#creative cognition
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Does Having ADHD Make You More Creative?
How to ADHD
View On WordPress
#actually neurodivergent#adhd and creativity#Art#brain storming#brains#conceptual expansion#creative#creative achievements#creative cognition#creative thinking#Creativity#creativity and adhd#divergent thinking#drawing#how to adhd#innovative thinking#Mind Map#motivation#Neurodivergence#neurodiversity#novel ideas#original#overcoming knowledge constraints#painting#problem solving#reward creativity#risk taking#sculpting#shower thoughts#stimulation
1 note
·
View note
Note
hi there! im a fan of your page 💕
can you give me the best studying techniques?
hi angel!! @mythicalmarion tysm for asking about study techniques 🤍 i'm so excited to share my secret methods that helped me maintain perfect grades while still having a dreamy lifestyle + time for self-care!! and thank you for being a fan of my blog, it means everything to me. <3
~ ♡ my non-basic study secrets that actually work ♡ ~




(don't mind the number formatting)
the neural bridging technique this is literally my favorite discovery!! instead of traditional note-taking, i create what i call "neural bridges" between different subjects. for example, when studying both literature + history, i connect historical events with the literature written during that time. i use a special notebook divided into sections where each page has two columns - one for each subject. the connections help you understand both subjects deeper + create stronger memory patterns!!
here's how i do it:
example:
left column: historical event
right column: literary connection
middle: draw connecting lines + add small insights
bottom: write how they influenced each other
the shadow expert method this changed everything for me!! i pretend i'm going to be interviewed as an expert on the topic i'm studying. i create potential interview questions + prepare detailed answers. but here's the twist - i record myself answering these questions in three different ways:
basic explanation (like i'm talking to a friend)
detailed analysis (like i'm teaching a class)
complex discussion (like i'm at a conference)
this forces you to understand the topic from multiple angles + helps you explain concepts in different ways!!
the reverse engineering study system instead of starting with the basics, i begin with the most complex example i can find and work backwards to understand the fundamentals. for example, in calculus, i start with a complicated equation + break it down into smaller parts until i reach the basic concepts.
my process looks like:
find the hardest example in the textbook
list every concept needed to understand it
create a concept map working backwards
study each component separately
rebuild the complex example step by step
the sensory anchoring technique this is seriously game-changing!! i associate different types of information with specific sensory experiences:
theoretical concepts - study while standing
factual information - sitting at my desk
problem-solving - walking slowly
memorization - gentle swaying
review - lying down
your body literally creates muscle memory associated with different types of learning!!
the metacognition mapping strategy i created this method where i track my understanding using what i call "clarity scores":
level 1: can recognize it
level 2: can explain it simply
level 3: can teach it
level 4: can apply it to new situations
level 5: can connect it to other topics
i keep a spreadsheet tracking my clarity levels for each topic + focus my study time on moving everything to level 5!!
the information architecture method instead of linear notes, i create what i call "knowledge buildings":
foundation: basic principles
first floor: key concepts
second floor: applications
top floor: advanced ideas
roof: real-world connections
each "floor" must be solid before moving up + i review from top to bottom weekly!!
the cognitive stamina training this is my absolute secret weapon!! i use a special interval system based on brain wave patterns:
32 minutes of focused study
8 minutes of active recall
16 minutes of teaching the material to my plushies
4 minutes of complete rest
the specific timing helps maintain peak mental performance + prevents study fatigue!!
the synthesis spiral evolution this method literally transformed how i retain information:
create main concept spirals
add branch spirals for subtopics
connect related concepts with colored lines
review by tracing the spiral paths
add new connections each study session
your notes evolve into a beautiful web of knowledge that grows with your understanding!!
these methods might seem different from typical study advice, but they're based on how our brains actually process + store information!! i developed these through lots of research + personal experimentation, and they've helped me maintain perfect grades while still having time for self-care, hobbies + fun!!
sending you the biggest hug + all my good study vibes!! remember that effective studying is about working with your brain, not against it <3
p.s. if you try any of these methods, please let me know how they work for you!! i love hearing about your study journeys!!
xoxo, mindy 🤍
glowettee hotline is still open, drop your dilemmas before the next advice post 💌: https://bit.ly/glowetteehotline

#study techniques#academic success#unconventional study methods#creative study tips#neural bridging#shadow expert method#reverse engineering study#sensory anchoring#effective studying#minimal study guide#glowettee#mindy#alternative learning#academic hacks#study inspiration#cognitive stamina#learning tips#study motivation#unique study strategies#self improvement#it girl energy#study tips#pink#becoming that girl#that girl#girlblogger#girl blogger#dream girl#studying#studyspo
97 notes
·
View notes
Text
perhaps interesting take during this fine holiday but… i really like when people write in first person for selfship stuff and things like that lol
#rambles.#i know a lot of people don’t like that pov but i do. at least in this context#because i can see the beauty of it from your perspective instead of pseudo-pretending like it’s ‘me’ ykwim#i know it’s a complicated topic tho since many people write for themselves to go back and read#so yeah ‘you’ makes sense in that regard. i get it#i guess it’s just a preference thing#because even tho i’m not a person who goes back and reads my own stuff very often (and who doesn’t write heavy selfship things in general)#i think i would still prefer to read stuff like that back in a first person pov?? because that’s how my brain works personally#and it’s easier for me when reading someone else’s stuff in that pov to separate myself from it and enjoy it from their perspective#rather than struggle with the cognitive dissonance stemming from ‘you’#anyways. many thoughts many possibilities i love the creative world#i will cease my rambling now
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Philosophy of Curiosity
The philosophy of curiosity explores the nature, origins, and implications of human curiosity, which drives individuals to seek knowledge, explore new experiences, and ask questions about the world around them. Curiosity has long been recognized as a fundamental aspect of human cognition and behavior, playing a central role in scientific inquiry, philosophical reflection, and everyday life. Here are some key aspects and theories within the philosophy of curiosity:
Epistemic Curiosity: Epistemic curiosity refers to the desire for knowledge and understanding, motivating individuals to seek information, explore new ideas, and engage in intellectual pursuits. Philosophers have debated the nature of epistemic curiosity, its origins in human cognition, and its role in shaping scientific progress and cultural development.
Aesthetic Curiosity: Aesthetic curiosity pertains to the exploration of beauty, art, and creativity, driving individuals to seek out new experiences, appreciate diverse forms of expression, and engage with works of literature, music, visual art, and other cultural artifacts. Aesthetic curiosity raises questions about the nature of artistic inspiration, cultural interpretation, and subjective experience.
Existential Curiosity: Existential curiosity concerns the exploration of existential questions about the nature of existence, meaning, and purpose, motivating individuals to reflect on their own lives, values, and beliefs. Existential curiosity encompasses inquiries into topics such as the nature of consciousness, the search for transcendence, and the quest for personal fulfillment.
Philosophical Curiosity: Philosophical curiosity involves the pursuit of philosophical inquiry, critical thinking, and self-reflection, prompting individuals to question assumptions, challenge conventional wisdom, and explore fundamental concepts such as truth, morality, justice, and reality. Philosophical curiosity underlies the practice of philosophy as a discipline and informs broader intellectual endeavors.
Ethical Curiosity: Ethical curiosity concerns the exploration of ethical questions and moral dilemmas, motivating individuals to consider the consequences of their actions, empathize with others, and strive for moral growth and development. Ethical curiosity raises questions about the nature of moral values, ethical principles, and the pursuit of the good life.
Cognitive Curiosity: Cognitive curiosity encompasses the exploration of cognitive processes, mental states, and psychological phenomena, driving individuals to understand how the mind works, how knowledge is acquired, and how beliefs are formed. Cognitive curiosity informs research in fields such as psychology, neuroscience, and cognitive science.
Cultural Curiosity: Cultural curiosity involves the exploration of diverse cultures, traditions, and worldviews, prompting individuals to learn about different societies, languages, and customs, and to appreciate the richness of human diversity. Cultural curiosity fosters intercultural understanding, global awareness, and cross-cultural communication.
Metacognitive Curiosity: Metacognitive curiosity pertains to the exploration of one's own cognitive processes and learning strategies, motivating individuals to reflect on their own thinking, monitor their own understanding, and adapt their learning strategies to achieve greater intellectual growth and self-improvement.
Overall, the philosophy of curiosity explores the multifaceted nature of human curiosity and its profound influence on knowledge, creativity, personal growth, and the human condition.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#chatgpt#education#psychology#Epistemic curiosity#Aesthetic curiosity#Existential curiosity#Philosophical curiosity#Ethical curiosity#Cognitive curiosity#Cultural curiosity#Metacognitive curiosity#Human cognition#Inquiry#Exploration#Intellectual curiosity#Human experience#Curiosity and creativity#Curiosity and learning
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Friendly reminder that ADHD doesn’t mean “Wow! Teehee I’m so silly and hyper! Oh! What’s this what’s that? I can’t sit still lol!” As someone with ADHD, it really hurts when characters and real people with ADHD are represented that way, so please keep this in mind if you’re writing about a character in a story who has it.
1: ADHD is on the neurodivergence spectrum, and is a cognitive disability. 2: While yes, we can struggle to sit still and get distracted, that’s generally more of a negative thing rather than something “quirky” 3: We can struggle with social interaction, get overwhelmed and overstimulated, feel a near-constant sense of unrest, find it hard to fall asleep, and much more things that can make life difficult for us.
Keep in mind: other people with similar disabilities are also often stereotyped in this way! Just because ADHD is imo the most common doesn’t mean this can’t happen with other mental disabilities as well! I once had a panic attack a few years ago at a school while wearing dark clothes and some people verbally and to my face labeled me as having depression (which I don’t).
What I listed above is only a small piece of something a bit more complicated, and though it’s not necessarily required to do heavy deep diving in this subject, it is still very important to properly represent people with mental disabilities and to not stereotype real people with real emotions.
Below are some resources talking about what ADHD actually is. Remember, if you ever have done this and accidentally stereotyped things like this, it’s never too late to make sure that doesn’t happen again.
#Writers#writerscommunity#writers on tumblr#writers and poets#writer stuff#creative writing#writeblr#writing life#writing#fanfic#archive of our own#ao3 writer#fanfiction#ADHD#adhd problems#actually adhd#adhd things#adhd brain#neurodivergence#neurodivergent#neurodiversity#mental health#mental illness#actually mentally ill#cognitive disability
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Human Brain vs. Supercomputers: The Ultimate Comparison
Are Supercomputers Smarter Than the Human Brain?
This article delves into the intricacies of this comparison, examining the capabilities, strengths, and limitations of both the human brain and supercomputers.

#human brain#science#nature#health and wellness#skill#career#health#supercomputer#artificial intelligence#ai#cognitive abilities#human mind#machine learning#neural network#consciousness#creativity#problem solving#pattern recognition#learning techniques#efficiency#mindset#mind control#mind body connection#brain power#brain training#brain health#brainhealth#brainpower
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
I just realized something awful
I’ve always had a problem
With things that don’t last
Did it even hurt me
If it’s over so soon?
It was only x minutes, x hours, x days
Was it really as bad as I thought?
Was it even real?
I thought that came from me
Just my personality
Something to work through
But now
My mom is telling me
It won’t last
You’re going to regret doing this now
It means less because it might change someday
You might change your mind
And I’m wondering
If the problem was ever me at all
~ella
#poetry#my poem#my poetry#asexual#asexuality#writeblr#creative#my mother#sometimes it’s hard to be someone’s child#manipulation#maybe#cognitive distortions#again maybe#idk it’s still weird in my head#original poem#original poetry
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
🪗
#man. if anything at all is worth not having him in my life#it's the life that i have now#and i kinda reject what would be an easy narrative to tell which is that i needed to lose him to gain what i have now#because i do think i was limited by that relationship but it's more complicated than that#and i genuinely believe a lot of it was just coincidence#but! my life has so much good in it i am literally flanked on all sides by family#of origin and of choice#and creative pursuits that I actually have cognitive space to care about#because all my creative energy is no longer being funneled into frantically trying to make that relationship work#people matter to me in ways that felt impossible when i was with him because he felt like the only person that mattered#and if i loosened that grip i was scared he'd disappear#spoiler alert he disappeared anyway#and lucky little me that void got filled with just. so much love and laughter and fulfillment and truth#thanks for listening diary
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

sick sad world
#my art#vent art#self portrait#the good part about enjoying being creative again is#feeling it even more when capitalism steals your creativity and cognitive energy
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Arcane s2 spoilers
I need to stop kinning Jinx and go eat breakfast and pretend that finale did NOT just kill her off

#sillyposting#she’s so erratic and sad and suicidal and full of love and rage and creativity and trauma and#*cradles her in my hands* I just think she’s neat#I think it’s so funny they killed off the suicidal character and frame it as being a loving sacrifice#and that she’s finally at peace now that she’s dead#surely this does not reinforce the cognitive distortions of suicidal people thinking everyone would be better off without them!#disclaimer:#I love a good tragedy okay!!!! but I’m so tired of this trope of always killing off mentally ill characters. especially suicidal ones#get new material PLEASE#anyway time to touch grass. Dunkin’ Donuts time ☕️🍩‼️
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Possibly one of THE most frustrating things about experiencing cognitive awareness whilst having hallucinations/delusions/splitting episodes is getting that feeling, as if you're in the passenger's seat of a car, you've just looked over to the driver's seat to see nobody there, so you try to move to grab the steering wheel, but you're bound by invisible chains that shackle you to the passenger's seat as the car you're in speeds down the road, so your only hope to make it out alive as you struggle against the invisible chains is either that you suddenly grow superhuman strength and bust out, or you wait for the car to eventually crash or run out of gas so you can cry for help from horrified bystanders.
Or maybe that's just a personal thing because this entire scenario is based on a recurring dream I've had since I was a little girl that has followed me into adulthood, who knows
#bpd#borderline personality disorder#actually bpd#bpd awareness#hallucinations#delusions#delulu#cluster b#cluster b personality disorder#personality disorder#cognitive skills#cognitive behavioral therapy#dbt#dialectical behavior therapy#adhd#diary entry#my thoughts#personal anecdote#dreams#recurring dream#dream journal#dream interpretation#mental health#mental illness#dark academia#light academia#gothic academia#chaotic academia#creative writing#journal entry
17 notes
·
View notes
Video
Landscape, asperity/kinship/collage/photogram by Russell Moreton Via Flickr: russellmoreton.blogspot.com/ The Unfolded Garment Embracing Subjectivity Pierced Assemblage on Photogram What is Philosophy? Gilles Deleuze, Felix Guattari Their book is a profound and careful interrogation of what it might mean to be a 'friend of wisdom', but it is also a devastating attack on the sterility of what has become, when 'the only events are exhibitions and the only concepts are products which can be sold'. Philosophy, they insist, is not contemplation, reflection or communication, but the creation of concepts www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0860916863/ref=pe_2724401_140...
#landscape#field#documents#recordings#texture#Russell Moreton#visual art#philosophy#Deleuze#Gauttari#collage#concept#mapping#asperity#subjectivity#materials#creative#body#form#fashion#corset#muse#otherness#textures#colour#moods#poetics#sensation#architectural#cognitive
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Elusive Spark: Untangling the Threads of Genius, Giftedness, and Emerging Intelligence
Human intelligence, a multifaceted tapestry woven with threads of logic, creativity, intuition, and adaptability, remains one of the most intriguing and debated subjects in science and philosophy. While standardized tests attempt to quantify this elusive quality, the true nature of intelligence eludes simple measurement. This article delves into the complex nuances of human intelligence, exploring the distinctions between genius, giftedness, and the burgeoning concept of “emerging” intelligence, all the while acknowledging the limitations of our current understanding.

Giftedness: Nurturing the Seeds of Potential
Giftedness, often identified in early childhood, typically manifests as exceptional aptitude in a specific domain, be it mathematics, language, music, or visual arts. These individuals possess an innate ability to learn and master new concepts quickly, often demonstrating advanced problem-solving skills and an insatiable curiosity within their chosen field. However, giftedness is not a monolithic trait. It encompasses a diverse spectrum of abilities and talents, each requiring unique nurturing and educational approaches to fully blossom.

Genius: The Dawn of Revolutionary Insights
Genius, a term often imbued with a sense of awe and reverence, represents a rare and extraordinary level of intellectual prowess. Geniuses are not merely adept at problem-solving; they are pioneers, forging new paths of understanding and reshaping the very landscape of their disciplines. Think Einstein’s theory of relativity or Mozart’s symphonies — groundbreaking contributions that fundamentally altered our perception of the universe and the possibilities of human expression. Genius, unlike giftedness, often transcends a single domain, encompassing an ability to connect seemingly disparate ideas and synthesize novel perspectives.

Emerging Intelligence: The Unfolding Enigma
A relatively nascent concept, “emerging” intelligence suggests a dynamic and evolving understanding of intellectual capacity. It challenges the traditional, static view of intelligence as a fixed attribute, instead positing that intelligence can emerge and develop throughout life, influenced by a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and personal experiences. This perspective emphasizes the potential for growth and adaptation, highlighting the plasticity of the human brain and its remarkable ability to rewire and reorganize itself in response to new challenges and learning opportunities.

The Interplay of Nature and Nurture
While the debate surrounding the relative contributions of nature versus nurture in shaping intelligence continues, the prevailing consensus points toward a complex interplay of both. Genetic predisposition undoubtedly lays the foundation for cognitive abilities, but the environment plays a crucial role in nurturing and cultivating these innate potentials. Access to quality education, enriching experiences, and a supportive social environment can significantly impact an individual’s intellectual development and unlock hidden talents.

Beyond the IQ Test: Embracing the Multiplicity of Intelligence
Standardized tests, while providing a useful benchmark for certain cognitive skills, fail to capture the full spectrum of human intelligence. They often prioritize logical-mathematical reasoning and verbal comprehension, neglecting other crucial aspects such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and practical skills. Howard Gardner’s theory of Multiple Intelligences, which proposes eight distinct types of intelligence — including musical, spatial, interpersonal, and bodily-kinesthetic — offers a more holistic perspective, acknowledging the diverse ways in which individuals can excel and contribute to society.
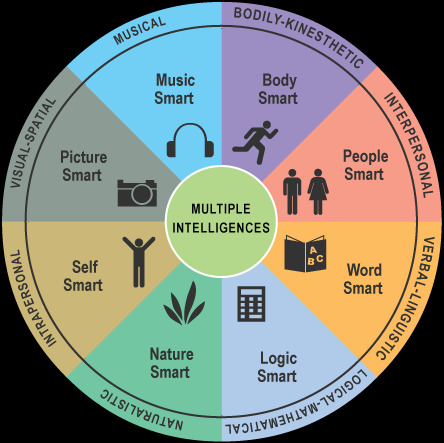
The Uncharted Territory of Potential
The concept of emerging intelligence underscores the limitations of our current understanding of human potential. It suggests that we may only be scratching the surface of what the human mind is capable of achieving. As neuroscience and cognitive psychology continue to advance, our comprehension of intelligence will undoubtedly evolve, revealing new dimensions and unlocking further possibilities for individual growth and societal advancement.

Conclusion: The Ongoing Quest for Understanding
The quest to unravel the mysteries of human intelligence is a journey that has captivated thinkers for centuries. While we may never fully comprehend the elusive spark that ignites genius or the intricate interplay of factors that shape intellectual development, our ongoing exploration of this fascinating realm continues to yield valuable insights. By embracing a more nuanced and holistic understanding of intelligence, we can foster a more inclusive and supportive environment where individuals of all abilities can thrive and contribute their unique talents to the world.
#Intelligence#Giftedness#Genius#EmergingIntelligence#Psychology#Neuroscience#Education#Cognition#HumanPotential#MultipleIntelligences#Talent#Creativity#Innovation
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Not knowing the scope of your own ignorance is part of the human condition. The problem with it is we see it in other people, and we don't see it in ourselves. The first rule of the Dunning–Kruger club is you don't know you're a member of the Dunning–Kruger club.”
— David Dunning
#quote of the day#David Dunning#dunning kruger#dunning kruger effect#quotes#skill#creative#art#artist#NFT#NFT art#NFT artist#ideas#idea#motivation#ignorance#cognitive#confidence#Psychology#mind#Justin Kruger
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Key Differences Between AI and Human Communication: Mechanisms, Intent, and Understanding
The differences between the way an AI communicates and the way a human does are significant, encompassing various aspects such as the underlying mechanisms, intent, adaptability, and the nature of understanding. Here’s a breakdown of key differences:
1. Mechanism of Communication:
AI: AI communication is based on algorithms, data processing, and pattern recognition. AI generates responses by analyzing input data, applying pre-programmed rules, and utilizing machine learning models that have been trained on large datasets. The AI does not understand language in a human sense; instead, it predicts likely responses based on patterns in the data.
Humans: Human communication is deeply rooted in biological, cognitive, and social processes. Humans use language as a tool for expressing thoughts, emotions, intentions, and experiences. Human communication is inherently tied to understanding and meaning-making, involving both conscious and unconscious processes.
2. Intent and Purpose:
AI: AI lacks true intent or purpose. It responds to input based on programming and training data, without any underlying motivation or goal beyond fulfilling the tasks it has been designed for. AI does not have desires, beliefs, or personal experiences that inform its communication.
Humans: Human communication is driven by intent and purpose. People communicate to share ideas, express emotions, seek information, build relationships, and achieve specific goals. Human communication is often nuanced, influenced by context, and shaped by personal experiences and social dynamics.
3. Understanding and Meaning:
AI: AI processes language at a syntactic and statistical level. It can identify patterns, generate coherent responses, and even mimic certain aspects of human communication, but it does not truly understand the meaning of the words it uses. AI lacks consciousness, self-awareness, and the ability to grasp abstract concepts in the way humans do.
Humans: Humans understand language semantically and contextually. They interpret meaning based on personal experience, cultural background, emotional state, and the context of the conversation. Human communication involves deep understanding, empathy, and the ability to infer meaning beyond the literal words spoken.
4. Adaptability and Learning:
AI: AI can adapt its communication style based on data and feedback, but this adaptability is limited to the parameters set by its algorithms and the data it has been trained on. AI can learn from new data, but it does so without understanding the implications of that data in a broader context.
Humans: Humans are highly adaptable communicators. They can adjust their language, tone, and approach based on the situation, the audience, and the emotional dynamics of the interaction. Humans learn not just from direct feedback but also from social and cultural experiences, emotional cues, and abstract reasoning.
5. Creativity and Innovation:
AI: AI can generate creative outputs, such as writing poems or composing music, by recombining existing patterns in novel ways. However, this creativity is constrained by the data it has been trained on and lacks the originality that comes from human creativity, which is often driven by personal experience, intuition, and a desire for expression.
Humans: Human creativity in communication is driven by a complex interplay of emotions, experiences, imagination, and intent. Humans can innovate in language, create new metaphors, and use language to express unique personal and cultural identities. Human creativity is often spontaneous and deeply tied to individual and collective experiences.
6. Emotional Engagement:
AI: AI can simulate emotional engagement by recognizing and responding to emotional cues in language, but it does not experience emotions. Its responses are based on patterns learned from data, without any true emotional understanding or empathy.
Humans: Human communication is inherently emotional. People express and respond to emotions in nuanced ways, using tone, body language, and context to convey feelings. Empathy, sympathy, and emotional intelligence play a crucial role in human communication, allowing for deep connections and understanding between individuals.
7. Contextual Sensitivity:
AI: AI's sensitivity to context is limited by its training data and algorithms. While it can take some context into account (like the previous messages in a conversation), it may struggle with complex or ambiguous situations, especially if they require a deep understanding of cultural, social, or personal nuances.
Humans: Humans are highly sensitive to context, using it to interpret meaning and guide their communication. They can understand subtext, read between the lines, and adjust their communication based on subtle cues like tone, body language, and shared history with the other person.
8. Ethical and Moral Considerations:
AI: AI lacks an inherent sense of ethics or morality. Its communication is governed by the data it has been trained on and the parameters set by its developers. Any ethical considerations in AI communication come from human-designed rules or guidelines, not from an intrinsic understanding of right or wrong.
Humans: Human communication is deeply influenced by ethical and moral considerations. People often weigh the potential impact of their words on others, considering issues like honesty, fairness, and respect. These considerations are shaped by individual values, cultural norms, and societal expectations.
The key differences between AI and human communication lie in the underlying mechanisms, the presence or absence of intent and understanding, and the role of emotions, creativity, and ethics. While AI can simulate certain aspects of human communication, it fundamentally operates in a different way, lacking the consciousness, experience, and meaning-making processes that characterize human interaction.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#metaphysics#ontology#AI Communication#Human Communication#Language Understanding#Natural Language Processing#Machine Learning#Cognitive Science#Artificial Intelligence#Emotional Intelligence#Ethics in AI#Language and Meaning#Human-AI Interaction#Contextual Sensitivity#Creativity in Communication#Intent in Communication#Pattern Recognition
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
you would think that finishing both of the books i’ve been reading on the same day would lead to a sense of satisfaction, because i’m keeping up nicely with my reading goals, or excitement, because i now get to select something else from my 563538373728 title “to read” list, but actually it’s horrible.
i just spent like 2.5 hours fully down the ADHD rabbit hole, listening to audiobook samples and experiencing ambivalence about narrators and debating what to get instead of doing literally anything else with my one wild and precious life.
ANYWAY. echopraxia by peter watts is next for fiction. 👍
what non-fiction AUDIOBOOKS SPECIFICALLY do you guys love? any subject, but good recordings and engaging narrators are a must.
#m#recommendations pretty please? 🥺#preferred topics: social sciences/cognitive science/bio & ecology/arts & creativity
6 notes
·
View notes
