#fatty acids
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
happy national chemistry week feat. an assortment of really great things i made while completing my chem minor:









#personal#chemistry#organic chemistry#inorganic chemistry#biochemistry#orgo#acetone#cyclopropane#borzoi#krebs cycle#proline#fatty acids#acid base chemistry#Lewis acids#ribbitol#nad+#nadh#chemistry memes#chemistry meme#I miss it 🥺
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
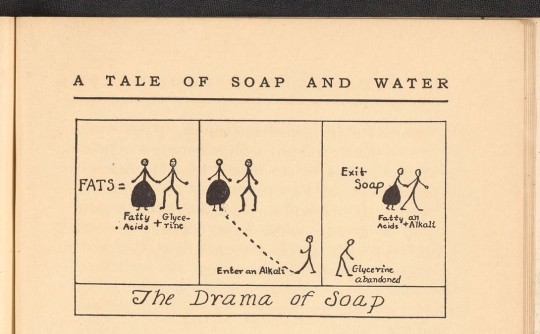
the saddest story ever told 🥺😢
This illustration from A Tale of Soap and Water by Grace T. Hallock demonstrates the process by which an alkali separates fatty acids from glycerin, making soap.
Citation: Hallock, Grace T. (Grace Taber). “A Tale of Soap and Water.” New York, New York: Cleanliness Institute, 1928. RA780 .H35 1928. Science History Institute. Philadelphia.
#soap#chemistry#drama#total drama#soap opera anyone?#fatty acids#glycerin#soap making#science illustrations#othmeralia
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lemons are an especially valuable citrus fruit with regards to bringing down cholesterol levels. This is because of their high satisfaction with vitamin C, a strong antioxidant that has been displayed to diminish the risk of heart disease.
#Cholesterol#Citrus fruit#Diet#Fatty acids#Fiber#Flavonoids#HDL#Health#Healthy eating#Healthy fats#Healthy Lifestyle#Heart disease#High cholesterol#L-ascorbic acid#LDL#Lemon#Lemon juice#Lemon water#nutrition#Plant sterols#Stanols#Stroke
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chemistry in nutrients, EPA

Omega-3 fatty acids, a class of polyunsaturated fatty acids, are important nutrients that our bodies cannot synthesize but are indispensable, the most important of which are ALA, EPA, and DHA.
EPA and DHA are mainly found in marine plant and animal oils and are also important ingredients in some fish oil-based health products. DHA, which was introduced yesterday, is important for the development and maintenance of brain and nerve tissue, while EPA plays a vital role in immune and inflammatory responses and promotes a healthy circulatory system, preventing cholesterol and fat from accumulating in artery walls.
In nature, EPA and DHA are mostly synthesized by aquatic phytoplankton in cold regions and are enriched through the food chain in the fish that feed on them (tuna, sardines, salmon, etc.), which is a good source for us to supplement EPA and DHA.

#omega 3#fatty acids#EPA#ALA#DHA#marine plant#animal oil#plant oil#stem studyblr#chemistry#molecule#organicchemistry#compound#organic#healthcare#nutrition#tuna#sardines#salmonfishing#kingdraw#did u know#interesting facts#information#pls share
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Well one type eaten is Moon jellyfish and Moon jellyfish contain no calories, no carbs, fat, or protein but they are eaten by many predators and even will be eaten by animals who don’t usually prey on moon jellies will eat them if moon jellies are readily available. But why?? What is the nutritional benefit? Surely animals don’t just consume low quality food for fun? They don’t!! A study conducted at the University of South Denmark collected moon jellyfish every two weeks and studied them for two years, finding that they actually have many valuable fatty acids in them. Such as polyunsaturated fatty acids, arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, and docosahexaenoic acid. The amount of fatty acid content found in jellyfish actually change across different developmental stages like mature jellies (you know they are mature due to their reproductive tissues) had the highest fatty acid content. Although jellyfish do contain fatty acids its not much since they’re mainly water, which is why turtles and other predators fill up heavily on jellyfish, for example salmon eat jellyfish like 20 times faster than they would shrimp. Also jellyfish are a good prey due to a good amount of them moving slowly through the water which means they can’t really swim away when being preyed upon.
-The fatty acids found in moon jellyfish like DHA, EPA, Arachidonic acid, and Polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential to many bodily processes. DHA and EPA are both omega-3 fatty acids and are found in fish oil supplements and cold water fatty fish like salmon (Usually found together which is why I put em in the same sentence). Arachidonic acids repairs skeletal muscle tissue at least in the human body so it wouldn’t be that wrong of an assumption that it would have similar benefits in animals that eat moon jellyfish.
https://www.earth.com/news/study-reveals-the-nutritional-appeal-of-moon-jellyfish/
#ceruleanmoonjellies#moon jellyfish#moon jellie#moon jellies#jellies#jelly#cnidaria#cnidarians#marine biology#marine science#aurelia#fatty acids
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Benefits of Lipids and Fatty Acids in Moisturisers
When it comes to achieving hydrated, healthy, and glowing skin, moisturisers play a vital role. Among the many components that make up a good moisturiser, lipids and fatty acids stand out for their incredible benefits. These skin-loving ingredients help restore the skin barrier, lock in hydration, and improve overall texture and appearance. But what exactly are lipids and fatty acids, and why are…
0 notes
Text

The Science Research Manuscripts of S. Sunkavally, p 464.
#gonorrhea#fatty acids#lingual lipase#tooth decay#hypertriglyceridemia#vitamin A toxicity#leprosy#skin temperature#antibody resistance#carbon-13#carbon-12#satyendra sunkavally#theoretical biology#manuscript
0 notes
Text
The fatty acid market is growing due to rising awareness of omega-3 and omega-6 health benefits, driving demand in food, supplements, and personal care. Innovations in encapsulation and healthier fat consumption trends further boost its appeal as a functional ingredient.
#Fatty Acids Market#Fatty Acids#Fatty Acids Market Size#Fatty Acids Market Share#Fatty Acids Market Growth#Fatty Acids Market Drivers#Fatty Acids Market Trends#Fatty Acids Market Forecast#Fatty Acids Market Analysis#Fatty Acids Market Report#Fatty Acids Market Scope#Fatty Acids Market Overview#Fatty Acids Market Outlook#Fatty Acids Industry#Fatty Acids Companies
0 notes
Text
The Impact of High Fructose Corn Syrup on Mitochondrial Function
The Impact of High Fructose Corn Syrup on Mitochondrial Function:
Analysis
High fructose corn syrup (HFCS), a widely used sweetener derived from corn, has become a major component of the modern diet, especially in processed foods and sugary beverages. HFCS is composed of glucose and fructose in varying proportions, with HFCS-55 (55% fructose, 45% glucose) and HFCS-42 (42% fructose, 58% glucose) being the most common formulations. While the impact of HFCS on metabolic health has been widely discussed, recent studies have shown that it can also exert a detrimental effect on mitochondrial function. This technical analysis explores the biochemical mechanisms by which HFCS damages mitochondria, contributing to cellular dysfunction and a range of metabolic diseases.
Mitochondrial Physiology and Biochemical Function
Mitochondria are highly specialized organelles responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of the cell, through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). This process occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and involves the electron transport chain (ETC) and ATP synthase. The mitochondria are also involved in regulating cellular metabolism, maintaining redox balance, calcium homeostasis, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Mitochondrial dysfunction, characterized by impaired ATP production, altered mitochondrial dynamics (fusion/fission), and excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, is a key factor in the pathogenesis of many chronic diseases, including obesity, insulin resistance, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Fructose Metabolism and Its Divergence from Glucose
The metabolism of fructose, particularly in the liver, diverges significantly from that of glucose, and it is this divergence that underpins much of the mitochondrial dysfunction associated with HFCS consumption. Unlike glucose, which is predominantly metabolized via glycolysis and the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle), fructose bypasses the rate-limiting step of glycolysis, catalyzed by phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), and is instead phosphorylated by fructokinase to form fructose-1-phosphate. This rapid metabolism of fructose in the liver can overwhelm metabolic pathways and lead to the accumulation of intermediate metabolites such as dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde, which can be further converted to fatty acids and triglycerides through de novo lipogenesis (DNL).
Excessive fructose consumption leads to the accumulation of triglycerides, particularly within hepatocytes, which is a hallmark of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The lipid accumulation in the liver, in turn, exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, contributing to insulin resistance and a cascade of metabolic disorders.
Mechanisms of Mitochondrial Damage Induced by HFCS
Increased ROS Production
One of the most significant consequences of excess fructose metabolism is the elevated production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS are byproducts of cellular respiration, primarily generated at complexes I and III of the electron transport chain. Under normal conditions, mitochondria have a robust antioxidant defense system, including enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which help neutralize ROS. However, when cells are exposed to an overload of fructose, the liver mitochondria become overwhelmed, leading to excessive ROS generation.
Fructose metabolism increases the NADPH/NADP+ ratio, enhancing the activity of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent oxidases such as NADPH oxidase (NOX), which further amplifies ROS production. These ROS cause oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), lipids in the mitochondrial membranes, and mitochondrial proteins. Such damage impairs mitochondrial function by decreasing mitochondrial membrane potential, disrupting the electron transport chain, and promoting mitochondrial fragmentation. Furthermore, mtDNA is particularly vulnerable to ROS due to its proximity to the electron transport chain and the lack of histone protection, leading to mutations that impair mitochondrial replication and protein synthesis.
Disruption of Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Mitochondrial biogenesis refers to the process by which new mitochondria are synthesized within a cell to meet the energy demands. This process is tightly regulated by several transcription factors, most notably peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α). PGC-1α activates the transcription of nuclear and mitochondrial genes involved in energy metabolism, mitochondrial dynamics, and antioxidant defenses.
Fructose consumption has been shown to inhibit PGC-1α expression in both liver and skeletal muscle cells. Reduced PGC-1α levels lead to impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, which limits the ability of cells to adapt to increased energy demands. This is particularly concerning in tissues with high metabolic demands, such as muscle, heart, and liver, where impaired mitochondrial function can exacerbate energy deficits and lead to insulin resistance, fatty liver disease, and other metabolic disorders.
Mitochondrial Permeability Transition and Apoptosis
Chronic exposure to high levels of fructose can lead to mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT), a process in which the mitochondrial inner membrane becomes permeable to ions and small molecules, disrupting mitochondrial function. MPT is typically induced by excessive ROS production, calcium overload, or changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential. The opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) leads to the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, and the release of pro-apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c into the cytoplasm. This, in turn, activates the caspase cascade, promoting apoptosis.
In the context of HFCS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, increased ROS and altered metabolic intermediates, such as ceramides, may trigger MPT and apoptotic pathways, leading to cell death and tissue damage. In tissues such as the liver and pancreas, this can exacerbate the pathological progression of fatty liver disease and insulin resistance.
Fatty Acid Accumulation and Impaired Beta-Oxidation
Excessive fructose consumption induces de novo lipogenesis (DNL) in the liver, leading to an increase in the synthesis of fatty acids, which are esterified into triglycerides and stored within hepatocytes. This accumulation of lipids can overwhelm the capacity of mitochondria to oxidize these fatty acids via beta-oxidation, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. The accumulation of lipotoxic intermediates such as ceramides and diacylglycerols further impairs mitochondrial function by inhibiting key enzymes involved in mitochondrial energy production.
Moreover, the excess fatty acids can impair mitochondrial membrane fluidity, reducing the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation. The lipid-induced mitochondrial dysfunction leads to further oxidative stress, creating a feedback loop that exacerbates the metabolic disturbances caused by high fructose intake.
Clinical Implications of HFCS-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction
The long-term consumption of HFCS has profound implications for human health, particularly in the context of metabolic diseases:
Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: HFCS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, particularly in liver and muscle cells, contributes to impaired insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis. As mitochondrial function declines, cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): The accumulation of fat in the liver, driven by increased fructose metabolism, leads to mitochondrial damage and dysfunction, which exacerbates the progression of NAFLD to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form of liver disease.
Cardiovascular Disease: Mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes can impair ATP production, leading to reduced contractile function and the progression of cardiovascular disease. The increased oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators associated with mitochondrial damage also contribute to vascular injury and atherosclerosis.
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Impaired mitochondrial function in neurons, driven by high fructose intake, may contribute to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, as mitochondria play a critical role in maintaining neuronal health.
Conclusion
High fructose corn syrup exerts a significant impact on mitochondrial function through several interconnected mechanisms. These include the increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), inhibition of mitochondrial biogenesis, induction of mitochondrial permeability transition, and the accumulation of toxic lipid intermediates. These disruptions in mitochondrial homeostasis contribute to the development of insulin resistance, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and other chronic metabolic diseases. Addressing the widespread consumption of HFCS and reducing dietary fructose intake could be crucial in mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction and preventing associated metabolic disease
#High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS)#Mitochondrial Function#Mitochondria#Oxidative Phosphorylation#Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)#Fructose Metabolism#ATP Production#Mitochondrial Biogenesis#PGC-1α#Mitochondrial Dysfunction#Insulin Resistance#Fatty Liver Disease(NAFLD)#Mitochondrial Permeability Transition (MPT)#Apoptosis#Beta-Oxidation#De Novo Lipogenesis (DNL)#Ceramides#Lipotoxicity#Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)#Type 2 Diabetes#Cardiovascular Disease#Neurodegenerative Diseases#Fatty Acids#Liver Mitochondria#Metabolic Disorders#Fructose-Induced Oxidative Stress#Cellular Metabolism#Mitochondrial Membrane Potential#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)#Lipid Accumulation
0 notes
Text
Nuances of Healthy and Unhealthy Fats with Practical Tips
Eating fat is essential to lowering body visceral fat and staying healthy, but not all fats are healthy. Over the years, I have written extensively about ketogenic diets and the critical role of fat in our health. Recently, I shared an article on the benefits of being fat-adapted, outlining compelling reasons and practical tips for readers. One of the most common questions I received from new…
#abdominal obesity#avocado oil#Balanced Diet#cholesterol#chronic inflammation#diabetes#Dietary Guidelines#EPA and DHA#fat-phobia#Fatty Acids#HDL and LDL#Healthy Eating#healthy fats#Heart Health#hormonal balance#hydrogenating vegetable oils.#immune health#insulin resistance#keto for meat eaters#keto for omnivores#keto for vegans#keto-carnivore#keto-omniore#keto-vegan#ketogenic diets#metabolic health#metabolic syndrome#Monounsaturated Fats#Nutrition Tips#nuts and seeds
0 notes
Text
ORGANIC RICE BRAN OIL
People frequently mistake emollients for moisturizers, although a moisturizer locks water into skin tissues, whereas an emollient softens and smoothes skin. It is a natural emollient with the benefits of essential fatty acids that penetrate deep into the skin and leave it smooth and silky. Pure Rice Bran Oil contains the properties of both an emollient and a moisturizer. It is high in linoleic and oleic fatty acids, which might imitate the skin's natural oil, sebum. They may penetrate deep into the skin's layers and trap moisture inside those small tissues. It also contains Vitamin E, which produces a protective layer on the epidermis (the first and outermost layer of skin).

#smooth skin#fatty acids#epidermis#excess sebum#usda certified#carrier oil#new launch#silky skin#small tissues
0 notes
Link
1 note
·
View note
Text
Study reveals the benefits and downside of fasting
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/study-reveals-the-benefits-and-downside-of-fasting/
Study reveals the benefits and downside of fasting


Low-calorie diets and intermittent fasting have been shown to have numerous health benefits: They can delay the onset of some age-related diseases and lengthen lifespan, not only in humans but many other organisms.
Many complex mechanisms underlie this phenomenon. Previous work from MIT has shown that one way fasting exerts its beneficial effects is by boosting the regenerative abilities of intestinal stem cells, which helps the intestine recover from injuries or inflammation.
In a study of mice, MIT researchers have now identified the pathway that enables this enhanced regeneration, which is activated once the mice begin “refeeding” after the fast. They also found a downside to this regeneration: When cancerous mutations occurred during the regenerative period, the mice were more likely to develop early-stage intestinal tumors.
“Having more stem cell activity is good for regeneration, but too much of a good thing over time can have less favorable consequences,” says Omer Yilmaz, an MIT associate professor of biology, a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research, and the senior author of the new study.
Yilmaz adds that further studies are needed before forming any conclusion as to whether fasting has a similar effect in humans.
“We still have a lot to learn, but it is interesting that being in either the state of fasting or refeeding when exposure to mutagen occurs can have a profound impact on the likelihood of developing a cancer in these well-defined mouse models,” he says.
MIT postdocs Shinya Imada and Saleh Khawaled are the lead authors of the paper, which appears today in Nature.
Driving regeneration
For several years, Yilmaz’s lab has been investigating how fasting and low-calorie diets affect intestinal health. In a 2018 study, his team reported that during a fast, intestinal stem cells begin to use lipids as an energy source, instead of carbohydrates. They also showed that fasting led to a significant boost in stem cells’ regenerative ability.
However, unanswered questions remained: How does fasting trigger this boost in regenerative ability, and when does the regeneration begin?
“Since that paper, we’ve really been focused on understanding what is it about fasting that drives regeneration,” Yilmaz says. “Is it fasting itself that’s driving regeneration, or eating after the fast?”
In their new study, the researchers found that stem cell regeneration is suppressed during fasting but then surges during the refeeding period. The researchers followed three groups of mice — one that fasted for 24 hours, another one that fasted for 24 hours and then was allowed to eat whatever they wanted during a 24-hour refeeding period, and a control group that ate whatever they wanted throughout the experiment.
The researchers analyzed intestinal stem cells’ ability to proliferate at different time points and found that the stem cells showed the highest levels of proliferation at the end of the 24-hour refeeding period. These cells were also more proliferative than intestinal stem cells from mice that had not fasted at all.
“We think that fasting and refeeding represent two distinct states,” Imada says. “In the fasted state, the ability of cells to use lipids and fatty acids as an energy source enables them to survive when nutrients are low. And then it’s the postfast refeeding state that really drives the regeneration. When nutrients become available, these stem cells and progenitor cells activate programs that enable them to build cellular mass and repopulate the intestinal lining.”
Further studies revealed that these cells activate a cellular signaling pathway known as mTOR, which is involved in cell growth and metabolism. One of mTOR’s roles is to regulate the translation of messenger RNA into protein, so when it’s activated, cells produce more protein. This protein synthesis is essential for stem cells to proliferate.
The researchers showed that mTOR activation in these stem cells also led to production of large quantities of polyamines — small molecules that help cells to grow and divide.
“In the refed state, you’ve got more proliferation, and you need to build cellular mass. That requires more protein, to build new cells, and those stem cells go on to build more differentiated cells or specialized intestinal cell types that line the intestine,” Khawaled says.
Too much of a good thing
The researchers also found that when stem cells are in this highly regenerative state, they are more prone to become cancerous. Intestinal stem cells are among the most actively dividing cells in the body, as they help the lining of the intestine completely turn over every five to 10 days. Because they divide so frequently, these stem cells are the most common source of precancerous cells in the intestine.
In this study, the researchers discovered that if they turned on a cancer-causing gene in the mice during the refeeding stage, they were much more likely to develop precancerous polyps than if the gene was turned on during the fasting state. Cancer-linked mutations that occurred during the refeeding state were also much more likely to produce polyps than mutations that occurred in mice that did not undergo the cycle of fasting and refeeding.
“I want to emphasize that this was all done in mice, using very well-defined cancer mutations. In humans it’s going to be a much more complex state,” Yilmaz says. “But it does lead us to the following notion: Fasting is very healthy, but if you’re unlucky and you’re refeeding after a fasting, and you get exposed to a mutagen, like a charred steak or something, you might actually be increasing your chances of developing a lesion that can go on to give rise to cancer.”
Yilmaz also noted that the regenerative benefits of fasting could be significant for people who undergo radiation treatment, which can damage the intestinal lining, or other types of intestinal injury. His lab is now studying whether polyamine supplements could help to stimulate this kind of regeneration, without the need to fast.
“This fascinating study provides insights into the complex interplay between food consumption, stem cell biology, and cancer risk,” says Ophir Klein, a professor of medicine at the University of California at San Francisco and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, who was not involved in the study. “Their work lays a foundation for testing polyamines as compounds that may augment intestinal repair after injuries, and it suggests that careful consideration is needed when planning diet-based strategies for regeneration to avoid increasing cancer risk.”
The research was funded, in part, by a Pew-Stewart Trust Scholar award, the Marble Center for Cancer Nanomedicine, the Koch Institute-Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center Bridge Project, and the MIT Stem Cell Initiative.
#acids#author#Biology#bridge#Cancer#cell#cell biology#cell types#Cells#Delay#diet#diets#Diseases#driving#effects#energy#fasting#fatty acids#Food#Foundation#growth#harvard#Health#how#humans#impact#inflammation#injuries#insights#intermittent fasting
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Chia Seeds - Natural Omega 3 | GFGV
#youtube#chia seeds#natural#omega 3#fatty acids#natural omega 3#super food#health#nutrition#get fit#good vibes#getfitgoodvibes
0 notes
Text
If you or someone you care about is in need of effective treatment, the psychiatric treatment in Irving, Texas at Excellent Care Psychiatry is here to provide comprehensive care for mental health. Today, let’s explore the significant influence of brain nutrition therapy exercise on the path to wellness.
0 notes