#empress china
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
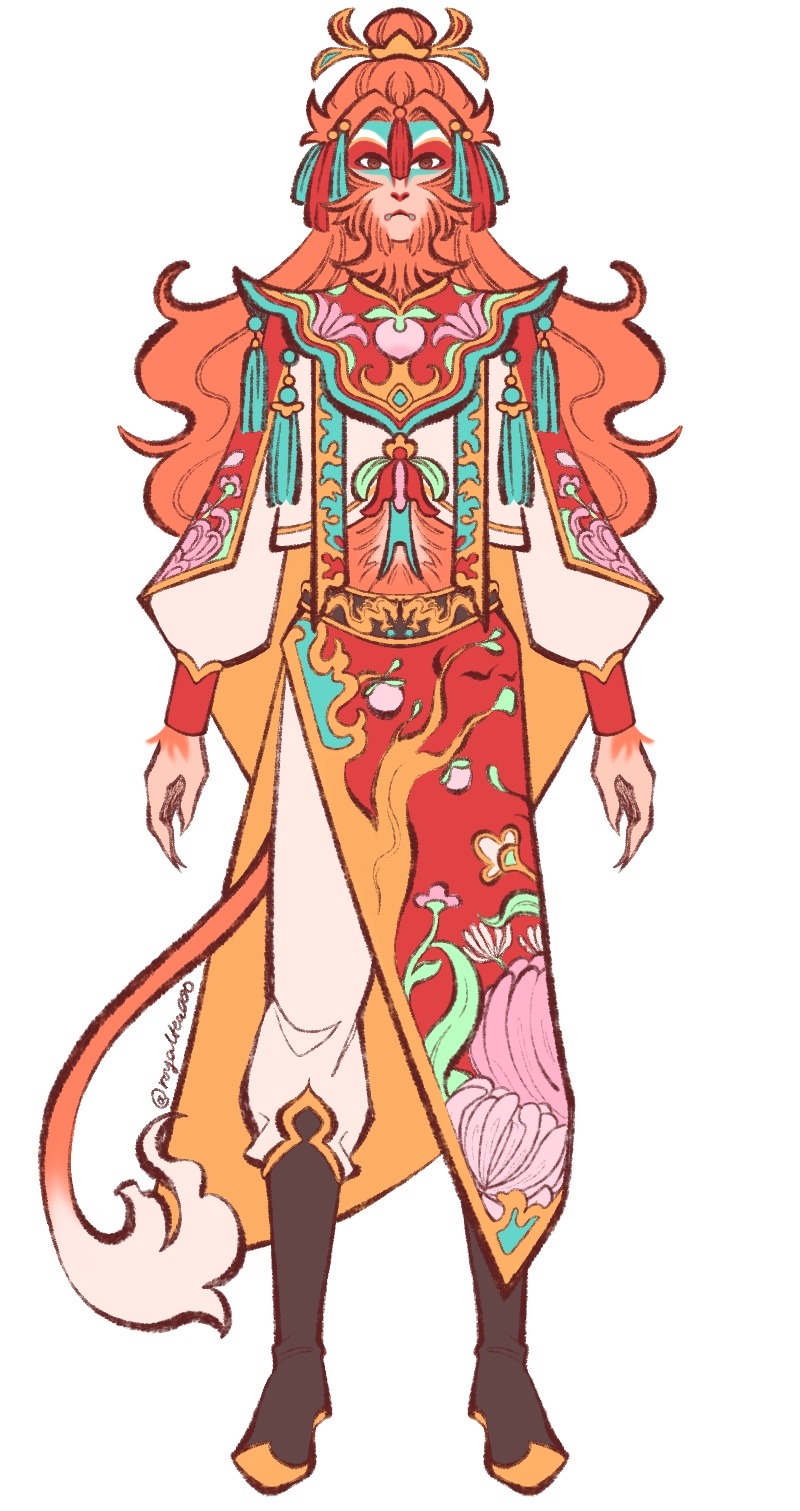
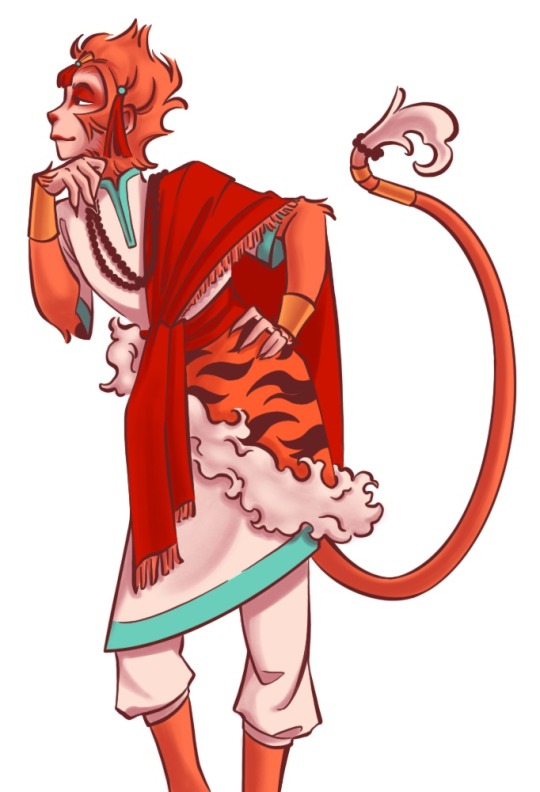
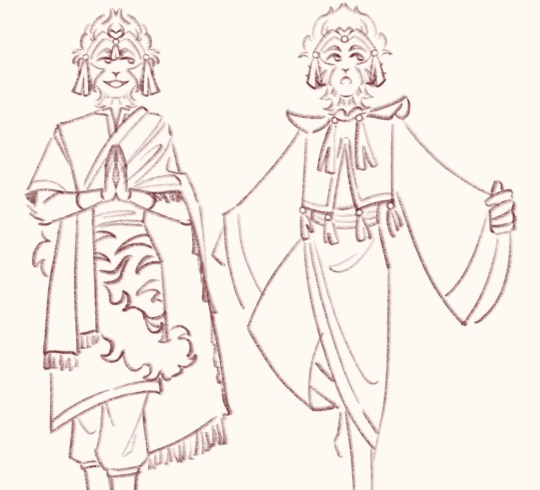
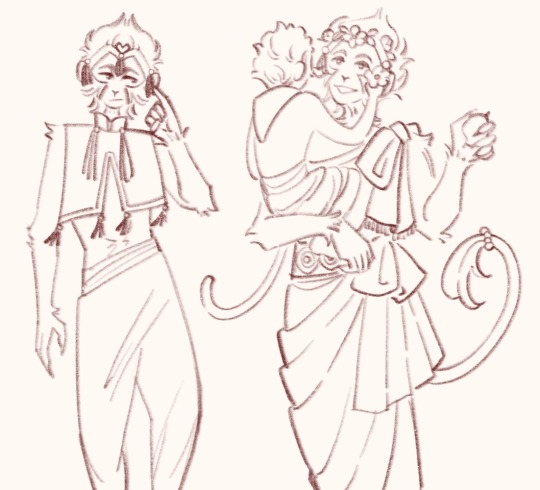




Qitian dasheng and other outfit concept sketches
#I always find it funny when in every iteration wukong is the only one to ever get outfit changes#he ran the fashion department pockets THROUGH#every season china’s Madonna gets a new dress cuz he’s the people’s prettiest little princess#jelly didn’t do a good enough job talking me out of that uglyass qtds design so you guys get to see it#I was going for a more empress dowager look to be unique but it doesn’t really suit him I think lol ^^#back to the drawing board#but I really do like that handsome monkey king sketch#the one with the small monkey in his arms#I like to think he’s actually very motherly to his children subjects <:3#that’s mother#I’m also trying my hand at giving him a more Indian outfit since that’s where they’re going -w-#not really satisfied with any of em lol#the crop top sketch is maybe him directly after getting out of the mountain and being petulant about the band#the tassels STAY ON#digital art#my art#jttw sun wukong#journey to the west#sun wukong#jttw fanart#monkey king#anyways lemme know what y’all think#I actually wanna hear other opinions on this :P#also if you couldn’t tell I’m obsessed with cloud collars at the moment#☁️ 🌺 🦢 ✨
283 notes
·
View notes
Text












PERIOD DRAMA APPRECIATION WEEK 2024 | Day 1 (July 29th): Favorite TV Shows
#perioddramaedit#perioddramaappreciationweek24#mcedit#borgiaedit#twqedit#kosemedit#ekaterinaedit#mfmmedit#blacksailsedit#theempressofchinaedit#musketeersedit#theamericansedit#bridgertonedit#chernobyledit#my edits#magnificent century#chernobyl 2019#borgia#the americans#miss fisher's murder mysteries#the musketeers#ekaterina#magnificent century: kosem#the empress of china#black sails#the white queen
377 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
“这个位子 我有何坐不得?” “我欲问鼎天下,试问谁与争锋”
"Why can't I sit in this seat?"
"I want to conquer the world, who can compete with me?"
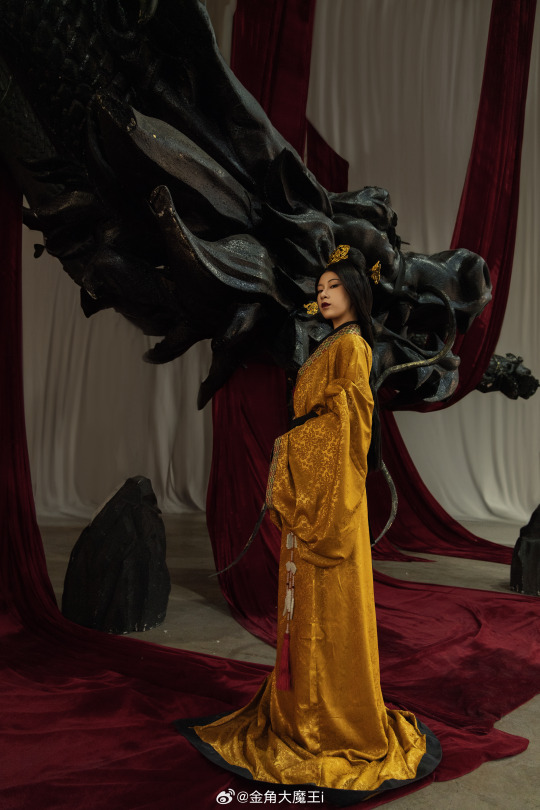
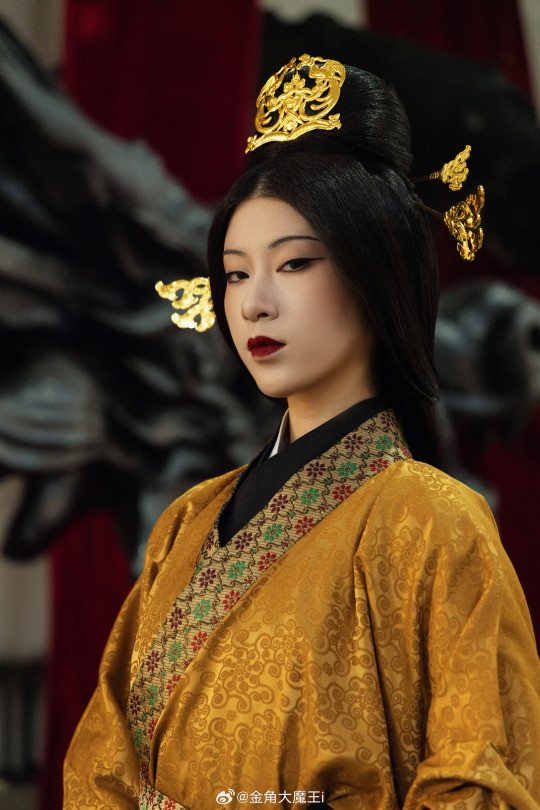
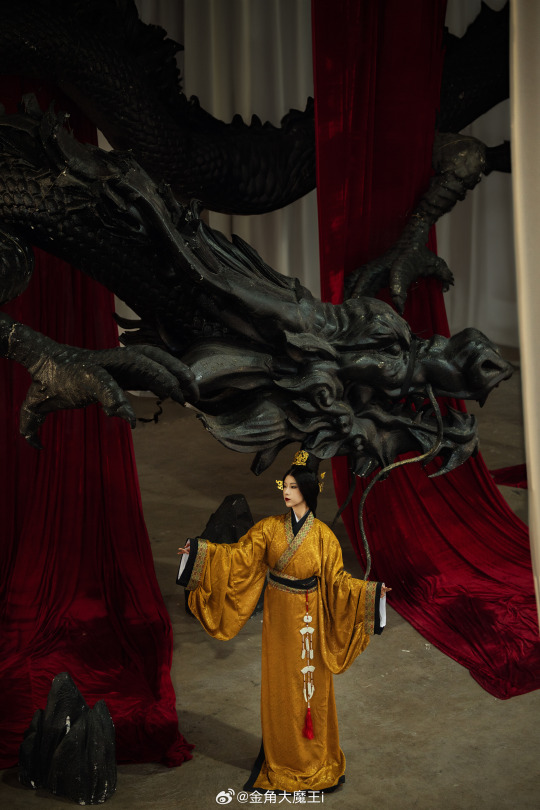
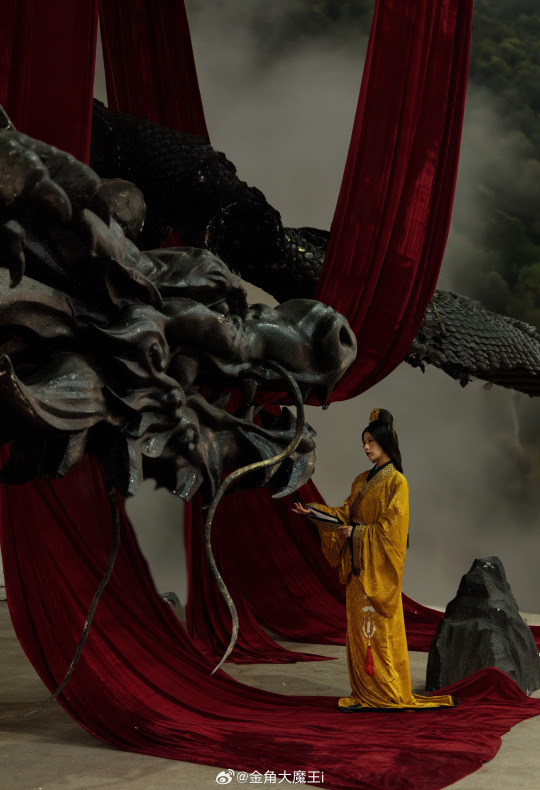








【About The First Empress of the Han Dynasty Empress Lü:Lǚ zhì(吕雉)】
Lü Zhi (241–18 August 180 BC), courtesy name E'xu (娥姁) and commonly known as Empress Lü (traditional Chinese: 呂后; simplified Chinese: 吕后; pinyin: Lǚ Hòu) and formally Empress Gao of Han (漢高后; 汉高后; Hàn Gāo Hòu), was the empress consort of Gaozu, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. They had two known children, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han) and Princess Yuan of Lu. Lü was the first woman to assume the title Empress of China and paramount power. After Gaozu's death, she was honoured as empress dowager and regent during the short reigns of Emperor Hui and his successors Emperor Qianshao of Han and Liu Hong (Emperor Houshao).
She played a role in the rise and foundation of her husband, Emperor Gaozu, and his dynasty, and in some of the laws and customs laid down by him. Empress Lü, even in the absence of her husband from the capital, killed two prominent generals who played an important role in Gaozu's rise to power, namely Han Xin and Peng Yue, as a lesson for the aristocracy and other generals. In June 195 BC, with the death of Gaozu, Empress Lü became, as the widow of the late emperor and mother of the new emperor, Empress Dowager (皇太后, Huángtàihòu), and assumed a leadership role in her son's administration. Less than a year after Emperor Hui's accession to the throne, in 194 BC, Lü had one of the late Emperor Gaozu's consorts whom she deeply hated, Concubine Qi, put to death in a cruel manner. She also had Concubine Qi's son Liu Ruyi poisoned to death. Emperor Hui was shocked by his mother's cruelty and fell sick for a year, and thereafter no longer became involved in state affairs, and gave more power to his mother. As a result, Empress dowager Lü held the court, listened to the government, spoke on behalf of the emperor, and did everything (臨朝聽政制, "linchao ting zhengzhi"). With the untimely death of her 22-year-old son, Emperor Hui, Empress dowager Lü subsequently proclaimed his two young sons emperor (known historically as Emperor Qianshao and Emperor Houshao respectively). She gained more power than ever before, and these two young emperors had no legitimacy as emperors in history; the history of this 8-year period is considered and recognized as the reign of Empress Dowager Lü. She dominated the political scene for 15 years until her death in August 180 BC, and is often depicted as the first woman to have ruled China. While four women are noted as having been politically active before her—Fu Hao, Yi Jiang, Lady Nanzi, and Queen Dowager Xuan—Lü was the perhaps first woman to have ruled over united China.
Lü Zhi was born in Shanfu County (單父; present-day Shan County, Shandong) during the late Qin Dynasty. Her courtesy name was Exu (Chinese: 娥姁; pinyin: Éxǔ). To flee from enemies, her father Lü Wen (呂文) brought their family to Pei County, settled there, and became a close friend of the county magistrate. Many influential men in town came to visit Lü Wen. Xiao He, then an assistant of the magistrate, was in charge of the seating arrangement and collection of gifts from guests at a banquet in Lü Wen's house, and he announced, "Those who do not offer more than 1,000 coins in gifts shall be seated outside the hall." Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han), then a minor patrol officer (亭長), went there bringing a single cent and said, "I offer 10,000 coins." Lü Wen saw Liu Bang and was so impressed with him on first sight, that he immediately stood up and welcomed Liu into the hall to sit beside him. Xiao He told Lü Wen that Liu Bang was not serious, but Liu ignored him and chatted with Lü. Lü Wen said, "I used to predict fortunes for many people but I've never seen someone so exceptional like you before." Lü Wen then offered his daughter Lü Zhi's hand in marriage to Liu Bang and they were wed. Lü Zhi bore Liu Bang a daughter (later Princess Yuan of Lu) and a son, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han).
Liu Bang later participated in the rebellion against the Qin Dynasty under the insurgent Chu kingdom, nominally-ruled by King Huai II. Lü Zhi and her two children remained with her father and family for most of the time during this period.
Even after Emperor Gaozu (Liu Bang)'s victory over Xiang Yu, there were still unstable areas in the empire, requiring the new government to launch military campaigns to pacify these regions thereafter. Gaozu placed Empress Lü Zhi and the crown prince Liu Ying (Lü Zhi's son) in charge of the capital Chang'an and making key decisions in court, assisted by the chancellor Xiao He and other ministers. During this time, Lü Zhi proved herself to be a competent administrator in domestic affairs, and she quickly established strong working relationships with many of Gaozu's officials, who admired her for her capability and feared her for her ruthlessness. After the war ended and Emperor Gaozu returned, she remained in power and she was always influential in many of the country's affairs.
In his late years, Emperor Gaozu started favouring one of his younger consorts, Concubine Qi(戚夫人), who bore him a son, Liu Ruyi, who was instated as Prince of Zhao in 198 BC, displacing Lü Zhi's son-in-law Zhang Ao (Princess Yuan of Lu's husband). Gaozu had the intention of replacing Liu Ying with Liu Ruyi as crown prince, reasoning that the former was too "soft-hearted and weak" and that the latter resembled him more. Since Lü Zhi had strong rapport with many ministers, they generally opposed Gaozu's decision but the emperor seemed bent on deposing Liu Ying. Lü Zhi became worried and she approached Zhang Liang for help, and the latter analysed that Gaozu was changing the succession on grounds of favouritism. Zhang Liang invited the "Four Whiteheads of Mount Shang", a group of four reclusive wise men, to persuade Gaozu to change his decision. The four men promised to assist Liu Ying in future if he became emperor, and Gaozu was pleased to see that Liu Ying had their support. Gaozu told Concubine Qi, "I wanted to replace (the crown prince). Now I see that he has the support of those four men; he is fully fledged and difficult to unseat. Empress Lü is really in charge!" This marked the end of the dispute over the succession and affirmed Liu Ying's role as crown prince.
In June 195 BC, Emperor Gaozu died and was succeeded by Liu Ying, who became historically known as Emperor Hui of Han. Lü Zhi was honoured by Emperor Hui as empress dowager. She exerted more influence during the reign of her son than she had when she was empress, and she became the powerful and effective lead figure in his administration.
Lü Zhi did not harm most of Gaozu's other consorts and treated them according to the rules and customs of the imperial family. For example, consorts who bore male children that were instated as princes were granted the title of "Princess Dowager" (王太妃) in their respective sons' principalities. One exception was Concubine Qi, whom Lü Zhi greatly resented because of the dispute over the succession between Liu Ruyi (Qi's son) and Liu Ying. Liu Ruyi, the Prince of Zhao, was away in his principality, so Lü Zhi targeted Concubine Qi. She had Qi stripped of her position, treated like a convict (head shaved, in stocks, dressed in prison garb), and forced to do hard labour in the form of milling rice.
Roles in the deaths of Concubine Qi and Liu Ruyi
Lü Zhi then summoned Liu Ruyi, who was around the age of 12 then, to Chang'an, intending to kill him together with his mother. However Zhou Chang (周昌), the chancellor in Liu Ruyi's principality, whom Lü Zhi respected because of his stern opposition to Emperor Gaozu's proposal to make Liu Ruyi crown prince, temporarily protected Liu Ruyi from harm by responding to Lü Zhi's order that, "The Prince of Zhao is ill and unfit for travelling over long distances." Lü Zhi then ordered Zhou Chang to come to the capital, had him detained, and then summoned Liu Ruyi again. Emperor Hui tried to save Liu Ruyi by intercepting his half-brother before the latter entered Chang'an, and kept Liu Ruyi by his side most of the time. Lü Zhi refrained from carrying out her plans for several months because she feared that she might harm Emperor Hui as well.
One morning in the winter of 195-194 BC, Emperor Hui went for a hunting trip and did not bring Liu Ruyi with him because the latter refused to get out of bed. Lü Zhi's chance arrived, so she sent an assassin to force poisoned wine down Liu Ruyi's throat. The young prince was dead by the time Emperor Hui returned. Lü Zhi then had Concubine Qi killed in an inhumane manner: she had Qi's limbs chopped off, eyes gouged out, ears sliced off, nose sliced off, tongue cut out, forced her to drink a potion that made her mute, and had her thrown into a latrine. She called Qi a "human swine" (人彘). Several days later, Emperor Hui was taken to view the "human swine" and was shocked to learn that it was Concubine Qi. He cried loudly and became ill for a long time. He requested to see his mother and said, "This is something done not by a human. As the empress dowager's son, I'll never be able to rule the empire" From then on, Emperor Hui indulged himself in carnal pleasures and ignored state affairs, leaving all of them to his mother, and this caused power to fall completely into her hands.
When Lu first came to the court, she planned to establish the Lu family members as "kings (nobles)". This was not only to commemorate her deceased relatives, but also to strengthen her power in the court. However, Wang Ling, the prime minister at the time, immediately pointed out that the great ancestor Liu Bang(Husband of Lu, founding emperor of Han Dynasty)once killed the white horse and agreed that "if someone who are not Liu family be come the king, the whole world should attack them." Therefore, the move of establishing a foreign surname as the king violated the ancestral system established by Liu Bang and was really inappropriate.
Faced with the obstruction of Wang Ling, Empress Lu responded by deposing him and insisting on honoring her deceased father and two brothers as King Lu Xuan, King Wu Wu, and King Zhao Zhao. After setting this precedent, Lu was out of control. She not only named her three nephews Lu Tai, Lu Chan, and Lu Lu as King Lu, King Liang, and King Zhao respectively, but also named her grandnephew Lu Tong. He was the King of Yan, and his grandson Zhang Yan was granted the title of King of Lu.
In addition, there are also quite a few people with the surname Lu who have been granted the title of marquis. As a result, it can be said that many princes surnamed Lu appeared in the court in the blink of an eye. They controlled the government and became the cornerstone and support for Empress Lu to control the right to speak in the court.
Empress Lu's life was emblematic of the intricate power dynamics of the Han Dynasty in ancient China. Born into a modest family, Lu rose to prominence through her marriage to Emperor Gaozu. Her astute political acumen and strategic alliances allowed her to wield significant influence behind the throne. As the mother of several emperors, she orchestrated their ascensions and manipulated court politics to consolidate power for her family. However, her ruthless pursuit of control and elimination of rivals earned her both admirers and enemies. In the end, her ambitions led to her downfall, as her unchecked power and manipulation of succession angered the nobility.As a result, after her death, the Lu family was retaliated and killed by the nobles and courtiers who supported the Han Dynasty, and the family was almost exterminated.Empress Lu's life illustrates the delicate balance of power, ambition, and intrigue in ancient Chinese imperial courts.
Literati in every dynasty in China often likened women who attempted to participate in government affairs and influence national policies to Empress Lü, saying they were vicious. One of them was Wu Zetian, the first official female emperor of China. However, compared with Empress Lü, Wu Zetian was more talented. Unlike Empress Lü, who was simply vicious, she ignored the system and stability of the empire and put personal and family interests first.
________________
📸Photo & Model :@金角大魔王i
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/NFVOXthxX
________________
#chinese hanfu#Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD)#hanfu#Empress Lü#Lǚ zhì(吕雉)#china history#chinese history#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#woman in history#漢服#汉服#中華風#金角大魔王i#historical fashion
323 notes
·
View notes
Photo

while I’m drawing f!sqq here’s one who’d use chenqie pronouns
#im scared of her and i hope u are too#demon realm say hello to your new mother#era unlikely cleavage#but it's FANTASY historical china after all#outfits referenced from the drama empress of china#rule 63#genderbend#shen qingqiu#scum villain#svsss#sqq#f!sqq#fem!shen qingqiu
816 notes
·
View notes
Text

Women warriors in Chinese history - Part 1
“In the nomadic tribes of the foreign princesses from the Steppes northwest to the northeast of the Chinese borders, women habitually rode horses and were frequently also skilled militarily. They had to be able to survive on their own and defend themselves when their men left camp to herd animals for months on end. Thus, unsurprisingly, many daughters of nomadic and semi-nomadic tribal chiefs were also capable fighters. Madam Pan 潘夫人 of “barbarian origins” during the Wei dynasty, the semi-barbarian Princess Pingyang 平陽公主 who helped establish the Tang dynasty, and the “barbarian queen,” Empress Dowager Xiao, are historical examples of this category of female generals.
While the barbarians to the north were known as fan 番, those belonging to peripheral areas from the southwest to the southeast were known as man 蠻. Like the nomadic princesses, these women of non-Chinese or Chinese ethnic minority groups did not bind their feet and could thus become formidable opponents. Indeed, the female battle units within the Taiping 太平 rebel forces that actually entered combat – rather than merely providing labour as most of the female units did –were reportedly made up in the main of women from the Miao 苗 tribes, aside from the Hakka (Kejia 客家) women of Guangxi.
Female bandit leaders or daughters and sisters of bandit leaders who occupied mountains or established strongholds in marginal lands are almost indistinguishable from the man barbarian princesses of tribal chieftains in novels and shadow plays. Such barbarian women generals and female bandit leaders were rarely privileged enough to be recorded by the historians. The three found most frequently, Madam Xi 洗夫人 (502– 557), Madam Washi 瓦氏夫人 (1498–1557),95 and Madam Xu 許夫人 (1271–1368), were all pro-Chinese. While the first two cooperated with the Chinese government, the third joined Chinese forces against the Mongols. A certain Zhejie 折節 or Shejie 蛇節, a female leader of the Miao tribe, also led a rebellion against Mongol troupes, but she eventually surrendered to them and was subsequently executed.
Real enemies of the Chinese empire, such as the Trv’vy sisters of Vietnam, are hardly ever mentioned by the Chinese, even though they are first recorded in the Han dynastic history. Even under such circumstances, of the women commanders in Chinese history studied by Xiaolin Li, a hefty per cent were from “minor nationalities.”
Female rebel leaders and women warriors in rebel forces tended to rise from peasantry and marginal groups such as families of itinerant performers, robbers, boatmen, and hunters. Many of them are beautiful and charismatic. Most of the rebel groups were basically bandits (known as haohan 好漢, “bravos” euphemistically) – how else could they have survived without a continuous source of income? Many of the bandit groups, like the sworn brothers of the Water Margin, lived in mountains and marshlands, awaiting a chance to start or join in an uprising with the hope of gaining power and legitimacy through either pardon (when they posed too great a threat to the state) or founding a new dynasty. Many had sisters, wives, or daughters who were also capable of leading armies.”
Chinese shadow theatre: history, popular religion, and women warriors, Fan Pen Li Chen
#history#women in history#warrior women#women's history#historyblr#warriors#quotes#women warriors#china#chinese history#asian history#Princess Pingyang#empress dowager chengtian#lady washi#taiping rebellion#trung sisters
167 notes
·
View notes
Text





⸺⸺ I love the way you look at me with all the frustration kept inside.
墨雨云间 · The Double · 2024
#墨雨云间#the double#cdramasource#dailyasiandramas#asiandramasource#chineseartistsinc#dramasource#chinesemedia#cdramanet#cdramagifs#cdramaedit#cdrama#chinese drama#*4#ep7#li meng#shen yurong#liang yongqi#in the west we say yess queen but in china we say yess empress (no we dont but im making it thing#the women in this so is so unhinged i love them all 💕💕💕 princess is evil(?) so what? i love an ambitious woman
140 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cornus elliptica 'Elsbry' / 'Elsbry' Evergreen Dogwood at the Sarah P. Duke Gardens at Duke University in Durham, NC
#Cornus elliptica 'Elsbry'#Cornus elliptica#Cornus#Cornaceae#Elsbry Evergreen Dogwood#Empress of China Evergreen Dogwood#Evergreen Dogwood#Dogwood#Plants#Flowers#Trees#Nature photography#photography#photographers on tumblr#Sarah P. Duke Gardens#Duke Gardens#Duke University#Durham#Durham NC#North Carolina#🌺🌻
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deep blue outfit of Empress Wu

#empress of china#武媚娘传奇#the empress of china#cdramaoutfit#cdrama#wu zetian#tang dynasty#fan bingbing#Wu Meiniang
93 notes
·
View notes
Text

Empress Wanrong of China, early 20th century
#manchu#mdpchina#china#20th c. china#photography#costume#mdpcostume#chinese costume#chinese dress#chinese empress
31 notes
·
View notes
Text


Period dramas dresses tournament: Red dresses Round 3- Group A: Wu MeiNiang, The empress of China (gifset) vs Lucille Sharpe, Crimson peak (gifset)
#period drama dresses tournament#tournament poll#tumblr tournament#polls#fashion poll#wu meiniang#wu zetian#the empress of china#lucille sharpe#crimson peak#red r3
102 notes
·
View notes
Text






PERIODDRAMA APPRECIATION WEEK 2023
Day 4: Favorite time period/era:
Tang dynasty:
The Tang dynasty, or the Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. The Lǐ family (李) founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire. (source: wikipedia) In general, garments were made from silk, wool, or linen depending on your social status and what you could afford. Furthermore, there were laws that specified what kinds of clothing could be worn by whom. The color of the clothing also indicated rank. During this period, China's power, culture, economy, and influence were thriving. As a result, women could afford to wear loose-fitting, wide-sleeved garments. Even lower-class women's robes would have sleeves four to five feet in width. (source)
Wu Zhou dynasty:
Zhou, known in historiography as the Wu Zhou was a short-lived Chinese imperial dynasty that existed between 690 and 705, when Wu Zhao (commonly known as Wu Zetian) ruled as empress regnant. Despite Wu's infamous rise to power, there is evidence that suggests women were granted more privileges during her reign, and China was in a state of great prosperity during her rule. Wu Zetian greatly enhanced the prestige and effectiveness of the civil service recruitment tests, filling government positions by skills demonstrated in written examinations, and opening them up to men of all classes. (source: wikipedia)
#luoyang#wind from luoyang#court lady#weaving a tale of love#the empress of china#jiu liu overlord#stand by me#cdrama#asian drama#stuff:mine#perioddramaweek2023
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
░ ✧ "OLD" FAN BINGBING in THE EMPRESS OF CHINA (2014)
GIF PACK • By clicking the source link, you'll find a page containing 112 gifs of chinese actress Fan Bingbing, in the show The Empress of China (2014), as older Wu Zetian/Meiniang. They were made by me, and can be used (creditless) for roleplays & similar personal uses, and (credited) in posted works such as edits/video edits. I don't care what themes you're using them for or if they're "problematic" so long as you're not hurting anyone.If you use this gifpack, please like and/or reblog this post, thank you!




Buy me a ☕?
#viscardi gifpacks#fan bingbing#the empress of china#wu zetian#wu meiniang#historical drama#costume drama#period drama#gif pack#gif hunt#gif set#rph resources#indie rph#rph br#rp resources#rp help#rph
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Empress Xiaolie of the Ming Dynasty (1534-1547)
Lady Fang was born in 1516 and grew up in the Nanjing area. She was selected to become an imperial concubine in 1531 at the age of 15. Despite never sharing a bed with the Jiajing Emperor she was chosen to become his third empress consort just nine days after Empress Zhang was deposed. The reason for her ascension is most likely because she had sided with the emperor during one of his disputes with court officials over honoring imperial ancestors. For the first several years as empress Lady Fang was described as being the favorite spouse of the emperor.
Their relationship would be damaged after the Renyin Palace Rebellion in 1542. In October of that year sixteen palace maids conspired to assassinate the emperor for being exceedingly cruel to the palace women. It’s reported that the Jiajing Emperor had up to 200 palace maids beaten to death during his reign. The maids attacked the emperor when she was spending the night with his favorite concubine, Consort Duan, and attempted to strangle him. During the attack one of the women became afraid and ran to Lady Fang. Lady Fang would rush in and save the emperor’s life.
As the emperor was in an extreme state of shock after this attempt, Lady Fang took control of the situation and had all sixteen maids and Consort Duan executed. The emperor was upset after Consort Duan’s execution and refused to believe she was involved with the attempt. He would blame Lady Fang for Consort Duan’s death and their relationship never recovered. Lady Fang reportedly became depressed after this.
In 1547, Lady Fang would become trapped in a fire. An eunuch asked the Jiajing Emperor if they should try to save her, but the emperor refused to answer and as a result Lady Fang burned to death. Despite blaming her for his favorite concubine's death and letting her burn to death, the emperor granted her all honors after her death.
Titles:
Lady Fang (from 1516)
Concubine De (from 1531)
Empress (from 1534)
Empress Xiaolie (posthumous from 1547)
13 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is me catching up with the challenge I'm doing this month - kind of. It was supposed to be "casual vs formal wear" - but I ran out of time after barely finishing the formal part. Well, goodnight everyone, I guess _._
-- support me on ko-fi��/ redbubble
#hanfu#empress#zhoudynasty#china#manga#mangaart#characterdesign#characterart#originalcharacter#originalstory#art#artist#digitalart#digitalartist#medibangpaint#queen
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
on one hand, i’m...content? with canon hetalia having china and japan being men because there really are multiple levels of regicidal, confucian mentor/protégé vibes that we can explore between yao and kiku through the prism of east asian masculinity (and how problematic these two prideful dickheads can be). but i will admit nyo!china and nyo!japan definitely offer a lot of interesting opportunities, when just thinking about how they might be associated with prominent deities in japanese and chinese tradition like amaterasu and nüwa. and also because tang dynasty china and heian japan overlap historically...on a purely aesthetic level, my silly brain also itches to draw things like these:

#hetalia#hws china#hws japan#granted 'the empress of china' might have exaggerated a bit#as period dramas often do#but low cut dresses were a thing in tang china
118 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sent to a foreign country as a tribute, Lady Ki (c.1320- after 1369) carved a place for herself and became a powerful empress, the last of the Yuan dynasty.
From maid to imperial consort
Lady Ki, also known as Öljei Khuduq, was born in Xingzhou, Gaoli (present-day Korea). The Korean state used to send a tribute of women to its neighbor, the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty, who controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas such as present-day Mongolia.
Lady Ki entered the palace and was assigned to Toghon Temür's service. Described as beautiful and clever, she quickly caught the young emperor’s attention and was elevated to the rank of consort.
The empress Danishiri was hostile to Lady Ki but was executed in 1335 or 1337 for having tried to protect her brother who was involved in a rebellion.
Toghon Temür then tried to name Lady Ki empress, but his decision was met with extreme hostility. Indeed, no Korean woman had held the dignity so far. Most empresses came from the Mongol Khongirad clan. He ultimately relented and chose a Mongol empress: Bayan Khuduq.
A powerful favorite
Lady Ki’s position was strengthened when she gave birth to a son, Ayushiridara (future emperor Zhaozong of Northern Yuan, r.1370-1378). Bayan Khuduq's son died young. Having a frugal and effaced personality, the empress was furthermore no match for Lady Ki. Ayushiridara was thus made heir apparent in 1355.
Empress Ki was influential and involved herself in political and military affairs. She for instance protected the high-ranking official Toqto'a but withdrew her support when he opposed the installation of her son as heir apparent.
She liked to read the Women’s Book of Filial Piety and sought examples of past empresses she could emulate. When a famine struck in 1359, she showed her generosity by having the officials distribute porridge to the hungry, using her own funds to have thousands of corpses buried and hiring monks to perform funeral services.
Lady Ki used her influence to promote her family’s interests. Her kinsmen in Korea were granted official ranks and titles. They repeatedly abused their power, which led the Korean king to execute Lady Ki’s entire clan.
When she learned about it, she asked her son to avenge her family and raise a force of 10,000 soldiers. The military campaign was a complete failure and the entire force was routed.
Empress before the fall
Bayan Khuduq died in 1365. No obstacles stood in Lady Ki’s way and she received the empress’s seal. It seems that she tried to make up for the mistakes of a poorly-performing emperor. Later historians indeed wrote that Toghon Temür preferred focusing on wine and women, though this could be an exaggeration to justify the fall of the Yuan Dynasty.
The government’s structure was disintegrating. Empress Ki conspired to force the emperor to abdicate and put her son on the throne but failed. She faced little consequences and was simply put under house arrest for 100 days. Her agressive defense of her son’s interests was in keeping with Mongolian political culture, which recognized the influence of strong women.
The Yuan dynasty fell in 1368 when the armies of the future Ming Emperor Hongwu entered the capital. Empress Ki fled to the north with Toghon Temür. What happened to her afterward is unclear, but she likely died the following year.
Her life was the inspiration for a 2013 Korean television drama, Empress Ki.
Feel free to check out my Ko-Fi if you like what I do! Your support would be much appreciated.
Further reading
Buell Paul D., Fiaschetti Francesca, Historical Dictionary of the Mongol World Empire
McMahon Keith, Celestial Women: Imperial Wives and Concubines in China from Song to Qing
Robinson David M., Empire's Twilight: Northeast Asia Under the Mongols
Xu Shindan, “Öljei Qudu”, in: Hong Lee Lily Xiao, Wiles Sue (ed.), Biographical Dictionary of Chinese Women, Volume II: Tang Through Ming 618 - 1644
#empress ki#history#women in history#women's history#historyedit#queens#empresses#powerful women#14th century#korea#korean history#china#chinese history#mongolia#kdramas#historyblr#historical figures#asian history
70 notes
·
View notes