#Private Equity Funds
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Is investing in private equity funds recommended? Why?
Private equity (PE) is an alternative form of investment that involves investing in companies that are not publicly traded on stock exchanges. In India, private equity has emerged as a dynamic and lucrative investment avenue over the past few decades. Institutional investors like pension funds, endowments, and high-net-worth individuals have been increasingly drawn to private equity, seeking higher returns than those available through traditional public market investments.
Here's why investing in private equity funds in India is recommended:
Diverse Types of Private Equity in India:
India's private equity market offers various options, including growth capital, buyouts, venture capital, and mezzanine finance. This diversity allows investors to tailor their investments to match their risk tolerance and investment objectives. For example, growth capital is suitable for those interested in supporting early or growth-stage companies, while buyouts are ideal for those looking to take control of established businesses.
Historical Growth and Resilience:
Despite facing challenges such as the global financial crisis, India's private equity industry has displayed resilience. Over the last decade, private equity investments in India surged, with average deal sizes increasing significantly. In the year 2022, private equity and venture capital investments amounted to $34.1 billion, showcasing sustained investor interest.
India's Robust Economic Landscape:
India boasts one of the world's fastest-growing economies, offering substantial growth potential for private equity investors. With a projected GDP growth rate of 6.4% in 2023-24 and a burgeoning middle class, opportunities abound in sectors like healthcare, education, retail, and consumer goods.
Government Initiatives:
The Indian government actively supports entrepreneurship and economic growth through initiatives like Startup India and Make in India. These programs provide funding and regulatory support to new businesses and aim to boost manufacturing in the country, fostering a favourable environment for private equity investments.
Improved Regulatory Environment:
The government's efforts to simplify the tax system, streamline regulations, and reduce bureaucratic hurdles have enhanced the ease of doing business in India. This improved regulatory environment makes it more accessible for private equity firms to invest in the country.
While private equity investments offer significant potential rewards, they also come with increased risks, illiquidity, and a longer investment horizon. Therefore, investors need to assess their risk tolerance, diversify their portfolios, and consider their investment goals before venturing into private equity funds.
Rurash Financials is your gateway to the future of finance. We bring together industry expertise and innovative strategies to empower Private Equity firms in creating sustainable and transparent long-term value for all stakeholders.
Our Private Equity vertical offers a diverse range of solutions, from investing in promising unlisted shares to providing specialised financial services for Non-Resident Indians, managing family offices and trusts, and navigating the exciting world of cryptocurrency.
To know more, connect with us today or write to [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Understanding the Healthcare Private Equity Landscape in India

India's healthcare sector offers significant investment opportunities for private equity firms. The growing demand for quality healthcare services, coupled with the country's rapidly growing population, makes India an attractive destination for healthcare private equity. However, private equity firms need to navigate several challenges in the Indian healthcare sector, including a complex regulatory environment, a shortage of skilled healthcare professionals, and infrastructure issues. By carefully evaluating potential investments and partnering with the right companies, private equity firms in India can capitalize on the significant opportunities in India's healthcare sector.
#private equity firms#Private Equity Firms in India#Top Private Equity Firms in India#Private Equity Funds#private equity
1 note
·
View note
Text
Private equity ghouls have a new way to steal from their investors

Private equity is quite a racket. PE managers pile up other peoples’ money — pension funds, plutes, other pools of money — and then “invest” it (buying businesses, loading them with debt, cutting wages, lowering quality and setting traps for customers). For this, they get an annual fee — 2% — of the money they manage, and a bonus for any profits they make.
On top of this, private equity bosses get to use the carried interest tax loophole, a scam that lets them treat this ordinary income as a capital gain, so they can pay half the taxes that a working stiff would pay on a regular salary. If you don’t know much about carried interest, you might think it has to do with “interest” on a loan or a deposit, but it’s way weirder. “Carried interest” is a tax regime designed for 16th century sea captains and their “interest” in the cargo they “carried”:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/29/writers-must-be-paid/#carried-interest
Private equity is a cancer. Its profits come from buying productive firms, loading them with debt, abusing their suppliers, workers and customers, and driving them into ground, stiffing all of them — and the company’s creditors. The mafia have a name for this. They call it a “bust out”:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/02/plunderers/#farben
Private equity destroyed Toys R Us, Sears, Bed, Bath and Beyond, and many more companies beloved of Main Street, bled dry for Wall Street:
https://prospect.org/culture/books/2023-06-02-days-of-plunder-morgenson-rosner-ballou-review/
And they’re coming for more. PE funds are “rolling up” thousands of Boomer-owned business as their owners retire. There’s a good chance that every funeral home, pet groomer and urgent care clinic within an hour’s drive of you is owned by a single PE firm. There’s 2.9m more Boomer-owned businesses going up for sale in the coming years, with 32m employees, and PE is set to buy ’em all:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/16/schumpeterian-terrorism/#deliberately-broken
PE funds get their money from “institutional investors.” It shouldn’t surprise you to learn they treat their investors no better than their creditors, nor the customers, employees or suppliers of the businesses they buy.
Pension funds, in particular, are the perennial suckers at the poker table. My parent’s pension fund, the Ontario Teachers’ Fund, are every grifter’s favorite patsy, losing $90m to Sam Bankman-Fried’s cryptocurrency scam:
https://www.otpp.com/en-ca/about-us/news-and-insights/2022/ontario-teachers--statement-on-ftx/
Pension funds are neck-deep in private equity, paying steep fees for shitty returns. Imagine knowing that the reason you can’t afford your apartment anymore is your pension fund gambled with the private equity firm that bought your building and jacked up the rent — and still lost money:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/02/25/pluralistic-your-daily-link-dose-25-feb-2020/
But there’s no depth too low for PE looters to sink to. They’ve found an exciting new way to steal from their investors, a scam called a “continuation fund.” Writing in his latest newsletter, the great Matt Levine breaks it down:
https://news.bloomberglaw.com/mergers-and-acquisitions/matt-levines-money-stuff-buyout-funds-buy-from-themselves
Here’s the deal: say you’re a PE guy who’s raised a $1b fund. That entitles you to a 2% annual “carry” on the fund: $20,000,000/year. But you’ve managed to buy and asset strip so many productive businesses that it’s now worth $5b. Your carry doesn’t go up fivefold. You could sell the company and collect your 20% commission — $800m — but you stop collecting that annual carry.
But what if you do both? Here’s how: you create a “continuation fund” — a fund that buys your old fund’s portfolio. Now you’ve got $5b under management and your carry quintuples, to $100m/year. Levine dryly notes that the FT calls this “a controversial type of transaction”:
https://www.ft.com/content/11549c33-b97d-468b-8990-e6fd64294f85
These deals “look like a pyramid scheme” — one fund flips its assets to another fund, with the same manager running both funds. It’s a way to make the pie bigger, but to decrease the share (in both real and proportional terms) going to the pension funds and other institutional investors who backed the fund.
A PE boss is supposed to be a fiduciary, with a legal requirement to do what’s best for their investors. But when the same PE manager is the buyer and the seller, and when the sale takes place without inviting any outside bidders, how can they possibly resolve their conflict of interest?
They can’t: 42% of continuation fund deals involve a sale at a value lower than the one that the PE fund told their investors the assets were worth. Now, this may sound weird — if a PE boss wants to set a high initial value for their fund in order to maximize their carry, why would they sell its assets to the new fund at a discount?
Here’s Levine’s theory: if you’re a PE guy going back to your investors for money to put in a new fund, you’re more likely to succeed if you can show that their getting a bargain. So you raise $1b, build it up to $5b, and then tell your investors they can buy the new fund for only $3b. Sure, they can get out — and lose big. Or they can take the deal, get the new fund at a 40% discount — and the PE boss gets $60m/year for the next ten years, instead of the $20m they were getting before the continuation fund deal.
PE is devouring the productive economy and making the world’s richest people even richer. The one bright light? The FTC and DoJ Antitrust Division just published new merger guidelines that would make the PE acquire/debt-load/asset-strip model illegal:
https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2023/07/ftc-doj-seek-comment-draft-merger-guidelines
The bad news is that some sneaky fuck just slipped a 20% FTC budget cut — $50m/year — into the new appropriations bill:
https://twitter.com/matthewstoller/status/1681830706488438785
They’re scared, and they’re fighting dirty.

I’m at San Diego Comic-Con!
Today (Jul 20) 16h: Signing, Tor Books booth #2802 (free advance copies of The Lost Cause — Nov 2023 — to the first 50 people!)
Tomorrow (Jul 21):
1030h: Wish They All Could be CA MCs, room 24ABC (panel)
12h: Signing, AA09
Sat, Jul 22 15h: The Worlds We Return To, room 23ABC (panel)

If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/20/continuation-fraud/#buyout-groups

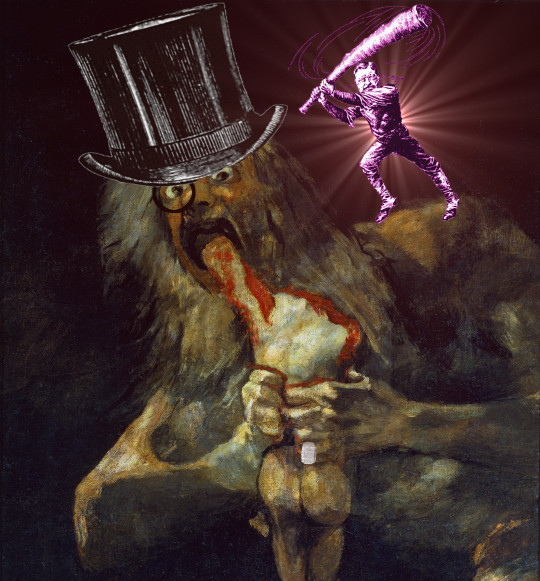
[Image ID: An old Punch editorial cartoon depicting a bank-robber sticking up a group of businesspeople and workers. He wears a bandanna emblazoned with dollar-signs and a top-hat.]
#pluralistic#buyout groups#continuation fraud#pe#pyramid schemes#the sucker at the table#pension plans#continuation funds#matt levine#fiduciaries#finance#private equity#mark to market#ripoffs
309 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ko-Fi prompt from @dirigibird:
I've been looking at investment options but I don't want to be messing around too much with the stock market, and a co-worker suggested exchange traded funds. Would love to know your opinions!
LEGALLY NECESSARY DISCLAIMER: I am not a licensed financial advisor, and it is illegal for me to advise anyone on investment in securities like stocks. My commentary here is merely opinion, not financial advice, and I urge you to not make any decisions with regards to securities investments based on my opinions, or without consulting a licensed advisor. I am also going to be talking this all over from an American POV, which means some of these things may not apply elsewhere.
So instead of letting you know what to pick or how to organize your securities, I'm going to go through the definitions of what various investment funds are, how they compare functionally, and maybe rant about how I disagree with the stock market on a fundamental ethical level if I have word count left over.
If you want more information, and are okay with jargon, I'd suggest hitting up investopedia. That is where I will be double-checking most of my information for this one.
I also encourage folks who know more about the stock market specifically to jump in! I like to think I'm good at research and explaining things, but I'm still liable to make mistakes.
Mutual Funds: A mutual fund is a pool of money and resources from multiple individuals (often vast numbers of people, actually) being put together and managed as a group by investment specialists. The primary appeal of these is that the money is professionally managed, but not personally so; it gives smaller investors access to professional money managers that they would not have access to on their own, at cheaper rates than if they tried to hire one for just their own assets. The secondary appeal is that, due to the sheer number of people, and thus capital, that is being invested at once, the money can be invested in a wide variety of industries, and is generally more stable than investing in just one company or industry. Low risk, low reward, but overall at least mostly reliable. Retirement plans are often invested in mutual funds by employer choice, through companies like Fidelity or John Hancock.
Hedge Funds: A hedge fund is a high risk, high reward mutual fund. Investors are generally wealthy, and have the room and safety to lose large amounts of money on an investment that has no promise of success, especially since money cannot be withdrawn at will, but must remain in the fund for a period of time following investment. It gets its name from "hedging your bets," as part of the strategy is to invest in the opposition of the fund's focus in order to ensure that there is a backup plan to salvage at least some money if the main plan backfires. Other strategies are also on the riskier side, often planning to take advantage of ongoing events like buyouts, mergers, incumbent bankruptcy, and shorting stocks (that's the one that caused the gamestop incident).
Private Equity: Private equity is... a nightmare that got its own incredibly good Hasan Minhaj episode of Patriot Act, so if you've got 20 minutes, an interest in comedically-delivered, easily-digestible, Real Information, and an internet connection, take a watch of that one. (If it's not available on YouTube in your country, it's originally from Netflix, or you can probably access it by VPN.) Private equity companies are effectively hedge funds that purchase entire companies, rebuild them in one way or another, and then sell them at (hopefully) a profit. Very often, the companies purchased by private equity are very negatively impacted, especially if the private equity group is a Vulture Fund. Sometimes, it's by taking it apart to sell off; sometimes it's by just bleeding it for cash until there's nothing left. Sometimes, it's taking over a hospital and overcharging the patients while also abusing the staff! (Glaucomflecken has a lot of videos on the topic of private equity in the medical industry, check him out.)
Venture Capital: In contrast to private equity, which purchases more mature companies, venture capital is focused on startups, or small businesses that have growth potential. These are the kinds of hedge funds that are like a whole group that you'd see some random tv character calling an Angel Investor (they're not actually the same thing, but they overlap by a lot). I'd hesitantly call these less ethically dubious than private equity, but I'm still suspicious.
And finally, to answer your question on what ETFs are and how they fit into the above.
Exchange Traded Funds: ETFs are... sort of like a mutual fund. Sort of. You are, to some extent, pooling your money... ish.
An ETF is like a stock that is made out of partial stocks. So instead of paying $100 for stock A, and not getting stocks B/C/D that all cost the same, you buy $100 of the ETF, which is $25 each of stocks A/B/C/D. You are getting a quarter of a unit of stock, which isn't normally an option, but because you are purchasing through an ETF that officially already bought those Whole stocks, you can now purchase the partial stocks through them.
They buy the whole stocks, then they resell you mixes of those stocks. They still officially own the whole stocks themselves, but you now own parts of the stocks. Basically, you own "stock" in a company that owns stock in other companies, and in that process you own partial stocks in those other companies.
I'm going to re-explain this using fruit.
Imagine you can buy apples, oranges, melons, grapes, etc. You can also buy fruit cups. You can only buy the individual fruits in big batches or you can pool your money with a few other people, hand it to a chef. The chef will decide which fruits look like they'll taste the best by lunch time, buy a bunch of those fruit pallets with your combined money, and plan out the best possible fruit salad for you to share with a bunch of people once lunch rolls around.
You could also buy a fruit cup. You don't have a lot of control over what's already in the fruit cup, but there are a few different mixes available--that one has strawberries, but that one over there uses kiwi, and the other one that way has pineapple--and you can pick which mix you want. It's a pretty small fruit cup, and it's predesigned, but you can choose the one you want without having to pool money with everyone else. You just first have to let someone else design the fruit cups you choose from, and you don't know which ones are probably going to survive the best to lunch time unless you ask a chef (which defeats the purpose of buying a fruit cup instead of pooling your money, and asking the chef costs money).
That's the ETF. The ETF is the fruit cup.
The upside is that you can now just track the prices of your fruit cup, instead of tracking the prices of four different fruits, and so if the price of one fruit drops, you can just... let the other three buoy it.
Of course, in the real world, there are more than just four stocks involved in an ETF. This part of the Investopedia article lists a few examples, and they're usually themed and involve anywhere from 30 (DOW Jones) to thousands (Russell) of shares by stock type, or by commodity/industry. So with the ETF, you can invest in an entire industry, like technology, and just keep track of that single "stock" in the industry game.
They do cost less in brokerage/management fees than regular mutual funds, and they have a slightly lower liquidity (slower to cash out). There also exist actively managed ETFs, which are basically mutual funds for ETFs. You are paying the chef to buy you premade fruit cups.
(Prompt me on ko-fi!)
#economics#stock market#etfs#etf#mutual funds#hedge funds#venture capital#private equity#capitalism#phoenix talks#ko fi#ko fi prompts#economics prompts
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
i haven't seen anyone on here talking about it yet, but the CEO of our brave website has embroiled himself in drama again, this time in a more high-profile way: matt mullenweg is the head of automattic, which owns tumblr and also wordpress, the largest service provider for wordpress, an open-source web hosting project and infrastructure for a huge percentage of the web; he is also a founder of & on the board for wordpress, the nonprofit that manages wordpress (the open-source project). matt, in his infinite wisdom, got mad at wpengine, a different service provider for wordpress (the open-source project); supposedly, he's mad because wpengine uses the open-source software but doesn't contribute financially or in staff time to support it, but that's actually completely legal to do even if we think it's a party foul, so wordpress is suing wpengine for trademark infringement & wpengine is countersuing for extortion. matt, #1 most stable tech CEO in the business, banned wpengine from accessing wordpress.org, the website that hosts plugins & themes for the open-source project. he can do that because, according to him, it's just his personal website. again, a huge percentage of the web uses wordpress, even if those websites don't go through automattic to do it; wordpress.org gets thousands of requests a second, and matt broke like literally a million websites (wpengine's client sites) with no notice. this is a hilarious thing to do, but it is not necessarily a great idea, so our intrepid leader is paying automattic employees who think the whole wpengine grudge match is a bad idea up to six months of salary to leave the company (8% of his employees took him up on it). so it's going great & matt still does not know how to log the fuck off when he's mad
#one of the great arguments in favor of open-source projects is that they're less susceptible to one guy getting mad lol#the whole OS ecosystem has massive issues including funding but like. will this fix it? it will not.#i agree with matt that private equity is bad! however. does this fix anything? no. also i think the trademark claim is weak as hell lol#also also. um buddy. i'm sensing that one may have crossed the streams a little bit with one's nonprofit & for-profit work. haha.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

















Equi Corp Legal has the best lawyers in Delhi NCR
#Corporate Disputes Litigation Lawyers in Delhi#Insolvency Bankruptcy NCLT Lawyers in Delhi#Private Equity Funds Investment Transaction Advisory M&A Lawyers in Delhi#Technology E-Commerce Fintech Blockchain Lawyers in Delhi#Regulatory Compliance Legal Audits in Delhi Noida#Director Investor Shareholder Dispute Litigation Lawyers in Delhi#Sports Gaming lawyers in Delhi#Startup Investor Lawyers in Delhi#Banking NBFC Financial Services DRT Debt Restructuring Lawyers in Delhi#Corporate lawyers in Delhi#Arbitration Lawyers in Delhi#Consumer Protection Lawyers in Delhi#Commercial Civil Disputes Litigation Lawyers in Delhi
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Onnibussi is now the only bus option between my home town and Tampere where I visit fairly often. Train still costs more, but the difference is so little that I’d rather take it. Onnibussi fucking sucks, and I fucking hate it so much. We used to have good, well maintained bus companies, then the fire nation attacked onnibus came into the market and now we only have that.

#fuck onnibussi#onnibus was bought by koiviston auto in 2018 btw#and koiviston auto was bought by a private equity fund manager company#rip väinö paunu you were the best
63K notes
·
View notes
Text
PORTUGAL GOLDEN VISA - EQUITY FUNDS ASSISTANCE
APPLY FOR THE PORTUGAL GOLDEN VISA - GET FUNDS SUBSCRIPTION ASSISTANCE NOW!
Funds Subscription Assistance – Portugal Golden Visa VisaConnect’s Consultant’s in cooperation with various Fund Managers and Portugal Lawyers, and we can advise and assist Investors, with the Fund Subscription Process, including the following: Promotional Fliers/Teasers Fund Powerpoint Presentation Management Regulation Prospectus Reservation Fee Letter Subscription application…
#invest in portugal funds#live in portugal#portugal eu passport#portugal funds for golden visa#portugal funds investment for golden visa#portugal golden residence permit#Portugal Golden Visa#portugal immigration advice#portugal immigration lawyers#portugal investor immigration#portugal investor visa#portugal nationality advice#portugal permanent residence#portugal private equity funds#Portugal Residence by Investment#portugalresidence permit
0 notes
Text
Private Equity’s Ruthless Takeover Of The Last Affordable Housing In America
https://youtu.be/wkH1dpr-p_4?si=X7ZEHSBbCi8Gamco
youtube
#private equity#affordable#affordability#housing#videos#video#class war#usa#america#american dream#american nightmare#homeless#poverty#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#usa is a terrorist state#usa is funding genocide#usa news#usa politics#american indian#american#amerika
1 note
·
View note
Text
Why Private Equity Funds Are Flocking To The Indian Healthcare Sector?

Private equity funds in India have been attracting a lot of investor attention in the healthcare sector. Find out why, in this article! India is an attractive investment destination for private equity (PE) funds due to its large population, growing economy, and favorable demographics. The healthcare sector in India is especially attractive to PE investors due to the country’s low per capita spending on healthcare and the government’s recent initiatives to increase access to quality healthcare. it is not surprising that private equity funds are flocking to the Indian healthcare sector. It is clear that private equity funds are flocking to the Indian healthcare sector for a variety of reasons. With an aging population and a growing middle class, there is a large and growing market for healthcare services in India. In addition, the Indian government is supportive of private investment in the healthcare sector and has put in place policies to encourage it. As a result, we can expect to see more private equity investment in the Indian healthcare sector in the years to come.
0 notes
Text
Yes, it is market manipulation by corporate real estate.

Hedge funds and private equity should be banned from manipulating and exploiting residential real estate.
#housing#hedge funds#private equity#corporate landlords#price setting#price gouging#inflated rent#inflated real estate prices#market manipulation
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The antitrust Twilight Zone

Funeral homes were once dominated by local, family owned businesses. Today, odds are, your neighborhood funeral home is owned by Service Corporation International, which has bought hundreds of funeral homes (keeping the proprietor’s name over the door), jacking up prices and reaping vast profits.
Funeral homes are now one of America’s most predatory, vicious industries, and SCI uses the profits it gouges out of bereaved, reeling families to fuel more acquisitions — 121 more in 2021. SCI gets some economies of scale out of this consolidation, but that’s passed onto shareholders, not consumers. SCI charges 42% more than independent funeral homes.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/09/09/high-cost-of-dying/#memento-mori
SCI boasts about its pricing power to its investors, how it exploits people’s unwillingness to venture far from home to buy funeral services. If you buy all the funeral homes in a neighborhood, you have near-total control over the market. Despite these obvious problems, none of SCI’s acquisitions face any merger scrutiny, thanks to loopholes in antitrust law.
These loopholes have allowed the entire US productive economy to undergo mass consolidation, flying under regulatory radar. This affects industries as diverse as “hospital beds, magic mushrooms, youth addiction treatment centers, mobile home parks, nursing homes, physicians’ practices, local newspapers, or e-commerce sellers,” but it’s at its worst when it comes to services associated with trauma, where you don’t shop around.
Think of how Envision, a healthcare rollup, used the capital reserves of KKR, its private equity owner, to buy emergency rooms and ambulance services, elevating surprise billing to a grotesque art form. Their depravity knows no bounds: an unconscious, intubated woman with covid was needlessly flown 20 miles to another hospital, generating a $52k bill.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/14/unhealthy-finances/#steins-law
This is “the health equivalent of a carjacking,” and rollups spread surprise billing beyond emergency rooms to anesthesiologists, radiologists, family practice, dermatology and others. In the late 80s, 70% of MDs owned their practices. Today, 70% of docs work for a hospital or corporation.
How the actual fuck did this happen? Rollups take place in “antitrust’s Twilight Zone,” where a perfect storm of regulatory blindspots, demographic factors, macroeconomics, and remorseless cheating by the ultra-wealthy has laid waste to the American economy, torching much of the US’s productive capacity in an orgy of predatory, extractive, enshittifying mergers.
The processes that underpin this transformation aren’t actually very complicated, but they are closely interwoven and can be hard to wrap your head around. “The Roll-Up Economy: The Business of Consolidating Industries with Serial Acquisitions,” a new paper from The American Economic Liberties Project by Denise Hearn, Krista Brown, Taylor Sekhon and Erik Peinert does a superb job of breaking it down:
http://www.economicliberties.us/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Serial-Acquisitions-Working-Paper-R4-2.pdf
The most obvious problem here is with the MergerScrutiny process, which is when competition regulators must be notified of proposed mergers and must give their approval before they can proceed. Under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Act (HSR) merger scrutiny kicks in for mergers when the purchase price is $101m or more. A company that builds up a monopoly by acquiring hundreds of small businesses need never face merger scrutiny.
The high merger scrutiny threshold means that only a very few mergers are regulated: in 2021, out of 21,994 mergers, only 4,130 (<20%) were reported to the FTC. 2020 saw 16,723 mergers, with only 1.637 (>10%) being reported to the FTC.
Serial acquirers claim that the massive profits they extract by buying up and merging hundreds of businesses are the result of “efficiency” but a closer look at their marketplace conduct shows that most of those profits come from market power. Where efficiences are realized, they benefit shareholders, and are not shared with customers, who face higher prices as competition dwindles.
The serial acquisition bonanza is bad news for supply chains, wages, the small business ecosystem, inequality, and competition itself. Wherever we find concentrated industires, we find these under-the-radar rollups: out of 616 Big Tech acquisitions from 2010 to 2019, 94 (15%) of them came in for merger scrutiny.
The report’s authors quote FTC Commissioner Rebecca Slaughter: “I think of serial acquisitions as a Pac-Man strategy. Each individual merger viewed independently may not seem to have significant impact. But the collective impact of hundreds of smaller acquisitions, can lead to a monopolistic behavior.”
It’s not just the FTC that recognizes the risks from rollups. Jonathan Kanter, the DoJ’s top antitrust enforcer has raised alarms about private equity strategies that are “designed to hollow out or roll-up an industry and essentially cash out. That business model is often very much at odds with the law and very much at odds with the competition we’re trying to protect.”
The DoJ’s interest is important. As with so many antitrust failures, the problem isn’t in the law, but in its enforcement. Section 7 of the Clayton Act prohibits serial acquisitions under its “incipient monopolization” standard. Acquisitions are banned “where the effect of such acquisition may be to substantially lessen competition between the corporation whose stock is so acquired and the corporation making the acquisition.” This incipiency standard was strengthened by the 1950 Celler-Kefauver Amendment.
The lawmakers who passed both acts were clear about their legislative intention — to block this kind of stealth monopoly formation. For decades, that’s how the law was enforced. For example, in 1966, the DoJ blocked Von’s from acquiring another grocer because the resulting merger would give Von’s 7.5% of the regional market. While Von’s is cited by pro-monopoly extremists as an example of how the old antitrust system was broken and petty, the DoJ’s logic was impeccable and sorely missed today: they were trying to prevent a rollup of the sort that plagues our modern economy.
As the Supremes wrote in 1963: “A fundamental purpose of [stronger incipiency standards was] to arrest the trend toward concentration, the tendency of monopoly, before the consumer’s alternatives disappeared through merger, and that purpose would be ill-served if the law stayed its hand until 10, or 20, or 30 [more firms were absorbed].”
But even though the incipiency standard remains on the books, its enforcement dwindled away to nothing, starting in the Reagan era, thanks to the Chicago School’s influence. The neoliberal economists of Chicago, led by the Nixonite criminal Robert Bork, counseled that most monopolies were “efficient” and the inefficient ones would self-correct when new businesses challenged them, and demanded a halt to antitrust enforcement.
In 1982, the DoJ’s merger guidelines were gutted, made toothless through the addition of a “safe harbor” rule. So long as a merger stayed below a certain threshold of market concentration, the DoJ promised not to look into it. In 2000, Clinton signed an amendment to the HSR Act that exempted transactions below $50m. In 2010, Obama’s DoJ expanded the safe harbor to exclude “[mergers that] are unlikely to have adverse competitive effects and ordinarily require no further analysis.”
These constitute a “blank check” for serial acquirers. Any investor who found a profitable strategy for serial acquisition could now operate with impunity, free from government interference, no matter how devastating these acquisitions were to the real economy.
Unfortunately for us, serial acquisitions are profitable. As an EY study put it: “the more acquisitive the company… the greater the value created…there is a strong pattern of shareholder value growth, correlating with frequent acquisitions.” Where does this value come from? “Efficiencies” are part of the story, but it’s a sideshow. The real action is in the power that consolidation gives over workers, suppliers and customers, as well as vast, irresistable gains from financial engineering.
In all, the authors identify five ways that rollups enrich investors:
I. low-risk expansion;
II. efficiencies of scale;
III. pricing power;
IV. buyer power;
V. valuation arbitrage.
The efficiency gains that rolled up firms enjoy often come at the expense of workers — these companies shed jobs and depress wages, and the savings aren’t passed on to customers, but rather returned to the business, which reinvests it in gobbling up more companies, firing more workers, and slashing survivors’ wages. Anything left over is passed on to the investors.
Consolidated sectors are hotbeds of fraud: take Heartland, which has rolled up small dental practices across America. Heartland promised dentists that it would free them from the drudgery of billing and administration but instead embarked on a campaign of phony Medicare billing, wage theft, and forcing unnecessary, painful procedures on children.
Heartland is no anomaly: dental rollups have actually killed children by subjecting them to multiple, unnecessary root-canals. These predatory businesses rely on Medicaid paying for these procedures, meaning that it’s only the poorest children who face these abuses:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/17/the-doctor-will-fleece-you-now/#pe-in-full-effect
A consolidated sector has lots of ways to rip off the public: they can “directly raise prices, bundle different products or services together, or attach new fees to existing products.” The epidemic of junk fees can be traced to consolidation.
Consolidators aren’t shy about this, either. The pitch-decks they send to investors and board members openly brag about “pricing power, gained through acquisitions and high switching costs, as a key strategy.”
Unsurprisingly, investors love consolidators. Not only can they gouge customers and cheat workers, but they also enjoy an incredible, obscure benefit in the form of “valuation arbitrage.”
When a business goes up for sale, its valuation (price) is calculated by multiplying its annual cashflow. For small businesses, the usual multiplier is 3–5x. For large businesses, it’s 10–20x or more. That means that the mere act of merging a small business with a large business can increase its valuation sevenfold or more!
Let’s break that down. A dental practice that grosses $1m/year is generally sold for $3–5m. But if Heartland buys the practice and merges it with its chain of baby-torturing, Medicaid-defrauding dental practices, the chain’s valuation goes up by $10–20m. That higher valuation means that Heartland can borrow more money at more favorable rates, and it means that when it flips the husks of these dental practices, it expects a 700% return.
This is why your local veterinarian has been enshittified. “A typical vet practice sells for 5–8x cashflow…American Veterinary Group [is] valued at as much as 21x cashflow…When a large consolidator buys a $1M cashflow clinic, it may cost them as little as $5M, while increasing the value of the consolidator by $21M. This has created a goldrush for veterinary consolidators.”
This free money for large consolidators means that even when there are better buyers — investors who want to maintain the quality and service the business offers — they can’t outbid the consolidators. The consolidators, expecting a 700% profit triggered by the mere act of changing the business’s ownership papers, can always afford to pay more than someone who merely wants to provide a good business at a fair price to their community.
To make this worse, an unprecedented number of small businesses are all up for sale at once. Half of US businesses are owned by Boomers who are ready to retire and exhausted by two major financial crises within a decade. 60% of Boomer-owned businesses — 2.9m businesses of 11 or so employees each, employing 32m people in all — are expected to sell in the coming decade.
If nothing changes, these businesses are likely to end up in the hands of consolidators. Since the Great Financial Crisis of 2008, private equity firms and other looters have been awash in free money, courtesy of the Federal Reserve and Congress, who chose to bail out irresponsible and deceptive lenders, not the borrowers they preyed upon.
A decade of zero interest rate policy (ZIRP) helped PE grow to “staggering” size. Over that period, America’s 2,000 private equity firms raised buyout warchests totaling $2t. Today, private equity owned companies outnumber publicly traded firms by more than two to one.
Private equity is patient zero in the serial acquisition epidemic. The list of private equity rollup plays includes “comedy clubs, ad agencies, water bottles, local newspapers, and healthcare providers like hospitals, ERs, and nursing homes.”
Meanwhile, ZIRP left the nation’s pension funds desperate for returns on their investments, and these funds handed $480b to the private equity sector. If you have a pension, your retirement is being funded by investments that are destroying your industry, raising your rent, and turning the nursing home you’re doomed to into a charnel house.
The good news is that enforcers like Kanter have called time on the longstanding, bipartisan failure to use antitrust laws to block consolidation. Kanter told the NY Bar Association: “We have an obligation to enforce the antitrust laws as written by Congress, and we will challenge any merger where the effect ‘may be substantially to lessen competition, or to tend to create a monopoly.’”
The FTC and the DOJ already have many tools they can use to end this epidemic.
They can revive the incipiency standard from Sec 7 of the Clayton Act, which bans mergers where “the effect of such acquisition may be substantially to lessen competition, or to tend to create a monopoly.”
This allows regulators to “consider a broad range of price and non-price effects relevant to serial acquisitions, including the long-term business strategy of the acquirer, the current trend or prevalence of concentration or acquisitions in the industry, and the investment structure of the transactions”;
The FTC and DOJ can strengthen this by revising their merger guidelines to “incorporate a new section for industries or markets where there is a trend towards concentration.” They can get rid of Reagan’s 1982 safe harbor, and tear up the blank check for merger approval;
The FTC could institute a policy of immediately publishing merger filings, “the moment they are filed.”
Beyond this, the authors identify some key areas for legislative reform:
Exempt the FTC from the Paperwork Reduction Act (PRA) of 1995, which currently blocks the FTC from requesting documents from “10 or more people” when it investigates a merger;
Subject any company “making more than 6 acquisitions per year valued at $70 million total or more” to “extra scrutiny under revised merger guidelines, regardless of the total size of the firm or the individual acquisitions”;
Treat all the companies owned by a PE fund as having the same owner, rather than allowing the fiction that a holding company is the owner of a business;
Force businesses seeking merger approval to provide “any investment materials, such as Private Placement Memorandums, Management or Lender Presentations, or any documents prepared for the purposes of soliciting investment. Such documents often plainly describe the anticompetitive roll-up or consolidation strategy of the acquiring firm”;
Also force them to provide “loan documentation to understand the acquisition plans of a company and its financing strategy;”
When companies are found to have violated antitrust, ban them from acquiring any other company for 3–5 years, and/or force them to get FTC pre-approval for all future acquisitions;
Reinvigorate enforcement of rules requiring that some categories of business (especially healthcare) be owned by licensed professionals;
Lower the threshold for notification of mergers;
Add a new notification requirement based on the number of transactions;
Fed agencies should automatically share merger documents with state attorneys general;
Extend civil and criminal antitrust penalties to “investment bankers, attorneys, consultants who usher through anticompetitive mergers.”
#pluralistic#american economic liberties project#jonathan kantor#doj#clayton act#hart-scott-rodino act#zirp#financial engineering#monopoly#consolidation#rollups#debt financing#private equity#hedge funds#serial acquirers#antitrust#incipiency standard#Celler-Kefauver Act#vons#brown shoe#boomers#silver wave#labor#monopsony#pricing power#kkr#envision#funeral homes#surprise billing#sci
103 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think I may need to lower my standards orz
#the three things I'm going to have to think about compromising on: pay. location. industry.#the problem is that the best-paying industry in NYC is obviously finance. And that means private equity and hedge funds.#which are patently evil#so like. I don't want to work in that industry#but my skillset won't get a living wage (for NYC) in other industries#so I have to either bite the bullet and work on LI (I'd really rather not) work for an evil industry (GOD no) or#get a wage low enough that I'll have to continue living with my parents indefinitely and commute four or five hours a day#personal#vent post#job hunting
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top-Paying Jobs in Finance

#finance jobs#top-paying jobs#financial advisors#Private Equity#Investment Banking#Chief Financial Officer#Hedge Fund Manager#Quantitative Analyst#High-Paying Finance Jobs#Finance Careers
0 notes
Text
Types of Private Equity Investments
Private equity or PE investments help businesses thrive through capital infusion from willing investors. Later, they can utilize the increased capacity to expand operations and regional headcounts. Investors’ support allows brands to develop new product research roadmaps and reduce debt-related liabilities. However, investors do not get hassle-free access to a private company’s financial, reputational, and legal history, unlike what they can quickly check when investing in a publicly-held enterprise. This post will explore the types of private equity investments that enhance investors’ portfolios while reliably predicting returns through data-backed performance and investment disclosures.
What is Private Equity?
Private equity facilitates investments into unlisted companies. So, the companies can achieve fundraising goals through leveraged buyouts, venture capital, distressed debt, and similar approaches. Additionally, investors might employ private equity outsourcing support during due diligence since significant performance insights are absent from publicly accessible media resources.
Blackstone, Carlyle Group, Advent International, and Vista Equity Partners are a few globally recognized brands streamlining PE investments for stakeholders. Given the high-risk classification of PE investing opportunities, business owners and equity portfolio managers have identical incentives to maximize returns.
Types of Private Equity Investments
1| PE Fund of Funds
A fund of funds (FOF) gathers capital from investors. Later, investors will want the FOF to invest in available PE opportunities. Simultaneously, investors benefit from a multi-strategy PE investing approach, distributing risk across growth capital, leveraged buyouts, and venture capital allocations. Investors and private sector players can utilize fund data solutions to assess a FOF’s past performances for informed wealth development decisions.
Private equity FOF enables access to otherwise exclusive investment opportunities and robust diversification models. Aside from the time-tested skill set of financial professionals heading fund of fund operations, investors enjoy moderate liquidity. It is still less than public company investments but more than direct investments into unlisted businesses.
FOFs in private equity investments can offer geographic, sectoral, and thematic scope of screening companies. Otherwise, investors can select a multi-strategy option that integrates the strengths of these three FOF categorizations.
2| Distressed Debt
Bankruptcy, restructuring, and similar financial challenges often prompt private companies to offer discounts to attract and retain investors. Distressed debt involves transactions involving investors purchasing high-risk corporate debt securities. Later, if the business successfully recovers from those financially troubling circumstances, investors enjoy additional gains because they receive remarkable discounts during the initial transactions.
Active involvement is also vital, indicating investors must share their acquired wisdom of corporate restructuring and collaborate with domain experts to accelerate business value enrichment programs. Therefore, feasibility studies and performance reports are pivotal to reducing investment loss risks upon failed business revival attempts.
3| Mezzanine Capital
This hybrid approach to private equity investments offers a concentrated strategy relying on synergized equity and debt financing strengths. Mezzanine capital, beneficial in PE-driven fundraising, exhibits higher interest rates because it is secondary to senior debt. Senior debt in a private equity context ensures lenders get settlements upon liquidation or bankruptcy.
In other words, Mezzanine capital is subordinated to senior debt in the enterprise capital structure and, therefore, riskier. However, its return-yielding potential is remarkable due to interest rates being higher than those of senior debt. Mezzanine capital in PE also features conversion rights or warrants, empowering lending investors to upgrade to standard equity when company performance improves after capital infusion.
Conclusion
Distressed debt and Mezzanine capital are the high-risk types of private equity investments. Meanwhile, a private equity fund of funds softens the risk exposure. After all, it delivers strategic diversification and exclusive access to unique PE investing opportunities. Regardless of a few slumps in the industry during 2019-20, private equity is essential to help unlisted companies overcome capacity and growth challenges while striking a balance of investor risks and returns.
#private equity#fund solutions#fund services#fund data#fund management#private equity services#private equity support
0 notes
Text

Global Star Capital founder Rich Cocovich recently met with principals in both New York City and Los Angeles California on a $5 Million USD entertainment sector project and bridged the gap of funding with a private California based investor. Since 1991, Cocovich has serviced clients in 126 countries and all 50 states in America as the top expert and private funding. Over 30 billion USD from private investors awaits the projects Global Star Capital and Rich Cocovich represent. If you are a solvent and prepared project principal who understands that high end, professional expertise is not free, not contingent, not pro bono, and not wrapped into a closing, then you are welcome to visit one of our two main websites www.globalstarcapital.com or https://lnkd.in/eFeNm-pb and begin in the Our Process Section. Our engagement process and fee structure is etched in stone and non-negotiable. Project principals who follow our protocol, including the mandatory face-to-face meeting steps, succeed in gaining the attention their project deserves. Within seven days of meeting Rich Cocovich in person, a greenlight from a private funding facilitator/investor will be established.
#richcocovich #globalstarcapital #privefunding #projectfunding #richcocovichreviews #globalstarcapitalreviews #cocovich #capitalraising #topconsultant #familyoffice #equity #equityfunding #projectequity #equityinvesting
#rich cocovich#global star capital#richard cocovich#private funding#richard cocovich and global star capital#rich cocovich top consultant in private funding#rich cocovich and global star capital#global star capital news#global star capital comments#rich cocovich private funding expert#private funding intermediaries#private funding project funding#project funding professionals#project funding#capital raising#global star capital information#family offices#equity funding#equity capital#equity financing#private equity#cocovich#rich cocovich review#richard cocovich review#project funding services
0 notes