#like this is actually a situation where that philosophy makes so much sense!!!!!!!
Text
The thing is I need the haters to at least get their facts right because if i have to see one more post complaining that Jamie was trying to use the leaked tape as some sort of point in his favour on the grander list of why he should be with Keeley instead of Roy...That quite literally wasn't what was happening, okay!!!! He said that solely and only because he knew it was the single thing he could say that would hurt Roy most, not because he thought it was a genuine argument for Keeley loving him more than Roy or whatever. In fact, it was so Roy-focused and deeply reactionary in nature that I'd argue he wasn't thinking about Keeley at all when he said it. She was an afterthought even in a quickly devolving argument that began centered around her. And yes, this absolutely is just as bad if not arguably worse Jamie behavior!!! But like damn, at least get it right before you start slamming him for it.
#jamie tartt#ted lasso#ted lasso spoilers#the amount of crazy crazy takes on this scene#different but related issue:#last week people were okay with ted trying to make 'hurt people hurt people' apply to jamie and his abusive father#but this week suddenly it can't apply to roy and jamie? I am TIRED#like this is actually a situation where that philosophy makes so much sense!!!!!!!#okay i gotta get off the internet for the day peace and love lassoers
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
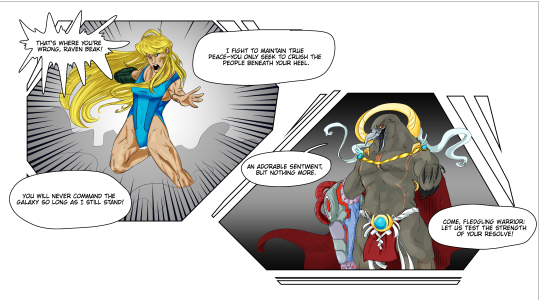
So I put the power of friendship and impractical outfits into Metroid Dread. No suits, no shields: we die in a giant laser hand cannon fight like true warriors.
#raven beak#chozo#a lot of effort for a bit#i thought back to that one piece i did a few years ago where i put raven beak in bikini armor and i said#'wouldn't it be funny to see him actually fight in something like that?'#because as we all know exposed flesh in combat is very humorous when large guns that shoot beams are involved#and then my train of thought fell to 'wouldn't it be funny if Samus was covered more than Raven Beak is'#'to subvert the sexy outfits thing a little bit but also drive home the 'god-emperor of Chozo Victoria's Secret' look he has going for him'#So the original sketch was created July 21 2023. And I redid it on April 10 2024.#and built Raven Beak bulky like a pro wrestler to really drive home the drama/hamminess of the situation but also to make him look stronger#my outfit design continues to be lacking but my commitment to the bit remains unmatched#... it's also so much easier to draw silly bikini armor that makes no sense than it is to put characters in regular clothes. or armor.#if you want a 'lore justification' for the lack of armor let's just say Raven Beak doesn't need the suit to be powerful.#and Samus is about to demonstrate that he has sorely underestimated her. by a mile. or a kilometer.#anyways the differences in their outfits match their upbringing and general philosophy#Samus opts for the more practical leotard offering her mobility and lightweight motion#Raven Beak guns for the full regalia that shows off as much muscle as possible while not skipping out on symbols of rank#and he NEVER leaves home without a cape#the cape is a must if shoulder-mounted black hole generators aren't available.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
someones lover boy feels like im banging on a glass wall trying to tell beau he has autism and there are coping mechanisms that can help him but nooooo SOMEONE had to set this in the 80s so he has to figure it all out himself without ever actually knowing the Thing behind it all
#there's something thematic in the autism of lover boy but i don't know what it is yet#anyway partially related but i saw a reel ages ago that like#described meltdowns as necessary for autistic people to regulate their emotions when they#get the Build Up (iykyk)#they were like oh when i find myself getting overwhelmed or pushed over the edge i let myself have a meltdown#like if you can get out of the situation and be alone and let yourself do what you need to do#and i was just like wow cause ive only seen meltdowns framed as like#the Explosion after everything bubbles up like....the consequence of it#which makes sense when so much of autism portrayals is external (aka how it affects non autistic ppl)#like cant remember a time where i've seen meltdowns defined as smth that is actually necessary to help me#anyway I WANT TO TELL BEAU THAT SO BADDDD i wish he knew that if he needs to just like cry until hes exhausted he can#like brother that is your body regulating itself#one of the challenges is i want him to develop and find coping skills + philosophies like this#but it kinda like. has to happen organically because he literally has no resources#except like. 1980s take on anxiety oops#idk maybe felix can help him out. felix being good at this stuff is already the plot twist i never expected from the Annoying Cocaine Man
1 note
·
View note
Note
I love your personality for dottore’s character! I like how he demonstrates his intelligence in a way that is not overbearing and cocky and how his actions have deep meanings behind them and not just for his satisfaction like most interpretations. how do you go about making such a character? Is it from purely your own perspective or is it influenced by other characters,books,philosophy concepts or any other piece of media?
Hi!
Some of his character is a personal interpretation but it’s based on a foundation from several other analyses and canon material that we have from the game.
Namely, some of the following Reddit threads:
Sadist or Scientist?
Dottore as a Villain and Sumeru’s Dysfunction
The Heresies of Il Dottore
There’s also a very long thread in this sub that’s living rent free
Along with the manga where we get a few crumbs for Celestia lore/Dottore’s perspective on allogenes, the Archon quest voicelines and Scara’s character quest, and Zandik’s notes found in the overworld.
@/ellalalala and localplaguenurse and haeresysabound also have their own analyses that prove really helpful and look at different facets of his character.
Most of it is a logical progression of how someone like him would think. He’s rational, observed before he acts, and doesn’t so much predict as follow the logic behind someone’s previous patterns of behavior. He’s arrogant to a fault but it’s posturing; a lot of people display that kind of behavior in the real world.
Most of the time, I start with a situation and, based on all of the above, I play, “what would Dottore do?”
He’s ultimately insatiably curious, chasing knowledge for the sake of it, just to see what happens.
Machines help him to understand the world and his interpretation of it. It goes to show how detached he is to consider a human body is nothing but a machine of its own, capable of surpassing the divine.
He’s more human than anyone because he seeks to understand and push the limitations; humans are naturally curious creatures who long to make the world better and leave a legacy behind.
But it’s not chaotic. It’s not The Joker style of curiosity where it’s bombastic and wild, a twisted version of a joke.
I’d argue that Webtorre is The Joker while Omega and in-game Dottore is Scarecrow.
And this is where myself (and others) differ because I do not think Dottore is a sadist. That he wants to harm people. It’s very obvious in several notes that, while not signed, are written in a manner that you know it’s Dottore. There’s one that lists several subjects and he considers the actions taken by a subordinate (I think it’s torturing one of them? Something drastic, will check) to be a waste of resources.
Is he apathetic? More than likely.
Does he enjoy seeing others suffer? Probably not. Why else would he be looking for a cure for Elezar, even as a byproduct to understanding the Withering?
He would probably actually be a failure at relationships precisely because he doesn’t know how to connect with people. If he would want to pursue a meaningful connection, there’s a lot stacked against him between trust issues built up over centuries, a detached worldview, and more than likely, a skewed sense of self (he’s arrogant but to a fault where he’s clearly still sensitive about how no one but himself sees him as a scholar). So many of the meaningful reasonings to his actions stem from this in particular.
My personal suggestions for additional insight would be:
Most renditions of the Scarecrow from Batman. How he sees fear is how I imagine Dottore understands knowledge. The more you have of it, the less you can fear, the better to understand the world around you.
I’ll put more here as they come to mind, because I’m definitely forgetting others at the moment.
#thank you for this!#dottore#il dottore#one day I will write an essay that additionally condenses all of this#there’s so much lore that needs to be extrapolated lol#but I am under a time crunch rn and this was what my brain spit at me
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Does it make sense?"
I think, ultimately, the thing that it comes down to for why I just can't see "the Jedi are intentionally written as dogmatic/dispassionate" or "Obi-Wan failed Anakin" or "the Jedi brought their own downfall" reads as valid anymore is because... it makes no sense that George Lucas - of all people - would write that.
Like, this is the guy who preaches the same lessons and philosophies that the Jedi do in the Prequels, every chance he gets (sometimes going all the way back to American Graffiti).
So ask yourself:
Does it make sense that he would intentionally make the characters to whom he gave his own values "dogmatic"?
He's a self-proclaimed "methodist-Buddhist". The Jedi are based on Buddhist monks.
youtube
Does it make sense that the buddhist would write a story about space-buddhists being "emotionless", "devoid of compassion" and "at fault for their own genocide"?
Lucas had an apprenticeship, that turned into a friendly/brotherly bond with his mentor Francis Ford Coppola. Their personalities were completely opposite (Coppola was more outgoing, George was more prudent) but they worked in sync, they completed each other.
youtube
Do you really think that this guy's intended narrative would be that "Qui-Gon would've been better-suited for Anakin as a teacher than Obi-Wan because the latter was prudent/strict and too different from the more passionate Anakin"?
George lays Anakin's downfall on Anakin's shoulders almost every time he talks about it. It's a corruption that was caused from within, he would be able to love without getting attached if he had joined the Jedi at an earlier age, but he didn't so his attachment and greed results in his turn to the Dark Side.
youtube
So does it make sense that Lucas' narrative would be that "the Jedi (aka EXTERNAL forces) pushed, denied and failed Anakin that they caused him to turn" instead of "it was Anakin's own fault because he wasn't able to let go"?
He has said multiple times that, aside from Anakin's downfall, the Prequels center on the Republic's downfall, never mentioned the Jedi once when describing what the Prequels are about.
youtube
If the Prequels were actually about "the fall of the Jedi and how they lost their way", wouldn't he have brought it up once?
And would he really have focused so much on the Senate and politics rather than adding more development to characters like Mace and Yoda?
I think the answer to all of these is "no".
Here's one more: Lucas stated so many times that this was a fairy tale, that all six Star Wars movies are meant for kids. The situation of the Prequels is more complex than the one in the Original Trilogy, but before, during and after the Prequels Lucas confirmed that the Star Wars morality is binary, it is black and white, good vs bad.
Would he really intentionally make the Prequels this subversive story wherein "actually, if you stop and think about it, the good guys are really the bad guys"?
Or is it just that:
We live in a time where movie audiences expect the "good guy" to be individualistic, flawed and non-conformist, and the Jedi are a community of nigh-incorruptible champions of good who've already completed their character arcs.
So the adults (aka not the target audience) who watched the Prequels at the time were turned off by these characters who they perceived as "holier than thou", having been conditioned by the times they lived in to think that there are skeletons in "Mr. Perfect's" closet.
Thus, they retconned the films (via comics, books, games and episodes) so that they could enjoy the Prequels more, and did so by:
injecting more realistic "gray morality" themes into the films and
projecting an oppressive "boys don't cry" philosophy onto the Jedi.
For lack of a better metaphor, "they put a skeleton in Mr. Perfect's closet so that they could finally find his existence bearable, and keep bringing up that skeleton to this day."
#jedi order#george lucas#star wars#long post#meta#in defense of the jedi#pro jedi#Youtube#trying something different#instead of posting quote collections I'm posting video compilations#hopefully it'll work#lucas quotes
280 notes
·
View notes
Note
At best plurality is akin to a philosophy, or way of life. No way of life is “truth” necessarily, though people tend to believe that their own way is The way. It’s an alternative explanation for natural brain phenomenon. Internal dialogue is normal; however, one can choose to decipher the “other” as separate if that so pleases them. As social beings, having internal dialogues is incredibly useful. They can help broaden one’s perspective of a situation, to see another side. It can also be helpful for brainstorming, in the creative process. And of course, it’s useful from a mental health perspective, such as managing depression or anxiety. I have “voices” in my head all the time. If I’m overly anxious about something, I might tell myself to chill in a manner that isn’t my typical tone or manner, and yes it can appear to come from “outside” me. What my brain is doing is borrowing from its environment. I could of course decide to focus on this “voice” and draw it out as its own separate entity. However, I don’t see the usefulness of that. That’s then living inside my own head, rather than being present in the here and now. I spent my whole youth living inside my head and all that did was isolate me. I find living in the here and working to forge connections with my environment and the people around me brings me a much higher quality of life. Again though, that is me and what makes sense for where I am in this current stage of my life.
It can be dangerous to spread this kind of rhetoric, that plurality is an objective reality, when you have a platform that may attract younger minds not yet fully developed. This way of thinking can create a hinderance in their development. It’s one thing to talk about it as something you experience that helps you. It’s an entirely other to encourage it in hopes of propagating it. The most current research shows, for example, that encouraging the idea of separate identities to clients actually hurts their progress.
First, before we get into the bulk of what you're saying, this blog is a fact first zone. If there is a study out there that has shown empirically that encouraging the idea of separate identities is harmful then I would like to see it and know what methods they used to come to such a conclusion.
So far, internal family systems has been shown to help people. Tulpamancy is shown to help people. And while DID specialists do tend to recommend treating them as parts of one whole person, they also paradoxically want to approach each alter as a separate individual to build up communication between the system.
Many spiritual beliefs that involve speaking to some invisible other have shown positive results as well.
So if you have research showing that people treating different identities as separate is harmful then it's up to you to show it. As of right now I have no reason to take your word for it.
With that out of the way, I really find this whole argument you're making to be pretty... basic.
Despite what you say, I don't think a majority of people actually have multiple autonomous voices in their head. Aside from, perhaps, when they're sleeping. (Whole other can of worms there.)
Having these separate agents with their own memories and senses of self is not nearly a philosophy. It is a psychological phenomenon, and one that occurs cross-culturally. Yes, some cultures will say that it is a spiritual possession, just like an earlier anon mentioned that they used to consider the people they communicate with ghosts. But if you look deeper and get past people's own personal explanations for what they experience, what you will find is a lot of commonality between these phenomena, regardless of whether somebody gives a spiritual or psychological explanation.
At the same time though, this does not seem to apply to everybody. There are singlets out there who are just one person. They may be different in different circumstances as people are. But they don't experience the type of experiences that are described by plurals and wouldn't relate to them.
To reduce plurality to just being a philosophical concept does a disservice to it. Because plurality isn't merely philosophical but has very distinct psychological characteristics and understanding how plurality works might help to solve some of the greatest mysteries about how human brains in general function.
#plural#syscourse#plurality#multiplicity#endogenic#pro endo#pro endogenic#systems#system#systempunk#syspunk#psychiatry#psychology#science#tulpamancy#tulpa#tulpas
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
circle, line
A circle and a line look different, right?

What about now?
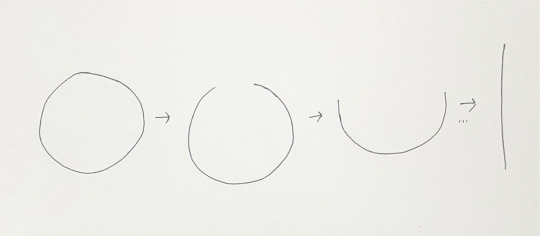
Time in gintama is a useless subject. Unfortunately, it is also a prerequisite to the gintama-human ontology. Thus, with a heavy heart, I look at lines, loops, and other unlikely time-mechanics in order to construct a gintama time for the gintama-human.
Throughout this pseudoscientific inquiry, I locate gintama time– which I eventually call [time], for lack of better notation– in my thematic abuse of two mathematical concepts: irrationality and uncountable infinity. To give away the end, [time] is an uncountable infinity born in irrationality. Which, even to its own creator, makes little sense.
Finally, this is my defense of the gintama time loop. Why? Well, I like loops and loop-like things, and, after all, we want good things to last, to repeat. So this turns out to be a love letter to algebraic topology. Sorry time loop fiction.
Onto more interesting things.
preliminary time notes
To think about time in gintama, I bracket [real world time] from [the narrative structure of gintama, which follows a time] and [time as characters in gintama experience it, i.e. personal time]. The latter two time-categories reflect [real world time] because gintama is written by an author, who, by virtue of existing, lives in [real world time]. That is, while narrative is fun because you can play with reality to make something new (e.g., time loop, time travel, non-chronological narratives in general), creation still requires building blocks, which are ultimately some sort of known assumption, that inevitably require some understanding of actual Time.
All this to say I look at [narrative time] and [personal time] through philosophies about [real world time], which themselves are not especially real; in other words, my methodology is kind of shit.
the situation– personal time
Otae announces the whole of gintama in chapter one.

This is gintama’s genetic code.
To speak of time here is to note a few things:
1. amanto possess advanced technology;
2. humans are forced to throw away their physical swords;
3. the sword of the soul.
The sword is a tool*; later chapters tell us that it “carries the soul”. So the sword represents, or, rather, is, something irreplaceable to humanity, that relates to the soul and personhood. This much is corroborated by the plot cycle.
With contrast to the sword, time appears impersonal. We conceive of time, at least scientifically, as the movement between past to present, present to future, stretching infinitely before and after, where our existence does not matter to its flow.
But would “time” exist without anyone to observe it?
Alternatively, how can “time” be experienced as time– as a movement– without anything to measure it?
The human must “create” “time”, if only because it would not be “time” without a person to observe and call it as such. What this person perceives, they conceptualize as movement (measurement); and thus there must be a prior position to reference, or, in the least, a default– a memory.
So “time” requires the present to be given by a prior; that is, for “time” to be experienced, the human who observes it needs already given into a past. The past itself (“knowledge” of the histories that make us who we are, “knowledge” of the tools that allow us to intend various things)– i.e., its inherent “given-ness” to us– depends upon it outliving those who live it. Thus various contexts, with their technologies, arts, and writing (though these are not really separable), function also to contain the essential past-as-memory for those who use and engage with them.
Alright, great, but what does this have to do with the dick-and-balls manga? Nothing, really, except for everything. The amanto (with futuristic technology, in futuristic contexts**) force humans to give up their swords. It would be ridiculous to talk about what the “sword” means here. Suffice to say that it carries (an assumed) cultural-historical weight, an (idealized) memory. We would expect that its dispossession disrupts temporality. And it does– hence the “time loop”.
People love to talk about cyclical time in gintama. It is the same situations, over and over again; that no one ages, injuries heal by the next chapter, and, more than serial-typical regressions, that there is a sense that things won’t work, that important change won’t last, that life “just gets worse and worse”. Time as lasting change– or what we like to call “linear time”– doesn’t feel like it exists.
To return to chapter one. Here the central conflict is not actually between amanto and human; it is between Shinpachi and Otae. Their dying father tells them that even if they give up their physical swords (memory, past), they are not to lose the sword in their soul (?unknown). Sword-less Shinpachi resents him. Rather than “cling to the past”, he tries to adapt to the “linear time” of the amanto: he works in modern food service, gives up on the dojo, and, most importantly, opposes Otae.
What does Otae do? We might expect her to inverse Shinpachi, that is, to “embrace” cyclicality, which would be to give up. She doesn’t. Otae tries to adjust, to make a living and survive, but, unlike her brother, she does so also to protect the “thing she can never take back”. This, as Shinpachi points out, is ridiculous, unrealistic, and makes no sense. And yet it is Otae who is thematically vindicated in the end.
From the first chapter, then, we can construct a sense of [personal time (to the characters)]. Again, for change to exist, there must be a prior form; that is, a certain sort of time is what makes change (technological, political, situational advancement) possible. Further, the self is involved in the process of time. Thus when the self is not whole (lacks the sword), time, and thereby change, becomes cyclical. So “time”, to the amanto, advances, because they can work with their external “selves” (technology, worlds, knowledge-memory) to “make change”. But time, to humanity, loops back on itself, is stopped, because humanity is bereft of its self and can only return to the starting point.
We notice that humans still live in a world where time progresses– where time goes on without them. There is a split between the time of the self and the time of the world. Shinpachi decides to do away with memory and join the world-time, the “linear time”, that is, the time of futuristic technology and change; but his sister, who goes along with this and drags the past with her, does much better.
For a more thorough application of this thought, please rewatch the monkey hunter arc.
*It is also (obviously) a dick.
**This reveals some connection between the concepts of “tool”, “context”, and time. Though I say so inverse-facetiously, since nothing about gintama can be taken as if it were serious.
time loop– narrative time
So what about infinity?
Personal time is not infinity. In a first sense, it simply is not infinite– characters die. In a second sense, even considering that memory can be (haphazardly) preserved beyond a lifetime, especially in a story, humanity as a whole is finite– there comes a point, eventually, where no one is left to do the remembering. And in a third sense, personal time is still a string of pasts that were once presents, into futures that will be presents; though this finite string might divide into an infinite number of presents, its divisibility renders it still essentially patterned, which is to say that it is not really “infinity”– it is still mathematically countable.
I mentioned a dysfunction of personal time into cyclical (“un-change-able”) personal time. This is associated with sword-less-ness, equivalently memory-loss, equivalently not being a whole self. The fun of stories is that “character” can be projected into the structure of the story itself; it would make sense for cyclical personal time to have some correspondence to, or at least effect on, narrative time, that is, narrative structure.
At this point I should be more general about the time loop.
The time loop is thought to stand opposed to “linear time” in the stagnation-change, lack-presence, circle(hole)-line([censored]) dichotomy. Specifically, the time loop is opposed to “linear time” in the sense that nothing (usually) changes in a time loop. Or, more exactly, change is slow, nothing gets “better” in any real sense. Again, only where time flows “linearly" can we build off of what is prior, can we intend and achieve a future, can we change for the better (or so we assume). Thus the time loop carries a sort of moral condemnation in its very structure— a karmic debt, if you will.
Characters in plots get thrown into time loops because something has gone wrong. Whether or not they are the direct cause, the character must “figure something out”, “learn a lesson”, that is, address the problem that created the time loop, which will almost always be related to a step within the story of their self-development, in order to escape it. The point of the story is to escape it. This is just how stories go.
Then the gintama narrative “time loop” is barely a time loop. It repeats itself, sure, and no one ages, but that’s because no one should age in a wsj serial and sorachi tried to be funny about it. Still, some lingering sense of futility, or maybe just the sheer repetition of the same event for 16 years of serialization, weighs on anyone who reads it. This kind of feels like time loop fiction; there should be a point to the plot cycles. What are they trying to force Gintoki to do, to show us in his character? What are they aiming for, what is driving the “time loop” in the first place?
Takasugi is driving the time loop.
(More specifically, Takasugi’s crushed eye-ball (soul), his eyelid; inaccessible past (memory), is driving the time loop.)
Another clarification. Personal time is time as experienced by the person; it is pure interiority. Thus, while the world moves on– personal time is time as movement– the person may not.
For the person to move on, they must be able to make change, that is, from a prior form, give birth to the next form. This is because only the person can observe, know, and experience “time”, which itself is a movement (a change in position) from past to present, present to future, that is defined by the person. So change and time-as-movement, within personal time, look synonymous.
Further, movement in personal time requires the given past– the memory, from before me, passed down to me by people and places and things and contexts that I outlive– to be held by me, to be part of the “I”, and thus for my bodily self and my non-embodied self to generate personal time together. In gintama, I locate “memory” as the sword. But gintama’s sword is also part of the Self; so personal time in which the Self can move is only born out of a whole self. Equivalently, personal time is not the Self, but it is intimately related to a change that can only be wrought by the Self, which is to say, both my body and my given memory are necessary to the movement of personal time.
In any case, “gin-tama” is about Gin-toki, and, quite literally, his soul, so we would suspect that narrative time is a projection of Gintoki’s personal time. But narrative time cycles weirdly, and Gintoki still has his sword. Alternatively: if Gintoki was not already a Self, that is, if he had to learn some lesson to become a Self through the time loop, how could he have saved any of the endless roster of villains that conveyor-belts around him? So maybe Gintoki holds his sword without remembering– except that he doesn’t, and the story makes this clear (“I haven’t lost a single thing”). He does, however, seem to possess a slightly different personal time. He and his sword remind antagonists of what they’ve forgotten, and these antagonists sometimes move forward with him into the next cycle. In other words, there is some sort of movement, a change, in the narrative, in the structure, associated with each loop.
But cycles stay cycles, up to a very particular moment.
At which point I revert to the most obvious advantage of narrative time: it interacts with the readers. Gintoki “is” a Self (in the sense that an electron is both a wave and a particle), who carries his sword, who remembers, who hasn’t lost a single thing. Yet the time around him repeats the same events, over and over again. Why? Well, in part for the above: every gintama villain needs to learn the same lesson. But every gintama villain is also Gintoki, and even if he remembers, we don’t. To risk being redundant, we, as readers, have no idea what actually happened to him until chapter 519, when it is fished (unwillingly, I think) out of Takasugi’s eyelid.
Then narrative time functions in several senses. It relates to Gintoki’s personal time, but indirectly; more generally it looks like a projection of the Losers’ personal times, where a Loser is one who has lost their sword. Still every Loser is also Gintoki, and every lost sword is lost memory, and even if Gintoki hasn’t forgotten anything– and even if Gintoki carries his past, his sword, with him– we, the readers, don’t. Surely enough, historical time in gintama only begins after chapter 519. The revelation must precede it.
So the gintama time loop is driven forward by whatever it takes for this memory to be revealed. Each iteration brings us closer, but there is no lesson for Gintoki to learn that would speed this up; the heart of it is that he is waiting, he has to wait, for memory to return, for his past to come back to him, and this past is exactly Takasugi.
Why? Takasugi is the past (his eye, his eyelid, is the past); his eye is therefore Gintoki’s sword, the sword of the soul we need for time to move on. But 10 years jump before Takasugi can make the approach, and even then only from behind. Worse, it takes hundreds more chapters for him to work up the resolve to face Gintoki head on. So if Gintoki somehow constrains the world to cyclical time, equally so does Takasugi.
In short, narrative time cannot move until Takasugi’s eye becomes Gintoki’s sword. Thus half of the loop is about Gintoki always standing up again, always waiting for Takasugi to face him, and the other half of the loop, that is, its motivation, is about Takasugi working up the guts, or whatever he does throughout the series, to finally come at Gintoki* face to face. Yes, I’m equating circles and lines, which is silly. But I did this in the beginning anyways. Rewatch the final.
So why does this matter? Readers well-versed in gintama sword theo-ontology may recognize that the sword which is memory is identical to the sword of the human. This is partly because I’ve defined personal time to require the whole Self (the human) to move, which itself requires both the sword-as-memory and its human wielder. It is also because I’ve equated Takasugi to memory instead of treating him like a character (sorry Takasugi). Nevertheless, creation of the human sword (the memory-sword) is now essential to creating time, and creating time is now equivalent to completing the Self, that is, to becoming “human”. Put another way, Shouyou isn’t killed until Gintoki kills him in 519.
More specifically, Gintoki killing Shouyou undoubtedly completes (undoes) his humanity**. It is also the only way for anyone in gintama to have a future, because it creates, gives birth, to time, the time of the series. Further, its revelation births time in the present just as its actuality births time in the past: the Gintoki who swings his human sword, who cries, in Takasugi’s eye, is the one who swings it at him now. Gintama doesn’t actually timeskip until Gintoki kills Utsuro in silver soul.
Then the movement of time, both personal and narrative, requires three things:
1. a memory-sword (the human sword) (the sword of the soul);
2. a human to wield it;
3. and a decision on how to swing
I have discussed one and two to exhaustion. Now we turn to three.
*Gintoki is always Takasugi, in every case. The inverse holds as well.
**It also completes Shouyou’s, but that is for later.
in defense of the time loop
Birthing time looks like an escape from the time loop.
This is where the division between time, self, and change becomes essential. Why does the time loop, in many treatments, depress its readers? For the same reason that any tragedy is depressing: fate, un-change-ability, specifically, un-change-ability of things we want to change.
The time loop is a “literalization” of tragedy. The person trapped in the time loop, at best, loses the ability to determine their future, accomplish their projects, do what they want and have it last, that is, to find lasting (exterior) meaning (this is all exterior). At worst, this person carries their incapacity into a loop that is the same tragedy, over and over again, which they are helpless to prevent or change in any way.
This setup is not exclusive to the time loop– other variations could be immortality, reincarnation, oracles, endless linear eternity, et cetera. In every instance, though, the tragedy is that people cannot change the things that matter. And while the time loop usually removes external change to provoke internal change in its protagonist, gintama characters also struggle with the impossibility of changing themselves.
More generally, though, real time isn’t actually cyclical or linear. We move through time, changing form, towards our death– and so the common thought of time is “linear time”, which is really about “linear change” and an inability to “go back”. But time is only known to us, only countable, because of its cyclicality. There are 60 seconds to a minute; 60 minutes to an hour; 24 hours to the day; and then this repeats the next minute, the next hour, the next day; and then the next month, and then the next season, and then the next year; and then it repeats all over again. Time is only measurable, knowable, existent to us because it repeats. If it wasn’t known beforehand, how could we measure the present, the future, against it? And for it to be knowable, it has to be familiar; and for it to be familiar, we must have encountered it before; and here is the inherent repetition– we can’t stop the cyclicality or flow of time anymore than we can avoid our deaths. Real time makes possible our “change” just as it is unchangeable, just as its existence is conditioned on unchangeability.
Gintama is a story, and story time works differently than real time, so maybe in the story we can separate “linear time” (change-ability) from “cyclical time”, from “time loop” (un-change-ability). Even still, what happens after you escape a time loop? Equivalently, what happens after you escape the tragedy? In the usual time loop– at least the usual time loop in our minds– the loop is escaped into linear time, or, more appropriately, it is escaped into the time where linear change is possible. But why is “linear time” the happy ending? Even granted that it exists (which is questionable), what makes linearity better than repetition, that is, why do people love “linear change”?
The Joui 4 lived “linear time” during the war. They fought enemies, and won. They progressed towards something, and believed in it, too; they were the main characters of a power-scaling, battle-shounen manga. And yet, their linear time ended, or more accurately, was never “linear”. Shouyou’s death, if anything, only proved the inherent impossibility of their shounen dreams. So narrative time twists into defeatist cycles, and Takasugi is doomed forever to repeat, and this is probably more accurate to the condition of the actual world they inhabit, because, most importantly, time was always like this, linear change as linear time never existed.
But again, the tragedy was never about the time loop. From its inception, the tragedy has always been about intentionality versus ruination, “I” as capable actor versus “I” as acted upon, and the utter inability of anyone to change any of this. We want out of the time loop because we can’t do anything; we want out because we can’t act out of ourselves to make external change in any way that lasts. Ultimately, we want out of the time loop because we discover that our intentionality actually means jackshit. The world does what I don’t want it to, and traps me in this; I cannot act, and yet it acts on me. My despair at the exterior world which rivets me to itself quickly translates to despair in, at, my self. I can’t make change, so what does being [x person] matter, so this is my fault, so there’s no point in changing myself, so I can’t change myself in any way that matters, because even if I do everything right, there’s no meaningful effect on the world that holds me captive, et cetera. Thus everyone wants out of the tragedy, the time loop.
Including gintama villains, who usually try to get out of it by killing themselves. This never works.
The time loop is tragic because it makes its inhabitants absolutely passive to it and acts on them eternally. The gintama cast is supposedly full of “losers”; its villain of the week, while beating Gintoki, calls him a masterless dog, a ghost, the one who lost, along with the rest of the samurai, et cetera; and the loser here is inherently passive against a winning actor. Nevermind that Gintoki never fought for the Romantic Japan that lost to the amanto– his loss is even more infinite for the narrowness of its scope.
And yet, you’re not supposed to kill yourself.
Escaping the time loop– or, more generally, the tragedy– never guarantees linear time, because we always have to end the book on the happily ever after. So what really happens after you escape the time loop– is linear time actually a relief? Either things start going wrong, which isn’t the linear time ideal, or you achieve every dream, you make possible every impossibility, and come to the end of the infinite series by continuing on within it infinitely. Is that really “happy”?
Alternatively: the cycles of narrative time drive towards the birth of a new time. But the tragedy of the cycles is intentionality/ruination, and the cycles can’t be escaped into their “opposite”. Gintoki, a human, with a human sword, kills Shouyou, and thereby brought forth a new time. And yet, this new time was still cyclical.
Then what’s the solution– killing yourself? Takasugi, repetition Personified, asks this to Gintoki the entire series. Why won’t you stay down?, [Why are you crying?], [Why can’t I comfort you?], Why keep living in this world? Villainy aside, he does have a point– if you look carefully, living in the gintama world is incredibly, incredibly stupid.
Gintoki says: no matter how many times I fall, no matter how many times I fight the same fight over and over again, no matter if it never ends, I will always stand up.
This is the height of stupidity.
[time]
So narrative cycles aim at the revelation of Gintoki’s memory, which would identify sword with eye, tool with wielder, that is, complete the “human”, and thereby give birth to a new (non-linear) time.
Here we get to mathematical infinity.
Mathematical infinity is not a number, or even properly a concept. It’s more like a sign at the edge of a cliff that says, there’s a cliff here, here’s the end of the world– except that this sign also signifies whatever, and everything, that might lie beyond the cliff, which cannot really be called “essence”, or even be said to exist in the first place. In other words, infinity is a marker for a point of no return, that in of itself is nothing.
Some things are said to be “infinite”. Usually, these are patterns. A line is infinite, as is a parabola; but these infinities are predictable, that is, countable, because patterns are rules. Their comprehensibility allows us to treat them like fancy numbers.
Conversely, some functions decompose into situations that are entirely ungraspable. This edge of knowledge, where it devolves into paradox and nonsense, looks like uncountable infinity.
Uncountable infinity is the infinity whose name itself means nothing. It signifies to something that is, by axiom, impossible impossibility, ungraspable. When infinity “interacts” with the mathematical world– or, rather, when we push far enough to reach it– we come to paradox, chaos, and unintelligibility. Certainly, science could advance sufficiently to reconcile the mysteries of particle physics; but the fun of mathematical concepts is that you can define them in any way you like, even if they’re fake. And uncountable infinity is, by my definition, the “thing” that is always uncountable.
So gintama narrative cycles aim at something, while those in cyclical personal times suffer for them. Cycles, better, change-less-ness, correspond to sword-less-ness, to lack of memory, and historical time only “restarts” when Takasugi brings us the past. Et cetera, et cetera, et cetera.
This doesn’t mean our new time won’t be cyclical.
In the end, “time” is associated with sense of Self. This is an unavoidable relation, because time is a human word, in a human language, that describes what is ultimately only known to us as human experience. But “Self” is (itself) a problematic concept. After all, what determines one’s Self? Relatedly, who, and/or what, and/or where, and/or why, gets to possess Selves at all?
Within concepts of Self is often embedded an instinct towards differentiation. The (western philosophical) impulse is to originate this difference in agency: that is, through my free determination of my Will, my Projects, my Actions, and et cetera, I differentiate “I” from “other” and thereby constitute Me. Needless to say, concepts of “agency” are inextricably linked to “change”. Thus, in this particular conception, “time” is bound to “Self”, is bound to “agency”, is bound to “change”, and to invoke any one is to invoke the other three.
Here, “knowing” (as agency) finds itself imperiled. That is, though the “unknowable” would strip agents of acting-ability, “knowing” would also consign existence, life, the universe, et cetera, to determinism. In both cases, “(un)-knowledge” renders the agent passive. Thus someone might long for an unknowable magic in order to undo determinism, just as they might long for the knowledge to successfully determine their life; yet the one who longs for agency could find agency a disappointment, a not-agency. Equally, if the time loop embodies both desires before they collapse into paradox (I can continue into the unknown future if I escape; something is tying me down, my knowledge is insufficient to escape), “linear time” does so as well.
But now we return to infinity, to irrationality, to uncountability, in short, to paradox. The bulk of the previous 5000 words has been to determine that the dichotomy is false. To be straight, knowing and not knowing, agent and non-agent, the linear and the cyclical, are not separable from each other. Their binary is an illusion, and the suggestion of one carries within it the absence of the other; they are synonymous at the exact and every moment they are not. Clearly, this is not not-knowing, and not knowing, and not not-either of them at the same time. I call this uncountable infinity, the mathematically irrational.
The mathematically irrational is paradox. Consider: we can graph, and look at, certain functions, and yet never grasp their value (put x(sin(1/x)) into desmos). Similarly, we know exactly what “pi” is– the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter– and we can define it, use it, find it in every instance. And yet, pi is an irrational number, because its decimals trail off into uncountable infinity. Knowing and not-knowing, united in the same action: irrationality is knowing in not-knowing, not-knowing in knowing, and also neither.
I will be ridiculous and find this paradox in gintama. I want to claim, in the first place, that the self never generated time at all; in the second, that this is never irreducible to agent/acted, knowing/unknown; and in the third, that time is generated by [time]. To do so, we must investigate the moment of its birth, in 519.
the cliff—519
Tools, given memory, etc., together with the persons who hold them, produce an actor-self, a time of possible change (a “linear” time). It is in 519 that Takasugi finally faces the camera.
Now Gintoki grasps the sword (memory, Takasugi). This should give us “linear” time.
But 519 is not so willing. Where we hope for capable agency, we find none. Instead linear/cyclical, active/passive, presence/distance, collapse into irrationality.
Take the archetypical moment. To Takasugi’s why, Gintoki says he’ll stand up. Specifically, he says, too bad– I (you) won’t fall.
Standing up is what Gintoki (a person, with a sword) does. It is how he defeats each suicidal villain, kills Shouyou, and kills Shouyou and Takasugi all over again. This is what the “time loop” would require of him.
Gintama antagonists, those paragons of rationality, tell us that it is irrational.
Otae is also irrational. Her irrationality doesn’t fix anything (⇔escape cyclical time, make change), and she knows so herself– “If I’ll suffer either way, I’d rather suffer protecting it.” 518 chapters later, Gintoki says: “I won’t fall until you [Takasugi] fall, until you stop, no matter how many times it takes, I’ll stand up again… even if I have to walk over my teacher’s corpse, even if I have to walk over your corpse, I’ll protect his disciple, our companion, Shoka Sonjuku’s Takasugi Shinsuke, his soul.”
So Gintoki stand(ing)s up until something– until Takasugi stops, until time is born– in order to protect Takasugi’s soul. This might look like an “end” to the cycle, but it doesn’t feel like one. “Even if I have to walk over your corpse”?
Alternatively, “saving” Takasugi should be the change that the cycles want to make, that would break them in any normal work of time loop fiction. It is “agency” (capable action, material change) at its purest. But Gintoki says he will stand up and kill Takasugi and stand up again. No matter how many times the same thing repeats, no matter if time never moves on, no matter if he is forced to kill the very person he’s trying to protect, Gintoki will stand up. How could Gintoki possibly care about escaping any cycle, when he is the one “perpetuating it”?
So gintama is not actually about escaping the time loop, which is the rational thing to do. Gintama is about, do you have the strength to keep living in the time loop, even if it never ends?, or, do you have the strength to kill your teacher and your friend, and lose everything all over again?, or, do you have the strength to eternally suffer for the thing that can never be taken back? In short: forget the capable actor– gintama is about being foolish, and irrational, and embracing the time loop by standing up.
If we look to chapter one, [standing up] is [protecting the thing that can’t be taken back]. Neither can be appropriately confined to cyclical or linear time. Otae says she’ll suffer either way, and Gintoki says he stands up to protect what Shouyou held precious, Takasugi’s soul.
Otae protects a thing that cannot be taken back. This is the past. Gintoki acts for– and this is also a protecting– the past. Takasugi is, in a literal sense, pierced by this past every moment of his life.
The past that we can recover, that we can fully integrate into ourselves, is the past that can be used to generate the future in “time”. Thus “accepting” the past “to move on” – accepting, making entirely part of oneself, making entirely interior – because only then can the past become knowable, comprehensible, and usable. The person must accept their past to change things, i.e., to make linear time. Time, change, and agency coincide.
Yet Otae’s past “cannot be taken back”. Certainly, even the accepted past cannot be “returned” to. But Otae’s past is the past that pierces Takasugi’s eye– that is, the past whose “revelation”, whose self-same existence, drives the completion/generation of gintama time itself.
So this is the past that “cannot be taken back”, in more than the literal sense. Takasugi is scandalized by its distance, even as he dies satisfied; Gintoki, ever-silent, still loses his composure at its provocation, is emptied by it, cries in 519 (in all of gintama), in 703. It is a past that refuses total use or incorporation; instead it acts on those who carry it, even after person is reconciled to sword (to its memory).
Its paradox in position. Though “the past” is always present (“I haven’t lost anything”, “how long will you keep looking at that crushed eye of yours”), it is simultaneously kept from us by an irreparable distance. Distance, of course, suggests space, which itself suggests a space that is surpassable. But this distance is not spatial– it is temporal. Gintoki carries the past, yet never reveals it to anyone, much less to us; in the end it is Takasugi who has to do the revealing, and even then only after 500 chapters. Further, its revelation actually increases the distance. We grow used to our proximity to Gintoki’s “point of view”, to our role, through him, as protagonist of the story; and here his defining moment is told not through his eyes, but through the eyes of the distant antagonist, whose breaking point is the discovery of the distance between him and Gintoki. Gintoki is reflected– more, revealed to have always been– across a distance that is unsurpassable.
This distance is equally time, because Takasugi and Gintoki were separated always, and only, by “the 10 years”. Takasugi comes to Edo– there is nothing stopping him, spatially, no physical restriction or meaningful law imposed, from making the approach– and yet he cannot make it. Or so we assume. We only know its universal separation axiom: 10 years, a distance between two points that could never be overcome or recuperated.
So the past is across an unsurpassable distance. In this sense, it cannot be taken back. It is simultaneously carried in, pierces, Takasugi’s eye, who struggles because he cannot reconcile it to himself. Just as it is always with him– “every time I look, the beast…”– it is also the one thing he cannot bear to see (your crying face). Though its revelation is necessary to New time, it is also what sent time into irregularity in the first place. And though it is irreparably distant, it pierces every moment of the present, which is to say: it degrades time, it makes things weird.
Its paradox in times. The cliff is pre-originary to everything by narrative position. Gintama narrative cycles press towards its revelation as first dilemma. It is before even the corpse field, before anything else. It drives each time Gintoki swings his sword and reenacts it. The very first moment that Shouyou finds Gintoki, is predated, predicated upon, generated, made possible by, the fact that Gintoki kills him with his sword.
From this past, Gintoki is (in the verb sense). It is ahead of him (in 519) and behind him (before 1). For its sake he “acts” towards a “change” (stands up) that he knows is impossible (“if I have to walk over even your corpse”*). In other words, for sake of this past, Gintoki lives as if he belongs to a “linear” time, even as he knows he doesn’t. The past brings forth itself again.
Finally, its paradox in agency. What is burned onto Takasugi’s eyelid is a single moment he cannot recover or recuperate. Instead, this moment acts on him, it pierces him, against his will. This sort of past is not an empty concept, that could be filled with any given circumstance. Takasugi is tortured because the content matters– because what happens on the cliff that day, matters.
The cliff is not what Takasugi, Gintoki, Shouyou, or anyone else, wanted. Worse, it is not what they fought for: Takasugi to save Shouyou, Gintoki to protect Shouyou’s disciples (in an act that he knows will destroy them), Shouyou to protect his children. Instead Takasugi is stripped of agency, and the eye that would acquire it; in the present he acts on everything because he is, in every moment, acted on. Equally, just as Shouyou tries to protect his students, he destroys them, and Gintoki, who is forced (acted on) to choose (acts on) between two wrongs, two denials of his self** (of linearity), that is, two losses, is the classic agent paradox most of all.
So the past cannot be taken back, and this not only in the sense that no one can return to it. The past cannot be taken back as a memory, nor can it be incorporated as part of the self, nor can it function as the essential memory that projects forward normal time, even as it is known at every single moment. It cannot be domesticated.
Gintoki killing Shouyou, and crying, is unacceptable. It is distance itself, just as it is proximity; it is simultaneously known (Takasugi sees it), unknown (no one can reconcile it), and neither (we still move on). It should not have happened. It is irrationality itself.
And yet, by virtue of being “a past”, in its relation to the present, in its position as driving force of the time of the entire series, it still is time. The human, with the human sword, who cuts off someone’s head, is [time] itself.
Clearly, this is something outside of normal time. The question becomes, who needs to be killed, and where, and why?
The one who gives birth to a future.
*–and he does.
**“No need. They’ll never hold a sword again.”
the future
That Gintoki kills Shouyou is essential.
The start of gintama’s “historical timeline” is the corpse field. Here the time that Gintoki sits in carries a heavy sense of eternity. The moment where Shouyou finds him could be forever; historical time is out of place.
What breaks this time is very particular. It is not that person and sword = human = time in the automatic sense, because Gintoki, who holds a successful sword (“before meeting you, I never lost to an adult”), remains inhuman. Rather, Shouyou, a human (to Gintoki), must give his sword to Gintoki for time to start. This is also what makes Gintoki human. Gintoki, the human, had to be given his humanity– and thereby time– by someone else.
Equivalently, it is not enough for gintama’s [being human] that the right person holds the right sword. Only a human can progress time, that is, give birth to the future, but reconciling self to past, sword to eye, escaping the time loop, is insufficient. That Shouyou finds Gintoki is predicated by the cliff; sword can only become eye through the cliff’s revelation (and the cliff happens concurrently); self and past are reconciled only after Gintoki kills Takasugi; and the Shimura dojo is restored only once the Shimura siblings kill their mentor. It isn’t enough just to hold the sword– you have to actually swing it.
This swing must be something irrational, because everything else is just the natural extension of a person with a sword (it is the person and the sword). Further, the person must make the swing themselves. For it to be a swing they make, they need to choose it. So the swing is a decision made in irrationality.
Swinging a sword at– beheading someone— who is clearly the irrational choice. What goes against the logic of the world, of time, of all the meaning you sought after? Gintoki fought to protect Shouyou’s disciples; but Takasugi tells us that he wanted to save Shouyou more than anyone. Narrative logic says that Shouyou’s disciples should die to save him, and the logic of their linear time– their humanities and their swords– is to rescue Shouyou and progress into the future. Gintoki swings against everything. And cries.
Gintoki stands up, is irrational, for the past that can never be taken back. This past completes his humanity (person, sword, swing) in the moment that it ruins it (he cries). Gintoki kills the one before him(先生) to make them the one behind (into the past); which itself is a loop, is a cycle, but also a line. It is a [being human] that gives birth to an irrational time.
Gintoki kills Shouyou even though it changes nothing. How does this birth time? “Time” comes out of a self, but Gintoki loses his self; “time” is what renders change possible, but Gintoki cannot “save” Shouyou or Takasugi. Certainly Gintoki knows this, and kills Shouyou in spite of it. But how does this bring forth a future at all?
Gintoki does kill Shouyou for something, for some reason, and this is concretely the survival (into the future) of Shouyou’s disciples. Abstractly, though the purpose is less clear– “even if I have to walk over your corpse” – it is still what drives (is the purpose of) every instance that Gintoki, or anyone, stands up.
Gintoki’s purpose is Shouyou’s purpose, and Shouyou dies to give birth to the “future” (a future that is born in irrationality). So when Utsuro comes to kill him, Shouyou sees also Gintoki, and smiles. Sakamoto calls this “hope”.
We are told that Shouyou gives birth to hope– his students��� almost as if to invoke the analogy. Shouyou’s disciples– his “children” – are him, because he gave birth to them, and they are not him, because they have a futurity beyond his imagination. Equally, this future is knowable, because the child is you, and time repeats, just as it is not, because the child is not you, and you will not be there to see it. This is the substance of “hope”.
With regards to the structure of his world, his time, and perhaps even his own humanity, Gintoki makes the irrational choice: he stands up. But to stand up is actually for, to give birth to, the uncountable future. Sakamoto tells us that Gintoki “gives birth” to this future in every shounen-bond he ever makes. And here is the paradox, something more generative than irrational dilemma– Gintoki’s “descendants” inherit his soul to be in ways unimaginable to him.
This future pierces every moment, and in the same moment it escapes. Take that Shouyou knows, and cannot know, what his disciples will be. Their possibility is imaginable, in the sense that he can delineate it– “I hope you all find your own bushidous” – but it is also uncountably infinite, because your child is not you and not beholden to your patterns. Equivalently, Otae’s happy memories end when her father dies, but she still keeps the sword of her soul, this unspeakable thing, that past, and it is her purpose in standing up.
Gintoki, with the sword he has been given by a human, kills Shouyou. This gives birth to an uncountable future– uncountable because it is born in irrationality, beyond the possibilities and expectations of pattern, either linear or cyclic– that is an uncountable infinity, and this is [time]. [time] drives, again, pierces, every second of all of time, and in the same moment it escapes. It is also irreparably beyond the one who births it. This is why gintama had to end.
So the human is constituted in the moment of death (⇔the moment of irrational swing), which is to release the future— [time]. In the same moment, humanity, and [time], escapes. But the moment of constitution (⇔ [time]) is what births the next instance of being human, that is, the rest of time.
In the moment before Gintoki’s irrational swing, each [time] was truly infinite. Here possibility is as unthinkable as Gintoki’s heart; there is no better way I can describe this than an uncountable infinity. Gintoki did what he should have (not) (not) have done. Neither he, nor Shouyou, nor Takasugi, Katsura, Oboro, or anyone, could have imagined any possibility for the future that was to come. In its sheer impossibility, this was infinity: the past that cannot be taken back.
But the past that cannot be taken back is also the sword of the soul. By definition, this generates an impossible impossibility, that slips away as soon as it is born; and as the uncountable, that is, the mother of all irrationality, and also its child, [time] has little to say about lines or circles, aside from that they are essentially the same. So gintama never cared about time loops or not: all that matters is if you follow [time] by standing up.
When Gintoki recovers his sword (Takasugi’s eye, Takasugi), he does so amidst a wreckage that looks like pine trees, as Takasugi (the one who finally stood before him, who now will stand behind) dies in his arms. Here, we find that the “cycle” repeats: Gintoki stands up, and the sun rises.
This is the dawn of a new, impossible day.
I don’t think that’s so bad.
#4 months later. i cant articulate the suffering this has brought me. anyways. happy 5 years since 703 LOL#goose tag#gintama
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
Work in Progress Wednesday - A Dark Alternative

“Callum!”
He started upon hearing Claudia’s voice, very much not in the mood to talk to anyone right now. She hurried across the grounds, clearly excited to see him. “Hey Claudia,” he didn’t try to even disguise his mood, hoping she’d pick up on it and leave him alone.
“Hey!” She beamed at him. “How was your trip? Ez said you went out rock hunting or something.”
“It was good.” Callum continued in the direction of his room. “Long though, I’m pretty tired, actually.”
Claudia walked quickly with him, seeming intent on continuing the conversation. “What’s on your head?” She snorted, reaching forward.
Callum frowned, assuming he’d got leaves or cobwebs caught up there and immediately flushing with embarrassment when Claudia pulled the flower crown from his hair. “Oh, eh-”
“Cute!” Claudia examined the chain. “Where did you get this?”
“Em, a friend.” Callum didn’t really want to elaborate, thoughts of Rayla making his heart ache right now. He reached for the flower crown, frowning when Claudia seemed reluctant to give it up, though she eventually relented.
“Who’s your friend?” Claudia sounded a little suspicious, which probably made sense. They pretty much knew everyone in each other’s social circles.
“Someone I know from before I moved to Katolis.” He kept his responses short and to the point, not wanting to engage Claudia any more than he absolutely had to. The whole… plan to maybe rekindle their thing had sort of fizzled out when he started spending more time with Rayla. He probably should have said something to her really. He’d sort of forgotten about Claudia and the whole thing though. Which just went to show how much of a crush he had on Rayla. She was pretty much all her thought about now.
The thought of discussing her with Claudia made him uncomfortable for multiple reasons though. He could already feel himself blushing about the flower crown and he didn’t want Claudia noticing and teasing him about it, maybe figuring out he had a crush on Rayla. Ugh, what if she told her father? After that weird conversation with Viren, the last thing Callum wanted was him knowing he spent a day alone with an elf. An elf who’d made him a flower crown. Viren would read way more into that than was there. There was no way he’d accept he and Rayla were just friends. Or maybe he wouldn’t care either way and would try and manipulate the information to try and make Callum look stupid or something?
“Ooooh, yes, the elf.” Claudia continued along with him, appearing oblivious to his attempt to exit the conversation. “What sort of elf was it again?”
Callum frowned, not sure what it was that Claudia could be interested in and not knowing how to avoid telling. “Moonshadow.”
Her eyes went wide as they dart to the flower crown clutched delicately in his hand. “Reeeeallly.” She grinned widely. “What does that mean then?”
“Mean?” Callum stopped, frowning at her. “Why would it mean something?”
“Well, Moonshadows are all into cryptic messages and that, aren’t they? Always weaving illusions.” She shrugged, looking excited. “That’s got to mean something.”
“I… no, I don’t think so.” Callum glanced at the little string of flowers in his hand. “Rayla’s not really like that.” He bit his lip, mind a mess. “She’s not really into the whole Moonshadow thing.”
“An elf who’s not into being an elf?” Claudia waved her hand dismissively. “How’s that work?”
Callum took a breath, feeling more awkward now. He didn’t want to explain anything about Rayla and her situation to Claudia. In fact, he didn’t want to discuss Rayla with Claudia at all. Especially not after everything Viren implied about him and his apparent “tastes”. “Elves are just people, Claudia.” He turned back in the direction of his room. “They all different, you know. Someone of them just aren’t into the philosophy or cultural stuff, you know?”
———
As I approach the last chapter of Fuel the Pyre, the tail end of Purgatory and slowly chip away on the final chapter of Zoom-mates, I’m cleaning up the first ~20 chapters of my dark magic AU, A Dark Alternative.
Set in a world where humans and elves lives a lot more closely, Callum and Rayla, childhood friends rekindle that friendship in the midst of political and personal turmoil.
Ticking the childhood friends to strangers to lovers tropes, copious pining, idiots in love, along with map making, world building and pastry pondering.
Projecting ~60 chapters (lets not discuss my track record), 40 of which are in a decent state of finished. Hoping to start posting mid-June/July.
27 notes
·
View notes
Note
Gwaine does not seem to like magic much in the later seasons and happily hunts down sorcerers (dragoon, the guy from 5x05, finna) Thoughts on that?
I’ve answered similar questions before! Unfortunately, Tumblr’s search function doesn’t like me, or I’d link to my older analyses 😔
As early as 3x04 (Gwaine’s introductory episode!), Gwaine is implied to have some bias against magic. Not as severe as Arthur’s, but any bias can be dangerous. When Merlin goes to Gaius and Gwaine about the Stulorne blades, this is the reaction he gets:
Gwaine: I've seen those blades in action. They're forged using sorcery.
There’s quite a bit of emphasis on the word “sorcery” here, both in Gwaine’s speech and in the overall use/placement of it. The fact that the blades are forged using sorcery tells our protagonists why they’re capable of deceiving people’s eyes, but it does not in itself imply danger unless you see magic as a danger.
Later, in 3x08, Gwaine remarks on magic with a similar attitude:
Gwaine: Wyverns. Distant cousins of the dragon. They're creatures of magic, so be careful.
Again, Gwaine expresses their capacity for harm by bringing attention to their magical origins. But the worst is in 3x12, when Gwaine does nothing to stop Arthur from holding his sword against the throat of a child simply because he’s a Druid. Rather, Gwaine pulls his sword on the rest of the Druids when they come out to save the boy. It’s Merlin who has to tell Arthur to let him go. So, Gwaine not only sees magic as dangerous, but he believes that magic and innocence (not as in guilt, but as in youth and vulnerability) are mutually exclusive. He dangerously adultifies a kid who’s <10yo.
Thrice, in the introductory era of the character, pretty solidly confirms his perspective. However, Gwaine doesn’t seem to approach magic as an innate evil the way Arthur does. He more or less ignores Grettir, despite his flagrant use of magic to turn Gwaine’s sword into flowers. In season 5, he sees clearly that the Diamair is a creature of magic, but leaves with an understanding that he owes it his life.
Gwaine’s philosophy is openly stated in 3x04: “Nobility is defined by what you do, not by who you are.” If he’s to be true to this logic, then he has to accept that one’s actions/beliefs determine one’s character, rather than their birth circumstances. He has to apply this to magical people and creatures. And he seems to, in relation to Grettir and the Diamair.
Perhaps not so much to those who he believes “chose” magic, for what he may assume is to the end of greed and power—some of the very traits he hates nobles for. However, there is only one instance to go off of, and it takes place in 5x05, where Gwaine’s like, 2 lines are the one that implies this, and the one telling someone to respect Arthur because he’s a king (even though Gwaine only respects Arthur despite that fact), so I’m inclined to ignore it.
As far as Dragoon goes, Gwaine seems to be under the impression that assassinating Uther would be evil, even though he has no motive for this. Uther had him banished and even threatened to cut his tongue out. I suppose he might just think that killing = evil, but considering how he’s employed to do just that—and it’s what he threatens Dragoon with—it doesn’t make a whole lot of sense. Perhaps because he sees sorcerers as a danger, he doesn’t disapprove of the magic ban, and therefore finds Uther’s death to be unjust?
They never really offer an explanation. I think the safest bet is that Gwaine assumes this means that Dragoon would want Arthur—who still holds the ban on magic in place—dead also. “Dragoon” actually plays into this idea.
It would be the same reason for the Finna situation. Arthur has already decided that she’s a threat, and Gwaine is receiving this information through his word alone. Gwaine’s exact quote is: “There’s a dangerous sorcerer at large,” who he wants to protect Merlin from. (It would be a very different story if Gwaine knew that Merlin was her accomplice—or rather, she is Merlin’s accomplice, heehee.)
So, while Gwaine doesn’t “happily” hunt down sorcerers—seriously, more like—he does show a bias against magic, believing it to be dangerous. However, he is also shown to overlook this bias from time to time, and I think it’s safe to say that he would have been able to make a repeat for Merlin if it came to it.
#if I haven’t answered your ask yet it’s cause i respond with 10 paragraphs almost every time#sir gwaine#merlin meta#bbc merlin#my meta#asks
30 notes
·
View notes
Note
Spooky, I'm so tired of seeing people say that "Megumi has no development/is badly written/sucks", especially on reddit, and now I almost started to cry because you started your last answer-meta about Megumi with "Megumi's actually the most complicated and well-written character in the manga", and let me tell you that's a lot coming from someone who writes such great metas!
Then I continue reading and you describe him in the same way that I perceive him but it's also like I'm seeing Megumi for the first time? it's difficult to express this but it always happens to me ... Megumi is so complicated that every time I read an analysis/meta about him this happens and I love it.
Sorry, I'm terrible at expressing myself and everything I wrote might be confusing but I needed to tell you, and also, Thank you for writing and sharing your metas! 🖤

Thank you for sending the ask, anon! I'm just happy you're a fan of Megumi and enjoy his character as much as I do. My friend @theanimepsychologist did a much better post than I did, explaining why exactly the complexity of Megumi's character is hard to miss. I wish I could just copy paste that whole post here and steal it, but I have some brief thoughts on why Megumi is oftentimes overlooked and it has to do with the fact that his development throughout the entire manga is hidden in the shadows.
I say Megumi's development is hidden in shadows, because in typical shonen manga tradition his character development goes hand in hand with him learning to use the Ten Shadows ability. It's outlined for him twice by both Gojo and Sukuna that Megumi should really be a lot more powerful than he is right now.


Megumi is your typical genius kid who everything comes so naturally to him he never learns to study, and therefore when moving up from high school to college begins to fall apart because he didn't learn the skills that would lead to his further development.
If you look at Megumi's situation, he should really be more powerful than he is. Megumi has the ten shadows, which is the strongest technique in the Zen'in, and apparently even capable of defeating a limitless user with the six eyes. Not only that, but he was handpicked and tutored by Gojo Satoru since he was a child, and he's clearly the student that Gojo takes the most interest in teaching.
Gojo and Yuta who have similiar natural talent are already at the level of special class at Megumi's age, and Yuta himself has only been a sorcerer for a year, but Megumi lingers at grade two. Gojo and Megumi himself are frustrated by his own lack of progression and neither of them can understand why.
In typical Gojo fashion, Gojo who only understands the world through the lens of sorcery, just suggests that Megumi get stronger at developing his ten shadows technique and everything else will work out. However, the reason Megumi can't advance isn't because he's not strong enough or not working hard enough, but because he's emotionally weak.
He falls apart mentally rather than physically, and we learn the reason why in his flashbacks to Tsumiki.

Megumi has no emotional reason to want to be a sorcerer, he doesn't even feel an obligation to save people does the way Yuji does, he was just groomed into it by Gojo. However, the loss of Tsumiki at middle school age makes Megumi falter, because the one reason he had for going forward is that he could possibly make Tsumiki safe because doing his job as a sorcerer gave them money to live... but then Tsumiki is out of the picture and Megumi is trapped in a life he doesn't want for no reason.
The difference between Megumi and Gojo that Gojo fails to notice, is that Gojo has an incredibly strong sense of self, and Megumi has no sense of self (which further inhabits his development). He's never once doing things for himself, despite calling himself selfish and espousing a much more selfish philosophy that Yuji does, his goals all focus around providing some kind of service or protection to others.
This is where Megumi's development starts becoming difficult to keep track of, because Megumi is a character who both changes a lot throughout the manga, and doesn't actually change at all. Which is a statement that makes no sense but let me explain: Megumi develops his ten shadows technique and on the outside is developing into a stronger sorcerer, but he never does the internal work and self reflection required to become emotionally strong.
Once again, Gojo in his great genius can only offer this advice to Megumi: Become strong, become a better sorcerer. This is because Gojo misses out that emotional issues are what is holding Megumi back. Megumi's first two major fights in the manga are losses, he's not strong enough to kill the curse on his own in the first chapter so Yuji eats the finger to help, he's not strong enough to stop Sukuna's rampage in Yuji's body, so Yuji dies in front of him.

It's two situations where Megumi reflects, "If I was strong enough, I would have been able to do X, Y, and Z, therefore it's my fault that this bad thing happened."
So we see Megumi throughout the arcs, continually developing his ten shadows technique to be stronger, while at the same time avoiding personal development. The biggest moment of this is origin of obedience, where he unlocks his partial domain expansion and then a few chapters later just avoids an emotionally difficult conversation with Yuji because he's scared to talk with him.


Megumi's desire is to feel free and grow into a better version of himself, but he stops at every opportunity to develop emotionally because that's harder. Gojo suggests that Megumi just pursue strength, so Megumi just starts finding himself in violence. Which is why the progression we do see in his character is him getting stronger and better at using his technique, coupled with him being more openly violent and more like his father the shadow of violence who is always chasing after him. This is what turns Megumi into Mr. "I'll totally kill people in the Culling Games if I need to."
Would Megumi at the beginning of the manga been okay with slaughtering normal people to get points in a game, maybe yes maybe no but he does advocate for just leaving a prisoner to die to curses because they committed a crime once. If anything his development post shibuya is just exaggerating a side to him that was already there. Megumi in times of crisis falls back on violence for survival because that's what Gojo taught him.
Megumi grows more confident with his abilities, he uses them in more creative ways, he even starts demonstrating himself as a leader among the group basically coming up with the strategy for the culling games. He's also more emotionally open with Yuji than he was in the past. There's definite emotional progression.
Beginning of the manga Megumi is lacking in confidence -> Yuji dies in front of him, he realizes his need to get stronger and starts applying himself -> In the Kyoto battle arc despite training with the second years he still falls short in the battle against Hanami -> Gojo reveals to megumi part of the reason he has a mental block against getting stronger is because he's downplaying himself for the sake of others, and afterwards Megumi starts imagining a better version of himself for the first time -> Megumi shows his strength at cooperating in Shibuya, fighting with Yuji, and then later Maki and the rest against Dagon -> Megumi is the one who convinces Yuji to keep fighting showing his emotional development and comes up with the strength for the culling games -> Megumi uses his domain expansion again but much more confidently than he did in origin of obedience.
There's clear progression here on Megumi's part that I can even give a general summary and map out, but at the same time the fundamental problem has not been solved, that Megumi doesn't have a thoroughly developed sense of self and self destructs. Gojo even says as much that part of the reason he's so limited in using his abilities is because he thinks he has Mahoraga to fall back on.
He tries to use Mahoraga in the fight against Sukuna, tries to use it against Todo of all people, tries to use it against the special grade spirit in origin of obedience and this time stops himself (making progress) only to once again default to using Mahoraga in Shibuya when he's cornered. Megumi doesn't try to personally develop himself because he considers his own life worthless and that behavior never stops. It keeps persisting until we get all the way to Sukuna taking over his body, which happened because Megumi ignored every warning from Yuji that Sukuna was planning for something. Because in that case he just assumed Sukuna would kill him and Megumi doesn't care about that because he doesn't value his own life.
Which is where we get the great paradox that is Megumi, he's the most developed character in the manga with a great deal of the manga focused on both his slow progression as a character, but also revealing more parts of his personality that the audience would not notice at first. People who saw Megumi advocate for leaving prisoners behind to die in the first arc of the manga, probably wouldn't assume he'd go so far as killing people in the culling games to get point, because it's quicker that way and he can justify killing bad people, but that's the natural extreme of that behavior to begin with.
We see more and more of Megumi's repressed anger, and his abandonment issues with his sister and his parents, so his character is moving, but we also don't see a lot of progression on those issues because Megumi's not focusing on trying to be a better person just being a better sorcerer.
In typical shonen manga fashion, the focus is put on Megumi getting stronger and learning to develop his technique ore. In atypical shonen manga fashion, Megumi is actually punished by the narrative for only caring about getting stronger. Sukuna's possession of him, and his loss of Tsumiki are both things caused by Megumi being ignorant until the last moment and keeping himself hidden in the shadows too, if he'd valued himself more he'd have steered clear of Sukuna and Yuji because of the danger, if he'd paid more attention to his sister he'd notice Yorozu in his body.
Which is what makes Megumi so unique, but also a little hard to understand because he is in so many ways a typical shonen jump character, and in other ways he's nothing like them because he's just Megumi.
108 notes
·
View notes
Note
I’m a queer anarchist, and your music has really helped me accept myself, so here goes…what advice do you have on loving my radical self? I find myself trying to look respectable and chill to avoid being a stereotype, opting out of actions to please my family, and just internalizing a lot of BS about what it means to be an anarchist in the world. Thank you so much!!
David Graeber, RIP, guy at Occupy Wall Street who coined the slogan "we are the 99%," often said he was a "small-a anarchist" and that anarchism was a thing he did, not an identity. That is probably the healthiest way to engage with anarchism in a modern world where political identities and political language have been turned into sports teams and brands, completely divorced from anything that the words behind them actually mean. US politics at least have turned into "are you a LIBERAL or a CONSERVATIVE" which sort of means something but also means nothing, and its meanings contradict each other to the point of uselessness. They're not real ideological frameworks, after all. Nobody can give you a coherent manifesto of US American "Liberalism" but it's the thing you're supposed to agree with if you don't think gay people should die?? Maybe??? It doesn't even have any connection with the philosophy of classical liberalism, which is closer to stereotypically Republican fiscal politics, EXCEPT for when the ostensible "left wing" liberals actually agree with that shit? Anyway yeah it's a mess and it's no wonder why the younger generation is desperately trying to find an alternative way of labeling themselves so as to signal that we're outside of all that bullshit.
So don't do that. Actually be outside of all that bullshit instead of coming up with an edgier sports team to root for. Not that you're necessarily doing that, but just, remember not to do that.
Focus on the material circumstances you live in: the state and money and laws and all that shit are just things somebody made up one day before you were born. You exist in a world you had no say in constructing. Your goal is to figure out how to survive, and then to thrive, and then to be happy, under these circumstances. And ideally make them better for everyone else.
Now as for opting out of actions to please your family. Sounds like you're stuck in a family situation where you're not free to go where you want and be yourself without scrutiny, and that sucks. From the perspective of an effective anarchist, remember that it's from each according to their ability, and you don't have to feel any guilt about not doing your part to change the world.
But from a queer perspective? That queerness sounds a lot more like what's causing your tension about making yourself look more respectable. And that plays into this feeling you have of being trapped by family, or by capitalism, or whatever forces are making you feel the need to put yourself in a box. Obviously you've woven your queer identity pretty deep with your anarchism, which is good, but that definitely makes the desire to express your anarchist identity a whole lot stronger. It can feel like the same thing as your sexual orientation or gender when it's such a deep part of your worldview.
And that makes for a big contradiction in a world where political labels have turned into deep personal identities at the expense of any coherent intellectualism. Whoops. Everybody else has been forced to pick a vapid red or blue choice and here you are with an extremely deep sense of pink and black. Uh oh.
But that's the great thing about queerness, is to be comfortable existing as a contradiction, as category-defying, as someone that doesn't need to be intellectually consistent because you simply ARE. So be you. Don't feel like you have to debate the chuds in your head to explain your existence.
88 notes
·
View notes
Text
Endlessly enamored with MFR!Techno’s position of ‘The only way I can be wanted is if I’m being used, and the only way to survive is to be wanted’. Like the philosophy’s seeds were planted with the Piglins but the Wither honed it to something consuming. And honestly, it’s why Philza terrifies him so much, because his unconditional love (obsession) is intent on the idea of Techno completely irrespective of actuality. All his life the only thing Techno could control about his environment was himself, and so the only way he knows to survive is to change himself to please his given “parent” in the equation. And because he can’t do that with Philza he simultaneously has more freedom and less control of the situation. And for a man who defined his existence in the boundaries of others expectations, it scares Techno more because he can’t figure out the rules.
Like he definitely found lines that could be crossed but never something that revoked his inherent worth. Thing is, Techno can handle when it’s him getting punished. It makes sense in his head, his mistake, his consequences, and now he knows where the boundary is and can work with the rules of the household. Like, he actually thrived in the Nether when he was getting beaten up, poisoned, and drowned, because Techno can handle pain and responds well to it. (To the degree some readers accepted his view that the Nether was better at face value, simply because Techno prefers blatant manipulation and physical threats because he knows how to deal with them). But with Philza the consequences always, always fall on the head of someone else, and for someone with a painful abundance of empathy, for someone who defines his worth on what he does for others, that’s infinitely worse for Techno.
#techno angst#technoblade#technoblr#mandatory family reunion#Sbi#dark sbi#emerald duo fic#tw abuse#something to nom on
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
Let's say Mc is pregnant but doesn't know it. But their belly is slightly showing more and the Ro's notice. How do they react and feel? Do they confront Mc about it?
Ooof, talk about difficult conversations…Let’s see…
Oswin, if he truly believed that MC could be pregnant without realizing it, wouldn’t want to just ignore it. It could put MC in an even more difficult spot if he just left it up to them. He would feel awkward (especially if he knew he wasn’t the father), but he’d sit MC down and would ask as directly as he could if it could be possible. He’d offer help as well. He’s learned from his mother some things about pregnancy, and he’d know a few good midwives that MC could go to. Overall his feelings are only of concern for MC’s wellbeing.
Zahn would be a little out of their depth. This is something they don’t know a lot about and it’s something that could be scary for MC. They’d want to know if it were them, so they’d try to talk about it with MC. They may feel out the waters a bit, asking leading questions to see if MC actually does know and is keeping it secret. If Zahn could possibly be the second parent, they’d be pretty determined to confront MC and see where they should go from there. They’d feel a bit scared and sympathetic overall.
Duri would be so conflicted. Generally they just want others to do their thing and have the privacy they need to do just that. Getting involved sort of conflicts with that philosophy. They may assume that MC knows and is just not sharing it with them because it’s not their business. If they knew that MC was romantically involved with anyone, they might ask that person to be sure they’re taking care of MC or ask them to make sure MC is okay. They would not confront MC directly, but would be more subtle, telling them that if they ever had anything going on, that Duri would be there for them. If there is a chance they are the second parent, they’ll feel less conflicted in speaking to MC about it. A lot of conflict and concern from Duri in this situation.
Rune: They approach things head-on. They’d believe it was best to address this asap and would do so with keeping privacy and comfort for the MC at the forefront. They’d speak candidly and then offer to check MC for pregnancy themselves with magic. They’re supportive and logical and behave the same way if there’s a chance they are the second parent to MC’s child. Their biggest feeling is the sense of doing what is right for the MC.
???: Unless he is romantically involved with MC, he’s going to consider this largely ‘not his business.’ It would much depend on the type of relationship that has formed between them. He would likely not know that MC doesn’t know. He wouldn’t assume it. Now, if he is romantically involved with MC, that’s another story, and he’d confront them gently about it and ask what sort of support they needed. His feelings depend on his relationship, but overall he’d be concerned.
Thank you for the Ask, Anon! ^_^
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
What does "less than one personality" mean?
Is it ableist, dehumanizing, or harmful?
Spiegel was the clinician who first put forth this idea in 1993, when MPD was being renamed to DID. It was said that those with DID did not have "multiple personalities", but rather "a dissociated identity," or "less than one personality".
I think Middleton explained the concept best.
Characteristically people with DID switch between different identity states, none of which has the full range of memory and the full range of affect that an integrated personality that's non-dissociative has.
One way of conceptualising it is, yes, people with this condition switch between different identity states, but it can be usefully conceptualised as not so much as having multiple personalities but having access to less than one personality in any context or in any time. So if they are confronted with a certain event, a person with DID in that particular state summons up what resources that they can lay their hands on in that state, but that may mean that that precludes them from the full access to other resources or memories that may help their decision-making, which sometimes represents a situation where they do things that appear very unusual or reactive in a way that is totally out of keeping with the circumstances.
Carolyn Spring also has a good description:
Dissociative disorders are characterised by ‘a disruption in the usually integrated functions of consciousness, memory, identity or perception of the environment’. So for example memories and feelings may not go together – memories may be recalled with no accompanying affect or emotions, or there may be overwhelming feelings with no conscious memory of their cause. There is also often a lack of a coherent sense of autobiography, and this itself leads to problems with a sense of identity – ‘Who am I?’ and ‘What has happened in my life?’ This all results from dissociation acting as a creative survival mechanism in the face of overwhelming trauma, whereby the mind shields itself by segregating the experience, or splitting it off into its constituent parts rather than experiencing it as what would be an unendurable ‘whole’.
As a concept, this has nothing to do with personhood or ability to function as separate people-- though many alters do lack access to significant portions of memory and emotional growth that would inhibit and disrupt their ability to act completely independent of the system, and it ignores the internal communication and teamwork that makes sharing information across alters a key part of healing and treating DID.
It's really frustrating when people without DID/OSDD start making really broad, misleading statements about this topic, and pushing it as something negative or wrong based on made up arguments.
Frequently, topics that have nothing to do with the concept are dragged into it (like personhood) in order to make it look and sound worse than it really is.
You see people say things like, "The phrasing I more often hear is that alters are each part of the whole collective personality. This is based on a philosophy that a "person" is the biological human, and they therefore have a singular "personality.""
I have never heard anyone say that, and it's extremely misleading and flat out wrong.
It's rare that people specify what the parts make up, but typically, it's "person" or "individual".
It is important to bear in mind that the parts ‘are not actually separate identities or personalities in one body, but rather parts of a single individual that are not yet functioning together in a smooth, coordinated, and flexible way’. The ultimate work of therapy is to facilitate an increased coordination between these parts, so that they can indeed function together and perhaps even merge or ‘fuse’. By working on increased communication and cooperation between parts, often there is a corresponding increase in levels of co-consciousness, which can help the DID client to feel in much better control of their life.
Even the ISSTD says "person".
Although the DID patient has the subjective experience of having separate
identities, it is important for clinicians to keep in mind that the patient is
not a collection of separate people sharing the same body. The DID patient
should be seen as a whole person, with the identities sharing responsibility for daily life. Clinicians working with DID patients generally must
hold the whole person (i.e., system of alternate identities) responsible for
the behavior of any or all of the constituent identities, even in the presence
of amnesia or the sense of lack of control or agency over behavior.
Now while the philosophical view could be SAID to lead to one person = one personality, it doesn't mean that the connotation behind that is appropriate in this case.
And it's not even true. Even if I was one "person"-- as in, I had a full, continuous memory stream, I would still have different "personalities" for different situations.
Like every person does.
Even we, as alters, can change and adjust our personalities based on situational needs.
Not only do we share this brain and body, but I am not the full person I would have been if I had integrated the trauma and full range of memories from my childhood and adolescence. I would probably be more scared of people, of commitment, I might be more or less scared of public speaking, of wearing more vibrant clothing, I might have different interests or pursued different avenues of education and work. How would my (MY, me, as an alter) advice to other survivors be different if I had access to all of the memories?
Who would we have become if we hadn't had to break apart the continuity of our memory and consciousness to survive?
We are now parts of one person, together holding one whole, continuous stream of memory (plus extra), living this life together as best as we can, with access to what we can offer each other in terms of advice and ideas from our own limited resources.
105 notes
·
View notes
Text
TriMax Vol. 2 and Wolfwood
First want to shout out to everyone participating in the book club!! I’m getting so much more out of this reread of TriMax, thanks to listening to everyone’s thoughts as we read along! I’m seeing things in a new light and getting details I never spotted before! I’m so grateful we get to dissect such a meaty story and characters together, because there’s so much and so many legit ways to interpret things! We love us all some deep space planet future gun LITERATURE around here!
Okay, now, I promised to have some actual THOUGHTS, and now just share funny panels, so here’s something that stood out to me: watching Wolfwood’s arc unfold and his growing understanding of who Vash is and what his goals are.
In volume 2 of Trigun, Wolfwood felt like a character whose story got truncated by the manga being dropped by the publisher. He clearly had a backstory and was going to play an important role, but Shenanigans meant whatever those original plans were didn't pan out. So instead we hit TriMax Vol1 and this relative stranger is the one who pulls Vash out of retirement. It’s pretty strange, and it must be extra strange if you’ve never seen either anime adaptation, which both expand on Vash and Wolfwood’s interactions and relationships before Vash hits his Eriks era. In that case it makes more sense for Wolfwood to go after Vash, by then an old friend, but I’m not going to give TriMax too much of a hard time, since, again, publishing Fuckery. And really it’s not handled poorly or anything, it’s just strange.
Anyway, Wolfwood’s role in Vol1 seems to be as an external force to push Vash along when he’d Rather Not, and to serve as a contrast/dissenting voice against Vash’s optimism and philosophy. See the family feud/hostage taking in particular. Wolfwood constantly argues that Vash is naive or trying to save everyone, and selfish for trying to not get his hands dirty. Given what Wolfwood (and the reader) know about Vash at this point, it’s an understandable conclusion to make. Even when his adoptive home and family were in danger, Vash didn’t do anything to stop the violence, to the point of trying to downplay the sexual harassment of a child. Vash didn’t push back against the bandits until Wolfwood pushed him. Why would Wolfwood believe Vash is anything other than a holier-than-thou prick who is too cowardly to make the kinds of choices Wolfwood’s had to make? (And though we didn’t know what those were at the time, Wolfwood clearly spoke from experience.)
Then we have Vash intervene in the family feud/hostage crisis, with his new red coat and everything. He uses his reputation to clear out the civilians, then his uncanny abilities to take out most of the hostiles without killing them, until he is confronted with the grieving father about to kill his daughter’s murderer. This is *exactly* the kind of situation Wolfwood warned him about, about family willing to take up violence if their loved ones are hurt, about having to make a deadly choice and become the devil. And we see Vash struggle! He empathizes with the father’s desire for revenge, directly mirrored against Vash’s own grief over Rem and hatred of his brother! But he chooses to intervene anyway, choosing not to beg for the murderer’s life, but for the father to not commit a terrible crime. In the end no one dies, and by not continuing the cycle of violence that led to his daughter’s death, the father is also spared. Vash found another way out.
This is the first time Wolfwood witnessed a demonstration of Vash’s philosophy in practice, proof that it’s about more than just ‘killing is wrong’, it’s also about empathy, and stopping future violence before it an happen.
Which brings us to Vol.2, where we really start to understand more about Wolfwood.
We know he’s a Gung-Ho-Gun, and we know he witnessed the Fifth Moon for himself, so the audience knows why he knows about Knives, and can guess why he’s helping Vash (since their goal is now ‘eternal suffering’). We know he doesn’t particularly want to be there, so what brought him here? He dreams of the kids at the orphanage he’s referenced before, begging their big brother to hold him, only for Wolfwood to smile sadly, then hold up his bloody hands and say he has no right to hug them anymore.
And then after Wolfwood kills Rai-dei, we get one of the most stunning panels in the manga.

And by stunning I do mean that literally. Every time I’ve read this volume, I have to stop for a moment when I hit this page. Others have talked about its composition in detail, so I won’t dig too much into it here. This is such a pivotal scene for both characters, their understandings of each other, and as a setup for Future Stuff.
Wolfwood has just seen Vash do something stupid and naive AGAIN, but turning his back to Rai-dei, who was about to attack Vash again. Wolfwood killed Rai-dei to protect Vash, then Vash lashed out in anger, saying he wasn’t going to go through with the attack. Probably. Wolfwood, fucking pissed about all this, demands Vash shoot him if he thinks what Wolfwood did was wrong. Wolfwood believes that Vash needs to dirty his hands, to become a demon (like Wolfwood has) in order to save people, and anything else is childish nonsense. In this moment he says he’s willing to give up his life if that means Vash would become the kind of person Wolfwood believes he has to be.
Then Vash plays his reverse uno, saying that he sees Wolfwood as the coward in this moment, for valuing his life so little, for being so ready to give up hope and toss his own life away. He sees Wolfwood has someone who was forced to play a role he never wanted, to become someone he didn’t want to be.
Vash reads Wolfwood like a book, and it disarms the situation. (Empathy again plays a role in ending a violent conflict!)
We already got a sense that Wolfwood is someone who loves very deeply, we saw that in the dream with the orphans. We see in that same dream that he’s someone who’s willing to bloody his hands, and hates himself for it. The next chapter opens with a flashback of child Wolfwood being shot for the first time, and as he suffers horrific pain, says that he thinks for the first time (!!!) that he didn’t want to die.
We see next chapter that this conflict gets under Wolfwood’s skin, he’s still thinking about it, even thinking that Vash putting others’ live above his own “makes me sick”. The next time we see them talk about ethics is on the way to Vash’s home while they’re in the cable car, Wolfwood reiterating that he has to make the choices he does because he has (human) limits. Then Vash admits that he doesn’t know if his way is the right one! In a moment of vulnerability we haven’t seen until now, Vash shares his doubts about his philosophy. In response, Wolfwood says nothing. He doesn’t take the moment to pry open the crack in the armor Vash shows him, just listens.
In this volume we’re starting to see the shape of Wolfwood’s story arc, of his conflict with Vash, and a growing understanding between them. I won’t say more to avoid story spoilers, but this volume does such a good job of planting the seeds of future arcs for both characters, with the “Shoot” scene in particular coming back in a big way more than once.
What I love LOVE about Trigun is that it’s not interested in determining who is morally superior, because moral absolutes do not exist. The narrative doesn’t put down Wolfwood’s philosophy, and though we see Vash succeed in his efforts to save people without loss of life, we see him fail just as often, if not more. Trigun invites us to understand why these people believe the world works a certain way, and how those ideas clash with reality. This is something that becomes much stronger later, we’re still very early in the story, but it’s something to keep in mind going forward.
One last thing to note, though it’s not as strong a thread in this volume, is that alongside Wolfwood’s growing understanding of Vash, is his growing fear of his inhumanity. We know Wolfwood witnessed the Fifth Moon, and that’s one thing, but we know from Wolfwood’s internal thoughts that Vash being inhuman is something that’s always on his mind, and always plays a factor when they’re arguing. To Wolfwood it’s the thing that separates them as people, Wolfwood has human limits, and Vash doesn’t, and that’s the only reason Vash can believe and behave the way he does. (Is he right? That’s a question for the future). This is also the chapter where he gets a closer look at Vash’s power, where he sees Vash CRY BLOOD, and then a wave of darkness paralyzes Wolfwood, and Vash emits some kind of blast or wave that doesn’t hurt or damage anything, but frightens both Wolfwood and Leonof. Again, this is a bigger factor later, but it’s worth remembering that Wolfwood is tackling his perception of Vash as monstrous and dangerous alongside his more emotional understanding of who Vash is.
That’s all for now. That’s a lot of words and I don’t have the energy to go back and edit this, so if you see typos, no you didn’t.
#trigun#trigunbookclub#this is.... a lot of words#sorry#hope someone things this is interesting!#kay writes things
78 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sanctuary, Pt. 13
When Sheppard left his conversation with Teyla, he stumbled slightly heading toward the door. Here, we find him and Chaya seated on a balcony or a protuberance of some kind with a view of the city. What is interesting is that the picnic basket is behind Chaya and not behind Sheppard which is what one would expect if he was the one hosting this midnight picnic. The basket should be behind him and he should be the one offering things to her.

They have a lot of things laid out between them. Chaya even makes reference to "such variety of foods" indicating that there's comprehensive selection of every kind of delicacy they have. Chaya also tells Sheppard that she has been perusing the "information machine" Weir got her "on" which means that she's getting a really thorough insight into all things earthling.
The picnic, tasting earth foods, is also gathering intel since she is "a being of pure energy". We don't even know whether she's actually capable of tasting things, but she sure is putting up an act:
Chaya: This is delicious.
Sheppard: Well, enjoy it while you can, 'cause it's the last of what we have.
Chaya: Then I am honored.
Sheppard: When McKay finds out, he's going to kill me.
The thing is, although Sheppard seems to pour her wine made from grapes they have traded with the Athosians later, his comment here that this is the last of it and that it's something McKay would care about indicates that what she is drinking to start with is coffee. Him referencing Athosian wine here would make no sense.
But what's really worth highlighting, and is entirely on brand for Sheppard, is that he has to mention McKay. Anywhere he goes, anyone he speaks with, he cannot not mention McKay. Things McKay does, says, or thinks, or has done, has said, or has thought, is something that Sheppard needs to report to other people at every available opportunity. Even here in what he calls a "romantic situation with a woman from another planet". It's a strange new situation but it's not enough for him to not want to talk about McKay while it's going on.

It should also be pointed out that it's when he lays back on his elbow and seems to relax into a lean that he brings up McKay. It's either the thought of McKay that made him lean into it or the leaning is what reminded him of McKay. And as soon as Sheppard has brought up McKay, she brings up Athar. She gives him a seductive smile and tells her that Athar will save him from McKay. Which should mean exactly nothing to Sheppard who hasn't made it a secret to her that he's not a believer.
In fact, even though Sheppard told her earlier that he respects that she believes, he doesn't share that. He has shown no interest in talking about religion or religions, and yet she persists.
Chaya: I'm fascinated by your many religions. So many beliefs. So many philosophies.
Sheppard: Yeah, we've got a few of those.
Chaya: So many contradictory faiths.
Sheppard: Yeah, it's a bit of a mess. More?
He gives noncommittal replies. He has not consented to discussing religion. He hasn't consented to much of what has been happening recently.

Whether or not one sees Chaya as using supernatural means or just her feminine wiles, this is where the attempted seduction happens. The one that Sheppard mentions in the case file that Lucius read (and it is not coincidental that we return to this episode in connection with Lucius who bedded several women without their consent; "sometimes all at once"). She has a sultry look about her, keeps her gaze intensely on him. It doesn't seem like she has total control over him because we see flashes of him breaking free of her influence but it is clearly making him more open to suggestion. One of the most notable times comes when she first mentions truthfulness:
Chaya: I wasn't completely truthful with you about something.

And then loneliness.
Chaya: On Proculus, when I told you I did not feel lonely… Coming here, and being with you… it reminded me what it was like not to be alone.

Sheppard springs up and puts distance between them, taking several steps away from her. John Sheppard is lonely. This feeling he shares with her. He's lonely because he has chosen to be alone rather than let people get hurt for being anywhere near him. He had isolated himself in the most remote part of his world. But this is not something he wants to discuss with anyone, ever. His reaction clearly surprises her.
Chaya: What?
Sheppard: Well, I mean, nothing. It's just that… this is the first time I've been in a romantic situation with a woman from another planet, and it just strikes me as really, um…
Chaya: Wrong?
Seppard: No. God, no! Just… just… funny. I'm sorry. I just thought that I would…


He feels funny. He feels funny being in this romantic situation with her. It's weird. It's strange. Even with the full force of her seductive stare, the wine, the night sky, the gentle ocean breeze what he feels is funny. He says "I just thought that I would--" and shakes his head. He can't find the words. Any words.

He doesn't know what he's here to do. Yes, he said that he had no intention of taking no for an answer from her but it's doubtful he ever intended for it to get this far. He's not heartless.
She is. She is literally without a heart, a being of pure energy. Even in a suggestible state (even if just for the wine and her lovely company), his reaction made it pretty clear that his intention was not to make out with her (he holds his hand up and says "No, God no."). It's also worth mentioning that it's a lie ("You said it yourself -- we're both human") that she uses to draw him in. And the last thing she tells him before he kisses her is a command ("Don't [leave]").
When he says "I'm not going anywhere" here, it's in response to her direct command.

Interestingly, this is the only time we see Sheppard kiss a woman other than when he's possessed by something (although an argument can be made here that he's not doing this out of his own volition either). Every other time, he is the one that is kissed. And twice when this happens, he confesses that he never sees it coming when they do. Even with the women that have the Ancient gene that seem to be drawn to him and that we can assume he is similarly physically drawn to. John Sheppard does not actively pursue women. All of this comes later, though.
So far, we haven't really seen him express interest in a woman. We were made to think that he had once had a crush on a woman on Earth who hadn't reciprocated it, but it's not made clear that was a woman, and once he smiled at a nurse. A few times he has introduced himself to women with a charming smile. Because he uses charm to gain something, it's difficult to tell whether or when he actually feels attraction. But this still seems out of character for him, on multiple levels.
Continued in Pt. 14
#stargate atlantis#sga#sga meta#john sheppard#sheppard is bi#rodney mckay#rodney is gay#ep. sanctuary#ep. conversion#ep. the long goodbye
15 notes
·
View notes