#Global Security Initiative
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Full text after break
Chinese President Xi Jinping on Tuesday made a speech at the Closing Ceremony of the BRICS Business Forum 2023, which was read out by Chinese Commerce Minister Wang Wentao.
Following is the full text of the speech:
Enhancing Solidarity and Cooperation To Overcome Risks and Challenges And Jointly Build a Better World
Your Excellency President Matamela Cyril Ramaphosa,
Members of the Business Community,
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Friends,
I wish to extend my warm congratulations on the success of the BRICS Business Forum in South Africa!
Ten years ago here in South Africa, we BRICS leaders witnessed the birth of the BRICS Business Council. Since then, the Council has stayed true to its founding mission. It has seized opportunities to deepen cooperation, contributing to economic and social development of BRICS countries and helping sustain global economic growth.
Right now, changes in the world, in our times and in history are unfolding in ways like never before, bringing human society to a critical juncture. Should we pursue cooperation and integration, or just succumb to division and confrontation? Should we work together to maintain peace and stability, or just sleepwalk into the abyss of a new Cold War? Should we embrace prosperity, openness and inclusiveness, or allow hegemonic and bullying acts to throw us into depression? Should we deepen mutual trust through exchanges and mutual learning, or allow hubris and prejudice to blind conscience? The course of history will be shaped by the choices we make.
An ancient Chinese thinker observed that “following the underlying trend will lead one to success, while going against it can only cause one to fail.” We humankind have achieved notable economic development and social progress over the past decades, and that is because we have drawn lessons from the two world wars and the Cold War, followed the historical trend of economic globalization, and embarked on the right path of openness and development for win-win cooperation. Our world today has become a community with a shared future in which we all share a huge stake of survival. What people in various countries long for is definitely not a new Cold War or a small exclusive bloc; what they want is an open, inclusive, clean and beautiful world that enjoys enduring peace, universal security and common prosperity. Such is the logic of historical advance and the trend of our times.
Ten years ago, I made a proposition of building a community with a shared future for mankind, calling on all countries to build this planet we all call home into a harmonious family. In the face of high winds, choppy waters and even treacherous storms, we in all countries need to uphold the correct views of the world, of history and of our overall interests, and act to translate the vision of a community with a shared future for mankind into reality.
—We need to promote development and prosperity for all. Many emerging markets and developing countries (EMDCs) have come to what they are today after shaking off the yoke of colonialism. With perseverance, hard work and huge sacrifices, we succeeded in gaining independence and have been exploring development paths suited to our national conditions. Everything we do is to deliver better lives to our people. But some country, obsessed with maintaining its hegemony, has gone out of its way to cripple the EMDCs. Whoever is developing fast becomes its target of containment; whoever is catching up becomes its target of obstruction. But this is futile, as I have said more than once that blowing out others’ lamp will not bring light to oneself.
Every country has the right to development, and the people in every country have the freedom to pursue a happy life. With that in mind, I have proposed the Global Development Initiative, with the goal of promoting development for all by the international community and boosting the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. With the support of many countries, solid gains have been made in pursuing this initiative, with cooperation flourishing in various fields. China will work with all other countries to speed up cooperation under the Global Development Initiative, strengthen drivers of global development, promote the reform of the World Trade Organization in a comprehensive and in-depth manner, meet common challenges together and make life better for people across the world.
—We need to achieve universal security. Recent years have seen a turbulent world; many countries and regions are plagued by wars and conflicts and many people are displaced. Members of the international community share the pressing hope to eradicate the root cause of conflicts and wars, and find a fundamental way to realize enduring peace and security globally. Facts have shown that any attempt to keep enlarging a military alliance, expand one’s own sphere of influence or squeeze other countries’ buffer of security can only create security predicament and insecurity for all countries. Only a commitment to a new vision of common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable security can lead to universal security.
Last year, I put forward the Global Security Initiative, and it has gained support from over 100 countries and international organizations. China stands ready to jointly pursue this initiative with all others. We should have dialogue and oppose confrontation, forge partnership but not alliance, and pursue win-win outcome and oppose zero-sum game, and work together to build a community of security.
—We need to stay committed to exchanges among civilizations and mutual learning. One flower alone cannot make a beautiful spring; only blossoming of a rich variety of flowers can bring spring to the global garden. Human civilization is colorful by nature. It is precisely because of their differences in history, culture and system that all countries need to interact with one another, learn from each other, and advance together. Deliberately creating division with the assertion of “democracy versus authoritarianism” and “liberalism versus autocracy” can only split the world and lead to clash of civilizations.
I have put forward the Global Civilization Initiative, calling for promoting diversity of global civilizations, the common values of humanity, and people-to-people and cultural exchanges and cooperation. China welcomes all other countries to get involved in cooperation under this initiative. We should encourage different civilizations to bring out their best and flourish together; we should break barriers to exchanges, and renew human civilization.
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Friends,
As an ancient Chinese philosopher observes, “Change is the nature of the universe.” The collective rise of EMDCs represented by BRICS is fundamentally changing the global landscape. EMDCs have contributed as high as 80 percent of global growth in the past 20 years, and their share in the global GDP has increased from 24 percent 40 years ago to more than 40 percent. Just as a line in a Chinese poem reads, “No mountains can stop the surging flow of a mighty river.” Whatever resistance there may be, BRICS, a positive and stable force for good, will continue to grow. We will forge stronger BRICS strategic partnership, expand the “BRICS Plus” model, actively advance membership expansion, deepen solidarity and cooperation with other EMDCs, promote global multipolarity and greater democracy in international relations, and help make the international order more just and equitable. The gathering between BRICS countries and more than 50 other countries in South Africa today is not an exercise of asking countries to take sides, nor an exercise of creating bloc confrontation. Rather, it is an endeavor to expand the architecture of peace and development. I am glad to note that over 20 countries are knocking on the door of BRICS. China hopes to see more joining the BRICS cooperation mechanism.
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Friends,
China stays committed to an independent foreign policy of peace and the building of a community with a shared future for mankind. As a developing country and a member of the Global South, China breathes the same breath with other developing countries and pursues a shared future with them. China has resolutely upheld the common interests of developing countries and worked to increase the representation and voice of EMDCs in global affairs. Hegemonism is not in China’s DNA; nor does China have any motivation to engage in major-power competition. China stands firmly on the right side of history, and believes that a just cause should be pursued for the common good.
At present, we Chinese, under the leadership of the Communist Party of China, are advancing the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation on all fronts by pursuing Chinese modernization. Chinese modernization aims to achieve common prosperity, material and cultural-ethical advancement, harmony between humanity and nature, and peaceful development for a huge population. Chinese modernization has created a new form of human advancement and presented a new future of modernization. We hope that other developing countries can draw on the outstanding achievements of human civilization and find their own paths to modernization in keeping with their national conditions.
Achieving high-quality development is a top priority in China’s goal of fully building itself into a modernized country. We are committed to applying a new development philosophy and creating a new development paradigm. In the past decade, China has contributed more than 30 percent of annual global growth. This year, the Chinese economy has maintained the momentum of recovery and growth. China enjoys several distinct advantages: a socialist market economy in systemic terms, a supersize market in terms of demand, a full-fledged industrial system in terms of supply, and abundant, high-caliber labor force and entrepreneurs in terms of human resources. The Chinese economy has strong resilience, tremendous potential and great vitality. The fundamentals sustaining China’s long-term growth will remain unchanged. The giant ship of the Chinese economy will continue to cleave waves and sail ahead.
China will remain an important opportunity for the world’s development. Our door is wide open to anyone who wants to engage in cooperation with us. As a supersize economy, China will remain firm in advancing high-standard opening-up. We will continue to expand market access, cut the negative list for foreign investment, and further open the modern services sector. We will steadily improve the business environment, provide national treatment to foreign-invested enterprises, foster a world-class, market-oriented business environment governed by a sound legal framework, and build a globally-oriented network of high-standard free trade areas. We will continue to advance ecological conservation, accelerate the building of a Beautiful China, actively and prudently move toward carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and pursue all-round green transition in economic and social development. Going forward, as it endeavors to achieve modernization for its more than 1.4 billion people, China will surely contribute even more to the global economy and provide even more opportunities for the global business community.
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Friends,
A formidable mission is a magnificent and glorious mission. As long as we work in unity and strengthen cooperation, we will not be intimidated by any risk or challenge on the way ahead, and we will surely steer the giant ship of human development to a brighter future!
Thank you.
#xi jinping#BRICS#brics summit#global development initiative#global security initiative#new cold war#communist party of china
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
China will educate thousands of foreign law enforcement officers for ‘more fair’ globe
China will educate thousands of foreign law enforcement officers for ‘more fair’ globe #Africa
#Africa#authoritarian tactics#Belt and Road Initiative#China#global security#Global Security Initiative#Indo-Pacific#law enforcement training#transnational crime#Wang Xiaohong
0 notes
Text
From Emerging Tech to Responsible AI - The Present and Future of Law Enforcement and Counter-terrorism.
The objective of this event is to officially launch and promote the second phases of two EU-funded pivotal projects in the field of emerging technologies: The AI and Law Enforcement Programme implemented by UNICRI and INTERPOL and CT TECH + implemented by UNOCT and INTERPOL. The event aims to highlight the significance and transformative potential of these independent yet related initiatives to strengthen both public safety and global security.
Watch From Emerging Tech to Responsible AI: The Present and Future of Law Enforcement and Counter-terrorism!

#counter terrorism#CT TECH +#unoct#UNICRI#global security#public safety#law enforcement#future of law#responsible AI#artificial intelligence#funded projects#initiatives#terrorism#panel discussion
0 notes
Text
#China Military Base#Cambodia#Strategic Projections#Military Expansion#Geopolitics#Southeast Asia#China-Cambodia Relations#Global Security#Defense Strategy#Regional Influence#Maritime Security#Military Presence#Belt and Road Initiative#International Relations#Strategic Alliances
0 notes
Text
Technological Competition: The New Cold War in AI Development
Introduction: The Global AI Race
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just a technological advancement—it is a tool for geopolitical dominance. The race to lead in AI development has quickly become the new "Cold War" for technological superiority, with countries vying for global influence through innovation. India and China, two rising powers in the global AI race, are engaged in this competition, not just for technological advancement, but for broader geopolitical positioning. The winner of this race will hold significant leverage in global markets, cybersecurity, and military might, reshaping the international order.
India and China’s AI Race: Strategic Motivations and Differing Paths
China’s approach to AI development is aggressive and expansive, driven by its ambition to become the global leader in AI by 2030, as outlined in its "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan" (2017). China sees AI as a key to enhancing its global competitiveness, strengthening its military, and asserting its dominance in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and national security. Its significant investments in AI infrastructure, research, and development underscore its commitment to becoming an AI superpower.
India, on the other hand, has taken a more measured approach, focusing on AI for social inclusion, economic growth, and democratic governance. India's AI strategy, outlined by NITI Aayog in 2018, emphasizes "AI for All," aiming to harness AI's potential to address societal challenges in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and education. While India’s strategy focuses on leveraging AI for inclusive growth, its efforts to scale AI innovations to compete globally are still in their nascent stages.
The contrasting motivations behind India and China’s AI policies—China’s for global dominance and India’s for societal benefit—reflect their broader geopolitical aspirations. However, the divergence in their AI strategies also highlights the technological gap between the two nations, which has significant implications for global power dynamics.
AI and Economic Competitiveness
AI is poised to reshape the global economy by enhancing productivity, automating processes, and fostering innovation. China’s early adoption and massive investments have given it a significant edge in AI-driven economic competitiveness. Chinese companies like Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu have integrated AI into various industries, creating a robust AI ecosystem that fuels their global expansion. China’s AI investments in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare have not only boosted its domestic economy but also positioned it as a critical player in global supply chains.
India, while progressing in AI research and development, faces challenges in scaling AI applications across industries. Although India has a growing start-up ecosystem and a strong IT sector, it lacks the infrastructural investments and comprehensive AI strategies seen in China. Nevertheless, India's potential to become an AI hub for the developing world cannot be overlooked. The Indian government’s focus on creating AI solutions for its vast and diverse population provides a unique model of AI deployment, one that prioritizes inclusivity and social welfare over sheer economic dominance.
Global Influence and Geopolitical Consequences
The AI race between India and China extends beyond economic competition; it is also about gaining geopolitical influence. China's AI strategy is intrinsically linked to its geopolitical ambitions. Through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and its growing investments in AI research, China is exporting its AI technologies to developing countries, influencing the global AI standards and creating dependencies on Chinese technology. This raises concerns about digital sovereignty and the spread of authoritarian AI governance models, particularly in surveillance and data control, which China uses to maintain its own domestic security.
India, on the other hand, is positioning itself as a counterbalance to China’s growing influence. By advocating for responsible AI development, India promotes a more ethical and democratic approach to AI governance. India’s participation in international forums, such as the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI), signals its intent to influence global AI standards while safeguarding democratic values.
However, to truly challenge China’s dominance, India must increase its investment in AI infrastructure, foster international collaborations, and scale up its AI research efforts. The challenge for India is to compete with China while adhering to its principles of transparency, data privacy, and ethical AI development.
The New Cold War: AI and Future Power Dynamics
As AI becomes the backbone of economic and military power, the competition between India and China will shape the future balance of power in Asia and beyond. China’s rapid progress in autonomous systems, AI-driven cybersecurity, and military applications presents a formidable challenge to India’s national security and sovereignty. India’s response must involve not only bolstering its AI capabilities but also forming strategic alliances with like-minded countries to resist China’s growing influence in AI governance and technology standards.
Conclusion
The AI race between India and China is more than just a competition for technological superiority—it is a battle for global influence and economic power. China’s aggressive push for AI dominance threatens to reshape the global order, while India’s democratic and inclusive AI model offers an alternative path. However, the technological gap between the two nations poses a significant challenge for India. As the new Cold War of AI intensifies, India must accelerate its AI investments and forge international collaborations to protect its interests and promote a more responsible and ethical AI-driven future.
#AI competition#New Cold War#AI race#India China rivalry#Global AI dominance#AI and geopolitics#Technological competition#AI for global power#China AI strategy#India AI strategy#AI in economics#AI and national security#Belt and Road Initiative#Responsible AI#AI for social good#Geopolitical influence#AI infrastructure#AI standards#Digital sovereignty#AI and global governance
0 notes
Text
Part II - United Nations Chiefs of Police Summit (UNCOPS 2024).
Geopolitical tensions, the climate crisis, global mistrust and the dark side of technology, which Secretary-General António Guterres has called the "looming threats of the 21st century", are affecting the well-being and livelihoods of communities worldwide and the planet itself. National and United Nations Police are on the frontlines of averting and addressing these transnational threats.
The United Nations Police contribute to the Action for Peacekeeping (A4P) initiative and A4P+ priorities by building and supporting or, where mandated, acting as a substitute or partial substitute for host-State police capacity to prevent and detect crime, protect life and property, and maintain public order and safety in adherence to the rule of law and international human rights law.
---
Objectives:
A common vision and concrete commitments to further equipping the United Nations Police - UNPOL to effectively contribute to A4P and A4P+ priorities. Awareness of interlinkages between national and United Nations policing to increase global security.
Collective appreciation of the role of national and United Nations policing in overcoming systemic challenges affecting peacekeeping.
Joint understanding of the needs of the United Nations Police, including related to safety and security, and concrete Member State and Secretariat commitments to meet demands.
A common roadmap to realize the Secretary-General's vision of "a transformed United Nations police that is people-centred, modern, agile, mobile and flexible, specialized, rights-based and norm-driven", and that is also innovative, data-driven and tech-enabled.
United Nations Headquarters
UN Web TV
Watch (Part 2) United Nations Chiefs of Police Summit (UNCOPS 2024)!

#geopolitical tensions#unhq#uncops#global security#substitute for host state police capacity#partial substitute for host state police capacity#police personnel#military police#action for peacekeeping initiative#safety and security#a4p+ transformation initiative#overcoming challenges#policing#peacekeeping#violence prevention#collective appreciation#role of national and united nations policing#tech enabled#human security#data driven#people-centered#armed conflicts#united nations police
0 notes
Text
this call was released anonymously (understandably) but my local Palestinian organizers who I literally trust with my life have endorsed it, and it seems to be gaining momentum in multiple cities, so I encourage you all to get involved:
"A proposal to coordinate a multi-city economic blockade on April 15th in solidarity with Palestine recently received overwhelming commitments to participate around the US and internationally.
The proposal states that in each city, we will identify and blockade major choke points in the economy, focusing on points of production and circulation with the aim of causing the most economic impact, as did the port shutdowns in recent months in Oakland, California and Melbourne, Australia, as just a few examples.
There is a sense in the streets in this recent and unprecedented movement for Palestine that escalation has become necessary: there is a need to shift from symbolic actions to those that cause pain to the economy.
As Yemen is bombed to secure global trade, and billions of dollars are sent to the Zionist war machine, we must recognize that the global economy is complicit in genocide and together we will coordinate to disrupt and blockade economic logistical hubs and the flow of capital."
ETA: since I posted, organizers in St. Louis, Seoul, Brussels, and the Netherlands have signed onto the agreement, so if you saw this before and your city wasn't listed look again. anyone with the capacity to do some outreach, and a few connections to start with, could take the initiative to bring their city or region on board. read the solidarity agreement and check out the resources, and if you know trustworthy people in your area who might be interested in this sort of thing, talk to them about it.
remember that this isn't a series of protests (although some cities are organizing protests in conjunction), it's a commitment to take mass direct action and to maintain a united front in the face of any state repression. many organizers are (and have already been) using an affinity group model to actually coordinate those direct actions. autonomous groups can take action on April 15th whether or not others in their city/region have committed to this agreement. just do your homework (look up know-your-rights info specific to where you live + general direct action safety tips) and take good care of each other Blockades: a short guide to getting in the way Basic blockading Practical Protest Techniques: using your body Blockading: a guide ACT UP civil disobedience guide
tumblr
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The future of food in a changing climate

Written by: Jagriti Shahi, Business Analyst at Global Launch Base
Introduction
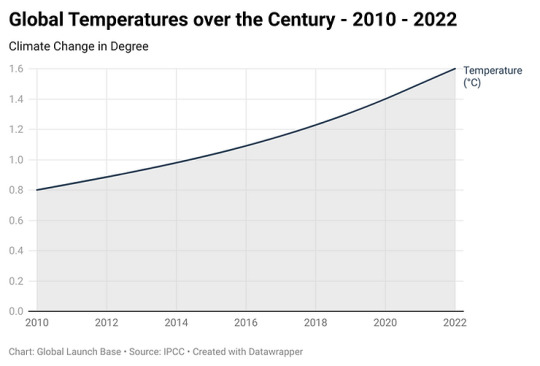
Figure 1: Global Temperature over the Century
This data shows that global temperatures have been rising steadily over the past few decades. The rate of warming is expected to accelerate in the coming years, if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has warned that if we do not take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, global temperatures could rise by as much as 5.2 degrees Celsius by the end of the century. This would have devastating consequences for the planet, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and mass extinctions. The data is clear that we are facing a serious challenge, and we need to take action now to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Climate Change and Food Production
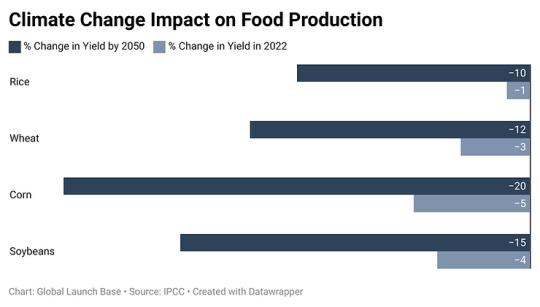
Figure 2: Climate Change Impact on Food Production
This data shows that the % change in yield of different crops by 2050 is already starting to be felt in 2022. For example, rice yields are already 1% lower in 2022 than they were in 2020. This is likely due to the combination of climate change and other factors, such as pests and diseases.
The trend is expected to continue in the coming years, as climate change continues to impact crop yields. This could have a serious impact on food security, as it will make it more difficult to produce enough food to feed the world's growing population.
The intricate relationship between climate change and food production is reshaping agricultural landscapes, challenging traditional practices, and compelling us to explore innovative solutions to ensure global food security. In this article, we delve into the intricate interplay between climate change and food production, highlighting the challenges faced and the potential pathways toward a more resilient future.
Altered Growing Conditions: One of the most immediate and palpable impacts of climate change on food production is the alteration of growing conditions. Rising global temperatures influence the length of growing seasons and shift the geographic suitability of certain crops. In some regions, this leads to reduced yields, as crops may experience stress due to excessive heat, prolonged droughts, or erratic precipitation patterns. Conversely, other areas might witness extended growing seasons, presenting opportunities to cultivate new varieties of crops.
Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: As the climate warms, pests and diseases that were once constrained by temperature limitations are expanding their ranges, posing significant threats to crops and livestock. The increased prevalence of pests can lead to reduced yields and necessitate more intensive use of pesticides, raising environmental concerns and potentially compromising food safety.
Water Scarcity and Agricultural Droughts: Climate change exacerbates water scarcity, a critical factor in agricultural productivity. Changing precipitation patterns and the intensification of droughts can jeopardize water availability for irrigation, which is essential for many crops. This can force farmers to compete for limited water resources, driving up costs and reducing overall agricultural output.
Impacts on Livestock Production: Livestock farming, a vital component of global food systems, is also vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Heat stress can lead to reduced livestock productivity, affecting meat and milk production. Moreover, changing forage availability due to altered precipitation patterns can challenge livestock feed supply, leading to increased costs for farmers.
Soil Degradation and Erosion: Climate change can exacerbate soil degradation and erosion, undermining agricultural sustainability. Intense rainfall events can lead to soil erosion, stripping away fertile topsoil and diminishing its ability to support crop growth. Soil degradation impacts soil structure, nutrient content, and water-holding capacity, posing a significant threat to long-term food security.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies: To address these challenges, a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies is required.
Adaptation: Farmers can adopt climate-resilient practices such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved water management. Planting diverse crop varieties can spread risk and enhance resilience to changing conditions. Agroforestry systems, which combine trees with crops or livestock, can stabilize soil, conserve water, and provide additional income sources. Implementing efficient irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting can help manage water scarcity.
Mitigation: Mitigating climate change through the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions is a critical step toward safeguarding food production. Sustainable land management, reforestation, and the adoption of renewable energy sources can contribute to lowering emissions from the agricultural sector.
7. Technological Innovations: Advancements in technology hold promise for enhancing climate resilience in food production. Precision agriculture utilizes data-driven approaches to optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and reduce waste. Climate-resilient crop varieties developed through traditional breeding or genetic modification can enhance yields under changing conditions.
8. Policy and International Cooperation: Global efforts are indispensable in addressing the complex challenges posed by climate change and food production. International agreements and policies can incentivize sustainable agricultural practices, support smallholder farmers, and promote technology transfer. Investment in research and development can drive innovation and provide farmers with the tools they need to adapt to changing conditions.
Key players in the market:
Impossible Foods: Impossible Foods is a food technology company that makes plant-based meat products that are indistinguishable from real meat. Impossible Foods' products use less water, land, and energy than traditional meat, and they emit significantly fewer greenhouse gasses.
Danone: Danone is a food and beverage company that has set a goal of becoming carbon neutral by 2050. Danone is working to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions across its entire value chain, from the farm to the fork.
Innovative Agricultural Practices
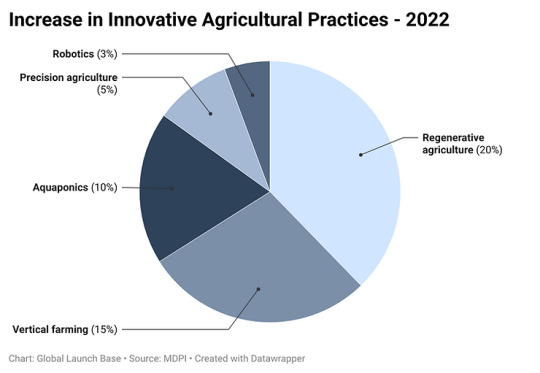
Figure 3: Increase in Innovative Agricultural Practices
This data shows that there is a growing interest in innovative agricultural practices. This is likely due to the increasing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional agriculture and the need for more sustainable food production methods.
Innovative Agricultural Practices: Navigating the Future of Sustainable Food Production
In a world where climate change and environmental degradation pose unprecedented challenges to traditional agricultural practices, innovation emerges as a beacon of hope. Innovative agricultural practices are essential not only for meeting the growing global demand for food but also for ensuring the long-term sustainability of our planet. In this article, we explore a spectrum of groundbreaking techniques that are transforming the way we cultivate crops, rear livestock, and manage natural resources.
Agroecology: Harmonizing Nature and Agriculture: Agroecology is a holistic approach that seeks to mimic natural ecosystems within agricultural systems. By fostering biodiversity, enhancing soil health, and minimizing external inputs, agroecological practices promote resilient and sustainable food production. Techniques such as intercropping, cover cropping, and crop rotation reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, mitigating the environmental impact of conventional agriculture.
Precision Agriculture: Merging Technology and Farming: Precision agriculture leverages cutting-edge technologies, including GPS, remote sensing, and data analytics, to optimize resource utilization and enhance productivity. By precisely mapping variations in soil and crop conditions, farmers can tailor irrigation, fertilization, and pest control measures, minimizing waste and maximizing yields. Drones, sensors, and automated machinery further streamline operations and minimize environmental footprint.
Vertical Farming and Hydroponics: Farming in Tight Spaces: Vertical farming and hydroponics redefine the boundaries of traditional agriculture by enabling food production in urban environments and underutilized spaces. Vertical farms stack crops in vertical layers, utilizing artificial lighting and controlled environments to optimize growth. Hydroponics, a soilless cultivation method, delivers water and nutrients directly to plant roots, reducing water usage and enabling year-round production.
Conservation Tillage and No-Till Farming: Preserving Soil Health: Conventional tillage practices disrupt soil structure and contribute to erosion, compaction, and carbon loss. Conservation tillage and no-till farming minimize soil disturbance, maintaining soil structure and organic matter. This enhances water retention, reduces erosion, and sequesters carbon, making farms more resilient to extreme weather events and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Aquaponics: Symbiotic Aquaculture and Hydroponics: Aquaponics integrates aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics in a mutually beneficial system. The fish waste provides nutrients for hydroponically grown plants, which, in turn, filter and purify the water for the fish. This closed-loop system conserves water, eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, and yields both protein and vegetables.
Controlled Environment Agriculture: Climate-Proofing Crop Production: Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) encompasses greenhouse and indoor farming, allowing year-round cultivation of crops under precisely managed conditions. CEA protects plants from extreme weather, pests, and diseases while optimizing resource efficiency. High-tech greenhouses use advanced climate control systems, enabling growers to fine-tune temperature, humidity, and light levels for optimal plant growth.
Permaculture: Designing Sustainable Ecosystems: Permaculture draws inspiration from natural ecosystems to create self-sustaining and regenerative agricultural systems. By integrating diverse plant and animal species, permaculture designs promote ecological harmony, resilience, and long-term productivity. Food forests, which emulate natural forests with layers of edible plants, exemplify permaculture principles and provide a wide array of harvestable foods.
Urban Agriculture: Nourishing Cities Locally: Urban agriculture transforms urban landscapes into productive spaces, mitigating the environmental impact of food transportation and enhancing food security. Rooftop gardens, community plots, and vertical farms bring fresh produce to city dwellers while fostering a sense of community and reconnecting people with their food sources.
Key players in the market:
Ceres Imaging: Ceres Imaging uses satellite imagery and artificial intelligence to help farmers make more informed decisions about their crops. Ceres Imaging's products can help farmers to identify pests and diseases early on, optimize their irrigation practices, and improve their yields.
AeroFarms: AeroFarms' vertical farms are located in urban areas, which helps to reduce the company's carbon footprint. AeroFarms also uses recycled materials in its farms and packaging, and it is committed to reducing its environmental impact.
Resilient Crop Varieties
The development of climate-resilient crop varieties through breeding and genetic modification is crucial. Scientists are working on crops that can withstand higher temperatures, require less water, and exhibit resistance to pests and diseases. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 offer precise methods to enhance desired traits, potentially revolutionizing crop production. However, careful consideration of ethical and environmental implications is essential in adopting such technologies.
As the world grapples with the uncertainties of a changing climate, ensuring a steady and nutritious food supply has become a paramount challenge. Resilient crop varieties, born from innovative breeding techniques and scientific advancements, offer a glimmer of hope in the face of shifting weather patterns, changing pest dynamics, and dwindling natural resources. In this article, we delve into the significance of resilient crop varieties and the transformative potential they hold for securing global food security.
1. The Need for Resilience
Traditional crop varieties, often developed for specific regions and historical climatic conditions, are increasingly vulnerable to the unpredictable and extreme weather events wrought by climate change. Droughts, floods, heatwaves, and new pest and disease pressures threaten agricultural productivity and food availability. Resilient crop varieties possess traits that enable them to withstand and recover from these challenges, ensuring a consistent supply of food even in the face of adversity.
2. Breeding for Resilience
The art and science of breeding resilient crop varieties involve a combination of classical breeding methods and cutting-edge technologies. Plant breeders select and cross plants with desirable traits, such as drought tolerance, disease resistance, and improved nutrient uptake. Advancements in molecular biology, genetic mapping, and gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 enable scientists to precisely manipulate plant genomes, accelerating the development of resilient varieties.
3. Drought-Resistant Varieties
Drought is a major concern for agricultural regions worldwide. Resilient crop varieties with enhanced water-use efficiency and deep root systems can thrive with limited water availability. Genetic modifications that control stomatal opening and closing, reducing water loss through transpiration, are being explored to confer drought tolerance.
4. Disease and Pest Resistance
Pests and diseases can devastate crop yields, leading to food shortages and economic losses. Resilient crop varieties can be engineered with natural pest repellents, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Genetic markers linked to disease-resistance genes are identified to expedite breeding efforts, resulting in more robust crops.
5. Heat and Cold Tolerance
Extreme temperatures, whether scorching heat or chilling cold, disrupt plant metabolism and growth. Resilient crop varieties can be developed with genetic traits that enable them to thrive in temperature extremes. Heat-tolerant crops might possess heat-shock proteins that protect cellular structures, while cold-tolerant crops could have antifreeze proteins that prevent ice-crystal formation.
6. Salinity and Soil Adaptation
As sea levels rise and agricultural lands become salinized, crops need to tolerate higher levels of salt in the soil. Resilient crop varieties can be bred to thrive in saline conditions, ensuring continued food production on affected lands. Breeding for improved nutrient uptake and utilization also contributes to healthier plants and improved yields.
7. Biodiversity and Resilience
Maintaining a diverse array of crop varieties is essential for building resilience. Traditional and heirloom varieties often possess unique traits that can be crucial for adaptation. Initiatives to conserve and promote local crop diversity are essential for safeguarding food security in a changing world.
8. Ethical and Environmental Considerations
While resilient crop varieties hold immense promise, ethical and environmental considerations must guide their development and deployment. Ensuring that genetic modifications do not inadvertently harm ecosystems or reduce genetic diversity is a critical aspect of responsible breeding practices.
Key players in the market:
Monsanto: Monsanto is a multinational agricultural biotechnology corporation that develops and markets crop seeds, herbicides, and other agricultural products. Monsanto has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, as well as some biotic stresses, such as pests and diseases.
Seminis: Seminis is a subsidiary of Bayer CropScience that develops and markets crop seeds. Seminis has a portfolio of resilient crop varieties that are tolerant to a variety of abiotic stresses, such as drought, heat, and salinity.
Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable management of natural resources is pivotal to food security in a changing climate. Efficient water management, such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation, conserves water and ensures its availability during dry spells. Soil health restoration through techniques like cover cropping and reduced tillage enhances soil's capacity to retain water and nutrients. Integrated pest management minimizes chemical use and maintains a balance between pests and their natural predators.
Resilience Through Resource Efficiency: Sustainable resource management serves as a cornerstone for building resilience in the face of climate-related uncertainties. Efficient utilization of resources, such as water, energy, and soil, is paramount to ensure that food systems remain productive and adaptable. Through water-efficient irrigation methods, reduced energy consumption, and soil health enhancement, sustainable practices bolster the capacity of agricultural systems to weather the impacts of altered climatic conditions.
Water: A Precious Commodity: In a changing climate, water scarcity and variability become magnified challenges for agricultural production. Sustainable resource management involves optimizing water use through techniques like drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and integrated water management systems. By safeguarding water sources, improving distribution, and minimizing wastage, we ensure a consistent supply of this invaluable resource to sustain food production.
Soil Health and Carbon Sequestration: Healthy soils play a pivotal role in both climate mitigation and adaptation. Sustainable resource management practices prioritize soil health through reduced tillage, cover cropping, and organic matter enrichment. These strategies not only enhance soil fertility and water retention but also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the atmospheric buildup of greenhouse gasses.
Biodiversity Conservation for Resilient Ecosystems: Preserving biodiversity within agricultural landscapes is central to sustainable resource management. Diverse ecosystems are more resilient to climatic fluctuations and provide natural pest control, pollination services, and soil fertility. Agroecological approaches, such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and maintaining habitat corridors, support diverse species and foster ecosystem health.
Circular Economy and Waste Reduction: A circular economy approach within food systems minimizes waste and resource depletion. Sustainable resource management encourages reducing food waste, adopting efficient packaging, and promoting composting or recycling of organic matter. By embracing a circular mindset, we reduce the burden on landfills, conserve resources, and limit the environmental footprint of food production and consumption.
Renewable Energy Integration: As we envision a climate-resilient food future, the integration of renewable energy sources into agricultural operations becomes essential. Sustainable resource management emphasizes transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy to power irrigation, processing, and distribution systems. Solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas facilities contribute to reducing emissions and enhancing overall sustainability.
Localized Food Systems and Resilient Communities: Sustainable resource management advocates for the development of localized food systems that prioritize regional resilience. By supporting small-scale farmers, community gardens, and farmers' markets, we enhance local food security and reduce the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
Policy, Collaboration, and Global Action: Effective sustainable resource management requires a collaborative effort encompassing policymakers, researchers, industries, and consumers. Governments can incentivize sustainable practices through policies, subsidies, and regulations. International cooperation is vital to share knowledge, innovations, and best practices, ensuring a collective response to the global challenge of climate change.
Key players in the market:
Veolia: Veolia is a French multinational water, waste management and energy services company. Veolia has a long history of sustainable resource management, and it is one of the world's leaders in the field. Veolia's water treatment plants are some of the most efficient in the world, and the company is also a leader in waste recycling and energy recovery.
Ecolab: Ecolab is an American multinational provider of water, hygiene and energy technologies and services. Ecolab is a leader in sustainable resource management, and the company has a number of programs and initiatives in place to reduce its environmental impact. Ecolab's water conservation programs have helped to save billions of gallons of water, and the company's energy efficiency programs have helped to reduce its energy consumption by millions of kilowatt-hours.
Climate-Resilient Livestock Farming
Livestock production is another area greatly affected by climate change. Heat stress reduces livestock productivity, and changing grazing patterns impact feed availability. Transitioning towards climate-resilient livestock farming involves improving animal genetics, optimizing feed formulations, and implementing better shelter and cooling systems. Alternative protein sources like insect farming and lab-grown meat might also play a significant role in ensuring a sustainable and climate-resilient protein supply.
Adapting to Changing Conditions: Climate-resilient livestock farming entails embracing adaptable practices that mitigate the impact of a changing climate on animal health, productivity, and well-being. Heat stress, a growing concern due to rising temperatures, can lead to decreased feed intake, reduced reproductive efficiency, and overall livestock productivity. Employing cooling measures such as shade structures, misting systems, and proper ventilation helps mitigate heat stress and maintain optimal livestock conditions.
Improved Breeding for Resilience: Selecting and breeding animals for climate resilience is a key facet of climate-resilient livestock farming. Breeding programs aim to develop livestock varieties that are better equipped to withstand heat stress, disease outbreaks, and changing feed availability. Genetic traits that confer heat tolerance, disease resistance, and efficient nutrient utilization contribute to animals better suited for a changing climate.
Sustainable Feed Sourcing: Climate-resilient livestock farming integrates sustainable feed sourcing practices to ensure the long-term availability of nutritious and environmentally friendly animal diets. Livestock production is a significant contributor to deforestation and land degradation, often driven by the demand for animal feed crops. Transitioning to alternative feed sources, such as algae, insect-based protein, and agroforestry byproducts, minimizes environmental impact while ensuring adequate nutrition for animals.
Precision Livestock Management: Advances in technology play a pivotal role in climate-resilient livestock farming through precision livestock management. Sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence enable real-time monitoring of animal health, behavior, and productivity. This data-driven approach enhances disease detection, facilitates targeted interventions, and optimizes resource utilization, contributing to both economic efficiency and animal welfare.
Agroecological Integration: Integrating livestock into agroecological systems fosters synergy between animal and crop production. Agroforestry, where livestock graze in wooded areas, enhances feed availability, carbon sequestration, and biodiversity. Rotational grazing, which involves moving animals between different pastures, prevents overgrazing, improves soil health, and enhances forage quality.
Alternative Livestock Systems: Exploring alternative livestock systems offers a promising avenue for climate resilience. Silvopasture combines trees with pasture, providing shade, forage, and carbon sequestration potential. Aquaculture and integrated fish-farming systems can complement traditional livestock production, diversifying income sources and protein supply.
Community Engagement and Knowledge Sharing: Climate-resilient livestock farming thrives in a collaborative environment where farmers, researchers, and communities exchange knowledge and best practices. Farmers' networks, extension services, and capacity-building initiatives facilitate the dissemination of climate-resilient techniques and encourage collective adaptation to changing conditions.
Policy Support and Incentives: Effective policies and incentives play a pivotal role in fostering climate-resilient livestock farming. Government support for research and development, funding for sustainable practices, and market incentives for climate-resilient products incentivize farmers to adopt and invest in these strategies.
Key players in the market:
Alltech: Alltech is a global animal nutrition company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Alltech has a program called Alltech Climate Challenge that helps livestock producers reduce their environmental impact. Alltech Climate Challenge provides farmers with training on climate-friendly livestock farming practices, such as methane mitigation and water conservation.
Zoetis: Zoetis is a global animal health company that develops and markets products and services for livestock producers. Zoetis has a program called Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture that helps livestock producers improve their environmental performance. Zoetis Sustainable Agriculture provides farmers with training on sustainable livestock farming practices, such as reducing antibiotic use and improving manure management.
Reducing Food Waste and Loss
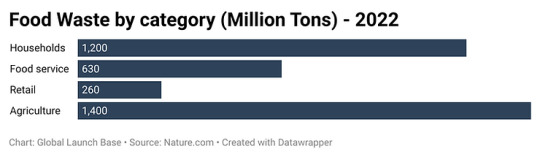
Figure 4: Food Waste by Category
This data shows that food waste is a major problem worldwide. It is estimated that one-third of all food produced for human consumption is wasted. This waste has a significant environmental impact, as it contributes to climate change, water pollution, and land degradation. Households are the biggest contributors to food waste, followed by food service and retail. Agriculture also contributes a significant amount of food waste, but this is often due to factors beyond human control, such as crop losses due to pests and diseases.
The Scale of the Challenge: Food waste and loss constitute a staggering paradox in a world where millions go hungry. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted annually. In a changing climate, this inefficiency takes on heightened significance, given the increased strain on agricultural resources and the urgent need to maximize production.
Climate Impacts and Food Loss: The impacts of climate change, including extreme weather events, temperature fluctuations, and altered growing seasons, exacerbate the problem of food waste and loss. Disrupted supply chains, reduced crop yields, and increased pest and disease pressures contribute to losses at every stage of the food system, from production to consumption.
Farm-Level Strategies: At the production level, climate-resilient agricultural practices are essential in minimizing food loss. Crop diversification, improved storage facilities, and effective pest management contribute to preserving harvests. Climate-smart irrigation and water management systems ensure that water resources are used efficiently, reducing losses due to drought-related crop failures.
Post-Harvest Innovations: Innovations in post-harvest technologies play a pivotal role in reducing food loss. Cold storage, modified atmosphere packaging, and controlled atmosphere storage systems extend the shelf life of perishable goods. Solar drying and value-addition techniques enable smallholder farmers to process excess produce into value-added products, minimizing waste and increasing income.
Efficient Distribution and Supply Chains: Efficient distribution and supply chains are central to addressing food waste. Improving transportation infrastructure, embracing digital solutions for real-time inventory management, and facilitating coordination between producers, distributors, and retailers can prevent perishable goods from spoiling before reaching consumers.
Consumer Behavior and Awareness: Shifting consumer behavior towards responsible consumption is essential in curbing food waste. Education campaigns, labeling initiatives, and community-driven efforts raise awareness about the consequences of wasting food and empower individuals to make conscious choices.
Food Rescue and Redistribution: Food rescue organizations and surplus food redistribution networks salvage edible food that would otherwise be discarded. These initiatives divert surplus produce from landfills to those in need, addressing both food waste and food insecurity simultaneously.
Policy and Industry Leadership: Government policies and private sector initiatives play a crucial role in reducing food waste and loss. Regulatory measures, tax incentives, and industry commitments to zero-waste goals drive systemic change across the food supply chain.
Key players in the market:
Too Good To Go: Too Good To Go is a Danish company that has developed an app that connects consumers with businesses that have surplus food. Businesses can list their surplus food on the app, and consumers can purchase it at a discounted price. Too Good To Go has helped to prevent millions of meals from being wasted.
RapidPricer: RapidPricer is an AI-powered pricing platform that helps retailers automate their pricing and promotions. The platform uses deep learning algorithms and machine vision to dynamically price products to match their real-time value based on competition, product lifecycle, and market conditions. With deep expertise in retail pricing, RapidPricer computes merchandising actions for real-time execution in a retail environment.
Policy and Global Cooperation
Mitigating the impact of climate change on food production requires global cooperation and effective policy measures. International agreements and frameworks can promote sustainable agriculture, support smallholder farmers, and facilitate technology transfer to developing countries. Financial incentives, subsidies for sustainable practices, and research funding can drive innovation and promote the adoption of climate-resilient technologies. 1. Policy as a Catalyst for Change Sound and visionary policies are the cornerstone of a resilient food system. Governments play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of food production, distribution, and consumption through regulations, incentives, and strategic planning. Policies that promote climate-resilient agriculture, sustainable resource management, and reduced food waste set the stage for a more secure and sustainable food future. 2. Climate-Smart Agriculture Policies Climate-smart agricultural policies harness innovative approaches to enhance productivity, mitigate climate impacts, and reduce emissions. By incentivizing the adoption of climate-resilient practices, such as crop diversification, agroforestry, and improved irrigation, governments foster adaptive capacity and mitigate the vulnerabilities of agriculture to a changing climate. 3. Research and Innovation Funding Government funding for research and innovation accelerates the development and adoption of climate-resilient agricultural technologies and practices. Support for breeding drought-tolerant crops, developing efficient irrigation systems, and advancing precision agriculture empowers farmers to overcome the challenges posed by climate change. 4. International Agreements and Frameworks The global nature of climate change demands international collaboration. Agreements like the Paris Agreement underscore the commitment of nations to combat climate change and lay the groundwork for coordinated efforts in the agricultural sector. Frameworks for technology transfer, capacity-building, and financial support ensure that countries with varying levels of resources can participate in climate-resilient food production. 5. Sustainable Trade and Supply Chain Policies International trade and supply chains are integral to global food security. Policies that promote sustainable trade practices, reduce trade barriers and ensure equitable access to markets contribute to stable food supplies and price stability, benefiting both producers and consumers. 6. Strengthening Smallholder Resilience Policies that specifically target smallholder farmers, who are often the most vulnerable to climate impacts, play a vital role in enhancing food security. Financial support, access to credit, and extension services empower smallholders to adopt climate-resilient practices and diversify their livelihoods. 7. Public-Private Partnerships Collaboration between governments, private sector entities, and civil society organizations amplifies the impact of climate-resilient policies. Public-private partnerships drive innovation, leverage resources, and facilitate knowledge exchange, ensuring that policies are implemented effectively and that a wide array of stakeholders are engaged. 8. Education and Consumer Awareness Policies that promote consumer education and awareness campaigns raise consciousness about sustainable consumption practices. Clear labeling, educational initiatives, and public awareness campaigns inform consumers about the environmental and social impacts of their food choices, influencing demand and driving market shifts.
Conclusion
The future of food in a changing climate is a complex challenge that demands immediate attention and collaborative efforts. Innovations in agriculture, sustainable resource management, and climate-resilient practices offer hope for ensuring food security for a growing global population. By embracing new technologies, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering international cooperation, we can navigate the challenges presented by a changing climate and build a more resilient and secure food future for generations to come. ------------------------------------ Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us. Contact Info: Website: www.globallaunchbase.com LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/ Email: [email protected]
#Climate change#Food security#Sustainable agriculture#Climate-resilient farming#Adaptation strategies#Agricultural innovation#Climate-smart technologies#Global food systems#Environmental impact#Crop diversity#Resource management#Food supply chain#Resilient livestock farming#Circular economy#Policy initiatives#Smallholder resilience#Sustainable sourcing#Climate challenges#Food waste reduction#Renewable energy integration
0 notes
Text
@khalilgaza67 Reached out to me and NEEDS YOUR HELP!
His is vetted and is currently still in gaza suffering through the genocide, with only €2,435 raised of his €30,000 target.
Below are excerpts from his gofundme campaign that I highly encourage you to read:
“My name is Khalil Abubaker, and I am reaching out to you from Gaza, a place that has been deeply affected by the ongoing war.
The past eight months have been incredibly challenging for my family and me. My father, who has always been our main supporter, has been unable to work due to the conflict. Like many others, he lost his job and exhausted all his savings trying to keep us afloat.”
Call for Help:
Our campaign goal is to raise €30,000. Initially, we will use €20,000 to cross the border into Egypt for myself, my father, my mother, and my youngest unmarried sister—half of our family members.
The remaining €10,000 will be used to settle in Egypt and cover the costs of necessary items, rent, transportation, and other expenses as we start a new life.
How You Can Help:
I've never spoken up like this before; in fact, I feel shy even asking my close friends outside the country to help because I know it's beyond their ability.
I truly believe in the kindness of strangers and in the power of the global community to help us get out of this dire situation. Every contribution, no matter how small, will bring us closer to securing a future away from the devastation.
We understand that not everyone may be able to contribute financially, but sharing our story with your network can also make a significant difference.”
To support Khalil and his family, You can donate to the gofundme and spread it around!
“From the depths of our hearts, we thank you for your kindness, support, and prayers. Together, we can give my family the hope and strength to overcome this harrowing time and start anew.
With gratitude and hope,
Khalil Abubaker”
#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#palestine aid#all eyes on palestine#free palestine#palestinian genocide#save palestine#i stand with palestine#rafah under attack#save rafah#free rafah#rafah#all eyes on rafah#gazaunderfire#gaza under attack#free gaza#gaza strip#gaza#gaza gofundme#gofundme palestine#palestine gofundme#gofundme#mutal aid#palestine donation
752 notes
·
View notes
Text
Satirical news publication The Onion has bought Infowars, the media organisation headed by right-wing conspiracy theorist Alex Jones, for an undisclosed price at a court-ordered auction.
The Onion said that the bid was secured with the backing of families of victims of the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting, who won a $1.5bn (£1.18bn) defamation lawsuit against Jones for spreading false rumours about the massacre.
[…] The Onion plans to rebuild the website and feature well-known internet humour writers and content creators.
“We are planning on making it a very funny, very stupid website,” said Ben Collins, a former NBC News journalist who is chief executive of The Onion’s parent company, in a statement.
The website also posted a jokey article, saying that Infowars “has shown an unswerving commitment to manufacturing anger and radicalizing the most vulnerable members of society".
[…] No price would be too high for such a cornucopia of malleable assets and minds. And yet, in a stroke of good fortune, a formidable special interest group has outwitted the hapless owner of InfoWars (a forgettable man with an already-forgotten name) and forced him to sell it at a steep bargain: less than one trillion dollars.
Make no mistake: This is a coup for our company and a well-deserved victory for multinational elites the world over.
What’s next for InfoWars remains a live issue. The excess funds initially allocated for the purchase will be reinvested into our philanthropic efforts that include business school scholarships for promising cult leaders, a charity that donates elections to at-risk third world dictators, and a new pro bono program pairing orphans with stable factory jobs at no cost to the factories.
As for the vitamins and supplements, we are halting their sale immediately. Utilitarian logic dictates that if we can extend even one CEO’s life by 10 minutes, diluting these miracle elixirs for public consumption is an unethical waste. Instead, we plan to collect the entire stock of the InfoWars warehouses into a large vat and boil the contents down into a single candy bar–sized omnivitamin that one executive (I will not name names) may eat in order to increase his power and perhaps become immortal.
559 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good News - July 15-21
Like these weekly compilations? Tip me at $kaybarr1735! (Or check out my new(ly repurposed) Patreon!)
1. Thai tiger numbers swell as prey populations stabilize in western forests

“The tiger population density in a series of protected areas in western Thailand has more than doubled over the past two decades, according to new survey data. […] The most recent year of surveys, which concluded in November 2023, photographed 94 individual tigers, up from 75 individuals in the previous year, and from fewer than 40 in 2007. […] A total of 291 individual tigers older than 1 year were recorded, as well as 67 cubs younger than 1 year.”
2. Work starts to rewild former cattle farm

“Ecologists have started work to turn a former livestock farm into a nature reserve [… which] will become a "mosaic of habitats" for insects, birds and mammals. [… R]ewilding farmland could benefit food security locally by encouraging pollinators, improving soil health and soaking up flood water. [… “N]ature restoration doesn't preclude food production. We want to address [food security] by using nature-based solutions."”
3. Harnessing ‘invisible forests in plain view’ to reforest the world

“[… T]he degraded land contained numerous such stumps with intact root systems capable of regenerating themselves, plus millions of tree seeds hidden in the soil, which farmers could simply encourage to grow and reforest the landscape[….] Today, the technique of letting trees resprout and protecting their growth from livestock and wildlife [… has] massive potential to help tackle biodiversity loss and food insecurity through resilient agroforestry systems. [… The UN’s] reported solution includes investing in land restoration, “nature-positive” food production, and rewilding, which could return between $7 and $30 for every dollar spent.”
4. California bars school districts from outing LGBTQ+ kids to their parents

“Gov. Gavin Newsom signed the SAFETY Act today – a bill that prohibits the forced outing of transgender and gay students, making California the first state to explicitly prohibit school districts from doing so. […] Matt Adams, a head of department at a West London state school, told PinkNews at the time: “Teachers and schools do not have all the information about every child’s home environment and instead of supporting a pupil to be themselves in school, we could be putting them at risk of harm.””
5. 85% of new electricity built in 2023 came from renewables

“Electricity supplied by renewables, like hydropower, solar, and wind, has increased gradually over the past few decades — but rapidly in recent years. [… C]lean energy now makes up around 43 percent of global electricity capacity. In terms of generation — the actual power produced by energy sources — renewables were responsible for 30 percent of electricity production last year. […] Along with the rise of renewable sources has come a slowdown in construction of non-renewable power plants as well as a move to decommission more fossil fuel facilities.”
6. Deadly cobra bites to "drastically reduce" as scientists discover new antivenom

“After successful human trials, the snake venom antidote could be rolled out relatively quickly to become a "cheap, safe and effective drug for treating cobra bites" and saving lives around the globe, say scientists. Scientists have found that a commonly used blood thinner known as heparin can be repurposed as an inexpensive antidote for cobra venom. […] Using CRISPR gene-editing technology […] they successfully repurposed heparin, proving that the common blood thinner can stop the necrosis caused by cobra bites.”
7. FruitFlow: a new citizen science initiative unlocks orchard secrets

“"FruitWatch" has significantly refined phenological models by integrating extensive citizen-sourced data, which spans a wider geographical area than traditional methods. These enhanced models offer growers precise, location-specific predictions, essential for optimizing agricultural planning and interventions. […] By improving the accuracy of phenological models, farmers can better align their operations with natural biological cycles, enhancing both yield and quality.”
8. July 4th Means Freedom for Humpback Whale Near Valdez, Alaska

“The NOAA Fisheries Alaska Marine Mammal Stranding Hotline received numerous reports late afternoon on July 3. A young humpback whale was entangled in the middle of the Port of Valdez[….] “The success of this mission was due to the support of the community, as they were the foundation of the effort,” said Moran. [… Members of the community] were able to fill the critical role of acting as first responders to a marine mammal emergency. “Calling in these reports is extremely valuable as it allows us to respond when safe and appropriate, and also helps us gain information on various threats affecting the animals,” said Lyman.”
9. Elephants Receive First of Its Kind Vaccine

“Elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus is the leading cause of death for Asian elephants (Elephas maximus) born in facilities in North America and also causes calf deaths in the wild in Asia. A 40-year-old female received the new mRNA vaccine, which is expected to help the animal boost immunity[….]”
10. Conservation partners and Indigenous communities working together to restore forests in Guatemala

“The K’iche have successfully managed their natural resources for centuries using their traditional governing body and ancestral knowledge. As a result, Totonicapán is home to Guatemala’s largest remaining stand of conifer forest. […] EcoLogic has spearheaded a large-scale forest restoration project at Totonicapán, where 13 greenhouses now hold about 16,000 plants apiece, including native cypresses, pines, firs, and alders. […] The process begins each November when community members gather seeds. These seeds then go into planters that include upcycled coconut fibers and mycorrhizal fungi, which help kickstart fertilization. When the plantings reach about 12 inches, they’re ready for distribution.”
July 8-14 news here | (all credit for images and written material can be found at the source linked; I don’t claim credit for anything but curating.)
#hopepunk#good news#tiger#thailand#habitat#rewilding#food insecurity#forest#reforestation#california#lgbtq#lgbtqia#students#law#trans rights#gay rights#renewableenergy#clean energy#snake#medicine#crispr#citizen science#farming#whale#humpback whale#elephant#vaccine#alaska#guatemala#indigenous
442 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Impact of Conflict on Polio Eradication: Gaza and Global Challenges
As Tuesday is the week day dedicated to Health and Beauty issues to FAMILY+ Blog, we will continue with another health article. This time we will talk about a very dangerous disease that unfortunately is coming back in zones of conflict. I’m talking about Poliomyelitis, commonly known as polio. This is a highly infectious viral disease that primarily affects children under the age of five. The…
#anti-vaccination#Community Health#Conflict Impact#countries in conflict#Disease Eradication#End Polio#End Polio Now#Eradicate Polio#Fight Polio#gaza updates#Global Efforts#Global Health#Global Wellness#health#Health Awareness#Health Crisis#Health For All#Health Initiatives#Health Security#Healthcare For All#Humanitarian Efforts#Polio Awareness#Polio Eradication#Polio Fight#Polio Plus#Polio Prevention#Poliomyelitis#Protect Kids#Public Health#Rotary International
0 notes
Text
The Intersection of AI and Geopolitics: India-China Relations
Introduction: The Intersection of AI and Geopolitics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the global landscape, especially in the realm of geopolitics. By transforming the way nations project power and compete, AI is ushering in new strategies in international conflict. The integration of AI into military, economic, and governance sectors has opened up new fronts, with the ability to conduct cyber warfare, enhance surveillance, and revolutionize decision-making processes. In this evolving geopolitical theatre, AI stands as a critical component in determining global dominance, reshaping not only international power dynamics but also introducing ethical challenges.
In the context of India-China relations, AI plays a pivotal role. Both nations are racing to harness AI's transformative potential, yet their strategies are distinct. While China focuses on AI as a tool for global supremacy and internal control, India aims to leverage AI for inclusive growth, addressing societal challenges and fostering innovation. The friction between the two reflects broader geopolitical concerns, where technology, data, and governance models shape the future of conflict and cooperation between these Asian giants.
How AI is Changing the Rules of International Conflict
The integration of AI into warfare has expanded the concept of conflict beyond physical battles. Nations now contend in cyberspace, utilizing AI for espionage, cybersecurity, and information warfare. AI can process vast amounts of data to identify vulnerabilities, predict attacks, and even automate military responses. China's AI ambitions, as seen through its "New Generation of Artificial Intelligence Development Plan" (2017), highlight its strategic objectives to lead in AI technology by 2030, leveraging AI for military and industrial dominance. This push underscores how AI is central to China's broader geopolitical goals.
India, on the other hand, focuses more on the societal applications of AI, aiming to solve problems in healthcare, agriculture, and education while also addressing security concerns. India’s AI strategy is grounded in fostering inclusive growth, underpinned by the #AIForAll vision, which emphasizes AI as a tool for economic and social development rather than solely a means of global dominance. Despite differing approaches, both nations recognize AI's transformative impact on national security and the need to protect data, control information, and outpace rivals in technological innovation.
Overview of the India-China Geopolitical Landscape
The geopolitical rivalry between India and China is shaped by historical tensions, territorial disputes, and their contrasting visions for global leadership. China’s assertiveness in the South China Sea, its Belt and Road Initiative, and the boundary disputes with India have heightened tensions in recent years. At the same time, both nations are key players in the global AI race, seeking to bolster their technological capabilities.
China’s AI strategy is a direct reflection of its ambitions to establish technological supremacy. The country has invested billions in AI research, development, and infrastructure, and aims to integrate AI into both civilian and military sectors. China’s AI-enabled surveillance state has raised concerns globally, particularly its mass surveillance programs targeting ethnic minorities like the Uighurs, demonstrating how AI can be employed for authoritarian control.
India, while lagging behind China in terms of AI investments, is steadily advancing its AI capabilities. India's approach to AI is more aligned with democratic values, with a focus on responsible AI development that respects privacy and data security. This reflects India’s broader geopolitical stance, positioning itself as a global leader in ethical AI and as a counterbalance to China’s more authoritarian approach.
Conclusion
The intersection of AI and geopolitics is creating a new paradigm of international relations, where technological supremacy may determine future global leaders. India and China, as key players in this race, present starkly different approaches to AI governance, security, and ethics. While China seeks dominance through AI-driven surveillance and military applications, India’s focus on inclusive growth and responsible AI positions it as a democratic alternative in the global AI landscape. However, as AI continues to shape the rules of conflict and cooperation, the India-China dynamic will remain a critical focal point for understanding the future of global power.
#AI and geopolitics#India China relations#Artificial intelligence#AI in conflict#India AI strategy#China AI ambitions#Cyber warfare#Geopolitical tension#AI and military#Technology and conflict#Global AI race#Surveillance state#Data security#AI ethics#AI in international relations#India vs China#Belt and Road Initiative#AI for all#Inclusive AI
0 notes
Text
Part I - United Nations Chief of police summit (UNCOPS 2024).
Geopolitical tensions, the climate crisis, global mistrust and the dark side of technology, which Secretary-General António Guterres has called the "looming threats of the 21st century", are affecting the well-being and livelihoods of communities worldwide and the planet itself. National and United Nations Police are on the frontlines of averting and addressing these transnational threats.
The United Nations Police contribute to the Action for Peacekeeping (A4P) initiative and A4P+ priorities by building and supporting or, where mandated, acting as a substitute or partial substitute for host-State police capacity to prevent and detect crime, protect life and property, and maintain public order and safety in adherence to the rule of law and international human rights law.
---
Objectives:
A common vision and concrete commitments to further equipping the United Nations Police to effectively contribute to A4P and A4P+ priorities. Awareness of interlinkages between national and United Nations policing to increase global security.
Collective appreciation of the role of national and United Nations policing in overcoming systemic challenges affecting peacekeeping.
Joint understanding of the needs of the United Nations Police, including related to safety and security, and concrete Member State and Secretariat commitments to meet demands.
A common roadmap to realize the Secretary-General's vision of "a transformed United Nations police that is people-centred, modern, agile, mobile and flexible, specialized, rights-based and norm-driven", and that is also innovative, data-driven and tech-enabled.
Related Sites and Documents
Concept Note
Website
Programme

#United Nations police#people-centred#safety and security#human security#data-driven#tech-enabled#collective appreciation#role of national and United Nations policing#overcoming challenges#A4P+ priorities#A4P#peacekeeping#detect crime#protect life#prevent crime#protect properties#action for peacekeeping initiative#partial substitute for host-State police capacity#substitute for host-State police capacity#unhq#looming threats of the 21st century#global security#Geopolitical tensions#transnational threats#chief of police#summit
0 notes
Text
"India has reached a key milestone in renewable energy, with the country’s total renewable energy capacity exceeding 200 gigawatts as of Oct. 10, 2024, according to the Central Electricity Authority. The renewable energy-based electricity generation capacity now stands at 201.45 GW, accounting for 46.3% of the nation’s total installed capacity.
This milestone is the result of years of efforts to harness India’s natural resources. From solar parks to wind farms and hydroelectric projects, the country has built a diverse renewable energy base, reducing fossil fuel dependence and enhancing energy security.
India's total electricity generation capacity has reached 452.69 GW, with renewable energy contributing a significant portion of the overall power mix as the country continued to increase its dependence on cleaner, non-fossil fuel energy sources and push towards its sustainability goals.
When factoring in the 8,180 MW of nuclear capacity, the total non-fossil fuel-based power now accounts for almost half of the country's installed electricity generation capacity, signalling a strong move towards clean energy leadership on the global stage.
Renewable Energy
A variety of renewable energy resources contribute to this impressive figure. Solar power leads the way with 90.76 GW, playing a crucial role in India’s efforts to harness its abundant sunlight. Wind power follows closely with 47.36 GW, driven by the vast potential of the coastal and inland wind corridors across the country.
Hydroelectric power is another key contributor, with large hydro projects generating 46.92 GW and small hydropower adding 5.07 GW, offering a reliable and sustainable source of energy from India’s rivers and water systems.
Biopower, including biomass and biogas energy, adds another 11.32 GW to the renewable energy mix. These bioenergy projects are vital for utilising agricultural waste and other organic materials to generate power, further diversifying India’s clean energy sources. Together, these renewable resources are helping the country reduce its dependence on traditional fossil fuels while driving progress towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Leading States In Renewable Energy Capacity
Several states in India have emerged as leaders in renewable energy capacity, making significant contributions to the nation's progress. These states are essential to advancing India’s renewable energy goals and fostering a sustainable energy future.
Rajasthan leads the pack with an impressive 29.98 GW of installed renewable energy capacity, capitalising on its extensive land and abundant sunlight.
Following closely is Gujarat, which boasts a capacity of 29.52 GW, driven by its strong focus on solar and wind energy projects. Tamil Nadu ranks third with 23.70 GW, leveraging its favourable wind patterns to generate substantial energy. While Karnataka rounds out the top four with a capacity of 22.37 GW, supported by a mix of solar and wind initiatives.
India's commitment to renewable energy is reflected in the annual electricity generation trends in recent years. The Government of India has introduced various measures and initiatives to promote and accelerate renewable energy capacity nationwide, aiming for an ambitious target of 500 GW of installed capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030."
-via NDTV, October 14, 2024
#india#renewables#renewable energy#wind power#green energy#clean energy#solar power#solar energy#climate action#climate hope#rajasthan#gujarat#tamil nadu#karnataka#south asia#asia#good news#hope
338 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The Congo’s strategic location in the middle of Africa and its fabulous natural endowment of minerals and other resources have since 1884 ensured that it would serve as a theatre for the playing out of the economic and strategic interests of outsiders: the colonial powers during the scramble for Africa; the superpowers during the Cold War; and neighbouring African states in the post-Cold War era. To prevent a direct confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union, the Security Council deployed from 1960 to 1964 what was then the largest and most ambitious operation ever undertaken by the UN, with nearly 20,000 troops at its peak strength plus a large contingent of civilian personnel for nation-building tasks.
This latter aspect of the Opération des Nations unies au Congo (ONUC) was a function of the fragile political revolution ... The Congo won its independence from Belgium on 30 June 1960. Patrice Lumumba’s MNC-L and its coalition of radical nationalist parties had captured a majority of seats in the lower house of parliament in the pre-independence elections in May. Lumumba became prime minister and head of government, while the Abako leader Joseph Kasa-Vubu became the ceremonial head of state. The victory of a militantly nationalist leader with a strong national constituency was viewed as a major impediment to the Belgian neocolonialist strategy and a threat to the global interests of the Western alliance.
Within two weeks of the proclamation of independence, Prime Minister Lumumba was faced with both a nationwide mutiny by the army and a secessionist movement in the province of Katanga bankrolled by Western mining interests. Both revolts were instigated by the Belgians, who also intervened militarily on 10 July, a day before the Katanga secession was announced. In the hopes of obtaining the evacuation of Belgian troops and white mercenaries, and thus ending the Katanga secession, Lumumba made a successful appeal to the UN Security Council to send a UN peacekeeping force to the Congo. However, the UN secretary-general, Dag Hammarskjöld, interpreted the UN mandate in accordance with Western neocolonialist interests and the US Cold War imperative of preventing Soviet expansion in the Third World. This led to a bitter dispute between Lumumba and Hammarskjöld, which resulted in the US- and Belgian-led initiative to assassinate the first and democratically elected prime minister of the Congo.
... Brussels’ failure to prevent a radical nationalist such as Lumumba from becoming prime minister created a crisis for the imperialist countries, which were determined to have a decolonization favourable to their economic and strategic interests with the help of more conservative African leaders. With Belgium’s failure to transfer power in an orderly fashion to a well-groomed moderate leadership group that could be expected to advance Western interests in Central and Southern Africa, the crisis of decolonization in the Congo required US and UN interventions. Working hand in hand, Washington, New York and Brussels succeeded in eliminating Lumumba and his radical followers from the political scene."
Georges Nzongola-Ntalaja, The Congo from Leopold to Kabila: A People's History, 2002
424 notes
·
View notes