#people skills and adaptability really make sense when you take into account the fact that he’s a red eared slider
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Shockingly underrated thing about Leo is that he’s legitimately charming when he wants to be?
He’s the Faceman! He’s persuasive! That’s not just some random title he gave himself with no backing to it. People will listen to him. Even if they think he’s being annoying or if they’re upset at him, people listen to him anyway! There’s a reason his bros push him out front to talk to people, and when this happens, that talking nearly always works.
Moreover, Leo knows people. He looks at them and takes into account how they act and what they’re like as he makes his way through the conversations. It’s easy to forget this aspect of Leo’s character because he only brings it out when he really needs (read: wants) to, but it really is a notable part of him that always love to see.
And I say charm in particular because he has a knack for not only getting people to pay attention, but for getting people to stay and listen to what he has to say.
#rottmnt#rise of the teenage mutant ninja turtles#rottmnt leo#rise leo#I feel like people equate Leo to a lot of loud gross boy behavior instead of looking at his actual accomplishments#which fair enough#he IS a loud gross boy a lot of the time#but his charisma really deserves a mention for how much it comes in clutch#that one cut animatic of the other people in the resistance wanting Leo to join them for karaoke like#and yes those inspiring speeches he gives his fam are also an example of charm#bro has! charisma! he can have his loser moments and at the same time show off how to manipulate through words#Leo knows people and if he really wants to he can talk them up#but yeah like - I see people calling him the face man a lot but not so much taking into account what that entails#he’s got a pretty face! and he’ll do the talking a lot! but that’s not all a face man is#another thing that is SHOCKINGLY underrated in fandom is Raph loving fighting???#I have no idea why but I feel like I don’t see this mentioned enough#he adores wrestling and roughhousing and training and just FIGHTING in general plz let my boy punch something#I have more I wanna say but it’ll have to wait until later it is very late haaa#anyway my main point behind this post is that Leo knows people and in turn knows what they WANT#it is this same perception that makes him REALLY GOOD at getting under people’s skin too#people skills and adaptability really make sense when you take into account the fact that he’s a red eared slider#it really is cool to see how much this part of Leo is addressed throughout the series#nearly always in very lowkey ways
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
Having shared my RINGS OF POWER s2 eulogy, and while assuring you all that I am also mourning the loss of one of the best things about the show, I would also like to take a moment to defend the decisions being made by the showrunners and writers here.
Before I get started, I just want to acknowledge the members of my writers' group. This post owes much to our discussions. Anyway, when it comes to Adar's death, there are three reasons why I'm not calling his death pointless, or blaming the showrunners for bad writing. The overall reason is this: Adar represents the show's efforts to treat Orcs like people. In this sense, his character was a blazing success. Look at us all, with a hopeless crush on an Orc? Success.
But let's go a bit deeper.
SIMON TOLKIEN'S EXECUTIVE MEDDLING
The fact that Simon Tolkien made an EXCELLENT call in asking the showrunners to keep Adar around for an extra season...still doesn't stop what he did from being executive meddling, or from causing tricky ramifications in the second season. Adar was a first-season antagonist, brilliantly well-written, but ultimately only intended to be a supporting character. The decision to keep him on, suddenly made him more charismatic, more mysterious, and more sympathetic. Given how he'd been set up as a warm-up baddie...season 2 suddenly turned around and made us think he was here to stay. The writers had cornered themselves: on the Tolkien Estate's behest, they had a dark horse who was about to run away with the show. I'm not going to fault them for going ahead with their original plan, because they would have had to retool subsequent seasons massively in order to fit in an Adar redemption arc, and you can't necessarily do that when the whole arc of your story is already planned.
JRR TOLKIEN'S LEGACY
All of us have written things we're not proud of. JRR Tolkien wrote a story world with something problematic hard-baked into the foundations: an entire race of beings for whom genetics determined ethics. Can you even imagine what it must have taken for him to get to the end of a long life spent in the dedicated pursuit of this story world, and to have the courage to admit that he might have been wrong? That really isn't something most authors are capable of. When Peter Jackson went to make LOTR and HOBBIT into movies, he did nothing to scrutinise this issue. His Orcs are flat: monstrous, comic, but never people.
TROP challenged that, and exercised significant skill, care, and wisdom in doing so. But they are still attempting a faithful adaptation of Tolkien's source material. We know where this story is going. Galadriel will end up in Lorien with her elf wifeguy. The Orcs will fall under Sauron's dominion and become his tools, enslaved to his will with the Ring. I did fantasise about Adar being Celeborn, and possibly some of his "children" getting to nope out of Sauron's dominion or even be turned into Elves. But we now know that was never on the table. The Orcs were always meant to fall to the Enemy. But here's the point: for the first time in the history of Tolkien works and adaptations, TROP allowed them the dignity of a fall. Going forward in the show, the Orcs won't be monstrous cannon fodder: they'll be people we knew, people we were pulling for, people whose deaths matter. They are, not a waste, but a tragedy.
TOLKIENIAN TRAGEDY
Look...there's nothing more Tolkienian than a beautiful disaster of a man who dies far too early.
And yes, I know that it's something we've seen before and wish storytellers would move away from - the Moment of Grace that never becomes anything more than a Moment. The villain who has a five minute redemption, then dies conveniently so that the heroes never have to work through the messy business of forgiveness and accountability (although I always did wonder how it would play to see a redeemed Adar, possibly Celeborn, living the rest of his life as a redeemed Uruk among people who hold an undying enmity with his children). It's happened so often that when I, Suzannah Rowntree, sit down to write a six book series where the irredeemable villain has to live and build a new and more accountable life for himself, there's startlingly little template for it, at least in Western media. We live in times that are starved for happy endings and genuine redemption arcs. I wanted so badly for Adar and his "children" to be blessed, and not cursed, by this narrative. So I get the rage. I get the grief.
But tragedy is still a valid art form. Again, all this is a function of the show successfully making the Orcs matter. And the reason the Orcs needed to matter is because they are about to be enslaved to Sauron. They were so close. They genuinely could have been good. Adar could have led them into an alliance with the Elves against their enemy - but instead, just like Celebrimbor, just like Galadriel, they are deceived by him. They turn to him out of fear that their father figure is treating them like cannon fodder, and now they have no one to advocate for them. And that's the tragedy of their situation.
We might all be a little tired of tragedy, but it's still valid, especially insofar as it never, ever forgets to treat its characters like people. Did the writers have to choose tragedy? No. Adar might have lived and undergone a redemption arc.
But the writers didn't have to give Adar a redemption arc, either. Any more than they had to so deeply humanise the Orcs and their father. It's not perfect writing, but it's not bad writing, either. Indeed, for a Tolkien adaptation trying to both honour the author's work and scrutinise his failings, in my opinion it's doing brilliantly.
And...honestly, I'm kind of happy that they left me wanting more, and better, for Adar. Because now I get to write that story myself.
#the rings of power#jrr tolkien#trop spoilers#trop#trop positivity#pro trop#the rings of power spoilers#adar#adariel#galadriel#trop season 2
48 notes
·
View notes
Note
My Prince,
If it would be to your liking, would you share your personal intelligence rankings, which you spoke of in the tags of a previous request, to the court?
Thank you, Your Highness.
Intelligence is classified by your ability to apply things you already know and the skills you already have. You can be bright but slow, or a quick thinker but lack experience. There's many things to take into account when talking about intelligence. This may not make sense, as I am a bit loopy from switching meds recently.
Loosely:
Giorno is obviously at the top. I think it's criminal that his intelligence is listed as a B on his stats. Giorno doesn't slack in any of the things I understand intelligence to be, he applies absolutely everything he has and somehow never misses. Giorno spent his entire childhood figuring social etiquette out the hard way, he's hard wired to figure out what to do and not to do as quickly as possible. To Giorno, survival means being the best of the best. Has he always been absolutely perfect? No. Has he always bounced back? Yes.
Trish is fairly young, it's a bit unfair to put her up against grown men. She takes after her father in many ways- one being how clever she is. She may not understand stands yet, or why she couldn't just stay home and never go out again, but she's very quick to adapt. Trish did well in high school, she had a high gpa and did lots of extracurricular activities, which just means that she's a hard worker. Her ability to adapt and her natural curiosity is what leads me to believe that she's on the higher end, it's just that she lacks experience pre canon. Post canon, she's a force to be reckoned with. A Trish that understands how to fully use her stand, how to do what her father did and make someone disappear entirely, and how to manipulate the public so they think her kidnapping victim lovely darling is on tour with her is a very dangerous Trish indeed. If this is strictly pre-canon, bump her down to the middle-lower end.
Some people may not like Guido being in the top three, but I'm fairly firm on it. Guido's a quick thinker and has managed to stay alive for this long. Does he understand things like infections and germs? Not really. Could he, if you explained it to him? Sure. Guido's street smart- he never went to college, but he reads a lot. He's a curious guy! If something interests him, he'll look into it. He's got great instincts and a ridiculous amount of luck, which isn't intelligence, but often will help him figure out what's going on. He checks for Sale's shadow under a truck, he yells at Narancia for not telling him the stove was on and it wasn't safe to fire his revolver. He knows what he's doing, even if it seems like he's just fucking around until something clicks. That's kinda scientific theory, isn't it? Fuck around and find out? Yeah, he gets it.
Pannacotta... the author Her Highness does not believe in IQ tests, as most people who claim to have a high IQ got it off of some online test made to stroke the quiz taker, but I believe Pannacotta is very intelligent. He's just not socially intelligent, which bumps Trish and Guido above him. He left behind his prissy, rich lifestyle in favor of being homeless for a little while before Bruno found him- he's left behind most manners and forgotten most unspoken rules. In this case, Trish and Guido outdo him. What worth does purely academic intelligence have if you cannot apply it, and it has nothing to do with the situation? Pannacotta is intelligent, but he isn't creative enough to apply what he has. Who makes a vaccine on the spot like that?????? If he wasn't so in his head all the time, he'd probably be a lot scarier. I mean, who thinks to put capsules in things you're not supposed to be touching anyway?
I think it's a bit silly to put Bruno so low when he is, in fact, an adult with a fully developed prefrontal cortex. I don't think Bruno is unintelligent at all, he's a man of average intelligence for his age. He's only so low because everyone above him is not average, even if they pretend to be. An older, more mature Pannacotta would have him in too many categories for comfort. Guido has him in reaction time and blind instinct, and while some may argue that isn't intelligence, it's applying what you've got. Bruno can be a little slow at times mentally, but never in combat. He pauses to make decisions that would take Giorno a split second. He makes mistakes that, although he makes up for later on, he still makes in the first place. He's formidable- he has experience and knows how to use it, but he's not very creative.
Narancia's not all there all of the time. It's not fair to say Narancia's stupid because he isn't good at math or academics in general, you can be smart and have weaknesses. But not Narancia. He's a little lacking. He doesn't try to make up for it at all, but he's figured some things out that he definitely shouldn't have before, saving him from dead last. Narancia has some crazy instincts, but he doesn't really know what to do with them. Instincts don't equal intelligence, but it helps. He'll take credit for anything you're willing to blame on him- FUCK yeah he figured out you're trying to escape 'cause you left some shit on the table. (He felt it in his tummy and got anxious that you're leaving him.)
Leone went through some schooling, but he barely passed. You could always argue that he was too depressed to do his work, but I personally don't believe so. Leone's slow and prone to picking the hard way- not because he's a masochist, but because he's been living off of going "Well, one of these is right." for the past three years. He's just happy he finally got a stable job. His instincts are terrible, his reaction time is shit, he has very slow realization in general- the list goes on. Does that mean you're getting off easy? Nope. He's still taller, and stronger. Doesn't take a lot of brains to pin someone, especially when it's muscle memory. Leone can bump himself up over Narancia eventually, but only because Narancia is emotionally stunted. You have him in the emotional maturity (aha. Leone and emotional maturity?) category, and what else? Get a grip. Leone knows how to do more- makeup and cosmetics is a skill, so is media literacy- but Nara's got him in reaction time, realizing that dots do in fact connect, and learning how to put you in your place at a faster rate.
#request granted#poor leone#a pass is a pass I respect it#yandere vento aureo#yandere leone abbacchio#yandere bruno bucciarati#yandere narancia ghirga#yandere guido mista#yandere giorno giovanna#yandere trish una
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Secrets chapter 7: T.A.H.I.T.I.

Pairing: Steve Rogers X OFC, Brock Rumlow X OFC.
Word count: 1101 words.
Summary: Sometimes keeping secrets can be dangerous or a heavy burden, which is what Kathleen has been doing for years. She will also be in charge of guiding Steve Rogers into this century; meanwhile, S.H.I.E.L.D. will be looking for a way to kick-start the Avengers Initiative by integrating her as one of the superheroes, but that won't be the only danger they face.
Warnings: Slightly distrust.
A/N: After long time working on this longfic, I finally post it. If you wanna be added to the taglist, let me know.
My native language is Spanish so I wanna improve my writing skills in English if you notice any mistakes, please let me know and I will correct them.
I don’t give any kind of permission that my fics to be posted on other platforms or languages (I translate myself my work) or the use of my graphics (my dividers are included in this), I did them exclusively for my fics, please respect my work and don't steal it. There are some people here who make dividers that anyone can use, mine is not this type, please look for the other's people. The only exception is the ones I gifted 'cuz now belong to someone else. If you find any of my works on a different platform and are not one of my accounts, please let me know. Reblogs and comments are always welcome.
DISCLAIMER: I don't own Marvel's characters (unfortunately), except for the original characters and the story.
Add yourself to my taglist here.
My other media where I publish: Ao3, Wattpad, ffnet, TikTok, Instagram, Twitter.
If you like it, please vote, comment, and give me feedback to improve my skills and reblog.
You can read it on Wattpad and Ao3 too. Secrets masterlist. Previous chapter. Next chapter.

Steve watched the two of them with crossed arms and a very serious expression; he was still trying to understand what had happened, even though he didn't understand how it was that he survived. Nothing made sense; in fact, he expected to be told at any moment that it was a joke.
"Cap, we'll have to take you somewhere else, where you'll be calm and recover."
Steve was not very convinced, but apparently, there was no other option, nevertheless he did not let his guard down, he never knew when something would happen, and even so, he agreed to accompany them.
The whole car ride was confusing for Steve, too much information, many changes, buildings where in his time there were none, the vehicles were different, and he even feared that if he touched something he would break it, the music was already too varied, during the ride he listened to several songs, everything was new to him, the world had definitely not stopped after he had been frozen, there were too many changes compared to the forties that he began to doubt if he could really adapt.
Steve still wasn't sure if he could trust them; he feared they were deceiving him. It seemed strange to him that at no time had the girl removed the gloves that covered her hands, not to mention the resemblance she bore to Katherine.
There was a cabin; it looked very quiet. He was told they would be there for two weeks, but he needed to know more.
"How do I know you're not fooling me or that you're not enemies?" he asked gruffly as he put on a straight face.
"You sound logical to believe that Captain, Director Fury has been looking for you for years until now, the biggest fear was that you would fall into enemy hands, when S.H.I.E.L.D. was founded they decided that the mission was simple, protect the world from threats, we take down terrorists or anyone who..."
"Of course, everything is weird, especially you; you are suspicious, you haven't taken off those gloves at any time, and your attitude," he spat as he pointed to the gloves the mutant was wearing. She smiled.
"They are to avoid direct contact with other people and try to avoid reading their minds." She took off the gloves and showed him her hands; there was nothing strange about them, but the ring on the index finger caught his attention. The figures they had were curious: a sun, a moon, a star, and a ray. "If you need to read my file when we leave here, you can ask for it." Believe me, I am one of the best agents that S.H.I.E.
"How did you get them?" Steve questioned. She looked at him blankly, not sure what he was referring to "Your powers," he said.
"I was born with them; I'm a mutant," she approached him and stretched out her hand, "may I?" She took his hand as he nodded, and so Steve began to see a few moments since they found him; he seemed calm. Maybe it wasn't a bad idea to trust her after all. "I guess he would have figured it out by now in case we cheated on him, or am I wrong?" She asked, and he nodded, then withdrew his hand. She noticed that Steve had his eyes on the ring.
The ring had a very special meaning for Kath, and it was related to the necklace she had; Wanda, Pietro, and Saori also had their own. Sometimes she wished they were there; everything would be better, easier, and more fun if they were. The only one who knew the meaning and importance was Brock; he wasn't going to let other people know.
"Agent Anzai, there is no need for such formality; tell me, Steve," he interrupted her.
"In that case don't call me that way either, you can call me Kathleen, Kathy, Kath, whatever you want, well it's time to start introducing you to the world of technology," the girl opened a box, which contained several mobile phones, all of them had been hers over the years, she believed it would be the easiest way to introduce him to telecommunications, They would start with the simplest until they reached the current ones, then they could move on to computers and other electronics, there were too many things to teach him, not only about technology, but also about culture, history and so on, she was not sure what things he would like, but she would find out as she went along.
After several hours, Steve had already managed to understand and learn how to use a mobile phone, at least the basics, even though they didn't work quite right in the beginning.
After a few days, Steve began to trust Kath a little. He began to notice several differences from Katherine, but evidently, he was convinced that she was her granddaughter.
Sometimes she told him about what happened in the army, even when she was on that ship on her last mission. Although it seemed a little strange that she barely told him about her, he still believed that she was hiding something, or maybe there was something else. Steve promised himself that at some point he would discover and know more about her; somehow he was going to find the information.
He would not ask her at the moment, since the one time he dared, he regretted it. That time was when he asked him what happened to Katherine; if Bucky had been alive...
There was practically no one from his time alive anymore; what was left were the descendants. Steve wasn't sure he could adapt properly, and he wasn't sure he could get all those years back either. How would he be able to go on?
Although there was also something about her that caught his attention—it seemed as if she had a sadness that she couldn't talk to anyone about—he was sure that the ring he saw had something to do with it, and he also discovered that she wore a bracelet with the same figures.
Sometimes it even seemed to him that she was talking to someone, but she was alone, and he was going to find out what she was hiding.
Steve closed his suitcase. Kath had told him that the next morning they were going back to New York, and he was going to stay at her house for a while. How different are the houses now?
He was also curious about what had happened to certain people's offspring.

Ꭲꭺꮐꮮꮖꮪꭲ:
@saiyanprincessswanie @sinceimetyou @unnuevosoltransformalarealidad
@navybrat817 @angrythingstarlight @shield-agent78 @charmed-asylum @pandaxnienke @real-fbi @smokeandnailz @white-wolf1940 @tenaciousperfectionunknown @xoxonotme @bluemusickid @leyannrae @harrysthiccthighss @marvelatthisone @caplanbuckybarnes @sapphire-rogers @lizzieolseniskinda @notyourtypicalrose @hallecarey1 @nana1000night @talia-rumlow @mylifeispainandiloveit @writingshae @alexxavicry @azulatodoryuga @daemonslittlebitch @sweater-daddiesdumbdork @jtargaryen18 @chaoticcollectivenightmare @endlesstwanted @chemtrails-club @marigoldreamer
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
(kind of extra rambling kind of respond to @digitalmagpie in comments but think may get long) (not mad just woke up with serious tone??)
so first am talking about severity labels & not autism levels, which autism levels do have defined how to distinguish between levels - i.e. social communication & restrictive repetitive (there a chart). think at least in past DSM, there no same similar chart for severity for autistic disorder, which muddy it a little, but there scales & official testing measures that can distinguish. they typically normed for children because 1) back then not much awareness for undiagnosed adults & 2) issue of severity more pressing in children (like if make it this far to adulthood without diagnosis, assumed you not severe, n while this assume can leave ppl out, but generally accurate for most. issue of true late autism regression both rare n also not really known at the time)
n also don’t see how comorbid condition would make mild severe harmful?
because either way both severity & levels of autism is about autism itself, like how most if not all disorders severity defined, not overall functioning/abilities/struggles (second one more like support needs).
DSM 5 autism spectrum disorder levels is explicitly only social communication, restrictive repetitive
DSM 4 autistic disorder severity, is look at social, communication, restrictive repetitive (social & communication separate)
adaptive functioning (which in sense include bADLs iADLs) actually not inherently included in autism severity & levels, that why you see children & adolescents online diagnosed as severe level 3 etc & videos of them learning independent living skills adaptive functioning skills. it also fairly established fact in autism research that autistics without ID have lower adaptive functioning skills than non autistic people of same age & IQ (yea yea IQ problematic etc but is often thing measured with)
for example mild depression doesn’t automatic become severe depression just because also have anxiety (like if depression more match others with mild depression, second diagnosis of anxiety won’t be enough reason change depression label to severe) - two disorders tend feed into eachother into bad loop n sometimes make both worse over time, n when that happen, depression labeled from mild to severe, but that still not inherent because there anxiety, but because depression got worse.
depression anxiety ocd ADHD all not autism - they can be result of live in unsupportive world not for autistic people, n can be very hard separate, but still inherently not autism. same even go for intellectual disability, a general disorder that impact near everything about person. ID not automatic mean severe or level 3 (& responsible clinicians do follow this), if someone with ID more fit mild moderate or level 1/2, then that should be their diagnosis. guideline for diagnosing people with known ID for autism, actually only diagnosed when that person struggle more with big autism categories (social, communication, restrictive repetitive) more than people with similar severity ID. it just you see more people diagnosed severe & level 3 with ID or congenital developmental genetic disorders because they really do tend happen together and/or their level 3 / severe autism make it hard for accurate IQ test this misdiagnosis
in practice it harder separate sometimes but that go for all comorbidity for all disorders. - what don’t understand is if autism severity should be null & void & not exist because most autistic people have comorbidities, then why shouldnt all severity be treated same way - get rid of because not including comorbid, or reranked to include comorbid? like it still not answer question of why autism treated different
& this thing about comorbidities kind of always go back to like. argument from LSN level 1 that their comorbidity cannot be separated from autism n should be more take into account so they’re not mild autism, but same time argue that people severe level 3 (or any ugly symptom) because just intellectual disability & not autism n need separated
n thing about levels & severity change over time, yeaaa, it unfortunately less known back then n even now. but by time, mean like over course of life, not switch back n forth between days or weeks or months (which sometimes what meant by some LSN level 1 people).
n it getting in way of support definitely issue, but think that more law issue & awareness issue (whole “mild/level 1 not need support” bs), still not inherent mild severity issue to me.
so again still don’t see what make autism so unique from other disorders that make mild severe uniquely bad for it?
really genuinely more n more sometimes struggle understand why so many people so against mild autism severe autism
all arguments don’t make sense to me when switch autism for another thing?
like mild depression not saying you have less depression than severe depression
n. to have mild depression mean your struggle clinically significant enough. but mild in comparison to what depression could be.
think lots disabled people feel like not struggle bad enough. which include severely disabled, not uniquely “mild” label thing? like me too? n also it not change what you able or not able do though?
if you argue there no mild depression severe depression it all just depression most people look at you silly
n don’t see it as inherently dehumanize either? like if have (& back when had) severe depression n people treat me bad abuse me for it (they did). think most people able know it fault of ableist people who abuse me, not caused by label of severe depression?
like to me mild severe just facts?
maybe it different because developmental disability which people treat as if nondisordered personality trait?
but then people argue against this also say have severe ADHD?
like why autism so special
genuine don’t understand
bc guess it really clear to me n not able ever imagine understand anyone think different… again
(if dont know you please don’t try explain it to me thanks)
216 notes
·
View notes
Note
You mention in posts how torture doesn’t make people obedient and usually makes them spiteful (which obviously makes sense), but isn’t it realistic for someone to comply out of fear rather than loyalty? Whether that was giving up information or obeying orders or something else entirely. I imagine it depends on the person, and they would probably still be willing to turn on their torturers if given the chance, but would it be possible for them to obey orders in hopes of avoiding more pain?
This is a much more nuanced and complicated topic then we’re taught to assume.
When it comes to giving up information it’s pretty clear cut. No, torture can’t lead to accurate information for a lot of interconnected reasons. I have about six separate masterposts covering the reasons for this.
One of those is the antagonism torture produces. Another is the memory problems torture causes. Another is the effect that the use of torture has on organisations and the chain of command. Another is the effect torture has on torturers.
Torture drastically increases the chances of memory loss and it also increases the chances of inaccurate memories. So not only is a torture victim less likely to talk, they’re more likely to be wrong if they do talk.
But the effects on victims aren’t the main reason torture doesn’t work as a way of getting information. You’re assuming that torturers have access to people who have information.
The reality is that torture destroys an organisation’s ability to gather accurate information. Most information comes from volunteers: when torture comes into play less people volunteer information. This means that an organisation which tortures is more likely to be questioning someone who knows nothing. That person is then abused until they start making things up.
Because there’s less access to volunteered information and because humans are very bad at telling when someone is lying, a lot of these made up stories are believed. And this then effects who else the organisation arrests and tortures. This creates a sort of spiral, with lies leading to more lies.
Additionally the torturers themselves make things worse. There’s less quality research on them, but the research and anecdotal accounts create a pretty clear picture of their behaviour. They undermine the chain of command, they lose the skills the originally had as they turn to torture, they’re aggressive, incredibly competitive and they have a… fracturing effect on their organisation.
Basically they’re incredibly difficult to work with and totally convinced of their own importance. And this effects their colleagues. It totally divides organisations. The worst case I’ve read about involved members of the same organisation killing each other over access to prisoners.
That’s a short run through of the main factors. Torture, in the legally defined sense, means all of these factors are in play. Plus a few more I’ve omitted to keep this shorter.
With all of that together you just can’t get accurate information.
If you want longer posts I’ve made on the subject I suggest looking for the ‘torture doesn’t work’ tag and the ‘torture as interrogation’ tag. You can also read the masterposts. If you want a much more in depth look at why torture consistently fails as a way of getting information I recommend O’Mara’s Why Torture Doesn’t Work and Rejali’s Torture and Democracy.
O’Mara is a neuroscientist and goes through the effects torture has on the brain in a way that’s accessible, explaining the damage torture causes and how that destroys the evidence torturers claim to be seeking. Rejali’s book is a breeze block but it’s really a must, it is the textbook on torture in a broad sense. He ties together information from across the globe creating a broader picture of what torture does, not just to victims but to societies.
The question of compliance under threat and pain… is more complicated.
People can be forced to do some things. That much is obvious from a brief glance at human history and things like slavery. But it’s important to listen to what people in these scenarios say.
And my opinion, based on what I’ve read, is that what these people say doesn’t support the idea that humans will easily obey instructions when they’re hurt or threatened. I think instead these people are making hard headed, rational choices in absolutely awful situations. I think when we don’t have these experiences of torture or slavery, it’s easy to look at the surface of the situation and assume that pain alone assures obedience. I think that happens because it’s hard for use to understand the rationale when we don’t have that lived experience.
Let me give some examples. So it probably goes without saying that slavery goes hand in hand with physical abuse. One of the major researchers on slavery, whose data I quote pretty regularly, assumes throughout his writings that pain is the deciding factor which ‘makes’ people obey.
But he also describes a couple of very obvious consistent patterns in the ways slavers behave. Slavers almost universally do the following things as well as using physical abuse:
Separate enslaved people from their community
Bar enslaved people from other forms of support
Make enslaved people financially/materially reliant on the slavers
Tell enslaved people that going to the police/authorities will lead to the enslaved person being arrested
Try to convince enslaved people that they will be better off if they comply, usually by framing it as a debt to be worked off with promises of riches after a period of time
Now here’s the thing: we know from studies on cults and studies on ICURE techniques that a lot of these strategies will result in obedience when there is no violence or physical abuse.
Given that I don’t think we can assume that violence is the deciding factor. In fact I think the evidence we have from forced confessions under torture suggests the violence may lead to less obedience and a lower ‘success’ rate then a set up that used emotional abuse or other exploitative techniques without violence.
We have two sources of historical data that are used for statistical studies on forced confessions. One is from historical France. We think that this data set only involved torture to force a confession; no other method of coercion just violence. The rate of forced confessions varied a little in different areas but over all it’s about 10%. The second data set is from the ‘London Cage’ a British prison during the second world war. Here we know that torture was combined with blackmail, bribery and other kinds of coercion. The rate of forced confessions there was about 30%.
And while this is just two studies, while the data is lacking… That is one hell of a jump.
Let’s circle back to ICURE. ICURE stands for Isolation, Control information, create Uncertainty, Repetition and Emotive responses. It’s a set of techniques which can, sometimes, change someone’s beliefs when it’s applied consistently over a long time.
Notice the effort slavers put in to isolating their victims. Notice that the behaviour pattern I’m describing means the slavers are creating uncertainty over seeking help and repeating those messages as well as messages that the victims will be better off if they just go along with it.
Slavers will generally also try to control the information their victims have access to, taking phones and blocking access to news sources and other resources. Now a lot of slavers will transport their victims to other states or countries putting a language barrier in place. They sometimes also use emotive responses in attempts to persuade victims to comply.
I’ve read multiple accounts where survivors of modern slavery described slavers telling them that the money they were making was being sent to the victim’s family and without it the family would not survive. (Sometimes the slavers do send small amounts to the families of their victims, sometimes they pocket everything.) I’ve also read accounts where gangs of slavers used religion and oaths taken in a religious setting to persuade their victims they’d be punished by God for not complying.
Even with all of this, all these techniques we know can sometimes ‘work’- lots of people refuse. Lots of people disobey. Lots of people escape. Lots of people actively sabotage the operations the slavers put together.
And if you look at that same history of slavery, that shows us people can sometimes be forced to work, you’ll see that this has always been true.
We have records of historic enslaved people attacking slavers, forming organised militias, forming parallel societies, sacking towns, taking over an entire Caribbean island and beating off four European armies in the process. We also have records of smaller acts. Sabotage, worship of banned deities, speaking banned languages, destruction of property, aiding in the escape of others.
What I’m saying is: this isn’t black and white. The evidence, modern and historical does not paint a clear picture of violence leading to obedience.
Instead I believe that it shows humans are resilient, stubborn, adaptable creatures. People can survive all kinds of horrible situations. It is more accurate, more human, to assume that people make rational choices.
Sometimes those choices involve short term compliance while looking for a better option or a way out. But we tend to hear less stories about the people who completely refuse to comply. We tend to treat that as an impossible fiction when it is a recorded historical and modern reality.
Bringing this back to writing as a general rule the more complicated the act the less likely you can force someone to do it. Because the more complicated it is the more opportunities they’ll have to sabotage it or use it against their abuser.
I recommend reading up on the history of Haiti pet. Then Brazil via Palmares.
I’ll end this by bringing it back to those statistics on forced confessions in historical France. Imagine the conditions with me for a moment. Unsanitary, cramped cells. Dehydration, starvation and disease. Plus the kinds of scarring torture that are conjured up in the minds of most Western people when the word ‘torture’ comes up; thumb screws, leg irons that tighten until the bone snaps, whips.
Picture it. Try to imagine the pain those people went through.
And remember that 90% of them did not comply long enough to sign their name.
Available on Wordpress.
Disclaimer
#writing advice#tw torture#tw slavery#tw racism#torture apologia#torture does not work#torture as interrogation#ways torture fails#resistance to torture#resistance to slavery#slavery#historical slavery#forced confessions#ICURE#coercion#compliance under threat#compliance under torture#writing victims#writing slavery#writing torture#writing responsibly
230 notes
·
View notes
Note
hi, rory! <3 what majors would the sc veterans take if they were in the modern world?
hi, anon !! thank you so much for this ask, this is heaven in disguise from all my schoolwork. tbh, the whole time i was working for a lab report, my mind will go back to this ask bc i wanted to have the association as accurate as possible hhhajshw
i asked one of my friends for help and thank God for them bc my single brain cell really said 'it's time for you to rest' after staring at one backlog. without further ado, here are the veterans' majors if they're studying in university:

first off, hange zoe, because if you ask me this question in real life, they would be the only one i can answer. every damn time i would think of them in a college setting, being a biology major is really hange's forte. at this point, this is what everyone would associate them with.
hange is all about experimenting and doing brilliant breakthroughs in any field of science but knowing that they have this unparalleled fascination with the unusual and unexpected life-forms (ahem titans ahem), the biology lab would be the surest place where you could find hange. i feel like biology is too broad so i will add that microbiology or bacteriology are just some of the specializations they will be taking in their time in college.
imagine, being lab partners with hange and immediately knowing that you will have one of the highest grades in the class because they're that well-versed in a specific lab report. and if you're partners with them for the rest of the academic year, you might as well have a shot at an immaculate grade. i'm not saying that you should depend on them too much though hHHHH, hange is still a member of the majority of the student body who relies heavily on caffeine to keep them invigorated. who isn't at this point?
so far, some of the biology majors that i encountered (well, more like chatted behind a screen — online classes suck), they have this energy that could drain my social battery too quickly and hange fits that description. (note that this doesn't apply to any college bc i observed this in mine soooo 🤭) they're the type to always go on a tangent on a certain science article or coerce you into joining this org thing. i can imagine levi just looking at hange like they're the one sucking his brain cells out whenever they speak about a documentary in bbc they watched the night before.
and if you're stuck on anything biology-related, hange will be the best person to ask help from. they're the first ray of sunlight you get while waking up. they're that approachable.

okay, so erwin smith.
don't come at me but he just radiates this ceo vibes and with that, one of his probably majors is business administration. i know this is so stereotypical of me but let's face it, erwin is a smooth talker through and through and if he doesn't take up marketing, business is one way to spend his college years. knowing his personality in attack on titan of establishing deals easily with a determined resolve, he fits the broadest description of being a business administration major. (again, don't come at me because my consultant for this statement is google and nobody comes after google sometimes hhhhh)
just for the benefit of myself, i will add what google says about this major, "[they] learn the mechanics of business through classes in fundamentals, such as finance, accounting and marketing ... students find ways to solve problems using data and they develop communication and managerial skills." and i thank you.
he's also probably the most well-spoken and most professional when conversing with others among his friends (and i'm not saying this to drag the other characters but this is what i pick up on) and that is exactly the qualities his major specializes. it is expected for them to strike deals and be a people person and who better character for the job than our very own erwin smith 🤩
now i mentioned 'one of the probable majors' and yes, aside from business administration, philosophy just exudes erwin smith. ngl, when i imagined erwin in a college setting, this major will always come first. his mind is just so sexy to me??? and i hope you guys think the same, too, because i don't want to be the only one who thinks that 👀 kidding aside, erwin is one of the smartest people in attack on titan and every time he speaks in one episode, my brain will instantly go mush, and that's what i feel when i hear philosophy majors talk.
philosophy majors (according to any other youtuber who does lookbooks for various majors hhhhhh) challenge what is unanswerable and analyze questions with no right answer. i feel like erwin, like hange, will talk all night to explain a theory. just imagine a date with him and you just listen to him rant about a topic that they should be making a report on. just listen to this man, okay?? it's adorable when he lets his guard down to include you in his little bubble of philosophies. he would also mention random things that he learned in classes, sometimes finding joy in knowing the philosophies of other people, or even deciphering levi's dream of an apocalyptic world. (it pisses levi off but he just leave him be.)
if you want a man who can do both of these majors, erwin smith is the answer 😉

sigh, mike zacharias.
this man holds so many talents and will forever amaze me.
i assume all of us here watched the movie perfume. and no, i'm not saying that mike is going to be a murderer but just like the main character of that film, making perfumes will be his forte with that sense of smell of his. and here, i conclude that mike will definitely take up chemical engineering.
he gives me the vibes that if it covers the one thing he does best, he will love his major. (mr. zacharias, can you please spare me that quality because i really need that now 😩) being in the labs while experimenting mundane things that can be found in the environment to create different scents is also a likely situation you can find him in, again, very much like hange. he's the type of student who really puts so much effort in staying afloat the honors list, even to the point of topping midterms in his major, for the sake of his dream. there will never be a moment where you will catch him complain about his major and professors.
he's that type of friend in college who agrees to any rant you say but in reality, he's got his life easy 😭
i headcanon mike owning a perfume shop after college just like how levi always dreamed of having a tea shop.
okay, imagine this little scenario if you're dating mike where he creates this unique perfumes as random gifts for you. they're not the typical perfumes that can seep through the room and can make you gag for no reason, they're subtle scents that will stay for the duration of the day. because again, he's got a sensitive nose, so making perfumes according to what his sense of smell dictates will always result in a revolutionary experiment. if you're randomly blurting out that you want a fusion of flowers and fruits as your perfume, say no more, he's your man.

now, the veteran who i find the hardest to associate a major with — levi ackerman.
after much deliberation and a break from plant physiology, i see him taking up law or criminology.
(i asked some of this from my mom because she attended law school :>>>)
levi is so organized and detailed in the things that he do and he fits in either of these majors since they require tedious memorizations and analysis of laws and crime scenes while being assertive enough to defend someone. he's the typical person who blurts out the true situation of a crime scene when watching film adaptations. yeah, he's that person, the one who sucks the enthusiasm out of you while watching a movie because he just had to correct some of the scenes. nevertheless, he means well though, he just wanted you to understand the reality unlike how films portray gruesome murders. movie nights always end up with levi ranting about half-assed mystery clichés.
levi's binder of readings are always too bright for everyone's good. his notes are full of highlighters and scribbles that it can blind someone. for one, he's always up all night studying his readings and cases for a practice court so by choosing neon highlighters, it's a way for him to wake up. there isn't one book in his possession that he doesn't highlight like it's a fricking coloring book. hange once jokingly said that his binder now acts like his bible and for once, he agrees because he was never seen without one. hange had a field day since levi never agrees with them.
when doing practice courts though, his go-to resting bitch face always come in handy when carrying out his role as one of the lawyers. he's just so sexy with his hands in the pockets of his slacks as he tries to justify his supposed client. the way he questions the accused definitely isn't hot because he's like one of the panelists in your thesis defense, the one who just comes up with questions that have you melting on the spot. he's dangerous i tell you. it also doesn't help if you accidentally hurt one of his friends or just landed randomly in his blacklist for being annoying as hell. relax though, he doesn't mean harm other than the fact that he's ready to throw some hands from all the pent-up rage he gathered in his body.
of course, i couldn't forget how he dresses up like a typical dark academia fanatic so look out for eye-candy.
if you want someone who can recite articles from the constitution, this man is perfect for you 😌

i had so much fun doing this !! again, i'm not generalizing every major i've talked about in these little headcanons, this is all for fun and based on the people i encountered in college. if you want more of this, don't hesitate to ask !! 😚
#attack on titan#aot#levi ackerman#aot x reader#attack on titan x reader#snk#levi ackerman x reader#attack on titan headcanons#hange zoe#hange zoe x reader#mike zacharias#mike zacharias x reader#erwin smith#college au#erwin smith x reader
161 notes
·
View notes
Text
Psycho Analysis: Suicide Squad Team A

(WARNING! This analysis contains SPOILERS! Seriously, as soon as you click that read more, you’re gonna be smacked with SPOILERS! Don’t say I didn’t give you ample warning this time!)
The world’s in danger yet again, and Amanda Waller is in need of some expendable forces to take on some dirty jobs in the name of preserving peace. Last time she did this, it seems like she hired the wrong people. Nice guy Will Smith Deadshot? Bland, boring Killer Croc? El Diablo, who became attached to a bunch of reprobates after spending a couple hours with them? The only one who was useful in that squad was Katana. She had their backs, could cut all of them in half with one sword stroke just like mowing the lawn, and her sword traps the souls of its victims. Unfortunately, she was decidedly not expendable, so what is a girlboss like Waller to do?
Easy: Assemble a brand new squad of criminals to do the dirty work. Harley and Boomerang are the only ones she brought back, because let’s be real, they’re the only ones we give a damn about. Filling out the rest of the squad are the stoic, craggy crackshot Savant; the handsome, German spear-thrower Javelin; the alien warrior Mongal; the frothing, psychotic animal Weasel; the confident and all-powerful TDK; and Blackguard, who is literally just a guy. Together, this team gets deployed to Corto Maltese to do what no one else can do, and with skills like theirs, they are absolutely unstoppable!
They all fucking die before the opening credits.
Motivation/Goals: Considering the goal of the squad is to shave time off their prison sentences by going on the mission, it’s ostensibly the reason every single one of these goons accepted the job. Savant and Weasel are pretty well established in this regard; we get to focus on Savant for much of the opening, so we can get a sense of him, and Weasel is stated to have murdered no less than 27 children. So, yeah, they need to do this mission.
The rest, though? Who knows! Why are Mongal, Javelin, and TDK in prison? How did they even get an alien like Mongal? What did they do to land in the position they’d need to go on a suicide mission? Why doesn’t this movie have flashy, intrusive cards explaining everything to us in a throwaway gag in a montage?!
Blackguard, at least, has some other motivation. He sold out the entire squad to the military of Corto Maltese, which is why they’re ambushed. Now, there’s actually some ambiguity here: Did he do this of his own volition, and was this a complete surprise, or is it, as it is heavily implied, all part of Waller’s plan and she let this happen as a diversion for the other team to get in unnoticed?
Honestly, though, it doesn’t matter what their goals are. They’re all dead within five minutes of the movie starting, with one exception.
Performance: So, the reason these guys are even worth talking about is because, despite their minuscule screentime, all of their actors manage to cram in enough humor and characterization that they’re all pretty fun and likable. Michael Rooker is as stony and stoic as ever as Savant (until he hilariously isn’t), Flula Borg’s Javelin is really sweet and charming in his interactions with Harley, and Pete Davidson’s Blackguard is just amazingly douchey and pathetic. Special mention goes to Nathan Fillion’s TDK, who has an utterly endearing and unwavering faith in his astoundingly crappy ability to… detach his arms. It’s honestly kind of beautiful. Then there’s Weasel as portrayed by Sean Gunn, who is just a hilarious crackhead of an animal man.
Final Fate: Literally every single one of them die horribly thanks to Blackguard’s betrayal. He’s the first to go, because as soon as he walks out saying “Hey guys, it’s me, the one who contacted you!” he literally has his face blasted clean off. The rest go soon after. Mongal, in one of the most astounding moments of idiocy I’ve ever seen, leaps on a helicopter despite Rick Flag telling her specifically not to. Her weight and strength send it careening out of control, which leads to it shredding Captain Boomerang to bits before exploding, burning her alive as she painfully screams and writhes in agony. TDK gets his arms shot into Swiss cheese, leading to him bleeding out since even detached they still are part of him. Javelin is also shot, but gets a dying moment with Harley where he passes her Checkov’s Javelin. Finally, after witnessing all of this carnage, Savant completely loses his shit and tries to swim away, leading to Waller blowing his head up.
You may be wondering what happened to Weasel. He appears to drown as soon as the Squad deploys, because despite being actually smart in this movie, Waller forgot to make sure everyone on the Squad could swim. Thankfully, this lovable child-murdering crackhead rodent was just sleeping, and wakes up in the first credit scene.
Best Scene: Obviously, it’s their one and only scene. It’s a magnificent slaughter that puts the X-Force scene from Deadpool 2 to shame.
Final Thoughts & Score: I’ve gotta hand it to James Gunn. Even though these losers are only onscreen for a few minutes, they all get to cram a lot of charm and personality into that time, to the point it’s actually kind of sad seeing them all die. It’s a beautiful mix of comedy and tragedy. Since their screentime is so limited, though, I’m mostly going to be grading them on style, performance, and so on rather than on villainy like normal. They are all bad guys, as they don’t really get a chance to redeem themselves like the other Squad, so I’m still counting them as villains, which means they could potentially score above an 8 (which is the highest score I’m willing to give heel-face turn villains, because they end up being better as characters in general than as villains).
I’m also not going to talk about Boomerang (I’ll talk about him when I review the original Squad) or Harley (because she not only lives, but deserves her own solo Psycho Analysis). Now here we go, from best to worst:
TDK
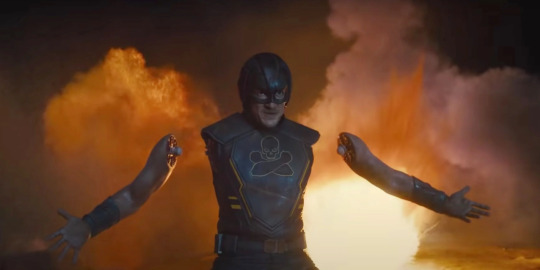
If you thought anyone but TDK would get top marks, you’re sadly mistaken. Seeing Nathan Fillion proudly wield the insanely lame power to detach his arms to lightly tap soldiers on the head and gently grab their guns is a sight I never knew I needed to see until this movie. The fact he just seems so darn proud about this power that he doesn’t even bother to use in any way that would be remotely useful is honestly really endearing. Frankly, the sheer fact they adapted Arms-Fall-Off Boy in any way is enough for me to give him a 10/10.
Weasel

Weasel is just disgustingly delightful. He’s just a horrible, nasty, ugly little bastard… But he’s kind of adorable? He clearly has no idea where he is at any given time and is just so goddamn freaky that I can’t help but love him. The fact that, despite being a character who in the comics is noteworthy only for dying on his first mission with the Squad, he manages to survive the entire movie is pretty impressive. Hopefully he comes back in the future, but either way he gets an 8/10 from me.
Javelin

Honestly, aside from Boomerang, his death stung the most. He’s just so cute and charming, and he doesn’t even get to fling his javelin at anyone! Thankfully, he passes it on to Harley, and boy does she ever get to use it! He’s so cute, I have to give him an 8/10. I just wish we got more of him.
Savant

Savant is just an absolutely hilarious bait-and-switch. We follow him through the prologue, with everything seeming to point to him as our main character and the Squad leader. He’s stoic, he’s cranky, and he has impeccable aim… and then we get to the beach and he just freaks the hell out and starts screaming and crying and running away like a little bitch. Seeing Michael Rooker act like he’s shitting his pants after playing a badass like Yondu is just the sort of hilarious subversiveness that James Gunn loves to do when you let him loose. The fact that he looks like, to paraphrase the TVTropes YMMV page for the movie, a “cyberpunk Tommy Wiseau” is the icing on this 7/10 cake.
Blackguard

I was prepared to hate this guy just based on how lame Pete Davidson’s costume was, and you know what? I do hate him. But I love to hate him. He’s just an utterly pathetic scoundrel and a coward, true to his name. The fact he is the first to die, as just about everyone predicted, and is killed absolutely gruesomely makes any annoyance he could provide moot, and his freeakout over being seated next to Weasel on the plane is actually kind of funny. I was originally going to give him a 6, but you know what? He can have a low 7/10. He’s like the only member of this particular Squad to actually do anything evil, so I gotta give him props for that.
Mongal

Let me make this perfectly clear: I do not blame James Gunn or actress Mayling Ng. I’m not actually mad at either of them for what they chose to do, because it is ultimately hilarious and sad. It suited the narrative of the film, and I’m not actually, genuinely mad.
With all that out of the way, Mongal is one hell of a stupid cunt. It is one thing to cause your own death with your stupidity, it is something else entirely to cause the death of a beloved character with your poorly planned attack. The fact she didn’t take into account how her weight and strength would effect an airborne helicopter makes one wonder if she is really supposed to be based on a character who can take on Superman and live to tell about it.
Let’s compare her to two similar characters to really show how bad she is. Like Blackguard, she is directly responsible for a death on the beach, Blackguard being responsible for everyone by selling them out and leading them into an ambush (and yes, I’m including him as well), and Mongal killing Boomerang with the chopper. The difference is, Blackguard’s betrayal was deliberate, he meant to sell the team out, he was actively doing something evil there, while Mongal killed Boomerang out of sheer idiocy.
Now, let’s compare her to Zeitgeist from the similar bloody massacre that occurred during X-Force’s deployment in Deadpool 2. Like Mongal, he accidentally kills a teammate. The difference is, in the case of Zeitgeist, he only accidentally melted Peter, it was a freak accident, and ultimately it does get undone by the end. Meanwhile, Mongal made a conscious, stupid decision and ended up killing her squadmate with her own idiocy. She sucks, hardcore. I don’t do this lightly, but I’m giving her a 1/10. Villains just don’t get much stupider than her.
I will giver her this, though: the makeup work on her is good. She’s lowkey kinda hot if I’m being honest. But being hot and having good makeup does not a good villain make.
#Psycho Analysis#The Suicide Squad#Savant#Michael Rooker#Javelin#Flula Borg#TDK#Nathan Fillion#Weasel#Sean Gunn#Mongal#Mayling Ng#Blackguard#Pete Davidson
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transcript Lingthusiasm Episode 52: Writing is a technology
This is a transcript for Lingthusiasm Episode 52: Writing is a technology. It’s been lightly edited for readability. Listen to the episode here or wherever you get your podcasts. Links to studies mentioned and further reading can be found on the Episode 52 show notes page.
[Music]
Gretchen: Welcome to Lingthusiasm, a podcast that’s enthusiastic about linguistics! I’m Gretchen McCulloch.
Lauren: I’m Lauren Gawne. Today, we’re getting enthusiastic about writing as a technology. But first, do you wish there was more Lingthusiasm to listen to? Even though this is Episode 52, we have almost a hundred episodes of Lingthusiasm. Some of them exist as bonus episodes over at our Patreon.
Gretchen: If you want to listen to those and have more Lingthusiasm in your earballs, you can go to patron.com/lingthusiasm. This also helps keep the show ad-free. If you like listening to a show without ads, help us keep doing that.
Lauren: The Patreon also fosters this wonderful linguistics enthusiastic community. In fact, we have a Discord server, which is basically just a wonderful chat space for people to talk about linguistics. There are over 350 people on the Lingthusiasm Discord right now.
Gretchen: If you wish you had other lingthusiasts to talk to to share your interesting linguistics anecdotes and memes and general nerdery, and you want more people like that to talk to, you can join the Patreon to also get access to the Discord. We launched the Discord community just a year ago, and it’s been really fun to see it grow and thrive and take on a life of its own since then. If you are already a patron, and you haven’t linked your Patreon and Discord account together, it’s there waiting for you. Feel free to come join us.
Lauren: We have Patreon supporter levels at a range of tiers. Some of them include additional merch. One of my favourite perks is the very scientific Lingthusiasm IPA quiz where we send you a short quiz and then we give you your own custom IPA character which is enshrined on our Wall of Fame.
Gretchen: It’s a fun quiz. We have fun looking at people’s answers.
Lauren: Our most recent bonus episode is a collection of some of our favourite anecdotes from interviews and from other episodes that didn’t quite make it into the original episode. We’re delighted to share those in that bonus episode.
Gretchen: You get to see a bit behind-the-scenes with that episode. Also, do you want more linguistics on your favourite other podcasts?
Lauren: Always.
Gretchen: Constantly. We’re also very happy to do podcast interviews on other shows about various topics. If there’re other podcasts that you like that you wish would do a linguistics episode and interview one of us, you should tell them that! We’re happy to come on. Tag us both or something on social media or tell your favourite podcasts that they could do a linguistics episode because we’d be happy to do that.
[Music]
Lauren: Gretchen, do you remember learning how to read?
Gretchen: Not really. I mean, I remember encountering the alphabet chart in my first year of school, but I already sort of knew the alphabet at that point. I guess there was some point when I didn’t know how to read, and there was some point when I did, but I don’t really have concrete memories of that. Do you remember learning how to read?
Lauren: I feel like I have more memories of learning how to write, just because that’s such a mechanical thing. I remember sitting there writing out a row of As. I definitely wrote the number “five” backward for way longer than I probably should have, which is a really common thing that happens when kids are learning to write because it is a combination of brain skills and fine motor skills. But reading in English is something I feel like I’ve always just been able to do. I mean, I guess in comparison learning to read Nepali, which is written in a different script – it’s written in the Devanagari script – I have more memories of that because I did that in my 20s. Even now, I still feel the real disconnect between being relatively able to chat and really struggling to read and write. I still have to put my finger under the words as I’m going through, whereas with English it just feels like the words are beaming straight into my brain because I learnt to read that language so early in my life.
Gretchen: Yeah, I read at this automatic level. I can’t see a sign that says, “Stop,” on it and not read it in Latin script. But in undergrad I took both Ancient Greek and Arabic. In Greek, I got to the point – because the script is sort of similar enough and I was familiar enough with the letters previously-ish – that I got to the point where I could very slowly sound out words as I was reading them out loud because we had to do a lot of reading aloud in Greek class. But in Arabic, I was very much at that hooked on phonics level where you’re like, /p/-/t/-/k/-/a/. There are a few words that I have as sight words in Arabic. One of them is the word for “and,” which is “waa”, and one of the words for “the,” which is “al”, and one of them is the word for “book” because “kitaab” just shows up all the time. But most of the words I had to painstakingly sound out each letter and then listen to myself as I was saying them. I’d be like, “Oh, it’s that word,” even if I knew it, which is this process that I must’ve gone through in English, but I don’t remember doing it for the Latin script.
Lauren: I think that is one of the things that makes it really hard for people who grow up in highly literate, highly educated societies to tease writing and reading apart from language. But actually, when you step back, you realise that writing is actually super weird.
Gretchen: It’s so weird! It’s this interesting – it really is a technology. It’s a thing you do on top of language to do stuff with language, but it’s not the language itself. There are thousands and possibly millions of languages that have never been written down in the history of humanity. We have no idea. We’ve never met a society of humans, or heard of a society of humans, without language. But those are spoken and signed languages, which are just kind of there. Writing, by contrast, was invented somewhere between 3 and 4 times in the history of humanity.
Lauren: That we know of.
Gretchen: That we know of.
Lauren: There might’ve been a society that did a very ephemeral form of snow writing that we have lost forever. But we have records of 3 or 4 times.
Gretchen: It’s been invented a handful of times. There are a few other cases where there are scripts that haven’t been deciphered by modern humans. Maybe they’re scripts, maybe they’re not – it’s not quite clear. But it’s definitely a handful of number of times. And then once other cultures come in contact with the technology of writing, they’re like, “Oh, this is cool. Let’s adapt this to our linguistic situation,” and it gets borrowed a heck of a lot. But it only got cemented a few times.
Lauren: It’s worth saying that “3 to 4” is a bit squishy because it’s not entirely clear if cuneiform, which is a very pointy form of writing from Babylonia, somehow inspired the Egyptian system that became what we know as the hieroglyphs or if they just happened around the same time by coincidence are something we may never really fully put together. That’s a very contested situation. That’s why we can’t even pin down the number of times we think it was invented.
Gretchen: Cuneiform is the one that’s made with the sharpened reed that you push into your clay tablets or, if you’re some people on the internet, into your gingerbread because there’s some really excellent examples of cuneiform gingerbread tablets people have made, which I just wanna – yeah, it’s really great. The Egyptian hieroglyphs people have seen. But yeah, it’s unclear whether they were in contact with each other and kind of heard of each other in a very loose sense and were inspired by each other because there was some amount of contact between those two areas, or if that was elsewhere. The other two – one is in Mesoamerica, in modern-day Mexico and that area, where they had a writing system there that, again, developed into lots of different scripts as it got borrowed from different areas, of which the best deciphered is the Mayan script from the 3rd Century BCE. There’s also the Olmec script, which is probably the oldest. The Zapotec script is also really old. There’s a bunch of scripts in the modern-day Mexico area that also developed independently.
Lauren: Then the final system arose in China around the Bronze Age a couple of thousand years BCE. Because this script was mostly found in its most earliest forms on oracle bones, it’s known as the “oracle bone” script.
Gretchen: What is an oracle bone?
Lauren: They are turtle bones that are used in divination.
Gretchen: Oh.
Lauren: Yeah.
Gretchen: And, again, the Chinese script, once it developed further, it was also, yeah, influenced a bunch of the other writing systems in the area.
Lauren: I find it super fascinating, with absolutely no historical knowledge or insight to bring to this, that in these three different places that were completely separate and going about their own cultural lives writing arose at a similar time around 3,000 to 4,000 years ago.
Gretchen: Yeah! You wonder what was in the water or something. Well, and it’s partially, I think, that there’s a certain level of writing makes it easier to do things like administrative bureaucracy if you’re trying to keep track of whether people paid their taxes or – it’s a very empire-y thing to have is to develop a writing system.
Lauren: Oh yeah. And it’s absolutely worth stating that it’s not like three people in these three different locations all woke up on the same Tuesday 4,000 years ago and were like, “I’m gonna write a long letter to someone.”
Gretchen: Did they have Tuesdays 4,000 years ago?
Lauren: What you see is this emergence of, “I’m just gonna make a couple of notes so I know how much money you owe me.” Some of the earliest cuneiform tablets we have are just, like, beer supply stock takes.
Gretchen: Like, “Three oxes and this many baskets of grain” or whatever.
Lauren: I feel like it’s very human to be like, “We love writing because it’s poetry, and I can send letters to people I love,” and it’s like, no, it’s actually, “I just wanted to know how much you owe me.”
Gretchen: The king just wants to know if these people have paid their taxes.
Lauren: So, what you get is – although I’m like, “Oh, it all happened within similar millennia,” it is actually centuries of development from just keeping tabs on a few items to a fully fleshed out written system.
Gretchen: What types of things people thought were important to write down – things like legal codes and stuff like that – one of the interesting things that I came across when I was looking this up was that there’s a person named Enheduanna, who is the earliest known poet whose name has been recorded. She was the high priestess of the goddess Inanna and the moon god Nanna in the Sumerian city-state of Ur. There we go. But authorship shows up much later than some anonymous civil servant keeping track of who’s registered which grain or some anonymous priest or something keeping track of who’s made various offerings. This idea of like, “Oh, you’re gonna write poetry,” is a step later.
Lauren: Filing your tax is what is actually one of the best links you have to those ancient civilisations.
Gretchen: There’s this Egyptian named Ptahhotep – that’s “Pta,” P-T, even though I know I’m not pronouncing it that way – he was a vizier in Egypt. He’s also one of the first named writers, the first book in history – or people call him the first book in history – because he wrote these Maxims of Ptahhotep. There may have been people who were writing on more perishable materials that didn’t get recorded and stuff like that. It’s this whole process of, “Okay, I’m going to draw these little diagrams of oxen or something or draw these little diagrams of this plant or this animal or whatever to record what types of things get recorded.” But then in order for it to actually become a writing system, there’s also this step of abstraction that has to happen. This is when you start saying, “Okay, well, the word for this very easily visualisable thing” – so I’m thinking of oxen because the word for “ox” in one of the Semitic languages, I think, was something like /alef/. And so, this “ox’s head” gets transformed into, “Okay, what if this is the sound at the beginning of the word for ‘ox’s head,’” which is /alef/, and it gets transformed into our modern letter A, which is “alpha.” “Alpha” in Greek is just the name of the letter. It’s not “an ox’s head” in Greek anymore because the Greeks borrowed it form the Phoenicians. This level of abstraction that has to go from, “Okay, I’m gonna draw an ox’s head” – if you turn a capital A upside down, it kind of looks like an ox’s head.
Lauren: It’s got its little horns, which are the feet of an A.
Gretchen: Yeah, and there’re all these related languages. You know, Arabic’s got alif at the beginning, even though it doesn’t look like an ox’s head anymore. Hebrew’s got an alef, and Greek’s got an alpha, and all of these alphabets that begin with A. It’s this level of abstraction where you can use this thing to stand for this thing that was associated with an ox.
Lauren: There’re a couple of main different ways that you can relate these abstract images that you’re putting down in writing to the language that you are trying to capture. Of course, being a linguistics podcast, I was gonna bring this straight back to the structure of language.
Gretchen: Well, I think it’s interesting to look at the structure of languages in different areas of the world, and how people reflect those in the writing systems that are developed for those languages. When they borrow a writing system for a language with a very different structure, they end up doing certain adaptations to account for not just like, “Okay, languages have different sounds,” but also those sounds are organised and structured in different ways with relationship to each other. The writing systems often reflect some of that history.
Lauren: The Latin alphabet that both of us are most familiar with has a very approximate correspondence between each character of the writing system and a sound in the language. And I say “approximate” because English spelling is a wonderful historical record of how some of those sound changes have changed over time. I’m just gonna keep this upbeat. You can fall down a giant well of English writing system problems, but to get to a point where the majority of letters have a pretty stable correspondence to sounds that we recognise as phones in the language, and that allows us to write out the words of English.
Gretchen: One of the things that’s true about a lot of the Indo-European languages is that they have a particular ratio between consonants and vowels in the words, where they have a fair bit of consonants in relationship to their vowels but not a ton. You can see this in the writing system because the writing system represents consonants and vowels separately. And yet, when the Greeks were borrowing the alphabet from the Phoenicians – Phoenician is a Semitic language like modern-day Arabic and Hebrew – that alphabet only had consonants in it – letters for consonants – because the vowels were not that important. This is still true of modern-day Semitic languages is they’re often written in writing systems that don’t represent the vowels or kind of optionally represent the short vowels, or sometimes they represent the long vowels, but they’re often written in writing systems where the vowels can be omitted. That’s not really a thing you can do very well in Indo-European languages and still have things understood because the vowels carry enough information that you need to represent them somehow.
Lauren: Even when you have a phonemic script, it’s not necessary to always represent all of the sounds to convey the language.
Gretchen: Right. Then conversely, there are other languages where the vowels are even more important and, in fact, every consonant comes with a vowel or virtually every consonant comes with a vowel. In those, you often get what are called “syllabaries,” where they represent one syllable at a time, because why bother with representing each of these things separately when in every context where you have a consonant there’s gonna be a nearby vowel – or in virtually every context there’s gonna be a nearby vowel – and so you can have a symbol that just represents the whole syllable there. That’s also a structure that doesn’t work very well for Indo-European languages because they don’t have that many vowels. There’s this spot of like they have important enough vowels that you need to represent the vowels somehow but not so important are vowels that you have to represent lots of vowels all the time, whereas languages like Japanese or Hindi – well, Hindi’s Indo-European, but it’s got more vowels, I guess.
Lauren: The Devanagari writing system is inherently focused on the syllable, which is a very different approach to reading. Each character of this writing system, if there’s no vowel specified, it just comes with a bonus vowel. It’s like, “Buy this consonant, get this free letter A sound.”
Gretchen: Right. That’s partly a feature of the writing system, but it can only be a feature of the writing system because it’s already a feature of the language. A similar thing goes for a language like Chinese, where a lot of things are based around a syllable.
Lauren: Then you can go a level of abstraction further where your character in the writing system represents a word-level thing and doesn’t have a direct relationship to the sound correspondence, which is what happens with the Chinese script.
Gretchen: I think it’s important to recognise that there is a phonetic component to Chinese characters. They often make use of – especially for words that are more abstract – it’s not just like, “Oh, here’s a bunch of little pictures that we’ve drawn,” because that’s not capable of conveying abstract concepts like grammatical particles and words for things that don’t come with easy pictures. And so, making use of, “Okay, a lot of our words are one or two syllables long, so here’s a word that’s relatively easy to visualise that sounds very similar to a word that is not as easy to visualise.” We can just add a thing to be like, “It sounds like this, but it’s got a meaning more related to this,” and you can be like, “Oh, it must be this more abstract word.” The classic example, which I’m definitely gonna do the tones wrong on, is that the word for “horse” is /ma/, and the word for mother is also /ma/ with a different tone, and you can add the little horse semantic component with the woman semantic component and be like, “Oh, it’s the word that sounds like ‘horse’ but has to do with something with a woman,” and then you end up with “mother.”
Lauren: This works for languages in China because they tend to be not as long as words in English. We like to add all these extra bits of morphology within our grammar, whereas, again, you get – not a direct rule force – but you get this general tendency where the writing system kind of fits with the vibe of the grammar of the language.
Gretchen: One example of that is in Japanese where they were heavily influenced by the Chinese script, but Japanese actually does have suffixes and other little grammatical words and things you need to change about words. They made some of the Chinese characters that had formerly only had semantic things into just like, “Oh, this makes this sound, and this makes this sound,” because they needed to be able to represent that morphological information that’s not super important in Chinese but is very important in Japanese. You end up adapting a script into something else when it gets borrowed in a different context. Another interesting example here is Farsi or Persian which is an Indo-European language that’s conventionally written with the same script as Arabic except it’s also had a couple of additional letters added because Persian has a P and Arabic doesn’t. They had to create a symbol for the sound P, which is why you get “Farsi” instead of “Parsi” because Arabic doesn’t pronounce that P. So, it makes the P into an F. Sometimes you get people adding additional letters like adding a letter for P. Sometimes you get adapting whole sets of a script.
Lauren: Sometimes you lose letters. English had distinct characters for /θ/ and /ð/ until it was technologically easier to just use the characters in the printing press that English had borrowed. It’s makes me a little bit sad. But also, it makes international people – maybe it’s a little bit easier.
Gretchen: We used to have a thorn for the /ð/ sound, but those early printing presses from continental Europe didn’t have thorns on them. I mean, Icelandic still has thorns. One of the things that I think is more interesting in the closer to modern era – not strictly modern era – is cultures and peoples that are familiar with the idea of writing yet take the idea of writing and say, “We’re gonna make our own homegrown script that actually works really well for our particular language.” One of my favourites is the Cherokee syllabary, which was invented by Sequoyah, who was a Cherokee man who didn’t know how to read in English, but he’d encountered the Latin-based writing system in English. He thought it was cool that the English speakers had this, and so he locked himself in shed for several years and came up with a syllabary for Cherokee. Some of the symbols on the Cherokee syllabary look something like Latin letters, but they stand for completely different things because he wasn’t just learning to read from English. Some of them are completely different. This became hugely popular among the Cherokee in the area. There were newspapers in this in the 1800s. There was very high literacy in Cherokee country. It was really popular. It’s even still found on modern-day computer keyboards and stuff like this. You can get Windows and stuff in Cherokee. It’s this interesting example of that’s one where we can say a particular person was inspired by writing systems but also created his own thing that became very popular.
Lauren: The thing that makes Cherokee so compelling to me is not only did he come up with an incredibly elegant, well thought out, suits the language system, but that he actually got uptake as well – that the community decided to use this as the writing system that they would learn to read and write in, and that it had uptake. It’s very easy to come up with ways of improving the technology of writing but, as I think you’re fond of saying, language is very much an open-source project. You can come up with really elegant solutions, but if no one else is gonna take them up, that’s not gonna be very helpful. So, Sequoyah’s work is doubly amazing for that reason.
Gretchen: People actually made printing presses with the Cherokee symbols and were using those. Another interesting case of this disconnect between a person or people coming up with a system and actual uptake of it is Korean, which has what I think linguists generally agree is just the best writing system.
Lauren: Yeah, we’re like, “Writing as a technology is amazing. All writing systems are equally valid. But Korean is particularly great.”
Gretchen: “But Korean’s really cool.” The thing that’s cool about it from a completely biased linguist perspective is that the writing system of Korean, Hangul, the script, is not just based on individual sounds or phonemes, it’s actually at a more precise level based on the shape of the mouth and how you configure the mouth in order to make those particular sounds. There’s a lot of, okay, here are these closely related sounds – let’s say you make them all with the lips – and you just add an additional stroke to make it this other related sound that you make with the lips. Between P and B and M, which are all made with the lips, those symbols have a similar shape. It’s not an accident. It’s very systematic between that and the same thing with T and D and N. Those have a similar shape because they have this relationship. It’s very technically beautiful from an analysis of language perspective.
Lauren: I love this so much that when we were prototyping a potential script for the Aramteskan language for the Shadowscent books, when I was constructing that language, I also started constructing a script that we never used anywhere, but it was helpful to think about how the characters would write and what writing implements they would use. If you look at the script, you’ll notice that the letter P and B are very similar, but B has an additional stroke. T and D are very similar, but D has an additional stroke. Very much feature driven. And then for the vowels – it’s roughly a quadrant in the writing space – the /i/ vowel is in the top left of the quadrant, the /u/ vowel is in the top right of the quadrant, the /a/ vowel is in the bottom left of the quadrant.
Gretchen: So clever!
Lauren: It was actually just for really selfish reasons that I decided to go with a feature-based system, and that is that it was easier for me to remember if I used the features of the language and made sure that the voiced sound was always identical to the voiceless one but just with an additional stroke. It meant that I only had to remember half the characters.
Gretchen: That’s very elegant. The easy to remember bit is also true about the Hangul script because it’s got so much regularity. The famous quote about Hangul is something like “A wise man can learn it in an afternoon and a foolish man can learn it in a day.”
Lauren: So catchy!
Gretchen: There’s probably a better version of that quote. What’s interesting about it from an adoption perspective is that Hangul was invented by Sejong the Great.
Lauren: Appropriately named.
Gretchen: Who has a national holiday now because of the script. But it was created in 1443. It’s not quite clear whether it was him personally doing everything or whether he had an advisory committee of linguists, but it’s really extremely well-adapted to the linguistic situation of Korean in particular. Even though it’s just also really cool for how it represents the inside of the mouth, but it’s really well adapted for Korean. It was invented in 1443, but it wasn’t popularised in use until several centuries later because for a long time Korean was also using, like Japanese, this adapted version of the Chinese script or adapted version of the Japanese script because of the cultural influences. In the early 20th century, they were doing a much bigger literacy push in Korea to be like, “What want everyone to learn how to read.” And they said, “Okay, we’re gonna have an orthographic reform, and we’re gonna use this script which has this very nice historical pedigree but also is much easier to learn than this complicated thing that we had done that wasn’t really designed for Korean.” It’s got this historical antecedence but also it came back in the modern-day. Now, everything in Korean is written in it. It’s because it’s really easy to learn how to read and write in. The historical uptake wasn’t immediate. It wasn’t during King Sejong’s lifetime where they were like, “Oh, yeah, now we’re all gonna use his script,” people were like, “Okay, king, you’ve got this hobby,” but it wasn’t popularised until later.
Lauren: Even when there is really strong abstraction, humans have this unavoidable tendency to think about the relationship between sounds and other senses. In sound-based writing systems – Suzy Styles, who has been on the podcast before and works on perception across the senses, did an experiment alongside Nora Turoman where they looked at whether people can guess, for writing systems they’re not familiar with, which character was the /u/ sound and which character was the /i/ sound. They found that for a whole variety of scripts there is a much higher than chance – because there’s only two choices. If was completely arbitrary, it would be 50/50. But people do tend, across the evolution of sound-based writing systems, to have /u/ that has a more rounded, bigger sound has properties in the writing system that re-occur. People continue to unavoidably link the sounds of the language to the written properties of the script in a very low-level way. I’ll link to that study. It’s really great.
Gretchen: That’s interesting. It’s not gonna be 100%, but there’s this slightly better than chance relationship.
Lauren: Yeah.
Gretchen: Visual representation of physical information is also something that shows up in ways of writing signed languages.
Lauren: Yeah. Everything we’ve talked about so far, I think, we’ve talked about for spoken languages, but it is possible to write signed languages as well.
Gretchen: There are several different systems in place. Some of them are language-specific like, “Oh, this is the system for writing ASL in particular,” and some of them are kind of like your linguist, International Phonetic Alphabet trying to provide a language-agnostic way of writing signed languages for research purposes but, in a way, that’s sort of impractical, like the IPA for general use. There’s an interesting set of systems. There isn’t as much agreement among representers of signed languages in writing which amounts of information are crucial information that has to be written down and which are optional bits of information that the reader can fill in from their own knowledge of the language and the signer.
Lauren: I think it’s worth flagging that that’s not just a discussion that arises for signed languages. It’s just that those conversations got thrashed out for spoken languages four millennia ago, and we weren’t around when people were arguing about whether intonation had any role in the – or people probably were arguing because it was an emerging thing.
Gretchen: Well, when people were arguing about like, “Do we write vowels or not,” which was a big thing. Do we write vowels? Do we write intonation? And punctuation followed quite a bit after – you know, punctuation wasn’t as much of a thing for several of the early centuries and millennia of writing. They didn’t do punctuation. There’s some level of ongoingness that’s still there. If you think about the internet efforts to try to write tone of voice very precisely and communicate sarcasm and irony and rhetorical questions very precisely, there’s some level of ongoing debate that’s still happening in the spoken language context but not nearly as much as is still happening in the signed language context.
Lauren: Also, just because of the way that signed language communities tend to be embedded within larger spoken language communities, people who sign as a primary language tend to also be educated in the mainstream spoken language, and so literacy gets developed in, say, a language like English.
Gretchen: I think that’s the case for a lot of smaller spoken languages as well where sometimes there’s this imperative of, “Okay, we want to be able to write things to each other” or something, but if there hasn’t been a history of a lot of published literature in that language that you’re trying to read, then it becomes a question of, “Should we teach this in school,” because there isn’t literature there, even though there would be oral literature. It becomes a chicken and egg problem of which comes first, or which do you start teaching first, when you’re constantly comparing stuff against a few very large spoken languages that have this very long writing tradition. It shows up in languages with a newer writing tradition.
Lauren: Education systems have a massive influence there. My grandmother, actually her strongest written language is German. Even though she and her sister speak to each other in Polish, they would write to each other in German because that’s the language they had been educated to write in. Even with people who don’t speak minority languages, the influence of the education system there is so massive.
Gretchen: Reading and writing, they’re separate skills even though they’re often taught together. Sometimes you can read a language that you can’t write or something like that. But it’s a big question. With signed languages, because video technology is now available, if we’d had good audio recording technology 4,000 years ago, the pressure to develop writing systems for spoken languages might not have been as strong – probably wouldn’t have been as strong – even though there are other useful things that writing can do even in the audio-video era. It’s easier to be like, “Well, you can just make a video of the signer,” and then you’d know exactly what they were trying to say and exactly how they wanted to say it. You wouldn’t have this level of abstraction of are you gonna try to write it down in a way that imperfectly represents what a person is gonna do when they’re producing it. It is still interesting looking at some of the signed language writing systems. Some of them, like Stokoe notation and HamNoSys, which stands for “Hamburg Notation System,” they try to very physically represent the characteristics of the signer – where their hands are, where their face is, and things like that. There’s another one that I can’t find the name of that is based on the ASCII alphabet, so you can type it into search engine boxes, which has some advantages as well but represents things more abstractly. It’s got this link with Korean, which was representing this very physical aspect of what the mouth is doing. Several of the signed language writing systems like Stokoe and HamNoSys also have this very physical representation what the body’s doing when it’s being produced. But I think they’re more popular among researchers than they are among actual D/deaf users who tend to use video a lot.
Lauren: I encounter Stokoe and HamNoSys in the gesture and signed linguistics literature. I haven’t really seen them too much outside of that.
Gretchen: I think that it’s easy to conflate a language with its writing system because we’re so used to thinking of English as sort of inextricably linked to the Latin alphabet. But there isn’t a reason, in theory, why you couldn’t write English in the Greek alphabet or in the Arabic alphabet or in a very adapted version of Chinese characters where you’d have to do a lot of adaptation. The same thing is true when you write languages that don’t originally use the Latin alphabet and you have romanisations of them. Writing systems are just as much political and contextual. Some of them have this very tight structural relationship to the properties of the languages they represent and some of them have looser relationships because they’ve been adapted to it later.
Lauren: It’s this slightly looser relationship to language as it’s spoken or signed that means that linguists don’t always include writing systems in, say, an Introduction to Linguistics course. We don’t often talk about writing systems. But when we were putting together the Crash Course series, we ended up making writing the topic of our final episode for the series.
Gretchen: I think partly because people are really interested in it, so why not do something about writing, and also because I think that you can use writing systems as a window into some of the interesting structural features of different languages and how the writing systems represent that. As somebody who’s really interested in internet linguistics and the rise of informal writing and how we represent tone of voice and things like that in modern-day writing, and that’s still a moving target evolutionarily speaking, I think it’s interesting to give that linguistic lens on writing systems even though they are imperfect representations of the languages that they represent.
Lauren: “Writing Systems” is Video 16 of Crash Course linguistics, which is wrapping up this month. If you’ve been holding out to watch all 16 of those episodes, you’ll be able to do so very soon or perhaps even now thanks to the temporal vagueness of podcasts.
Gretchen: Crash Course is the YouTube series that we’ve been working on basically all of 2020. It’s especially popular with high school or undergraduate teaching. If you know people that age, or who teach people that age, that may be a useful thing to send to people. We hope that people find it useful as a resource for self-teaching or for instructing in various capacities.
[Music]
Lauren: For more Lingthusiasm and links to all the things mentioned in this episode, go to lingthusiasm.com. You can listen to us on Apple Podcasts, Google Podcasts, Spotify, SoundCloud, YouTube, or wherever else you get your podcasts. You can follow @Lingthusiasm on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and Tumblr. You can get IPA scarves, “Not judging your grammar, just analysing it” mugs, and other Lingthusiasm merch at lingthusiasm.com/merch. I tweet and blog as Superlinguo.
Gretchen: I can be found as @GretchenAMcC on Twitter, my blog is AllThingsLinguistic.com, and book about internet language is called Because Internet. Have you listened to all the Lingthusiasm episodes and you wish there were more? You can access to 48 bonus episodes to listen to right now at patreon.com/lingthusiasm or follow the links from our website. Patrons also get access to our Discord chat room to talk with other linguistics fans – like, do you remember learning how to read – and other rewards as well as helping keep the show ad-free. Recent bonus topics include an AMA with a lexicographer and our favourite stories and anecdotes that we just didn’t have time for in some of the earlier episodes. Can’t afford to pledge? That’s okay, too. We also really appreciate it if you could recommend Lingthusiasm to anyone who needs a little more linguistics in their life. And, hey, tell your other favourite podcasts that they could a linguistics episode, and get us on! It’d be fun.
Lauren: Lingthusiasm is created and produced by Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne. Our Senior Producer is Claire Gawne, our Editorial Producer is Sarah Dopierala, and our music is “Ancient City” by The Triangles.
Gretchen: Stay lingthusiastic!
[Music]

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
#linguistics#lingthusiasm#language#episode 52#transcripts#writing#writing techonology#cuneiform#chinese oracle bones#scripts#orthography#technology#cherokee syllabary#hangul#olmec script#mayan script#stokoe notation#hamnosys
81 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is Nicky the only one headcanoned by people as bad with languages or are Nile and Booker seen the same way too (Andy is of course excluded from that due to her age and Joe is universally depicted as skilled with languages) ? I would expect Nile to be seen as bad with languages due to the American education system but it doesn’t seem to be the case.
Hello! Post-response me would like to apologise once again for the length of this post :(
I have personally not found a single fic where either Booker or Nile were depicted bad with languages; at most I found fics where Nile cannot speak languages other than English yet and you have the rest of the Guard routinely teaching her this and that idiom.
So, no, in my experience the only one that I saw people actively headcanon as bad at languages is Nicolò. Even though exactly as you point our if we want to go by stereotypes the one that should have been hc’d as such should have been Nile precisely because the large majority of Anglos are monolingual and the way languages are taught in their educational systems is horrendous to say the least (I will never forget my experiences studying Arabic in a Canadian university).
As it stands, Nile is shown using a couple of words of Pashtu, and if I remember correctly it is mentioned that she speaks Spanish in her presentation card, but if it’s the average American knowledge of Spanish “mi casa es su casa” then I would not call that speaking it. But these are just suppositions :)
So canon doesn’t give us much, that we know. And this is where headcanons come in. Like I was saying, usually people would not write Nile as multilingual but as someone who is in the process of learning several languages.
No one is indicated that she is bad at it, although if you ask pratically anyone in the world they will tell you that Americans and Brits are the worst at both learning and speaking other languages, because in those cultures there is a deep imperialist bias engrained – whether they are aware or not – that everyone in the world speaks English, so they can spare the effort to try to pronounce properly another language, or, God forbid, learn it at all. Nothing indicates us that Nile butchers or not other languages, and no one ever takes it into account.
As for Booker, he is French so normally Anglos would have also made fun of his way of talking if it had not been for Matthias.
And now I reach my point. The main reason why Nicolò is consistently depicted as terrible at languages is because of Luca’s Italian accent, and the fact that you can see he is not as fluent in English as Marwan and Matthias are, who are like him not native speakers. This even though the man speaks five languages.
I am not going into the whole mess with interviews with native English speakers who treated him as if he were dumb just because he could not really understand their accent (I myself often have to slow down and ask for a repeat, because some accents are just not as immediately intelligible as Anglos think), given that it has been discussed at length.
The only thing I want to stress is how this headcanon is extremely imperialistic, condescending and plays once again into the harmful stereotype of the dumb, illiterate Southerner.
Linguistic discrimination is a thing, and it’s a thing everywhere. By linguistic discrimination I don’t just mean that against people who cannot speak a major language (or the “official” language of the country they are in), but it also affects accents.Accents have everything to do with geography and class: it is a marker of where you are from, and plays into prejudices linked to the social standing and the class usually associated to that accent. Now, languages are a natural process, in continuous evolution and adaptation, whereas standardised languages (including a standardised pronunciation) are artificial choices. Just think of British vs American English: they are both theoretically the same language, but they diverge in several instances in terms of both vocabulary and pronunciation.Whip this up to the max when it comes to speaking a language that is not your own. The sounds and grammar structures of your mother tongue have an impact on the way you process a different language. That’s why it’s difficult for Spanish-speakers to pronounce S + consonant at the beginning of a word, or why Slavic languages have a harder H sound (again at the beginning of a word). Even when you have the grammar and pronunciation down to a T and are virtually indistinguishable from a native speaker, it does not mean that people who lose their accents and speak like a BBC tv host are any better at languages than people whose accent is still noticeable, or whose speech flow may be slower.
Having an accent does not qualify the level of fluency in a set language. Not speaking like a dictionary does not qualify the level of your intelligence (and I cannot believe I have to even say that).
And yet having an accent is politicised for classist and racist purposes. If someone does not blend in 100% with the majority, it means that something is lacking in them: usually it means they do not have the same level of education, which means they probably come from a lower class, or that they also are foreigners. So they are less than, just because their speech is deemed as not up to par with that of the majority.
@lucyclairedelune meant this when she brought up the example of Gloria from Modern Family, saying “you don’t know how intelligent I am in Spanish”. I want to make an example that is closer to my heart. Elena Ferrante in her wondrous Neapolitan Quartet described the life of a girl who was trying to escape from the material and psychological misery of the slums of Naples in the 60s. To do so she migrates North to study at one of Italy’s most prestigious university: here, however, she is bullied for her accent that clearly marks her origins and (prejudicially, since people of the South were in general poorer) status, class, and, finally, categorises her as less intelligent. Just because of her accent when speaking standard Italian. As a Southern Italian woman, I have often felt like I had to mask my own accent, both in Italy and abroad, to be taken seriously. This regardless of my academic qualifications or how many languages I speak.
When people describe Nicolò as bad at languages simply because Luca has an accent and speaks English slower and less fluently than his co-stars, this is the context that this treatment plays in. Subconsciously (or consciously) it adds to the image that a big chunk of the fandom is painting of him as dumb and ignorant. No one else. And the fact that (luckily) no one ever uses Nile’s monolingualism as a marker for being less intelligent is also because being American is still taken as the standard, as well as the fact that unfortunately Nile (like Yusuf) is going through positive discrimination by which she cannot have any complexity or flaws (starting from hardly ever acknowledging the fact that she herself was part of an invader/occupying foreign force which has bombed and killed civilians in Afghanistan, and was in the midst of a military operation exactly in this sense).
According to that specific discourse, Nicolò is being given every single possible flaw, in order to be opposite to Yusuf. Again, because this fandom, with its Anglocentrism and Puritan incapacity of overcoming black-and-white oppositions, cannot seem to accept that we have a beautiful interracial, interreligious same-sex couple of complex individuals, who can both be smart at the same time. I myself think that Yusuf historically is better at languages than Nicolò, as he was a merchant (and an artist), and I love this difference about them, but conflating intelligence with proficiency in one single language (because it’s only proficiency English that we have been discussing, let’s be honest, if the show had been shot in German we would not be talking about Luca’s issues with the language probably) is an utterly imperialistic, condescending and ridiculous thing to do.
I probably lost the train of my thought (and I had two beers in the meantime, so I am too tired to reread), but what I mainly wanted to highlight is that this mocking attitude towards Nicolò is rooted in both a wider downgrading trend of his character, and on a general approach towards non-English speakers that Anglos have virtually everywhere.
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Regulate Emotions and Not Be Scared of Them
Adapted from Calming the Emotional Storm by Sheri Van Dijk MSW
Because a lot of us have grown up in emotionally invalidating environments, we were taught to think of our emotions and how we express them as wrong, inappropriate, not okay, etc., leaving us to feel either angry, ashamed, guilty, upset whenever these emotions do arise. Because of the suppression, ignoring, and avoiding of our feelings, emotions have become foreign to us and paved the way for the many mental health problems we’re dealing with, as well as unhealthy coping mechanisms that can be detrimental to our physical health.
Thankfully we can learn not to be afraid of our emotions and to embrace them for the purposes that they serve. We can unlearn all the conditioning done to us over the span of our lives to make dealing with our emotions in a healthy way. Like all skills in life, it takes time and practice, so do not get discouraged. Your feelings are valid, but you should also know how to manage them effectively.
Here are some ways you can learn to start regulating your emotions:
MINDFULNESS
Mindfulness is intentionally being aware of our present moment in time, and instead of judging whatever we may be experiencing in that moment, we let it be. We are just an observer. The purpose of mindfulness is to train our brains to pay attention to where we want it to go as opposed to letting it wander aimlessly (to negative thoughts, negative self-talk), but also to look at our current experiences with acceptance and openness.
It sounds easier said than done, but trust me, with practice we can learn to focus on what we are feeling at any given moment by creating self-awareness. This allows us the time and a calm mind to choose how we react to the situation. Mindfulness also helps to improve concentration and memory because we’re allowing our minds to focus on one thing instead of letting everything and anything come into it.
CHOOSE HOW TO ACT
Reacting without thinking has consequences, and they’re generally negative. In order to choose how to react, we have to understand that we have 3 different ways of thinking about things: from our emotional self, from our reasoning self, and from our wise self.
Emotional Self - when our emotions control our behaviors. Instead of thinking about how to react in a situation, we just react emotionally . Examples: when you’re angry and you lash out verbally or physically; anxiety → avoiding the situation; depression→ isolating yourself. Acting from the emotional self is generally not the best in the long run, but the challenge is the fact that our emotions make it hard for us to consider the consequences of our reactions, hence the important of self-awareness.
Reasoning Self - when we use logical thinking. When doing so, we’re not taking into account the emotions we may be feeling at the time and will likely minimize them. This generally comes up when we’re making decisions. Example: you may have been offered a job that makes your commute go from 10 mins to 1 hour: better pay, the job is closer to your elderly parents; sounds ideal. However, you might forget about your emotional attachment to your current home, the neighborhood, or even your current coworkers.
Wise Self - finding the perfect balance between the emotional self and reasoning self, and following our gut instincts about what’ll be best for us in the long run. We’re trying to consider what we think in a situation and the feelings associated with it, plus the consequences for the actions we intend to take. Thus, choosing how to react.
LEARNING ABOUT EMOTIONS
“Emotion” and “feeling” are used interchangeably, but emotions are more than just how we feel. With emotions comes a full-system response: it affects body chemistry and body language in addition to what we are feeling. Example: anger → you might feel flushed, increased heart rate, increased breathing, tense muscles, plus the angry thoughts. Not everyone experiences the emotions the same way however, but there are definitely commonalities that help us identify these emotions if we’re not able to yet.
Emotions have purposes though: to motivate, to communicate, and to validate. (You can find a more expanded explanation on these here)
It’s important to also name our emotions and recognize exactly what it is because it may have been something we’ve been suppressing for so long that it’s become foreign to us, or we’ve been using a blanket term like feeling “upset” or “bad” when we’re likely feeling scared, guilty, sad, grief, etc. Knowing exactly what we’re feeling will help us narrow down an appropriate response.
QUIETING OUR EMOTIONS
Emotions communicate with us, and these messages can be positive, neutral, or negative--often they’re negative. We generally inherit the feelings we have about our emotions from societal conditioning or even from our families. When we understand the reason why we think and feel these ways about them, it will help us change the way that we look at them in reality, which helps us manage your emotions.
When we judge our emotions or even ourselves for feeling them because of our conditioning of being made to feel that way towards them, it makes us more vulnerable to reacting from our emotional selves. The more we judge them, the more they control us. How can we fix that? We learn to validate our emotions! Validation means accepting and understanding them--we must recognize that they’re happening, acknowledge them, give ourselves permission to feel them, and eventually let them go.
LEAVE OUT THE JUDGMENTS
Judgments have a huge impact on negative emotions (obviously), but some people surprisingly don’t believe that they add to our emotional load (crazy, right?). Learning to become nonjudgmental can really help to decrease emotional pain, making it a lot easier to manage the remaining emotions. Of course, the challenge is realizing how automatic a lot of our judgments are, and this is where self-awareness and mindfulness come into play.
Another thing that may happen with increasing this awareness however, is that we may start judging ourselves for being judgmental. There’s no need to feel shame for it! We’ve been conditioned as a society to be like this, but this is how we begin to unlearn this behavior.
Here are some things to note on judgments: they don’t provide helpful information, self-judgment are a form of verbal abuse, they negatively impact relationships, but some of them can be necessary (for survival purposes). It’s also important to not that becoming nonjudgmental doesn’t completely eradicate judgments, it’s more about being aware of them and the language we use when we form opinions from them.
ACCEPTING THINGS ARE THEY ARE
Suffering is the extra painful emotions that arise when we refuse to accept the pain in our lives. When this happens, it makes it more difficult for us to cope and function normally and leads us into unhealthy coping mechanisms. As humans, we naturally want to fight the things that cause us pain (physical and emotional), and this instinct is a survival/protective mechanism that can sometimes bring us more harm than good. Of course this makes sense when it comes to physical pain, but our brain does this as a natural function as well, but in doing so, our brains are working against us without realizing it, causing suffering instead of alleviating pain. This is called fighting reality, and this is where emotional regulation comes into play.
When we learn to stop fighting reality and accept it, we can reduce our suffering. When we learn to accept the reality of our situations, it eventually loses power over us. We eventually stop thinking about the situation and the suffering starts to go away and your anger will go down.
#emotions#dealing with emotions#mental health#free therapy#mental illness#depression#anxiety#bpd#ptsd#bipolar disorder#ocd#invest in your health#you got this#your feelings are valid#mindfulness#acceptance#emotional intellgience#emotional dysregulation#emotional regulation
28 notes
·
View notes
Note
world walker to date is one of my most favorite fanfics ever. it's so well-written! not too op, with real difficulties and plot, but still light-hearted and funny! <3 <3 <3 <3 <3 i hope life smoothens out for you so we can get an update of this awesome story! :D :D :D
Aaaa thanks Anon!! This ask made me super happy - I'm glad you like World Walker and that it hit the right balance between angst and comedic moments (tbh that's one of the things that's really hard to get right). Things are still hectic but as soon as they're not that chapter is getting finished!!!
Since it might be a while, have a post-World Walker scene from the pov of a couple civilians. It was written to try out Cryptid as Izuku's hero name (/^o^)/
(Note: this scene isn't canon to World Walker and was written before I knew how the story would end.)
“Why do you even think this is going to work?” Yua hovers around Mariko’s efforts in the Denny’s parking lot, careful to avoid stepping on the complicated design taking place under Mariko’s second piece of chalk. The first one was sacrificed to ward off a raccoon. They specifically chose to do this after midnight for the ambiance, but Yua is starting to have second thoughts.
It’s very dark, and they’re both fem-presenting teenagers with emitter quirks in a deserted part of town.
This is not a good place to be.
“I got the pattern off a hero,” Mariko assures her. “You know how I was in the gym when Uravity's fight hit school, right?”
Yes, and Yua is trying desperately to forget the worst day of her life, thank you.
“Uravity and Cryptid dug me out, but it was weird, because he drew this symbol on a piece of the roof and it just- stayed. In the air. Even when nothing was supporting it.” Mariko pauses, beaming at the magic circle that’s mostly made of lines and squiggles to complete the aesthetic. One of the symbols doesn't look right. It slides out of focus, and Yua carefully steps back, because hell no.
“How is that supposed to help us summon a ghost-”
“Finished! Start filming, hurry, hurry, hurry!” Mariko drops her piece of chalk as Yua scrambles to swipe open her camera. Before Yua can stop her, Mariko has drawn a pocket knife, cut the pad of her thumb, and is smearing blood on the unsanitary parking lot ground.
Delightful.
Her hand is going to get so infected.
That’s right about when the air above the circle tears itself apart.
Mariko shrieks. Yua almost runs, then remembers herself and makes sure her phone is pointed at the sliver of starlight shining out of thin air. She knows her horror film tropes. Whatever they released into the world is taking them first, but she can at least get a video account to warn people of what they did.
Eaten by a demon or some shit. That’s a bomb-ass obituary.
Pro Hero Cryptid crashes out of the portal, one hand protectively wrapped around a bowl half-full of salad. His Uravity sweatshirt mostly obscures Froppy sweatpants, but Yua is more alarmed by the fact that Cryptid looks surprisingly human. No needle-sharp teeth, no starlit eyes. Spinach flutters to the ground around the hero in a gentle shower of greenery that nestles in his curly hair as if adding to the foliage. He stares blankly at them, then at the scribbles under his feet, before pointing a truly pissed-off look at the sky.
“Are you serious?” Cryptid yells at the city skyline. A spinach leaf falls off his shoulder. “Right in front of my salad?”
“Holy shit,” Yua whispers, and discovers that she can, in fact, be more embarrassed than the time their teacher made the whole class sing ‘Happy Birthday’ while she stood in silent mortification on a chair. “We summoned him.”
Mariko claps both hands over her mouth to keep in her laughter, eyes wide. “We really did.”
This seems to draw the hero’s attention back to them.
“You two okay? Yes? Nobody’s hurt? Oh, thank goodness.” Cryptid stabs a fork into his vegetables, shoves it into his mouth, and makes grabby hands for the chalk. Mariko passes it over with a potent mix of awe and glee.
“I am so sorry,” Yua breathes.
Mariko sniffs. “I’m not.”
“And I’m glad to be summoned,” Cryptid finishes with a sunshine-smile. He’s very… human. The wrinkled eyebrows he directs at Mariko’s chalk art do not resemble the otherworldly creature that showed up during All Might’s last battle. “Better for me to be dropped here than for y’all to get… hm. Yeah, this is good.”
Hm?
Hm??
What does ‘hm’ mean?
Yua reaches over and frantically swats at Mariko’s sweatshirt in an attempt at telepathically communicating her many, many feelings concerning accidentally summoning a hero into this godsforsaken Denny’s parking lot.
“How did you find a stasis glyph?” Cryptid mumbles around his fork.
“Copied it from you. My quirk lets me mimic actions if I see them without blinking.” Mariko peers around his shoulder at the lines taking form.
“That’s such a cool quirk,” Cryptid tells her instantly. “Do you need a clear line of sight? Is it only capable of copying real-life actions or can you use recordings? Oh, are you limited to your own flexibility and strength, or is this a mirror skill instead of a mimic? You could use that for anything, it’s a very adaptable power.”
Yua cautiously edges closer to give the camera a better angle at the ground while Mariko preens. “What are you even doing?”
“Editing. Here, look- right there, you tied it down with intent contrary to the meaning.” Cryptid shuffles over so she can see and points out a circled section. He smudges out the blurry patch.
Mariko watches eagerly as the hero replaces it with a mishmash of lines that Yua can actually make sense of. “I don’t understand any of what you just said, but hell fuckin’ yeah, you funky lil’ cryptid.”
“Oh, sorry. I get called whenever the void gets angry, and this is the language it speaks,” Cryptid says, like this makes sense. He taps the lines eagerly. “Put a stasis glyph on the ground and continents will stop shifting, which is a whole lot of bad news."
"Uh huh," Mariko says. Yua swats at her again, because there's no way she understands and going along with this for entertainment value alone is going to get them into some sort of horror movie B-Plot.
Cryptid just looks amused. "Next time you need to experiment, use a paper base instead of the concrete. It’s safer. And- is that blood?”
“Maybe,” Mariko says, partially as a dare for him to say anything because she isn’t really the type to listen to anyone, regardless of if they’re a hero. “It worked, didn’t it?”
“Huh. Yeah, you got me there.” Cryptid puts his bowl of salad on the ground and fishes around in his Uravity sweatshirt for a tiny med kit.
“Where’d we go wrong,” Mariko asks, like they are ever going to try this again. Yua hisses for her to stop and is ignored with the extreme confidence of someone determined to keep making the same continuous mistake until success is summoned through stubborn willpower alone.
“You didn’t need to hurt yourself.” Cryptid bandages her hand, slips away the medkit, and says gravely, “Blood never brings anything good.”
“Holy shit,” Yua repeats as Cryptid takes a bite of salad and goes right back to his art project like this happens every other Tuesday. Mariko glares at her, but honestly, this is the wildest thing.
The hero keeps saying things.
“Not to lecture either of you, but it’s a bad idea to mess around with unborn languages without supervision.” Cryptid hands back the chalk and takes another bite of his salad. “This stuff can blow up in your face. So, can I escort you guys anywhere? Because it’s a little dark and this isn’t exactly the safest part of town.”
That’s about when Yua realizes something under the spinach is glowing.
11 notes
·
View notes
Note
Headcanons for the greek gods as omegas?
(I assume you mean as Omegaverse and not for them all to be Omegas cus there’s no way Ares is Omega lol)
This is gonna be the 12(.5) Olympians and the royal couple of the underworld
Zeus: Alpha, a very obvious Alpha. Leader of the Olympian pack. If we're going with the personality he has in the myths then he's the kind of douchebag Alpha who thinks it's his right to go around knotting whoever he fancies; I imagine his pheromones are pretty powerful too. Like, send-you-into-an-surprise-heat kind of powerful. If we're going with how the ancient Greeks actually saw Zeus though he's the absolute best provider. Big dad vibes towards everyone who's even a little bit younger than him (which... y’know, given that he's a god is almost everyone).
Hera: Omega. The kind of Omega that has a dominant, leader's streak; the kind born to be the leader's mate. She has that Omega's need for love and attention (which Zeus really needs to work on giving her smh) and likes to pamper her body (see: pool that she bathes in every night that somehow magically makes her not a virgin anymore... yeah idk either, blame the ancient Greeks). She does, however, lack a natural maternal instinct (see: yeeting baby Hephaestus off of mt. Olympus), so I feel like she could potentially also be a Beta.
Poseidon: Alpha. Originally he was actually the leader of the Olympian pack (no that's not a headcanon - the Macedonians actually considered Poseidon to be the head of the Olympians). I imagine him to be a kind of rugged-looking Alpha - like an strong old fisherman with rough palms and speckled grey hair - with an air of calm and control that can switch to chaotic and aggressive in an instant's notice - like the ocean itself.
Hestia: Omega. Absolutely 100% Omega. The kind of Omega who's very presence makes you feel soothed, her hugs are warm and soft (not just because she always wears fluffy cardigans), her nest is absolute perfection - beautiful, calming to be in, and cosy - and she's always got something divine (if you'll excuse the pun) in the oven. Always purring kin the kitchen. Absolute biggest mama vibes. She smells like a bakery; chocolate and pastry. Holy shit I love Hestia.
Demeter: Alpha. Considered her, perhaps, as an Omega on account of her being a fertility agriculture goddess but she just doesn't strike me as the placating, gentle type. Quite the opposite. She fought stubbornly for her daughter to remain at her side, and she's the goddess of law too - she's not the rolling-over-showing-her-neck type at all. I picture her as an absolute Unit; muscles for days from all the years harvesting crops. The no-nonsense kind of Alpha.
Aphrodite: Omega. The hypersexual kind of Omega. I believe I've seen them called 'Pack Omegas' - the type that do best when they're in a relationship with lots of people, practically (or literally) a whole pack. Also the beauty-obsessed kind of Omega. Takes ten hours to get her clothes, hair, and makeup done yet somehow she turns the whole process into a mesmerising dance. She turns everything into a mesmerising dance. Another I imagine with knock-out strong pheromones that have Alphas falling to their knees for her. She smells like roses.
Athena: Alpha. Another leader-type Alpha - literally has Athens named after her, and she's very proud of her people... despite some of the absolute nonsense she's had to witness from them throughout the ancient years. A very adept and skilled fighter and strategist - likes to know everything about a situation before rushing in. She's an incredibly supportive and wise lead Alpha, the kind that the pack feels they can go to with whatever problem they might have. I feel like she could also easily be a Beta, but she's got such a strong sense of being dominant and in charge it's hard to see her as anything but an Alpha.
Ares: Alpha. Less of a leader-type Alpha, lbr, more of a team player. The kind of Alpha that runs into things without thinking, relying on instinct and, on the battlefield, pure rage. Your average Aggressive Type Alpha who's ready to kill for anyone in his pack. Can come across as a bit of a meat head... and can be a bit of a meat head at times... Yet I imagine him as a really loving, doting mate, which initially surprises a lot of people; seeing this big burly 6ft< Alpha who smells like fire and blood smiling dopily as picks out the perfect dainty jewellery for Aphrodite.
Hephaestus: Beta. My poor poor bastard boy. Very crafty and creative (see: trapping his mother in a beautiful trick throne he built as revenge for yeeting him off the mountain as a baby). Likes to think his creations through and plan genius contraptions. He could very easily also be an Alpha, what with the fact he's a blacksmith, which is a rather Alpha job. But I guess I lean towards Beta because, even though he's a bit of a social outcast on account of his leg and general appearance, he's clearly desperate to be more socially involved with the pack and doesn't want to be a lone wolf.
Artemis: Alpha. Surprisingly nonsexual for an Alpha. Very much a lone wolf. Loves spending her days out in the forest. You wouldn't think she's an Alpha to look at her, but she'd surprise you with how strong she is. Also very good at using her opponent's strength against them. Because of her build, she's considered the protector of Omegas; most Omegas would feel very safe in her presence. She's got this mysterious edge to her that just uncontrollably draws you in... like the moon.
Apollo: Omega. Ah, sweet darling disaster bisexual... I just imagine him being very soft and sensitive (not that he can't kick ass on a battlefield, see: his involvement in the battles of the Iliad). He has an artist's soul and an angel's voice. His serenades are totally his courting gifts. I imagine him revelling in being doted on, and always eager for fuss and attention. He has a beautiful Omegan frame, and he loves decorating himself in luxurious garb and crowns of flowers and leaves. He smells like laurel and somehow also sunshine. No one knows how this is possible but he does.
Hermes: Beta. And nooo I'm not just saying that because he's my favourite and that's the dynamic I best identify with (>_>) He really is such a Beta though. I've a headcanon that Beta's love travelling and exploring and he's literally the God of that so y'know. He's also so quick thinking and witty: represented himself in a what was basically a godly court case where he was guilty of thievery and won when he was literally a baby. He's hardly ever submissive to anyone but he hardly ever uses aggression or physical force to get his way/get out of trouble. He smells like ripe strawberries and the metallic tinge of coins.
Dionysus: Beta. The eccentric, outgoing, party type Beta; wants to be surrounded by friends having a good time all the time. He smells like booze; in the morning it's a little off-putting, but in the evening its literally intoxicating. I imagine his mortal Maenads needing only his scent to drive them into a frenzy. Not the kind of Beta you'd expect to also have the Supportive Beta streak, but he absolutely does; he lives to support his friends and gives the kind of advice you don't realise is advice at first and later hits you like an epiphany, and it was exactly what you needed to hear.
Persephone: Beta. Difficult one, but I had to go with Beta because she strikes me as a very gentle, delicate goddess of spring that could easily have her classified as Omega, but in winter she's the no-nonsense, dominant queen of the underworld that could have her classified as an Alpha. Overall, I think this shows her adaptability, which is a very Beta trait. Also, she's not really as needy and dependent as an Omega traditionally is. Things might have happened to her beyond her control, but she very much took back control and has both Hades and Demeter wrapped around her little finger. Of course, she smells like pomegranates, and spring blossom.
Hades: Omega. I have such a soft spot for soft!Hades. But he's kind of the reverse of Artemis in that you would not think to look at him that he's an Omega, you'd assume he's an Alpha, especially considering his position as ruler of the underworld. But he's a softy at heart, and adores material possessions (which I consider a bit of an Omegan trait). He mopes all the way through spring and summer at the lack of Persephone's presence, cooped up in his nest the whole time until autumn rolls around and she comes back into his life. He has a very earthy scent.
bonus:
Hermaphrodite: All three! Thought I'd include Hermaphrodite because they flashed through my mind and I wondered what might be classified as intersex in a/b/o. Of course, that depends on how you hc biology for the dynamics but I thought what would perhaps make Hermaphrodite an outcast/outlier could be their body, scent, and instincts being a mix of all three dynamics.
thanks for the ask 💞
#omegaverse#a/b/o#alpha/beta/omega#oemgaverse dynamics#a/b/o dynamics#alpha/beta/omega dynamics#omegaverse headcanons#a/b/o headcanons#alpha/beta/omega headcanons#greek mythology#greek gods and goddesses#omegaverse theoi#a/b/o theoi#omegaverse greek gods#a/b/o greek gods#long post#ask#anonymous#mine#does hermes know i would take a bullet for him??#probably actually. he'd probably let me take the bullet as he sipped a juice box
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top 20 BEST Animated Series of the 2010s-4th Place
To anyone who plans on making a reboot of their favorite show in the future, you might want to take notes on this next pick. Because if you ask me, this next series that I'm going to talk about is the best example of how to do a reboot properly.
#4-Ducktales (2017-2021)
The Plot: Scrooge McDuck is the richest duck in the world, who made it big by also being one of the greatest adventurers of all time...ten years ago. Sadly, after an unfortunate accident with the family, Scrooge is forced to live the life of a normal businessman-er-duck. Up until Donald Duck asks Scrooge to watch over his nephews: Huey, Dewey, and Louie. What starts off as a single day of babysitting soon turns into a life of adventure as Scrooge gets back into the adventuring spirit to show his new family what the world really has to offer.
Now I want to make one thing clear: As of the moment of me writing this review, I have seen a total of zero episodes of the original Ducktales. That being said, despite my limited knowledge of the series, I still think it’s fair of me to point out how this is hands down the best reboot as of late (and I’ll explain more as to why that is later). And besides, from what I’ve heard from fans who have watched the original, Ducktales (2017) is a pretty faithful adaptation of the beloved franchise. The reason is that I believe this show remembers the two most important rules of making a reboot.
The first rule of a reboot is to try something new while still being faithful to the source material. Doing something like that is simple as a writer just needs to keep what the fans love and change what they hated. And trust me when I say that the writers of Ducktales (2017) knows how to do just that. For the most part, the show is about a family going on crazy globe-trotting adventures while still learning that family is the best adventure of all, much like the original. As for the characters, most of them keep their fun personalities. Scrooge is still a stingy miser with the heart for adventure, Launchpad is still the lovable idiot who can’t fly a plane, and Donald Duck still remains the one who gets stuck with all the bad luck. Then some characters have their personalities/roles revamped into something that improves upon the original. The best example is Fenton, who is still the wannabe superhero but is now a scientist in this show, wherein the old one was just Scrooge’s accountant. This way, both the hero and the man-DUCK-who’s behind the mask are equally capable of saving the day. There’s also Mrs. Beakley, who was originally a nanny that nagged Scrooge’s ear off for putting the kids in danger. In the reboot, she’s treated more as the anchor of reality to the more oddball characters, who also used to be a kick-butt super spy in her younger years. It is still the same role, but a different interpretation.
Now, some characters receive grand changes to their original personalities. But from what I’ve heard, those changes are made for the better. And there are no characters that need it more than the children. More specifically, Huey, Dewey, and Louie. This show does something that I’m eternally grateful for, and that’s giving each of these three their own distinct personalities and quirks. For years I couldn’t for the life of me tell the triplets apart. They had the same design, the same voice, the same personality, and the only difference people had to go off of are their different colors (which really didn’t do much to help). Here, they have different designs, voices, and now defining character traits for each of them. Huey is the smart and responsible boy scout, Dewey is the annoying attention seeker, and Louie is the best character in the entire show, and I WILL FREAKING FIGHT YOU ON THAT! And let us not forget the most appreciated change: Webby. From what I’ve heard, fans hated the original Webby, as she was nothing more than just the stereotypical girl of the group. Here, she’s given an actual personality and a fun one to boot. Webby is the ecstatic thrill-seeking adventurer who is skilled in combat training (thanks to her grandma) and is (of course) a socially awkward girl who wants to make friends. Like I said, this show took the idea that the fans hated and changed it into something that they’ll love. Which makes sense why the writers mastered this because they themselves are real fans of the show.
It is clear how much the writers are fans of the Ducktales franchise as they filled Ducktales (2017) with many references. And not just references to the original series but also references to the classic comics by Carl Barks and even the NES video game from the 1980s (seriously, this show will make you feel things about the “Moon Theme” you wouldn’t think was possible!). Even the show’s animation seems to be a homage to both the cartoon and comics. Not only do the characters and backgrounds have a more comic book style to them, but the characters also work on a mix of realistic and cartoony logic. And let me just say, it is refreshing to see characters in a Disney show have cartoon logic to them since Wander Over Yonder got canceled. And it’s not just Ducktales that the series reference, but even classic Disney movies (of course) and other shows in the Disney Afternoon lineup. And when it comes to these references, it’s more than just a subtle wink to the fans. The writers actually go out of their way to write a story around these beloved characters, so people who don’t get the joke won’t be one-hundred percent lost. For instance, without giving anything away, the writers found a brilliant way to reintroduce Darkwing Duck in this universe that feels right for this famous character. And if you ask me personally, these are the best ways to handle references for a reboot. Make them work within the story, even if you don’t fully get the joke.
This brings me to the second most important rule of a reboot: Make a quality product even though it is based on something else. Let us pretend that the original never existed. Would Ducktales (2017) still be as good as it is now? Personally, as a person who has never seen the original, I think it is.
This is another show that mixes slice of life episodes with adventure ones, similar to My Little Pony: Friendship is Magic. And just like Friendship is Magic, both are equally interesting because the characters themselves make them so. No matter what situation the Duck Family are in, the audience will care about it because the characters care about it. In fact, I think Ducktales (2017) handles the mix of slice of life and adventure much better than Friendship is Magic. In MLP: FiM, the adventure-based episodes force the characters to stick to their simple personality traits to move the story forward, and character-based ones help them grow. In Ducktales (2017), because the characters regularly go on adventures, they grow as characters no matter the situation. For example, my favorite episode is “The Great Dime Chase” where the main plot is Louie finding Scrooge’s #1 dime after accidentally spending it. While in that same episode, Dewey and Webby try to solve a mystery around the boys’ mom. We get a great lesson about the importance of hard work and a fascinating plot of an overarching mystery within the season, all taking place within the same episode. Both are interesting, neither feels as though it overshadows the other, and the characters develop along the way.
Another thing this show mixes well is comedy and drama. A lot of shows recently tried way too hard to find that perfect mix. Ducktales (2017) is one of the few examples that nails it. The comedy is hilarious, the drama is endearing, and neither feels like it’s prioritized over the other. The show starts off with this mix as well, where others that I’ve talked about seem to start off as purely comedic only to take themselves more seriously later on. That isn’t entirely a bad thing, but I feel as though Ducktales (2017) is the best way to go about the method. That way, fans won’t be complaining about how much “better” the show used to be in its first batch of episodes, much like Star V.S. the Forces of Evil.
Unfortunately, while I recommend this show, it’s not without its fair share of issues. Or rather, issue, as there really is only one problem I have with it. And that problem can be summed up with one name: Dewey Duck. For the most part, I dislike Dewy. Because he’s nothing more than a Ben Schwarts character. No disrespect to Ben Schwarts himself, but lately, it feels as though he only plays the one character from time to time: The egotistical attention seeker slowly and surely learning to be a better person who realizes that not everything is about him. That’s the character he plays in both Rise of the Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles and Sonic the Hedgehog (2020), and it’s the character he plays here. And the thing about these characters is that they’re not as lovable as Ben Schwarts thinks they sound. In fact (and, again, I mean no disrespect to the actor. I’m sure he’s a lovely person in real life), every single one of these characters comes off as kind of annoying rather than as the lovable rapscallions I’m sure they’re meant to be. However, there is one thing worth mentioning about Dewey. While he’s portrayed as annoying when used for comedy, Dewey is surprisingly a compelling character when used for drama. The thing is, he’s rarely used for dramatic moments and is meant as a source of comedy. Hence why I said I disliked him for the most part.
Other than that, there aren’t really that many problems with the show. Well, there are, but they’re mostly nitpicks that the series more than makes up for. Is it weird that the kids are voiced by adults? Yes, but the actors do a great job at being sincere and have great comedic timing than any kid could have. Are there changes to characters that fans might not enjoy? Probably, but I have yet to have seen anyone that has annoyed me as much as Dewey has. Are the villains just evil for the sake of being evil? Yes, but that’s not really a big deal. In fact, a villain doesn’t need a heartbreaking backstory as to why they’ve become so evil. They just need to have a great personality that’s fun to watch, which every villain in the show has (aside from season two’s antagonist who’s basically a Disney surprise villain. And I hate them with a fiery passion). Does it feel as though the show suffers from “too many characters” syndrome? It sometimes does, but each character has such a fun and unique personality that I find it hard to forget most of them.
So really, Ducktales (2017) is the best reboot in recent memory. This is crazy, seeing as how lately it feels as though Disney doesn’t even know how to properly reboot their own movies to save their lives. This is why I feel as though people should take notes on what Ducktales (2017) does if they ever feel like rebooting something they loved as a kid. Because this is more than just a retelling of the same story that people know by heart. This is a fantastic show with even better characters, stories, and tone. Whether you’ve been a fan since the beginning, or a part of the new generation of viewers, odds are you’ll be screaming Whoo-Ooo with every episode.
(Also, a word of warning to those who haven’t watched the show yet: Beware the theme song. Trust me when I say it’ll be stuck in your head until the day you die)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Project Clypse
Hello there stranger! If you don’t know who I am, or you’re too lazy to read my name, I’m AveryScarlet! You can simply call me Avery or Av. And if you know me on fanfiction.net, mostly through my works Mercury Alchemist or Final Fantasy Versus XV, welcome! Now, for a while now, I’ve been wanting to write up my own original story. Issue with me, thanks to college in the past, I haven’t properly developed the mindset to write a full-blown novel. I’ve gotten so used to typing up a chapter or two in a month before publishing them that I can’t properly focus as an actual writer should.
As much as I want to focus on writing some of my fanfiction, I can’t because I’m focusing on studying for NCLEX. So if you’re waiting for the next chapter for FF Versus XV... It’s almost done! It’s just gonna take a while. But as you can see below, I’ve been working on something else. I’m sure you’re confused as to who these characters are in the chat and why I’m pushing so many out. Well. I’ll tell you. This is my way of practicing for a story I’ve been... REALLY wanting to write for a long time. It doesn’t have a definite name, so I’m calling it Project Clypse. Which partially comes from the group my main characters are in.
Now, I thought of writing up their character bio’s but..... I’m not really that good at it as I used to be. I used to for when I was active in RP’s but I’m so rusty that I doubt I can keep up with whomever I’m chatting with. So, I’m just summarizing certain details you need to know about them! Not all of it because that'd be spoiling the story of every character. Now, with all that’s said and done, let me start explaining key points of Project Clypse.
Premise/Background
The story is centered on a world called Avarus, which you can say is sort of like Earth, except it was made with someone else's version of life. Or, it used to be. Avarus is one of the few remaining worlds that has an active patron God, who has chosen to go under the alias Belial. The world was originally created and governed by another, Belial’s younger sister, Soleil. After Avarus’ creation, and the birth of man, she was killed by an unknown assailant. But before she died, she was cursed to experience an endless cycle of death and rebirth into various random worlds. She will live a short mortal life, then die from either natural or unnatural causes.
According to Belial, this curse is bestowed only to Celetials who have performed a dire sin. While there is no definite way to lift the curse, Belial hopes that by locating and retrieving her while she's still alive, or at the very least obtain her soul, then he could find the proper means to spare his sister of her cursed fate and return Avarus's true patron Goddess. Because of her demise, life on the planet started to decay. To prevent its destruction, Belial forced the planet to stop rotating, hoping to delay it long enough for him to find Soleil.
However, there were dire consequences to this act. His actions indirectly causing the world to cease rotating; time became non-existent as a result. This, inevitably, killed off most of the remaining life in the world due to the imbalance of the ecosystem as one half of the planet became stuck in perpetual darkness, and the other being dried up caused prolonged exposure to the sun's light.
The only life that Belial was able to salvage was her sisters creation; humanity. Those that survived after the planet ceased its rotation found themselves unable to age. They can still die, but their bodies will no longer decay. During the first Century since Soleil’s death, the God went through various countermeasures to keep the world and the life still inhabits it safe until he can find his sister.
However, a strange plague began to manifest. Soon, it began to devour most of the remaining populace, creating a dark entity in the process; the Astrals (will explain in a different section).
While Belial was successful in wiping out the infected, the God realized that he cannot keep the last remnants of humanity safe. Not while there are still Astrals lurking about. So he put them to sleep, sealed them in a place that only he knows. However, because of the sudden absence of time and life, the world began to deconstruct itself each time he departed in search for her in other worlds. Realizing he cannot manage Avarus and search for his sister at the same time, he found an alternative. Since his conception, he had noticed a peculiar type of living being popping up now and then in a variety of sentient species. So he sought them out.
Eventually, gathered enough to temporarily replace humanity and trick the world itself into thinking life still exists. At first, he gathered adults since he knew nothing can grow in Avarus once they’ve lived in the world for a certain period of time, but because of their attachments to the worlds they originated from, it was difficult to convince them to remain. Then he thought up of another solution, one which he knew his sister would frown upon. Children. With their young minds, they’ll easily forget their place of origin and can be easily trained in the necessary skill in traversing through different worlds. And, after learning that the Astrals have branched out to those said worlds, learn how to handle their sudden enemy.
Their goal is simple; to locate and, if possible, retrieve Soleil and eradicate the Astrals.
Main Characters
Note: Just in case you did not know... I. Cannot. Draw. As much as it pains me to do this, but I need you guys to have some sort of idea on how they look like. I cannot find the original artists of the artworks; mostly because google imaging is shit and Pinterest tends to... Send you elsewhere. So of you know the artist, please PM me so I can give them credit. If you know they don't want their works republished, I'll remove it and try to figure something out. I take no credit whatsoever on the art! I merely scoured the internet for any references I could use. If you're wondering why I'm not.using actual people... You know how awkward that is?
Anyway, much of these are concepts so expect changes in the future. I tried to discuss as little as possible about each character. And let me tell ya.... That was a lot I had to cut off, so if the explanation is a bit messy, that was from me trying to select what to remove to avoid revealing too much.
. . .
Sound
‘I have to be better. I have to be a better leader. I have to be a better lover. I have to be a better sibling. If I don’t... then I’ll lose everything again. If I must, I’ll sacrifice my identity for a third time if it means protecting them.’

Credits to: T0Q00(?) - Okay, on Pinterest it has the person’s name AND link to their twitter account. The thing is... it’s empty. Their entire page is empty. At least I found the artist’s name?
Also known as the Glutton King, Sound is one of the leaders of his faction, Tunera Clypse and a member of Mythral. He is a first generation Nors. While not as lazy as Noise, he’s not really a fan of getting involved in fights with people. When it comes to killing Astrals; that’s an entirely different story.
Outwardly, he displays laid back, playful, and very concerning outlandish behavior. And by outlandish, I mean his... eating habits. Sound likes to experiment with his stomach. He’ll do absolutely ANYTHING to eat whatever he deems as edible. He also - absolutely - lacks any sense of shame (ex. walking out of the shower and to his room without a towel, slapping Noise’s butt). Although limited to communicate via writing, he makes sure that every single thing he writes is worth reading. Many are even surprised at just how fast he writes his messages. Then again, after years of practice, it’s expected he’d adapt.
Sound is self-aware of the fact that he’s a fictional character and will randomly break the fourth wall, causing much confusion to his friends several times. While not as dark as his previous self, Fell, he maintains some of his views towards life and tends to be as vocal - via writing - of his previous self's beliefs.
As a Cursed Blood, his curse forces him to conceal his face behind a customized Fox Mask. Depending on the amount of facial skin that was exposed, a person can live up to several minutes to several hours before inflicted with sudden death. If a person were to see the entirety of his face, they will die on the spot from unknown causes. He has a Physical Curse as well, which causes him to inflict a certain degree bad-luck to whoever hears his voice. While it’s rarely anything life-threatening, Sound is forced to become selectively mute. Although he tries his best to remain silent, he tends to accidentally let it a few words or sounds slip. Which usually occurs when he sneezes, and when he does, it is immediately advised by his friends to duck and cover.
After undergoing the Ascension Ceremony, he joined the faction Tunera Clypse and then gave up his original name, becoming the next Sound. Unbeknownst to him, his actions later in life has caused him to unknowingly become the Vessel of Gluttony. It is unknown if his eating habits is the reason he became the vessel or it’s the other way around. Either way, he has shown to be fully capable of controlling the abilities that comes with being a Vessel. Sound merely chooses not to use them.
. . .
Ayane Koronashi
“If my brother had left the orphanage that day without me, I would simply smile. If Ulric presented me his latest girlfriend, I’d smile. Smiling is all I can ever do without being a nuisance. I could never show them my pain. I want to cry but my curse renders me incapable of doing so. But now it’s better. I’m better.”

Also known as the Black Fox. Ayane is the younger twin sister of Sound. Like her twin, she is also a member of Tunera Clypse and Mythral; as well as a first generation Nors. Despite being an active member, unless accompanied by her brother, Ayane is rarely allowed to participate in any scouting or combat-related missions. The main reason for this is her curse. While also a Cursed Blood like her brother and some of their friends, the unnatural causes that led to sudden conversion to a cursed blood caused her condition to be unstable. At the beginning, she was unable to retain her original form and would take the shape of a fox.
After some time and practice, she has learned to maintain most of her former human appearance, leaving only a pair of fox ears to replace her human ears and a tail (not by choice) as an extra ligament. Not only that, some of her internal organs remain similar to that of a fox. Because of this, she is unable to eat certain foods that are potentially poisonous to her (or generally unhealthy). She was told that eventually, if nothing is done, she will permanently take the complete form of a fox. She cannot surgically remove the fox parts as they will simply grow back.
Side-note: No, they did not try or plan to remove her fox ears. The curse replaced her human ears so they cannot remove them without indirectly making her deaf.
Her personality is the somewhat similar to Sound’s, but is far more excitable and outgoing than her brother. Just like a fox, she is clever and witty, which she demonstrates many times during combat. She has a tendencyto steal things without her knowledge. While this isn’t necessarily kleptomania, as objects appear in her hands at random, she still tries get over her childhood habit. She does have a tendency to be reckless, though this is stems from her need to be useful as her curse leaves her unable to perform all of the necessary abilities that is required of a Nors.
Another thing to know is her intense hatred towards cats. Which will be explored at a later time.
As a Cursed Blood, she can take the form of a fox. While the size varies, depending on her emotional state, she is commonly seen to change into the size similar to an elephant. If she performs multiple transformations, she will regress to a regular sized fox and sleep for an extensive period of time. She has been recommended to avoid constantly rely on her full fox form as it will hasten the progression of her curse.
After undergoing the Ascension Ceremony, she followed her brother and joined the same faction as him, but unlike him, did not join as a core member so she did not have to give up her original name. Because of the current state of her body caused by her Cursed Blood, her emotions has unknowingly lead her to become thenext Vessel of Envy.
. . .
Reihana Toelle Ur Kamaria
“Why was I born like this... what did I deserve to be cursed like this!? All I want is to hold someone without fearing I’ll crush them. I can’t be the receiver forever!”

Or Rei for short. Is a member of Mythral and is a second generation Nors. As a floater, Rei rotates between the three factions, but she usually works with Tunera Clypse. Known for her terrifying brute strength, Rei is feared by many and is challenged on a near daily basis. Because of her strength and seemingly indestructible nature, she is (much to her annoyance) sometimes used as a human shield. While she is able to take on an army by herself, Rei tries not to go all out in fear of accidentally killing her allies in the crossfire. In terms of mental maturity, aside from Xavier, she is slightly more competent and is level-headed enough to not participate in childish activities. Most of the time.
Rei prefers to ‘punch first, talk later’ when confronted, though the talking never happens as her opponents is either obliterated or immediately knocked out after one hit. While she can be aggressive at times, she merely acts out on this person's due to the rumors that were spread when word of her curse began to circulate. Those closest to her have witnessed her carefree and adventurous nature. She is also cautious and careful of her surroundings, becoming more thoughtful in the usage of her strength as a result.
As much as she loves the thrill and adrenaline that comes from combat, she prefers not to fight too often. Mostly because it usually leads to unnecessary mass destruction. She craves for proper physical contact, but due to her curse, she forces herself to avoid it as much as possible.
Being the physically oldest, next to Percy, she tends to act like the big sister of the group, which Rei has admitted she finds embarrassing. Still, she works hard in trying to act as moral support for her friends. That doesn’t stop her from losing her temper when a certain line is crossed.
As a Cursed Blood, she is cursed with immeasurable strength. Her strength doubles based on who or whatever is the strongest in a world that she sets foot in. That, of course, excludes Celestial’s as the strength of the divinity is almost non-existent. By default, back in Avarus, her usual strength is enough to crumble an entire building. In other worlds, it depends. To help control and regulate her strength during combat, she uses a large amount of Astral Dust to create form-fitting gauntlets around her lower arm. She was meant to become the Vessel of Wrath but was instead changed to be the candidate for the Vessel of Pride.
. . .
Perseus Vlahos
"I used to believe that being a hero will allow you to cement your place in history. But over time, I learned that the farther in time your name is shared in time, you become nothing more than a mere legend. Or worse, a myth. Stories can be altered, changed. If that’s the case, I’d rather not be remembered at all. I didn’t work this hard just to be written off as a bedtime story.”

Christened under the name ‘Percy the Naive’ by his best friend, later life-long rival, Wilhelm, he is the current wielder of the legendary sword; Excalibur, and member of Infernum Poncitator. Grandson of Rayner, Percy is one of the few third generation Nors in Avarus. He is a kind young man and is respected amongst his peers (well, most of them) and superiors, so much so that he has been offered the position of leader of the faction. Percy refuses as not only deems himself unworthy, but out of respect for those that have lived in Avarus longer.
He displays many the ideal traits of a knight, eventually becoming viewed as an ideal knight by others. However, deep down, Percy perceives himself as the opposite. He feels he is a dishonorable fraud and is not proud of his status as Excalibur's chosen wielder. If he was given a chance to do it over again, Percy would immediately abandon his decision never search and locate the sword.
After joining Avarus, in a short span of time, Percy was able to easily establish himself as a sort of leader figure within his faction. While serious most of the time, especially during missions, due to his time with other Nors, has displayed a degree of patience and tolerance towards whoever he is assigned. Still, he never forgets their main objective and takes charge if he deems the assigned leader incompetent. Which happens more times than he refuses to count. He tries to maintain a cool head, but will severely reprimand others if the situation calls for it.
Proficient in the ways of the sword, he garnered the attention of (the then Mongrel) Mitchell. He was very reluctant in taking in a squire. But eventually, Percy relented after the younger boy attempted to fight against an Astral and nearly lost his life. He plans to one day pass down Excalibur to Mitchell once he gains the strength to surpass Percy.
At the moment, Percy is the current Vessel of Wrath.
. . .
Noise (***** Rallus)
“I tried all of my life to give my dad a reason why he shouldn't be treating his body the way he did. I tried all of my life to keep my friend in line so I'd never have to be the one to discipline him. And yet... If only I didn't try so hard, they'd still be alive.”

Author’s Note: Yeah I... legit do not know who this belongs to. There’s the artist’s signature so that’s the good thing. Problem is....
After escaping from the confines of his original world, Eingesperrt City, and, with the help Sound, joined Avarus and assumed the title of Noise. Unlike others that were gathered in the past, Noise is a regular human being. Something only Sound knows. Regardless of the danger, he became one of the leaders for Tunera Clypse, later joining Mythral after adapting to his new lifestyle.
He wears one of the Artifacts in order to copy and use only one ability of his choosing. As long as a piece of original user is within the Artifact, Noise can use it for as long as he wants. However, if its been removed and replaced with something else, the previous copied ability cannot be used ever again.
Since his recruitment, Noise adopted an extremely lazy personality. He’s so lazy that somehow even snoring consumes too much energy. To make sure he’s awake most of the time, Sound forced Noise to set up a sleep schedule, so that when he’s ready, he has enough energy to do SOMETHING. However, no matter where he is, he’ll take every opportunity to take a nap. He doesn’t care. As long as he gets to close his eyes, Noise is fine to sleep wherever, even if it involves napping righ at the edge of a volcano.
He’ll get annoyed if anyone that dares try to wake him up and he’ll be in a fowl mood for the rest of the day. The only exception is the fox girl and his lover. Despite this, he displays a certain degree of kindness. It’s just really hard to tell if what he’s doing is truly an act of kindness or he’s just too lazy to do things such as delivering a ‘motivational speech’. He can be blunt when he has to be, and he tends to come off as a jackass rude because of his personality. However, this is his way of showing he cares. Noise will flat out tell you if he dislikes you.
Another thing to know about him is his crude sense of humor. Combined with his blunt and rude nature towards people, mostly acquaintances and strangers, it always leads to various... Misunderstandings. Worst case scenario? A fight. He'd improve if he could, but he won't.
Look, if you haven't figure out that he's lazy after reading all this, gooood luck.
For reasons unknown, despite becoming the next Vessel of Sloth, it remains dormant within him. They thought of extracting it to learn the causes that led up to its current dormant state, but Sound intervened in time as he knew that extracting it by force will kill the the vessel.
. . .
Michael/Raphael/Gabriel/Uriel/Saraqael/Raguel/Remiel/etc
‘Dragons are raised under the false pretense that they are the supreme species above all others. But that merely obscures the truth; the truth that we’re just as vulnerable as anyone else. There are various ways to kill aside from piercing our hearts with a spear.”

Author’s Note: Just so you know, HE’S BLONDE and has green eyes! This was the only option I have that closely resembles how I envisioned him! There was another because he gives off the same atmosphere when you look at him but... he’s from an otome game. And I only learned that recently so, if the same goes for this one? WELP. Oh and he has patches of dark brown scales on part of his skin.
Neither a Quietus Nors nor a resident of Avarus, Michael is a dragon. His version of his race if capable of transformation, but can only change into the form of the last creature they devoured. Whole. Rather than his true form, in order to remain working in Avarus, chose to work in the form of the former Prince of Edrakon, a world where dragons were enslaved and cruelly treated as mere objects. Despite his appearance not being his own, he maintains an intimidating and powerful aura, which is easily distinguishable even within a large crowd.
Due to the high esteem he holds towards his race and his pride as a Dragon, he can come off as domineering, even becoming critical towards other versions of his race if he finds something illogical or nonsensical in their appearance and their abilities. While he does act this way, he finds it absolutely disgusting to find dragons place themselves in a position of power and abuses their power in controlling another species. Another aspect of him is that he looks down on dragons with physical defects, which is mostly directly aimed as himself due to his extremely poor eyesight. Thus, forcing him to rely on his human form to watch glasses. He also has a very confusing naming system; where he changes his name based on the date, time and temperature.
Micheal held the potential required to become a Nors, but because of his age, he was unable to undergo the necessary steps to fully integrate into Avarus. While others are reluctant to have him join their ranks, several others, for different reasons, allowed him to remain. This eventually allowed others to accept his addition to the organization.
As the one in charge of organizing and handling most of Avarus’ internal affairs, a job the Nors, even the Ex-Anima/Animus, are reluctant in taking up such an important position; he takes his job very seriously. Although he does express some contempt towards humans, this does not extend to the people he works with. He cares about them to a certain degree, which is shown by he constantly reprimands whoever acts risky during a mission.
He is the current Vessel of Pride, something he only learns of later on. Despite the fact Micheal is a vessel, Belial believes this is only temporary. He isn’t particularly close with Belial, but he respects the God enough to follow his orders.
. . .
Ulric Soknawo
'In my tribe, I was considered an outcast. You can thank the unnatural union that birthed me. Now? It hasn’t changed much, but at least I’m no longer considered the runt of the pack.’

Whose other name is Kuckunniwi, is a former member of the Aniwaya Tribe. In their world, his people are Natives who worshipped a guardian Wolf Spirit. According to them, in return for their unyielding loyalty and devoted nature, it granted the people with the power to take the form of the spirit they have worshipped for many generations. So long as they use that power to protect the forest, it shall provide them protection. Ulric is the third, second youngest, illegitamate son of the Tribal chief Tamaska and grandson of Wolfram.
As per tradition, all tribesmen are given two names, one for their human form while the other is for their inner wolf. Despite being allowed to use either name like others of his tribe, he refuses to be use his wolf name due to the meaning behind it. After being discovered by Ayane, she brought and recruited him to Avarus. Ulric is considered to be a Third Generation Nors due the fact his father was (oddly) not born a Nors, or had to potential to be converted into one.
Ulric tends to act like the stereotypical lone-wolf, choosing to remain in solitude and observe from a distance. He likes to spend his quiet time alone, though he does allow others to sit next to him when asked. Many have pointed out that he never smiles, but, as much as he hates to quote Noise, states that if there is no reason to smile, there is no reason to put so much effort in abusing his facial muscles.
As much as he loves being a wolf, he finds certain aspects of his second nature to be... aggravating. Depending on the season and the weather, it deals a the effects his wolf instincts on his human nature. Because of the two separate natures continually clashing, he tends to act irritable and his temper worsens, especially during the night. Ulric holds a strong belief that one’s nature, regardless of your race, should never control a one's personal feelings.
He holds an unyielding loyalty to his loved ones, almost to the point of willing to kill for them if the situation calls for it, but his actions are subtle and tends to be the exact opposite of how he truly feels. Only two people in his life have been able to decipher his behavior, and he cherishes them for it. Ulric has a bit of a temper as well but is able to keep it in check. His temper, however, is what led him to becoming a Cursed Blood. His curse forces him to foresee the deaths of whomever he romantically falls in love (or at least feel an interest) with.
Any attempts at interfering will only hasten their death.
. . .
Xavier Wozwald Hawthorne
'Murderers are dumbasses, always killing because of their unchecked emotions and pented up desires. Hence why most of them clumsily try to hide their crime. Serial killers are more... sofisticated with their craft, but their ego always gets in the way. If they weren’t complete dumbasses, they would have lived a long comfortable life. I should know.’

Note: Yes, this is obviously Vflower. Did I know that before? No. Do I plan to change the art reference? Yes, but only when I find one that’s not a god dang real-life person’s online avatar. XD Seriously, each time I thought I found one... it’s an utaite or vtuber.
Is a member of Mythral and a First Generation Nors. Like Rei, he is a Floater, which allows him to particiate in mission for all three factions. However, he prefers to work with those in Tunera Clypse as, since they mostly handle scouting and recruiting missions. As long as he doesn’t remain in Avarus for too long, he's fine with accepting any mission related to Tunera. Xavier will still accept missions from other factions, but that's merely to fill up his quota.
Despite appearing around the age 12-14; which was not by choice, Xavier is in fact mentally older than most of his fellow Nors. Known for his sharp tongue, Xavier is one of the few known Nors to have been granted permission to travel outworld immediately after undergoing the Ascenscion Ceremony.
Due to the experiences his past life went through, Xavier has a very grim outlook of the world and displays little to no respect towards authority figures. And that includes his current patron God; Belial, which only worsens after being told by the God that he is unable to help Xavier grow into the appropriate intended size. Unlike most Nors, he displays a high degree of critical thinking and intelligent. He is, if not more, level-headed than one of his friends; Percy. Though that doesn’t stop the teasing. While confident in his abilities in terms of combat, Xavier knows the limits of his current smaller body.
In order to compensate, he creates an excessively large scythe as compensation, but he's too proud to admit this.
Because of his level of maturity, he has been labeled as a 'Midget Grandpa'. Which he fails at trying to prove otherwise by collecting certain tthings that are considered out of date by their standards. Eventually, it became a soft of hobby for him to collect such things.
Xavier tends to display a sadistic nature while in combat, choosing to taunt his opponent by constantly pointing our their obvious flaws deficits and toy with them until the last minute. Most times, he will use his child-like appearance to his advantage to further torment his opponent/victim. Comically enough, if his opponent is a cold-blooded criminal, Xavier will compliment and , depending on their actions, congratulate them; much to the annoyance of those involved.
Like Sound, he has both a Physical and Blood-based Curse, but unlike the latter, Xavier was born with both. His Physical Curse has caused severe permanent scarring on his right arm, making it appear similar to third degree burns. If freed from any type of coverage, such as bandages, his arm will painfully be set a blazed, forcing him to conceal his arm at all times. As a Cursed Blood, Xavier has a similar effect of a Siren, except his hypnotic singing forces someone to commit suicide. Every time he uses this curse, he temporarily falls into a coma.
. . .
Succu(bus) Kilmer

Like her name suggests, Succu is a succubus, but belongs to a different version of her species. Due to being a demon, she is forbidden to reveal her true name. Succu is neither a Nors nor a Cursed Blood. She’s more of an illegal immigrant after sneaking her way into a group of Nors when they were scouting for potential recruits. There have been many attempts in trying to relocate her back to her original world, but she is able to seduce her attackers and slip away. Eventually, Belial declared that she will be allowed to remain as a resident, so long as she contributes in their mission to locate Soleil.
While they do seduce those of the opposite sex, her source of food is not as grotesque as several others. She does seduce her victim, but moves her body in a way that her victims find alluring. Succu will then massage certain parts of their body as a means to relax them. To assure that they will not attempt to escape, she will release pheremones that nulls the victims senses. What she devours isn’t the flesh of her victim nor does she devour their soul, she merely devours the emotions she was able to invoke until her hunger is quenched.
Succu is flirtaceous and very... very.... VERY- Well, you get the point. While she doesn’t flaunt her beauty, she does know how to use it to her advantage. However, despite many approaching her, Succu has only eyes for one, and is willing to wait as long as possible for that person to reciprocate her feelings. Succu, although assertive and open with her feelings, is not the type to force them onto someone.
She does like to express herself by getting physical - very physical. Not the way that you’re thinking, you perverts. She finds it more convenient to allow her actions to talk rather than saying things verbally. Since she’s an outsider, she notices several things that not even Pery or Ulric have noticed, and both are outsiders as well considering the fact they grew up outworld before being recruited. Regardless, she remains silent for the sake of remaining by her beloved’s side.
Succu is often mistaken as the Vessel of Lust due to her nature, and, on her part, finds it’s tiresome to prove that she is not.
Side Characters
Tank Mortem
A former member of Tunera Clypse and Mythral, Tank has been assigned to act as one of the engineers in maintaining the Infernian Generator due to his body’s condition and the issues of his mental state. He seldom participates in missions but, despite being given strict orders not to, joins in anyway. Due to the limits of his mental capacity, Tank has difficulty interacting with others. Quite literally.
Beatrix Staccato
Is a researcher and inventor in charge of the tools and weaponry utilized by most Nors and Ex-Animus. Having taken over most of the unfinished projects since the passing of his master, Beatrix has dedicated all of his time in improving the welfare of the world and its inhabitants. However, most of his experiments tend to be a bit... over the top. If he’s not thinking of new potential products that may benefits the Nors, he’ll make whatever comes at the top of his head, and most of the time it’ll lead him to make the most outrageous and unnecessary items. Beatrix prefers to remain in his lab/home at all times, rendering his social interactions with the three factions to be limited via holographic meetings.
‘Nyx’ Pierrot
Leader of Vanidicus Persona, she is one of the oldest Nors - next to Constantine - making her the default leader of her faction. Much about her is a mystery. Even her behavior can be viewed as... questionable. Not outlandish, that’s Sound’s department. Her behavior is so odd that it’s enough to baffle even Belial. She takes her leadership over her faction very seriously, however, as part of her nature, the requirements in joining and maintaining your membership vastly deviates from the original. However, looks can be deceiving. Aside from her seniority, there is a reason why she was given the position of leader.
Mitchell Pierrot
He prefers to be called as ‘Mitch’ after being told, and proven, by his sister how much of a tongue twister his name is if repeated constantly in a single conversation. While he is the younger brother of Nyx, Mitch opted to become a submember of Tunera Clypse upon undergoing the Ascension Ceremony to be in the same faction as his mentor, Perseus Vlahos. Compared to the Nors in his batch, he is viewed as weak by many as he is unable to perform the abilities that is expected of him to develop after becoming a Nors.
Constantine L. Refrain
Nothing is truly known about him except that he’s a chronic smoker. Nobody truly knows who he is, no one even knows which faction he belongs to. It’s nearly impossible to question these things as he is constantly surrounded by a shroud of - barely tolerable - smoke. All that is known is that he’s been around longer than most of the Ex-Animus. Constantine usually frequints the Silent Siren Bar, staying there for hours until he’s either drunk or needs to receive another pack of cigarretes from Beatrix. He says they’re for medicinal purposes buuuuut...
I’m pretty sure black smoke isn’t normal.
Stefan Mal Sorcier
Is Percy’s second pupil. Although, it was more like Percy was forced into taking in another after his continual refusal to become leader of Infernum Poncitator. Outwardly, he is aloof and always appears smiling, which unsettles Mitchell even when they’re alone. His politeness is found unusual by many and causes others to feel wary around him. Even the dragon finds himself is unable to remain in the same vicinity as the young man. Despite being full of many secrets, Percy accepts him as is and tries his best to teach him all he can, which Stefan appreciates.
Kyline Necro
Considered as the mascot ambassador of Avarus, like the soul that was fused with her upon birth, she mostly lounges around and has little participation in any missions in and out of Avarus. This has caused her to be disliked by many, most especially Ayane. The only person Kyline has gotten close to is Noise; mostly because they share the same favored sleeping spot. On a side, she acts a physician, or surgeon if you like to get technical. She has a strange fondness of picking apart and replacing specific limbs with doll parts.
Yu-Yan Chi Ryou
Was once one of the strongest Nors from Xavier’s batch until he was inflicted by an unknown disease during one of his missions. While there is no name for the disease, it has caused much of his bones to undergo crystallization; rendering him immobile due to the pain that comes from even the smallest of movements. Since he is incapable in participating in any activities, Yu-Yan has since been forced to be confined to a wheel chair for the rest of his life.
Anita Eine Kleine
Is the fighting instructor of the Mongrels and a member of Infernum Poncitator. Anita is a highly-skilled caster, able to conjure and manipulate various elements. She absolutely hates the term ‘witch’, even going as far as to cast a minor curse in making a person temporarily mute if they refer to her as one. Which Sound found rather offensive when he found out about the curse, something she deeply apologized for. She participates in some Scouting Missions but only if personally requested by someone from Tunera Clypse.
Victor Stein
Is Beatrix’s (only living) research assistant. He is the sole survivor of the Night of the Black Moon. Although having physically recovered, the damage to his mental state has left a deep scar on his psyche. He fears yet obsesses over the sensation of pain. There is not one instance where he isn’t found sowing over his own intact skin. While Victor knows his addiction found uncomfortable by others, he finds it extremely difficult to control his urges.
Wolfram
Grandfather of Ulric and most of his siblings, he is an Ex-Anima (or retired Nors) and a former member of the original Mythral. As the more experienced and one of the longest surviving resident of Avarus, he acts as a mentor to those who seek his guidance. However, in terms of combat, his skills are very limited as he has become permanently stuck in his wolf form. The only grandchildren he's ever personally met are Ulric and Seeing, who have both ironically became his favorite. While acting as a mentor, he is rather strict, constantly parting lessons in order to make sure none make the same mistakes he committed when he was younger, many of which he refuses to share.
Diantha Anemone
Despite being still a Liberi, Dia still participates in many activities meant to be done only by Nors. She originally wanted to become a part of Tunera Clypse due to the many adventures imparted by Sound. But after having a first hand experience in one, it traumatized her to the point where she wants to merely work as a Librarian, a position many people avoid.
Echo & Yell
Fellow teammates of Sound and Noise. As part of the four heads leaders that overwatch many of Tunera Clypse's activities, both in and out of Avarus. They mostly take charge of delegating the members while the other two take an active role in leading many scouting missions off-world. Contradicting her name, like Sound and Noise, her personality is the completely opposite. Due to her sociophobia, she is extremely shy and is unable to speak when talked to, only whispering her sentences as she talks. Yell, however, is the only one whose personality fits the mantle she inherited. Due to her curse, she has to raise her voice after every two hours. If not, she will fall into a coma, and she can only be awaken by *************.
Important Figures
Belial

Credits to: @airtrees0507 (Again, another artist who... disappeared from the internet. How do I keep finding refrences where the artist is just gone?)
Is a Celestial and the younger brother of Soleil. However, despite his godly status, he does not have any of the expected gifts. Neither a god of creation, life, or death, he has been given the title God of Void by his peers. Because of this, he is incapable of maintaining Avarus by himself, forcing him to use alternative (and questionable) means in preserving the world his sister created. Like his title, Belial is unable to express emotions, giving blank demeanor. He does, however, hold some semblence of emotions within him. Yet despite this, he has little to no understanding of life, death and emotions. Even after centuries since he over his sister’s role as Patron God, he still has no understanding to all living things, almost to the point of coming off as insensitive and heartless.
Belial has a deep devotion to his sister, having gone through great lengths to make sure to maintain her world and willingly sacrifice the lives of many. Despite knowing her distaste towards such acts, he holds onto the hope of one day finding her.
Soleil

Credits: Um... Lucare Eu??? Sorry, I’m just basing it off the signature. Once again, can’t find the artist themself so...
The true patron goddess of Avarus and the older sister of Belial. Aside from her status as the original creator and caretaker of her world and the life that once flourished within it, not much is known about her. While her exact cause of death is unknown, she was cursed to live an endless cycle of death and rebirth in various worlds. In order to restore the world she created and loved dearly, Belial dedicated his life in searching for her soul and freeing her of her curse. As a Celestial, she was said to have chosen to take the form of her first ever creation and first mortal friend.
It is said that, despite having blessed with the gift of creation, she was known to be a lonely goddess. Those that new her describe as someone that’s physically there but is spiritually detached.
The Oracle

Is a title given to those with the ability to commune and guide the spirits to the Empyrean Plain, more specifically Avarus’ residences due to the absence of Soleil. The Oracle acts as the divine anchor on the world to aid Belial in prolonging the world’s existence. They are also the main source of Belial’s divine power; both of which are maintained through her prayers. The gender and species of the Oracle is non-specific, but it if preferred by Belial if they are humanoid and have the ability of speech for the sake of communication.
The current Oracle is Aniela Fischl, who, unlike her predecessors, is able to foresee various futures. She does so by carefully peeking through the leylines and selects various possibilities that solely benefit Avarus. No one is allowed to meet her except Belial and her assigned Seekers.
The Seekers
The guardians, caretaker, and acting medians between the Oracle and the residents of Avarus. Their duty is to ensure that the chosen Oracle remains within the Spiral Tower and that he/she fulfills their duty, even going as far as to grant their wish regardless of the consequenses. Each Seeker has only one desire, and that’s to protect the Oracle at all times.
Races
Liberi
Age Range: Birth or 5 to 10 years
Although that is the official term, ‘Mongrel’ is what they are commonly referred as. It is the used for the for the children taken to or born in Avarus. Mongrels spend most of their young lives training within the safe walls of the Aldebaran Academy. They are forbidden from leaving as, according to Belial, they are the extremely fragile during this point of their lives. Regardless of their age, depending on how well they’ve performed in training, they will be given the right of undergoing the Ascension Ceremony. Those who fail are xxxxxxxx xx.
Due to their young age, their behavior is more sporadic than that of a normal child. Their reflexes are enhanced, almost to the point where it becomes difficult to contain them. Mongrels lack common sense so they tend to act out without fully understanding the impact their actions have. While childish and friendly by nature, Travellers are advised to approach with caution. Those who act beyond the expected norm are called Prodigies.
Quietus Nors
Age Range: (Physically) 14-19, (Mentally) 10 or above
Or simply called, Nors. After their graduation, every Nors is immediately sent to work. Depending on the final results of their training prior to undergoing the ceremony/procedure, each is individually assigned into one of the three factions ; Infernum Poncitator, Vanidicus Persona, and lastly, Tunera Clypse (formerly called Tunera). Those that are assigned to neither of the factions are assigned to more menial jobs alongside the Ex-Animus,
Despite their young minds, they have quickly adapted into their new forms. Due to time becoming almost non-existant in Avarus, Nors age at a rapidly slow rate. Though known to be childish by nature due to the gap of their young minds to their bodies, they dangerously lack empathy and display little to no compassion and remorse towards others. In worst cases, some act selfishly on their own accord. On a positive note, they lack any emotions that may hinder their mission in locating Soleil; such as fear.
Only two of the three current generations of Nors differ greatly from the first:
First Generation Nors - Are those converted or directly born within Avarus with the blood of two Nors. Those born in the first generation share two specific physical characteristics; raven black hair and golden eyes. They all share the same abilities upon conversion/birth, but it depends on the individual which ones they should master. Unless they happen to be a Cursed Blood, they are unable to obtain different abilities to call their own. They are required to undergo the Ascension Ceremony.
Second Generation Nors - In terms of personality, they are considered half as bad as those in the first gen. Unlike the previous, second generation Nors are considered slightly weaker, however, they have a better chance of obtaining other abilities outside of Avarus. Their hair is slightly lighter shade of black but their eyes remain the same. They too are required to undergo the Ascension Ceremony.
Third Generation Nors - While rare, they do tend to appear once in a while. It’s not exact how one falls into this category. The closest is being the grandchild or who has an anscestor that was a Nors. Because of their circumstances, these Nors are far weaker as they cannot use any of the standard abilities. Third Generation Nors are far difficult to locate as their potential doesn’t surface until they are of a much later age, rendering them incapable of taking necessary training to hone their abilities and undergoing the Ascension Ceremony. They do not share the common personality or physical traits of a Nors. One thing every Nors in this generation share are sky blue eyes, which emit a faint glow when in the dark.
Ex-Animus (or Anima for singular)
Age Range: (Physically) 30 to 40, rarely appears in their early 20′s
Are individuals who are retired from their duties as a Nors. Although Nors generally age at an excessively slow rate (due to the effects of Avarus), after a number of cycles (which refers to the number of batches that underwent the Ascension Ceremony), they will be given the order to retire. Regardless whether they are willing to or not, there is nothing they can do once the order has been issued. Once one becomes an Ex-Anima, they are completely cut off from their original faction and are unable to leave Avarus for the rest of their life.
Not only that, they are unable to defend themselves like they used to as they can no longer control Astral Dust and use the abilities from their time as a Nors,Basically. Basically, Ex-Animus’ are left to fend for themselves.
Factions
Every Nors is allowed to join any of the three factions; Infernum Poncitator, Vanidicus Persona , and Tunera Clypse. There is an option to not join any of the factions; they are called ‘Floaters’.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
100 Humans on Netflix
So there’s this neat Netflix Original show called 100 Humans. I immediately got interested in it because they take this group of various humans from different backgrounds, age groups, and so on, and they use them to conduct experiments to get answers to interesting questions.
So, right away I had concerns about this show because
If you know anything about data and statistical research, you know 100 people is a very small sample size and does not breed accurate results
However, I’m very curious and wanted to see what they came up with anyway. I watched all 8 episodes and, honestly, I enjoyed watching it for the most part. However, I have a LOT of issues with the show and how it was conducted and I want to list them out here.
If you’re interested in watching 100 Humans or have already watched it, please consider the following before taking any of the show’s data as fact.
100 people is a very small sample size. This is because, the more people you have, the more weight each increment in your percentages has. With 100 people, each person represents 1 entire percent. That’s a lot. That means even a few people giving incorrect answers, having off-days, or giving ridiculous results (such as you can see in the spiders georg meme), can sway the entire result of an experiment into unreasonable territory. This is why most scientific studies attempt to get data from many hundreds or even thousands of people. The bigger the sample size, the more accurate it is to the entirety of the world.
I’ll put the rest under the cut because it gets long
The 3 hosts, who I’ll refer to as the scientists (regardless of if they actually are, because I’m not sure and don’t feel like googling it) repeatedly make false statements. For example, in one episode, they told their humans to “raise your hand if you believe you’re less bigoted than the average person here,” to which 94 people raised their hands. One of the scientists then made the statement, “If that were true, it would mean only 6% of Americans are bigoted.” This statement is entirely false. The only way to actually determine a true meaning to that would be to determine at what percentage of bigotry you are considered a real bigot. You also must consider that believing you’re more bigoted than other people in a small group, who you already have an impression of, is not necessarily indicative of how you feel you measure up to America as a whole. Anyway, I could go on and on. The only way to accurately summarize the results of that question would be to say that 44% of the humans had an inflated sense of righteousness or something of the sort.
The 3 scientists, both in person and in narration, for the sake of entertainment (if that’s what you call it) continually made “jokes” that poked fun at different groups, implied men are shit, etc. Maybe that’s fun for some people, but the kind of jokes they were making to amp up the hilarity of their host personas was genuinely just uncomfortable and made me feel even more like they couldn’t be trusted to go about unbiased research.
The scientists continually drew conclusions where the results should have been labeled inconclusive
The scientists made blanket statements about certain groups based on 1 element of research that would not stand up to further evaluation. For example, when explaining that ~93% (i think it was about that number) of Americans have access to clean, drinkable, tap water and yet some large number of single use bottled waters are sold every year, one scientist said it was because people believe bottled water is safer and cleaner than tap water. I am going to do my next survey on this to see if my own perception is flawed, but I simply don’t believe that all of the people who buy bottled water do so because they think its cleaner than “tap” (as if all tap is the same.) I know there have been studies about people drinking unlabeled bottled water and tap water and not being able to tell the difference, but this neglects to account for the fact that different houses pipes can affect the taste of the tap water running through them, people can use disposable bottles of water for certain activities or events too far away from tap for people to refill their reusable bottles easily, and so so so much more. Anyway, it just really bothers me to see “scientists” making these kinds of generalizations when they’re the ones whose results we’re supposed to trust.
The show was incredibly cisnormative. There was an entire episode based on comparing men and women that made me extremely uncomfortable with its division of people by men and women. There was the implication that all men have penises and all women have vaginas. There were implications that reproduction is a necessity in picking a partner. It was just a shitshow. There was one comment by one subject who asked, when being told to separate by men and women, “What if I’m transgender?” Obviously I can’t say for sure, but this person didn’t appear to be transgender and the sort of tone it was asked in makes me think it was literally something they asked him to say in order to get inclusivity points with the viewers and to “prove” that they’re not transphobic by having them divide up, because they said to go to the side you identify with. This whole thing is a) harmful to nb folks who would not have had a side to go to and b) completely negating the fact that the way we were socialized can have an effect on our social responses. That means that for a social experiment, a trans person could sway the results of one side due to their upbringing and the pressures society put on them before/if they don’t pass. This is all assuming they had any trans people there, which is potentially debatable. I also take issue with this entire fucking episode because just, the amount of toxicity in proving one sex is better than the others is really gross and actually counterproductive to everything feminist and progressive. Not to mention, them implying that they’re trying to support trans people only to reinforce the notion that a trans man is inherently lesser for being a man when even prior to hatching, he would have also been force fed propaganda and societal pressure implying he’s less than for supposedly being a woman is really gross and makes me angry. The point of what I’m saying is that it’s actually not woke to hate men as a way of bringing women up because there are men who are minorities who are being hurt by the rise of aggression being directed at them for their gender. Anyway enough about that.
The tests drew false conclusions because they did not account for how minorities adapt to a world that’s not made for them. This is specifically directed at the episode where subjects were asked to match up 6 people into couples. There were 3 women and 3 men and the humans were asked to put them together into pairs. they could ask the people 1 question each but then had to match them up with only that information. The truth is, the people brought in were 3 real life couples already, which the humans didn’t know until after they matched them. The couples were m/f, m/m, and f/f. I think that’s great, but the problem is, literally none of the humans asked any of them their sexuality as their question and most people didn’t even consider they could match up same-sex people. One girl even thought that they had told her to make m/f pairings, even though they didn’t. The scientists concluded from the experiment that the humans have a societal bias toward people, and assume they’re all straight, even if they, themselves, are not straight. I personally believe that was the wrong conclusion to draw. You could see some of the queer humans were shocked that they hadn’t considered some of the pairings might be gay. But, I don’t think it’s because they believe everyone they meet is straight, I believe this says more about what they expected from the scientists themselves. If someone is in a minority and they go to do something organized, like a set of experiments, they are going to be judging the quality and setup of the experiments by those designing them. I feel that the lack of consideration that the couples might be gay has a lot more to do with queer people having adapted to a world where queers are rarely involved or included in equal volume to the cishets. The queer humans taking part in the experiment and failing to guess gay couples shows that they have adapted to a world where they are excluded rather than a belief that every random person that they meet is straight. My point is further supported by an expert they had on the show who explained that, statistically, it was entirely likely that they were all straight and that even queers will account for being minorities by going with what’s most likely. The truth is, we are surrounded by a whole lot of straight people. It makes sense to assume only 6 people are all straight and that, if any aren’t, they may be bi.
The scientists frequently broke an already small sample size into even smaller groups. The group was very frequently broken in half, in thirds, or into sets of 10 people. These sample sizes tell us almost nothing actually conclusive.
The experiments/tests frequently were affected by peoples abilities, unrelated to what was being tested. For example, one test that was broken down into 6 people and 6 control people competing at jenga was meant to show whether needing to pee helps or hurts your focus. first of all, sample sizes of 6 are a fucking joke. Second, this completely ignores these 6 people’s actual ability to play Jenga. If someone sucks at jenga with or without needing to pee, them losing Jenga when they need to pee says exactly fuck all about whether needing to pee affected their focus. They should have tested people’s Jenga skills beforehand, counted the amount of moves they made before the tower fell, and then did it again after hours of not peeing to compare their results. This test made no logical sense at all.
The scientists ignored the social effect of subjects knowing each other as well as duration of events during their last experiment. They were testing to see if people with last names near the end of the alphabet get a shittier deal because they go last in everything where things are done by name order. They tested this by doing a fake awards ceremony where they gave out some 30 awards to people, gauging the applause to see whether the people at the end got less hype and therefore felt worse about themselves than those in the beginning who got the fresh enthusiasm of the audience. the results showed that the applause remained fairly consistent throughout the awards. The issues with this test are numerous, but here are the three I take most issue with. 1) the people here all got to know each other very well over the week it took to make the show. People who know each other and have become friends are much more likely to cheer for each other with enthusiasm, regardless of how long it’s been. On the other hand, polite applause from a crowd at, say, a graduation, where you are applauding people you don’t know, WILL start off more raucous and grow very quiet except for individual families near the end. 2) the duration of the test was a half hour, which is not very long at all and doesn’t say much to test the limits of enthusiasm. Try testing the audience at a graduation with a couple hundred graduates that also involves the time it takes to walk all the way up to a stage a hundred feet away, accept a diploma, and then wait for the next person. These kinds of events take hours and nobody keeps up their enthusiasm that long unless they’re rooting for someone in particular. 3) this study tested only one of many many ways name order affects a person. Cheering and applause is only one factor. It does not take into account people having their resumes looked at in alphabetical order and therefore people at the beginning of the alphabet being picked before anyone ever looks at a W name’s resume. It doesn’t take into account a small child’s show and tell day being at the very end of the school year, after 6 other people have brought in the same thing they planned to. No one cares about their really cool trinket because they’ve seen a bunch like it already. This test doesn’t take into account how many end-of-the-alphabet people just get straight up told, “we ran out of time. maybe next time,” when next time doesn’t really exist. I feel genuinely bad for the girl who suggested this experiment because the scientists straight up said something akin to, “lmao her theory was bs ig /shrug” even though it was their own shitty research abilities that led to their results.
They did one experiment intending to see how many people have what it takes to be a “hero.” The request for this test was made by someone curious about the effect of adrenaline and if it really works how some people say. The scientists thought it an adequate method to determine an answer by testing their reflexes with a weird crying baby sound and then dropping a doll from above while they were distracted with answering questions. The scientists looked up before the doll dropped to indicate a direction of attention. While this does give some answers about peoples intuition, reflexes, and ability to use context clues, its entirely an unusual situation, makes no sense in reality, fails to take adrenaline into consideration literally at all, and has a lot more to do with chance. The person dropping the doll literally couldn’t even drop it in the same place from person to person. Some got it dropped into their lap and others almost out of arm’s reach. This, like a few of the other mentioned experiments, was during the last episode, which felt lazy and thrown together last minute, with very little scientific basis to any of the results. The last episode was weak and disappointing overall.
One of the big issues I have with this show is actually their repeated use of the same group. They said at the end that they had done over 40 tests. Part of doing studies is getting varied samples of people in order to get more widespread results. Using the same 100 or less people (already a tiny sample) repeatedly is a terrible research method. You’re no longer studying humans at large. You’re studying these specific humans. You can’t take the same group with the same set of inadequacies, the same set of skills, and the same set of biases and then study them extensively and in many different ways like this. Your results are inherently skewed toward these specific people and their abilities. I expected them to at least get a new group each episode - every 5 or so studies - but no. They keep the same group all week, which makes the entire season. This is inexcusable in research imo.
The next issue is contestant familiarity. The humans all getting to know each other is great, socially, but it also destroys the legitimacy of many of the studies that involve working together or comparing yourselves and your beliefs
Many tests had issues with subject dependency. One study, meant to compare age groups and their ability to work together to complete the task of putting together a piece of ready to assemble furniture had each group with members they relied on entirely. A few people built the furniture while one person sat across the room, looking at instructions with their back to the others. They had to relay the instructions through a walkie talkie to another contestant and that other contestant had to relay it to the people they’re watching build the chair. You cannot study a group’s ability to build something with instructions by the ability of one single person to communicate. You’re testing that individual and the rest of them on two completely different capabilities. One person fails at being able to communicate and everyone else becomes unable to build the furniture. Even if everyone else in the group is more effective than all the other groups at building ready to assemble furniture, they might end up falling in last because of their shitty communicator who is literally not able to convey simple instructions. (yes, this actually happened in the test)
One test judged the subjects at their speed of getting ready, to see if men or women are faster at getting ready. While most elements of this test were just fine, the part I took issue with was that they did this test without regard to social convention. They told the subjects they were going on a field trip and to get ready by a certain time. Then, they gave them many things to get distracted by, like refreshments to pack with them, a menu to preorder lunch from, and so on. The part that upsets me about this test is that they ignored social convention entirely, to the point that subjects were judged based on their conventional actions and expectations more than their actual speed at getting ready. The buses promptly shut their doors and left at the time they were supposed to but there was no final call to get on the buses. In general, when a group is to be taken somewhere by bus, there will be an announcement to load up and leave. You could clearly see many of the subjects were ready to go and were just standing around talking while they waited for fellow subjects to finish getting ready. I have no doubt that, if given a final call, most of them would have loaded up within a couple minutes. However, they were relying on the social convention of announcing departure and were therefore, left behind entirely (for a nonexistent field trip). These people who were left behind were counted as being late and not making the time cutoff. If one were to look at the social element of this situation, if everyone there believed there would be a warning before departure, the fact that 24 to 14 women to men were loaded onto the buses at departure doesn’t necessarily indicate the women were faster to get ready. It seems to me that it’s more likely to indicate anxiety at being late and a belief that they need not impede on anything lest they be reprimanded or have social consequences for taking too long - something women are frequently bullied for. There’s also the chance that many who boarded without final call are more introverted or antisocial. Plus, we can’t forget to include the people who have anxiety about seating. If someone is overweight, has joint pain, or has social anxiety, they will be more likely to board early to get a seat they feel comfortable in. If they had counted up all of the people socializing and waiting on the sidewalks nearby, they may have found that there were more men who were ready to board up at a moment’s notice. I’m not saying I think men are faster to get ready, I’m just saying that we can’t know based on who boarded without a final call. If people believe they will have a last minute chance to board, a large number of them will take the last few minutes to socialize with their new friends until they’re told they have to board. Therefore, this test cannot be considered conclusive without counting and including the people who were ready and not boarded as a third subset.
Honestly, I could go on and on about how sensationalist and unscientific this show is, but I just don’t have 6 more hours to contribute to digging up every single flaw with it. There’s A Lot.
My point is, if you feel like watching this show, which I don’t necessarily discourage inherently, I just beg you to go into it with a critical eye. Enjoy the fun of it and the social aspects, but please don’t rely on the information provided and please don’t spread it as fact, because it’s not.
It’s entertainment, not science.
#100 humans#netflix#tv#show#science#scientific research#research#studies#study#studyblr#statistics#stats#sociology#data#netflix original#analysis#review#netflix review#show review#tv review#ghostpost#logical fallacy#logic#correlation#causation
10 notes
·
View notes