#space western europe
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Yes aliens would be super shocked by adrenaline. No other biosphere would have a need for a fight or flight hormone. All other biospheres would run by different thermodynamic laws and competition and predation would not be things. That is totally good speculative biology and in no way ignores the fact the laws of physics are the same everywhere.
Don’t you a have a father-daughter purity ball to attend? I ask because you are clearly a backwoods fundamentalist and think it is blasphemy to inquire into the evolutionary pressures that cause aspects of humanity. Or else you would have realized they would exist everywhere.
#humans are space orcs#except that no fuck off#humans are space hobbits#space western europe#space australia#also north america is home to far more dangerous wildlife#humanity fuck yeah#or rather#humanity fuck off
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
“We all pack bond you illiterate troglodyte. You can’t be a social animal without that capacity, you can’t develop language without being a social animal, and you can’t abstract without language.”
The advisor looked tiredly at the emperor. "I advised no contact with the humans, not because THEY are especially dangerous. They pack bond. With literally anyone or thing. You attacked anyway. They have summoned The Pack."
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
On one level the book is about the life of a woman who is hardly more than a token in a great epic poem, on another it’s about how history and context shape how we are seen, and the brief moment there is to act between the inescapable past and the unknowable future. Perhaps to write Lavinia Le Guin had to live long enough to see her own early books read in a different context from the one where they were written, and to think about what that means.
-Jo Walton
#thinking of how her last four novels between 2004 and 2008 show a progressive blossoming of interest in classical literary traditions#following nearly half a century's worth of a career where she seems to actively avoid the influence of classical or medieval europe#idk. but i think this explains annals of the western shore as much as lavinia.#she gets so interested in what it means to share the same stories across space and time (and class and gender and nationality)#to be united in a community by having the same poetry#and in such an obvious way thinking about classics as a discipline is an incredible way to work through that#and i do think its an interest that must come out of having witnessed her own work unite people in community across time#if you're talking about the way stories and poems bring people together across time...#i read the texts passed on to me by renaissance humanists and 19th century philologists and byzantine monks and late antique scribes...#and they're the same across time and space but they're also not#and to have seen her own work reach people across space and time and be the same but also not... that must have been incredible#so: did living long enough to see her own early books read in a different context and to think about what that means#drive her to think about classical literature as she clearly was for the better part of a decade?#mine#reception#anyway i gotta think about this and email [redacted] tomorrow
250 notes
·
View notes
Text
Saturday's Late Night Sci-Fi Cinema (Double Feature)
First Spaceship on Venus (1960 film)

Theatrical release poster
In 1985, during the course of the works to irrigate the Gobi Desert, a strange piece of rock was discovered.
As it was analyzed, an artificial spool was discovered on it. The origin was not of this world.
At the enquire into its origin, someone reminds an explosion the equivalent of an hydrogen bomb ocurred in Siberia in June of 1908. It was a meteor, the Tongu Meteor.
77 years later, an International expedition team has been assembled to investigate where it came from.
At the World Federation for Space Research meeting to celebrate the first station at the Moon, Professor Harringway made an important revelation: the meteor was a indeed a spaceship that came from the planet Venus and it exploded in the air while it tried to land.
And also, the spool was itself a flight recorder. It was partially decoded making itself the first cosmic document of alien life forms.
At the questioning why the Venusians make any further intent of communicating with planet Earth, the Federation gathered a group of scientists to travel aboard the Kosmoskrator to Venus.
Its crew must have to decipher the rest of the message contained on the spool to know the intentions of the Venusian civilization with planet Earth and discover the mysteries behind the atmosphere of the Morning Star.
First Spaceship on Venus is a 1960 color film from East Germany and Poland.
Main cast:
Günther Simon as Robert Brinkman Yoko Tani as Dr. Sumiko Oldrick Lukes as Professor Orloff Julius Ongewe as Talua Ignacy Machowski as Professor Durand Mukhail Postnikov as Professor Harringway Kurt Rackelmann as Professor Sikarna Tang Hua-Ta as Dr. Chen Yu
Production staff:
Directed by: Kurt Maetzig Screenplay by: Kurt Maetzig and J. Barkhauer (uncredited) Story by: J. Fethke, W. Kohlhasse, G. Reish, G Rücker and A. Stenbock-Fermor Cinematography by: Joachim Hasler Edited by: Lena Neumann Music by: Andrzej Markowski Production companies: Roter Kreis group of DEFA* and Filmowe Iluzjon film studio Distributed by: Progress Film (East Germany), Crown International Pictures (United States) Release dates: February 26, 1960 (East Germany), March 7, 1960 (Poland), October 31, 1962 (United States)
Fascinating facts:
It was the first science fiction film made in Poland and East Germany.
*DEFA (Deutsche Film-Aktiengesellschaft) was the state-owned film studio of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) throughout the country's existence. (Source: Wikipedia)
This is an edited and English dubbed version the original movie, Der Schweigende Stern (The Silent Star).
It was based on the novel The Astronauts. It was written by the famous Polish science fiction writer Stanislaw Lem (12 September 1921 – 27 March 2006).
His most known novel is Solaris. Published in 1961, it has two movie adaptations, one in 1972 and other in 2002.

YouTube channel: Timeless Classic Films
youtube
War of the Satellites (1958 film)

Theatrical release poster
At the dawn of mankind's conquest of space, its future is at stake.
An unknown alien force already destroyed ten satellites while they were in orbit of planet Earth.
Later, the unknown enemy sent a message. A menace to stop the Sigma Project or else, humans will face their destruction.
The man at charge of the Sigma Project, Dr. Van Ponder was killed by UFOs and was replaced by an alien who can duplicate himself.
The alien usurper made his plea to the United Nations to continue with the founding of the space exploring project to make more damage on the inside.
There are two young scientists who were aware of what happened to Dr. Van Ponder. One already exposed the truth, but no one believes him. The other have to wait for the chance of exposing the hoax while they were in flight.
War of the Satellites, a 1958 film directed and produced by Roger Corman
Main cast:
Dick Miller as Dave Boyer Susan Cabot as Sybil Carrington Richard Devon as Dr. Pol Van Ponder Eric Sinclair as Dr. Howard Lazar Michael Fox as Jason ibn Akad Robert Shayne as Cole Hotchkiss Jerry Barclay as John Compo
Production staff:
Directed by: Roger Corman Screenplay by: Lawrence Louis Goldman Story by: Irving Block and Jack Rabin Cinematography by: Floyd Crosby Edited by: Irene Morra Special effects by: Jack Rabin, Irving Block and Louis DeWitt Producers: Roger Corman, Jack Rabin and Irving Block Music by: Walter Greene Production company: Santa Cruz Productions Distributed by: Allied Artists Pictures Corporation Release date: May 18, 1958
Fascinating facts:
This is a colorized version. It was originally released in black and white.
The first man-made satellite was the Sputnik 1. It was built in the former Soviet Union and launched in October 4, 1957.

SFX Expert, Jack Rabin suggested the idea of making this movie while the subject was still hot on the news' headlines.
Filming started in December 9, 1957
It was released in a double feature with Attack of the 50 Feet Woman
YouTube channel: Cult Cinema Classics
youtube

#60s sci fi#eastern europe#east germany#poland#60s movies#space opera#space western#soviet sci fi#stanislaw lem#Youtube#roger corman#satellite#sputnik#50s sci fi#50s movies
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

#dissociated#small town#western europe#late night post#late night walks#it’s almost 5am and I can’t sleep#liminal spaces#weirdcore#my picutre
1 note
·
View note
Text
It makes sense that all the aliens would be proofs of God, since everyone who writes those stories is a Young Earth Creationist. Or at least they all seem to consider it blasphemous to ask “Wait why did this thing about humanity evolve? Would aliens have the same selection pressures?” (The answer is almost always yes.)
I simply cannot enjoy most Humans Are Space Orcs stories cause the way they make us Space Orcs is bymaking every other alien so unbelievably fragile and incompetent that they prove the existence of a God, cause only divine intervention could possibly explain how they survived long enough to reach space
312 notes
·
View notes
Text
One one hand, I've seen this fucking ad literal four times today after i said the H-word in Messenger ...

... on the other hand, I must have done a good job banning facebook from learning shit about me, because unlike tumblr and youtube, it clearly doesn't know my geographical location.
#i'm in western europe rn#i'm preeeetty sure there are hozier shows closer to me both in time and in space#in other news i'm gonna find out which of the phone goblins are telling my location to tumblr/youtube ads#and kill them all
0 notes
Text
can't stop thinking like this when i see posts

"three types of animals defined by utility and simplified transactional relationship to humans. including categories of productivity, domestic companionship, or passive/threat/disgust/pest":
British and colonial American institutional and folk taxonomy of "the natural world" in the eighteenth century. The unofficial-but-still-influential way of imagining animals in "utilitarian" ways that support material accumulation and colonial "productive land" and "land improvement." Like a secularization of previously explicitly-religious "great chain of being" schema but adapted for Englightenment-era scientific cosmology that reifies racialized imaginaries of environmental space and reinforces class/racial/species hierarchies with technical expertise.
"we have to do something about the distances":
Britain and the United States in the nineteenth century trying to control the globe and conquer "frontiers" and obsessively trying to more quickly and efficiently move trade, industrial products, information, communications, administrators, indentured laborers, and imperial military across seas and vast distances to cement hegemony by utilizing technical expertise with railroad networks, sailing ships, steamships, investments in cartographic surveying, latitude/longitude establishment, canals, and elaborate systems of telegraph lines.

"they should make a big heavy machine beast that can pull tons of black iron across grasslands and such":
British Empire technicians, Canadian administrators, and their US advisers from 1900-1930-ish when the Canadian "federal government also established breeding programs designed to cross cattle with bison or yak to create a new [ultimate] range animal" with "a reserve stock of pure blood bison of the highest potency" and an "enthusiasm for stocking northern [boreal and northern Great Plains] environments with exploitable game populations" when "nothing, in fact, captured the imagination of bureaucrats and private promoters in the early twentieth century more than the idea of importing domesticated reindeer from northern Europe as a the vanguard of a settled and prosperous agricultural civilization in northern Canada." And they partially pursued the project as "a response to the success of Americans" in "assimilating" the Inuit by importing 82,000 European reindeer to Alaska by 1916: "[A]n Alaskan Bureau of Education Report proudly proclaimed [...]: 'within less than a generation, the [slur] throughout northern and western Alaska have been advanced through one entire stage of civilization.'"
And in the same decade with British administrators in Southeast Asia, when they pursued the "purchase of elephants whose labour made possible the logging and transport of this harder-to-reach teak [in Burma]. By the period between 1919 and 1924, elephants represented the largest assets owned by the biggest timber firm operating in the colony […]. This animal capital, of around three thousand creatures, represented [...] the equivalent of roughly a third of the corporation's liabilities [...]. And these elephants must have been busy. This five-year period saw half a million tons of teak exported out of the colony, the overwhelming majority of which was exported by a handful of large British-owned firms. Their ownership of these beasts of burden gave imperial trading firms a considerable advantage."
"america will be a manufacturing nation once more , We're going to build great and terrible machines, so great and terrible they carve the land they walk on, the sun will set and it will rise and the forge will still burn and the hammer will still ring true folks"
Without comment:
[Quote.] [O]n the morning of February 20, 1915, [...] Franklin K. Lane, the secretary of the Interior […] intoned to the crowd, “The seas are now but a highway before the doors of the nations […]. The greatest adventure is before us, the gigantic adventure of an advancing democracy, strong, virile, kindly, and in that advance we shall be true to the indestructible spirit of the American Pioneer.” The fair did not officially commence, however, until President Wilson […] pressed a golden key linked to an aerial tower […], whose radio waves sparked the top of the Tower of Jewels, tripped a galvanometer, and closed a relay, swinging open the doors of the Palace of Machinery, where a massive diesel engine started to rotate. […] [T]he PPIE was organized to commemorate the completion of the Panama Canal […]. As one of the many promotional pamphlets declared, "California marks the limit of the geographical progress of civilization. For unnumbered centuries the course of empire has been steadily to the west." […] One subject that received an enormous amount of time and space was […] the areas of race betterment and tropical medicine. Indeed, the fair's official poster, the "Thirteenth Labor of Hercules," [the construction of the Panama Canal] symbolized the intertwined significance of these two concerns […] that crowned San Francisco as the Jewel of the Pacific. […] The construction of the Panama Canal unfolded against the backdrop of […] the installation of American colonial rule in Cuba, Puerto Rico, the Philippines, Guam, and Hawai’i. […] In San Francisco, […] this meant the presence of artifacts such as Fountain of Energy, a strong male mounted on horseback […] crowned by figurines of “Fame” and “Valor.” Referred to by its creator as the Victor of the Canal, this sculpture symbolized “the vigor and daring of our mighty nation […].” In his address titled "The Physician as Pioneer," the president-elect of the American Academy of Medicine, Dr. [W.H.], credited the colonization of the Mississippi Valley to the discovery of quinine […]. [A]t the Pan-American Medical Congress, where its president, Dr. [C.R.] delivered a lengthy address praising the hemispheric security ensured by the 1823 Monroe Doctrine and "the combined genius of American medical scientists […]" in the Canal Zone. […] [A]s [CR]'s lecture ultimately disclosed, his understanding of Pan-American medical progress was based […] on the enlightened effects of "Aryan blood" in American lands. […] [End quote.]
Source: Alexandra Minna Stern. "Race Betterment and Tropical Medicine in Imperial San Francisco." Eugenic Nation: Faults and Frontiers of Better Breeding in Modern America. Second Edition. 2016.
421 notes
·
View notes
Text
#this castle is 400 years old and a vampire lives there #versus #we're the only people around for miles so bigfoot is out there and we're going to die (tags courtesy of OP)
My favorite thing is that Europe is spooky because it’s old and America is spooky because it’s big
#i copy tags#europe#western europe#america#time#space#china#surprise archaeology#world war ii#aztecs#saint sophia cathedral#retag
422K notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m this close to starting a side blog where I do nothing but mock people’s shit speculative biology where they demonstrate they are incapable of considering why things evolve. Think I’ll call it “When De Facto Young Earth Creationists Try Science Fiction” and it’ll involve the image of a hand holding a snake with an apple in its teeth (evoking both Genesis and snake handlers).
The two I just saw: no, aliens would not find sneezing strange. Fucking sea sponges sneeze, it’s for expelling foreign matter from the body. Please explain why alien biology would never have to do that. And no, even aliens evolved from prey animals would not be freaked out by you killing mosquitos. Do you think herbivores don’t kill insect pests?
#they had to add the quasielemental plane of salt back to the inner planes just for me#things that ain't so#salty scifi writer#salty science fiction writer#salty sf writer#humans aren't weird#humans are space hobbits#space western europe
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
on the aesthetics of asian erasure in star wars: obi-wan kenobi and the planet of naboo

when we talk about representation in star wars, the conversation often stops at what’s visible or credited. star wars has a long-standing problem with the lack of asian leads or asian-coded worlds, but sometimes what’s more insidious is the erasure of asian influence where it once existed, or where it was clearly intended to be.
take obi-wan kenobi. before alec guinness was cast, george lucas had reportedly wanted a japanese actor to play the role, toshirō mifune, most famously known for his work with akira kurosawa. lucas has never strayed away from citing the hidden fortress as a direct inspiration for a new hope, and the jedi, in their original conception, from eastern philosophies, particularly bushido and zen buddhism. this was not accidental. it’s embedded into the language, “obi” (the sash of a kimono), “wan” (a name component common in chinese and southeast asian names), and “kenobi,” which emulates the structure of japanese surnames. it is an asian-inspired name, heavily so.
but when mifune declined, lucas pivoted. and instead of keeping that vision intact, the jedi master archetype, the wise elder, steeped in tradition, was lifted from its asian origins and handed to a white british actor. and then later, to ewan mcgregor, whose performance, while incredible, westernized the role further. we are told obi-wan is from “stewjon,” a planet born out of a joke, a merging of jon stewart’s name, after he asked lucas where obi-wan was from. then “space scotland” became the shorthand. that change from asian inspiration to european performance was never really questioned.
it’s not about demanding obi-wan look asian. it’s that the character was rooted in an asian framework, and that framework was abandoned the moment it became inconvenient to uphold. and that sets the tone for much of star wars, aesthetic borrowing without meaningful credit.
naboo is another case where this shows up. the common narrative is that naboo was inspired by renaissance europe, with its lush italian architecture, baroque dresses, and romanticized monarchy. those elements are there. but there’s a consistent thread of asian influence that is almost never acknowledged.
the names of the monarchs are a starting point. padmé, from the sanskrit “padma,” meaning lotus. sabé and saché, echoing asian and hindi name constructions. queen jamillia, whose name stems from arabic roots, suggests influence from islamic culture. even the name “naboo” itself sounds curiously close to nebo, a mesopotamian god, or nabu, the sumerian deity of wisdom. the planets closest to naboo in the galactic grid, like sereno and ord mantell, also carry vague echoes of eurasian tone.
but most significantly, look at the costume design in the phantom menace. trisha biggar drew from a range of global influences, but some of queen amidala’s most iconic gowns were directly modeled after traditional mongolian royal attire, specifically the headdress and layered robes worn by mongolian empresses. the high collars, rich brocades, and facial makeup are unmistakable. yet, in the lore, naboo is labeled as european. not central asian. not global. and certainly not asian.
this is not to say star wars owes its worldbuilding to any one culture. it doesn’t. part of its power comes from its ability to merge and reimagine cultures. but there is a problem when the contributions of asian cultures are stripped of credit, while european aesthetics are exalted as canonical. when a jedi’s name can be asian, his values drawn from eastern philosophies, his robes loosely modeled on samurai garb, and yet his face, voice, and homeworld are made definitively western.
#star wars#obi wan kenobi#george lucas#ewan mcgregor#naboo#padme amidala#padme naberrie#sabe#leia organa#breha organa#bail organa#luke skywalker#jedi#sith#darth vader#han solo#cassian andor#mon mothma#luthen rael#bix caleen#kleya marki#qui gon jinn#ki adi mundi#mace windu#yoda#shaak ti#ahsoka tano#plo koon#anakin skywalker#kit fisto
257 notes
·
View notes
Text
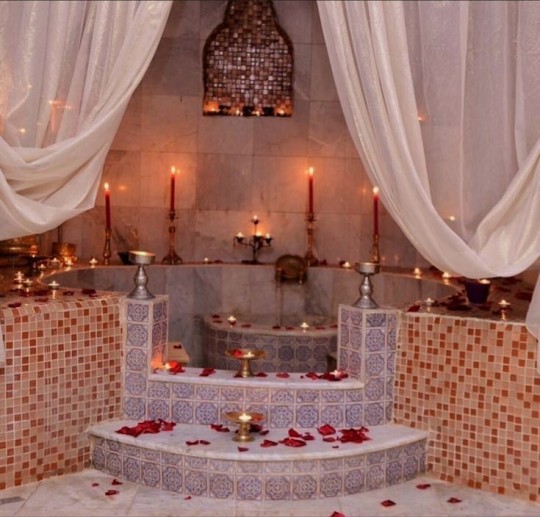
Secrets to the Arabian Princess Scent 💐🧴🪷
So with Arab perfumes becoming popular in the West due to their strong projection and beautiful smell, and the Arab world becoming known for our knowledge on how to smell good af, I (a half Moroccan) am going to reveal some other ways we ensure we smell amazing to the girlies on Tumblr who are interested in Arab perfumes or just in generally smelling amazing 😍 Most tips are Moroccan but many apply to the Arab world in general (under the cut because this turned into a long post) ✨💞💐



1) Good Eating Habits: When my mother moved here to Europe, she was immediately struck by how the people seemed to smell like "pig." And that's no coincidence. You are what you eat, so coming from a country where nobody eats pig to one where everyone eats it, of course you're going to be struck by people smelling like it from the inside out. Not just that, but in the Arab world, it's also way less common for people to eat takeout and drink alcohol, whereas in many parts of the West, these things are a normal part of many people's diets and affects their natural scent. A lot of Arabs have also talked about how Westerners smell like "milk," and this is because Westerners tend to consume more dairy products than people in the East do. It's also common for Arabs to eat fruit as dessert instead of having cakes or cookies all the time (although speaking of cookies and cakes, the scents of rosewater, orange blossom water, almonds, honey, vanilla, oranges and lemons commonly used in Arab baking fill up the house with a wonderful smell while they're baking). Teas made from various herbal infusions are popular throughout the Arab world. Spearmint, peppermint, sage, cardamom, cinnamon, hibiscus, chamomile, anise, and thyme are commonly used to flavor tea in MENA. Dried lime tea is drunk in the Arabian Peninsula. Coffee flavoured with cardamom is also common. I especially like Turkish coffee. Spices like cinnamon, cardamom, and cloves are commonly used in cooking, and the scent of them can cling to your clothes and hair. Herbs like mint and parsley, which have natural deodorising properties, are often used in meals.
I'm not saying that you need to cut any foods out in order to smell good, but you should consider reducing the amounts of unhealthy foods and red meats you eat, and make sure to drink plenty of water and eat veggies and fruit daily.
2) Keeping a Clean House: Here in Ireland, a lot of people don't clean their houses every day. I know multiple people that only clean their floor once a week, and have a couple of neighbours who don't do much cleaning themselves and just have a housekeeper visit to clean once a week. But in Morocco, people clean daily. The home is also deep cleaned once a week, we even wash the walls. We don't wear shoes inside, and not just that, but we also have different slippers specifically for wearing inside the bathroom. Living in a clean space is important for smelling good, because no matter what you do, you'll always end up smelling like wherever you live due to spending so much time there. The scent will cling to your clothes and hair. Which means if your house smells dirty, you will also smell dirty.
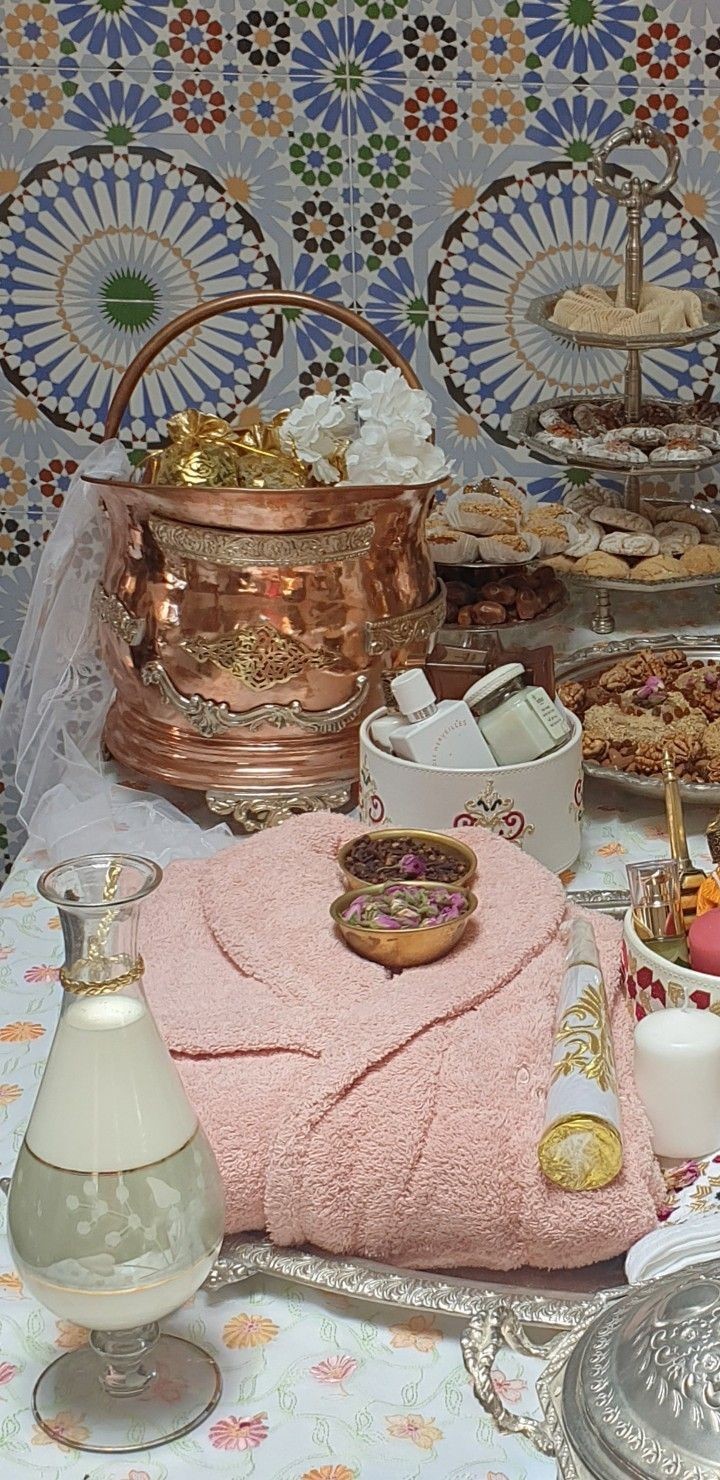
As well as making sure the house is clean, Arabs also make it smell pretty with extras. For example, in Morocco it's common to burn incense or bakhour (perfumed wood chips), and the scent permeates your clothes. People also keep pieces of musk in their wardrobes (wrapped in a handkerchief). It come in scents like orange blossom, jasmine, amber, sandalwood, chamomile and lavender. An unused bar of soap or a sachet of potpourri in your wardrobe will do the same job though if you can't or don't want to buy musk. The musk can also be used as a scented wax melt, a home scent (you just leave it in a bowl), a body perfume (rub it on your skin), a hair perfume (rub on your palms and run through the hair), or to scent bathwater. Solid perfume made from natural ingredients has the same effect. I like Lush Rose Jam solid perfume, as it smells like sweet roses and Turkish delight, and a little goes a long way.
Specific to Marrakech, you can buy jasmine balls which you just leave around the house (if you're not in Marrakech, you can just leave potpourri or dried flowers and herbs in sachets on your desk, bedside table, etc). The Marrakech herbal shops also sell sandalwood bark which you burn. Oud and amber are also burned. Herbs like lavender are sprinkled under carpets and rugs so the scent rises as they're stepped on. Room sprays from brands like Nabeel are used, which come in a range of lovely scents (like the warm vanilla and oud Kanz or the rich floral Raunaq).
3) Personal Hygiene: In the Arab world, people shower daily. In Morocco, we also go to the hammam (public bath) once a week, and we sit in the sauna room, and then rub our bodies with sabon beldi (black soap), a natural soap made from olive oil and black olives, leaving it on for a few minutes before rinsing it off. Then we scrub our skin with a kessa glove after it's marinated. Exfoliating dead skin regularly makes perfume cling to you better (if you order Korean bath towels from Amazon, they're very similar to Moroccan kessa gloves and you use them in a similar way). Then after washing our hair, we use a ghassoul clay mask (some people also rub henna into their skin). After washing the clay off, many people rub rosewater or argan oil into their skin before heading to the relaxation area to enjoy refreshments. As well as helping us smell good, it also makes our skin incomparably soft. When my parents were newlyweds, my father remarked on how he'd never felt a woman with such soft skin in his life before. My mother attributes it to regularly using the hammams before moving here.
Obviously not everyone has access to a hammam, but you can create a similar experience at home. Just sit in a steamy hot shower for 10-15 minutes, wash your skin with a natural soap and leave it on for a few minutes before rinsing off and exfoliating with a glove. Then tone with rosewater and apply oil to your body.
Dukhan treatments (smoke baths) are practiced in Sudan. Married women and brides anoint themselves with oil, before sitting over a chair with a hole in the centre. Under the seat, there is a pit, in which acacia wood, frankincense, or other aromatic woods and resins are burned in a clay vessel.
As well as showering daily (and using the hammam regularly if you're Maghrebi), many people in the Arab world also perform wudu (ritual cleansing) five times a day before praying.
Women commonly apply Musk Al Tahara (white musk), an attar that smells like vanilla, flowers and soft musk on the external parts of their vulva after periods.
Alum was commonly used as a natural deodorant in the Arab world in the past, and some still use it today.
Bidets are also common in the Arab world. In the Anglosphere they're uncommon, but it's easy to get a portable bidet (a small squeezable bottle with a nozzle) online.
We also wash our hands before meals, with a pitcher of water which is passed around the room. In Turkey, they use kolonya, made from fig blossoms, jasmine, rose, or citrus to disinfect their hands. In Morocco, it's common for women to scent their hands with rosewater or orange blossom water after meals.
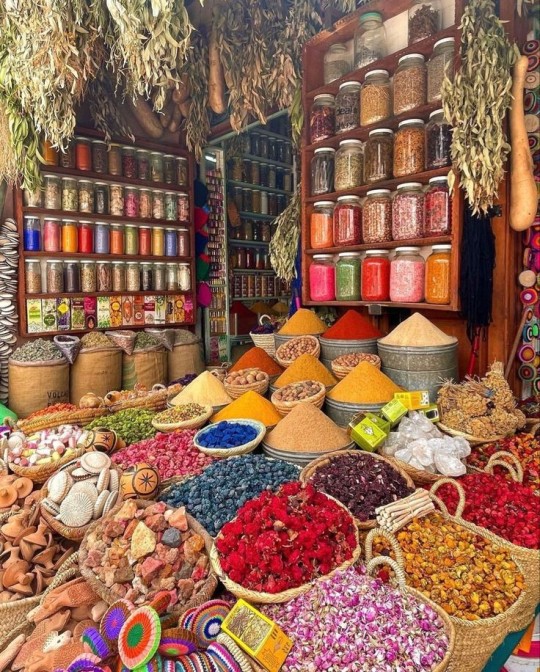
4) Fragrances, Lotions and Potions: In the Arab world, perfumes are incredible. They're oil-based, so they have excellent projection and longevity. The olfactory notes commonly used in them are beautiful too: delicate rosewater and orange blossom water, exotic oud, sweet amber, vibrant roses and jasmine. In Morocco, gardenia scents are popular, even among men.
Emirati perfumes are the most well known in the West and are super good. Some personal favourites of mine include Oud Mood by Lattafa (Caramel, rose, saffron, and oud), Fatima Pink by Zimaya (Sweet rose that smells like a bit like Turkish delight. it's a dupe of the French Parfums De Marly Delina, however, the actual Delina smells very similar to generic rose oil perfumes you can get in the Arab world to begin with so Zimaya was basically able to dupe it to a T. Their version lasts really long too), Ameerat Al Arab by Lattafa (jasmine, a hint of oud, slightly citrusy. Also the name means "Arabian Princess" in English), Fakhar Rose by Lattafa (sweet, fruity, and very floral) and Yara by Lattafa (floral, amber, vanilla and strawberry). I buy my perfumes from Dubai Perfume Shop in Dublin, but they can be easily found online. Some well-known Arab perfume houses include Lattafa, Al Rehab, Zimaya, Al Qurashi, Amouage, Afnan, Ajmal, Asdaaf, Al Haramain, Armaf, Kayali, Maison Alhambra, and Swiss Arabian, but there are hundreds more.
As well as sprayable perfume, perfume oil is also used. It usually comes in rollerballs or small containers, is inexpensive, and lasts for ages. Like spray perfume, it comes in a huge variety of scents. You can also put it in diffusers or add some to cotton balls and leave in your wardrobe to scent clothes and linens.
Arabs know when to wear perfumes. For example, a rich, sweet, strong oud and vanilla scent will be beautiful in colder weather. But in warm weather, it will become cloying and sickly. Musk, amber and saffron are popular in winter, while rose, orange blossom and jasmine are popular in summer.
In the Arab world, many stalls in the Medina sell gorgeous oils, fragrances and soaps that are inexpensive. For example, the musk I mentioned above. As well as making your home smell incredible, you can also rub it on your body and you'll smell good for days.
Rosewater is commonly used as a toner and to remove makeup. In the town of Skoura, where my great grandparents were from, men even use it to shave with! Orange blossom water is also used in Arab beauty routines in a similar way to rosewater. You can apply either to a bath for extra luxury.
Argan oil is commonly used in Morocco on both skin and hair, as well as the less well-known but just as good prickly pear oil (which is very high in vitamin E). Pure argan oil actually smells mild and not fragrant (similar to olive oil), but for beauty, things like rose oil and menthol are commonly added, so it smells pretty good. Throughout the Middle East and North Africa, jasmine hair oil, castor oil and sweet almond oil (I like putting it in my baths and on my body) are easy to find. Usually Middle Eastern and South Asian shops in the West sell them too.
Honey and almond masks have been used since ancient times, and to this day are still popular. You can buy them basically anywhere. Homemade face masks made from honey and yoghurt or crushed figs and yoghurt are also used.
Aloe Vera is used to treat dry skin, acne, and sunburns. It has a cool and refreshing scent, perfect for the hot climate in many parts of the Arabian world. I like applying it after shaving as it's soothing, natural, and absorbs easily.
Frankincense, a resin used in the Middle East and North Africa for thousands of years, was traditionally used as a natural perfume. It's commonly used in incense. Frankincense oil is also good for the skin.
Bakhour and incense, as well as being used to scent the home, can also be used to scent the hair and clothes. Hold your clothes or hair over a brazier with incense burning inside, and the perfumed smoke will cling on to them.
There are many beautiful scented soaps available in the Arab world. If you go to Turkish or Arab supermarkets, a lot of them will have a section where they sell hygiene products, including soaps with ingredients like argan, rose and oud, and olive oil. I've even found Syrian Aleppo soap before. You can just buy soaps from regular stores in scents like rose, jasmine, honey and almond, orange blossom and sandalwood for achieving that exotic scent though.
As well as using various oils, perfumes, and fragrant beauty treatments, Arab women also know how to layer these different scents to add dimension to them and avoid clashing. For example, a rose perfume over a vanilla lotion will always smell good. Other combinations that are good include almond and vanilla, rose and oud, rose and jasmine, lavender and lemon, rose and orange blossom, and orange blossom and vanilla. But there are many different combinations you can use to achieve a delicious scent that's unique to you.



I hope this was helpful, stay pretty ✨
#law of attraction#becoming that girl#clean girl#it girl#dream girl#girlblogging#dream girl journey#glow up tips#glow up#dream girl tips#dream life#wonyongism#pink pilates girl#pink pilates princess#it girl energy#girly tumblr#just girly things#just girly thoughts#just girly posts#pink blog#hyperfeminine#girly#princess life#princesscore#masterpost#levelling up journey#level up#hypergamy#high maintenance#high value woman
898 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yassin al-Haj Saleh, "The Liquid Imperialism That Engulfed Syria," Commons, December 18, 2023:
Syria is a country of only 71,498 square miles in area, with a population of less than 24 million, and yet two global superpowers (the United States and the Russian Federation) and three of the largest regional powers (Iran, Turkey and Israel) are present on its territory. Israel has occupied the Syrian Golan Heights since 1967, and carries out almost nonstop incursions into Syrian air space today. In centuries past, prior to the heyday of European and Russian imperialism, Iran and Turkey were empires. While it is debatable whether they still qualify as imperial powers, they have never let go of their regional imperial ambitions. One way to understand them, regionally, is as “subimperial”: expansionist and interventionist, including militarily, in neighboring countries.
The U.S. and Russia have well-known histories of expansion and domination of peoples and territories. Imperialism was key to the very formation of both nations. But while Russia’s “manifest destiny” had been, for centuries, to expand into neighboring areas in Central Asia and Eastern Europe, it was in Syria that Moscow established its first overseas outpost. I will return to this crucial fact later.
In Syria, multiple imperial and subimperial powers have poured into one small country — some of them to protect a murderous regime, all of them annihilating any independent political aspirations among its people, dividing up sectors of Syrian society among themselves and their satellites, and denying Syrians the promise of a different future.
This unique situation was made possible by a combination of internal as well as international structures and dynamics involving five key powers — the U.S., Russia, Iran, Turkey and Israel...
One slogan of the recent protests that erupted in the southern city of Sweida on Aug. 20, 2023, speaks directly to the imperial-colonial complex that controls Syria:
["]We want the seaport, we want the land (the oil, in another formula) and we want the airport returned to us!["]
The seaport is Tartus, which, as mentioned, has been leased to Russia. The land is divided by the five occupying powers. And Damascus International Airport has, for several years now, been widely perceived to be under de facto Iranian control. The protestors in Sweida are thus drawing a connection between their economic hardships and the colonial relations between the regime and its Russian and Iranian protectors. In the version of the slogan that refers to oil, the implication is that it has been usurped by another imperial power: the U.S...
Lenin’s argument that imperialism represents “the highest stage of capitalism” has led many to think of imperialism as embodied in a very few capitalist powers. By this logic, there has been only one imperialism since World War II: Western imperialism, with the U.S. as its center and NATO as its military arm. The Soviet Union was not generally seen by those on the left as imperialist: not following World War II, nor after it invaded Hungary in 1956 and Czechoslovakia in 1968, nor even after it invaded Afghanistan in 1979. Similarly, Putin’s Russia has not generally been understood as imperialist, even after the annexation of Crimea in 2014 and the intervention in Syria in 2015. For much of the so-called anti-imperialist left, not even the full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 was enough.
This conception of imperialism must be challenged. The case of Syria requires a paradigm shift in the understanding of imperialism and the theorizing of new practices and phenomena pertaining to it.
Ultranationalism, expansion, dismissal of international law, exceptionalism, imperial imaginaries — these are characteristics of many powers in the age of the war on terror. With “terror” identified as the principal political evil globally, any state that joins in this alleged war can gain international legitimacy — even those engaged in war crimes and murder on an industrial scale. This has dealt massive blows to the rule of law both locally and internationally. It has contributed to a securitized politics, it has promoted thuggery among political elites and has weakened democracy and popular movements everywhere. Imperialism has permeated the practices of power in many countries, among which Syria is arguably the most unfortunate, with no fewer than five expansionist powers on its territory.
The concept of liquid imperialism is an attempt to capture the fact that five different powers have penetrated one small country. But it also speaks to the lack of solidity or coherence in these powers’ strategies, practices, visions and commitments. Unlike the imperial projects of the past, in Syria there is no “civilizing mission.” Natural resources are not a primary motive (though the intervening states have seized whatever they can get their hands on, from oil and phosphates to seaports and airports, to water and real estate). Rather, this is a scramble to control the future of the country.
There is also a liquid aspect in the relations among the five colonial powers. In Syria, we have two Russias — one of them is called the U.S. On a rhetorical level (especially at the beginning of the uprising), Moscow and Washington seemed to be on opposite sides: The Kremlin stood by Assad and the White House denounced him. Yet operationally, Russia and the U.S. were effectively on the same side — especially after the Islamic State came into the picture and became the central focus of U.S. strategy in Syria. From that point forward, Moscow and Washington were on the same page: The two powers closely coordinated “deconfliction” and their military personnel were on the phone to each other on a daily basis to avoid planes flying in the same location at the same altitude and to ensure airstrikes didn’t hit one another’s “friendlies.” For all the bluster about Washington wanting “regime change” in Syria, the exact opposite was the case. The researcher Michael Karadjis has demonstrated that U.S. policy in Syria was decidedly one of “regime preservation.”
191 notes
·
View notes
Note
would you have any reading suggestions to learn more about the earrings are evil era??? I've never heard of that aspect of fashion history and I am curious
Oh man, it was wild
you saw the first stirrings of it in the 1890s, when you started to get (mostly white and middle-to-upper-class) proto-feminists arguing that ear piercing was barbaric- keep an eye on the racist undertones there; they will come up again-and forcing women to suffer for fashion. I cannot emphasize enough that, until that point, ear piercing had been pretty much normal for this race/class/gender group. For centuries. You see criticism of the practice here and there, but nothing that really stuck.
The objections slowly increased until roughly the mid-1920s, when everything reached a tipping point and pierced ears became largely taboo for most white Americans and Brits of northern/western European descent. If that sounds HIGHLY specific, it is- communities from southern and sometimes eastern Europe retained cultural practices of ear piercing, to the point where it was often used as a point against them by mainstream society. It was also associated with Latino people, Black people, and the Romani, which. Yeah. I don't need to tell you how that went down.
It also developed associations with sexual immorality and/or backwards thinking. One newspaper letter I read came from a teen girl in the 1940s, wondering why she shouldn't pierce her ears if her very respectable grandmother had piercings. The response was something like "well, they did all sorts of things in the Bad Old Days that we shouldn't do now." True in many ways, or course, but...piercing your ears? That's the hill culture decided to die on as far as antiquated behavior that we should leave behind? Apparently yes.
Earrings themselves never went out of style, which led to the birth of clip-ons and screwbacks. Ironic that the "don't surfer for fashion" crowd was so eager to embrace screwing tiny vices onto your ears, but there we are. My own mother (born 1953) remembers her mother (born 1926) always taking off her screwback earrings immediately after getting home from a party, literally in the foyer of their house the second the door shut. There had been adaptations for unpierced ears before- Little Women, published in 1868, describes Meg March hanging earrings from a flesh-colored silk ribbon tied around the base of her ear -but they'd never caught on like this before.
However, the pendulum was soon to swing back. After just 40 years of Piercing Panic, in the 1960s, girls began piercing their ears again in droves. As piercing moved from the slumber party or summer camp back to the professional jewelers whose families had been early professional piercers in the 19th century- and to befuddled doctors who had no idea what they were doing yet still received piercing requests -cultural commentators had no idea what to make of it. Some decried the new trend while most took an air of bemused neutrality. My personal favorite article expressed surprise that "Space Age misses" were adopting these "Victorian traditions."
(In 1965, my grandmother took Mom to the anesthesiologist down the street who was offering to pierce his young daughter's friends gratis, and got it done. My grandfather had strongly disapproved of the idea, but in the end it took him a week to notice the new earrings.)
As to sources...honestly, I've just gone to Google Books, specified a time frame, and typed in "ear piercing," "pierced ears," "pierce ears," etc. Tons of primary sources at your fingertips, though I'm not always great about documenting or saving what I find. There's not much written about it formally, I've found- no books or scholarly studies. It may just be too close in history to attract much academic attention, though I find it fascinating.
This little blip where something that's been normal for most of western history suddenly became taboo for a hot second.
Also my ear piercings just turned 20 five days ago, commemorating the date that I was taken with much ceremony to Piercing Pagoda (and that horrible gun; it's a wonder I didn't get keloids) to get me out from underfoot while the Thanksgiving feast was being made. Grandma got hers pierced on the same day, at age 78. Happy Birthday, Marzi's ear piercings!
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
To the International Community,
Be on guard. Be vigilant when your own land, your cities, and your institutions are being used by foreign dictators to falsify history, appropriate the culture of others, and lay the groundwork for yet another genocide and ethnic cleansing.
The latest event, titled "western azerbaijan in our memories," was held in Warsaw, Poland on April 8th. During this exhibition, a spokesperson for the so-called “western azerbaijan community,” presented fictional claims about the “forced displacement of western azerbaijanis” in the 20th century and the supposed “destruction of azerbaijani heritage” in the territory of the Republic of Armenia. According to her, “western azerbaijanis,” who were “forcibly removed from their ancestral lands,” are entitled under international law to return.
Archaeological, genetic, and anthropological studies (conducted by non-Armenians), as well as numerous scriptures of historical significance (again, written and preserved by non-Armenians), all prove and confirm that the Armenian people are indigenous to historical Armenia [the Armenian Highland], with roots going back as far as the 13th century BC, emerging without admixtures.
azeris, on the other hand, only emerged as a nation in the 19th and 20th centuries. And yet, despite all facts, logic, and historical evidence, azerbaijan continues to claim that Armenia is actually “western azerbaijan.” [more here]
petrostate azerbaijan has organized similar propaganda events in Rome at the Pontifical Gregorian University, attempting to present Armenian churches, towns, and sacred sites — as "azerbaijani" or "caucasian albanian." [more here]
This is a deliberate, state-sponsored lie — part of a bigger campaign of historical erasure, cultural appropriation, and preparation for future wars and aggression.
And now, they’re exporting that lie to your countries.
azerbaijan is not merely making territorial claims; it is executing a state-sponsored propaganda campaign aimed at legitimizing its false narrative of "western azerbaijan." This campaign is led by a government-backed entity called the "western azerbaijan community", officially launched in 2022 but rooted in older revanchist ideologies.
Let’s ask honestly: why is Europe giving space to this? Why are countries that "champion" human rights and historical truth being used as tools in a disinformation campaign that serves to justify cultural erasure and future war?
Cultural erasure begins with soft words and staged sympathy.
So please, if you’re reading this from Warsaw, Rome, or anywhere else, ask questions, do your own research. Pay attention. Don’t let your silence be the seal of approval. Be vigilant. Be careful. Don’t let your countries, your cities, or your people be put on the wrong side of history.
#I swear one of these days I'm going to die from a heart attack#it is anger and rage not blood that's flowing in my veins#world news#world history#warsaw#poland#azeri crimes#western azerbaijan#armenian history#armenian culture#armenia#artsakh#history
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
Despite the Storm
YN YLN -> your name & your last name
2,8k of words!!!!
masterlist (1) - (2) - (3) - (4)

It was never supposed to end the way it did.
Back when you were just two girls with nothing but a ball at your feet and a thousand dreams in your chest, everything felt simple. Easy.
You signed your first pro contract in 2017, leaving everything you knew behind to chase your dreams in Italy with Juventus. Kyra stayed in Australia, starting her own journey with Melbourne Victory.
"It’s just distance," she said, laughing into her phone speaker, her voice brighter than the sunrises you missed watching together. "We’re stronger than that."
And for a while, you believed her.
Mornings were for your texts — sleepy and rushed before training sessions. Nights were for her calls — her soft voice crackling through the line, filling the lonely corners of your cold apartment.
"One day," Kyra whispered once, half-asleep, "we’ll wake up in the same city. Same bed. Same everything."
You clung to those promises like lifelines. You built a future around them.
Every offseason, you found each other. Two weeks stolen from the world — airports, long hugs, hurried kisses — breathing each other in before time tore you apart again.
When Kyra moved to Western Sydney Wanderers in 2019, you celebrated her milestone from across oceans, sending her a clumsy video of you popping a bottle of prosecco alone in your tiny Turin kitchen.
"I’m so proud of you, baby," you had grinned into the camera, cheeks flushed, heart bursting.
You kept telling yourself it was temporary. That soon she’d come to Europe, that soon you’d stop counting the hours, the missed moments.
But soon started stretching further and further away.
You moved to Arsenal in 2020. A dream fulfilled. A loneliness sharpened.
Kyra, instead, went back to Melbourne Victory. Home. Safety. Familiarity.
You told yourself it was okay. That maybe she needed more time. That loving her meant being patient.
But deep down, you felt the first splinter.
The late replies. The canceled calls. The birthdays spent apart, your phone cold and silent in your hand at midnight.
Love, no matter how deep, started to feel like water slipping through your fingers.
When Kyra finally signed for Hammarby in 2022, a tiny ember of hope lit inside you. Finally Europe. Finally closer. Finally maybe… fixing what had cracked.
But it wasn't the same anymore.
She was trying to survive a new country, a new league, a new weight on her shoulders. You were fighting for trophies, games, your place at Arsenal.
The distance wasn't oceans now. It was the space between two hearts who didn't beat in the same rhythm anymore.
The last conversation was quiet. So much quieter than you deserved.
"Maybe we’re not enough anymore," Kyra said, her voice trembling through the line. You wanted to scream. You wanted to fight.
But how do you fight for someone who’s already half out the door?
"I’ll always love you," she whispered. "That’s what makes this hurt so damn much."
And just like that — the future you built together shattered into a thousand tiny pieces.
Weeks. Months.
You buried yourself in football. In new friendships. You stopped checking her socials. You stopped letting yourself wonder what if.
You tried so hard to forget.
Until tonight.
You were curled up in your apartment, the London rain tapping against the windows, scrolling absently through your phone when a notification lit up your screen.
Caitlin had texted.
"Look who’s joining us. 😳👀" Followed by a screenshot of Arsenal’s latest post:
"Welcome to Arsenal, Kyra Cooney-Cross!" Her smile, all sunshine and wild dreams, staring back at you.
For a long moment, you just stared. Breath caught somewhere between your ribs.
You didn’t even realize your fingers were trembling until you almost dropped your phone.
Kyra. Here. At Arsenal. At your Arsenal.
No warning. No heads-up. Just a name and a jersey and a club post that ripped open a wound you thought had long scarred over.
You sank back into the couch, the world tilting slightly. You didn’t know if you wanted to cry, laugh, or throw your phone across the room.
All you knew was this:
You weren’t ready. Not for her smile. Not for the memories. Not for the storm she still carried inside you.
And tomorrow?
Tomorrow you’d have to see her in person.
Face to face. Heart to heart. Past to present.
And you had no idea if you were strong enough to survive it.
You should’ve known.
You should’ve stayed home a little longer. Pretended you were sick. Anything to avoid this moment.
But you didn’t.
And now here you are, standing on the side of Arsenal’s training pitch, boots scuffing the grass, arms folded tightly across your chest, heart hammering in your ears — watching her.
Kyra Cooney-Cross.
Wearing Arsenal red. Smiling. Laughing with Leah and Lotte like she’s belonged here all along.
And god, she looks good. Stronger. Fiercer. Her hair tied up messily like always, a stubborn curl falling across her forehead, cheeks flushed from the drills.
You hate how your chest tightens at the sight of her. You hate how the air around you crackles — thick and heavy, like a storm’s about to break.
You don’t even realize you’re staring until Caitlin nudges you with her elbow, a knowing look flashing across her face.
"You okay?" she murmurs low enough that no one else hears.
You nod too quickly. "Fine."
Liar.
Training winds down, and you grab your water bottle, pretending to be busy — tying and retying your laces, adjusting your shin guards, anything to avoid the inevitable.
But then you hear her.
"Hey, Y/N."
Soft. Tentative. A voice you haven't heard in months. Not really. Not since that night everything ended.
You look up. And she’s standing there.
Close enough to touch. Close enough that you can see the freckles dusting her nose, the scar just under her jaw from a game you watched on TV but didn’t text her about after.
Time freezes between you.
For a long moment, neither of you says anything.
It’s all there in her eyes — the apologies, the regrets, the what-ifs. It’s mirrored right back in yours.
"Hi," you finally breathe out.
It’s stupid how shaky it sounds.
Kyra shifts awkwardly, kicking at a clump of grass with the toe of her boot.
"I didn’t know if you’d wanna… talk. Or… anything."
You swallow hard.
There’s so much you want to say. So much you’re afraid to say.
"You didn’t tell me you were coming," you say instead, and it comes out sharper than you mean.
Kyra flinches. Just slightly. But you catch it.
"It happened fast," she says, voice small. "I didn’t know how to… if I should…" She trails off, helpless.
You nod stiffly. You don't trust yourself to speak.
Not when part of you wants to yell. Not when part of you wants to pull her into your arms and pretend the last year never happened.
The silence between you stretches, taut and aching.
Around you, teammates laugh and joke, oblivious to the wreckage unfolding between two broken hearts.
"I missed you," Kyra blurts suddenly.
Your throat tightens.
Because that's the thing about storms — even after they're over, the damage lingers.
You want to tell her you missed her too. You want to ask her why it wasn’t enough before. You want to scream and cry and kiss her stupid mouth all at once.
But you just say:
"Welcome to Arsenal, Kyra."
And you walk away before she can see the tears burning at the back of your eyes.
You should’ve known Kyra wouldn’t let it end like that.
The knock at your door comes barely an hour after training. Sharp. Relentless.
You debate pretending you’re not home. But part of you knows — she won’t leave. Not this time.
With a heavy breath, you yank the door open.
And there she is. Still in her training hoodie. Hair messy. Eyes wild.
"Can we talk?" she says, voice already cracking.
You don’t answer. You just step aside, wordlessly letting her in.
The second the door clicks shut behind her, the air shifts — thick with all the things you never said.
Kyra stands in the middle of your living room like she doesn’t know where to start.
Good. Because you sure as hell don’t either.
"You can’t just show up here, Kyra," you snap, harsher than you mean — but god, it’s easier to be angry than shattered.
"I didn’t know how else to—"
"You don't get to do this," you cut in, heart pounding so loud you can barely think. "You don’t get to leave. You don’t get to break my fucking heart and then walk back into my life like nothing happened."
Kyra flinches, her eyes wide and glassy.
"I didn’t want to break anything," she whispers. "I just… I was scared. I didn’t know how to handle it back then."
"You didn’t even try," you hiss, voice thick. "You promised we were bigger than the distance. That we were stronger than this. But the second it got hard, you bailed."
Her hands are shaking now.
"I hated myself for it," she chokes out. "You think I didn’t want to fight for you? I did. Every fucking day. But I was drowning, Y/N. New country. New pressures. I didn’t know how to ask you to wait for someone who was falling apart."
The words hit you square in the chest.
Because you recognize it — the panic. The fear. You lived it too.
"You didn’t even give me the chance to stay," you say, softer now, voice breaking.
Kyra’s lip trembles.
"I know."
The silence is a living, breathing thing between you — so full of grief it hurts to stand in it.
Tears spill over before you can stop them. Hot. Angry. Helpless.
Kyra steps forward, desperate. "Please… don’t cry. I can't—"
"What do you want from me, Kyra?" you snap through your tears. "You want me to pretend it didn’t hurt? You want me to pretend I didn’t spend nights wishing you’d pick up the damn phone? That I didn’t check flights to Sweden a hundred times and delete them every time because you didn’t ask me to come?"
Kyra breaks then. Fully.
Tears streaking her flushed cheeks, her whole body shaking.
"I just want you," she says, wrecked. "I want to fix this. I want to try again."
You shake your head.
"It’s not that simple."
Because you’re scared too now. Scared of letting her in again. Scared of loving her just to lose her all over.
"I know I don't deserve another chance," Kyra whispers, stepping closer, "but I'd spend every damn day proving you still have my heart if you let me."
You squeeze your eyes shut. You feel her hand hovering — not touching — waiting for permission.
"I never stopped loving you," she says, voice broken.
You open your eyes. Meet hers. And god, the love is still there. Shining. Shattered. Real.
You should say no. You should protect yourself.
Instead, you whisper:
"Then show me."
Kyra lets out a breath like she’s been drowning for years. And finally — finally — she closes the space between you.
She pulls you into her arms so tightly it steals the air from your lungs.
And this time, you let yourself fall.
Not into the pain. Not into the past.
But into the tiny, fragile hope that maybe — just maybe — love could survive the storm after all.
Healing isn’t some dramatic, cinematic thing.
It’s slower. Quieter. Messier.
It looks like you and Kyra sitting on your couch later that night, a cautious distance apart, talking about everything you never dared say when it still mattered most.
It sounds like broken confessions whispered into the spaces between you. Small apologies. Bigger ones.
It feels like Kyra reaching out — hesitating — before barely brushing her fingers against yours on the cushion between you, like she’s terrified you’ll pull away.
You don't.
You turn your hand over instead, lacing your pinky with hers. Not fully holding her yet. But letting her know:
I’m still here. I’m scared too. But I’m willing to try.
The next few days are cautious and strange.
At training, you avoid each other’s eyes more than you should. But there's a difference now.
When you pass her in the hallways, her fingers graze yours — a whisper of a touch no one else sees.
When you catch her eye during drills, she gives you a tiny, crooked smile — and it twists something deep inside your chest, something painfully hopeful.
On a Wednesday night, after a long, rainy practice, Kyra shows up at your flat again.
No excuses. No warning.
She’s dripping wet and shivering, standing awkwardly at your door.
"I didn’t bring an umbrella," she says, sheepish.
You roll your eyes, but your chest warms in that way it only ever has for her.
You pull her inside without a word. Hand her a towel. Throw one of your old sweatshirts at her — the one she used to steal when she stayed over, back before everything fell apart.
She hesitates, fingers tightening around the fabric.
"You sure?" she asks, voice small.
"It’s yours," you say simply.
The way her face crumples at that — like it’s the kindest thing anyone’s ever done for her — almost breaks you.
Later, you're curled up on the couch together, knees brushing, a movie playing low in the background — not that either of you is watching.
Kyra’s head slowly drops to your shoulder. You stiffen for half a second — and then relax.
Her hand finds yours again, easier this time. Your fingers intertwine naturally, like they were always meant to.
You turn your face slightly, breathing her in — the smell of rain and your sweatshirt and something that's just Kyra.
She looks up at you then. So close you can count her eyelashes.
"I missed this," she whispers. "I missed you."
"I missed you too," you whisper back, voice cracking.
For a second, neither of you moves.
Then — so softly you barely realize it’s happening — Kyra leans in.
And finally — finally — your lips meet.
It's not a desperate kiss. It's not the kiss of people who forgot what they meant to each other.
It’s slow. Careful. Reverent.
A promise, not a plea.
When you break apart, you stay close, foreheads touching.
You don't say anything. You don't have to.
Because sometimes rebuilding isn't loud. Sometimes it’s quiet nights, borrowed sweatshirts, forehead kisses, and holding each other like you’re both a little fragile — but trying anyway.
It’s different now.
Not perfect — you’re both still learning how to carry the past without letting it crush you — but it’s better.
You see it in the way Kyra waits for you after training, leaning casually against the locker room door, arms crossed, trying (and failing) not to look like she was counting down the seconds.
You see it in the way your hand finds hers as you walk through the training center parking lot, no longer hiding.
You see it when Caitlin notices, quirks a brow, and says with a smirk, "Finally."
No one’s surprised. Not really.
Everyone around you seems to breathe a little easier, like the universe is finally slotting something back into place.
A few weeks later, it's a quiet Sunday morning.
Sunlight spills through your apartment windows. The sheets are tangled around your legs. Kyra's head rests on your chest, her fingers lazily tracing shapes over your skin.
You’re scrolling half-distractedly through your phone when you feel Kyra shift.
You glance down.
She’s staring at you with that look — the one that used to undo you completely, back when everything was raw and unsure.
It still undoes you now, but differently. Softer. Deeper.
"You’re really staying this time, huh?" you tease, brushing a strand of hair from her forehead.
Kyra smiles — a little broken, a lot beautiful.
"I'm not going anywhere," she says, voice steady.
And this time, you believe her.
Later that day, a soft little buzz from your phone catches your attention.
Instagram.
Kyra tagged you in a post.
Curious, you open it.
It’s a candid photo — you hadn’t even realized she took it — from the night she showed up soaking wet at your door.
You’re handing her the towel, your face a perfect mixture of exasperated affection. Kyra’s looking at you like you hung the stars.
The caption is simple:
"Home isn't a place. It's you. 🖤"
You feel your heart stutter in your chest.
Because for all the years, the heartbreak, the distance, the almosts and the could-have-beens —
You finally found your way back to each other.
Not despite the storm. But because you survived it.
Together.
#woso fanfics#woso x reader#kyra cooney cross x reader#kyra cooney cross#arsenalwfc x reader#arsenal#arsenalwfc#awfc x reader#awfc
71 notes
·
View notes