#English dialects
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Friendly reminder that Steve and Bucky probably have absolutely wild Brooklyn accents. Maybe it’s mellowed out over the years but sometimes, woild, goil, woist, poifume. Cwafee. Wourder. Fugeddaboutit.
#1940s stucky#stevebucky#stucky#prewar stucky#brooklyn idiots#otp brain rot#circa 1918#star spangled ding dongs#english dialects#it’s just his neurosis that oughta be coibed he’s psychologically distoibed I’M DISTOIBED#steve rogers#bucky barnes
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

8 notes
·
View notes
Text
my favorite part of all this dialect research I did is watching Georgian period pieces with upperclass british gentry and knowing they wouldn't have spoken in RP and might have rather sounded a bit like pirates to my 21st century North American ear.
#linguistics#english language history#english dialects#dialect#regional dialects#simon roper does really great stuff on youtube and y'all gotta follow him there ok
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi linguists of tumblr! I know there are some of you out there.
Can y'all explain the "I dunno" noise? idk if this is a southern thing specifically or if it's all over the place, but where I live people commonly just. Make A Noise, no vowel sounds, just a hum that (so far as I can tell) goes low pitch-high pitch-middle pitch (fooled around on a keyboard a bit to see if I could assign intervals. Kinda like anywhere from an augmented sixth to an octave up then maybe a third down, but that last note bounces a little?) that we all just acknowledge to mean "I don't know".
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
podficcer resource
IDEA: international dialects of english archive
0 notes
Text
Studying linguistics is actually so wonderful because when you explain youth slang to older professors, instead of complaining about how "your generation can't speak right/ you're butchering the language" they light up and go “really? That’s so wonderful! What an innovative construction! Isn't language wonderful?"
#linguistics#gen z slang#english#as people in the reblog pointed out!#most gen z slang comes from (or was appropriated from) aave#honestly I was just excited to talk about how people in my field actually get excited about non standard uses of English#instead of ridiculing speakers#and I tagged incorrectly and didn’t point out the very real issues of language and power and appropriation inherent in modern slang#in that much of it was appropriated#and even that which experiences language change in the wider culture still originated in aave#aave is just as linguistically valid as any other English dialect because it is a proper language#and the grammar is incredible!!!#habitual be is fantastic and an excellent example of how a richer case system or a certain case can render an adverb unnecessary#and the phonology is just beautiful#anyway I’m very sorry#I fucked up
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dialect notes! Dialect notes! Dialect notes!
Because I missed my calling in academic research, I've spent a non-zero amount of time going down rabbit holes on early North American dialect for Along The Northern Heights. Is it worth doing all this research for a fanfiction of a PBS kids show from 20 years ago? Well it gives me considerable amounts of joy to write, so yes.
Anyway! I want to share a massive infodump, because writing gives me goodfeels and so does sharing! Please let me know if I am inaccurate or wrong about anything. I am not an academic and furthermore I do not want to spread misinformation.
MASSIVE WORD BLOCK UNDER THE CUT
A Pregame With Disclaimers About "Good" English
The history of Modern English is rife with Big Oof moments, and I'm not just talking about The Great Vowel Shift or Noah Webster deciding that the "u" in "colour" was silly. Especially in the late 18th century, there was a push to make accents more uniform and to establish a single "Good" English - and there is so much aggression towards what those scholars considered "Bad" English. And, in my extremely uneducated opinion, it seems like it's a conveniently moving target, just like "whiteness." In the context I'm in when writing, it positively reeks of shitting on any of the world's population groups that aren't Southeastern England. And, being from the United States, I know all too well the absolute shit that's been lobbed at AAVE for not being "Good" English.
This "Good" vs "Bad" way of looking at dialect is reductive, destructive, and boring, and I think it goes without saying I don't condone it in the slightest.
A Further Pregame With Received Pronunciation, or RP
the "generic" British dialect many of us outside the UK think of when we think of a British accent (a shame, I think, because the UK is so dialect-diverse and there are some absolute bangers on that damp island!) There are certainly a myriad of reasons for this, but probably the most common reasons/claims I've heard through my life are
A) 19th-century upper-class British folk wanting to have a more separate dialect from the other classes.
B) associations with the way the Royal Family has spoken English since at least Queen Victoria (a generic reasoning that we see happen along populations: imitating those in power)
C) 20th-century RP became "generic" in a similar way that the broad North American dialect* now associated with the United States and, to some degree, Canada, did - that is, it was further developed and use encouraged as the easiest to understand when recorded and played-back on period audio recording equipment (specifically radio and television.)
*a timeout is to be made here for the so-called Mid-Atlantic dialect at the dawn of "talkies" and early Hollywood. Its the delightful way of talking you'll hear in old black-and-white movies: slightly musical cadence, and combining the broad north american dialect with a bit of the non-rhoticity of RP. This dialect was mostly affectation and as anyone with living American relatives born before 1960 can tell you, mid-20th-century Americans largely did not speak it in normal settings.
Now, all of this is to say, RP as a dialect doesn't really appear until mid-19th century (although it would seem the loss of rhoticity we so associate with RP was a gradual shift starting in the very end of the 18th century.) Furthermore, the ways that we, 21st-century denizens, know RP don't come into their own until the 20th century and proliferation of audio-based mass media.
On to My Actual Point : 18th Century American Dialect (non-AAVE)*
*I make this distinction because the history of AAVE is a massive topic all on its own and I feel even less qualified to speak on it
It can't be ignored that the base strata making up Anglo-American speech patterns would have been as varied as where the original settlers/invaders came from, nor can it be ignored that the American Colonies were made up of more than just Anglo-Saxon descendants. Even back then, they were a mosaic of cultural interaction, which is why Thomas Paine declared America (at least the white part) a European, and not British, culture.
That being said, multiple primary sources indicate that the dialect of Anglo-Americans at the late 18th/very early 19th century was similar to "well-bred" Londoner dialect of the time (assuming there's enough of a distinction here from broad Southeastern UK,) and that this particular dialect was broadly spoken with less regional variance than the family of dialects in the UK.
This is made clear in vol 3 of Timothy Dwight's Travels in New-England and New-York, a collection of letters sent to colleagues in England:
"I shall not, I believe, offend against either truth or propriety if I say, that the English language is in this country pronounced more correctly than in England. I am not, indeed, sanguine enough to expect, that you will credit the assertion, nor that you will believe me to be a competent judge of the subject. Still I am satisfied that the assertion is true. That you may not mistake my meaning, I observe, that by a correct pronunciation I intend that of London; and, if you please, that of well-bred people in London."
(Dwight, Timothy. Travels in New-England and New-York vol 3 p 265)
Now in context he is only speaking of the New England region, and he does make a disclaimer here that he's not "a competent judge" of the subject, and we are certainly ignoring his hope that he won't be cited on the matter. But, his observation holds true from other primary accounts, especially William Eddis' Letters From America, which are composed of his observations (mostly of Maryland gentry) from 1769 to 1777. (His letters also happen to be an invaluable primary source for observations on culture and political commentary on the rising crisis between the colonies and Britain, from the perspective of a loyal well-to-do British subject.)
On the uniformity of language, Eddis has this to say:
"In England, almost every county is distinguished by a peculiar dialect; even different habits, and different modes of thinking, evidently discriminate inhabitants, whose local situation is not far remote; but in Maryland, and throughout the adjacent provinces, it is worthy of observation, that a striking similarity of speech universally prevails; and it is strictly true, that the pronounciation of the generality of the people has an accuracy and elegance, that cannot fail of gratifying the most judicious ear."
(Eddis, William. Letters from America, Historical and Descriptive. p 59)
if the odd comma placements are making it hard to read, you're not alone. 18th century writing is choc-full of what we might today consider run-on sentences, comma splices, or just generally cumbersome. Here's me paraphrasing as best I can:
"In England, almost every county has its own dialect, habits, and modes of thinking, noticeably different inhabitants that don't live very far from each other; but in Maryland and adjacent provinces, there is a notable similarity of speech, and its absolutely true that the generalized accent/pronunciation has an accuracy and elegance that won't fail to gratify a discerning ear."
----------------------------------------------------------
All this background I'm giving comes to this point: late 18th-century "well-bred" Londoner is the dialect I have chosen to loosely base what I write in Along The Northern Heights. I listen to alot of Simon Roper's work on youtube regarding the topic. I would say these two are probably the most valuable videos on the accent.
youtube
youtube
He makes disclaimers about not being formally qualified to speak on linguistics, and I would be remiss to not pass along those disclaimers.
That being said, what's in my mind is pastiche of that, the local "country" (read: appalachian) dialect in rural Virginia, the dialect work used in Turn:Washington's Spies and HBO John Adams, as well as some of the dialect you hear in PBS Masterpeice's Poldark, and various media I've watched/read from Living History re-enactors about reconstructing dialect.
------------------------------------------------------------------
Since I've made it a headcanon feature that James Hiller has a bit of a brogue that he feels pressured to correct, but slips into when he is excited or upset, I'd like to dig more into less-"proper" dialects of the time, and, if possible, the less-proper Philly accent. For shits and giggles, here's what I suspect is a dramatization of a modern-day Philly accent:
And then a very similar, a very real Baltimore Baldmer accent:
youtube
Honestly? Hearing both of these warms the cockles of my heart, because my late grandparents (especially grandma. *Especially* grandma) spoke with a Baltimore accent, which has similarities with the Philly accent. My aunts and uncles all speak it; its been normalized and blended with a virginia rural accent in mine (I say wadder, my grandma said wooder. I say toosdaye, my grandma said toosdee. I say ahn, grandma said ooowan. I say y'all, grandma said all youse/all you. I say "d'jeet," she said d'jeet, and you can pull d'jeet from my cold dead hands.)
In addition, you have the modern-day "High Tide" dialect of Okracoke, the Carolina Brogue.
youtube
youtube
trouble with Carolina Brouge, which is disappearing, is that its got too much modern-day southeastern drawl to really use as a basis for an 18th century Philly boy. Though it does seem like drawing out the "A" in water into wooder/woader is a commonality.
Anyway. That's been my infodump. I spent too long on this!
#liberty's kids#my writing#linguistics#language#English language#me infodumping#infodump#hyperfixations#dialect writing#english dialects#british dialects#north american dialects#18th century English#Okracoke brogue#Youtube
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heute die englischen Dialekten
0 notes
Text
#i need to know#English#english dialects#share if you can#text#macdonald's#food#english poll#english colloquialisms#colloquial#share pls#share#tumblr#poll#tumblr poll#silly poll#science#curious
1 note
·
View note
Text

Miniature dog and khait effigies for a Wardi funeral. These are clay figurines that have been painted and decorated with great care by a skilled artist. Both include real hairs from the individual animals they have been modeled after. The dog is collared, showing that it is a loyal pet rather than a lowly feral scrounger. The khait is fully bridled and ready to carry the deceased in their journey.
---
It is believed that the souls of the deceased, once freed of their bodies, undergo a month-long journey to reach rebirth in the lunar lands. This journey is full of perils. It begins in the realm of the earth where the soul is naked and vulnerable and traveling through complete darkness. Evil spirits dwell within this realm and may try to capture the soul or lead them astray, and the way is twisting and obscured in shadows. Even after escaping this darkness, the soul still must travel an arduous and winding path through the realm of the sky in order to reach their destination.
A khait and a dog are traditionally offered as funerary goods (in addition to food, water, wine, clothing, weapons, and other needs) to assist the soul in their travels- the khait will ease their passage in their long journey and carry them swiftly, and the dog will navigate through earthly darkness and dense cloud by scent, and protect the soul from harm.
Ideally, one of the deceased's own living khait and hunting/guard dogs will be killed at the funeral (typically the most beloved of their animals, as who would be better company than that?) so that they can have familiar and loyal helpers in their lonely journey. However, there are tremendous class barriers to ownership and disposability of a khait, and well-bred working dogs (while significantly more accessible) aren't ubiquitously available, and many people do not consider captured feral dogs to be a worthy replacement. As such, funerals with full animal offerings tend to be limited to higher status individuals.
Everyday people still need protection on their journeys, and animal effigies can be appropriate replacements for the real thing. These effigies are usually designed with great specificity to represent known individual animals that have already died (often including the animal's actual hair, as seen here). The soul of the represented animal will recognize the effigy as its body, and can be called into the icon so that it may accompany the deceased. These effigies (along with any other necessary grave goods) will be placed onto the pyre and burned along with the body so that the traveling soul will be sent off with everything they need.
Some folk traditions have semi-legendary local animal spirits who will be represented instead of a personally familiar animal. This often develops around a small community 'sharing' one historically extant animal for their funeral effigies as a matter of practicality, developing a sense of attachment to this animal as an aspect of shared identity, and adding layers of legend to the animal's story with the passage of time.
For example, a very popular legendary guide in the northeastern rural parts of Ephennos is Chisnops-Inreña (which very closely translates to 'Orange Son Of A Bitch'), a legendary livestock guardian dog. The animal was said to have been the biggest, meanest, ugliest motherfucker around, but was an unshakably loyal and fierce guardian, as noble as a dog (not the noblest of animals by any means) can possibly be. He is said to have fought off everything from jackals to lions to cattle thieves in his day, and died protecting his herdsman master from an infamous man-eating king hyena, only succumbing to his own wounds when the great beast lay dead. His spirit was later used as a guide in his master's funeral, and local legend states that the same spirit has been seen following herdsmen and their cattle ever since, as not even death could keep him from his duties. Such a dog would make an excellent guide and protector in the journey to the afterlife, and effigies of him are favored in the funerals of northeastern Ephenni pastoralists.

A lovingly crafted Orange Son Of A Bitch
#Partly a rehash of prev post BUT WITH PICS!!!!!!!#chisnops more literally means 'bitch-born'. The word 'bitch' doesn't have the same breadth of connotations as in english#and pretty directly means 'female dog' but calling someone 'chisnops' is functionally Very close to 'son of a bitch'#Inrenna is a color word for orange. Most of the western Wardi dialects pronounce double N syllables like ñ (in- /rey/ - nya)#while others will enunciate like 'in- /reyn/- nah'. Spelled it inreña here to indicate Ephenni dialect
438 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rare Language Learning: Polari
If you have ever used the words:
- Naff
- Butch
- Camp
You have unknowingly been speaking the sociolect known as Polari, the language of queer people primarily used in the 30s to the 70s. Polari is now an endangered language, as labelled by the University of Cambridge
Something of note: Many resources out there imply (or state) that Polari was a language invented and used solely by white cis gay men, which is decidedly untrue. Many words of Polari come from drag culture, lesbians, and the Romani people and their language. The use of ‘the language of British gay men’ may be a more palatable title to the general public, but it is not to me. I did my best to curate a variety of resources, but unfortunately much of queer history has been lost many more decades than I’ve been alive, if you have any other resources for studying Polari I would love to read them, message me or leave a link in the replies.
Articles
Learn Polari, the Secret Language of the Gays ⚢ Out Magazine
Polari: The code language gay men used to survive ⚢ BBC
Polari and the Hidden History of Gay Seafarers ⚢ National Museums Liverpool
The Story of Polari, Britain’s Secret Gay Language ⚢ Fabulosa!
Polari People ⚢ Fabulosa!
Polari: a language born from prejudice ⚢ Englishpanish
The secretive gay language that gave LGBTQ people a voice ⚢ GAYTIMES
A brief history of Polari: the curious after-life of the dead language for gay men ⚢ The Conversation
Study Material
The Polari Bible ⚢ Internet Archive
Fantabulosa: A Dictionary of Polari and Gay Slang ⚢ Internet Archive
Sociolinguistics / Polari ⚢ StudySmarter
FlashCards ⚢ Quizlet
New Polari Translator ⚢ LingoJam
Polari: A sociohistorical study of the life and decline of a secret language. ⚢ Dissertation, University of Manchester
Polari: a language born from prejudice ⚢ Englishpanish
Simon Bowkett: a short blog in Polari for LGBT+ History Month ⚢ Civil Service LGBT+ Network
#academia#studyblr#university studyblr#uni#university#student#linguistics#language study#language learning#langblr#languages#endangered languages#queer history#queer history month#lgbtq community#lgbtq history#lgbtq history month#lgbt#lgbt history month#queer academia#queer community#linguistic#Polari#Polari language#dialect#sociolect#pride#uk history#English history#university student
795 notes
·
View notes
Text
Map of British English dialects
by Ryan Starkey (Starkey Comics)
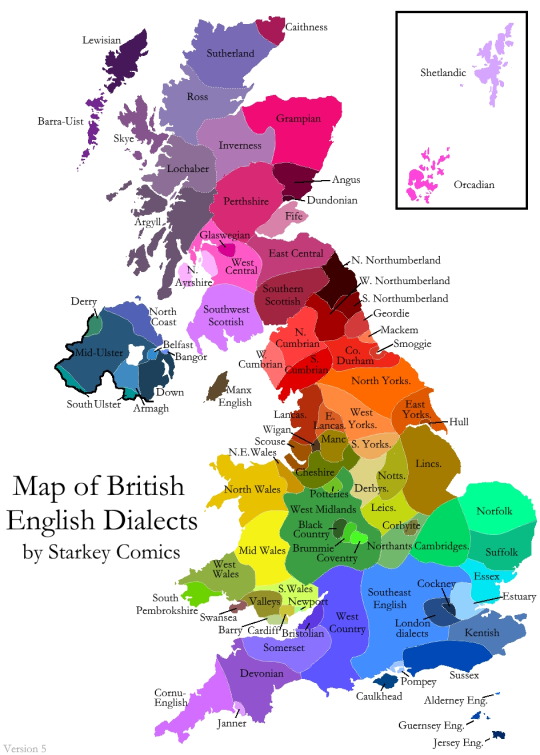
Author Ryan Starkey accompanies the map with a great article:
I’ve spent the last few years pooling together every study, survey, map, and database I can find, and then subjecting my image to several rounds of peer feedback. […] The end result is an image which is, to my knowledge, the most detailed map of British dialects ever made.
He also discusses “Why this map is wrong, and always will be”, and just how difficult it is to create a precise map of dialect regions.
Why is there so much dialect diversity in the U.K.? Because the longer a language is in a region, the more it tends to diversify. This is partly why, for example, there is a much larger variety of dialects spoken in the Eastern U.S. than the Western U.S.
Further Reading
The stories of English (David Crystal)
This is the perfect book to read if you want to know more about the history of dialect diversity in English, because the entire focus of the book is to show that English is not just one unified language (hence the plural “stories” in the title). It’s one of my favorite popular language books.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Do you ever became incredibly frustrated with your own language? No? Just me? Hwæt mickle mess!
From the US but i spell grey with an e because e just feels like a much greyer letter than a
77K notes
·
View notes
Text
Observation that nobody asked for time!
When doing all the soft research I've done for writing in 18th cent dialect, I've noticed a quirk in my own accent/dialect.
It's a broadly north american dialect, with a touch of southeastern and a helping of Maryland/tidewater. But when speaking fast or informally/relaxed, I sometimes pronounce "you" as "ye." As in "yeh" (or sometimes "ya") not "yeee." so then:
"you've got something on your face," (which I might pronounce fully if I'm actually trying to speak clearly/speaking with a stranger)
becomes "yehv got somethin' on yeh face," or, if I'm VERY chill, "y'got sum'in' on y'face."
I guess the problem I have is when transcribing that, and when I apply it to my fics when I think it might be appropriate, I really, REALLY want to use "ye" and not "yeh" because it looks/reads easier, (and in practice that "h" isn't actually there, which makes it so so so easy to cram it into other words like above,) but I'm assuming most people will read it as yeee and not yeh.
...I don't know where I was going with this but yeah. Actual linguists of tumblr, pipe in.
#dialect writing#tricorn on the cob hyperfixates#English dialects#North American English#linguistics#linguistics of tumblr#linguistics interest#my squirrelly ass brain wants to rewrite this entire post in dialect
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is based off of that one tiktok from @sorruna where it’s the audio from Spider-Man: Into the Spider-verse.
——
Dick Grayson was a sneaky, intelligent little shit.
He was also dumb. These things are not mutually exclusive.
To this day, one of his best kept secrets- one of the many, many that he had now- was something he’d take to his grave.
Or to Jason’s grave, at least.
Dick sat down and began telling the story to ears that would never truly hear it.
——
Batman’s voice rumbled behind him as Dick, in his Robin suit, stood blankly on top of a roof.
“I know you snuck out last night, Robin.”
Dick froze, train of thought about his dinner derailed. Holy busted, Batman! Quick! Play dumb!
“Who’s Robin?” He asked, the years of performing in front of a large crowd coming to save his ass.
Not that dumb!
Batman sent him a dry look, reprimand already poised on his lips. Dick, however, was nothing but a good performer. Nay, a dedicated performer.
Quick! Do something out of character! He shouted at himself, panicking visibly. He stepped backwards, an idea appearing in his head. In his defense, it sounded like an amazing idea at the time. He had no idea it would blow up into a Justice League issue. If he had known… Dick would have lied better, probably. There was no way he was going to let B bench him for weeks!
“Who the fuck are you?!” He yelped. Dick apologized mentally to Alfred and his parents. Batman paused, stunned.
“That’s my question. Who are you?!” Bruce asked, immediately hostile. His son doesn’t curse. Well, not in any normal way anyways. Dick quickly backpedaled by yelling at him with a heavy Vlax dialect, missing his parents terribly as he screamed stranger danger in rudimentary Romany. After this, he was going to have to convince Bruce to get him a language tutor. He refused to forget one of the only ties he had left to his parents.
“Wait, wait- you’re my son.” Bruce replied back, in perfect Romany. He looked more convinced but still skeptical.
“My dad is a circus performer! Not a flying rat!” Dick screeched back. He couldn’t help but feel touched about Bruce seeing him like a son.
“Oy! Keep it down out there, you assholes! Some of us like our sleep, damn!” A random Gothamite screamed out of their window.
“Yo, shut the fuck up! The vigilantes are helping to keep the rent low, motherfucker!” Another Gothamite shouted back.
….
Needless to say, Bruce quickly brought Dick back to the cave- with precautions to make sure he didn’t figure out where the Cave was if Dick was actually someone else.
——
“You would have loved it, Little Wing. B was running around like a headless chicken. The memory loss protocol was actually made because of me, you know.” Dick chuckled, sniffling as he talked to the carved gravestone.
It did not reply.
——
The blood tests came back. Yeppers, Dick sarcastically thought, who woulda thought I’m me?
Reinforcements were called in.
Meaning, Batgirl.
“Watch him while I contact Justice League Dark.”
“You think it’s magic?” Barbara asked.
“Yes. There was no one else near our vicinity that could affect Dick like this. He has no head wounds.”
“Eesh. Okay, go. I’ll watch him.”
Bruce disappeared in his zeta tube, looking harried. So, to everyone that’s not a Bat, he looked absolutely terrifying.
“What did you get yourself into now, Boy Wonder?” Barbara sighed. Dick was careful to keep any signs of recognition out of his face.
“Stop calling me that! Where are my parents?!” He asked back. Barbara coughed and looked uncomfortably away.
That’s right, Babs. I’m pulling out the orphan card. Feel bad. Dick hid his feral grin.
“They’re… uh, busy.” Busy being dead, Barbara thought, immediately wincing at her own thoughts. Apparently, Dick thought the excuse was lame too, and he sent her an incredulous look.
“Would you like refreshments, Master Dick?”
“What?”
Alfred held out some cookies on a platter, giving Babs a quelling look as she tried to reach for his share.
“Oh, wow, these are really good!” Dick said as he shoveled cookies into his mouth. He tried to replicate the reaction he had when he tried these for the first time, and from Alfred’s satisfied look, Dick nailed it.
——
“Robin doesn’t remember who he is.” Batman rumbled as he all but dragged Zatanna and Constantine by the scuff of their jackets towards the zeta tubes.
“Hey, wait-”
“We have no time.” Batman snarled, tossing the two magic users into the zeta. He punched in the destination.
When they got there, he glared at the two magic users until they got into the cave.
“Damn, Bats. Really living up to your name, huh?”
“Not bad,” Zatanna said as she looked around.
“Robin,” Batman- Bruce- reminded them. He did a quick glance over to check on his kids, and found them satisfactorily uninjured. Though, Barbara was looking worse for wear. Bruce quickly found out why as she stalked to him.
“You deal with him.” She muttered. “I’m going home.”
Bruce blinked and nodded. “Get home safe.”
Zatanna and Constantine followed Batman as he walked towards Robin. It was odd to see the normally laughing child frown.
“It’s you! The kidnapper! Where are my parents?!”
Bruce winced which, for him, was akin to a full body flinch and recoil. No wonder Barbara was so tired.
“Fix it.”
“Don’t get your knickers in a twist, Batsy.” Constantine grumbled.
“Well help, Batman. Though… I’m not sure if he should be doing that.”
Bruce sharply turned his head back to where Dick was. Emphasis on was. Because now, he’s halfway up the giant dinosaur the Robin had insisted they keep.
“Robin, get down from there!”
“Stranger Danger!” Dick hollered back.
Batman- Bruce Wayne- sighed.
“That’s high level magic,” Zatanna hummed. “I can’t feel anything, but I know for sure that he won’t die. Magic like that either dissipates naturally or…”
“Lasts forever,” Constantine finished.
Bruce groaned, shooting off a grappling line and swooping upwards to catch Dick as he fell from the giant dinosaur.
——
“I pretended to get my memories back later,” Dick chuckled. “And pretended to forget the whole thing. Bruce was so relieved that I stopped knocking things over and trying to do cartwheels in high places that he totally forgot I snuck out.”
Dick patted the headstone.
“But between you and me? I’m pretty sure Alfred knew. I think B pissed him off that week.”
#y’all is the Romani language spelled Romany#idk if im reading that wrong but did you know the Vlad dialect is the most widespread?#nightwing#dick grayson robin#dick grayson#dick grayson’s gaslight gatekeeper girl boss moment#Bruce Wayne#Batman#Batman and the trials of parenthood#google what to do when your vigilante child seems to have forgotten that he’s a vigilante#Batman using the magic Justice League like a wiki how#minors angst disguised as crack#also my favorite thing to write is brice and dick coping by talking to graves#but not actually talking to the grave’s owner who is actually alive#dick gets better about it#Bruce? not really#English is the fucking worst#Jason Todd#jason Todd’s grave
739 notes
·
View notes