#GeospatialData
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
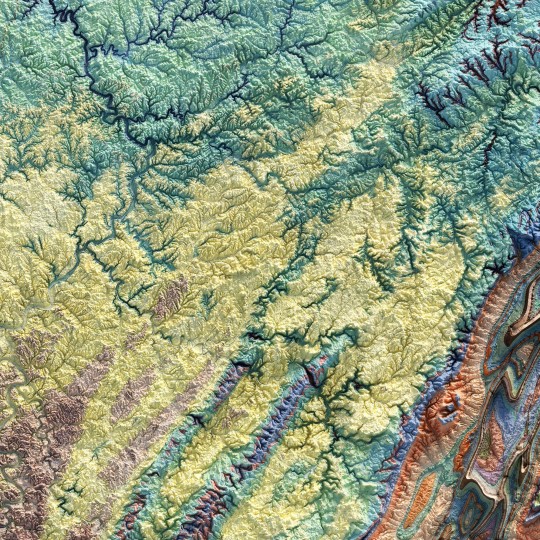


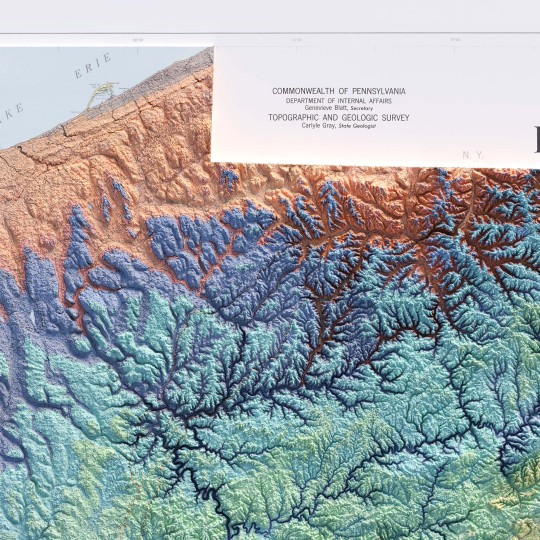

From the 1960s, a (restored) school geological map of Pennsylvania, obviously with shaded relief!
🗺️ 𝗠𝗔𝗣 𝗜𝗡𝗙𝗢 Geologic map of Pennsylvania, Topographic and Geologic Survey, Commonwealth of PA, 1960. Source: David Rumsey Collection.
If you like our work, want to see our daily updates (or want to say hello to our studio), consider to follow our Instagram or Twitter account. Otherwise if are interested in our prints or have a custom request check our shop.
#Pennsylvania#pittsburgh#usmap#mapdesign#GeologyPA#VintageMap#PennsylvaniaHistory#ShadedRelief#GeologicHeritage#PAExploration#RockFormation#GeologicalTreasure#EarthScience#PennsylvaniaGeology#GeologicWonders#LandscapeHistory#GeologicalArt#ElevationData#GeologicMapping#BedrockGeology#NaturalHistory#GeospatialData#GeologicFeatures#MapArt#vizart
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate QGIS 3 Guide – Learn GIS Mapping & Automation
Unlock the secrets of QGIS 3 with this in-depth Udemy course! 📌 Learn GIS workflows, mapping techniques & data visualization.
🌍 ONLY $12.99 from $19.99 (48% off)!
#QGISGuide#GISAutomation#LearnMapping#DataScienceMapping#GeospatialData#GISDevelopment#QGISTools#RemoteSensingGIS#GISAnalysis#MappingExperts
0 notes
Text
The rapid evolution of deep technology is transforming geospatial mapping, pushing the boundaries of how spatial data is captured, processed, and utilized. AI, machine learning, blockchain, and cloud computing are making geospatial technology more intelligent, automated, and efficient. Among the biggest beneficiaries of this transformation are BIM modeling services and 3D BIM modeling, which leverage deep tech to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making across industries.
#DeepTech#GeospatialMapping#AIinGeospatial#BIM#3DBIMModeling#SmartCities#GeospatialData#MachineLearning#Blockchain
0 notes
Text
Exploring (NYSE:PL) Role in Space-Based Data Solutions
Planet Labs PBC (NYSE:PL) specializes in satellite imagery and geospatial data, providing insights for industries such as agriculture, defense, and environmental monitoring. With a vast satellite network, the company delivers real-time earth observation solutions, supporting decision-making across multiple sectors. Its advancements in space technology enhance global data accessibility and efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Drone Land Survey: Revolutionizing Land Mapping with Precision and Efficiency

Introduction
In the world of land surveying, accuracy, efficiency, and safety are paramount. Traditional methods, while reliable, can be time-consuming, labor-intensive, and sometimes risky. Enter drone land surveys—a game-changing technology that is transforming the industry. Drones are now being used to conduct land surveys faster, more accurately, and at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods. In this blog, we’ll dive into what drone land surveys are, why they’re so effective, and how they can benefit your next project.
What is a Drone Land Survey?
A drone land survey involves using unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR sensors, and GPS technology to capture detailed aerial data of a piece of land. This data is then processed using specialized software to create accurate maps, 3D models, and topographic surveys. Drone land surveys are used in a variety of industries, including construction, agriculture, mining, and urban planning.
Why Drone Land Surveys Are a Game-Changer
Unmatched Speed Drones can cover large areas of land in a matter of minutes or hours, compared to the days or weeks it might take using traditional ground-based methods. This makes them ideal for time-sensitive projects.
Cost-Effective By reducing the need for heavy equipment, large teams, and extended fieldwork, drone surveys significantly lower costs. They also minimize the risk of human error, which can be expensive to correct.
High Precision Modern drones are equipped with advanced sensors and GPS technology, allowing them to capture data with centimeter-level accuracy. This level of precision is essential for creating detailed topographic maps and 3D models.
Enhanced Safety Drones can access difficult or hazardous terrain, such as steep slopes, unstable ground, or disaster zones, without putting surveyors at risk.
Versatility Drone land surveys can be used for a wide range of applications, from measuring land boundaries to monitoring construction progress and assessing environmental changes.
How Drone Land Surveys Work
Planning the Survey Before the drone takes off, the survey area is mapped out using specialized software. This ensures that the drone captures all necessary data efficiently.
Data Collection The drone is equipped with cameras and sensors that capture high-resolution images, elevation data, and other relevant information as it flies over the land.
Data Processing The collected data is processed using photogrammetry or LiDAR software to create detailed maps, 3D models, or contour lines. This step often involves stitching together hundreds or thousands of images to form a cohesive model.
Analysis and Reporting The final output is analyzed and presented in a format that meets the project’s requirements, whether it’s a topographic map, volumetric analysis, or a detailed 3D rendering.
Applications of Drone Land Surveys
Construction Drones are used to monitor construction progress, track stockpile volumes, and create as-built surveys.
Agriculture Farmers use drone surveys to assess crop health, plan irrigation systems, and optimize land use.
Mining Drones help in calculating stockpile volumes, monitoring mine sites, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
Environmental Monitoring Conservationists use drones to map forests, monitor wildlife, and assess the impact of natural disasters.
Urban Planning City planners rely on drone surveys to create detailed maps for infrastructure development and zoning.
Choosing the Right Drone for Land Surveys
When selecting a drone for land surveys, consider the following factors:
Payload Capacity: Ensure the drone can carry the necessary cameras and sensors.
Flight Time: Longer flight times allow for larger areas to be covered in a single mission.
GPS Accuracy: High-precision GPS is essential for accurate data collection.
Software Compatibility: The drone should be compatible with industry-standard mapping software.
Popular drones for land surveying include the DJI Phantom 4 RTK, senseFly eBee X, and WingtraOne.
The Future of Drone Land Surveys
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of drone land surveys are only expected to grow. Innovations like AI-powered data analysis, real-time mapping, and improved battery life will make drones even more efficient and accessible. Additionally, the integration of drones with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT), will open up new possibilities for industries worldwide.
Conclusion
Drone land surveys are revolutionizing the way we collect and analyze spatial data. With their unmatched speed, accuracy, and versatility, drones are becoming an indispensable tool for professionals across various fields. Whether you’re a land surveyor, a farmer, or a construction manager, incorporating drone technology into your workflow can save time, reduce costs, and improve the quality of your projects.
If you haven’t yet explored the potential of drone land surveys, now is the time to take flight. The sky’s the limit when it comes to what you can achieve with this cutting-edge technology!
Call to Action Ready to elevate your land surveying projects? Contact us today to learn more about how drone technology can benefit your business. Let’s map the future together!
#DroneLandSurvey#LandSurveying#AerialSurvey#GISMapping#DroneTechnology#PrecisionSurvey#GeospatialData#SurveyingSolutions#LandMapping#UAVSurveying#AccurateSurvey#DroneData#SurveyingInnovation#LandSurvey#DroneMapping
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Power of Surveys: Understanding Their Importance and Types
A survey is a method of collecting information by doing relevant research and using technology to analyze the data, and condition of a specific area or mapping out the construction area. This data is important for planning, designing, and constructing different projects. Dolphin Engineer understand the importance of surveys in various industries. The survey is an essential part of our service, we have been providing accurate reports and reliable results to our clients for over two decades. In this blog, we understand the importance of surveys and the different kinds of surveys we do.
Why survey are important?
Surveys provide researchers with reliable, usable, primary data to inform. They are important because the data comes directly from the individuals you have identified in your goal. Surveys give you a detailed, systematic way to view and analyze your data. Surveys play a major role in gathering data, opinions, and feedback from clients. Accurate survey data also helps avoid costly mistakes and rework, making the project more cost-efficient. Additionally, surveys ensure that projects comply with local, state, and federal regulations, preventing legal issues and fines.
Types of surveys we do-
Topographical Survey- Topographic Surveys are worn to recognize and map the shape of the ground and existing features on the plane of the earth or a little above or below the earth's surface (i.e. trees, buildings, streets, walkways, manholes, utility poles, retaining walls, etc.). This type of topographic survey can be very favorable to homeowners, industrial owners, or even for land under an edifice. Land may include hills, trees, fences, buildings, and ravines. If the purpose of the survey is to serve as a base map for the design of a residence or building of some type or design a road or driveway.

Water Supply Survey- A pipeline survey is the initial step in planning and installing a safe water, gas, or oil pipeline. Dolphin Survey Engineering provides a significant and lucrative alignment for pipe laying and prepares the necessary land accusation planning by Cadastral. Solar Power Plant Surveys- We conduct surveys for the installation of solar power stations. Solar power stations have a basic need to capture as ample sunlight available as possible. There are certain conditions where the resource is available in ample like deserts while some areas get the bare minimum of sunlight in certain parts of the year.
River Survey- Dolphin Engineering are expert in river surveys we have a group of professionals who perform their work in the best manner. River survey helps in analyzing the depth and width of the river and also helps in analyzing the flow of the waves. It helps to gather accurate information about the river. This survey helps in analyzing the temperature of the river. This survey includes two things cross-sections and contour maps.
Bathymetric Survey The bathymetric test helps in measuring the depth of the water body. This survey helps in gathering information regarding underwater and also helps in preparing the map. There are various techniques used to measure the depth. This survey helps in collecting accurate information about the sea.
Conclusion
Surveys are a powerful tool that can help organizations, governments, and individuals make informed decisions, identify trends, and understand public perspectives. Dolphin Engineer, we understand the importance of surveys and offer a range of survey services to our clients. Whether you need topographical surveys, River surveys, or Solar Power Plant surveys, we have the expertise and equipment to deliver accurate and reliable results.
Contact us today to learn more about our survey services and how we can help you achieve your goals.
#Surveying#Engineering#TopographicalSurvey#WaterSupplySurvey#SolarPowerSurvey#RiverSurvey#BathymetricSurvey#DolphinEngineer#DataAnalysis#ConstructionPlanning#AccurateReports#ReliableResults#CostEfficiency#RegulatoryCompliance#Mapping#ProjectDesign#SurveyServices#EngineeringServices#InfrastructurePlanning#GeospatialData
0 notes
Text
How to add Location in Google Maps | YMA PRO TECH
Open Google Maps, find the location, right-click (tap and hold on mobile) to drop a pin. Click the pin, select "Add a missing place," enter the name, category, address, and details. Adjust pin placement if needed. Add photos/videos. Review and submit. Wait for Google's verification process.
youtube
#GoogleMaps#AddLocation#NewPlaceOnMaps#MapUpdates#LocalBusiness#PlacesNearMe#MapContributions#MapEditing#UserGeneratedContent#CrowdsourcedMaps#LocalGuides#MapMaking#MapData#OpenStreetMap#CitizenCartography#DigitalMapping#GeoSpatialData#LocationBasedServices#MapYourWorld#MappingCommunity#MapEverything#GeoTags#PlaceMarkers#PinDropping#MapCollaborations#LocationSharing#CrowdsourcedPlaces#MapYourCity#Youtube
0 notes
Video
youtube
Space Tech for Weighing Trees | Nature IS | Episode 102 with Florian Reber
#youtube#carbon#geospatialtechnology#climatescience#carbonsequestration#aitraining#geospatialdata#forestconservation
0 notes
Text
Conference
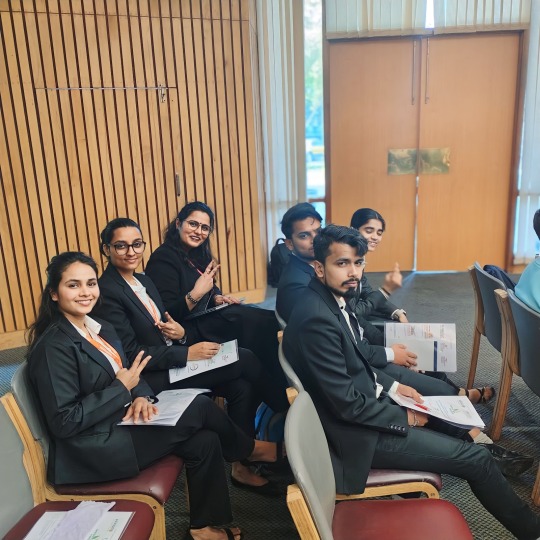






Students of MBA Department along with Dr. Ritu Soryan (HOD MBA) and Prof. Dr. BMK Prasad, Director General, Dronacharya Group of Institutions, Greater Noida attended the "Strategic Workshop on GeoWwise Green Credits: India's Pioneering Initiative" held at India International Centre, New Delhi on 8th February, 2024. Dr. Yogita Shukla, CEO of the addGEO Foundation, warmly welcomed the students.
The aim of the conference is to delve into the nuances of how geospatial information and technology is fundamental to robust water resource management and help communities earn green credits.
#greencredits#geospatialtechnology#geospatialdata#regenerativeeconomy#technology#mbadepartment#students#college#engineeringcollege#g20#cbseboard#delhincr#aicte#aktu#topprivateengineeringcollegeingreaternoida#bestengineeringcollegeindelhincr#DronacharyaGroupofInstitutions#multipleplacement#greaternoida#uttarpradesh
1 note
·
View note
Text
Unlocking the Power of Location-Based Services: Your Ultimate Guide!
A location-based service (LBS) is a service provided by software for mobile device apps that requires information on the location of the mobile device. The application collects geodata, which are real-time data obtained by one or more monitoring technologies.
Technological advances and the rising availability of geolocation, GPS, and mobile data technologies have made LBS more sophisticated and accessible. This allows for the development of new and creative market applications and solutions. These elements will contribute to driving the market expansion. In addition, according to a research report by Astute Analytica, the Global Location-Based Services Market is likely to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.2% over the projection period from 2023 to 2031.
What are the various types and elements needed to run location-based services?
Push:
The application starts the location process when triggered or at daily intervals. The application then displays appropriate information to the user or device based on their geographic location. In this case, a user gets emailed an advertisement or discount after the application detects that he or she is close to a particular retail outlet.
Pull:
The application user begins the location-based service procedures. A user using a mobile map application, like Waze, to identify the nearest automated teller machine is an example of a query-based on-location service. Few services also allow users to look into concerts, restaurants, or athletic events and utilize apps like Yelp, or Google Maps.
The following four essential elements are necessary for location-based services to function:
An application that makes use of location-based services.
A geodata collection placement system.
A mobile network for data transmission or reception.
Analytics software that runs on an outside server to calculate and present relevant data to users based on their geographic location.
What technologies are utilized to track a person's location?
Based on the demand, mobile device hardware type, and available enabling technologies, various tracking mechanisms are frequently employed for location-based services:
GPS: The Global Positioning System is a network of satellites that exist only to assist in the location of objects on Earth. These satellites can be pinged by any device equipped with a GPS receiver (including various smartphones). This function enables the gadget to link up with a minimum of four satellites.
Wi-Fi: Wi-Fi location tracking differs from previous approaches. Usually, a device only links to one Wi-Fi network at a time, thus removing the chance of triangulation. Instead, IP addresses are used in this location tracking.
Each network has an actual IP address that informs the rest of the internet where it is so that data may be sent over the internet infrastructure appropriately. When a user's phone joins a Wi-Fi network, it combines with the physical IP address of that network, enabling location services to determine their current location.
Cellular technology: Cellular tracking functions similarly to GPS. User device links to cellular towers rather than satellites. In general, they'll be within the reach of at least two of the towers, allowing the system to utilize triangulation to pinpoint their location.
#LocationBasedServices#GeolocationTech#GPSNavigation#MobileApps#GeospatialData#ProximityMarketing#GeoTargeting#LocationAnalytics#GISTechnology#RealTimeLocation#GeoMarketing#Geofencing
1 note
·
View note
Text

Join the location-based services revolution! According to a report, the market is set to reach USD 39.2 billion by 2025, with a growth rate of 17.6% from 2020. Don't miss out on leveraging this technology for your business.
For more information,https://hirinfotech.com/digital-marketing/ or contact us at info@hirinfotech.com
0 notes
Text
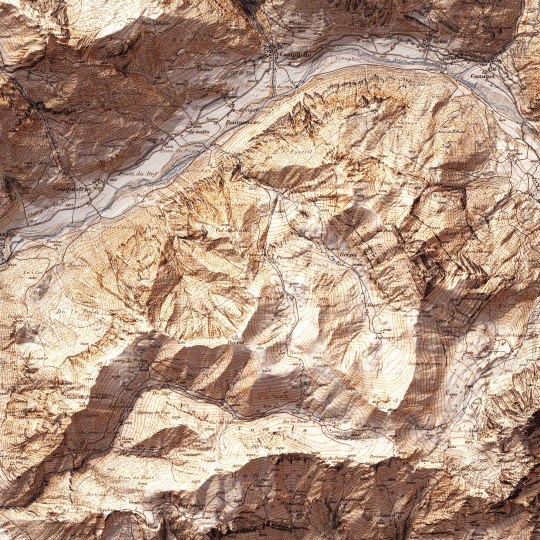
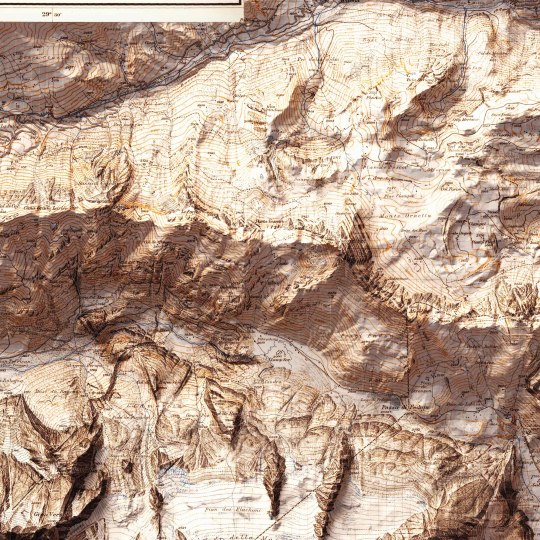
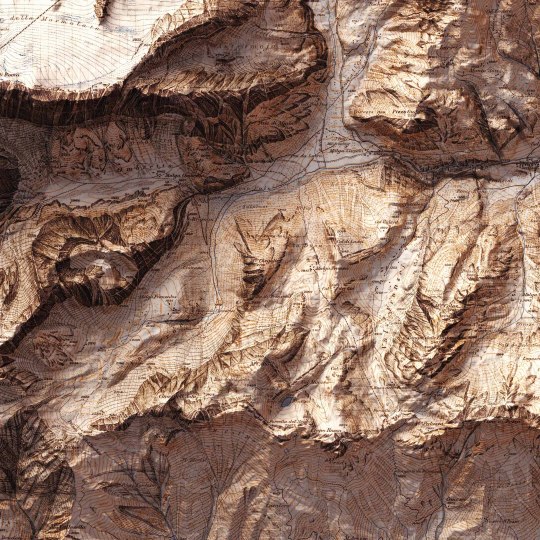




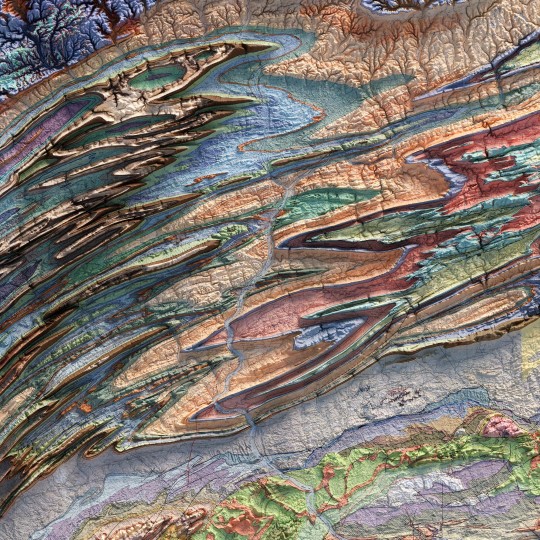
Today we show you the queen of the Dolomites: the Marmolada. The original map was made in 1926 by Freytag-Berndt. We restored it and gave it new life with shaded relief. If you like our work, want to see our daily updates (or want to say hello to our studio), consider to follow our Instagram or Twitter account. Otherwise if are interested in our prints or have a custom request check our shop.
#mountains#mountainlife#mountainlovers#dolomites#dolomitesunesco#dolomitesitaly#marmoladaglacier#marmolada#marmoladapassofedaia#cartography#cartographyart#mapart#digitalmaps#shadedrelief#geography#dataviz#geospatialdata#geospatial#gis#3dlandscape#vizart
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate QGIS 3 Guide – Learn GIS Mapping & Automation!! Unlock the secrets of QGIS 3 with this in-depth Udemy course! 📌 Learn GIS workflows, mapping techniques & data visualization.
🌍 ONLY $12.99 from $19.99 (48% off)!
#QGISGuide#GISAutomation#LearnMapping#DataScienceMapping#GeospatialData#GISDevelopment#QGISTools#RemoteSensingGIS#GISAnalysis#MappingExperts
0 notes
Text
GeoBIM Integration Data Formats and Models for Converging GIS and BIM
The rapid evolution of technology has revolutionized industries by integrating once-disparate systems, creating opportunities to streamline processes, enhance accuracy and optimize decision-making. GeoBIM, the convergence of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM Modeling), is at the forefront of this alteration, merging geospatial intelligence with detailed building data to discover unmatched potential in urban planning, construction and asset management.
The global geospatial analytics market is projected to grow from USD 78.5 billion in 2023 to USD 141.9 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 12.6%. Similarly, the GIS market is expected to expand by USD 21.57 billion within the same period, driven by the integration of BIM and GIS technologies. These trends underline the increasing importance of GeoBIM in addressing complex challenges across industries.
However, the seamless integration of GIS and BIM depends on effective data formats and models that ensure interoperability, scalability and precision. This blog delves into the critical data formats and models facilitating GeoBIM integration, highlighting their real-world applications beyond traditional infrastructure development.
Understanding GeoBIM: A Convergence of Spatial and Built Data
GeoBIM represents the fusion of GIS’s spatial analysis capabilities with BIM’s detailed, object-oriented design models. While GIS excels in managing, analyzing and visualizing geographic data across large areas, BIM focuses on creating highly detailed digital representations of physical assets, such as buildings and utilities. The synergy between these two domains allows stakeholders to visualize, simulate and optimize projects throughout their lifecycle—from planning and design to construction and maintenance.
GeoBIM represents a paradigm shift by combining GIS’s spatial analysis and contextual mapping with BIM’s precise 3D modeling and detailed data about building components. This integration enables stakeholders to:
Visualize Projects in Context: GeoBIM overlays BIM models on geospatial data, helping stakeholders understand how a building or infrastructure fits within its environment.
Enhance Decision-Making: By combining spatial and building data, organizations can perform comprehensive analyses that inform urban planning, disaster management and sustainability initiatives.
Optimize Asset Management: GeoBIM provides real-time insights into building performance, maintenance schedules and surrounding environmental factors, improving operational efficiency.
Why Data Formats and Models Matter in GeoBIM
In GeoBIM, data formats and models are crucial for seamless integration between GIS and BIM platforms. Standardized formats ensure smooth data exchange, visualization and analysis, preventing issues like data loss and misinterpretation. Without proper alignment, integration efforts can lead to costly errors.
For instance, integrating geotechnical data with BIM models is vital for managing natural disasters like earthquakes and floods. This integration relies on standardized data formats to ensure accurate and efficient data exchange.
Additionally, using standardized data formats like CityGML and 3D Vector Scene objects in GIS enables high-quality visualization of textured building overlays on GeoBIM models, enhancing stakeholder communication and participation.
In the end, selecting appropriate data formats and models is essential for effective GeoBIM integration, ensuring data integrity and facilitating successful project outcomes.
Data Formats in GeoBIM: Harmonizing Information for Seamless Integration
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC):
IFC is the primary open standard for BIM data, developed by buildingSMART. It provides a rich, object-oriented schema for representing 3D geometries, materials and semantic data. IFC files support the exchange of building models across different BIM software, ensuring consistency in collaborative projects.
Use Case: A study in Remote Sensing explores BIM and GIS integration for urban disaster management, highlighting how detailed building data enhances disaster response. Similarly, a paper from CEUR Workshop Proceedings discusses using GIS and BIM to assess and visualize flood damage. Both underscore the value of combining IFC-based building models with GIS flood data for improved flood risk management.
CityGML (City Geography Markup Language):
CityGML is a widely used standard for representing 3D city models and large-scale infrastructure projects. It allows for multi-level detail (LoD) representation, enabling users to switch between broad, city-wide views and intricate building models.
Use Case: City planners in Helsinki use CityGML to integrate building designs with topographical data, optimizing solar energy potential for urban districts.
LandInfra (Land and Infrastructure):
LandInfra, developed by OGC, focuses on land development and infrastructure projects. It provides a unified schema that bridges GIS and BIM data related to roads, bridges and utility networks.
Use Case: Transportation agencies use LandInfra to integrate road networks with underground utility models, reducing excavation risks during road expansion projects.
Esri Shapefile (SHP) and GeoJSON:
SHP and GeoJSON are prevalent GIS data formats that store vector data (points, lines and polygons). They allow GIS applications to overlay spatial data on BIM models.
For instance, a study on integrating BIM, IoT sensors and Building Automation Systems (BAS) discusses how such integration can lead to a more efficient energy management system.
5. Esri Multipatch
Description: Multipatch is a GIS format used by Esri to represent 3D features. It is commonly used for importing 3D BIM models into GIS environments.
Use Case: Multipatch enables BIM models to be visualized within GIS for spatial analysis.
Example: For flood risk assessment, a multipatch BIM model of a building can be overlaid onto floodplain maps to evaluate vulnerabilities.
Models Facilitating GeoBIM Integration
Beyond data formats, conceptual and logical models ensure that data from GIS and BIM systems aligns for comprehensive analysis.
1. LOD (Level of Detail) for GeoBIM LOD defines the detail and complexity of BIM models. For GeoBIM, LOD levels are extended to support geographic scales, balancing between BIM’s granular detail and GIS’s broader scope. This includes two key dimensions:
Element LOD (eLOD): Refers to the geometric detail of individual BIM elements, evolving from basic shapes (e.g., LOD 200) in early design to highly detailed, construction-ready models (e.g., LOD 400).
Information LOD (iLOD): Focuses on the depth of non-graphical data, such as specifications, performance metrics and lifecycle details, enriching BIM models with actionable insights.
For instance: Urban planners can start with LOD 200 for zoning and feasibility studies, upgrading to LOD 400 for detailed construction phases, leveraging both eLOD for accuracy and iLOD for informed decision-making.

These models ensure that data schemas in BIM and GIS platforms align, providing a unified framework for asset tracking, lifecycle management and spatial analysis.
For instance, Transportation agencies can align BIM bridge models with GIS datasets to monitor infrastructure health and predict maintenance schedules.
Future Trends and Innovations:
Digital Twins: GeoBIM facilitates the creation of digital twins, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of physical assets. For example, HNTB Corporation utilized GIS technology to develop a 5D digital twin for a transportation project, integrating 3D models with time and cost dimensions to improve project management.
5D and 6D Modeling: Incorporating time and cost dimensions into BIM-GIS integration leads to more comprehensive project management. The integration of BIM and GIS data in the cloud has been shown to enhance efficiency in project workflows.
Cloud Collaboration: Cloud platforms are enabling real-time collaboration, allowing stakeholders to access GeoBIM data globally. This approach fosters collaborative workflows and processes throughout the project lifecycle. Key Challenges in GeoBIM Data Integration:

Heterogeneous Data Sources: BIM operates at high precision on a micro-level (e.g., building components), while GIS handles macro-level data across extensive geographic areas.
Differing Coordinate Systems: BIM models often use local coordinate systems, whereas GIS relies on global coordinate reference frameworks.
Data Granularity: BIM data is highly detailed, while GIS datasets may generalize features to optimize for large-scale analysis.
The Road Ahead: Future Trends in GeoBIM Data Formats and Models
As digital twin technology gains traction, the demand for high-fidelity, interoperable data formats will rise. Emerging trends, such as the integration of AI-driven analytics into GeoBIM workflows, promise to unlock new dimensions of project optimization and predictive maintenance. Magnasoft, with its expertise in GIS and 3D modeling, is at the forefront of these advancements, providing tailored solutions that drive innovation across sectors.
GeoBIM’s potential extends far beyond traditional applications, shaping the future of industries ranging from energy and healthcare to telecommunications and resource management. By embracing the right data formats and models, organizations can unlock unprecedented value, transforming the way they design, build and manage assets.
Explore Magnasoft’s GeoBIM solutions to discover how data-driven integration can revolutionize your projects.
0 notes
Text
#aitools#ai#artificialintelligence#digitaltwin#indoormapping#newtech#geospatialdata#datamapping#gis#mapping#geospatialtechnology#gismapping#dmapping#geospatial#dmap#digitaltwins#machinelearning#lidar#onpassiveai#onpassive#assetmapping#maps#fieldmapping#aitechnology#dataextraction#earth#voxelmaps#utilitymapping#onpassiveaitools#dmodeling
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Power of Lidar Technology: Transforming Surveys and Mapping Solutions

In today’s fast-evolving world, lidar technology has emerged as one of the most groundbreaking tools for precise surveying services. Whether it's for aerial surveys, topographic surveys, or advanced mapping solutions, lidar offers exceptional accuracy and efficiency. Let’s explore how this cutting-edge technology is reshaping industries and driving innovation.
What is Lidar Technology?
Lidar technology stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D models of terrain, structures, and vegetation. When combined with remote sensing, lidar helps gather geospatial data quickly and safely, making it indispensable for various industries such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure development.
The Role of Aerial Surveys in Modern Mapping Solutions
Aerial surveys powered by lidar technology are one of the most effective ways to collect data over large areas. Drones and aircraft equipped with lidar sensors capture high-resolution data of landscapes, buildings, and other features in real-time. These surveys play a vital role in mapping solutions for everything from land development projects to flood risk assessment.
Unlike traditional methods that require time-consuming fieldwork, lidar offers a much faster, safer, and more accurate alternative. With lidar technology, businesses and governments can make more informed decisions while saving time and money.
Why Remote Sensing and Geospatial Data Matter
Remote sensing through lidar provides a unique advantage in collecting geospatial data from areas that are difficult to access or hazardous. Whether it’s mapping forests, assessing flood zones, or surveying coastal regions, lidar can capture highly detailed information with precision.
This data is used to create topographic surveys that show the elevation and contours of the land, making it invaluable for urban planning, construction, and environmental studies. By having access to detailed, accurate data, professionals can plan projects more effectively, manage natural resources, and predict potential issues before they arise.
Innovation in Aviation: How Lidar Is Changing the Game
In the world of innovation in aviation, lidar technology has brought about a transformation. Drones equipped with lidar sensors are now being used for everything from forest inventory management to land surveying. These aircraft can fly over difficult terrain, gathering data without putting human surveyors at risk.
This technological advancement in aerial surveys is particularly valuable in India, where vast areas of land need to be mapped for development and environmental monitoring. By leveraging drones with lidar sensors, businesses and governments can gather high-quality data in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
The Future of Lidar Technology
As the demand for accurate geospatial data continues to rise, the future of lidar technology looks promising. The integration of remote sensing and lidar will only continue to grow, opening up new possibilities for surveying services and mapping solutions.
Whether you’re involved in urban planning, environmental conservation, or infrastructure development, lidar technology provides the tools necessary for smarter decision-making and more efficient planning.
Conclusion
The impact of lidar technology on industries worldwide cannot be overstated. From topographic surveys to aerial surveys, lidar is revolutionizing the way we collect, analyze, and visualize data. As it continues to evolve, this technology will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of mapping and surveying.
If you’re looking for a reliable lidar survey company to help with your next project, Atom Aviation offers cutting-edge surveying services with expertise in lidar technology. Whether for land development, environmental monitoring, or infrastructure planning, we have the solutions you need.
#LidarTechnology#AerialSurveys#MappingSolutions#GeospatialData#RemoteSensing#SurveyingServices#InnovationInAviation#TopographicSurveys
1 note
·
View note