#this is a valuable experience
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
i had a terrible, awful, bad day yesterday (I mean. two days ago, since it's already after midnight here). I'm not sure if I even should share details, but let's just say being (partially) responsible for evacuating almost 700 people definitely wasn't on my bucket list for that day
and it is mentally taxing, I still feel like the stress of it all didn't fully leave my body. and I have to go to work tomorrow (I mean. today. since it's already after midnight) and everyone knows what happened and to whom and I know they're all just curious but I'm not sure if I'm mentally capable of answering all their questions. I DIDN'T SIGN UP FOR BEING A MINOR CELEBRITY AT MY JOB I SIGNED UP SO I COULD BE NICE TO PEOPLE AND SOMETIMES SLEEP AT WORK
#i would write down specifically what happened but#let's just say i like to be somewhat anonymous on the internet#+ it was literally something that never happened before. not just to me but to ANYONE#(not like. never ever)#(but not in this city. not to people that work where i do. not on that scale.)#and if I write about it too openly#my employers potentially could figure out my identity#i doubt they browse tumblr but if they do then they WILL know who I am#and since the employers & the bosses (& the way company handled this case) are part of the reason the day was fucking awful-....#yea i dont wanna them to read it#i like my job and i'd like to keep it. and i'm alredy on thin ice#but now im just. so tired guys#so tired and YET im proud of myself.#of the way i handled it. of all things i did. people literally thanked ME for it????#i know that better than me would fail in my position.#this is a valuable experience#not just for me but for the entire company#so the empoyers should fucking APOLOGIZE to me and utilize my experience for something better. for their own good lol#dont mess with me i have the power of rage and labour unions on my side#personal#ramblings
0 notes
Text
"Haha Dream BBQ is so random and incomprehensible" "did they take drugs to make this lol" "you're actually not meant to understand anything in this series it's ok" "Joel G just makes up stuff on the spot based on what would be funny" "it's just random for random's sake" "is this AI" "stop theorising, it's not that deep" SHUT UPPPPPPPPPP

#ena dream bbq#ena joel g#random art does not exist. all human made art is made with intention.#like. sure. ena is intentionally surreal and aburdist and weird. and im sure some things were less thought out#but to say its all just random bullshit does SO much disservice to the creators behind this project#and disservice to your OWN intelligence in giving up and refusing to work those braincells of yours to create your own interpretation#like. There Are Things To work with here. there are a Lot Of Things#you just have to actually Think and connect the pieces and do introspection on what this Means to YOU#like. you dont wanna think hard. fine. if you wanna just enjoy the experience thats fine too#but then you have to still ackowledge that youre getting SOMETHING out of this (unless youre actually not and are just a hater)#even if its just emotionally. even if its jus unconsciouslly#there Is Meaning There#its just not linear#so think about it!!! thats whats fun about this series!!!#it forces everyone to think about it instead of just following the one 'canon'!!!!#there probably isnt one right answer here!!!#but that doesnt make it any less valuable!!!!#just. auuuughh#i have a lot of thoughts about this#the ena team would not put in this much effort and creativity and symbolism and themeing just for shits and giggles#ok ill stop being a hater now. and I WONT go in the opposite direction and start wining about how a lot of theories (on youtube at least)#seem to ignore the more emocionally significant and symbolic themes in favour of basic or emotionally shallow takes.....#ggrhrgrh (through gritted teeth)... everyones interpretation is valid.. everyones interpretation is valid#whatevr. im just rambling. idk. i hope you get what i mean#negative#fandom critical#my own post
191 notes
·
View notes
Note
Dragon age really was over before it started, huh
Real and it pisses me off badly.
Incredibly fun world-building, a story so engaging fans fight over it, talented devs who love the studio and actually understand what makes single-player RPGs special, a GOTY win under the belt, tons of supplementary media + merch sales, iconic characters, and still a troubled development every single time. I hate it so much, I hate those that contributed to it, I hate how common this all is.
But I'm proud of everyone who did what they could with what they had. Even the few folks who drive me insane out of my mind ballistic sicko-mode. Because at the end of the day: they fought for DA. They really did. Which is more than I wouldve done in their shoes. One (1) disparaging comment about a project I'm devoting 40+ fucking hours a week to and I would've crashed out big time.
#replies#id be online talking crazy and burning bridges like nahhh im naming names and @-ing people#it aint even happen to me and im shaking goddd its just not RIGHT to do this to people#real breathing people who want to get interesting art out there instead of battle pass junk food !#and yknow also even strictly from a business perspective isnt a connective series valuable?#every new DA fan I know goes back and buys ALL the previous games to experience them + build a world state#thats gotta count for something man idk
157 notes
·
View notes
Text












Happy Birthday Owen Wilson! ♡ (November 18th, 1968)
#and we love him for it 🥰💖#owen wilson#celebrating this monumental occasion with an appreciation of one of the most valuable experiences of our time#the cowboy owen wilson cinematic universe™ of course#which even this isn't the entirety of but uh. for completely coincidental reasons i may have gotten distracted while making the set lol#happy birthday beloved!! man of all time forever and always 🥳#shanghai noon#zoolander#night at the museum#the royal tenenbaums#starsky and hutch#drillbit taylor#armageddon#shanghai knights#marvelcastedit#owenwilsonedit#movieedit#dianagifs#(also have to mention how surreal it is for those california naturals ads to have taken place THIS year they feel soooo long ago 😭😭)
275 notes
·
View notes
Text
house of eazy
#jay eazy#house of leaves#LISTEN!!!!#hol#jayeazy#this is. not the funniest thing ive done. but valuable learning experience for a new video editing software i started using#enjoy :]#oh and the song is hallways of always by ulver
1K notes
·
View notes
Text










"But... Those aren't the emotions I wanted!"
#uchu sentai kyuranger#uchuu sentai kyuranger#kyuranger#naga ray#hebitsukai silver#hebitsuki metal#tenbin gold#lucky (kyuranger)#balance#balance (kyuranger)#lucky#shishi red#super sentai#flashing lights#flashing lights tw#tokuedit#please do not repost#umbrella.posts#umbrella.edits#umbrella.gifs#translation: over-time#subtitles added by me#mutual got to this scene so now we can post it#ever think about how much naga loves his friends and wants to learn with them bc the experience of learning with them is just as valuable#as the emotions themselves? do you ever think about how control is something that naga needs to learn to balance? you ever think about naga
94 notes
·
View notes
Text

brush test slash rendering practice with ayem
#morrowind#almalexia#the elder scrolls#tes#tes fanart#art#id in alt#ok that's all the tags this needs ANYWAY#i started this 1. for experimenting with coloring from dark to light#2. because i wanted to draw someone kind of back turned to the camera#3. rendering practice for hair particularly#4. to go from sketch to rendering rather than doing lines to see if that doesn't smooth out my workflow a bit#5. because i've never actually used this brush past flat coloring#and out of those 1. i don't think i had enough of an idea of the palette or process to jump into dark to light painting so i did scrap that#and go with my usual “flat color with one of the mid shadow tones add shadows add light”#i do think that painting from shadows out is a thing people do digitally i just think this wasn't the drawing to test it on for me#i think i'd need to look at some other peoples processes and start with a more fleshed out idea of where to go#2 and 3 i think worked out. i'm gradually figuring hair out which i think is sick#4 i also think worked out for me which is also sick because i do get caught on lines a lot. they're fun sometimes but i think some drawings#benefit better from not having them and that it might be a bit faster#and of course everything i do is so that i can draw slightly faster and better for next artfight#as for 5. i have mixed feelings on this brush but that might be because i hate change. and also because i started this drawing on the 15th#of november and finished it yesterday. so im kind of just sick of working on and looking at it#it was a valuable learning experience and i think it came out well! i am also going to drop to my knees and rejoice when i can finally#close this file out and free medibang paint from under it so i can work on Literally Anything Else#thank you almalexia for being my test subject i should've used a reference for your armor when i did the sketch but i didn't#maybe the crown looks weird because of it maybe it doesn't. not my problem anymore i can draw other elves again#my art#iiii think i forgot a my art tag last time
118 notes
·
View notes
Note
Mr. Cube I have a question of utmost importance for you as literally the only Magneto main I know of. HOW... DO YOU PLAY HIM. Do you have any tips. I want to look at him.
So You Want To Be Pretty OK As Magneto In Marvel Rivals

(3 March, 2025) a beginner's guide written by your resident magneto main snapperoni because now i get an excuse to talk about marvel rivals magneto extensively and in gross detail
*this guide will be treating you as though you have never used magneto in your life and will go into extreme depths at explaining his abilities as well as what it means to be a tank player. if you feel confident in understanding his abilities, feel free to skip the abilities section and head straight to the bottom for talk on strategy and tips
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
TLDR ROLE INTRODUCTION ABILITIES Melee/Greatsword Primary Fire/Iron Volley Secondary Fire/Mag Cannon Metallic Curtain Metal + Iron Bulwark [TEAM-UP ABILITY] Metallic Fusion [ULTIMATE] Meteor M [PASSIVE] Magnetic Descent TIPS AND STRATEGIES Iron Volley + Mag Cannon Combo Bubble and Shield Usage Two Tanks Are Better Than One Metallic Fusion How to Use Meteor M CLOSING THOUGHTS
-----------------------
Too Long, Didn't Read:
Magneto is a poke tank meant to be played at medium-to-close range whose priorities should lie in acting as a living wall for his teammates. preserving his abilities mostly for himself yet sharing them when the situation calls for it.
While his priorities should be defense-based, when it comes to going on the offensive you want him to target strategists and duelists and only engage in tanks if the rest of the team is with you. As far as aiming goes, he's very friendly and isn't hitscan reliant, and you should find yourself picking up his aim style easily with time.
He's not a super flashy character like the rest of the cast, but he's far from useless and, at this moment in time, stands as one of Rival's best tank options alongside Doctor Strange and Hulk, whether you're running two tanks or running solo.
Overall, the two-star difficulty he is awarded is very fitting: available to newcomers to pick up and start playing, however offers a little something extra to those with a better understanding of him; he's generally straight forward as far as tanks go, but picking up a few extra tips and tidbits never hurt anyone. Except your enemies, of course.
-----------------------
Role Introduction: Vanguard/Tank
As a vanguard unit, Magneto's top priority should be taking the brunt of the team's damage on the front line and should give the team either opportunities to push forward, or shoot behind the cover you provide.
With 650HP (without shields), while he has average health for a vanguard, his defensive kit allows him to be a formidable wall when his abilities are used tactfully and you work in tandem with your support/s. Unlike dive tanks like Venom and Captain America, Magneto is much more stationary, and his kit rewards playing defensively and close to the team.
A common misconception with FPS games is that your top priority is to get the most eliminations as possible and to exclusively hunt for the next kill (unless that is the objective of the specific map you're playing on, then kill away). There are several errors with this philosophy: for starters, you begin to neglect the objective, which can lead to a game loss.
The amount of kills you have won't matter if you stay off point and the other team takes the objective. No matter what anyone says, don't stress about your eliminations so long as you know you're protecting your team, securing the point, and overall providing value to the game (though it is important to be able to land a shot....).
Moreover, playing under this philosophy is a sure-fire way to not only get you killed and remove your time away from the field (which should truly be your game philosophy: die as little as possible), but specifically as a tank you'll bring your teammates down with you as they lose what should be a reliable line of defense. As a tank, you should be opening up opportunities for your teammates to get the eliminations and protecting your strategist/support units.
All of that said, tank is not for the passive player: as tank, you need to be firm about the playing field being yours and making sure the enemy team knows they're going to have a hard time taking it from you. Fitting for Magneto, really.
-----------------------
Ability Review
Before dissecting Magneto's abilities, I will preface and say I calculated his damage using Doctor Strange (600HP) and Scarlet Witch (250HP) as damage dummies. The numbers I have here may not be accurate, so to circumvent this potential error I'll describe how many shots it takes to use a specific skill in order to eliminate certain enemies.
Melee/Greatsword
Attack speed: ~1 second
Damage Output: 40 (About seven swings to KO a 250HP enemy)
Utilizing Doom Bot remains, Magneto swings with a grandiose blade. The problem with this sword is it's not only one of- if not the- slowest melees in the game as of right now, but it has very little to compensate for its poor speed. Should very rarely be used in place of a well-aimed primary fire.
Primary Fire/Iron Volley

Reload time: ~1 Second
Damage Output:
Direct Damage: 80 (About four shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Edge Damage: 40 (About seven shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Fall-Off Damage: 40 (About seven shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Magneto's Iron Volley asks that you lead/predict your shots. Moreover, his Iron Volley will explode automatically once reaching 25M(eters), whether it hits a target or not. At 25M, your shot will no longer do 80 damage, but will do half instead. As noted before, Magneto's primary fire will explode when it comes into contact with a wall, floor, or enemy. As such, the explosion has a small hitbox- doing just about half of a regular, direct shot. Because of this, you shouldn't be too stressed if you're not the greatest at aiming: Magneto's primary fire makes up for any minor imperfections and is rather generous so long as you're in the general area of your target.
Secondary Fire/Mag-Cannon
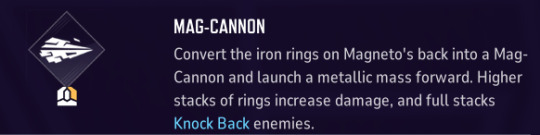
Reload Time (Without Bulwark Aid):
One Ring: ~4 Seconds
Two Rings: ~8 Seconds
Full Power: ~12 Seconds
Damage Output:
One Ring: 40 (About seven shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Two Rings: 80 (About four shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Three Rings/Full Power: 100 (About three shots to KO a 250HP enemy)
Edge Damage: N/A
Similar to Iron Volley, you will need to lead your shot when firing off a Mag-Cannon. Unlike his primary fire however, Magneto's secondary fire will keep going until it hits a wall or enemy. Moreover, it doesn't suffer any damage fall-off, nor does it offer any edge damage. How many rings you possess show both on Magneto physically, but they can also be tracked by the purple arrows below your crosshair. As a bonus, the Mag-Cannon momentarily stuns and pushes back any targets it hits which can either cancel an enemy's advancement, or open the floor for a follow-up attack.
Metallic Curtain


Recharge Time: 3 Seconds
Replenish-to-Full Time: 10 Seconds
Duration: 1.5 Seconds
Shield HP: N/A
Putting up an impenetrable wall just shy of two seconds allows Magneto and his allies to pull back safely from oncoming damage or provide just enough cover to make an adequate push forward. Not to mention, this indestructible wall scoffs in the face of any ult coming your way. Once the shield has been spent, a white bar will appear on the right side of your crosshair. This bar indicates how long you can hold your shield up the next time you use it before it's fully charged, where then the bar will fade. Finally, you can put your shield down early. While this means you'll have to wait the full three seconds for it to be available again, this means your shield will have more durability the next time you use it.
Metal Bulwark + Iron Bulwark

Recharge Time: 12 seconds
Duration: ~3 Seconds
Shield HP: To be calculated, but it does exist: be cautious of the damage you and your teammates take.
Magneto can spring a magnetic bubble over either himself or an ally. The bubble not only negates any incoming damage and protects allies from Scarlet Witch's Reality Erasure, but once the bubble has popped or faded Magneto will regain some Mag Cannon rings relative to the damage absorbed.
[TEAM-UP ABILITY] Metallic Fusion/Chaos

Recharge Time: 30 seconds
Duration: 10 seconds
Damage Output:
Direct Damage: 100 (About six shots to KO a 600HP enemy)
Edge Damage: N/A
Being his only team-up ability as of writing this post, this father-daughter duo ability allows Magneto to fire at an impressive 100 damage per second as he finally finds use in his otherwise-inadequate greatsword, adding a truly dangerous ability to his typically defensive kit. It's as though every shot taken was a Mag Cannon with a wider hitbox- however this hitbox varies from being vertical or horizontal and thus can be a little unpredictable if you aren't aiming carefully. Is used best at medium-close range, but don't neglect its potential to snipe enemies from across the map.
[ULTIMATE] Meteor M



Duration: 4 Seconds
Magnetic Range:
Lowest to the ground: 30M
Nearest to the skybox: 5M
Damage Output (No Charge):
Edge: 150 (About over half of a 250HP enemy's health bar)
Direct: 300 (About half of a 600HP enemy's health bar)
Damage Threshold Before Explosion: To be calculated, however can be tracked by the counter below the crosshair
Automatically floating into the air, Magneto stays true to his name and acts as a magnet for all incoming projectiles; extracting enemy projectiles to build the power of his metal meteor and granting Magneto the ability to float freely, Magneto's ultimate doubles both as an offensive and defensive ability. You're able to see your magnetic field + blast radius by observing the purple ring on the ground. Remember: you can rise and descend freely so long as your ultimate is up, use this wisely. I affectionately refer to the meteor as "rock", however this ultimate has garnered a reputation for not doing as much as some believe it should. Hopefully this guide helps you in ensuring your meteors make the impact they deserve.
[PASSIVE] Magnetic Descent

Manipulating the magnetic field around him, Magneto decreases his fall speed by 50% when holding the jump button. Nuff said. People have a hard time aiming up in FPS's so if you find yourself with the opportunity to float around a bit (especially using Rocket's jump pack) then by all means terrorize from above as you descend.
-----------------------
Tips and Strategy
Iron Volley + Mag Cannon Combo

A basic tip, but a valuable one nonetheless. To eliminate an enemy with 250HP- assuming you land all your shots directly- it takes about 3 seconds, four shots. Again, this is assuming you hit all your shots and if the enemy doesn't regenerate any health. Alternatively, utilizing the PRIMARY-SECONDARY-PRIMARY combo allows you to not only stun an opponent with your secondary fire, but it should take nearly half of the time spent then if you only used primary fires, so make sure to use your secondary shots responsibly. Remember that your primary fire has, at max, 25M of utility: afterwards, it won't be able to do much. Fine for picking off low-health enemies while they're fleeing, but don't expect to hit any enemies close to the skybox or far away from you without moving in a little bit first- that's what your secondary fire's for. As Magneto, your targets should be squishy characters like support and DPS. Because of his relatively-slow DPS, Magneto doesn't fair well against other tanks and shouldn't engage in 1v1's if possible (they're not unwinnable, but they could be a great distraction and leave your team vulnerable).
While I'm here, I'm just going to stress to not use your melee. Like. At all. You're much better just using your primary fire. At most you can set it up as Hulk's turning into Bruce if you'd like but that should really be it: your primary fire is much more effective than your sword.
Bubble and Shield Usage
As a tank, you want to act as a wall for your teammates, and this can be done effectively by being more conservative and selfish with your shields: you are the wall. Remember. Draw the enemy's fire towards you by being an irritant. While Magneto is healthy in shields, remember you have natural cover from stage obstacles and structures as well. Magneto can be regarded as a 'poke' tank: a tank who is meant to attack sporadically and in short bursts. He is best played at a medium distance from the enemy front line and to not to be wholly damage focused when he is much more defense focused. 'Poking' the enemy from behind structures is not only a great way to conserve your abilities, but it utilizes Magneto's primary and secondary fires well due to their moderately-slow start up and overall DPS, letting him take cover when need be.
While attacking on the front line, once you notice your health start to dip below half or you feel as though the crowd is about to overwhelm you, raise your Metallic Curtain and step back to give yourself some air. Bubble yourself as a last resort if you still need to back up- be sure to fire your Mag Cannon beforehand so you'll immediately have it replenished if your bubble pops during your escape. It's important to remember Magneto has zero movement abilities and it takes 5 seconds for him to traverse 30M: it doesn't sound too bad, but when there's a large crowd in front of you, you'll wish he could move faster. Don't push too far ahead, and be aware of exits around you.
That being said, be conscious of your teammates. This is a TEAM game after all. We've covered Magneto and Scarlet Witch's team-up ability before and how valuable it is. As a result, you'll need to learn to play well with any Scarlet Witches on your team, and this means having your bubble ready to protect her when she decides to ult (this also means making sure to check the scoreboard occasionally for your teammate's ult charge as well as, again, being ability-conscious of those around you). Only when she's in immediate danger do you bubble her, not before: this ensures the bubble lasts long enough for her to get her ult off (or there's a better chance it'll be executed, anyhow). If you feel as though you won't be able to react fast enough, then you can try to bubble her beforehand; don't stress out about timing the bubble perfectly, just make sure she's protected. In general, bubble your duelists when they're deep in a crowd to give them a chance to escape (but don't stress out about protecting them. After all, there's only so much you can do before you put yourself in danger or use a bubble inappropriately when someone else could have better benefited from it). Besides Wanda, it's naturally best to look after your support units and to make sure they're not being overwhelmed. Don't helicopter them and neglect the rest of the team, but just make sure to check on them every now and then. Ultimately, your bubble priority should be Supports -> Yourself -> Others. After all, your support/s can't help you or the team if they're dead.
Two Tanks Are Better Than One
Magneto has the fortitude to be able to tank by himself comfortably, however the rare days you find yourself partnered up with a second tank, know these are the days you can be more generous with your bubbles and shields to your teammates. Your second tank will help cover with you and should make it easier for you to escape the crowd when need be, so bubble-hogging is less of a necessity. Make sure to help your tank too if they're in a bind and they're out of defenses/movement abilities (but again, not at the detriment of yourself or your supports: once more, Magneto can tank by himself if need be so long as you use your abilities carefully).
Metallic Fusion
It's tempting to want to use Magneto and Scarlet Witch's team-up ability the second you have it, however it's best to save it for crowd control. That being said, once it is active, make the absolute most of it: there's no consequence to holding down the primary fire, so just let loose and go crazy (with reason, of course: don't run in and get yourself killed and don't forget your teammates).
How to Use Meteor M
Someone asked me this midmatch once and I scrambled to come up with an answer. Both because the round was about to start in five seconds but also because I truly didn't know the answer at the time. The longer I've played though, I think I finally have the answer- or a better one besides "spray and pray" at least. As noted before, Meteor M is a fickle ultimate and how you use it is dependent on the situation (many such cases about anything, honestly). At times, you'll want to play higher to the skybox to ensure your meteor doesn't explode immediately. Alternatively, a quick throw of the meteor might do the trick in some situations where it's both safe to build meteor charge close to the ground, and the faster you remove a target/s, the better. This is also dependent on how many projectiles are being thrown out onto the field: if you're in a situation with predominantly melee opponents, it's best to use your meteors to single-out troublesome duelists and supports- there's little chance your meteor's going to exceed 30+ charge in those kinds of matches. Generally, you'll want to use it to counter support ults like Cloak + Dagger and Luna Snow (NOTE: a raw meteor will NOT KO an ulting Luna. You need at least 30+ charge before a direct hit can KO her. Cloak + Dagger can be KO'd from the get-go with a direct hit). Don't be afraid to throw out a meteor if you see a cluster of low health/squishy enemies without any defenses, however. Just remember it's ok to hold onto an ult if it means it gets greater value later on, and that you shouldn't hunt exclusively for team wipes. If you find yourself popping ult and the crowd's dispersed, support units should be your default priority (unless there's a duelist/DPS unit using their ultimate: take them out instead if you can). Initiating Meteor against Punisher's Final Judgement can be tricky if you aren't fast enough, as Frank's ammunition will quickly push your meteor to its limit. If you don't throw your meteor fast enough, you could potentially risk your teammates their lives and waste an ultimate in the process. Use your meteor against Punisher with caution. Similar notes to be said about Star-Lord's Galactic Legend, only now your problem is also throwing at a flying enemy. If he's close enough to your 25M range, I personally would shoot him down with a regular primary/secondary as his DPS isn't nearly as grand as Punisher's and a meteor could be superfluous. Otherwise, focus on getting to cover and protecting your vulnerable teammates. You'll especially want to be wary of enemy tanks and their shields as they'll without a doubt cancel out your ult with ease, more specifically enemy Magneto's and Doctor Stranges. Be cautious that Captain America can deflect your ultimate, though I personally have had minimal trouble with Captains. In general, you should track enemy ability usage, but especially the prior two if you hope to pop your rock soon.
-----------------------
Closing Thoughts
Ultimately, improving at Marvel Rivals in general comes with time and willingness to acknowledge you're bad at the game sometimes but to not let that stop you from playing who you wanna play, whether you're playing as Magneto or not. While you can do your best to improve your aim in Rivals' practice area, things like game sense are something that can only really be accumulated through experience and playing the game.
Sometimes I watch back old games/moments of mine to figure out where I could've gone wrong to improve next time, but you don't HAVE to do that: just play the game, have fun, and love Magneto.
And throw a rock at every support you see for me okbyethankyouforreading
-----------------------
Bonus: My Credentials so you can determine if i'm reliable or not. or something.

[PS: every hero Not Mags/Wanda/Adam is purely my brother i swear im loyal]
#marvel rivals#magneto#snap chats#idk how valuable my opinion is i'm just a plat player but like Hey Its Something focus on my hours and trust me vJLAERKEAKJ#hours mean nothing if you dont learn from being balls... whatever... moving on...#i'm not checking this over i'm just throwing it into the wind no one's going to read this anyway#i thought of having more gifs to show stuff but i thought thatd be overdoing it <- this whole post is overdoing it#maybe ill pin this to the top of my blog idk. took a long time to type...#NO ONE'S GONNA READ ALL THAT WHY DID I TYPE ALL THAT#i think ive gotten enough inquiries about My Magneto Playing to finally write a semi-professional guide about it vJELKJAEKL#wrote all of this to get my PhD in Magnetism thats right baby#WHATEVER if you read all of that i love you i'm giving you a box of mochi donuts#if you take anything away from this post uhhhh Please Dont Forget Your Teammates THIS IS A TEAM GAME#ok thank you.... i hope you enjoy my. nonsense#yk im so glad my school group hates me cause i got to spend all day doing this jvLKAKJ#NO TELL ME WHY i try contacting my group last week to ask when we can meet and no one says anythign#and now people getting cross with me for us not meeting sooner... i TRIED NONE OF YALL EVER ANSWER ME#WHATEVER. whatever...#for a mfer just talking about teamwork My Team is making me want to eat gravel#anyway!!!! again if you read All That hope you enjoyed my inisght and input#again this is just from my experience playing magneto and some tank experience from overwatch so#take it how you see fit#if you guys care one of my fave rivals/ow youtubers is flats and he's always got great input for tank players#check him out if you like :)
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
My first SynthV Cover! "I H8 U!!" with Stardust Infinity!🌟
youtube
#Please be nice to me#I dont know how to tune or mix and YOU CAN TELL#Its all manual tuning and as someone with 0 prior vocal synth experience EVERYONE MAKES IT LOOK SO EASY?!?#you people are so awesome omg how do you make songs sound that good#Mixing the harmonies was so hard - i couldnt get them to sound the way i wanted#It was a nice and valuable experience though#normally i just consume but actually looking behind the curtains a bit was fun :D#Stardust#Stardust Infinity#MEDIUM5#SynthV#Synthesizer V#Eggtan#I H8 U!!#SynthV Cover#Youtube
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
i know a lot of people like to make fun of young queer people who use a bunch of microlabels and engage in niche or "cringe" aesthetics but im gonna be so honest, i love them so much. i 100% was that kid and while now i don't really use or think about any of the labels i used back then, that doesn't make that time any less valuable and valid (and it doesn't make someone less valid if they do keep using that terminology into their adult life!). queer kids who are figuring themselves out and are learning about new fun words for genders and pronouns and sexualities deserve to run wild and be loud and happy and not carry and be impacted by the shame that many of us have been taught to hold.
my cousin is a year younger than how old i was when i first realized i was queer and they've vaguely known they were queer for a couple years now. personally, i think that's pretty awesome. recently they've gotten into the very stereotypical scene kid aesthetic and i make a point to compliment them on it every time i see them. almost every time i see them they have a new adjustment as to how they view their gender/sexuality and i always tell them that that's really cool and i give them a hug. recently they told me they have a boyfriend and listed like 3 separate labels as to how he defines his gender and i asked them if i was remembering the definitions of all those words correctly (which i was because, like i said, i was that kid lol).
it's just all these small things that seem so trivial or "weird/cringe" that so many people look down on queer kids for engaging in and i'll never understand it. i think it is so unbelievably cool that these people are figuring themselves out and finding new terms and identities and things that they can be and they're just so excited by it. being excited by queerness is cool! wanting to engage in niche subcultures is cool! allowing yourself to be who you are in that moment without the worrying guilt of having to get it "right" is wonderful and awesome and cool and how it should be!! please do not teach the queer kids to be ashamed of themselves in a time where they should be able to run wild and figure out their identities in a way that truly makes them happy!!!!
#sorry for rambling but this is something im genuinely very passionate about#theres this idea of “oh theyll grow out of it”#okay and??#something something “show me a permanent state of self”#and even more infuriating is the idea of “they make the queer community look bad by having all these microlabels!!”#or “those labels/sexualities/genders arent real!"#fun fact buddy#gender and sexuality and even LANGUAGE#ISNT REAL#NONE OF ITS REAL#ITS ALL SOCIALLY CONSTRUCTED FICTIONAL CONCEPTS#IT MAKES NO SENSE TO WANT OTHER PEOPLE TO PLAY BY THESE FICTIONAL RULES YOU MADE UP FOR THESE FICTIONAL CONCEPTS#also cishet people aren't gonna respect you any more as a queer person just because you're one of the “normal” ones#and if they do. boy oh boy i have news for you.#they never respected you and your queerness in the first place#the purpose of queerness is not and never has been to be palatable#it is about being yourself and self expression and radical acceptance of the full range of human gender and sexuality#it is about finding joy in the very thing that people deem you an outcast for being#will these kids likely “grow out of it”? yes but that doesnt make their experiences any less real and true and valuable#imo queer kids exhibit one of the most true forms of queerness which is self-discovery#the way they radically embrace this thing about themselves they are largely taught to feel shame for is beautiful and commendable#we should honestly all be learning from them#and also supporting them!! this is a very crazy stage of life! let queer kids in your life know you love and support them!!#in every stage of their journey!!!#sorry ive been having a very rambly day today#but i just think about this every time i see my cousin#and i see myself in them and i know how awful i felt bc i had no one who cared/supported me in that#and i just want to make sure they have at least one person#who they know thinks theyre cool as fuck and is on their side 100%#also my cousin thinks im cool! which is crazy!! and i wouldve gone WILD if i knew that someone i thought was cool that *I* was cool!!!
18 notes
·
View notes
Text






























Magnificent Century: Sultan Suleiman & Ibrahim Pasha + Anything (requested by @ohhmichelettoohh)
+ Touch
#Muhteşem Yüzyıl#Magnificent Century#mcedit#Muhtesem Yuzyil#Ibrahim Pasha#Sultan Suleyman#Sultan Suleiman#weloveperioddrama#perioddramaedit#period drama#historical drama#request#New Home New Rules#External and Internal Shocks#The Troubled Days#Faint Hope#Huge Disappointment#The Unjust Orders#Make Way We Are Waiting for a Holy War#Know Your Place#God Forbid Anyone To Experience This#Precautions#Plan for a Plan#The Last Hope#MC 2x20#Blackmail and Its Implications#A Valuable Lesson#The Loss#Death Trap#Deceitful Truths
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
[EOA2] Years In The Future, But Not Many: Adolescence and Time in Act 2 of Homestuck
‘Stories of cultural evolution and of individual adolescent development prioritize the ending; they are primarily narratives of fulfillment.’ – Nancy Lesko (2001)
Act 2 of Homestuck takes place in a single afternoon, and also spans the whole history of life on earth, from before the Pacific Ocean formed to a post-apocalyptic wasteland. As time flashes and contorts and makes a maze of sequential storytelling, our main characters remain frozen at thirteen years old, locked in time at the end of the world. The modern teenager is culturally constructed as a person who is always waiting and preparing, running to keep up with milestones and punished for stepping outside a correct order. Teenagers’ only, and very difficult, job is to adequately prepare for adulthood – an adulthood that is always years in the future, but not many.
This essay looks at adolescence as it is theorized in society and in young adult literature, with a focus on its temporal dimension. It then applies these theories to Act 2 of Homestuck, asking to what extent Homestuck recreates, explores or subverts dominant ideas of adolescence with its characterizations and nonlinear storytelling. It’s about 8,000 words; to skip the theoretical background and just read the Homestuck analysis, Ctrl+F for ‘Paragraphs in the future…’ and read from that section onwards.
This essay is also hosted on ao3 and has a bibliography.



Background: Normal Teenagers, Normal Development
‘A child’s social, and ontological purpose is therefore, it would seem, not to stay a child… any signs of entrenchment or backtracking, like play for example, may be interpreted as indicators of a failure to ‘develop’’ – Chris Jenks (2009)
All current adults have experienced childhood and adolescence – it is ‘the only truly common experience of being human’ (Jenks). Adolescence was not theorized in academia until the late 1800s, but had a social meaning much earlier; in 1818, Isaac Taylor published Advice to the Teens, Or, Practical Help Towards the Formation of One’s Own Character at the tender age of fifty-nine. G Stanley Hall, the first scholar of adolescence, was also fifty-nine in 1904 when he characterized the teenage experience as ‘storm and stress’, a time of turbulence, mood and behavioral changes, and conflict with authority.
In this early era of research, children and adolescents were studied in terms of their deviations from the ‘normal adult’, who was explicitly characterized as a middle-class white man. Young people were seen as speedrunning all stages of human evolution before reaching this ‘enlightened’ state at the onset of adulthood; the entirety of history recreated in each individual life. Those seen as ‘further down’ the evolutionary ladder – people of color and the working class in addition to adolescents – were viewed as biologically determined, controlled by their hormones and ‘underdeveloped’ brains, making it the job of those more ‘advanced’ to restrict their behavior. In this way, minors became a marginalized group, and adolescence became a training ground. By positioning teenagers as not yet capable of rational thinking and decision making, it was easy to justify controlling them until they were ‘ready’ to be full members of society.
Modern social scientists generally believe that our idea of ‘the adolescent’ was constructed in the early 20th century, in response to specific social conditions – but many people, including parents, teachers, journalists and young adult fiction authors, retain ideas about the ‘inherent nature’ of teenagers. Science surrounding the ‘teenage brain’ is picked up by popular media and adopted as proof of a biological basis of behavior, and two studies found that preservice teachers saw their future teenage students as ‘incomplete people’. Teenagers have long been described as overly emotional, as unstable due to raging hormones, as disrespectful and rebellious towards authority, delinquents and criminals, lacking individuality, lazy and disengaged, loud and disruptive, politically inactive, hedonistic, immature, as wasting their youth and health, and as not to be taken seriously. In the 21st century, the discourse shifts slightly: teenagers are just as much of a problem, but now they are entitled, inattentive, lacking in intelligence, work ethic and critical thinking skills, reliant on technology, spending too much time indoors, self- and celebrity-obsessed, irresponsible with money, overly sensitive and nihilistic towards the future. When these beliefs are dispersed throughout society and reiterated from all angles, it is no surprise that young people internalize them, and fulfill the prophecy they are told is unavoidable.
Politically, the ‘correct’ development of young people is crucial. The youth are the future adults, and as future adults, it is crucial that they advance society in the ‘right’ direction, and continue along the same path as the current adults. Hand in hand with the idea of teenagers’ inherent nature is the idea that their future trajectory can be changed through the right guidance and the right policy. Placed in a political spotlight, young people are always the ones to be concerned about, never able to formally raise their own concerns. Teenagers are denied the right to vote in countries they will likely be citizens of for their whole lives, and if they attempt to enter political arenas, are widely disparaged with their ideas seen as unrealistic and overly radical. They should instead be waiting their turn, with the expectation that their views will become more moderate by the time they are ‘mature’ enough to guide society.
In her re-theorization of adolescence Act Your Age! A Cultural Construction of Adolescence, Nancy Lesko points out that adolescence is defined through chronological age, and therefore through time. Pointing to theories of the clock as the technology that best defines the modern age, she discusses how youth are kept to a schedule of universalized milestones. One example is age graded schools, where all students are expected to turn thirteen during the seventh grade, and to all achieve the same defined educational standard at this age. Activities such as learning to drive and entering paid work are legally prohibited until a certain age, but people are expected to do these shortly after reaching these milestones, or they will be seen as falling behind. Physical markers of puberty are expected in narrow age ranges, and teenagers are medically pathologized if their bodies mature too fast or too slow. Social development, such as the expectation that adolescents will have their first kisses and first romantic relationships in their early teens, also qualify as milestones. Placed in narrowly age-grouped environments, young people will continually compare themselves to their peers, and those who reach milestones on time are socially rewarded by each other as well as by adults.
These milestones are not end points in themselves, but simply necessary steps along a path of becoming, always focused on the adult a teenager will be. Adults are positioned as superior in society, and to develop as a child is to become more adultlike. When a young person is given increased freedom and responsibility, it is bestowed by adults with the expectation that they will make the decisions of the adult – a teenager told they no longer have a curfew is probably still expected to come home at an adult-defined ‘reasonable time’, otherwise, the curfew will likely be reinstated.
The significance of adolescent decisions and experiences are often minimized. A first heartbreak, a failure to qualify for a sports team, or a decision between two potential friend groups or two academic tracks has a major impact on a teenager’s day to day life, but adults are typically dismissive, framing the issues from their perspective – when the teen is older, they will surely realize the insignificance of this training-ground decision to the arena of real life. Future reflections are privileged over in the moment feelings.
Time, more broadly, has been theorized by philosophers in many different ways, and studies have shown that humans intuitively understand time as both linear (happening one moment after another, continuous and unstoppable) and spatial (held in memory, with moments from the past able to be recaptured and moments from the future rehearsed). Western society heavily privileges the linear view, where time is measurable, unidirectional, and correlated with progress. Once a milestone has been reached, regression is unacceptable. A teenager putting away their Lego sets to get a part time job would be criticized for quitting that job and returning to their toys, and a high school that sees a year-on-year decline in standardized test results is seen as ‘failing’, regardless of other metrics (such as students’ mental health). Individuals and societies must continue to grow and advance with time; a logic which guides our current economic system as well as previous colonial projects. The fear of a society in decline is arguably the primary driving force behind the general obsession with youth, and with the ways the current adolescent generation is inferior to the previous.
This runs contrary to real experiences of time, which involve expansion, compression, twists, circles, loss, gain, running out and having too much. Time passes faster for a fifty year old compared to a fifteen year old. It passes faster when spending time with friends than when waiting for a bus in the rain, faster when anxiously preparing for a final exam than when waiting for results with fingers crossed. Adolescence, in its entirety, passes faster for a teenager raised in poverty who helps provide income and childcare at the age of fourteen than for an upper middle class teenager given a sizable income until they leave college at twenty-two. The past is returned to, over and over again, by adults who relive their high school yearbooks, watch television shows set in high schools, and reconceptualize their own adolescence by watching their children. My personal experience of time changed radically when I took on a seven year project, and started planning for a long term future as well as a short. Time is important not only in how it is spent, but in how it is captured, preserved, and shared.
Technological developments have further changed the experience of time for people of all ages. Writing in 2008, Judy Wajcman discusses the common belief that the pace of life is speeding up, as studies have found that across the second half of the twentieth century, people subjectively experienced feeling more rushed with decreased time for leisure. Some possible explanations discussed are how mobile communication has led to people organizing their lives around blocks of time instead of physical locations, as more activities are available ‘on the go’. There are greater expectations for people to do multiple tasks simultaneously, and mobile devices allow for people to plan and coordinate their time, and therefore optimize it for maximum productivity. Communication and the search for information happen at beyond-human speeds, and time that would historically have been ‘waiting time’ becomes obsolete.
For teenagers especially, social media has changed the experience of time, with young people feeling increased pressure to post frequently, respond to messages in the moment, and record their lives. One teenager explained social media as ‘kind of like documenting your life – you can look back in ten years time, you'll have all these pictures and comments’ while another, discussing taking photographs at Madame Tussauds, suggested that ‘the images became significant after the visit when they could be used to “tell stories” to others, providing digital prompts and enabling conversation about culture’ (Manchester & Pett, 2015). As affordable cultural spaces for teenagers decline, with fewer discos, malls and parks as well as a cultural shift away from parents allowing their children to roam outside, teenagers’ use of time also changes, and young people – especially the working class – report finding themselves with nothing to do.
In contrast, some middle-class young people have the opposite problem, their lives a far cry from the ‘leisure class’ of their peers fifty years before. Some schools begin careers education in middle school, and high achieving youth with college prospects are encouraged to fill their time with extracurriculars, volunteer work and academic preparation, held up against their peers who are using their time more effectively now, and are sure to see better futures because of it. In this way, some teenagers find themselves quite literally waiting for the time to pass and the next stage of life to arrive, while others find themselves working against the clock, trying to complete all preparatory work in time for their entry into adulthood. Despite attempts at standardization, real experiences of both adolescence and time are highly variable, responsive to individual differences, social positions, and new technologies.
Background: Narratives About Youth
‘Behind every disempowered teen narrator is an empowered adult author conveying ideology about the superiority of adult norms.’ – Petrone et al. (2015)
As teenagers became a distinct marketing group, new culture industries grew up around them. The first teen movies, focused on delinquent teenage boys committing crimes due to lack of adequate parenting, were released in the 1950s. In his book The Road to Romance and Ruin: Teen Films and Youth Culture, Jon Lewis argues that via these movies, adults projected their own discontent with modern society onto the teenage characters they created. He views all narrative as ideological, as even the most rebellious and anti-establishment teen movies end up reinforcing adult authority, with characters coming to regret their deviance and ‘reform’ themselves, or being punished for their actions.
Young adult literature was slower to develop, but grew in popularity throughout the 1970s and 80s. So named because it focuses on similar themes to adult books but intended for a younger audience, young adult books can work in any genre, but focus on teenage protagonists and coming of age narratives. Whether real or fantastical, these protagonists navigate the rules and power structures of the world around them, go through some type of trial and eventually learn a lesson crucial to adulthood. It has been argued that the classical narrative is inherently adolescent, as stories by their nature deal with development and change; postmodern fiction does not always follow these rules but it is true for many works for all age groups.
Jon Lewis also discusses the ‘notion of cause and effect’ as it applies to teenagers being ‘at once a mass movement and a mass market’. Many people have argued that the ‘teenager’ was partly created by marketing industries, who, noticing young people’s increased free time and money in the 1950s, created products to fill that niche. Other scholars assert the agency of young people in creating their own subcultures, saying that teen culture arises spontaneously, with adolescents just as likely to adopt a symbol not specifically marketed to them – such as the safety pin’s role in punk culture – as to be swayed by intentional marketing.
In media, the product being sold is an identity to embody. The protagonist of a teen movie can be both relatable and aspirational – they reflect both who the viewer is, and who they want to be. A teenage protagonist is described as ‘relatable’ and ‘authentic’ if they appear to reflect experiences of actual teenagers, who are conceptualized here as a monolith. Petrone et al. point out that such an analysis would seem ridiculous if a character were described as an ‘authentic adult’. They advocate for a more nuanced discussion of ideas surrounding adolescence in fiction – a Youth Lens, which questions how literature represents adolescence, what assumptions the story makes about youth and how that frames plots and characterizations, and to what extent the text reinforces or subverts the dominant understandings. They believe this could pave the way for more varied representations of teenagers, which could positively impact young readers, as ‘writers who foreground examples of youth who do not follow conventional expectations of adolescence can shift how youth might be understood’.
Young adult literature is typically written by adult authors, capturing a reflection of teen culture instead of the reality. It is also regulated by adults – editors and publishers who decide whether a book can be marketed for young adults, and librarians and bookstore owners who decide whether to categorize it as such. Mature themes – including mental health, death, drug abuse, sex, and structural issues such as racism – do feature in young adult fiction, but there are no formal guidelines, and any book seen as ‘going too far’ is liable to be kept away from teenagers.
Writing about young adult fantastical fiction, Alison Waller shows how fantasy narratives reinforce adult norms just as much as realistic fiction; the expectations of growth on a young witch, werewolf or ‘chosen one’ are not radically different from those on real life teenagers. A common theme in dystopian and high fantasy fiction sees a teenage protagonist framed as the only hope for the future, a person prophesized to both change and save their world. Although this narrative may seem progressive as it allows for radical change, in reality these characters are generally guided by wiser adult characters who influence their decisions, and the story is not so different from the real life expectation that the next generation will save us from the problems caused by the previous.
In time travel narratives specifically, a protagonist may go back in time to a situation where they have improved agency and a subjectively better life, but by the end of the story, will voluntarily decide that returning to the present is the right thing to do. A temporary move backwards gives this character the tools they need to succeed at the next stage of life, and overall, their chronological and developmental trajectory is not disrupted. Where a secondary character chooses the past over the future, the narrative tends to treat them with anxiety, positioning them as cautionary tales or as mistakes in need of fixing.
Novels, movies and video games are typically released as completed works – the creators know how the story ends before the work is released. This may not apply to books in a series, and also does not apply to many television shows, comic books, or audio dramas. In a format such as the sitcom, the growing up narrative is complicated – a teenage character may learn a lesson about sensitivity to others’ emotions in one episode, and return to their previous self-centered ways in the next, thereby allowing ‘adolescent’ to be a primary descriptor of the character, not a state to be grown out of. Creators who are teenagers themselves, such as published British author Rachael Wing and many online writers producing fanfiction and original fiction about characters their age, also present a new paradigm. Although they may be influenced by the judgments of adults, they are still writing based on their present experiences instead of memories and observations.
The internet expands possibilities for both narratives and creators. A work posted serially online has the chance to respond in real time to a young audience, and there are far fewer restrictions on what can be posted on the internet, meaning that stories can be made accessible to young adults even if a major publisher or a parent would disapprove. As the internet itself is an ‘adolescent’ rather than a ‘mature’ medium, exploring the possibilities of the medium itself could go hand in hand with disrupting a typical coming of age narrative.
Paragraphs in the future…
‘Try not to be so linear, dear.’ (p.421)
Homestuck is written by Andrew Hussie, a former teenager who turned 30 while writing Act 2 in 2009. Its principal characters are teenagers and like most stories, it is written from memories of being a teenager and observations of what teenagers are like today. Its first act is entirely linear, but Act 2 begins to explore time, continuity, and cause and effect. Readers can no longer assume that a page takes place after its preceding page, and the main characters – John, Rose, Dave and the Wayward Vagabond – all exist at different points along the timeline.
I believe that Act 2 represents time as it is actually experienced by teenagers, where growth and personal development are not always linear and not always in sync with that of others. John, Rose and Dave are all growing up in the 2000s USA, and are all subject to roughly the same cultural expectations as described in the earlier sections, just as the overall work is written in that context. Looking at each character in turn, I will discuss to what extent they conform to dominant conceptions of ‘the teenager’ and how they experience time within the narrative, with a view to asking whether Homestuck could offer a new understanding of adolescence.
John Egbert
‘And even meanerwhile, in the present. Sort of. Once again, the slippery antagonist eludes you.’ (p.385)
As the principal character and the first introduced, John’s time is arbitrarily defined as ‘the present’ – pages 334 and 385 both say as such. However, at the end of act 1, John is transported to a ‘realm untouched by the flow of time’ (p.421) and while time continues to pass for him, it’s not necessarily in step with Earth time, indicated by the ??:?? timestamps on his Pesterlogs. As such, John’s ‘normal’ development has been stalled on the day he becomes a teenager, and he’s locked off from the future of his society.
For John, time and space are linked. Although he has been removed from time and therefore from normal expectations, he’s still stuck in his house, the one piece of his culture that he brought with him. The picture John’s dad pinned to the fridge and the green slime pogo ride John continues to define himself by in this act both keep him tied to his childhood. While he’s here, John can’t escape a multitude of authority figures. His dad has been kidnapped, but still leaves notes around the house congratulating John on his maturity – ‘You are strong enough to lift the safe. You are now a man… I know you will take this responsibility seriously’ (p.546).
With Dad gone, Nannasprite steps in, having not seen John since he was very young. She restores John’s bedroom door to its hinges and restores the family order in the house, giving advice, controlling what John knows, and baking unprecedented amounts of cookies. Nannasprite calls John a ‘good boy’ (p.428), and the Wayward Vagabond’s first command to John is ‘BOY.’ (p.252), a word with assumptions about both John’s gender and current stage of life. Rose and WV also have guardianlike roles over John, able to control how he spends his time.
John is younger than Rose and Dave by a few months, but retains far more childlike qualities. His priorities lean towards play and silliness, as shown when he captchalogues shaving cream in case he suddenly needs to make a Santa beard (p.488) or makes a tent out of cruxite dowels (p.615), and he isn’t in any hurry to reach the signifiers of adulthood, such as shaving (p.544) or taking personal responsibility (p.643). The trait John most shares with the stereotypical teenager is poor emotional regulation – both his excitement and his frustration are obvious on his face and regularly interfere with his behavior (for example, p.429, p.637).
He passes the time instead of using the time, and is easily swayed by his peers. He has a drive for autonomy and self preservation, and will attempt to stand up for himself, but usually ends up deferring to the authority of his friends or guardians. He’s not very self-motivated except when it comes to putting bunnies back in boxes, and he enjoys consuming media, not all of which is age-appropriate – three of the movies on his wall are R-rated, including Con Air. He also plays popular video games and buys media merchandise such as T-shirts and posters, so falls into a mainstream youth marketing demographic.
As a prophesized savior positioned to undertake a hero’s journey, John is a classic young adult protagonist. He demonstrates the idea that the youth are our only hope, though they still require guidance from previous generations and are defined by their opposition to adulthood (seen through Nannasprite’s presence). However, despite Skaia influencing Earth since before life itself existed (p.757), it wasn’t until its power was harnessed into a video game that it began to threaten the world – youth’s popular culture is the thing that sends us all into decline, even if that culture was created and marketed by adults.
The earth already being ‘done for’ (p.427) allows for a subversion of the typical progress narrative. Page 757 indicates that Sburb may be influenced by ancient technology from outside of Earth, The end goal is not known, making John’s narrative defined by the journey and not by the ending, highlighting adolescence as a meaningful experience in and of itself, not only because of where it leads. And Sburb is already poking fun at John’s culture – the echeladder (p.405) parodies the milestone progression of youth, filled with meaningless and generic titles placed in an arbitrary order.
John’s destiny to ascend through the Seven Gates to Skaia, fighting with the light kingdom and attempting to overcome the dark forces’ destined win, could be read as an ascension from childhood to adulthood. John would be moving away from the sinful childlike state where young people are ruled by their base instincts of hunger, sleep, hormones and emotions, towards a rational and enlightened adulthood. But an inversion of this metaphor would work, too. John could move away from his culture’s ideal adult that he’s been told he’ll become – a person who is cynical, conformist, an obedient worker, driven by money and personal success – back towards the childlike state, retaining the open-mindedness, sense of whimsy and possibility, and creativity of childhood. Earth is done for, and so there’s no reason John should still be tied to the linear march of the culture he came from. He is perfectly positioned to imagine a new paradigm of adolescence, if he can break away from the ties – his house and his guardians – that try to tie him down to the ‘old ways’.
Rose Lalonde
‘To hear his mammoth belly gurgle is to know the Epoch of Joy has come to an abrupt end.’ (p.302)
In the narrative, Rose’s time is defined as the near future. Although her story directly overlaps with John’s, putting them at the same point in time, Rose is three timezones ahead and refers to other timezones as ‘younger’ (p.174). It’s night time for her, which visually distinguishes her panels and gives her story a more adult atmosphere. She is future oriented and proactive, planning for the next thing, and typically portrayed as one step ahead of John.
Rose has experienced the passage of time quickly, and has not had the luxury of lingering in childhood as John has. With a mother who is inattentive towards raising her and communicates through daily arguments (p.389) and ‘notes’ on the fridge (p.366), Rose likely had to develop independence and adult traits at a young age. She would be considered ‘precocious’, a word typically carrying a negative or judgmental tone describing a young person whose achievements or inclinations are happening ‘too soon’. In the narrative, Rose is continually running out of time, watching the battery on her laptop slowly drain and the forest fire surrounding her house creep closer. This anxiety of something yet to come positions Rose as a teenager who is awaiting the future and making use of every possible moment to prepare for it.
Educationally, she has a larger vocabulary than the average person her age, and likely a higher reading level. Practically, she understands construction and generator safety, has a good grasp of modern technology such as computers as well as classic skills such as knitting, and the hand eye coordination to do these things well. She demonstrates abstract and critical thinking, and attempts – with varying levels of success – to understand the consequences of her actions. She shows an understanding of a world greater than herself when she wishes Jaspers had been allowed to decompose (p.414) and avoids allocating her grimoire to her strife specibus (p.297). Despite being raised by a rich mother, she enjoys a challenge and is willing to work hard, rejecting childlike wish-fulfillment fantasies such as princesses and wizards.
Rose is a teenager who attempts to fill her time with activities she sees as productive and as bettering her as a person. She has internalized adult values and would prefer to get there too soon than be left behind, and she works hard to define herself through timeless, sophisticated hobbies such as literature, knitting and the violin, generally resisting mass culture that would be typically marketed to teens; unlike John she disrupts the idea of the teenager as mindless consumer or as defined by her peers’ interests. She tries to avoid juvenile behavior and scorns it in others (p.249) and is very attuned to cultural expectations, feeling a nebulous pair of eyes upon her judging the appropriateness of her actions, which affects her decisions (p.370), almost as if she is trying to skip the complicated, messy parts of being a modern teenager and move directly from childhood into rational adulthood.
It’s rare for Rose to regress into childlike behavior, such as the ‘W’ mustache (p.370) and the Youth Roll (p.379), and she usually ends up regretting or correcting the behavior afterwards (p.398, p.380). Her disdain for her mother suggests that she is self-correcting and trying to parent herself in response to these ‘slips’. Notably on page 440, Rose works on her GameFAQs, which are intended as an informative guide to future players. Accidentally slipping into a frustrated and self-berating personal anecdote, she strikes out the passage and again criticizes her own regression, which is immediately followed by a narrative shift into Rose’s actual past.
Rose struggles with patience, and with waiting for other people to catch up to her. She understands the seriousness of her situation; for her adolescence is a time of survival, her decisions now liable to affect her entire future. Act 2’s title, ‘Raise of the Conductor’s Baton’, appears in the text in relation to Rose - ‘Somewhere a zealous god threads these strings between the clouds and the earth, preparing for a symphony it fears impossible to play. And so it threads on, and on, delaying the raise of the conductor's baton’ (p.307). This certainly links to Rose’s experience of time, her living in expectant mode for a terrifying, looming future.
Primarily Rose strives for the ‘positive’ markers of adulthood, such as responsibility and educational attainment, but she also tries to be casual regarding sex, such as claiming to enjoy Dave’s bro’s websites (p.419). The only markers of adulthood she openly rejects are alcohol and domestic chores, both of which the text associates with Rose’s mother, who Rose views as a cautionary tale and the ‘wrong’ kind of adult. Through Rose’s relationship with her mother, there is space to question the idea put forward by other media that teenagers become dangers to society through poor parental oversight; Rose is certainly a rebellious and anti-authority teen, but her ‘rebellion’ consists of asserting her own capability and responsibility, such as turning down alcohol in favor of water (p.388).
Rose sees herself as the more responsible of the two of them, but it remains uncertain whether the narrative will legitimize this. By being positioned in a guardianlike role over John she disrupts the typical adult-youth dynamic, and is given a chance to prove her chesslike skills of thinking several steps ahead while staying responsive to new information, evidenced by her GameFAQ updates. However, in the final page of the act, Rose’s ability to manage her own life reaches its limits, and it is her mother who saves her by opening a secret passage, having apparently planned for this all along. Here Rose’s independence is taken from her and she is once again the teenager who needs a firm guiding hand, despite apparently working much harder than her mother. This reinforces a typical authority structure and is dismissive of Rose’s legitimate problems with her mother, as despite her flaws she is still a necessary figure in Rose’s life.
In future acts, Rose’s character arc could go multiple ways, particularly once she enters the Medium and is presumably separated from her mother. The story could legitimize her drive to grow up at a young age and allow her to take on a leadership role that she does seem well positioned for, given her ability to keep a clear head and solve problems in real time. In this narrative, Rose would not be punished or put back in her ‘rightful place’ for speeding through time, instead, her early development would allow her to be valuable to the group, and to challenge herself in ways a thirteen-year-old would not have access to in the real world. Alternatively, Rose could have an arc that allows her to go ‘back in time’ and reclaim her more youthful traits, taking on some of John’s silliness, handing over responsibility or making bad and uninformed decisions when in a new context, for example when she becomes a client player. This could also be subversive if returning from a more adultlike to a more childlike state is portrayed as a valid and meaningful journey in its own right, instead of as someone who grew up too fast returning to their ‘correct’ place in time.
Dave Strider
‘You just don’t have time for this bullshit. You’ll catch up later.’ (p.332)
Dave’s narrative time is defined as the past. His story begins on page 308, at the same moment where John’s story began on page 1. John and Rose are several hours ahead of him by now, and Dave’s storyline is constantly racing to catch up. Like any teen looking around and watching their peers maturing physically and socially while they fail to keep up, Dave is always missing information and excluded from his friends’ activities. The narrator makes sly references to Dave being in the past and unaware of what’s to come (p.314) like a nagging thought in the back of his head, and in every page, he has the relic of a five-year-old movie stamped on his face.
In reality, Dave is not failing to meet developmental milestones – quite the opposite. In a world where the athletic achievement of young men is prized and adults are expected to be in control of their own bodies, Dave is physically fit with quick reflexes, able to fight, jump, dodge and perform an ‘acrobatic fucking pirouette’ (p.579, p.665), even without regular access to food. The original, early 20th century Boy Scouts prepared boys for military service primarily through obedience, a sense of duty, and personal responsibility towards physical development; Dave’s brother with his strict sword-training and Saw trap regime is instilling similar values.
Dave does participate in mainstream culture, evidenced by his regular reading of GameBro and his desire to be ‘cool’ and to like the same things as his brother – but he’s not only a consumer of culture, he’s also a producer. He writes a blog, ostensibly on a regular schedule, and produces a webcomic, combining creative and analytical pursuits. He regularly refers to himself as ‘busy’ (p.309, etc) and says he ‘doesn’t have time’ for things (p.310, 332), has ‘a lot on [his] plate’ (p.333), and that it’s ‘hard to get any work done’ (p.381). Dave sees his internet projects as work, as commitments he needs to make time for, and he’s not afraid to push back against the player’s commands if he thinks they wouldn’t be a good use of his time.
He has the Complete Bullshit desktop application and keeps up with his brother’s projects, and likely other internet culture too, to stay on the cutting edge of irony that he prides himself on. It seems like Dave’s time is largely full and he struggles to fit everything in. He is very aware of the constantly changing, modern society that he lives in and wants to stay on the pulse of these changes. Less than six months after Obama’s election, a black president is no longer noteworthy to Dave (p.287), and he creates remixes with electronic samplers instead of playing classical instruments like his friends. He’s always online and always keeping in real time contact with his friends; he ‘pesters [Rose] like clockwork’ (p.415). Trying to keep the beat of an ever-shifting internet meme culture to stay cool and avoid being outdated at all costs is exhausting, and it’s no wonder Dave sometimes struggles to keep up.
Living in the city, a place where the pace of life is quickest, in a time of rapid technological and cultural change already creates a ‘racing against the clock’ mindset, and Dave’s relationship with his brother compounds this. By modeling himself on Jigsaw, a villain who created complex, physically violent traps with strict time limits, he forces Dave to be constantly on guard, constantly expecting the next danger, yet often a moment too late for it, behaving like an intense ‘no pain, no gain’ style sports coach. On the surface, Dave’s sunglasses, frown and monosyllables look like a rebellious teen movie protagonist, but beneath that, Dave best corresponds to a real life high achieving teenager who is put under pressure to achieve even more by the adults around them.
Dave’s story so far has focused on the ‘campaign of one-upmanship’ between himself and his brother as he fights for his brother’s Sburb game discs – his brother is an obstacle to both his plot development and his emotional development (for example, admitting that he’s uncomfortable with his brother’s hobbies). This is likely setting up a ‘loss of innocence’ story, where Dave has to come to terms with harsh realities of the adult world by recognizing that an authority figure is imperfect. This is a fairly typical growing up narrative that does not disrupt conventional ideas of linear growth, as the adult world is widely seen as darker, more serious, and something young people need to be protected from.
However, I think Dave’s status as a subcultural producer places him outside a typical youth/adult binary. Dave is not overall presented as adultlike, as he follows trends and is fully subservient to the adult in his life, and his hobbies – Sweet Bro and Hella Jeff, sweet bro’s hella blog, and remixing music – don’t place him on a typical path to adulthood. By establishing that Dave sees these as responsibilities, and as things he creates for a real audience of at minimum four people and potentially many more, Dave’s teenage experiences and creations are given importance without needing to be legitimated by adults (such as the narrator or his brother).
Dave’s self-motivation when it comes to his creative pursuits also disrupts ideas of teenagers as lazy or needing to be shaped by outside forces; he’s capable of sticking to a self-imposed schedule. However, his creative drive is part of a real-time responsiveness to internet culture – if he is taken to the Medium, outside the normal progression of time, would he be able to maintain this? An arc that focuses on Dave as a creator instead of Dave as a soldier could do more to complicate a typical youth narrative.
Wayward Vagabond
‘The APPEARIFIER cannot appearify something if it will create a TIME PARADOX’. (p.752)
The Wayward Vagabond is not a human adolescent, and does not come from the same culture as John, Rose and Dave – they discover the concepts of ‘cutlery’ and ‘politeness’ in Act 2, so are a long way from internalizing age-based ideals. As such, although WV exists in the future – their story taking place 413 years after the human characters’ – they are not more advanced, or more adult, than the others.
Alone in a wasteland and free from social influences, WV does not regulate their eating, is described as physically weak, expresses black and white opinions on governance, and loses track of time playing pretend games. At the same time, they show a good understanding of art, chess strategy and precise movements and distances. They pick up social and technological skills quickly and are very attuned to positions in space (p.743), but far less attuned to positions in time (p.755). Many of their actions are similarly nonsensical to John’s, and these moments of whimsy frame WV as childlike.
However, WV has a privileged position in time. Not only are they in the future, but they have the technology to experiment with temporal mechanics. Through a set of screens they are able to look back at and directly influence events from the past; they have authority over at least one young person, and can appearify objects from other points in time.
Being an adult and a child at the same time feels like a time paradox to us, just as appearifying a rotten pumpkin they ate earlier is a time paradox to WV. Having authority over a young person who, if he continued to grow in linear time, would be long dead by the time WV enters the bunker is also a paradox of normal development. By mixing childlike and adultlike traits, WV draws attention to the way roles in society are socially mediated and may not exist outside of their cultural moment. By living in a post-apocalyptic wasteland where advanced technology is lost to the ravages of nature, WV represents a type of person who could live in the future if the world does not follow a path of strict linear progress, but simply of change.
The appearifier and command station in WV’s bunker fundamentally change the function of time in the narrative. Although WV’s mastery of time is limited by the need to avoid paradoxes, if characters take actions to influence or improve the past, they disrupt the norm of future orientation and give equal importance to the past. Indeed, the pages titled ‘Years in the future…’ are not presented as the desirable end goal of the narrative, nor are they a terrible fate to be avoided. They are interesting asides to the story, but they are asides, with the bulk of them taking place in pages hosted outside of the main story. The story structure lets the past and present be centered in themselves, not just through their leading to the future.
The Narrator
‘Maybe you could go bug someone somewhere else for a while? Or at the very least, somewhen else.’ (p.440)
The position of any given Homestuck page within the timeline is uncertain until established by the narrator, who regularly exercises their power to shift back and forth, and to conceal these movements until the player has made a fool of themself. In this way, the narrator is positioned as an adult with perfect knowledge of the timeline, viewing adolescence in its totality. They have transcended the limitations of adolescence and have moved onto a real and meaningful time of life, and will occasionally reference their superior knowledge of future events with winks to the audience while keeping characters out of the loop – ‘you can’t imagine how a video game could save someone’s life’ (p.314) or ‘only… babies who poop in their diapers believe in [monsters]’ (p.387).
However, moments of the narrator criticizing or speaking condescendingly to the teenage characters is surprisingly rare. It happens occasionally, like with ‘This is COMPLETE BULLSHIT.’ (p.458) or ‘The circle of stupidity is complete’ (p.490) but the vast majority of narrative criticism is directed towards the Wayward Vagabond, the only character the narrator regularly speaks directly to. The narrator calls WV stupid on multiple occasions (for example, p.437, p.746), and tells them to defer to Rose’s decision making (p.277), but the majority of narrative text criticizing the kids’ behavior is actually just reporting their own thoughts, either towards themselves – ‘It seems the woman has you at a clear disadvantage’ (p.373) – or towards each other, such as ‘What the hell is that nincompoop doing?’ (p.508). When a command would lead to a bad decision, it’s generally the character who refutes it, not the narrator (p.489). In this way, although the narrator does have superior knowledge, they give center stage to adolescent perspectives.
Implicitly, the narrator controls the flow of time in the story – deciding who to switch to and in what moment of their story, allowing characters to speak or moving focus away from them – and the narrator is willing to indulge the characters in their non-plot critical diversions, rarely hurrying them along when they take extended time to read books or rearrange their sylladex, but allowing the minutiae of their experiences to matter. The narrator lists characters’ interests without judgment – adult characters are interested in clowns, wizards, puppets and sugary foods, while adolescent characters are interested in computer programming, knitting and specimen preservation, with no clear line on ‘acceptable’ interests for a given age group.
Zooming out a layer, Act 2 posits the idea of John, Rose and Dave’s stories available for viewing through a screen, four hundred and thirteen years in the future. As well as reflecting the existence of the webcomic itself, this contrasts the idea of adolescence as a transient state. The 13-year-old versions of these characters are frozen in time on the Wayward Vagabond’s screen. Born in the mid-1990s, these characters are among the first to grow up with social media, and with an internet moving away from anonymity. Their lives being recorded on the command terminal, in Rose’s GameFAQ screenshots (p.510) and in Bro’s Jigsaw puppet (p.570) are not a million miles from the teenagers documenting each other’s lives on Facebook in 2009 – and at the time of Act 2’s writing, it’s not yet certain what the real world impacts of this will be on current young people’s experiences of time.
Conclusion
‘Temporal movement into the future is understood as linear, uni-directional, and able to be separated from the present and the past… a conception of growth and change as recursive, as occurring over and over again as we move into new situations, would reorient us.’ - Nancy Lesko (2001)
Written in 2009, Homestuck carries the baggage of over a hundred years of public discourse around the teenager. Adulthood is seen as the most important stage of life, with teenagers as flawed, incomplete versions who need to be corrected before reaching the end goal of conventional adult society through conforming to a series of linear milestones. The expected development of real teenagers is reflected in the stories told about them, which focus on characters ‘coming of age’ and successfully internalizing adult norms.
By introducing nonlinear storytelling in Act 2, Homestuck represents time as teenagers actually experience it, which gives the comic a chance to explore and question dominant ideas of adolescence and adolescent time. John and Rose have relationships with guardian figures, including the narrator, that reinforce adult superiority, and all three kids have communication breakdowns between themselves and their guardians – but the skills and interests of teenagers are also given importance, and adults are not exempt from narrative criticism. The narrator is happy to indulge the teenagers just as often as to correct them.
The end of Act 2 positions Sburb as an organic entity of sorts, not necessarily created by adults in universe. Sburb encourages linear gameplay with progression up the Echeladder and through the Seven Gates, but the Medium’s position outside of time, and the fact that restoring the Earth is not the game’s goal, allow for narratives of change that are not necessarily narratives of progress, as the characters’ future in rational adult society no longer exists. The comic’s focus on creativity – both the potential of Skaia and with Dave’s role as an artist – means the story could focus on the importance of not losing childlike traits along the path to adulthood.
The narrative structure allows teenage characters to be nonlinear, to move between past and future moments, to experience sudden growth and moments of regression, to overtake their friends and then fall behind. The real-time nature of Homestuck’s creation allows readers to linger in the characters’ day to day moments and to experience their present alongside them, instead of tightly focusing on their plot development, and the reader submitted commands central to Act 2 mean that real life teenagers likely contributed to their own story. Homestuck is still early on in its story, but has already laid the groundwork for a novel conceptualization of time, and therefore an understanding of adolescence as more than just its ending.
#eoa2#milestone#analysis#homestuck#to be honest i think i aimed too high with this and that what i wanted to do here is beyond what im currently capable of#but it was a very valuable experience! and i hope to work on these skills over the next couple years#and to look back at this and see lots of improvement over time!#i do also think theres a lot of good in the bones of this even if the execution isnt great! and so its still important to post :)#chrono
32 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is how I feel in most transmasc spaces.
#butchy babbles#trans ftm#trans man#transmasc#trans masc#transmasculine#transman#transgender#trans#tboy#tman#trans male#PLEASE do not get the wrong idea from this. i'm not saying that transmascs who're boys are inherently less valuable or more annoying -#or ect. than transmascs who're men. all i'm saying is that there's a lot of emphasis on boyhood in the general transmasc community and as a-#fat hairy man that doesn't resonate with me! i personally feel like i went from being a girl to a man. i was never a boy#that's my own personal experience with gender and THAT DOES NOT MEAN I THINK LESSER OF TBOYS. I'M JUST NOT ONE OF THEM.
46 notes
·
View notes
Note
May I request happy man and green monster being sappy? I have loved that ship since I was little lmao
yup

#ratboy genius#fanart#green monster#happyman#shipping#ship art#I never draw kissing stuff so this has been a valuable learning experience
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
I cannot think of a worse or less productive argument for me to try and get into than discussing anti-intellectualism with online academics.
#i am in support of like critical thinking#and checking sources#and being open to being wrong#and asking questions#but when they fight about people who dont have degrees in a subject trying to say their education is just as good?#its like#i dont know man they wont likely get very far career wise if theyre genuinely unfounded in their expertise#and like yeah it can be an arrogant argument to make#but uh i think my expertise is about as valuable as soneone with a technical writing degree and no work experience#at this point i no longer plan to go back to school unless i decide to change industries#because i have enough work experience to allow me to continue in my industry#and if someones wrong why not suggest studies or books if theyre super into the subject?#they might say no?#yeah man i dont know that seems frustrating but generally probably fine#i dont know man#i see people acting like someone will talk their way into doing surgery becusse its their Special Interest#and uh#yeah i dont know i actually dont think theyd get that far and still know nothing about surgery
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
so many things are like. i can't tell if everyone around me is acting and exaggerating or if they're serious. i just don't experience any of what they're describing. every description of "love" just ends up confusing me, i never had "dreams" for the future, i don't reminisce on happy memories. am i just an outlier empty husk of a human or am i taking people too literally and they're being metaphorical or something???
#i like watching video essays and just. it sounds like people's relationship to media is so much richer than mine?#like people remember their first time playing a game or watching something???#and those memories are valuable to them???#i don't remember any of that stuff. it's never important to me#ill recall the content fine. but my reaction? what i felt? no idea#and i.... never really feel the urge to soak in atmosphere or anything#games are a series of tasks rather than an experience to immerse myself in
9 notes
·
View notes