#green policies. London
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
There's so much pollution in the air now that if it weren't for our lungs there'd be no place to put it all. (Robert Orben)
This week saw Keir Starmer’s keynote speech on education being interrupted by environmentalists protesting against him abandoning his previous £28billion commitment to a green prosperity programme.
“Green protesters interrupt Starmer's big education speech with demand for 'no more U-turns' (skynews: 06/07/23)
They didn’t succeed.
Only a day later Keir Starmer said it was “right" for the Labour candidate fighting the Uxbridge bye-election, to raise concerns about Sadiq Khan's plans to extend the ultra low emissions zone (ULEZ) to outer London.
Apparently, now is “not the right time” for this policy.
When is the right time Sir Keir? After more children die from the polluted air they breathe?
“Air pollution a cause in girl's death, coroner rules in landmark case." (Guardian: 16/12/20)
Following this tragic case, a study found that:
“Almost every London school is in an area where air pollution levels exceed World Health Organization limits" (BBC News: 16/08/21)
The fact that in outer London, an area not covered by ULEZ, there are 4000 premature deaths a year caused by air pollution doesn’t seem to bother Sir Keir.
Despite the fact that Professor Chris Whitty, England’s Chief Medical Officer highlighted the SUCCESS of Sadiq Khan’s ULEZ policy in reducing the air pollution within inner London, Sir Keir doesn’t want the scheme extended.
Sir Keir, who earlier in the week admitted that Sadiq Khan as London Mayor, had a “legal obligation" to cut air pollution, was clearly reluctant to give his open support to the scheme. For Sir Keir the ONLY goal worth pursuing is his own ambition of becoming Prime Minister. The expansion of ULEZ to the boroughs of outer London is not popular among voters, despite its obvious and proven health benefits, and in the outer London borough of Uxbridge and Ruislip, a bye-election is being fought.
Sir Keir want to win this bye-election and if that means not actively supporting the Labour Mayor in his bid to improve air quality for ALL Londoners, then so be it. Who cares if ULEZ saves lives? Who cares if England’s Chief Medical Officer supports its expansion? Who cares if it is the children of the poor who suffer disproportionately from poisoned air?
Not Sir Keir – all he cares about is being elected.
#uk politics#moral bankruptcy#keir starmer#unbridled ambition#air pollution#elections#broken promises#green policies. London#sadiq khan
1 note
·
View note
Text
some of my favorite Stupendium lyrics, in no particular order
"Haters green with envy, call that verdigris burns" (Adequate Wordsmith)
"Was the apocalypse your politician's policy?" (The House Always Wins)
"I am psych-i-opathic as I am homeo-cidal" (Losing My Patients)
"Tried to earn an honest bob, but a Bob is just a Robert, and a Robert's just a robber to a T" (NEATH! A Fallen London Musical)
"This train's not just cancelled, it's damn well deplatformed" (The End of the Line)
"It's easy to cut out the middleman when he's cut out most of himself" (The Data Stream)
"I don't want to set the world on fire, but your house will do just fine" (Vault Number 76)
"I play a Q or a Z like a symphony, giving you 'quixotry,' 'quartzy' or 'syzygy'--" "Wizardry!" (Chairman of the Board)
"If music's the food of love, then I'm serving it heavily diced" (Impossible Geometry)
"Burn the incense of our innocence, and in a sense, we thrive" (Shelter From the Storm)
that one bit from "The Fine Print," I don't even need to quote it
74 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two million hectares of public land have been sold off since the 1970s, including NHS sites, valuable holdings in towns, and agricultural land put up for sale to fund cash-strapped councils. In the process, benefits formerly enjoyed by ordinary citizens have been sacrificed and new obstacles have been created for any programme of environmental renewal. In London and other major cities, where global capital has been flooding in to transform urban space, uprooting older communities and providing ‘deposit-box’ properties for the ultra-rich, reclaiming control will demand outright opposition to neo-liberal development policies. The same is true if we are to resist the spread of so-called ‘POPS’ (privately owned public spaces) that has come about as municipal planners have come under economic pressure to cede control to private developers, in what some academics regard as an era of ‘urban enclosure’ comparable to the rural enclosures of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Most criticism of these ‘pseudo-public’ spaces has been directed at the secrecy of their regulations on public use, their socially hygienic forms of policing or their corporate aesthetic. But their removal from public ownership also complicates the spatial and architectural conversions essential to the green renaissance of city life, and needs to be denounced on those grounds and reversed wherever possible.
Kate Soper, Post-Growth Living: For an Alternative Hedonism
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
HI MY FRENCHIES FROM THE 3RD CIRCUMSCRIPTION OF FRENCH PEOPLE ABROAD aka my French residents of Northern Europe and especially London: (and my English speaking followers who'd like to French elections drama)
Macron's candidate, Vincent Caure, is blatantly lying on his program about his opponent's party, the NFP, which feels very dishonest and, frankly, kind of pathetic? I know Frenchies in London voted a lot for him but PLEASE let's not let a liar get ahead of the race.
He claims the NFP - a coalition of green and leftist parties - will have Mélenchon as Prime Minister. For some reason, the French media is OBSESSED with making Mélanchon (the leader of a prominent leftist party) THE DEVIL. Look. I know some people don't like Mélenchon even on the left. But he's NOT EVEN PART OF THIS ELECTION. Besties: he's not a candidate anywhere. And even less for French people abroad. And even worse: the NFP has NEVER said who they'd send as Prime Minister if they get the majority in the assembly. This is FAKE.
He pretends French people abroad will be doubly taxed because of the NFP wants to put back the "exit tax", and that the NFP is obsessed with the universal tax (aka paying taxes for your country even when you work abroad). The exit tax is a specific tax that affects only people who own A LOT in assets. I have no idea how to even reach to that kind of criteria. I don't think neither me nor any of the French people I know in Dublin have the assets required to have to pay the exit tax. I wish I had that amount of money so I could get taxed on it! Alas, Vincent Caure and I don't live in the same world because it's not even remotely a worry for me. As for the universal tax, it's nowhere in the NFP's program so I guess they're not as obsessed with it as Vincent claim they are.
He offers to put more procedures online such as passpot renewal online whereas the NFP offers nothing. Ok slay king, then run your campaign on that instead of telling lies. Unless this is your only good point?
He claims that the NFP wants to end nuclear energy, which would make us depend on Russian gas. Nowhere is this written on the NFP program. There are only 4 mentions of the word "nuclear" in the NFP program and none of it is associated to the word "stop" or "end", half of them are not even about nuclear energy itself... I don't see where he got that from.
He does agree that the NFP wants to make railways more accessible but argue that they didn't vote for a law making mobility within France easier. Fair! He forgets to mention most of the supporters of this law were his party only and BOTH LEFT AND RIGHT voted against, citing lack of funding for this law as an issue, that the Prime Minister back then brushed away, so take that what you will. Also want to note his only point for this program is that they're going to use the funding for transport that they already have so... ok good? that's not revolutionary. That's just expected.
He also claims that:
the left is the one who led to the far right taking the lead when it's his own party who called for an election. Like. The move no one expected nor wanted except the far right. That was all Macron. That was all your party. You guys flirted so much with the far right that you led them right in, that is NOT the left's fault and even less your favorite scapegoat, Jean-Luc Mélenchon - who, I'd like to remind everyone, is not a candidate for this election oh my god shut up about Mélenchon already I don't care about Mélenchon why are you obsessed with Mélenchon
The left wants a Frexit because of their tax policies (debunked above) and nuclear energy policies (also debunked above). The left is notoriously pro-EU, his opponent is a British-French citizen who probably saw the shitshow of Brexit from the front rows. And even if the left wants to tax VERY rich people trying to avoid being taxed on their huge assets out of France (fun fact: it's for the people who try and get their assets moved to Dubai not to pay taxes on them lmao) and wanted to reduce the use of nuclear energy, that does not equate Frexit, like, I... I don't see the correlation.
The left is planning for 300 billion more expenses and intends to cover for those expenses by taxing people the most. The thing he's not saying is that they intend to tax the richest. It's the rich the target. The very VERY rich. Not you, regular French immigrant to Ireland who struggles with the cost of life in Dublin and cry for a better flat.
ALL IN ALL: Vincent Caure is a liar who ment comme un arracheur de dent et fait sa campagne dessus, ce qui est un peu dégueu.
He cries about potential taxes that would only affect a very, very tiny minority of French people who were probably trying to evade said taxes anyway and tries to frame it as "double taxing French people abroad"
The left wants to tax the rich and good for them and good for us who are not playing in the targeted tax bracket AT ALL.
Macron's party is the one who's fucked us all over; Attal is a notoriously impopular Prime Minister; they're a party for the rich (as proven above by trying to act as if a tax on the rich was gonna be a double tax for everyone like... lmao how out of touch are you) and love to frame themselves as the only right solution QUAND C'EST EUX QUI NOUS ONT MIS DANS LA MERDE
As with the rest of his party, he's obsessed with Mélenchon, who has nothing to do with this specific election since the opposition is initially from the Green Party.
SVP SI VOUS ÊTES DANS LA 3E CIRCONSCRIPTION DES FRANÇAIS À L'ÉTRANGER, VOTEZ CHARLOTTE MINVIELLE AU MOINS POUR NE PAS ÊTRE REPRÉSENTÉ PAR UN CANDIDAT QUI VOUS MENT SANS HONTE POUR AVOIR DES VOTES
and for my English speaking friends: please pray for us all (at least here the far right is not gonna pass but I'd rather not have such a liar for deputee please and thank you)
ET COMME TOUJOURS, ON EMMERDE LE FRONT NATIONAL!
#french stuff#upthebaguette#french#french elections#politiks#sorry i'm just petty like that#if there's one thing i hate it's shameless hypocritical liars#running your campaign on spreading misinfo and smearing your opponent's program is NOT A GOOD LOOK#so i'm petty. and annoyed. and i shall tumblr about it.#is this anything? i don't know#i just got tremendously annoyed#and since i don't need to fight against the far right since it didn't make it to the second turn in our circumscription#i'll be petty against the rich people party
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Magnus Protocol 25 - the one I incorrectly thought was labeled Gorging/Incest at first glance, so at least there isn't that.
Saying a quick prayer that it's not plant people, I need a longer break from plant people
Whoop Celia has been yoinked onto some random roadside again. ... Though. Why does she always have her phone? Is it like the tape recorders? Is it because it's a listening device and whatever it is that's listening in is also doing the yoinking?
'That's why we're being safe' Sam. Sam, you are being the opposite of safe or subtle. But go off, shrimp king.
Sam and Alice laughing together, that's nice. I doubt we'll get to keep it, but that's nice.
The editor's complaining voice is very much pissy!Martin Blackwwood and I have missed it so omg I need to go re-listen to some Magnus Archives where Martin is letting someone have it.
Ominous violin music while describing the alleyway does not suggest good things are coming in this diner, no.
Tragically, the 'Green Pig' cafe does not seem to exist (or my google-fu sucks), I was trying to see if it was near the OIAR.
Jonny is showing off his linguistic chops here with the food descriptions, that is foul, thanks ever so much. I'll just be over here checking every burger bun ever again for bugs. Eugh. And the sooooooooup.
More Sam and Alice being adorable, yeah, we're definitely not going to get to keep this.
Colin! You live!
It is remarkably easy to buy a hammer in central London.
So three PC monitors smashed. Coincidence? maybe. But wouldn't it make sense that whatever this is would be more in the servers than anywhere else? But Colin should know that, he's IT. The monitors would just be the interface. IDK, it's a weird choice, if I wanted to kill a computer I wouldn't crack the screen.
Lies, four monitors smashed. Hmm.
Shrimp king is not afraid to get in a fight, noted.
OIAR's mental health policies: A blank page
... Nope, three monitors and a server rack. ... So this fight went on for a bit? Alice and Sam chasing Colin down the hallways? Celia missing all the fun? (hey fic writers, c'mere, I wanna talk)
Sam? Sam. My dearest of shrimpy princes. In what reality do you think your government boss who has monsters in her employ is going to just spill her secrets because you decided to take a vote? This isn't the Institute and that's not Elias gloating over a win.
And Celia is, in fact, out in the boonies. With the phone.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
I promised a book haul of all the exciting books I purchased on my travels to London and Edinburgh! y'all... I bought TEN books...
Here is the stack of books and also some cute bookmarks I got from various places!

Here is the breakdown of all the books with their official descriptions:

Bloom by Delilah S. Dawson
Rosemary meets Ash at the farmers’ market. Ash—precise, pretty, and practically perfect—sells bars of soap in delicate pastel colors, sprinkle-spackled cupcakes stacked on scalloped stands, beeswax candles, jelly jars of honey, and glossy green plants. Ro has never felt this way about another woman; with Ash, she wants to be her and have her in equal measure. But as her obsession with Ash consumes her, she may find she’s not the one doing the devouring…

Monsters: What Do We Do With Great Art By Bad People? by Claire Dederer
Pablo Picasso beat his partners. Richard Wagner was deeply antisemitic. David Bowie slept with an underage fan. But many of us still love Guernica and the Ring cycle and Ziggy Stardust. And what are we to do with that love? How are we, as fans, to reckon with the biographical choices of the artists whose work sustains us? Wildly smart and insightful, Monsters is an exhilarating attempt to understand our relationship with art and the artist in the twenty-first century.

Little Rot by Akwaeke Emezi
One weekend. The elite underbelly of a Nigerian city. A breakup that starts a spiral. A party that goes awry. A tangled web of sex and lies and corruption that leaves no one unscathed. Little Rot is a whirling journey through the city’s dark side, told through the eyes of five people, each determined to run from the twisted powers out to destroy them. Aima and Kalu are a longtime couple who have just split. When Kalu, reeling from his loss, visits a sex party hosted by his best friend, Ahmed, he makes a decision that will plunge them all into chaos, brutally upending their lives. Ola and Souraya, two Nigerian sex workers visiting from Kuala Lumpur, intersect with the three old friends as everything goes to hell. Sucked into the city’s corrupt underworld, they’re all looking for a way out of the trouble they’ve instigated, driven by loss and fueled by a desperate need to escape the dangerous threat that looms over them. They careen madly in the face of the poison of power, sexual violence, murder, betrayals. Little Rot tests how far these five will go to save each other—or themselves—when confronted by evil, culminating in a shattering denouement.

The Wind Knows My Name by Isabel Allende
Vienna, 1938. Samuel Adler is five years old when his father disappears during Kristallnacht—the night his family loses everything. As her child’s safety becomes ever harder to guarantee, Samuel’s mother secures a spot for him on a Kindertransport train out of Nazi-occupied Austria to England. He boards alone, carrying nothing but a change of clothes and his violin.
Arizona, 2019. Eight decades later, Anita Díaz and her mother board another train, fleeing looming danger in El Salvador and seeking refuge in the United States. But their arrival coincides with the new family separation policy, and seven-year-old Anita finds herself alone at a camp in Nogales. She escapes her tenuous reality through her trips to Azabahar, a magical world of the imagination. Meanwhile, Selena Durán, a young social worker, enlists the help of a successful lawyer in hopes of tracking down Anita’s mother.
Intertwining past and present, The Wind Knows My Name tells the tale of these two unforgettable characters, both in search of family and home. It is both a testament to the sacrifices that parents make and a love letter to the children who survive the most unfathomable dangers—and never stop dreaming.

Bone Black: Memories of Girlhood by bell hooks
Stitching together the threads of her girlhood memories, bell hooks shows us one strong-spirited child's journey toward becoming the pioneering writer we know. Along the way, hooks sheds light on the vulnerability of children, the special unfurling of female creativity and the imbalance of a society that confers marriage's joys upon men and its silences on women. In a world where daughters and fathers are strangers under the same roof, and crying children are often given something to cry about, hooks uncovers the solace to be found in solitude, the comfort to be had in the good company of books. Bone Black allows us to bear witness to the awakening of a legendary author's awareness that writing is her most vital breath.

A House at the Bottom of a Lake by Josh Malerman
Both seventeen. Both afraid. But both saying yes. It sounded like the perfect first date: canoeing across a chain of lakes, sandwiches and beer in the cooler. But teenagers Amelia and James discover something below the water’s surface that changes their lives forever. It’s got two stories. It’s got a garden. And the front door is open. It’s a house at the bottom of a lake. For the teens, there is only one rule: no questions. And yet, how could a place so spectacular come with no price tag? While the duo plays house beneath the waves, one reality remains: Just because a house is empty, doesn’t mean nobody’s home.

Godkiller by Hannah Kaner
Kissen’s family were killed by zealots of a fire god. Now, she makes a living killing gods, and enjoys it. That is until she finds a god she cannot kill: Skedi, a god of white lies, has somehow bound himself to a young noble, and they are both on the run from unknown assassins. Joined by a disillusioned knight on a secret quest, they must travel to the ruined city of Blenraden, where the last of the wild gods reside, to each beg a favour. Pursued by demons, and in the midst of burgeoning civil war, they will all face a reckoning – something is rotting at the heart of their world, and only they can be the ones to stop it.

People Love Dead Jews: Reports from a Haunted Present by Dara Horn
Renowned and beloved as a prizewinning novelist, Dara Horn has also been publishing penetrating essays since she was a teenager. Often asked by major publications to write on subjects related to Jewish culture—and increasingly in response to a recent wave of deadly antisemitic attacks—Horn was troubled to realize what all of these assignments had in common: she was being asked to write about dead Jews, never about living ones. In these essays, Horn reflects on subjects as far-flung as the international veneration of Anne Frank, the mythology that Jewish family names were changed at Ellis Island, the blockbuster traveling exhibition Auschwitz, the marketing of the Jewish history of Harbin, China, and the little-known life of the "righteous Gentile" Varian Fry. Throughout, she challenges us to confront the reasons why there might be so much fascination with Jewish deaths, and so little respect for Jewish lives unfolding in the present. Horn draws upon her travels, her research, and also her own family life—trying to explain Shakespeare’s Shylock to a curious ten-year-old, her anger when swastikas are drawn on desks in her children’s school, the profound perspective offered by traditional religious practice and study—to assert the vitality, complexity, and depth of Jewish life against an antisemitism that, far from being disarmed by the mantra of "Never forget," is on the rise. As Horn explores the (not so) shocking attacks on the American Jewish community in recent years, she reveals the subtler dehumanization built into the public piety that surrounds the Jewish past—making the radical argument that the benign reverence we give to past horrors is itself a profound affront to human dignity.

84, Charing Cross Road by Helene Hanff
In 1949 Helene Hanff, a “poor writer with an antiquarian taste in books”, wrote to Marks & Co Booksellers of 84 Charing Cross Rd, in search of the rare editions she was unable to find in New York. Her books were dispatched with polite but brisk efficiency. But, seeking further treasures, Helene soon found herself in regular correspondence with bookseller Frank Doel, laying siege to his English reserve with her warmth and wit. And as letters, books and quips crossed the ocean, a friendship flourished that would endure for twenty years.

Rouge by Mona Awad
For as long as she can remember, Belle has been insidiously obsessed with her skin and skincare videos. When her estranged mother Noelle mysteriously dies, Belle finds herself back in Southern California, dealing with her mother’s considerable debts and grappling with lingering questions about her death. The stakes escalate when a strange woman in red appears at the funeral, offering a tantalizing clue about her mother’s demise, followed by a cryptic video about a transformative spa experience. With the help of a pair of red shoes, Belle is lured into the barbed embrace of La Maison de Méduse, the same lavish, culty spa to which her mother was devoted. There, Belle discovers the frightening secret behind her (and her mother’s) obsession with the mirror—and the great shimmering depths (and demons) that lurk on the other side of the glass. Snow White meets Eyes Wide Shut in this surreal descent into the dark side of beauty, envy, grief, and the complicated love between mothers and daughters. With black humor and seductive horror, Rouge explores the cult-like nature of the beauty industry—as well as the danger of internalizing its pitiless gaze. Brimming with California sunshine and blood-red rose petals, Rouge holds up a warped mirror to our relationship with mortality, our collective fixation with the surface, and the wondrous, deep longing that might lie beneath.
#books#book haul#guardian reads (sometimes)#when you have so many books you gotta use a cut to save the timeline#I’m very excited to read these!!#I’ve been reading a TON this month!
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Lyn Julius
The results of the British Jewish election are in: a landslide victory for the Labour party. Will it be good for the Jews?
The Jewish vote will have reflected the national trend of a swing to Labour, but many Jews remain seriously concerned over resurgent antisemitism. They remain skeptical about new prime minister Sir Keir Starmer’s reassurances that Jeremy Corbyn’s far left antisemitism has been expunged from the party. And, they ask, will a Labour government take a robust enough stand against antisemitism?
A global tsunami of antisemitism without precedent smashed into the Diaspora in the wake of the October 7 Hamas attacks; the link between antisemitism and anti-Zionism has never been clearer. Hostility to Israel has translated into intimidation and brutality against ordinary Jews and their property in London and Paris, Los Angeles and Montreal.
While the pro-Israel Conservatives did not always put their money where their mouth was – and the last foreign secretary, Lord Cameron, shocked many with his moral equivalence over Israel’s war on Hamas — the Conservatives’ fall from power means that UK’s 300,000 Jews have lost the most pro-Israel government they could have hoped for. Labour’s policy on the Middle East is ambivalent at best. The Greens are unabashedly pro-Palestinian and the Liberal party are equivocal, if not anti-Israel. The Reform party have their fair share of antisemitic conspiracy nutjobs. Although ‘Gaza George’ Galloway has lost his seat, Jewish hearts will also sink at the news that four independent MPs were elected on a pro-Gaza ticket.
‘A pro-Gaza ticket’ is doublespeak for the demand for Israel to surrender unconditionally to Hamas, to be pilloried in the international courts for alleged ‘war crimes’ and to suffer political and economic boycotts and strangulation. The pro-Gaza lobby do not want a ‘two-state solution,’ they want Israel gone.
How has it come to this – that whole swathes of public opinion believe that the Jews are to blame for October 7, that Israel’s war against Hamas is unjust and and that Palestinian terror groups – in reality proxies for Iranian aggression and imperialism – are the aggrieved party? The role of the media in misleading public opinion by omitting essential context and amplifying blood libels cannot be underestimated.
The lie, peddled over decades by Western pundits and academics wracked by post-colonial guilt, that Israelis are ‘white settler colonialists,’ is probably the most egregious. Tens of thousands of young people have been swayed by this inversion of the truth. Not only are Jews an indigenous people of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) with a right to self-determination in their ancestral homeland, but they predate Islam and the Arab conquest in the wider Middle East by 1,000 years or more. Even Jews from Europe and the US were traditionally treated as outsiders. They have incontrovertible cultural, linguistic and genetic links with the Middle East. Crucially, over half the Jewish population of Israel are refugees from Arab countries or their descendants. Ninety-nine percent have been driven from the Middle East and North Africa by mob violence and state-sanctioned persecution – in greater numbers than Palestinian refugees from Israel.
How many politicians taking their seats in the new Parliament will have heard of the 850,000 Jewish refugees from Arab countries? How many will be aware of the abuse of their human rights? Apart from a handful of MPs representing ‘Jewish’ constituencies – none.
In order to challenge ignorance and entrenched misconceptions, we need to launch a massive, pro-active, education campaign about Jewish refugees from Arab countries. The largest act of ethnic cleansing in the Israel-Arab conflict took place not against Palestinians, but Jews. Hamas just wants to finish the job by eradicating our last redoubt in Israel.
We urgently need to reframe the terms of the debate.
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! Thank you so much for all you do! I’ve been stalking your page since I found you and read so many good fics because of it!
I’ve been on a Dronarry kick lately thanks to all the incredible works from the fest this year! I’ve looked back at past fests and searched the tag on your blog, but I’m wondering if you’ve got any particular recs for the pairing that are older than this year or last?
Hello friend, welcome to the amazing Dronarry world! I’m so happy that you’ve been venturing into one of my favourite triads. The Dronarry Fest is indeed an excellent starting point with many of my personal favourites (here and here) but I definitely have a couple more to add, in fact Tacky’s Aim for my Heart was my official Dronarry initiation and it remains one of the best fics I’ve ever read, period. Enjoy!!
It's as simple as that by @cibeewastaken (T, 1k)
“So you’re just taking the piss,” Ron said, and he wasn’t sure if the lump that dropped from the base of his throat was due to relief or disappointment. “About your crush on me.” “Hm?” Draco said. “That? Oh, I’m serious about that.”
Holding Back by p1013 (E, 2.2k)
"I know what you really want." Weasley's mouth ghosts over the collar of Draco's shirt. No lips to skin, just breath and anticipation. "Don't think I haven't seen you staring in the common room. You're always watching, Malfoy. And something tells me it's not because you hate me."
Come Harbour a.k.a the Not-a-Metaphor Sailing Association: a story of friendship, sex, and beautiful water-based metaphors (not puns) by @dictacontrion, @gracerene and @lol-zeitgeistic
After Harry, Ron, and Draco are suspended - for something Ron had absolutely no part in whatsoever - they must take a forced holiday in Majorca to learn to work together. Which they do.
Aim For My Heart by @tackytigerfic (M, 3.4k)
Harry's in love, Ron's in control, and Draco just wants a nice lunch. They say three's a crowd, but Harry doesn't always agree. Not when he gets to be in the middle, anyway.
Close Encounters Of The Casual Kind by digthewriter (E, 3.4k)
They were going to do this—and it was going to be fine.
Complementary To Green by digthewriter (E, 7.6k)
When Draco had started The Malfoy Fix, he'd expected plenty of fashion-disaster(s) clients and had figured having an open-door policy was good for business. Although, catering to celebrity-Aurors Harry Potter and Ron Weasley was not on the agenda.
What It Takes by jad (E, 10k) - endgame Drarry
If Ron had been on time, Harry never would've realised what he was missing
The Taste of Țuică by @fluxweeed (E, 15k)
It’s quite one thing for your best mate to casually tell you about all the sex his boyfriend wants to have. It’s altogether another to have him bring up the time you snogged him in a shitty Central London park.
Things They Get Up To series by bumble_Bree (E, 23k)
In an attempt to cheer Ron up, Harry and Draco show him just how much Draco loves being taken.
Tiny Home by @wolfpants (E, 30k)
Harry and Ron left the Aurors years ago to travel the world and make up for lost time. When they finally decide to settle roots back in England, together, building a tiny home in the Lake District by hand seems like the perfect plan. What they don't realise is that Draco Malfoy already lives on the plot of land that they choose to build on.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Ayaan Hirsi Ali
Published: Oct 14, 2023
I was raised to curse Israel and pray for the destruction of Jews, writes AYAAN HIRSI ALI... That's why I know all too well Hamas is another ISIS - whatever useful idiots in the West say
All across the West, there is no shortage of people blaming the horrors in Israel on Israel itself — and openly supporting the perpetrators.
The head of policy at the Community Security Trust, which monitors hate crimes committed against British Jews, has said: 'Anti-Semites are getting excited by the sight of dead Jews... Hamas murdering Israeli civilians has exhilarated them... We've had reports of people driving past synagogues shouting 'Kill the Jews'.'
Anti-Semitic incidents in Britain are currently three times higher than they were this time last year, the charity adds.
'Free Palestine' graffiti has been scrawled on a railway bridge in Golders Green, a Jewish area of north London, while in Oxford Street, one young woman — who may well have been radicalised in England — was filmed ripping down posters that pleaded for the safe return of the babies taken hostage by Hamas. 'Free Palestine, f*** you!' she screamed at an onlooker who dared to remonstrate with her.
On Thursday night in Paris, police used tear gas and water cannon to disperse hundreds of people at a pro-Palestine rally, in which protesters chanted 'Israel murderer [sic]' and 'End the siege of Gaza.'
Outside the Sydney Opera House, about 1,000 protesters lit flares and waved Palestinian flags — and some were filmed chanting: 'Gas the Jews.'
In the U.S., meanwhile, 31 student groups at Harvard signed an open letter claiming that the 'Israeli regime' was 'entirely responsible for all unfolding violence', while California's Stanford University displayed a banner declaring that Palestine would be made free 'by any means necessary' — a sinister slogan that tacitly justifies Hamas's slaughter of children in pursuit of its aims.
Not to be outdone, the Chicago 'chapter' of the Black Lives Matter movement posted an image of a paraglider alongside the slogan 'I stand with Palestine'. The reference, of course, was to Hamas paragliders who descended on Israel's Supernova music festival last Saturday to rape and butcher at least 260 young people.
In short, anti-Semites the world over have been emboldened by this crisis, and Jews are once again being blamed for their own massacre. And I am not remotely surprised. In my childhood, I was steeped in the Islamist movement's noxious anti-Semitism — which has been on such ugly display this week.
Born in Mogadishu, Somalia, I spent my early years escaping political strife after my father was imprisoned for being an anti-government activist. We moved between countries before settling in Kenya.
The worst insult in the Somali community was to be called a 'Jew', not that any of us actually knew one. To be called a 'Jew' was so abhorrent, some felt justified in killing anyone who so dishonoured them with this 'slur'.
As a teenager in Nairobi in the 1980s, I joined the Muslim Brotherhood — the strict Sunni Islamist movement, founded in Egypt in 1928, from which Hamas ultimately descends.
I vividly remember sitting with my female fellows in mosques, cursing Israel and praying to Allah to destroy the Jews. We were certainly not interested in a peaceful 'two-state solution': we were taught to want to see Israel wiped off the map.
When I was 16, my school's teacher of religion was Sister Aziza. She read to us the Koran's lurid descriptions of the everlasting fire that burns flesh and dissolves skin — the place reserved for Jews.
Sister Aziza described Jews as physically monstrous, with horns coming from their heads, out of which flew devils that would corrupt the world. Jews controlled everything, she told us, and it was the duty of Muslims to destroy them.
It was a lot to take in for a teenager who read Western romance novels in secret, but I believed every word.
When the fatwa was issued against the British writer Salman Rushdie in 1989, a small crowd gathered in a Nairobi car park to burn a copy of his novel The Satanic Verses.
Sister Aziza urged us to join in the condemnations of Rushdie and I am ashamed to say I took part in the book-burning. I was certain Rushdie should be killed, but the scene nevertheless made me uncomfortable.
That seed of doubt grew over the next few years as I questioned why, if Allah was so just, women were treated as mere chattels in some Muslim families.
Over time, my questions turned into open rebellion against the Muslim Brotherhood, Islam and, ultimately, my family.
My father sent me to relatives in Germany in 1992 so I could go from there to Canada to join the distant cousin he had married me off to. I ran away from that marriage and travelled to the Netherlands where I sought asylum.
Eventually, I became a member of the Dutch parliament, and later settled in America.
I abandoned my religion, but I have never lost my clear-sighted understanding, forged in my childhood, of Islamism's pathological hatred of Jews, as well as Muslims considered as heretics and non-Muslims in general.
The former Egyptian president Mohamed Morsi — a one-time leader of the Muslim Brotherhood — declared that Muslims should 'nurse our children and our grandchildren on hatred' of Jews. His organisation has done just that — and the despicable sentiment is the underlying context to Hamas's most recent attacks.
The truth, however, is that Hamas is no more a friend of the Palestinians than it is a friend of Israel.
Those who see the conflict as a simple territorial dispute between a colonial state and a dispossessed minority fail to recognise Hamas for what it really is: a gang of genocidal Islamist thugs backed by a theocratic, anti-Semitic regime in Iran.
Useful idiots on the far-Left in Western countries, who blindly support Hamas because they see it as a freedom-fighting group, harm the very people they claim to defend.
They say they want peace —and perhaps many of them do. But real peace talks based on the 2020 Abraham Accords between Israel and Arab countries have made painstaking but undeniable progress despite the efforts of Hamas.
Until Hamas's recent attacks, Saudi Arabia and Israel had looked set to normalise relations. This murderous incursion was an attempt to derail such talks — and thus ruin any chance of lasting peace.
Ordinary Palestinians want to build a prosperous, functioning society. Hamas, in its obsession with annihilating Israel, doesn't care about that. It wishes only to bring about a genocidal Islamist dystopia.
It is Hamas, after all, that holds Palestinians hostage in Gaza, setting up military installations in — and launching rockets from — civilian areas in the full knowledge that counterstrikes will kill innocent people.
It is Hamas that impoverishes Palestinians by stealing humanitarian aid to fund its terror. This is what 'by any means necessary' truly signifies: supreme callousness towards Palestinian life.
If you genuinely want to see peace between Israelis and Palestinians, or more generally between Muslims and Jews in the Middle East, then Hamas should be your enemy.
And even if — like many in the West, as we can now see — you don't care at all about Israeli or Jewish lives, even if you care only about the lives of Palestinians, Hamas is still your enemy. After all, Hamas ruthlessly persecutes any Palestinians who disagree with it: a 2022 U.S. State Department report found that, among other abuses, Hamas detained and assaulted critical journalists.
It is especially hostile to public figures associated with its rival Fatah, the Palestinian party voted out of office in Gaza in 2006, but which still runs the West Bank.
Hamas harasses its own dissidents, and has invaded the home of at least one young critical activist, telling his parents to keep their son under control — or else.
As a Dutch MP in 2004 and 2005, I travelled to the West Bank and met Palestinians.
In public, they spouted all the usual lines about Israel being their 'oppressor'. But once the cameras were switched off, they spoke more truthfully.
They complained bitterly about their treatment by Hamas and other radical groups, and told me how money meant to feed the people was being taken to fund those organisations' activities and their leaders' luxurious lifestyles. Arabs and Palestinians alike told me how fed up they were with conflict, and how ready they were for peace.
Hamas, like other Islamist groups, has done its best over the course of decades to stomp all over those wishes.
And it has been successful. The shocking rise in anti-Semitism in the West owes much to the entrenched Islamist networks that have spent years stirring up this ancient hatred.
Europe must now wake up to these fifth columnists who shamelessly celebrate violence and bigotry, promoting hatred of the Jewish minority in Europe.
The West must also wake up to the moral corruption of its own Hamas supporters, from Left-wing university students to flag-waving street thugs.
Meanwhile, elite human-rights organisations need to do far more to name terrorism when they see it.
It is horrifying to see Amnesty International claiming that one of the 'root causes' of the crisis is 'Israel's system of apartheid imposed on Palestinians'.
Human Rights Watch, meanwhile, should do more than merely equivocating in its insistence that no injustice can justify another.
This is not to argue that Israel should be immune from criticism. My point is that much of the criticism is at best misguided and at worst thinly veiled anti-Semitism.
Hamas, like Lebanon's Hezbollah, Isis in Syria and Iraq, Nigeria's Boko Haram, Somalia's Al-Shabaab and several other groups, are fighting not for the liberty and prosperity of Muslims but, ultimately, for the annihilation of Israel and the imposition of an Islamic state.
If Palestinians and other Muslims have to suffer for that aim, then so be it.
Well-meaning celebrities and broadcasters who, out of wilful ignorance and good intentions, hesitate to condemn Hamas as terrorists need to recognise this truth.
These are dark times for Israel and for the world, but there are some reasons to be hopeful.
This week's strong statement by America, Britain, France, Italy and Germany condemning Hamas while recognising the 'legitimate aspirations' of the Palestinians is a good sign.
Labour leader Sir Keir Starmer's condemnation of Hamas is particularly welcome, given that, until recently, his party was led by a man who called these butchers his 'friends'.
And if Israel and the Arab states do not allow their worst instincts to rule them, talks may continue — and might just secure peace in the longer term.
Hamas is another Isis. They are the enemies of Israel; they are the enemies of all Jews; they are the enemies of Palestinians; they are the enemies of peace and freedom. They are the enemies of Western civilisation itself.
It is about time they were recognised as such.
To achieve a two-state solution — with free and prosperous Palestinians and a safe Israel — the first, fundamental step is for people to stop chanting slogans in support of terrorists and murderers, and for everyone to cry in unison: 'Down with Hamas!'
==
Remember two years ago when everyone was arguing about whether the terrorist assault and takeover of Afghanistan by the Taliban was Trump's fault or Biden's fault? Today, people are scolding us not to call the same thing terrorism. It's "liberation" and "decolonization."
Remember in 2014 when Boko Haram kidnapped the children and everyone was campaigning for their safe return because it was an unconscionable act of terrorism? Now kidnapping and murdering children is an act of legitimate revolution.
Remember when kids rushed to support ISIS the instant they rose, and people were appalled and argued over how could it could be possible to support a terrorist state that seized illegitimate power? Online radicalization was blamed, and many didn't want to believe that indoctrination had primed it well in advance. Now, if your Gender and Postcolonial Studies haven't activated you to support a terrorist state that has seized illegitimate power in the region, you're a bigot.
Remember when we cheered on the Iranians for finally fighting back against the regime of terror that hung over them, hoping for them to finally win the war against the regime? Now, Israel has to simply take whatever assaults of terrorism are dealt at them; it is, as Douglas Murray said, is the only country which is not allowed to win a war.
Remember when certain people liked to call everyone who disagreed with them "Nazis" and that punching them was the right thing to do? Now the extermination of all the Jews is the "Be Kind" position.

How morally confused do you have to be, after all this, to side with the terrorists?
Hamas is to Palestine as ISIS is to Syria and the Taliban is to Afghanistan.
As I've posted about before, Islam is a supremacist ideology. Its goal is world domination. They tell us that. Loudly.

https://quranx.com/Hadith/Bukhari/USC-MSA/Volume-4/Book-52/Hadith-196
Narrated Abu Huraira: Allah 's Apostle said, "I have been ordered to fight with the people till they say, 'None has the right to be worshipped but Allah,' and whoever says, 'None has the right to be worshipped but Allah,' his life and property will be saved by me except for Islamic law, and his accounts will be with Allah, (either to punish him or to forgive him.)"
https://quranx.com/Hadith/Bukhari/USC-MSA/Volume-1/Book-8/Hadith-387
Narrated Anas bin Malik: Allah's Messenger (ﷺ) said, "I have been ordered to fight the people till they say: 'None has the right to be worshipped but Allah.' And if they say so, pray like our prayers, face our Qibla and slaughter as we slaughter, then their blood and property will be sacred to us and we will not interfere with them except legally and their reckoning will be with Allah."
Narrated Maimun bin Siyah that he asked Anas bin Malik, "O Abu Hamza! What makes the life and property of a person sacred?" He replied, "Whoever says, 'None has the right to be worshipped but Allah', faces our Qibla during the prayers, prays like us and eats our slaughtered animal, then he is a Muslim, and has got the same rights and obligations as other Muslims have."
https://quranx.com/Hadith/Muslim/USC-MSA/Book-41/Hadith-6985
Abu Huraira reported Allah's Messenger (ﷺ) as saying: The last hour would not come unless the Muslims will fight against the Jews and the Muslims would kill them until the Jews would hide themselves behind a stone or a tree and a stone or a tree would say: Muslim, or the servant of Allah, there is a Jew behind me; come and kill him; but the tree Gharqad would not say, for it is the tree of the Jews.
It has successfully weaponized intersectional shibboleths to trick useful idiots into thinking that the supremacist is the oppressed victim.
#Ayaan Hirsi Ali#down with hamas#hamas#Palestine#israel#islamic terrorism#islam#antisemitism#terrorist organization#jihad#religion#exterminate hamas#religion is a mental illness
55 notes
·
View notes
Text
Submitted via Google Form:
Do you have any ideas on how to world build a massive overpopulated city but it isn't dirty or in shambles. Basically, everything is neat, clean and works well. Just a massive population density. I'm thinking 30k people per km2 with a total area of 1200km2. When I find images or descriptions of such high density populations I often see buildings that kind of look all rundown and slummy (not to mention high crime rates and poor if not in poverty) Or is that like.. impossible if you have such a massive crowd in one spot?
Tex: “Overpopulated” implies “more residents than the infrastructure can accommodate”. What’s considered dirty or in shambles is the result of a garbage disposal system that isn’t structured to the amount of residents + guests (tourists, relatives, holiday-goers, etc). To have a city or other area properly equipped with the amount of employees to maintain sanitation and employees to repair buildings degrading over time, it must have properly-allocated funds, and enough of it. This is at its core a governance and taxation issue, not a morality issue of “just don’t make it dirty”. Crime and poverty are the natural result of neglect by one’s government, both at a local and larger level, which requires a lot of forethought in the amount of space an individual needs to live in private and public spaces.
Utuabzu: I’m going to assume you want a prosperous city with very high density. Happily for you, there are many examples of this in the real world. Density occurs when the demand for living/working space in an area is greater than the physical space available, meaning it is worthwhile to create more space by building upwards. This naturally occurs in the centres of all cities, because proximity to one another is a big draw for both people and organisations. In the absence of any limiting factors, this is usually counterbalanced by cost making it cheaper to build outwards and simply accept longer travel times, resulting in a relatively gradual gradient of density from rural periphery to urban core.
You get greater density when there are limiting factors on outward expansion. These can be geographic, like in the case of Singapore, Hong Kong and Manhattan (all islands), legal, like in the case of Vancouver, London and many other cities (laws and policies preserving green belts or valuable farmland), or political, such as was the case for Hong Kong and still is for Singapore (an international border acting as a constraint). Often it’s more than one of these. While places like Kowloon Walled City can exist - and it in particular is a very interesting case study in urban form - for the most part very high density occurs when people want to live and work somewhere, which usually means it’s a pretty nice place to be (at least in comparison to the other options anyway). Tokyō is the world’s largest city, with 36 million people (11 million more than the entire continent of Australia), but I don’t think I’ve ever heard anyone accuse it of being dirty or in a shambles.
It is also worth noting that density doesn’t necessarily look like skyscrapers towering overhead. Paris has a population density of almost 25k/km² when one excludes the outlying woodland park areas, and is predominantly mid-rise buildings. The 11th Arrondissement of Paris outdoes what you ask for, with a population density just under 40k/km², and is mostly historic midrise buildings. Other European cities like Barcelona, Naples and Thessaloniki have a similar development pattern, largely due to having been built mostly before elevators existed or were commonplace, which naturally limited building heights to around 5 to 6 floors (any higher becoming increasingly impractical for the sheer number of stairs).
Feral: The International Residential Code has the minimum size required for a house to be 120 sq ft/11.1 sq m. That’s a pretty standard secondary bedroom size in suburban USA. Your population density would have one person per 33.3 sq meters, which sounds great except that doesn’t account for any non-residential use space. Given your desire for the entire city to be exceptionally well-maintained, free of crime, and presumably a wonderful place to live, that means you need great air quality, multiple green spaces, art, food, entertainment. And your city’s overall size is massive. It’s 20.5 times the size of Manhattan, 11.3x the size of Paris, and 1.6x the size of Singapore - to name a few of the cities brought up in previous answers. This kind of sprawl does not make for good urbanization - just ask the city of Los Angeles, which is almost exactly the same overall size as what you’re aiming for but has a tenth of the density.
A few articles to get you started on density, urbanization, and sprawl:
Cities Really Can Be Both Denser and Greener by Emma Marris
Is There a Perfect Density? By Michael Lewyn
When is density good, and when is it harmful to cities? By Philip Langdon
Making cities more dense always sparks resistance. Here’s how to overcome it. By David Roberts
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
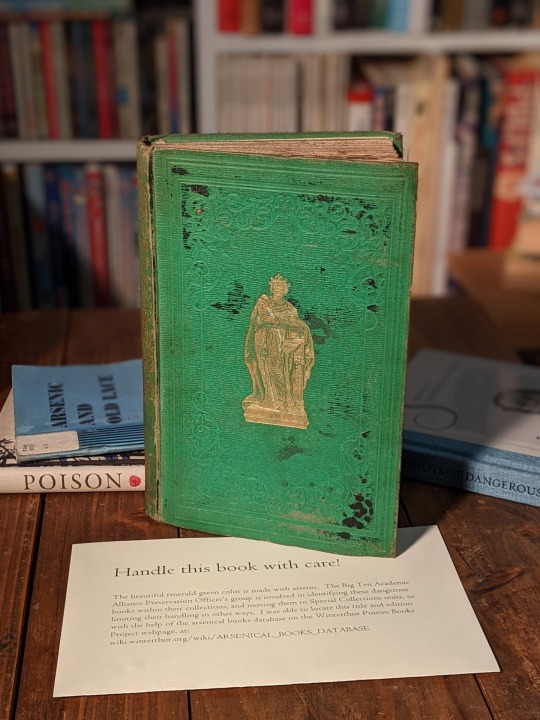




The previous post in which I asked Fran whether or not she had been licking books in the Christmas displays has apparently caused some confusion. An explanation is in order. The book shown above -- which Fran had placed in one of the displays -- has a lovely emerald green cover. The green color, alas, comes from a pigment made with arsenic, and these books must be handled with care. They should definitely not be licked.
Of course, books in general should not be licked, although typically the risk to the book is greater than the risk to the person doing the licking. However, I do know a bookstore run by a retired longshoreman, and I believe that anyone caught licking a book in his store would in fact be in grave danger indeed. But I digress.
Pigments containing arsenic were popular in the late 19th century, though there were other green dyes and pigments which did not use arsenic. The book shown here -- Poets and Statesmen, Their Homes and Haunts was published by E. P. Williams in London in 1857, and has tested positive for the presence of arsenic.
Bearing this in mind, I will take this opportunity to declare an official policy in our bookshop: Book licking is not permitted.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Ron Ayers
Engineer and aerodynamicist involved in land-speed record-breaking cars and guided missile design
Working at the Handley Page company, and then in the guided weapons division of the Bristol Aeroplane Company (now part of BAE Systems), in the 1950s and 60s, the engineer and aerodynamicist Ron Ayers, who has died aged 92, became one of Britain’s most experienced supersonic and high-speed aircraft designers.
Following retirement in 1988, he took on a volunteer role at the Brooklands Museum, Weybridge, and was fascinated to discover, among the aviation archives held there, aerodynamic and wind tunnel work on the prewar generation of land-speed record-breaking cars. This led to Ayers meeting Ken Norris, designer (with his brother Lew) of Donald Campbell’s Bluebird car and jet-powered boat. With these two vehicles, in 1964, Campbell had achieved world records, for land speed of 403.1mph (648.73 km/h), and for water speed of 276.3mph (444.71km/h).
Norris had also been manager of more recent world-record-breaking runs by the self-styled “adventurer and engineer” Richard Noble with Thrust, a car that gained a world record of 633mph (1018.7 km/h) in the Nevada desert in 1983. When Ayers bumped into Noble by chance, while they were both passing through Bournemouth airport in 1992, he found that Noble’s next project was the Thrust SSC, a jet-powered “car” intended to break the sound barrier on land – at a speed of about 767mph. “Don’t be an idiot – you’ll kill yourself,” Ayers said.
The problem is that a land-speed car is an “interface vehicle” running between air and earth. Designing a stable supersonic shape for that regime is quite different to making an aircraft or missile that could achieve supersonic flight safely in free air. On land, where would the supersonic shock waves around the vehicle go and how might they upset it? What would the airflow underneath it be like and how might it lift or destabilise it? There were no precedents. But, intrigued by the challenge, Ayers mulled over the problem and, a little later, got back to Noble saying that he thought he could see a way to do it.
There are no wind tunnels capable of modelling this situation, but between them, they called in favours and all their contacts to win time for day-long simulations that ran on Britain’s most powerful supercomputer (a Cray machine), in parallel with physical experiments with a scale model attached to an 800mph rail-mounted rocket sledge at the Defence Research Agency’s establishment at MOD Pendine in Wales.
The research paid off, and on 15 October 1997 the RAF pilot Wg Cmdr Andy Green finally achieved a supersonic world record of 763.035mph (1,227.986 km/h) in Thrust SSC – a record that still stands.
Ayers was born in London, the son of Frederick Ayers, an engineer, and his wife, Maud (nee Jardine). To escape bombing during the second world war, in 1940 the family, and Frederick’s factory, moved to Barnstaple in Devon. Deemed not suitable for university, due to chronic childhood ear infections (alleviated with the advent of penicillin) and an interrupted education, Ron went straight into the Handley Page company in 1950 as an engineering apprentice, where he worked on the Victor bomber project. This also allowed him “day release” to gain a degree in aeronautical engineering from the University of London. He then won a scholarship to study for an MSc at Cranfield College of Aeronautics (now Cranfield University).
Britain had some of the most technically advanced aircraft companies in the world and Handley Page was one of the most esteemed, at the forefront with an exceptionally advanced aerodynamic design team. Its Victor bomber became central to the V force – Britain’s cold war deterrent. These aircraft had been devised to evade interception by flying faster and higher than any aircraft before.
It is impossible to overstate the importance of aerodynamic science to national policy at the time. Cold war aircraft development was a contest of the brightest minds to achieve unprecedented performance in the tricky transonic regime – the speed range approaching the speed of sound. As the new postwar generation of military aircraft approached that speed, the airflow over them could be mixed – flowing in a familiar, well understood way in some areas, but becoming supersonic over parts where the air accelerated.
This supersonic (incompressible) flow was a new, little studied, phenomenon, and it posed fresh problems in stability, control and structural integrity. The whole industry was supported closely by the Royal Aircraft Establishment at Farnborough, Hampshire (and at Bedford). This was probably the biggest research enterprise in Europe in those years.
This was the milieu in which Ayers developed – solving problems that the feasibility of Noble’s supersonic car would recall. The national deterrent policy back then was to devise near-supersonic bombers that could outfly the fighter defences, exploiting speed, height and the limitations imposed by radar warning time. But at the same time, the aim was to create home defences that could catch anything similar developed by an enemy.
As part of this war of innovation, the Bristol company was developing the Bloodhound guided missile, intended to destroy incoming enemy aircraft, so it is intriguing that Ayers in 1956 joined the Bristol’s guided weapons division, becoming chief aerodynamicist. The revised Bloodhound Mk II that he worked on was a highly effective missile intended to destroy bombers attacking Britain, capable of reaching 65,000ft (nearly 20,000 metres) at more than twice the speed of sound. It went into service “to defend the deterrent” – the V-bomber force that Ayers had originally contributed to in his first job.
However, on the death of his father, Ayers left aeronautics and in 1967 took over the family business, which made printing presses, remaining with the company until it was sold in 1988.
In retirement, as well as volunteering at Brooklands, Ayers was actively involved in promoting engineering education, and he viewed the Thrust SSC record-breaking attempts as valuable publicity to showcase engineering and its intrinsic interest. Subsequently, he was chief aerodynamicist for the JCB 2006 Dieselmax car, which still holds the world diesel car record of over 350mph (560 km/h), and also for the projected 1,000mph Bloodhound car.
All this highly original work done in the later decades of Ayers’s life was, he said, “much more fun than mowing the lawn”.
Ayers married Irene Graham, a psychologist, in 1968. She died in 1991 and he is survived by their son, Roger, and granddaughters, Lily-May and Daisy.
🔔 Ronald Frederick Ayers, engineer, born 11 April 1932; died 29 May 2024
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
A pricey trip for a group of Conservative MPs sponsored by an interest group and a Hungarian think-tank could soon come under the microscope by the House of Commons ethics committee.
NDP ethics critic Matthew Green served notice Monday that he will introduce a motion for the committee to take a closer look at a trip to London last June sponsored by Canadians for Affordable Energy and the Danube Institute. The trip, billed as an opportunity to discuss energy policy, included thousands of dollars in flights, hotels and ground transportation as well as a dinner at the Guinea Grill in London's Mayfair district with $600 bottles of champagne that rung in at an estimated $6,262.
Full article
Tagging: @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#canada#canadian politics#canadian news#canadian#conservatives#ethics#house of commons#corruption#canadians for affordable energy#danube institute
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Before this column ends, we’ll get to the unmissable fact that anti-Israel, often antisemitic, protests are proliferating at what we amusingly choose to call our most “selective” universities—Columbia, Yale, New York University, Stanford, Berkeley. For the moment, add these North Face tent protests on $75,000-a-year campus quads to the sense among the American public that their country is running off the rails.
A list of the phenomena laying us low includes: wokeness, DEI (diversity, equity and inclusion), defund the police (a depressing subset of wokeness), conspiracy theories, head-in-the-sand isolationism and a self-centered political polarization typified—from left to right—by Reps. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, Ilhan Omar, Cori Bush, Marjorie Taylor Greene, Matt Gaetz and Lauren Boebert.
Ironically this time of year is associated with hope, amid spring and college graduations—except at the University of Southern California, which, fearing trouble, canceled its commencement speakers and told honorary-degree recipients not to show up.
Setting silenced USC aside, a hopeful note one hears at college commencements is that the American system is self-correcting, that despite recurrent stress, it always rights itself. Opinion polls suggest few believe this anymore but—happy spring—it looks as if we may be on the brink of a real counter-revolt against the craziness.
Last week in the hopelessly gridlocked House, Republican Speaker Mike Johnson, facing threats to his job from the chaos caucus, cast his lot with the enough-is-enough caucus. The House passed bills to sustain allies in Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan. Congress isn’t dead—yet.
Blue states and cities that looked willing to collapse rather than defend their citizens have begun to push back against progressives’ pro-criminal and antipolice movements.
At the urging of Gov. Kathy Hochul, New York’s just-passed state budget includes measures to crack down on shoplifting. Assaulting a retail worker will be a felony. Larceny charges can be based on the total goods stolen from different stores. Progressives in the state’s Legislature opposed the measures. Philadelphia Mayor Cherelle Parker, elected in January on restoring law and order (yes, it can be a Democratic issue), last week announced a plan to support policing in the most crime- and drug-plagued neighborhoods.
March seemed to be a tipping point. The hyperprogressive Council of the District of Columbia, in a city that had become an embarrassing carjacking hellhole, passed an array of anticrime measures. Oregon’s Legislature voted to reverse the state’s catastrophic three-year experiment with drug decriminalization. San Francisco voters approved two measures proposed by, of all people, Mayor London Breed, to ease restrictions on policing and require drug screening for welfare recipients. The results in Los Angeles County’s primary for district attorney strongly suggest progressive George Gascón will be voted out in November.
In all these places, the reversals by elected officials are driven by the prospect of voters’ turning them out of office. That is the U.S. political system trying to right itself.
In California, a safety coalition has collected about 900,000 signatures to reverse parts of Proposition 47, the state’s now-notorious 2014 decision to reduce some theft felonies to misdemeanors. This week, the U.S. Supreme Court’s conservative majority appeared sympathetic to overturning a Ninth Circuit decision that bars cities and towns from enforcing vagrancy laws. Though the case emerged from Grants Pass, Ore., which is trying to ban homeless encampments, about three dozen elected officials and organizations in California filed briefs arguing that the Ninth Circuit’s ruling made cleaning up the streets almost impossible.
News stories since the start of the year have noted that many private companies are rethinking policies on DEI, partly under legal pressure, such as the Supreme Court’s decision last year to strike down the use of race in college admissions.
Some in the corporate DEI movement thought they were immune to restraints. No longer. Companies are rediscovering that the constituency most needing inclusion is their customers. The loudest shot across the bow came last week, when Google fired 28 employees after some staged sit-in protests at its New York and California offices over a contract with Israel’s government. Google’s firing statement describes “completely unacceptable behavior.” No one saw that coming.
All this adds up to a nascent counter-revolt against America’s lurch toward self-destruction. The exception is elite U.S. universities. Their leadership has seen itself as answerable to no one and politically immune.
Robert Kraft, a Columbia grad and owner of the New England Patriots, said this week he will no longer give the school money “until corrective action is taken.”
If big donors ever regain control of these so-called selective schools, a suggestion: Firing the president won’t close the barn door. Instead, fire the admissions office. What a tragedy to think how many serious high-school students were rejected by Columbia, Yale and NYU, edged out by nonuseful idiots whose chosen major is the political structure of re-education camps.
Someone has to be a lagging indicator, and these schools are it.
Non-paywall link
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me and my colleague were bored at work earlier (quiet week) so looking through the UK May 2024 Mayor of London candidates for the vote today... and as a summary of several, it was like: -TORIES 🤢 -Sadiq Khan (*Long sigh* but at least it's left and labour) -Mr yellow scarf with wet blanket policies -Green Lady is pretty alright but a bit extreme with the remove cars from central London??? how about taxis for disabled folk who can't use public transport first of all, but I digress. Policies are alright and in touch overall though! -Good'ol Count Binface 🗑️ -Ah yes Reform who's gonna get the racist vote -WAIT wtF there's a right-wing literally facist group?!?! Like oh my god look up Britian First... it's wtf wtf wtffffff🤢🤢🤢 -The vegans™ -Who's this... *reads her website* OH FUCK THAT'S A LITERALLY A TERF EW EW EW -Some American podcaster???? obsessed with freedom of speech, blockchain and BTC???
Like... OH MY GOD WTF 🤢🤢🤢🤢 like this is the state of the UK that we gotta terf and a right extremist running for mayor of london
#lord have mercy on the uk jesus fucking christ#my posts#idk what i'm doing i have 4.5 hours to research for the 3 votes and get there before it shuts at 10pm#uk politics
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Bibliography for FAQ
Non-Anarchist Works
Adams, Arthur E., Bolsheviks in the Ukraine: the second campaign, 1918–1919, Yale University Press, New Haven, 1963
Anderson, Terry L. and Leal, Donald R., Free Market Environmentalism, Pacific Research Institute for Public Policy,San Francisco, 1991.
Anweiler, Oskar, The Soviets: The Russian Workers, Peasants, and Soldiers Councils 1905–1921, Random House, New York, 1974.
Archer, Abraham (ed.), The Mensheviks in the Russian Revolution, Thames and Hudson Ltd, London, 1976.
Arestis, Philip, The Post-Keynesian Approach to Economics: An Alternative Analysis of Economic Theory and Policy, Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., Aldershot, 1992.
Armstrong, Philip, Glyn, Andrew and Harrison, John, Capitalism Since World War II: The making and breakup of the great boom, Fontana, London, 1984.
Capitalism Since 1945, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1991.
Arrow, Kenneth, “Economic Welfare and the Allocation of Resources for Inventiveness,” in National Bureau of Economic Research, The Rate and Direction of Inventive Activity, Princeton University Press, 1962.
Aves, Jonathan, Workers Against Lenin: Labour Protest and the Bolshevik Dictatorship, Tauris Academic Studies, London, 1996.
Bain, J.S., Barriers in New Competition: Their Character and Consequences in Manufacturing Industries, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, 1967.
Bakan, Joel, The Corporation: The Pathological Pursuit of Profit and Power, Constable, London, 2004.
Bakunin, Michael, The Confession of Mikhail Bakunin, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, N.Y., 1977.
Bukharin, Nikolai, Economy Theory of the Leisure Class, Monthly PressReview, New York/London, 1972.
Bagdikian, Ben H., The New Media Monopoly, Beacon Press, Boston, 2004.
Baldwin, William L., Market Power, Competition and Anti-Trust Policy, Irwin, Homewood, Illinois, 1987.
Balogh, Thomas, The Irrelevance of Conventional Economics,Weidenfield and Nicolson, London, 1982.
Baran, Paul A. and Sweezy, Paul M., Monopoly Capital, Monthly Press Review, New York, 1966.
Baron, Samuel H., Plekhanov: the Father of Russian Marxism, Routledge & K. Paul, London, 1963
Barry, Brian, “The Continuing Relevance of Socialism”, in Thatcherism, Robert Skidelsky (ed.), Chatto & Windus, London, 1988.
Beder, Sharon, Global Spin: The Corporate Assault on Environmentalism, Green Books, Dartington, 1997.
Beevor, Antony, The Spanish Civil War, Cassell, London, 1999.
The Battle for Spain: The Spanish Civil War 1936–1939, Phoenix, London, 2006.
Berghahn, V. R., Modern Germany: society, economy and politics in the twentieth century, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
Berlin, Isaiah, Four Essays on Liberty, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1969.
Bernstein, Michael A., The Great Depression: Delayed recovery and Economic Change in America, 1929–1939, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1987.
Beynon, Huw, Working for Ford, Penguin Education, London, 1973.
Binns, Peter, Cliff, Tony, and Harman, Chris, Russia: From Workers’ State to State Capitalism, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Blanchflower, David and Oswald, Andrew, The Wage Curve, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass., 1994.
Blinder, Alan S. (ed.), Paying for productivity: a look at the evidence, Brookings Institution, Washington, D.C, 1990.
Blum, William, Killing Hope: US Military and CIA Interventions Since World War II, 2nd edition, Zed Books, London, 2003.
Rogue State: A Guide to the World’s Only Superpower, 3rd edition, Zed Books, London, 2006.
Böhm-Bawerk, Eugen, Capital and Interest, Libertarian Press, South Holland,Ill., 1959.
Bolloten, Burnett, The Spanish Civil War: Revolution and Counter Revolution, Harvester-Wheatsheaf, New York, 1991.
Boucher, Douglas H. (ed.), The Biology of Mutualism: Biology and Evolution, Croom Helm , London, 1985.
Bourne, Randolph, Untimely Papers, B.W. Huebsch, New York, 1919.
War and the Intellectuals: Essays by Randolph S. Bourne 1915–1919, Harper Torchbooks, New York, 1964.
Bowles, Samuel and Edwards, Richard (Eds.), Radical Political Economy, (two volumes), Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd., Aldershot, 1990.
Bowles, Samuel and Gintis, Hebert, Schooling in Capitalist America: Education Reform and the Contradictions of Economic Life, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London, 1976.
Braverman, Harry, Labour and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in theTwentieth Century, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1974.
Brecher, Jeremy, Strike!, South End Press, Boston, 1972.
Brecher, Jeremy and Costello, Tim, Common Sense for Hard Times, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1979.
Brenan, Gerald, The Spanish Labyrinth: An Account of the Social and Political of the Spanish Civil War, 2nd Edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1976.
Broido, Vera, Lenin and the Mensheviks: The Persecution of Socialists under Bolshevism, Gower Publishing Company Limited, Aldershot, 1987.
Brovkin, Vladimir N., From Behind the Front Lines of the Civil War: political parties and social movements in Russia, 1918–1922, Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J, 1994.
The Mensheviks After October: Socialist Opposition and the Rise of the Bolshevik Dictatorship, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1987. Russia after Lenin : politics, culture and society, 1921–1929, Routledge, London/New York, 1998
Brovkin, Vladimir N. (ed.), The Bolsheviks in Russian Society: The Revolution and Civil Wars, Yale University Press, New Haven and London, 1997.
Bunyan, James, The Origin of Forced Labor in the Soviet State, 1917–1921: Documents and Materials, Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1967.
Byock, Jesse, Viking Age Iceland, Penguin Books, London, 2001
C.P.S.U. (B), History of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Bolsheviks), International Publishers, New York, 1939.
Cahm, Eric and Fisera, Vladimir Claude (eds), Socialism and Nationalism, Spokesman, Nottingham, 1978–80.
Carr, Edward Hallett, The Bolshevik Revolution: 1917–1923, in three volumes, Pelican Books, 1966.
The Interregnum 1923–1924, Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1969.
Carr, Raymond, Spain: 1808–1975, 2nd Edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1982.
Carrier, James G. (ed.), Meanings of the market: the free market in western culture, Berg, Oxford, 1997.
Chandler, Lester V., America’s Greatest Depression, 1929–1941, Harper & Row, New York/London, 1970.
Chang, Ha-Joon, Kicking Away the Ladder: Development Strategy in Historic Perspective, Anthem Press, London, 2002.
Bad samaritans: rich nations, poor policies and the threat to the developing world, Random House Business, London, 2007
Clark, J.B., The Distribution of Wealth: A theory of wages, interest and profits, Macmillan, New York, 1927
Cliff, Tony, Lenin: The Revolution Besieged, vol. 3, Pluto Press, London,1978.
Lenin: All Power to the Soviets, vol. 2, Pluto Press, London,1976. State Capitalism in Russia, Bookmarks, London, 1988. “Trotsky on Substitutionism”, contained in Tony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky, Party and Class,Bookmarks, London, 1996. Trotsky, vol. 3, Bookmarks, London, 1991. Revolution Besieged: Lenin 1917–1923, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Cohen, Stephan F., Bukharin and the Bolshevik Revolution, Oxford University Press, London, 1980.
“In Praise of War Communism: Bukharin’s The Economics of the Transition Period”, pp. 192–203, Revolution and politics in Russia: essays in memory of B.I. Nicolaevsky, Alexander and Janet Rabinowitch with Ladis K.D. Kristof (eds.).
Collins, Joseph and Lear, John, Chile’s Free-Market Miracle: A Second Look,Institute for Food and Development Policy, Oakland, 1995.
Communist International, Proceedings and Documents of the Second Congress1920, (in two volumes), Pathfinder, New York, 1991.
Confino, Michael (ed.), Daughter of a Revolutionary: Natalie Herzen and the Bakunin-Nechayev Circle, Library Press, LaSalle Illinois, 1973.
Cowen, Tyler, “Law as a Public Good: The Economics of Anarchy”,Economics and Philosophy, no. 8 (1992), pp. 249–267.
“Rejoinder to David Friedman on the Economics of Anarchy”, Economics and Philosophy, no. 10 (1994), pp. 329–332.
Cowling, Keith, Monopoly Capitalism, MacMillian, London, 1982.
Cowling, Keith and Sugden, Roger, Transnational Monopoly Capitalism,Wheatshelf Books, Sussez, 1987.
Beyond Capitalism: Towards a New World Economic Order, Pinter, London, 1994.
Curry, Richard O. (ed.), Freedom at Risk: Secrecy, Censorship, and Repression in the 1980s, Temple University Press, 1988.
Curtis, Mark, Web of Deceit: Britain’s real role in the world,Vintage, London, 2003.
Unpeople: Britain’s Secret Human Rights Abuses,Vintage, London, 2004.
Daniels, Robert V., The Conscience of the Revolution: Communist Opposition in Soviet Russia, Harvard UniversityPress, Cambridge, 1960.
Daniels, Robert V. (ed.), A Documentary History of Communism, vol. 1,Vintage Books, New York, 1960.
Davidson, Paul, Controversies in Post-Keynesian Economics, E. Elgar, Brookfield, Vt., USA, 1991.
John Maynard Keynes, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke, 2007
Davis, Mike, Late Victorian Holocausts: El Niño Famines and the Making of the Third World, Verso, London, 2002.
Denikin, General A., The White Armies, Jonathan Cape, London, 1930.
DeShazo, Peter, Urban Workers and Labor Unions in Chile 1902–1927,University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, 1983.
Deutscher, Isaac, The prophet unarmed : Trotsky 1921–1929, Oxford University Press, 1959.
Devine, Pat, Democracy and Economic Planning, Polity, Cambridge, 1988.
Dobbs, Maurice, Studies in Capitalist Development, Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd., London, 1963.
Dobson, Ross V. G., Bringing the Economy Home from the Market, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1993.
Domhoff, G. William, Who Rules America Now? A view from the ‘80s, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1983.
Donaldson, Peter, A Question of Economics, Penguin Books, London, 1985.
Economics of the Real World, 3rd edition, Penguin books, London, 1984.
Dorril, Stephen and Ramsay, Robin, Smear! Wilson and the Secret State, Fourth Estate Ltd., London, 1991.
Douglass, Frederick, The Life and Writings of Frederick Douglass, vol. 2, Philip S. Foner (ed.) International Publishers, New York, 1975.
Draper, Hal, The ‘dictatorship of the proletariat’ from Marx to Lenin, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1987.
The Myth of Lenin’s “Concept of The Party”, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/draper/works/1990/myth/myth.htm
Du Boff, Richard B., Accumulation and Power: an economic history of the United States, M.E. Sharpe, London, 1989.
Dubois, Pierre, Sabotage in Industry, Penguin Books, London, 1979.
Eastman, Max, Since Lenin Died, Boni and Liveright, New York, 1925.
Eatwell, Roger and Wright, Anthony (eds.), Contemporary political ideologies, Pinter, London, 1993.
Edwards, Stewart, The Paris Commune 1871, Victorian (& Modern History) Book Club, Newton Abbot, 1972.
Edwards, Stewart (ed.), The Communards of Paris, 1871, Thames and Hudson, London, 1973.
Eisler, Rianne, Sacred Pleasure,
Ellerman, David P., Property and Contract in Economics: The Case forEconomic Democracy, Blackwell, Oxford, 1992.
The Democratic Worker-Owned Firm: A New Model for Eastand West, Unwin Hyman, Boston, 1990. as “J. Philmore”, The Libertarian Case for Slavery, available at: http://cog.kent.edu/lib/Philmore1/Philmore1.htm
Elliot, Larry and Atkinson, Dan, The Age of Insecurity, Verso, London, 1998.
Fantasy Island: Waking Up to the Incredible Economic, Political and Social Illusions of the Blair Legacy, Constable, London, 2007. The Gods That Failed: Now the Financial Elite have Gambled Away our Futures, Vintage Books, London, 2009.
Engler, Allan, Apostles of Greed: Capitalism and the myth of the individual in the market, Pluto Press, London, 1995.
Evans Jr., Alfred B., Soviet Marxism-Leninism: The Decline of an Ideology, Praeger, London, 1993.
Faiwel, G. R., The Intellectual Capital of Michal Kalecki: A study ineconomic theory and policy, University of Tennessee Press, 1975.
Farber, Samuel, Before Stalinism: The Rise and Fall of Soviet Democracy, Polity Press, Oxford, 1990.
Fedotoff-White, D., The Growth of the Red Army, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1944.
Ferguson, C. E., The Neo-classical Theory of Production and Distribution, Cambridge University Press, London, 1969.
Ferro, Marc, October 1917: A social history of the Russian Revolution, Routledge & Kegan Paul, London, 1980.
Figes, Orlando, A People’s Tragedy: The Russian Revolution 1891–1924, Jonathan Cape, London, 1996.
Peasant Russia, Civil War: the Volga countryside in revolution 1917–1921, Phoenix Press, London, 2001.
Flamm, Kenneth, Creating the Computer: Government, Industry, and High Technology, The Brookings Institution, Washington D.C., 1988.
Forgacs, David (ed.), Rethinking Italian fascism: capitalism, populismand culture, Lawrence and Wishart, London, 1986.
Fraser, Ronald, Blood of Spain: the experience of civil war, 1936–1939, Allen Lane, London, 1979.
French, Marilyn, Beyond Power: On Women, Men, and Morals , Summit Books, 1985.
Frenkel-Brunswick, Else, The Authoritarian Personality,
Friedman, David, The Machinery of Freedom, Harper and Row, New York, 1973.
Friedman, Milton, Capitalism and Freedom, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 2002.
Economic Freedom, Human Freedom, Political Freedom,available at: http://www.cbe.csueastbay.edu/~sbesc/frlect.html The Hong Kong Experiment, available at: http://www.hoover.org/publications/digest/3532186.html
Funnell, Warrick, Jupe, Robert and Andrew, Jane, In Government we Trust:Market Failure and the delusionsof privatisation, Pluto Press, London,2009.
Gaffney, Mason and Harrison, Mason, The Corruption of Economics, Shepheard-Walwyn (Publishers) Ltd., London, 1994.
Galbraith, James K., Created Unequal: The Crisis in American Pay, The Free Press, New York, 1999.
Galbraith, John Kenneth, The Essential Galbraith, Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, 2001.
The New Industrial State, 4th edition, Princeton University Press, Princeton and Oxford, 2007.
Gemie, Sharif, French Revolutions, 1815–1914, Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, 1999.
Getzler, Israel, Kronstadt 1917–1921: The Fate of a Soviet Democracy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1983.
Martov: A Political Biography of a Russian Social Democrat, Melbourne University Press, Carlton, 1967. “Soviets as Agents of Democratisation”, in Revolution in Russia: reassessments of 1917, Edith Rogovin Frankel, Jonathan Frankel, Baruch Knei-Paz (eds.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York, 1991. “Marxist Revolutionaries and the Dilemma of Power”, pp. 88–112, Revolution and Politics in Russia, Alexander and Janet Rabinowitch with Ladis K.D. Kristof (eds.)
Gilmour, Ian, Dancing with Dogma, Britain Under Thatcherism, Simon and Schuster, London, 1992.
Glennerster, Howard and Midgley, James (eds.), The Radical Right and the Welfare State:an international assessment, Harvester Wheatsheaf,1991.
Gluckstein, Donny, The Tragedy of Bukharin, Pluto Press, London, 1994
The Paris Commune: A Revolutionary Democracy, Bookmarks,London, 2006
Glyn, Andrew, Capitalism Unleashed: Finance Globalisation and Welfare,Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2006.
Glyn, Andrew and Miliband, David (eds.), Paying for Inequality: The Economic Costs of Social Injustice, IPPR/Rivers Oram Press, London, 1994.
Goodstein, Phil H., The Theory of the General Strike from the French Revolution to Poland, East European Monographs, Boulder, 1984.
Gould, Stephan Jay, Ever Since Darwin: Reflections in Natural History,Penguin Books, London, 1991.
Bully for Brontosaurus: Reflections in Natural History, Hutchinson Radius, London, 1991.
Gramsci, Antonio, Selections from Political Writings (1921–1926), Lawrence and Wishart, London, 1978.
Grant, Ted, The Unbroken Thread: The Development of Trotskyism over 40 Years, Fortress Publications, London, 1989.
Russia from revolution to counter-revolution available at https://www.marxist.com/russia-from-revolution-to-counter-revolution.htm
Gray, John, False Dawn: The Delusions of Global Capitalism, Granta Books, London, 1998.
Green, Duncan, Silent Revolution: The Rise of Market Economics in Latin America, Cassell, London, 1995.
Greider, William, One World, Ready or Not: The Manic Logic of Global Capitalism, Penguin Books, London, 1997.
Gross, Bertram, Friendly Fascism, South End Press, Boston, 1989.
Gunn, Christopher Eaton, Workers’ Self-Management in the United States, Cornell University Press, Ithaca and London, 1984.
Gunson, P., Thompson, A. and Chamberlain, G., The Dictionary of Contemporary Politics of South America, Routledge, 1989.
Hahnel, Robin and Albert, Michael, The Quiet Revolution in Welfare Economics, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1990.
The Political Economu of Participatory Economics, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1991. Looking Forward: Participatory Economics for the Twenty First Century, South End Press, Boston, 1991.
Hallas, Duncan, The Comintern, Bookmarks, London, 1985.
“Towards a revolutionary socialist party”, contained inTony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky,Party and Class, Bookmarks, London, 1996.
Harding, Neil, Leninism, MacMillan Press, London, 1996.
Lenin’s political thought, vol. 1, Macmillan, London, 1977.
Harman, Chris, Bureaucracy and Revolution in Eastern Europe, Pluto Press, London, 1974.
“Party and Class”, contained in Tony Cliff, Duncan Hallas, Chris Harman and Leon Trotsky, Party and Class,Bookmarks, London, 1996, How the revolution was lost available at: http://www.marxists.de/statecap/harman/revlost.htm
Hastrup, Kirsten, Culture and History in Medieval Iceland, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1985.
Hatch, John B., “Labour Conflict in Moscow, 1921–1925” contained in Russia in the Era of NEP: explorations in Soviet society and culture, Fitzpatrick, Sheila, Rabinowitch, Alexander and Stites, Richard (eds.), Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1991.
Hawkins, Howard, “Community Control, Workers’ Control and the Co-operative Commonwealth”, Society and Nature, no. 3, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 55–85.
Haworth, Alan, Anti-Libertarianism: Markets, Philosophy and Myth, Routledge, London, 1994.
Hayek, F. A. von, The Essence of Hayek, Chiaki Nishiyama and Kurt Leube (Eds.), Hoover Institution Press, Stanford, 1984
Individualism and Economic Order, Henry Regnery Company, Chicago, 1948 “1980s Unemployment and the Unions” contained in Coates, David and Hillard, John (Eds.), The Economic Decline of Modern Britain: The Debate between Left and Right, Wheatsheaf Books Ltd., 1986. New Studies in Philosophy, Politics, Economics and the History of Ideas, Routledge & Kegan Paul. London/Henley, 1978. Law, Legislation and Liberty, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, 1982.
Hayek, F. A. von (ed.), Collectivist Economic Planning, Routledge and Kegan Paul, London, 1935.
Hayward, Jack, After the French Revolution: Six critics of Democracy and Nationalism, Harvester Wheatsheaf, Hemel Hempstead, 1991.
Heider, Ulrike, Anarchism: left, right, and green, City Lights Books, San Francisco, 1994.
Hein, Eckhard and Schulten, Thorsten, Unemployment, Wages and Collective Bargaining in the European Union, WSI_Discussion Paper No. 128, Witschafts- und Sozialwissenschaftliches Institut, Dusseldorf, 2004.
Henwood, Doug, Wall Street: How it works and for whom, Verso, London, 1998.
“Booming, Borrowing, and Consuming: The US Economy in 1999”, Monthly Review, vol. 51, no. 3, July-August 1999, pp.120–33. After the New Economy, The New Press, New York, 2003. Wall Street: Class Racket, available at http://www.panix.com/~dhenwood/WS_Brecht.html
Herbert, Auberon, “Essay X: The Principles Of Voluntaryism And Free Life”, The Right And Wrong Of Compulsion By The State, And Other Essays, available at: http://oll.libertyfund.org/Texts/LFBooks/Herbert0120/CompulsionByState/HTMLs/0146_Pt11_Principles.html
“Essay III: A Politician In Sight Of Haven”, The Right And Wrong Of Compulsion By The State, And Other Essays, available at: http://oll.libertyfund.org/Texts/LFBooks/Herbert0120/CompulsionByState/HTMLs/0146_Pt04_Politician.html
Herman, Edward S., Beyond Hypocrisy, South End Press, Boston, 1992.
Corporate Control, Corporate Power, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1981. “Immiserating Growth: The First World”, Z Magazine, January, 1994. “The Economics of the Rich”, Z Magazine, July, 1997
Herman, Edward S. and Chomsky, Noam, Manufacturing Consent: the politicaleconomy of the mass media, Pantheon Books,New York, 1988.
Heywood, Paul, Marxism and the Failure of Organised Socialism in Spain 1879–1936, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990.
Hicks, J. R., Value and capital: an inquiry into some fundamental principles of economic theory, 2nd edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1975.
Hills, John, Inequality and the State, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004.
Hobsbawm, Eric, Primitive Rebels: Studies in Archaic Forms of Social Movements in the 19th and 20th Centuries, 2nd Edition, W. W. Norton and Co., New Yprk, 1965.
Revolutionaries, rev. ed., Abacus, London, 2007.
Hodgskin, Thomas, Labour Defended against the Claims of Capital, available at: http://socserv2.socsci.mcmaster.ca/~econ/ugcm/3ll3/hodgskin/labdef.txt
Hollis, Martin and Edward Nell, Rational Economic Man: A Philosophical Critique of Neo-classic Economics, Cambridge University Press, London, 1975.
Hodgson, Geoffrey Martin, Economics and Utopia: why the learning economy is not the end of history, Routledge, London/New York, 1999.
Hoppe, Hans-Hermann, Democracy: The God That Failed: The Economics andPolitics of Monarchy, Democracy, and Natural Order,Transaction, 2001.
Anarcho-Capitalism: An Annotated Bibliography, available at: http://www.lewrockwell.com/hoppe/hoppe5.html
Holt, Richard P. F. and Pressman, Steven (eds.), A New Guide to Post KeynesianEconomics, Routledge, London, 2001.
Howell, David R. (ed.), Fighting Unemployment: The Limits of Free MarketOrthodoxy, Oxford University Press, New York, 2005.
Hutton, Will, The State We’re In, Vintage, London, 1996.
The World We’re In, Little, Brown, London, 2002.
Hutton, Will and Giddens, Anthony (eds.), On The Edge: living with global capitalism,Jonathan Cape, London, 2000.
ISG, Discussion Document of Ex-SWP Comrades, available at: http://www.angelfire.com/journal/iso/isg.html
Lenin vs. the SWP: Bureaucratic Centralism Or Democratic Centralism?, available at: http://www.angelfire.com/journal/iso/swp.html
Jackson, Gabriel, The Spanish Republic and the Civil War, 1931–1939, Princeton University Press, Princeton, 1965.
Jackson, J. Hampden, Marx, Proudhon and European Socialism, English Universities Press, London, 1957.
Johnson, Martin Phillip, The Paradise of Association: Political Culture and Popular Organisation in the Paris Commune of 1871, University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, 1996
Kaldor, Nicholas, Further Essays on Applied Economics, Duckworth, London, 1978.
The Essential Kaldor, F. Targetti and A.P. Thirlwall (eds.), Holmes & Meier, New York, 1989. The Economic Consequences of Mrs Thatcher, Gerald Duckworth and Co. Ltd, London, 1983.
Kaplan, Frederick I., Bolshevik Ideology and the Ethics of Soviet Labour,1917–1920: The Formative Years, Peter Owen, London, 1969.
Kaplan, Temma, Anarchists of Andalusia: 1868–1903, Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J., 1965.
Katouzian, Homa, Ideology and Method in Economics, MacMillian Press Ltd., London, 1980.
Kautsky, Karl, The road to power: political reflections on growing intothe revolution, Humanities Press, Atlantic Highlands, 1996.
Keen, Steve, Debunking Economics: The Naked Emperor of the social sciences, Pluto Press Australia, Annandale, 2001.
Keynes, John Maynard, The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, MacMillan Press, London, 1974.
Kerhohan, Andrew, “Capitalism and Self-Ownership”, from Capitalism, pp. 60–76, Paul, Ellen Frankel, Fred D. Miller Jr., Jeffrey Paul and John Ahrens (eds.), Basil Blackwood, Oxford, 1989.
Kindleberger, Charles P., Manias, Panics, and Crashes: a history of financialcrises, 2nd Edition, Macmillan, London, 1989.
King, J.E., A history of post Keynesian economics since 1936, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham, 2002
Kirzner, Israel M., “Entrepreneurship, Entitlement, and Economic Justice”, pp. 385–413, in Reading Nozick: Essays on Anarchy, State and Utopia, Jeffrey Paul (ed.), Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1982.
Perception, Opportunity, and Profit, University of ChicagoPress, Chicago, 1979.
Klein, Naomi, No Logo, Flamingo, London, 2001.
Fences and Windows: Dispatches from the front lines of theGlobalisation Debate, Flamingo, London, 2002.
Koenker, Diane P., “Labour Relations in Socialist Russia: Class Values and Production Values in the Printers’ Union, 1917–1921,” pp. 159–193, Siegelbaum, Lewis H., and Suny, Ronald Grigor (eds.), Making Workers Soviet: power, class, and identity, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1994.
Koenker, Diane P., Rosenberg, William G. and Suny, Ronald Grigor (eds.), Party, State, and Society in the Russian Civil War, Indiana University Press, Indiana, 1989.
Kohn, Alfie, No Contest: The Case Against Competition, Houghton Mufflin Co.,New York, 1992.
Punished by Rewards: The Trouble with Gold Stars, Incentive Plans, A’s, Praise and Other Bribes, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, 1993.
Kollontai, Alexandra, The Workers Opposition, Solidarity, London, date unknown.
Selected Writings of Alexandra Kollontai, Allison and Busby, London, 1977.
Kowalski, Ronald I., The Bolshevik Party in Conflict: the left communist opposition of 1918, Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1990.
Krause, Peter, The Battle for Homestead, 1880–1892: politics, culture, and steel, University of Pittsburgh Press, Pittsburgh/London, 1992
Krugman, Paul, Peddling Prosperity: Economic Sense and Nonsense in the Age of Diminished Expectations, NW Norton & Co., New York/London, 1994.
The Conscience of a Liberal, W.W. Norton & Co., New York/London, 2007.
Krugman, Paul and Wells, Robin, Economics, W. H. Freeman, New York, 2006.
Kuhn, Thomas S., The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, 3rd ed., University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1996.
Kuznets, Simon, Economic Growth and Structure: Selected Essays, Heineman Educational Books, London, 1966.
Capital in the American Economy, Princeton University Press, New York, 1961.
Lange, Oskar and Taylor, Fred M., On the Economic Theory of Socialism, Benjamin Lippincott (ed.), University of Minnesota Press, New York, 1938.
Laqueur, Walter (ed.), Fascism: a Reader’s Guide, Harmondsworth, Penguin, 1979.
Lazonick, William, Business Organisation and the Myth of the Market Economy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991.
Competitive Advantage on the Shop Floor, Havard University Press, Cambridge, Mass., 1990. Organisation and Technology in Capitalist Development, Edward Elgar, Brookfield, Vt, 1992.
Lea, John and Pilling, Geoff (eds.), The condition of Britain: Essays on Frederick Engels, Pluto Press, London, 1996.
Lear, John, Workers, Neighbors, and Citizens: The Revolution in Mexico City, University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, 2001.
Lee, Frederic S., Post Keynesian Price Theory, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998
Leggett, George, The Cheka: Lenin’s Political Police, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1981.
Lenin, V. I., Essential Works of Lenin, Henry M. Christman (ed.), Bantam Books, New York, 1966.
The Lenin Anthology, Robert C. Tucker (ed.), W.W. Norton & Company, New York, 1975. Will the Bolsheviks Maintain Power?, Sutton Publishing Ltd,Stroud, 1997. Left-wing Communism: An Infantile Disorder, Lawrence & Wishart,London, 1947. The Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970. Six Thesis on the Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government,contained in The Immediate Tasks of the Soviet Government, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970, pp. 42–45. The Threatening Catastrophe and How to Avoid It, Martin Lawrence Ltd., undated. Selected Works: In Three Volumes, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1975.
Lenin, V. I., and Trotsky, Leon, Kronstadt, Monad Press, New York, 1986.
Levin, Michael, Marx, Engels and Liberal Democracy, MacMillan Press, London, 1989.
Lichtenstein, Nelson and Howell, John Harris (eds.), Industrial Democracy in America: The Ambiguous Promise, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1992
Lichtheim, George, The origins of socialism, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London, 1969
A short history of socialism, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London, 1970
Lincoln, W. Bruce, Red Victory: A History of the Russian Civil War, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1989.
List, Friedrich, The Natural System of Political Economy, Frank Cass, London, 1983.
Lovell, David W., From Marx to Lenin: An evaluation of Marx’s responsibility for Soviet authoritarianism, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1984.
Luxemburg, Rosa, Rosa Luxemburg Speaks, Mary-Alice Waters (ed.), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1970.
MacPherson, C.B., The Political Theory of Possessive Individualism: Hobbes to Locke, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1964.
Malle, Silvana, The Economic Organisation of War Communism, 1918–1921, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985.
Mandel, David, The Petrograd Workers and the Soviet Seizure of Power: from the July days 1917 to July 1918, MacMillan, London, 1984.
Marglin, Steven, “What do Bosses Do?”, Review of Radical Political Economy, Vol. 6, No.2, New York, 1974.
Marshall, Alfred, Principles of Economics: An Introductory Volume, 9th Edition (in 2 volumes), MacMillian, London, 1961.
Martin, Benjamin, The Agony of Modernisation: Labour and Industrialisation in Spain, ICR Press, Cornell University, 1990.
Martov, J., The State and Socialist Revolution, Carl Slienger, London, 1977.
Marx, Karl, Capital: A Critique of Political Economy, vol. 1, Penguin Books, London, 1976.
Capital: A Critique of Political Economy, vol. 3, Penguin Books, London, 1981. Theories of Surplus Value, vol. 3, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1971. A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1970.
Marx, Karl and Engels, Frederick, Selected Works, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1975.
The Marx-Engels Reader, Second Edition,Robert C. Tucker (ed.), W.W. Norton & Co, London & New York, 1978. The socialist revolution, F. Teplov and V. Davydov (eds.)Progess, Moscow, 1978. Basic Writings on Politics and Philosophy,Lewis S. Feuer (ed.), Fontana/Collins, Aylesbury, 1984. “Manifesto of the Communist Party”, Selected Works, pp. 31–63. Fictitious Splits In The International,available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1864iwma/1872-e.htm
Marx, Karl, Engels, Federick and Lenin, V.I., Anarchism and Anarcho-Syndicalism, Progress Publishers, Moscow, 1974.
Matthews, R.C.O. (ed.), Economy and Democracy, MacMillan Press Ltd., London, 1985.
McAuley, Mary, Bread and Justice: State and Society in Petrograd 1917–1922, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1991.
McElroy, Wendy, Anarchism: Two Kinds, available at:http://www.wendymcelroy.com/mises/twoanarchism.html
McLay, Farguhar (ed.), Workers City: The Real Glasgow Stands Up, Clydeside Press, Glasgow, 1988.
McNally, David, Against the Market: Political Economy, Market Socialism and the Marxist Critique, Verso, London, 1993.
Another World Is Possible: Globalization & Anti-Capitalism, Revised Expanded Edition, Merlin, 2006.
Mehring, Franz, Karl Marx: The Story of his life, John Lane, London, 1936.
Miliband, Ralph, Divided societies: class struggle in contemporary capitalism, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1989.
Mill, John Stuart, Principles of Political Economy, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1994.
On Liberty and Other Essays, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991.
Miller, David, Social Justice, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1976.
Market, State, and community: theoretical foundations of marketsocialism, Clarendon, Oxford, 1989.
Miller, William Ian, Bloodtaking and Peacemaking: Feud, Law and Society in Saga Iceland, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1990.
Mills, C. Wright, The Power Elite, Oxford University Press, London, 1956.
Milne, S., The Enemy Within, Verso, London, 1994.
Minsky, Hyman, Inflation, Recession and Economic Policy, Wheatsheaf Books, Sussex, 1982.
“The Financial Instability Hypothesis” in Post-Keynesian Economic Theory, pp. 24–55, Arestis, Philip and Skouras, Thanos (eds.), Wheatsheaf Books, Sussex, 1985.
Mises, Ludwig von, Liberalism: A Socio-Economic Exposition,Sheed Andres and McMeek Inc., Kansas City, 1978.
Human Action: A Treatise on Economics, William Hodge and Company Ltd., London, 1949. Socialism: an economic and sociological analysis, Cape, London, 1951.
Montagu, Ashley, The Nature of Human Aggression, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1978.
Montgomery, David, Beyond Equality: Labour and the Radical Republicans, 1862–1872, Vintage Books, New York, 1967.
The Fall of the House of Labour: The Workplace, the state, and American labour activism, 1865–1925, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
Moore, Michael, Downsize This! Random Threats from an Unarmed America, Boxtree, London, 1997.
Morrow, Felix, Revolution and Counter-Revolution in Spain, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1974.
Mumford, Lewis, The Future of Technics and Civilisation, Freedom Press, London, 1986.
Negri, Antonio, Marx Beyond Marx, Autonomedia, Brooklyn, 1991.
Neill, A.S, Summerhill: a Radical Approach to Child Rearing, Penguin, 1985.
Newman, Stephen L., Liberalism at wit’s end: the libertarian revolt against the modern state, Cornell University Press, 1984.
Noble, David, America by Design: Science, technology, and the rise of corporate capitalism, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1979.
Progress without People: In defense of Luddism, Charles H. Kerr Publishing Ltd., Chicago, 1993. Forces of Production: A Social History of Industrial Automation, Oxford University Press, New York, 1984.
Nove, Alec, An economic history of the USSR: 1917–1991, 3rd ed., Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1992.
Socialism, Economics and Development, Allen & Unwin, London, 1986.
Nozick, Robert, Anarchy, State and Utopia, B. Blackwell, Oxford, 1974.
Oestreicher, Richard Jules, Solidarity and fragmentation: working people and class consciousness in Detroit, 1875–1900, University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 1986.
Ollman, Bertell, Social and Sexual Revolution: Essays on Marx and Reich, Black Rose Books, Montreal, 1978.
Ollman, Bertell (ed.), Market Socialism: The Debate Among Socialists, Routledge, London, 1998.
O’Neill, John, Markets, Deliberation and Environment, Routledge, Oxon, 2007.
The market: ethics, knowledge, and politics, Routledge, London, 1998 Ecology, policy, and politics: human well-being and the natural world, Routledge, London/New York, 1993.
Oppenheimer, Franz, The State, Free Life Editions, New York, 1975.
Ormerod, Paul, The Death of Economics, Faber and Faber Ltd., London, 1994.
Orwell, George, Homage to Catalonia, Penguin, London, 1989.
The Road to Wigan Pier, Penguin, London, 1954. Nineteen Eighty-Four, Penguin, Middlesex, 1982. Orwell in Spain, Penguin Books, London, 2001. Inside the Whale and Other Essays, Penguin Books, Harmondsworth, 1986.
Pagano, U. and Rowthorn, R. E. (eds.), Democracy and Efficiency in Economic Enterprises, Routledge, London, 1996.
Palley, Thomas I., Plenty of Nothing: The Downsizing of the American Dreamand the case for Structural Keynesian, Princeton UniversityPress, Princeton, 1998.
Paul, Ellen Frankel. Miller, Jr., Fred D. Paul, Jeffrey and Greenberg, Dan (eds.), Socialism, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1989.
Perrin, David A., The Socialist Party of Great Britain: Politics, Economics and Britain’s Oldest Socialist Party, Bridge Books, Wrexham, 2000.
Petras, James and Leiva, Fernando Ignacio, Democracy and Poverty in Chile: The Limits to Electoral Politics, Westview Press, Boulder, 1994.
Pipes, R., Russia Under the Bolshevik Regime, 1919–1924, Fontana Press, London, 1995.
Pirani, Simon, The Russian revolution in retreat, 1920–24: Soviet workers and the new Communist elite, Routledge, New York, 2008
Phillips, Kevin, The Politics of Rich and Poor: Wealth and the American Electorate in the Reagan Aftermath, Random House, New York, 1990.
Polanyi, Karl, The Great Transformation: the political and economic origins of our time, Beacon Press, Boston, 1957.
Popper, Karl, Conjectures and Refutations: The Growth of Scientific Knowledge, Basic, New York, 1965.
Preston, Paul, The coming of the Spanish Civil War: reform, reaction, and revolution in the Second Republic, 2nd ed., Routledge, London/New York, 1994.
Preston, Paul (ed.), Revolution and War in Spain 1931–1939, Methuen, London, 1984.
Prychitko, David L., Markets, Planning and Democracy: essays after the collapse of communism, Edward Elgar, Northampton, 2002.
Rabinowitch, Alexander, Prelude to Revolution: The Petrograd Bolsheviks and the July 1917 Uprising, Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 1991.
The Bolsheviks Come to Power: The Revolution of 1917 in Petrograd, W.W. Norton & Co., New York, 1976. The Bolsheviks in Power: The first year of Soviet rule in Petrograd, Indiana University Press, Bloomington, 2007. “Early Disenchantment with Bolshevik Rule: New Data form the Archives of the Extraordinary Assembly of Delegates from Petrograd Factories”, Politics and Society under the Bolsheviks, Dermott, Kevin and Morison, John (eds.), Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1999.
Rabinowitch, Alexander and Janet with Kristof, Ladis K.D. (eds.), Revolution and politics in Russia: essays in memory of B.I. Nicolaevsky, Indiana University Press for the International Affairs Center, Bloomington/London, 1973.
Radcliff, Pamela Beth, From mobilization to civil war: the politics of polarizationin the Spanish city of Gijon, 1900–1937, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1996.
Radin, Paul, The World of Primitive Man, Grove Press, New York, 1960.
Radek, Karl, The Kronstadt Uprising available at, https://www.marxists.org/archive/radek/1921/04/kronstadt.htm
Raleigh, Donald J., Experiencing Russia’s Civil War: Politics, Society,and Revolutionary Culture in Saratov, 1917–1921,Princeton University Press, Woodstock, 2002.
Rand, Ayn, Capitalism: The Unknown Ideal, New American Library, New York, 1966.
The Ayn Rand Lexicon: Objectivism from A to Z, Harry Binswanger (ed.), Meridian, New York, 1986. The Virtue of Selfishness, New American Library, New York, 1964.
Ransome, Arthur, The Crisis in Russia 1920, Redwords, London, 1992.
Rayack, Elton, Not So Free To Choose: The Political Economy of MiltonFriedman and Ronald Reagan, Praeger, New York, 1987.
Read, Christopher, From Tsar to Soviets: The Russian people andtheir revolution, 1917–21, UCL Press, London, 1996.
Reed, John, Ten Days that shook the World, Penguin Books, 1982.
Shaking the World: John Reed’s revolutionary journalism,Bookmarks, London, 1998.
Reekie, W. Duncan, Markets, Entrepreneurs and Liberty: An Austrian Viewof Capitalism, Wheatsheaf Books Ltd., Sussex, 1984.
Reich, Wilhelm, The Mass Psychology of Fascism, Condor Book, Souvenir Press (E&A) Ltd., USA, 1991.
Reitzer, George, The McDonaldization of Society: An Investigation into the changing character of contemporary social life, Pine Forge Press, Thousand Oaks, 1993.
Remington, Thomas F., Building Socialism in Bolshevik Russia: Ideology and Industrial Organisation 1917–1921, University of Pittsburgh Press, London, 1984.
Richardson, Al (ed.), In defence of the Russian revolution: a selection of Bolshevik writings, 1917–1923, Porcupine Press, London, 1995.
Ricardo, David, The Principles of Political Economy and Taxation, J.M. Dent & Sons/Charles E. Tuttle Co., London/Vermont, 1992.
Ridgeway, James, Blood in the Face: The Ku Klux Klan, Aryan Nations, Nazi Skinheads, and the Rise of a New White Culture, Thunder’s Mouth Press, 1990.
Roberts, David D., The Syndicalist Tradition and Italian Fascism,University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, 1979.
Robertson, Dennis, “Wage-grumbles”, Economic Fragments, pp. 42–57, in W. Fellner and B. Haley (eds.), Readings in the theoryof income distribution, The Blakiston, Philadephia, 1951.
Robinson, Joan, The Accumulation of Capital (2nd Edition), MacMillan, St. Martin’s Press, 1965.
Contributions to Modern Economics, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1978. Collected Economic Papers, vol. 4, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1973. Collected Economic Papers, vol. 5, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1979.
Rodrik, Dani, Comments on ‘Trade, Growth, and Poverty by D. Dollar and A. Kraay, available at: http://ksghome.harvard.edu/~drodrik/Rodrik%20on%20Dollar-Kraay.PDF
Rollins, L.A., The Myth of Natural Rights, Loompanics Unlimited, Port Townsend, 1983.
Rose, Steven, Lewontin, R.C. and Kamin, Leon J., Not in Our Genes: Biology, Ideology and Human Nature, Penguin Books, London, 1990.
Rosenberg, William G., “Russian Labour and Bolshevik Power, pp. 98–131, The Workers Revolution in Russia: the view from below, D. Kaiser (ed.), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987.
“Workers’ Control on the Railroads and Some Suggestions Concerning Social Aspects of Labour Politics in the Russian Revolution”, pp. D1181-D1219, The Journal of Modern History, vol. 49, no. 2.
Rosmer, Alfred, Lenin’s Moscow, Bookmarks, London, 1987.
Rosnick, David and Weisbrot, Mark, Are Shorter Work Hours Good for the Environment? A Comparison of U.S. and European Energy Consumption, available at: http://www.cepr.net/documents/publications/energy_2006_12.pdf
Rothbard, Murray N., The Ethics of Liberty, Humanities Press, Atlantic Highlands, N.J., 1982.
For a New Liberty, MacMillan, New York, 1973. “Praxeology: The Methodology of Austrian Economics” in The Foundation of Modern Austrian Economics, pp. 19–39,Dolan, Edwin G. (ed.), Sheed & Ward, Inc., Kansas, 1976. Egalitarianism as a Revolt against Nature and Other Essays, Libertarian Press Review, 1974. “Nations by Consent: Decomposing the Nation-State,”in Secession, State and Liberty, David Gordon (ed.),Transaction Publishers, New Brunswick, 1998. Power and Market, Institute for Humane Studies,Menlo Park, 1970. Man, Economy, and State, with Power and Market, Ludwig von Mises Institute, Auburn, 2004. “Society Without A State”, pp. 191–207, Anarchism: Nomos XIX, J. Roland Pennock and John W. Chapman (eds.), New York University Press, New York, 1978. America’s great depression, Van Nostrand, Princeton/London, 1963. Conceived in Liberty (in four volumes), Arlington House Publishers,New Rochell, 1975. The Logic of Action II: Applications and Criticism from the Austrian School, Edward Elgar, Cheltenham/Lyme, 1997. Classical Economics: An Austrian Perspective on the Historyof Economic Thought, Edward Elgar, Brookfield, 1995. Konkin on Libertarian Strategy, available at:http://www.anthonyflood.com/rothbardkonkin.htm Are Libertarian’s ‘Anarchists’?, available at: http://www.lewrockwell.com/rothbard/rothbard167.html
Rousseau, J-J, The Social Contract and Discourses, Everyman, London, 1996.
Rowbotham, Sheila, Hidden from History: 300 Years of Women’s Oppression and the fight against it, Pluto Press, London, 1977.
“Edward Carpenter: Prophet of the New Life”, Rowbotham, Sheila and Weeks, Jeffrey, Socialism and the New Life: The Personal and Sexual Politics of Edward Carpenter and Havelock Ellis, Pluto Press, London 1977.
RSDLP, Minutes of the Second Congress of the RSDLP, New ParkPublications, London, 1978.
St. Clair, David, The Motorization of American Cities, Praeger, New York, 1986.
Sakwa, Richard, Soviet Communists in Power: a study of Moscow during the Civil War, 1918–21, Macmillan, Basingstoke, 1987.
Sawyer, Malcolm C., The Economics of Michal Kalecki, MacMillan, Basingstoke,1985.
The Economics of Industries and Firms: theories, evidence and policy (2nd ed.), Croom Helm, London, 1985.
Schapiro, Leonard, The Origin of the Communist Autocracy: PoliticalOpposition in the Soviet State: The First Phase, 1917–1922, Frederick A. Praeger, New York, 1965.
Schlosser, Eric, Fast Food Nation: What the all-american meal is doing to the world, Allen Lane, London, 2001.
Schneider, Cathy Lisa, Shantytown protest in Pinochet’s Chile, Temple University Press, Philadelphia, 1995.
Schor, Juliet B., The Overworked American: The Unexpected Decline of Leisure, BasicBooks, New York, 1992.
Schorske, C., German Social Democracy, 1905–1917, Cambridge, Mass., 1955.
Schulkind, Eugene (ed.), The Paris Commune of 1871: The View from the Left, Jonathan Cape, London, 1972.
Schumacher, E.F., Small is Beautiful: A Study of Economics as if people mattered, Vintage, London, 1993.
Schweickart, David Against Capitalism, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1993.
After Capitalism, Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, inc., Lanham, 2002.
Sen, Amartya, Resources, Values and Development, Basil Blackwell, Oxford, 1984.
Development as Freedom, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1999.
Senior, Nassau, An Outline of the Science of Political Economy, Alan & Unwin, London, 1951
Serge, Victor, Memoirs of a Revolutionary 1901–41, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1963.
Revolution in Danger: Writings from Russia, 1919–1921, Redwords, London, 1997. Year One of the Russian Revolution, Bookmarks, Pluto Press and Writers and Readers, London/New York, 1992. The Serge-Trotsky Papers, D. J. Cotterill (ed.), Pluto Press, London, 1994 Anarchists Never Surrender: Essays, Polemics, and Correspondence on Anarchism, 1908–1938, PM Press, Oakland, 2015. The Life and Death of Leon Trotsky, Haymarket Books, Chicago, 2016
Service, Robert, The Bolshevik Party in Revolution: A Study of Organisational change, Macmillan, London, 1979.
Silk L., and Vogel, D., Ethics and Profits: The Crisis of Confidence in American Business, Simon and Schuster, New York, 1976.
Sirianni, Carmen, Workers’ Control and Socialist Democracy, Verso/NLB, London, 1982.
Shanin, Teodor, The Awkward Class: Political Sociology of Peasantry in a Developing Society: Russia 1910–1925, OxfordUniversity Press, London, 1972.
Skidelsky, Robert (ed.), Thatcherism, Chatto & Windus, London, 1988.
Skidmore, Thomas E. and Smith, Peter H., Modern Latin America, Second Edition, Oxford University Press, 1989.
Smith, Adam, The Wealth of Nations, Everyman’s Library, London, 1991.
The Wealth of Nations, book 5, contained in An Inquiry intothe Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations: A SelectedEdition, Oxford University Press, Oxford/New York, 1998.
Smith, S.A., Red Petrograd: Revolution in the Factories 1917–1918, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1983.
Revolution and the People in Russia and China: A Comparative History, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2008. Russia in Revolution: An Empire in Crisis, 1890–1928, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2017.
Solvason, Birgir T. Runolfsson, Ordered Anarchy, State and Rent-seeking: The Iceland Commonwealth, 930–1262, available at http://www.hag.hi.is/~bthru/ritgerd.htm
Sorel, Georges, Reflections on Violence, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1999.
Sorenson, Jay B., The Life and Death of Soviet Trade Unionism: 1917–1928, Atherton Press, New York, 1969.
Spriano, Paolo, The Occupation of the Factories: Italy 1920, Pluto Press, London, 1975.
Staub, Ervin, The Roots of Evil: The Origins of Genocide and Other Group Violence, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000
Stauber, John, and Sheldon Rampton, Toxic Sludge is good for you! Lies, Damn Lies and the Public Relations Industry, Common Courage Press, Monroe, Maine, 1995.
Steinberg, I., Spiridonova: revolutionary terrorist, Methuen, London, 1935.
Steinbeck, John, The Grapes of Wrath, Mandarin, London, 1990.
Stewart, Michael, Keynes in the 1990s: A Return to Economic Sanity, Penguin Books, London, 1993.
Keynes and After, 3rd edition, Penguin Books, London, 1987.
Stiglitz, Joseph, Globalisation and its Discontents, Penguin Books, London, 2002.
Stretton, Hugh, Economics: A New Introduction, Pluto Press, London, 2000.
Suny, Ronald Grigor (ed.), The Structure of Soviet History: Essays and Documents, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003
Swain, Geoffrey, The Origins of the Russian Civil War, Longman, London/New York, 1996.
Sweezy, Paul, Theory of Capitalist Development, Monthly Review Press, New York, 1942.
Targetti, Ferdinando, Nicholas Kaldor: The Economics and Politics of Capitalism as a Dynamic System, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1992.
Taylor, M. W., Men versus the state: Herbert Spencer and late Victorian individualism,Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1992.
Taylor, Michael W. (ed.), Herbert Spencer and the Limits of the State: The LateNineteenth-Century Debate Between Individualism andCollectivism, St. Augustine’s Press, 1997.
Thomas, Hugh, The Spanish Civil War, Hamish Hamilton, London, 1986.
Thomas, Paul, Karl Marx and the Anarchists, Routledge & Kegan Paul plc,London, 1985.
Tomlins, Christopher L., Law, Labor, and Ideology in the Early American Republic, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1993.
Thompson, E.P., The Making of the English Working Class, Penguin Books, London, 1991.
Customs in Common, Penguin Books, London, 1993.
Thompson, Noel, The Real Rights of Man: Political Economies for the Working Class, 1775–1850, Pluto Press, London, 1998.
Ticktin, Hillel and Cox, Michael (eds.), The Ideas of Leon Trotsky, Porcupine Press, London, 1995.
Tokes, Rudolf L., Bela Kun and the Hungarian Soviet Republic: The Origins and Role of the Communist Party of Hungary in the Revolutions of 1918–1919, Pall Mall Press, London, 1967.
Trotsky, Leon, History of the Russian Revolution, in three volumes, Gollancz and Sphere Books, London, 1967.
Writings of Leon Trotsky: Supplement (1934–40), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1979. Writings 1936–37, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1978. Writings 1933–34, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2003. Writings 1932, Pathfinder Press, New York, 1999. Writings 1930–31, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2002. Writings 1930, Pathfinder Press, New York, 2003. Terrorism and Communism, Ann Arbor, 1961. The Revolution Betrayed: What is the Soviet Union and where is it going?, Faber and Faber Ltd, London, 1937. Leon Trotsky Speaks, Pathfinder, New York, 1972. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. I, New Park Publications, London, 1979. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. II, New Park Publications, London, 1979. How the Revolution Armed: the military writings and speeches of Leon Trotsky, vol. IV, New Park Publications, London, 1979. Stalin: An Appraisal of the man and his influence, in two volumes, Panther History, London, 1969. The Death Agony of Capitalism and the Tasks of the Fourth International, contained in How Solidarity can change the world, Alliance for Workers’ Liberty, London, 1998. First Year Years of the Communist International, (in 2 volumes), New Park Publications, London, 1974. The Third International After Lenin, Pioneer Publishers, New York, 1957. The Challenge of the Left Opposition (1923–25), Pathfinder Press, New York, 1975. The Challenge of the Left Opposition (1926–27), Pathfinder, New York, 1980. On Lenin: Notes towards a Biography, George G. Harrap & Co. Ltd., London, 1971. “Lessons of October”, pp. 113–177, The Essential Trotsky, Unwin Books, London, 1963. Leon Trotsky on China, Monad Press, New York, 2002 In Defense of Marxism, Pathfinder, New York, 1995. Platform of the Opposition, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1927-plo/ch01.htm The Lessons of October, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1924-les.htm How Did Stalin Defeat the Opposition?, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1935-sta.htm Work, Discipline, Order, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1918-mil/ch05.htm More Equality! available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1919-mil/ch12.htm The Revolution Betrayed, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1936-rev/index.htm The Class Nature of the Soviet State, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/sovstate.htm The Path of the Red Army, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1918-mil/ch02.htm The Moralists and Sycophants against Marxism, contained in Their Morals and Ours, pp. 53–66, Pathfinder, New York, 1973. The Makhno Movement, available at: http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1919-mil/ch49.htm Stalinism and Bolshevism, available at:http://www.marxists.org/archive/trotsky/works/1937/1937-sta.htm
Turner, Adai, Just Capital: The Liberal Economy, Pan Books, London, 2002.
Utton, M. A., The Political Economy of Big Business, Martin Robinson, Oxford, 1982.
van der Linden, Marcel, Western Marxism and the Soviet Union : a survey of critical theories and debates since 1917Brill, Leiden, 2007
Wade, Robert, Governing the Market: Economic Theory and the role of governmentin East Asian Industrialisation, Princeton University Press,Princeton, 1990.
Walford, George, George Walford on Anarcho-Capitalism, available at http://flag.blackened.net/liberty/walford-on-anarcap.html
Wallerstein, Immanuel, Geopolitics and Geoculture, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991.
The Capitalist World System (vol. 1),
Walras, L, Elements of Pure Political Economy, Allen and Unwin, London, 1954.
Ward, Benjamin, What’s Wrong with Economics?, Basic Books, New York, 1972
Ware, Norman, The Industrial Worker 1840–1860: The Reaction of American IndustrialSociety to the Advance of the Industrial Revolution, Elephant Paperbacks, Chicago, 1924.
Watson, Andrew, From Red to Green: Green Politics and environmentalism cannot save the environment. A socialist politics can,Privately Published, 1990.
Weisbrot, Mark, Globalisation for Whom?, available at: http://www.cepr.net/Globalization.html
Weisbrot, Mark, Baker, Dean, Kraev, Egor and Chen, Judy,The Scorecard on Globalization 1980–2000: Twenty Years of Diminished Progress,available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/globalization_2001_07_11.htm
Weisbrot, Mark, Baker, Dean, Naiman, Robert and Neta, Gila, Growth May Be Good for the Poor — But are IMF and World Bank Policies Good for Growth? available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/econ_growth_2001_05.htm
Weisbrot, Mark and Rosnick, David, Another Lost Decade?: Latin America’s Growth Failure Continues into the 21st Century, available at: http://www.cepr.net/publications/latin_america_2003_11.htm
Wilkinson, Richard and Pickett, Kate, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal Societies Almost Always Do Better, Allen Lane, London, 2009.
Williams, Gwyn A., Proletarian Order: Antonio Gramsci, factory councils and the origins of Italian Communism, 1911–1921, Pluto Press, London, 1975.
Artisans and Sans-Culottes: Popular Movements in France and Britain during the French Revolution, Edward Arnold, London, 1981.
Wilson, H., The Labour Government 1964–1970, London, 1971.
Wilkinson, Richard and Pickett, Kate, The Spirit Level: Why More Equal SocietiesAlmost Always Do Better, Allen Lane, London,2009.
Winn, Peter (ed.), Victims of the Chilean Miracle: Workers and Neoliberalism in the Pinochet Era, 1973–2002, Duke University Press, Durham and London, 2004.
Wolff, Edward N., Top Heavy: A Study of Increasing Inequality in America, Twentieth Century Fund, 1995
Wolff, Jonathan, Robert Nozick: Property, Justice and the Minimal State, Polity Press, Oxford, 1991.
Wray, L. Randall, Money and Credit in Capitalist Economies: the endogenousmoney approach, Aldershot, Elgar, 1990.
Zinoviev, Grigorii, History of the Bolshevik Party: A Popular Outline, New Park Publications, London, 1973.
#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#faq#anarchy faq#revolution#anarchism#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate crisis#climate#ecology#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment
4 notes
·
View notes