#medieval history
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
As I approach the end of my undergraduate degree in archaeology, I wanted to make a small thank you gift for my dissertation supervisor. She specialises in the early medieval period and is a big cat fan so I found a funky image from a Medieval Manuscript and embroidered a version of it for her!
The original image (final image!) is from the Peterborough Bestiary, produced in Peterborough, England during the early 14th century and now housed at Corpus Christi College, University of Cambridge (MS 53, fol. 197v).





#artwork#art#original art#embroidery#medieval archaeology#medieval history#medieval#cats#medieval animals#sewing#self taught artist
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

I started reading Roland Betancourt's Byzantine Intersectionality because it has a chapter on transwomen, but it turns out that the book is heavily focused on transmasculinity and race in the Byzantine world.
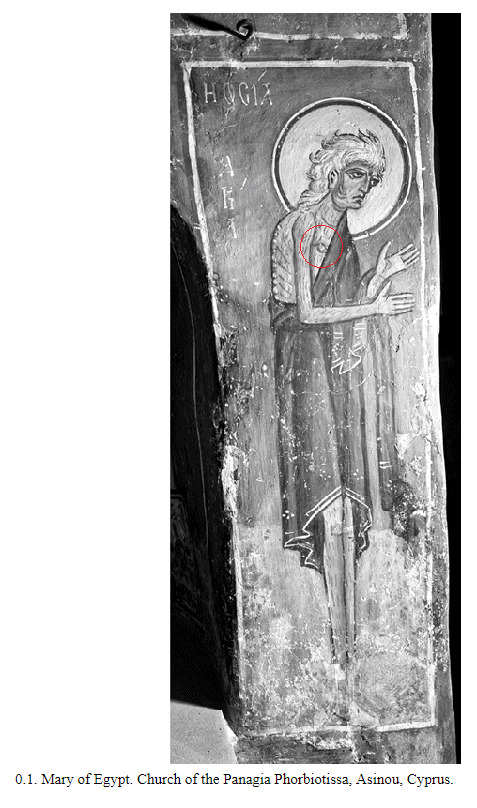

Specifically I wanted to show you this discussion on artistic representation of top surgery and the likelihood that this actually represents top surgery.
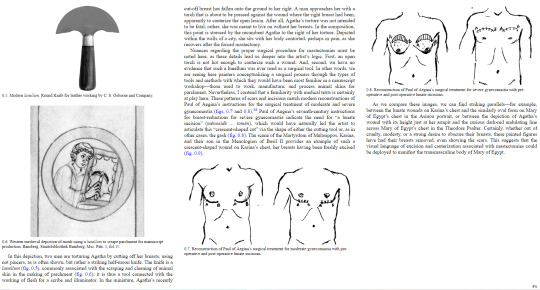
Anyway this is really fucking cool
5K notes
·
View notes
Text

really just an excuse to draw medieval kyubey
#also cause i was thinking abt anime#my art#medieval art#madoka kaname#puella magi madoka magica#puella magi#illuminated manuscript#medieval#medieval history#medievalist#medieval meme#homura akemi#mami tomoe#sayaka miki
133 notes
·
View notes
Text

Urban Women presents a different and lesser-known image of the late Middle Ages, from 1250 to 1550. The authors trace the lives of women protesting, marrying, making love, working, and engaging in the daily life of Low Countries towns. In doing so, this book gives voice to wealthy businesswomen, laborers, religious women, criminals, and sex workers, spotlighting the remarkable figures who shaped a "women's town" within a man's world.
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
"As far as we know, Ende was a Spanish illustrator who lived in the late 10th century and is regarded as the first female European artist to be recorded. She spent a portion of her life at San Salvador de Tábara Monastery in Tábara, Kingdom of León in Medieval Spain. According to the research of John Williams, one of the most eminent experts in Spanish medieval art, Ende may not have been a nun but rather belonged to a group of noble women from León who, during those years, rejected both convent life and instead managed their wealth and in a sense decided to go their way.
The Tabara scriptorium, which generated some of the Spanish Middle Ages’ most significant codices, was a cultural lighthouse at the time. Ende felt tremendously at ease working and living at Tábara Monastery, according to her illuminated manuscripts. Above all, it brought Ende closer to the dominant cultural movement of the day, recognizing the need to preserve sacred passages and everlasting images, working for her faith and herself."

#ende#history#women in history#women's history#10th century#female painters#female artists#spain#spanish history#middle ages#medieval history#medieval#medieval women
615 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gauntlets owned by Emperor Maximilian I (1459-1519)
#photography#plate armor#design#armor design#gauntlets#art#history#medieval history#red#red aesthetic#medieval#world history#dark academia
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

#history#medieval history#ish?#oh i am Deeply in my feelings about this#people have always been people#(will always be people)#“i was his closest neighbor”#(they had not wanted him to go without flowers)#excuse me i just need to cry for real. thanks.
11K notes
·
View notes
Text


Medieval heart-shaped music book, circa 1460-1477.
National library of France.
#beauty#oddities#antiques#middle ages#medieval history#curiosities#medieval art#european culture#french culture
2K notes
·
View notes
Text


Carolingian sword uncovered in Dendermonde, Belgium, dated 750-850 AD
from the Royal Military Museum, Brussels
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Lots of pop culture fiction about the Middle Ages likes to tackle the concept of witch trials (even though that didn't even become a thing until the mid-1400s and didn't hit the stride we think of it with today until the 1600s) in one of three ways:
"actually they were really witches with magic powers! (Bad)"
"actually they were really witches with magic powers! (Good)"
"they weren't witches at all they were smart women of science more sophisticated and advanced than those STUPID inbred people could comprehend so they killed them because they thought that medicine was evil"
no they were just weird people. How do you treat weird people?
#death bed#death bed: a souls like rpg#ttrpg#ttrpg tumblr#indie ttrpg#middle ages#witches#witch#witchcraft#ttrpg community#tabletop#ttrpgs#rpg#eureka#eureka: investigative urban fantasy#medieval history#medieval#medieval women#15th century#dark souls#dark souls 2#dark souls 3#soulsborne#fromsoft
510 notes
·
View notes
Text

#medieval#medieval history#archive#museum#Europe#goth architecture#gothic#whimsigoth#whimsicore#moody#dark#aesthetic#green aesthetic#rosieandthemoon#dreamcore#esoteric#occult#fairycore#goth#whimsical#fairy aesthetic#witchy#witchcore#gothcore#gothblr#fantasy vibes#fantasy aesthetic#medieval aesthetic#portals#magick
6K notes
·
View notes
Text









“i desire violently—and i wait”- Anaïs Nin
#medieval#old art#art history#knight#medieval times#medieval era#medieval art#medieval aesthetic#medieval armor#medieval ages#medieval animals#medieval period#medieval tradition#mood board aesthetic#moodboard aesthetic#moodboard#medieval illustration#medieval painting#medieval style#medieval setting#medieval fantasy#medieval history#medieval knight#medieval core
969 notes
·
View notes
Text

gadzooks! my game? It be'eth changed!
#me when i put a disproportionate amount of effort into a joke#game changer#dropout#game changer fanart#sam reich#dropout fanart#dimension 20#medieval art#illuminated manuscript#medieval#medieval history#medieval meme#history meme
19K notes
·
View notes
Text

Sword Hilt with Design of Lion Heads, Arabesque Scrollwork, and Arabic Inscription. Hamadan, Iran. 13th Century CE.
Saint Louis Art Museum.
#Iran#Iranian#iranian history#Persia#Persian#middle eastern history#asian history#medieval#medieval history#saint louis art museum#art#culture#history#military history#sword
295 notes
·
View notes
Text

I think we need to bring whatever the hell was going on at 17th-century conclaves back. Who's with me.
#history#medieval history#history of religion#conclave 2025#conclave-the-non-pope-yaoi-so-far-as-we-know version#also fond of the part where the 13th century viterbans literally took the roof away to force the cardinals to get a shift on
283 notes
·
View notes