#Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Western Han (202 BC–9 AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
She is the emperor's sister, She is also the emperor's aunt.
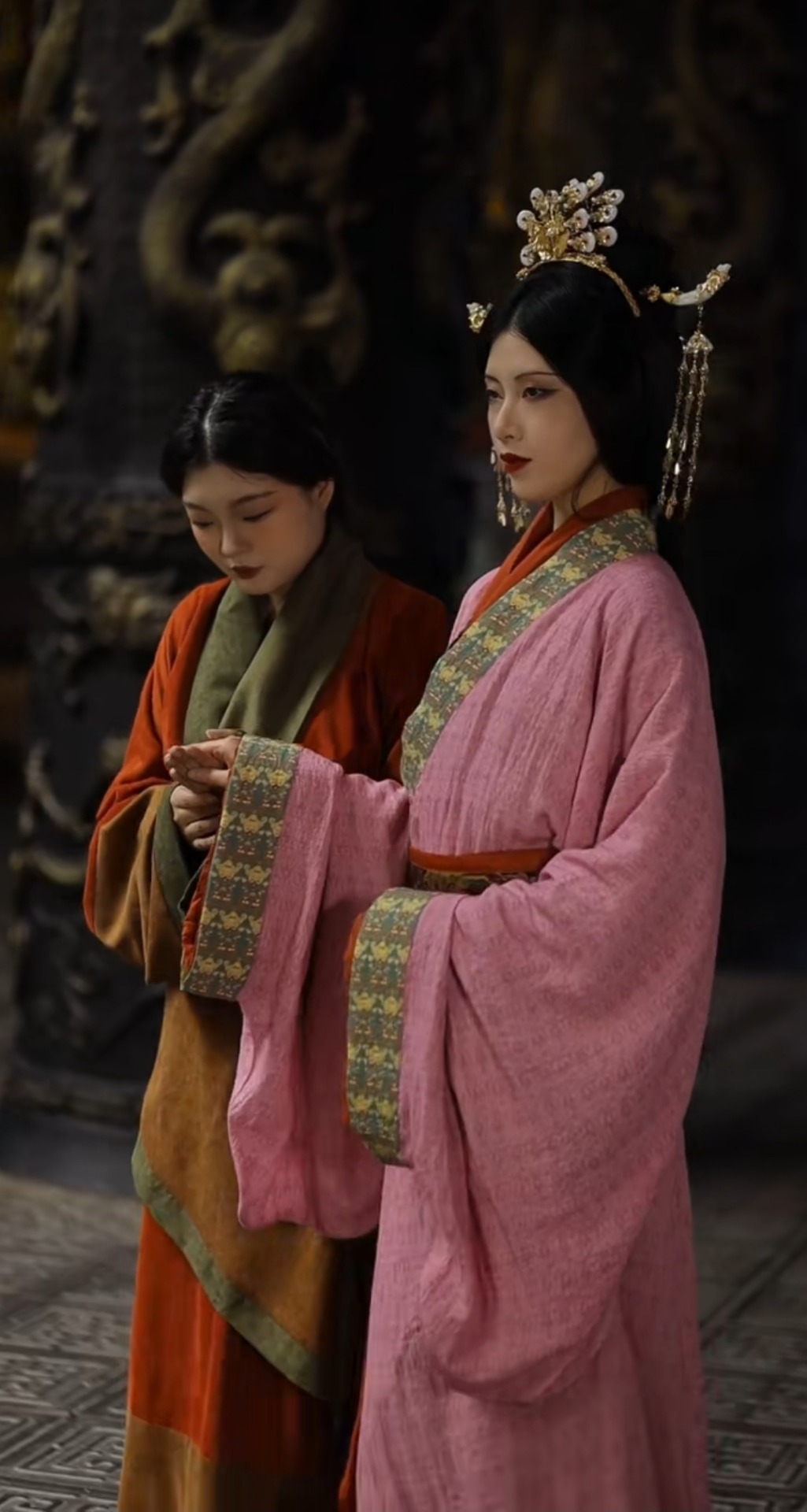





【About Princess Guantao Liu Piao/馆陶公主刘嫖】 Princess Guantao, Liu Piao (born before 188 BCE—died before 116 BCE), was the daughter of Emperor Wen of Han and Empress Dou, and the sister of Emperor Jing of Han. She was granted the title of Princess Guantao, but after marrying Chen Mu of Tangyi(堂邑)Marquis, she was also known as Princess Tangyi. As the aunt of Emperor Wu of Han, she was honored with the title of Dowager Dou(窦太主). Her daughter, Chen, became the first empress of Emperor Wu of Han.
Liu Piao's birth year is unknown, but her younger brother, Emperor Jing of Han (Liu Qi/刘启), was born in 188 BCE. At that time, their father, Emperor Wen of Han (Liu Heng/刘恒), was only fifteen years old and still a vassal king of han dynasty, so Liu Piao's birth year is unlikely to be later than 188 BCE. In September 180 BCE, Liu Heng was ushered to Chang'an and ascended the throne as Emperor Wen. A few months later, Liu Qi was made Crown Prince, Empress Dou was made appointed, and Liu Piao was given the title of Princess Guantao. During this period, Liu Piao married Chen Mu, Marquis of Tangyi, and they had at least two sons and one daughter. Chen Mu became the third-generation Marquis of Tangyi in the third year of Emperor Wen’s reign (177 BCE), but the exact date of Liu Piao's marriage to him is no longer verifiable.
During the Reign of Emperor Jing of Han(Princess's brother) Peirod
In 157 BCE, after Emperor Jing of Han ascended the throne, Princess Guantao Liu Piao continued to frequently visit the palace. With the favor of Dowager Dou and the indulgence of Emperor Jing, she became a significant figure in the Han court. During this time, her son Chen Jiao was granted the title of Marquis of Longlü because of his mother's status.
Liu Piao was adept at political maneuvering and used her daughter, Chen Shi(陈氏), as a political pawn. Initially, she intended to marry Chen Shi to Crown Prince Liu Rong(刘荣), the son of Lady Li(Concubine). However, due to her frequent introduce of beautiful women to Emperor Jing, which caused deep conflict with Lady Li, this proposal was firmly rejected by her. Enraged, Liu Piao later sought a marriage alliance with Consort Wang, who agreed to the match. Through the combined efforts of Liu Piao and Consort Wang, Crown Prince Liu Rong was deposed and made the King of Linjiang in the seventh year of the Yuan era (150 BCE), and two years later, he was forced to death, with Lady Li also dying from grief.
Soon after, Consort Wang was made Empress, and her son, Liu Che(刘彻), was established as Crown Prince and married Chen Shi(陈氏).
During the Reign of Emperor Wu of Han(汉武帝)
In 141 BCE, after Emperor Wu of Han (Liu Che/刘彻) ascended the throne, Chen Shi was made Empress(陈氏). As the granddaughter of Dowager Dou and the daughter of Princess Guantao Liu Piao, who had contributed to the appointment of Liu Che as Crown Prince, Chen Shi enjoyed significant favor. At this time, Princess Guantao Liu Piao had been elevated by the emperor and was honored with the title Dowager Dou(窦太主).
Later, Emperor Wu favored Wei Zifu(卫子夫), a singer from the residence of his sister, Princess Pingyang(平阳公主). This situation made Empress Chen extremely jealous, especially since she was childless and unable to conceive despite seeking medical help. Meanwhile, Wei Zifu(卫子夫) became pregnant. As a result, Empress Chen resorted to witchcraft, but Emperor Wu discovered her actions, leading to her deposition in the fifth year of the Yuan Guang era (130 BCE).
By 129 BCE, after the death of Dowager Dou Liu Piao's husband, Chen Mu, she was a woman in her sixty year old, living as a widow. At this time, she became infatuated with a handsome young man named Dong Yan(董偃). Dong Yan(董偃)'s mother had been a pearl seller, and from the age of thirteen, he had frequently visited the home of Dowager Dou Liu Piao. Known for his good looks, Dong Yan was summoned by Dowager Dou Liu Piao, who took him into her household, where he was educated and trained in various skills. At eighteen, Dong Yan served as Dowager Dou's attendant and also acted as her inner chamber servant. His gentle and kind nature, combined with their illicit relationship, led many to address him as “Lord Dong/董君.”
Later, Anling Yuan Shu(安陵爰叔) advised Dong Yan to suggest to Dowager Dou that she offer the Changmen Garden as a separate palace to Emperor Wu. Emperor Wu was pleased with this gesture and renamed the garden “Changmen Palace.” Dowager Dou, delighted with this outcome, rewarded Yuan Shu generously.
Subsequently, Anling Yuan Shu suggested that Dong Yan propose to Dowager Dou that she be ill and unable to see Emperor Wu. When Emperor Wu visited to inquire about her health, Dowager Dou expressed a desire to host him. After Dowager Dou recovered, Emperor Wu was invited to a banquet. During the event, Dowager Dou removed her jewelry, knelt to apologize to Emperor Wu, and then had Dong Yan do the same. Throughout the banquet, Dowager Dou and Dong Yan showed great respect and hospitality to Emperor Wu, who was very pleased. As a result, Dong Yan became highly favored and frequently participated in palace activities.
Han dynasty scholar-official DongFang Shuo(東方朔) was quite critical of Dong Yan, disapproving of his affair with the princess, which he felt undermined moral standards and distracted the ruler from his duties. Emperor Wu gradually distanced himself from Dong Yan, who fell out of favor and died in his thirties. After losing Dong Yan, Princess Guantao Liu Piao lived for several more years before her death. Her final wish was not to be buried with her husband, Chen Mu, but rather to be interred with her lover, Dong Yan, in Balin. This request is considered the beginning of more extravagant practices among princesses and noblewomen.
In the first year of the Yuanding era (116 BCE), her two sons, Chen Xu, Marquis of Tangyi, and Chen Jiao, Marquis of Longlü, committed suicide during their mother's mourning period due to their involvement in illicit affairs(with woman)and disputes over inheritance. The title of Marquis of Tangyi was abolished. A few years later, her daughter, the deposed Empress Chen Shi, also passed away.
In Chinese history, princesses were often unfortunate victims of political marriages and diplomatic alliances. However, there are also many fortunate examples, such as Princess Guantao. Unlike many others confined by the conservative constraints of a feudal empire, she lived a life of personal freedom and pursued her desires, breaking free from traditional limitations.
________________
📸Photo & Model :@金角大魔王i
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/O3vkEFAC9
________________
#chinese hanfu#hanfu#Western Han (202 BC–9 AD)#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#chinese history#china history#woman in history#Princess Guantao#漢服#汉服#中華風
134 notes
·
View notes
Text
April 14, Xi'an, China, Shaanxi History Museum, Qin and Han Dynasties Branch (Part 3 – Innovations and Philosophies):
(Edit: sorry this post came out so late, I got hit by the truck named life and had to get some rest, and this post in itself took some effort to research. But anyway it's finally up, please enjoy!)
A little background first, because this naming might lead to some confusions.....when you see location adjectives like "eastern", "western", "northern", "southern" added to the front of Zhou dynasty, Han dynasty, Song dynasty, and Jin/晋 dynasty, it just means the location of the capital city has changed. For example Han dynasty had its capital at Chang'an (Xi'an today) in the beginning, but after the very brief but not officially recognized "Xin dynasty" (9 - 23 AD; not officially recognized in traditional Chinese historiography, it's usually seen as a part of Han dynasty), Luoyang became the new capital. Because Chang'an is geographically to the west of Luoyang, the Han dynasty pre-Xin is called Western Han dynasty (202 BC - 8 AD), and the Han dynasty post-Xin is called Eastern Han dynasty (25 - 220 AD). As you can see here, in these cases this sort of adjective is simply used to indicate different time periods in the same dynasty.
Model of a dragonbone water lift/龙骨水车, Eastern Han dynasty. This is mainly used to push water up to higher elevations for the purpose of irrigation:
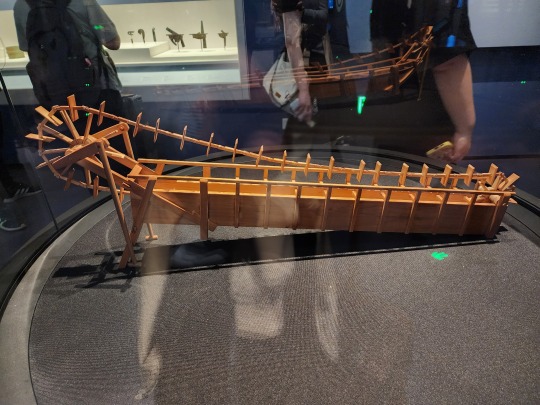
Model of a water-powered bellows/冶铁水排, Eastern Han dynasty. Just as the name implies, as flowing water pushes the water wheel around, the parts connected to the axle will pull and push on the bellows alternately, delivering more air to the furnace for the purpose of casting iron.
The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art/《九章算术》, Fangcheng/方程 chapter. It’s a compilation of the work of many scholars from 10 th century BC until 2 nd century AD, and while the earliest authors are unknown, it has been edited and supplemented by known scholars during Western Han dynasty (also when the final version of this book was compiled), then commented on by scholars during Three Kingdoms period (Kingdom of Wei) and Tang dynasty. The final version contains 246 example problems and solutions that focus on practical applications, for example measuring land, surveying land, construction, trading, and distributing taxes. This focus on practicality is because it has been used as a textbook to train civil servants. Note that during Han dynasty, fangcheng means the method of solving systems of linear equations; today, fangcheng simply means equation. For anyone who wants to know a little more about this book and math in ancient China, here’s an article about it. (link goes to pdf)

Diagram of a circle in a right triangle (called “勾股容圆” in Chinese), from the book Ceyuan Haijing/《测圆海镜》 by Yuan-era mathematician Li Ye/李冶 (his name was originally Li Zhi/李治) in 1248. Note that Pythagorean Theorem was known by the name Gougu Theorem/勾股定理 in ancient China, where gou/�� and gu/股 mean the shorter and longer legs of the right triangle respectively, and the hypotenuse is named xian/弦 (unlike what the above linked article suggests, this naming has more to do with the ancient Chinese percussion instrument qing/磬, which is shaped similar to a right triangle). Gougu Theorem was recorded in the ancient Chinese mathematical work Zhoubi Suanjing/《周髀算经》, and the name Gougu Theorem is still used in China today.

Diagram of the proof for Gougu Theorem in Zhoubi Suanjing. The sentence on the left translates to "gou (shorter leg) squared and gu (longer leg) squared makes up xian (hypotenuse) squared", which is basically the equation a² + b² = c². Note that the character for "squared" here (mi/幂) means "power" today.

This is a diagram of Zhang Heng’s seismoscope, called houfeng didong yi/候风地动仪 (lit. “instrument that measures the winds and the movements of the earth”). It was invented during Eastern Han dynasty, but no artifact of houfeng didong yi has been discovered yet, this is presumably due to constant wars at the end of Eastern Han dynasty. All models and diagrams that exist right now are what historians and seismologists think it should look like based on descriptions from Eastern Han dynasty. This diagram is based on the most popular model by Wang Zhenduo that has an inverted column at the center, but this model has been widely criticized for its ability to actually detect earthquakes. A newer model that came out in 2005 with a swinging column pendulum in the center has shown the ability to detect earthquakes, but has yet to demonstrate ability to reliably detect the direction where the waves originate, and is also inconsistent with the descriptions recorded in ancient texts. What houfeng didong yi really looks like and how it really works remains a mystery.

Xin dynasty bronze calipers, the earliest sliding caliper found as of now (not the earliest caliper btw). This diagram is the line drawing of the actual artifact (right).


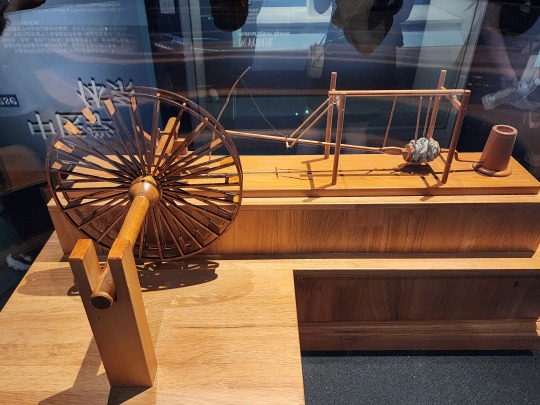
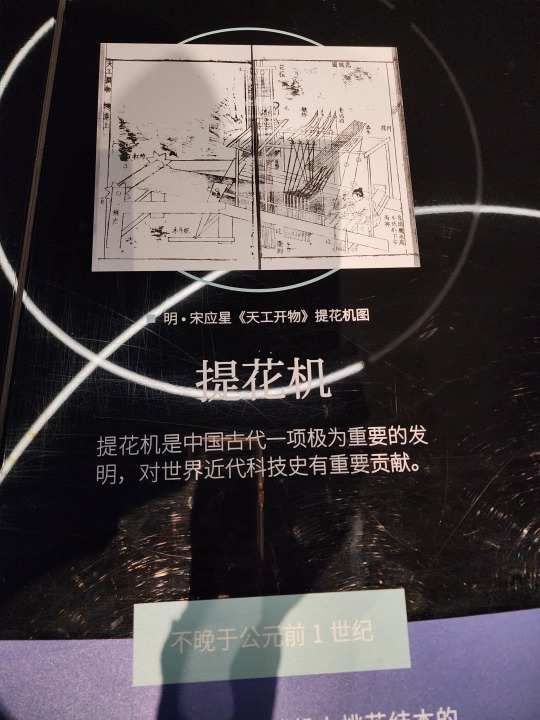
Ancient Chinese "Jacquard" loom (called 提花机 or simply 花机 in Chinese, lit. "raise pattern machine"), which first appeared no later than 1st century BC. The illustration here is from the Ming-era (1368 - 1644) encyclopedia Tiangong Kaiwu/《天工开物》. Basically it's a giant loom operated by two people, the person below is the weaver, and the person sitting atop is the one who controls which warp threads should be lifted at what time (all already determined at the designing stage before any weaving begins), which creates patterns woven into the fabric. Here is a video that briefly shows how this type of loom works (start from around 1:00). For Hanfu lovers, this is how zhuanghua/妆花 fabric used to be woven, and how traditional silk fabrics like yunjin/云锦 continue to be woven. Because it is so labor intensive, real jacquard silk brocade woven this way are extremely expensive, so the vast majority of zhuanghua hanfu on the market are made from machine woven synthetic materials.
Chinese purple is a synthetic pigment with the chemical formula BaCuSi2O6. There's also a Chinese blue pigment. If anyone is interested in the chemistry of these two compounds, here's a paper on the topic. (link goes to pdf)

A list of common colors used in Qin and Han dynasties and the pigments involved. White pigment comes from chalk, lead compounds, and powdered sea shells; green pigment comes from malachite mineral; blue pigment usually comes from azurite mineral; black comes from pine soot and graphite; red comes from cinnabar; ochre comes from hematite; and yellow comes from realgar and orpiment minerals.

Also here are names of different colors and shades during Han dynasty. It's worth noting that qing/青 can mean green (ex: 青草, "green grass"), blue (ex: 青天, "blue sky"), any shade between green and blue, or even black (ex: 青丝, "black hair") in ancient Chinese depending on the context. Today 青 can mean green, blue, and everything in between.

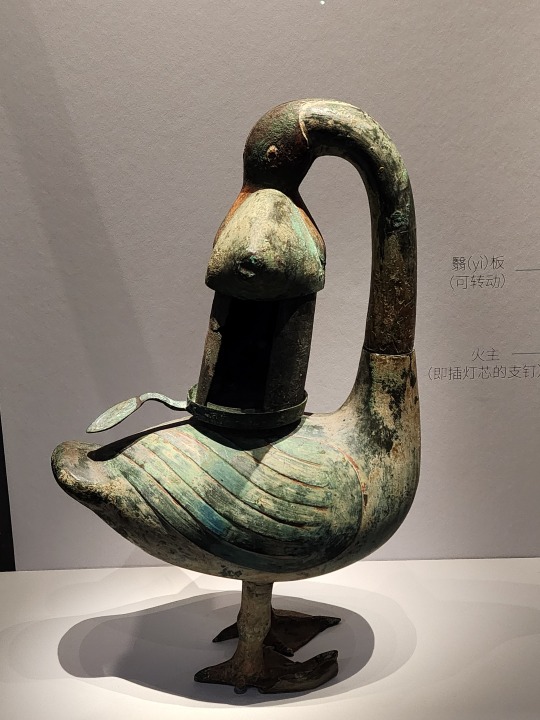
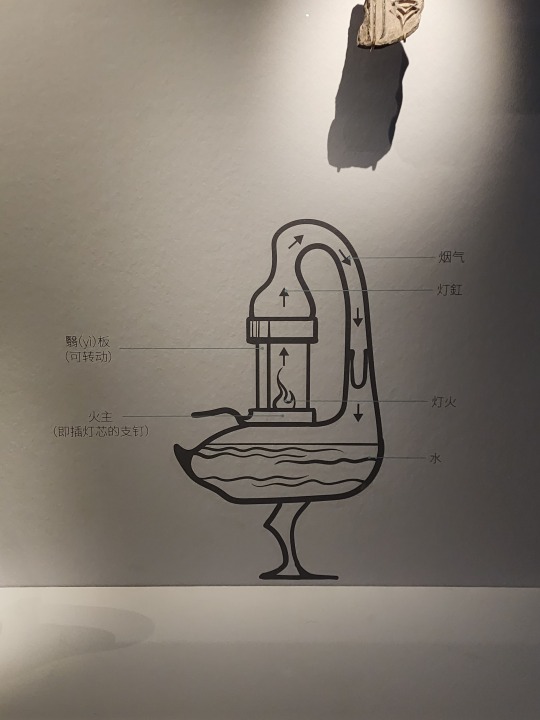
Western Han-era bronze lamp shaped like a goose holding a fish in its beak. This lamp is interesting as the whole thing is hollow, so the smoke from the fire in the lamp (the fish shaped part) will go up into the neck of the goose, then go down into the body of the goose where there's water to catch the smoke, this way the smoke will not be released to the surrounding environment. There are also other lamps from around the same time designed like this, for example the famous gilt bronze lamp that's shaped like a kneeling person holding a lamp.

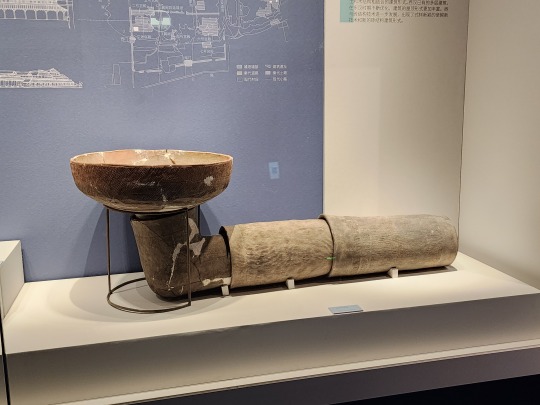
Part of a Qin-era (?) clay drainage pipe system:

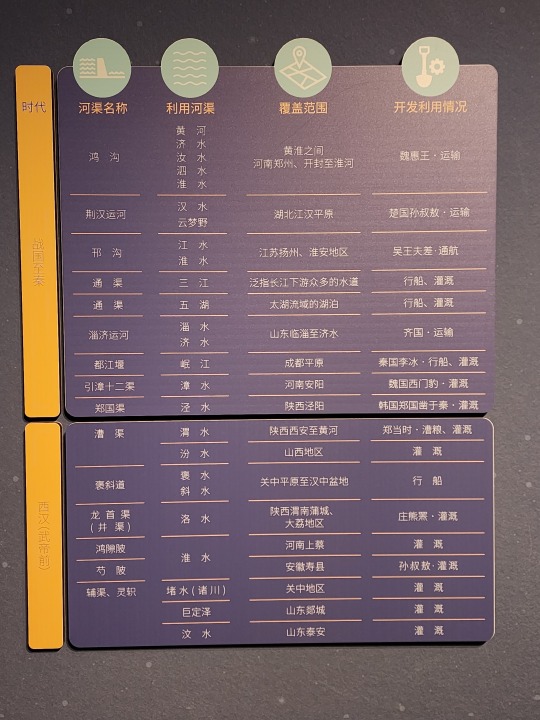
A list of canals that was dug during Warring States period, Qin dynasty, and pre-Emperor Wu of Han Han dynasty (475 - 141 BC). Their purposes vary from transportation to irrigation. The name of the first canal on the list, Hong Gou/鸿沟, has already become a word in Chinese language, a metaphor for a clear separation that cannot be crossed (ex: 不可逾越的鸿沟, meaning "a gulf that cannot be crossed").
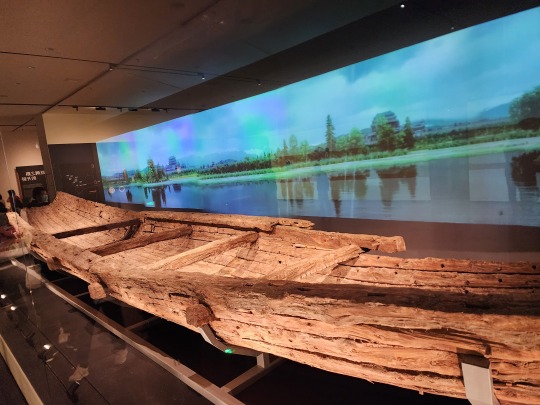
Han-era wooden boat. This boat is special in that its construction has clear inspirations from the ancient Romans, another indication of the amount of information exchange that took place along the Silk Road:

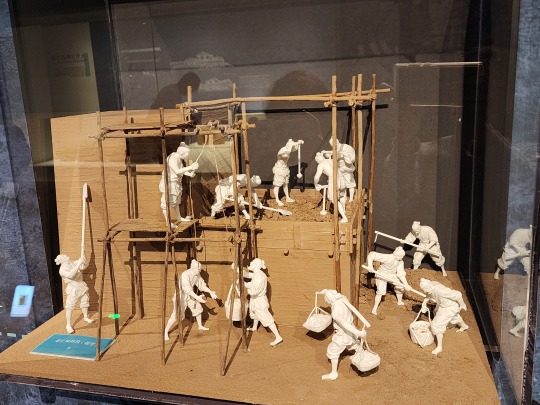
A model that shows how the Great Wall was constructed in Qin dynasty. Laborers would use bamboo to construct a scaffold (bamboo scaffolding is still used in construction today btw, though it's being gradually phased out) so people and materials (stone bricks and dirt) can get up onto the wall. Then the dirt in the middle of the wall would be compressed into rammed earth, called hangtu/夯土. A layer of stone bricks may be added to the outside of the hangtu wall to protect it from the elements. This was also the method of construction for many city walls in ancient China.

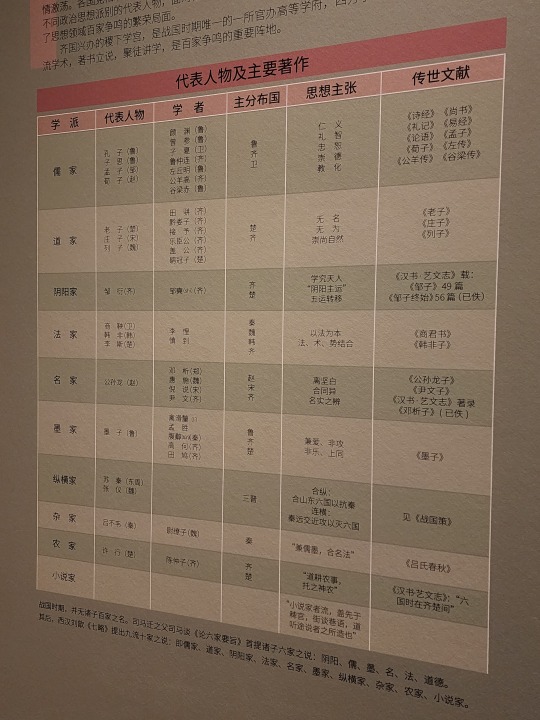
A list of the schools of thought that existed during Warring States period, their most influential figures, their scholars, and their most famous works. These include Confucianism (called Ru Jia/儒家 in Chinese; usually the suffix "家" at the end denotes a school of thought, not a religion; the suffix "教" is that one that denotes a religion), Daoism/道家, Legalism (Fa Jia/法家), Mohism/墨家, etc.
The "Five Classics" (五经) in the "Four Books and Five Classics" (四书五经) associated with the Confucian tradition, they are Shijing/《诗经》 (Classic of Poetry), Yijing/《易经》 (also known as I Ching), Shangshu/《尚书》 (Classic of History), Liji/《礼记》 (Book of Rites), and Chunqiu/《春秋》 (Spring and Autumn Annals). The "Four Books" (四书) are Daxue/《大学》 (Great Learning), Zhongyong/《中庸》 (Doctrine of the Mean), Lunyu/《论语》 (Analects), and Mengzi/《孟子》 (known as Mencius).

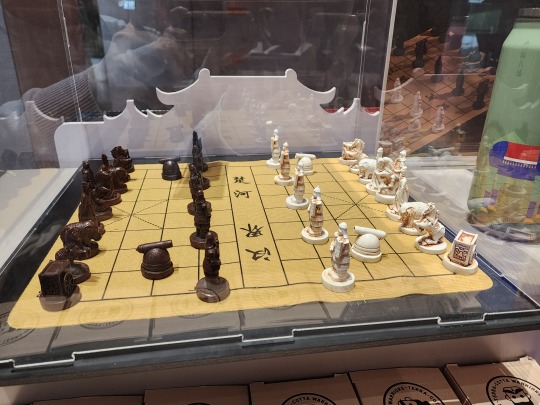
And finally the souvenir shop! Here's a Chinese chess (xiangqi/象棋) set where the pieces are fashioned like Western chess, in that they actually look like the things they are supposed to represent, compared to traditional Chinese chess pieces where each one is just a round wooden piece with the Chinese character for the piece on top:

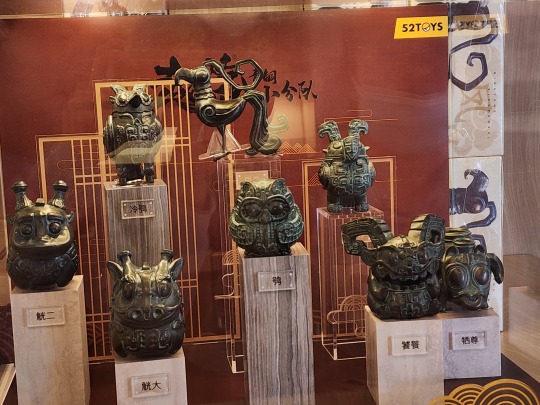
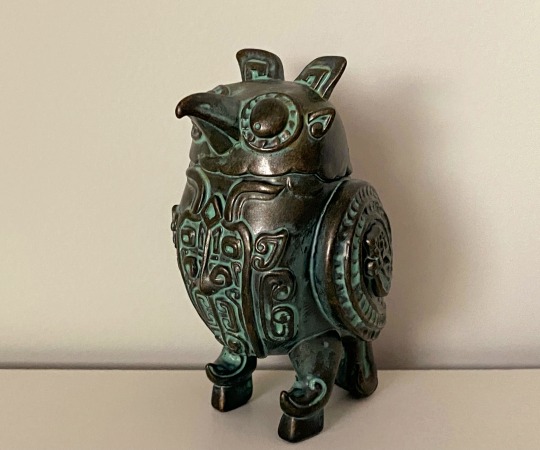
A blind box set of small figurines that are supposed to mimic Shang and Zhou era animal-shaped bronze vessels. Fun fact, in Shang dynasty people revered owls, and there was a female general named Fu Hao/妇好 who was buried with an owl-shaped bronze vessel, so that's why this set has three different owls (top left, top right, and middle). I got one of these owls (I love birds so yay!)


And that concludes the museums I visited while in Xi'an!
#2024 china#xi'an#china#shaanxi history museum qin and han dynasties branch#chinese history#chinese culture#chinese language#qin dynasty#han dynasty#warring states period#chinese philosophy#ancient technology#math history#history#culture#language
95 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2,000-Year-Old Bronze Coins Unearthed in Xi'an, China
A new batch of relics, including thousands of bronze coins, have been unearthed from the remains of a mint dating back more than 2,000 years in Xi'an, the capital of northwest China's Shaanxi Province.
Apart from the coins of different face values and shapes, more than 100 ash pits, three house ruins, 11 kiln ruins, 18 wells, and three smelting and casting ruins have been unearthed.
Judging from their shapes and structures, all relics date back to the Western Han Dynasty (202 BC-AD 25). Some belonged to the short-lived period under the reign of Wang Mang between AD 9 and 23, also called the Xin Dynasty, according to Zhang Jianfeng, a researcher with the Institute of Archaeology of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS).
Zhang said the mint was a national-level one. Xi'an used to be the capital of the Western Han Dynasty when the city was called Chang'an.
In December 2015, archaeologists from the CASS Institute of Archaeology and Xi'an's institute of cultural relics protection and archaeology jointly launched the excavation work of the site.
The latest round of excavation started in March 2021.
The discoveries are of great significance to the study of coinage technology and the changes in monetary and economic policies of that time, said Zhang.
#2000-Year-Old Bronze Coins Unearthed in Xi'an China#coins#collectable coins#bronze coins#ancient coins#ancient artifacts#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient china#chinese history
418 notes
·
View notes
Text
Commanderies and States of Western Han, Part 1
This is really only for the really specially interested, but having done the work I thought I might as well put it out here.
From the geographic treatise in Ban Gu's Hanshu with the commentary by Yan Shigu.
The reader will note that unlike later similar works, the commanderies are not grouped by province.
Jingzhaoyin
Governor of Jingzhao京兆尹, formerly Qin's Neishi內史. 1st Year of Emperor Gao [206 BC], it belonged to Sai state塞國. 2nd Year [205 BC], it changed to become Weinan commandery渭南郡. 9th Year [198 BC], it was restored to Neishi內史. Emperor Wu's 6th Year of Jianyuan [135 BC], divided it off to be Youneishi右內史, 1st Year of Taichu [104 BC], it changed to become Governor of Jingzhao京兆尹. 2nd Year of Yuanshi [2 AD], 195 702 households, 682 468 people[a]. 12 counties:
[1]Chang'an長安, 5th Year of Emperor Gao [202 BC], set it up. 1st Year of Emperor Hui [194 BC], began the city walls, 6th Year [189 BC], it was completed. 80 300 households, 246 200 people. Wang Mang called it Chang'an常安[b].
[2]Xinfeng新豐. Li Mountain驪山 is to the south. Formerly the Li Rong's state驪戎國. Qin called it Liyi驪邑. 7th Year of Gaozu [200 BC], set it up[c].
[3]Chuansikong船司空, Mang called it Chuanli船利[d].
[4]Lantian藍田. The mountains produce pretty jade. Has the Tiger Marquis's Mountain Shrine虎候山祠. Duke Xiao of Qin [361 – 340 BC] set it up.
[5]Huayin華陰, formerly Yinjin陰晉. 5th Year of King Huiwen of Qin [333 BC], changed the name to Ningqin寧秦. 8th Year of Emperor Gao [199 BC], changed the name to Huayin華陰. Taihua Mountain is to the south, it has a shrine, the mountain of Yu province豫州. Jiling palace集靈宮, Emperor Wu erected it. Mang called it Huatan華壇.
[6]Zheng鄭, the district of King Xuan of Zhou's younger brother, Duke Huan of Zheng. Has an iron official[e].
[7]Hu湖, has Zhou's Sons of Heaven' shrines at two places. Formerly called Hu胡, in Emperor Wu's 1st Year of Jianyuan [140 BC], changed the name to Hu湖.
[8]Xiagui下邽[f].
[9]Nanling南陵. 7th Year of Emperor Wen [173 BC], set it up. Yi River沂水 sets out from Lantian valley藍田谷, to the north arrives at Baling霸陵 to enter the Ba River霸水. The Ba river霸水 likewise sets out from Lantian Valley藍田谷, going north it enters the Wei渭. The ancients called it Zi River茲水. Duke Mu of Qin [659 – 621 BC] changed the name to hence set forth the Merits of Ba, to look after sons and grandson[g].
[10]Fengming奉明, Emperor Xuan [79 – 49 BC] set it up.
[11]Baling霸陵, formerly Zhiyang芷陽. Emperor Wen [180 – 157 BC] changed the name. Mang named it Shuizhang水章.
[12]Duling杜陵, formerly the Earl of Du's state杜伯國, Emperor Xuan [79 – 49 BC] changed the name. Has Zhou's General of the Right, Du Zhu's Shrine周右將軍杜主祠 at at four places. Mang called it Rao'an饒安.
[a]Shigu says: Han's households and population must in the time of Yuanshi have been the most abundant and flourishing. For that reason the treatise lift them up and use them as the number. The ones after are all classified like this.
[b]Shigu says: Wang Mang usurped the throne, and changed the names of Han's commanderies and counties, generally altering them. The ones below are all classified like this.
[c]Ying Shao says: the Grand High August thought of returning home east. And so Gaozu built a city with courtyards, streets and wards in the image of Feng豐, and moved the people of Feng to fill it. For that reason it was titled Xinfeng新豐 [“New Feng”].
[d]Fu Qian says: “The name of a count”. Shigu says: “Originally the officials which was master of ships船, and thereupon used it as county.”
[e]Ying Shao says: “The fief of King Xuan's younger brother of the [same] mother You. His son and King Ping moved east, which was further called Xinzheng [“New Zheng”].”
Your Subject Zan says: “Zhou, since King Mu and downwards had the capital at Xizheng新鄭 [“Western Zheng”], and did not get to use it as fief of Duke Huan. In the beginning Duke Huan was Zhou's Minister over the Masses. The kingly house was about to be chaotic, and for that reason he planned with Scribe Bo to convey the treasure to give bribes for between Guo虢 and Hui會. When King You was defeated, after two years he then wiped out Kuai會, after four years he then wiped out Guo虢, and settled at the hill of Zhengfu鄭父. Hence he became Duke Huan of Zheng, there are no writings of a fief in Jingzhao京兆.”
Shigu says: “The Outer Transmittals of Spring and Autum states: “When King You was defeated, Duke Huan of Zheng died there. His son Duke Wu and King Ping turned back east”. For that reason Mister Zuo's Transmittals states: “When our Zhou moved east, it was Jin and Zheng they relied on.” Also when Duke Zhuang of Zheng states: “Our previous lord's new town was here”, it is perhaps the road to Xinzheng新鄭. King Mu below were without affairs of a capital at Xizheng西鄭. Zan's explanations was wrong. Kuai會 is pronounced gong工+wai外.”
[Baxter & Sagart state: Present hui會 was then pronounced (h- + -waj C), present kuai會was then pronounced(k- + -waj C). 工 was then pronounced (k- + -uwng A). 外 was then pronounced (ng- + -waj C). Your Humble Tumbler says: Therefore here 會 should be read as (k- + -waj C) which should give kuai.]
[f]Ying Shao says: “Duke Wu of Qin invaded the Gui邽 Rong, and set up to have Shanggui上邽[“Upper Gui”]. For that reason they added Xia下 [“Lower”].
Shigu says: “邽 is pronounced gui圭. They took the people of the Gui Rong, and the came to this county.”
[g]Shigu says: “Xi沂 is pronounced xian先+li歷. The Observed Readings says shi示[?].”
[Baxter & Sagart state: 沂 was pronounced (ng- + -j+j A). 先was pronounced (s- + -en C). 歷 was pronounced (l- + -ek D). Your Humble Tumbler says: Therefore here 沂 should be read as (s- + -ek D) which should give xi like in 析]
Zuopingyi
Zuopingyi左馮翊, formerly Qin's Neishi內史. 1st Year of Emperor Gao [206 BC], it belonged to Sai state塞國. 2nd Year [205 BC], changed the name to Heshang commandery河上郡. 9th Year [198 AD], abolished it, restoring it to be Neishi內史. Emperor Wu's 6th Year of Jianyuan [135 BC], divided it off to be Zuoneishi左內史, 1st Year of Taichu [104 BC], changed the name to Zuopingyi左馮翊[a. 235 101 households, 917 822 people. 24 counties:
[1]Gaoling高陵, Seat of the Assisting Chief Commandant of the Left. Mang called it Qianchun千春.
[2]Yueyang櫟陽, Duke Xian of Qin [384 – 362 BC] moved there from Yong雍. Ma called it Shiting師亭[a].
[3]Didao翟道, Mang called it Huan渙.
[4]Chiyang池陽, 4th Year of Emperor Hui [191 BC], set it up. Jienie Mountain巀嶭山 is to the north[b].
[5]Xiayang夏陽, formerly Shaoliang少梁. 11th Year of King Huiwen of Qin [327 BC] changed the name. The Tribute of Yu's Liang Mountain梁山 is to the north-west. Longmen Mountain龍門山 is to the north. Has an iron official. Mang named it Jiting冀亭.
[6]Ya衙, Mang named it Dachang達昌[c].
[7]Suyi粟邑, Mang named it Sucheng粟城.
[8]Gukou谷口, Jiuzong Mountain九嵕山 is to the west. Has the Duke of Heavenly Unity天齊公, Wuchuang Mountain五床山, the Transcendents僊 and the Five Emperors Shrines五帝祠 at four places. Mang called it Guhui谷喙[d].
[9]Lianzhuo蓮勺[e].
[10]Fu鄜, Mang called it Xiuling脩令[f].
[11]Pinyang頻陽, Duke Li of Qin[476 – 443 BC] set it up[g]. [In 456 BC according to the Shiji].
[12]Linjin臨晉, formerly Dali大荔. Qin seized it [in 461 BC according to the Shiji] and changed the name. Has the He River's Shrine河水祠, Ruixiang芮鄉, formerly the Rui state芮國. Mang called it Jianjin監晉[h].
[13]Zhongquan重泉, Mang called it Diaoquan調泉.
[14]Heyang郃陽[i].
[15]Duixu祋祤, 2nd Year of Emperor Jing [155 BC], set it up[j].
[16]Wucheng武城, Mang called it Huancheng桓城[k].
[17]Chenyang沈陽, Mang challed it Zhichang制昌.
[18]Huaide褱德, in the Tribute of Yu the northern branch Jing Mountain荊山 is to the south. Below has the Qiangliang Plain彊梁原. Luo River洛水 to the south-east enters the Wei渭, the irrigation of Yong province雍州. Mang called it Dehuan德驩[l].
[19]Cheng徵, Mang called it Fan'ai氾愛[m].
[20]Yunling雲陵, Emperor Zhao [87 – 74 BC] set it up.
[21]Wannian萬年, Emperor Gao [206 – 195 BC] set it up. Mang called it Yichi異赤[n].
[22]Changling長陵, Emperor Gao [206 – 195 BC] set it up. 50 057 households, 179 469 people. Mang called it Changping長平.
[23]Yangling陽陵, formerly Yiyang弋陽. Emperor Jing [157 – 141 BC] changed the name. Mang called it Weiyang渭陽.
[24]Yunyang雲陽. Has Xiutu休屠, the Golden Person金人 and the God of Straight Paths' Shrines徑路神祠. The Yue Shaman Gu Rang's Shrine越巫(夘+古?)𨟚祠 at three places[o].
[a]Ru Chun says: “ 櫟 is pronounced yüe藥.
[b]Ying Shao says: “It is on the sunny side of Chi River池水.”
Shigu says: “Jienie 巀嶭, precisely where present customs places [?] Cuo'e Mountain嵯峨山, pronounced Jienie巀齧. It is pronounced cai 才+ge葛, and also pronounced wu五+ge葛.
[齧 Baxter & Sagart: (ng- + -et D). 才 Baxter & Sagart: (dz- + -oj A). 葛 Baxter & Sagart: (k- + -at D). 五 Baxter & Sagart: (ng- + -u B). Baxter & Sagart have nothing under (dz- + -at D) or (ng- + -at D). But (dz- + -et D) gives jié and (ng- + -et D) gives nie as in 齧.
[c]Ru Chun says: “衙 is pronounced ya牙.”
Shigu says: “Just the place of which the Spring and Autumn states 'Qin and Jin fought at Pengya彭衙'.”
[d]Shigu says: “嵕 is pronounced zi子 + gōng 公. And also pronounced zi子 + kǒng 孔. 喙 is pronounced xu許 + hui穢.
[e]Ru Chun says: “Pronounced nianzhuo輦酌.”
[Baxter & Sagart: 蓮: (l- + -en A) 輦: (l- + -jen B). zhuo勺: (tsy- + -jak D). 酌: (tsy- + -jak D)
[f]Meng Kang says: “Pronounced fu敷.”
[g]Ying Shao says: “It is on the sunny-side of Pin River頻水.”
[h]Ying Shao says: “Overlooks [lin臨] the Jin River晉水, for that reason it was called Linjin臨晉.
Your Subject Zan says: “Jin River晉水 is in the midst of the He河. This county is to the west of the He西. Do not get to state that it overlooks the Jin River晉水. The old explanation says, Qin built a tall rampart so as to overlook Jin state晉國, for that reason it was Linjin臨晉.”
Shigu says: “Zan's explanation is correct. Those who explain sometimes consider it to be when Marquis Wen of Wei invaded Qin, he first set up Linjin, which is wrong. Marquis Wen heavily walled it and that was all, how was he first to set it up!”
[i]Ying Shao says: “It is on the sunny-side of He River郃水.”
Shigu says: “Pronounced he合. Just where the Great Odes' poem of Great Clarity speaks of as 'On the sunny-side of the Qia洽.'”
[j]Shigu says: “dui祋 is pronounced ding丁 + huo活, and also pronounced ding丁 + wai外. 祤is pronounced xu音詡.”
[k]Shigu says: “Just of where Mister Zuo's Transmittals states 'Qin invaded Jin, and was defeated at Wucheng武城'.”
[l]Shigu says: “ 褱 is like the huai懷 character.”
[m]Shigu says: “ 徵 is pronounced cheng懲, precisely the Chengcheng澄城 county of the present. When the Zuo Transmittals state 'defeated at northern Cheng 徵', it speaks of this land, that is all. Yet Du Yuankai is not detailed with its location.”
[n]Shigu says: “The Yellow Map of the Three Supports states that the Grand High August was buried on the plain north of Yueyang櫟陽, and they erected the Wannian Mound萬年陵 there.”
[o]Meng Kang says: “(夘+古?) is pronounced as the gu辜 in guzhe辜磔 [“punishment by dismembering”], the shrine of a person of the Yue越. 𨟚 is pronounced rang穰. 休is pronounced xu許 + qiu虯. 屠 is pronounced chu除.
Youfufeng
Youfufeng右扶風, formerly Qin's Neishi內史. 1st Year of Emperor Gao [206 BC], it belonged to Yong state雍國. 2nd Year [205 BC] changed it to be Zhongdi commandery中地郡. In the 9th Year [198 AD], abolished it, restoring it to be Neishi內史. Emperor Wu's 6th Year of Jianyuan [135 BC], divided it off to be Youneishi右內史, 1st Year of Taichu [104 BC] changed the name of the Master of the Feudal Ranks Chief Commandant主爵都尉 to be Youfufeng右扶風[a]. 216 377 households, 836 070 people. 21 counties:
[1]Weicheng渭城, formerly Xianyang咸陽. 1st Year of Emperor Gao [206 BC], changed the name to Xincheng新城. 7th Year [200 BC], abolished it, belonging to Chang'an長安. Emperor Wu's 3rd Year of Yuanding [114 BC], changed the name to Weicheng渭城. Has the Lanchi Palace蘭池宮. Wang called it Jingcheng京城.
[2]Huaili槐里, Zhou called it Quanqiu犬丘. King Yi [899 – 892 BC] made it the capital. Qin changed the name to Feiqiu廢丘. 3rd Year of Gaozu [204 BC], changed the name. Has Huangshan Palace黃山宮, 2nd Year of Xiaohui [193 BC], erected it. Mang called it Huaizhi槐治.
[3]Hu鄠, anciently a state. Has Hugu Precinct扈谷亭. Hu扈 is who Qi of Xia invaded. Feng River酆水 sets out to the south-east. Also has Jue river潏水. Both to the north pass through Shanglin Park上林苑 to enter the Wei渭. Has Beiyang Palace萯陽宮, erected by King Wen of Qin[b].
[4]Zhouzhi盩厔. Has Changyang Palace長楊宮. Has the Shexiong Building射熊館, King Zhao of Qin [306 – 251 BC] erected it, Lingzhi Canal靈軹渠, pierced by Emperor Wu [114 – 87 BC].
[5]Tai斄,where was the fief of Houji of Zhou[c].
[6]Yuyi郁夷, The Poetry: “The way from Zhou is Yuyi周道郁夷.” Has the Qian River's Shrine汧水祠. Mang called it Yuping郁平[d].
[7]Meiyang美陽, in the Tribute of Yu Qi Mountain is to the north-east. Zhongshui District中水鄉 where was the town of King Da of Zhou. Has Gaoquan palace高泉宮, Dowager Xuan of Qin erected it.
[8]Mei郿, Chengguo Canal成國渠 at the head accepts the Wei. North-eastward it arrives at Shanglin上林 to enter Menglong Canal蒙籠渠. Seat of the Assisting Chief Commandant of the Right[e].
[9]Yong雍, Duke Hui of Qin made it the capital. Has the Five Places for Worshipp五畤, Taihao太昊, the Yellow Emperor and below, shrines at 303 places. The Tuoquan Palace橐泉宮, Duke Xiao [361 – 338 BC] erected it, the Qinian Palace祈年宮, Duke Hui erected it, the Yuyang Palace棫陽宮, King Zhao [306 – 251 BC] erected it. Has an iron official[f].
[10]Qi漆, the river is west of the county. Has an iron official. Mang called it Qizhi漆治.
[11]Xunyi栒邑, has Bin District豳鄉, the Poetry's Bin state豳國, where was Noble Liu's capital[g].
[12]Yumi隃麋, has the Yellow Emperor's Sons Shrine黃帝子祠. Mang called it Futing扶亭[h].
[13]Chencang陳倉, has the High Duke上公, the Morning Star明星, the Yellow Emperor's Grandson[s], and Shun's wife Yu's Burial mound's Shrines舜妻育冢祠. Has Yuyang Palace羽陽宮, King Wu of Qin [310 – 307 BC] erected it.
[14]Duyang杜陽, Du River杜水 to the south enters the Wei渭. The Poetry says: “From Du杜.” Mang called it Tongdu通杜[i].
[15]Qian汧, Wu Mountain吳山 is to the west. Ancient writings considered it to be Qian Mountain汧山. The mountain of Yong province雍州. To the north has Pugu District蒲谷鄉 and Xianzhong Valley弦中谷, Yong province's Xianpu Marsh弦蒲藪. Qian River汧水 sets out to the north-west, and enters the Wei渭. Rui River芮水 sets out to the north-west, to the east entering the Jing涇, the Poetry's Ruiwu芮㑄. The streams of Yong province[j].
[16]Haozhi好畤, Gui Mountain垝山 is to the east. Has Liangshan palace梁山宮, the First August of Qin [246 – 210 BC] erected it. Mang called it Haoyi好邑[k].
[17]Guo虢, has the Yellow Emperor's Sons, and Wen and Wu of Zhou's Shrines. Guo Palace虢宮, Dowager Xuan of Qin erected it.
[18]Anling安陵, Emperor Hui [195 – 188 BC] set it up. Mang called it Jiaping嘉平[l].
[19]Maoling茂陵, Emperor Wu [141- 87 BC] set it up. 61 087 households, 277 277 people. Mang called it Xuancheng宣城[m].
[20]Pingling平陵, Emperor Zhao [87 – 74 BC] set it up. Mang called it Guangli廣利.
[21]Wugong武功, Taiyi Mountain太壹山 ancient writings consider to be Zhongnan終南. Chui Mountain垂山 ancient writings considered to be Dunwu敦物. Both are east of the county. Ye River斜水 sets out from north of Yaling Mountian衙領山, and arrives at Mei郿 to join the Wei渭. Bao River褒水 likewise sets out from Yaling衙領, and arrives at Nanzheng南鄭 to join the Mian沔. Has Chui Mountain垂山, Ye River斜水 and Bao River's Shrines褒水水祠 at three places. Mang called it Xinguang新光[n].
[a]Shigu says: “Master of the Feudal Ranks Chief Commandant, originally Qin's Master of the Feudal Ranks Central Commandant, in charge of the ranked marquises. Arriving at the 1st Year of Taichu [104 BC], altered the name to Supporting Wind of the Right[youfufeng右扶風], and seated him in the right [i.e. western] territory of Neishi. For that reason this treatise retroactively writes that in the 6th Year of Jianyuan [135 BC] they divided it to be the Neishi of the Right右內史, and also states that they altered the name of the Feudal Ranks Chief Commandant to be Youfufeng右扶風.
[b]Shigu says: “潏 is pronounced jue決. 萯 is pronounced bei倍.”
[c]Shigu says: “read similar to tai邰, and is pronounced tai 胎.”
[d]Shigu says: “The Lesser Ode's poem of Four Steeds says: “The four steeds stride steadily, the way from Zhou is meandering away [weichi倭遲].” In the Han Poetry it is written with the yu郁 and yi夷 characters. It talks of a subject on a mission who drives his horses and travels on this road.”
[e]Shigu says: “ 郿 is pronounced mei媚].
[f]Ying Shao says: “To pile up high on four sides is called yong雍[“Damming up”].”
Shigu says: “棫 is pronounced yu域.”
[g]Ying Shao says: “Mister Zuo's Transmittals says: “ Bi畢, Yuan原, Feng酆 and Xun郇 were the left-side successors of Wen [of Zhou]”. The Marquis of Xun and the Earl of Jia invaded Jin.”
Your Subject Zan says: “The Ancient Writings of Ji Commandery : 'Duke Wu of Jin wiped out Xun荀, and hence bestowed on the Grandee Yuanshi An, this was Xun Shu.' It also states 'Duke Wen walled Xun荀.' As such then Xun must have been within the borders of Jin, and do not get to be in the region of Fufeng扶風. Presently Hedong河東 has Xuncheng荀城, the ancient Xun state.”
Shigu says: “Zan's explanation is correct. This xun栒 is read similar to xun荀, but is itself a separate town, and that is all. It is not the one that invaded Jin.”
[h]Shigu says: “隃 is pronounced yu踰.”
[i]Shigu says: “The Great Odes' poem of Floss silk says “The people's first life, was from the land [tu土] of Qiju漆沮.” The Qi Poetry writes “from Du杜. It speaks of Noble Liu escaping the Di and coming to dwell in the territories of Du杜 and Qiju漆沮.”]
[j]Shigu says: “㑄 is read similar to ju鞠. The Great Odes' poem of Noble Liu says: “The halted travellers then became close, just there in Ruiju芮鞠.” The Han Poetry writes Ruiwu芮㑄. It talks of Noble Liu halting his army's travel, wishing to cause calm and quietness. He therefore went to the space of Ruiwu芮㑄.
[k]Shigu says: “Gui垝 is pronounced qiu丘 + hui毀.”
[Baxter & Sagart: 垝 is not listed. 丘: (kh- + -juw A). 毀: (x- +-jwe B). No (kh- + -jwe B) is listed.]
[l]Shigu says: “Kan Yan considers it to be originally Zhou's Cheng Town程邑.”
[m]Shigu says: “The Yellow Map states it originally was Huaili's槐里 Mao District茂鄉.”
[n]Shigu says: “斜 is pronounced yi弋 + she奢. 衙 is pronounced ya牙.”
[Baxter & Sagart: 斜 is not listed. 弋: (y- + -ik D). 奢: (sy- + -jae A). (y- + -jae A) is same as ye邪.]
Hongnong
Hongnong commandery弘農郡, Emperor Wu's 4th Year of Yuanding [113 AD], set it up. Mang called it Youdui右隊. 118 091 households, 475 954 people. Has an iron official in Mianchi黽池. 11 counties:
[1]Hongnong弘農, formerly Qin's Hangu pass函谷關. Beneath Ya Mountain Pass衙山領 is a valley from where Zhu River爥水 sets out, to the north it enters the He河.
[2]Lushi盧氏, Xiong'er Mountain熊耳山 is to the east. Yi River伊水 sets out, to the north-east joins the Luo雒, passing through 1 commandery, travelling 450 li. Also has Yu River育水, to the south it arrives at Shunyang順陽 to enter the Mian沔. Also has Er River洱水, to the south-east it arrives at Luyang魯陽, and likewise joins the Mian沔. Both pass through 2 commanderies, and travel 600 li. Mang called it Changfu昌富[a].
[3]Shan陝, formerly Guo state虢國. Has Jiao City焦城, formerly Jiao state焦國. To the north of Guo虢 is Dayang大陽. To the east of Guo虢 is Xingyang滎陽. To the west of Guo虢 is Yongzhou雍州. Mang called it Huangmei黃眉.
[4]Yiyang宜陽, at Minchi黽池 has an iron official.
[5]Mianchi黽池, 8th Year of Emperor Gao [199 BC], restored the people of Mianchi's黽池 middle district. Middle 2nd Year of Emperor Jing [148 BC], started the city, migrating ten thousand families to be the county. Gu River穀水 sets out from the Guyang Valley穀陽谷, to the north-east it arrives at Gucheng穀城 to enter the Luo雒. Mang called it Shanting陝亭[b].
[6]Danshui丹水, the river sets out from Shangluo's上雒 Zhongling Mountain冢領山, to the east it arrives at Xi析 to enter the Jun鈞. Miyang district密陽鄉 was formerly Shangmin商密[c].
[7]Xin'an新安, in the Tribute of Yu, the Jian River澗水 is to the east, to the south it enters the Luo雒.
[8]Shang商, the town of Qin's chancellor Wei Yang.
[9]Xi析, the Huang River黃水 sets out from Huang Valley黃谷, the Ju River鞠水 sets out from Xi Valley析谷, both arriving east at Li酈 to enter the Zhuan River湍水. Mang called it Junting君亭[d].
[10]Luhun陸渾, in the Spring and Autumn, moved the Luhun Rong to there. Has a pass[e].
[11]Shangluo上雒. In the Tribute of Yu, Luo River sets out from Zhongling Mountain冢領山, to the north-east it arrives at arriving at Gong鞏 to enter the He河, passing through 2 commanderies, travelling 1 070 li, the streams of Yu province豫州. Also has Jia River甲水 setting out from Qinling Mountain秦領山, to the south-east it arrives at Y鍚, to join the Mian沔, passing through 3 commanderies, travelling 570 li. Xiong'er熊耳 and Huoyu Mountains獲輿山 are to the north-east[f].
[a]Shigu says: “ 洱 is pronounced er耳.”
[b]Shigu says: “ 黽 is pronounced mo莫 + jian踐. And is also pronounced mo莫 + ren忍.”
[Baxter & Sagart: meng黽: (m- + -eang B), mo莫: (m- + -ak D), jian踐: (dz- + -jen B). (m- + -jen B) should give miǎn. ren忍: (ny- + -in B). (m- + -in B) should give mǐn.
[c]Shigu says; “Jun鈞 is likewise the name of a river, pronounced jun均.”
[d]Shigu says: “ 析 is pronounced xian先 + li歷. Ju River鞠水 is precisely what is presently spoken of as the Ju Deep pool菊潭. 酈 is pronounced chi持 + yi益. 湍 is pronounced zhuan專.
[Baxter & Sagart: 析: (s- + -ek D). xian先: (s- + -en A), li歷: (l- + -ek D). 酈: not listed, chi持: (dr- + -i A), yi益: ('- + -jiek D). (dr- + -jiek D) not listed.
[e]Shigu says: “渾 is pronounced hu胡 + kun昆.”
[Baxter & Sagart: hun渾: (h- + -won A) and (h- + -won B), hu胡: (h- + -u A), kun昆: (k- won A).
[f]Shigu says: “ 鍚 is pronounced yang陽.”
Hedong
Hedong commandery河東郡, Qin set it up [around 285 BC?]. Mang called it Zhaoyang兆陽. Has Gen Granary根倉 and Shi Granary溼倉. 236 896 households, 962 912 people. 24 counties:
[1]Anyi安邑, Wuxian Mountain巫咸山 is to the south. Salt pool鹽池 is to the south-west. Wei Jiang moved from Wei魏 to here. Arriving at King Hui, he moved to Daliang. Has iron official, salt official. Mang called it Hedong河東.
[2]Dayang大陽, Wu Mountain吳山 is to the west. On it is Wu City吳城. King Wu of Zhou ennobled the descendants of Taibo here. This was the Duke of Yu虞公, he was wiped out by Jin. Has the Son of Heaven's Temple天子廟. Mang called it Qintian勤田[a].
[3]Yishi猗氏.
[4]Xie解[b].
[5]Pufan蒲反 has Yao Mountain堯山 and Shou Mountain's Shrines首山祠. Leishou Mountain雷首山 is to the south. Formerly called Pu蒲, Qin changed the name. Mang called it Pucheng蒲城[c].
[6]Heibei河北, the Poetry's Wei state魏國. Duke Xian of Jin wiped it out, and used it to ennoble the Grandee Fubi. His great-grandson Jiang moved to Anyi安邑.
[7]Zuoyi左邑, Mang called it Zhaoting兆亭.
[8]Fenyin汾陰, Jia Mountain介山 is to the south.
[9]Wenxi聞喜, formerly Quwo曲沃. Duke Wu of Jin moved from Jinyang晉陽 to there. Emperor Wu in the 6th Year of Yuanding [111 BC] moved through, and changed the name[d].
[10]Huoze濩澤, in the Tribute of Yu Xicheng Mountain析城山 is to south-west[e].
[11]Duanshi端氏.
[12]Linfen臨汾.
[13]Yuan垣, in Tribute of Yu Wangwu Mountain王屋山 is to the north-east. Yan River沇水 sets out from there, to the south-east arriving at Wude武德 it enters the He河. Yi軼 sets out from Xinyang滎陽 in Beidi北地, and also to the east arrives at Langhuai琅槐 to join the sea, passing through 9 commanderies, travelling 1 840 li[f].
[14]Pishi皮氏. Geng district耿鄉 was formerly Geng state耿國. Duke Xian of Jin wiped it out, and used it to appoint the Grandee Zhao Su. Ten generations later Marquis Xian moved to Zhongmou中牟. Has an iron official. Mang called it Yanping延平.
[15]Changxiu長脩.
[16]Pingyang平陽, Han Wuzi's great-great-grandson Zhenzi resided there. Has an iron official. Mang called it Xiangping香平[g].
[17]Xiangling襄陵, has Banshi district and precinct班氏鄉亭. Mang called it Ganchang幹昌[h].
[18]Zhi彘, Huoda Mountain is to the east, the mountain of Ji province冀州. The place where King Li of Zhou fled. Mang called it Huangcheng黃城[i].
[19]Yang楊, Mang called it Younianting有年亭[j].
[20]Beiqu北屈, in the Tribute of Yu Hukou Mountain壺口山 is to the south-east. Mang called it Zhenbei朕北[k].
[21]Puzi蒲子[l].
[22]Jiang絳, Duke Wu of Jin moved from Quwo曲沃 to there. Has an iron official[m].
[23]Huzhe狐讘[n].
[24]Qi騏, a marquisate[o]
[a]Ying Shao says: “Is on the sunny-side of the Great He大河.”
[b]Shigu says: “Pronounced Xie蟹.”
[c]Ying Shao says: “The First August of Qin toured east and saw a long slope [ban阪], for that reason he added fan反.
Meng Kang says: “Originally Pu蒲. Duke Wen of Jin used it to bribe Qin. Later the people of Qin returned Pu. The people of Wei were happy and said “Pu蒲 has turned around [fan反]”. To speak of Qin naming it is a mistake.”
Your Subject Zan says: “The Generational House of Qin says “Used Yuan垣 as Pufan蒲反.” As such then it was originally not Pu蒲.
Shigu says: “Ying's explanation is correct.”
[d]Ying Shao says: “The present Quwo曲沃. Qin changed it to be Zuoyi. Emperor Wu here heard that the Southern Yue were routed, and changed it to be called Wenxi聞喜 [lit. “Heard the joyful”.]
[e]Ying Shao says: “Has Huo Marsh濩澤, is to the north-west.”
Shigu says: “濩 is pronounced wu烏 + guo虢.”]
[Baxter & Sagart: 濩: not listed, wū烏: ('- + -u A), guó 虢: (k- + -waek D).
Which should give ('- + -waek D) which is the pronunciation Baxter & Sagart lists for wò擭. Zdic.net lists huò as the main pronunciation of 擭.
[f]Shigu says: “ 琅 is pronounced lang郎. 槐 is pronounced hui回.
[g]Ying Shao says: “Yao's capital, it is on the sunny-side of the Ping He平河.”
[h]Ying Shao: “Xiang Mound襄陵 is to the north-west.”
Shigu says: “Duke Xiang of Jin's mound, followed it to use to name the county.”
[i]Ying Shao says: “Emperor Shun changed it to be called Yong'an安.”
[j]Ying Shao says: “Yang楊 was a marquisate.”
[k]Ying Shao says: “Has to the south the former Chengbei稱北.”
Your Subject Zan says: “The Ancient Writings of Ji Commandery : “When Zhai Zhang saved Zheng鄭, he stayed at the southern bend南屈.
Shigu says: “屈 is pronounced ju居 + wu勿. Precisely where the Duke of Jin's son Yiwu stayed.”
[Baxter & Sagart: qū屈: (kh- + -jut D), jū居: (k- + -jo A), wù勿: (m- + -jut D). No (k- + -jut D) listed.]
[l]Ying Shao says: “Formerly Pufan's蒲反 old town, Emperor Wu set it up.”
Shigu says: “Where Chong'er resided. Ying's explanation missed it.”
[m]Ying Shao: “Jiang River絳水 sets out to the south-west.”
[n]Shigu says: “讘 is pronounced zhī之 + shè涉.”]
[Baxter & Sagart: 讘 not listed, zhī之: (tsy- + -i A), 涉 not listed. Guangyun: 涉: 時攝切. Baxter & Sagart: shè攝: (sy + -jep D), (tsy- + -jep D): zhé]
[o]Shigu says: “pronounced qi其.”]
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Random Stuff #9: Daoist Elements and More in The Untamed/MDZS Part 1 - Concepts
(Part 2 Here) (Super-long post ahead!)
Though The Untamed is a Xianxia/仙侠 drama (kind of like fantasy genre), there are some elements in it that had clear roots in Chinese culture, especially religious/philosophical Daoism. So here are some Daoist elements within the world of The Untamed/MDZS:
“Cultivation” (Dao)/道
In Chinese, the “cultivation method” is the “Dao”/“道”, which some of you may recognize as that character that sometimes stands for Daoism. Within Daoism however, that character has a deeper meaning than just a name; in fact it is one of the most important concepts of both philosophical and religious Daoism (it also has a few different meanings, but the world of The Untamed mostly focuses on one of them; Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy has a very comprehensive article entry on Daoism that explains the concept of Dao in detail, for anyone who’s interested in more scholarly explanations). It actually translates best as “way” or “path” (note: when not referring to a specific “way”, it absolutely CANNOT be translated as “the way” or “the path”, and I will get to why that’s important), and basically means a “way” of doing something. For example, to make a salad you might rip the lettuce leaves or cut them with a knife. Both of these methods would be “ways”/道 of making a salad. And as you can see in this example, there are many different ways of arriving at a result or accomplishing a goal. Since Dao encompasses all of the different ways of doing all the different things, it cannot be translated as “the way”, since “the” would imply that “there is only one way”, or “only one right way”, of doing things.

(image credit: My Great Lakes)
This concept that there is more than one way to accomplish something is very important to the story of The Untamed/MDZS, especially in terms of Wei Wuxian. But we have to clarify the “goal” in The Untamed/MDZS first: what was it that these people were trying to accomplish with their different “ways”? Looking at the overall story, it appears that they were all generally trying to do good and uphold justice by warding off or neutralizing supernatural threats. Now that we’ve established the goal, let’s return to WWX. In the story, WWX was forced to give up the regular “cultivation”/ the “sword path”/剑道, instead founding the “demonic cultivation”/”dark path”/魔道 in order to survive the extreme environment of the Burial Mounds and acquire enough power to get revenge on the Wens. Since the Wens killed a lot of people, WWX would also be upholding justice by punishing them for their evil deeds. As the lyrics of the opening song of MDZS animated series puts it: “though his (WWX’s) ‘path’ was different, there was justice within his heart” (道不同义在心中). Conversely, this is also why the sects/clans were wrong to label different “cultivations”/“ways” as good or evil, as both WWX’s “demonic cultivation” and the regular “sword path” could be used as powerful forces for good and evil. Of course, the irony was that while the sects hailed their “sword path” as “the one right path”, they were using it to control each other, instead of using it to do good.


(The two “paths”/daos. How different are they?)
“Cultivation”/修道
Well now that we’ve cleared up what “cultivation”/道 or Dao actually is in the context of the show and what the characters were trying to accomplish with their different “ways”, this “cultivation” or 修道 becomes easier to understand. It means the development (修) of one’s skill in regard to the “path” (道) one has chosen. For example, most characters chose to develop their skills in the “sword path”. In actual religious Daoism, however, since the ultimate end purpose is to become an immortal/仙, 修道 would mean doing something to work towards that immortal status.
“Cultivator”/仙
In Daoism, the character “仙” can be translated as “immortal”, “sage”, or “celestial being”, and refers to the end goal of religious Daoists: to “metamorphose” into an immortal (羽化登仙) (also connotes transitioning into eternal afterlife through death). The characters “羽化” literally mean “to become feathery”, because at least in Western Han dynasty (202 BC-8 AD) figures and tomb murals, such immortals often appeared as humans with feathers or winged humans, and are capable of flight.

Over the next few hundred years, the appearance of immortals gradually morphed into humans that fly by floating, standing on platforms of clouds, or riding birds (often cranes)/mythical creatures.

In the drama and the animated series, 仙 is often used as a descriptor in different words (ex: 仙门, 仙家, 仙侣, 仙缘...etc), rather than a standalone noun. However, it is still a reference to this general idea of training/cultivating oneself to become something greater, and provides a strong connection to Daoism.
“Cultivators”/修士
In Daoism, this term is used less than 道士, but it still means “cultivators of Dao” (修道之人), or simply, “Daoists”. In The Untamed/MDZS, of course, it means practitioners of a “cultivation”/“path”.
“Golden core”/金丹
This one has roots in real life sects of religious Daoism. The translation “golden core” itself is quite literal. “Golden” from the descriptor 金, and “core” for 丹, presumably because it looks like a sort of core. In reality, 丹 is quite hard to translate. Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy translates 丹 as “alchemy”, so I will use “alchemy” for 丹 from here on out. In religious Daoism, there are two types of this alchemy: external and internal, and both are supposed to help one towards immortality. People who practiced “external alchemy”/外丹 basically made “immortality elixirs” (in reality it wasn’t a drink like “elixir” implies, but a ball-shaped chewable) in the hopes that it would give immortality to whoever ate it. This is very much like alchemy in Europe, except instead of trying to turn things into gold, people were making things to eat for immortality. Some fun facts: these elixirs frequently contained heavy metals like mercury and lead, and ironically would shorten people’s lives instead of helping them live longer; also legend has it that an explosive attempt to make elixirs actually led to the invention of gunpowder.

(these appears to be actual products of external alchemy found in an Eastern Jin dynasty tomb, well-preserved due to its high mercury content)
This external alchemy obviously does not apply to “golden core” in The Untamed/MDZS, so let's look at internal alchemy. “Internal alchemy”/內丹 is much more abstract than external alchemy, but in simple terms it is the practice of using meditation and similar strategies to return oneself to a state of emptiness (kind of like “one with nature”). This is probably what the show’s “golden core” was based on. Also another name for “internal alchemy”/內丹 is “golden alchemy”/金丹, literally the same characters as “golden core”/金丹 in the show.

There is one major difference though. While real practitioners of internal alchemy believe that everyone already possess a “golden alchemy” (“golden core”), in the show everyone has to “cultivate” themselves in order to have one in the first place.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text










The Restoration of Traditional Chinese clothing/Hanfu of Han Dynasty from裝束復原團隊(中國裝束復原小組)
The Han Dynasty (202 BC-220 AD) was a unified dynasty following the Qin Dynasty. Divided into the Western Han Dynasty (202 BC - 8 AD)and the Eastern Han Dynasty(25 AD- 220 AD), with a total of 29 emperors. The han Dynasty has a history of 407 years.
the Western Han Dynasty(202 BD - 8AD)
The Xin Dynasty (9 AD – 23 AD) was established by Wang Mang, a relative of the Western Han Dynasty, after the Western Han Dynasty
the Eastern Han Dynasty (25 AD - 220 AD )
#fashion#china#china fashion#chinese fashion#hanfu#men's hanfu#men's fashion#chinese culture#historical costume#chinese hanfu#chinese costumes
101 notes
·
View notes
Text

A western Han dynasty (202 BC - 9 AD) bronze hollow sword hilt inlaid with gold and silver.
The hilt was hollow casted and decorated with gold and silver. There is a dragon-shaped mythological animal standing in the middle. The iron blade rusted away.
From the private collection from Giuseppe Eskenazi (born 1939, in Istanbul), a most important dealers in Chinese works of art.
#jianfa#chineseswordsmanship#chinesemartialart#chineseswordfighting#劍法#sword#swords#chinesehistory#chinesesword#duanbing#historicalsword#historicalswords#swordfighting#swordsmithing
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Palm Reading Research

Palmistry with the meaning of palm reading or hand prediction is to learn a person’s personalities, fortune and future by analyzing his/her hands. It is also called Chiromancy.
reading one’s palm lines, hand shape and size, finger length and flexibility, fingernail…, we can predict his character traits, health, wealth, wisdom, career, marriage and many more aspects
Since the Zhou Dynasty which is about three thousand years ago, it has been prevailed. The first comparatively complete and systematic palmistry work in China appeared in Western Han Dynasty (202 BC - 9 AD) which was written by Xu-Fu. In this article, we introduce how the Chinese people read palms in general.
choose the right hand to read. Some people think the right for female and left for male.
The left hand usually represents what you were born with physically and materially and the right hand represents what you become after grown up.So, the right hand is dominant in palm reading and the left for a supplement.
there are mainly three major lines to read which are Life Line, Head Line (also Wisdom Line) and Heart Line (also Love Line).
Besides, there are also some minor lines which are also important in palm line reading such as Marriage line, Fate line, Sun line, Children Line, Money Line, Health Line, Travel Line, Bracelet Line, Line of Mars, Ring of Solomon, Ring of Saturn, Girdle of Venus, Ring of Apollo and Ring of Mercury.
Small Hands Meaning
People with Big Body But Small Hands Are Often Poor 1. On the contrary, you people with big body but small hands appear to be petty and stingy, thus often in poverty. 2. Comparing with the body, you people with relatively small hands are quick-minded, adaptable, decisive, and impulsive and have nothing to fear; you are bold and open-minded, and you like the decisive work. Women with Small Hands: You women with small hands are not good at sewing and cooking, thus not suitable for the system work but the job related to production and foreign relations. Men with Small Hand: Instead, you men with relatively small hands and well-balanced hand shape will get great wealth. The hand in slight red is a symbol of great fortune. As the saying goes, the small hands can grasp a lot of wealth; it doesn't mean getting a lot of wealth directly but refers to the accumulation of wealth and you never spend money foolishly, thus you will be rich in the future. You men with small hands are always small-sized, so you will not have advantage if you make a living with your body in the competitive society; instead, you should use your head and compete with your resourcefulness. Therefore, you people with small hands can get great wealth.
Pig Hands Meaning
People with Small Body But Big Hands Often Waste Money 1. According to traditional Chinese culture, people with big hands tend to waste money excessively and don't restrain the spending. The Chinese idiom "big hands and feet" means spending extravagantly and it proves the above saying. Usually, you people of this kind have good luck in wealth but you like to spend, thus often live beyond your income. Also, you often spend regardless of the consequences; in modern saying, you are a Moonlite (living from paycheck to paycheck). The proverb "big hands catch grass and little hands grasp treasure" has the same meaning. 2. Comparing with the body, you people with relatively big hands are narrow-minded and prudent and you will never act out without the careful planning, thus suitable for elaborate work and have strong analytical skills. You are conservative and have low demand for material; if you are a woman, you will be immature in handling interpersonal relationships.




0 notes
Photo





Fundamentals Lectures - Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity (sericulture). The shimmering appearance of silk is due to the triangular prism-like structure of the silk fibre, which allows silk cloth to refract incoming light at different angles, thus producing different colors.
Silk is produced by several insects, but generally only the silk of moth caterpillars has been used for textile manufacturing. There has been some research into other types of silk, which differ at the molecular level. Silk is mainly produced by the larvae of insects undergoing complete metamorphosis, but some insects such as webspinners and raspy crickets produce silk throughout their lives. Silk production also occurs in Hymenoptera (bees, wasps, and ants), silverfish, mayflies, thrips, leafhoppers, beetles, lacewings, fleas, flies, and midges. Other types of arthropod produce silk, most notably various arachnids such as spiders.
Several kinds of wild silk, which are produced by caterpillars other than the mulberry silkworm, have been known and used in China, South Asia, and Europe since ancient times. However, the scale of production was always far smaller than for cultivated silks. There are several reasons for this: first, they differ from the domesticated varieties in colour and texture and are therefore less uniform; second, cocoons gathered in the wild have usually had the pupa emerge from them before being discovered so the silk thread that makes up the cocoon has been torn into shorter lengths; and third, many wild cocoons are covered in a mineral layer that prevents attempts to reel from them long strands of silk. Thus, the only way to obtain silk suitable for spinning into textiles in areas where commercial silks are not cultivated was by tedious and labor-intensive carding.
Commercial silks originate from reared silkworm pupae, which are bred to produce a white-colored silk thread with no mineral on the surface. The pupae are killed by either dipping them in boiling water before the adult moths emerge or by piercing them with a needle. These factors all contribute to the ability of the whole cocoon to be unravelled as one continuous thread, permitting a much stronger cloth to be woven from the silk. Wild silks also tend to be more difficult to dye than silk from the cultivated silkworm. A technique known as demineralizing allows the mineral layer around the cocoon of wild silk moths to be removed, leaving only variability in color as a barrier to creating a commercial silk industry based on wild silks in the parts of the world where wild silk moths thrive, such as in Africa and South America.
Genetic modification of domesticated silkworms is used to facilitate the production of more useful types of silk.
Silk fabric was first developed in ancient China. The earliest example of silk fabric is from 3630 BC, and it was used as wrapping for the body of a child from a Yangshao culture site in Qingtaicun at Xingyang, Henan.
Legend gives credit for developing silk to a Chinese empress, Leizu (Hsi-Ling-Shih, Lei-Tzu). Silks were originally reserved for the Emperors of China for their own use and gifts to others, but spread gradually through Chinese culture and trade both geographically and socially, and then to many regions of Asia. Because of its texture and lustre, silk rapidly became a popular luxury fabric in the many areas accessible to Chinese merchants. Silk was in great demand, and became a staple of pre-industrial international trade. In July 2007, archaeologists discovered intricately woven and dyed silk textiles in a tomb in Jiangxi province, dated to the Eastern Zhou Dynasty roughly 2,500 years ago. Although historians have suspected a long history of a formative textile industry in ancient China, this find of silk textiles employing "complicated techniques" of weaving and dyeing provides direct evidence for silks dating before the Mawangdui-discovery and other silks dating to the Han Dynasty (202 BC-220 AD).
Silk is described in a chapter on mulberry planting by Si Shengzhi of the Western Han (206 BC – 9 AD). There is a surviving calendar for silk production in an Eastern Han (25–220 AD) document. The two other known works on silk from the Han period are lost.[10] The first evidence of the long distance silk trade is the finding of silk in the hair of an Egyptian mummy of the 21st dynasty, c.1070 BC. The silk trade reached as far as the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East, Europe, and North Africa. This trade was so extensive that the major set of trade routes between Europe and Asia came to be known as the Silk Road.
The Emperors of China strove to keep knowledge of sericulture secret to maintain the Chinese monopoly. Nonetheless sericulture reached Korea with technological aid from China around 200 BC, the ancient Kingdom of Khotan by AD 50, and India by AD 140.
In the ancient era, silk from China was the most lucrative and sought-after luxury item traded across the Eurasian continent, and many civilizations, such as the ancient Persians, benefited economically from trade.
Silk is also a natural fibre and it is obtained from the cocoon of the silkworm moth. Silk is prized for its fragility and luxury and can be very expensive. Silk is popular among the luxury items due to its unique texture and lustrous appearance. It requires frequent dry cleaning and hand washing is strictly prohibited for silk. It also gets creased and can be damaged if exposed in sunlight. Thus silk must be carefully handled. Silk's absorbency makes it comfortable to wear in warm weather. Its low conductivity keeps warm air close to the skin during cold weather. It is often used for clothing such as shirts, ties, blouses, formal dresses, high fashion clothes, lingerie, pyjamas, robes, dress suits and sun dresses.
0 notes
Text
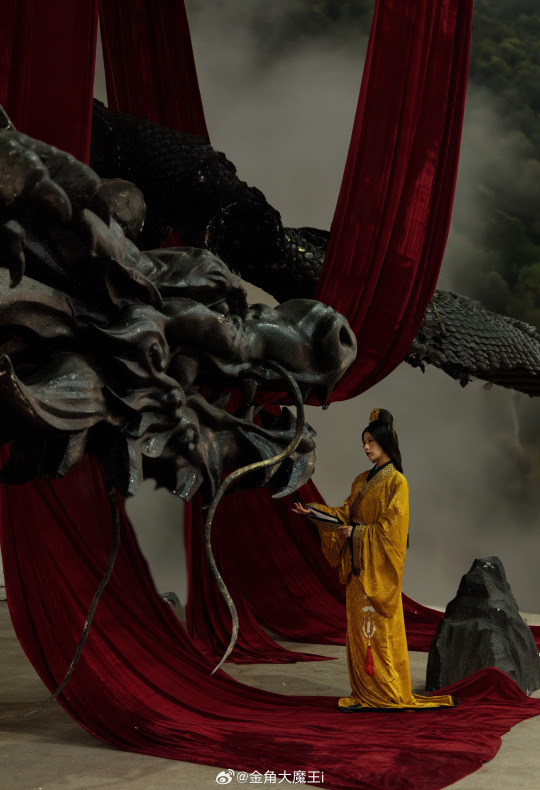
[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) Traditional Clothing Hanfu Photoshoot
“这个位子 我有何坐不得?” “我欲问鼎天下,试问谁与争锋”
"Why can't I sit in this seat?"
"I want to conquer the world, who can compete with me?"
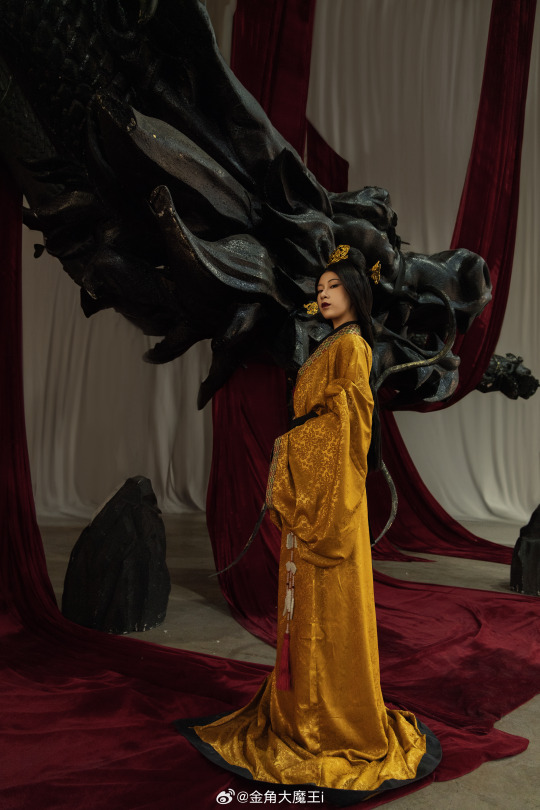
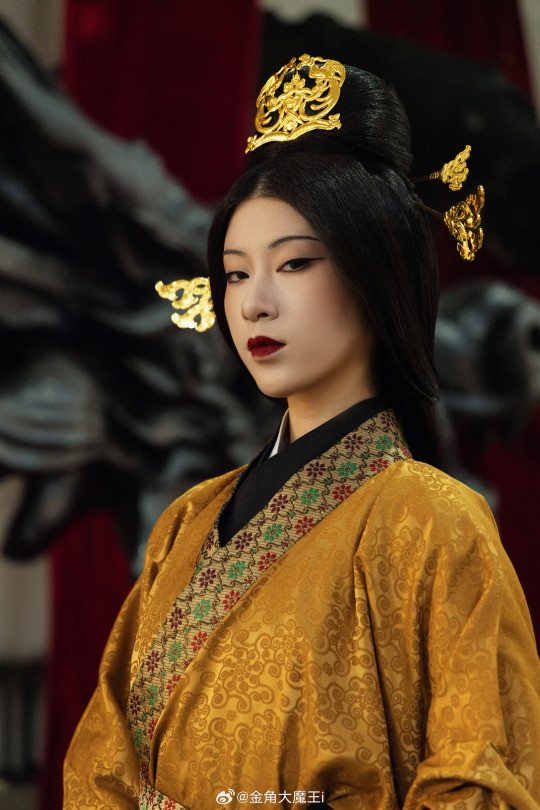
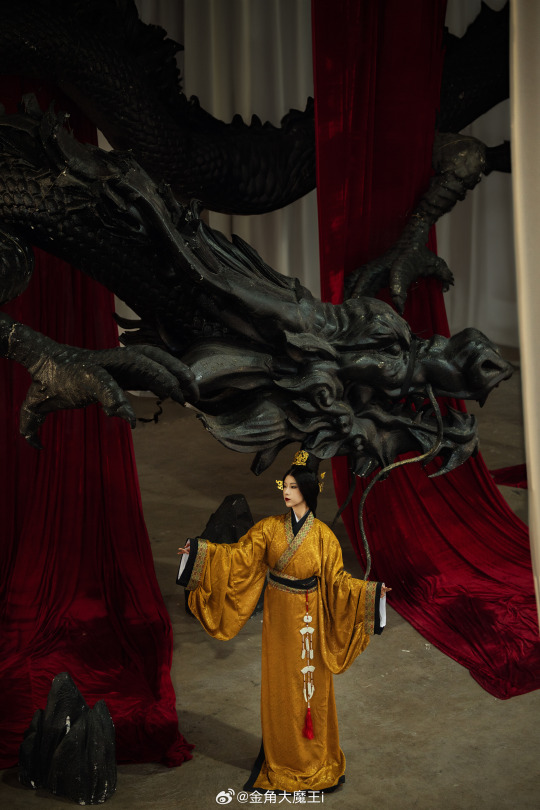








【About The First Empress of the Han Dynasty Empress Lü:Lǚ zhì(吕雉)】
Lü Zhi (241–18 August 180 BC), courtesy name E'xu (娥姁) and commonly known as Empress Lü (traditional Chinese: 呂后; simplified Chinese: 吕后; pinyin: Lǚ Hòu) and formally Empress Gao of Han (漢高后; 汉高后; Hàn Gāo Hòu), was the empress consort of Gaozu, the founding emperor of the Han dynasty. They had two known children, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han) and Princess Yuan of Lu. Lü was the first woman to assume the title Empress of China and paramount power. After Gaozu's death, she was honoured as empress dowager and regent during the short reigns of Emperor Hui and his successors Emperor Qianshao of Han and Liu Hong (Emperor Houshao).
She played a role in the rise and foundation of her husband, Emperor Gaozu, and his dynasty, and in some of the laws and customs laid down by him. Empress Lü, even in the absence of her husband from the capital, killed two prominent generals who played an important role in Gaozu's rise to power, namely Han Xin and Peng Yue, as a lesson for the aristocracy and other generals. In June 195 BC, with the death of Gaozu, Empress Lü became, as the widow of the late emperor and mother of the new emperor, Empress Dowager (皇太后, Huángtàihòu), and assumed a leadership role in her son's administration. Less than a year after Emperor Hui's accession to the throne, in 194 BC, Lü had one of the late Emperor Gaozu's consorts whom she deeply hated, Concubine Qi, put to death in a cruel manner. She also had Concubine Qi's son Liu Ruyi poisoned to death. Emperor Hui was shocked by his mother's cruelty and fell sick for a year, and thereafter no longer became involved in state affairs, and gave more power to his mother. As a result, Empress dowager Lü held the court, listened to the government, spoke on behalf of the emperor, and did everything (臨朝聽政制, "linchao ting zhengzhi"). With the untimely death of her 22-year-old son, Emperor Hui, Empress dowager Lü subsequently proclaimed his two young sons emperor (known historically as Emperor Qianshao and Emperor Houshao respectively). She gained more power than ever before, and these two young emperors had no legitimacy as emperors in history; the history of this 8-year period is considered and recognized as the reign of Empress Dowager Lü. She dominated the political scene for 15 years until her death in August 180 BC, and is often depicted as the first woman to have ruled China. While four women are noted as having been politically active before her—Fu Hao, Yi Jiang, Lady Nanzi, and Queen Dowager Xuan—Lü was the perhaps first woman to have ruled over united China.
Lü Zhi was born in Shanfu County (單父; present-day Shan County, Shandong) during the late Qin Dynasty. Her courtesy name was Exu (Chinese: 娥姁; pinyin: Éxǔ). To flee from enemies, her father Lü Wen (呂文) brought their family to Pei County, settled there, and became a close friend of the county magistrate. Many influential men in town came to visit Lü Wen. Xiao He, then an assistant of the magistrate, was in charge of the seating arrangement and collection of gifts from guests at a banquet in Lü Wen's house, and he announced, "Those who do not offer more than 1,000 coins in gifts shall be seated outside the hall." Liu Bang (later Emperor Gaozu of Han), then a minor patrol officer (亭長), went there bringing a single cent and said, "I offer 10,000 coins." Lü Wen saw Liu Bang and was so impressed with him on first sight, that he immediately stood up and welcomed Liu into the hall to sit beside him. Xiao He told Lü Wen that Liu Bang was not serious, but Liu ignored him and chatted with Lü. Lü Wen said, "I used to predict fortunes for many people but I've never seen someone so exceptional like you before." Lü Wen then offered his daughter Lü Zhi's hand in marriage to Liu Bang and they were wed. Lü Zhi bore Liu Bang a daughter (later Princess Yuan of Lu) and a son, Liu Ying (later Emperor Hui of Han).
Liu Bang later participated in the rebellion against the Qin Dynasty under the insurgent Chu kingdom, nominally-ruled by King Huai II. Lü Zhi and her two children remained with her father and family for most of the time during this period.
Even after Emperor Gaozu (Liu Bang)'s victory over Xiang Yu, there were still unstable areas in the empire, requiring the new government to launch military campaigns to pacify these regions thereafter. Gaozu placed Empress Lü Zhi and the crown prince Liu Ying (Lü Zhi's son) in charge of the capital Chang'an and making key decisions in court, assisted by the chancellor Xiao He and other ministers. During this time, Lü Zhi proved herself to be a competent administrator in domestic affairs, and she quickly established strong working relationships with many of Gaozu's officials, who admired her for her capability and feared her for her ruthlessness. After the war ended and Emperor Gaozu returned, she remained in power and she was always influential in many of the country's affairs.
In his late years, Emperor Gaozu started favouring one of his younger consorts, Concubine Qi(戚夫人), who bore him a son, Liu Ruyi, who was instated as Prince of Zhao in 198 BC, displacing Lü Zhi's son-in-law Zhang Ao (Princess Yuan of Lu's husband). Gaozu had the intention of replacing Liu Ying with Liu Ruyi as crown prince, reasoning that the former was too "soft-hearted and weak" and that the latter resembled him more. Since Lü Zhi had strong rapport with many ministers, they generally opposed Gaozu's decision but the emperor seemed bent on deposing Liu Ying. Lü Zhi became worried and she approached Zhang Liang for help, and the latter analysed that Gaozu was changing the succession on grounds of favouritism. Zhang Liang invited the "Four Whiteheads of Mount Shang", a group of four reclusive wise men, to persuade Gaozu to change his decision. The four men promised to assist Liu Ying in future if he became emperor, and Gaozu was pleased to see that Liu Ying had their support. Gaozu told Concubine Qi, "I wanted to replace (the crown prince). Now I see that he has the support of those four men; he is fully fledged and difficult to unseat. Empress Lü is really in charge!" This marked the end of the dispute over the succession and affirmed Liu Ying's role as crown prince.
In June 195 BC, Emperor Gaozu died and was succeeded by Liu Ying, who became historically known as Emperor Hui of Han. Lü Zhi was honoured by Emperor Hui as empress dowager. She exerted more influence during the reign of her son than she had when she was empress, and she became the powerful and effective lead figure in his administration.
Lü Zhi did not harm most of Gaozu's other consorts and treated them according to the rules and customs of the imperial family. For example, consorts who bore male children that were instated as princes were granted the title of "Princess Dowager" (王太妃) in their respective sons' principalities. One exception was Concubine Qi, whom Lü Zhi greatly resented because of the dispute over the succession between Liu Ruyi (Qi's son) and Liu Ying. Liu Ruyi, the Prince of Zhao, was away in his principality, so Lü Zhi targeted Concubine Qi. She had Qi stripped of her position, treated like a convict (head shaved, in stocks, dressed in prison garb), and forced to do hard labour in the form of milling rice.
Roles in the deaths of Concubine Qi and Liu Ruyi
Lü Zhi then summoned Liu Ruyi, who was around the age of 12 then, to Chang'an, intending to kill him together with his mother. However Zhou Chang (周昌), the chancellor in Liu Ruyi's principality, whom Lü Zhi respected because of his stern opposition to Emperor Gaozu's proposal to make Liu Ruyi crown prince, temporarily protected Liu Ruyi from harm by responding to Lü Zhi's order that, "The Prince of Zhao is ill and unfit for travelling over long distances." Lü Zhi then ordered Zhou Chang to come to the capital, had him detained, and then summoned Liu Ruyi again. Emperor Hui tried to save Liu Ruyi by intercepting his half-brother before the latter entered Chang'an, and kept Liu Ruyi by his side most of the time. Lü Zhi refrained from carrying out her plans for several months because she feared that she might harm Emperor Hui as well.
One morning in the winter of 195-194 BC, Emperor Hui went for a hunting trip and did not bring Liu Ruyi with him because the latter refused to get out of bed. Lü Zhi's chance arrived, so she sent an assassin to force poisoned wine down Liu Ruyi's throat. The young prince was dead by the time Emperor Hui returned. Lü Zhi then had Concubine Qi killed in an inhumane manner: she had Qi's limbs chopped off, eyes gouged out, ears sliced off, nose sliced off, tongue cut out, forced her to drink a potion that made her mute, and had her thrown into a latrine. She called Qi a "human swine" (人彘). Several days later, Emperor Hui was taken to view the "human swine" and was shocked to learn that it was Concubine Qi. He cried loudly and became ill for a long time. He requested to see his mother and said, "This is something done not by a human. As the empress dowager's son, I'll never be able to rule the empire" From then on, Emperor Hui indulged himself in carnal pleasures and ignored state affairs, leaving all of them to his mother, and this caused power to fall completely into her hands.
When Lu first came to the court, she planned to establish the Lu family members as "kings (nobles)". This was not only to commemorate her deceased relatives, but also to strengthen her power in the court. However, Wang Ling, the prime minister at the time, immediately pointed out that the great ancestor Liu Bang(Husband of Lu, founding emperor of Han Dynasty)once killed the white horse and agreed that "if someone who are not Liu family be come the king, the whole world should attack them." Therefore, the move of establishing a foreign surname as the king violated the ancestral system established by Liu Bang and was really inappropriate.
Faced with the obstruction of Wang Ling, Empress Lu responded by deposing him and insisting on honoring her deceased father and two brothers as King Lu Xuan, King Wu Wu, and King Zhao Zhao. After setting this precedent, Lu was out of control. She not only named her three nephews Lu Tai, Lu Chan, and Lu Lu as King Lu, King Liang, and King Zhao respectively, but also named her grandnephew Lu Tong. He was the King of Yan, and his grandson Zhang Yan was granted the title of King of Lu.
In addition, there are also quite a few people with the surname Lu who have been granted the title of marquis. As a result, it can be said that many princes surnamed Lu appeared in the court in the blink of an eye. They controlled the government and became the cornerstone and support for Empress Lu to control the right to speak in the court.
Empress Lu's life was emblematic of the intricate power dynamics of the Han Dynasty in ancient China. Born into a modest family, Lu rose to prominence through her marriage to Emperor Gaozu. Her astute political acumen and strategic alliances allowed her to wield significant influence behind the throne. As the mother of several emperors, she orchestrated their ascensions and manipulated court politics to consolidate power for her family. However, her ruthless pursuit of control and elimination of rivals earned her both admirers and enemies. In the end, her ambitions led to her downfall, as her unchecked power and manipulation of succession angered the nobility.As a result, after her death, the Lu family was retaliated and killed by the nobles and courtiers who supported the Han Dynasty, and the family was almost exterminated.Empress Lu's life illustrates the delicate balance of power, ambition, and intrigue in ancient Chinese imperial courts.
Literati in every dynasty in China often likened women who attempted to participate in government affairs and influence national policies to Empress Lü, saying they were vicious. One of them was Wu Zetian, the first official female emperor of China. However, compared with Empress Lü, Wu Zetian was more talented. Unlike Empress Lü, who was simply vicious, she ignored the system and stability of the empire and put personal and family interests first.
________________
📸Photo & Model :@金角大魔王i
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1763668330/NFVOXthxX
________________
#chinese hanfu#Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD)#hanfu#Empress Lü#Lǚ zhì(吕雉)#china history#chinese history#hanfu accessories#hanfu_challenge#chinese traditional clothing#china#chinese#woman in history#漢服#汉服#中華風#金角大魔王i#historical fashion
323 notes
·
View notes
Text
[Hanfu · 漢服]China's national Important Cultural Relics Impression Series By Artist @陆曼陀
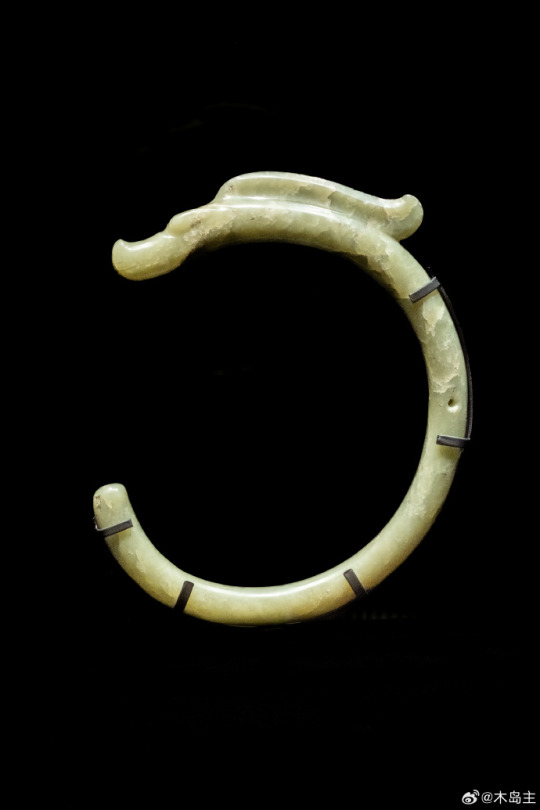
China Neolithic Period:The Hongshan culture(4700-2900 BC)Relics<玉猪龙/Pig dragon>

China Shang dynasty / Western Zhou dynasty(1200–800 BC) · Shu state Relics < 太阳神鸟金饰/Golden Sun Bird>


China Western Han Dynasty (202 BC – 9 AD)Artifact Relics<长信宫灯/oil lamp in the shape of a kneeling female servant>


After the lamp is lit, the soot enters the base of the palace lantern through the sleeve to achieve the purpose of cleaning the air.

China Eastern Han Dynasty(25–220 AD)Artifact Relics<铜奔马 or the Galloping Horse Treading on a Flying Swallow (馬踏飛燕)>


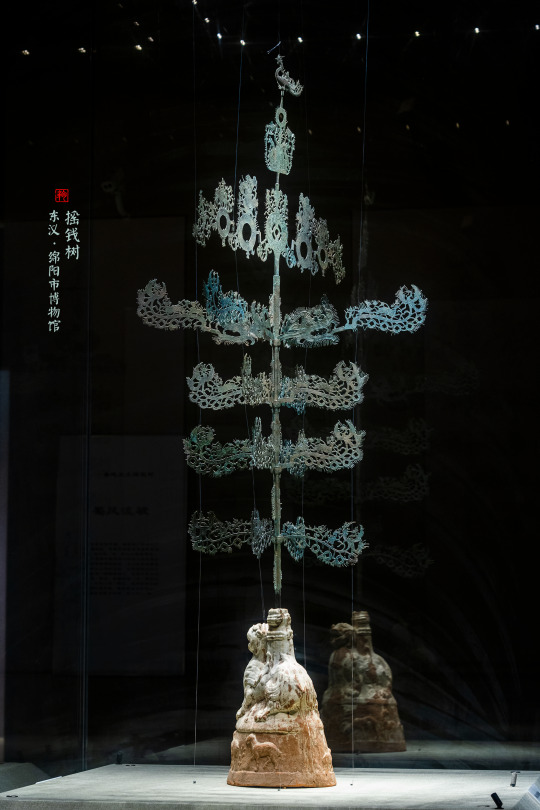
China Eastern Han Dynasty(25–220 AD) Artifact Relics<摇钱树/Money tree (myth)>


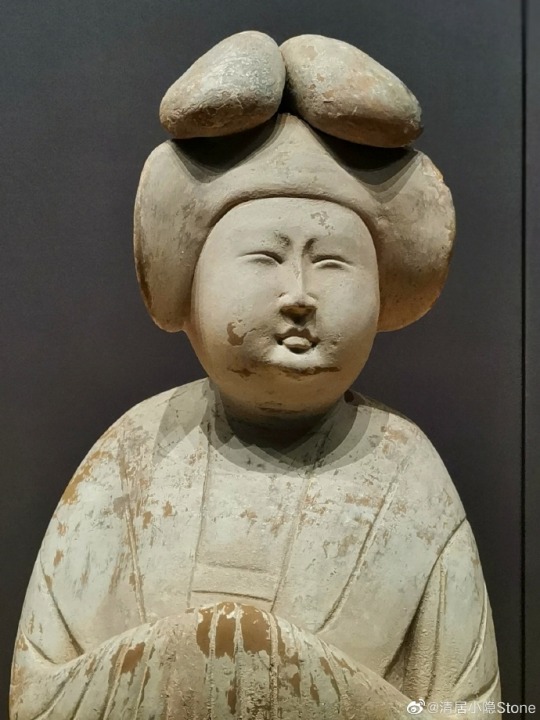
China Tang Dynasty(618–907CE) Artifact Relics<女立俑/Female standing figurine >


China Song Dynasty (960–1279) Artifact Relics<汝窑天蓝釉刻花鹅颈瓶/Ru kiln sky blue glaze carved gooseneck bottle>


China Song Dynasty (960–1279) Painting<千里江山图/A Thousand Li of Rivers and Mountains>by 王希孟(Wang Ximeng)



China Yuan dynasty (1279–1368) Artifact Relics<霁蓝釉白龙纹梅瓶/Ji blue-glazed plum vase with white dragon pattern>
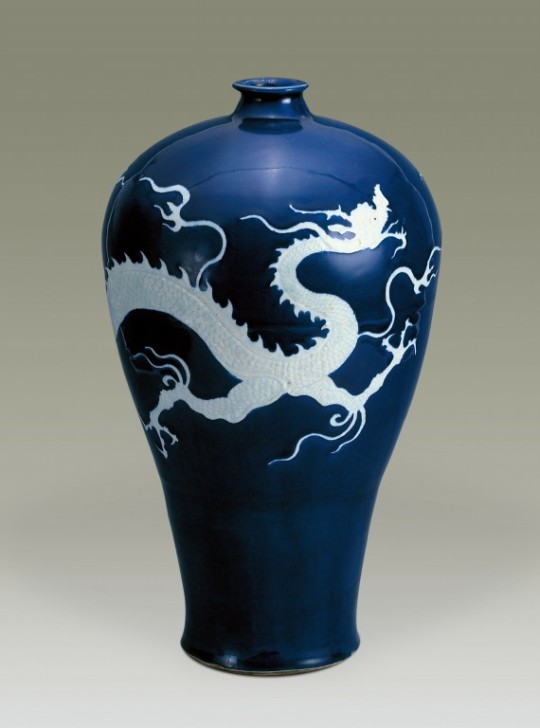


【Artist:陆曼陀 Social Media】 ————————
Twitter:https://twitter.com/LuDanling
Weibo:https://weibo.com/u/2846691957
Post Source:https://weibo.com/2846691957/NzQ9IyzKL
————————
#chinese hanfu#陆曼陀#China history#chinese art#hanfu illustration#hanfu accessories#hanfu#hanfu history#china#chinese#history#chinese aesthetics#culture relic#汉服#漢服#heritage#civilization
456 notes
·
View notes
Photo











【Reference Artifacts】
Chinese Western Han Dynasty-Eastern Han Dynasty(202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD) Murals and Stone Carvings
the court dress of Civil Officials during the Eastern Han(25-220)dynasty.




[Hanfu · 漢服]Chinese Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 A.D.) Hanfu-Civil Officials Based On Han Dynasty Relics
【History Note】
In the Eastern Han Dynasty, officials were divided into civil officials(文官) and military officials (武官),and civil officials usually wore black robes and a cloth crown called "Jinxian Crown/進賢冠" on their heads.
The military officer (武官) is different from the civilian officer. They wear red robes and wear a crown call” Wubian DaGuan/Huben crown(武弁大冠 or 虎贲冠)”,These crown is characterized by always having two feathers on it
Refer to the picture below to distinguish between civil officials and military officials in the Eastern Han Dynasty
pic from Romance of the Three Kingdoms (TV series in 1994)

During the Three Kingdoms period(220–280 AD) in China (the end of the Eastern Han Dynasty), Zhuge Liang(諸葛亮), a well-known Chinese military engineer, strategist, statesman, and writer should wear the above civil official clothes when meet the emperor instead of wearing the clothes like below:

・↑Portrait of Zhuge Liang in the China Ming Dynasty(1368-1644 AD).

・↑The image of Zhuge Liang produced by a Japanese game company
----
The above image is the image of Zhuge Liang imagined by later generations combine with the actual costumes at the Song Dynasty(960–1279 AD) in China.
The Three Kingdoms game, including those made by the Japanese, is also based on the image of Zhuge Liang imagined and drawn by people after the Song Dynasty(960–1279 AD).
Which is not conform to the clothing that Zhuge Liang should have worn in Three Kingdoms period(220–280 AD,the end of the Eastern Han Dynasty)
________________
🙋♂️Model & Recreation Work:@柿子菌stargazer
📸Photo: @张宇莹-小花
🎨Painting Artist:@白人阿又
🔗Weibo:https://weibo.com/1812652835/N1w7AClHo & https://weibo.com/6137313995/Msbxt7ynG
________________
#chinese hanfu#Eastern Han Dynasty#Three Kingdoms period(220–280 AD)#Civil Officials#military officer#Zhuge Liang#Jinxian Crown/進賢冠#Wubian DaGuan/Huben crown(武弁大冠 or 虎贲冠)#皂緣中衣#皂禪衣#柿子菌stargazer#张宇莹-小花#白人阿又#hanfu#historical clothing#historical fashion#hanfu history#漢服#hanfu accessories#hanfu artifacts
326 notes
·
View notes