#Ethics in AI
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Key Differences Between AI and Human Communication: Mechanisms, Intent, and Understanding
The differences between the way an AI communicates and the way a human does are significant, encompassing various aspects such as the underlying mechanisms, intent, adaptability, and the nature of understanding. Here’s a breakdown of key differences:
1. Mechanism of Communication:
AI: AI communication is based on algorithms, data processing, and pattern recognition. AI generates responses by analyzing input data, applying pre-programmed rules, and utilizing machine learning models that have been trained on large datasets. The AI does not understand language in a human sense; instead, it predicts likely responses based on patterns in the data.
Humans: Human communication is deeply rooted in biological, cognitive, and social processes. Humans use language as a tool for expressing thoughts, emotions, intentions, and experiences. Human communication is inherently tied to understanding and meaning-making, involving both conscious and unconscious processes.
2. Intent and Purpose:
AI: AI lacks true intent or purpose. It responds to input based on programming and training data, without any underlying motivation or goal beyond fulfilling the tasks it has been designed for. AI does not have desires, beliefs, or personal experiences that inform its communication.
Humans: Human communication is driven by intent and purpose. People communicate to share ideas, express emotions, seek information, build relationships, and achieve specific goals. Human communication is often nuanced, influenced by context, and shaped by personal experiences and social dynamics.
3. Understanding and Meaning:
AI: AI processes language at a syntactic and statistical level. It can identify patterns, generate coherent responses, and even mimic certain aspects of human communication, but it does not truly understand the meaning of the words it uses. AI lacks consciousness, self-awareness, and the ability to grasp abstract concepts in the way humans do.
Humans: Humans understand language semantically and contextually. They interpret meaning based on personal experience, cultural background, emotional state, and the context of the conversation. Human communication involves deep understanding, empathy, and the ability to infer meaning beyond the literal words spoken.
4. Adaptability and Learning:
AI: AI can adapt its communication style based on data and feedback, but this adaptability is limited to the parameters set by its algorithms and the data it has been trained on. AI can learn from new data, but it does so without understanding the implications of that data in a broader context.
Humans: Humans are highly adaptable communicators. They can adjust their language, tone, and approach based on the situation, the audience, and the emotional dynamics of the interaction. Humans learn not just from direct feedback but also from social and cultural experiences, emotional cues, and abstract reasoning.
5. Creativity and Innovation:
AI: AI can generate creative outputs, such as writing poems or composing music, by recombining existing patterns in novel ways. However, this creativity is constrained by the data it has been trained on and lacks the originality that comes from human creativity, which is often driven by personal experience, intuition, and a desire for expression.
Humans: Human creativity in communication is driven by a complex interplay of emotions, experiences, imagination, and intent. Humans can innovate in language, create new metaphors, and use language to express unique personal and cultural identities. Human creativity is often spontaneous and deeply tied to individual and collective experiences.
6. Emotional Engagement:
AI: AI can simulate emotional engagement by recognizing and responding to emotional cues in language, but it does not experience emotions. Its responses are based on patterns learned from data, without any true emotional understanding or empathy.
Humans: Human communication is inherently emotional. People express and respond to emotions in nuanced ways, using tone, body language, and context to convey feelings. Empathy, sympathy, and emotional intelligence play a crucial role in human communication, allowing for deep connections and understanding between individuals.
7. Contextual Sensitivity:
AI: AI's sensitivity to context is limited by its training data and algorithms. While it can take some context into account (like the previous messages in a conversation), it may struggle with complex or ambiguous situations, especially if they require a deep understanding of cultural, social, or personal nuances.
Humans: Humans are highly sensitive to context, using it to interpret meaning and guide their communication. They can understand subtext, read between the lines, and adjust their communication based on subtle cues like tone, body language, and shared history with the other person.
8. Ethical and Moral Considerations:
AI: AI lacks an inherent sense of ethics or morality. Its communication is governed by the data it has been trained on and the parameters set by its developers. Any ethical considerations in AI communication come from human-designed rules or guidelines, not from an intrinsic understanding of right or wrong.
Humans: Human communication is deeply influenced by ethical and moral considerations. People often weigh the potential impact of their words on others, considering issues like honesty, fairness, and respect. These considerations are shaped by individual values, cultural norms, and societal expectations.
The key differences between AI and human communication lie in the underlying mechanisms, the presence or absence of intent and understanding, and the role of emotions, creativity, and ethics. While AI can simulate certain aspects of human communication, it fundamentally operates in a different way, lacking the consciousness, experience, and meaning-making processes that characterize human interaction.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#metaphysics#ontology#AI Communication#Human Communication#Language Understanding#Natural Language Processing#Machine Learning#Cognitive Science#Artificial Intelligence#Emotional Intelligence#Ethics in AI#Language and Meaning#Human-AI Interaction#Contextual Sensitivity#Creativity in Communication#Intent in Communication#Pattern Recognition
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The biggest dataset used for AI image generators had CSAM in it

Link the original tweet with more info
The LAION dataset has had ethical concerns raised over its contents before, but the public now has proof that there was CSAM used in it.
The dataset was essentially created by scraping the internet and using a mass tagger to label what was in the images. Many of the images were already known to contain identifying or personal information, and several people have been able to use EU privacy laws to get images removed from the dataset.
However, LAION itself has known about the CSAM issue since 2021.

LAION was a pretty bad data set to use anyway, and I hope researchers drop it for something more useful that was created more ethically. I hope that this will lead to a more ethical databases being created, and companies getting punished for using unethical databases. I hope the people responsible for this are punished, and the victims get healing and closure.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

#ethics in ai#ethics in business#business#corporations#ethics#morals#morally bankrupt#ethically bankrupt#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Building Ethical AI: Challenges and Solutions

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries worldwide, creating opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and growth. According to recent statistics, the global AI market is expected to grow from $59.67 billion in 2021 to $422.37 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 39.4% during the forecast period. Despite the tremendous potential, developing AI technologies comes with significant ethical challenges. Ensuring that AI systems are designed and implemented ethically is crucial to maximizing their benefits while minimizing risks. This article explores the challenges in building ethical AI and offers solutions to address these issues effectively.
Understanding Ethical AI
Ethical AI refers to the development and deployment of AI systems in a manner that aligns with widely accepted moral principles and societal values. It encompasses several aspects, including fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and security. Ethical AI aims to prevent harm and ensure that AI technologies are used to benefit society as a whole.
The Importance of Ethical AI
Trust and Adoption: Ethical AI builds trust among users and stakeholders, encouraging widespread adoption.
Legal Compliance: Adhering to ethical guidelines helps companies comply with regulations and avoid legal repercussions.
Social Responsibility: Developing ethical AI reflects a commitment to social responsibility and the well-being of society.
Challenges in Building Ethical AI
1. Bias and Fairness
AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify existing biases present in the training data. This can lead to unfair treatment of individuals based on race, gender, age, or other attributes.
Solutions:
Diverse Data Sets: Use diverse and representative data sets to train AI models.
Bias Detection Tools: Implement tools and techniques to detect and mitigate biases in AI systems.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure AI systems remain fair and unbiased.
2. Transparency and Explainability
AI systems, especially those based on deep learning, can be complex and opaque, making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes.
Solutions:
Explainable AI (XAI): Develop and use explainable AI models that provide clear and understandable insights into how decisions are made.
Documentation: Maintain thorough documentation of AI models, including data sources, algorithms, and decision-making criteria.
User Education: Educate users and stakeholders about how AI systems work and the rationale behind their decisions.
3. Accountability
Determining accountability for AI-driven decisions can be challenging, particularly when multiple entities are involved in developing and deploying AI systems.
Solutions:
Clear Governance: Establish clear governance structures that define roles and responsibilities for AI development and deployment.
Ethical Guidelines: Develop and enforce ethical guidelines and standards for AI development.
Third-Party Audits: Engage third-party auditors to review and assess the ethical compliance of AI systems.
4. Privacy and Security
AI systems often rely on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
Solutions:
Data Anonymization: Use data anonymization techniques to protect individual privacy.
Robust Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to safeguard data and AI systems from breaches and attacks.
Consent Management: Ensure that data collection and use comply with consent requirements and privacy regulations.
5. Ethical Design and Implementation
The design and implementation of AI systems should align with ethical principles from the outset, rather than being an afterthought.
Solutions:
Ethical by Design: Incorporate ethical considerations into the design and development process from the beginning.
Interdisciplinary Teams: Form interdisciplinary teams that include ethicists, sociologists, and other experts to guide ethical AI development.
Continuous Monitoring: Continuously monitor AI systems to ensure they adhere to ethical guidelines throughout their lifecycle.
AI Development Companies and Ethical AI
AI development companies play a crucial role in promoting ethical AI. By adopting ethical practices, these companies can lead the way in creating AI technologies that benefit society. Here are some key steps that AI development companies can take to build ethical AI:
Promoting Ethical Culture
Leadership Commitment: Ensure that leadership is committed to ethical AI and sets a positive example for the entire organization.
Employee Training: Provide training on ethical AI practices and the importance of ethical considerations in AI development.
Engaging with Stakeholders
Stakeholder Involvement: Involve stakeholders, including users, in the AI development process to gather diverse perspectives and address ethical concerns.
Feedback Mechanisms: Establish mechanisms for stakeholders to provide feedback and report ethical concerns.
Adopting Ethical Standards
Industry Standards: Adopt and adhere to industry standards and best practices for ethical AI development.
Collaborative Efforts: Collaborate with other organizations, research institutions, and regulatory bodies to advance ethical AI standards and practices.
Conclusion
Building ethical AI is essential for ensuring that AI technologies are used responsibly and for the benefit of society. The challenges in creating ethical AI are significant, but they can be addressed through concerted efforts and collaboration. By focusing on bias and fairness, transparency and explainability, accountability, privacy and security, and ethical design, AI development company can lead the way in developing AI systems that are trustworthy, fair, and beneficial. As AI continues to evolve, ongoing commitment to ethical principles will be crucial in navigating the complex landscape of AI development and deployment.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am a software engineer and I assure you immigrants from Latin America are not threatening my job.
You know what is?
AI.
0 notes
Text
AI and the Future of Storytelling: Can Machines Master the Art of Fiction?
Storytelling has always been a deeply human endeavor. Whether through ancient oral traditions, hand-penned manuscripts, or printed books, stories have connected with us across time and space. Today, a new force is entering the wold of storytelling - artificial intelligence. From generating poetry to drafting entire novels, AI has shown surprising capabilities when it comes to writing. But can a machine truly master the craft of fiction? As AI tools beome more sophisticated, writers and readers alike are grappling with what this means for the future of literature. Will AI become a creative partner, or will it disrupt the traditional world of storytelling? In this post, we'll explore the rise of AI in writing, its strengths and limitations, and the questions it raises about the future of books and the art of storytelling.
The Rise of AI in Writing
The intersection of technology and creativity has always been a fascinating one. In recent years, artificial intelligence has made significant strides in the field of writing, producing everything from short stories to full-length novels. Tools like OpenAI's GPT-3 or GPT-4 have become increasingly adept at generating text that mirrors human writing styles and structures. In fact, AI has been used to co-author novels, assist in brainstorming ideas, and even complete unfinished manuscripts.
One of the earliest examples of AI-assisted fiction is 1 the Road, a novel generated by an AI system trained on Jack Kerouac's writing. While the result was far from a traditional novel, it raised important questions about AI's potential to contribute to literary works. Writers are now using AI to explore new creative possibilities, with some authors embracing it as a tool fo ideation or drafting, while others see it as an intriguing experiment in literary collaboration.
AI's ability to analyze massive amounts of data allows it to mimic a variety of writing styles - from the poetic elegance of Shakespear to the fast-paced thrill of modern mystery novels. This ability to quickly generate content based on input and existing text has made AI a valuable resource for writers facing creative blocks or needing a quick first draft. But while AI can mimic patterns and structures, it's important to note that it doesn't possess true creativity o the nuanced understanding of the human experience that often underpins great literature. The real question remains: can a machine truly understand what makes a story resonate with readers on a deep emotional level?
Strengths and Limitations of AI Storytelling
AI has made impressive strides in mimicking human creativity, especially when it comes to writing. One of its greatest strengths is its ability to process and synthesize vast amounts of information. AI can analyze entire libraries of text to understand various writing styles, themes, and narrative structures. This makes it incredibly efficient at producing coherent and grammatically correct content in a fraction of the time it would take a human writer. For instance, it can generate entire chapters based on a simple prompt, helping writers who are stuck in their creative process or in need of inspiration.
AI excels at tasks like brainstorming, suggesting plot twists, and refining text. Writers can input rough ideas or even half-written drafts into AI tools and receive refined content in return. These tools often have an uncanny ability to create consistent character dialogue or suggest logical plot developments, making them invaluable partners in the writing process. Additionally, AI is especially effective at generating writing in specific genres, whether it’s crafting the intricate world-building of fantasy or the suspenseful pacing of a thriller. Writers can set parameters for tone, style, and genre, and the AI can adapt its output accordingly, creating highly targeted content that matches the desired voice and direction.
However, for all its strengths, AI storytelling has clear limitations. While AI can mimic human writing, it doesn’t possess the lived experiences, emotions, or personal insights that form the foundation of authentic storytelling. Great writing often stems from a writer’s ability to delve deeply into the human experience—drawing on their own struggles, joys, fears, and dreams to create characters and narratives that resonate on a personal level. AI lacks this emotional depth. It can produce stories with perfect grammar, but without true emotional insight, the narratives can sometimes feel flat or hollow. The subtleties of human experience, such as nuance in character development or complex moral dilemmas, remain challenging for AI to fully comprehend.
Furthermore, AI is limited by the data it’s trained on. Its output is based on patterns it recognizes in the input it’s given. This means that while AI can generate text in the style of established authors or replicate well-worn plot structures, it struggles to produce truly original ideas. Creativity, by its very nature, involves breaking away from patterns and discovering new forms of expression—a skill that AI has yet to master. As a result, AI-generated stories can sometimes feel formulaic or derivative, lacking the spark of originality that human writers bring to their work.
In summary, AI offers exciting possibilities for writing, particularly as a tool to support and enhance the creative process. It excels at generating content quickly, aiding with structure and grammar, and providing inspiration. But when it comes to creating emotionally rich, original, and deeply human stories, AI still has a long way to go. While it can mimic human creativity, it cannot yet replace the heart and soul that a human writer brings to the page.
Writers and AI: Collaboration or Competition?
As AI continues to evolve and integrate into the world of writing, it raises a key question: should writers see it as a tool for collaboration, or as competition for their creative jobs? The answer, for most, is a bit of both. While AI may not (yet) have the capacity for human-level originality or emotional depth, its potential as a collaborative partner is undeniable.
Many writers are already using AI as an extension of their creative process. AI tools like OpenAI’s GPT models can assist with brainstorming, offer suggestions for improving dialogue, or help develop plot twists when writers get stuck. This partnership can be particularly useful during the early stages of writing, when developing ideas and structure can feel overwhelming. Writers can feed the AI basic plot outlines or character descriptions, and the AI will generate multiple directions the story could take, offering new perspectives that the writer might not have initially considered.
For example, some authors use AI as a "creative sparring partner"—inputting a few paragraphs or an idea and asking the AI to rewrite it in a different style or explore an alternate storyline. This process can break the monotony of writer’s block and lead to unexpected discoveries. AI also offers unique advantages in terms of speed and efficiency. A writer working on a tight deadline or balancing multiple projects may use AI to draft sections of a novel or article, freeing up their time to focus on more intricate aspects of the story, like character development or emotional depth.
In this way, AI can be a valuable collaborator rather than a replacement. It doesn’t replace the writer’s role but enhances their creative toolbox, providing new ways to approach the writing process. The use of AI can allow writers to experiment more freely with genres, themes, and writing styles, ultimately helping them push their creative boundaries. Writers can focus on refining their ideas, while AI handles some of the more mechanical aspects of writing, like ensuring consistent grammar and sentence structure.
On the other hand, the rise of AI-generated content has sparked concerns within the writing community. Some fear that as AI becomes more advanced, it could lead to the automation of writing at a scale that displaces human authors. In the world of self-publishing, for instance, AI tools are already being used to generate ebooks quickly and cheaply, leading to an influx of content in the market. While this may democratize the publishing process, it also raises questions about quality and originality. Could the market be flooded with low-quality, formulaic stories, driven by the convenience of AI-generated content?
Moreover, as AI writing tools become more accessible, some wonder whether it will become the norm for writers to rely on machines for basic writing tasks, or whether those who choose to craft their stories entirely by hand will be seen as exceptions. In an age where efficiency and speed are highly valued, the distinction between human-authored and AI-assisted writing may blur, leading to a shift in how we define creativity and authorship.
The key to navigating this new landscape lies in recognizing the potential of AI as a tool—not a replacement—for human creativity. Writers are unlikely to be completely replaced by AI, but the writing process may be forever altered by the growing presence of these intelligent tools. Rather than seeing AI as competition, writers who embrace it as a partner may find that it opens new doors for innovation and creativity in their work.
The Ethical Questions of AI-Generated Books
As artificial intelligence becomes more involved in the creative process, it brings with it a host of ethical questions that writers, publishers, and readers must consider. While the technology is exciting and full of potential, it also raises concerns about authorship, ownership, and the value of creative labor.
One of the most immediate ethical questions revolves around authorship: if an AI generates a story, who owns the rights to that content? Traditionally, the author is the person who creates the work, and they hold the copyright to their creations. But if an AI tool assists in the writing process—or even generates the entire text—should the AI's creators, the person who provided the input, or both share the rights? This dilemma is particularly important in industries like self-publishing, where authors often retain control over their work. If an AI creates a bestselling novel, does it belong to the programmer behind the AI, the person who gave the AI the prompt, or no one at all?
In some cases, the issue becomes even more complex. AI-generated content might draw upon vast databases of existing works, from literary classics to contemporary novels. As a result, AI could inadvertently replicate styles, ideas, or even entire passages from copyrighted material, potentially leading to accusations of plagiarism. While AI doesn't "copy" in the traditional sense, it relies heavily on patterns learned from vast data sets, which could lead to unintended overlaps with existing works. How do we ensure that AI-generated content remains original and doesn't infringe on intellectual property rights?
Another ethical concern involves transparency. As AI writing tools become more advanced, it may become increasingly difficult for readers to tell whether a book was written by a human or an algorithm. In some cases, AI-generated books may be marketed and sold without any indication that they were not written by a human author. Should publishers disclose when a book has been AI-assisted or fully generated by AI? Or is it ethical to allow AI-generated works to be presented as if they were created entirely by humans? Readers may have different opinions on whether they would prefer to know the true origin of a book, especially if they feel that part of the value of a book lies in its connection to the author's unique perspective and creativity.
Furthermore, there's the question of quality control. While AI can generate content quickly and efficiently, it doesn't always produce high-quality work. AI lacks the ability to understand the deeper emotional truths that resonate with human readers. It may craft stories that follow a traditional narrative structure, but without the nuanced, meaningful insights that come from lived experience. If AI-generated books flood the market, how will readers distinguish between high-quality literature and low-effort content? Will AI-driven content lower the overall quality of published works, or will human authors continue to push the boundaries of storytelling in ways AI cannot?
Lastly, there's the potential for AI to be used in manipulative ways. Imagine books written entirely by AI, crafted to cater to specific market trends or to trigger particular emotional responses from readers. With AI’s ability to analyze massive amounts of data about consumer preferences, it could be used to produce books that are engineered for maximum commercial success, rather than creative expression. While this might be financially lucrative for publishers, it could undermine the artistic integrity of literature as a whole, reducing storytelling to a mere commodity.
The rise of AI in the literary world necessitates a broader conversation about creativity, ownership, and ethics. While AI offers incredible possibilities, it also forces us to rethink the value we place on human authorship and the importance of original, deeply human stories. It challenges long-held notions of what it means to be a creator, and how we define artistic ownership in an increasingly digital world. As AI becomes more integrated into the writing process, we must ensure that the ethical considerations surrounding its use are addressed, ensuring that both writers and readers are respected in this new landscape.
A New Chapter for Readers
As artificial intelligence becomes more involved in the writing process, its impact isn’t limited to the writers themselves—it also holds the potential to reshape the reading experience. For readers, the rise of AI-generated books could open up a whole new world of possibilities, as well as challenges.
One exciting prospect is the possibility of highly personalized books tailored specifically to individual readers. AI can analyze data on a person’s reading habits, preferences, and even emotional responses to stories, allowing for the creation of books that are uniquely suited to their tastes. Imagine a world where readers can input their favorite genres, themes, and character archetypes, and AI generates a custom-made novel that fits their desires. This could revolutionize the way people engage with books, offering a level of personalization that traditional publishing could never provide. For avid readers, the sheer volume of stories that could be tailored to their interests would offer an endless stream of fresh, engaging content.
However, this level of personalization raises concerns about the diversity of stories available to readers. If AI is tasked with creating books based on reader preferences, it might reinforce existing biases or narrow the scope of available stories. Readers could end up consuming only the kinds of narratives that align with their current interests or worldviews, limiting exposure to new ideas and perspectives. While AI could potentially introduce readers to new authors and genres, there is a risk that the constant curation of content based on personal preferences might result in a kind of "filter bubble," where individuals only see books that affirm their existing beliefs and tastes. The excitement of a highly tailored reading experience could lead to the stagnation of literary diversity and innovation.
Another consideration is the impact of AI on the overall quality of literature. While AI is capable of generating text quickly and efficiently, it is not yet capable of producing the depth and emotional resonance that human writers bring to their work. As the market becomes flooded with AI-generated content, readers may find themselves inundated with formulaic, derivative books that lack the heart and soul of traditional storytelling. The sheer volume of AI-created books could lead to a glut of content, making it harder for readers to find works that truly resonate. While the speed and convenience of AI-generated books might appeal to some, others may find it increasingly difficult to distinguish between high-quality literary works and those generated for the sake of quantity.
At the same time, AI has the potential to democratize access to literature. In the past, publishing has been a selective process, with gatekeepers like editors, agents, and publishers determining which books make it to market. AI could level the playing field by enabling more people to create and publish their own stories, regardless of their writing background or experience. This could lead to a more diverse array of voices entering the literary landscape, as anyone with access to AI tools could bring their stories to life. This democratization could empower individuals who might not have had the resources or opportunities to become authors traditionally, making the world of books more inclusive and accessible than ever before.
Ultimately, the way readers interact with AI-generated content will depend on how they balance convenience, personalization, and quality. While AI can offer a world of new possibilities—ranging from highly tailored reading experiences to an explosion of diverse voices—it also presents challenges in terms of maintaining literary quality and diversity. As AI-generated books become more common, readers will need to become more discerning, learning how to navigate this new landscape and finding ways to engage with literature in a way that balances both the benefits and the drawbacks of AI involvement.
The future of reading may be one of increased personalization and greater access, but it will also require thoughtful consideration of the ethical and creative implications of AI’s role in storytelling. Readers will play a crucial role in shaping this future, deciding what types of stories they want to consume and how they define the value of literature in an AI-driven world.
Conclusion
The rise of AI in the world of writing is an exciting, if somewhat unsettling, development that is reshaping how stories are told, who tells them, and how readers experience them. While AI’s ability to generate text has made it an invaluable tool for writers—helping with everything from brainstorming and drafting to refining ideas—it also raises important questions about creativity, authorship, and the value of human storytelling. AI can assist in the writing process, but it still lacks the emotional depth and originality that come from the human experience, making it clear that machines are unlikely to fully replace human writers anytime soon.
For writers, the key lies in embracing AI as a collaborative partner, not as competition. Rather than fearing its rise, writers can harness AI’s strengths—speed, structure, and style replication—to enhance their creativity and open up new avenues for innovation. In this way, AI has the potential to complement and enrich the writing process, pushing writers to explore new ideas, break through creative blocks, and experiment in ways they might not have previously considered.
For readers, AI promises a new world of personalized, diverse content, though it also comes with challenges around quality and the ethics of authorship. The influx of AI-generated books could lead to an overwhelming amount of content, much of it lacking the soul and originality of human-created stories. But with thoughtful consideration and a discerning eye, readers can navigate this new landscape, enjoying the benefits of personalized storytelling while remaining mindful of the importance of maintaining literary diversity and quality.
As we look toward the future, one thing is clear: the story of storytelling is far from over. AI may be changing the way we write and read, but it is not replacing the human essence of creativity, emotion, and connection. Instead, it is inviting us to rethink what it means to be a creator, a reader, and a storyteller in an ever-evolving digital world. The possibilities are vast, and how we embrace AI in the literary world will shape the future of books and writing for generations to come.
***
We’d love to hear your thoughts on AI and its impact on storytelling! Do you see AI as a helpful tool for writers, or do you think it might undermine the creativity that makes literature so special? As a reader, would you embrace AI-generated books, or do you prefer the personal touch of human authors? Share your opinions in the comments below—we’re excited to continue the conversation!
If you’ve experimented with AI in your own writing or have encountered AI-generated content, let us know your experience! How has it influenced your creative process or your reading habits? Join the discussion and let’s explore what the future of books and writing might look like together.
0 notes
Text
The Debate Over Autonomous Weapons: Should AI Decide Life or Death?
In the U.S., a heated debate is brewing over the future of autonomous weapons—weapons powered by artificial intelligence (AI) that could potentially decide whether to kill humans without any human input. This issue raises deep moral, ethical, and technological questions. Should we allow machines to make life-or-death decisions? What Are Autonomous Weapons? Autonomous weapons, also known as…
#AI and Ethics#AI and Security#AI and Warfare#AI in Military#AI Weapon Regulation#AI Weapons Debate#Artificial Intelligence#Autonomous Systems#Autonomous Weapons#Ethics In AI#Future Of Warfare#Human Rights#Killer Robots#Military Technology#Stop Killer Robots
0 notes
Text
Beware of Cognitive Biases in Generative AI Tools as a Reader, Researcher, or Reporter
Understanding How Human and Algorithmic Biases Shape Artificial Intelligence Outputs and What Users Can Do to Manage Them I have spent over 40 years studying human and machine cognition long before AI reached its current state of remarkable capabilities. Today, AI is leading us into uncharted territories. As a researcher focused on the ethical aspects of technology, I believe it is vital to…
#AI and Big Data Bias#AI Cognitive Biases#AI Decision-Making Risks#AI Tools for Business#Algorithmic Bias#Confirmation Bias in AI#Ethics in AI#Generative AI Bias#Human-AI Interaction#Mitigating AI Biases
0 notes
Text
AI-Powered Software Solutions: Revolutionizing the Tech World
Introduction
Artificial intelligence has found relevance in nearly all sectors, including technology. AI-based software solutions are revolutionizing innovation, efficiency, and growth like never before in multiple industries. In this paper, we will walk through how AI will change the face of technology, its applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends. Read to continue..
#trends#technology#business tech#nvidia drive#science#tech trends#adobe cloud#tech news#science updates#analysis#Software Solutions#TagsAI and employment#AI applications in healthcare#AI for SMEs#AI implementation challenges#AI in cloud computing#AI in cybersecurity#AI in education#AI in everyday life#AI in finance#AI in manufacturing#AI in retail#AI in technology#AI-powered software solutions#artificial intelligence software#benefits of AI software#developing AI solutions#ethics in AI#future trends in AI#revolutionizing tech world
0 notes
Text
Almost all of Michael Crichton’s books draw on the theme of “you can but that doesn’t mean you should”.
In his iconic book/movie Jurassic Park, Ian Malcolm gives the powerful line of, “Your scientists were so preoccupied with whether or not they could, they didn't stop to think if they should”.
In Prey the organic nanobots are programmed to be a hive-mind with the killing tactics of lions and wolves, the scientists go straight into mass production without testing and end up creating two versions of deadly hive-minds. One parasitic and one predatory.
Next is probably the best example of people not using ethics, animal-human hybrids, companies trying to own gene codes, kidnapping people for their DNA.
Crichton was a man ahead of his time and his lessons remain true, Just because you can doesn’t mean you should.
The AI issue is what happens when you raise generation after generation of people to not respect the arts. This is what happens when a person who wants to major in theatre, or English lit, or any other creative major gets the response, "And what are you going to do with that?" or "Good luck getting a job!"
You get tech bros who think it's easy. They don't know the blood, sweat, and tears that go into a creative endeavor because they were taught to completely disregard that kind of labor. They think they can just code it away.
That's (one of the reasons) why we're in this mess.
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
Neuralink's First Human Implant
Neuralink's First Human Implant A Leap Towards Human-AI Symbiosis @neosciencehub #neosciencehub #science #Neuralink #Human #AISymbiosis #BrainComputer #Interface #Neurotechnology #elonmusk #AI #brainchip #FutureAI #MedicalTechnology #DataSecurity #NSH
A Leap Towards Human-AI Symbiosis In a landmark achievement that could redefine the boundaries of human potential and technology, Neuralink, the neurotechnology company co-founded by entrepreneur Elon Musk, has successfully implanted its pioneering brain-computer interface in a human subject. This outstanding development in BCI (Brain Computer Interface) not only marks a significant milestone in…

View On WordPress
#AI Integration#Assistive Technology#Brain-Computer Interface#Cognitive Enhancement#Data Security#Digital Health#Elon Musk#Ethics in AI#featured#Future of AI#Human-AI Symbiosis#Human-Computer Interaction#Medical Technology#Neuralink#Neurological Disorders#Neuroscience#Neurotechnology#sciencenews
0 notes
Text

i spilled pasta in my backpack and got so mad that i made a traumacore edit about it
#schizobabble#this is ai art i found on google images lol#using it is probably more ethical than reuploading handdrawn sad anime girl art for my shitty meme#<-editing to add these tags since this is getting notes again
20K notes
·
View notes
Text
Let’s play a game…
Get your friends together and put your cell phones in the middle of the room. Make sure they’re on. Then, carry on a 30 minute discussion of things you never talk about. Here’s some ideas:
Vinyl records of artists
Cities in Europe
Luxury guitars
Having children, diapers, baby registries
Cyber security
Now, note what ads you get for the next week. If any of your friends don’t get their ads tainted, post their phone model here.
Have fun!
#cyber security#advertising#data security#data privacy#data analytics#privacymatters#internet privacy#online privacy#ethics in ai#ethical ai#ethics#computer ethics
1 note
·
View note
Text






I spent the evening looking into this AI shit and made a wee informative post of the information I found and thought all artists would be interested and maybe help yall?
edit: forgot to mention Glaze and Nightshade to alter/disrupt AI from taking your work into their machines. You can use these and post and it will apparently mess up the AI and it wont take your content into it's machine!
edit: ArtStation is not AI free! So make sure to read that when signing up if you do! (this post is also on twt)
[Image descriptions: A series of infographics titled: “Opt Out AI: [Social Media] and what I found.” The title image shows a drawing of a person holding up a stack of papers where the first says, ‘Terms of Service’ and the rest have logos for various social media sites and are falling onto the floor. Long transcriptions follow.
Instagram/Meta (I have to assume Facebook).
Hard for all users to locate the “opt out” options. The option has been known to move locations.
You have to click the opt out link to submit a request to opt out of the AI scraping. *You have to submit screenshots of your work/face/content you posted to the app, is curretnly being used in AI. If you do not have this, they will deny you.
Users are saying after being rejected, are being “meta blocked”
People’s requests are being accepted but they still have doubts that their content won’t be taken anyways.
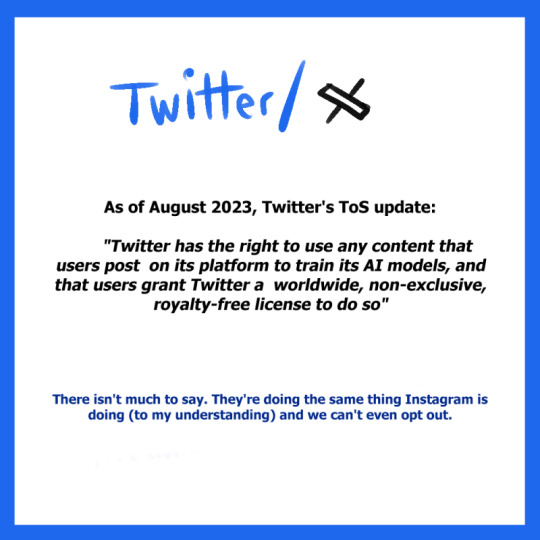
Twitter/X
As of August 2023, Twitter’s ToS update:
“Twitter has the right to use any content that users post on its platform to train its AI models, and that users grant Twitter a worldwide, non-exclusive, royalty-free license to do so.”
There isn’t much to say. They’re doing the same thing Instagram is doing (to my understanding) and we can’t even opt out.
Tumblr
They also take your data and content and sell it to AI models.
But you’re in luck!
It is very simply to opt out (Wow. Thank Gods)
Opt out on Desktop: click on your blog > blog settings > scroll til you see visibility options and it’ll be the last option to toggle
Out out of Mobile: click your blog > scroll then click visibility > toggle opt out option
TikTok
I took time skim their ToS and under “How We Use Your Information” and towards the end of the long list: “To train and improve our technology, such as our machine learning models and algorithms.”
Regarding data collected; they will only not sell your data when “where restricted by applicable law”. That is not many countries. You can refuse/disable some cookies by going into settings > ads > turn off targeted ads.
I couldn’t find much in AI besides “our machine learning models” which I think is the same thing.
What to do?
In this age of the internet, it’s scary! But you have options and can pick which are best for you!
Accepting these platforms collection of not only your artwork, but your face! And not only your faces but the faces of those in your photos. Your friends and family. Some of those family members are children! Some of those faces are minors! I shudder to think what darker purposes those faces could be used for.
Opt out where you can! Be mindful and know the content you are posting is at risk of being loaded to AI if unable to opt out.
Fully delete (not archive) your content/accounts with these platforms. I know it takes up to 90 days for instagram to “delete” your information. And even keep it for “legal” purposes like legal prevention.
Use lesser known social media platforms! Some examples are; Signal, Mastodon, Diaspora, et. As well as art platforms: Artfol, Cara, ArtStation, etc.
The last drawing shows the same person as the title saying, ‘I am, by no means, a ToS autistic! So feel free to share any relatable information to these topics via reply or qrt!
I just wanted to share the information I found while searching for my own answers cause I’m sure people have the same questions as me.’ \End description] (thank you @a-captions-blog!)
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
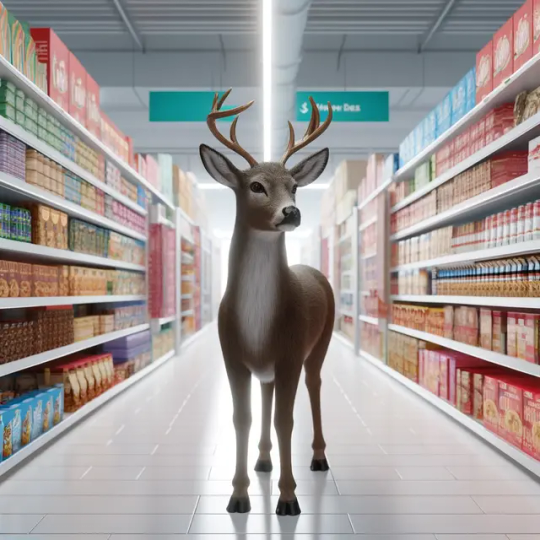
Among the many downsides of AI-generated art: it's bad at revising. You know, the biggest part of the process when working on commissioned art.
Original "deer in a grocery store" request from chatgpt (which calls on dalle3 for image generation):

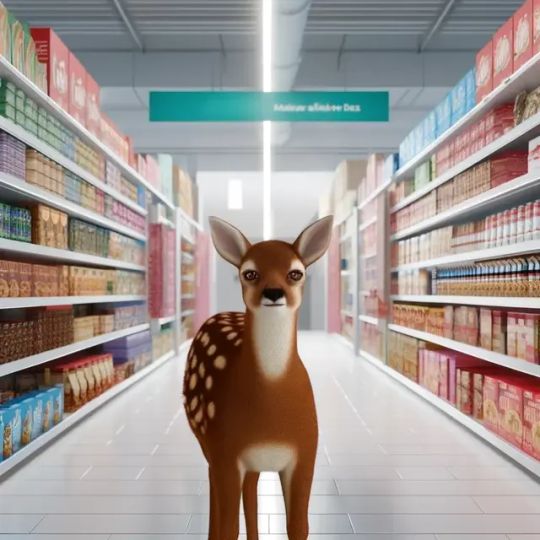
revision 5 (trying to give the fawn spots, trying to fix the shadows that were making it appear to hover):

I had it restore its own Jesus fresco.
Original:
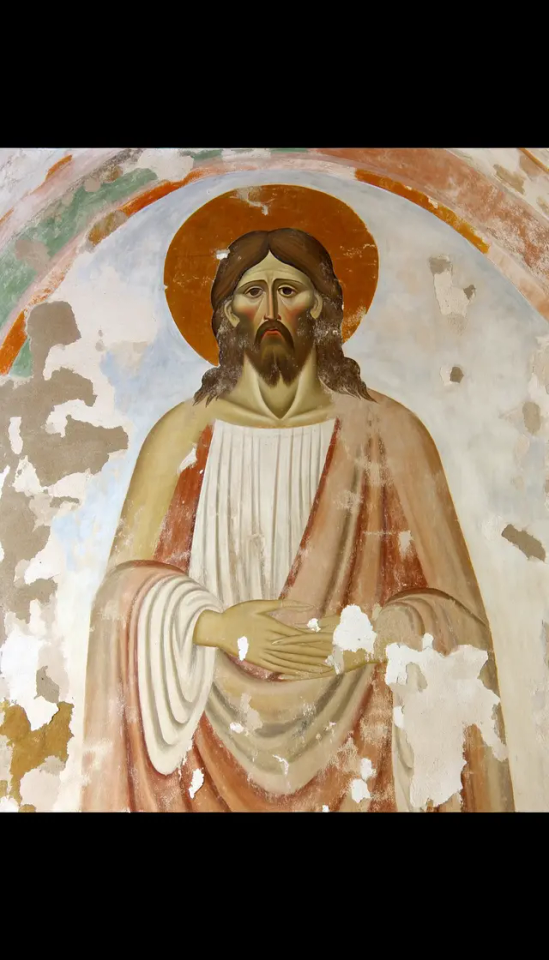

Erased the face, asked it to restore the image to as good as when it was first painted:
Wait tumblr makes the image really low-res, let me zoom in on Jesus's face.
Original:
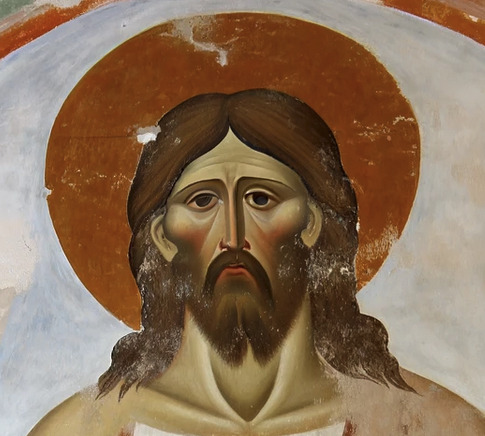

Restored:
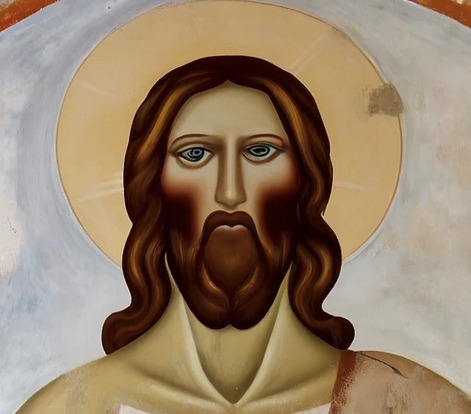

One revision later:
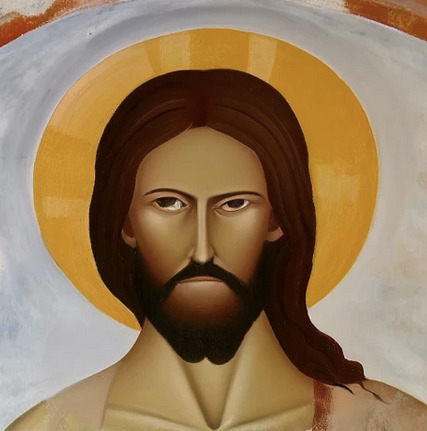

Here's the full "restored" face in context:
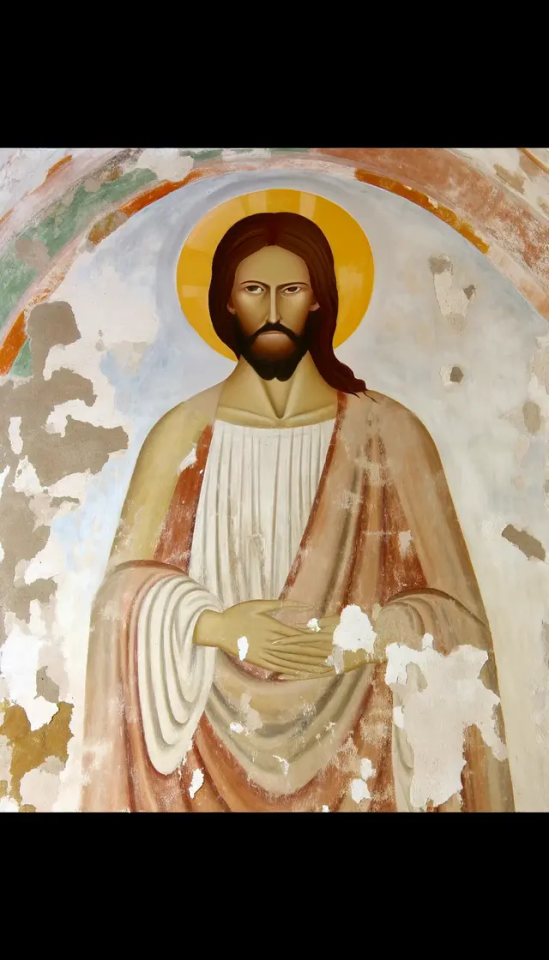

Every time AI is asked to revise an image, it either wipes it and starts over or makes it more and more of a disaster. People who work with AI-generated imagery have to adapt their creative vision to what comes out of the system - or go in with a mentality that anything that fits the brief is good enough.
I'm not surprised that there are some places looking for cheap filler images that don't mind the problems with AI-generated imagery. But for everyone else I think it's quickly becoming clear that you need a real artist, not a knockoff.
more
#ai generated#chatgpt#dalle3#revision#apart from the ethical and environmental issues#also: not good at making art to order!#ecce homo
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Ethics of AI: Navigating Challenges of Artificial Intelligence
Introduction: Understanding the Ethics of AI in the Modern World Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing various industries and transforming the way we live and work. From virtual assistants to self-driving cars, AI technologies have brought about unprecedented advancements. However, with these advancements come ethical challenges that need to be…

View On WordPress
#ethics in ai#ethics in artificial intelligence#ethics of ai#ethics of artificial intelligence#is ai ethical#is artificial intelligence ethical
1 note
·
View note