#Greco-Roman period
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Archaeologists Unearth Mummies with Golden Tongues in Egypt
Archaeologists have unearthed several ancient tombs with dozens of mummies—including some with golden tongues.
Researchers made the findings during excavations at the ancient city of Oxyrhynchus, an extensive archaeological site located around 100 miles south-southwest of Cairo near the modern-day municipality of Al-Bahnasa in Minya Governorate.
Oxyrhynchus was "very important" during ancient Egypt's Greco-Roman period, which spanned hundreds of years from the late fourth century B.C. until the 7th century, Esther Pons Mellado and Maite Mascort, co-directors of a Spanish archaeological mission at the site.
"[It[ was the second city of Egypt after Alexandria. There was a great business and cultural relationship between these two cities," they said.
The Greco-Roman period began with Alexander the Great's conquest of Egypt—then controlled by the Persians—in 332 B.C. An ancient Greek state known as the Ptolemaic Kingdom was subsequently established in 305 B.C., which ruled Egypt until 30 B.C. when the region was conquered by the Romans.


The territory became a province of the Roman Empire, which eventually divided into a western and eastern portion—with Egypt belonging to the latter. The Roman period ended around A.D. 641 when Arab forces conquered Egypt.
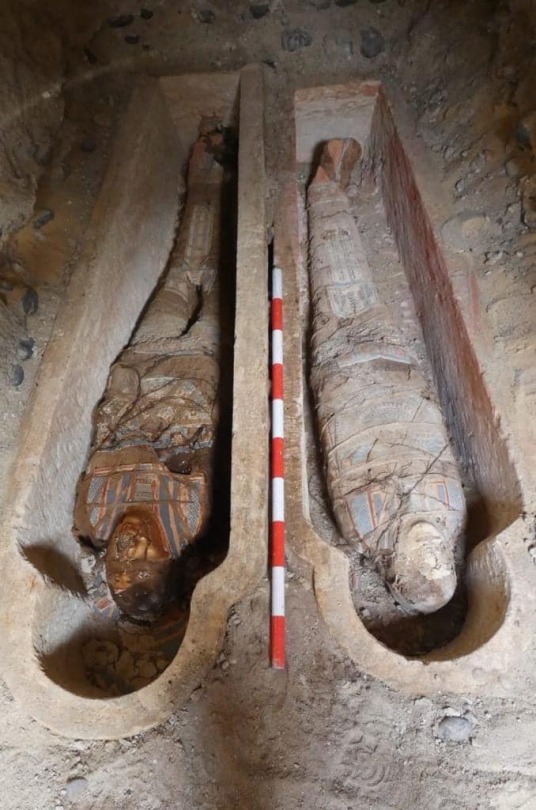
The latest excavations at Oxyrhynchus took place in November and December 2023. Over the course of these investigations, Pons Mellado, Mascort and colleagues discovered several tombs from the Greco-Roman era, as well as human remains and artifacts.
The finds include two tombs dating to the Roman period, built with limestone blocks. In these tombs, the archaeologists uncovered more than 20 mummified individuals covered in multi-colored wrappings, as well as papyri with Greek texts and mud seals with Egyptian iconography.
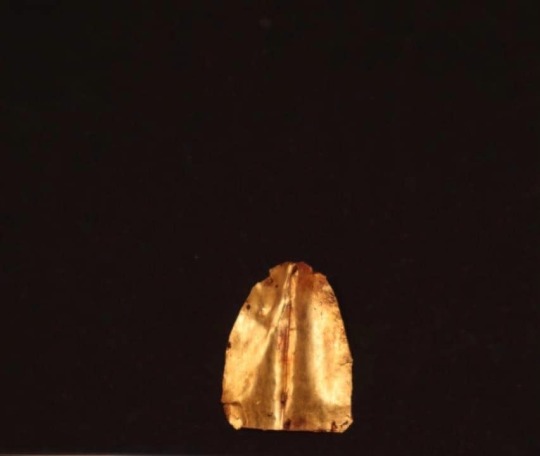
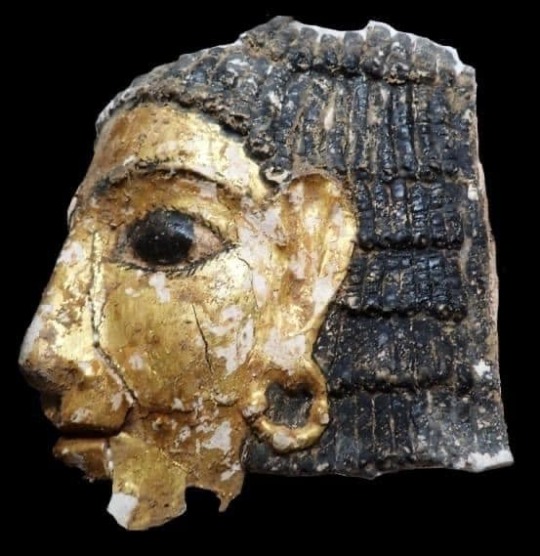
Two of these mummies were found to have pieces of gold shaped into the form of a human tongue placed where their real tongue was. Such golden tongues have previously been found at Oxyrhynchus and, indeed, other archaeological sites in Egypt.


"Until now we have found 16 golden tongues in Oxyrhynchus," Pons Mellado and Mascort said.
Experts think the ancient Egyptians may have placed gold tongues on some human remains to enable the spirits of the deceased to communicate with Osiris—the god of the underworld—and to help them cross into the afterlife.
"The Egyptian people deposited the golden tongues on the tongue to restore vital functions to the dead and also so that the body remained intact in the afterlife. For the Egyptians, gold was the flesh of the gods," Pons Mellado and Mascort said.
In addition to the Roman-era tombs, the archaeologists also discovered three "hypogea"—or underground tombs—dating to the Ptolemaic period that had been excavated beneath the natural rock.
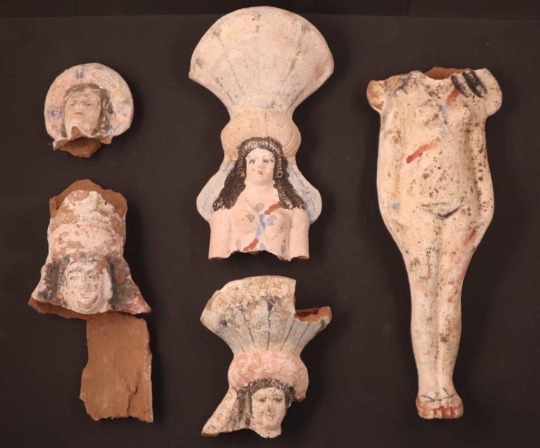
In these hypogea, the researchers uncovered several more mummies covered in colorful wrapping, a number of anthropomorphic stone sarcophagi (some of which were closed) and various terracotta statues depicting the goddess Isis-Aphrodite, among other artifacts. This deity is a form of the Egyptian goddess Isis combined with the fertility aspects associated with the Greco-Roman goddess Aphrodite.


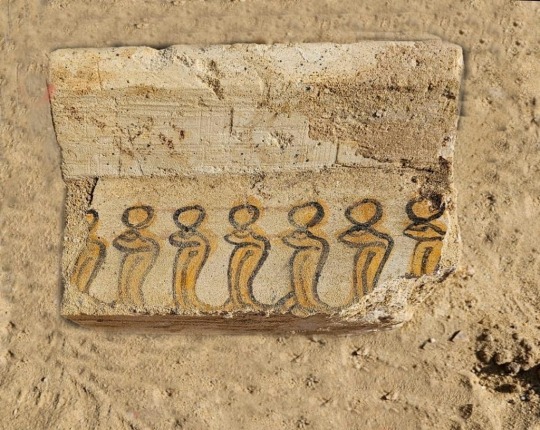
In one of the hypogea, the team also found many multi-colored limestone blocks with decorations, including depictions of humans, snakes, pigeons and plants.
All these findings are very important for the history of the funerary world in Oxyrhynchus," Pons Mellado and Mascort said.
"It is the first time that we have found an Oxyrhynchus terracotta with the image of Isis-Aphrodite, and the first time that this kind of piece has appeared in this area of Middle Egypt. The limestone blocks with decoration [are also very important]."
The limestone blocks—another new finding at Oxyrhynchus—appear to have come from some kind of construction, although the nature of the structure is unclear.
By Aristos Georgiou.


#Archaeologists Unearth Mummies with Golden Tongues in Egypt#ancient city of Oxyrhynchus#Greco-Roman period#ancient graves#ancient tombs#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient egypt#egyptian history#roman history
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
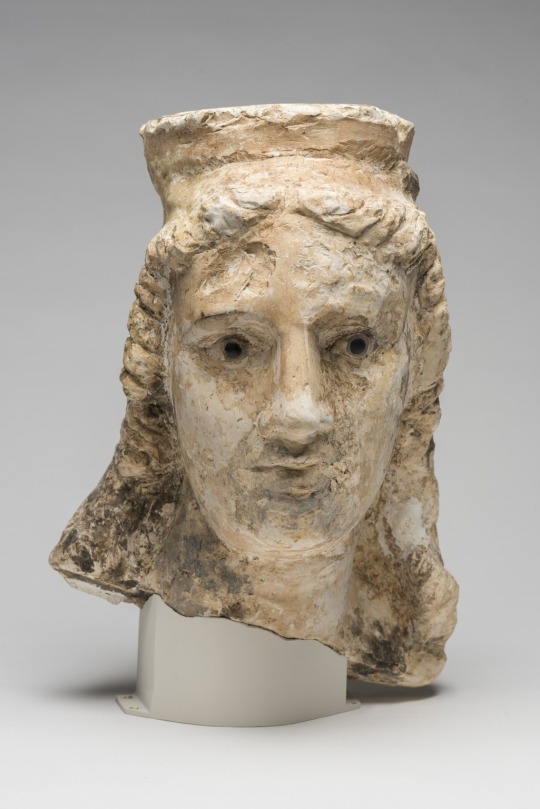



~ Female Head.
Culture: Graeco-Egyptian
Place of origin: Akhmim, Egypt
Date: 1st century B.C.-A.D. 1st century
Period: Ptolemaic Period-Roman Period
Medium: Limestone, stone, pigment
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient egypt#ancient sculpture#roman#ancient history#archaeology#Greco-Roman#female head#portrait#akhmim#Egyptian#egyptology#Egypt#ptolemaic#roman period#1st century B.C.#a.d. 1st century
283 notes
·
View notes
Note
If you could escape to any other time period or world for one hour at a time, where/when would you go, and why?
Such a hard question to answer because there are so many different time periods to choose from.
If I could escape to any other time period for an hour, I would choose the turn of the century around 30 AD. I would love to experience not just the life of Jesus but also the rich interactions of the Romans, Greeks, Jews, and other Middle Eastern cultures and customs. Being able to witness these civilizations in their prime, with their buildings and structures standing as they were originally intended, would be awe-inspiring. The chance to observe the political and social dynamics of the time, to walk through ancient cities like Jerusalem or Rome before they became ruins, and to see how everyday life unfolded in such a pivotal era in human history would be an unforgettable experience. So for an hour I'd like to see all the hustle and bustle from everyone and everything.
So for 30 AD, I would be in:
The Early Roman Empire under Emperor Tiberius.
The Second Temple Period for Jewish history.
The Greco-Roman period for cultural interactions.
In a single sentence... I would like to visit 30 AD, the start of the 1st century during the early Roman Empire, in the midst of the Second Temple Period, when Roman, Jewish, Greek, and Middle Eastern cultures were thriving and interacting in ways that shaped the world.
#ask me anything#question#answer#time period#escape#dark academia#light academia#classical#academia aesthetic#escapism#academia#books and libraries#classic literature#books#architecture#1st century#early roman empire#second temple period#greco roman#romans#greeks#jews#jesus#culture#history#historical#academic#aesthetic#tumblr#bearwistleflute
14 notes
·
View notes
Text

Dionysus made me do it. 🐆🌿🍇
#Grecian#greco roman#ancient rome#ancient greece#Hellenistic#Hellenistic Period Revival#Hellenic#Greek Pantheon
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
The above image depicts two Hyena cubs, humorously labeled as "German Shepherd pups." Dogs are common pets in the early twenty-first century. Hyenas are dangerous, undomesticated wild animals that are illegal to own in a large number of places on account of "exotic animal laws."
It is evident that the above is a joke, both because most people in the early 21st century would not mistake a hyena for a dog (the distinct ears, muzzle, and fur pattern make it explicit), and because the humorist made a reference to "laughter." Hyenas are known to make an unusual sound that resembles human laughter and have, since at least the third century, been associated with laughter. A group of Hyenas is called a "Cackle" for that reason.
An early twenty-first century viewer of the above image would recognize the hyenas, recognize the fact that they laugh BECAUSE they are hyenas, and would find humor in the idea that somebody could make such a silly mistake. They would understand that these hyenas are not actually for sale, and would understand that it is a fictional narrator making the mistake, not the image creator.

#period novel details#explaining the joke ruins the joke#not explaining the joke means people 300 years from now won't understand our culture#it's interesting how a lot of animal stereotypes EXPLICITLY go back to the greco-roman world#you can imagine Roman four year olds laughing like hyenas or roaring like lions when they play#I think that kind of long reaching cultural influence is fascinating
38K notes
·
View notes
Text
Karnak and Luxor Temple Complexes Egypt

View On WordPress
#18th Dynastic Theban Triad#Abu El-Haggag Mosque#Alexander the Great#Amenhotep III of the 18th Dynasty#Amun The Creator God#Amun-Ra Suen God#Ancient Egyptian Culture#Ancient Egyptians#Ancient Greeks#Arabic word Khurnaq#Avenue of the Sphinxes#Colonnada of Amenhotep Ill and Tutankhamun#East Bank Nile River#Egypt Greco-Roman Period#Egypt Middle Kingdom#Egypt New Kingdom#Egyptian Hieroglyphs#Egyptian Ipet-isut (The Most Selected of Places)#Egyptian New Kingdom#Egyptologist#Egyptologist Professor Gaston Maspero#Emperor Diocletian#Festival of Opet#Gebel el-Silsila Area South-Western Egypt#General Ptolemy#God Amun#God Hathor#Goddess Mut#Hatshepsut Obelisks#Horemheb
1 note
·
View note
Text
"Priestess of Isis", "Enchantress" and "Sylph": Occult References in Ellen Hutter’s character in “Nosferatu” (2024)
In another post I analyzed Ellen Hutter’s character in the 2024 adaptation of “Nosferatu” through literary lenses of the Gothic female genre. Now, I want to dwell on her occult and mystical symbolism, and how this translates in her connection with Count Orlok, the undead demon of the story, who’s bound to her. But how and why? And what exactly is she in this story?
“In heathen times you might have been a great priestess of Isis.”
Von Franz tells this to Ellen in their last scene together, because he recognizes her spiritual power and ability to communicate with the spiritual world. Her “hysterical fits” and “epilepsies” also mirror the trance-like states of Pagan priestesses. She inhabits the “borderland”, a peripheral area, a portal between the two worlds: the physical (matter) and the spiritual.

“The pupil is expanded. It does not contract naturally to the light. […] A second sight. She’s no longer here. […] She communes now with another realm.”

“Somnambulists afflicted with these perversions [hysterics and lunatics] oft possess a gift: a sight into the borderland. […] I believe she has always been highly conductive to cosmic forces, uniquely so.”
Von Franz says demons usually obsess over “those whose lower animal functions dominate”, because they like them and seek them out. He elaborates: hysterics and lunatics. However, he says this before he actually gets to know Ellen, and he quickly realizes that’s not the case here. Because Ellen is the one who awoke Orlok from his centuries old sleep. Which is confirmed by three characters in the narrative: Orlok, Ellen herself and Von Franz.
O’er centuries, a loathsome beast I lay within the darkest pit… ‘til you did wake me, enchantress, and stirred me from my grave. You are my affliction.

Which leads me to the next topic:
Why Isis, of all deities?
Isis and Osiris
Isis is one of the major Egyptian deities. She’s more commonly known for her role as “Mother Goddess” of Horus, the Sun god. Isis had mighty magical powers, greater than that of all other gods, she governed the natural world, healing and wield power over Fate itself.
“Destiny!” Ellen cries out to Anna, while looking at the sea. “Providence!” Herr Knock screams throughout the narrative. “You run in vain! You cannot out-run your destiny!” Von Franz laughs in religious fervor as Thomas tries to save Ellen.
Isis is also connected with the themes of death, sex and rebirth in Egyptian cosmology, due to the myth of Isis and Osiris; which are also the core themes of Robert Eggers’ adaptation of “Dracula/Nosferatu”, so it’s not coincidental.
The “Osiris Myth” is one of the major surviving pieces of Egyptian mythology. It’s a ancient tale, with its early versions dating back to the 5th Dynasty (c. 24th century B.C.). It has known several adaptations throughout Egyptian history. The most complete version is in “The Moralia” by the 1st-century scholar Plutarch of Chaeronea, a collection of essays about Greco-Roman culture; that became very popular during the Renaissance era (14-16th centuries) and the Enlightenment period (18th century) in Europe.
Isis and Osiris were brothers, and according to Ancient Egyptian religion, they were in love with one another before they were born, and enjoyed each other in the dark before they came into the world. They eventually married.
Osiris had two facets as a God: in life, he was the God of fertility, agriculture, and vegetation, being considered a “Shepherd God”; in death, he was the God of the Underworld, the judge and Lord of Dead, the afterlife and resurrection. The pharaohs of Ancient Egypt were associated with Osiris in death, because as he rose from the dead, so would they unite with him and gain eternal life through imitative magic. Which appears to be the whole deal between Orlok and Herr Knock in “Nosferatu”, as Knock seeks to gain immortality like Orlok, by serving him.
On Earth, Osiris was believed to take on the form of a bull (the sacred bull Apis). What I find interesting here is that in both the 2016 script and the 2023 script of “Nosferatu”, Orlok’s physicality is actually compared to a bull:


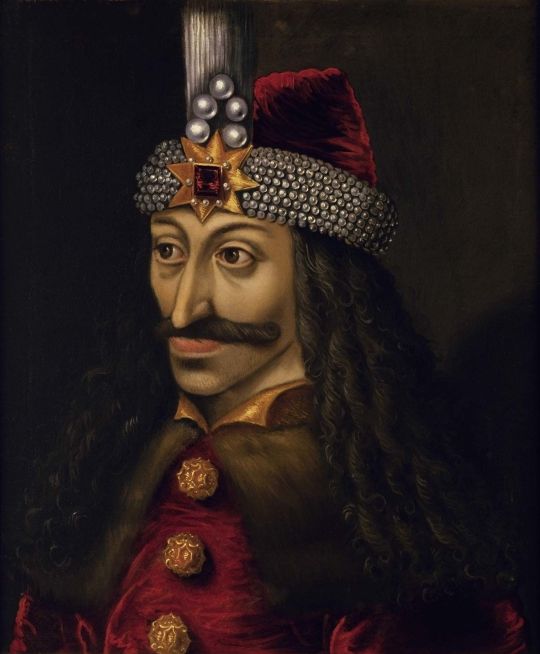
Osiris became king of Egypt, and taught the people how to farm and live peacefully in their villages; he had a reputation for being a powerful and wise king, loved and respected by the Egyptian people. We don’t know exactly how Eggers’ Orlok was in life, other than him being a Romanian or Hungarian nobleman and a Solomonar sorcerer who sought to achieve immortality. But if we go by Vlad III (Drakule or Dracula, the infamous “Vlad the Impaler”) biography, he’s actually considered a Romanian national hero because he defended the Romanian people from foreigner invaders (Germanics and Turks, mostly). Just throwing this out there, because it’s unsure if this is intentional or not.
Osiris and Isis had a brother, Seth (or Typhon in Plutarch essays), the God of deserts, storms, disorder and violence, who murdered Osiris to take his throne. He tricked Osiris into climbing into a wooden chest/coffin, shut the lid, sealed it shut, and threw it down the Nile River, knowing Osiris would never be able to survive. In some versions, it’s said Seth cut Osiris body into pieces and scattered them throughout Egypt. Interestingly enough, there’s a similar legend associated with Vlad the Impaler, who died in battle against the Ottomans, and, according to Leonardo Botta, the Milanese ambassador in Buda(pest), Vlad’s enemies cut his corpse into pieces, too. and his remains were never found.
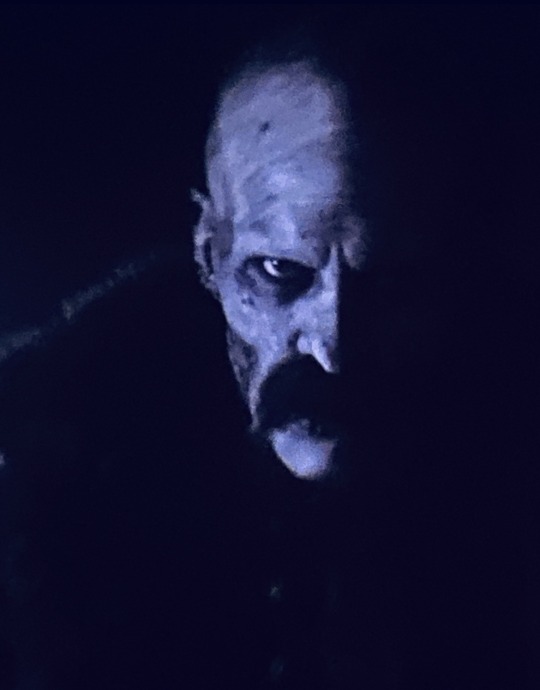


Isis is the epitome of the mourning widow in this myth, as she mourns Osiris’ death deeply. Here enters the symbolism of the lilacs in "Nosferatu", the symbolic flowers of Ellen and Orlok: in the Victorian era, they were associated with widows because they represented a memento of a deceased lover.
Can this also be a nod to “Bram Stoker’s Dracula” (1992) by Francis Ford Coppola? Where Dracula himself is the grieving widower because Elisabeta commits suicide? In the 1992 adaptation, Mina also speaks of “flowers of such frailty and beauty as to be found nowhere else”. What flowers is Mina talking about? It’s unclear, but Lilacs are native flowers to the Balkans, after all.
Isis sought for Osiris’ mangled body and with help of tree other Gods (Nepthys, Thoth and Anubis), they sew Osiris’ body back together, and then wrapped it head to toe in strips of linen, creating a mummy. Interestingly enough, Orlok’s corpse appears almost mummified at the end of the story.

In the Osiris myth, Isis uses powerful magic (incantations and magic spells) to bring her dead lover back to life; similar to Ellen who resurrects Orlok with her summoning prayer. In one version, this happened on a night of the full moon; in “Nosferatu” (2024) we also have a full moon connected to Ellen and Orlok, in the prologue, when he reveals his rotten corpse to her:
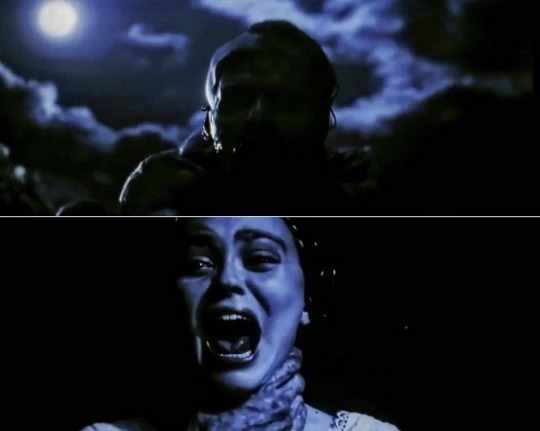

According to Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, it’s Isis sorrow, sexual desire and anger that empower her magic to be able to bring Osiris back to life. When Ellen prays for a companion of “any celestial sphere” in the prologue, she’s crying (sorrow), she’s upset because her father recoils from her now that’s she’s no longer a child (anger) and she’s in her teenage years/puberty (sexual desire). Like Isis with Osiris, it’s the combination of these emotions that power her magic to unconsciously resurrect Orlok.
However, Osiris can’t remain among the living, because he has to return to the Underworld and become King of the Afterlife. But before he goes, Osiris and Isis conceive Horus, the God of the sun and the sky, who will restore peace and order to the universe. In “Nosferatu” (2024), Von Franz says that “with Jove’s holy light” before dawn, redemption will come to the people of Wisburg and the curse of Nosferatu will be vanquished. “Jove” is Jupiter, the “King of the skies”, who’s connected with the Egyptian Horus. Horus and Ra are often merged together in Ancient Egyptian religion, making Isis and Osiris the metaphorical parents of the Sun.

In “Nosferatu” (2024), as Orlok and Ellen complete their covenant, consummate their wedding and he drinks from her, the sun is also the metaphorical result of their union. As dawn breaks, the sunlight vanquishes them both from the physical world, as they both die in the material realm.

After being buried by Isis, Osiris goes into the Underworld to rule over it. And from then on, Isis herself is also associated with funeral rites, as she would guide the souls of the dead, helping them entering the afterlife. Through her magic, Isis helped resurrecting the souls of the dead, as she did with Osiris, acting as a mother to the deceased, providing protection and nourishment.

At the end of "Nosferatu" (2024) we see Ellen fulfilling her role as “priestess of Isis” (or as Isis herself?), as the Goddess of healing, who ends the blood plague in Wisburg, but also guides her dead lover Orlok/Osiris with her into the Underworld... where he'll rule as king? Unclear.
Since we are discussing the Egyptian Gods, I have to mention Greta the Cat, Ellen’s domestic cat. Her name is an obvious homage to Greta Schröder, the actress who played Ellen Hutter in the original 1922 “Nosferatu”. Indeed, cats are predators to rats, however, the Egyptian Goddess Bastet is considered to be Isis’ daughter. She's the "cat goddess" for cats were considered sacred in Ancient Egypt. Bastet was associated with sun gods like Horus and Ra. Bastet was the goddess of pregnancy, childbirh, and protection against contagious diseases and evil spirits.
Enchantress
Orlok calls Ellen “enchantress”, but what does this mean? “Enchantress” is not only a female archetype, but has root in historical realities. Enchantresses were practitioners of feminine magic: oracles, healers, herbalists, midwives and shamanic shapeshifters. They were what’s commonly known as “witches”. These female magicians studied and practiced their art in goddess temples, mystery schools, alchemy schools and hedge schools.
The alchemists of the Middle-ages studied these dynastic lineages of “wise women”, and they had several names: enchantresses, chantresses, encantrices, or incantrix. Many physicians who founded "medicine" and "science" studied these wise women, mainly healers and their use of medicinal plants and herbs.
Ellen’s character appears to fit that of a “incantrix”. Women who used words, incantations, songs, spells and prayers to shape reality. It’s the priestess of an old religion (as Von Franz also calls her); gifted with magic power and authority to command the elements or the body by the power of their word.

Heptagrams
Orlok seal (or sigil) meaning has already been widely discussed by others (symbols of Ancient Dacian religion, mainly the figure of Zalmoxis), but what I want to mention here is the heptagram itself, the seven-pointed star. Heptagrams have several occult meanings, including warding off evil which, for obvious reasons, doesn’t fit Orlok’s character. It has meaning in Alchemy, too, as representative of the seven planets and seven substances.

The heptagram, however, is used by Aleister Crowley in his occult system Thelema (from Ancient Egyptian text) to represent a goddess/archetype: Babalon, which is also connected with Isis, Nuit, Lilith, Kali, among other goddesses and deities. At its core, it’s a goddess of female empowerment and liberation, of divine feminine. According to this occult belief, Babalon has several manifestations (sort of incarnation) and is a spiritual gateway to wisdom and enlightenment through chaos and female sexuality.

In “Nosferatu” (2024), when Ellen and Thomas are returning home, there’s a man in the streets rambling bits from the “Book of Revelations” (Apocalipse) from the Bible: “And I saw a beast rising out of the sea, owith ten horns and seven heads, with ten diadems on its horns and blasphemous names on its heads.” (Revelations, 13:1).
Indeed this passage is about Orlok arrival and how he’ll spread plague among the town. However, we have a character in the “Book of Revelations” which is connected to all of this: the Whore of Babylon, the “Mother of Prostitutes and All Abominations of the Earth”, and she rides this Beast, which is the same as Crowley’s Babalon. What Crowley did was a positive reinterpretation of this biblical figure, symbolizing liberated female sexuality by embracing the powers of the Divine Harlot.
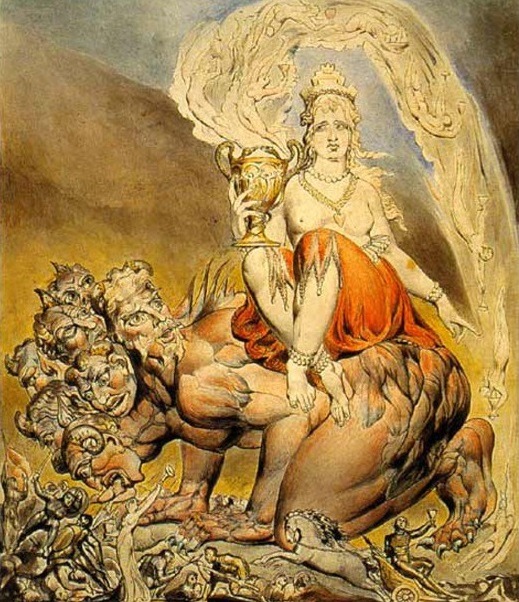


Also known as the “Scarlet Woman” and “Great Mother”, this complex and mysterious figure was established in 1904 in “The Book of Law”, however her roots are far older, and can be found in the Enochian tradition, a magical system by John Dee and Edward Kelly, dated from the late 16th century. In the 2016 script of “Nosferatu”, Orlok spoke Enochian, so it’s clear Robert Eggers is very much aware of all of this.
Initiatrix, Creator and Destroyer, Babalon is the “Great Mother” because she represents matter, Mother Earth. Like Isis, she’s the Archetypical Mother, the Womb, the Great Sea and the Divine Blood itself. According to Crowley, the “whore/harlot” facet is about enjoying sex without the burden of reproduction; and the “mother of abominations” connects with destruction like natural catastrophes, plagues, etc. She’s the ruler of the cosmological sphere and both good and evil (as evil as elemental forces can be or are considered as).
Crowley is a man who was born and raised in the Victorian era where sexuality was to be silenced and repressed, which provides context to his occultist beliefs and his “sex magick” theories. Victorian physicians and scientists were obsessed with classification of sexual perversions, too. “Hysteria” being one example among many. Which is the historical context for Eggers adaptation of “Nosferatu”/“Dracula”, so these references are quite fitting.
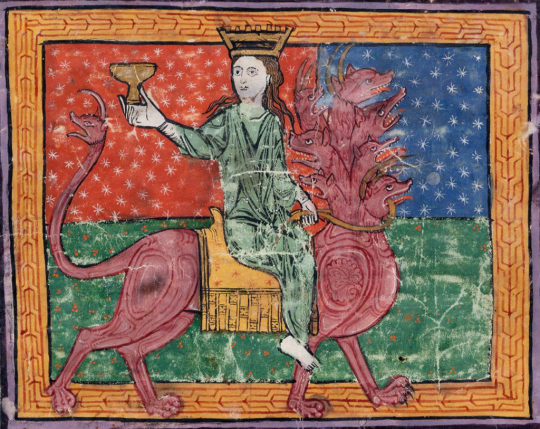

According to the Thelema, Babalon is the “Sacred Whore”, and her primary symbol is the Chalice or Graal (symbolic womb). She’s a consort to the Beast, who has seven heads, which is symbolically represented in her heptagram sigil. Crowley described her: “She rides astride the Beast; in her left hand she holds the reins, representing the passion which unites them. In her right she holds aloft the cup, the Holy Grail aflame with love and death. In this cup are mingled the elements of the sacrament of the Aeon”.
To Crowley these were not actual beings but titles/archetypes (sort of speak) in his Sex Magick beliefs: the “Scarlet Woman” is the High Priestess, and the “Beast” is the Hierophant. This fits Ellen (the priestess) and Orlok (warlock, black sorcerer) in “Nosferatu” (2024). The “Scarlet Woman” is a gateway to both the moon and the sun, and we see both associated with Ellen.
Orlok is described as a “beast” several times in the film, including by himself and by Von Franz, who also mentions Ellen’s “dark bond with beast”, and how she gave her love to the beast: "and lo the maiden fair did offer up her love unto the beast, in close embrace until the first cock crow, her willing sacrifice thus broke the curse and freed them from the plague of Nosferatu."
Orlok says Ellen’s passion is bound to him, like Babalon’s passion is united with the Beast. Babalon as “mother of abominations” also fits with how Ellen unleashed Orlok and his blood plague onto the world, bringing destruction and apocalypse.

Your passion is bound to me. […] I cannot be sated without you. […] Remember how once we were? A moment. Remember?
Thelemic followers of the Beast have been trying to call into being an older, more primeval, female force that is lacking in the Modern Age. Interestingly enough, this was the reason why Orlok became interested in Ellen in the 2016 script (which was later changed, because in the 2023 version it’s Ellen who summons Orlok): “I have sought a creature from the depths. A Eve that remembers her Eden. You are such one.” Both Crowley but more notoriously Jack Parsons have tried a bunch of incantations to conjure Babalon into being.
Oddly enough, the conjuring ritual we see Herr Knock performing at the beginning of “Nosferatu” (2024) is very similar to one of the incantations of Babalon performed by Jack Parsons: Air dagger, blood and channeling of windstorms and the Air element, over a heptagram. He also compares Ellen to a sylph; a nymph of the air element from alchemy and hermetic literature. We are told by Von Franz this is Solomonari sorcery, but is it really?

In Ophidian Thelema, Babalon is the Goddess of magick (“Heka”), of the Liberation of the Spirit (ecstasy), of the Liminal Point, of the Underworld, of Vengeance and of the Principles of Life. Their priestesses use the female body (vulva and womb) to channel their power during their magic rituals. This is similar to Ellen’s “hysterical fits” when she’s communicating with Orlok in the spiritual world, especially since “hysteria” was considered a disease caused by “wandering womb”. In the film, we also see Ellen's womb being talked about between Von Franz and Dr. Sievers during her examination, when they say her menstruation is liberal and she has too much blood in her.

The “liberation of spirit” is in the form of a Serpent, which manifests in the flesh. This notion was present in the “Book of Law”, where its said there’s the dove, and there’s the serpent, and a choice must be made. While the dove represents religion, the serpent represents the spirit. In one scene, Ellen says Orlok is like a serpent in her body; and he replies it’s not him, but her own nature, a nature she denies. Babalon says “my vocation is the serpent.”
The priestesses of Babalon are also in control of their “trances” when they access the spiritual world. In “Nosferatu” (2024) there’s a interesting scene between Ellen and Thomas (the infamous sex scene), when Ellen “comes back” from her transe when he says he’ll call for Dr. Sievers. Does this indicate Ellen is actually in control of her trance-like states?
Babalon is the guardian of the Seven Principles of the Underworld, a place of darkness and transformation. Orlok tells Ellen in the prologue “you are not for the living. You are not for human kind.” Babalon is also the goddess of the liminal point, who can access other realms. As Goddess of vengeance, Babalon punishes when life is out of balance, and exerts violence and corruption upon those who are in the wrong. Ellen unleashes Orlok onto the world, and we can interpret him bringing plague into Wisburg as Ellen’s reckoning against a society that ostracizes her and will never accept her.

All rites and initiations of the Underworld Goddesses include rites of sex and death. Which is what we see with Ellen at the end of “Nosferatu” (2024). By Thelemic occult tradition, she, the manifestation of Babalon, has sex with the Beast (Orlok), “representing the passion which unites them” and her womb (Holy Grail; cup) is “aflame with love and death” (sexual climax, orgasm, with an un-dead vampire).
I will work the work of wickedness; I will kill my heart; I will be loud and adulterous; I will be covered with jewels and rich garments; I will be shameless before all men; I will, for token thereof, will freely prostitute my body to the lusts of each and every living creature that shall desire it; I claim the Mystery of Mysteries, BABALON the Great, and the Number 156, and the robe of the Woman of Whoredomes and the Cup of Abomination. “The Great Beast: The Life of Aleister Crowley”, John Symonds, 2016

Orlok being the Beast and Ellen the manifestation of Babalon explains why she’s promise to him in the narrative, and was never meant to marry Thomas: in Thelemic tradition, the Beast is the consort of Babalon, after all. Orlok's interest in Ellen isn't predatory for its own sake; he sees her as his rightful and fated spiritual consort, which fits the "bride of Dracula" theme of the Bram Stoker original story.
This probably also mirrors the 1992 adaptation by Francis Ford Coppola, where Van Helsing calls Lucy the “Devil’s concubine”: "Hear me out, young man. Lucy is not a random victim attacked by mere accident. Do you understand? No. She is a willing recruit, a breathless follower, a wanton follower. I dare say, a devoted disciple. She is the devil's concubine! Do you understand me? Yet, we may still save her precious soul." In this adaptation, Lucy is full Crowley and Parsons “Scarlett Woman”, with red garments and red hair.


Orlok also gives Ellen three nights to accept him/her nature and complete their covenant. Some are mistakenly associating this with Jesus Christ. These “three days” are possibly connected with another Goddess associated with Babalon: Inanna (or Ishtar), the ancient Mesopotamian Goddess of love, war, fertility, sensuality and divine law. The most famous myth about this deity is her descent into the Underworld, where she spends three days and three nights dead, until she re-ascends (rebirth).
Ellen also goes through the “Myth of Inanna” in “Nosferatu” (2024), which is the theme of the heroine descending into the “Underworld”, to suffer, to be stripped bare, to die, and to be reborn in the aftermath. This is the primal Shamanic crisis. Ellen also goes through three days and nights of suffering and death (witnessing her friends and the townsfolk of Wisburg dying by the blood plague) until she joins Orlok and is reborn.
Ellen and Orlok are involved in sex magick, at the end, clearly. But with what purpose? Sex magick to Crowley has several purposes and strong creative power, conjuring, invocation, etc. He believed deliberate acts of sexual transgression were a radical form of super-human power that promised to explode the narrow boundaries of Western Christian society and open the way for a whole new era of human history. Which is probably what’s happening here? A symbolic ending to the sexually repressed Victorian era as Western societies moved toward a more open-minded and accepting view of sexuality? Or it’s Ellen reborn as a Goddess of the Underworld (return to spiritual state), after going through a initiation rite of sex and death, as she breaks free from her human form? Or both?
Or it can be a nod to Crowley idea of sex magick to unleash supreme creative power to generate a godlike child? This can mirror the Osiris and Isis myth, of Horus (the Sun) as their metaphorical child, like it is for Ellen and Orlok here, as the end result of their union.
Alchemy
Alchemy, at its core, is the transmutation of base materials (lead, etc.) into noble materials (gold), and the pursuit of immortality (“philosopher’s stone”). Occultists reinterpreted this as a spiritual quest of self-transformation, purification and regeneration of the human soul. Hence physical death being seen as a gateway to another life (rebirth); which is the symbolism of the final scene of “Nosferatu” (2024).

Both Ellen and Orlok evolve from a diseased and corruptive state (physical world) into regenerative and perfect state (spiritual world), after being purified by fire (the Sun). Their old selves are empty shells, as their spirits ascend. This also finds parallel in the myth of Isis and Osiris, as they both went from “daemons” to Gods in the Plutarch essay.
And this also finds parallel in the 1992 adaptation when Vlad/Dracula ascends to the Heavens and is reunited with Elisabeta’s soul. Is this intentional? Are we dealing with reincarnation themes in Eggers' adaptation, as well? According to occultists both Babalon and the Beast have had many manifestations (reincarnations) in the physical world throughout the centuries, after all.

Orlok asking Ellen to remember their shared past, is also an interesting nod to Vlad and Mina in the Coppola's adaptation (their OST is called "Love Remembered"): "I have crossed oceans of time to find you." and “I have sought a creature from the depths. A Eve that remembers her Eden. You are such one.” in the 2016 "Nosferatu" script. Which didn't change all that much in 2023, except we don't have an actual explanation for Orlok interest in Ellen, other than her waking him from his centuries old sleep (resurrection).
#nosferatu 2024#robert eggers#ellen hutter#count orlok#lily rose depp#bill skargard#von franz#dr sievers#ellen x orlok#orlok x ellen
234 notes
·
View notes
Text
Not quite.
There is one other lil dude who gets the full frontal:
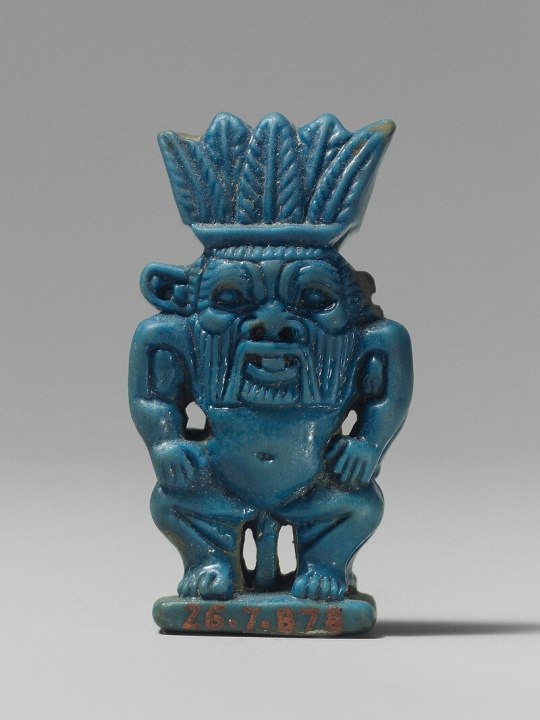

Say hello to Bes. He's a very old deity and one of the most enduring ones - possibly because he was the protector of pregnant women and children; driving away both snakes and evil spirits.
And I think this is why both Bes and Medjet are depicted like this; their power lies in their gaze!
tis the season to remember Medjed aka The Smiter, an invisible egyptian deity with laser eyes and nonbinary swagger:
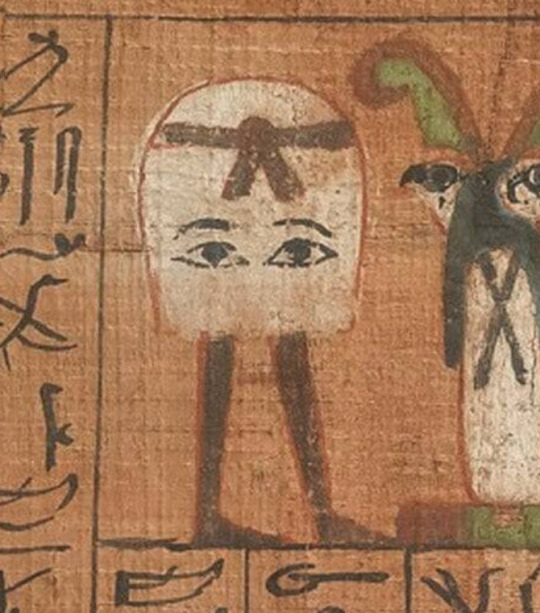

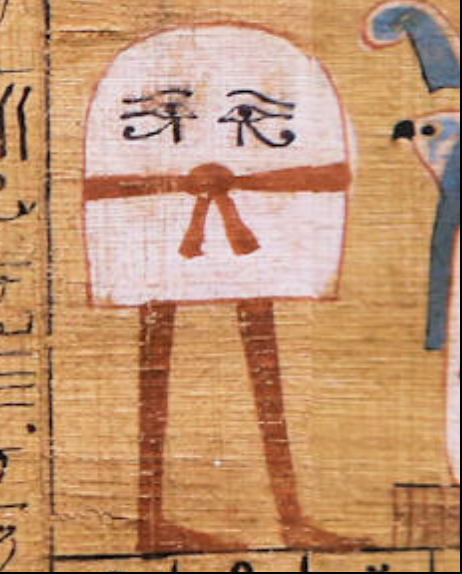

rotating them gently in my mind as they do a spiffy little dance number
#and yes#I know this is an amulet#but wall paintings of him look exactly like this as well#he's never in profile#it's just that most images of him are from the Greco Roman period#where things get a bit mooshy stylistically#this was one of the few I could find that are older#but mentions of him go back to the Old Kingdom#and afaik we got depictions of him from the Middle Kingdom?#anyway#he was a really important folk deity for his entire run#and we've just got more normal people stuff from the Greco Roman period than the ones before
44K notes
·
View notes
Text

33 Greco-Roman Family Tombs Found in Aswan, Egypt
An Egyptian-Italian archaeological mission has uncovered 33 family tombs from the Greco-Roman period near the Aga Khan Mausoleum in Aswan, Egypt.
The joint mission, led by Dr. Mohamed Ismail Khaled, Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, and Professor Patrizia Piacentini from the University of Milan, made the announcement earlier this month. The tombs, discovered west of Aswan’s Nile, date back to the Late Period and the Greco-Roman era, spanning from the sixth century BCE to the third century CE.
The Aga Khan Mausoleum, the resting place of Aga Khan III, Sir Sultan Muhammed Shah, who passed away in 1957, now sits above a necropolis with over 400 tombs. Dr. Khaled noted that it adds a new historical dimension to the Aga Khan area. The tombs vary in architectural style, with some featuring arched entrances and open courtyards made from mudbrick, while others are directly carved into the mountain rock. This diversity reflects the social stratification of the period.
Among the notable finds are mummified remains and funerary objects, including clay figures, sacrificial tables, ceramics, and painted cartonnages. An intriguing discovery within a stone coffin revealed the mummified remains of an adult and a child, likely adhered together by embalming fluids. Further analysis is planned to understand their relationship.



Anthropological and radiological studies have provided insights into the health conditions of buried individuals. Dr. Patricia Piachenti from the University of Milan noted that 30% to 40% of the deceased were infants, children, or adolescents. This high mortality rate among the young offers clues about prevalent diseases during that period. The remains of several adult women showed signs of pelvic bone trauma, suggesting childbirth complications or other medical conditions. Other mummies exhibited evidence of anemia, malnutrition, chest diseases, tuberculosis, and osteoporosis.
“Initial studies reveal that many individuals suffered from infectious diseases and bone disorders,” said Dr. Piacentini. “Some adult females showed signs of medical interventions such as amputations and bone trauma, indicating that ancient Aswan had developed some medical practices.”
Dr. Ayman Ashmawy, Head of the Egyptian Antiquities Sector, said that the lower parts of the necropolis were likely reserved for the middle-class residents of Aswan Island, including physicians, artisans, merchants, and storekeepers. The upper parts of the necropolis, however, appear to have been reserved for the wealthier upper class. This social stratification is reflected in the differing architectural styles and the types of artifacts found within the tombs.



The discoveries also include remains of colored cartonnage, clay and stone figurines, wooden coffins, and offering tables. The tombs’ architectural complexity reflects the advanced skills of the ancient craftsmen who overcame the challenges of digging into rock and constructing low-ceilinged funerary rooms and galleries.
The mission has employed the latest technology, including X-ray and CT scans, to analyze the mummies and artifacts. These technologies have allowed researchers to create three-dimensional reconstructions of the mummies and identify items such as bracelets found on some individuals.
By Dario Radley.



#33 Greco-Roman Family Tombs Found in Aswan Egypt#Aga Khan Mausoleum#Late Period#Greco-Roman era#ancient grave#ancient tomb#ancient mausoleum#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
2,000-Year-Old Fayum Portraits from Roman Egypt: also known as "mummy portraits," these funerary paintings were often fastened to the coffins of the people they depicted

Above: Fayum portrait of a woman from Roman-occupied Egypt, c.100-110 CE
Fayum portraiture was a popular funerary practice among the upper-class families of Roman Egypt from about 50 CE to 250 CE. Given the high mortality rates for children during this period, many of these portraits depict children and youths, but adults were often featured, too.

Above: portrait of a youth wearing a golden wreath, c.130-150 CE; the wreath and the background of the portrait are both gilded
The population of the Faiyum Delta, where most of these portraits were found, largely contained individuals with both native Egyptian/North African and Greek heritage. The Greek lineages can be traced back to the Ptolemaic period, when the Greeks gained control of Egypt and began to establish settlements throughout the region, gradually leading to a cultural diffusion between the Greek and Egyptian populations. The Romans eventually took control of Egypt in 31 CE, absorbing it into the Roman Empire and colonizing much of North Africa, but the demographics of the Faiyum Delta remained largely unchanged.

Above: portrait of a man with a mole on his nose, c.130-150 CE
Many of these Fayum portraits reflect the same blend of ethnic and cultural roots, depicting individuals with both Greek and native Egyptian heritage (a claim that is supported by both archaeological and genetic evidence). Some portraits may also depict native Egyptians who did not have any European ancestry, but had been integrated into Greco-Roman society.

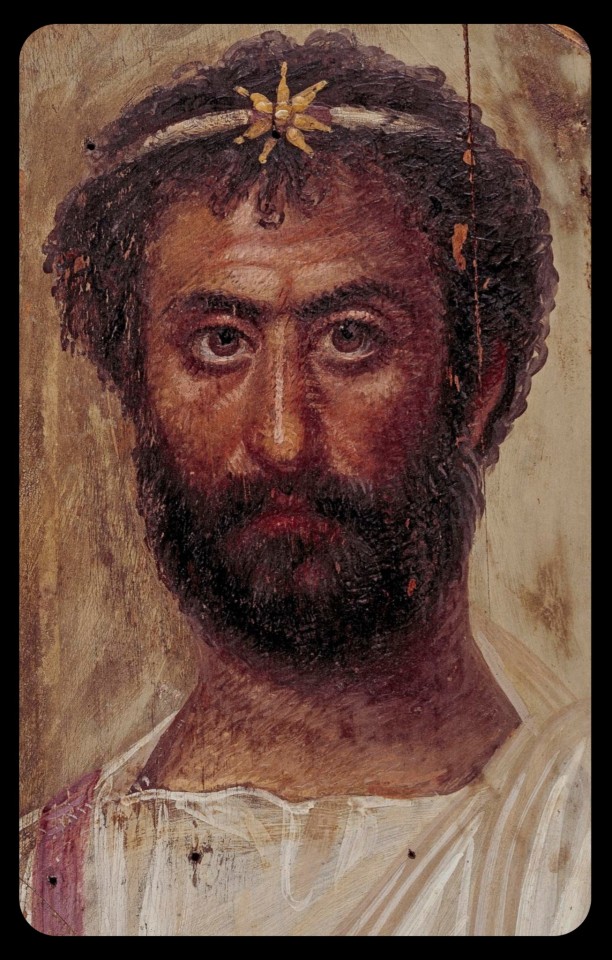
Above: portrait of a bearded man, c.170-180 CE
These representations of native Egyptians provide us with unique insights into the actual demographics of Roman-occupied Egypt (and the ancient world at large). Non-European peoples are rarely included in depictions of the classical world; it's also interesting to see the blend of cultural elements that these portraits represent.

Above: portrait of a priest of Serapis, c.140-160 CE; the man in this portrait is shown wearing a fillet/crown that bears the seven-pointed star of the Greco-Egyptian god, Serapis
As this article explains:
In the 1800s and early 1900s, Western art historians didn’t know what to make of these portraits. Scholars of Roman history labeled them Egyptian. Scholars of Egyptian history labeled them Greco-Roman. These binary academic classifications failed to capture the true complexity of the ancient (or, indeed, modern) Mediterranean. In reality, Fayum portraits are a syncretic form, merging Egyptian and Greco-Roman art and funerary practices. They reflect the cosmopolitanism of both Roman and Egyptian history.
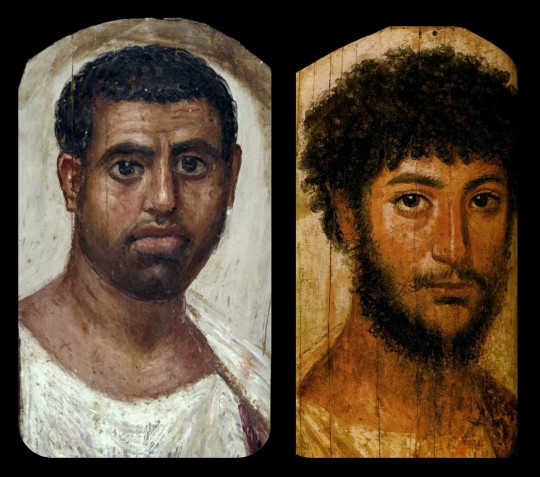

Above: portrait of a man, c.80-100 CE (left); portrait of a bearded officer, sometimes referred to as "Perseus," c.130-175 CE (right)

Above: portrait of a young woman in red, c.90-120 CE
Nearly 1,000 of these portraits are currently known to exist.

Above: portrait of a man wearing a gilded ivy wreath, c.100-150 CE

Above: portrait of a bearded man, c.150-170 CE
Sources & More Info:
Curationist: Fayum Portraits
Harvard Art Museums: Giving the Dead their Due: an Exhibition Re-Examines Funerary Portraits from Roman Egypt
Getty Museum: APPEAR Project
Getty Museum: Faces of Roman Egypt
National Geographic: Ancient Egypt's Stunning, Lifelike Mummy Portraits
The Athens Centre: The Myth of Whiteness in Classical Sculpture
Forbes: Whitewashing Ancient Statues: Whiteness, Racism and Color in the Ancient World
#archaeology#artifact#anthropology#history#ancient history#art#fayum portraits#roman egypt#ancient rome#ethnography#painting#portrait#north africa#people of color#egypt#religion#greco roman#greek#classical antiquity#fayum#mummy portraits#romano egyptian#representation
417 notes
·
View notes
Text




~ Oracle statue of Aphrodite Arsinoe II.
Period: Hadrian; Greco-Roman Period
Place of origin: Egypt
Medium: Dolomite
#ancient#ancient art#history#museum#archeology#ancient egypt#ancient sculpture#ancient history#roman#archaeology#egypt#egyptology#Egyptian#ancient roman#oracle#aphrodite#Aphrodite Arsinoe II#hadrian#Greco-Roman#dolomite
717 notes
·
View notes
Text
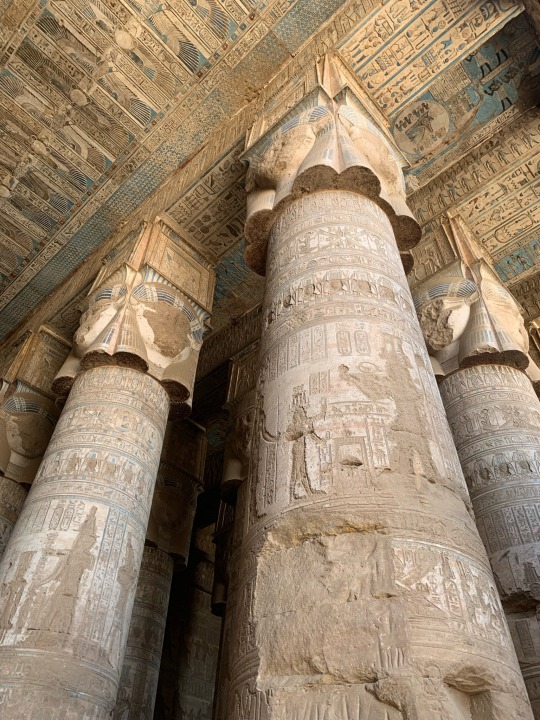
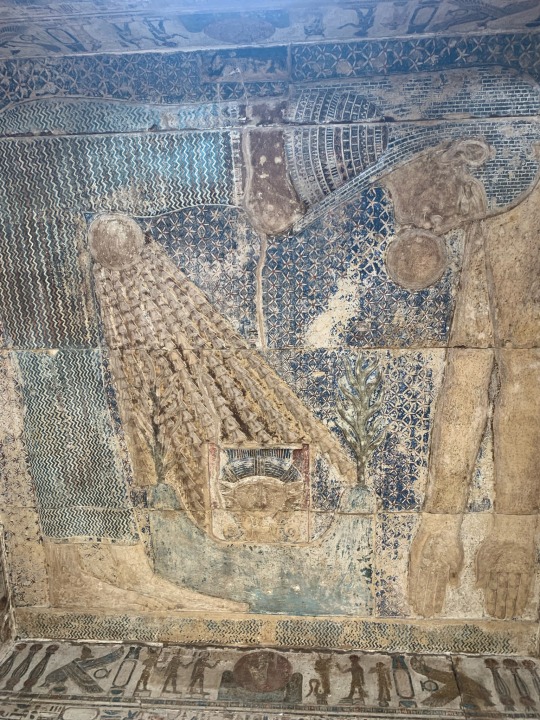
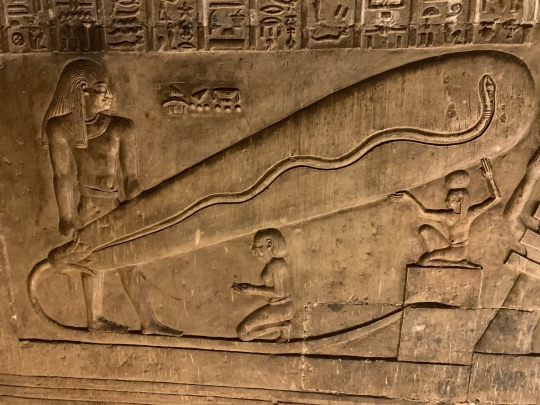
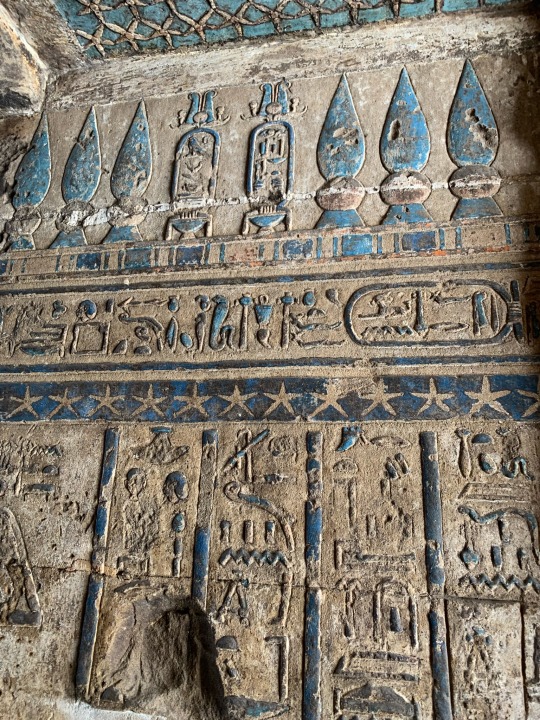
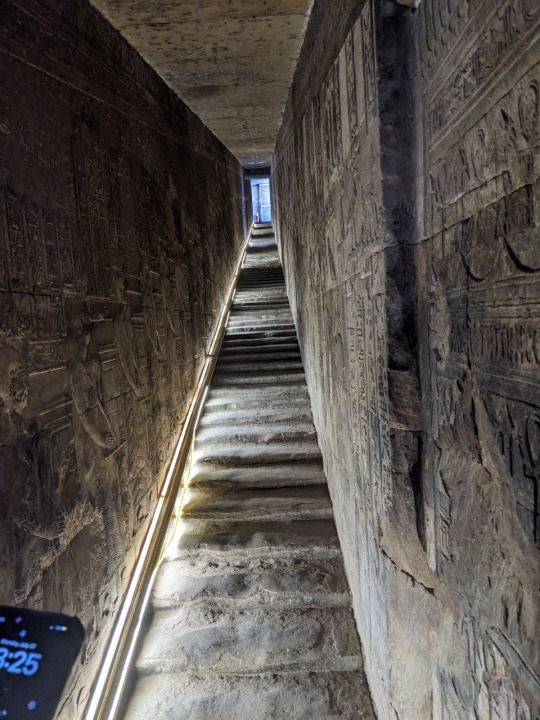










Scenery and imagery from the Hathor temple at Dendera, built in the Greco-Roman period
photos taken by me in August, 2023
Some parts of this temple, when I visited, were off limits. However it was very hard to distinguish what was and wasn’t off limits, so my companion and I wandered everywhere. We also bought passes to the different hidden chambers of the temple; well worth the price in my opinion. You descend or ascend cramped, steep stairs to get to seemingly secret and certainly hidden tunnels filled with vivid imagery of the Gods and worship. Unfortunately, the Dendera calendar filled with zodiacs, has been stolen and replaced with a black cast of what it once was. The original now rests in a museum in Europe.
#ancient egypt#dendera#Hathor#egyptian mythology#egyptian hieroglyphs#ancient history#egyptian gods#egyptian art#egyptology#ancient art#hieroglyphs#egypt
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Dress
1800-1805
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
"The Empire silhouette is readily identified with its origins in the chiton of ancient Greco-Romans, which was a tubular garment draped from the shoulders and sometimes belted beneath the bust. Several re-interpretations have occurred throughout costume history but none have been as notable as the period bridging the rectangular panierred skirts of the 18th century and the conical hoop skirts of the 19th century. The neoclassic style was adopted in all forms of decoration after the French Revolution and was upheld during the Napoleonic Wars partly due to Napoleon Bonaparte's (1769-1821) alliance with Greco-Roman principles. In fashion, the style began as children's wear made from fine white cotton, but was adopted by women in the form of a tubular dress with skirts that were gathered under the bust with some fullness over a pad at the back. As the style progressed the skirts began to flatten at the front and solely gather from the bodice at the center back. The style persisted until the 1820s when the waist slowly lowered and the skirts became more bell shaped."
188 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi :)) do you have any advice on writing stories about Celtic mythology? Ive been trying to use Wikipedia to learn more about it but I find the format of it isn’t very digestible for me and I end up not understanding it well
Writing Notes: Celtic Mythology
The ancient Celtic pantheon consisted of over 400 gods and goddesses who represented everything from rivers to warfare.
With perhaps the exception of Lugh, the Celtic gods were not universally worshipped across Iron Age Europe but were very often limited to only several regions or a specific area.
Another difficulty in examining the Celtic pantheon is the paucity of written records produced by the Celts themselves; quite often a god (deivos/deiva) is named in only a single surviving inscription.
To further complicate our lack of knowledge, the Celts often gave all-embracing powers and attributes to their gods which means that they can rarely be easily categorised.
Celtic votive inscriptions from the Roman period often name a Celtic god with a Roman equivalent noted alongside, a practice known as the interpretatio romana. The following are a few major deities or those with multiple or significant inscriptions.
Andarta - a Celtic goddess whose name may derive from the Celtic word for the bear animal.
Borvo (also Bormo) - a god whose name likely derives from the Celtic word meaning 'to boil' and so indicates his frequent association with natural hot springs.
The Dagda - an Irish-Celtic god whose name is usually preceded by the definite article. His name likely means 'the good god', probably in the sense of being 'many-skilled'. His common attributes are a great club, which can both kill and bring the dead back to life, and a giant cauldron that can produce an inexhaustible quantity of food, especially porridge.
Danu (also Dana) - a Celtic mother-goddess who gives her name, which means 'stream' or 'the waters of heaven' to various places and the River Danube.
Genii Cucullati - mysterious Celtic divinities which are not given a name but appear in groups or alone and wear hooded cloaks in art. Depictions typically have them near a single better-known god and holding either an egg or a scroll.
Nemetona - a goddess whose name derives from the Celtic term for a sacred grove of trees (nemeton). Votive inscriptions naming the goddess survive from both England and Germany, some of which indicate she is the partner of Mars. The goddess had temples dedicated to her at Klein-Winternheim and Trier, both in eastern Germany.
Suleviae - this is a group of Celtic sister goddesses who were venerated in Britain, Germany, and Rome (where there were many Celtic mercenaries). The trio was most likely seen as protective figures and associated with regeneration.
Read the full list here. More Celtic mythology concepts and themes:
Albion - Ancient Celts referred to Britain—not including Ireland—as Albion and only later as Britannia. The Romans connected Albion through their word albus, meaning “white,” with the white cliffs of Dover. Geoffrey of Monmouth reported that the Celts believed a certain Albion who ruled the island was a giant fathered by a god of the sea. Others believe the island was named for a princess who came to the island with fifty women who in their former home had killed their husbands.
Belenus - Also known in Celtic Ireland and Britain by various names—Bel, Belinos, Beli, Bile—Belenus is a god of Celtic Gaul whom Julius Caesar compared to the Greco-Roman Apollo as a solar god of light and reason. He carries a solar disk on the chariot that he presumably uses to travel daily across the sky. His British name is the source for Billingsgate in London. Fires in honor of the god were lit for Celtic festivals of Beltaine (“Bel’s Fires”) on May 1.
Cernunnos - A horned Celtic god of Gaul (modern France) and parts of the British Isles, Cernunnos was a god offertility, like the Italian goddess *Ceres. He carries a club and is lord of the animals. Perhaps because of his association with planting and seeds, he was associated with the underworld. The Romans linked him to Mercury, who led souls to the underworld, and to Apollo, as he provided light for the dead in their graves. Sometimes he is equated with Dispater and the Irish Dagda.
Decapitation - An important theme in Celtic mythology in general and Irish and Welsh mythology in particular. The story of Bricriu’s Feast is a decapitation myth, as is the Welsh story of Bran. The theme influenced the Arthurian myths and the medieval English romances such as Sir Gawain and the Green Knight. Earlier decapitation stories are found in the Bible—including the tales of David and Goliath, Judith and Holofernes, and Salome and John the Baptist. There is also decapitation in the Greek myth of Perseus and Medusa, and in the Mesopotamian myth of Gilgamesh and Humbaba. The decapitation theme—especially when associated with a “green man” such as Gawain’s Green Knight, the Aztec Corn King, or many Native North American Corn Mothers—may well have its roots in sacrificial rituals of fertility. Heads that have been cut away from the body, as in the case of Bran’s head, continue to function and talk in Celtic mythology, suggesting a belief in the head’s being the seat of the soul as well as of power and fertility.
Dis Pater - In the Gaulish, that is, continental Celtic mythology, Dis Pater was the Roman name provided by Julius Caesar for a god claimed by the Gauls as their father god, or ultimate progenitor. The name given by Caesar suggests that the Romans saw a connection between this deity and the otherworld or underworld. As, literally, “underworld father,” Dis Pater is naturally associated in Caesar’s mind with the Roman Pluto. The Irish cognates would probably be the Dagda, the father god of the Tuatha De Danaan, and Donn, the god of the dead.
Druids - The priestly class in early Celtic societies, especially continental Celts. They were judges and seers with great moral authority, who ranked above all other classes. As such, they were the equivalent of their Indo-European brothers, the Indian brahmans. The Romans in Gaul developed myths about the druids such as the one suggesting that they practiced human ‘sacrifice. The Irish filidh may be said to have somewhat diminished druidic standing. The great Celtic bards Taliesen and Amairgen had druidic qualities and authority.
Epona - It was primarily the continental Celts who revered Epona, the horse goddess. She was naturally adopted as a favorite by the Roman cavalry and was celebrated at an annual Roman festival. Epona has certain earth goddess aspects, such as her strong association with fertility, sexuality, and water. In Welsh mythology, Epona appears to have had a cognate in the fertility-warrior goddess Rhiannon, who rode about Wales on a white horse dispensing gifts, in the traditional great goddess manner, from her bag or womb bundle.
Irish mythology
Lugus - His name, referring to brightness, indicates that the continental Celtic god Lugus, whom Julius Caesar equated with the Roman Mercury, was a cognate of the Irish Lugh and the Welsh Lleu. Lugus was a god of the arts.
Maponos - Son of the continental Celtic mother goddess Matrona, has a Welsh cognate in Mabon, as Matrona has one in Modron. Maponos was the divine child— the puer aeternus—of Celtic mythology.
Matrona - In the continental Celtic tradition, Matrona, whose counterpart in Welsh mythology was Modron, was the mother goddess whose son was the divine child Maponos (Welsh Mabon).
Nehalenia - A Germanic and possibly continental Celtic sea goddess who protected voyagers.
Taranis - (Taranus) was compared by Julius Caesar to the Roman god Jupiter. Taranis was the thunder and storm god of the continental Celts of Gaul. He was an aspect of the typically Indo-European triad of Esus, Taranis, and Teutates.
Arthurian Mythology
Annwn - (Caer Feddwid) is a name for the Welsh Otherworld, where a magic cauldron exists. In a medieval Arthurian tale, Preiddeu Annwn (The Spoils of Annwn), Arthur and his knights go to Annwn to obtain the cauldron, which, as indicated by the possession of the Cauldron of Plenty by the Dagda, the father god of the Irish Tuatha De Danaan, was a symbol of sacred kingship. Arthur and the few of his men that remained return empty-handed. The tale is seen as a prototype for the story of the Holy Grail.
Camelot - The castle and primary dwelling place of King Arthur, the seat of the fellowship known as the Round Table. It was at Camelot that the Holy Grail appeared to the knights of the Round Table. Many places in England to this day claim to be the site of the legendary castle. Camelot was first mentioned by Chretien de Troyes in his twelfth-century work Lancelot. Supposedly Camelot was destroyed after Arthur’s death. During the early stylish and optimistic years of the American presidency of John F. Kennedy, it became customary to speak of Kennedy and his followers in the White House, and of the administration as a whole, as “Camelot.”
Chretien de Troyes - A French poet of the 12th century C.E., Chretien wrote metrical romances about the ‘Welsh-British ‘hero ‘King Arthur and his knights of the ‘Round Table. Most famously, he wrote Perceval or the Story of the Grail, about ‘Percival (Parsifal) and the ‘quest for the ‘Holy Grail; and Lancelot, or the Knight of the Cart.
Fisher King - In the Arthurian story, the Fisher King is a somewhat ambiguous figure who is encountered in various conflicting versions by hero-knights of the Round Table— particularly Percival—during the quest for the Holy Grail. The King is in some sense wounded, a fact that affects the fertility of the land he rules. Some say that the King—Pelles, Parian, or Pellam—was guardian of the Grail but that he had sinned and was thus unable to speak when the Grail appeared before him. The King can be cured of his wounds or his speechlessness only when certain questions are asked of him. But when Sir Percival comes to the Fisher King’s castle and the Grail passes by him in procession, he fails to ask any questions about it, and the King remains under the terrible spell.
Galahad - Originally Gwalchafed in Welsh, Sir Galahad was a knight of King Arthur’s Round Table in medieval Arthurian sagas. His story had strong heroic mono- mythic elements. Galahad was the son of Sir Lancelot and the Lady Elaine, whom Lancelot had been tricked by a potion into thinking was his beloved Guinevere. Galahad was brought up by a nun and then knighted by his father and taken to Arthur’s court. He was, above all, pure, and it was this quality that made it possible for him, of all knights, to succeed in the quest for the Holy Grail. Galahad appears in Arthurian lore in a thirteenth-century French cycle of romances. La queste del saint graal (“The Quest for the Holy Grail”). In Sir Thomas Malory’s Le morte d’Arthur, Galahad achieves apotheosis; he is taken up to Heaven.
Guinevere - In the Arthurian romances, including those of Chretien de Troyes, the Welsh historian Geoffrey of Monmouth, and Sir Thomas Malory, Guinevere (Welsh Gwenhwyfar) is the wife of King Arthur and the beloved of Sir Lancelot. There are conflicting tales of Guinevere’s origins. Some traditions hold that she was the daughter of Leodegan, who gave the Round Table to Arthur when the latter married his daughter. Her love for Lancelot led to the disruption of Camelot and the fellowship of the knights of the Round Table, and eventually to Arthur’s death. Some say she married Mordred after Arthur’s death. More often it is said that she retired to a nunnery.
Holy Grail - or Sangreale in Old French, was an important quest object in the Arthurian tradition, particularly connected with Percival, as in the Perceval of Chretien de Troyes (c. 1185) and the slightly later Parfval of Wolfram von Eschenbach. Whatever the original source of the legends of the Grail, Christianity associated it with one of the vessels used by Jesus at the Last Supper.
King Arthur - Legendary British king who appears in a cycle of medieval romances (known as the Matter of Britain) as the sovereign of a knightly fellowship of the Round Table. It is not certain how these legends originated or whether the figure of Arthur was based on a historical person. The legend possibly originated either in Wales or in those parts of northern Britain inhabited by Brythonic-speaking Celts.
Lancelot - The son of King Ban of Benwick or Brittany, Sir Lancelot, or Lancelot of the Lake—so called because he was raised by Vivienne, the mysterious Lady of the Lake, who stole him at birth—was one of the noblest knights of King Arthur’s Round Table. But his love affair with Arthur’s queen, Guinevere, would lead to the downfall of Camelot and the fellowship of knights. Sir Galahad was Lancelot’s son by the Lady Elaine, who tricked him into thinking she was Guinevere and so made love with him. Galahad would succeed in the quest for the Holy Grail where his father had failed. Lancelot rescued Guinevere when she was about to be burned at the stake for adultery. When Guinevere and Lancelot fled to Brittany, Arthur followed them and his illegitimate son or nephew, Mordred, usurped his throne. This led to a war in which both Mordred and Arthur were killed. When Guinevere retired to a nunnery, Lancelot, too, took religious vows. The Lancelot story is found in the works of Chretien de Troyes and Sir Thomas Malory.
Mabinogion - The “Welsh Mabinogion is found in two fourteenth-century manuscripts, the White Book of Rhydderch and the Red Book of Hergest. The collection, based on oral narratives, probably took literary form between the mid-eleventh to the early twelfth centuries.
Malory - Sir Thomas Malory is the fifteenth-century English author of Le Morte d’Arthur, an important compilation of Arthurian material. He is said to have created his great prose work while in prison.
Merlin - Probably has an antecedent in the legendary Scottish and/or Irish mad prophet Myrddin (Merddin). The Welsh historian Geoffrey of Monmouth, in his twelfth-century History of the Kings of Britain, established Merlin’s position as the motivating wizard in the Arthurian legend. It was Merlin who helped arrange for the liaison between Uther and Igraine that would lead to the conception and birth of King Arthur. After Arthur’s birth Merlin took the child to one Hector, this in keeping with the monomythic heroic divine child’s being raised by a menial or commoner. It was Merlin who arranged for the ceremony through which Arthur would prove himself to be the king by removing a sword from a rock. There are many versions of Merlin’s life. It was said by some that he was conceived as a result of the union between a sleeping nun and a demon. In Sir Thomas Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, based on many earlier sources—many of them specifically about Merlin—the magician falls in love with an enchantress, Nimue (perhaps the Lady of the Lake), a femme fatale who imprisons him under a rock.
Welsh Mythology
Has come to us from various sources, all much more directly affected and distorted by time and non-Celtic elements than is the case in the much more isolated Ireland.
There are the two Latin texts especially concerned with the Arthurian legends—the early-ninth-century Historia Brittonum by Nennius and the twelfth-century Historia Regum Britanniae by Geoffrey of Monmouth—and there are, of course, oral sources, including, traditionally, poems questionably attributed to the semi-mythic sixth-century poet-prophet Taliesin, whose Irish equivalent was Amairgen, the poet-warrior.
But Welsh mythology, including the remnants of a pre-Christian Welsh pantheon, is more essentially contained in the “four branches” of a collection of eleven medieval tales known in modern times as the Mabinogion {Mabinogi) and in the various traditions associated with King Arthur.
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 ⚜ More: References ⚜ Writing Resources PDFs
Hi, consuming a lot of media on the topic would be important for your story. These are just a few excerpts from the sources I was able to find, which you can go through in the links above (+ the other references the authors mentioned). Find the right balance between your research and the direction you want your own story to go. Hope this helps with your writing!
#anonymous#celtic#mythology#writeblr#dark academia#literature#writing reference#creative writing#writers on tumblr#spilled ink#writing prompt#writing inspiration#writing ideas#light academia#writing resources
86 notes
·
View notes
Text










previous ➸ next | beginning
Oh dear, young, idiotic King Nikomachos II, son of Demosthenes of Mycenae. Or, rather some smaller provincial kingdom of north-western Lakonia, to rather generalise, from which his great Eurypontid house needed to expel him; with a reign that proves as just as trivial and hedonistic as he. Powdered in rouge as an effeminate leukochrōs, Nikomachos, deformed and ill-bred, possibly a bastard of helot whisper and beheld among five elder sisters, the boy’s kingship was a jest among all the Peloponnese behind closed doors. Yet, in his Kastro Koiláda Chalkou, the scrutiny of the Ekkelisa could not reach him and his whore-bride to be, Eurynome, for the luxury and the splendour of Dionysos and Demeter’s sweet ecstasy were irresistibly intoxicating. For who has time for leading trade routes and waring territory when the pig has only just been carved?
so, what is this? i actually am not sure yet, will it be gameplay, will it be story? we will find out at some point, but i just desperately wanted to play with the late bronze age because as an ancient history and linguistics major, it is my duty. i have always been deeply in love with my hellenistic greco-roman history and thought it would be quite fun to delve into a period i am not as familiar with with the Mycenaeans, to see what i can learn. also considering the beautifully accurate amount of cc clothing for this era, particularly by @clepysdra which i feel the classical age is lacking in among historical cc compared to the bronze age. BUT in speaking of accuracy, those that noticed i referenced the Eurypontid house of the diarchic Spartans, the Ekkelisa and the names of my sims themselves, for the sake of my own enjoyment, i WILL be snatching names for funsies with no relation to their historical origin, but i do want to try my best to make this accurate to Mycenaean culture/dress/relgion, etc. but i am still learning about this fascinating time. i also want to give the BIGGEST praise and thank you to @kyriat-sims for her absolutely beautiful early civilisation save that she’s created, as well as the build featured in this post (which you can find HERE and HERE) as although i tweaked the interior to my manic over-cluttered taste, the castle shell itself is done by her and it’s so brilliant <3
#cardamon#the delusions have got to me again#now you may have noticed my ultimate decades challenge has disappeared#and i don’t know what to tell ya#sometimes i just get struck with new inspiration and the adhd tells me to make it happen now#so now we’re here#hopefully i can make something out of it#:D#ts4#the sims 4#ts4 historical#ts4 legacy#ts4 early civilisation#ts4 greece#eurynome#nikomachos#ts4 ancient greek#leukochrōs#the ancient greek feminisation of the male face by painting it white
121 notes
·
View notes
Note
so I've been watching a lot of videos abt food that's uniquely Hong Kong and y'know with all the changes happening there I had a thought like hm is this preservation and documentation of cultural foods that are at risk of being lost?
and then I thought gosh this sounds familiar likkke everywhere we see violent colonization occur not only are lives and freedom lost but also language culture food
and then I wanted to ask you as a historian: has this always been the case? have people always had low key anxiety about culture "loss" or did they think of it a diff way? is this framing of colonization and cultural loss a recent one?
I'm realizing this is a big question and we are all le tired from les recent events, so pls view this as a no pressure ask, I just uh figured you're the only historian I have real access to haha
This is an important question that I don't currently have the mental wherewithal to answer in great depth, but I think it's important to speak to briefly. And I'll put it this way: yes, human beings have always felt that their culture, their way of life, their present existence, their friends and family, and the forces at work against them are tenuous, uncontrollable, and prone to sudden and violent destruction. I'd say it's one of the key themes of being human. I'll cite the famous example of the 8th-century Old English elegy The Ruin of the Empire, known usually as The Ruin:
This is what many of us would consider the dark and distant past, wherein an unknown person in Anglo-Saxon England is observing the ruins of the Roman Empire in Britain and reflecting on how fragile and frightening the present day feels, as if all the glory has faded into the past, as if things will not be "great" anymore, and the present is just moving inexorably toward darkness:
Bright were the castle buildings, many the bathing-halls, high the abundance of gables, great the noise of the multitude, many a meadhall full of festivity, until Fate the mighty changed that. Far and wide the slain perished, days of pestilence came, death took all the brave men away; their places of war became deserted places, the city decayed. The rebuilders perished, the armies to earth.
And yet... that was the 8th century. That was a very long time ago. A lot of history has happened since then, and despite everything, it's still here. People have always looked at the danger and fragility of their present situation and yearned for the perceived stability of the past. Indeed, the reason we have the myth of the "Dark Ages" is largely thanks to the 14th-century Italian humanist Petrarch, who looked at the (also objectively very, very crappy) 14th century, which is similar to now in a lot of ways, and built the shining myth of the Greco-Roman era as a bygone golden age that society needed to reinstate if it was going to save itself from self-inflicted destruction. This in turn gave rise to the Renaissance, which was intensely a cultural project to reclaim and re-instate a seemingly "better" past in the face of present-day chaos and uncertainty. This included a strict reifying of gender roles (etc. etc. Was There a Renaissance For Women?) and turn toward "purer" social ideals.
Anyway: these concepts have been shaped and articulated differently in various historical periods. But yes, the basic feeling that we are losing ourselves somehow, that the past was better and more stable, that the present challenges can be solved by insular reactionary politics, and so forth, is a very, very common human experience. For better or worse: both tangible and intangible artifacts have always been lost, destroyed, subject to violent sociopolitical conquest attempts, written out of history, and used for oppressive political and cultural processes. Part of the reason the right wing is doing so well worldwide right now is because they are tapping into a very, very old "put the strongman in charge and everything will go back to how [good] it used to be" mythology that is also as old as dirt and time, and which humans just keep doing when things feel existentially scary. This "weaponized nostalgia" is even more of an issue in the age of rampant disinformation, AI, and fake-news bubbles which can totally create what is accepted as reality, very often to the benefit of illiberal, right-wing, authoritarian forces. That is very hard to deal with and overcome, and I don't think we're anywhere near doing it.
That, therefore, is the bad news. The good (as it were) news is that at least these cultural processes and human instincts are not new, and indeed have continued for a long, long time. And even when these old things are destroyed, new ones emerge as well. So yeah.
108 notes
·
View notes