#Historical cautionary tales
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Opinion | Lessons from Alexandria: A Cautionary Tale for Modern American Politics
By Jet Espinosa In a city once hailed as a beacon of knowledge and tolerance, Alexandria drew people from across the ancient world. It was a place where scholars, thinkers, and believers from diverse backgrounds came to share and preserve their wisdom. With libraries that housed invaluable knowledge in science, philosophy, medicine, and the arts, Alexandria was a symbol of progress and…

View On WordPress
#Alexandria library destruction#American democracy#Ancient Alexandria#Cultural diversity#Enlightenment and progress#Freedom of belief#Historical cautionary tales#History repeating itself#Intellectual freedom#Knowledge and tolerance#Lessons from ancient civilizations#Lessons from history#Modern American politics#Political power and religion#Politics and religion#Protecting democracy#Religious influence in politics#Religious tolerance#Role of religion in government#Separation of church and state
0 notes
Text
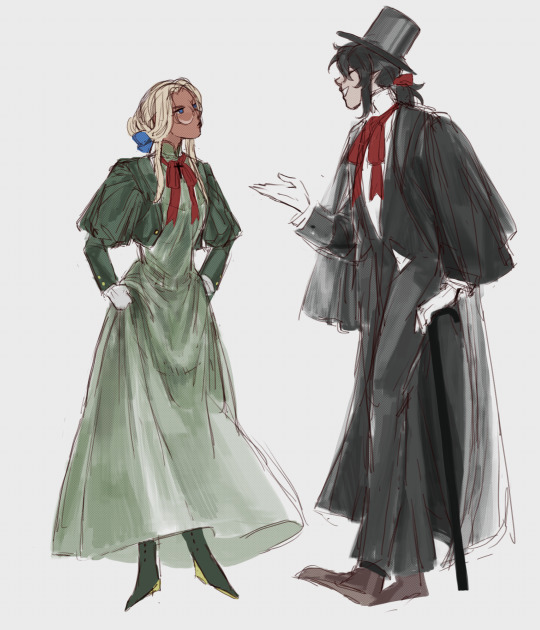

the scorpion and the frog
#hellsing#alutegra#i need period drama hellsing#the clothes might be historically inaccurate because i just shove every reference up together#did not have the time to differentiate between victorian or ewardian or regency something something#alucard hellsing#integra hellsing#the scorpion and the frog is my favourite fable#there are so many ways to interpret it more than just a cautionary tale#personally i see it as a tragic romance#all of my otps follow the same damn trope everytime#someone who believed that it is in their nature that they are unlovable#and someone who trusted them regardless even fully aware of their destructive nature#but as fairytales mostly go isnt true love can break the spell#so i think there are several ways that the tale of the scorpion and the frog can be retold#the scorpion and the frog
901 notes
·
View notes
Text
When you actually Americanize Starlight Express, Electra suddenly becomes a Reaganite boogeyman of Amtrak as a “welfare queen”- A “Dark Side of the (T)Rainbow” esque fascinating synchronicity
(Yes, that term is racially loaded and I am using it very deliberately for reasons to be explained later.)
MASSIVE DISCLAIMER: I was way too wishy washy on this in the original version of the post (which got picked up by some bigger names and spread around) so I want to make this very clear. This is all a giant “Immer Pünktlich!” situation where the original creators could have never foreseen how it comes off wildly different in another country. Most of the traits discussed here were not present in the workshop version of the character. They just arose later on mainly through pure coincidence. I am VERY aware of Electra’s original intent and origins. I would be astounded if Brits in the 80s knew this much about the long-suffering US passenger rail network, even most Americans today don’t know if they don’t actually ride these trains or live in the northeast. Starlight’s central themes of bootstrapping and “being under your own control” are associated with conservatives like Thatcher and Reagan, but that’s basically it in terms of actually intended elements. This is a wild reinterpretation of things by someone with a wildly different viewpoint than the original creatives.
People often make fun of how Electra makes such a big deal of being electric and futuristic when electric trains are just kind of the norm in most countries with substantial rail networks. But when you take into account that toothpaste-era Electra is considerably Amtrak-coded and look into the politics and railroad history of what they’d be like irl…. Their framing goes from kind of stupid to pointedly malicious in oddly specific ways.
You know what else WAS the norm in the US (and still is in much of Europe) until Reagan started treating it as a radical freak? The big bad “liberal agenda” of the government actually funding things like social programs and infrastructure, including railroads. And you know what kind of trains are almost completely dependent on that kind of government support? Electric ones. EVERY SINGLE REPLICA NATIONAL represents a country that (at least circa the 80s) had a nationalized rail network that actually invested in electrification. It’s not impossible for private companies to fully fund themselves but very hard, especially now.
Who are “electric train politics” heavily associated with in the US? Black people, LGBT people, damn near every minority, which coincidentally, Electra regularly was early on.
You may not realize this if you’re from elsewhere, but the US has very, very little rail electrification vs other rich countries. You have some commuter rail and local transit systems in a number of cities, the Northeast Corridor and Keystone Corridor, and that’s…. about it. Intercity service between a line of the big northeastern cities and that’s it. The rest is all diesel domain irl. Behold the wikipedia page for electrified lines in the US and see just how many are GONE. (Passenger service is also absolutely threadbare if not nonexistant in most of the non-electric network and often offensively slow, not even local road speed. But that’s a whole separate can of worms)
Why is this? Heavy simplification, but the government subsidized highways and airports instead after WWII and that along with antiquated laws and losing mail service made passenger rail a massive money pit for most the railroads forced to continue it. Instead of passenger rail service and infrastructure improving like basically all the other Nationals’ countries, routes dropped like flies and many railroads sank into financial ruin until Penn Central’s collapse in the late 60s. That’s when the government finally stepped in and took over passenger services as Amtrak. Electrification infrastructure and equipment was dated then due to years of desperate finances, and while there was active rail investment in the 70s to improve, Reagan’s administration was hostile to it and it’s been an on and off uphill battle since to get enough funding to keep things going, let alone improve or expand. Literally left decades behind by the system. The 2013 tour is the most accurate version of Electra as a realistic reflection of electric passenger rail in the US- a guy who’s been at it since the 80s that still looks like a decades-old vision of the future in a notably cheap, torn up, worn out costume. Actually the AEM-7 locomotives used then date to 1978, even older than that.
“Electra must be rich” sounds like something a stingy conservative politician would say about Amtrak needing billions of dollars (to just be barely functional due to years of neglect). Yes, they were intended to be a celebrity for separate reasons early on, but the massive contrast between being shown as “rich” but representing an infamously NOT rich rail system really feels like something a nasty conservative politician would try as a smear campaign in another timeline. Oooo handouts bad. Oooo you must be so extravagant if you need that much. You “welfare queen” sucking government funds to blow on exotic pets and glitter and other frivolities. You “strapping young buck buying T-bone steaks with food stamps”. Those are Reagan’s quotes, not mine, I hate even typing them out but god, can it be more obvious? Painting those who need government assistance (usually coded as black) as extravagant has been weaponized to destroy social programs and further inequality. The gap between Electra and reality always felt kind of jarring for me, but the longer I thought about it, the more I realized how much uglier the implications were.
“Or unreliable”- electric trains have so few moving parts they tend to be notably reliable in terms of the physical locomotive/multi unit*. A lot of their issues are actually due to structural failures with powerlines, and this is ESPECIALLY true with the NEC and other ooold electric commuter lines in the US. This has also limited the maximum speed of trains at times. See video below for more on this, also explains a lot of the stuff I’ve mentioned earlier. Huh. Gee whiz. Someone held back and suffering due to structural problems being blamed as personal failing. What DOES that sound like?
youtube
*technically CC 40104 used as Electra’s helmet actually was an unreliable model because it was a weird complicated niche thing with four voltages for a uniquely European situation but that’s downright cherry picking. The other Nez Casse engines with that styling actually were reasonably reliable and realistic Amtrak Electra from the 80s to 2018 would be an AEM-7 (common fanon choice too) that was also fine.
When you think about it, the likes of “only you have the power within you” and “needn’t beg the world to turn around and help you” might be the most offensive things you could say specifically to an electric train in the US besides“lol they shoulda replaced your line with even moar I-95 lanes”
Anyways, isn’t it funny how people conveniently ignore how steam preservation was actually very popular (compared to almost any other obsolete tech) in the 80s and had been since at least the 60s? You had steam engines pulling the 1976 Freedom Train. A small, relatively “young”, mechanically functional steam engine would have tourist railroads FIGHTING over them back then. That was the era when the majority of the steam engines left in Barry Scrapyard were scooped up and preserved, Crown Metal Company was making new build ones for amusement parks, and some tourist railroads even bought new builds from the last company in China building steam engines for regular service.
But you know what did go out of favor in the late 30s and was treated as downright laughable to go back to after the 50s, just like the regular revenue use of steam locos in the US?
The kind of small-government conservatism Reagan preached. And the steam engines in the show promote. Barry Goldwater was openly mocked for it in the mid-60s. It was thought genuinely unthinkable to go back to.
So, those laughably historically inaccurate depictions of electric and steam engines. Isn’t it uncanny how near-perfectly those unrealistic traits of them align with other things?
Also a funny aside: probably 90% of those new build Crown Metal steam engines were dressed up in western themes. Literally cowboy actors, just like Reagan was.
(I’ve got an extended unhinged analysis of Starlight accidentally resembling the rise of Reaganism and it unexpectedly spreading world over and destroying everyone else’s railroads too. That’s still in progress though. But these two aspects are so freakishly dead-on I really needed to get them out.)
#stex electra#stex#starlight express#yeah this’ll piss people off but i’m even surprised by how much historical justification this angle has#the sad story of american electrified rail really should be known more than it is. It’s a real cautionary tale#it’s telling that i’ve seen multiple big boys and centennials but i don’t think i’ve ever seen a GG1 OC#(besides my own that I haven’t actually posted publicly)
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
particular thanks to @lyricwritesprose for the analysis
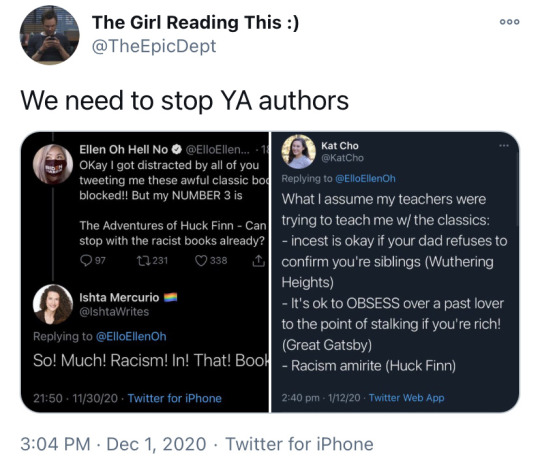
#media literacy#god I worry so much so often#particularly horrified because... like damn#I too! I too was on the 'eh but huck finn probably shouldn't be taught - that language is hurtful and damaging' train#and I definitely think there is something to be said about finding books that center poc voices#but I was never assigned huck finn in school#I read it in elementary school on my own time and just remember thinking that it was racist because jim seemed like a caricature#and perhaps I do need to reexamine my criteria for judging whether books should be taught or not#because when I agreed with the removal of it from curricula it was because the language could be theoretically hurtful#and as a white person I certainly don't feel comfortable saying that it isn't#but rather than pushing for huck finn to get off the lists#maybe we could push for Their Eyes Were Watching God to get *on* the lists#additive activism rather than punitive activism#or Song of Solomon#or Go Tell It on the Mountain#or any number of fantastic books that offer a nuanced and important historical perspective on bigotry#the thing is#tho#all of those books use slurs and offensive language too#so if that's my reasoning for wanting Huck Finn off the list... *sighs@self*#I guess I'll go ahead and be the cautionary tale#be careful why you argue for a book's removal—ask yourself if you really want that logic applied universally#anyway this analysis of huck finn is thoughtful and worth reading and I'm glad I came across it#it makes me wish huck finn was taught *well* in schools
229K notes
·
View notes
Text
When most Americans think of fascism, they picture a Hitlerian hellscape of dramatic action: police raids, violent coups, mass executions. Indeed, such was the savagery of Nazi Germany, Stalinist Russia, and Vichy France. But what many people don’t appreciate about tyranny is its “banality,” Timothy Snyder tells me. “We don’t imagine how a regime change is going to be at the dinner table. The regime change is going to be on the sidewalk. It’s going to be in your whole life.”
Snyder, a Yale history professor and leading scholar of Soviet Russia, was patching into Zoom from a hotel room in Kyiv, where the specter of authoritarianism looms large as Ukraine remains steeped in a yearslong military siege by Vladimir Putin. It was late at night and he was still winding down from, and gearing up for, a packed schedule—from launching an institution dedicated to the documentation of the war, to fundraising for robotic-demining development, to organizing a conference for a new Ukrainian history project. “I’ve had kind of a long day and a long week, and if this were going to be my sartorial first appearance in Vanity Fair, I would really want it to go otherwise,” he joked.
But the rest of our conversation was no laughing matter. It largely centered, to little surprise, on Donald Trump and how the former president has put America on a glide path to fascism. Too many commentators were late to realize this. Snyder, however, has been sounding the alarm since the dawn of Trumpism itself, invoking the cautionary tales of fascist history in his 2017 book, On Tyranny, and in The Road to Unfreedom the year after. It’s been six years since the latter, and Snyder is now out with a new book, On Freedom, a personal and philosophical attempt to flip the valence of America’s most lauded—and loaded—word. “We Americans tend to think that freedom is a matter of things being cleared away, and that capitalism does that work for us. It is a trap to believe in this,” he writes. “Freedom is not an absence but a presence, a life in which we choose multiple commitments and realize combinations of them in the world.”
In an interview with Vanity Fair, which has been edited for length and clarity, Snyder unpacks America’s “strongman fantasy,” encourages Democrats to reclaim the concept of freedom, and critiques journalists for pushing a “war fatigue” narrative about the Russian invasion of Ukraine. “There’s just something so odd about Americans being tired of this war. We can get bored of it or whatever, but how can we be tired?” he asks. “We’re not doing a damn thing.”
Vanity Fair: The things we associate with freedom—free speech, religious liberty—have been co-opted by the Republican Party. Do you think you could walk me through how that happened historically and how Democrats could take that word back?
Timothy Snyder: Yeah. I think the way it happened historically is actually quite dark there. There’s an innocent way of talking about this, which is to say, “Oh, some people believe in negative freedom and some people believe in positive freedom—and negative freedom just means less government and positive freedom means more government.” And when you say it like that, it just sounds like a question of taste. And who knows who’s right?
Whereas historically speaking, to answer your question, the reason why people believe in negative freedom is that they’re enslaving other people, or they are oppressing women, or both. The reason why you say freedom is just keeping the government off my back is that the central government is the only force that’s ever going to enfranchise those slaves. It’s the only force which is ever going to give votes to those women. And so that’s where negative freedom comes from. I’m not saying that everybody who believes in negative freedom now owns slaves or oppresses women, but that’s the tradition. That’s the reason why you would think freedom is negative, which on its face is a totally implausible idea. I mean, the notion that you can just be free because there’s no government makes no sense, unless you’re a heavily drugged anarchist.
And so, as the Republican Party has also become the party of race in our country, it’s become the party of small government. Unfortunately, this idea of freedom then goes along for the ride, because freedom becomes freedom from government. And then the next step is freedom becomes freedom for the market. That seems like a small step, but it’s a huge step because if we believe in free markets, that means that we actually have duties to the market. And Americans have by and large accepted that, even pretty far into the center or into the left. If you say that term, “free market,” Americans pretty generally won’t stop you and say, “Oh, there’s something problematic about that.” But there really is: If the market is free, that means that you have a duty to the market, and the duty is to make sure the government doesn’t intervene in it. And once you make that step, you suddenly find yourself willing to accept that, well, everybody of course has a right to advertise, and I don’t have a right to be free of it. Or freedom of speech isn’t really for me; freedom of speech is for the internet.
And that’s, to a large measure, the world we live in.
You have a quote in the book about this that distills it well: “The countries where people tend to think of freedom as freedom to are doing better by our own measures, which tend to focus on freedom from.”
Yeah, thanks for pulling that out. Even I was a little bit struck by that one. Because if you’re American and you talk about freedom all the time and you also spend all your time judging other countries on freedom, and you decide what the measures are, then you should be close to the top of the list—but you’re not. And then you ask, “Why is that?” When you look at countries like Sweden, Norway, Denmark, France, Germany, or Ireland—that are way ahead of us—they’re having a different conversation about freedom. They don’t seem to talk about freedom as much as we do, but then when they do, they talk about it in terms of enabling people to do things.
And then you realize that an enabled population, a population that has health care and retirement and reliable schools, may be better at defending things like the right to vote and the right to freedom of religion and the right to freedom of speech—the things that we think are essential to freedom. And then you realize, Oh, wait, there can be a positive loop between freedom to and freedom from. And this is the big thing that Americans get a hundred percent wrong. We think there’s a tragic choice between freedom from and freedom to—that you’ve got to choose between negative freedom and positive freedom. And that’s entirely wrong.
What do you make of Kamala Harris’s attempt to redeem the word?
It makes me happy if it’s at the center of a political discussion. And by the way, going back to your first question, it’s interesting how the American right has actually retreated from freedom. It has been central for them for half a century, but they are now actually retreating from it, and they’ve left the ground open for the Democrats. So, politically, I’m glad they’re seizing it—not just because I want them to win, but also because I think on the center left or wherever she is, there’s more of a chance for the word to take on a fuller meaning. Because so long as the Republicans can control the word, it’s always going to mean negative freedom.
I can’t judge the politics that well, but I think it’s philosophically correct and I think we end up being truer to ourselves. Because my big underlying concern as an American is that we have this word which we’ve boxed into a corner and then beaten the pulp out of, and it really doesn’t mean anything anymore. And yet it’s the only imaginable central concept I can think of for American political theory or American political life.
Yeah, it’s conducive to the joy-and-optimism approach that the Democrats are taking to the campaign. Freedom to is about enfranchisement; it’s about empowerment; it’s about mobility.
Totally. Can I jump in there with another thought?
Of course.
I think JD Vance is the logical extension of where freedom as freedom from gets you. Because one of the things you say when freedom is negative—when it’s just freedom from—is that the government is bad, right? You say the government is bad because it’s suppressive. But then you also say government is bad because it can’t do anything. It’s incompetent and it’s dysfunctional. And it’s a small step from there to a JD Vance–type figure who is a doomer, right? He’s a doomer about everything. His politics is a politics of impotence. His whole idea is that government will fail at everything—that there’s no point using government, and in fact, life is just sort of terrible in general. And the only way to lead in life is to kind of be snarky about other people. That’s the whole JD Vance political philosophy. It’s like, “I’m impotent. You’re impotent. We’re all impotent. And therefore let’s be angry.”
Did you watch the debate?
No, I’m afraid I didn’t. I’m in the wrong time zone.
There was a moment that struck me, and I think it would strike you too: Donald Trump openly praised Viktor Orbán, as he has done repeatedly in the past. But he said, explicitly, Orbán is a good guy because he’s a “strongman,” which is a word that he clearly takes to be a compliment, not derogatory. You’ve written about the strongman fantasy in your Substack, so I’m curious: What do you think Trump is appealing to here?
Well, I’m going to answer it in a slightly different way, and then I’ll go back to the way you mean it. I think he’s tapping into one of his own inner fantasies. I think he looks around the world and he sees that there’s a person like Orbán, who’s taken a constitutional system and climbed out of it and has managed to go from being a normal prime minister to essentially being an extraconstitutional figure. And I think that’s what Trump wants for himself. And then, of course, the next step is a Putin-type figure, where he’s now an unquestioned dictator.
For the rest of us, I think he’s tapping—in a minor key—into inexperience, and that was my strongman piece that you kindly mentioned. Americans don’t really think through what it would mean to have a government without the rule of law and the possibility of throwing the bums out. I think we just haven’t thought that through in all of its banality: the neighbors denouncing you, your kids not having social mobility because you maybe did something wrong, having to be afraid all the damn time. African Americans and some immigrants have a sense of this, but in general, Americans don’t get that. They don’t get what that would be like.
So that’s a minor key. The major key, though, is the 20% or so of Americans who really, I think, authentically do want an authoritarian regime, because they would prefer to identify personally with a leader figure and feel good about it rather than enjoy freedom.
You mentioned the word banality, which makes me think of Hannah Arendt’s theory of the “banality of evil.” What would the banality of authoritarianism look like in America?
So let me first talk about the nonbanality of evil, because our version of evil is something like, and I don’t want to be too mean, but it’s something like this: A giant monster rises out of the ocean and then we get it with our F-16s or F-35s or whatever. That’s our version of evil. It’s corporeal, it’s obviously bad, and it can be defeated by dramatic acts of violence.
And we apply that to figures like Hitler or Stalin, and we think, Okay, what happened with Hitler was that he was suddenly defeated by a war. Of course he was defeated by a war, but he did some dramatic and violent things to come to power, but his coming to power also involved a million banalities. It involved a million assimilations, a million changes of what we think of as normal. And it’s our ability to make things normal and abnormal which is so terrifying. It’s like an animal instinct on our part: We can tell what the power wants us to do, and if we don’t think about it, we then do it. In authoritarian conditions, this means that we realize, Oh, the law doesn’t really apply anymore. That means my neighbor could have denounced me for anything, and so I better denounce my neighbor first. And before you know it, you’re in a completely different society, and the banality here is that instead of just walking down the street thinking about your own stuff, you’re thinking, Wait a minute, which of my neighbors is going to denounce me?
Americans think all the time about getting their kids into the right school. What happens in an authoritarian country is that all of that access to social mobility becomes determined by obedience. And as a parent, suddenly you realize you have to be publicly loyal all the time, because one little black mark against you ruins your child’s future. And that’s the banality right there. In Russia, everybody lives like that, because any little thing you do wrong, and your kid has no chance. They get thrown out of school; they can’t go to university.
We don’t imagine how a regime change is going to be at the dinner table. The regime change is going to be on the sidewalk. It’s going to be in your whole life. It’s not going to be some external thing. It’s not like this strongman is just going to be some bad person in the White House, and then eventually the good guys will come and knock him out. When the regime changes, you change and you adapt, and you look around as everyone else is adapting and you realize, Well, everyone else adapting is a new reality for me, and I’m probably going to have to adapt too. Trump wants to be a strongman. He’s already tried a coup d’état. He makes it clear that he wants to be a different regime. And so if you vote him in, you’re basically saying, “Okay, strongman, tell me how to adapt.”
Yeah, we could talk about Project 2025 all day. This new effort to bureaucratize tyranny—which was not in place in 2020—could really make the banal aspect a reality because it’s enforced by the administrative state, which is going to be felt by Americans at a quotidian level.
I agree with what you say. If I were in business, I would be terrified of Project 2025 because what it’s going to lead to is favoritism. You’re never going to get approvals for your stuff unless you’re politically close to administration. It’s going to push us toward a more Hungary-like situation, where the president’s pals’ or Jared Kushner’s pals’ companies are going to do fine. But everybody else is going to have to pay bribes. Everyone else is going to have to make friends.
It’s anticompetitive.
Yeah, it’s going to generate a very, very uneven playing field where certain people are going to be favored and become oligarchs. And most of the rest of us are going to have a hard time. Also, the 40,000 [loyalists Trump wants to replace the administrative state with] are going to be completely incompetent. When people stop getting their Social Security checks, they’re going to realize that the federal government—which they’ve been told is so dysfunctional—actually did do some things. It’s going to be chaos. The only way to get anything done is to have a phone number where you can call somebody at someplace in the government and say, “Make my thing a priority.” The chaos of the administration state feeds into the strongman thing. And since that’s true, the strongman view starts to become natural for you because it’s the only way to get anything done.
You’ve studied Russian information warfare pretty extensively. A few weeks ago the Justice Department indicted two employees of the Russian state media outlet RT for their role in surreptitiously funding a right-wing US media outfit as part of a foreign-influence-peddling scheme, which saw them pull the wool over a bunch of right-wing media personalities. Do you think this type of thing is the tip of the iceberg when it comes to Russian information warfare?
Of course. It’s the tip of the iceberg, and I want to refer back to 2016. It was much bigger in 2016 than we recognized at the time. The things that the Obama administration was concerned with—like the actual penetration of state voting systems and stuff—that was really just nothing compared to all of the internet stuff they had going. And we basically caught zilcho of that before the election itself. And I think the federal government is more aware of it this time, but also the Russians are doing different things this time, no doubt.
I’m afraid what I think is that there are probably an awful lot of people who are doing this—including people who are much more important in the media than those guys—and that there’s just no way we’re going to catch very many of them before November. That’s my gut feeling.
While we’re on Russia, I do want to talk about Ukraine, especially since you’re there right now. I think one of the most unfortunate aspects of [the media’s coverage of] foreign wars—the Ukraine war and also the Israel-Hamas war—is just the way they inevitably fade into the background of the American news cycle, especially if no American boots are on the ground. I’m curious if this dynamic frustrates you as a historian.
Oh, a couple points there. One is, I’m going to point out slightly mean-spiritedly that the stories about war fatigue in Ukraine began in March 2022. As a historian, I am a little bit upset at journalists. I don’t mean the good ones. I don’t mean the guys I just saw who just came back from the front. [I mean] the people who are sitting in DC or New York or wherever, who immediately ginned up this notion of war fatigue and kept asking everybody from the beginning, “When are you going to get tired of this war?” We turned war fatigue into a topos almost instantaneously. And I found that really irresponsible because you’re affecting the discourse. But also, I feel like there was a kind of inbuilt laziness into it. If war fatigue sets in right away, then you have an excuse never to go to the country, and you have an excuse never to figure out what’s going on, and you have an excuse never to figure out why it’s important.
So I was really upset by that, and also because there’s just something so odd about Americans being tired of this war. We can get bored of it or whatever, but how can we be tired? We’re not doing a damn thing. We’re doing nothing. I mean, there’s some great individual Americans who are volunteering and giving supplies and stuff, but as a country, we’re not doing a damn thing. I mean, a tiny percentage of our defense budget—which would be going to other stuff anyway—insead goes to Ukraine.
And by the way, Ukrainians understand that Americans have other things to think about. I was not very far from the front three days ago talking to soldiers, and their basic attitude about the election and us was, like, “Yeah, you got your own things to think about. We understand. It’s not your war.” But as a historian, the thing which troubles me is pace, because with time, all kinds of resources wear down. And the most painful is the Ukrainian human resource. That’s probably a terribly euphemistic word, but people die and people get wounded and people get traumatized. Your own side runs out of stuff.
We were played by the Russians, psychologically, about the way wars are fought. And that stretched out the war. That’s the thing which bothers me most. You win wars with pace and you win wars with surprise. You don’t win wars by allowing the other side to dictate what the rules are and stretching everything out, which is basically what’s happened. And with that has come a certain amount of American distraction and changing the subject and impatience. I think journalists have made a mistake by making it into a kind of consumer thing where they’re sort of instructing the public that it’s okay to be bored or fatigued. And then I think the Biden administration made a mistake by not doing things at pace and allowing every decision to take weeks and months and so on.
What do you think another Trump presidency would mean for the war and for America’s commitment to Ukraine?
I think Trump switches sides and puts American power on the Russian side, effectively. I think Trump cuts off. He’s a bad dealmaker—that’s the problem. I mean, he’s a good entertainer. He’s very talented; he’s very charismatic. In his way, he’s very intelligent, but he’s not a good dealmaker. And a) ending wars is not a deal the way that buying a building is a deal, and b) even if it were, he’s consistently made bad deals his whole career and lost out and gone bankrupt.
So you can’t really trust him with something like this, even if his intentions were good—and I don’t think his intentions are good. Going back to the strongman thing, I think he believes that it’s right and good that the strong defeat and dominate the weak. And I think in his instinctual view of the world, Putin is pretty much the paradigmatic strongman—the one that he admires the most. And because he thinks Putin is strong, Putin will win. The sad irony of all this is that we are so much stronger than Russia. And in my view, the only way Russia can really win is if we flip or if we do nothing. So, because Trump himself is so psychologically weak and wants to look up to another strongman, I think he’s going to flip. But even if I’m wrong about that, I think he’s incompetent to deal with a situation like this. Because he wants the quick affirmation of a deal. And if the other side knows you’re in a hurry, then you’ve already lost from the beginning.
175 notes
·
View notes
Note
was thinking about this earlier but the dynamic of cannibalism being associated with high society and the culinary elite (hannibal comes to mind specifically) while also simultaneously being associated with the socially isolated and economically impoverished (as in texas chainsaw massacre) is so interesting to me i want to read 10 million books on why it happens so much in media....
i can only speak from a place of personal opinion and general knowledge, because i haven't read that many papers or in-depth studies on cannibalism, but i think it often comes down to an interesection between the themes of the story you're telling and class structures and divisions. cannibalism is a compelling form of narrative symbolism because it's undeniably impactful and hard to ignore. when portrayed as a practice associated with the culinary and social upper class, it might be used as a critique of the rich and powerful and their lack of ethics and willingness to consume and destroy others for their own self-interest by showing them literally preying on and consuming their victims, or a horror story/cautionary tale about how having everything can lead you to never be satisfied and turn to increasingly extreme measures to feel like life is worth living, or a dark fantasy of indulgence and excess. when associated with the poor, marginalized and isolated, it's often based in bigotry and harmful stereotypes of the "primitive" "inhuman" "savage" "other", however it might also function as a revenge fantasy where the most oppressed and exploited members of society turn on their oppressors and take "eating the rich" to its most literal extreme, exposing the fragility of class divisions and pointing out that those in positions of social and economic power are hardly the mythic titans their propaganda tries to make them out to be, but ultimately just as mortal and made of flesh and blood as any other human being, and not immune to being dragged down from their position at the top of the food chain and torn to pieces by the crowd (as well as reminding the audience of their own fragile mortality and precarious position in the social order, and the humanity we all share in common - however cannibalism often divides the perpetrators from both their victims and the audience, so this is rarer than the other interpretations mentioned).
cannibalism and power often go hand in hand. cannibalism has historically been used as both a means of displaying your power over defeated opponents and delivering a final, humiliating blow to their image by consuming their flesh, and a means of othering and dehumanizing your opponent by portraying them as the cannibalistic monster.
both the very rich and very poor also tend to be perceived as more distant from the people who make and consume these stories, making them easier to project fiction onto and transform into symbols and narrative devices (or, in the worst cases, dehumanize) than those who occupy the same social spheres as the creator. they can be held at an arm's length without discomfort and, depending on the target audience, may be a source of fascination due to the differences in their lived experiences. it adds to the fantasy, and makes any inaccuracies, exaggerations and fabrications feel more plausible because the majority of the audience probably don't have any personal experiences of being in those positions to draw on.
#cannibalism#classism#like this is literally just my interpretation based on my knowledge of media studies literary analysis and sociology#i cant say with any certainty whether its a True and Accurate assessment
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Of Sauron [Hypothetical] Redemption
Is Sauron redeemable?
This question is particularly active in the Sauron x Galadriel fandom, for obvious reasons. But it can be of interest to any Tolkien fan, really. Brace yourselves, this is a long read and we are going deep into Tolkien legendarium, here.
To many, the idea that Sauron is redeemable is absurd in itself because of how Tolkien describes him as “the second visible incarnation of evil”; “reincarnation of Evil, and a thing lusting for Complete Power” (Letter 131); or “shadow of Morgoth” (The Silmarillion). All of this means that Sauron is absolute and pure evil, yes? And hence, he has no possibility of redemption, whatsoever?

Not quite.
For starters, there’s an idea that needs to be deconstructed here: Tolkien lore being “black and white”, or pure Evil vs. pure Good. It isn’t.
And this was actually, a grievance Tolkien himself had ever since his work first got published. The critics and the public, seemed determined to judge his books on an absolute dichotomy, without any nuance. Ironic, many are doing the same until this day (and probably the reason why Christopher Tolkien hated the Peter Jackson adaptations so much).
Some reviewers have called the whole thing simple-minded, just a plain fight between Good and Evil, with all the good just good, and the bad just bad. Pardonable, perhaps (though at least Boromir has been overlooked) in people in a hurry, and with only a fragment to read, and, of course, without the earlier written but unpublished Elvish histories. But the Elves are not wholly good or in the right. Not so much because they had flirted with Sauron; as because with or without his assistance they were 'embalmers'. They wanted to have their cake and eat it: to live in the mortal historical Middle-earth because they had become fond of it (and perhaps because they there had the advantages of a superior caste), and so tried to stop its change and history, stop its growth, keep it as a pleasaunce, even largely a desert, where they could be 'artists' – and they were overburdened with sadness and nostalgic regret. Tolkien Letter 154
Tolkien admits his lore doesn’t deal with “absolute evil” because he doesn’t believe in such a thing:
In my story I do not deal in Absolute Evil. I do not think there is such a thing, since that is Zero. I do not think that at any rate any 'rational being' is wholly evil. Satan fell. In my myth Morgoth fell beasts and monsters, and the Unknown. The defence of the realm may then indeed become symbolic of the human situation. Before Creation of the physical world. Tolkien Letter 183
Tolkien's Sauron
Did Tolkien created Sauron as a nuanced villain in his lore? What does he say about him?
And there is Sauron. In the Silmarillion and Tales of the First Age Sauron was a being of Valinor perverted to the service of the Enemy and becoming his chief captain and servant. He repents in fear when the First Enemy is utterly defeated, but in the end does not do as was commanded, return to the judgement of the gods. He lingers in Middle-earth. Very slowly, beginning with fair motives: the reorganising and rehabilitation of the ruin of Middle-earth, 'neglected by the gods', he becomes a reincarnation of Evil, and a thing lusting for Complete Power – and so consumed ever more fiercely with hate (especially of gods and Elves). All through the twilight of the Second Age the Shadow is growing in the East of Middle-earth, spreading its sway more and more over Men – who multiply as the Elves begin to fade. The three main themes are thus The Delaying Elves that lingered in Middle-earth; Sauron's growth to a new Dark Lord, master and god of Men; and Numenor-Atlantis. Tolkien Letter 131
Mairon, the Maia of Aulë, was not evil in the beginning (because nothing is, in Tolkien lore). He was corrupted by Morgoth. He repents of his crimes under Morgoth but doesn’t do penitance. During the Second Age, he begins his rise to power, being a cautionary tale of “the road to hell is paved with good intentions”.
In Season 1 of "Rings of Power", we saw "repentant Mairon" aka Halbrand:


In Season 2, Annatar was introduced, and he symbolizes "Sauron the reformer", who wants to rebuilt Middle-earth with good intentions:


Sauron was of course not 'evil' in origin. He was a 'spirit' corrupted by the Prime Dark Lord (the Prime sub-creative Rebel) Morgoth. He was given an opportunity of repentance, when Morgoth was overcome, but could not face the humiliation of recantation, and suing for pardon; and so his temporary turn to good and 'benevolence' ended in a greater relapse, until he became the main representative of Evil of later ages. But at the beginning of the Second Age he was still beautiful to look at, or could still assume a beautiful visible shape – and was not indeed wholly evil, not unless all 'reformers' who want to hurry up with 'reconstruction' and 'reorganization' are wholly evil, even before pride and the lust to exert their will eat them up. Tolkien Letter 153
During the Second Age, Sauron begins his rise to power, with good intentions, at first. However, his pride and lust for power becomes too great, and he aspires to become a “God of Men” (no longer a mere Maia).
And this is probably Sauron's greater crime (sin) in the legendarium, since Eru himself is called to intervene: Sauron was first defeated by a 'miracle': a direct action of God the Creator, changing the fashion of the world, when appealed to by Manwë [...] reduced to 'a spirit of hatred borne on a dark wind', I do not think one need boggle at this spirit carrying off the One Ring, upon which his power of dominating minds now largely depended (Letter 211).

Because of his admiration of Strength he [Sauron] had become a follower of Morgoth and fell with him down into the depths of evil, becoming his chief agent in Middle Earth. When Morgoth was defeated by the Valar finally he forsook his allegiance; but out of fear only; he did not present himself to the Valar or sue for pardon, and remained in Middle Earth. When he found how greatly his knowledge was admired by all other rational creatures and how easy it was to influence them, his pride became boundless. By the end of the Second Age he assumed the position of Morgoth's representative. By the end of the Third Age (though actually much weaker than before) he claimed to be Morgoth returned. Tolkien Letter 183 (note)
Let's dig in the "Sauron the supervillain":
The corrupted, as was Melkor/Morgoth and his followers (of whom Sauron was one of the chief) saw in them the ideal material for subjects and slaves, to whom they could become masters and 'gods', envying the Children, and secretly hating them, in proportion as they became rebels against the One (and Manwë his Lieutenant in Eä). Tolkien Letter 212

In my story Sauron represents as near an approach to the wholly evil will as is possible. He had gone the way of all tyrants: beginning well, at least on the level that while desiring to order all things according to his own wisdom he still at first considered the (economic) well-being of other inhabitants of the Earth. But he went further than human tyrants in pride and the lust for domination, being in origin an immortal (angelic) spirit. In The Lord of the Rings the conflict is not basically about 'freedom', though that is naturally involved. It is about God, and His sole right to divine honour. The Eldar and the Númenóreans believed in The One, the true God, and held worship of any other person an abomination. Sauron desired to be a God-King, and was held to be this by his servants; if he had been victorious he would have demanded divine honour from all rational creatures and absolute temporal power over the whole world. Tolkien Letter 183
What these quotes tell us, is this: while Sauron isn’t “absolute evil” (because Tolkien himself didn’t deal with this in his legendarium, nor did he believed such a thing exists), Sauron's will (desires; intentions; goals) came pretty close to “wholly evil”.
Sauron is unmistakable evil, obviously distinguishable from “good”: he’s not a grey character, nor an anti-hero in any way, shape or form. He’s a full-on villain, some might even say a "super-villain", really. However, he’s not pure irredeemably wicked evil in Tolkien lore.
Why?
Tolkien's Ideas of Redemption
This goes back to Tolkien’s religious beliefs (Christian-Catholic) and how they are present in his legendarium; in 1953, he wrote this about the Orcs:
the Diabolus Morgoth did, and started making things 'for himself, to be their Lord', these would then 'be', even if Morgoth broke the supreme ban against making other 'rational' creatures like Elves or Men. They would at least 'be' real physical realities in the physical world, however evil they might prove, even 'mocking' the Children of God. They would be Morgoth's greatest Sins, abuses of his highest privilege, and would be creatures begotten of Sin, and naturally bad. (I nearly wrote 'irredeemably bad'; but that would be going too far. Because by accepting or tolerating their making – necessary to their actual existence – even Orcs would become part of the World, which is God's and ultimately good.) I have represented at least the Orcs as pre-existing real beings on whom the Dark Lord has exerted the fullness of his power in remodeling and corrupting them, not making them. That God would 'tolerate' that, seems no worse theology than the toleration of the calculated dehumanizing of Men by tyrants that goes on today. Tolkien Letter 153
In 1965, W.H. Auden asked Tolkien if the notion of Orcs (an entire race that should be seen as irredeemably wicked) was not heretical:
With regard to The Lord of the Rings, I cannot claim to be a sufficient theologian to say whether my notion of Orcs is heretical or not. I don't feel under any obligation to make my story fit with formalized Christian theology, though I actually intended it to be consonant with Christian thought and belief, which is asserted somewhere, Book Five, page 190,1 where Frodo asserts that the orcs are not evil in origin. Tolkien Letter 169
And now you know the reason behind Orc families in "Rings of Power".
Tolkien himself went back and forward with this notion, or even if the Orcs had “souls”, to begin with, but in the end his faith probably got the best of him. We also see this with his thoughts on Gollum:
In which case (as I believe) salvation from ruin will depend on something apparently unconnected: the general sanctity (and humility and mercy) of the sacrificial person [...] Gollum had had his chance of repentance, and of returning generosity with love; and had fallen off the knife-edge. Tolkien Letter 191
On the importance of repentance, even among the Valar:
The Fall or corruption, therefore, of all things in it and all inhabitants of it, was a possibility if not inevitable. Trees may 'go bad' as in the Old Forest; Elves may turn into Orcs, and if this required the special perversive malice of Morgoth, still Elves themselves could do evil deeds. Even the 'good' Valar as inhabiting the World could at least err; as the Great Valar did in their dealings with the Elves; or as the lesser of their kind (as the Istari or wizards) could in various ways become self-seeking. Aulë, for instance, one of the Great, in a sense 'fell'; for he so desired to see the Children, that he became impatient and tried to anticipate the will of the Creator. Being the greatest of all craftsmen he tried to make children according to his imperfect knowledge of their kind. When he had made thirteen, God spoke to him in anger, but not without pity: for Aulë had done this thing not out of evil desire to have slaves and subjects of his own, but out of impatient love, desiring children to talk to and teach, sharing with them the praise of Ilúvatar and his great love of the materials of which the world is made. The One rebuked Aulë, saying that he had tried to usurp the Creator's power; but he could not give independent life to his makings. He had only one life, his own derived from the One, and could at most only distribute it. 'Behold' said the One: 'these creatures of thine have only thy will, and thy movement. Though you have devised a language for them, they can only report to thee thine own thought. This is a mockery of me.' Then Aulë in grief and repentance humbled himself and asked for pardon. And he said: 'I will destroy these images of my presumption, and wait upon thy will.' And he took a great hammer, raising it to smite the eldest of his images; but it flinched and cowered from him. And as he withheld his stroke, astonished, he heard the laughter of Ilúvatar. 'Do you wonder at this?' he said. 'Behold! thy creatures now live, free from thy will! For I have seen thy humility, and taken pity on your impatience. Thy making I have taken up into my design.' This is the Elvish legend of the making of the Dwarves; but the Elves report that Iluvatar said thus also: 'Nonetheless I will not suffer my design to be forestalled: thy children shall not awake before mine own.' And he commanded Aule to lay the fathers of the Dwarves severally in deep places, each with his mate, save Dúrin the eldest who had none. There they should sleep long, until Ilúvatar bade them awake. Nonetheless there has been for the most part little love between the Dwarves and the children of Iluvatar. And of the fate that Ilúvatar has set upon the children of Aulë beyond the Circles of the world Elves and men know nothing, and if Dwarves know they do not speak of it. Tolkien Letter 212
This is pure Christian doctrine.
Even though Tolkien legendarium is not a copy-paste from the Bible (and it has several other inspirations), it’s pretty clear that Eru Ilúvatar represents the Christian God. And even though God himself had different interpretations throughout History, I think we should see it as the God from Tolkien’s time (and our time, too): “God the Father” (which makes sense with what Tolkien created on his lore).
In Catholicism (Tolkien’s religion), God is just (God’s justice) but he’s also merciful, and he loves all of his children, even those who fallen into sin. No one is unredeemable in the eyes of God (no matter how deep one has fallen), if one truly repents and makes amends for his sins ("the virtue of penance"). God is always willing to give their faithful a second chance, if they accept him as their one true God, and make penitence in His service (whatever that might be).
In the lore, we know that the Children of Ilúvatar are Elves and Men. However, all the deities (Valar and Maiar) were also created by Eru. From a Christian perspective, the Valar are archangels, and the Maiar are angels. This is an on-going debate within Theology, because some agree that angels are “sons of God”, while others don’t. For the sake of the argument, I’ll just add this: Job 38:7 - when the morning stars sang together and all the sons of God [angels] shouted for joy. But more on that later.
This means that Sauron is, indeed, redeemable. But he has to make that choice, himself. "Free will"; another major theme in Tolkien lore.
And, the true question, here, isn’t “is Sauron redeemable?” but “is Sauron capable of repentance”?
In Tolkien “canon”, meaning the events of “The Silmarillion”, “The Hobbit”, up until the end of “The Lord of the Rings” trilogy (First to the dawn of the Fourth Age) the answer is no.
After the One ring is destroyed by Frodo, Sauron’s spirit is left so diminished and weak, he can never rise to power, again, according to Gandalf:
If [the One Ring] is destroyed, then [Sauron] will fall; and his fall will be so low that none can foresee his arising ever again. For he will lose the best part of his strength that was native to him in his beginning, and all that made or begun with that power will crumble, and he will be maimed for ever, becoming a mere spirit of malice that gnaws itself in the shadows, but cannot again grow or take shape. And so a great evil of this world will be removed.
However, this is not as simple. Sauron/Mairon is an immortal spirit by definition. He can’t never truly die, since he’s one of the spiritual forces that first helped shaped the world in the Ainulindalë (the Music of the Ainur), and no soul can be annihilated or reduced to zero (non-existent) in Tolkien legendarium.
Sauron/Mairon’s whereabouts and fate after the dawn of Fourth Age are unaccounted for, because Tolkien didn’t get the chance to finish his story. We, truly, don’t know where he went, if we stayed on Middle-earth, or to the Undying Lands of Valinor (to finally face the judgement of the Valar for his crimes), because he could go whenever he wanted in Arda, really.
One theory is that Manwë, the King of the Valar, might have come to Mordor to capture Sauron after the One ring is destroyed, based on this description from “Return of the King”:
And as the Captain gazed south to the Land of Mordor, it seemed to them that, black against the pall of cloud, there rose a huge shape of shadow, impenetrable, lightning-crowned, filling all the sky. Enormous it reared above the world, and stretched out towards them a vast threatening hand, terrible but impotent [Sauron’s spirit]: for even as it leaned over them, a great wind took it, and it was all blown away, and passed, then a hush fell.”


Basically this scene but a “great wind” carries away that shadow
Manwë is the one with the power over air and winds, and when Sauron repented the first time (after Morgoth’s defeat), he went to Eönwë, the herald of Manwë, to beg forgiveness for his past crimes. His fellow Maia told him that he couldn't be the one to grant him pardon, because that’s above his station, and he needs to face trial before the Valar, namely from Manwë.
Since we know that Sauron’s pride prevented him from doing this, it would actually make sense for Manwë himself to capture Sauron after his defeat, bringing him to Valinor.
When Thangorodrim was broken and Morgoth overthrown, Sauron put on his fair hue again and did obeisance to Eönwë, the herald of Manwë, and abjured all his evil deeds. And some hold that this was not at first falsely done, but that Sauron in truth repented, if only out of fear, being dismayed by the fall of Morgoth and the great wrath of the Lords of the West. But it was not within the power of Eönwë to pardon those of his own order, and he commanded Sauron to return to Aman and there receive the judgment of Manwë. Then Sauron was ashamed, and he was unwilling to return in humiliation and to receive from the Valar a sentence, in might be, of long servitude in proof of his good faith; for under Morgoth his power had been great. Therefore when Eönwë departed he hid himself in Middle-Earth; and he fell back into evil, for the bonds that Morgoth had laid upon him were very strong. The Silmarillion
Many use Gandalf’s quote as “proof” that Sauron remained on Middle-earth like a shadow of malice, or a ghost. However, Tolkien made the distinction between himself and what his characters say, in Letter 153: “There is, to me, a wide gulf between the two statements, so wide that Treebeard's statement could (in my world) have possibly been true [...] Treebeard is a character in my story, not me; and though he has a great memory and some earthy wisdom, he is not one of the Wise, and there is quite a lot he does not know or understand.”
Gandalf is wise, indeed, but he’s not of the same rank as the Valar (he’s a servant to them), nor he, like Eönwë, has either the power or the permission to pass sentences on other Maiar’s fates. Which means, his quote is his own opinion on the subject, and not actual "canon" on what happened to Sauron after the One was destroyed.
For the sake of argument, let’s assume Manwë captured Sauron: was he sent to the Void like his former master, Morgoth?
Based on The Silmarillion it could appear that way:
Among those of his servants that have names the greatest was that spirit whom the Eldar called Sauron, or Gorthaur the Cruel. In his beginning he was of the Maia of Aulë, and he remained mighty in the lore of that people. In all the deeds of Melkor the Morgoth upon Arda, in his vast workds and in the deceits of his cunning, Sauron had a part, and was only less evil than his master in that for long he served another and not himself. But in after years he rose like a shadow of Morgoth and a ghost of his malice, and walked behind him on the same ruinous path down into the Void.
However, this, again, is not that simple, because The Silmarillion was not only published by Christopher Tolkien, and it contains elements outdated and reviewed by Tolkien himself, but it’s also a tale written by the Eldar, and it contains “opinions” and “facts” from which the Eldar themselves had little knowledge about (namely everything that’s connected to the Maiar and the Valar).
This means, not everything that’s in The Silmarillion is true or actually happened (canon): it’s like “Fire & Blood” by George R.R. Martin, a collection of facts, opinions, gossip, myths, etc. written by the Elves. The truth is in Tolkien’s essays and letters, really. And this is why “Rings of Power” can afford to play with the events of this book.
Tolkien did confirm, in his Letter 297, that Morgoth was overthrown and extruded from the World (the physical universe). But his crimes were far worse than Sauron's:
the Diabolus Morgoth did, and started making things 'for himself, to be their Lord', these would then 'be', even if Morgoth broke the supreme ban against making other 'rational' creatures like Elves or Men. They would at least 'be' real physical realities in the physical world, however evil they might prove, even 'mocking' the Children of God. They would be Morgoth's greatest Sins, abuses of his highest privilege. Tolkien, Letter 153
Morgoth is a Vala (God/archangel), and he did not only corrupted Elves into Orcs, but also Maiar (angels) into Balrogs and other servants of his (demons), including Mairon himself. Mairon, like all the other Maiar (including the fallen ones), was created by Eru, but got corrupted by Morgoth, which means, the way Eru sees him is key. Does he sees Mairon as "equal" to Morgoth, or as victim of Morgoth's corruption? Food for thought. Because if he's just a victim, the Void isn't his fate.
A lot of fans in the Tolkien fandom have the headcanon that the immortal servants of Morgoth were sent to the Void, alongside him, but Tolkien never wrote about this, and their fates are a mystery. I might be mistaken here, but I think only Ungoliant’s fate is mentioned in the legendarium, and very enigmatic, too: went to the forgotten south of the world before the (first) rising of the Sun, and there disappeared from history.
Then, we have the fact that Satan/Lucifer is Melkor/Morgoth because he’s the one who corrupts God’s creation and he’s the symbolic archangel (like Lucifer was). Him being dragged in chains and imprisoned until the end of time, also parallels a biblical event.
Sauron is a satanist, a follower of Satan/Morgoth. Tolkien also makes this distinction in his letters: Satanic rebellion and evil of Morgoth and his satellite Sauron; in which Evil is largely incarnate, and in which physical resistance to it is a major act of loyalty to God (Letter 156). Tolkien also calls Sauron "a reincarnation of Evil"; that "evil" being Morgoth (diabolus).
Sauron’s crimes
His biggest crimes in Tolkien legendarium aren’t the forging of the One ring, nor the whole “rings of power” project to enslave the Free people’s of Middle-earth, nor even the Fall of Númenor. Because, as Tolkien, told us: “in The Lord of the Rings the conflict is not basically about 'freedom', though that is naturally involved. It is about God, and His sole right to divine honour” (Letter 183).
Sauron’s biggest sins in Tolkien lore are:
Pride
Idolatry (worship of false gods): Thou shall have no other Gods before me. Mairon turned his back on Eru (God) to serve Morgoth (Devil), and this act of treason is a crime against Eru himself;
Rebellion: against Eru’s authority, by siding with Morgoth;
Heresy: he forsake his worship of Eru (his creator) for Morgoth; and also converted many Númenoreans to his Morgoth cult, in the hopes of angering the Valar enough to destroy Númenor;
Blasphemy: he cut down Nimloth, the White Tree of Númenor, a symbol of the Faithful, and in its place raised a great Temple devoted to Morgoth in which human sacrifices were performed to asks for immortality, and persecuted the Faithful;
Usurpation of God’s authority: self-proclaim God. That’s why he’s called “shadow of Morgoth”; because Sauron is a mere Maia, a servant to a God, not an actual God.
Would any of these sins sent Sauron into the Void with his former master? Again, it would depend on how Eru judges him, really.
The Void is quite a mysterious place in the legendarium; it’s located outside Time and Space, it’s the absence of the Secret Fire of Eru (“the Flame Imperishable”), his power of Creation. We only know that Morgoth was imprisoned there, and set free at the end of time.
Eru already punished Sauron once, by removing his ability to take on physical form after the Fall of Númenor; and after the One ring was destroyed, Sauron himself is little more than a shadow of his former self, his spirit severely diminished, powerless, and unable to cause any damage, at all. That’s his punishment, already.
But in order to get any redemption, that choice would have to come from Mairon. He would have to truly and honestly repent for all of sins (confession), starting by forsaken Morgoth and recognizing Eru as his one true God, and, then, fulfill a fitting penitence for his crimes. We are talking about an immortal spirit here, this process can take thousands of years or even millenniums.
#tolkien lore#tolkien legendarium#tolkien world#sauron#mairon#sauron rop#the lord of the rings#lord of the rings#sauron rings of power#rings of power#the rings of power#saurondriel
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
#this post is an act of violence against me personally (affectionate)
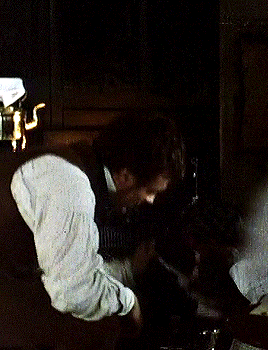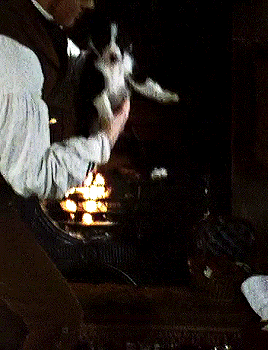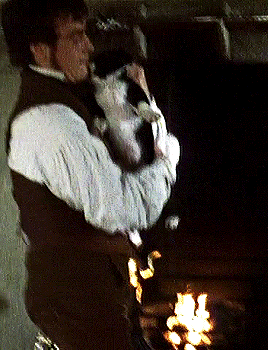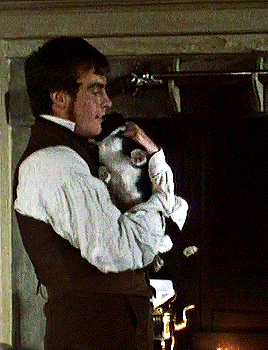





Toby Stephens as Gilbert Markham in THE TENANT OF WILDFELL HALL Part I.
#HEY Y'ALL#remember when#toby stephens#was a himbo shepherd/farmer who fell for the mysterious artist next door#and was a WAY better father to her kid than her piece of absolute shit husband was?#and then he cuddled with a puppy???#I SURE DO#i should revisit this one; gotta love how tara fitzgerald was the heroine of this AND the awful aunt in jane eyre#the woman has the bronte RANGE#the tenant of wildfell hall#(additional reminder that this was one of the -- if not THE -- first stories to have a woman seek a divorce/escape from an abusive husband#and actually get A HAPPY ENDING instead of being treated as a cautionary tale. anne bronte gets ALL of my love and admiration for that.)#historical#as queue wish
840 notes
·
View notes
Text
Welcome to another round of W2 Tells You What You Should See, where W2 (me) tries to sell you (you) on something you should be watching. Today's choice: 琅琊榜/Nirvana in Fire.

Nirvana in Fire is a 2015 historical series best described as either a complicated succession drama set in the premodern Chinese imperial palace, or the story of a man who didn't die a decade ago and has decided to make it everyone else's problem.

And really, I almost feel silly giving my glib little summary, because Nirvana in Fire is so well-known of a property. It's a classic for a reason, and that reason is that it's legitimately very good. This show is what happens when you adapt a solid story, get a bunch of very talented actors, and throw a huge amount of money at it. It's incredibly popular and highly acclaimed, and it earned all of the hype.
Still, while I bet there are few people adjacent to c-drama stuff who've never heard of Nirvana in Fire, I'm sure there are plenty who haven't watched it. After all, it looks like one of those slow, serious shows with a lot of ponderous talking and no joy. If that's the impression you've been given, I could imagine looking at the 54-episode commitment and saying, I don't need that in my life.

I am here to tell you you're wrong. It is a banger of a show. It's tense. It's funny. It's heartbreaking. It’s exceptionally clever. It’s jaw-droppingly stupid. It’s romantic. It’s tragic. It has smart plots and bizarre subplots. And that's not even touching the thing with the yeti.
So in case you're one of those people who's heard of Nirvana in Fire, but has put off watching it for one reason or another, I'm here with five reasons I think you should try it.
1. Epic Shit
Did you like the Lord of the Rings? More specifically, did you really like the second Peter Jackson film? Great, then you're all set for this.

I guess I could have called this Game of Thrones without the dragons, but that's not actually the vibe at all. Game of Thrones is much more sensational and salacious, with all the blood and butts and what-not. The Tolkien comparison is more apt, I think, because Nirvana in Fire is equally about as wholesome as you can get in a property where dudes are still getting stabbed all the time.
This is a show about vengeance. And yeah, justice for the fallen, sure, that's fine too. But mostly it's about a bunch of good people joining forces to make sure the bastards who did wrong pay, with their lives as necesary.

The problem, though, is that these bastards are incredibly powerful, which means that a pure brute-force approach isn't going to work. Accordingly, this quickly becomes a story about the power of smart teamwork to exact retribution on some people who can (and did!) legally get away with murder -- and our heroes are some of the people with their necks most on the line if anything goes wrong.

Don't let the Middle Earth comparison fool you into thinking this is all epic swordfights. It's not. (I mean, for one thing, as well-funded as this project is, it doesn't have Peter Jackson Money.) The vast majority of the tension in the show comes from dialogue and slow, terrible realizations. The fight scenes are almost a relief from the nail-biting intensity of intimate conversations about getting a letter from somebody's ex-wife or returning a book.
All told, the show has that incredible almost-RPG vibe of going through all the little subquests and cutscenes you find along the way to defeat the final boss. The plot carefully unravels a multi-tendriled mystery told to you by people in incredible costumes. It doesn't get much more epic than that.

(Nirvana in Fire is also a cautionary tale about how you should be very careful with who gets invited to your birthday party.)
2. A chronically ill protagonist
Okay, right in the first episode, it is established that the main character has three whole completely different names and an old nickname. I'm going to call him Mei Changsu for the duration of this rec post, but let the record show that I could just have easily gone with one of the other three.

What you learn in that same first episode is that Mei Changsu used to be a palace insider, the cocky son of a noble family, only now nearly everyone he used to know thinks he's dead. Also, he's not far off from being actually dead -- he has an unspecified terminal condition that's mostly managed, provided he stays in his little mountain hideaway with his handsome doctor bestie and doesn't return to his old stomping ground and start kicking over hornets' nests.
So guess what he's about to do.

I have to make a note of how brilliant the casting is here: Hu Ge is an action actor! He is a kickpuncher of a man! And I think it's great that you can sort of see his frustration, as well as Mei Changsu's, at having to spend the whole series wrapped in countless layers of fabric and/or lying in bed while everyone around him gets to be the badass action heroes.


Mei Changsu's not faking it, either -- he's actually dying. He expends his energy where he thinks it's necessary, and sometimes that means he has to spend the following week in bed. He's constantly frustrated with himself for what he can't do anymore. He's racing a clock, and that clock is his own failing body. If he dies, the only hope anyone here has for justice dies with him.
He gets two love interests that the show treats pretty much equally. One's a lady general who wasn't even a love interest in the book. The other's the handsome prince who was initially going to be his textual romantic partner in same book, until the author hopped genres from danmei to general historical drama. I can't even call this a love triangle, because there's no competition. He just gets a wife and a husband -- in that he gets neither, because circumstances and his own illness keep him distant from them. He lies to both of then about his condition (among other things). He wants to be with them both and knows he can't be with either. And they in turn have to learn to accept what of him they can and can't have.


(Also, Nihuang (her) and Jingyan (him) are both incredibly gorgeous, which is exactly what bisexual genius Mei Changsu deserves.)


Obviously this isn't a perfect representation of life with chronic illness, largely because Mei Changsu is an incredily wealthy man who lives in a universe with what's basically magic medicine. However, I've seen the story's treatment of him and his condition resonate with a lot of chronically ill viewers, so even with the fantasy layer on it, there's definitely something there.
3. Dave
I have already told the story of how Meng Zhi became "Dave," but long story short, he's such a Dave that I legitimately forget his character's real name. He embodies Daveness. He's The Ultimate Dave.

Dave is an excellent fighter, a loyal friend -- and a terrible liar. He's possbly the only straightforward character in the entire show. When he's asked to be duplicitous, he's comically bad at it. Dave will never do a heel turn. I was misled at first by his semi-evil facial hair, but I have seen the error of my ways. Dave is pure lawful good.
And the reason I list Dave as such a selling point is that having a Dave means you always know what's going on. This is because Dave never knows what's going on, and he has no ego about that, so he asks questions, and other characters have to explain to him what just happened, and that is how you figure out what's going on.
It's an incredibly smart move on the drama's part, because some of the (very fun) schemes are so complicated that there's no way for you, the viewer, to understand them just by watching. Without the internal monologues and omniscent narration of a book, the machinations are opaque. You need things explained -- but why would the schemers explain their schemes? Well, Dave needs some exposition, so here you go.

So if you're worried that you might be left feeling stupid by a show where so many sneaky people are hatching so many complex plans, worry not! Like the good man he is, Dave has your back.
4. A Million Amazing Antagonists
If you like bad guys, this is a show for you. This show has brilliant bad guys all the way down. It has bad guys at every turn. It has bad guys for every taste. Welcome to Big Liang's Big Bad Guy Emporium, where we guarantee you'll walk out of here with a bad guy you like, or your money back!





(And yes, this set of pictures is also to say that their costume budget was entirely well-spent.)
Without getting too far into spoilers, I will say that the basic situation underlying the whole series is this: The emperor has done a lot of bad things, and he has enlisted a bunch of people's help in hiding those bad things, so much so that many of those other people have done even more bad things the emperor didn't even know about -- and then everyone has gone to great lengths to cover those up as well. Our protagonists spend the whole series unraveling this colossal shitshow and bringing people to task for their crimes.
So really, if you're going to spend 54 episodes taking down the baddies, they've got to be baddies you love to see taken down. And these are -- in part because all of them have crystal-clear, rock-solid motivations for their actions. Nobody here is a moustache-twirling comic-book-villain baddie. They're all bad for reasons that are very understandable in their individual contexts. And not a single one of them is going to go down without a fight.
5. World's Best Mom

(Sidebar: The fact that four out of five of my reasons to watch the show are individual or groups of characters should be your strongest indicator that this is an intensely character-driven story.)
This is not a Dead Mom Show. Okay, some moms are dead, but mostly this is a Moms Are Alive And Often Cause Problems Show, which is a lot of what makes the palace drama so delicious. But there is one Good Mom who stands out above all the rest: Consort Jing.

Played with perfect grace and devastating politeness by the stunning Liu Mintao, Consort Jing is a skilled doctor and excellent baker who starts the show with a low-level status among the women of the palace. She swallows down all kinds of mistreatment because she's not in a place to oppose it -- and when she can retaliate, it must only be through soft power. She loves her jock son with all her heart, but because of both their relatively poor positions in the hierarchy, she doesn't get to see him all that much. She wants to be an asset to him, while all the time she has to fear becoming a liability.

She is also the smartest person in any room that she's in, unless she's in a room with Mei Changsu, and even then it may be a tie.

There are lots of great characters in the show that I could have highlighted here, and plenty of them are women, but Consort Jing in particular never ceases to impress me. She is trapped in a gilded cage, married to a man who [lengthy list of spoilers that are traumatic to her in particular], and held hostage by how every time she even looks like she's out of line, it puts both her and her boy in danger. She's the most vulnerable of any of our good guys. Kind of like Wang Zhi, she's got to be clever or she's dead.
Consort Jing is not part of Mei Changsu's original plan. She figures out his plan and makes herself part of it -- and entirely remotely, as she and he aren't even in the same room until episode 40 or so. She puts herself in great danger to make sure he succeeds, not because it will necessarily do her any good, but because Jingyan needs him. This woman has been captain of the Mei Changsu/Jingyan ship for like twenty years already.
Oh, and did I mention her outfits?



I love you, Consort Mom.
Are you ready to watch it yet?
Get it on Viki! Get it on YouTube! Get it on YouTube but in a different playlist! (And also maybe get it on Amazon? Not in my region, but maybe in yours.)
I will warn you that it does take off running -- I think I saw someone say it introduces nineteen characters in the first episode? I was worried that I'd be too innundated by situations and flashbacks and names to be able to follow. By the second or third episode, though, I was rolling with it. So if you feel like you're struggling at the beginning, stick with it a bit. See if you don't feel it start to click.
...Man, reading over this post has left me going, oh, but I missed that! and that! and that guy! And yeah, the truth is that there are just so many great things about the show that limiting myself to only five (and being limited to only thirty images) was tough. I'm sure that people reblogging will add their own must-see elements.
Truly, this is a show that deserves its reputation. It may not be for everyone, but if this is the kind of thing that you like, it is a shining example of that thing.
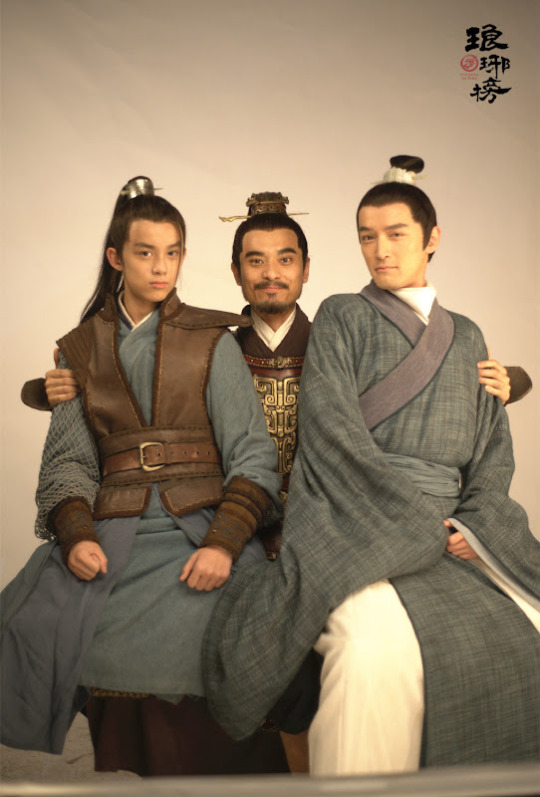

Besides, you have to love a production where everyone was clearly having just a whole lot of fun being big ol' costumed dorks.
488 notes
·
View notes
Text
"....and here we have the image of the Terran deity of truth, Eycha-Bomba-ur-Guy, not be confused with the deity Bomb-ur, the god of abundance from the ancient Tolki-eena religion, which predates the Utubar religion entirely. Archeological excavations of the primitive holo-relics of Terra dates the Utubar religion to the two kingdoms period of the Amaz-U-na, and App-le-ple empires, in the Memetiscan era.
As stated before Eycha-Bomba-ur-Guy is a deity of truth and religious texts proclaim that he emerges whenever the principles of truth are violated. The legends we have been able to uncover from the ruins of Terra talks of a well where he is supposed to reside in and that every terran year he appears unexpectedly in order to shame the liars seeking fortune in the Holos of the kingdom of Utuba in a ruthless public sermon.
(Unfortunately we have not been able to uncover physical evidence of the kingdom as of now. Much of the information we have on the Utuba come from the Utuba Com-men-tits, the famous historical document that confirmed the theory that the Utuba people, consisting of the mortal Viu-wah, the priestly Saab-scriba, and godly Cree-atar, recorded history collectively.)
In his endeavor to champion truth Eycha-Bomba-ur-Guy is confronted by many adversaries and we can see how these battles play out in the religious iconography of the period. One of his many opponents is Tomm-y-Tallaar-ico, a rather comical figure who relentlessly takes credit for the achievements of others' and boasts about it throughout Terra. Some scholars believe him to be a fictional figure created to warn children to stay away from lying and boasting, especially because the Utuba Com-men-tits records one of the claims made by the minor deity as his mother being proud of him, which by the very nature of the deity is implied to be a false claim.
(Parental figures and their approval seems to be very important to the Terrans. Scholars have found multiple worshipful holos with terms such as Daddy, Zaddy, Mother, Mommy, and Muscle Mommy as evidence to this theory. Deviant behaviour seems to be referred to as 'Fatherless' behaviour. 'Yo Mamma' statements seem to be considered a damning insult. In addition, the ritualistic chant "Excuse me? Sorry. Mommy? Sorry. Mommy? Sorry", which is believed to be the only surviving part of the the lost Litany for Forgiveness, the pair to the Litany against Fear from the Epic of the Dune, validates the theory that Terrans craved parental approval.)
Much more sinister than the Tomm-y-Tallaar-ico is the Jayme-som-Erton, a figure that only talks in the voice of others. A negative deity presiding over plagiarism, Jayme-som-Erton pretends be your ally while making profit off of your work. After Eycha-Bomba-ur-Guy defeated him in a lengthy duel the Utuba Com-men-tits faithfully records that Jayme-som-Erton's own voice can only speak lies and to be wary of the others among the Cree-ator class that use his tricks to prosper in Utuba.
Eycha-Bomba-ur-Guy's legendary victory over Jayme-som-Erton was followed by the complete erasure of the Cree-ator's presence in the Utuba kingdom's religion beyond being used as a cautionary tale. This presents another aspect of Terran religion, called Can-cellat-Ion, a ritualistic deicide of the gods that have wronged them. Undoubtedly this is an evidence of the might of the ancient Terrans. Several pieces of historical evidence from the records known as Twee-et-er (theorized to be named after a blue avian like figure who many believe might be related to the legendary heroes Twee-dle-dee, and Twee-dle-dum) refer to multiple conflicts called the War of the Fans which lead to the Can-cellat-Ion being performed. Ancient Terrans were indeed a fearsome species. (To be noted that some deities do recover while others do not. Criteria for survival unknown.)
In the coming chapters, we'll look into more deities from Terra's various pantheons, such as the eternal enmity between the Goddess Doll-y-Par-tonn and her nemesis Jol-e-Ne. The deity Trish-a-Payt-As, whose children are harbingers for the death of malignant royals is also important to look into. The deity seems to have had hostility towards the Brie-ti-ish royals specifically as legends say they were hit twice by the deity's wrath. Also of particular interest are Ea-Nasir, a deity of trickery and mischief, and ancient literature such as the Gonch-ar-Ov, a lost epic saga whose holo-copy researchers are still trying to uncover today. Both of these are a part of the Tumb-L-Er mystery religion, whose intricate rites and rituals still remain too complex to decode...."
-Excerpt from Chapter 9, "Deities from the Holo", from Scholar Jaarp-r-Saar's The Complexities of Terran Religions.
#hbomberguy#tommy tallarico#james somerton#humans are space orcs?#I don't know about that last one#this came to me in a dream#I can never reproduce this monstrosity#like what is this?#ea-nasir#Goncharov#Dolly Parton#Jolene#Trisha Paytas#King Charles#what a set of tags
258 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mad Queen Misogyny
All the mad queen Dany takes, from both D&D and the audience, are just plain misogyny. They are literally just repeats of common misogynistic ideas. D&D have given a few reasons for why they wrote the mad queen ending for Dany, and all of them are the same old misogynistic tropes of fantasy and mythology.
The Mad Queen:

I'm going to start this off by going into how the mad queen trope itself is rooted in misogyny. This is one of the oldest tropes in fantasy/fairytales. Whether it's Snow White's evil step mother or the Queen of Hearts, literature is riddled with mad queens.
The idea of the mad queen is informed by the desires of men to keep women out of power. Yes there are historical women who were horrible people and unstable when in power. However, those examples are not enough to justify the amount of times the trope occurs, especially since some of the examples occur after many stories have already been written (ie, Mary I and medieval fairytales). These fictional women were written as cautionary tales of what happens when a woman is placed in power.
By writing the mad queen Dany arc in GOT, D&D are perpetuating an old trope rather than "subverting" anything as they claim. The most powerful woman in the world turning out to be a war mongering and mass murdering tyrant isn't subversive in any way. The only reason it was surprising was because it came out of nowhere narratively.
ASOIAF fans who constantly try to justify this turn for Dany's book character are attempting to do the same thing D&D did. They want to employ an ancient trope to justify their dislike for her in name of being "subversive".
The Violent Woman:

A trope that stretches back all the way to the Ancient Greeks is that of the angry, homicidal woman in power. From Hera to Medea, the myths are full of women who commit atrocities simply because of anger. This trope isn't just about avenging a slight or retribution on the guilty; it's about a woman taking out her anger on innocent parties.
Daenerys has fallen into the role of the avenger many times throughout both the show and and book. She killed Mirri Maz Duur for the murder of her son and husband. She killed the Undying for attempting to trap/kill her. She kills Kraznys mo Nakloz and many other slavers for the atrocities they commit constantly on the people they enslaved.
In the show, she imprisoned Xaro Xhoan Daxos and Doreah in a vault for killing Irri and helping the warlocks steal her children. She killed the Khals who threatened to rape her. She kills the Tarleys for rebelling against the Tyrells, thus getting them killed, and refusing to bend the knee.
Every time Dany killed up until season eight, it was purely because those she killed harmed her or her allies/children. That is why none of her past kills justify her burning KL. The people of KL did nothing to her; it's not an established part of her character to harm innocents out of anger. She even outright condemns the killing of innocents in earlier seasons.
The inconsistencies show how D&D chose to blatantly ignore the complexities of Dany's character in favor of a sexist trope. They perpetuated the idea that a woman in power who is angered will ultimately commit injustice and atrocities.
Dany antis in the ASOIAF fandom are no different from D&D. A common argument used by Dany and Targaryen antis is that they are bound to be corrupt and tyrannical because they have dragons. Essentially saying that Dany was doomed to be the villain the moment she hatched her children.
They point to her dragons' existence and her conquest in Essos as reasons for her "villain arc", despite the fact that none of her actions reflect the things they claim. Dany is simply being condemned for being a woman with power; it's expected of her to be a tyrant for those reasons alone.
The Woman Scorned:

This reasoning given by D&D in a behind the episode interview is probably the excuse that I hate the most. They said that one of the reasons for Dany's descent into madness was because Jon Snow refused to kiss her back once he found out they were aunt and nephew. This is an insanely misogynistic trope.
Used time and again by writers (mostly male), this trope is about a woman who becomes an antagonist due to rejection, unrequited love, or betrayal from a lover. In the case of Dany and GOT, it's Jon refusing to continue their romantic relationship.
For some reason, this is seen as a breaking point for Dany. A woman who has endured poverty, homelessness, sexual slavery, a traumatic miscarriage and death of a spouse/protector, and the stresses of war was broken by a man refusing to kiss her. Doesn't that sound fucking stupid? Well that's because it is.
Dany has never felt entitled to people's love (with the exception of shitty writing from D&D) let alone someone's sexual/romantic reciprocation. It's out of character and flat out insulting to women to believe that is enough to make Dany into a mass murdering tyrant.
Once again, there are members of the fandom who espouse this reasoning into their own theories and metas. Jonsas especially are guilty of this; some claiming that Jon's rejection of Dany in favor of Sansa will be a catalyst for the "mad queen".
An offshoot of this thinking, is the idea that Dany went/will go mad because she was rejected by the realm.
In the show, the Northmen are dismissive or outright hostile to Dany when she arrives (even after she saves them). Due to this rejection by the Westerosi people, Dany decides "let it be fear" and chooses to burn KL to the ground.
Once again, this idea isn't grounded in her past actions at all. Dany has always known she needs to earn people's love and respect as a ruler, why should she change her mind the moment she steps onto Westerosi soil? The answer is simple: she's a woman, so she can't possibly be able to deal with rejection.
Fans theorize constantly that Dany is going to go mad and destroy KL and Westeros because the people will definitely reject her in favor of Young Griff/Jon Snow/any other king they can think of. This theory is simply clinging to misogynistic ideas about women and it's disgusting in every iteration (it also dismisses the fact that there are people in Westeros excited about the idea of Dany and her dragons in the books but that's a different post).
The Woman Bereft:

This argument is probably the least outright in its misogyny. The idea that a woman who has lost everything will lose her mind isn't a new one and it can be played in a non-sexist way. However, GOT played it completely in the sexist roots of the trope.
Throughout seasons seven and eight, Dany loses basically everything. All but one of her children, her closest advisor and best friend Missandei, Ser Jorah, a massive chunk of her army, her other advisors, most of her allies, and is rejected by Westeros and Jon. That's a lot of loss to endure.
However, Dany has endured severe loss before and never reacted by murdering a city full of innocents. Again, this decision and descent isn't backed up by anything else in her storyline.
The sexism of this idea, that loss produces mad women, is that it's rarely applied to men in the same situations. For example: Tyrion lost everything he cared about, yet he's never written by D&D to be in danger of becoming a mass murderer. He even outright says he wishes he'd poisoned the whole court, but is never portrayed as a mad man by D&D or fans.
Dany is expected to go insane after enduring loss because she's a woman. She's perceived as being fundamentally weaker, mentally as well as physically, so she must be more vulnerable to madness than the male characters.
The Foreign Seductress:

The idea of the foreign seductress is a xenophobic and racist stereotype. For Dany, her antis use the instances of her exercising sexual autonomy and her life in Essos as fodder for this disparaging trope.
In the books and the show, Dany pursues sexual and romantic relationships outside of marriage. This is something that doesn't fall in line with the medieval setting of the world. In Westeros and Essos, it's common for men to do that, but not women, due to systematic misogyny. Because of this, Dany's antis often feel free to argue that because she doesn't act "pure", she is wrong and evil. Dany's bound to become a villain because she isn't a chaste and "good" woman.
In the same way, Dany is painted as wrong for wanting to take her family's throne purely because she wasn't raised in Westeros. She's perceived as a foreign invader by both her antis and D&D.
D&D wrote many scenes of outright xenophobia from the Northmen, Sansa, and Arya towards Dany and her forces without ever condemning those ideas. In fact, they justify them by writing the mad queen ending. The fact that Dany isn't "one of them" is used as an excuse for her descent.
Dany antis also employ this rhetoric, especially when people compare Dany's conquest for the IT to the Starks' desire to retake Winterfell. It's good for the Starks to want to retake their throne because they were raised in Winterfell, but Dany has no right to her ancestral home because she wasn't raised in Westeros.
However, this idea is never applied to Young Griff, who was also not raised in Westeros. Despite this, people will talk about how excited they are for his story and how sad it is that he's totally going to be murdered by his evil aunt. Once again a double standard is applied to Dany.
All this is because Dany is a woman who refuses to conform to patriarchal standards and was raised in a foreign country.
Never Good Enough:

Dany antis and D&D thrive on applying a different set of standards to Dany than other characters. They do this an a way that's reminiscent of the double standards set for women even today.
No matter what Dany does, it's never good enough for them. She dealt with Viserys and his death in the wrong way. She didn't protect her people in the right way. She tried to abolish slavery in the wrong way. She saved the goddamn world wrong. Like nothing Dany does is right in their eyes.
In their minds, Dany should've died in AGOT being a perfectly passive woman. She refused to submit to those (men) around her, and for that they punish her.
She's wrong for fighting the slavers, she's wrong for trying to avenge murdered children, she's evil for killing to protect herself. D&D used each of her actions throughout the show that they seemed too aggressive as justification for what they wrote. Dany's antis do the exact same thing in their theories.
The mad queen Dany theory is rooted completely in misogyny. It has no true justification in the narrative and every argument conjured up is just as sexist as the trope they want to perpetuate.
#daenerys targaryen#asoiaf#anti got#anti jonsa#anti sansa stans#anti dany antis#anti targaryen antis#asoiaf fandom#fandom misogyny#fandom critical#anti d&d#asoiaf meta
162 notes
·
View notes
Text
Opinion | Lessons from Alexandria: A Cautionary Tale for Modern American Politics
By Jet Espinosa In a city once hailed as a beacon of knowledge and tolerance, Alexandria drew people from across the ancient world. It was a place where scholars, thinkers, and believers from diverse backgrounds came to share and preserve their wisdom. With libraries that housed invaluable knowledge in science, philosophy, medicine, and the arts, Alexandria was a symbol of progress and…

View On WordPress
#Alexandria library destruction#American democracy#Ancient Alexandria#Cultural diversity#Enlightenment and progress#Freedom of belief#Historical cautionary tales#History repeating itself#Intellectual freedom#Knowledge and tolerance#Lessons from ancient civilizations#Lessons from history#Modern American politics#Political power and religion#Politics and religion#Protecting democracy#Religious influence in politics#Religious tolerance#Role of religion in government#Separation of church and state
0 notes
Text
C. Wright Mills argued that people are often unaware of their connection to broader historical narratives. This can limit their understanding of how their actions impact the world and their potential to shape it. History, with its cycles of wars, revolutions, and personal struggles (education, economic circumstances, health) offers both cautionary tales and opportunities for learning. Whether we engage with these lessons or not, the echoes of the past continue to resonate.

Guernica, 1937. Pablo Picasso. Oil on canvas.
195 notes
·
View notes
Text


Fun stuff from Dr. Balls — an essay collection published on the Silmarillion Writers Guild across the upcoming year that intertwines fanfiction and nonfiction in the pursuit of Celebrían + most women in the legendarium turn up at some point ✨
Head over here or click ‘Read More’ below for a brief introduction to and overview of the essays in the collection, which can all be read independently. Fans of Crablor and Mr. Balls, you will enjoy Chapter 5 & 6, which should be out in the summer.
—————
“But there is also something deeply strategic in the act of spectacle. To make a ‘lost woman’ like Celebrían into a vast, operatic, hyper-visible character is to place her where she cannot be ignored… no longer dependent on the fragile benevolence of the archive. She becomes impossible to overlook. Across this collection, Celebrían will be written, rewritten, and repeated, until her absence is not only rectified but reversed — until she looms larger than the moment of violence that defines her. To put it bluntly, she takes her story back, and does whatever the hell she wants with it.”
The introductory essay, ‘Dazzling Despair: Life, Death and a Spectacularly Lost Woman’ considers the radical potential of performing one’s own ‘death’. On the fictional front: Celebrían’s search for the Elessar transforms loss into an act of deliberately poetic spectacle.
Read ‘Dazzling Despair’ here.
Would honestly love to hear what you think of this so far — feel free to comment here or DM me as well. I really want to make sure my tone isn’t too jargon-y and that it flows well: combining fanfiction and nonfiction is something I haven’t done before.
Introduction and Overview
An Elopement with Life is a 9-part essay collection that intertwines literary fanfiction with the nonfiction essay form, exploring the idea of a Celebrían who stays in Middle Earth.
The fictional narrative follows a year in the life of Celebrían who, across conversations with various 'lost women' of the legendarium, makes the deliberate choice to not-sail to Valinor. The essays use Celebrían and “courtesan laments” as a general framework but traverse a wider thematic landscape, engaging with historiography, investigative environmental journalism, and critical queer/disability theory to unpack how mythic and literary narratives shape our understanding of loss, resilience, and reclamation.
The introductory essay Dazzling Despair considers the radical potential of performing one’s own ‘death’, as Celebrían’s search for the Elessar transforms loss into an act of deliberately poetic spectacle. The Art of Dying Twice deconstructs Lúthien’s legendary defiance, revealing how even the most celebrated figures of resistance may be vexing in their contradictions. Sea-cure is an intertextual meditation on the sea’s ambivalence—both vessel of liberation and instrument of dispossession—as Elrond attempts to communicate with the Valar across an unfathomable divide. The Poster Child examines the distortions of historical memory, positioning Celebrían as an uneasy object of mythmaking who must navigate her own commodification into a cautionary tale, paralleling a “poster child” in narratives of disability.
The collection then shifts toward a mode of speculative investigative journalism with The Crab-Eaters and The Crab-Saviours, in which Celebrían, Arwen, and the elusive Fëanorian wives cross paths with an eccentric cryptid who runs a farm of extinct-yet-not-extinct shellfish, mirroring the author and their partner’s real-world pursuit of brutalised waterfowl in the United Kingdom. Does Your Mother Know? takes on the ethics of retribution, as Celebrían and Elrond are at odds after she demands to see her sons' orc hunt, raising fraught questions about complicity, cycles of violence, and the power of bearing witness.
The collection concludes with the two-part essay The Bravest Girl in Arda, where Celebrían, alongside her father Celeborn, constructs a living reconstruction of Taur-im-Duinath, a sunken forest in Beleriand. This final couplet articulates restoration as a quiet, persistent act: the renewal of the self through reconnection with the nonhuman world, the submerged histories that whisper beneath dominant narratives, and the “little revolutions” that exist under the weight of the great ones — resonating with Tolkien’s own attentiveness to the dignity of small acts and overlooked labours. Across the collection, An Elopement with Life engages with resilience as both concept and praxis, unfolding through a dialectic of rupture and repair, disappearance and re-emergence, myth and materiality, and the histories we choose—or refuse—to inherit.
Zara is an essayist and novelist who works broadly across queer world literatures and ecocriticism. She holds degrees from SOAS, St. Andrews and Oxford.
The work will update every 6-8 weeks, hosted exclusively on the SWG, and each essay in the collection can be read standalone.
Go to Collection.
#tolkien#lord of the rings#the silmarillion#lotr#elrond peredhel#celebrían#tolkien meta#nerdanel#maglor#elwing#balroballs writes
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
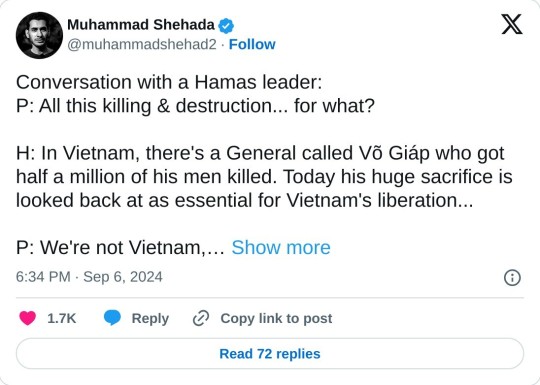
Conversation with a Hamas leader: P: All this killing & destruction… for what?
H: In Vietnam, there's a General called Võ Giáp who got half a million of his men killed. Today his huge sacrifice is looked back at as essential for Vietnam's liberation…
P: We're not Vietnam, every liberation struggle is unique to its context.
H: Oppressed people always win against colonizers…
P: Not everywhere. Native Americans, Aboriginals, and Maoris never managed to drive the colonizers out!
H: We're not native Americans, every case is different…
P: But you weren't you just comparing us to Vietnam?
[Long argument]
H: So what is your alternative? Nothing else works with Israel, not Mahmoud Abbas' diplomacy, not non-violence, not the international community, not the UN…
In domestic Palestinian politics, Hamas always wins every argument not by the appeal of its ideology, but by the long foiling & betrayal of every single alternative Palestinians ever tried.
Palestinians tried the biggest non-violent protest in Gaza's modern history, the 2018-19 Great March of Return, tens of thousands marching to the fence every Friday bare-chested raising the Palestinian flag (never Hamas')… The IDF took potshots at over 30,000 protesters for sport & bragged about the joy of hunting down people's kneecaps!
Palestinians tried international advocacy, only to be smeared, shut down, labelled "antisemties", detained, harassed, made into cautionary tales…
Palestinians tried negotiations, accepted 22% of their historic homeland & called for international law to be respected, only to be called rejectionists, maximalists, uncompromising & "never miss an opportunity to miss an opportunity" (although Israel's Knesset officially rejects the two-state solution in absolute terms).
Palestinians tried to knock on the doors of every UN agency and international court, only to be called "diplomatic terrorists" & for whatever historic decision we got to remain mere ink on paper; never to be implemented…
Palestinians tried collaborating with Israel & providing it with ultimate security (the Palestinian authority), only to be weakened, humiliated, smeared, abandoned, defunded & called "terror supporters"…
Some Palestinians tried even converting to Judaism, only to be automatically rejected out of hand by Israel. One, who changed his name to Davidi ben Abraham & studied the Torah in depth, was literally shot at a checkpoint by an Israeli soldier who got mad at "Davidi" for daring to call himself "Jewish". How dare he?
These failures upon failures have only ever lent credence to Hamas & strengthened it.
As always: Palestinian nonviolence requires global non-silence!
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
what i read in aug. 2023:
(previous editions) bold = favourite
race, gender, sexuality
the blind side was always trash
he’s the trans son of an anti-trans influencer. it's his turn to speak
'the eurocentric fallacy': the myths that underpin european identity
is there a sinister side to the rise of female robots?
i call myself a spinster, but that doesn’t mean l’ll be single forever
politics & current affairs
the land beyond the drug war (usa)
how torture, deception and inaction underpin the uae’s thriving sex trafficking industry
wa mp james hayward found guilty of child sex abuse, disqualified from parliament (australia)
a north korean defector captivated us media. some question her story (usa)
history, culture, & personal essays
loneliness: coping with the gap where friends used to be
inside barbados' historic push for slavery reparations
ahead of time: on poetry and mourning
dreaming of water with tiger salamanders
i stole my neighbour's tragedy to write a short story
nuclear tech: war, power, & oppenheimer
the cautionary tale of j. robert oppenheimer
315 nuclear bombs and ongoing suffering: the shameful history of nuclear testing in australia and the pacific
revisiting hiroshima in iran (journal of international security, open access)
japan releases treated wastewater from fukushima nuclear plant into pacific ocean
spectre of maralinga hangs over aukus nuclear waste for indigenous communities (aus/us)
the dark history oppenheimer didn't show
don't let the victors define morality – hiroshima was always indefensible
if you're interested in more peer-reviewed resources on the american bombings of hiroshima/nagasaki please let me know!
#studyblr#studyspo#reading recommendations#academia#reading list#reading lists#university#productivity#student#dark academia
313 notes
·
View notes