#british dialects
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Right, starting a war again

#this is only using the most common terms so unfortunately no scufflers or stotties here#ive seen so many maps which confine terms to specific counties which is crazy because all my friends are from the same city as me and we#still cant agree if its a cob a cake a bun or a roll#id say cob but thats just cause its what my parents say#on its own its a cob. a sandwich made with it is a butty#uk#british polls#uk polls#british memes#british dialects#dialects#british
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dialect notes! Dialect notes! Dialect notes!
Because I missed my calling in academic research, I've spent a non-zero amount of time going down rabbit holes on early North American dialect for Along The Northern Heights. Is it worth doing all this research for a fanfiction of a PBS kids show from 20 years ago? Well it gives me considerable amounts of joy to write, so yes.
Anyway! I want to share a massive infodump, because writing gives me goodfeels and so does sharing! Please let me know if I am inaccurate or wrong about anything. I am not an academic and furthermore I do not want to spread misinformation.
MASSIVE WORD BLOCK UNDER THE CUT
A Pregame With Disclaimers About "Good" English
The history of Modern English is rife with Big Oof moments, and I'm not just talking about The Great Vowel Shift or Noah Webster deciding that the "u" in "colour" was silly. Especially in the late 18th century, there was a push to make accents more uniform and to establish a single "Good" English - and there is so much aggression towards what those scholars considered "Bad" English. And, in my extremely uneducated opinion, it seems like it's a conveniently moving target, just like "whiteness." In the context I'm in when writing, it positively reeks of shitting on any of the world's population groups that aren't Southeastern England. And, being from the United States, I know all too well the absolute shit that's been lobbed at AAVE for not being "Good" English.
This "Good" vs "Bad" way of looking at dialect is reductive, destructive, and boring, and I think it goes without saying I don't condone it in the slightest.
A Further Pregame With Received Pronunciation, or RP
the "generic" British dialect many of us outside the UK think of when we think of a British accent (a shame, I think, because the UK is so dialect-diverse and there are some absolute bangers on that damp island!) There are certainly a myriad of reasons for this, but probably the most common reasons/claims I've heard through my life are
A) 19th-century upper-class British folk wanting to have a more separate dialect from the other classes.
B) associations with the way the Royal Family has spoken English since at least Queen Victoria (a generic reasoning that we see happen along populations: imitating those in power)
C) 20th-century RP became "generic" in a similar way that the broad North American dialect* now associated with the United States and, to some degree, Canada, did - that is, it was further developed and use encouraged as the easiest to understand when recorded and played-back on period audio recording equipment (specifically radio and television.)
*a timeout is to be made here for the so-called Mid-Atlantic dialect at the dawn of "talkies" and early Hollywood. Its the delightful way of talking you'll hear in old black-and-white movies: slightly musical cadence, and combining the broad north american dialect with a bit of the non-rhoticity of RP. This dialect was mostly affectation and as anyone with living American relatives born before 1960 can tell you, mid-20th-century Americans largely did not speak it in normal settings.
Now, all of this is to say, RP as a dialect doesn't really appear until mid-19th century (although it would seem the loss of rhoticity we so associate with RP was a gradual shift starting in the very end of the 18th century.) Furthermore, the ways that we, 21st-century denizens, know RP don't come into their own until the 20th century and proliferation of audio-based mass media.
On to My Actual Point : 18th Century American Dialect (non-AAVE)*
*I make this distinction because the history of AAVE is a massive topic all on its own and I feel even less qualified to speak on it
It can't be ignored that the base strata making up Anglo-American speech patterns would have been as varied as where the original settlers/invaders came from, nor can it be ignored that the American Colonies were made up of more than just Anglo-Saxon descendants. Even back then, they were a mosaic of cultural interaction, which is why Thomas Paine declared America (at least the white part) a European, and not British, culture.
That being said, multiple primary sources indicate that the dialect of Anglo-Americans at the late 18th/very early 19th century was similar to "well-bred" Londoner dialect of the time (assuming there's enough of a distinction here from broad Southeastern UK,) and that this particular dialect was broadly spoken with less regional variance than the family of dialects in the UK.
This is made clear in vol 3 of Timothy Dwight's Travels in New-England and New-York, a collection of letters sent to colleagues in England:
"I shall not, I believe, offend against either truth or propriety if I say, that the English language is in this country pronounced more correctly than in England. I am not, indeed, sanguine enough to expect, that you will credit the assertion, nor that you will believe me to be a competent judge of the subject. Still I am satisfied that the assertion is true. That you may not mistake my meaning, I observe, that by a correct pronunciation I intend that of London; and, if you please, that of well-bred people in London."
(Dwight, Timothy. Travels in New-England and New-York vol 3 p 265)
Now in context he is only speaking of the New England region, and he does make a disclaimer here that he's not "a competent judge" of the subject, and we are certainly ignoring his hope that he won't be cited on the matter. But, his observation holds true from other primary accounts, especially William Eddis' Letters From America, which are composed of his observations (mostly of Maryland gentry) from 1769 to 1777. (His letters also happen to be an invaluable primary source for observations on culture and political commentary on the rising crisis between the colonies and Britain, from the perspective of a loyal well-to-do British subject.)
On the uniformity of language, Eddis has this to say:
"In England, almost every county is distinguished by a peculiar dialect; even different habits, and different modes of thinking, evidently discriminate inhabitants, whose local situation is not far remote; but in Maryland, and throughout the adjacent provinces, it is worthy of observation, that a striking similarity of speech universally prevails; and it is strictly true, that the pronounciation of the generality of the people has an accuracy and elegance, that cannot fail of gratifying the most judicious ear."
(Eddis, William. Letters from America, Historical and Descriptive. p 59)
if the odd comma placements are making it hard to read, you're not alone. 18th century writing is choc-full of what we might today consider run-on sentences, comma splices, or just generally cumbersome. Here's me paraphrasing as best I can:
"In England, almost every county has its own dialect, habits, and modes of thinking, noticeably different inhabitants that don't live very far from each other; but in Maryland and adjacent provinces, there is a notable similarity of speech, and its absolutely true that the generalized accent/pronunciation has an accuracy and elegance that won't fail to gratify a discerning ear."
----------------------------------------------------------
All this background I'm giving comes to this point: late 18th-century "well-bred" Londoner is the dialect I have chosen to loosely base what I write in Along The Northern Heights. I listen to alot of Simon Roper's work on youtube regarding the topic. I would say these two are probably the most valuable videos on the accent.
youtube
youtube
He makes disclaimers about not being formally qualified to speak on linguistics, and I would be remiss to not pass along those disclaimers.
That being said, what's in my mind is pastiche of that, the local "country" (read: appalachian) dialect in rural Virginia, the dialect work used in Turn:Washington's Spies and HBO John Adams, as well as some of the dialect you hear in PBS Masterpeice's Poldark, and various media I've watched/read from Living History re-enactors about reconstructing dialect.
------------------------------------------------------------------
Since I've made it a headcanon feature that James Hiller has a bit of a brogue that he feels pressured to correct, but slips into when he is excited or upset, I'd like to dig more into less-"proper" dialects of the time, and, if possible, the less-proper Philly accent. For shits and giggles, here's what I suspect is a dramatization of a modern-day Philly accent:
And then a very similar, a very real Baltimore Baldmer accent:
youtube
Honestly? Hearing both of these warms the cockles of my heart, because my late grandparents (especially grandma. *Especially* grandma) spoke with a Baltimore accent, which has similarities with the Philly accent. My aunts and uncles all speak it; its been normalized and blended with a virginia rural accent in mine (I say wadder, my grandma said wooder. I say toosdaye, my grandma said toosdee. I say ahn, grandma said ooowan. I say y'all, grandma said all youse/all you. I say "d'jeet," she said d'jeet, and you can pull d'jeet from my cold dead hands.)
In addition, you have the modern-day "High Tide" dialect of Okracoke, the Carolina Brogue.
youtube
youtube
trouble with Carolina Brouge, which is disappearing, is that its got too much modern-day southeastern drawl to really use as a basis for an 18th century Philly boy. Though it does seem like drawing out the "A" in water into wooder/woader is a commonality.
Anyway. That's been my infodump. I spent too long on this!
#liberty's kids#my writing#linguistics#language#English language#me infodumping#infodump#hyperfixations#dialect writing#english dialects#british dialects#north american dialects#18th century English#Okracoke brogue#Youtube
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

The main issues with this article are that it's WRONG!!
List of British words not widely used in the United States. Lists of words having different meanings in American and British English. List of American words not widely used in the United Kingdom.
#British slang#British dialects#That's not what THAT means#seriously my hometown has two distinct and acdemically recognised dialects#Not all people from the SAME TOWN use the same slang#Not all British people use the same slang
133K notes
·
View notes
Text
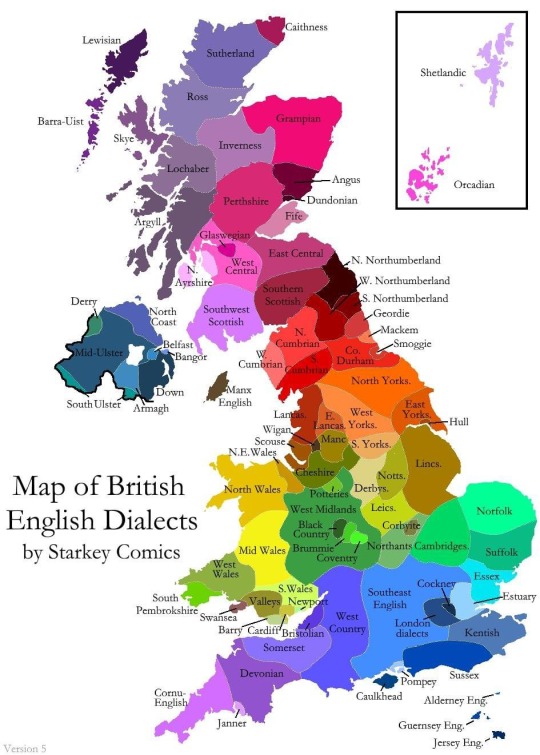
Also every native British and Irish language
1 note
·
View note
Text
sometimes, a lot more often than necessary i would say, dan and/or phil will say something and everyone will go ?? that's how british people pronounce that word ???? and you have to realise that a lot of the time the answer is no. they don't. dan and phil do, because there's many things wrong with them, but that doesn't always mean it's like.. normal
#other times it is just a weird british thing though to be fair#swear to god i've never heard anyone say cashews like that though#i'm not british i can't say for certain there isn't some obscure dialect in which that's normal#but it certainly isn't either of theirs
214 notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought my accent deafness wasn’t so bad anymore… I was wrong. The whole conversation between Gwen and Brett I kept thinking “huh, he has an interesting accent. Can’t quite place it tho” ITS FUCKING AMERICAN
#seriously does anyone know if the actor is actually American? cause something about it felt off#might just be me tho#I’ve gotten so used to the different British accents (that I think I can now place pretty well)#that I forgot Americans exist#the accent deafness also goes for Norwegian dialects btw#I’m bad at it#I can tell when someone has a dialect#but can never place it confidently#tmagp#echoing thoughts#echoing thoughts tmagp
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
In all the discussions of British vs American English, I've never seen anyone bring this up.
In British English, this is a handbag:


and this is a purse:



A handbag is a bag, generally big enough to fit (at least) a phone, a purse, keys, tissues, maybe even a water bottle or umbrella, and whatever other miscellaneous things people carry around with them on a daily basis. A purse is much smaller, and is designed for money and cards. We do also have a gendered distinction between a purse (to simplify, an item like this aimed at women) and a wallet (an item like this aimed at men).
Whereas it seems (and Americans, do feel free to expand on this in the notes) that in American English a “purse” refers to the first item. I still haven't quite worked out whether the word can refer to both items or just the first one.
The difference in usage means that as someone from the UK, every time an American says something like, I don't know, “that guy grabbed that lady's purse and ran away!”, it makes me think “wait why did she have her purse out?”, and every time they refer to putting away some decently large item like a book “in their purse”, it makes me think “holy hell how massive is their purse?” before remembering that ohhhhh, they're most likely referring to what I would call a handbag.
#linguistics#english language#language#languages#british english#american english#uk english#us english#us vs uk#dialects#writing#writers#united kingdom#great britain#britain#my posts
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
watching masters of the air they are inventing new kinds of accents on this show. never before seen. one night only. transatlantic is putting it mildly and demurely
#AND it’s boring#callie speaks#austin butler still doing elvis voice and everyone else is british + attempting a regional 1940s american dialect in the CRAZIEST way#spielberg drunk as fuck on set as an exec producer like i like a BIG choice….
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
So do you have any ff7 language and accent headcanons?
MY LINGUIST HEART IS EXPLODING TY yes ofc I do let’s see…and I’ll almost assuredly be talking cultural hcs too because language and culture are inextricably entwined
I’ll start with Banora/Mideel (I am much more familiar with Banora) since I mentioned that most recently! That area gives me such uk vibes, especially Banora. Not to mention that Genesis already has such a borderline posh voice. I like to hc that Reeve comes from somewhere around there and that Cait Sith’s voice is his native accent! But then I am torn because with the Rhapsodos family…greek names…ancient greek values and similarities displayed in Genesis and Angeal…so tempting. So I kind of imagine Banora at least as kind of a mix of those cultures (which would work pretty well I think, I know of quite a few overlaps in values between homeric and anglo-saxon values, and greek folklore does give me a similar vibe to celtic folklore) (ah you see there I go, using language and culture interchangeably already)! Ancient Greek at least is a very lyrical-sounding language (it’s theorized that the different accents were used to show differences in pitch) and I feel like it would fit perfectly in Genesis’ voice especially! Also I like to hc that his parents’ names are Peleus and Thetis for the Achilles reference >:)
For Gongaga and Nibelheim I’m more mainstream, love the Zack speaking Spanish and Cloud speaking Old Norse hcs so much! Don’t have much else to say about Gongaga, wonderful as is. Nordic Nibelheim is so special to me bc people always conflate ‘norse’ with vikings when that’s so not all there is ;-; there’s the Vanir as well as the Aesir! And even just thinking about it for so little time rn the Fenrir myth does fit him
Wutai is meant to be based off Japan (I’m fairly sure, I know so much less than I should about that part of the world so anyone feel free to add on). I do love that—people who have different first languages actually think differently, because their brains learn to process and codify things differently based on what the grammar of their language focuses on and how their words are constructed and so forth (it’s very much a chicken or the egg type situation). And with Japanese being in an entirely different language family, the breakdowns in communication that can occur due to people not doing enough research on the differences in cultural thought can be massive and disastrous. Which works so realistically well for the whole Shinra vs Wutai conflict.
As for Midgar, cities are often little islands dialect and accent wise. Lots of different accents and languages and dialects from all over the place mixing together to create something new. I like to hc that being surrounded by so many conflicting accents Sephiroth can mimic them pretty well, even though Hojo tried to knock everything out of him but the ‘normal’ ‘educated’ accent (there is no such thing as not having an accent. Your speech is marked inherently by being different from another person’s speech). Hehehe I like to imagine that spending so much time with Genesis and Angeal and actually liking and wanting to be like them he’s picked up quite a few Banoran mannerisms :) like me when I lived in the uk for a few months and suddenly now I say “you’ve not” instead of “you haven’t” and still pronounce “vase” and “island” weird take me back there nowwwww
#also fair note that when I say accents I am not only thinking of the phonetics but also the differences in phrasing and word choice that’s#probably more dialect than accent but eh close enough#my linguistics brain cannot just think about the sound it automatically analyzes the content too and I forget that other people may not#honestly I often think about the latter more often than the sound#also I acknowledge that I am an ignorant white person so if I did anything wrong feel free to yell at me so I learn 👍#also obligatory psa that there is not just one ‘british accent’ there are a bunch of different uk accents#star rambles#star essays#ff7#genesis rhapsodos#angeal hewley#zack fair#cloud strife#wutai#banora#mideel#nibelheim#gongaga#final fantasy vii#final fantasy 7#crisis core#sephiroth#asks
22 notes
·
View notes
Text

JUST REALIZED I NEVER POSTED THIS HERE nationality hcs :]
#PIKERO'S CANONICALLY VIET IN CASE PEOPLE DON'T KNOW HE'S SO DEAR TO ME AND IM NOT EVEN VIET#arupek is too filipino coded its scary#badjao is an indigenous group mostly known as “sea nomads” and their culture revolves around the sea and fishing btw#aru speaks a bit of bisaya and a mindanao dialect (idk which one im sorry)#chaco forgets which words are spanish and which ones are filipino so he mixes them up#bado grew up in africa so his filipino is very conyo/taglish#british hallritt is the reason his cooking is bad i fear#fragaria memories#fragmem#fragaria memories headcanon#hallritt#merold#puruth#romarriche#rimicha#sanah#cielomort#kurode#willmesh#klarkstella#louterstella#myunna#badobarm#chaco#arupek#tuxam#hangyon#pikero#>> quincyposting
40 notes
·
View notes
Text


silly little guys doing silly little things..
#some oc and Wheatley interaction#I love my little oc core I just don’t know what to call him#me not beinig able to choose a consistent design for human Wheatley#also the thought of just making as many cores with as many different British dialects as I can is so funny#their relationship is not based on the xfm arguments Karl and Steve get into noooo not at all what are you talking about#portal 2#portal fanart#wheatley portal 2#core oc#portal 2 fanart#Wheatley#oc#thatsonehellofanart#human wheatley
61 notes
·
View notes
Text
Names for the number 0 in English
"Zero" is the usual name for the number 0 in English. In British English "nought" is also used and in American English "naught" is used occasionally for zero, but (as with British English) "naught" is more often used as an archaic word for nothing. "Nil", "love", and "duck" are used by different sports for scores of zero.
There is a need to maintain an explicit distinction between digit zero and letter O,[a] which, because they are both usually represented in English orthography (and indeed most orthographies that use Latin script and Arabic numerals) with a simple circle or oval, have a centuries-long history of being frequently conflated. However, in spoken English, the number 0 is often read as the letter "o" ("oh"). For example, when dictating a telephone number, the series of digits "1070" may be spoken as "one zero seven zero" or as "one oh seven oh", even though the letter "O" on the telephone keypad in fact corresponds to the digit 6.
In certain contexts, zero and nothing are interchangeable, as is "null". Sporting terms are sometimes used as slang terms for zero, as are "nada", "zilch" and "zip".
Zero" and "cipher"
"Zero" and "cipher" are both names for the number 0, but the use of "cipher" for the number is rare and only used in very formal literary English today (with "cipher" more often referring to cryptographic cyphers). The terms are doublets, which means they have entered the language through different routes but have the same etymological root, which is the Arabic "صفر" (which transliterates as "sifr"). Via Italian this became "zefiro" and thence "zero" in modern English, Portuguese, French, Catalan, Romanian and Italian ("cero" in Spanish). But via Spanish it became "cifra" and thence "cifre" in Old French, "cifră" in Romanian and "cipher" in modern English (and "chiffre" in modern French).
"Zero" is more commonly used in mathematics and science, whereas "cipher" is used only in a literary style. Both also have other connotations. One may refer to a person as being a "social cipher", but would name them "Mr. Zero", for example.
In his discussion of "naught" and "nought" in Modern English Usage, H. W. Fowler uses "cipher" to name the number 0.
O" ("oh")
In spoken English, the number 0 is often read as the letter "o", often spelled oh. This is especially the case when the digit occurs within a list of other digits. While one might say that "a million is expressed in base ten as a one followed by six zeroes", the series of digits "1070" can be read as "one zero seven zero", or "one oh seven oh". This is particularly true of telephone numbers (for example 867-5309, which can be said as "eight-six-seven-five-three-oh-nine"). Another example is James Bond's designation, 007, which is always read as "double-o seven", not "double-zero seven", "zero-zero seven", or "o o seven".
The letter "o" ("oh") is also used in spoken English as the name of the number 0 when saying times in the 24-hour clock, particularly in English used by both British and American military forces. Thus 16:05 is "sixteen oh five", and 08:30 is "oh eight thirty".
The use of O as a number can lead to confusion as in the ABO blood group system. Blood can either contain antigen A (type A), antigen B (type B), both (type AB) or none (type O). Since the "O" signifies the lack of antigens, it could be more meaningful to English-speakers for it to represent the number "oh" (zero). However, "blood type O" is properly written with a letter O and not with a number 0.
In sport, the number 0 can have different names depending on the sport in question and the nationality of the speaker.
"Nil" in British sports
Many sports that originated in the UK use the word "nil" for 0. Thus, a 3-0 score in a football match would be read as "three-nil".[1] Nil is derived from the Latin word "nihil", meaning "nothing", and often occurs in formal contexts outside of sport, including technical jargon (e.g. "nil by mouth") and voting results.
It is used infrequently in U.S. English, although it has become common in soccer broadcasts.
"Nothing" and "oh" in American sports
edit
In American sports, the term "nothing" is often employed instead of zero. Thus, a 3-0 score in a baseball game would be read as "three-nothing" or "three to nothing". When talking about a team's record in the standings, the term "oh" is generally used; a 3-0 record would be read as "three and oh".
In cricket, a team's score might read 50/0, meaning the team has scored fifty runs and no batter is out. It is read as "fifty for no wicket" or "fifty for none".
Similarly, a bowler's analysis might read 0-50, meaning he has conceded 50 runs without taking a wicket. It is read as "no wicket for fifty" or "none for fifty".
A batsman who is out without scoring is said to have scored "a duck", but "duck" is used somewhat informally compared to the other terms listed in this section. It is also always accompanied by an article and thus is not a true synonym for "zero": a batter scores "a duck" rather than "duck".
A name related to the "duck egg" in cricket is the "goose egg" in baseball, a name traced back to an 1886 article in The New York Times, where the journalist states that "the New York players presented the Boston men with nine unpalatable goose eggs", i.e., nine scoreless innings.
"Love" and "bagel" in tennis
In tennis, the word "love" is used to replace 0 to refer to points, sets and matches. If the score during a game is 30-0, it is read as "thirty-love". Similarly, 3-0 would be read as "three-love" if referring to the score during a tiebreak, the games won during a set, or the sets won during a match. The term was adopted by many other racquet sports.
There is no definitive origin for the usage. It first occurred in English, is of comparatively recent origin, and is not used in other languages. The most commonly believed hypothesis is that it is derived from English speakers mis-hearing the French l'œuf ("the egg"), which was the name for a score of zero used in French because the symbol for a zero used on the scoreboard was an elliptical zero symbol, which visually resembled an egg.
Although the use of "duck" in cricket can be said to provide tangential evidence, the l'œuf hypothesis has several problems, not the least of which is that in court tennis the score was not placed upon a scoreboard. There is also scant evidence that the French ever used l'œuf as the name for a zero score in the first place. (Jacob Bernoulli, for example, in his Letter to a Friend, used à but to describe the initial zero–zero score in court tennis, which in English is "love-all".) Some alternative hypotheses have similar problems. For example, the assertion that "love" comes from the Scots word "luff", meaning "nothing", falls at the first hurdle, because there is no authoritative evidence that there has ever been any such word in Scots in the first place.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the first use of the word "love" in English to mean "zero" was to define how a game was to be played, rather than the score in the game itself. Gambling games could be played for stakes (money) or "for love (of the game)", i.e., for zero stakes. The first such recorded usage quoted in the OED was in 1678. The shift in meaning from "zero stakes" to "zero score" is not an enormous conceptual leap, and the first recorded usage of the word "love" to mean "no score" is by Hoyle in 1742.
In recent years, a set won 6-0 ("six-love") has been described as a bagel, again a reference to the resemblance of the zero to the foodstuff. It was popularised by American announcer Bud Collins.
Null
In certain contexts, zero and nothing are interchangeable, as is "null". However, in mathematics and many scientific disciplines, a distinction is made (see null). The number 0 is represented by zero while null is a representation of an empty set {}. Hence in computer science a zero represents the outcome of a mathematical computation such as 2−2, while null is used for an undefined state (for example, a memory location that has not been explicitly initialised).
In English, "nought" and "naught" mean zero or nothingness, whereas "ought" and "aught" (the former in its noun sense) strictly speaking mean "all" or "anything", and are not names for the number 0. Nevertheless, they are sometimes used as such in American English; for example, "aught" as a placeholder for zero in the pronunciation of calendar year numbers. That practice is then also reapplied in the pronunciation of derived terms, such as when the rifle caliber .30-06 Springfield (introduced in 1906) is accordingly referred to by the name "thirty-aught-six".
The words "nought" and "naught" are spelling variants. They are, according to H. W. Fowler, not a modern accident as might be thought, but have descended that way from Old English. There is a distinction in British English between the two, but it is not one that is universally recognized. This distinction is that "nought" is primarily used in a literal arithmetic sense, where the number 0 is straightforwardly meant, whereas "naught" is used in poetical and rhetorical senses, where "nothing" could equally well be substituted. So the name of the board game is "noughts & crosses", whereas the rhetorical phrases are "bring to naught", "set at naught", and "availeth naught". The Reader's Digest Right Word at the Right Time labels "naught" as "old-fashioned".
Whilst British English makes this distinction, in American English, the spelling "naught" is preferred for both the literal and rhetorical/poetic senses.
"Naught" and "nought" come from the Old English "nāwiht" and "nōwiht", respectively, both of which mean "nothing". They are compounds of no- ("no") and wiht ("thing").
The words "aught" and "ought" (the latter in its noun sense) similarly come from Old English "āwiht" and "ōwiht", which are similarly compounds of a ("ever") and wiht. Their meanings are opposites to "naught" and "nought"—they mean "anything" or "all". (Fowler notes that "aught" is an archaism, and that "all" is now used in phrases such as "for all (that) I know", where once they would have been "for aught (that) I know".)
However, "aught" and "ought" are also sometimes used as names for 0, in contradiction of their strict meanings. The reason for this is a rebracketing, whereby "a nought" and "a naught" have been misheard as "an ought" and "an aught".
sometimes used as names for 0, in contradiction of their strict meanings. The reason for this is a rebracketing, whereby "a nought" and "a naught" have been misheard as "an ought" and "an aught".
Samuel Johnson thought that since "aught" was generally used for "anything" in preference to "ought", so also "naught" should be used for "nothing" in preference to "nought". However, he observed that "custom has irreversibly prevailed in using 'naught' for 'bad' and 'nought' for 'nothing'". Whilst this distinction existed in his time, in modern English, as observed by Fowler and The Reader's Digest above, it does not exist today. However, the sense of "naught" meaning "bad" is still preserved in the word "naughty", which is simply the noun "naught" plus the adjectival suffix "-y". This has never been spelled "noughty".
The words "owt" and "nowt" are used in Northern English. For example, if tha does owt for nowt do it for thysen: if you do something for nothing do it for yourself.
The word aught continues in use for 0 in a series of one or more for sizes larger than 1. For American Wire Gauge, the largest gauges are written 1/0, 2/0, 3/0, and 4/0 and pronounced "one aught", "two aught", etc. Shot pellet diameters 0, 00, and 000 are pronounced "single aught", "double aught", and "triple aught". Decade names with a leading zero (e.g., 1900 to 1909) were pronounced as "aught" or "nought". This leads to the year 1904 ('04) being spoken as "[nineteen] aught four" or "[nineteen] nought four". Another acceptable pronunciation is "[nineteen] oh four".
Decade names
See also: Aughts
While "2000s" has been used to describe the decade consisting of the years 2000–2009 in all English speaking countries, there have been some national differences in the usage of other terms.
On January 1, 2000, the BBC listed the noughties (derived from "nought") as a potential moniker for the new decade. This has become a common name for the decade in the U.K.and Australia, as well as some other English-speaking countries. However, it has not become the universal descriptor because, as Canadian novelist Douglas Coupland pointed out early in the decade, "[Noughties] won't work because in America the word 'nought' is never used for zero, never ever".
The American music and lifestyle magazine Wired favoured "Naughties", which they claim was first proposed by the arts collective Foomedia in 1999.However, the term "Naughty Aughties" was suggested as far back as 1975 by Cecil Adams, in his column The Straight Dope.
interchangeable, as is "null". However, in mathematics and many scientific disciplines, a distinction is made (see null). The number 0 is represented by zero while null is a representation of an empty set {}. Hence in computer science a zero represents the outcome of a mathematical computation such as 2−2, while null is used for an undefined state (for example, a memory location that has not been explicitly initialixed).
Slang
Sporting terms (see above) are sometimes used as slang terms for zero, as are "nada", "zilch" and "zip".
"Zilch" is a slang term for zero, and it can also mean "nothing". The origin of the term is unknown.
Silvio Pasqualini Bolzano inglese ripetizioni English insegnante teacher
#dialects#lexicography#lexicology#linguistics#english#american english#languages#mathematics#math#maths#geometry#colloquialism#informal#sports#numerology#vocabulary#definition#british english#dictionary#encyclopedia#score#slang#etimologia#linear algebra#lexicon#arithmetic#calculator#calculations#calculus#fraction
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
For the linguists out there, what is Red3yz’ accent? The wikis say he lives in the UK, which I definitely hear in the way he pronounces some words, but I feel like maybe he’s from America originally? Particularly in how he pronounces his ‘r’s, I feel like it’s very American, but I’m really bad with distinguishing accents lol!
Or if there are any old hc fans who remember him talking about it somewhere that would be rad too! Again the wikis say the UK but don’t have references for where he talks abt it
(A regular vid so you can hear him talking)
#I feel like this might be a dumb question#coz there’s a lot of British/european accents in general I’m unfamiliar with#so maybe he just has a dialect I’ve never heard before#or maybe he talks abt it in an obvious place I didn’t see#rae chats#idk idk it’s all I can think abt when I hear him talk#red3yz#also I scrolled thru every post on here tagged red3yz and found no art so. mayhaps expect art soon
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
A big thing that annoys me way more than it should is people acting like all Southern accents are the same. Y'all cannot just plaster whatever southern state you want onto a character with an accent and call it a day. Character with an obviously Texan accent? Not from North Carolina, I don't care if it's your headcanon, it doesn't work that way. There's a character that's supposed to be from Tennessee? Why do they sound like they're from Georgia?
#people are always like 'not every northerner has a new york accent'#'british accents aren't all the same'#'there are different dialects for each spanish speaking country'#okay show the same understanding towards all accents then???#i put so much care into figuring out how my characters would talk from state to state and even country to country and region to region#but then i see other people and they're like 'HMMM this definitely north carolinian character is from texas'#'because southern. southern mean the same and interchangeable'#and the accent differs from region to region within the state as do the words/phrases we use!#i can immediately tell whether someone is from upstate south carolina or the coastal regions of SC#i was surrounded by a bunch of people from upstate sc for example that said 'lord OF mercy/lord'a mercy' in exasperation#while everyone in the area i'm actually from says 'lord HAVE mercy' (the correct one btw)#also: you CAN have a mixed dialect it's not impossible#but your accent probably won't be#i don't really have an accent but the words i use are a frankenstein of my mom's middle SC and my dad's western georgia dialect#probably delete later
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
My one compliant with Prodigy is that Zero said math.
They are British! They smoke fags behind Tesco! They won't drink tea made in a microwave! They eat beans on toast!
They'd say maths! They know it's a plural word, they know mathematics contains multitudes! They wouldn't say math!
#the universal translator did them DIRTY#does picard ever say either?#or julian?#i know picard says lad but i can't think of any other britishisms from the top of my head#the universal translators... they take the dialect away....#i know picard is French but hes british isnt he#prodigy#star trek prodigy#if anyone saw me misspell prodigy no you didn't
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

i always draw rex so angry its funny at this point
#boy why you so mad#i need to learn how to write in a british accent for accuracy#i am not as versed in writing dialects as my boyfriend is#my art#scp ocs#scp foundation#scp original character#rex turner#víctor penz
7 notes
·
View notes