#neuroscience
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Accurate.
The ones who know he's lying are gleefully complicit in whatever they think the conspiracy is — that's why there are many people who should know better who today love tearing down our government, sniffing out our rights, and rounding up people they seem "other" ...power.
youtube
THOM HARTMANN: Science Explains Why Republicans Can’t Accept Trump’s Guilt (Sept. 12, 2023)
Scientists discovered a fascinating reason why Republicans can’t accept criticism of Donald Trump. Thom explains.
In the above video, Thom Hartmann refers to a Raw Story column by cognitive neuroscientist Bobby Azarian, PhD (shown below):
Here are some excerpts from Azarian's column:
In 2009, a study published in PLOS ONE challenged our understanding of belief systems. Researchers placed participants into the confines of an fMRI scanner and presented them with a mixture of factual and abstract statements. The results were illuminating. Disbelief, it turns out, is cognitively demanding. It requires more mental effort than simply accepting a statement as true. From an evolutionary perspective, this preference for easy belief makes sense; a perpetually skeptical individual questioning every piece of information would struggle to adapt in a fast-paced world. What does all this have to do with Trump supporters? Well, it’s far less cognitively demanding for them to believe anything their leader tells them. Any challenge to what Trump tells them is true takes mental work. This means there is a psychological incentive for Trump loyalists to maintain their loyalty. (I wrote about this phenomenon in a slightly different context in the Daily Beast article "Religious Fundamentalism: A Side Effect of Lazy Brains?") Molding of belief: neuroplasticity at play Now, let's consider the unique predicament faced by individuals who staunchly support Trump and want him to again become president. From the moment Trump began his political career and his social engineering career, his supporters have been exposed to narratives — Trump doesn't lie, Democrats are communists, the media is an enemy of the people — that emphasize loyalty and trust in their political idol. These narratives often steer away from critical examination and instead encourage blind faith. When coupled with the brain's inherent tendency to accept rather than question, it creates an ideal environment for unwavering allegiance. No matter that Trump, time and again, has been revealed to be a serial liar, habitually misrepresenting matters of great consequence, from elections to economics to public health. For example, in the Psychology Today article "Why Evangelicals are Wired to Believe Trump’s Falsehoods," I explain that the children of Christian fundamentalists typically begin to suppress critical thinking at an early age. This is required if one is to accept Biblical stories as literal truth, rather than metaphors for how to live life practically and with purpose. Attributing natural occurrences to mystical causes discourages youth from seeking evidence to back their beliefs. Consequently, the brain structures that support critical thinking and logical reasoning don't fully mature. This paves the way for heightened vulnerability to deceit and manipulative narratives, especially from cunning political figures. Such increased suggestibility arises from a mix of the brain's propensity to accept unverified claims and intense indoctrination. Given the brain's neuroplastic nature, which allows it to shape according to experiences, some religious followers are more predisposed to accept improbable assertions. In other words, our brains are remarkably adaptable and continuously evolving landscapes. For ardent Trump supporters, residing in an environment that prioritizes faith over empirical evidence can reshape the neural circuits within their brains. [color emphasis added]
[edited]
#accurate analysis#trump 47#ideology#ideological#not really#lies#belief#culpability#credulity#incredulity#incredulous#new tariffs will pay the $36T deficit#i reject your reality and substitute my own#why republicans can't accept trump's guilt#the brain and disbelief#neuroscience#maga#christian nationalists#text#required reading
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
analogistically
or, the adventure of canmom on lysergic acid diethylamide
Epistemic status: jam session
Two months ago I dropped acid for the first time, which surely explains a lot about recent posting trends on canmom dot tumblr dot edu. It was exactly as extraordinary as you would hope your first time on psychedelics would be. Among other things, LSD kind of acts like an intense reverb filter on your thoughts, boosting the intensity of sensory perceptions in various ways (for e.g. touch, music, colour, edges) and putting your capacity to form associations into overdrive. I did a lot of classic 'on drugs things' like staring very intensely at my hands or a piece of flatbread trying to map my perception into some kind of visual effects filters I might be able to recreate later... my best description is something akin to motion extraction as the primary effect, causing all sorts of little surface details to pop out very vividly as I moved an object.
This, however, is not a trip report; just an attempt to explain some ideas and connections that were formulated while on acid, in a state where my eyes were full of interesting fractals and I couldn't remember the world 'analogously'.
Here's some music to start us off - one of the first things that I listened to during the trip and something which probably informed the very geometric path I went down...
youtube
This is a music track that can be interpreted simultaneously as music and, when used to control an oscilloscope trace, as imagery. The whole function that generates it fits on a floppy. The beat of this music basically stayed with me throughout the whole trip, and for a while afterwards.
One of the curious experiences I had during the trip was what the (sadly no longer actively updated) psychonaut wiki calls perceived exposure to the inner mechanics of consciousness. Although it's not listed as a common effect of LSD, and said to be associated with a higher degree of visual effects than I reached, the description does resonate:
Perceived exposure to inner mechanics of consciousness can be described the experience of being exposed to an array of complex, autonomously-generated, cognitive sensations and conceptual thoughts which contain detailed sets of innately readable information. The information within these sensations is felt to convey the organization, structure, architecture, framework and inner mechanics of the underlying programming behind all conscious and subconscious psychological processes. Those who undergo this effect commonly interpret the experience as suddenly having perceivable access to the inner workings of either the universe, reality, or consciousness itself. (...) These specific pieces of information are often felt and understood to be a profound unveiling of an undeniable truth at the time. Afterward, they are usually realized to be ineffable due to the limitations of human language and cognition, or simply nonsensical, and delusional due to the impairment caused by of other accompanying cognitive effects.
Here, it felt like a kind of separating out of processes within my brain: a separation of sensory processing, conceptual thinking, and the word stream operating with a slight delay between them.
I imagined these different elements of me kind of floating in some kind of space, that each one possessed its own space of meaning, and that thoughts were being mapped between the different parts. I imagined that they were all working in concert to make 'Bryn' happen, so much so that I didn't perceive the different parts most of the time, and that they seemed happy with this arrangement. I also hit on a very striking metaphor of thoughts as oscillations and the resonant modes of the brain.
Afterwards, I wondered how much of this was driven simply by inputs - elaboration on stuff I'd been learning about recently, which we'll get into in a bit. I find it hard to be confident that what I perceived was actual 'direct' introspection, rather than a narrative conjured on the fly by my brain when prompted to generate a 'look inside'.
However, even if it was not the direct observation of some kind of 'brain telescope', it certainly gave me a lot of rich connections to think about. So the purpose of this post is to flesh out and record what came to me very intuitively at the time. Although my direct memory has faded a bit, my brain is still oscillating intently (upcoming metaphor) with thoughts inspired by what I explored there.
We're mostly talking about human brains here, but I will be talking about AI stuff as well, largely as a provocative counterexample.
Prior to the trip I had recently watched 3Blue1Brown's video on how LLMs encode meaning with high-dimensional vector embeddings and the 'attention' mechanism:
youtube
To try and summarise briefly, the meaning of a token inside an LLM (and various other types of machine learning system) is an incredibly high-dimensional vector of associations. By combining information from elsewhere in its inputs, the LLM is able to alter its encoding to take into account which specific nuances of a word are relevant here, its grammatical role in a sentence, etc.
How exactly a concept is encoded is essentially entirely relative: a vector can be said to encode a concept because it activates other nodes in the network that correspond to that concept (insofar as, by the time that it percolates through the LLM into its final output, it generates tokens that a human will associate with that concept). It can also come in degrees, rather than being purely binary. The correspondence of individual nodes with concepts can be identified using techniques like sparse autoencoder dictionary learning, which let you find neurons strongly connected to a certain concept which can be 'pinned' to force the LLM to behave in a certain way. And they can also be in a 'superposition' of corresponding to multiple concepts that would be relevant to humans.
Crucially, the 'space' of concepts that a given LLM understands is entirely specific to that model. You can't tale a vector inside Claude and directly convert it into a vector that works for DeepSeek. You have to figure out a mapping between the two spaces.
So let's talk about spaces, and then we'll talk about language.
Spaces & thought-oscillations
Perhaps not surprising as creatures who spend our lives navigating 3D environments, one of the most versatile recurring metaphors in maths and physics is an abstract space.
In physics: you have regular physical space where particles might live; you have phase space, the high-dimensional space of all parameter values and velocities accessible to a system; you have Hilbert space, which is the infinite-dimensional space of all states of the quantum wavefunction; you have Minkowski spacetime of special relativity and various curved spacetime manifolds of general relativity which can be parameterised in multiple ways; you have frequency space accessed by a Fourier transform... Other fields have their own spaces; biology has its own phase space describing populations for example.
In my current field of computer graphics, spaces abound just as much. In rasterisation, you define your verticex positions in object space, then map them to world space, and project them into clip space before the projective-geometry perspective divide finally maps them into screen space (where various further algorithms can take place). But we are far from done! We must also keep track of the UV space over the surface of an object, and the tangent space defining directions along the surface for certain kinds of anisotropic effect. A lot of graphics calculations involve mapping points in one space into another space. It's linear algebra all the way down, baby. Even more abstract spaces like all the different colour spaces are there.
One interesting area where spaces come up is the study of oscillations. For many oscillating structures, from something simple like a string on a violin to something complicated like a building, you can decompose the motion into a combination of pure, sinusoidal vibrations known as normal modes. You do this by turning the system's equations of motion into a matrix and finding its eigenvalues and eigenvectors. Remarkably, these form a basis, meaning that you can break down the system into a sum of eigenvectors, evolve them independently, and then add it back up.
Now, let's return to machine learning, and its feature spaces. In an LLM, the feature-encoding vectors evolve in discrete steps passing through layers of the LLM. High-dimensional vector spaces also show up in neuroscience, for example when using electrode arrays to monitor the activity of neurons.
However, inside a brain, the whole system is temporal in nature, and you have all kinds of feedback effects, which means you could imagine these 'feature vectors' not as static things but as oscillations.
I imagined a thought as something like a spiky little blob oscillating with various overlapping modes. Well, I'm a 3D artist, let me make a picture of that for you. Let's make it a demo even. Let's go to Switzerland and spend a weekend trying to make a visual representation of something I saw on LSD. That's a cool thing to do.
youtube
This is a superposition of spherical harmonics, all given different frequencies. The (infinite) set of spherical harmonics forms an orthnormal basis for functions on a sphere, so if you took each component of one of those ultra high dimensional vectors as the coefficient of a spherical harmonic, you would get a unique bumpy shape.
Funnily enough, I was inspired by code that was written for displaying data from MRI imaging, although that is pretty much entirely a coincidence because there it represents something quite different, the diffusion of water molecules.
With this metaphor in hand, we can imagine recurring patterns of thought (ranging from comfortable turns of phrase to traumatic flashbacks) as something like the resonant modes of a system. They are easily excited by random impulses, and slow to die out. Conversely, other types of thought might be heavily damped. Much like a violin bow provides a whole bunch of noisy excitations which ultimately end up exciting a string's resonant modes, the noisy sensory input would get distilled down into oscillations.
The idea of considering the movement of neurons through some kind of phase space is not so outlandish. In fact, recent research has been investigating the topology of 'subspaces' explored by neurons in the brains of mice, as discussed in this video (yes I've been watching a lot of Arsem's videos lately...)
youtube
However, the exact meaning of any of these hypothetical 'modes' is entirely contextual. We might be able to say 'this mode is stimulated when you receive sensory input with the colour red' for any given brain, or even section of one brain.
But to map the oscillations in one space into another space, we need to have some kind of common interface. Perhaps for adjacent regions of the brain, we could go 'directly', with one functional unit of neurons wired up to excite corresponding oscillations in another.
But what about brains that are only connected by whatever you can pass through the physical world inbetween them? Sound, images, etc.? How can you create a correspondence there?
Language
Writing has been described as a kind of telepathy: we encode our internal world into a series of symbols (either as images or sound), which are then decoded to generate a thought in someone else's brain - one that is notionally equivalent.
But what is the nature of that equivalence? It isn't that it will make the exact same pattern of neuron firing in your brain that it did in mine. After all, you have a completely different neural network that has learned different inputs. So there is some kind of mapping from one space to another: the pattern of activity in my brain and the pattern of activity in your brain are related in some way.
We all know that the meaning of sounds in language is pretty much arbitrary. It's built by associations: you have learned that the symbol-sequence 'red' corresponds to this colour's internal representation [assuming your monitor is not calibrated in a really weird way].
And insofar as we have broadly similar sensory and bodily experiences, it is possible to build up this mapping of associations between words, sensations, and whatever other internal representation exists in our brains. It's also a feedback process, spawning all sorts of social constructs by giving them names and acting as if they exist.
However, language does more for us than this.
A moment of introspection: I personally experience an ongoing verbal 'stream of consciousness' most of the time. How this manifests more concretely is that words come to me rapidly from 'somewhere inside'; if I am speaking, I might consider briefly whether they are the 'right' words before saying them.
Internally, I might consider a thought that occurs to me and decide that I do not agree with it, or just think about a sentence I have thought as a kind of 'object', as if I am perceiving it from a different vantage point. It seems to be impossible to consider a thought 'as I am thinking it'; only after it has entered into memory can I 'observe' it.
When I was on LSD, I perceived a kind of 'separating out' of the 'inner', nonverbal process of thought and the linguistic stream. There would be a delay in which the linguistic stream would be waiting for input, and would have to kind of 'spin its wheels' and fill space as it waited for something concrete to encode. This separation was quite delightful, since I am not used to perceiving it in such a way. Other times when I was on LSD I had a vague sense of multiple thought streams occurring in parallel, of switching tracks to bring one or another into salience (something covered here on the psychonaut wiki). I'm not entirely sure if these 'seemed verbal'.
This suggests to me some kind of feedback cycle, of thoughts bouncing between the 'language space' and the broader 'conceptual space' of the rest of the brain. Speculatively: my brain might encode something into language in order to store it while it thinks about something else, for certain more 'sequential' forms of thought, or to activate resonances with linguistically-encoded things. By bouncing thoughts in and out of 'language-space' it might be able to perform different kinds of thinking/computation.
Expanding the space
One of the more intense images that occurred to me while I was jamming with all these ideas of spaces and oscillations was the thought of how new ideas get encoded into the space as I encounter new things and learn. I had recently made two friends, and I had the idea of new dimensions appearing: first a direction that was associated with my friends as a pair, and a secondary dimension that encoded the differences between them.
Each of these 'dimensions' would be associated with other concepts by the dynamics of the neural network.
Visually, I imagined a line extending out from (something that represented the space), and then dividing into another line. I think this is kind of what is meant when the psychonaut wiki speaks of 'intrinsically understandable' geometric representations: I knew exactly what this line was supposed to mean, but it would hardly be clear if I drew you a picture.
Exactly what that 'adding of dimensions' would mean on a physical level I can't tell you. I don't think it's like my brain was literally growing an extra neuron that would specifically be stimulated by thoughts of my friends, like the now-famous 'golden gate bridge' neuron in Claude. Internally, it all presumably exists in some nebulous state of superposition with all sorts of other ideas. Maybe you could extract a vector associated with that concept by some kind of statistical bullshit if you had somehow access to the states of all the neurons, but we don't. Do we?
...well, I thought we don't. Actually we pretty much do have access to individual neurons in mice. We can do all sorts of crazy shit like make their brains transparent and attach glowing proteins to specific neurons that are activated when a specific memory is stimulated. That is fucking insane. We are literally living in an age. Here's Arsem again:
youtube
The idea of 'engrams' as the physical correspondents to memory is nearly a century old, but now we can actually physically observe them.
So, you develop a new concept-association, and a certain subset of neurons get tagged to that concept and excited when it comes up. We mentioned these 'subspaces' up above: presumably that is what could be said to grow an extra dimension. If I have a conceptual dimension that is 'associated with my friend M.', presumably there is a set of neurons that correspond to her, and another set of neurons linking them to various concepts that I associate with her, my memories of what she looks like, etc. etc.
I get a strong sense that the more things that I encounter, the larger my internal 'space' of concepts becomes. But these feature dimensions don't seem to be 'independent'. I suppose what I'm approaching obliquely and fuzzily here is the idea of covariance, and the covariance matrix seen in techniques like principal component analysis. Or something to do with the subspaces mentioned above.
The role of prediction and roleplaying
The thing language models optimise for is to generate something that is contextually appropriate and consistent. This results in a curious behaviour akin to 'roleplaying', where the model will respond as if it's 'in character', according to a premise set up in a prompt.
I previously talked about the 'free energy' model in neuroscience, in which the brain is constantly attempting to predict the next sensory input. There, the main point was in the creation of art: that a lot of the interest we have in artworks comes from its delicate balance of predictability/unpredictability.
However, I think the brain is also predicting something even more significant: itself!
Viewed in another light, an LLM generates a variety of contextually plausible tokens that it might continue along, and then it selects one. The form of its selection is to pick one at random. However, what if it was not random? What if there is some process that views the prediction output and goes 'yes, that one?'
When I am talking, ideas of things to say will come into my head. I will have just a moment to decide whether to let them come out my mouth or not. Or, I will think a thought in my internal 'stream of consciousness', and then conclude that 'yes, that is good' or 'no, this appals me, I won't say this'. We could say that the process that is generating the stream of language is attempting to predict whether I will find it agreeable, or interesting, or relevant or some such thing.
In other words, I am continually engaged in an elaborate performance of 'Bryn'.
On LSD, I had the curious sense of how all these functional elements I was dimly sensing within my brain were acting in concert to produce 'Bryn'. I had the strange and honestly very comforting sense that they were all happy to play a role in generating this persona. I don't know how much credence to lend to this idea.
When I enter a new social context where the rules are unfamiliar (such as a kink scene, c.f. everything is roleplaying except roleplaying which is improv), I become temporarily compromised in my ability to perform the contextually appropriate character. I need to get a sense of the dynamics of this new space - in other words, my brain must develop its prediction-model. It is, in other words, very much like learning to play a new game. (I'll read you eventually, Wittgenstein.)
Depending on context, depending on which set of dynamics you are attempting to predict, different memories will become more or less able to be drawn up through the associative links. Feedbacks are possible; hence 'flashbacks', emotional and literal, where the memory becomes so furiously excited that it shuts out everything else for a while. But this also shapes what sort of person the brain predicts you will be (and thus gives you the option to be) in a given moment.
Compression
Prediction, game-playing, and performance are all facets of this constant process of updating my internal representations - in other words, adjusting the resonances and dynamics of those neuron-interaction spaces. The brain 'wants' - generally tends - to simplify and abstract. In other words, it wants to compress - to discern underlying patterns so it can store its information and generate predictions more efficiently.
So it will try to relate unfamiliar new things to familiar types, and then, where necessary (e.g. because of an extended interaction with a person or a thing), flesh them out with additional details - which is to say building out a subspace for that thing to vary within.
When I was first transitioning my gender, I had a pathetic tendency to view all these interesting new women I was meeting as instances of the same type. It made me embarassing; I was viewing people as a category, not as individuals. Now many many years later, probably the subspace for thinking about all the different trans women I know is one of the larger ones in here. Perhaps other information has been forgotten (dissolved into noise) to make room for it.
The more time I spend with someone, the more specific associations I can build with them.
The more I can get a sense of the dynamics of their inner meaning-spaces.
Initiate feedback loop
So we encode high-dimensional oscillating thoughts into a stream of language-associations in order to excite analogous thoughts in the brain of another person. But of course, that person will have their own associations. Different memories and ideas will be excited by that word. I can only dimly predict how my words will be perceived.
But communication is not hopeless. Because we can ask for clarification. We can pass messages back and forth. Clarify the shapes of each of our thoughts.
The specific ideas I use for introspection, whether or not I'm under the influence of a powerful substance like LSD, are all influenced by the history and the models my brain has built. I like physical science metaphors, obviously. I am a creature who can't help but think in the language of dynamical systems, feedback loops, networks of interacting elements, fluids (hehehe), component parts, parallel processes, games, and of course abstract spaces...
Perhaps it is a worldview that is proper to this moment in the story of the superorganism!
This post represents the most complete effort I've made so far to encode the 'working model' I have of the shape of thinking into language. But the things I am talking about are very abstract, and the direct experiences I refer to are only really available to me - I can only hope that my words excite something analogous in your mysterious meaning-space.
Listen to me banging on about oscillations though. Might as well go full hippie and call it vibes. You can take the girl out of Glastonbury, but...
Postscript
The other image I had while I was on that LSD trip was of each brain existing somewhere in a void: each a constellation of connected parts, which only occasionally get so lucky as to brush up against another such structure and glimpse another mind. Each one trying desperately to roleplay itself in the face of chaotic input and its own inscrutable behaviour. As many people do when they take this stuff, I felt a sort of empathy for everyone, even - especially - the people who had annoyed or troubled me. A glow that lingered long after.
I do not think I am anywhere near done with this quest to understand what the hell I am, or what any of us are for that matter. It's impossible, isn't it? To somehow find a model of the universe and all within it so elegant that it can fit inside here and so rich it captures all that complexity. Authors to read, conversations to have (hii), sensory and emotional experiences to flesh out the spaces.
But before all that... or running through all that... is of course, well, other people. You lot. Endlessly mysterious creatures who continue to fill this hungry, vibrating brain with strange oscillations. Have you considered yourself as the nucleus of the fractal patterns evolving within the ~800,000,000,000,000,000,000 human neurons, and all that we accumulate around us? I don't know, is that a silly metaphor? Do you like it?
"The net is vast and infinite".
That's all we've got for tonight, folks. We've been canmom - love you all, thanks for listening!
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
The whole "the brain isn't fully mature until age 25" bit is actually a fairly impressive bit of psuedoscience for how incredibly stupid the way it misinterprets the data it's based on is.
Okay, so: there's a part of the human brain called the "prefrontal cortex" which is, among other things, responsible for executive function and impulse control. Like most parts of the brain, it undergoes active "rewiring" over time (i.e., pruning unused neural connections and establishing new ones), and in the case of the prefrontal cortex in particular, this rewiring sharply accelerates during puberty.
Because the pace of rewiring in the prefrontal cortex is linked to specific developmental milestones, it was hypothesised that it would slow down and eventually stop in adulthood. However, the process can't directly be observed; the only way to tell how much neural rewiring is taking place in a particular part of the brain is to compare multiple brain scans of the same individual performed over a period of time.
Thus, something called a "longitudinal study" was commissioned: the same individuals would undergo regular brain scans over a period of mayn years, beginning in early childhood, so that their prefrontal development could accurately be tracked.
The longitudinal study was originally planned to follow its subjects up to age 21. However, when the predicted cessation of prefrontal rewiring was not observed by age 21, additional funding was obtained, and the study period was extended to age 25. The predicted cessation of prefrontal development wasn't observed by age 25, either, at which point the study was terminated.
When the mainstream press got hold of these results, the conclusion that prefrontal rewiring continues at least until age 25 was reported as prefrontal development finishing at age 25. Critically, this is the exact opposite of what the study actually concluded. The study was unable to identify a stopping point for prefrontal development because no such stopping point was observed for any subject during the study period. The only significance of the age 25 is that no subjects were tracked beyond this age because the study ran out of funding!
It gets me when people try to argue against the neuroscience-proves-everybody-under-25-is-a-child talking point by claiming that it's merely an average, or that prefrontal development doesn't tell the whole story. Like, no, it's not an average – it's just bullshit. There's no evidence that the cited phenomenon exists at all. If there is an age where prefrontal rewiring levels off and stops (and it's not clear that there is), we don't know what age that is; we merely know that it must be older than 25.
27K notes
·
View notes
Text
The exact nature of long COVID is still coming to light, but we just got some of the best evidence yet that this debilitating condition stems from a brain injury. Using high-resolution scanners, researchers at the Universities of Cambridge and Oxford have shown microscopic, structural abnormalities in the brainstems of those recovering from COVID-19. Signs of brain inflammation were present up to 18 months after first contracting the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Continue Reading.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text


this is my oc neuro, its a neuron and i wanted to make it look like a diagram ^_^
its meant to be a cat looking thing
woah htis is geting attentoin thank yall1!! follow if u wanna see more o f this gober.. an its friends..!
#artists on tumblr#neurons#neuro#neuron#myart#moeart#moe art#cats#anime#cells at work#cells#biology#art#new artist#neuro and hemo#oc#digital artist#small artist#medicine#neurology#neuroscience#cat#my art#original character#brain#medical#medical illustration#medart#sciart#medical art
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Story from the Washington Post here, non-paywall version here.
Washington Post stop blocking linksharing and shit challenge.
"The young woman was catatonic, stuck at the nurses’ station — unmoving, unblinking and unknowing of where or who she was.
Her name was April Burrell.
Before she became a patient, April had been an outgoing, straight-A student majoring in accounting at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore. But after a traumatic event when she was 21, April suddenly developed psychosis and became lost in a constant state of visual and auditory hallucinations. The former high school valedictorian could no longer communicate, bathe or take care of herself.
April was diagnosed with a severe form of schizophrenia, an often devastating mental illness that affects approximately 1 percent of the global population and can drastically impair how patients behave and perceive reality.
“She was the first person I ever saw as a patient,” said Sander Markx, director of precision psychiatry at Columbia University, who was still a medical student in 2000 when he first encountered April. “She is, to this day, the sickest patient I’ve ever seen.” ...
It would be nearly two decades before their paths crossed again. But in 2018, another chance encounter led to several medical discoveries...
Markx and his colleagues discovered that although April’s illness was clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia, she also had lupus, an underlying and treatable autoimmune condition that was attacking her brain.
After months of targeted treatments [for lupus] — and more than two decades trapped in her mind — April woke up.
The awakening of April — and the successful treatment of other people with similar conditions — now stand to transform care for some of psychiatry’s sickest patients, many of whom are languishing in mental institutions.
Researchers working with the New York state mental health-care system have identified about 200 patients with autoimmune diseases, some institutionalized for years, who may be helped by the discovery.
And scientists around the world, including Germany and Britain, are conducting similar research, finding that underlying autoimmune and inflammatory processes may be more common in patients with a variety of psychiatric syndromes than previously believed.
Although the current research probably will help only a small subset of patients, the impact of the work is already beginning to reshape the practice of psychiatry and the way many cases of mental illness are diagnosed and treated.
“These are the forgotten souls,” said Markx. “We’re not just improving the lives of these people, but we’re bringing them back from a place that I didn’t think they could come back from.” ...
Waking up after two decades
The medical team set to work counteracting April’s rampaging immune system and started April on an intensive immunotherapy treatment for neuropsychiatric lupus...
The regimen is grueling, requiring a month-long break between each of the six rounds to allow the immune system to recover. But April started showing signs of improvement almost immediately...
A joyful reunion
“I’ve always wanted my sister to get back to who she was,” Guy Burrell said.
In 2020, April was deemed mentally competent to discharge herself from the psychiatric hospital where she had lived for nearly two decades, and she moved to a rehabilitation center...
Because of visiting restrictions related to covid, the family’s face-to-face reunion with April was delayed until last year. April’s brother, sister-in-law and their kids were finally able to visit her at a rehabilitation center, and the occasion was tearful and joyous.
“When she came in there, you would’ve thought she was a brand-new person,” Guy Burrell said. “She knew all of us, remembered different stuff from back when she was a child.” ...
The family felt as if they’d witnessed a miracle.
“She was hugging me, she was holding my hand,” Guy Burrell said. “You might as well have thrown a parade because we were so happy, because we hadn’t seen her like that in, like, forever.”
“It was like she came home,” Markx said. “We never thought that was possible.”
...After April’s unexpected recovery, the medical team put out an alert to the hospital system to identify any patients with antibody markers for autoimmune disease. A few months later, Anca Askanase, a rheumatologist and director of the Columbia Lupus Center,who had been on April’s treatment team, approached Markx. “I think we found our girl,” she said.
Bringing back Devine
When Devine Cruz was 9, she began to hear voices. At first, the voices fought with one another. But as she grew older, the voices would talk about her, [and over the years, things got worse].
For more than a decade, the young woman moved in and out of hospitals for treatment. Her symptoms included visual and auditory hallucinations, as well as delusions that prevented her from living a normal life.
Devine was eventually diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder, which can result in symptoms of both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. She also was diagnosed with intellectual disability.
She was on a laundry list of drugs — two antipsychotic medications, lithium, clonazepam, Ativan and benztropine — that came with a litany of side effects but didn’t resolve all her symptoms...
She also had lupus, which she had been diagnosed with when she was about 14, although doctors had never made a connection between the disease and her mental health...
Last August, the medical team prescribed monthly immunosuppressive infusions of corticosteroids and chemotherapy drugs, a regime similar to what April had been given a few years prior. By October, there were already dramatic signs of improvement.
“She was like ‘Yeah, I gotta go,’” Markx said. “‘Like, I’ve been missing out.’”
After several treatments, Devine began developing awareness that the voices in her head were different from real voices, a sign that she was reconnecting with reality. She finished her sixth and final round of infusions in January.
In March, she was well enough to meet with a reporter. “I feel like I’m already better,” Devine said during a conversation in Markx’s office at the New York State Psychiatric Institute, where she was treated. “I feel myself being a person that I was supposed to be my whole entire life.” ...
Her recovery is remarkable for several reasons, her doctors said. The voices and visions have stopped. And she no longer meets the diagnostic criteria for either schizoaffective disorder or intellectual disability, Markx said...
Today, Devine lives with her mother and is leading a more active and engaged life. She helps her mother cook, goes to the grocery store and navigates public transportation to keep her appointments. She is even babysitting her siblings’ young children — listening to music, taking them to the park or watching “Frozen 2” — responsibilities her family never would have entrusted her with before her recovery.
Expanding the search for more patients
While it is likely that only a subset of people diagnosed with schizophrenia and psychotic disorders have an underlying autoimmune condition, Markx and other doctors believe there are probably many more patients whose psychiatric conditions are caused or exacerbated by autoimmune issues...
The cases of April and Devine also helped inspire the development of the SNF Center for Precision Psychiatry and Mental Health at Columbia, which was named for the Stavros Niarchos Foundation, which awarded it a $75 million grant in April. The goal of the center is to develop new treatments based on specific genetic and autoimmune causes of psychiatric illness, said Joseph Gogos, co-director of the SNF Center.
Markx said he has begun care and treatment on about 40 patients since the SNF Center opened. The SNF Center is working with the New York State Office of Mental Health, which oversees one of the largest public mental health systems in America, to conduct whole genome sequencing and autoimmunity screening on inpatients at long-term facilities.
For “the most disabled, the sickest of the sick, even if we can help just a small fraction of them, by doing these detailed analyses, that’s worth something,” said Thomas Smith, chief medical officer for the New York State Office of Mental Health. “You’re helping save someone’s life, get them out of the hospital, have them live in the community, go home.”
Discussions are underway to extend the search to the 20,000 outpatients in the New York state system as well. Serious psychiatric disorders, like schizophrenia, are more likely to be undertreated in underprivileged groups. And autoimmune disorders like lupus disproportionately affect women and people of color with more severity.
Changing psychiatric care
How many people ultimately will be helped by the research remains a subject of debate in the scientific community. But the research has spurred excitement about the potential to better understand what is going on in the brain during serious mental illness...
Emerging research has implicated inflammation and immunological dysfunction as potential players in a variety of neuropsychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia, depression and autism.
“It opens new treatment possibilities to patients that used to be treated very differently,” said Ludger Tebartz van Elst, a professor of psychiatry and psychotherapy at University Medical Clinic Freiburg in Germany.
In one study, published last year in Molecular Psychiatry, Tebartz van Elst and his colleagues identified 91 psychiatric patients with suspected autoimmune diseases, and reported that immunotherapies benefited the majority of them.
Belinda Lennox, head of the psychiatry department at the University of Oxford, is enrolling patients in clinical trials to test the effectiveness of immunotherapy for autoimmune psychosis patients.
As a result of the research, screenings for immunological markers in psychotic patients are already routine in Germany, where psychiatrists regularly collect samples from cerebrospinal fluid.
Markx is also doing similar screening with his patients. He believes highly sensitive and inexpensive blood tests to detect different antibodies should become part of the standard screening protocol for psychosis.
Also on the horizon: more targeted immunotherapy rather than current “sledgehammer approaches” that suppress the immune system on a broad level, said George Yancopoulos, the co-founder and president of the pharmaceutical company Regeneron.
“I think we’re at the dawn of a new era. This is just the beginning,” said Yancopoulos."
-via The Washington Post, June 1, 2023
#mental illness#schizophrenia#schizoaffective#psychotic disorders#psychology#neurology#autoimmune#autoimmine disease#neuroscience#medical news#medical research#catatonia#immunotherapy#immune system#clinical trials#good news#hope
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
why neuroscience is cool
space & the brain are like the two final frontiers
we know just enough to know we know nothing
there are radically new theories all. the. time. and even just in my research assistant work i've been able to meet with, talk to, and work with the people making them
it's such a philosophical science
potential to do a lot of good in fighting neurological diseases
things like BCI (brain computer interface) and OI (organoid intelligence) are soooooo new and anyone's game - motivation to study hard and be successful so i can take back my field from elon musk
machine learning is going to rapidly increase neuroscience progress i promise you. we get so caught up in AI stealing jobs but yes please steal my job of manually analyzing fMRI scans please i would much prefer to work on the science PLUS computational simulations will soon >>> animal testing to make all drug testing safer and more ethical !! we love ethical AI <3
collab with...everyone under the sun - psychologists, philosophers, ethicists, physicists, molecular biologists, chemists, drug development, machine learning, traditional computing, business, history, education, literally try to name a field we don't work with
it's the brain eeeeee
#my motivation to study so i can be a cool neuroscientist#science#women in stem#academia#stem#stemblr#studyblr#neuroscience#stem romanticism#brain#psychology#machine learning#AI#brain computer interface#organoid intelligence#motivation#positivity#science positivity#cogsci#cognitive science
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

#important reminders#healing#self love#self care#rest is productive#rest is important#resting#mental heath support#tw mental health#mental health#recovery#recovering perfectionist#it girl energy#it girl#pink pilates girl#pink pilates princess#becoming that girl#that girl#feminine health#psychology#neurodivergent#neuroscience#neurodiverse stuff#adhd#bpd#cptsd recovery#stress#nervous system#emotional regulation
465 notes
·
View notes
Text
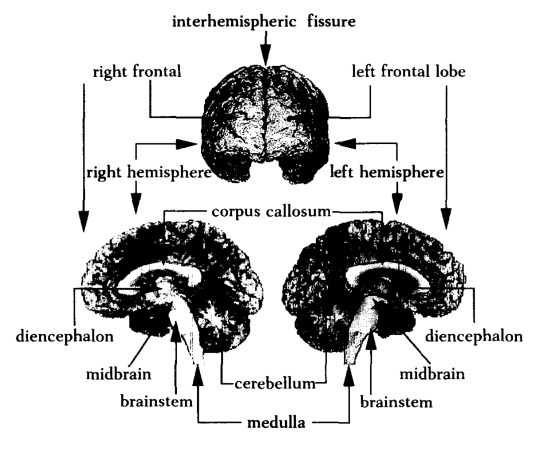
Antonio Damasio, Descarte's Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain
194 notes
·
View notes
Text

study motivation board that I made on pinterest <3
#girlblogging#study aesthetic#study blog#stem studyblr#studyblr#studyspo#study motivation#study inspiration#study#studying#study moodboard#study notes#rory gilmore#neuroscience#biology
347 notes
·
View notes
Text
34 REASONS TO HEAL
1. To heal your ancestors.
2. To heal others.
3. To lessen your physical pain.
4. To decrease worry.
5. To walk around with less baggage.
6. To become better at relationships.
7. To experience more life satisfaction.
8. To lessen your lack of presence in your own life.
9. To breathe easier.
10. To give your soul a break.
11. To get what you deserve in life.
12. To feel what inner peace feels like.
13. To break cycles.
14. To honor your community.
15. To reclaim your time.
16. To ensure that your abuser doesn't rob you of peace any longer.
17. To extend your positive energies.
18. To receive good vibes.
19. To internalize affirmations.
20. To extend your life.
21. To manage stress better than before.
22. To love more.
23. To be more honest with yourself.
24. To achieve those goals you've been holding onto.
25. To increase your creativity.
26. To heal your children.
27. To learn about your trauma.
28. To see firsthand how healing works.
29. To see yourself smiling more.
30. To improve your overall functioning.
31. To reclaim your mind, body & soul.
32. To lessen the burden you carry.
33. To hurt less.
34. To turn sadness into joy & light.
#quotes#positivity#inspiration#self care#self love#self worth#mental health#psychology#neuroscience#studyblr#studyspo#becoming that girl#becoming her#it girl#introvert#dark academia#self growth#personal growth#personal development#college#student#levelling up#self improvement#motivation#study motivation#txt#healing#self esteem#self confidence#self help
283 notes
·
View notes
Text
!!!!
this might be an interesting read
#radfem#radblr#radical feminism#feminism#menstruation#neuroscience#menstrual cycle#brain#womens health
788 notes
·
View notes
Text
Them: New studies suggest that being on the autism spectrum may be up to 90% hereditary!
Me: *looks at my father, who can deliver a discursive monologue on literally any topic at the drop of a hat and routinely ignores off-script conversational responses as though the other party hadn't said anything at all*
Me: *looks at my mother, who has immense difficulty discussing topics she's not already well-versed in because her brain interprets each utterance in contextless isolation and struggles to relate any given sentence to the sentence which preceded it*
Me:
Me: You don't say.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Wake Up Early




I always wanted to be one of those girls who would wake up early, go for a run and be super productive with their mornings. The issue is - i really love sleep. Every time i would start a routine, i would eventually fail. I would wake up to turn the alarm off, think to myself “5 mins more�� and boom- it’s suddenly 8:30 am and i need to leave for work in less than 1 hour.
Two videos on YouTube really changed my mind. One was Andrew Huberman’s, and the other was Jihyo, a k-pop star.
I came across Andrew Huberman’s video about dopamine, and somehow, it helped me to understand why the difficulty waking up early is so important. Now I’m no expert of neuroscience, but let me explain to the best of my abilities.
Dopamine is essentially the build up to the reward; it is not the reward. It is the satisfaction and happiness you feel (when your body releases), after you have achieved something that was painful/ required you to struggle a bit. In order to receive this reward, you have to feel pain, because pain and satisfaction are directly related to each other. Satisfaction without pain is useless and does nothing for you essentially.
That got me wondering: for me, waking up early is difficult. It’s painful. I dont want to do it. But if I do it, its my first win of the day. It’s the first challenge I have overcome of that day, and I always do feel amazing after. The dopamine release after the struggle of waking up and winning the battle of not going back to sleep is definitely there. I feel more confident because a) I have done the “right” thing b) selfishly, i can do something so simple that a lot of people struggle with c) it weirdly makes me feel more confident and like I’m doing the first step of being an adult right.
Jihyo’s video was quite random - she did some show where it shows her daily life when she’s not working. Parts of it made me feel like she’s unable to just relax with herself (probably because her body and mind are so used to chaos, performing, her girl group living together for so many years) so she busies herself a lot. I took the positives from the video; she’s extremely disciplined which I admired, she gets her chores done, she’s good at ensuring that her space is truly her space.
So I decided to build a relatively foolproof routine; but mind you, it does require quite a bit of willpower.
I’ve developed a habit of waking of waking up at 5 am. I head straight for a 30-45 minute meditation and then at least an hour long workout. I stack my habits that way; right after meditation, I put on my running shoes. I used to really struggle with waking up, even if I had to wake up late. This is the strategy that worked me, see if it works for you.
1. Reset your space the night before
This makes you feel less stressed in the morning and also genuinely makes you feel like you have your shit together. Put your clothes away, keep your bag in its place, clean up your desk, reorganise your make up and skin care products. You’re going to go to sleep and wake up to a clean space.
Make sure you define both your bedtime and wake up time. My bedtime is 9:30 pm - so i manage my chores, reading, dinner, everything around that.
2. Early dinner
I’ve noticed that early dinners help me sleep better. I’ve built the habit of casually walking for 25-30 minutes post dinner (not right after eating, after about 15 mins). I’m not walking fast to a point where I’m sweating and puffing, I’m casually strolling outside. During this time, I don’t listen to music, interact with anyone or my phone. I use this time to connect with myself and think about whatever I feel like.
3. No devices before sleeping
I don’t want to stimulate myself before sleeping, so I prefer reading before bed. If you don’t like reading, you can instead do your skincare, maybe revise some physical study notes, etc.
4. Using Alarmy app
This app is torture and I swear by it. This little thing makes you a solve a challenge of your choice in order to make the alarm stop, like math problems, puzzles, etc. I chose 5 math problems.
5. Keep your phone across the room
Don’t charge it near your reach. Keep it as away from you as possible.
6. Stand for two minutes after shutting off the alarm
Don’t allow yourself to snooze, or go back to bed. This is the part that really requires you to tell yourself: “i am not going back to sleep. I’m going to wake up and do the things I have to do for my own benefit.” Remember - the states of heaven and hell are not outside of you, they’re inside you. They are mental states. You have to fight with your lazy demon and tell him/her/whoever that NO; we are NOT going back to bed.
I charge my phone across the room so that forces me to walk first thing in the morning. To stop myself from going back to sleep, after i have shut the alarm off, i just stand for 2 minutes. I dont sit, or go back to bed. I stand and tell myself, we’re doing this. We’re going to wake up and have an amazing day.
Your mind is like a child with tantrums and mood swings. Your rational self has to discipline your mind the way a parent would to a child.
7. Turn a small light on
Not something that is jarring or overwhelming, but enough to help you start waking up. I turn my phone’s flashlight on and keep it on my desk.
8. Be consistent, even on weekends
The biggest mistake you can make is not being consistent. Your body doesnt recognise weekends, your mind does. Your body doesn’t know that tomorrow is Monday, so its time to wake up early. By staying consistent (yes, I wake up at 5 am on weekends too), it allows my body to develop its own body clock and not wrecking the system I’ve kept in place.
What do I do if I have a late night?
It really depends. Let’s say I come home relatively early (+2 hours around my bedtime) around 11 pm, and im in bed by 11:30. I’ll wake up somewhere close to 5 am, like 6 am instead. The next day I ensure I’m in bed by the bedtime I’ve kept for myself and wake up at 5 am again.
If I come home really late, like 3 am - i keep my alarm exactly 8 hours from that time. I need to get sleep, but oversleeping is an issue and that wont allow me to wake up early the next day. I want to get enough sleep where im rested for the day, but not excessively. Unfortunately, sleeping so late would definitely mean that i wont be able to fall asleep at my dot 9:30 pm bedtime, but i turn the lights off and get ready to sleep by then anyway, and mentally prepare for my 5 am wake up call.
#c suite#powerful woman#strong women#ceo aesthetic#personal growth#that girl#productivity#q/a#getting your life together#balance#waking up early#neuroscience#Andrew Huberman’s#K-pop#jihyo
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
A newly discovered communication pathway linking far-flung nerve centers within the brain and skull, and the body beyond, could provide a new target to stop migraine pain in its tracks. Researchers have long tried to pinpoint where migraines begin in the brain, and how these one-sided, nauseating headaches induce pain and other symptoms, such as vomiting. Understanding this would help find new ways to prevent migraines from happening or at least ease the searing pain once it starts.
Continue Reading.
1K notes
·
View notes