#12 May 1870
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text



















The Manitoba Act was given the Royal Assent on May 12, 1870, paving the way for Manitoba to become a province of Canada on July 15, 1870.
#The Forks#Manitoba Act#12 May 1870#Royal Assent#anniversary#travel#Saint Boniface Cathedral#Canadian history#summer 2012#vacation#cityscape#Assiniboine River#Lower Fort Garry National Historic Site of Canada#Red River#Esplanade Riel Pedestrian Bridge#Winnipeg#landscape#architecture#tourist attraction#Oodena#Lyons Lake#original photography#prairie province#Canada#landmark
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

[Image above: D. T. Suzuki (11 November 1870 - 12 July 1966) was a Japanese Buddhist scholar and doctor of literature. ]
A message from 23 nights temple Q&A: Part 2 [Part 1]
Next question was, want to know more about Tendai Buddhism and how to do face-to-face learning outside of Japan:
More than 1,400 years after its introduction, Buddhism in Japan was born from the founders of sects in Japanese history and culture. Today, about 13 major sects exist, including the Tendai sect. Of these, three are Zen sects: the Soto, Rinzai and Obaku.
Among them the most representative are, Saicho, founder of the Tendai sect, whose head temple is Enryaku-ji on Mt. Hiei; Kukai, founder of the Shingon sect, who brought esoteric Buddhism to Japan, whose head temple is Kongobu-ji on Mt. Koya; and Dogen, author of the Shobogenzo, a philosophy book said to be a manual for Zen meditation practice and originator of mindfulness. Founder of the Soto sect, whose main temple is Eiheiji Temple.
Buddhism means 'Buddha's teachings'. In the beginning, everything was transmitted orally and it was only after Buddha's death that documents and scriptures were created. All of the Buddhist scriptures that remain today were described by the memory of Buddha's disciples. In the meantime, it underwent various transformations through the views of translators and other factors, and representative gurus from different countries established and divided into sects. The Tendai sect is one of these sects, founded by Master Saicho. Incidentally, my trusted teacher is a Zen monk of the Soto sect, and he says that one should not be confined to a sect. It is because Dogen, the founder of the Soto sect, taught that the Buddha's teaching is one and that we should not be obsessed with sects.
Those wishing to study face-to-face or Buddhist thought outside Japan should visit your local Buddhist temple or Zen centre. You can easily find one by hitting the usual keywords. However, not all are good teachers. It is recommended to search patiently for a teacher or centre that suits you. For international learners, books by Japanese Buddhist scholar D.T. Suzuki are relatively accessible. He wrote on Zen in English and introduced Japanese Zen culture to the rest of the world. He was also a prolific translator of Chinese, Korean, Japanese, Vietnamese and Sanskrit literature.
In fact, the teachings of Zen that we are learning are not like there is a holy scripture that says this is the absolute truth, nor is there a founder who says that this is the absolute truth.
And it is best not to decide on a teacher based on sect or culture, but to knock on the door of a person you can identify with. More importantly, he or she may not only be in the temple.

二十三夜堂からのメッセージ Q&A: その2 [その1]
次の質問は、天台宗についてもっと知りたい、日本国外で対面で学ぶ方法を知りたいというものでした:
伝来から1400年余りの年月を経て、日本の歴史文化のなかで、宗派の開祖たちから生まれたのが「日本の仏教。 現在、大きな宗派として存在しているのは、天台宗を含め約13宗派。その中で禅宗は、曹洞宗、臨済宗と黄檗宗の3宗。
中でも代表的なのは、天台宗の開祖の最澄、総本山は比叡山延暦寺、日本に密教をもたらした、真言宗の開祖の空海、総本山は高野山金剛峯寺、そして、坐禅修行のマニュアルとも言われている哲学書「正法眼蔵 (しょうぼうげんぞう)」の著者でマインドフルネスの元祖、曹洞宗の開祖の道元、大本山は永平寺など、が挙げられる。
仏教とは「ブッダの教え」という意味である。当初、全ては口頭で伝えられており文書·経典ができたのはブッダ没後のことだ。今日残っている仏教経典はすべて、ブッダの弟子たちの記憶によって記述されたもの。その間訳者の見解などを通して様々な変形を繰り返し、各国の代表的な教祖が宗派を立ち上げ分かれていった。天台宗はその一つで、最澄が立ち上げた宗派である。因みに私の信頼できる先生は曹洞宗の禅僧だが、彼は宗派に囚われるべきではないと言っている。というのも曹洞宗の開祖である道元禅師が「ブッダの教えは一つであり、宗派に執われるな」と教えていたからだ。
国外で対面学習や仏教思想を学びたいとご希望の方々は、ローカルの仏教寺院、または禅センターを訪ねてみると良いと思います。お決まりのキーワードを叩けば、すぐに見つかります。但し、全てが良い先生とは限りません。自分に合った先生やセンターを根気よく探すことをお勧めします。海外の方々は、日本の仏教学者、鈴木大拙氏の本が比較的手に入りやすいと思います。彼は英語で禅に関する著作を発表し、日本の禅文化を世界に紹介し、また中国語、韓国語、日本語、ベトナム語、サンスクリット語などの多作な翻訳者でした。
実際、私たちが学んでいる「禅」の教えは、これが絶対の真理だという聖典があるわけでも、これが絶対の真理だという教祖がいるわけでもありません。
宗派や文化で師を決めるのではなく、ご自分が共感できる門を叩くのが最良かと思います。もっと言えば、その人はお寺にのみいらっしゃるとも限りません。
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
Part II C the larger paintings and the early furniture
Saint Cecile playing music

Fig 30 : Dominiquin (Domenico Zampieri, dit Il Domenichino), Sainte Cécile avec un ange tenant une partition musicale, 1600/1625, 160 x 120 cm, Louvre, INV 793; MR 181.
Painted by Domenichino(fig 30) in the early 17th century it depicts saint Cecile playing cello while looking at the sky with a angel under the traits of an infant holding her partition. The artist chose to depict the saint wearing an outfit contemporary the artist’s life, which would have been anachronistic for a saint who live in the 3rd century. The painting was sold by Jabach to Louis XIV in 1662[22] and was placed, according to Piganiol, on the unique fireplace of the time on the southern wall.
King David playing the Harp

Fig 31: Dominiquin (Domenico Zampieri, dit Il Domenichino), Le Roi David jouant de la harpe, vers 1619, 240 x 170 cm, huile sur toile, Château de Versailles, MV 5359
Painted by Domenichino (fig 31)around the same time as the painting previously discussed, it depicts King Davis paying the harp. Just like in the saint Cecile’s painting the main protagonist is assisted by an angel depicted as young boy holding the partition, while he is looking at the sky. But unlike the previous painting, in which background is dark, the one in the King David painting appears to follow the code of a state portrait : with a tapestries with golden fringes filling the upper right corner, and a column displayed on the left. It was purchased by Louis XIV to the heir of Mazarin in 1665[23].
2.3 The Furniture
The 1684 winter set :

Fig 32 : 3d Recreation of set 1109, in the central salon in the Sims 4 engine
The 20th of November 1684 a large delivery of furniture is registered for the royal apartments in Versailles. Several sets of crimson velvet are placed in the King’s apartment. In the room where the King dresses the delivery mentions two armchairs, 16 stools 8 portiere tapestries covered in crimson velvet with gold fringes, and braids, registered under the number 1109[24](fig 32)while no specific seasonal use is mentioned it is nevertheless possible infer that the set in question was meant to used for winter, as the table cloth and daybed delivered alongside for the council cabinet under the number 1103[25], is, as late as 1740[26], still mentioned in said cabinet and used as a winter set, probably until 1749[27].
The 1700 summer set :

Fig 33 : 3d Recreation of set 1870, in the central salon in the Sims 4 engine
In May 1700, Doublet delivered three new summer sets for King’s apartment under the numbers 1870,1871 and 1872, the set destined for the central salon, the 1870(fig 33), contained :
-8 portiere tapestries made of 3 pieces of brocade each
-3 armchairs and 12 folding stools covered in brocade, with gold fringes and braids, with their wood sculpted and gilded [28]
The brocade in question was described as “silver background brocade, with flowers embroidered in gold and silver, contoured with silk of different colors, with gold braids at the edge and taffeta lining.”[29], the brocade discharge includes several brocades with silver background used by doublet when making the upholsteries and portieres for those three sets. The 6th brocade listed is the one used for the confection of set 1870, its description goes as follow :”brocade from Lyon with silver background, flowers patterns of gold and silver surrounded by thin contours of red, green and purple silk”[30], the descrition is almost identical to the original but includes however the specific colors used for the outline of the silver and gold raised patterns, the origin of that brocade can be traced to a delivery from the 12th of June 1698, initially destined for the royal chapel in Versailles, and who was given at the time the number 135[31].
[22] See number 53 of Le Brun’s inventory
[23] See number 125 of Le Brun’s inventory
[24] AN O1/3305, f⁰ 153 v⁰ ; Jules Guiffrey Inventaire général du mobilier de la couronne sous Louis XIV (1663-1715). Partie 2, p. 348, number 1109
[25] Ibid
[26] AN O1/3453 f⁰ 4 r⁰
[27] AN O1/3314 f⁰ 145 v⁰
[28] AN O1/3307 f⁰ 417 v⁰
[29] Ibid
[30] Ibid f⁰ 420 r⁰
[31] Ibid f⁰ 360 r⁰
#ts4 historical#sims4cc#sims 4 custom content#sims4rococo#ts4cc#sims4#history#histoire#historical research#historical#versailles#palace of versailles
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Young Person's Introduction to Late 19th-Century Western Fashion
hello fellow youths
General information Banner, Bernadette. "Exposing Victorian Influencers Who 'Facetuned' Their Photos. (Photo Manipulation was EVERYWHERE)." YouTube. July 17, 2021. English Heritage. "Fashion Through History: Episode 1 – Victorians." YouTube. February 9, 2023. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "100 Years of Fashion // The Fashionable Plus Size Silhouette from 1820-1910." YouTube. June 5, 2021. Victoria and Albert Museum. "100 Years of Fashionable Womenswear: 1830s – 1930s | V&A." YouTube. July 18, 2023. Zebrowska, Karolina. "Victorian Fashion Is Not What You Think It Is." YouTube. March 19, 2019.
Accessories Banner, Bernadette. ""Afro-Victorian": Bringing Historical Black Women's Dress into the 21st Century w Cheyney McKnight." YouTube. October 20, 2021. Cox, Abby. "A Fashion Historian Explains the History of the Handbag." YouTube. January 26, 2023. Rudolph, Nicole. "Dangerous Things in Victorian Pockets : Mens Pocket History." YouTube. March 2, 2024. Rudolph, Nicole. "The Controversial History of Color Season Analysis." YouTube. November 4, 2023. Zebrowska, Karolina. "Disgusting and Creepy Victorian Fashion Trends." YouTube. October 17, 2018.
Bustles and hoopskirts Donner, Morgan. "Weirdest Victorian Invention: The Bustle-Chair (and we made one)." YouTube. November 20, 2020. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "100 Years of Underwear // The Changing Plus Size Shape from Regency to Victorian to Edwardian." YouTube. May 1, 2021. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "All About Bustles! A Deep Dive into 1870s Fashions." YouTube. December 26, 2023. Rudolph, Nicole. "Why were Victorian Hips Controversial?" YouTube. September 12, 2021.
Cosmetics Birchwood, Vasi. "1800s Makeup Is Not What You Think." YouTube. July 21, 2023. English Heritage. "Queen Victoria Makeup Tutorial | History Inspired | Feat. Amber Butchart and Rebecca Butterworth." YouTube. May 20, 2019. Zebrowska, Karolina. "I Used Only Victorian Cosmetics For a Week." YouTube. July 26, 2023.
Fabrics Rudolph, Nicole. "Did Silk Spontaneously Combust in the Victorian Era?" YouTube. August 8, 2021. Rudolph, Nicole. "The History of Elastic." YouTube. July 4, 2021. Rudolph, Nicole. "The Truth About Arsenic in the Victorian Era." YouTube. January 24, 2021.
Gowns Bullat, Samantha. "Dress Historian Analyzes Victorian Mourning Clothing of the Mid-19th Century." YouTube. March 14, 2021. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "All About 1860's Fashion // What did Civil War-era fashion look like?" YouTube. November 12, 2022. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "How did fashion evolve from 1850-1859? // 1850's Fashion Deep Dive." YouTube. October 1, 2022. Rudolph, Nicole. "Victorian Fast Fashion? The Truth about the History of Disposable Clothing." YouTube. February 6, 2022. SnappyDragon. "Were the Pre-Raphaelites painting accurate medieval dress . . . or Victorian fairtytalecore?" YouTube. April 26, 2024. Zebrowska, Karolina. "19th Century Fashion - How To Tell Different Decades Apart?" YouTube. November 17, 2017.
Hair care and styling Banner, Bernadette. "Following a Victorian Home Made Hair Care Routine (1889)." YouTube. September 11, 2021. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "Getting Dressed in an 1888 Daisy Costume // Easy Bustle-Era Hair Tutorial." YouTube. November 13, 2020. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "Getting Dressed in the 1870s & 1874 Hairstyle Tutorial." YouTube. February 23, 2020. Rudolph, Nicole. "Why did Victorian Women Cut their Hair Short?" YouTube. December 18, 2022. Laundry and housekeeping English Heritage. "A Tour of the Laundry - The Victorian Way." YouTube. September 6, 2019. English Heritage. "How to Wash Up - The Victorian Way." YouTube. March 18, 2021. English Heritage. "Laying the Table at Christmas – The Victorian Way." YouTube. December 14, 2022. Walkley, Christina, and Vanda Foster. Crinolines and Crimping Irons: Victorian Clothes: How They Were Cleaned and Cared for. Peter Owen Limited: London, 1978.
Outerwear and working wear Birchwood, Vasi. "What Irish Working Women Wore in the Late 19th Century | I Made the Clothing of My Irish Ancestors." YouTube. June 23, 2023. English Heritage. "The Real Mrs Crocombe | Part Four: A Victorian Cook's Outfit." YouTube. July 5, 2018. Stowell, Lauren. "It's Hot: Let's Look At Some Bathing Suits." American Duchess. August 18, 2023. Rudolph, Nicole. "The History of Jeans, T-shirts, and Hoodies: Time Travel 101." YouTube. March 20, 2022. Zebrowska, Karolina. "The 1851 Women's Pants That Made The Victorians Go Crazy." YouTube. March 2, 2020.
Shoes Rudolph, Nicole. "100 years of Antique Boots." YouTube. February 10, 2024. Rudolph, Nicole. "How to Make Regency & Victorian Shoes: Beginner Shoemaking." YouTube. June 27, 2021. Rudolph, Nicole. "The Myth of Tiny Feet "Back Then"." YouTube. September 26, 2021.
Undergarments Banner, Bernadette. "I Wore a (Medical) Corset for 5 Years. How do Victorian Corsets Compare?" YouTube. November 7, 2020. Banner, Bernadette. "Making Some Frilly Victorian Underwear || 1890s Combinations." YouTube. February 9, 2019. Birchwood, Vasi. "What Victorians Wore to Bed." YouTube. May 5, 2023. Cox, Abby. "I made weird Victorian underwear (it's a knit onesie) & a pretty 1890s corset || historical sewing." YouTube. March 21, 2021. Lady Rebecca Fashions. "How 8 Different Historical Corsets Affect the Same Plus Size Body." YouTube. December 12, 2020. Rudolph, Nicole. "100 Years of Corset History: How 8 Corsets affect the same body." YouTube. November 29, 2020. Zebrowska, Karolina. "How Did Victorian Ladies Stay Warm in Winter? || THE EXPERIMENT." YouTube. January 22, 2021. Zebrowska, Karolina. "How Did Victorian Women Deal With Their Periods?" YouTube. October 17, 2019.
#victorian era#history#fashion#karolina zebrowska#youtube#video#nicole rudolph#bernadette banner#abby cox#lady rebecca fashions#american duchess#shoes#hair care#hairstyle#morgan donner#1800s#1860s#us history#american history#cosmetics#gilded age#reconstruction era#1850s#1870s#menstruation#1880s#1890s#gibson girl#reference#edwardian era
135 notes
·
View notes
Text

Norton's Birth Year and some facts about his age at the time of the DeRoss tragedy
Alice: age 6 when her parents die in the tragedy
Year of the tragedy: 1887, based on the Official Artbook
Alice is 21 in the final game, so the final game was in 1902.
Norton is 28 in the final game.
-> Norton was born in 1874 and age 12 on the day of the tragedy in 1887.
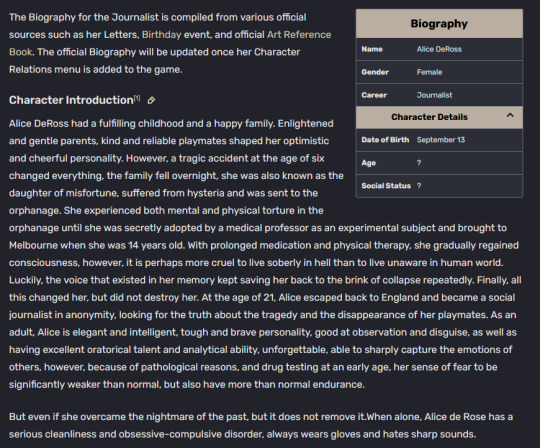
Alice's birthday: September 13.
If Alice is 6 during the tragedy, and the tragedy was in 1887, that tragedy had to have happened between September 13, 1887 and December 31, 1887.
Norton's birthday is March 19.
-> Thus why Norton we know was 12 at the time of the tragedy.
12 was the minimum age allowed for boys to work underground in coal mines (Metalliferous Mines Regulation Act, 1872). Legislation in 1860 set a requirement for a minimum level of formal education before children were permitted to work. It made it so 10 and 11 year old boys could only be employed in British collieries if they had earned an educational certificate or if they attended school at least 2 days a week for at least 3 hours per day. (Females were prohibited by an Act in 1842.)


The Education Act of 1870, which applied to England and Wales, made attendance at school compulsory for children between the ages of 5 and 10. For Scotland, an Act was introduced in 1872 that made school compulsory for children between 5 and 13. There were exceptions to these 2 acts, such as for children engaged in apprenticeships or those being appropriately home schooled.
The 1872 Act also made it so boys between 12 and 16 couldn’t work more than 54 hours in 1 week or 10 hours in 1 day. It also required between 8 and 12 hours between periods of employment (defined as starting when they leave the surface and ending when they return to the surface).
It did have provisions for 10 year olds to labor part time where seams were especially thin. At the same time, surface work was regulated, a minimum age of 12 being required for both boys and girls for full-time employment (and 10 years for part-time work).
Norton says in his 2nd letter “Over the last 20 years, I lived like a rat in the gutter”. Based on what we know, he was likely restricted to work above ground until at least age 12, and even afterwards had restrictions on his hours and what he could do and such until at least age 16.

In which case, this comment, based on the context, may have just been referring to him growing up poor. It may imply his father died when he was 8, at which point life became very hard for him, especially as Norton’s mother is never referenced. As I discussed in a previous post, with how rare divorce was, Norton’s mother is more likely to be dead.

#idv#identity v#norton campbell#prospector#Fool's Gold#fools gold#idv norton#identity v norton#idv prospector#identity v prospector#idv fools gold#identity v fools gold#idv fool's gold#identity v fool's gold#sirenjose analyses and theories
125 notes
·
View notes
Note
I noticed there are dates on your top liners list, ranging from the 1870s to the 2000's. I think on my alt you told me it was one of the last made, and the last in current use (as a hotel [and apparently haunted house according to the third video?]).
Anyway, I was wondering if you had an overview on the history of Ocean Liner design and how they've changed over the years, both technical in terms of operation, and aesthetic from the point of view both as a theoretical passenger and a learned liner enthusiast!
Plus any fun details about your examples would be nice as well.
Svjsvphsvpusvpusv okay. I am going to need to split this up into multiple posts, because I can not convey all this information with the 10 Pic limit. So periodically, check the reblogs of this post. I will periodically be adding more to it over time. Also, I'm not really citing any sources because this is mostly from memory, so there MAY be some mistakes. Also, I'm typing all this on my phone, so... please forgive the formatting, grammar, and spelling mistakes.
To begin, let's quickly discuss what an ocean liner is. An ocean liner is a ship you travel on to cross the ocean. It's called a liner because it goes in a line across the ocean. In this sense, “cruise liners” don't really exist. The proper term is cruise ship. Many people mistake liners for cruise ships and vice versa, but they are different in both function and design. As wikipedia puts it, “Though ocean liners share certain similarities with cruise ships, they must be able to travel between continents from point A to point B on a fixed schedule”. This means liners need to be both durable, and fast, something cruise ships are neither of. Cruise ships also almost never do trans-Atlantic crossings unless absolutely necessary. They just aren't built to handle the Atlantic at its worst. Cruise ships usually stay relatively close to land and reschedule for bad weather. For example, the only liner still in service is the RMS Queen Mary 2, built in 2004. Her construction used 60% more steel than a cruise ship of the same size. She also has a top speed of about 30 knots, whereas a cruise ship never really needs to exceed about 18. So, to summarize, an ocean liner is a ship you use to cross the ocean. A cruise ship, while it may take you to numerous excursions, is essentially the destination itself, and it will return you to where you started once the voyage is over. Last thing before we start, GRT. Gross Registered Tonnage is essentially a measure of the total usable internal volume of a ship. Generally, this is a much better measure of the size of a ship than length. For example, the RMS Adriatic was 729 ft long. The Titanic was 882 feet long. Only 150 feet longer, no big difference, right? WRONG. The Adriatic was 25,000 GRT. Titanic was 46,000 GRT. Britannic, which was the same length as Titanic, but 2 feet wider, was 48,000 GRT. Nearly double the size of Adriatic, even though she's not much longer. The Lusitania was 787 feet, and she was 31,000 GRT. So even though Britannic was only about 12% longer, she was about 55% bigger. Last thing, a knot is a unit of speed 1 knot is 1.150779 miles per hour, or 1.852 kilometers per hour.
Anyway, now that we have that sorted out, let's get into the history >:3
So, it starts with the steam engine. At the start of the 19th century, if you wanted to get from Europe to America (or vice Versa), you needed to book passage in a sailing ship. In just 4 short months, you can cross the ocean :D! Between extremely unsanitary conditions and the high chance of you not making it to your destination at all, something needed to change. There were some experiments with bolting steam engines to old sailing vessels, and these were very successful, but really only proofs of concept. Railway engineer Sir Isambard Kingdom Brunel realized that if ocean travel could work like the railway, travel between continents could be much more efficient and safe. With a sailing ship, you were dependent on the wind and weather, so your departure and arrival dates couldn't be predicted with any guarantee of certainty. With a steam engine, the ship could move at a consistent speed over a set distance, regardless of the conditions. Now, ocean travel was consistent, regimented, and much safer. All of these came together in 1838 with the launch of Brunel's SS Great Western, which crossed the Atlantic in 18 days, going at 8.66 knots. She was 1,700 Gross Registered Tons (GRT, a measure of internal volume) and 234 ft 11 in long (71.6 meters). She was the first ocean liner. Granted, she was essentially just a sailing ship with paddle wheels attached to a very rudimentary steam engine, she even Still had sails, and she had a hull made from oak, but she was the first commercial venture to bring passengers across the ocean on a regimented schedule. She was also the first purpose built liner.
Now, these very early years of ocean liners aren't really my specialty, so I'll cover some major events.
In 1839, Sir Samuel Cunard was awarded the first British transatlantic steamship mail contract, and in 1840, formed what would later be known as the Cunard Line, one of the most famous lines ever, And still around to this day.
In 1858, Sir Isambard Kingdom Brunel was back at it again with the SS Great Eastern. With this ship, Brunel set out to solve a problem: He wanted to make a ship big enough to carry enough coal to not need to stop and refuel on the voyage to Australia. The Great Eastern was the largest ship in the world by a WIDE margin. Before Great Eastern, the largest ship in the world was the SS Adriatic of the Colin's Line. She was 3,670 GRT, and 354 feet (108 meters) long. The Great Eastern was a whopping 18,915 GROSS REGISTERED TONS. 5.5 TIMES BIGGER! SHE WAS 692 FEET LONG. As wikipedia puts it, “Her length of 692 feet (211 m) was surpassed only in 1899 by the 705-foot (215 m) 17,274-gross-ton RMS Oceanic, her gross tonnage of 18,915 was only surpassed in 1901 by the 701-foot (214 m) 20,904-gross-ton RMS Celtic and her 4,000-passenger capacity was surpassed in 1913 by the 4,234-passenger SS Imperator.” IT IS WITH HONOR THAT I INTRODUCE YOU TO BRUNEL'S “GREAT BABE”, THE SS GREAT EASTERN.
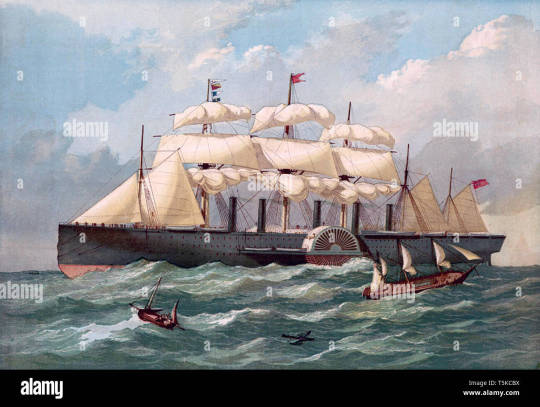


LOOK AT ‘ER! AIN'T SHE A BEAUT? IN A WORLD WHERE MOST SHIPS DIDN'T HAVE ANY FUNNELS, AND THE ONES THAT DID ONLY HAD ONE, THE GREAT EASTERN WAS THE ONE AND ONLY F I V E F U N N E L E D L I N E R. Even though she later lost one in an explosion, which was never replaced. She was rigorously mocked for her size and number of funnels, which is strange considering the 4 funneled superliner boom just 50 years later.
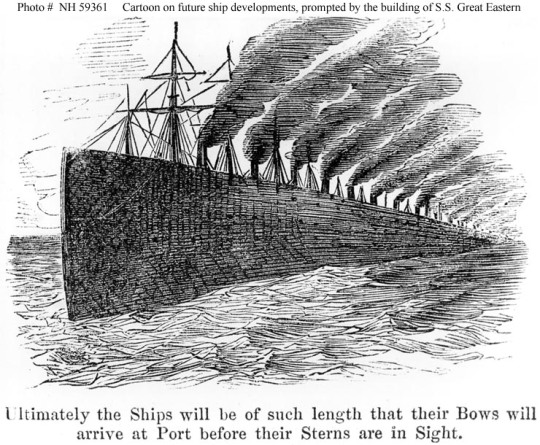

She FAMOUSLY didn't work, and the stress of trying to MAKE her work ended up sending Brunel to an early grave. SHE INDIRECTLY KILLED ONE OF THE GREATEST ENGINEERS OF ALL TIME! She then spent nearly a decade laid up as a glorified billboard:

She damaged or sunk at least 10 ships in her short Career, had a penchant for spontaneously exploding (which is where her 5th funnel went), and when she was scrapped in 1890, all of her size records were still at least 9 years from being bested. She was NEVER profitable, and the DEFINITION of an outlier. Whenever discussing the largest ships in the world from 1848 to 1890, it goes without saying that the Great Eastern is not included. There is a REASON she's on my top 25, and I've only skimmed the surface. She was a hot mess, and I love her for it. I'd be happy to make a post entirely dedicated to her.
Next, we have the birth of the White Star Line. In 1870, they got their first ship: The SS Oceanic. (Not the RMS Oceanic of 1899 mentioned previously).
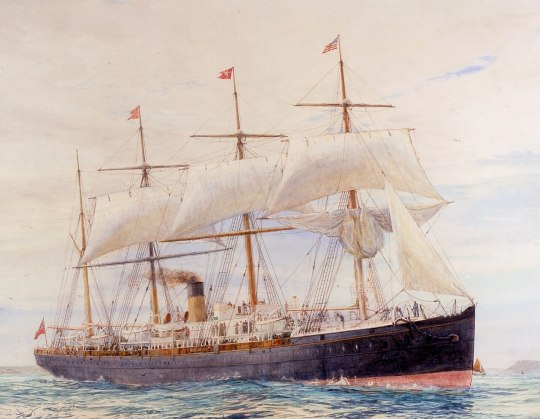



Many consider her and her 5 sisters to be the first “modern” liners, in the sense that they were starting to evolve past glorified sailing ships. She was 420 ft 4 in (128.12 meters) and 3,707 GRT. While her size PALED in comparison to the MIGHTY GREAT EASTERN, she was the “largest” ship in the world. Again, the great eastern kinda doesn't count. As modern as she was, Oceanic still had sails, and she had an INCREDIBLE top speed of… 14.5 knots. It was fast for the time. In fact, she won White Star Line their first Blue Riband for the fastest trans-Atlantic crossing. The ships of the Oceanic class were the Oceanic, Atlantic, Baltic, Republic, Adriatic (not the aforementioned RMS Adriatic, OR the SS Adriatic of the Colins Line), and Celtic. One of the big innovations of these ships was that they had a longer length to width ratio. Most sailing ships have a 6:1 ratio of length to width. The Oceanic class increased it to 9:1. With a thinner hull form, it reduced drag and allowed for a higher speed, albeit at the cost of stability. She was also one of the first ships at sea to use electricity. Not for lights, though. Those were still oil lamps. No, the electricity was for buttons in the cabins, which, when pressed, would summon a steward. Founder of the White Star Line, Thomas Ismay, realized that most of the profits of shipping lines came from The hundreds of steerage passengers, rather than the ultra wealthy first class/saloon Class passengers, so he made sure that he had THE BEST steerage accommodations by a scenic mile. He wanted to make sure that he'd be the one getting their business. Her steerage accommodations (3rd class) were fuckimg REVOLUTIONARY in their standards. In an era where poor people were treated like literal cattle, the steerage accommodations on the Oceanic class must have seemed like heaven on earth. Certainly better than anything they would have ever experienced on land. Steerage passengers had FRIGGIN PORTHOLES, which was a new thing for them because, like I said, before White Star, no one gave a shit about poor people. Also, for decks beneath the water line, there were skylights that reached all the way down to the bottom decks. The designers went through great pains to make sure everyone had fresh air and natural sunlight. Which, again, not something you'd find on other ships of the era, as basic as it seems. Anyway, the SS Atlantic, the White Star Line's second ever ship, was their first loss at sea. While we associate the line with Disaster today, history shows quite a different story. In their 65 years of operation, from 1870 to 1935, they operated at least 89 ships. They only lost 5 during peacetime disasters. This is a genuinely phenomenal track record, especially for the time. The aforementioned Collins Line lost literally 2/5ths of their ships (although they did have a much smaller fleet, so it's not an entirely fair comparison). Anyway, the SS Atlantic ran aground near Halifax Nova Scotia, with a loss of 535 people, leaving only 429 survivors. In the 30 minutes the ship took to fully sink, not a single lifeboat could be launched. I'd highly recommend Part-Time Explorer's videos on the subject.
In part 2, we'll cover from 1874 to 1900, with some of the most famous ships of all time. Like I said, this early stuff is where I'm weakest. Part 2 is where I'll become REALLY knowledgeable. >:3
#ss great eastern#great eastern#ss great western#great western#ocean liners#ocean liner#oceanliner#rms titanic#titanic#cunard#colins line#ss oceanic#ss atlantic#ss baltic#ss adriatic#ss republic#ss Celtic#oceanliners#rms oceanic#rms celtic#rms Adriatic#ss imperator
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Arsenic Poisoning of Episode 3
Hello hi I'm a history major currently doing research of the Victorian use of arsenic in textiles, and I figured, why not see how much arsenic poisoning Lokius would have gotten at the fair?
Poor Mobius is about to have a rough time. I'm assuming Loki has some genetics that make his less susceptible to arsenic poisoning. But Mobius's sweet tooth would be the most likely to get him into trouble.
First of all, arsenic was EVERYWHERE. It was in upholstery, paint, playing cards, curtains, clothing, pesticides, paper stationery, wallpaper, candy wrappers, even dust. The most common pigment was Scheele's green, which was used to produce a very vibrant green.




Let's look at the fair. What from here would they have come into contact with? They spent a good chunk of a day there, and Mobius seems like a fun guy. Let's assume they were in buildings. Many of the buildings were temporary constructions, so I would assume they would not be the most furnished, like a home would, but they could have stopped by the domestic product exhibit by the Pratt Institute. And they may have come across artificial flowers in decorations, stopped to look at gloves or in an art hall, or Mobius could have played a few rounds of cards painted with arsenic green. He might have accidentally brushed against someone wearing a green arsenic-dyed dress and had the offset sit in his skin for a while. Here is an illustration of the wounds direct contact with arsenic could cause.
Here you can look through photos and an account of the fair.
Arsenic was sold in grocery stores before restrictions were passed in Parliament (my research focuses on the UK right now, but I'm going to apply it to Chicago. I am also assuming many things from the UK were shipped to Chicago for the fair). The Arsenic Restrictions Act of 1851 limited the sale of arsenic to 10 pounds or less and to pharmacists. Not very effective, if you ask me, and according to this cartoon and this one.
(Quick background info was that Parliament was hesitant to pass arsenic restriction laws, which even led to an increase in the use of arsenic. Arsenic was not just in the green pigments, but for the purpose of this post and because it's the Loki series, I'm focusing on green.)

Doctors had widely suspected arsenic in domestic textiles and products caused arsenic poisoning since the 1870s. Most of the time, symptoms disappeared once the patients left the room/house because they weren't around the arsenic wallpaper/cloth/etc. But arsenic was so widespread at the end of the 19th century, I firmly believe that Mobius would have been seriously ill at the end of episode 3. Here are symptoms noted by two different doctors.



This is not even mentioning the fact that arsenic had a history of being in sweets and other foods. As mentioned in the second image, candies were sometimes wrapped in paper dyed with arsenic, but arsenic was also used to dye confectionery, and also substitute other ingredients, whether accidental or in an attempt to cut costs. In 1858, a confectioner accidentally mixed 12 pounds of arsenic into a batch of peppermint. 200 people got sick and 21 died in the Bradford Sweets Poisoning.
One historian, James C Whorton, posits that arsenic was added to lower costs and that the Arsenic Restriction Act actually did nothing to restrict arsenic being released into the public.


This brings us to another point. We know that at the fair, knockoffs were a large business there. If even before the fair, there was the temptation to lower costs by carelessly replacing it with arsenic, then it might be probable to assume some candies had a strong presence of arsenic at the fair, given how prevalent knockoffs were. Poor Mobius, unless he was very careful to do his research, probably ate a few. This is where the sweet tooth gets him in trouble. Loki didn't eat anything, the most he would have encountered was probably fabric and dust.
A report from 1900 shows that arsenic was suspect in glucose products. Glucose is sugar, which is used to make caramel and molasses, which are used in the making of: you guessed it, Crackerjack. The Crackerjack of the 1893 World's Fair was made with molasses, which is from refining the sugar cane, but arsenic mixed with molasses was also used as a pesticide so it would perhaps not be uncommon to have arsenic-laced molasses in the vicinity, especially at a fair showing off new agricultural developments. Given that this report is from 1900, I am assuming arsenic may have been more prevalent in sugar before 1900.



So Mobius could have been exposed to any amount of this during the day at the fair. What about onscreen? When they reach the bar, Mobius could have brushed against clothing containing arsenic given how crowded it was. We see him think about ordering a beer. Also not a good idea, Mobius.

I would also say Timely might have had exposure standing next to the stage curtains. But Loki's magic when they leave also kicks up a lot of dust. If we look back at the first image, we can see the concentration of arsenic in dust. Inhaling that wouldn't have done Mobius any good either.
There are several factors that we did not see onscreen that I could only guess that they did. But Timely's lab may have had arsenic in it, and given how dusty it seemed to be, that very well could have also been a place that added to Mobius's exposure. Many physicians reported arsenic poisoning, likely from their work.
This post will likely be edited for a while as I continue my research (it's also 1 am and I wrote this in an hour) and then I'll do a full bibliography (if you want a certain source, ask in the notes and I'll post it), but this is my conclusion that Mobius would probably have been ill after returning to the TVA if we lean into his sweet-tooth side, so Lokius hurt/comfort fics anyone??
#lokius#loki series#loki laufeyson#loki#mobius m mobius#mcu loki#mobius#loki x mobius#loki season 2#loki season two
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
wrote in that Narnian accent post that the Pevensies would be using the equivalent of 1820s slang when they come back in PC, and got distracted looking up period slang. I found this article (12 Lost American Slangisms From The 1800s) and honestly I think we should bring some of these back. let's all start saying we're going to "wake snakes" (do a mischief) again
full list for your perusal:
Too high for his nut — beyond someone's reach. "That clay-bank hog wants the same pay as a Senator; he's getting too high for his nut," according to a grammar-corrected version of the Oakland, Calif., Tribune on Jan. 12, 1885.
Bottom fact — an undisputed fact. "Notwithstanding all the calculations of the political economists, the great bottom fact is that one man's honest, steady work, rightly applied, especially if aided by machinery and improved modes of conveyance and distribution, suffices to supply the actual needs of a dozen burdensome loafers," according to the Brooklyn Daily Eagle of Jan. 31, 1871.
To be Chicagoed — to be beaten soundly, as in a baseball shutout. "Political corruption ... if the clergy only keep to that topic, Lincoln will be Chicagoed!" from the Plymouth, Ind., Weekly Democrat of June 7, 1860.
See the elephant — to see all the sights of a town, especially the edgier aspects. "A young Sioux Indian from Haskell Institute ... said he was going to Chicago to hunt buffalo. He was told there was no game of that kind there, but that if he wanted to see the elephant he was on the right track," the Lawrence, Kan., Daily Journal reported on Sept. 2, 1891. Also sometimes used by members of the military to describe going to war.
How came you so — inebriated. Describing an illustration, a reporter in the Gettysburg, Pa., People's Press of May 22, 1835, wrote: "A gentleman a little 'how came you so' with his hat on the back of his head, is staggering about in the presence of Miss Fanny, who appears to be quite shocked."
Lally-cooler -- a real success. "That north show window of Shute & Haskell's is a 'lally-cooler,' " the Jan. 4, 1890, Salina, Kan., Republican noted.
Shinning around -- moving about quickly. "It is shinning around corners to avoid meeting creditors that is sapping the energies of this generation," opined the Dallas, Texas, Daily Herald on Oct. 31, 1877.
Shoddyocracy — people who get rich selling shoddy merchandise or services. "A lady of the shoddyocracy of Des Moines found, on returning from a walk, some call cards on her table," observed the Harrisburg, Pa., Telegraph of June 30, 1870.
Some pumpkins -- a big deal. "If there was any kind of trading," noted the Grant County Herald in Wisconsin on July 17, 1847, "in which Simon B. ... flattered himself he was decidedly 'some pumpkins,' it was a horse-trade."
Like Thompson's colt -- doing something unnecessarily, like jumping a fence when the rails have been removed. "Thompson's colt," a reporter in the Saint Paul, Minn., Globe of Nov. 20, 1882, wrote, "was such an infernal idiot, that he swam across the river to get a drink."
Tell a thumper -- construct a clever lie. "When anyone told a thumper more palpably outrageous than usual, it was sufficiently understood ..." Reminiscences of the Turf by William Day, 1891.
Wake snakes — get into mischief. "So I went on a regular wake snakes sort of a spree, and I went here and there turnin', twistin' and doublin' about until I didn't know where or who I was," a man testified in court as to why he was intoxicated, according to the New Orleans, La., Times Picayune of Aug. 15, 1842.
#language#slang#1800s slang#period slang#historical language#19th century#nova actually post stuff#some of these feel *exceedingly* tumblr#good omens fandom i trust you to have fun with wake snakes#also: bottom fact#no comment. but like. i know tumblr#not to brag but i'm some pumpkins#given this site's obsession with halloween#etc#(i know wake snakes isn't used as a verb in the example but language is fluid and “do a mischief” isn't proper grammar either)#the higher the queuer
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
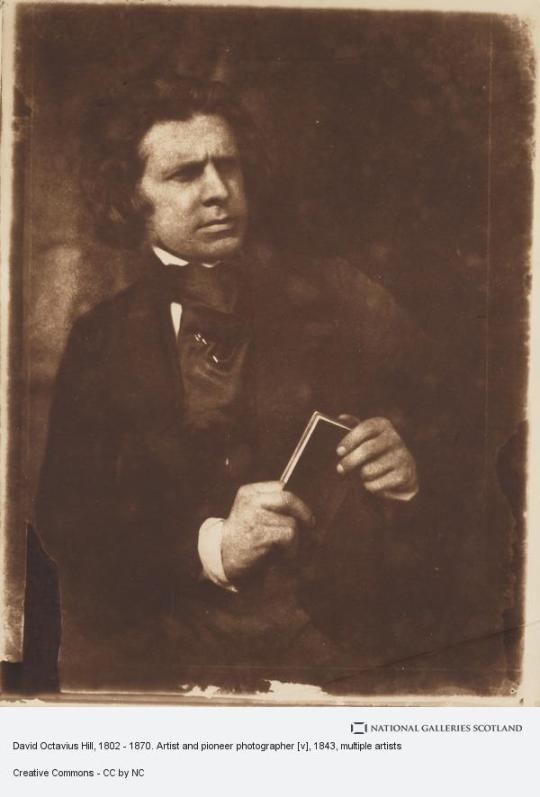
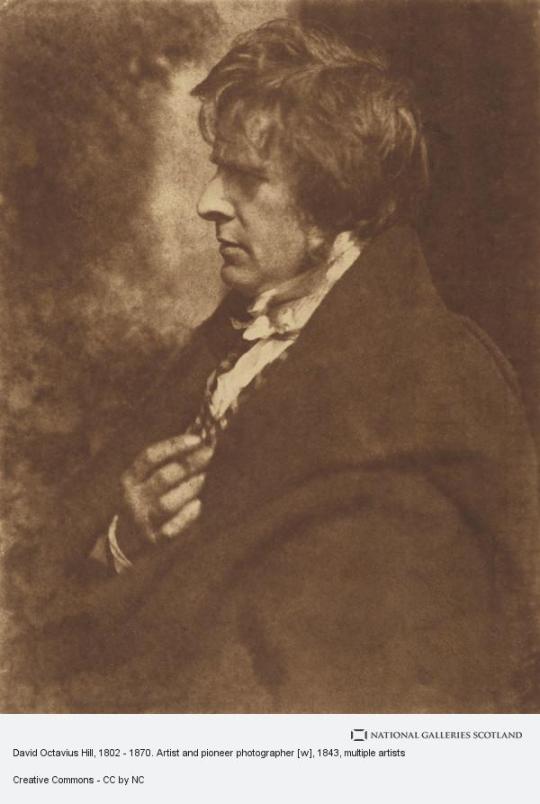
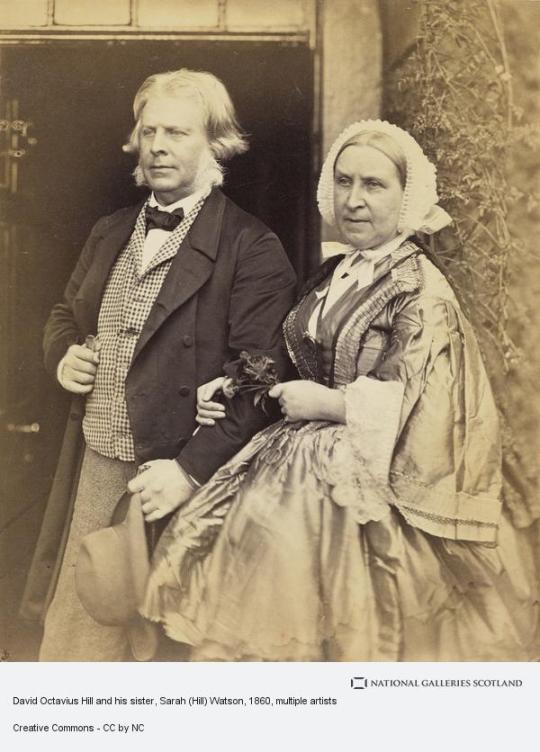
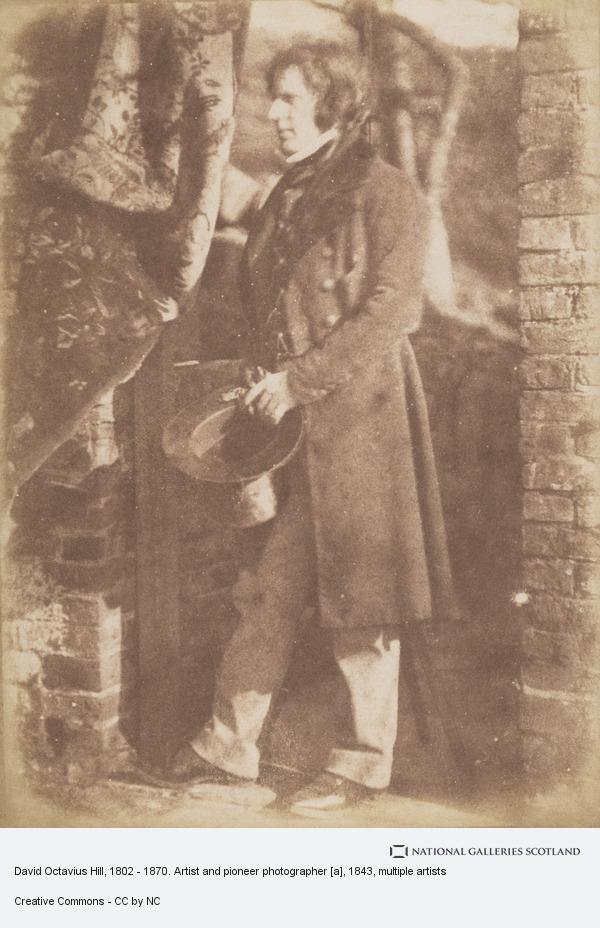
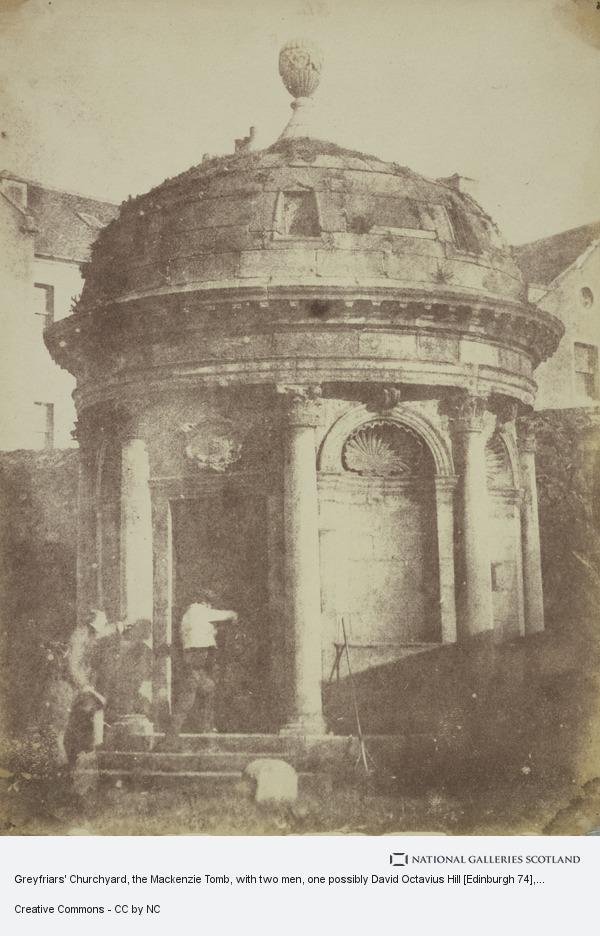
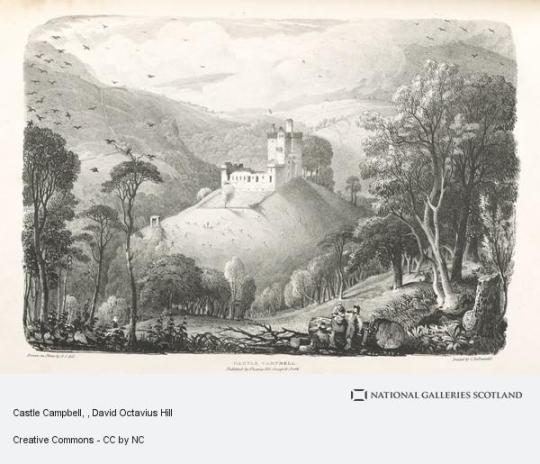










On 17th May 1870 David Octavius Hill, the painter and pioneering Scottish photographer, died.
Hill was one of several pioneering photographers Scotland produced during the 19th century. If you follow my posts you have definitely seen lots of his pictures.
David Octavius Hill was born in Perth, the son of a book publisher. He was educated at Perth Academy and the School of Design in Edinburgh. Hill was an acceptable landscape painter and illustrator (illustrating some novels for Sir Walter Scott). Always involved in the art world, he helped organize the Royal Academy of Scotland and served as secretary from its inception until his death. He was a respected artist in his time, but not one that would be recognized today had he not become involved with Robert Adamson.
David Octavius Hill was present in 1843 at the meeting of the Church of Scotland and witnessed the succession of 457 ministers to reassemble as the Free Church of Scotland. Hill was so moved he pledged to paint a portrait of all 457 ministers together. Sir David Brewster, who had studied for the clergy of the Church of Scotland was also at the meeting. He suggested the use of the Calotype as a sketching tool.
Adamson, who had opened his studio at Rock House just weeks before, entered into a joint venture with Hill to photograph all 457 men of the new Free Church of Scotland. The subjects were posed outside. One set was designed to appear indoors but was actually outdoors with furniture and drapery against a wall of the building.
David Octavius Hill’s 12 ft-wide Disruption Painting, widely thought to be the first time a painter based his work on photographs. The work, which was begun in 1843 and took 23 years to complete, includes everyone involved in signing the agreement that set up the Free Church of Scotland in the 19th century.
Hill and Adamson mainly made Calotype documentary portraits that beautifully speak of their time. They photographed not only the churchmen, but also a variety of subjects: landscapes, architecture, friends and family. Their environmental portraits were among the earliest recorded, utilizing the new medium of photography. They worked together on their project for four and a half years, until Adamson’s early death in 1848.
After Adamson’s premature death at age 27, Hill temporarily abandoned photography and returned to painting. Hill became a member of the Photographic Society of Scotland in 1856 and ran a studio with Alexander McGlashan from 1861 to 1862 publishing Some Contributions Towards the Use of Photography as an Art. Hill sold the remnants of his studio with Adamson in 1869. The property on Calton Hill is now holiday accommodation.
Hill is buried in Dean Cemetery, Edinburgh - one of the finest Victorian cemeteries in Scotland. He is portrayed in a bust sculpted by his second wife, Amelia, who is buried alongside him.
Pics are mainly of Hill, with several pieces of his artwork.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Researching African American Ancestors
Due to the long history of slavery in the United States, family history research can be challenging for many African Americans.
Census takers rarely recorded the names of enslaved people and seldom listed family members together. Enslaved people were often subjected to forced name changes, family separation, and other injustices that continue to cause challenges when finding people from the past.
But some strategies can help.
Getting started
Download our guide to African American family history.
Gather information:
Family Bibles
Journals, diaries, and letters
Photographs
Obituaries and newspaper clippings
Birth, marriage, and death certificates
Family group sheets, pedigree charts, and books of remembrance
Interview your family members and ask whether they have any records. Take note of names, dates, and places.
Start a family tree and add anything you've discovered.
Search family trees by clicking the Search tab and selecting Public Member Trees. To narrow your search results, add information one field at a time until you get results you can use.
Follow the strategies below.

Tracing your family backward
In the United States, federal censuses are taken every 10 years. Trace your ancestors backward in censuses starting with your immediate family, recording each detail you find.
Enslaved people were not usually named in censuses. Slavery was abolished in 1865, so the first census that included the names of most African Americans was the 1870 U.S. Federal Census.
If you can trace your ancestor back to the 1870 census, you've got a good start. The next step is to find out whether they appeared in the 1860 U.S. Federal Census.
In 1860, about 10% of African Americans were free. If your ancestor was free in 1860, they should be listed in the census. If you can't find them in the 1860 census, they were likely among the 90% of African Americans still enslaved.
Look too for your ancestor in the Mortality Schedules. These are indexes of people who died during the 12 months before the census date. Mortality schedules are available for the 1850–1880 censuses. These schedules often included the names of both freedmen and enslaved people, but sometimes the names of enslaved people were excluded from the index.
Trace your ancestors backward until you can't find them anymore. At that point, it's time to find the name of the last enslaver.

Finding the last enslaver
To find pre-1870 records that include your African American ancestor, you may need to find records for the enslaver.
If your ancestor has an uncommon last name, search censuses for white people with the same surname as your ancestor in the same area. When you find them, make a list; these are possible enslavers. Only about 15% of formerly enslaved people took the enslaver's surname. Start with the 1860 U.S. Federal Census.
Search the Freedmen's Bureau for your ancestor's name. The Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands was established in 1865 to help newly freed African Americans transition to life outside slavery. The names of former enslavers were often included in labor contracts, sharecropping agreements, and marriage records. Read more about the Freedmen's Bureau Records & Freedman's Bank Records.
Search the U.S. Colored Troops Military Service Records and the Civil War Pension Index. First, identify an ancestor in the Colored Troops Military Service Records, then use the information you find to locate the same person in the Civil War Pension Index, which often lists the names of enslavers.
Search the Freedman’s Bank Records. The Freedman's Savings and Trust was an institution chartered by Congress to benefit of newly-emancipated people. This publication reproduces fifty-five volumes of signatures and personal identification data of thousands of depositors who maintained accounts with the bank. These records usually show account numbers, dates of application, and the depositor's name, age, complexion, place of birth, place raised, occupation, spouse, children, family members' names, remarks, and signature. These registers of deposits sometimes included the name of a formerly enslaved person, their family members, and the former enslaver.
Search the Wills and probate records. Enslavers’ wills and probate records often list enslaved people by name.
Search U.S. Interviews with Former Slaves, 1936-1939. This database contains more than 2,300 first-person accounts of slavery and 500 black-and-white photographs of people who were formerly enslaved. It’s searchable by any word, so references to specific names can be found easily. Enslavers were often named in these narratives.

Searching slave schedules
If you know the enslaver's name and your ancestor's likely year of birth, try searching for the enslaver in the 1850 slave schedules and 1860 slave schedules. For help searching or understanding slave schedules, see Searching Slave Schedules.
More resources
The African American history page on Ancestry contains information about our DNA test and links to search databases.
The African American Historical Record Collection features interviews with people who were formerly enslaved, slave manifests, slave emancipation records, and more.
AfriGeneas provides resources for African-related genealogy with a vision of finding and documenting the last slaveholder and the first African in each family.
Cyndi's List has an index of genealogy sites about African American research.
The National Archives contain both African American research and links to resources.
The Hutchins Center for African & African American Research is a Harvard research center that supports research on the history and culture of people of African descent and provides a forum for collaboration.



#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#brownskin#afrakans#brown skin#african culture#afrakan spirituality#african ancestry#research ancestry#research family'#research family#research african family
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
May 11, 2024
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
MAY 12, 2024
If you google the history of Mother’s Day, the internet will tell you that Mother’s Day began in 1908 when Anna Jarvis decided to honor her mother. But “Mothers’ Day”—with the apostrophe not in the singular spot, but in the plural—actually started in the 1870s, when the sheer enormity of the death caused by the Civil War and the Franco-Prussian War convinced writer and reformer Julia Ward Howe that women must take control of politics from the men who had permitted such carnage. Mothers’ Day was not designed to encourage people to be nice to their mothers. It was part of women’s effort to gain power to change society.
The Civil War years taught naïve Americans what mass death meant in the modern era. Soldiers who had marched off to war with fantasies of heroism discovered that newly invented long-range weapons turned death into tortured anonymity. Men were trampled into blood-soaked mud, piled like cordwood in ditches, or withered into emaciated corpses after dysentery drained their lives away.
The women who had watched their hale and healthy men march off to war were haunted by its results. They lost fathers, husbands, sons, and brothers. The men who did come home were scarred in both body and mind.
Modern war, it seemed, was not a game.
But out of the war also came a new sense of empowerment. Women had bought bonds, paid taxes, raised money for the war effort, managed farms, harvested fields, worked in war industries, reared children, and nursed soldiers. When the war ended, they had every expectation that they would continue to be considered valuable participants in national affairs, and had every intention of continuing to take part in them.
But the Fourteenth Amendment, which established that Black men were citizens, did not explicitly include women in that right. Worse, it introduced the word “male” into the Constitution when it warned states against preventing “male inhabitants” from voting. In 1869, the year after the Fourteenth Amendment was added to the Constitution, women organized two organizations—the National Woman Suffrage Association and the American Woman Suffrage Association—to promote women’s right to have a say in American government.
From her home in Boston, Julia Ward Howe was a key figure in the American Woman Suffrage Association. She was an enormously talented writer who in the early years of the Civil War had penned “The Battle Hymn of the Republic,” a hymn whose lyrics made it a point to note that Christ was “born of woman.”
Howe was drawn to women’s rights because the laws of her time meant that her children belonged to her abusive husband. If she broke free of him, she would lose any right to see her children, a fact he threw at her whenever she threatened to leave him. She was not at first a radical in the mold of reformer Elizabeth Cady Stanton, who believed that women had a human right to equality with men. Rather, she believed strongly that women, as mothers, had a special role to perform in the world.
For Howe, the Civil War had been traumatic, but that it led to emancipation might justify its terrible bloodshed. The outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870 was another story. She remembered:
“I was visited by a sudden feeling of the cruel and unnecessary character of the contest. It seemed to me a return to barbarism, the issue having been one which might easily have been settled without bloodshed. The question forced itself upon me, ‘Why do not the mothers of mankind interfere in these matters, to prevent the waste of that human life of which they alone know and bear the cost?’”
Howe had a new vision, she said, of “the august dignity of motherhood and its terrible responsibilities.” She sat down immediately and wrote an “Appeal to Womanhood Throughout the World.” Men always had and always would decide questions by resorting to “mutual murder,” she wrote, but women did not have to accept “proceedings which fill the globe with grief and horror.” Mothers could command their sons, “who owe their life to her suffering,” to stop the madness.
"Arise, women!” Howe commanded. “Say firmly: ‘We will not have great questions decided by irrelevant agencies. Our husbands shall not come to us, reeking with carnage, for caresses and applause. Our sons shall not be taken from us to unlearn all that we have been able to teach them of charity, mercy and patience. We, women of one country, will be too tender of those of another country, to allow our sons to be trained to injure theirs.’”
Howe had her document translated into French, Spanish, Italian, German, and Swedish and distributed it as widely as her extensive contacts made possible. She believed that her Women’s Peace Movement would be the next great development in human history, ending war just as the antislavery movement had ended human bondage. She called for a “festival which should be observed as mothers’ day, and which should be devoted to the advocacy of peace doctrines” to be held around the world on June 2 of every year, a date that would permit open-air meetings.
Howe organized international peace conferences, and American states developed their own Mothers’ Day festivals. But Howe quickly realized that there was much to be done before women could come together on a global scale. She turned her attention to women’s clubs “to constitute a working and united womanhood.”
As Howe worked to unite women, she came to realize that a woman did not have to center her life around a man, but rather should be “a free agent, fully sharing with man every human right and every human responsibility.” “This discovery was like the addition of a new continent to the map of the world,” she later recalled, “or of a new testament to the old ordinances.” She threw herself into the struggle for women’s suffrage, understanding that in order to create a more just and peaceful society, women must take up their rightful place as equal participants in American politics.
While we celebrate the modern version of Mother’s Day on May 12, in this momentous year of 2024 it’s worth remembering the original Mothers’ Day and Julia Ward Howe’s conviction that women must have the same rights as men, and that they must make their voices heard.
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#letters from an american#Heather Cox Richardson#julia ward howe#Elizabeth Cady Stanton#Mothers' Day#war#women#women's rights#human rights#Civil War#mother
16 notes
·
View notes
Photo










The Manitoba Act was given the Royal Assent on May 12, 1870, paving the way for Manitoba to become a province of Canada on July 15, 1870.
#Lower Fort Garry National Historic Site of Canada#The Forks Historic Port#travel#Winnipeg#Lyons Lake#Trans-Canada Highway#prairie#flora#Canada Goose#Esplanade Riel Pedestrian Bridge#Armature of the Oodena Celebration Circle#Assiniboine River#Red River#Great Plains#Manitoba Act#12 May 1870#anniversary#Canadian history#Canada#Manitoba#landscape#cityscape#countryside#vacation#summer 2012
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo

La Mode illustrée, no. 24, 12 juin 1870, Paris. Toilettes de Mme Bréant-Castel, r. Nve des Pls. Champs. Collection of the Rijksmuseum, Netherlands
Description de toilettes (Bibliothèque Forney):
Costume en toile mexicaine écrue, composée d'une jupe ronde, d'une tunique drapée et d'un paletot. La garniture de la jupe se compose de sept rubans de velours noir sur lesquels sont jetés de distance en distance des bouquets de fleurs des champs composés de coquelicots, épis, bluets et pâquerettes, brodés en soie de couleurs naturelles. Même garniture sur la tunique, mais moins large (cinq rubans de velours noir). Même garniture sur le paletot, mais plus étroite (trois rubans de velours). Le paletot a des doubles manches très-larges et fendues, et secondes manches étroites.
Robe de foulard bleu, à fines rayures bleues plus foncées. Confection en taffetas noir.
Costume en cachemire blanc, composé d'une jupe ronde, d'une tunique non drapée et d'un paletot à doubles manches (larges, fendues, et sous-manches étroites). Le costume entier est garni d'une bordure brodée genre cachemire de l'Inde.
—
Costume in ecru Mexican canvas, consisting of a round skirt, a draped tunic and an overcoat. The trimming of the skirt is made up of seven black velvet ribbons on which are thrown at intervals bouquets of wild flowers made up of poppies, ears of corn, cornflowers and daisies, embroidered in natural-coloured silk. Same trim on the tunic, but narrower (five black velvet ribbons). Same trim on the overcoat, but narrower (three velvet ribbons). The overcoat has very wide and split double sleeves, and narrow second sleeves.
Blue scarf dress, with fine darker blue stripes. Made in black taffeta.
Costume in white cashmere, consisting of a round skirt, an undraped tunic and an overcoat with double sleeves (wide, split, and narrow under-sleeves). The entire costume is trimmed with an Indian paisley-like embroidered border.
#La Mode illustrée#19th century#1870s#1870#on this day#June 12#periodical#fashion#fashion plate#color#description#rijksmuseum#Forney#dress#flowers#stripes
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
The napoleonic marshal‘s children
After seeing @josefavomjaaga’s and @northernmariette’s marshal calendar, I wanted to do a similar thing for all the marshal’s children! So I did! I hope you like it. c: I listed them in more or less chronological order but categorised them in years (especially because we don‘t know all their birthdays). At the end of this post you are going to find remarks about some of the marshals because not every child is listed! ^^“ To the question about the sources: I mostly googled it and searched their dates in Wikipedia, ahaha. Nevertheless, I also found this website. However, I would be careful with it. We are talking about history and different sources can have different dates. I am always open for corrections. Just correct me in the comments if you find or know a trustful source which would show that one or some of the dates are incorrect. At the end of the day it is harmless fun and research. :) Pre 1790
François Étienne Kellermann (4 August 1770- 2 June 1835)
Marguerite Cécile Kellermann (15 March 1773 - 12 August 1850)
Ernestine Grouchy (1787–1866)
Mélanie Marie Josèphe de Pérignon (1788 - 1858)
Alphonse Grouchy (1789–1864)
Jean-Baptiste Sophie Pierre de Pérignon (1789- 14 January 1807)
Marie Françoise Germaine de Pérignon (1789 - 15 May 1844)
Angélique Catherine Jourdan (1789 or 1791 - 7 March 1879)
1790 - 1791
Marie-Louise Oudinot (1790–1832)
Marie-Anne Masséna (8 July 1790 - 1794)
Charles Oudinot (1791 - 1863)
Aimee-Clementine Grouchy (1791–1826)
Anne-Francoise Moncey (1791–1842)
1792 - 1793
Bon-Louis Moncey (1792–1817)
Victorine Perrin (1792–1822)
Anne-Charlotte Macdonald (1792–1870)
François Henri de Pérignon (23 February 1793 - 19 October 1841)
Jacques Prosper Masséna (25 June 1793 - 13 May 1821)
1794 - 1795
Victoire Thècle Masséna (28 September 1794 - 18 March 1857)
Adele-Elisabeth Macdonald (1794–1822)
Marguerite-Félécité Desprez (1795-1854); adopted by Sérurier
Nicolette Oudinot (1795–1865)
Charles Perrin (1795–15 March 1827)
1796 - 1997
Emilie Oudinot (1796–1805)
Victor Grouchy (1796–1864)
Napoleon-Victor Perrin (24 October 1796 - 2 December 1853)
Jeanne Madeleine Delphine Jourdan (1797-1839)
1799
François Victor Masséna (2 April 1799 - 16 April 1863)
Joseph François Oscar Bernadotte (4 July 1799 – 8 July 1859)
Auguste Oudinot (1799–1835)
Caroline de Pérignon (1799-1819)
Eugene Perrin (1799–1852)
1800
Nina Jourdan (1800-1833)
Caroline Mortier de Trevise (1800–1842)
1801
Achille Charles Louis Napoléon Murat (21 January 1801 - 15 April 1847)
Louis Napoléon Lannes (30 July 1801 – 19 July 1874)
Elise Oudinot (1801–1882)
1802
Marie Letizia Joséphine Annonciade Murat (26 April 1802 - 12 March 1859)
Alfred-Jean Lannes (11 July 1802 – 20 June 1861)
Napoléon Bessière (2 August 1802 - 21 July 1856)
Paul Davout (1802–1803)
Napoléon Soult (1802–1857)
1803
Marie-Agnès Irma de Pérignon (5 April 1803 - 16 December 1849)
Joseph Napoléon Ney (8 May 1803 – 25 July 1857)
Lucien Charles Joseph Napoléon Murat (16 May 1803 - 10 April 1878)
Jean-Ernest Lannes (20 July 1803 – 24 November 1882)
Alexandrine-Aimee Macdonald (1803–1869)
Sophie Malvina Joséphine Mortier de Trévise ( 1803 - ???)
1804
Napoléon Mortier de Trévise (6 August 1804 - 29 December 1869)
Michel Louis Félix Ney (24 August 1804 – 14 July 1854)
Gustave-Olivier Lannes (4 December 1804 – 25 August 1875)
Joséphine Davout (1804–1805)
Hortense Soult (1804–1862)
Octavie de Pérignon (1804-1847)
1805
Louise Julie Caroline Murat (21 March 1805 - 1 December 1889)
Antoinette Joséphine Davout (1805 – 19 August 1821)
Stephanie-Josephine Perrin (1805–1832)
1806
Josephine-Louise Lannes (4 March 1806 – 8 November 1889)
Eugène Michel Ney (12 July 1806 – 25 October 1845)
Edouard Moriter de Trévise (1806–1815)
Léopold de Pérignon (1806-1862)
1807
Adèle Napoleone Davout (June 1807 – 21 January 1885)
Jeanne-Francoise Moncey (1807–1853)
1808: Stephanie Oudinot (1808-1893) 1809: Napoleon Davout (1809–1810)
1810: Napoleon Alexander Berthier (11 September 1810 – 10 February 1887)
1811
Napoleon Louis Davout (6 January 1811 - 13 June 1853)
Louise-Honorine Suchet (1811 – 1885)
Louise Mortier de Trévise (1811–1831)
1812
Edgar Napoléon Henry Ney (12 April 1812 – 4 October 1882)
Caroline-Joséphine Berthier (22 August 1812 – 1905)
Jules Davout (December 1812 - 1813)
1813: Louis-Napoleon Suchet (23 May 1813- 22 July 1867/77)
1814: Eve-Stéphanie Mortier de Trévise (1814–1831) 1815
Marie Anne Berthier (February 1815 - 23 July 1878)
Adelaide Louise Davout (8 July 1815 – 6 October 1892)
Laurent François or Laurent-Camille Saint-Cyr (I found two almost similar names with the same date so) (30 December 1815 – 30 January 1904)
1816: Louise Marie Oudinot (1816 - 1909)
1817
Caroline Oudinot (1817–1896)
Caroline Soult (1817–1817)
1819: Charles-Joseph Oudinot (1819–1858)
1820: Anne-Marie Suchet (1820 - 27 May 1835) 1822: Henri Oudinot ( 3 February 1822 – 29 July 1891) 1824: Louis Marie Macdonald (11 November 1824 - 6 April 1881.) 1830: Noemie Grouchy (1830–1843) —————— Children without clear birthdays:
Camille Jourdan (died in 1842)
Sophie Jourdan (died in 1820)
Additional remarks: - Marshal Berthier died 8.5 months before his last daughter‘s birth. - Marshal Oudinot had 11 children and the age difference between his first and last child is around 32 years. - The age difference between marshal Grouchy‘s first and last child is around 43 years. - Marshal Lefebvre had fourteen children (12 sons, 2 daughters) but I couldn‘t find anything kind of reliable about them so they are not listed above. I am aware that two sons of him were listed in the link above. Nevertheless, I was uncertain to name them in my list because I thought that his last living son died in the Russian campaign while the website writes about the possibility of another son dying in 1817. - Marshal Augerau had no children. - Marshal Brune had apparently adopted two daughters whose names are unknown. - Marshal Pérignon: I couldn‘t find anything about his daughters, Justine, Elisabeth and Adèle, except that they died in infancy. - Marshal Sérurier had no biological children but adopted Marguerite-Félécité Desprez in 1814. - Marshal Marmont had no children. - I found out that marshal Saint-Cyr married his first cousin, lol. - I didn‘t find anything about marshal Poniatowski having children. Apparently, he wasn‘t married either (thank you, @northernmariette for the correction of this fact! c:)
#Marshal‘s children calendar#literally every napoleonic marshal ahaha#napoleonic era#Napoleonic children#I am not putting all the children‘s names into the tags#Thank you no thank you! :)#YES I posted it without double checking every child so don‘t be surprised when I have to correct some stuff 😭#napoleon's marshals#napoleonic
76 notes
·
View notes
Text


'Signora Savelli': a very large soprano mystery
A carte de visite photograph of Elisa Savelli (sometimes Eliza Savelli, real name Miss Sewell, fl. 1870s/1880s), English soprano, who created the role of Bi-bi in the English version of Offenbach’s Vert-Vert, produced at the St. James’s Theatre, London, 2 May 1874
‘A great success has been achieved at Milan by a young English prima donna now singing there under the name of Mdlle. Savelli. She has been received with great favour in many different rôles, especially in ”La Traviata” and ”Martha.” Mdlle. Savelli, who, in addition to her musical acquirements, is very beautiful, will probably appear in London next season.’ (The Illustrated Police News, &c, London, Saturday, 20 August 1870)
‘SIGNORA ELISA SAVELLI, Prima Donna Assoluto Soprano, ‘Has returned to London, after a brilliant and successful career of four years in Italy, singing to Milan and other Principal Cities. Will shortly appear at one of our large Theatres, being especially Engaged from Milan, to represent the Principal Par in the Opera ”Le Roi Carote.” Disengaged up till the 3d June. Apply, Mr. Carte, 20, Charing-cross.’ (The Era, London, Sunday, 12 May 1872, advertisement)
‘ALHAMBRA THEATRE ROYAL. ‘The Manager, Mr. John Baum, begs to inform the nobility and gentry that, on the 3d of June, will be produced, on a scale of magnificence hitherto unapproached in London, the Grand Opera Bouffe Feerie, LE ROI CAROTTE, in which upwards of 1,000 dresses will appear upon the stage. Music by Mons. J. Offenbach. Words translated and adapted to the English stage by Henry S. Leigh, Esq. ‘The artistes engaged include Mdlle. Elise Savelli, [Anetta] Scasi, and Cornelia D’Anka; Messrs, Selle, Connell, Warboys, and [Harry] Paulton. ‘Two Premier Danseuses, Mdlle. Nini and Bertha Linda, who will make their first appearance in London. A powerful chorus has been carefully selected, and with the magnificent Orchestra will be under the immediate direction of Mons. [Georges] Jacobi.’ (Reynolds’s Newspaper, London, Sunday, 26 May 1872, advertisement)
‘ALHAMBRA THEATRE ROYAL. – FIRST NIGHT of LE ROI CAROTTE. ‘ALHAMBRA THEATRE ROYAL. -FIRST APPEARANCE of the celebrated Prima Donna Mdlle. ELISA SAVELLI, from Milan, Naples, &c. …’ (The Daily News, London, Monday, 3 June 1872, advertisement) The Alhambra, extract from a review of Le Roi Carotte ‘… Mdlle. Cornelia D’Anka, who was Cunégonde, as usual, captivated all hearts by her handsome face and figure. Her vocal ability, too, enabled her to render good service, and it was manifestly impossible for the audience to be anything but pleased with so fascinating an artiste, even when she kept them waiting, which, we are compelled to say, she did more than once. The loving Rosee had a capital representative in Mdlle. Elisa Savelli, who was literally overwhelmed with bouquets for her rendering of a charming and plaintive air in which she envies the flowers and the birds, and sighs for release from captivity. Miss [Violet] Cameron was Coloquinte, the sorceress, and she only calls for remark by reason of the scantiness of her dress… .’ (The Era, London, Sunday, 9 June 1872)
The Alhambra, extract from a further review of Le Roi Carotte ‘… Mdlle. Elisa Savelli is also brilliantly successful as Rosee du Soir, and sings the air in the third act so well as to gain an encore, and the duet with Mdlle. Anetta Scasi, ”Guide me! guide me!” is equally successful and qually meritorious on the part of both ladies… .’ (The Era, London, Sunday, 4 August 1872)
‘ALHAMBRA THEATRE ROYAL. – ‘Seventy-ninth Night, and during the week, LE ROI CAROTTE. Principal Characters:- Miss Kate Santley (her First Appearance), Annetta Scasi, and Elisa Savelli; Messrs F.H. Celli, E. Connell, Worboys, Robins, and Harry Paulton. 250 Coryphees. The Opera commences at 8.15; terminated at 11.40. ‘The coolest and best ventilated Theatre in London.’ (The Era, London, Sunday, 1 September 1872, advertisement)
‘SIGNORA SAVELLI. – This talented vocalist, who has become quite a favourite at the Alhambra, on Monday evening, at two hours’ notice, undertook the role of Robin Wildfire in Le Roi Carotte, and created what we may truthfully term a furore. She is we understand specially engaged for the part of the Princess in The Black Crook [1st performance, Christmas Eve, 1872], now in active preparation.’ (The Era, London, Sunday, 1 December 1872)
The Alhambra, The Black Crook ‘… On the acting in the piece high praise may be bestowed, Mdlle. Savelli, who carried off the principal honours of the evening, sustains the part of Desirée with grace and skill, and is none the less impressive because she always avoids exaggeration… .’ (The Times, London, Friday, 27 December 1872
‘ITALIAN OPERA CONCERT. – A concert will be given this (Saturday) evening at the Victoria Rooms by several artistes of the Royal Italian Opera. The Brighton Gazette speaks highly of the vocal powers of Madame Savelli and Signor Brennelli, two of the artistes who will take part in the concert.’ (The Bristol Mercury and Daily Post, Bristol, Saturday, 19 September 1885)
‘MADAME ELISA SAVELLI, ‘Prima Donna, Soprano Dramatica, for Italian and English Opera. ‘Madame Savelli’s beautiful and artistic rendering of ”Convien Parti” (Donnizetti) was much admired, as was also her rendering of the ”Stella Confidenta,” which was enthusiastically encored. She is possessed of a magnificent soprano voice of rich and powerful quality such as is rarely heard. – Bristol Times and Mirror. ‘Address all communications to Mr Gilbert Tail, 6, York-street, Covent-garden, W.C.’ (The Era, London, Saturday, 3 October 1885, advertisement)
‘On Saturday next Her Majesty’s Theatre is announced to open at popular prices, with a company selected in Italy and France. Well-known operas will be given, commencing with Il Trovatore, Faust, Rigoletto, Lucia, Il Barbiere, La Traviata, Ernani, Fra Diavolo, LaGioconda, and, later on (never performed in England), La Ione. Mesdames Savelli, Dalti, Appia, Potentini, Signori Debiliers, Mascheroni, Genoesi, Fernando, Gualterio Bolton, Tamberlik, and Brennelli, are among the engagements.’ (The Era, London, Saturday, 20 February 1886)
Her Majesty’s Theatre, Haymarket… ‘Those present last night when the ”house of amber curtains” reopened its door with a performance of Verdi’s ”Il Trovatore” would scarcely have felt inclined to declare that Italian opera was a thing of the past unless some bright, particular star condescended to brighten it with her presence, for a large and friendly audience had gathered together to hear this old and hackneyed work, who certainly were not attracted by any particular bright star, seeing there was nothing of the sort upon the premises… . The heroine was, vocally speaking, well rendered by a Madame Elisa Savelli, who, if we are not mistaken, some fifteen years or so since was known as a Miss Sewell. Time has, however, not improved her personal appearance, as she is now considerably too broad for her length, and, in the bridal dress of which satin, bore a curious resemblance to Miss Minnie Warren, the wife of General Tom Thumb. Being accommodated with a tall, stern lady as a made of honour (Mdlle. Corona) made this lack of symmetry all the more apparent… . (Reynolds’s Newspaper, London, Sunday, 28 February 1886
Her Majesty’s Theatre ‘… In Saturday’s representation Madame Savelli was cast for Leonora, and Signor Fernando for her ill-fated troubadour lover; … In her performance as Leonora Madame Savelli displayed considerable vocal and dramatic power in the declamatory portions of her music, with an occasional tendency to exaggerated effort and a strained use of her upper notes. She was favourably received throughout, especially in the great scenes with Manrico and the Count… .’ (The Daily News, London, Monday, 1 March 1886
London, Sunday Night ‘Her Majesty’s Theatre was re-opened last night for a season of Italian opera at cheap prices… . The Leonora was, curiously enough, taken from the Alhambra, where she sang some years ago as Mdlle. Savelli, the foreign equivalent of her own English name of Miss Sewell. Although still in fairly good voice the lady has now attained well night the physical proportions of a Titiens and Parepa combined, and her appearance in bridal costume was irresistibly comical… .’ (The Glasgow Herald, Glasgow, Monday, 1 Marcy 1886)
‘On Saturday night, during the performance of Il Trovatore at Her Majesty’s, a mishap occurred which, but for the presence of mind of certain individuals, might have resulted in serious consequences to Madame Savelli, the Leonora of the evening. Madame Savelli’s figure is not exactly like Madame Sarah Bernhardt’s, and in moving backwards to execute a fall at the end of the opera she tumbled ”all of a heap” beneath the ponderous roller of the descending curtain, and had not the stage-manager and an attendant run forward and dragged her out of her dangerous position, she might have been seriously injured. The audience expressed their sympathy with Madame Savelli’s narrow escape by calling her enthusiastically before the curtain.’ (The Era, London, Saturday, 6 March 1886)
Il Trovatore, Her Majesty’s, Saturday, 27 February 1886 ‘… Without ranking ourselves with those unimaginative individuals who cannot overlook certain personal disqualifications for a role when its rendering is illuminated by genius, we must say that we had to ”make believe very much” indeed to accept a portly, matronly lady of Madame Savelli’s physique as an ideal Leonora. There is something cruet, to our thinking, in calling upon a person of Madame Savelli’s liberal proportions and limited dramatic and vocal acquirements, to face a London audience in such a part. No one felt more keenly than ourselves the failure of the singer to reach the higher notes of her role, and to embody the emotional characteristics of the heroine; and no one sympathised more with the lady in her difficulty in assuming kneeling and falling attitudes. The fault, we felt, was not so much hers as that of those who permitted her to appear in a wrong position – literally and metaphorically… .’ (The Era, London, Saturday, 6 March 1886)
#classical music#opera#music history#bel canto#composer#classical composer#aria#classical studies#maestro#chest voice#Elisa Savelli#soprano#classical musician#classical musicians#classical history#history of music#historian of music#musician#musicians#diva#prima donna#Assoluto Soprano#His Majesty's Theatre#Her Majesty's Theatre
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mod 3: Gymnosperms
Pinus Needle T.S.
It is circular in outline in P. monophylla, semicircular in P. sylvestris and triangular in P. longifolia, P. roxburghii, etc.
Outermost layer is epidermis, which consists of thick-walled cells. It is covered by a very strong cuticle.
Many sunken stomata are present on the epidermis.
Each stomata opens internally into a substomatal cavity and externally into a respiratory cavity or vestibule.
Below the epidermis are present a few layers of thick-walled sclerenchymatous hypodermis. It is well developed at ridges
In between the hypodermis and endodermis is present the mesophyll tissue.
Cells of the mesophyll are polygonal and filled with chloroplasts. Many peg-like infoldings of cellulose also arise from the inner side of the wall of mesophyll cells.
Few resin canals are present in the mesophyll, adjoining the hypodermis. Their number is variable but generally they are two in number.
Endodermis is single-layered with barrel-shaped cells and clear casparian strips.
Pericycle is multilayered and consists of mainly parenchymatous cells and some sclerenchymatous cells forming T-shaped girder, which separates two vascular bundles. Transfusion tissue consists of tracheidial cells.
Two conjoint and collateral vascular bundles are present in the center. These are closed but cambium may also be present in the sections passing through the base of the needle.
Xylem lies towards the angular side and the phloem towards the convex side of the needle.
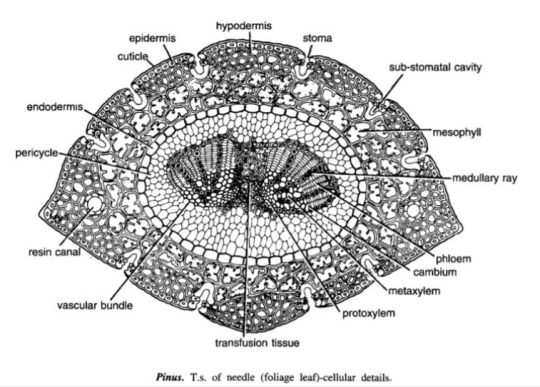
Idk where to find xeric nature info
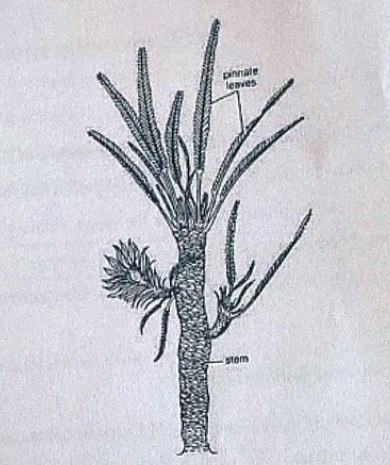
Williamsoniaceae
Occurrence of Williamsonia
Williamsonia belongs to family Williamsoniaceae of Bennettiales.
It has been reported from Upper Triassic period but was more abundant in Jurassic.
This was earlier discovered under the name Zamia gigas by Willamson in 1870 but has now been named as Williamsonia.
Professor Birbal Sanhi (1932) described W. sewardiana from Rajmahal Hills of Bihar (India).
External Features of Williamsonia
Williamsonia resembled Cycas in appearance, but its best-knows species is W. sewardiana. The plant had an upright, branched, and stout stem covered by persistent leaf bases.
A terminal crown of pinnately compound leaves was present. For the stem genus Bucklandia, Sharma (1991) opined that features of leaf bases such as their shape, size and arrangement pattern are of taxonomic significance.
He observed that leaves in Williamsoniaceae show syndetocheilic stomata with rachis possessing collateral endarch vascular bundles.
Reproduction in Williamsonia
The fructifications of Williamsonia were large and attained a diameter of about 12 cm.
They were borne on a peduncle.
Many spirally arranged bracts were present around the base of the floral axis.
In W. gigas the cones were present among the crown of leaf bases while in W. sewardinia they were present on the short lateral branches.
Williamsonia plants were unisexual.
Female Flower
The female 'cones' of W. gigas and W. sewardiana have been investigated in detail. Instead of 'strobili' or 'cones', Sporne (1965) proposed to use the term 'flower'.
The conical receptacle was surrounded by many perianth-like bracts. The ovules were stalked.
The apex of the receptacle was naked and sterile. The nucellus was surrounded by a single vascularize integument, which was fused with the nucellus. The nucellus had a well-marked beak and a pollen chamber. In young ovules the micropylar canal was long and narrow.
In mature ovules, the canal widened because of the formation of nucellar plug and disappearance of interlocking cells. In the apical part of the endosperm, Sharma (1979) observed 2 or more archegonia.
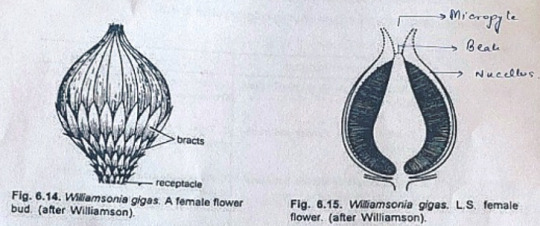
Male Flower
Male flowers consisted of a whorl of microsporophyll's which were united to form a more or less cuplike structure. In majority of the investigates species the sporophylls were un-branched but in some species they were also pinnately branched.
Sitholey and Bose discovered W. santalensis from Upper Gondwana, and observed that microsporophyll's in the species were bifid.
One of the branches of microsporophyll was fertile while the other was sterile. The fertile part has finger-like structures called synangia. Each synangium had two rows of chambers enclosing microsporangia.
The fertile branch of the bifid sporophyll possessed many purse-like capsules, in each of which there were present many monocolpate pollen grains.

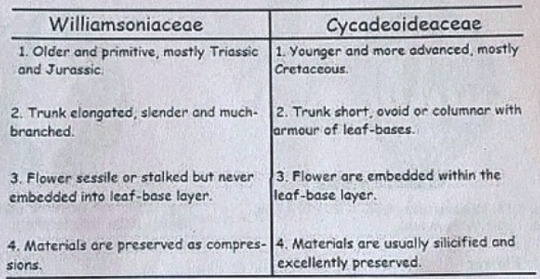
Cycadeoideaceae
Classification:
Division - Cycadeoidophyta
Order - Cycadeoideales
Family - Cycadeoideaceae
Genus - Cycadeoidea
Introduction:
Cycadeoidea is the only genus of family Cycadeoidaceae, represented by thirty species. They are entirely extinct and resemble cycads in the outward stumpy appearance of trunk and an apical crown of pinnate compound leaves. This fossil group of plants flourished during the Triassic to Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic era. They are reported from various places in the world, in India the Cycadeoidales are found in Rajmahal Hills in Bihar. The petrified trunks of C. entrusca are the oldest fossil ever collected by man.
External Features:
The genus Cycadeoidea had a short, branched, or unbranched spherical, conical, or irregular trunk. The diameter of the trunk is 50cm and the highest rarely reached a meter except in C. jenneyana, it attended the height of several meters. These trunks are covered by rhomboidal leaf bases having multicellular hairs in between. Crown of 10ft long pinnate compound leaves are present at the top.
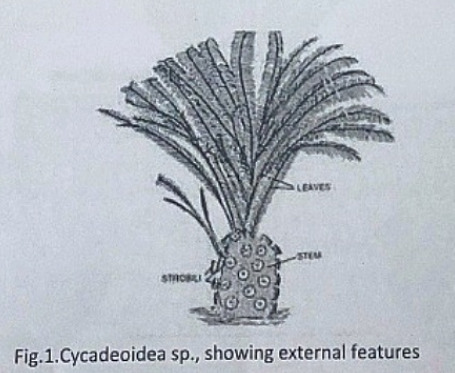
Anatomy of Stem:
The transverse section of the stem shows roughly a circular outline. The epidermis is not very distinct due to the presence of heavy armor of leaf bases. The cortex is parenchymatous and traversed by mucilage canals and numerous leaf traces. The primary vascular structure consists of a ring of endarch, collateral, conjoint, and open vascular bundles encircling the pith. Pith is wide and parenchymatous. A ray-like extension passes between the vascular bundles that make their appearance discrete.
There is a cambium ring with a thin zone of secondary wood. The secondary wood encircles the primary xylem and consists of tracheids with scalariform and bordered pits. The secondary medullary rays traverse the secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
The C-shaped leaf traces arise singly from the primary vascular strand and entering the cortex divided into several masarch strands and enters straight into the leaf.
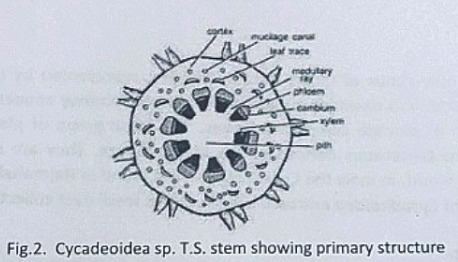
Anatomy of Leaf:
The pinnules show xerophilous structure. The upper and lower epidermis is heavily cutinized and thick walled. The mesophyll cells are distinguished into palisade and spongy parenchyma. The vascular bundles are mesarch and surrounded by bundle sheath.
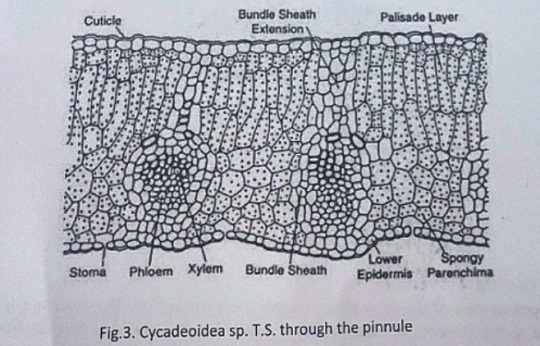
Reproduction:
The reproductive structure is represented by flowers. In most of the species, the flowers are bisexual and arise in the axil of each leaf.
Structure of Flower:
The flowers are bisporangiate, stalked, and partially sunken in the leaf base armor. Rach such mature flower is 5-10cm in diameter and 10cm long. From the base of such flowers about 100 to 150 hairy bracts arise in close spiral little below the apex. These bracts formed a perianth like structure and protect the megasporangiate and microsporangiate parts of a flower. The microsporophyll or androecium forms a whorl united at the base into a sheath. The megasporophyll or gynaecium consists of numerous stalked ovules born around a central receptacle. Between the ovules, interseminal scales with expanded tips are present. These expanded tips fused to form a continuous surface with pores, through which the micropyle of ovules extended. The vascular supply of flowers consists of many branches from leaf traces.
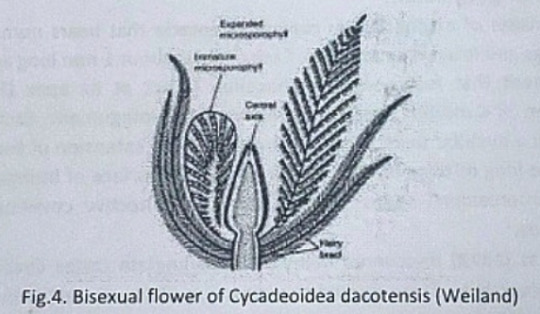
Microsporophyll or Androecium:
The microsporophyll is 10-12cm long, consists of a central rachis bearing numerous pinnae. The pinnae bear two rows of bean-shaped shortly stalked pollen capsules or synangia. These pollen capsules are born on the trabeculae within the fertile region of microsporophyll. A line of dehiscence is also visible at the base of each microsporophyll. This suggest that the entire microsporophyll might have been shed as a unit. The pollen capsule or synangia measures about 3.5x2.5mm and its wall is several layers thick, the outer layer made up of palisade like cells, and the inner layer is made up of thin-walled cells followed by a tapetum. The tapetum was not demarcated. A ring of microsporangia arranged around the periphery of each synangium. The microsporangia dehisce longitudinally and release the microspores into the synangial cavity. At maturity, the synangia liberate these microspores outside by an apical opening that splits into two valves. The liberated microspores or pollens are oval, measures up to 68µ that represents the male gametophytes. Pollen grains of Cycadeoidea are multicellular.
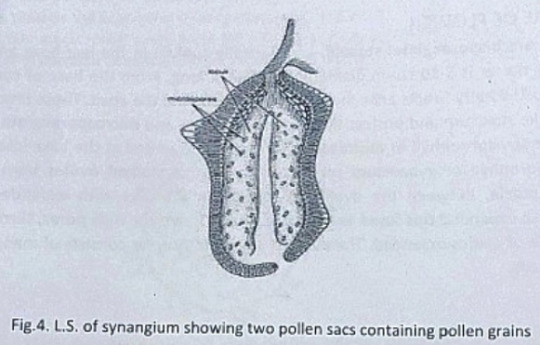
Megasporophyll or Gynoecium
The gynoecium consists of a spherical or conical receptacle that bears numerous stalked orthotropous ovules and interseminal scales. Each ovule is about 1mm long and consists of the single integument that fused with the nucellus except at its apex.
According to Lignier, in C. morieri, nucellus is free from the integument. Each ovule has a pollen chamber and a nucellar beak. This nucellar beak is the extension of the integument. The ovules also have long micropyle, extended from the flat surface of interseminal scales. The fused tips of interseminal scales form an external protective covering or pericarp surrounding the seeds.
Crepet and Delevoryas discovered many of bisporangiate cones from the Cretaceous of black hills. They studied the structure of these ovules in detail. These ovules are urn-shaped and resemble with the ovules of C. wellsii. According to them the micropyle of these ovules are funnel-shaped due to the constriction below the flaring. The inner wall of the micropyle is lined with large cells, considered to be epidermal cells. The integument has three distinct layers. The outer fleshy layer of radially elongated cells, the middle stony layer made up of thick-walled cells, and the inner layer is fleshy.
The young nucellus is made up of thin-walled cells. The cells at the micropylar end are much elongated (80µ long) in comparison to the cells of the chalazal end. The cell at the nucellar tip is pointed up tp whereas cells on either side are bend outward to give the nucellus a distinct shape.
Crepet and Delevoryas reported a linear tetrad or row of three cells in the center of the nucellus.
The seeds are somewhat elongated or oval and possessed two cotyledons.
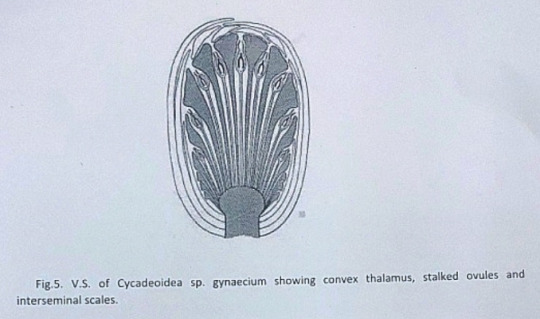
#exam season#send help#biology#notes#science#botany#gymnosperms#pines#pine trees#pine needles#plants#plant science#plant biology#nature#long post
8 notes
·
View notes