#trade ad
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Sip Monster Tears
19 notes
·
View notes
Text

When June Foray passed away on July 26th 2017, just shy of her 100th birthday, I was asked to do the artwork for the WB tribute ad for her. Here is one of the prelims for that print art. Having had the pleasure of working with June as she voiced her iconic Granny character, it was an honor to draw this for her.
#Spike Brandt#Looney Tunes#Merrie Melodies#WB#WB Studios#Granny#Sylvester#Sylvester J Pussycat#Tweety#Tweety Bird#Tweety Pie#June Foray#tribute#memorial#trade ad#acknowledgment#appreciation#voice actor#voice actress#iconic voiceactor
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

"What is the hottest TV agency today?" (1954)
#vintage#retro#advertising#vintage ad#black and white#old ad#1950s#TV#ad agency#advertising agency#trade ad#house ad
15 notes
·
View notes
Text

Follow the tale of a Krazy Kat from skid row to Park Row to Hollywood Blvd.
"Motion Picture News," August 1, 1925.
41 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rare trade ad from the booklet "Universal Pictures of 1982" for Tommy Lee Wallace's "Halloween 3". This is the only time this particular ad was used and is notably missing the "Season of the Witch" subtitle.
#halloween 3#trade ad#collectibles#booklets#movie ads#vintage ads#rare#season of the witch#tommy lee wallace#john carpenter#debra hill#horror collectibles#horror memorabilia#posters#ads
9 notes
·
View notes
Photo
2nd Highest Rated Saturday Daytime Show (1968)

Now In Color
#60s#cbs#warner bros#warner bros seven arts#the road runner show#the bugs bunny road runner hour#saturday morning tv#looney tunes#advertisement#trade ad
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
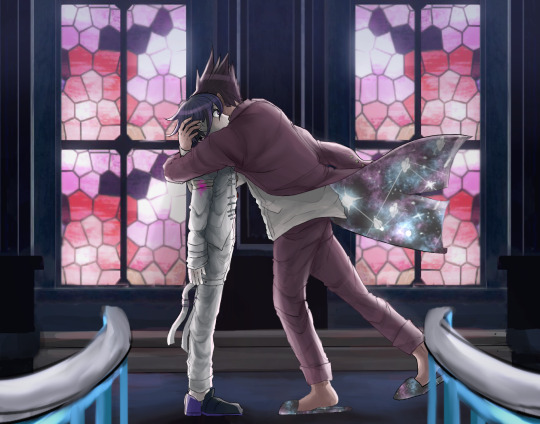
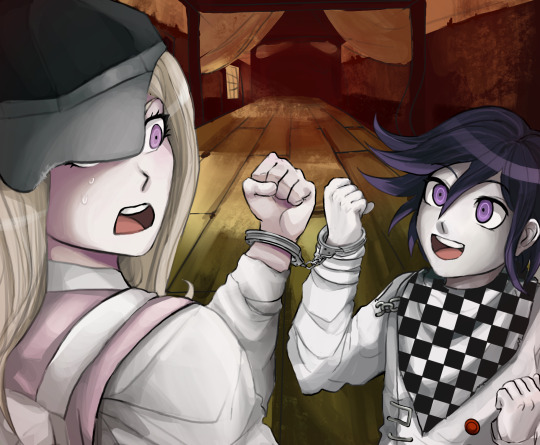


some fake screenshots I drew in 2022 for the fic that is leagues better than drv3, I’d trade my life for yours by grayimperia! this fic changed my life
depicted: [spoilers] the end of the chapter 5 trial, and the chapter 3 handcuff incident
#I purposefully added in some wonkiness for extra authenticity#danganronpa#drv3#danganronpa v3#kaito momota#kokichi ouma#kaede akamatsu#itmlfy#i’d trade my life for yours#oumota#fanart
652 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dracula’s Daughter (1936)
film industry trade ad from Universal Weekly Vol.38 #4, Feb, 22, 1936
source
#dracula's daughter#gloria holden#otto kruger#marguerite churchill#edward van sloan#1930s horror#1930s movies#1936#lambert hillyer#universal horror#classic horror#universal weekly#vintage movie ads#trade ads
173 notes
·
View notes
Text
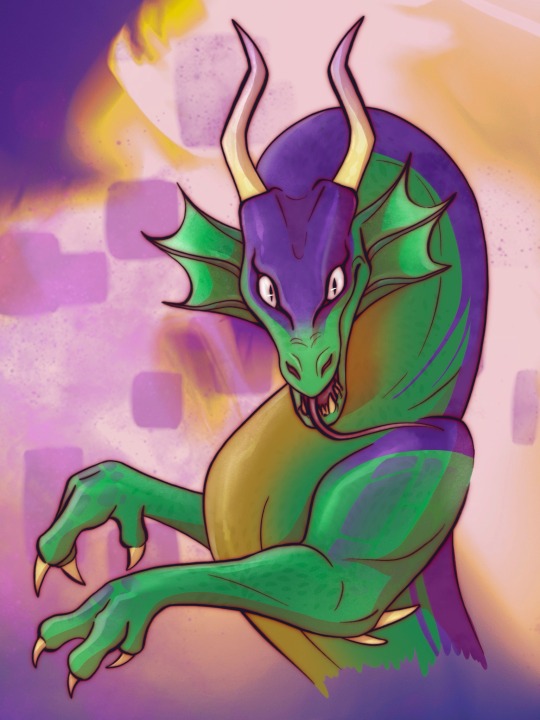
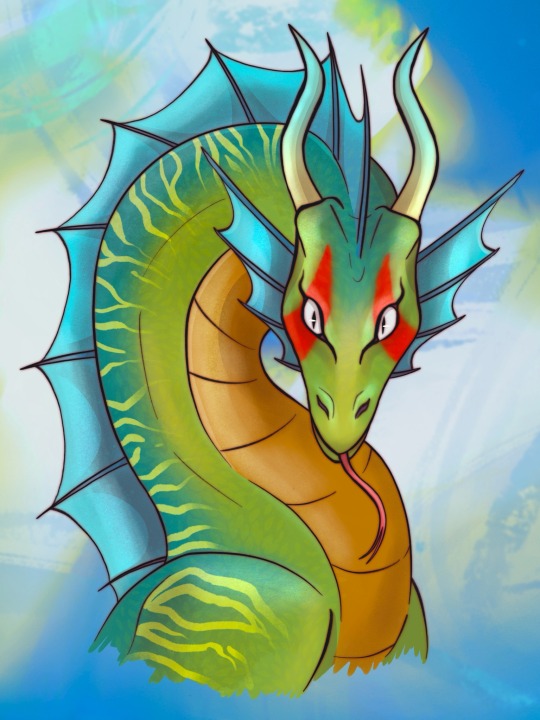





Dragons meet Dragons!
Got to do an art trade with @paintedkinzy-88 and their RISE dragon au!
#I really enjoyed getting to see the similarities and differences between each dragon design#I added a little sketch page with just some fun scenarios that came to me as I was drawing the dragon art#I though I was the only dragon AU so this was so much fun to find and get to draw!!!#art trade#my art#tmnt dragons#tmnt spitfire au#tmnt spitfire#rottmnt spitfire#rottmnt spitfire au#rottmnt art#rottmnt#rise turtles#rise tmnt#tmnt rise#rise fanart#rottmnt au#rise au#tmnt au#tmnt art#tmnt#tmnt fanart#teenage mutant ninja turtles#rise of the tmnt#rise of the turtles#rise of the teenage mutant ninja turtles#art 4 others#the hits
720 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cold Iron in folklore, fiction, and RPGs
'Gold is for the mistress—silver for the maid! Copper for the craftsman cunning at his trade.' 'Good!' said the Baron, sitting in his hall, 'But Iron—Cold Iron—is master of them all!' — Rudyard Kipling, “Cold Iron”
Folklore

Drudenmesser, or "witch-knife", an apotropaic folding knife from Germany
The notion that iron (or steel) can ward against evil spirits, witches, fairies, etc is very widespread in folklore. You hang a horseshoe over your threshold to deny entry to evil spirits, you carry an iron tool with you to make sure devils won't assault you, you place a small knife under the baby's crib to ward it from witches, and so on. Iron is apotropaic in many many cultures.
In English, we often come across passages that refer to apotropaic cold iron (or cold steel). "All uncouth, unknown Wights are terrifyed by nothing earthly so much as by cold Iron", says Robert Kirk in 1691, which I believe is the earliest example. "Evil spirits cannot bear the touch of cold steel. Iron, or preferably steel, in any form is a protection", says John Gregorson Campbell in 1901.
Words
So what is cold iron? In this context, it’s just iron. The “cold” part is poetic, especially – but not only – if we’re talking about either blades (or swords, weapons, the force of arms) or manacles and the like. It just sounds more ominous. There are “cold yron chaines” in The Fairie Queene (1596), and a 1638 book of travels tells us that a Georgian general (in the Caucasus) vowed “to make the Turk to eat cold iron”.
Green’s Dictionary of Slang defines “cold iron” as a sword, and dates the term to 1698. From 1725 it appears in Cant dictionaries (could this sense be thieves’ cant, originally? why not, plenty of words and expressions started as underworld slang and then entered the mainstream), and from ~1750 its use becomes much more common.
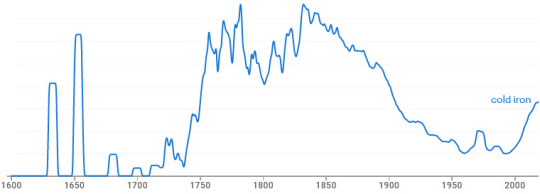
NGram Viewer diagram for 1600-2019.
In other contexts, cold iron is (surprise!) iron that’s not hot. So let’s talk a bit about metallurgy.
Metals

In nature, we can find only one kind of iron that’s pure enough to work with: meteoritic iron. It has to literally fall from the sky. Barring that very rare occurrence, people have to mine the earth for iron ore, which is not workable as is. To separate the iron from the ore we have to smelt it, and for that we need heat, in the form of hot charcoals. Throwing the ore on the coals won’t do much of anything, it’s not hot enough. But if we enclose the coals in a little tower built of clay, leaving holes for air flow, the temperature rises enough to smelt the ore. That’s called a bloomery.

clay bloomery / medieval bloomery / beating the bloom to get rid of the slag
What comes out of the bloomery is a bloom: a porous, malleable mass of iron (that we need) and slag (byproducts that we don’t need). But now we can get rid of the slag and turn the porous mass to something solid, by hammering the hot bloom over and over. And once the slag is off, by the same process we can give it a desired shape in the forge, reheating it as needed. This is called “working” the iron, hence “wrought iron” objects, i.e. forged.
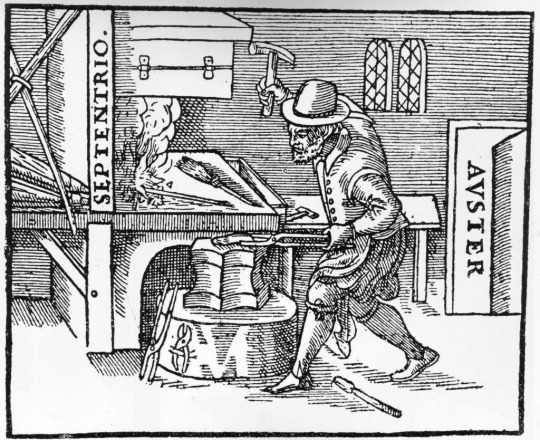

a blacksmith in his forge, with bellows, fire, and anvil (English woodcut, 1603)
This is the lowest-tech version, possibly going back to ~2000 BCE in Nigeria. If we add bellows, the improved air flow will raise the temperature. So smelting happens faster and more efficiently in the bloomery, and so does heating the iron in the forge, making it easier to work with. And that’s the standard process from the Iron Age all through the middle ages and beyond (although in China they may have skipped this stage and gone straight to the next one).
If we make the bloomery bigger and bigger, with stronger and stronger bellows, we end up with a blast furnace, a construction so efficient that the temperature outright melts the iron, and it’s liquified enough to be poured into a mould and acquire the desired shape when it cools off. This is “cast iron”.

a blast furnace
So in all of this, what’s cold iron? Well, it’s iron that went though the heat and cooled off. (No heat = no iron, all you got is ore.) If it came out of a bloomery, or if it wasn’t cast, it’s by definition worked, hammered, beaten, wrought, and that happened while it was still hot.
Is there such a thing as “cold-wrought” iron? No. In fact, “working cold iron” was a simile for something foolish or pointless. A smith who beats cold iron instead of putting it in the fire shows folly, says a 1694 book on religion, so you too should choose your best tools, piety and good decorum, to educate your children and servants, instead of beating them. When Don Quixote (1605) declares he’ll go knight-erranting again, Sancho Panza tries to dissuade him, but it’s like “preaching in the desert and hammering on cold iron” (a direct translation of martillar en hierro frío).
Minor work can be done on cold iron. A 1710 dictionary of technical terms tells us that a rivetting-hammer is “chiefly used for rivetting or setting straight cold iron, or for crooking of small work; but ’tis seldom used at the forge”. Fully fashioning an object out of cold iron is not a real process – though a 1659 History of the World would claim that in Arabia it’s so hot that “smiths work nails and horseshoes out of cold iron, softened only by the vigorous heat of the sun, and the hard hammering of hands on the anvil”. [I declare myself unqualified to judge the veracity of this statement, let's just say I have doubts.] And there is of course such a thing as “cold wrought-iron”, as in wrought iron after it’s cooled off.
Either way, in the context of pre-20th century English texts which refer to apotropaic “cold iron”, it’s definitely not “cold-wrought”, or meteoritic, or a special alloy of any kind. It’s just iron.
Fiction

The old superstition kept coming up in fantasy fiction. In 1910 Rudyard Kipling wrote the very influential short story “Cold Iron” (in the collection Rewards and Fairies), where he explains invents the details of the fairies’ aversion to iron. They can’t bewitch a child wearing boots, because the boots have nails in the soles. They can’t pass under a doorway guarded by a horseshoe, but they can slip through the backdoor that people neglected to guard. Mortals live “on the near side of Cold Iron”, because there’s iron in every house, while fairies live “on the far side of Cold Iron”, and want nothing to do with it. And changelings brought up by fairies will go back to the world of mortals as soon they touch cold iron for the first time.
In Poul Anderson’s The Broken Sword (1954), we read:
“Let me tell you, boy, that you humans, weak and short-lived and unwitting, are nonetheless more strong than elves and trolls, aye, than giants and gods. And that you can touch cold iron is only one reason.”
In Peter S. Beagle’s The Last Unicorn (1968) the unicorn is imprisoned in an iron cage:
“She turned and turned in her prison, her body shrinking from the touch of the iron bars all around her. No creature of man’s night loves cold iron, and while the unicorn could endure its presence, the murderous smell of it seemed to turn her bones to sand and her blood to rain.”
Poul Anderson would come back to that idea in Operation Chaos (1971), where the worldbuilding’s premise is that magic and magical creatures have been reintroduced into the modern world, because a scientist “discovered he could degauss the effects of cold iron and release the goetic forces”. And that until then, they had been steadily declining, ever since the Iron Age came along.
There are a million examples, I’m just focusing on those that would have had a more direct influence on roleplaying games. However, I should note that all these say “cold iron” but mean “iron”. Yes, the fey call it cold, but they are a poetic bunch. You can’t expect Robin Goodfellow’s words to be pedestrian, now can you?
RPGs

And from there, fantasy roleplaying systems got the idea that Cold Iron is a special material that fey are vulnerable to. The term had been floating around since the early D&D days, but inconsistently, scattered in random sourcebooks, and not necessarily meaning anything else than iron. In 1st Edition’s Monster Manual (1977) it’s ghasts and quasits who are vulnerable to it, not any fey creature. Devils and/or fiends might dislike iron, powdered cold iron is a component in Magic Circle Against Evil, and “cold-wrought iron” makes a couple of appearances. For example, in AD&D it can strike Fool’s Gold and turn it back to its natural state, revealing the illusion.
Then Changeling: The Dreaming came along and made it a big deal, a fundamental rule, and an anathema to all fae:
Cold iron is the ultimate sign of Banality to changelings. ... Its presence makes changelings ill at ease, and cold iron weapons cause horrible, smoking wounds that rob changelings of Glamour and threaten their very existence.... The best way to think about cold iron is not as a thing, but as a process, a very low-tech process. It must be produced from iron ore over a charcoal fire. The resulting lump of black-gray material can then be forged (hammered) into useful shapes. — Changeling: The Dreaming (2nd Edition, 1997)
So now that we know how iron works, does that description make sense? Well, if we assume that the iron ore is unceremoniously dumped on coals, it does not. You can’t smelt iron like that. If we assume that a bloomery is involved even though it’s not mentioned, then yes, this is broadly speaking how iron’s been made since the Iron Age, and until blast furnaces came into the picture. But the World of Darkness isn’t a pseudo-medieval setting, it’s modern urban fantasy. So the implication here is that “cold iron” is iron made the old way: you can’t buy it in the store, someone has to replicate ye olde process and do the whole thing by hand. Now, this is NOT how the term “cold iron” has been used in real life or fiction thus far, but hey, fantasy games are allowed to invent things.
Regardless, 3.5 borrowed the idea, and for the first time D&D made this a core rule. Now most fey creatures had damage reduction and took less damage from weapons and natural attacks, unless the weapon was made of Cold Iron:
“This iron, mined deep underground, known for its effectiveness against fey creatures, is forged at a lower temperature to preserve its delicate properties.” — Player’s Handbook (3.5 Edition, 2003)
Pathfinder kept the rule, though 5e did not. And unlike Changeling, this definition left it somewhat ambiguous if we’re talking about a material with special composition (i.e. not iron) or made with a special process (i.e. iron but). The community was divided, threads were locked over this!
So until someone points me to new evidence, I’ll assume that the invention of cold iron as a special material, distinct from plain iron, should be attributed to TTRPGs.
#long post#cold iron#d&d#Changeling: The Dreaming#World of Darkness#Peter S. Beagle#The Last Unicorn#Rudyard Kipling#Poul Anderson#The Broken Sword#how to rogue#pathfinder#rogues in fiction#Operation Chaos#rogue superstitions#words of the trade#thieves' cant#ad&d#d&d history#1st edition#fey#3.5#fluff#trs
405 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Inspector, hot on the heels of The Pink Panther.
Motion Picture Exhibitor, December 1, 1965.

48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Series A & Series B: The Wacky World Of Tex Avery & Sonic Underground

#00s#dic animation#dic entertainment#sonic underground#sonic the hedgehog#the tex avery show#wacky world of Tex Avery#Russian#trade ad#advertisement
30 notes
·
View notes
Text

YCAO!Ethubs err
ch6 spoilers ig?????
#stufffsart#ycao au#bdoubleo100#bdoubleo#etho#ethoslab#ethubs#hermitcraft#hermitshipping#hermitblr#mcytblr#.... ADDED BACK THE BLACK STREAKS TO ETHO'S HAIR IM SORRY he looks missing without them u_u#i think abt this part then i think about the immediate scene change after with etho at the police station and horrors beyond comprehension#tbf [REDACTED]'s debut there rocked tho LOVE that guy#LOL trade offer: YOU get free ethubs art - I get to talk about ycao. awesome? awesome
933 notes
·
View notes
Note
What’s the architecture/layout of old Bur, how do modern people perceive the ruins?
The city in its peak was very large and spread over both shoreline and a network of small islands. These islands comprised a waterfront district connected by a network of bridges and canals, where a large portion of its non-agricultural lower class lived.
It had a fairly well organized and efficient freshwater+sanitation system across most of its span (the canal district had less effective plumbing largely due to logistical difficulties, most of its wastewater was instead flushed by rain powered cisterns). The water system was powered by the Hsuke river and made fresh water readily accessible throughout the majority of the city (though few homes had direct freshwater plumbing). It had several major public baths, and the homes of the wealthiest members of society had their own private bathing pools.
In this part of the world, it is broadly regarded as once being one of the most beautiful cities to have ever existed. It was particularly noted for its water gardens (still a fixture of present day Burri culture) which were absolute marvels of engineering for that period, with the majority of these being entirely artificial and supported by its network of aqueducts. These hosted thousands of ornamental plants, fish, and fowl, as well as fruiting trees and shrubs. They were treated as a public work meant to benefit all citizens, and existed throughout the city.
The palace in particular was noted as impressive, in part for its architecture but mainly for its gardens. These hosted 'exotic' plants and a menagerie of animals from across the empire's territory, and existed in part as a symbol of the state's power and reach. It was a trend for emperors to bring in the fiercest animal from each conquered province to the grounds, with the an-nechoi being the beast of choice from the lands across the sea to the east, with one (Probably erroneously) cited as killing thirty servants in the process of moving it into the gardens.
The palace was located within the temple district. This district housed over a hundred shrines to the various lesser deities of the pantheon, and temple complexes to the seven chief deities (the firstborn gods who created the world, all other gods were later descendants). Old Burri temples were Kinda similar in shape to a ziggurat, though had an accessible interior space and a central tower which housed the shrine. At this time, the chief gods were believed to physically inhabit their temples. Each god had its own high priest permitted to attend to their shrine, with the emperor being the high priest to Inanariya (king of the gods) and the only person permitted to directly commune with this deity. The foundations to these temples are relatively intact in the present day, though none of the towers remain (collapsed in earthquakes with no one to rebuild them).
The city was heavily fortified, having one external wall surrounding most of its length, and an internal wall surrounding the palace/temple district (which doubled as a fortress).
---
The period of sea level rise began with a 500ish year period of mostly gradual increase, which occurred slowly enough that most infrastructure could adapt very easily and the problem went unnoticed by most (the city of Bur experienced most of its Growth during this time). It then culminated with about a century of (relatively) rapid rise, which is the direct cause of the city's abandonment.
The canals flooding had always been a problem during storms, but this began to occur with notable frequency, alongside the water level as a whole rising quickly enough to be noticed on an immediate human timespan. The canal district was maintained for a while by rerouting some of its waterways and building up barriers, but it was the first part of the city to be abandoned. Things got more serious when the mainland parts of the city grew increasingly impacted by storm surges that never seemed to fully retract, and major parts of its surrounding farmland were hit by surges and tidal waves, and rendered too saline to remain arable.
The actual single biggest cataclysm was the collapse of the city's mainland sewage system. It was built with flood canals as a failsafe, but these were built to withstand heavy rain rather than an encroaching ocean. Storm surges would cause large segments of the city to be flooded with sewage (including some of the freshwater plumbing), and serious disease outbreaks would follow.
These issues were enabled/exacerbated by earthquakes (the region is geologically active and this isn't unusual) that further damaged and mingled the sewage and freshwater systems. One earthquake and its subsequent tidal wave was a turning point, and the resulting breakdown of (already strained) infrastructure rendered a large swath of the city uninhabitable in the space of about a week. This also just caused immediate damage to much of the city's architecture/walls, and collapsed the tower of the temple to Inanariya (never a good sign). This is when the full exodus began, first with people flocking to un-flooded parts of its city and farmlands, and those who could afford it fully relocating to other cities/towns.
All of this issues were compounded by the 1st Burri Empire already being in a period of collapse at this time. This was largely a matter of simple overextension. Its borders were constantly under attack by rival states/its victims, sometimes with great success. Bur's own population had burgeoned well past what the imperial core land could sustain, and its cities relied predominantly on extraction of foreign grain/goods to feed their people. It lost most of its eastern land holdings in a fairly rapid timespan (overextended with wars at multiple fronts), which caused frequent famines in its core.
This put pressure on its final emperors to invest in increasingly desperate expansionist projects, while attempting to keep up public morale with lavish public works and objectively stupid vanity projects. The attempt to excavate a canal at the Viper seaway's 'tail' (one of the few eastern regions it retained secure control of at that point) was in part a desperate act to revive its economy by opening up/monopolizing a new trade system. The amount of money and manpower sunk into this ultimately doomed project was followed by Bur being fully ousted from its eastern holdings, and was one of the final straws in its collapse.
People in the city of Bur proper were dealing with the double front of starvation and their homes + streets + immediate water supply being flooded with seawater and literal human feces. These issues impacted the lower classes first and most severely, but ultimately transcended class boundaries. Famine grew more and more rampant, not only with the loss of the colonial holdings that supported the population but of farmland in the imperial core- much of the city of Bur's immediate farmlands were unproductive due to repeat inundation with saltwater during surges, and the farmland along the Yamage river to the north was rapidly being captured and pillaged by the Hsem (historical enemies, a nomadic group with a khait warrior culture from further west).
All this was fucking unlivable in of itself, but also had very obvious implications in the context of Burri emperors also being high priests and the chief intermediary between the gods and the people. Not only was the government failing to sustain its citizens to begin with, but signs of divine disapproval were deeply apparent.
So the last days of the 1st Burri empire were a chaotic period of civil unrest, most acute in and around city of Bur proper. This involved near-constant peasant revolts and several attempted coups. The last Burri emperor (of the First empire) ultimately fled the capital of Bur and reestablished in Titenegal, declaring it the new capital. This was then sacked by the Hsem within a year and after that it was fucking Joever.
The city of Bur was functionally abandoned by this point. People still Lived There and there were several attempts to set up a new government, all of which failed in the short term. After the collapse was complete, its inhabitants were mostly just peasants who built up new homes further inland and sustained themselves on the remaining farmland. Few people lived permanently in the city proper due to all of its intact infrastructure being effectively non-functional without the governmental bodies/human labor to sustain it.
---
It should also be noted that it was Extremely not just Bur that was flooded, the sea level rise was worldwide (resulting from a collapsing ice sheet) and almost Every coastal city during this period experienced the same issue. Bur's demise was just notably dramatic in that it was once the most heavily populated human city that has Ever Existed, and directly correlated with the fall of the empire it hosted.
The flooding was fairly gradual, but it's been 7 centuries since the first Burri empire's collapse and the fall of its capital city, and many contemporary records were lost to the immediate chaos and to the large span of time since. Cultural memory tends to reframe the flood VERY rapid on a human scale, many of the stories describe the city being swallowed in a single wave as an act of divine punishment (the popular notion at the time that the last emperors deeply displeased and shamed the gods has stuck into the narrative, often exaggerated into stories of them being horrifically debauched blasphemers guilty of the worst disgraces imaginable). Even more conservative accounts tend to imagine the totality of the destruction taking place over the span of about a year (merging the memories of the immediate earthquake devastation with more gradual elements of its slow flooding). People widely believe that most of its residents drowned in the city's cataclysmic demise, and that the ruins are now Extremely haunted.
The state of the flooding is not 'completely under the sea' and you can still walk/wade through most of the inland ruins (the canal district is effectively submerged, with most structures that Would be above the water level having collapsed against the strain). As such, some people Do Live Here. These people are mostly smugglers and pirates using the ruins as a hideout, and/or opportunistic hunters and fishermen who won't let ghosts stop them. Entering the city ruins is currently forbidden (largely Because of the criminal nature of basically every motive to go here (even hunting, which is considered poaching)), but enforcement of this rule/active patrols to prevent entry are inconsistent.
The majority of Old Bur's inhabitants are animals. The un-flooded parts of the city and its gardens are now a host to a thriving community of native plants and animals (and a few descendants of escaped non-native zoo animals/ornamental plants that adapted well to the conditions).
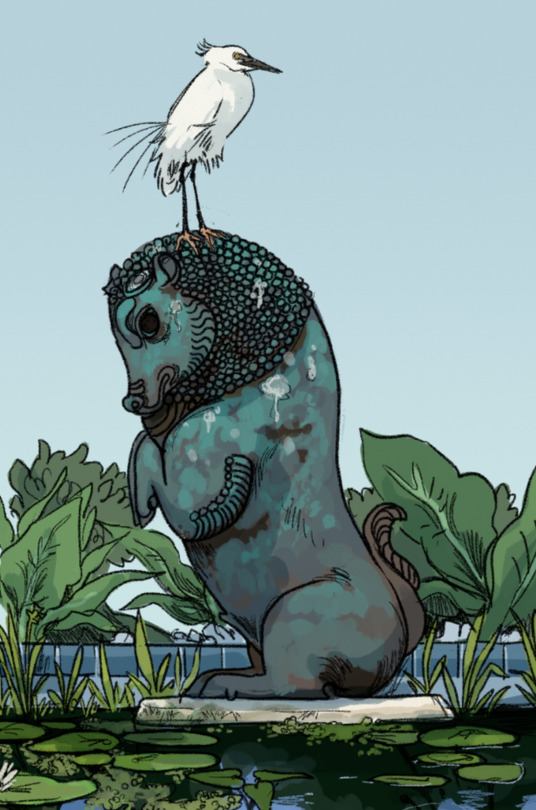

The egret shown here is a foreign species originally brought as an ornamental bird. In the centuries since its first import, it has become widespread and occurs on both sides of the Mouth seaway. It can hunt in both freshwater and saline environments, and a very large population lives permanently in the ruins of Old Bur.
Its common name is the ghost egret. Contemporary Burri folklore holds that the ghost egrets of Old Bur are literal ghosts, carrying the souls of those who died in the cataclysmic floods.
#[[JUST REALIZED you didn't even fucking. ask about the timeline of the flooding I just kinda went for it]]#[[its relevant to its contemporary state I guess????]]]#Added the photo without linking to the original post becasue it is WILDLY outdated.#Among other things I cited the population of the original city of Bur at 'over a million people'. Which is contextually ridiculous#Also (because this probably gets confusing) everything here describes the first of two empires out of Bur which was by far#the larger one. The second had a similar pattern in its downfall (overextension - famines at home - war and revolts at multiple fronts)#but was significantly less dramatic and had a much cleaner rebound (it ended in a successful coup that the contemporary#Burri Republic directly descends from)#I used to describe 3 Burri empires which. I don't know why I did that because the 1st of the three was an ANCIENT land empire#stemming from further west where contemporary Bur was its easternmost extent of Conquered lands. This collapsed like ~1500+#years before present and has no directly obvious impact on modern conditions whatsoever (it DID have major impacts#though: it's what first brought khait to this region and some of its ancient roads are still used in the largest continuous land#trade network in the northern hemisphere)
94 notes
·
View notes
Text

My part of the art trade with @cadavvera <3
#adding one to the collection of jean getting stoned#it was fun to draw#my art#art trade#disco elysium#jeanposting#jean vicquemare#jean heron vicquemare#cw weed#cw drugs#cw cigarettes#cw alcohol
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
CN 25th Anniversary Concept Sketch (2017)

Rough suggestion for trade ad featuring Scooby Doo, Bugs Bunny, Daffy Duck and Tom & Jerry celebrating Cartoon Network’s 25th anniversary in 2017.
#10s#cartoon network#hanna barbera#warner bros#mgm#scooby doo#bugs bunny#daffy duck#tom and jerry#concept art#character designs#conceptual art#trade ad#25th anniversary#spike brandt
65 notes
·
View notes