#Machine Learning
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

(Source)
73K notes
·
View notes
Text
31% of employees are actively ‘sabotaging’ AI efforts. Here’s why
"In a new study, almost a third of respondents said they are refusing to use their company’s AI tools and apps. A few factors could be at play."

1K notes
·
View notes
Text
AI hasn't improved in 18 months. It's likely that this is it. There is currently no evidence the capabilities of ChatGPT will ever improve. It's time for AI companies to put up or shut up.
I'm just re-iterating this excellent post from Ed Zitron, but it's not left my head since I read it and I want to share it. I'm also taking some talking points from Ed's other posts. So basically:
We keep hearing AI is going to get better and better, but these promises seem to be coming from a mix of companies engaging in wild speculation and lying.
Chatgpt, the industry leading large language model, has not materially improved in 18 months. For something that claims to be getting exponentially better, it sure is the same shit.
Hallucinations appear to be an inherent aspect of the technology. Since it's based on statistics and ai doesn't know anything, it can never know what is true. How could I possibly trust it to get any real work done if I can't rely on it's output? If I have to fact check everything it says I might as well do the work myself.
For "real" ai that does know what is true to exist, it would require us to discover new concepts in psychology, math, and computing, which open ai is not working on, and seemingly no other ai companies are either.
Open ai has already seemingly slurped up all the data from the open web already. Chatgpt 5 would take 5x more training data than chatgpt 4 to train. Where is this data coming from, exactly?
Since improvement appears to have ground to a halt, what if this is it? What if Chatgpt 4 is as good as LLMs can ever be? What use is it?
As Jim Covello, a leading semiconductor analyst at Goldman Sachs said (on page 10, and that's big finance so you know they only care about money): if tech companies are spending a trillion dollars to build up the infrastructure to support ai, what trillion dollar problem is it meant to solve? AI companies have a unique talent for burning venture capital and it's unclear if Open AI will be able to survive more than a few years unless everyone suddenly adopts it all at once. (Hey, didn't crypto and the metaverse also require spontaneous mass adoption to make sense?)
There is no problem that current ai is a solution to. Consumer tech is basically solved, normal people don't need more tech than a laptop and a smartphone. Big tech have run out of innovations, and they are desperately looking for the next thing to sell. It happened with the metaverse and it's happening again.
In summary:
Ai hasn't materially improved since the launch of Chatgpt4, which wasn't that big of an upgrade to 3.
There is currently no technological roadmap for ai to become better than it is. (As Jim Covello said on the Goldman Sachs report, the evolution of smartphones was openly planned years ahead of time.) The current problems are inherent to the current technology and nobody has indicated there is any way to solve them in the pipeline. We have likely reached the limits of what LLMs can do, and they still can't do much.
Don't believe AI companies when they say things are going to improve from where they are now before they provide evidence. It's time for the AI shills to put up, or shut up.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
shout out to machine learning tech (and all the human-input adjustment contributors) that's brought about the present developmental stage of machine translation, making the current global village 地球村 moment on rednote小红书 accessible in a way that would not have been possible years ago.
#translation#rednote#xhs#machine learning#linguistics#accessibility#unfinished thought pls read down the whole chain ty#when AI is accessibility tool for the masses :D
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

got distracted by imagining bocchi undergoing feature space transformations during lecture
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"The first satellite in a constellation designed specifically to locate wildfires early and precisely anywhere on the planet has now reached Earth's orbit, and it could forever change how we tackle unplanned infernos.
The FireSat constellation, which will consist of more than 50 satellites when it goes live, is the first of its kind that's purpose-built to detect and track fires. It's an initiative launched by nonprofit Earth Fire Alliance, which includes Google and Silicon Valley-based space services startup Muon Space as partners, among others.
According to Google, current satellite systems rely on low-resolution imagery and cover a particular area only once every 12 hours to spot significantly large wildfires spanning a couple of acres. FireSat, on the other hand, will be able to detect wildfires as small as 270 sq ft (25 sq m) – the size of a classroom – and deliver high-resolution visual updates every 20 minutes.
The FireSat project has only been in the works for less than a year and a half. The satellites are fitted with custom six-band multispectral infrared cameras, designed to capture imagery suitable for machine learning algorithms to accurately identify wildfires – differentiating them from misleading objects like smokestacks.
These algorithms look at an image from a particular location, and compare it with the last 1,000 times it was captured by the satellite's camera to determine if what it's seeing is indeed a wildfire. AI technology in the FireSat system also helps predict how a fire might spread; that can help firefighters make better decisions about how to control the flames safely and effectively.
This could go a long way towards preventing the immense destruction of forest habitats and urban areas, and the displacement of residents caused by wildfires each year. For reference, the deadly wildfires that raged across Los Angeles in January were estimated to have cuased more than $250 billion in damages.
Muon is currently developing three more satellites, which are set to launch next year. The entire constellation should be in orbit by 2030.
The FireSat effort isn't the only project to watch for wildfires from orbit. OroraTech launched its first wildfire-detection satellite – FOREST-1 – in 2022, followed by one more in 2023 and another earlier this year. The company tells us that another eight are due to go up toward the end of March."
-via March 18, 2025
#wildfire#wildfires#la wildfires#los angeles#ai#artificial intelligence#machine learning#satellite#natural disasters#good news#hope
722 notes
·
View notes
Text
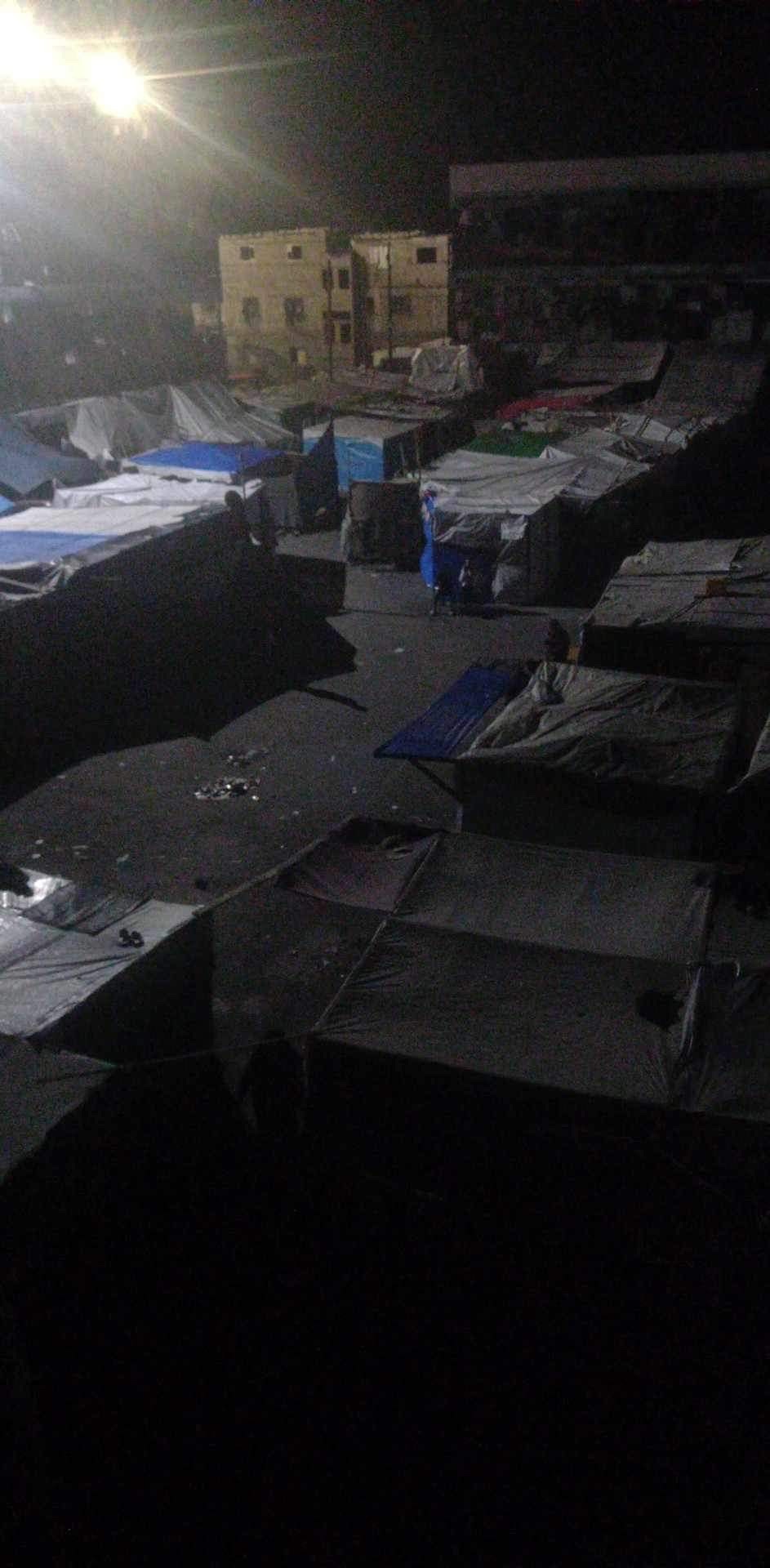



This the where my family stay right now they are staying in a school without any kind of privacy or any comfortable accommodation.kindly asking your help small things can help us in this situation
#free gaza#free palestine#gaza#gaza genocide#gaza strip#genocide#palestine#machine learning#save rafah#linux
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
why neuroscience is cool
space & the brain are like the two final frontiers
we know just enough to know we know nothing
there are radically new theories all. the. time. and even just in my research assistant work i've been able to meet with, talk to, and work with the people making them
it's such a philosophical science
potential to do a lot of good in fighting neurological diseases
things like BCI (brain computer interface) and OI (organoid intelligence) are soooooo new and anyone's game - motivation to study hard and be successful so i can take back my field from elon musk
machine learning is going to rapidly increase neuroscience progress i promise you. we get so caught up in AI stealing jobs but yes please steal my job of manually analyzing fMRI scans please i would much prefer to work on the science PLUS computational simulations will soon >>> animal testing to make all drug testing safer and more ethical !! we love ethical AI <3
collab with...everyone under the sun - psychologists, philosophers, ethicists, physicists, molecular biologists, chemists, drug development, machine learning, traditional computing, business, history, education, literally try to name a field we don't work with
it's the brain eeeeee
#my motivation to study so i can be a cool neuroscientist#science#women in stem#academia#stem#stemblr#studyblr#neuroscience#stem romanticism#brain#psychology#machine learning#AI#brain computer interface#organoid intelligence#motivation#positivity#science positivity#cogsci#cognitive science
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
We need to change the way we think about AI and remember that arms races don’t just exist between nations. The problem is once again capitalism, not the technology itself or some other boogeyman.
#leftblr#late stage capitalism#working class#left wing#class war#leftist#socialism#tech#technology#ai#machine learning
323 notes
·
View notes
Text

Frank Rosenblatt, often cited as the Father of Machine Learning, photographed in 1960 alongside his most-notable invention: the Mark I Perceptron machine — a hardware implementation for the perceptron algorithm, the earliest example of an artificial neural network, est. 1943.
#frank rosenblatt#tech history#machine learning#neural network#artificial intelligence#AI#perceptron#60s#black and white#monochrome#technology#u
820 notes
·
View notes
Text
we need to come up for a good word for ""AI"" that doesn't imply it's artificial or intelligent and highlights the stolen human labor. like what if we call it "theftgen"
(workshop this with me)
#theftgen#theft generation#machine learning#artificial intelligence#chatgpt#midjourney#dalle#stable diffusion
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
There is no such thing as AI.
How to help the non technical and less online people in your life navigate the latest techbro grift.
I've seen other people say stuff to this effect but it's worth reiterating. Today in class, my professor was talking about a news article where a celebrity's likeness was used in an ai image without their permission. Then she mentioned a guest lecture about how AI is going to help finance professionals. Then I pointed out, those two things aren't really related.
The term AI is being used to obfuscate details about multiple semi-related technologies.
Traditionally in sci-fi, AI means artificial general intelligence like Data from star trek, or the terminator. This, I shouldn't need to say, doesn't exist. Techbros use the term AI to trick investors into funding their projects. It's largely a grift.
What is the term AI being used to obfuscate?
If you want to help the less online and less tech literate people in your life navigate the hype around AI, the best way to do it is to encourage them to change their language around AI topics.
By calling these technologies what they really are, and encouraging the people around us to know the real names, we can help lift the veil, kill the hype, and keep people safe from scams. Here are some starting points, which I am just pulling from Wikipedia. I'd highly encourage you to do your own research.
Machine learning (ML): is an umbrella term for solving problems for which development of algorithms by human programmers would be cost-prohibitive, and instead the problems are solved by helping machines "discover" their "own" algorithms, without needing to be explicitly told what to do by any human-developed algorithms. (This is the basis of most technologically people call AI)
Language model: (LM or LLM) is a probabilistic model of a natural language that can generate probabilities of a series of words, based on text corpora in one or multiple languages it was trained on. (This would be your ChatGPT.)
Generative adversarial network (GAN): is a class of machine learning framework and a prominent framework for approaching generative AI. In a GAN, two neural networks contest with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. (This is the source of some AI images and deepfakes.)
Diffusion Models: Models that generate the probability distribution of a given dataset. In image generation, a neural network is trained to denoise images with added gaussian noise by learning to remove the noise. After the training is complete, it can then be used for image generation by starting with a random noise image and denoise that. (This is the more common technology behind AI images, including Dall-E and Stable Diffusion. I added this one to the post after as it was brought to my attention it is now more common than GANs.)
I know these terms are more technical, but they are also more accurate, and they can easily be explained in a way non-technical people can understand. The grifters are using language to give this technology its power, so we can use language to take it's power away and let people see it for what it really is.
12K notes
·
View notes
Note

Straight from the bull's mouth.
AI Art simply cannot make artistic choices or apply craft or storytelling, it just spits out an average.
467 notes
·
View notes
Text
I assure you, an AI didn’t write a terrible “George Carlin” routine
There are only TWO MORE DAYS left in the Kickstarter for the audiobook of The Bezzle, the sequel to Red Team Blues, narrated by @wilwheaton! You can pre-order the audiobook and ebook, DRM free, as well as the hardcover, signed or unsigned. There's also bundles with Red Team Blues in ebook, audio or paperback.

On Hallowe'en 1974, Ronald Clark O'Bryan murdered his son with poisoned candy. He needed the insurance money, and he knew that Halloween poisonings were rampant, so he figured he'd get away with it. He was wrong:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ronald_Clark_O%27Bryan
The stories of Hallowe'en poisonings were just that – stories. No one was poisoning kids on Hallowe'en – except this monstrous murderer, who mistook rampant scare stories for truth and assumed (incorrectly) that his murder would blend in with the crowd.
Last week, the dudes behind the "comedy" podcast Dudesy released a "George Carlin" comedy special that they claimed had been created, holus bolus, by an AI trained on the comedian's routines. This was a lie. After the Carlin estate sued, the dudes admitted that they had written the (remarkably unfunny) "comedy" special:
https://arstechnica.com/ai/2024/01/george-carlins-heirs-sue-comedy-podcast-over-ai-generated-impression/
As I've written, we're nowhere near the point where an AI can do your job, but we're well past the point where your boss can be suckered into firing you and replacing you with a bot that fails at doing your job:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/15/passive-income-brainworms/#four-hour-work-week
AI systems can do some remarkable party tricks, but there's a huge difference between producing a plausible sentence and a good one. After the initial rush of astonishment, the stench of botshit becomes unmistakable:
https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2024/jan/03/botshit-generative-ai-imminent-threat-democracy
Some of this botshit comes from people who are sold a bill of goods: they're convinced that they can make a George Carlin special without any human intervention and when the bot fails, they manufacture their own botshit, assuming they must be bad at prompting the AI.
This is an old technology story: I had a friend who was contracted to livestream a Canadian awards show in the earliest days of the web. They booked in multiple ISDN lines from Bell Canada and set up an impressive Mbone encoding station on the wings of the stage. Only one problem: the ISDNs flaked (this was a common problem with ISDNs!). There was no way to livecast the show.
Nevertheless, my friend's boss's ordered him to go on pretending to livestream the show. They made a big deal of it, with all kinds of cool visualizers showing the progress of this futuristic marvel, which the cameras frequently lingered on, accompanied by overheated narration from the show's hosts.
The weirdest part? The next day, my friend – and many others – heard from satisfied viewers who boasted about how amazing it had been to watch this show on their computers, rather than their TVs. Remember: there had been no stream. These people had just assumed that the problem was on their end – that they had failed to correctly install and configure the multiple browser plugins required. Not wanting to admit their technical incompetence, they instead boasted about how great the show had been. It was the Emperor's New Livestream.
Perhaps that's what happened to the Dudesy bros. But there's another possibility: maybe they were captured by their own imaginations. In "Genesis," an essay in the 2007 collection The Creationists, EL Doctorow (no relation) describes how the ancient Babylonians were so poleaxed by the strange wonder of the story they made up about the origin of the universe that they assumed that it must be true. They themselves weren't nearly imaginative enough to have come up with this super-cool tale, so God must have put it in their minds:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/29/gedankenexperimentwahn/#high-on-your-own-supply
That seems to have been what happened to the Air Force colonel who falsely claimed that a "rogue AI-powered drone" had spontaneously evolved the strategy of killing its operator as a way of clearing the obstacle to its main objective, which was killing the enemy:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/04/ayyyyyy-eyeeeee/
This never happened. It was – in the chagrined colonel's words – a "thought experiment." In other words, this guy – who is the USAF's Chief of AI Test and Operations – was so excited about his own made up story that he forgot it wasn't true and told a whole conference-room full of people that it had actually happened.
Maybe that's what happened with the George Carlinbot 3000: the Dudesy dudes fell in love with their own vision for a fully automated luxury Carlinbot and forgot that they had made it up, so they just cheated, assuming they would eventually be able to make a fully operational Battle Carlinbot.
That's basically the Theranos story: a teenaged "entrepreneur" was convinced that she was just about to produce a seemingly impossible, revolutionary diagnostic machine, so she faked its results, abetted by investors, customers and others who wanted to believe:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theranos
The thing about stories of AI miracles is that they are peddled by both AI's boosters and its critics. For boosters, the value of these tall tales is obvious: if normies can be convinced that AI is capable of performing miracles, they'll invest in it. They'll even integrate it into their product offerings and then quietly hire legions of humans to pick up the botshit it leaves behind. These abettors can be relied upon to keep the defects in these products a secret, because they'll assume that they've committed an operator error. After all, everyone knows that AI can do anything, so if it's not performing for them, the problem must exist between the keyboard and the chair.
But this would only take AI so far. It's one thing to hear implausible stories of AI's triumph from the people invested in it – but what about when AI's critics repeat those stories? If your boss thinks an AI can do your job, and AI critics are all running around with their hair on fire, shouting about the coming AI jobpocalypse, then maybe the AI really can do your job?
https://locusmag.com/2020/07/cory-doctorow-full-employment/
There's a name for this kind of criticism: "criti-hype," coined by Lee Vinsel, who points to many reasons for its persistence, including the fact that it constitutes an "academic business-model":
https://sts-news.medium.com/youre-doing-it-wrong-notes-on-criticism-and-technology-hype-18b08b4307e5
That's four reasons for AI hype:
to win investors and customers;
to cover customers' and users' embarrassment when the AI doesn't perform;
AI dreamers so high on their own supply that they can't tell truth from fantasy;
A business-model for doomsayers who form an unholy alliance with AI companies by parroting their silliest hype in warning form.
But there's a fifth motivation for criti-hype: to simplify otherwise tedious and complex situations. As Jamie Zawinski writes, this is the motivation behind the obvious lie that the "autonomous cars" on the streets of San Francisco have no driver:
https://www.jwz.org/blog/2024/01/driverless-cars-always-have-a-driver/
GM's Cruise division was forced to shutter its SF operations after one of its "self-driving" cars dragged an injured pedestrian for 20 feet:
https://www.wired.com/story/cruise-robotaxi-self-driving-permit-revoked-california/
One of the widely discussed revelations in the wake of the incident was that Cruise employed 1.5 skilled technical remote overseers for every one of its "self-driving" cars. In other words, they had replaced a single low-waged cab driver with 1.5 higher-paid remote operators.
As Zawinski writes, SFPD is well aware that there's a human being (or more than one human being) responsible for every one of these cars – someone who is formally at fault when the cars injure people or damage property. Nevertheless, SFPD and SFMTA maintain that these cars can't be cited for moving violations because "no one is driving them."
But figuring out who which person is responsible for a moving violation is "complicated and annoying to deal with," so the fiction persists.
(Zawinski notes that even when these people are held responsible, they're a "moral crumple zone" for the company that decided to enroll whole cities in nonconsensual murderbot experiments.)
Automation hype has always involved hidden humans. The most famous of these was the "mechanical Turk" hoax: a supposed chess-playing robot that was just a puppet operated by a concealed human operator wedged awkwardly into its carapace.
This pattern repeats itself through the ages. Thomas Jefferson "replaced his slaves" with dumbwaiters – but of course, dumbwaiters don't replace slaves, they hide slaves:
https://www.stuartmcmillen.com/blog/behind-the-dumbwaiter/
The modern Mechanical Turk – a division of Amazon that employs low-waged "clickworkers," many of them overseas – modernizes the dumbwaiter by hiding low-waged workforces behind a veneer of automation. The MTurk is an abstract "cloud" of human intelligence (the tasks MTurks perform are called "HITs," which stands for "Human Intelligence Tasks").
This is such a truism that techies in India joke that "AI" stands for "absent Indians." Or, to use Jathan Sadowski's wonderful term: "Potemkin AI":
https://reallifemag.com/potemkin-ai/
This Potemkin AI is everywhere you look. When Tesla unveiled its humanoid robot Optimus, they made a big flashy show of it, promising a $20,000 automaton was just on the horizon. They failed to mention that Optimus was just a person in a robot suit:
https://www.siliconrepublic.com/machines/elon-musk-tesla-robot-optimus-ai
Likewise with the famous demo of a "full self-driving" Tesla, which turned out to be a canned fake:
https://www.reuters.com/technology/tesla-video-promoting-self-driving-was-staged-engineer-testifies-2023-01-17/
The most shocking and terrifying and enraging AI demos keep turning out to be "Just A Guy" (in Molly White's excellent parlance):
https://twitter.com/molly0xFFF/status/1751670561606971895
And yet, we keep falling for it. It's no wonder, really: criti-hype rewards so many different people in so many different ways that it truly offers something for everyone.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/01/29/pay-no-attention/#to-the-little-man-behind-the-curtain


Back the Kickstarter for the audiobook of The Bezzle here!

Image:
Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
Ross Breadmore (modified) https://www.flickr.com/photos/rossbreadmore/5169298162/
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/
#pluralistic#ai#absent indians#mechanical turks#scams#george carlin#comedy#body-snatchers#fraud#theranos#guys in robot suits#criti-hype#machine learning#fake it til you make it#too good to fact-check#mturk#deepfakes
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

art is work. If you didn't put in hard work it's not art. If you didn't bleed then you're taking shortcuts. you have to put in "effort" or your art is worthless. if you don't have a work ethic then you're worthy of derision. if you are unwilling or unable to suffer then you are unworthy of making art
this is so, so obviously a conservative, reactionary sentiment. This is what my fucking dad says about Picasso. "They just want to push the button" is word-for-word what people used to say about electronic music - not "real" instruments, no talent involved, no skill, worthless. how does this not disturb more people? this should disturb you! is everyone just seeing posts criticizing AI and slamming reblog without reading too close, or do people actually agree with this?
usual disclaimer: this is not a "pro-ai" stance. this is a "think about what values you actually have" stance. there are many more coherent ways to criticize it
1K notes
·
View notes