#Virus Omicron
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang Selatan | 0813-8299-9966 | Garda Pest
Memerlukan Info Untuk Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang Selatan ? Segera Hubungi Customer Service Garda Pest Control di 0813-1344-4221 Layanan 24 Jam – Harga Terjangkau – Teknisi Profesional dan Tersertifikasi Assphami, Dapatkan Promo Diskon 10% atau Free Disinfektan Virus 1 Unit Mobil Untuk Pemesanan Via Aplikasi. Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang Selatan Pada tahun 2023, dunia terus…

View On WordPress
#Jasa Disinfektan#Jasa Disinfektan Bandung#Jasa Disinfektan Bank#Jasa Disinfektan Bekasi#Jasa Disinfektan Covid 19#Jasa Disinfektan di Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Kantor Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Mobil Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Rumah Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan Jogja#Jasa Disinfektan Rumah#Jasa Disinfektan Rumah Setelah Covid#Jasa Disinfektan Sekolah#Jasa Disinfektan Virus Varian Baru#Jasa Penyemprotan Disinfektan#Jasa Penyemprotan Disinfektan Covid#Jasa Semprot Disinfektan#Virus Omicron#Virus Varian EG.5#Virus Varian Eris
0 notes
Text
Ok futurama covid episode is a little taxing but I gotta give them credit for the omicron variant joke
#veesaysthings#futurama#for those who don’t know: there’s a group of recurring characters on futurama from the planet Omicron Persei 8#and they’ve been appearing on the show like almost since the beginning#so of course in the episode about the ‘explovid’ virus they made a joke about these characters getting the ‘omicron variant’#like the joke was right there so slightly low hanging fruit#but it’s hilarious that they had the whole omicron setup years before covid ever existed
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Evolusi dan Dampak Varian Baru COVID-19 Terkini
COVID-19 terus menjadi ancaman global, meskipun vaksinasi dan pengobatan telah berkembang pesat. Salah satu tantangan terbesar yang dihadapi oleh dunia adalah munculnya varian-varian baru dari virus ini. Menurut www.igcp585.org, varian Omicron dan subvarian XBB, misalnya, telah menjadi sorotan utama karena sifat mutasinya yang cepat dan dampaknya terhadap tingkat infeksi, keparahan penyakit,…
0 notes
Text

[x]
#Forbiddenclothes#covid#vaccines#public health#pandemic#plandemic#shot#boosters#omicron#CDC#WHO#virus#china#one world government#politics#vaxxed#medicine#big pharma#health care#us healthcare#insurance#scam#scamdemic
1 note
·
View note
Text
The global death rate did decline dramatically after Omicron.
0 notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
By Anthony Robledo
The side effects of newly discovered COVID-19 strain XEC might not be as severe, but is part of the more contagious variant class, experts say.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines XEC as recombinant or hybrid of the strains KS.1.1 and KP.3.3., both from the Omicron family that became the predominant strain in the U.S. late December 2022.
The variant, which first appeared in Berlin in late June, has increasingly seen hundreds of cases in Germany, France, Denmark and Netherlands, according to a report by Australia-based data integration specialist Mike Honey.
XEC has also been reported in at least 25 U.S. states though there could be more as genetic testing is not done on every positive test, RTI International epidemiologist Joëlla W. Adams said.
"We often use what happens in Europe as a good indication of what might happen here," Adams told USA TODAY Friday. "Whenever we're entering into a season where we have multiple viruses occurring at the same time, like we're entering into flu season, that obviously complicates things."
What is the XEC variant? New COVID strain XEC is a recombinant strain of two variants in the Omicron family: KS.1.1 and KP.3.3.
The hybrid strain was first reported in Berlin late June but has spread across Europe, North America and Asia with the countries Germany, France, the Netherlands and Denmark leading cases.
Is the XEC variant more contagious? While there's no indication the XEC strain will increase the severity of virus, it could potentially become a dominant strain as Omicron variants are more contagious. However, current available COVID-19 vaccines and booster shots are particularly protective against XEC as it is a hybrid of two Omicron strains.
"These strains do have the advantage in the fact that they are more transmissible compared to other families, and so the vaccines that are currently being offered were not based off of the XEC variant, but they are related," Adams said.
Like other respiratory infections, COVID-19 and its recent Omicron variants will increasingly spread during the fall and winter seasons as students return to classes, kids spend more time inside and people visit family for the holidays, according to Adams.
How can we protect ourselves from XEC and other variants? The CDC continues to monitor the emergence of variants in the population, according to spokesperson Rosa Norman.
"At this time, we anticipate that COVID-19 treatments and vaccines will continue to work against all circulating variants," Norman said in a statement to USA TODAY. "CDC will continue to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and vaccines against circulating variants."
The CDC recommends that everyone ages 6 months and older, with some exceptions, receive an updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccine to protect against the virus, regardless whether or not you have previously been vaccinated or infected.
Norman urged Americans to monitor the agency's COVID Data Tracker for updates to new variants.
KP.3.1.1:This dominant COVID-19 variant accounts for over 50% of cases, new CDC data shows
What is the dominant strain of COVID in the US? COVID-19 variant KP.3.1.1 is currently the dominant strain accounting for more than half of positive infections in the U.S. according to recent CDC projections.
Between Sept. 1 and Sept. 14, 52.7% of positive infections were of the KP.3.1.1 strain, followed by KP.2.3 at 12.2%, according to the agency's Nowcast data tracker, which displays COVID-19 estimates and projections for two-week periods.
KP.3.1.1 first became the dominant strain in the two-week period, starting on July 21st and ending on August 3rd.
"The KP.3.1.1 variant is very similar to other circulating variants in the United States. All current lineages are descendants of JN.1, which emerged in late 2023," Norman previously told USA TODAY.
COVID XEC symptoms There is no indication that the XEC variant comes with its own unique symptoms.
The CDC continues to outline the basic COVID-19 symptoms, which can appear between two to 14 days after exposure to the virus and can range from mild to severe.
These are some of the symptoms of COVID-19:
Fever or chills Cough Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing Fatigue Muscle or body aches Headache Loss of taste or smell Sore throat Congestion or runny nose Nausea or vomiting Diarrhea
The CDC said you should seek medical attention if you have the following symptoms:
Trouble breathing Persistent pain or pressure in the chest New confusion Inability to wake or stay awake Pale, gray or blue-colored skin, lips, or nail beds
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
COVID-19 Crisis: OCTA says Metro Manila positivity rate may peak by next week
As the number of new cases of COVID-19 infection continues to rise here in the Philippines, OCTA Research announced that the positivity rate in Metro Manila may peak next week, according to a Manila Bulletin news report. To put things in perspective, posted below is an excerpt from the Manila Bulletin news article. Some parts in boldface… The Covid-19 positivity rate in Metro Manila may peak…
View On WordPress
#anti-vaccine#anti-vaxxers#Carlo Carrasco#China virus#Coronavirus#COVID-19#COVID-19 booster#COVID-19 Crisis#COVID-19 vaccine#disease#free COVID-19 vaccines#health#journalism#Manila Bulletin#Metro Manila#National Capital Region (NCR)#NCR#news#OCTA Research Group#Omicron#Omicron variant#Philippines#Philippines blog
0 notes
Text
h3n2 | h3n2 virus | virus | corona virus | omicron virus | covid 19 | covid cases | covid news | covid news india
After Corona now H3N2 wreaks havoc, one person lost his life in Karnataka, you should also take these precautions It is being told that the old man suffering from the H3N2 virus died on March 1 itself and after his death, people in the surrounding areas of his village have also been investigated. Image Source: Pixabay Representational One person has died due to the H3N2 virus in…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Omicron Much Less Likely to Cause Long COVID, Study Finds
March 10, 2023 – Health care workers infected with the COVID-19 Omicron variant were far less likely to experience significant long COVID symptoms than those who contracted the original SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to new research out of Switzerland. The results, which will be presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases conference in April and have been peer…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
the COVID 2024-2025 vaccine is now available in some areas, please look into getting yours ASAP
i am a COVID survivor who is dealing with long COVID and permanent lung damage due to having caught the virus in October of 2023. this isn't a flu or a cold. this disease causes serious, permanent long term damage. i'm still struggling with even worse brain fog than i already had previously and sometimes it becomes extremely hard for me to breathe, even in good conditions.
COVID has been surging like crazy in the US this summer due to folks socializing more closely and masking no longer being required in most places. social distancing does not happen here anymore. we need to protect ourselves even while there are not mandates and rules in place stating that you MUST be masked (you still should be masking).
the CDC is stating that everyone ages 6 months and older should get the 2024–2025 COVID-19 vaccine:

even if you have been vaccinated in the past you still need to keep up with current vaccines as their protection decreases over time, and COVID continues to mutate and become different strains that are resistant to previous vaccines. staying up to date and masking are the only ways to stay safe. viruses mutate to adapt to their hosts, and COVID is no different.
there are currently 5 variants of the Omicron strain of COVID that are responsible for the uptick in recent cases:

from a COVID survivor who doesn't want to go through this shit a second time: vaccinate. wear your masks. wash your hands. social distance. quarantine when sick. take this seriously. it's been 4 years and COVID has done nothing but prove it is here to stay unless we make a huge change in our society.
#covid#covid 19#disability#pandemic#disabled#actually disabled#covid survivor#cripple punk#physical disability#crip punk#cpunk#punk#our writing
734 notes
·
View notes
Text
Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang | 0813-8299-9966 | Garda Pest
Memerlukan Info Untuk Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang ? Segera Hubungi Customer Service Garda Pest Control di 0813-1344-4221 Layanan 24 Jam – Harga Terjangkau – Teknisi Profesional dan Tersertifikasi Aspphami, Dapatkan Promo Diskon 10% atau Free Disinfektan Virus 1 Unit Mobil Untuk Pemesanan Via Aplikasi. Jasa Disinfektan Rumah di Tangerang Pada tahun 2023, dunia terus memperhatikan…

View On WordPress
#Jasa Disinfektan#Jasa Disinfektan Bandung#Jasa Disinfektan Bank#Jasa Disinfektan Bekasi#Jasa Disinfektan Covid 19#Jasa Disinfektan di Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Kantor Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Mobil Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan di Rumah Jakarta#Jasa Disinfektan Jogja#Jasa Disinfektan Rumah#Jasa Disinfektan Rumah Setelah Covid#Jasa Disinfektan Sekolah#Jasa Disinfektan Virus Varian Baru#Jasa Penyemprotan Disinfektan#Jasa Penyemprotan Disinfektan Covid#Jasa Semprot Disinfektan#Virus Omicron#Virus Varian EG.5#Virus Varian Eris
0 notes
Note
What is the greatest of all speculative fiction novels?
What makes a novel great is very subjective. Dune and 1984 are among the most famous, Frankenstein is often credited with inventing the genre, and Valhalla is the top favorite novel of nearly four people. It's also half off from the publisher right now.
But most people familiar with "Far Beyond the Machine" by Rudy T.F. Cloutier agree that if nothing else, it is the novel that best predicted the future. Written in 1972, it depicts the then-distant future of 2022 where the world population is passing 8 billion people and a virus called "The Omicron" is wreaking havoc across the globe. Meanwhile, the USSR has broken up and Russia has declared war on Ukraine.
The plot is a fairly typical spy story in which the heroic Agent 909 has been tasked with recovering a hard drive with critical information about the Russian plans. Surprisingly for a 1972 novel written when a 1MB hard drive weighed several pounds, the drive in the novel is stated to hold 16GB but is only the size of a thumbnail.
Most surprisingly, the novel features the use of "Motorolas," in reference to the then upcoming, just-announced 1973 release of the first public mobile phone. In the world of Cloutier's 2022, these are described not as giant cordless beasts like the real thing, but as tiny handheld computers that can look up any information in the encyclopedia, give directions to a safe-house, take and send photos, and even in once scene, access a computer-dating service.
Though the book is celebrated for its exceedingly prophetic vision of 2022, its sequel was not at all well received, with critics claiming its vision of 2026 as a post-apocalyptic wasteland where rich fascists have seized America and condemned its citizens to slavery and death for their own financial gain was too depressing, and the new main character Agent 020 was derided as a "Mary Sue."
277 notes
·
View notes
Text
Updated vaccines against Covid-19 are coming, just as hospitalizations and deaths due to the virus are steadily ticking up again.
Today, the US Food and Drug Administration authorized new mRNA booster shots from Moderna and Pfizer, and a panel of outside experts that advises the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention voted to recommend the shots to everyone in the United States ages 6 months and older. Once Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Mandy Cohen signs off on the recommendations and the vaccines are shipped, people can start getting the boosters.
The recommendation is projected to prevent about 400,000 hospitalizations and 40,000 deaths over the next two years, according to data presented at the meeting by CDC epidemiologist Megan Wallace.
This year’s mRNA vaccines are different from the 2022 booster in a key way. Last year’s shot was a bivalent vaccine, meaning it covered two variants: the original one that emerged in China in 2019, plus the Omicron subvariant BA.5, which was circulating during much of 2022. This fall’s booster drops the original variant, which is no longer circulating and is unlikely to return. It targets just the Omicron subvariant XBB.1.5, which was dominant throughout much of 2023.
Pfizer and Moderna’s vaccines work by introducing a tiny piece of genetic material called messenger RNA, or mRNA, that carries instructions for making SARS-CoV-2’s characteristic spike protein. Once it is injected, cells in the body use those instructions to temporarily make the spike protein. The immune system recognizes the protein as foreign and generates antibodies against it. Those antibodies stick around so that if they encounter that foreign invader again, they will mount a response against it.
Since the start of the Covid-19 pandemic, the virus has acquired new mutations in its spike protein and elsewhere. These mutations result in new variants and subvariants that diverge from the original virus. When enough mutations accumulate, these new versions can more easily evade the antibodies created by previous vaccine doses or infections.
The constantly evolving nature of the virus is the reason health regulators decided last year to update the original mRNA vaccines, which were designed against the version of the virus that first appeared in 2019. This year, once again, the virus has changed enough to warrant an updated booster.
In June, an advisory committee to the FDA recommended that this fall’s booster be a monovalent vaccine—targeting only the then-dominant XBB.1.5 subvariant.
At that meeting, committee members reviewed evidence suggesting that the inclusion of the original variant may hamper the booster’s effectiveness against newer offshoots. “The previous bivalent vaccine contained the ancestral spike and thus skewed immune responses to the old spike,” says David Ho, a professor of microbiology at Columbia University whose research, which is not yet peer-reviewed, was among the evidence the FDA panel reviewed. “This is what we call immunological imprinting, and it results in lack of immune responses to the new spike.” He thinks taking out the old variant should optimize the immune response.
But over the past few months, even newer Omicron offshoots have arrived. Currently, EG.5.1, or Eris, is the dominant one in the United States, United Kingdom, and China. Meanwhile, a variant called BA.2.86, or Pirola, has been detected in several countries. Pirola has raised alarm bells because it has more than 30 new mutations compared to XBB.1.5.
Even though the new boosters were formulated against XBB.1.5, they’re still expected to provide protection against these new variants. “The reason is, while antibodies are important in protection against mild disease, the critical part of the immune response that’s important for protecting against severe disease is T cells,” says Paul Offit, a professor of vaccinology at the University of Pennsylvania and member of the FDA’s vaccine advisory committee.
These cells are a different part of the immune response. Unlike antibodies, which neutralize a pathogen by preventing it from infecting cells, T cells work by eliminating the cells that have already been invaded and boosting creation of more antibodies. Both the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech Covid vaccines produce long-lasting T cells in addition to antibodies.
It’s why, Offit says, when the Omicron wave hit in late 2021 and peaked in January 2022, the US didn’t see a dramatic increase in hospitalizations and deaths even as cases rose significantly: People’s T cells kicked into gear, even when their antibodies didn’t recognize the Omicron variant.
“In some ways,” says Offit, when it comes to vaccine booster development, “it almost doesn’t matter what we pick to target” because the coronavirus has yet to evolve away from T cell recognition. “Everything works.”
Scientists think T cells are able to protect against severe Covid because they’re recognizing parts of the virus that have remained unchanged throughout the pandemic. “I suspect that as we continue to vaccinate, there are some conserved regions [of the virus],” says Jacqueline Miller, Moderna’s head of infectious diseases. “So even with the accumulation of mutations, we’re still building on previous immunity.”
People who have hybrid immunity—that is, have had a Covid infection and have also been vaccinated—seem to have the best immune responses to new variants, she says, which suggests that previous exposure shapes and improves immune responses to new variants. Preliminary studies show that antibodies generated by previous infections and vaccinations should be capable of neutralizing Pirola.
Earlier this month, Moderna issued a press release saying that clinical trial data showed that its updated booster generated a strong immune response against Pirola, as well as the more prevalent Eris variant.
In a statement to WIRED, Pfizer spokesperson Jerica Pitts said the company continues to closely monitor emerging variants and conduct tests of its updated monovalent booster against them. Data presented at Tuesday’s CDC meeting showed that Pfizer-BioNTech’s updated booster elicited a strong neutralizing antibody response against both Eris and Pirola.
The FDA expects that Covid-19 vaccines will continue to be updated on an annual basis, unless a completely new variant emerges that requires a different approach. “We will always be a little behind the virus,” says Ho. “In this instance, we won’t suffer too much, but that might not be the case going forward. Surveillance is imperative.”
813 notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm sorry I'm sending so many asks. I've been struggling like this for a year now, and it's barely gotten easier, but you've often been a good help with my anxiety. I really appreciate everything you do. It's hard to have hope.
I've had a really bad moment again recently. I have to be honest, the worst thing, that makes me the most anxious out of everything else, is COVID. Because it feels like nobody is paying attention, and that there is no good news. There is never any good news. COVID is always the catalyst for the worst of my anxious slumps. It's really bad. COVID is very, very scary. If you somehow have anything for that, I'd be thankful. Often I've only been able to set my heart on nasal vaccines, or next gen vaccines in general, but they're not going fast enough whatsoever.
I'm sorry, again. I don't want to try and treat you like a therapist. I just trust you. If this is too overwhelming, you can just delete it, but if you do, I'd like to know. Just so I'm not waiting for it to be answered.
I just ravaged through someone's doomy collapse blog, again, after stumbling on it in my rising anxiousness, and it was not good. I think I'm clearly too open-minded of a person to some degree, and I feel so pulled around by information that I see. I don't want to be placated, out of the loop, or lied to, but I don't want to feel hopelessly depressed. Everything is too complex. I feel like I've been through this maze, top to bottom, over and over again, and again. I just wish I knew how much truth their words held, or anyone else's words held.
And I wish we were all masking, at the very least. I'm holding myself back from swearing. I don't know if you'd have a good way to counteract general "collapse" thoughts, either. But that's also a thing.
<3 I'm touched by your trust.
I just found some good news about COVID - the first genuinely good covid-related news article I've seen in a while, instead of all of the "ah but young abled people are fine!" bs - and remembered this ask.
"As new varieties of the coronavirus took center stage during the COVID-19 pandemic, the odds of developing long COVID dropped. Those who were vaccinated against the virus saw the biggest plunge over time.
For every 1,000 unvaccinated people, 104 developed long COVID up to one year after an infection during the pre-delta phase of the pandemic. That fell to 95 per 1,000 during the delta variant’s era and 78 during omicron’s reign. Among vaccinated people, just 53 out of 1,000 developed long COVID up to a year after infection during delta and only 35 during omicron, researchers report July 17 [2024] in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The study of U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Health Care System data looked at people who had a COVID infection from March of 2020 — the month the pandemic began — to the end of January in 2022. The researchers, from the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System, compared the rates of long COVID during three phases of the pandemic among those who had and had not gotten vaccinated...
A comparison of omicron infections with infections from prior eras found that 72 percent of the drop in the long COVID rate during omicron was attributable to vaccines. The remainder was due to changes in the virus and improvements in medical care and the use of antiviral treatments during the omicron phase.
Even with the steep decline in the occurrence of long COVID for vaccinated people, there is still a risk, the researchers write. With “the large numbers of ongoing new infections and reinfections, and the poor uptake of vaccination,” they continue, this “may translate into a high number of persons” with long COVID."
-via ScienceNews, July 17, 2024
--
Masking continues to be important. The virus continues to be a problem. But especially given the decline in masking, I'm really encouraged to see this news. Because long covid IS scary. And I'll take any good news on this front that I can get.
It's especially encouraging because it shows how much staying on top of your vaccinations really does matter and really can prevent long covid.
I'm also really hopeful (though I don't have a related background and have no idea how realistic my hopes are) that this trend has been continuing past the end of the study (2022).
#dyingpleasehelp#covid#long covid#covid 19#covid isn't over#coronavirus#pandemic#covid19#epidemiology#virology#good news#hope
205 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello! First of all, thank you for the wonderful content! It's a real joy, and an enrichment, food for both the brain and the heart! I was wondering if through your treasures, you could find some writing notes/words/concepts/vocabulary relating to genetic engineering? Like...creating a virus, and a vaccine for it, modifying the virus so it has certain specific effects.... Thank you in advance!
Writing Notes: Virus & Vaccine
References How Viruses Work; Replication Cycle; Mutation, Variants, Strains, Genetically Engineering Viruses; Writing Tips; Creating your Fictional Virus & Vaccine
Virus - an infectious microbe consisting of a segment of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
It is a tiny lifeform that is a collection of genes inside a protective shell. Viruses can invade body cells where they multiply, causing illnesses.
It cannot replicate alone; instead, it must infect cells and use components of the host cell to make copies of itself. Often, a virus ends up killing the host cell in the process, causing damage to the host organism.
Well-known examples of viruses causing human disease include AIDS, COVID-19, measles and smallpox. Examples of viruses:
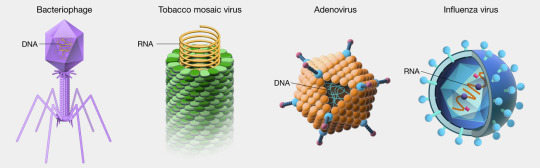
Viruses are even smaller than bacteria and can invade living cells—including bacteria. They may interfere with the host genes, and when they move from host to host, they may take host genes with them.
Bacteriophages (also known as phages)—viruses that infect and kill bacteria.

Size differential between virus and bacterium
Viruses are measured in nanometers (nm).
They lack the cellular structure of bacteria, being just particles of protein and genetic material.
How Viruses Work
Viruses use an organism’s cells to survive and reproduce.
They travel from one organism to another.
Viruses can make themselves into a particle called a virion.
This allows the virus to survive temporarily outside of a host organism. When it enters the host, it attaches to a cell. A virus then takes over the cell’s reproductive mechanisms for its own use and creates more virions.
The virions destroy the cell as they burst out of it to infect more cells.
Viral shedding - when an infected person releases the virus into the environment by coughing, speaking, touching a surface, or shedding skin.
Viruses also can be shed through blood, feces, or bodily fluids.
Virus Replication Cycle
While the replication cycle of viruses can vary from virus to virus, there is a general pattern that can be described, consisting of 5 steps:
Attachment – the virion attaches to the correct host cell.
Penetration or Viral Entry – the virus or viral nucleic acid gains entrance into the cell.
Synthesis – the viral proteins and nucleic acid copies are manufactured by the cells’ machinery.
Assembly – viruses are produced from the viral components.
Release – newly formed virions are released from the cell.
Mutations, Variants, and Strains
Not all mutations cause variants and strains. Below are definitions that explain how mutations, variants, and strains differ.
Mutation - errors in the replication of the virus’s genetic code; can be beneficial to the virus, deleterious to the virus, or neutral
Variants - viruses with these mutations are called variants; the Delta and Omicron variants are examples of coronavirus mutations that cause different symptoms from the original infection
Strains - variants that have different physical properties are called strains; these strains may have different behaviors or mechanisms for infection or reproduction
Genetically Engineering Viruses
Using reverse genetics, the sequence of a viral genome can be identified, including that of its different strains and variants.
This enables scientists to identify sequences of the virus that enable it to bind to a receptor, as well as those regions that cause it to be so virulent.
Vaccine - a special preparation of substances that stimulate an immune response, used for inoculation
Vaccines & Fighting Viruses with Viruses
Common pathogenic viruses can be genetically modified to make them less pathogenic, such that their virulent properties are diminished but can still be recognized by the immune system to produce a robust immune response against. They are described as live attenuated.
This is the basis of many successful vaccines and is a better alternative than traditional vaccine development which typically includes heat-mediated disabling of viruses that tend to be poorer in terms of immunogenicity.
Viruses can also be genetically modified to ‘fight viruses’ by boosting immune cells to make more effective antibodies, especially where vaccines fail. Where vaccines fail, it is often due to the impaired antibody production by B-cells, even though antibodies can be raised against such viruses – including HIV, EBV, RSV & cold-viruses.
Related Articles: Modified virus used to kill cancer cells ⚜ Genetic Engineering ⚜ Engineering Bacterial Viruses ⚜ Benefits of Viruses
A Few Writing Tips
As more writers look to incorporate infectious diseases into their work, there are quite a few things writers should keep in mind:
Don’t anthropomorphize. Really easy to do, but scientifically wrong. Viruses don’t want to kill you; bacteria don’t want to infect you; parasites don’t want to make your blood curdle. None of these things are big enough to be sentient to want to do anything. They just do it (or don’t do it).
Personal protective equipment. This includes wearing gloves, lab coats, safety glasses, and tying your hair back if it’s long. It is the same as Edna Mode’s “no capes.” Flowing hair looks cool all the way to the explosive ball of flames that engulfs someone’s head.
Viruses are small. You can’t see viruses down a normal microscope—they need a special microscope called an electron microscope. These are highly specialized and take a long time to make the preparations to be able to see the virus. Normally viruses are detected by inference—measuring part of them using an assay that can amplify tiny amounts of material, for example PCR.
Viruses don’t really cause zombie apocalypses.
Vaccines work. But they take time. The best vaccine in the world will still only prevent infections two weeks after it is given. Drugs are quicker, but still take some time. But the good news is an infection is not going to kill you (or turn you into a zombie) quickly, so they both have time to work.
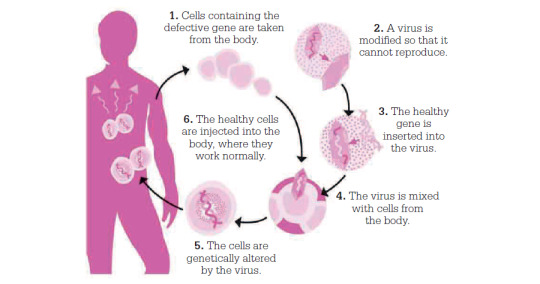
Scientists use viruses as a vector to introduce healthy genes into a patient’s cells:
Your Fictional Virus & Vaccine
When creating your own fictional virus, research further on the topic and consider choosing a specific one as your basis/inspiration.
Here's one resource. For some of them, you'll need a subscription to access, but those that are available give you a good overview of the virus, as well as treatment options.
You can do the same for creating your fictional vaccine:
Here's one resource. And here's one on vaccine developments.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ⚜ Writing Notes & References
Lastly, here's an interesting article on how science fiction can be a valuable tool to communicate widely around pandemic, whilst also acting as a creative space in which to anticipate how we may handle similar future events.
Thanks so much for your kind words, you're so lovely! Hope this helps with your writing. Would love to read your work if it does :)
#writing notes#virus#vaccine#writeblr#dark academia#spilled ink#writing reference#writing prompt#literature#science#writers on tumblr#creative writing#fiction#novel#light academia#lit#writing ideas#writing inspiration#writing tips#science fiction#writing advice#writing resources
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
"“It’s not your fault,” I told 16-year-old Cara, whose mother died of a SARS-CoV-2 infection [Cara] gave her. To be clear, the doctor confirmed Cara (not her real name) had passed on the virus and Covid was entered on the death certificate as the cause of death.
Cara’s mother had not been outside their home in the weeks preceding her death.
When masks were dropped in the “Omicron’s mild” phase of the pandemic, Cara continued as the lone masker at school to protect her immunocompromised mother, who was undergoing chemotherapy. It was tolerable until a child psychotherapist said on the national airwaves that some girls would continue to mask anyway “to hide their acne”.
His words were used to bully her. Cara left, but without support from teachers she struggled. Her parents pleaded with the school to use the Hepa filter they bought. The school refused.
Cara eventually returned to school unmasked, caught Covid and infected her mam. It killed her. Cara self-harms because she blames herself. She hasn’t been to school since.
Research shows that more than 70pc of Sars-CoV-2 transmission in households started with a child.
The incidence was highest during unmitigated in-person schooling. In a recent paper, Dr Pantea Javidan, of Stanford’s Centre for Human Rights, described the ways children’s rights to life, health and safety during the ongoing pandemic have been falsely rendered oppositional to education and development.
Methods used to manufacture consent to forcibly, repeatedly infect children, according to Dr Javidan, include minimising harms to children (“kids don’t get it or spread it”, “it’s mild”) and moral panic around mental health and educational attainment.
Regarding mental health, in August a study looking at paediatric psychiatric emergencies found school openings – not lockdowns – were associated with an increase in the number of emergency psychiatric visits.
In May, a study found that children with and without congenital heart defects showed increased risks for a variety of cardiovascular outcomes (including cardiac arrest, clots, palpitations) after Sars-CoV-2 infection.
In July, a study found that children and teenagers experienced cognitive impairment 12 months post-Covid infection, consistently correlated with poorer sleep and behavioural and emotional functioning.
Last month alone, several studies were published documenting Covid paediatric harms.
One found that children and adolescents experience prolonged symptoms post-Sars-CoV-2 infection in almost every organ system.
Study co-author Professor Lawrence C Kleinman said: “We have convincing evidence that Covid is not just a mild, benign illness for children. This is a new chronic illness in children. We need to be prepared to deal with it for a generation.”
Another study analysing paediatric and adult hospitalisations found teenagers were at greatest risk of severe disease among all children. Yet another study showed compelling connections between viral infection and subsequent autoimmune disease. Early in the pandemic, some children showed negligible Covid symptoms, only to later develop organ failure.
Researchers found the children’s immune systems had latched on to a part of the coronavirus that closely resembles a protein found in the heart, lungs, kidneys, brain, skin, eyes and GI tract and launched a catastrophic attack on their own tissues. “Experts” who claimed asymptomatic paediatric Sars2 infections equals mild were catastrophically wrong.
Covid is consistently a leading cause of US child mortality. Paediatric mortality has increased markedly with each year of the pandemic in the US, UK and elsewhere. In 2022, over six times as many children died from Covid than from flu in the US."
87 notes
·
View notes