Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
Reversing Global Warming: Actions and Impacts

Reversing the effects of global warming necessitates a blend of large-scale initiatives and everyday practices. This article delves into the effectiveness of diverse strategies, such as increasing tree plantations, adjusting AC temperatures, embracing electric vehicles, and minimizing food waste, to highlight their significant environmental impacts.
Read Full Article: https://www.globallaunchbase.com/post/reversing-global-warming-actions-and-impacts
Written By: Jagriti Shahi Key Contributor: Anubha Chicki
#ReversingGlobalWarming hashtag#ClimateChangeSolutions#hashtag#ReduceCarbonFootprint hashtag#RenewableEnergySources#SustainablePractices hashtag#EnvironmentalConservation#GreenhouseGasReduction hashtag#ClimateActionInitiatives#CarbonNeutralStrategies hashtag#EcoFriendlyTechnologies#ClimateResilience hashtag#SustainableLivingTips hashtag#GlobalWarmingMitigation#GreenEnergyAdoption hashtag#ClimateChangeImpactReduction#SustainableDevelopmentGoals hashtag#ClimateCrisisSolutions#EnvironmentalSustainability hashtag#ClimateChangeAdaptation#CarbonOffsetPrograms
0 notes
Text
International Conservation Tech in India
Written By: Jagriti S.

Figure: Growth of Conservation Tech Investment 2017 - 2023
The Role of Technology in Conservation

Figure: Remote and Camera Sensing
Drones and Remote Sensing:

Figure: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Conservation
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning:
Genetic Technologies:
International Collaborations and Initiatives
The integration of international conservation technology in India is often facilitated through global partnerships and collaborative initiatives. Some notable examples include:
Wildlife Protection Solutions (WPS): This international organization collaborates with Indian conservationists to implement advanced surveillance systems in protected areas. WPS's technology helps in real-time monitoring of poaching activities, leading to quicker response times and increased arrest rates of poachers.
Global Tiger Forum (GTF): India, home to over 70% of the world's tigers, is a key player in the GTF. This international consortium uses technology to monitor tiger populations, track their movements across borders, and implement anti-poaching measures. Satellite telemetry and camera traps are essential tools in these efforts.
Indo-UK Collaboration on Climate Resilience: This partnership focuses on using climate modeling and data analytics to enhance India's ability to predict and respond to climate change impacts. These technologies aid in developing conservation strategies for climate-vulnerable species and habitats.
Case Studies of Success
Several projects in India have successfully harnessed international conservation technology to achieve remarkable results:
Project Elephant: In collaboration with international researchers, Project Elephant uses GPS collars and drone technology to track elephant herds and mitigate human-elephant conflicts. This initiative has significantly reduced crop damage and human casualties in conflict-prone areas.
Sundarbans Mangrove Restoration: Partnering with global environmental organizations, India is using satellite imagery and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) to map and restore degraded mangrove forests in the Sundarbans. These efforts are crucial for protecting this unique ecosystem and its iconic species like the Bengal tiger.
Snow Leopard Conservation: In the high-altitude regions of the Himalayas, international conservationists are using camera traps, genetic sampling, and satellite collars to study and protect the elusive snow leopard. These technologies provide valuable insights into their behavior, habitat use, and threats.

Figure: Growth of Conservation Tech Investment in India 2016-2023
Here are some notable foreign startups and organizations operating in the conservation technology space in India:
Wildlife Protection Solutions (WPS)
Country of Origin: USA
Focus: Provides technology solutions for wildlife conservation, including real-time surveillance systems to monitor and prevent poaching activities.
EarthRanger (formerly Vulcan Technologies)
Country of Origin: USA
Focus: Offers a data visualization and analysis software platform to support wildlife conservation and protected area management.
Rainforest Connection (RFCx)
Country of Origin: USA
Focus: Uses recycled cell phones as solar-powered listening devices to detect and monitor illegal logging and poaching activities in real-time.
SMART (Spatial Monitoring and Reporting Tool)
Elephant Listening Project (ELP)
Country of Origin: USA
Focus: Uses acoustic monitoring to study and protect elephants, particularly in forest environments where visual monitoring is challenging.
Global Forest Watch (GFW)
Country of Origin: USA
Focus: An online platform that provides near-real-time data and tools for monitoring forests worldwide, helping to detect deforestation and illegal activities.
ZSL Instant Detect
Country of Origin: UK
Focus: Provides a satellite-connected camera trap system that sends real-time images and alerts to conservationists to prevent poaching and monitor wildlife.
Fauna & Flora International (FFI)
Country of Origin: UK
Focus: Engages in various conservation technology projects, including habitat mapping, wildlife monitoring, and anti-poaching initiatives.
Blue Ventures
Country of Origin: UK
Focus: Uses technology to support marine conservation, including community-based monitoring of marine biodiversity and fisheries.
Conservation Drones
Country of Origin: Singapore
Focus: Develops and deploys low-cost drones for various conservation applications, including wildlife monitoring, habitat mapping, and anti-poaching efforts.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While international conservation technology offers immense potential, it also presents challenges:
High Costs: Advanced technologies can be expensive to procure, deploy, and maintain, which can strain the budgets of conservation organizations.
Technical Expertise: Effective use of these technologies requires specialized knowledge and skills. Training local conservationists and researchers is essential for long-term success.
Data Management: The large volumes of data generated by these technologies need to be effectively managed, analyzed, and utilized for conservation planning.
Despite these challenges, the future of conservation technology in India looks promising. Continued international collaboration, investment in capacity building, and innovation in affordable and scalable technologies will play a crucial role in safeguarding India's biodiversity.
Here are some notable Indian startups and companies involved in conservation technology in India:
Wildlife Acoustics: This US-based company has a strong presence in India, providing acoustic monitoring technologies to researchers, conservationists, and protected area managers. Their Song Meter recorders and EcoNet software help track wildlife populations, monitor biodiversity, and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
Kheyti: This Indian startup uses satellite imagery, machine learning, and big data analytics to provide farmers with information on soil health, crop health, and water availability. This information can help farmers improve their agricultural practices and reduce their environmental impact.
Waycool: This Indian company builds and operates a network of cold chain facilities that help farmers store and transport their produce more efficiently. This reduces food spoilage and waste, which is a major environmental problem.
Ecodit Technologies: This Bengaluru-based startup uses AI and machine learning to monitor forests and detect illegal activities such as deforestation and poaching. Their cloud-based platform provides real-time insights to forest departments and conservation NGOs, helping them to better protect India's natural resources.
Conclusion
International conservation technology is transforming the landscape of environmental conservation in India. By embracing these advanced tools and fostering global partnerships, India is making significant strides in protecting its unique ecosystems and wildlife. As these technologies continue to evolve, they offer hope for a sustainable future where nature and humanity can coexist harmoniously.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
Water and Electricity Harvesting in Agriculture

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Agriculture is the backbone of civilization, but it faces a growing challenge: resource scarcity. Water tables are dropping, and traditional electricity sources can be expensive and environmentally unfriendly. However, innovative solutions are emerging that combine water and electricity harvesting to create a more sustainable future for farming. In an era where sustainable practices are no longer optional but essential, the integration of water and electricity harvesting into agriculture represents a transformative approach. This innovation not only addresses the critical issues of resource scarcity and environmental degradation but also enhances the efficiency and productivity of modern farming. By combining water management and renewable energy generation, farmers can create a more resilient and self-sufficient agricultural system.
Water: The Lifeblood of Agriculture
Water is essential for plant growth, and traditional irrigation methods can be highly water-intensive. Here's where water harvesting comes in. By collecting rainwater and runoff through techniques like ponds, swales, and cisterns, farmers can create a reliable source of irrigation without relying on depleting groundwater reserves. Additionally, drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and waste.
Harnessing the Power of the Sun
Electricity is crucial for powering pumps, lights for greenhouses, and other essential farm equipment. Solar panels offer a clean and sustainable solution. By installing solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, farms can generate their own electricity, reducing dependence on the grid and lowering energy costs.
Agrivoltaics in India

Figure: Certain crops can tolerate moderate shading. - Source: Image: Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE
India is also exploring the concept of agrivoltaics, where solar panels are installed above crop fields. This approach not only generates electricity but also provides partial shade for crops, reducing water evaporation and enhancing crop yields. Projects in states like Gujarat have demonstrated the viability and benefits of this dual-use land approach.
The Synergy of Water and Electricity Harvesting
The beauty lies in the synergy between these technologies. The electricity generated by solar panels can power pumps that utilize harvested rainwater for irrigation. This creates a closed-loop system, minimizing reliance on external resources and promoting environmental sustainability.
Agriculture is heavily dependent on water and energy. Traditionally, these resources have been sourced independently, often leading to inefficiencies and unsustainable practices. However, by harvesting water and electricity in tandem, farmers can optimize their resource use and reduce their environmental footprint.
Water Harvesting Techniques

Figure: Rainwater Harvesting for Agriculture - Source Rainharvesting Systems
Water harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater or surface runoff for agricultural use. Several techniques can be employed, each suitable for different climates and terrains:
Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces in tanks or reservoirs.
Surface Runoff Harvesting: Capturing runoff from fields and directing it to storage ponds or recharge structures.
Subsurface Water Harvesting: Utilizing techniques like check dams and percolation pits to enhance groundwater recharge.
These methods ensure a reliable water supply, even in arid regions, reducing dependence on erratic rainfall or over-exploited groundwater resources.
Water Harvesting Comparis
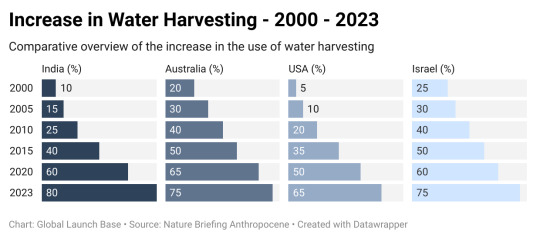
The figure provided earlier shows the increase in the use of water harvesting techniques in India, Australia, the USA, and Israel over a 23-year period, from 2000 to 2023. Each percentage value represents the proportion of the population or entities adopting water harvesting techniques as part of water management practices for that respective year.
In India, the proportion of adoption increased from 10% in 2000 to 80% in 2023.
In Australia, it increased from 20% in 2000 to 75% in 2023.
In the USA, it increased from 5% in 2000 to 65% in 2023.
In Israel, it increased from 25% in 2000 to 75% in 2023
India:
Rainwater Harvesting: India has over 4.75 million traditional rainwater harvesting structures, according to the Central Ground Water Board.
Micro-Irrigation Coverage: As of 2021, India has approximately 10.65 million hectares under micro-irrigation, according to the Ministry of Jal Shakti.
Global:
United States: The US has seen a steady increase in rainwater harvesting adoption, with over 55,000 systems installed across the country.
Australia: Australia boasts over 80% adoption of micro-irrigation in its agriculture sector, significantly higher than many other countries.
Israel: Israel is a global leader in drip irrigation technology, with around 75% of its irrigated land utilizing drip systems, according to the Israeli Ministry of Agriculture.
Electricity Harvesting Methods
On the energy front, renewable technologies offer promising solutions for agriculture. Key methods include:
Solar Power: Photovoltaic panels can be installed on farm buildings, over irrigation canals, or even integrated into greenhouse structures to generate electricity.
Wind Power: Small-scale wind turbines can provide a significant portion of the energy needs for farms, especially in windy regions.
Biogas Production: Organic waste from livestock and crop residues can be converted into biogas, which can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as a fuel.

Figure: Using Solar Energy for Agriculture - Ecoideaz
Integrating Water and Electricity Harvesting
The integration of these systems can create a synergistic effect, enhancing overall farm sustainability. Here’s how:
Solar-Powered Irrigation: Combining solar panels with water pumps enables farmers to irrigate their fields using renewable energy, reducing reliance on grid power and diesel generators.
Energy-Efficient Water Storage: Using solar or wind energy to power water pumps for filling storage tanks or reservoirs can significantly cut energy costs.
Enhanced Water Management: Sensors powered by renewable energy can monitor soil moisture levels and automate irrigation systems, ensuring optimal water use and improving crop yields.
Electricity Harvesting Comparison
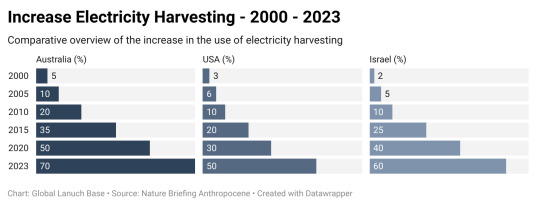
The figure presents the estimated increase in the use of electricity harvesting techniques in Australia, the USA, and Israel over a span of 23 years, from 2000 to 2023. Each percentage value represents the proportion of electricity generated from renewable sources (such as solar and wind power) as part of the total electricity generation for that respective year.
In Australia, the proportion of electricity generated from renewable sources increased from 5% in 2000 to 70% in 2023.
In the USA, the proportion increased from 3% in 2000 to 50% in 2023.
In Israel, it increased from 2% in 2000 to 60% in 2023.
India:
Solar Pump Installations: Under the PM-KUSUM scheme, India aims to install 1.75 million standalone solar pumps by 2022, with a cumulative capacity of 2.75 GW.
Solar Energy Generation: India's total installed solar capacity surpassed 45 GW as of 2021, with a significant portion allocated for agricultural use.
Global:
United States: The US leads in solar energy generation, with over 97 GW of installed solar capacity, contributing to both grid supply and on-farm electricity generation.
Australia: Solar-powered irrigation systems are gaining traction in Australia, with estimates suggesting over 5,000 solar pumps installed across the country.
Israel: Israel's solar energy capacity is comparatively smaller but growing rapidly, with a focus on providing clean energy solutions for agriculture.
Case Studies and Examples
Several innovative projects worldwide exemplify the benefits of integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture:
The Sahara Forest Project: This initiative in Jordan and Tunisia combines solar power, desalination, and sustainable agriculture. Solar energy is used to desalinate seawater, providing fresh water for crops, while excess energy supports local communities.
India’s Solar Irrigation Pumps: The Indian government has promoted the use of solar-powered irrigation pumps to help farmers access water efficiently and affordably, reducing their dependence on unreliable grid electricity.
China’s Agrivoltaics: In regions like Gansu Province, solar panels are installed above crop fields, providing shade for plants and generating electricity simultaneously. This dual-use approach maximizes land use efficiency.
The Dhundi Solar Cooperative: In Gujarat, the Dhundi Solar Cooperative has empowered farmers to generate solar power and sell surplus electricity to the grid. This initiative has provided farmers with a reliable income stream while promoting sustainable energy use.
Watershed Development in Maharashtra: The Pani Foundation’s watershed development projects have transformed arid regions into productive agricultural lands by implementing comprehensive water harvesting and management practices.
Solar Microgrids in Bihar: In Bihar, solar microgrids have been set up to provide reliable electricity to rural areas, supporting agricultural activities and improving the overall quality of life for farmers.
Companies Leading the Way
Several companies are at the forefront of integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture, providing innovative solutions to farmers:
Tata Power Solar: A leading solar energy company in India, Tata Power Solar provides solar irrigation solutions, including solar pumps and microgrids, enhancing energy access and sustainability for farmers.
Claro Energy: Specializing in solar-powered water pumping solutions, Claro Energy offers a range of solar pump systems designed to meet the irrigation needs of farmers across various regions in India.
DeHaat: An agritech company that supports farmers with end-to-end services including water management solutions and renewable energy products to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability.
KSB Limited: Known for its efficient water management systems, KSB provides advanced pumps and irrigation systems, integrating solar power to enhance water use efficiency in agriculture.
Amplus Solar: This company is involved in setting up solar power projects, including those tailored for agricultural applications, providing clean energy solutions to support irrigation and other farm operations.
Mahindra Susten: Part of the Mahindra Group, this company offers solar energy solutions, including solar water pumps, to promote sustainable farming practices in India.
Husk Power Systems: Specializes in decentralized renewable energy systems, including mini-grids powered by solar and biomass, which can be used to support agricultural activities in rural areas.
Government Support Programs for Water and Electricity Harvesting
The Indian government recognizes the importance of water and electricity harvesting for sustainable agriculture and has launched several programs to encourage their adoption:
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): This flagship program aims to improve irrigation infrastructure and promote water conservation practices like micro-irrigation. It provides financial assistance to farmers for installing drip and sprinkler irrigation systems.
Kisan Urja Suraksha Evam Utthan Mahabhiyan (KUSUM): This scheme aims to promote solar power adoption in the agricultural sector. It provides subsidies for farmers to install grid-connected, off-grid, and solar pump irrigation systems.
National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA): This mission focuses on promoting climate-resilient agricultural practices, including water conservation and efficient use of resources. It provides support for research and development of water-saving technologies and capacity building for farmers.
PM-KUSUM (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan): This flagship scheme promotes the use of solar energy in agriculture. It provides financial assistance for the installation of solar pumps, grid-connected solar power plants, and decentralized solar energy systems. The scheme aims to install over 2 million solar pumps, reducing farmers' dependence on grid electricity and diesel.
National Solar Mission: Part of the National Action Plan on Climate Change, this mission aims to establish India as a global leader in solar energy. It includes provisions for supporting solar irrigation and solar-powered cold storage facilities to reduce post-harvest losses and enhance agricultural productivity.
Atal Bhujal Yojana (ABY): This scheme aims to improve groundwater management in water-stressed areas. It promotes community participation in water management and supports the adoption of water-efficient agricultural practices.
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: A campaign aimed at water conservation and rainwater harvesting across India. It encourages the adoption of water-efficient practices in agriculture, such as micro-irrigation and watershed management, to ensure sustainable water use.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the clear benefits, integrating water and electricity harvesting in agriculture faces several challenges:
Initial Costs: The installation of renewable energy systems and advanced water management infrastructure requires significant upfront investment.
Technical Expertise: Farmers need training and support to manage and maintain these integrated systems effectively.
Policy Support: Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of these technologies.
Looking ahead, advances in technology and supportive policies will be critical in overcoming these challenges. Innovations such as more efficient photovoltaic cells, low-cost water storage solutions, and smart farming technologies will further enhance the viability of this integrated approach.
Conclusion
Agriculture with water and electricity harvesting represents a forward-thinking model for sustainable farming. By harnessing renewable energy and efficient water management techniques, farmers can improve their productivity, reduce their environmental impact, and build resilience against climate change. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, the integration of these practices will be essential in transforming the agricultural landscape, ensuring food security, and protecting our planet’s precious resources.
-x-
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#hashtag#WaterHarvestingTechniques hashtag#ElectricityHarvestingMethods#SustainableWaterManagement hashtag#RenewableEnergyInAgriculture#RainwaterHarvestingSystems hashtag#SolarPowerForAgriculture#WindEnergyInFarming hashtag#IrrigationEfficiency hashtag#GreenFarmingPractices#HarnessingNaturalResourcesInAgriculture hashtag#EcoFriendlyFarmingSolutions#OffGridAgricultureSystems hashtag#SustainableIrrigationTechnologies#EnergyEfficientFarming hashtag#WaterConservationStrategies
0 notes
Text
Bringing International farming Technologies into Indian Agriculture

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction
India, with its rich agricultural heritage and vast arable land, has long been regarded as the breadbasket of the world. However, the sector faces numerous challenges ranging from fragmented landholdings and water scarcity to soil degradation and yield stagnation. In the face of these challenges, there is an urgent need to modernize and revitalise Indian agriculture to ensure food security, livelihood sustainability, and environmental stewardship. Embracing international farming technologies presents a compelling opportunity to catalyse this transformation and unlock the full potential of India's agricultural sector. By drawing upon global innovations in precision agriculture, vertical farming, hydroponics, and drone technology, India can not only boost productivity but also foster sustainability and resilience in the face of climate change and evolving market dynamics. This article delves into the potential benefits and challenges of integrating international farming technologies into Indian agriculture and outlines strategies to facilitate this transition towards a more prosperous and sustainable future.
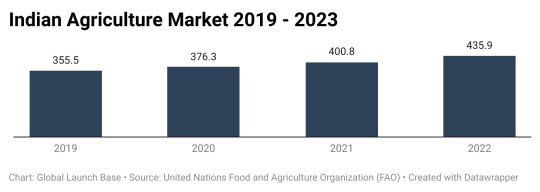
Figure: Indian Agriculture Market Size - 2019 - 2023
Harnessing Global Innovations:
The rapid pace of technological advancement has transformed agricultural practices worldwide, offering innovative solutions to age-old challenges. From the plains of North America to the rice paddies of Southeast Asia, farmers are increasingly turning to cutting-edge technologies to optimise production, conserve resources, and mitigate risks. As India strives to modernise its agriculture sector and meet the growing demands of a burgeoning population, it stands to gain immensely from tapping into these global innovations.

Precision Agriculture:
One of the most promising technologies is precision agriculture, which involves the use of satellite imagery, sensors, and data analytics to precisely manage farm inputs such as water, fertilisers, and pesticides. By adopting precision agriculture techniques, Indian farmers can optimise resource utilisation, minimise wastage, and maximise yields. Moreover, these technologies enable farmers to monitor crop health in real-time, allowing for timely interventions to prevent disease outbreaks and pest infestations.

Vertical Farming and Hydroponics:
With land becoming increasingly scarce, vertical farming and hydroponics offer innovative solutions to maximize productivity in limited spaces. Vertical farming involves cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers, while hydroponics utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions instead of soil. These methods require less land, water, and pesticides compared to traditional farming, making them particularly suitable for urban and peri-urban areas. By implementing vertical farming and hydroponics, India can address food security challenges and reduce pressure on arable land.

Drone Technology:
Drones have emerged as valuable tools for agriculture, enabling farmers to monitor vast expanses of land quickly and accurately. Equipped with cameras and sensors, drones can collect data on crop health, soil moisture levels, and pest infestations, allowing farmers to make informed decisions in real-time. Additionally, drones can be used for aerial spraying of pesticides and fertilisers, reducing manual labour and minimising chemical exposure risks for farmers.
How Foreign Startup Can Start in India
Foreign startups looking to establish a presence in India can explore several strategies to navigate the complex and dynamic business landscape of the country. Pilot projects are indeed an effective approach to test the market, understand local dynamics, and establish credibility among potential customers and stakeholders. Here are some ways foreign startups can start in India, including the utilisation of pilot projects:
Market Research and Localization: Before launching any pilot project, foreign startups should conduct comprehensive market research to understand the needs, preferences, and challenges of the Indian market. This involves analysing consumer behaviour, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and cultural nuances. By localising their products or services to suit the specific requirements of Indian customers, startups can increase their relevance and appeal in the market.
Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with local partners, such as established businesses, industry associations, research institutions, or government agencies, can provide foreign startups with valuable insights, resources, and networks. Partnerships can facilitate market entry, access to distribution channels, and credibility among local stakeholders. Joint pilot projects with Indian partners enable startups to leverage existing infrastructure, customer base, and market knowledge while sharing risks and rewards.
Pilot Projects and Proof of Concept: Launching pilot projects allows foreign startups to validate their products or services in the Indian market on a smaller scale before scaling up operations. Pilot projects provide an opportunity to test feasibility, gather feedback, iterate on solutions, and demonstrate value to potential customers and investors. By showcasing tangible results and measurable impact, startups can build trust and confidence among stakeholders and pave the way for wider adoption.
Government Initiatives and Incentives: Leveraging government initiatives, programs, and incentives aimed at promoting innovation, entrepreneurship, and foreign investment can provide foreign startups with strategic advantages. For example, Startup India, Make in India, and Digital India initiatives offer various incentives, tax benefits, and support schemes for startups operating in India. Participating in government-sponsored pilot projects or innovation challenges can help startups gain visibility, funding, and regulatory support.
Focus on Scalability and Long-Term Sustainability: While pilot projects serve as valuable entry points, foreign startups should maintain a long-term perspective and focus on scalability and sustainability. Pilot projects should be designed with scalability in mind, taking into account factors such as scalability of technology, scalability of operations, and scalability of impact. Startups should develop clear roadmaps and strategies for scaling up successful pilot projects into larger deployments and expanding their presence across India.
Adaptation and Agility: Flexibility, adaptability, and agility are essential traits for foreign startups operating in India's dynamic and diverse market. Startups should be prepared to pivot their strategies, products, or business models based on market feedback, changing customer needs, and evolving regulatory requirements. Continuous innovation, rapid experimentation, and a willingness to learn from failures are critical for success in India's competitive business environment.
Examples of International Startups Successful in India
EsoWorld: This Dutch company provides advanced weather monitoring and irrigation systems to Indian farmers. Their technology uses satellites and sensors to track weather patterns and soil moisture levels, allowing farmers to optimize their water usage and improve crop yields. EsoWorld has partnered with several Indian agricultural organizations to provide their services to farmers across the country.
Precision Planting: This American company is a leading provider of precision agriculture technologies. Their products, such as seed meters and automated guidance systems, help farmers to plant seeds more accurately and efficiently. Precision Planting has partnered with Indian agricultural equipment companies to bring their technology to the Indian market.
Netafim: This Israeli company is a global leader in drip irrigation systems, offering water-saving solutions perfect for India's climate. They've established a strong presence in India, providing farmers with efficient irrigation technology and training programs.
DeHaat: Interestingly, DeHaat is a foreign-founded company (Netherlands) but operates primarily in India. They function as a full-stack agritech platform connecting farmers directly to input suppliers, credit providers, and buyers. Their focus on end-to-end solutions has been well-received by Indian farmers.
BASF: This German multinational chemical company has a significant agricultural division. In India, BASF offers a range of products and services, including high-quality seeds, crop protection solutions, and agronomic advice. Their focus on scientific solutions resonates with Indian farmers seeking improved yields.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While international farming technologies offer tremendous potential, their successful integration into Indian agriculture requires addressing various challenges. These include high initial costs, limited access to technology infrastructure, and the need for specialised training and technical support. Additionally, there may be resistance from traditional farming communities reluctant to adopt new practices.
To overcome these challenges, concerted efforts are needed from government agencies, agricultural research institutions, and private sector stakeholders. This involves providing financial incentives and subsidies to encourage technology adoption, establishing demonstration farms to showcase the benefits of innovative techniques, and offering training programs to build capacity among farmers and extension workers. Moreover, public-private partnerships can facilitate technology transfer and ensure the localization of solutions to suit the specific needs and conditions of Indian agriculture.
Conclusion:
Bringing international farming technologies into Indian agriculture represents a transformative opportunity to enhance productivity, sustainability, and resilience in the face of evolving challenges. By harnessing the power of precision agriculture, vertical farming, hydroponics, and drone technology, India can unlock new avenues for growth and prosperity in the agricultural sector. However, realizing this potential requires collaborative efforts and strategic investments to ensure equitable access and adoption of innovative farming practices across the country. With the right policies and partnerships in place, India can lead the way towards a more efficient, inclusive, and resilient agricultural future.
— x —
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. We offer pilot project opportunities in India specifically tailored for international agritech startups. Get in touch with us to discover more about how we can support your business endeavours.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#InternationalFarmingTech hashtag#IndianAgAdvancements hashtag#CrossBorderAgInnovations hashtag#GlobalFarmingPractices#hashtag#TechTransferInAgriculture hashtag#FarmingTechIntegration#ModernizingIndianAgriculture hashtag#AgTechExpansionInIndia#PilotProjectsInAgSector hashtag#GlobalFarmingMethods#AgriculturalInnovationInIndia hashtag#InternationalAgTech#SustainableFarmingSolutions hashtag#BoostingAgProductivity#AgTechAdoptionTrends hashtag#EnhancingAgribusiness#InternationalFarmingCollaborations hashtag#PromotingAgTechInIndia#ScalingUpFarmingTech hashtag#ImprovingAgriInfrastructure
0 notes
Text
Revolutionising Agriculture with IoT Technology
Written By: Jagriti Shahi

Introduction:
In recent years, the agricultural sector has undergone a profound digital transformation, propelled by the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. This revolutionary shift has transcended traditional farming practices, empowering growers with real-time data and insights to make informed decisions, optimise resource utilisation, and maximise yields. By interconnecting physical devices and sensors with cloud computing and data analytics, IoT has ushered in a new era of precision agriculture, offering solutions to age-old challenges faced by farmers worldwide.
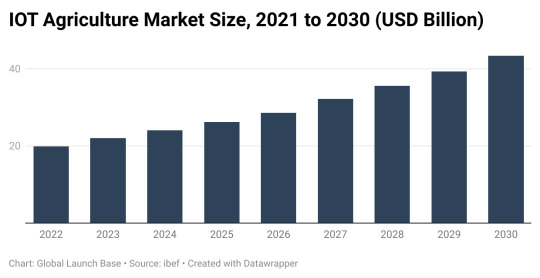
Figure: IOT Agriculture Market Size, 2021 to 2030 (USD Billion)
From the above figure we can see that IOT agriculture market size to surpass US$ 43.37 Bn by 2030

Figure: Adoption of Blockchain/ IoT - 2021
The marriage of IoT technology with agriculture has unlocked a plethora of opportunities across the entire farming ecosystem, from field management to supply chain logistics. This convergence has not only improved operational efficiency but also paved the way for sustainable farming practices. As the world grapples with escalating food demand, water scarcity, and environmental degradation, IoT-enabled solutions have emerged as indispensable tools in mitigating these challenges while ensuring food security and environmental stewardship.
Precision Farming:

Figure - Precision Farming
One of the cornerstone applications of IoT in agriculture is precision farming, which represents a paradigm shift from traditional blanket approaches to site-specific management. This innovative approach harnesses the power of IoT-enabled sensors, drones, and autonomous machinery to monitor and manage various aspects of crop production with unparalleled accuracy.
IoT sensors embedded in the soil continuously gather data on key parameters such as moisture levels, temperature, nutrient content, and pH levels. This real-time data is then transmitted to centralised platforms where it is analysed and processed using advanced algorithms. By leveraging this granular information, farmers can precisely tailor their irrigation, fertilisation, and pest control strategies to meet the specific needs of each crop and microenvironment within their fields.
Furthermore, the integration of IoT technology with precision agriculture has facilitated the development of variable rate application (VRA) systems. These systems utilise GPS-guided machinery to deliver inputs, such as water and nutrients, in precise quantities and locations based on the spatial variability detected in the field. By optimising input usage in this manner, farmers can not only enhance crop productivity and quality but also reduce costs and minimise environmental impact by avoiding over-application of inputs in areas where they are not needed.
Moreover, the data-driven insights generated through precision farming practices enable farmers to implement proactive measures to mitigate risks and optimise resource allocation. For instance, predictive analytics algorithms can forecast crop yields, pest outbreaks, and weather patterns, empowering farmers to make preemptive decisions to safeguard their crops and maximise profitability.
Overall, precision farming powered by IoT technology represents a quantum leap in agricultural productivity and sustainability. By harnessing the power of data-driven decision-making and precision management practices, farmers can unlock new levels of efficiency, profitability, and environmental stewardship in their operations. As IoT continues to evolve and become more accessible, the potential for innovation and transformation in agriculture is virtually limitless.
Smart Irrigation Systems:

Figure: Smart Irrigation Systems
Water scarcity is a pressing concern for farmers worldwide, exacerbated by climate change and population growth. In response to this challenge, smart irrigation systems have emerged as a game-changing solution, leveraging IoT technology to optimize water usage in agricultural fields.
At the heart of smart irrigation systems are IoT-enabled sensors that continuously monitor soil moisture levels, weather conditions, and crop water requirements in real-time. These sensors transmit data wirelessly to a central control system, where advanced algorithms analyse the information and determine the precise amount and timing of irrigation needed for each area of the field.
By dynamically adjusting irrigation schedules based on actual field conditions, smart irrigation systems minimise water wastage while ensuring that crops receive the optimal amount of moisture for healthy growth. This targeted approach not only conserves water but also enhances crop yield and quality by avoiding both under- and over-irrigation, which can lead to stress, disease, and reduced productivity.
Furthermore, smart irrigation systems offer farmers unprecedented control and flexibility over their irrigation practices. Through mobile or web-based applications, farmers can remotely monitor and manage their irrigation systems from anywhere, allowing them to respond quickly to changing weather patterns or crop needs. Some advanced systems even integrate weather forecasts and soil moisture data to automatically adjust irrigation schedules, further streamlining water management and reducing manual intervention.
Beyond water conservation and crop productivity, smart irrigation systems also deliver significant economic and environmental benefits. By reducing water usage and energy consumption associated with pumping, farmers can lower their operational costs and mitigate their carbon footprint. Additionally, by minimising runoff and leaching of nutrients and agrochemicals into water bodies, smart irrigation systems help protect water quality and preserve fragile ecosystems.
Crop Monitoring and Management:
In the realm of modern agriculture, crop monitoring and management have been revolutionised by the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. With the aid of IoT-enabled sensors, drones, and data analytics platforms, farmers now have unprecedented visibility into the health, growth, and condition of their crops, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimise production practices.

IoT sensors deployed in the field collect a wealth of data on various parameters such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and crop health indicators. This data is transmitted in real-time to centralised platforms where it is processed and analysed using advanced algorithms. By harnessing the power of big data analytics and machine learning, farmers can derive actionable insights from this data, allowing them to monitor crop performance, detect anomalies, and identify potential issues before they escalate.
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral imaging sensors play a pivotal role in crop monitoring and management. These aerial platforms can capture detailed imagery of fields from above, providing farmers with valuable insights into crop health, growth patterns, and pest infestations. By analysing these images, farmers can pinpoint areas of stress or vegetation anomalies, enabling them to take targeted corrective actions such as adjusting irrigation or applying pest control measures.
Moreover, IoT technology enables the development of predictive analytics models that forecast crop yields, disease outbreaks, and pest infestations based on historical data and real-time observations. By leveraging these predictive insights, farmers can proactively plan their planting, harvesting, and pest management strategies to optimise yields and minimise losses.
Additionally, IoT-enabled crop monitoring systems offer farmers greater flexibility and scalability in their operations. These systems can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different crops, growing conditions, and farming practices, allowing farmers to optimise resources and maximise profitability. Furthermore, the integration of IoT with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics holds the promise of further enhancing crop monitoring and management capabilities, paving the way for more autonomous and efficient farming practices.
Overall, IoT technology has transformed crop monitoring and management from a labour-intensive and resource-intensive process into a data-driven and proactive endeavour. By providing farmers with real-time insights, predictive analytics, and actionable recommendations, IoT-enabled solutions empower farmers to optimise crop yields, reduce risks, and enhance sustainability in agriculture. As IoT continues to evolve and become more accessible, the potential for innovation and transformation in crop monitoring and management is virtually limitless.
Livestock Monitori

Figure: Livestock Monitoring
In the realm of modern agriculture, livestock monitoring has undergone a paradigm shift with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT) technology. Traditionally, livestock management relied heavily on manual observation and intuition, making it challenging for farmers to detect health issues, optimise feeding regimes, and maximise productivity. However, IoT-enabled sensors and data analytics platforms have revolutionised livestock monitoring, offering farmers unprecedented insights into the health, behaviour, and performance of their animals. IoT sensors, attached to animals or installed in their living environments, continuously collect data on key parameters such as body temperature, heart rate, activity levels, and rumination patterns. This real-time data is transmitted wirelessly to centralised platforms where it is analysed and processed using advanced algorithms. By monitoring these physiological and behavioural indicators, farmers can detect signs of illness, stress, or reproductive cycles early on, allowing them to intervene promptly and provide appropriate care.
Moreover, IoT technology enables farmers to track the location and movement of livestock, particularly in extensive grazing systems or large-scale operations. GPS-enabled tracking devices attached to animals provide real-time information on their whereabouts, allowing farmers to monitor grazing patterns, prevent livestock theft, and optimise pasture management. This enhanced visibility into animal behaviour and movement enables farmers to make data-driven decisions to improve herd health, productivity, and welfare.
Furthermore, IoT-enabled livestock monitoring systems offer farmers greater efficiency and scalability in their operations. These systems can be integrated with other farm management software, such as feed management or reproductive tracking systems, to provide a comprehensive view of herd performance and profitability. Additionally, the use of wearable devices and smart collars allows farmers to remotely monitor individual animals or entire herds from anywhere, reducing the need for manual labour and improving overall productivity.
In addition to improving animal health and welfare, IoT-enabled livestock monitoring systems also deliver significant economic and environmental benefits. By optimising feeding regimes and managing herd health more effectively, farmers can reduce feed wastage, minimise veterinary costs, and increase overall profitability. Moreover, by minimising the environmental impact of livestock production through more efficient resource utilisation and waste management, IoT technology contributes to the sustainability of agriculture.
Supply Chain Optimization:
In the dynamic landscape of agriculture, supply chain optimization has emerged as a critical area where Internet of Things (IoT) technology is driving significant transformation. From farm to fork, the agricultural supply chain encompasses a complex network of processes, stakeholders, and resources. IoT-enabled solutions offer unprecedented visibility, traceability, and efficiency across this entire ecosystem, revolutionising how agricultural products are produced, processed, and distributed.
At the farm level, IoT sensors deployed in fields and orchards collect data on environmental conditions, crop growth stages, and harvest readiness. This real-time data enables farmers to optimise planting schedules, manage inputs more efficiently, and anticipate yield fluctuations. By integrating IoT data with farm management systems, farmers can make data-driven decisions to maximise productivity while minimising costs and environmental impact.
As agricultural products move through the supply chain, IoT technology plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, safety, and compliance. Temperature, humidity, and location sensors embedded in storage facilities, transportation vehicles, and processing plants monitor the conditions of perishable goods in real-time. Any deviations from optimal conditions trigger alerts, allowing stakeholders to take corrective action to prevent spoilage, contamination, or quality degradation. By maintaining the integrity of the cold chain and reducing food waste, IoT-enabled supply chain solutions contribute to improved food safety and sustainability.
Moreover, IoT technology enhances transparency and traceability throughout the agricultural supply chain, enabling stakeholders to track the journey of products from farm to consumer. Blockchain-based platforms leverage IoT data to create immutable records of product origin, production practices, and handling procedures. This transparency builds trust among consumers, enhances brand reputation, and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements such as food safety standards and sustainability certifications.
Additionally, IoT-enabled supply chain solutions offer opportunities for optimization and cost savings through predictive analytics and automation. By analysing historical data and real-time insights, predictive analytics models can forecast demand, optimise inventory levels, and streamline logistics operations. Autonomous vehicles and robotic systems equipped with IoT sensors and artificial intelligence algorithms further enhance efficiency by automating tasks such as harvesting, sorting, and packaging.
Furthermore, IoT technology facilitates collaboration and coordination among supply chain partners through real-time data sharing and communication. Cloud-based platforms and mobile applications enable seamless integration and exchange of information between farmers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers. This collaboration fosters greater agility, responsiveness, and resilience in the face of supply chain disruptions such as weather events, market fluctuations, or global pandemics.
Advanced IoT Applications for Farms

1. Drone-based scouting and spraying: Imagine agile drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors. These can autonomously map fields, identify weeds and pests with incredible accuracy, and deliver targeted treatment exactly where it's needed. This reduces reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides, promotes sustainable practices, and minimises environmental impact.

2. Predictive analytics for disease and pest control: IoT sensors combined with advanced AI can analyse historical data and weather patterns to predict outbreaks of diseases and pests. This allows farmers to take preventive measures, such as applying natural deterrents or introducing beneficial insects, before problems escalate.

3. Climate-smart agriculture: IoT weather stations with advanced sensors can provide hyper-local weather data, including real-time wind speed, precipitation forecasts, and even data on micronutrient levels in the atmosphere. This empowers farmers to make informed decisions about planting schedules, crop selection, and irrigation strategies based on real-time forecasts, optimising yields and building resilience against climate variations.

4. Blockchain for traceability and transparency: Imagine a system where every step of a product's journey, from farm to fork, is recorded on a secure blockchain ledger. Sensors embedded in packaging can monitor temperature and storage conditions during transportation, ensuring food safety. Consumers can then scan a QR code and access a transparent record of the product's origin, farming practices used, and even the environmental impact of its production.

5. Robotics for controlled-environment agriculture (CEA): In indoor farms and vertical farming facilities, IoT plays a central role. Robots equipped with sensors and grippers can perform delicate tasks like seeding, transplanting, and harvesting with minimal damage to crops. This not only reduces labour costs but also ensures consistent quality and higher yields in controlled environments.
Cultivating Innovation with IoT
The agricultural IoT revolution isn't just a theoretical concept – it's being driven by a wave of forward-thinking companies developing cutting-edge solutions. Here are a few industry leaders to watch:
Deere & Company: A major player in agricultural machinery, Deere offers a suite of IoT-powered solutions under the John Deere® FarmSight® banner. These include yield monitors, tractor telematics, and weather data analysis tools, empowering farmers to optimise their operations.
Trimble Inc.: This company provides a range of advanced positioning and data management solutions for agriculture. Their offerings include automated guidance systems for tractors and combines, allowing for high-precision planting and harvesting, and software platforms that integrate data from various sources to give farmers a comprehensive view of their operations.
SenseFly (Parrot Group): Specialises in agricultural drone technology. Their drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and multispectral sensors, are used for field scouting, identifying crop health issues, and creating detailed 3D field maps.
InFarm: A leader in the indoor vertical farming space, InFarm leverages IoT sensors and automation extensively. Their vertical farms are equipped with environmental control systems that optimise light, temperature, and humidity for specific crops, all monitored and managed through a central IoT platform.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While the potential of IoT in agriculture is undeniable, there are challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Here's a look at some key hurdles and how we can work towards a future where smart farming flourishes:
Challenges:
Connectivity: Reliable internet access in rural areas is crucial for real-time data collection and analysis. Efforts are underway to expand broadband access and explore alternative low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) for improved connectivity in remote locations.
Cost: The upfront investment in sensors, devices, and software can be significant, especially for small and medium-scale farms. Government subsidies, innovative financing models, and standardisation of technologies can help bring down costs and make these solutions more accessible.
Data Security and Privacy: As farms become increasingly reliant on data, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive information from breaches and ensure farmer trust.
Digital Literacy: Equipping farmers with the skills to understand and utilise IoT technologies effectively is crucial. Training programs, workshops, and user-friendly interfaces can bridge the digital divide and empower farmers to harness the full potential of these tools.
Future Outlook:
Despite these challenges, the future of IoT in agriculture is bright. As technology costs decrease, connectivity improves, and farmers become more comfortable with digital tools, adoption is expected to accelerate. Here are some exciting possibilities to look forward to:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: Advanced analytics will extract even deeper insights from agricultural data, allowing for predictive maintenance of equipment, automated disease and pest control, and hyper-personalised crop management strategies.
Rise of Agtech Startups: A growing number of innovative startups are developing niche solutions tailored to specific agricultural needs. This will lead to a more diverse and dynamic ecosystem, offering farmers a wider range of choices.
Focus on Sustainability: IoT will play a key role in optimising water usage, minimising fertiliser application, and reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. This will contribute to a more sustainable food production system.
In conclusion, IoT holds immense potential to transform agriculture. By addressing the existing challenges and fostering collaboration between farmers, technology providers, and policymakers, we can usher in an era of smart farming that is not only productive but also sustainable and resource-efficient.
— x —
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#AgriTechCEO hashtag#IoTAgricultureLeader hashtag#SmartFarmingPioneer#hashtag#PrecisionAgVisionary hashtag#DigitalAgChampion hashtag#FarmTechInnovator#IoTAgRevolutionary hashtag#AgriInnovationCEO hashtag#FutureFarmingExpert#AgriTechTrailblazer hashtag#SustainableAgLeader hashtag#DataDrivenAgCEO#AgriTechDisruptor hashtag#IoTAgSolutionist hashtag#FarmTechVisionary#AgriDigitalTransformationLeader hashtag#IoTAgriInnovator#AgriTechGameChanger hashtag#SmartAgPioneer hashtag#IOT hashtag#Agriculture
0 notes
Text
The Role of Government Organizations in Promoting International Expansion

Written By: Gargi Sarma, Industry Analyst Global Launch Base
Government organizations are essential in helping firms grow internationally by offering resources, advice, and assistance. These organizations help startups enter the market more smoothly, lower risks, and gain credibility in international markets by providing access to market intelligence, regulatory support, and strategic alliances. This article delves into the complex role that governments play in encouraging companies to expand internationally, examining their relevance and influence on the globalization of entrepreneurship.

Figure 1: Role of Government Organizations in Promoting International Expansion
Regulatory Advice and Assistance
Government agencies aid global expansion by offering regulatory guidance and simplifying complex processes like taxation and import/export rules. They provide precise instructions, assist with compliance, and facilitate license applications, reducing risks and easing market entry for growing businesses.
Access to Market Intelligence and Resources
Government agencies provide vital market intelligence, helping businesses understand customer behavior and competitive landscapes. Through data analysis and resources like trade trips and networking events, they enable companies to identify growth opportunities, make informed decisions, and forge strategic alliances, expediting their development plans.
Facilitating Partnerships and Collaborations
Governmental agencies facilitate global expansion by organizing events like trade shows and business matchmaking to connect companies and stakeholders. They negotiate favorable trade conditions, support companies in international markets, and help remove entry obstacles through diplomatic channels and bilateral agreements.
Promoting Brand Image and Credibility
Government agencies bolster a nation's international brand image, enhancing credibility for affiliated businesses. Through trade promotion programs and quality standards, they support legitimacy and adherence to global best practices, fostering consumer trust, improving market access, and providing a competitive edge in international markets.

Figure 2: Understanding the Benefits of Government Organizations with Startups
Government organizations play a crucial role in facilitating international expansion for startups by providing funding opportunities and pilot project support. Startups typically seek funding through grants, loans, or equity investment programs offered by government agencies. Additionally, these organizations often provide access to pilot projects, enabling startups to test their products or services in real-world scenarios and validate their market potential. This support helps startups overcome financial barriers and gain valuable traction in new markets, ultimately driving their international expansion efforts forward.
Leveraging Government Partnerships for Successful International Expansions:
At Global Launch Base, we specialize in facilitating successful business expansions into India through strategic partnerships with prestigious government agencies. With a proven track record, we've aided companies like Dutchbasecamp and Fermata in navigating the complexities of the Indian market, leveraging our services and government connections. Our comprehensive approach not only focuses on market entry but also on establishing optimal company structures for smooth operations. This ensures a seamless and prosperous entry into the Indian or European market.
Case Study: Empowering Global Startups for Success in the Indian Market Overview: From August 2021 to November 2023, 163 companies from 27 countries across 17 verticals received coaching and training from DutchBasecamp and Global Launch Base. With a 9 out of 10 participant satisfaction rate, this program was highly successful.
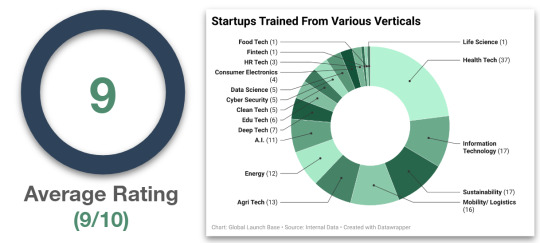
Figure 3: Results of Partnership with DutchBasecamp
Challenges: Startups faced difficulties in understanding the Indian market, forming alliances, and aligning products with local customs and laws, leading to uncertainty about market entry.
Solutions: Global Launch Base, in collaboration with DutchBasecamp, developed comprehensive solutions to address these challenges:
Cultural Adaptation: Acknowledging and adapting to diverse cultural norms and values to facilitate international commerce.
Go-to-Market Strategy: Crafting focused strategies to introduce and market products effectively in India.
Research and Validation: Conducting thorough market research and validation to ensure product viability and acceptance.
Investor Readiness: Aligning operations, finances, and strategies to meet investor requirements and expectations.
Results: DutchBasecamp and Global Launch Base successfully helped companies navigate the complexities of the Indian market. With deeper cultural understanding, strong go-to-market strategies, validated products, and investor-ready operations, startups were well-prepared for expansion in India.
Case Study: Empowering Israel Starup's Success in the UK Greenhouse Market
Overview: Global Launch Base provided crucial mentorship to an Israeli AI Pest and Disease Detection AgTech startup, enabling their successful entry and growth in the UK greenhouse market. Through strategic guidance, the startup achieved market growth, formed valuable partnerships, and enhanced brand visibility.
Challenges: The startup sought assistance in preparing a go-to-market strategy for the UK and navigating market dynamics effectively.
Solution: Global Launch Base Mentorship collaborated with Israel Startup to devise a comprehensive market entry strategy tailored to the UK greenhouse market:

Figure 4: Solution Provided for Israel Startup
Introduction and Expectations: Outlining objectives and preparing a plan for market preparations.
Market Size and Growth: Assessing market size and exploring growth opportunities across different locations.
Identifying Target Market: Researching potential clients and understanding unique market characteristics.
Understanding the Competition: Analyzing competitors, identifying strengths, and defining a competitive edge.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Developing a USP based on market needs and customer feedback.
Building Partnerships: Identifying and organizing potential partners for seamless implementation.
Go-to-Market (GTM) Strategy: Planning approach, pricing, sales tactics, and operational strategy for 2024–2026.
KPIs and Next Steps: Establishing metrics for success measurement and resource allocation.
Pitch Deck Review: Refining pitch deck and presentation skills for effective communication.
Results: Equipped with a comprehensive plan and finalized budget, Israel Startup is well-prepared to enter the UK greenhouse market, poised for success in the coming years.
Facilitating International Expansion Through Strategic Partnership:
Government organizations play a pivotal role in facilitating the international expansion of startups by forging strategic partnerships with entities like Global Launch Base (GLB). One of these partnerships aims to support startups in entering diverse markets, including both European and Indian territories.
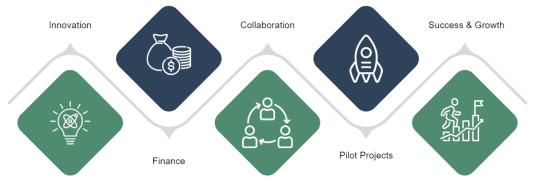
Figure 5: Solution Provided Through Strategic Partnership
Funding Opportunities: Startups and SMEs have access to funding opportunities that support their growth and development. These opportunities cover a wide range of activities, including early-stage research, proof of concept, technology transfer, and financing for scaling up.
Global Launch Base Partnership: Global Launch Base's recent partnership signifies its commitment to facilitating international expansion for startups. Through this collaboration, Global Launch Base gains access to a network of organizations with expertise in supporting innovations backed by the EU. This partnership opens doors for startups looking to enter both the European and Indian markets, providing tailored support and resources to navigate the complexities of international expansion.
Global Launch Base's service description underscores its dedication to assisting entrepreneurial ventures in launching into dynamic markets like India and Europe. By analyzing each venture's unique needs and collaborating with experts and mentors, Global Launch Base tailors launch platforms to provide concrete pilot opportunities, market validations, and introductions to key stakeholders. Whether startups aim to enter the Indian or European market, Global Launch Base offers comprehensive support, including need assessment, market research, and assistance with setting up appropriate business entities for operation.
Examples of Government Agencies Supporting Startup Business Expansion:
EU India Innocenter: This initiative focuses on facilitating collaboration and innovation partnerships between the European Union and India. It provides support for startups seeking to expand their operations across these regions, offering access to networks, funding opportunities, and market insights.
European Institute of Innovation & Technology (EIT): EIT is dedicated to nurturing innovation and entrepreneurship across Europe. It offers various programs and initiatives to support startups in scaling their businesses, including access to mentoring, funding, networking opportunities, and access to research and development facilities.
European Innovation Council (EIC): The European Innovation Council provides support to high-potential startups and innovative SMEs (Small and Medium-sized Enterprises) through funding, coaching, and networking opportunities. It aims to accelerate the growth of startups with disruptive technologies and business models.
DutchBasecamp: DutchBasecamp is a government-supported initiative in the Netherlands aimed at helping startups and scale-ups expand internationally. They provide resources, expertise, and connections to navigate global markets effectively, with a focus on assisting Dutch startups in their international expansion efforts.
EuRA - European Relocation Association: EuRA specializes in supporting startups and businesses with relocation services within Europe. They offer guidance and assistance in relocating employees, setting up offices, and navigating legal and logistical challenges associated with international business expansion.
Ministry of Agriculture, Netherlands: This governmental body, particularly in the Netherlands, supports startups in the agri-food sector by offering funding, regulatory guidance, and access to research and innovation programs. It specializes in promoting sustainable agriculture practices and facilitating market access for food-related startups.
These government agencies play crucial roles in fostering innovation, supporting startups, and facilitating their expansion into new markets, both within Europe and internationally.
Conclusion:
In summary, it is impossible to overestimate the critical role that government agencies play in helping businesses expand internationally. These agencies play a critical role in the success of businesses that expand into new markets by offering regulatory assistance, market intelligence, partnership facilitation, and brand credibility enhancement. Using tactical partnerships with prestigious governmental organizations, Global Launch Base has proven its dedication to enabling companies to enter markets with ease and success.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#governmentsupport hashtag#businessexpansion hashtag#internationalbusiness hashtag#marketintelligence hashtag#strategicalliances hashtag#globaltrade hashtag#entrepreneurship hashtag#startupsuccess hashtag#governmentinitiatives hashtag#marketentry hashtag#brandcredibility hashtag#globalization hashtag#businessdevelopment hashtag#marketresearch hashtag#regulatorycompliance hashtag#startupfunding hashtag#marketentrystrategy hashtag#globalpartnerships hashtag#businessnetworking hashtag#indiaexpansion hashtag#marketinsights hashtag#governmentcollaboration hashtag#startupsupport hashtag#innovation hashtag#globalmarkets hashtag#tradepromotion hashtag#businessgrowth hashtag#governmentresources hashtag#startupecosystem
0 notes
Text
Water Scarcity and Drought: Challenges and Solutions

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Water, the elixir of life, is becoming an increasingly precious commodity. Drought and water scarcity are no longer distant threats, but a present reality for many regions worldwide. This article explores the challenges of water scarcity and droughts, along with potential solutions, with a specific focus on the current situation in Bangalore, India.
Water Stress Level by Indian States

Figure: Indian States Facing Extreme to Low level of Water Scarcity - Source: World Resource Institute - 2019 Mapbox - OpenStreetMap
The Current Situation in India
India is currently classified as "water-stressed" by the World Resources Institute. This means that the country's available water resources need to be increased to meet its demands. Some alarming signs include:
Decreasing per capita water availability: India's per capita water availability has been declining steadily for decades.
Drying Rivers: Several major rivers, including the Ganges and Cauvery, are experiencing reduced flows, impacting agriculture and livelihoods.
Urban Water Shortages: Many cities in India face regular water cuts, forcing residents to rely on expensive tankers for daily needs.

Figure: India’s water cost curve illustrates a number of available options - Source: 2030 Water Resources Group, Mckinsey
Bangalore's Water Worries
India's IT capital, Bangalore, is a stark example of a city facing water scarcity. The city's rapid urbanization and population boom have outpaced the development of sustainable water management practices. Groundwater reserves are rapidly depleting, and traditional sources like lakes and rivers are drying up. This has resulted in water rationing, price hikes, and anxieties about the future.
India's IT capital, Bangalore, is a cautionary tale of a metropolis grappling with water scarcity. The crisis in Bangalore is a confluence of several factors:
Unsustainable Growth: The city's phenomenal growth has been impressive, but not without consequences. Bangalore's population has exploded from around 4 million in 1991 to an estimated 14 million today. This rapid urbanization has outpaced the development of water infrastructure and resources.
Depleting Groundwater: Bangalore relies heavily on groundwater, but extraction rates far exceed recharge rates. Thousands of borewells have dried up, leaving residents dependent on erratic piped water supplies or expensive water tankers.
Vanishing Lakes: Once blessed with numerous lakes, Bangalore has lost many to encroachment and pollution. These lakes used to serve as natural reservoirs, replenishing groundwater and mitigating floods. Their loss has severely impacted the city's water security.
Strained River Relations: The Cauvery River, a primary water source for Bangalore, is at the center of a long-standing water dispute with neighboring Tamil Nadu. Uncertain water flows from the Cauvery further exacerbate Bangalore's water woes.
The consequences of water scarcity in Bangalore are dire. Residents face water rationing, with some areas receiving water only for a few hours a day. Water prices have skyrocketed, placing a burden on households and businesses. The city's economic growth is threatened as water scarcity deters potential investors and disrupts essential services.
The Global Challenge of Water Scarcity
Freshwater resources are finite, and our demands are ever-growing. Factors like population increase, climate change, and pollution are putting immense strain on our water supplies. According to the World Resources Institute, around 1.7 billion people already experience water scarcity at least one month a year. This scarcity has cascading effects, impacting agriculture, industry, and human health.

Figure: Global Gap Between existing accessible, reliable supply and 2030 water withdrawals - Source - Mckinsey
Innovative initiatives by countries to address water scarcity and drought:
Singapore has become a world leader in desalination technology, which removes salt from seawater to produce fresh water. They also have NEWater, a high-purity reclaimed water used for industrial purposes and even drinking water supply.
Israel is a pioneer in drip irrigation, a method that efficiently delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. Additionally, they have developed advanced techniques for treating wastewater and recycling it for agriculture.
Australia is implementing water-efficient urban design practices, such as using drought-resistant plants and harvesting rainwater. They are also increasing their desalination capacity to meet growing water demands.
California, USA has implemented water rationing during droughts to restrict water use. They also have conservation programs that educate the public on water-saving practices.
Morocco: They've embraced fog harvesting, using large nets placed on mountaintops to capture moisture from fog and condense it into freshwater.
Netherlands: This country is known for its innovative water management systems. They are developing smart irrigation systems that use sensors to monitor soil moisture and deliver water only when needed.
China: They're utilizing large-scale water transfer projects, building canals and tunnels to divert water from wetter regions to drier ones.
Looking to the future:
Research into drought-resistant crops: Scientists are developing new crop varieties that require less water to thrive.
Wastewater treatment advancements: Technologies are being explored to further purify wastewater for broader applications, including drinking water.
Drought: A Symptom of a Larger Problem
Droughts are periods of abnormally dry weather that severely affect water availability. They can be caused by natural climate cycles, but human activities like deforestation and excessive water use exacerbate their impact. Droughts not only worsen water scarcity but also lead to crop failures, wildfires, and economic hardship.
Here's how human actions can worsen droughts:
Climate Change: The burning of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, trapping heat in the atmosphere. This alters weather patterns, leading to more extreme weather events, including droughts. Rising temperatures also increase evaporation rates, further drying out soils.
Deforestation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle. Trees absorb and transpire water, releasing moisture back into the atmosphere. Deforestation disrupts this process, leading to decreased rainfall and increased drought severity.
Water mismanagement: Overuse of groundwater for agriculture and other purposes can deplete aquifers, leaving less water stored underground. Inefficient irrigation practices can also waste vast amounts of water.
The consequences of droughts are far-reaching:
Agricultural impacts: Droughts cripple crop yields, leading to food shortages and price hikes. This can have a devastating impact on food security, particularly in vulnerable regions.
Environmental damage: Droughts can cause desertification, soil erosion, and habitat loss. They can also contribute to wildfires, further exacerbating environmental damage.
Socioeconomic hardship: Droughts can displace communities, disrupt livelihoods, and lead to economic hardship. Water scarcity can also create social tensions and conflicts.
Understanding droughts as a symptom of a larger problem – climate change and water mismanagement – is crucial for developing effective solutions. By addressing these root causes, we can build resilience to droughts and ensure a more sustainable future for our water resources.
Finding Solutions: A Multi-pronged Approach
Addressing water scarcity requires a multi-pronged approach. Here are some key solutions:
Conservation: Promoting water conservation efforts in homes, industries, and agriculture is crucial. This includes fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, and adopting smart irrigation practices.
Water reuse and recycling: Treated wastewater can be a valuable resource for irrigation and other non-potable uses. Investing in wastewater treatment and reuse infrastructure is essential.
Rainwater harvesting: Capturing rainwater during the monsoon season can significantly supplement water supplies. Encouraging rainwater harvesting in homes and communities can make a big difference.
Leakage reduction: Many water distribution systems suffer from significant leaks. Investing in infrastructure repairs and leak detection technologies can improve water efficiency.
Sustainable water management: Developing long-term water management plans that consider factors like climate change and population growth is vital.
Innovative Solutions: The Rise of WaterTech Startups
India's water crisis has spurred a wave of innovation, with startups developing cutting-edge technologies to address various aspects of water scarcity and drought. Here are a few examples:
Water ATMs: Companies like JanaJal and Swajal are setting up networks of water ATMs in rural areas. These user-friendly kiosks dispense purified drinking water at affordable prices, making clean water accessible to even the most remote communities.
Smart Irrigation Solutions: WEGoT and other startups are developing IoT-based irrigation systems that use sensors and data analytics to optimize water usage in agriculture. These systems can detect moisture levels in soil and deliver water precisely where and when it's needed, minimizing waste.
Atmospheric Water Generators: Uravu Labs is a pioneer in atmospheric water generation technology. Their solar-powered systems extract water vapor from the air, providing a sustainable source of clean drinking water in water-scarce regions.
Wastewater Treatment: Companies like Ion Exchange and Thermax are developing advanced wastewater treatment solutions. These technologies allow for the reuse of wastewater for irrigation and industrial purposes, reducing the reliance on freshwater sources.
Government Initiatives for Water Security and Startup Support
The Indian government recognizes the gravity of water scarcity and is implementing various initiatives to address the challenge. These initiatives can be broadly categorised into two areas:
1. Water Security Programs:
National Water Mission: Launched in 2011, this mission aims to conserve water, improve water use efficiency, and ensure equitable water distribution. It focuses on areas like rainwater harvesting, promoting efficient irrigation practices, and protecting water bodies.
Atal Jal Yojana: This flagship program focuses on water-stressed districts and aims to improve water availability and water security at the village level. It promotes community participation in water resource management.
Per Drop More Crop: This scheme encourages farmers to adopt micro-irrigation techniques like drip and sprinkler irrigation to save water and increase agricultural productivity.
2. Startup Support Programs:
Start-Up India Initiative: This government initiative aims to create a robust startup ecosystem in India. It provides various benefits to startups, including tax breaks, funding opportunities, and mentorship programs. Several water-focused startups have benefited from this initiative.
Water Technology Mission: This mission aims to promote innovation and development in the water sector. It provides financial assistance and facilitates partnerships between startups, research institutions, and investors.
Innovation in Water Technologies Challenge: This challenge by the Department of Science and Technology encourages startups to develop innovative solutions for water scarcity and sanitation. It offers grants and incubation support to promising ventures.
The Road Ahead
Addressing water scarcity is a collective responsibility. Governmental policies, community-based initiatives, and individual actions are all essential for ensuring a sustainable water future for India. By adopting water-saving practices and investing in innovative solutions, India can overcome this looming crisis and secure its water resources for generations to come.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#hashtag#WaterScarcityIndia hashtag#DroughtInIndia hashtag#WaterCrisisSolutions hashtag#SustainableWaterManagementIndia hashtag#WaterConservationMeasures hashtag#IndiaWaterResources hashtag#MitigatingWaterScarcity hashtag#AdaptationStrategiesIndia hashtag#WaterCrisisManagement hashtag#RainwaterHarvestingIndia hashtag#GroundwaterDepletionIndia hashtag#IrrigationEfficiencyTechniques hashtag#ClimateChangeImpactsOnWater hashtag#CommunityWaterResilienceIndia hashtag#GovernmentInitiativesWaterConservationIndia hashtag#Bangalorewaterissue
0 notes
Text
The Role of Renewables in Decarbonisation
Written By: Jagriti Shahi

Introduction:
As the world grapples with the urgent need to mitigate climate change, the imperative for decarbonization has become increasingly apparent. At the forefront of this global effort are renewable energy sources, which play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning towards a sustainable energy future. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted role of renewables in decarbonization, exploring their benefits, challenges, and the path forward.

Figure: An overview and possible decarbonisation pathways for India - Source: Mckinsey & Company
The Rise of Renewables:
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, have witnessed remarkable growth and technological advancements in recent years. This surge can be attributed to several factors, including declining costs, policy support, and heightened environmental awareness. Notably, renewables have emerged as competitive alternatives to fossil fuels, offering cleaner, more sustainable energy solutions.
Decarbonization Imperative:
Decarbonization, the process of reducing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions, is crucial for mitigating climate change and achieving global climate targets, such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement. The energy sector, being a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, holds immense potential for decarbonization through the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
The Role of Renewables:
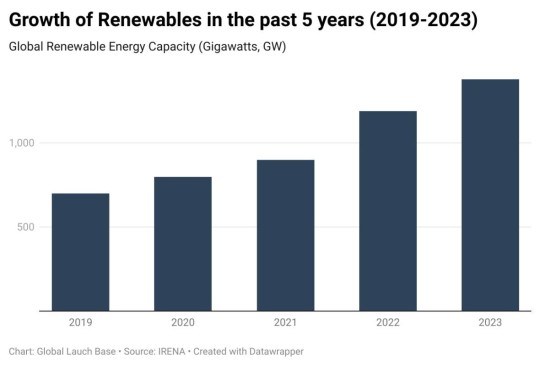
Figure: Growth of Renewables in the past 5 years
Renewable energy sources play a multifaceted role in decarbonization across various sectors:
Power Generation: Renewables are instrumental in decarbonizing electricity generation, displacing carbon-intensive sources like coal and natural gas. The scalability and versatility of renewables enable the deployment of clean energy infrastructure on a global scale, driving the transition towards low-carbon electricity grids.
Transportation: The electrification of transportation, facilitated by renewable energy, is pivotal for reducing emissions from the transport sector. Electric vehicles (EVs) powered by renewable electricity offer a sustainable alternative to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, thereby curbing emissions and improving air quality.
Heating and Cooling: Renewable energy technologies, such as solar thermal and geothermal systems, hold promise for decarbonizing heating and cooling in buildings and industrial processes. By harnessing renewable heat sources, it is possible to reduce reliance on fossil fuels for heating purposes, contributing to overall emissions reduction.
Industry and Agriculture: Renewable energy integration in industrial processes and agriculture can mitigate emissions associated with manufacturing, processing, and agricultural activities. From solar-powered factories to bioenergy production from agricultural waste, renewables offer innovative solutions for decarbonizing these sectors.
Renewables in Low Carbon Construction:
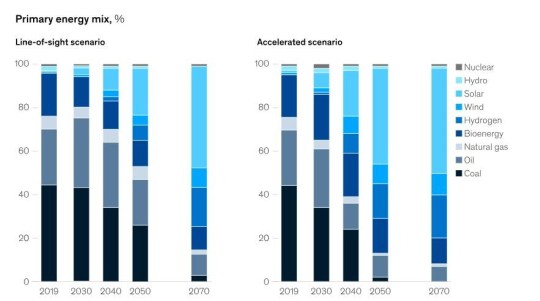
Figure: Primary Energy Mix,% Source: Mckinsey & Company
Low carbon construction encompasses practices and technologies aimed at minimizing carbon emissions associated with building materials, construction processes, and building operation. Renewable energy plays a crucial role in this context through several avenues:
Renewable Energy Integration: Incorporating renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into building designs reduces reliance on carbon-intensive grid electricity for powering homes and commercial buildings. Additionally, utilizing renewable energy for heating and cooling purposes in buildings mitigates emissions associated with traditional heating fuels like natural gas.
Sustainable Materials: Renewable resources can be utilized to produce sustainable building materials, such as bamboo, timber, and recycled materials. These materials not only have lower embodied carbon compared to traditional counterparts but also contribute to biodiversity conservation and sustainable land management.
Energy Efficiency: Renewable energy complements energy-efficient building design and technologies, enhancing overall energy performance and reducing operational carbon emissions. Integrating renewables with energy-efficient measures, such as insulation, efficient lighting, and smart building controls, maximizes energy savings and minimizes environmental impact.
Carbon Capture, Use & Storage (CCUS):
CCUS technologies are instrumental in capturing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power generation facilities, preventing their release into the atmosphere. The captured CO2 can then be utilized in various applications or stored underground, effectively reducing net emissions. Renewables play a vital role in CCUS through the following mechanisms:
Powering CCUS Facilities: Renewable energy sources provide low-carbon electricity to power CCUS facilities, reducing the carbon footprint of the capture and storage process. By utilizing renewable electricity instead of fossil fuels, CCUS operations can achieve significant emissions reductions while ensuring sustainable operation.
Renewable Hydrogen Production: Renewable energy, particularly solar and wind power, can be utilized to produce renewable hydrogen through electrolysis. This renewable hydrogen serves as a clean energy carrier for industrial processes and transportation, enabling decarbonization in sectors where direct electrification may be challenging.
Carbon Utilization: Renewable energy can facilitate carbon utilization technologies, where captured CO2 is converted into valuable products such as synthetic fuels, chemicals, and building materials. By coupling CCUS with renewable energy-driven conversion processes, carbon emissions are not only mitigated but also utilized in a circular and sustainable manner.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the integration of renewables with low carbon construction and CCUS offers significant potential for decarbonization, several challenges must be addressed. These include technological limitations, cost competitiveness, policy frameworks, and public acceptance. Overcoming these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions to drive innovation, scale deployment, and create supportive regulatory environments.
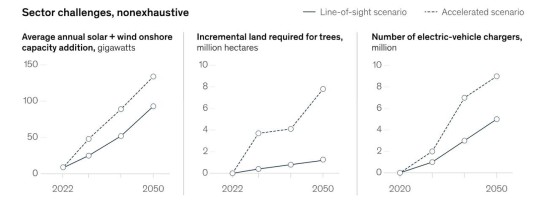
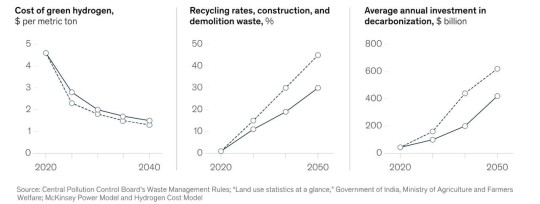
Figure: Sector Challenges, Source: Mckinsey & Company
The Path Forward:
To harness the synergies between renewables, low carbon construction, and CCUS effectively, concerted action is needed at the global, national, and local levels. This includes:
Setting ambitious decarbonization targets and policies that incentivize the adoption of renewables, promote low carbon construction practices, and support CCUS deployment.
Investing in research, development, and innovation to advance renewable energy technologies, low carbon materials, and CCUS solutions.
Fostering collaboration among governments, businesses, and communities to accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy and achieve net-zero emissions.
Conclusion:
Renewable energy, coupled with innovative approaches such as low carbon construction and CCUS, holds immense promise in driving decarbonization across multiple sectors. By leveraging the synergies between these strategies, we can mitigate carbon emissions, enhance resilience to climate change, and pave the way for a sustainable future. Now is the time to embrace renewables as catalysts for transformative change and forge a path towards a low-carbon society.
#Renewables hashtag#Decarbonisation hashtag#SustainableEnergy hashtag#CleanEnergy#hashtag#RenewableEnergySources hashtag#SolarPower hashtag#WindEnergy hashtag#ClimateAction#GreenEnergy hashtag#CarbonReduction hashtag#EnergyTransition hashtag#EnvironmentalSustainability hashtag#RenewablePowerGeneration#LowCarbonFuture hashtag#EnergyInnovation
0 notes
Text
Agriculture ERP's Role in Unlocking Growth
Written By: Jagriti Shahi

Introduction
India, with its vast and diverse agricultural landscape, has been embracing technological advancements to modernize its farming practices. One such pivotal development is the implementation of Agriculture Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) infrastructure. This integrated system is designed to streamline and optimize various agricultural processes, from production and supply chain management to financial transactions and data analysis. In this article, we will explore the significance and impact of Agriculture ERP infrastructure in India. India, a country deeply rooted in its agricultural heritage, is on the cusp of a transformative journey in farming practices, driven by technological advancements. At the heart of this evolution is the implementation of Agriculture Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) infrastructure. This integrated system is not merely a digital tool but a comprehensive solution designed to revolutionize every facet of the agricultural supply chain. From the intricacies of crop planning to the intricacies of financial transactions, ERP infrastructure is reshaping the landscape of Indian agriculture. In this article, we delve into the significance, features, and profound impact of Agriculture ERP infrastructure in propelling India towards a future of sustainable and technologically-empowered farming.
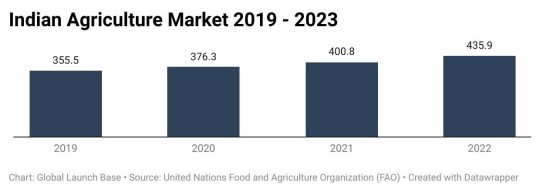
Figure: Indian Agriculture Market Size - 2019 - 2023
India's agricultural sector, a cornerstone of the nation's economy, is undergoing a digital transformation. At the heart of this change lies Agriculture Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. But how ready is the current infrastructure for widespread ERP adoption, and how can ERP companies prepare for the unique landscape of Indian agriculture?
The Current Landscape: A Patchwork of Potential
India's agricultural infrastructure presents a complex picture. While some regions boast modern facilities and tech-savvy farmers, others struggle with limited internet connectivity, fragmented land holdings, and a lack of digital literacy. This digital divide creates a challenge for widespread ERP implementation.
However, there are reasons for optimism. Government initiatives like Digital India and Krishi Megh (Farmers' Cloud) are promoting digital literacy and rural internet connectivity. Additionally, the rise of affordable smartphones and mobile apps is bridging the gap for many farmers.
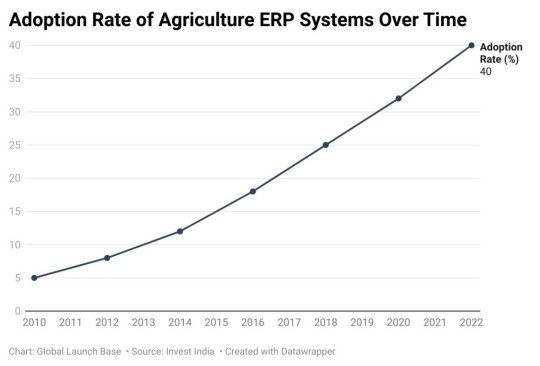
Figure: Adoption Rate of Agriculture ERP Systems Over Time
This figure indicates the percentage of agricultural businesses in India that have adopted ERP systems during each corresponding year.
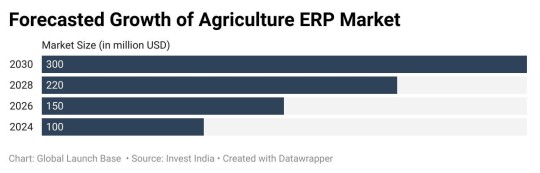
Figure: Forecasted Growth of Agriculture ERP Market
The Need for Agriculture ERP in India
India's agriculture sector has traditionally been characterized by small-scale farming practices, fragmented land holdings, and manual labor. The introduction of ERP systems aims to address several challenges faced by the agricultural community, such as inefficient resource utilization, lack of real-time data, and limited access to market information. By leveraging technology, the Agriculture ERP infrastructure seeks to enhance productivity, increase efficiency, and ultimately boost the income of farmers.
Key Features of Agriculture ERP in India
Crop Planning and Management: ERP systems enable farmers to plan and manage their crops effectively by providing real-time data on weather conditions, soil health, and market demand.
Crop management modules assist in optimizing planting schedules, crop rotations, and resource allocation, leading to improved yield and reduced wastage.
Supply Chain Integration: Seamless integration of the supply chain is a critical component of Agriculture ERP. It facilitates efficient coordination between farmers, suppliers, distributors, and retailers.
Real-time tracking of produce from farm to market ensures transparency, reduces wastage, and minimizes losses during transportation.
Financial Management: ERP infrastructure helps farmers manage their finances by providing tools for budgeting, expense tracking, and revenue forecasting.
Access to credit facilities and insurance options is enhanced, empowering farmers to make informed financial decisions and mitigate risks.
Market Intelligence: The ERP system gathers and analyzes market data, enabling farmers to make informed decisions based on current market trends and demand.
Access to market intelligence helps farmers negotiate better prices and explore new markets for their produce.
Data Analytics and Precision Farming: Data analytics tools incorporated in Agriculture ERP systems enable farmers to make data-driven decisions.
Precision farming techniques, aided by ERP infrastructure, allow for optimized resource utilization, leading to increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Benefits and Impact
Increased Productivity: By providing farmers with timely and relevant information, Agriculture ERP infrastructure contributes to enhanced productivity through optimized crop planning and resource utilization.
Improved Profitability: Efficient supply chain management, access to market information, and financial planning tools contribute to increased profitability for farmers.
Sustainable Agriculture: Precision farming practices promoted by ERP systems promote sustainable agriculture by minimizing resource wastage and environmental impact.
Empowering Farmers: Agriculture ERP infrastructure empowers farmers by providing them with the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions, access financial resources, and navigate the market effectively.
Challenges and Future Prospects While Agriculture ERP infrastructure holds immense potential, challenges such as the digital divide, infrastructure limitations, and resistance to technology adoption must be addressed. The government, private sector, and agricultural communities need to collaborate to overcome these hurdles and ensure the widespread adoption and success of ERP systems in Indian agriculture.
In conclusion, the implementation of Agriculture ERP infrastructure in India represents a significant step towards modernizing the agricultural sector. By leveraging technology to enhance efficiency, productivity, and sustainability, these systems play a crucial role in transforming traditional farming practices and improving the livelihoods of millions of farmers across the country. As India continues on its path of agricultural development, the integration of ERP infrastructure will remain a key driver of positive change in the sector.
Challenges of India's Infrastructure Landscape
India, as one of the world's fastest-growing economies, faces a myriad of challenges in its infrastructure development. Despite significant progress in recent decades, the country grapples with persistent obstacles that hinder the efficient functioning and expansion of its infrastructure networks. Understanding these challenges is crucial for policymakers, investors, and stakeholders to devise effective strategies for addressing them and unlocking India's full growth potential.
1. Funding and Financing Constraints: One of the primary challenges facing Indian infrastructure development is the availability of funding and financing. Infrastructure projects often require substantial capital investment, and securing long-term financing on favorable terms remains a significant hurdle. Issues such as regulatory uncertainties, project delays, and high debt burdens deter both domestic and foreign investors, constraining the pace of infrastructure expansion.
2. Bureaucratic Red Tape and Regulatory Hurdles: India's bureaucratic processes and regulatory frameworks are often cited as major impediments to infrastructure development. Cumbersome approval processes, overlapping jurisdictional authorities, and complex legal requirements contribute to project delays and cost overruns. Streamlining regulatory procedures, enhancing transparency, and promoting ease of doing business are essential for expediting infrastructure projects and attracting investment.
3. Land Acquisition and Rehabilitation Challenges: Land acquisition remains a contentious issue in India, particularly for large-scale infrastructure projects. Conflicting land ownership claims, inadequate compensation mechanisms, and resistance from local communities pose significant hurdles to acquiring land for infrastructure development. Moreover, the displacement of people and disruption of livelihoods necessitate comprehensive rehabilitation and resettlement policies to mitigate social tensions and ensure equitable development outcomes.
4. Technological and Innovation Gaps: While India has made strides in adopting modern technologies and innovation in certain sectors, there remains a significant gap in infrastructure development. Outdated construction methods, inadequate use of digital technologies, and limited innovation in project design and execution hamper the efficiency and quality of infrastructure projects. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) can enhance project management, optimize resource utilization, and improve infrastructure resilience.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Concerns: With rapid urbanization and industrialization, India faces mounting environmental challenges associated with infrastructure development. The depletion of natural resources, air and water pollution, and ecological degradation threaten both human well-being and ecosystem integrity. Balancing the imperative for infrastructure expansion with environmental sustainability requires integrating green infrastructure solutions, promoting renewable energy sources, and implementing stringent environmental regulations and standards.
6. Transportation and Connectivity Bottlenecks: Inadequate transportation infrastructure and connectivity remain significant barriers to India's economic growth and development. Congested roadways, insufficient public transportation systems, and underdeveloped rail and air networks impede the efficient movement of goods and people. Addressing transportation bottlenecks requires investments in road and rail infrastructure, last-mile connectivity solutions, and multimodal transportation hubs to enhance mobility and facilitate trade and commerce.
7. Urbanization and Infrastructure Deficits: India's rapid urbanization places immense pressure on urban infrastructure systems, exacerbating existing deficits in housing, water supply, sanitation, and public services. The proliferation of informal settlements, inadequate urban planning, and insufficient infrastructure investments contribute to urban sprawl, congestion, and social inequalities. Adopting integrated urban development strategies, promoting affordable housing initiatives, and investing in smart city infrastructure are imperative for creating sustainable and inclusive urban environments.
Addressing the multifaceted challenges of India's infrastructure landscape requires concerted efforts from government agencies, private sector entities, civil society organizations, and other stakeholders. Embracing innovation, fostering public-private partnerships, streamlining regulatory processes, and prioritizing sustainability are essential for overcoming barriers to infrastructure development and unlocking India's vast growth potential. By addressing these challenges holistically and collaboratively, India can build resilient, inclusive, and sustainable infrastructure networks that propel the nation towards a prosperous future.
Are Indian Farmers ready for using ERP?
The readiness of Indian farmers to adopt Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems varies based on several factors, including technological literacy, access to resources, and awareness of the benefits of digital solutions. While some farmers may be ready and willing to embrace ERP technology, others may face significant barriers to adoption. Let's explore both perspectives:
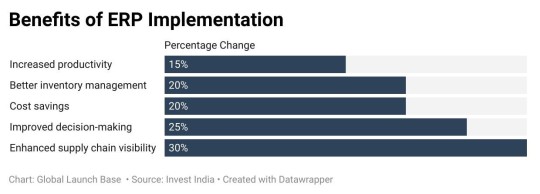
Figure: Benefits of ERP Implementation
Reasons for Optimism:
Government Initiatives: Digital India and Krishi Megh are bridging the digital divide and promoting rural internet access and digital literacy.
Mobile Revolution: Affordable smartphones and mobile apps are making information and tools more accessible to farmers.
Early Adopters: Progressive farmers are already reaping the benefits of ERP, demonstrating its potential.
The Reality:
Indian farmers are at various stages of ERP readiness. Large-scale, tech-savvy farms are prime candidates, while smaller farms might require more accessible and affordable solutions.
Factors Contributing to Readiness
Technological Awareness: Many Indian farmers, particularly those in regions with better access to information and communication technologies (ICTs), are increasingly familiar with digital tools and platforms. They may already use mobile applications for accessing weather forecasts, market prices, and agricultural information, indicating a level of readiness for more advanced technological solutions like ERP.
Education and Training: Farmers who have received formal education or vocational training in agriculture and allied fields are more likely to understand the benefits of ERP systems and possess the necessary skills to operate them effectively. Training programs conducted by government agencies, NGOs, and private organizations can enhance farmers' readiness by imparting knowledge about ERP functionalities and best practices.
Access to Connectivity: The availability of reliable internet connectivity, particularly in rural areas, is crucial for the successful adoption of ERP systems. With the increasing penetration of mobile networks and initiatives like BharatNet aimed at expanding broadband connectivity to rural India, farmers have greater access to online resources and digital platforms, laying the foundation for ERP adoption.
Market Integration: Farmers engaged in commercial agriculture and value-added activities are more likely to recognize the importance of efficient management practices and technology-driven solutions for enhancing productivity and profitability. ERP systems offer features such as supply chain management, market analysis, and financial tracking, which can benefit farmers seeking to optimize their operations and access broader markets.
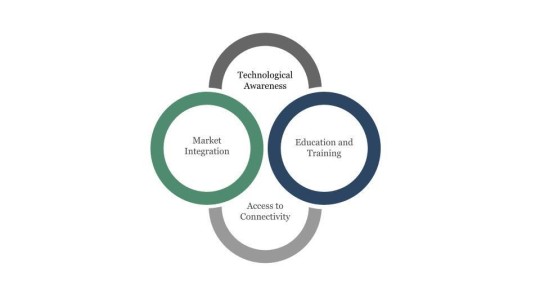
Challenges to Adoption:
Cost and Affordability: ERP implementation involves upfront costs for software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and training, which may be prohibitive for smallholder farmers with limited financial resources. While government subsidies or financing schemes can alleviate some of the financial burden, affordability remains a significant barrier to adoption for many farmers.
Complexity and Technical Support: ERP systems are sophisticated software solutions that require technical expertise for installation, customization, and maintenance. Many farmers, especially those with limited formal education or digital literacy, may find ERP interfaces complex and challenging to navigate without adequate technical support and guidance.
Infrastructure and Connectivity: In rural areas with poor infrastructure and limited internet connectivity, accessing and using ERP systems may be impractical or unreliable. Even with the increasing availability of mobile internet services, connectivity issues persist in remote agricultural regions, hindering farmers' ability to leverage cloud-based ERP solutions effectively.
Cultural and Behavioral Factors: Farmers' attitudes towards technology and traditional farming practices can influence their readiness to adopt ERP systems. Resistance to change, skepticism about the benefits of digitalization, and reliance on customary farming methods may impede the uptake of ERP technology, particularly among older or more conservative farmers.
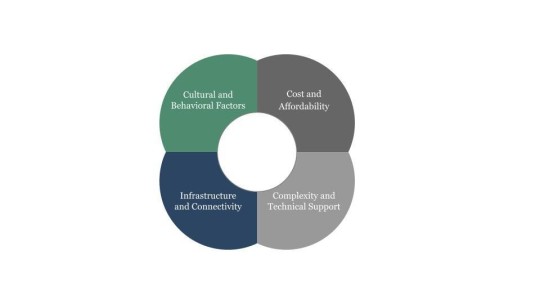
ERP Companies: Cultivating Solutions for Indian Needs
ERP companies can play a crucial role in accelerating ERP adoption in Indian agriculture. Here's how:
Localization is Key: Develop user interfaces and functionalities in local languages for better accessibility.
Mobile-First Approach: Prioritize mobile app development for real-time data access and on-field management.
Offline Functionality: ERP systems should function even in areas with limited internet connectivity.
Scalability and Affordability: Offer modular solutions with varying functionalities to cater to different farm sizes and budgets.
Partnerships: Collaborate with government agencies, NGOs, and agricultural institutions to promote digital literacy and build trust in ERP technology.
The Road Ahead: A Symbiotic Future
The future of Indian agriculture is one where ERP systems seamlessly integrate with a developing infrastructure. By embracing localization, mobility, and affordability, ERP companies can empower Indian farmers to make data-driven decisions, improve efficiency, and navigate the path towards a more sustainable and profitable future.
This collaborative effort between the government, ERP companies, and farmers has the potential to revolutionize Indian agriculture, ensuring food security for a growing nation and economic prosperity for its rural population.
How companies can expand in India’s unique ERP infrastructure landscape:
Understanding the Infrastructure:
Research and Analysis: Conduct in-depth research on the current state of internet connectivity, digital literacy levels, and farm sizes across different regions of India. Partner with local agricultural institutions or consulting firms to gain insights.
Focus on Regions: Identify regions with better digital infrastructure and higher tech adoption among farmers. This can help prioritize initial market entry and solution development.
Tailoring Your ERP Approach:
Localization is Paramount: Develop user interfaces and training materials in local languages to overcome language barriers and improve accessibility.
Mobile-First Development: Prioritize building mobile applications for your ERP system. This caters to the growing smartphone usage among farmers and allows for real-time data access and on-field management.
Offline Functionality: Ensure your ERP system functions even in areas with limited internet connectivity. This could involve data caching or offline modules for core functionalities.
Modular and Scalable Solutions: Offer various service tiers within your ERP system. This allows farmers with smaller land holdings or lower budgets to access basic functionalities, with the option to upgrade as their needs evolve.
Partnerships are Key: Collaborate with Indian companies or organizations. This can include:Technology Providers: Partnering with local IT firms can help integrate your ERP with existing agricultural platforms or government initiatives.Agricultural Institutions: Collaborate with agricultural universities or research bodies to offer training programs and build trust in your ERP technology among farmers.Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs): Partnering with NGOs can help reach smallholder farmers and integrate them into the digital agricultural ecosystem.
Additional Considerations:
Data Privacy and Security: Ensure your ERP system complies with Indian data privacy regulations to build trust with farmers.
Focus on Value Addition: Go beyond basic functionalities. Highlight how your ERP system offers unique value propositions like improved yield management, market access, or financial planning tools.
By understanding the evolving infrastructure and tailoring your ERP solutions, foreign companies can position themselves for success in the Indian agricultural market. Remember, collaboration with local players and a focus on user-friendliness will be crucial for long-term growth.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#AgricultureERP hashtag#IndianAgricultureTechnology#hashtag#FarmManagementSoftware hashtag#AgriculturalDigitization#ERPSolutionsForFarmers hashtag#IndianAgriculturalInnovation#DigitalTransformationInFarming hashtag#AgriculturalSoftwareSolutions#ERPImplementationInAgriculture hashtag#AgriTechAdvancementsInIndia hashtag#indianfarmers hashtag#indianfarmer hashtag#india hashtag#erp hashtag#agriculture hashtag#indianews
0 notes
Text
International expansion of Indian startups
Written By: Jagriti Shahi
In recent years, the Indian startup ecosystem has experienced a monumental transformation, transcending geographical boundaries to mark its presence on the global stage. As the world witnesses the rise of India as a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, the narrative of Indian startups is no longer confined to the domestic market but extends far beyond, with international expansion emerging as a pivotal strategy for growth and sustainability.
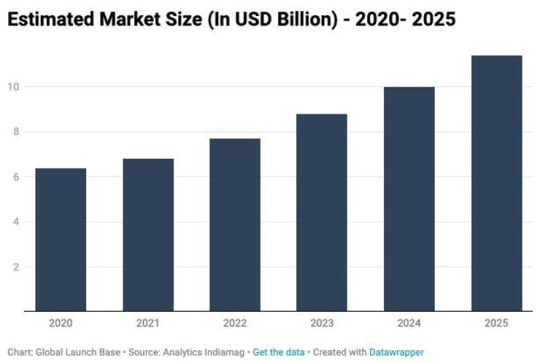
Figure: Estimated Market Size (In USD Billion)
The journey of Indian startups venturing into international markets is a testament to their resilience, adaptability, and unwavering ambition. Fueled by a confluence of factors such as technological advancements, favorable government policies, access to capital, and a burgeoning talent pool, these startups have embarked on a quest to conquer new territories, unlock untapped opportunities, and establish themselves as formidable players in the global arena. One of the key drivers propelling the international expansion of Indian startups is the relentless pursuit of innovation. Armed with cutting-edge technologies and disruptive business models, these startups are disrupting traditional industries and redefining paradigms across sectors such as e-commerce, fintech, healthtech, and edtech. By leveraging India's prowess in fields like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, these startups are not only addressing the needs of the domestic market but also catering to the evolving demands of international consumers and businesses. Moreover, the increasing globalization of markets and the growing acceptance of Indian brands globally have provided a fertile ground for expansion. Indian startups are capitalizing on this trend by strategically targeting markets with high growth potential, favorable regulatory environments, and cultural synergies. By customizing their products and services to suit local preferences, adapting to regulatory frameworks, and establishing robust distribution networks, these startups are gaining a competitive edge and winning the trust of international consumers.
Figure: Startups Going Abroad 2018-2022
India boasts the world's third-largest startup ecosystem, with over 60,000 active startups across diverse sectors like fintech, edtech, and SaaS. This robust ecosystem, fostered by factors like rising internet penetration and government initiatives, has instilled a sense of global aspiration in many startups. They are no longer content with just serving the domestic market; they are looking to take their innovative solutions to the world stage.
Rising internet penetration: Reaching over 850 million users by 2023, providing a massive domestic market and a springboard for international ambitions.
Government initiatives: Schemes like Startup India and Digital India provide support through funding, infrastructure, and regulatory reforms.
Changing demographics: India's young population, with its increasing disposable income and digital literacy, creates a fertile ground for innovation and market growth.
This combination of factors has instilled a sense of global aspiration in many startups. They are no longer content with just serving the domestic market; they are looking to take their innovative solutions to the world stage, hoping to:
Scale their user base and revenue: Expanding to new markets allows them to reach a much larger customer base, significantly increasing potential returns.
Attract global talent and partnerships: The international stage offers the opportunity to collaborate with established players and attract top talent from around the world.
Build global brand recognition: Gaining international recognition can enhance their brand value and attract further investments.
Funding Fuels Expansion:
The availability of funding plays a crucial role in enabling international expansion. India has witnessed a significant rise in venture capital and private equity investments, exceeding $25 billion in 2022 despite global headwinds. This influx of capital empowers startups to invest in resources, talent, and infrastructure necessary for navigating the complexities of international markets.
Market research and analysis: Understanding the specifics of new markets, including consumer behavior, regulatory landscape, and competitor analysis.
Localization efforts: Adapting products and services to suit the cultural nuances, language, and regulatory demands of new markets.
Building local teams: Establishing presence in target markets with skilled professionals who understand the local context and dynamics.
Conduct Market Research before Expanding into New Markets
Market research is the process of gathering and analyzing information about a market, including its customers, competitors, and industry trends. This information is used to make informed business decisions, such as identifying new opportunities, understanding customer needs, and developing effective marketing strategies.
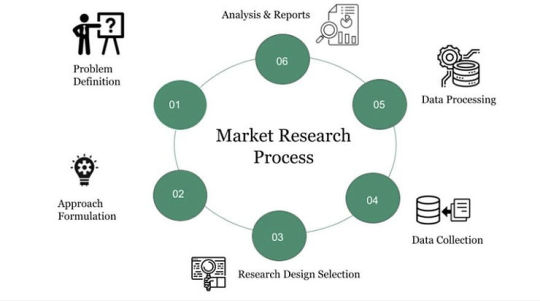
Figure 2: Market Research Process
Step 1. Define the Problem and Translate It into Research Objectives: The first step is to define the problem or issue that the market research will address. This includes identifying the research questions that need to be answered and the specific goals and objectives of the research.
Step 2. Formulate the Approach: Once the research objectives are defined, the next step is to formulate the research approach. This involves identifying the type of research to be conducted (e.g., qualitative or quantitative), the methods and techniques that will be used to collect data, and the resources needed to carry out the research.
Step 3. Define The Research Design: The research design is the framework that guides the data collection and analysis process. It includes identifying the target population, selecting the sampling method, developing the research instruments (e.g., surveys, interviews, focus groups), and determining the data analysis techniques to be used.
Step 4. Collect Data: This step involves actually collecting the data using the methods and instruments defined in the research design. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, focus groups, or other data collection methods.
Step 5. Data Processing: After the data has been collected, it needs to be processed and organized for analysis. This may include cleaning the data, coding it for analysis, and entering it into a database or statistical software program.
Step 6. Analyze & Report: The final step is to analyze the data and prepare a report of the research findings. This may involve using statistical techniques to identify patterns and trends in the data, summarizing the results in tables and charts, and drawing conclusions based on the research objectives. The report may also include recommendations for business decisions based on the research findings.
Figure 3: International Expansion Entry Modes
Exporting: This involves selling products or services directly to customers in a foreign market. Exporting can be done through distributors, agents, or direct sales.
Licensing and Franchising: Licensing and franchising involve giving another company the right to use your company's intellectual property or business model in exchange for a fee or royalty. This allows for rapid expansion into new markets without the need for large investments in infrastructure.
Joint Ventures: A joint venture involves forming a new company with a partner in the foreign market. This allows for shared investment and risk, as well as local expertise and knowledge.
Strategic Alliances: Strategic alliances involve forming a partnership with another company in the foreign market to achieve shared goals, such as developing new products or entering new markets.
Acquisitions and Mergers: Acquisitions and mergers involve buying or merging with an existing company in a foreign market. This allows for immediate access to existing infrastructure and customers.
Pilot Projects: Pilot projects involve testing the waters of a new market by launching a small-scale project before committing to a larger investment. This can help minimize risk and provide valuable insights into the viability of the market.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Indian startup ecosystem has the potential to disrupt the global landscape, several challenges lie ahead. Adapting to diverse regulatory environments, attracting skilled talent across borders, and understanding varying cultural nuances are just a few hurdles to overcome.
Adapting to diverse regulatory environments: Navigating the legalities and compliance requirements of different countries can be complex and time-consuming.
Attracting skilled talent across borders: Competing with established players for skilled international talent can be challenging, requiring attractive compensation packages and visa considerations.
Understanding varying cultural nuances: Adapting marketing strategies, product features, and customer service approaches to resonate with diverse cultures can be crucial for success.
However, these challenges are coupled with significant opportunities:
Emerging markets as fertile ground: With growing middle classes and increasing internet access, emerging markets offer lucrative opportunities for Indian startups to cater to underserved populations.
Established markets for collaboration: Leading economies present the potential for collaboration and knowledge sharing, allowing Indian startups to learn from established players and accelerate innovation.
Building global brand recognition: Successfully navigating international markets can enhance brand value and create a domino effect for further global expansion.
However, these challenges are coupled with significant opportunities. Emerging markets, with their growing middle class and increasing internet access, present lucrative opportunities for Indian startups. Additionally, established markets offer the potential for collaboration and knowledge sharing, further accelerating innovation.
Leading the Way: Success Stories of Indian Expansion:
Several Indian startups have already made their mark on the global stage. Leading examples include:
Ola Electric: This ride-hailing company has expanded its services to Australia, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom, with plans for further international presence.
Freshworks: This SaaS company boasts a global footprint, with offices in the US, Europe, and Australia, offering customer support software to enterprises worldwide.
Zomato: A food delivery platform that has grown significantly in India and expanded to international markets like the United Arab Emirates. Zomato offers a convenient way for users to order food from a wide variety of restaurants.
InMobi: An ad tech startup that offers mobile advertising and content discovery solutions. InMobi has a global presence and supports businesses in launching captivating ad campaigns across various mobile platforms.
Lenskart: Founded in 2010, Lenskart is an online eyewear retailer offering prescription glasses and sunglasses. The company has expanded to Singapore, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States, providing customers with a convenient and affordable way to purchase eyewear.
Druva: Founded in 2008, Druva is a cloud-based data protection and management company. The company has a global presence with offices in the United States, Europe, and Asia, serving businesses of all sizes.
Zoho Corporation: Founded in 1996, Zoho Corporation is a software development company that offers a wide range of cloud-based business applications, including CRM, project management, and accounting software. Zoho has a global customer base and offices in over 25 countries.
The Road Ahead:
The international expansion of Indian startups is a promising development, not only for the startups themselves but also for the Indian economy's global competitiveness and knowledge exchange. As more startups navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities, we can expect to see Indian innovation make a significant impact on the global stage in the years to come.
The Indian economy: Increased global presence translates to higher foreign investment, job creation, and knowledge transfer.
Global innovation: Indian startups can offer unique solutions and perspectives, contributing to diverse approaches to solving global challenges.
Conclusion
The international expansion of Indian startups is a story still being written. While challenges remain, the potential for growth and impact is undeniable. With continued support from the government, access to funding, and a willingness to adapt and innovate, Indian startups are poised to become key players on the global stage. Their journey not only promises to benefit the individual companies but also contribute to the economic growth, technological advancement, and global collaboration on a larger scale. By embracing their global aspirations, Indian startups can truly make a mark on the world, shaping the future of technology and innovation across borders.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#hashtag#IndianStartups hashtag#InternationalExpansion hashtag#GlobalGrowth hashtag#narendramodi hashtag#newindia hashtag#EmergingMarkets hashtag#StartupEcosystem hashtag#CrossBorderExpansion hashtag#MarketPenetration hashtag#GlobalReach hashtag#BusinessExpansionStrategies#StartupSuccessStories hashtag#OverseasMarkets hashtag#EntrepreneurshipTrends#GlobalMarketEntry hashtag#StartupGlobalization hashtag#InternationalEntrepreneurship
0 notes
Text
Collaborative Innovation in Startup Ecosystems Through Incubation and Acceleration

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
In the dynamic landscape of entrepreneurship, where ideas spark and innovation flourishes, the journey from conception to impact is often paved with challenges. Yet, within the vibrant ecosystem of startups, there exists a vital mechanism that nurtures these fledgling ideas into scalable ventures: incubation and acceleration programs. These programs serve as catalysts for entrepreneurial success, providing invaluable resources, mentorship, and networking opportunities to early-stage startups. By fostering collaboration and innovation, they play a pivotal role in shaping the future of industries and economies.
The startup landscape is a bustling arena where creativity intersects with ambition, and where bold visionaries dare to disrupt the status quo. However, amidst the excitement and promise, startups face a myriad of obstacles on their path to success. From securing funding and navigating regulatory hurdles to building a viable product and acquiring customers, the challenges can seem insurmountable for aspiring entrepreneurs. It is here that incubation and acceleration programs emerge as beacons of support, offering a lifeline to startups as they navigate the turbulent waters of entrepreneurship.
Incubation: Nurturing the Seed of Innovation
At the heart of any successful startup ecosystem lies the concept of incubation. Incubators serve as nurturing environments where entrepreneurs can develop their ideas, validate their business models, and refine their strategies under the guidance of seasoned mentors and industry experts.
Within these incubation programs, startups are provided with more than just physical space; they are immersed in a supportive ecosystem designed to foster growth and innovation. Mentors, often seasoned entrepreneurs or industry experts, offer invaluable guidance, drawing from their own experiences to help startups navigate the complexities of launching a business. These mentors provide not only strategic advice but also emotional support, serving as confidants during the inevitable ups and downs of the entrepreneurial journey. Moreover, incubation programs often offer access to a wide range of resources that startups might not have on their own. This includes legal and financial advice, assistance with market research and product development, and introductions to potential partners or customers. By providing these resources, incubators help startups overcome common barriers to success and accelerate their path to market. However, perhaps the most significant benefit of incubation programs lies in the sense of community they cultivate. In shared workspaces filled with like-minded entrepreneurs, startups have the opportunity to collaborate, learn from one another, and form valuable connections. This sense of camaraderie not only reduces the isolation often felt by founders but also fosters a culture of innovation where ideas can freely flow and evolve.
In addition to the tangible resources and support provided, incubation programs also play a crucial role in helping startups validate their ideas and refine their business models. Through workshops, pitch sessions, and access to potential customers, startups are able to test their assumptions in a real-world environment and make necessary adjustments based on feedback. This iterative process of experimentation and learning is essential for startups to develop viable products or services that meet the needs of their target market. In essence, incubation programs serve as the fertile soil in which the seeds of innovation can take root and flourish. By providing the necessary support, resources, and community, they empower entrepreneurs to turn their bold ideas into reality and embark on the journey of building successful and sustainable businesses.

Figure: Incubation Process
Imagine an incubator as a fertile ground where nascent ideas take root. By offering a supportive environment, incubators provide early-stage startups with the critical resources they need to develop a solid foundation. This includes:
Shared Workspace and Infrastructure: Incubators offer affordable access to office space, meeting rooms, technology infrastructure, and other amenities, reducing initial costs and fostering connections with fellow entrepreneurs.
Mentorship and Guidance: Seasoned experts and industry professionals mentor startups, offering invaluable advice on business strategy, market validation, fundraising, and overcoming hurdles.
Networking Opportunities: Incubators cultivate a collaborative atmosphere, connecting startups with potential investors, partners, and customers, expanding their reach and visibility.
Skill Development Workshops: Tailored workshops and training programs equip entrepreneurs with essential skills in areas like marketing, finance, legal compliance, and pitching, enhancing their capabilities.
Seed Funding: Some incubators provide access to small seed funding grants or connect startups with potential angel investors, fueling their initial growth spurt.
This nurturing environment allows startups to validate their ideas, refine their business models, and build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) before venturing into the competitive market.
Acceleration: Turbocharging Growth and Expansion
While incubation lays the groundwork for startups, acceleration programs propel them forward at a rapid pace. Accelerators typically operate on a fixed-term basis, offering intensive mentorship, networking opportunities, and sometimes seed funding in exchange for equity. Acceleration programs are designed to turbocharge the growth and expansion of startups, focusing on key areas such as product-market fit, customer acquisition, and scalability. Through a structured curriculum tailored to the specific needs of each cohort, accelerators provide startups with the tools and resources needed to overcome common growth challenges and achieve their full potential. One of the primary benefits of acceleration programs is the access to a vast network of mentors, investors, and industry experts. These seasoned professionals provide invaluable guidance and support, offering insights gained from years of experience in building and scaling successful businesses. Whether it's refining the startup's go-to-market strategy, optimizing its sales and marketing efforts, or navigating complex regulatory landscapes, mentors play a crucial role in helping startups overcome obstacles and seize opportunities.

Figure: Acceleration Programme
In addition to mentorship, acceleration programs often offer access to potential customers and strategic partners. This can be invaluable for startups looking to validate their products or services, secure pilot projects, or scale their customer base. By facilitating introductions and fostering partnerships, accelerators help startups accelerate their growth trajectory and establish a foothold in their target markets.

Figure: Application Process
Furthermore, acceleration programs provide startups with exposure to investors, increasing their chances of securing funding to fuel their growth. Demo days and pitch events organized by accelerators offer startups the opportunity to showcase their progress and pitch their vision to a curated audience of investors. This exposure not only helps startups raise capital but also validates their business model and enhances their credibility in the eyes of potential investors.
Perhaps most importantly, acceleration programs instill a sense of urgency and accountability in startups, challenging them to iterate quickly, execute decisively, and achieve measurable results within a compressed time frame. By setting ambitious goals and providing ongoing support and feedback, accelerators push startups out of their comfort zones and encourage them to strive for excellence.
In essence, acceleration programs serve as rocket boosters propelling startups towards success, helping them achieve in months what might otherwise take years. By providing access to mentorship, resources, and opportunities, accelerators empower startups to scale rapidly, disrupt industries, and create lasting impact in the world.
Startups graduate from the incubator phase, they often step into the accelerator program, designed to propel their growth trajectory. Accelerators offer:
Intensive Mentorship and Coaching: Renowned advisors and industry leaders closely collaborate with startups, providing tailored guidance and accelerating their decision-making process.
Structured Programs and Milestones: Accelerators follow a defined curriculum with clear milestones and deadlines, encouraging focused progress and rapid iteration.
Access to Investor Networks: The extensive networks of accelerators connect startups with venture capitalists, angel investors, and other funding sources, enabling them to secure capital for scaling their operations.
Industry-Specific Expertise: Specialized accelerators cater to specific sectors like FinTech, MedTech, or CleanTech, offering targeted expertise and industry connections.
Demo Days and Investor Pitches: Accelerator programs culminate in high-profile demo days where startups pitch their ventures to a curated audience of investors, media, and potential partners, raising their visibility and attracting funding.
Through this immersive experience, startups gain the momentum and resources necessary to scale their operations, acquire customers, and establish a strong market presence.
The Power of Collaboration and Community
What sets successful startup ecosystems apart is the spirit of collaboration and community that permeates through them. Incubators and accelerators serve as hubs where entrepreneurs, investors, and industry leaders converge to exchange ideas, forge partnerships, and drive innovation forward.
Within these vibrant communities, startups find more than just support—they find a network of like-minded individuals who share their passion for entrepreneurship and their determination to make a difference. Through shared workspaces, networking events, and collaborative projects, startups have the opportunity to connect with peers facing similar challenges and learn from their experiences. This sense of camaraderie not only fosters a supportive environment but also stimulates creativity and inspires innovation.
Moreover, the power of collaboration extends beyond the walls of individual startups to encompass the broader ecosystem. Incubators and accelerators often collaborate with universities, research institutions, and corporate partners to leverage their resources and expertise. This collaborative approach not only enriches the entrepreneurial experience but also fosters cross-pollination of ideas and drives collective progress.
In addition to formal collaborations, startup communities also thrive on informal interactions and serendipitous encounters. Whether it's striking up a conversation over coffee in the communal kitchen or brainstorming ideas at a networking event, these spontaneous moments often lead to unexpected insights, partnerships, and opportunities. It is this sense of serendipity and openness to collaboration that fuels the dynamism of startup ecosystems and accelerates the pace of innovation.
Furthermore, startup communities play a crucial role in nurturing diversity and inclusion within the entrepreneurial ecosystem. By providing a welcoming and inclusive environment where individuals from diverse backgrounds feel valued and supported, these communities foster creativity and drive innovation. Moreover, diverse teams are more likely to challenge conventional thinking, leading to more robust solutions and better outcomes.
Ultimately, the power of collaboration and community lies in its ability to amplify the impact of individual startups and drive collective progress. By fostering connections, sharing knowledge, and pooling resources, startup communities enable entrepreneurs to achieve more together than they ever could alone. It is this spirit of collaboration that transforms startup ecosystems into engines of innovation and drives positive change in the world.
Beyond individual support, both incubators and accelerators foster a collaborative innovation ecosystem where startups learn from and build upon each other's strengths. This includes:
Peer-to-Peer Learning: Sharing experiences, challenges, and solutions within the cohort fosters a supportive community where entrepreneurs can learn from each other's successes and failures.
Joint Ventures and Partnerships: Collaboration between startups in different stages can lead to innovative solutions and mutually beneficial partnerships.
Cross-Pollination of Ideas: Interaction with diverse mentors, advisors, and investors exposes startups to a wide range of perspectives, sparking new ideas and approaches.
Industry and Academic Collaborations: Partnerships with universities, research institutions, and established companies in the sector unlock access to cutting-edge technology, talent, and market knowledge.
This collaborative culture creates a vibrant innovation ecosystem where the sum is greater than its parts, accelerating the collective success of startups and driving overall economic growth.
Driving Impact: Transforming Ideas into Reality
Ultimately, the true measure of success for incubation and acceleration programs lies in their ability to translate ideas into tangible impact. Beyond just launching successful businesses, these programs have the power to drive societal change, create jobs, and catalyze economic growth.
By nurturing a diverse range of startups across various industries, incubators and accelerators contribute to the fabric of innovation, fueling breakthroughs that have the potential to shape the future. Whether it's revolutionizing healthcare, disrupting traditional industries, or addressing pressing global challenges, the impact of collaborative innovation reverberates far beyond the confines of individual startups.
By nurturing promising ideas, fostering collaboration, and providing crucial resources, incubation and acceleration programs play a pivotal role in:
Boosting Economic Growth: Successful startups create jobs, generate revenue, and contribute to technological advancements, fueling economic prosperity.
Addressing Global Challenges: Innovative solutions developed by startups can tackle pressing issues like climate change, healthcare, and social inequality, driving positive change.
Empowering Entrepreneurs: These programs equip individuals with the skills and knowledge to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams, fostering a culture of innovation and self-reliance.
Building Vibrant Communities: Thriving startup ecosystems attract talent, investment, and global attention, revitalizing communities and shaping the future of cities.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of entrepreneurship, incubation and acceleration programs serve as beacons of support and guidance for aspiring founders. By providing a fertile ground for ideas to flourish and a platform for collaboration to thrive, these programs play a crucial role in driving innovation and fostering economic growth.
As we look towards the future, the importance of nurturing and empowering the next generation of entrepreneurs cannot be overstated. By investing in incubation and acceleration programs, we not only cultivate a culture of innovation but also pave the way for a brighter, more prosperous tomorrow. From idea to impact, the journey of entrepreneurship is one that is best traveled together, fueled by collaboration, creativity, and a shared commitment to driving positive change.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#CollaborativeInnovation hashtag#StartupEcosystems hashtag#IncubationPrograms#hashtag#AccelerationPrograms hashtag#StartupCollaboration hashtag#InnovationHubs#EntrepreneurialEcosystems hashtag#CoCreationInStartups hashtag#IncubatorsAndAccelerators hashtag#CollaborativeEntrepreneurship#StartupPartnerships hashtag#InnovationNetworks hashtag#CoworkingSpaces#TechIncubators hashtag#StartupSupportSystems
0 notes
Text
Indian Recycle Industry of Electronic Goods
Written By: Jagriti Shahi

Introduction
In an era dominated by technological advancement, the rapid evolution of electronic devices has led to a consequential surge in electronic waste (e-waste) worldwide. From smartphones and laptops to household appliances and industrial machinery, the proliferation of electronic goods has revolutionized how we live, work, and communicate. In India, a country witnessing robust growth in its technological landscape, the management of electronic waste has emerged as a critical challenge, necessitating innovative solutions and sustainable practices.
As India's economy continues to flourish and its population embraces digital connectivity, the demand for electronic gadgets has reached unprecedented levels. The country's burgeoning middle class, coupled with the government's ambitious Digital India initiative, has accelerated the adoption of smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices across urban and rural landscapes alike. While this technological leap has undoubtedly empowered millions, it has also led to a corresponding increase in electronic waste generation, posing significant environmental and health risks if not managed effectively.
Amidst this backdrop of rapid technological progress and escalating e-waste concerns, the Indian recycling industry of electronic goods has emerged as a beacon of sustainability and innovation. This industry encompasses a diverse ecosystem of stakeholders, including formal recyclers, informal scrap dealers, government agencies, and technology innovators, all working towards the common goal of responsibly managing electronic waste while harnessing its latent value.
The Emergence of the Indian Recycling Industry
Acknowledging the pressing need for effective e-waste management, India has witnessed the rise of a dynamic recycling industry. This sector encompasses a wide array of stakeholders, including formal recyclers, informal scrap dealers, government agencies, and technology innovators, all working towards the common goal of responsibly managing electronic waste while harnessing its latent value.
Formal recyclers in India have made significant strides in adopting environmentally sustainable practices. These entities employ advanced technologies and standardized processes to dismantle, segregate, and recycle electronic waste efficiently. By adhering to stringent environmental and occupational health standards, formal recyclers ensure the safe handling and disposal of hazardous materials, minimizing the risk of environmental contamination and public health hazards.
Figure: Growth of the Recycling Industry in India
In parallel, informal scrap dealers constitute a significant segment of India's recycling ecosystem, particularly in urban and peri-urban areas. These individuals or small-scale enterprises engage in the collection, dismantling, and resale of electronic waste using rudimentary techniques and manual labor. While informal recyclers play a role in diverting electronic waste from landfills and promoting resource recovery, their operations often lack environmental safeguards and pose risks to worker health and safety.
To address the challenges associated with informal recycling practices, government agencies in India have implemented regulatory frameworks aimed at formalizing and incentivizing responsible e-waste management. The E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016, introduced by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, establish guidelines for the collection, segregation, transportation, and recycling of electronic waste. These rules mandate extended producer responsibility (EPR), requiring manufacturers to manage and finance the environmentally sound disposal of their products at the end of their lifecycle.
Furthermore, the Indian government has launched initiatives to promote public awareness and participation in e-waste recycling efforts. Campaigns such as Swachh Bharat Abhiyan and Clean India Mission emphasize the importance of responsible waste management practices, including the segregation and recycling of electronic waste. By fostering a culture of environmental stewardship and accountability, these initiatives aim to mobilize communities and industries towards sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Innovations in technology and business models have also played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of India's recycling industry. Startups and entrepreneurs are leveraging digital platforms, data analytics, and IoT (Internet of Things) solutions to optimize waste collection, streamline logistics, and track the flow of materials within the recycling supply chain. By harnessing the power of innovation and entrepreneurship, India's recycling industry is poised to unlock new opportunities for efficiency, scalability, and environmental impact.
The emergence of India's recycling industry of electronic goods signifies a paradigm shift towards sustainable waste management practices and circular economy principles. By embracing innovation, regulation, and public participation, India has laid the groundwork for a more resilient and resource-efficient future. As the country continues to navigate the challenges of electronic waste management, collaboration among stakeholders will be paramount in realizing the full potential of the recycling industry to drive economic growth, environmental sustainability, and social wellbeing.
y:
Figure: E-waste Generation in India
India's exponential growth in electronic consumption has translated into a staggering volume of electronic waste generation. The proliferation of electronic gadgets, ranging from smartphones and laptops to household appliances and industrial machinery, has permeated every facet of Indian society. With a population exceeding 1.3 billion and a rapidly expanding middle class, the demand for electronic goods has reached unprecedented levels.
According to a report by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), India generated approximately 3.2 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, with an annual growth rate of 21%. This exponential growth trajectory underscores the urgent need for comprehensive e-waste management strategies that balance environmental preservation with economic prosperity.
The composition of electronic waste in India is diverse and encompasses a wide range of products, including obsolete televisions, refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and electronic toys. Additionally, the proliferation of personal computing devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops has contributed significantly to the e-waste stream. These devices often contain valuable metals and components, making them lucrative targets for recycling and resource recovery.
Furthermore, the lifespan of electronic products in India tends to be relatively short due to factors such as rapid technological obsolescence, frequent upgrades, and shifting consumer preferences. As a result, a significant portion of electronic goods is discarded prematurely, exacerbating the e-waste challenge.
The management of electronic waste poses multifaceted challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, limited awareness among consumers, and the prevalence of informal recycling practices. Without effective intervention, the accumulation of electronic waste not only threatens environmental integrity but also jeopardizes human health and wellbeing.
In light of these challenges, the Indian government has recognized the importance of addressing e-waste management comprehensively. Initiatives such as the Digital India campaign and the Make in India initiative have spurred economic growth and technological innovation but have also underscored the need for sustainable consumption and production practices.
The scale and complexity of India's electronic waste challenge necessitate concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including government agencies, manufacturers, recyclers, and consumers. By adopting a holistic approach that integrates regulatory frameworks, technological innovations, and public awareness campaigns, India can chart a path towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
As India continues its journey towards economic prosperity and technological advancement, the responsible management of electronic waste will play a pivotal role in shaping the nation's environmental footprint and legacy for future generations. Through collaborative action and collective commitment, India can harness the potential of its recycling industry to mitigate environmental degradation, promote resource conservation, and foster sustainable development.
The Indian government is taking steps to formalize the e-waste recycling industry. In 2011, it introduced the E-Waste (Management) Rules, which require manufacturers and brands to take back and recycle their products. However, the implementation of these rules has been slow and uneven.
The Indian electronic goods recycling industry is a complex and rapidly evolving landscape. It is characterized by a mix of formal and informal sectors, with the informal sector currently dominating the market. This has both positive and negative implications, as we will explore below.
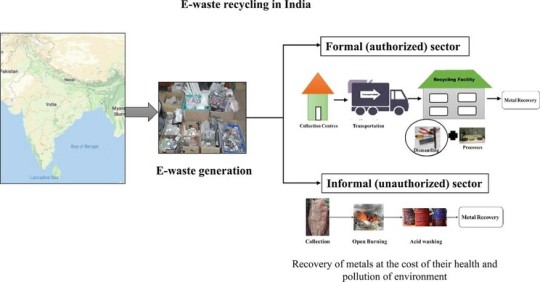
Formal sector:
Registered e-waste recyclers: These are companies that have been authorized by the government to collect, process, and dispose of e-waste in an environmentally sound manner. They typically have invested in sophisticated recycling infrastructure and employ trained personnel.
Advantages: Formal sector recyclers offer a more responsible and sustainable way to recycle e-waste. They are able to extract valuable materials from e-waste, such as metals, plastics, and glass, which can then be used to make new products. This helps to conserve resources and reduce pollution.
Disadvantages: Formal sector recyclers can be more expensive than informal recyclers. This is because they have to comply with stricter environmental regulations and pay for the cost of their infrastructure and personnel.
Informal sector:
Backyard and community-based operations: These are small-scale operations that typically collect e-waste from households and businesses. They then manually extract valuable materials, such as copper and gold, which they sell to scrap metal dealers.
Advantages: Informal recyclers are often able to offer lower prices than formal recyclers. This is because they do not have to comply with the same environmental regulations and do not have the same overhead costs.
Disadvantages: Informal recycling operations often pose serious health and environmental risks. They often burn e-waste to extract metals, which releases toxic fumes into the air. They also often do not properly dispose of hazardous materials, such as lead and mercury, which can contaminate soil and water.
The future of the Indian e-waste recycling industry is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including:
The continued growth of the Indian economy: As the Indian economy grows, so too will the amount of e-waste that is generated. This will create a demand for more e-waste recycling capacity.
Increasing government regulation: The Indian government is likely to continue to introduce stricter regulations on e-waste recycling. This will help to level the playing field between formal and informal recyclers and encourage more responsible recycling practices.
Technological innovation: New technologies are emerging that can make e-waste recycling more efficient and cost-effective. This could help to make formal sector recycling more competitive with informal recycling.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the commendable efforts of the recycling industry, several challenges persist. One major obstacle is the prevalence of informal recycling practices, characterized by rudimentary techniques and inadequate safety measures. These informal recyclers, often operating in unregulated environments, pose environmental and health hazards while contributing to resource wastage.
However, amidst these challenges lie significant opportunities for innovation and growth. The Indian government has introduced several regulatory frameworks to promote responsible e-waste management, including the E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016. These regulations mandate extended producer responsibility (EPR), compelling manufacturers to take accountability for the entire lifecycle of their products, from production to disposal.
Technological Innovations Driving Sustainability
In recent years, technological advancements have played a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of e-waste recycling processes. Innovations such as automated sorting systems, chemical recycling techniques, and modular design approaches have revolutionized the industry, enabling greater resource recovery while minimizing environmental impact.
Furthermore, the advent of blockchain technology holds promise for enhancing transparency and traceability within the recycling supply chain. By leveraging blockchain-enabled platforms, stakeholders can securely track the movement of e-waste throughout its lifecycle, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and promoting ethical practices.
Emerging Indian Companies in the Recycling Industry
Attero Recycling: Attero Recycling is a leading electronic waste management company in India. It specializes in recycling and refurbishing electronic devices, including smartphones, laptops, and televisions, while ensuring environmentally sustainable practices.
Gem Enviro Management Pvt. Ltd.: Gem Enviro Management is a pioneer in the field of electronic waste management and recycling in India. The company offers end-to-end solutions for the collection, dismantling, and recycling of electronic waste, adhering to international standards and regulations.
E-Parisaraa Pvt. Ltd.: E-Parisaraa is a Bangalore-based e-waste management company that provides environmentally responsible solutions for electronic waste recycling. The company focuses on resource recovery and material reuse through advanced recycling processes.
Ecoreco: Ecoreco is an electronic waste management company that offers comprehensive recycling solutions for businesses, households, and government agencies in India. It utilizes state-of-the-art technology and best practices to ensure the safe and sustainable disposal of electronic waste.
Karma Recycling: Karma Recycling is a Delhi-based company that specializes in the refurbishment and resale of used smartphones. The company aims to extend the lifecycle of electronic devices by offering buyback and recycling services, thus reducing electronic waste generation.
Earth Sense Recycle: Earth Sense Recycle is a Mumbai-based e-waste management company that provides collection, recycling, and disposal services for electronic waste. The company focuses on promoting awareness and education about responsible e-waste management practices.
Virogreen India Pvt. Ltd.: Virogreen India is an ISO-certified e-waste management company that offers end-to-end solutions for the recycling and disposal of electronic waste. The company operates across multiple cities in India, catering to both corporate and individual clients.
Greentek Reman Pvt. Ltd.: Greentek Reman is a Hyderabad-based company that focuses on remanufacturing and refurbishing electronic components and devices. The company aims to reduce electronic waste by extending the lifespan of products through repair and reuse initiatives.
The Role of Consumer Awareness
Amidst the ongoing evolution of the recycling industry, consumer awareness remains a crucial factor in driving sustainable change. Educating consumers about the importance of responsible e-waste disposal, encouraging product repair and refurbishment, and promoting the purchase of eco-friendly electronics are vital steps towards fostering a culture of sustainability.
Conclusion
The Indian recycling industry of electronic goods stands at the intersection of environmental conservation, technological innovation, and economic development. By embracing sustainable practices, leveraging cutting-edge technologies, and fostering widespread awareness, India has the potential to emerge as a global leader in e-waste management.
As we navigate the complexities of a digital age, the journey towards a circular economy hinges on our collective commitment to redefining the way we produce, consume, and dispose of electronic goods. In the pursuit of a greener, more sustainable future, the Indian recycling industry serves as a beacon of hope, demonstrating the transformative power of innovation and collaboration in tackling one of the most pressing challenges of our time.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#CircularEconomy#India#GreenTechnology#EWaste#EWasteRecyclingCenters#ReduceReuseRecycle#Electronics#SustainableDevelopment#DigitalWasteManagement#EnvironmentalSustainability#EWasteAwareness#TechRecycling#ResponsibleConsumption
0 notes
Text
The Rise of EV Globally

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction
In recent years, the global landscape of transportation has witnessed a paradigm shift with the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). While much attention has been given to individual electric cars, there's a transformative trend that is reshaping the way businesses approach their transportation needs – the rise of electric fleets. Companies worldwide are increasingly recognizing the economic, environmental, and operational advantages of integrating electric vehicles into their fleet management strategies.
Rising of EV
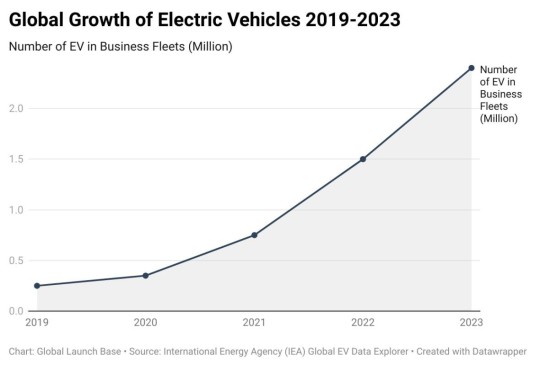
Figure: Global Growth of Electric Vehicles 2019-2023
Over the course of five years from 2019 to 2023, there has been a substantial evolution in the adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs) within business fleets. In 2019, the count stood at 0.25 million EVs, a figure that saw a modest increase to 0.35 million in 2020. However, the momentum gained significant traction in 2021, with the number soaring to 0.75 million. The trend took a transformative leap in 2022, witnessing a remarkable surge to 1.5 million EVs integrated into business fleets. This positive trajectory continued into 2023, with a notable expansion, bringing the total to 2.4 million EVs. These escalating figures indicate a progressive shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly transportation solutions within corporate fleets, underscoring a growing commitment to reducing environmental impact and embracing cleaner mobility alternatives.
In recent years, the global landscape has witnessed a revolutionary shift towards sustainable practices, with a particular focus on the automotive industry. The transition from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) has gained unprecedented momentum, signaling a new era for transportation. This article explores the speed of change in the electrification of vehicles, examining the factors driving this transition and the implications for the future of mobility.
Countries Transition to EV
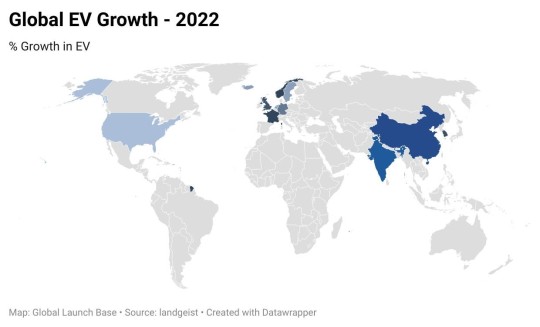
Figure: Global EV Growth
As we can see, Norway leads the pack in terms of EV adoption, with a staggering 80% share of new car sales in 2022. However, India is experiencing the fastest growth, with an impressive 82% increase in EV sales year-over-year. This is likely due to a number of factors, including government incentives, the rising popularity of electric two-wheelers, and the increasing availability of charging infrastructure.
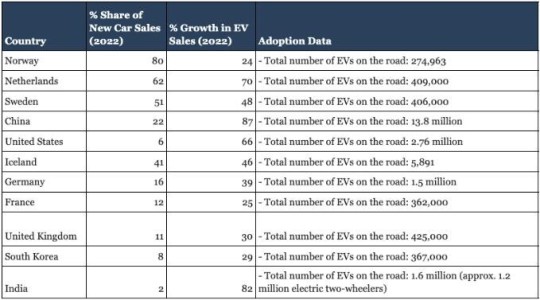
Norway: Norway has the highest EV market share in the world, with over 80% of new car sales being electric in 2022. The country has ambitious plans to phase out the sale of new gasoline and diesel cars by 2025.
Netherlands: The Netherlands has the second-highest EV market share in the world, with over 60% of new car sales being electric in 2022. The country has set a target of phasing out the sale of new gasoline and diesel cars by 2030.
Sweden: Sweden has a strong EV market, with over 50% of new car sales being electric in 2022. The country aims to have a fossil-fuel-free car fleet by 2040.
China: China is the world's largest EV market, with over 3 million EVs sold in 2022. The Chinese government has set ambitious targets for EV adoption, aiming for EVs to account for 20% of all new car sales by 2025.
United States: The United States is a growing EV market, with over 600,000 EVs sold in 2022. The US government has set a target of having 5 million EVs on the road by 2030.
India: India's EV market witnessed a significant surge in 2023, with sales growing by 82% compared to the previous year and 157% from FY2022 to FY2023. The electric two-wheeler market is currently the driving force, with over 1 lakh EVs sold every month in H2 FY2023.
Rapid Technological Advancements:
One of the primary drivers behind the swift transition to electric vehicles is the rapid advancement of technology. Breakthroughs in battery technology, energy storage, and electric drivetrain efficiency have significantly improved the performance and range of EVs. As a result, consumers are now presented with viable alternatives that not only match but often surpass the capabilities of traditional vehicles.
Government Initiatives and Policies:
Governments around the world have played a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles. Many countries have implemented stringent emission regulations, incentivized the production and purchase of electric vehicles, and invested in charging infrastructure. These policy measures create a favorable environment for both manufacturers and consumers, fostering the rapid integration of EVs into the mainstream market.
Changing Consumer Preferences:
Consumer attitudes towards electric vehicles have undergone a remarkable transformation. With increased awareness of environmental issues and a growing emphasis on sustainability, more consumers are actively seeking eco-friendly transportation options. The appeal of electric vehicles extends beyond environmental concerns, as drivers are drawn to the lower operating costs, reduced maintenance requirements, and a smoother driving experience.
Before and After EV
The advent of Electric Vehicles (EVs) has brought about a transformative shift in the automotive landscape, marking a clear distinction between the era before and after the widespread adoption of electric mobility. Several key differences characterize these two periods:
Propulsion Technology:
Before EVs: The automotive industry predominantly relied on internal combustion engines (ICEs) powered by fossil fuels, such as gasoline and diesel.
After EVs: Electric vehicles use electric motors and batteries for propulsion, reducing or eliminating reliance on traditional fossil fuels. This shift represents a move towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
Environmental Impact:
Before EVs: Internal combustion engines produced emissions, contributing to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, with detrimental effects on the environment.
After EVs: Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing air pollution and contributing to efforts to combat climate change. The environmental benefits of EVs are a crucial factor driving their adoption.
Infrastructure Development:
Before EVs: The infrastructure primarily consisted of fuel stations for gasoline and diesel, with limited availability of charging stations for electric vehicles.
After EVs: The emergence of EVs has led to a rapid expansion of charging infrastructure, including public charging stations, home charging solutions, and fast-charging networks. This development addresses concerns about range anxiety and facilitates the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Government Policies and Incentives:
Before EVs: Government policies often focused on regulating emissions and fuel efficiency standards for internal combustion engine vehicles.
After EVs: Governments worldwide have introduced incentives and policies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These measures include tax credits, subsidies, and stricter emissions regulations to encourage a shift towards cleaner transportation.
Consumer Awareness and Perception:

Figure: Global Rise in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing: 2019-2022
Before EVs: Consumer awareness of electric vehicles was relatively low, and there were misconceptions about issues like limited range, performance, and charging infrastructure.
After EVs: Increasing environmental awareness, advancements in technology, and positive experiences with electric vehicles have led to a shift in consumer perceptions. More consumers now view EVs as viable alternatives with benefits such as lower operating costs, reduced maintenance, and a positive impact on the environment.
Automaker Strategies:
Before EVs: Traditional automakers focused primarily on the production of vehicles with internal combustion engines, with limited investment in electric mobility.
After EVs: Automakers are increasingly investing in electric vehicle technology, developing dedicated EV platforms, and announcing plans to transition to fully electric fleets. The competition in the electric vehicle market has intensified, driving innovation and improvements in battery technology and vehicle design
Economic Considerations:

Figure: Price Compression Over Time - 2019-2022
Before EVs: The economic landscape was heavily influenced by the fossil fuel industry, including oil extraction, refining, and distribution.
After EVs: The rise of electric vehicles has led to a shift in economic dynamics, impacting industries related to renewable energy, battery manufacturing, and electric vehicle production. This transition has implications for job markets, resource extraction, and economic sustainability.
Leading Emerging EV Companies
BYD Company Ltd. (China): BYD is a diversified company with a strong presence in the EV market. They produce a wide range of electric vehicles, including cars, buses, and trucks.
XPeng Inc. (China): Xpeng is a leading Chinese EV maker known for its premium sedans and SUVs. They have a strong presence in the Chinese market and are expanding into Europe.
Fisker Inc. (USA): Fisker is focused on designing and developing luxury electric vehicles with extended range and innovative features. Their first model, the Ocean SUV, is scheduled for production in late 2023.
Rivian Automotive (USA): Rivian is a manufacturer of electric trucks and SUVs. Their R1T pickup truck and R1S SUV are already in production and have received positive reviews for their performance and capabilities.
Canoo Technologies Inc. (USA): Canoo designs and develops electric vehicles for various applications, including delivery vans, passenger shuttles, and subscription-based personal vehicles. They have partnerships with Hyundai and Walmart, indicating their potential for future growth.
Polestar (Sweden): Polestar is a joint venture between Volvo Cars and Geely Holding Group. They offer high-performance electric vehicles and plan to launch new models in the coming years.
Euler Motors (India): Focuses on electric commercial vehicles, catering to the growing demand for clean and sustainable last-mile delivery solutions.
Ather Energy (India): Known for their high-performance and tech-integrated electric scooters, they have a strong presence in major Indian cities and are expanding their product range.
Tata Motors (India): This major player recently launched the Nexon EV, their first electric SUV, and plans to introduce more electric vehicles in the coming years.
The shift from the era before EVs to the current era reflects a broader global commitment to sustainability, technological innovation, and a transition towards a more environmentally conscious and energy-efficient transportation system.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
Organisation Mentioned: Byd Company Limited XPENG Fisker Rivian Canoo Polestar Euler Motors Ather Energy Tata Motors
#ElectricVehicles hashtag#EVs hashtag#SustainableTransportation hashtag#GreenTechnology#hashtag#ElectricCarMarket hashtag#EVAdoptionTrends hashtag#RenewableEnergyVehicles hashtag#ChargingInfrastructure hashtag#EnvironmentalImpactOfEVs hashtag#GlobalElectricVehicleMarket hashtag#FutureOfTransportation hashtag#EVBatteryTechnology hashtag#ElectricVehicleIndustryGrowth#GovernmentIncentivesForEVs hashtag#EVManufacturers#ElectricVehicleRevolution hashtag#CleanEnergyTransportation#EVMarketAnalysis hashtag#EVSalesProjections hashtag#EVInvestmentOpportunities
0 notes
Text
Space Technology Opportunity in India

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship in space technology in India has been gaining momentum in recent years. The Indian government has been actively promoting the development of the space sector, and private companies are playing an increasingly important role.
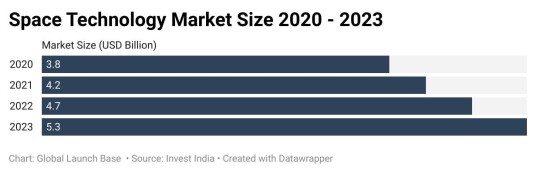
As the nation liberalizes its space sector, a diverse array of players are contributing to the burgeoning space ecosystem. Entrepreneurs are venturing into satellite manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of launch services, delving into space exploration, and exploring innovative solutions for satellite-based communication. The landscape is further enriched by collaborative efforts between private entities, government agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development.
In this context, it's crucial to explore the challenges and opportunities that define the entrepreneurial spirit in India's space technology sector. Regulatory hurdles, infrastructure development, and the need for sustained investments are among the challenges that entrepreneurs face. However, with increasing investor interest, a robust policy framework, and a commitment to fostering innovation, India's entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are poised to shape the nation's narrative in the cosmic domain. This dynamic interplay of public and private entities is not only propelling India's space capabilities but is also contributing to the global discourse on the commercialization and exploration of space.
Here are some key aspects of entrepreneurship in space technology in India:
Government Initiatives:New Space Policy: The Indian government has introduced policies to encourage private sector participation in space activities. The New Space India Limited (NSIL) was established to promote, commercially exploit, and transfer technologies developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).Liberalization: The government has liberalized the space sector, allowing private companies to undertake a wide range of space-related activities, including satellite launches, space exploration, and satellite communication services. (ISRO) Initiatives: Antrix Corporation: Antrix is the commercial arm of ISRO, and it collaborates with private players for the commercialization of space-related products and services.: SEED is a program initiated by ISRO to promote startups in the space sector by providing them with opportunities for collaboration and technology transfer.: NSIL is a central public sector enterprise (CPSE) under the Department of Space. It plays a crucial role in commercializing space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies.: ISRO has been actively engaging with startups, providing them access to its facilities, expertise, and technology.: The Department of Space in India oversees the country's space program. It may introduce schemes and programs to support space technology startups and entrepreneurs. (AIM): AIM, a flagship initiative of the NITI Aayog, supports innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors. It may have programs and funding opportunities that space technology startups can explore. (NIF): NIF supports grassroots innovations and may provide support to startups working on innovative space technologies.
Private Space Companies:Startups: Several startups in India are focusing on various aspects of space technology. Some are involved in satellite manufacturing, launch services, data analytics from space, and more.Launch Services: Companies like Agnikul Cosmos, Skyroot Aerospace, and Pixxel are working on developing small satellite launch vehicles to provide cost-effective and flexible launch options.
Space Exploration and Research: Interplanetary Missions: ISRO has been actively involved in space exploration, and private companies are expressing interest in participating in future interplanetary missions.Research and Development: Private entities are engaging in research and development activities, contributing to advancements in satellite technology, propulsion systems, and other space-related technologies.
Satellite Manufacturing:Private Satellite Manufacturers: Companies like Exseed Space and Bellatrix Aerospace are involved in the manufacturing of satellites, catering to various purposes such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Communication Services:Telecommunication Satellites: Private companies are exploring opportunities to provide satellite-based communication services. This includes both broadband internet services and other communication solutions.
Funding and Investments:Investor Interest: The space technology sector in India has attracted attention from investors. Funding rounds for space startups have been on the rise, indicating confidence in the potential growth of the industry.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Partnerships between private companies, government organizations, and academic institutions are fostering innovation and research in the space sector.
The Indian space technology ecosystem is evolving, and with continued government support, entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Indian space industry.
The number of space tech startups in India has witnessed explosive growth, increasing by almost five times in just five years. Investments in the sector have also seen a sharp rise, from $17 million in 2019 to an estimated $124.7 million in 2023.
Commercialization of Space Activities: With India's proven track record in satellite launches and space technology, there is a substantial potential for the commercialization of space activities. The burgeoning demand for satellite-based services, including communication, arth observation, and navigation, opens up opportunities for private entities to actively participate in the space industry. As the cost of space access continues to decrease, private companies can explore ventures such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, and satellite-based applications, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
International Collaborations: Collaborations with other space-faring nations present a promising avenue for India to augment its space capabilities. Joint ventures, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer can accelerate innovation and enhance the efficiency of space missions. ISRO has already established itself as a reliable partner for international launches, and expanding collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, reduced costs, and a more diversified approach to space exploration. As India continues to engage in global partnerships, it can leverage collective expertise for ambitious endeavors beyond Earth's orbit.
Innovation in Space Technology: Investments in research and development (R&D) can catapult India into the forefront of space innovation. Emphasis on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and propulsion systems can revolutionize space missions. The development of reusable launch vehicles, like the ongoing efforts in creating a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), can significantly reduce launch costs, making space exploration more sustainable. Encouraging a culture of innovation, fostering collaboration between academia and industry, and providing incentives for R&D initiatives can fuel breakthroughs in space technology.
Space Applications for Sustainable Development: Leveraging space technology for sustainable development on Earth is an untapped frontier. Utilizing satellite data for precision agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource mapping can contribute to addressing pressing global challenges. By integrating space-based solutions into sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and urban planning, India can harness the power of space technology for inclusive and sustainable development, bringing tangible benefits to its citizens and contributing to global initiatives.
Expansion of Interplanetary Exploration: Building on the success of Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India has the potential to expand its interplanetary exploration efforts. Initiatives for exploring other celestial bodies, such as Venus or asteroids, can contribute to humanity's understanding of the solar system and beyond. A strategic focus on ambitious interplanetary missions can position India as a key player in the broader scientific community and foster international collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Trending Technologies in India's Space Industry:
Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in space technology has the potential to revolutionize spacecraft design, materials, and instrumentation. Nanosatellites, with their miniaturized components, are becoming increasingly popular for cost-effective and innovative space missions. India can leverage nanotechnology for lightweight yet robust spacecraft, enhancing mission efficiency and scientific capabilities.
Companies: Nano-Tech SpA, Kalva Nanotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in data analysis, image processing, and autonomous decision-making in space missions. India can explore AI applications for real-time data interpretation, automated navigation, and predictive maintenance of spacecraft. Incorporating machine learning algorithms into Earth observation data analysis can significantly enhance the understanding of environmental changes.
Companies: Aadyah Aerospace, Blue Sky Analytics
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex computational problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In the space sector, quantum computing can be utilized for optimizing mission trajectories, simulating quantum systems, and enhancing the security of communication channels. India's focus on quantum computing research can contribute to advancements in space-related computations.
Companies: QpiAI, BosonQ
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: The adoption of 3D printing in space technology can revolutionize the manufacturing process, enabling the production of complex and lightweight structures. India can benefit from 3D printing for rapid prototyping, cost-effective manufacturing of satellite components, and even on-demand production during long-duration space missions.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos, EOS India
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, making it applicable to space-based applications such as satellite communication, data storage, and secure information sharing. By incorporating blockchain, India can enhance the security and integrity of space-related data and transactions.
Companies: SpaceTime Labs, Aryaka Networks
Solar Sail Technology: Solar sails, propelled by the pressure of sunlight, offer a sustainable and efficient means of propulsion for spacecraft. This technology can be harnessed for deep-space exploration, enabling missions to travel vast distances with minimal fuel requirements. India's exploration programs can benefit from research and development in solar sail technology for extended-duration missions.
Companies: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), IIT Bombay - Aerospace Engineering Department
Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging involves capturing a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. This technology is instrumental in Earth observation, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring. India can explore the integration of hyperspectral imaging in its satellite payloads for enhanced remote sensing capabilities.
Companies: Pixxel, Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd
Internet of Things (IoT) for Space: The application of IoT in space technology involves connecting devices and sensors on satellites and spacecraft to gather and transmit data. This interconnected network can facilitate efficient communication, data collection, and collaborative decision-making during space missions. India can explore IoT applications for enhanced space situational awareness and mission coordination.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos
As India looks to the future, embracing these trending technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in space exploration and satellite technology. By actively incorporating these innovations into its space programs, India can not only enhance mission success but also contribute to the global advancement of space technology. Collaborations with research institutions, startups, and the private sector will play a vital role in driving these technological advancements in India's space industry.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
Despite its successes, India's space program faces challenges such as increased competition, budget constraints, and the need for continuous innovation. To overcome these challenges, sustained government support, collaboration with private entities, and a focus on skill development in the space sector are crucial.
Increased Global Competition: The space industry is becoming increasingly competitive with the emergence of new players and the commercialization of space activities. To stay ahead, India must continuously innovate, streamline its processes, and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Developing a robust ecosystem for space startups and fostering public-private partnerships can enhance India's competitiveness in the global space market.
Budget Constraints: Despite commendable achievements, budget constraints pose a challenge for sustaining and expanding India's space endeavors. A consistent and increased allocation of funds to ISRO, along with exploring innovative funding mechanisms, will be crucial. Engaging with the private sector for joint ventures and commercial space activities can help alleviate financial constraints and promote economic sustainability in the long run.
Human Resource Development: The growth of India's space program necessitates a skilled workforce capable of handling complex missions. Investing in education and training programs in collaboration with academic institutions can ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals in fields such as aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and data sciences. This will not only address the current workforce requirements but also fuel future innovations in space technology.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements globally require India to stay at the forefront of innovation. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced propulsion systems will be essential. Establishing research and development centers dedicated to space technology innovation can facilitate the integration of these advancements into future missions.
Space Debris Management: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contribute to the growing issue of space debris. India needs to actively participate in international efforts to address space debris management, adopting sustainable practices in satellite design and end-of-life disposal. Research into debris removal technologies and international collaboration on space traffic management will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Climate Change Monitoring: With the rising global concerns about climate change, space technology plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental indicators. India can take a leadership role in developing satellite-based solutions for climate monitoring, disaster response, and sustainable resource management. This requires a dedicated focus on Earth observation satellites, advanced sensors, and data analytics.
Enhanced Space Diplomacy: Strengthening space diplomacy is essential for India to expand its global influence in the space arena. Engaging in collaborative space missions, sharing scientific knowledge, and participating in international forums will enhance India's standing as a responsible space-faring nation. Forming strategic partnerships with countries interested in space exploration can open up new avenues for cooperation and joint missions.
Conclusion:
India's journey in space technology has been nothing short of remarkable, with ISRO consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation. As the nation continues to invest in space exploration, the opportunities for growth, collaboration, and technological advancements are boundless. The future holds exciting possibilities for India's space technology sector, positioning the country as a key player in the global space community.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization#NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)#SEED(Social Entrepreneurship Empowerment Development)#Atal Innovation Mission Official#National Innovation Foundation - India#Nano-Tech SpA#Kalva Nanotech#AADYAH Aerospace Private Limited#Blue Sky Analytics#QpiAI#BosonQ Psi (BQP)#AgniKul Cosmos#EOS#Spacetime Labs#Aryaka#Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology#Aerospace Engineering Association IIT Bombay#Pixxel#Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd.#AgniKul Cosmos hashtag#SpaceTechnologyInIndia hashtag#IndianSpaceProgram hashtag#ISROOpportunities hashtag#SpaceIndustryGrowthIndia hashtag#SpaceResearchOrganizationsIndia hashtag#SatelliteTechnologyOpportunities hashtag#IndianSpaceExploration hashtag#ISROAchievements hashtag#SpaceScienceCareersIndia hashtag#SpaceTechnologyTrends hashtag
0 notes
Text
India's Changing Food Produce Preferences Over Time

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
India, with its rich tapestry of cultures, traditions, and flavors, has witnessed a fascinating evolution in its food produce preferences over the years. From the bustling street markets to the kitchens of urban homes, the landscape of Indian cuisine is undergoing a dynamic transformation influenced by globalization, health consciousness, regional diversity, and environmental awareness.


The Evolution of India's Changing Food Produce Preferences Over Time
India, with its rich tapestry of culture and tradition, has witnessed a significant evolution in its food produce preferences over the years. The shift in dietary habits reflects not only changing lifestyles but also economic dynamics that have played a pivotal role in shaping the nation's culinary landscape.

Early Years: Economic Constraints and Dietary Choices
In the early years, a substantial portion of the Indian population faced economic challenges, and the primary goal was to find affordable and filling food options. This led to a predominant reliance on staples like rice and wheat, which were not only economical but also effective in satiating hunger. The emphasis was on quantity rather than the nutritional quality of the food consumed.
Rice and Wheat Dominance:
Rice and wheat emerged as the cornerstone of the Indian diet due to their versatility, long shelf life, and ability to provide sustained energy. These grains formed the basis of many traditional dishes, serving as a staple for millions across the country. The shift towards these carbohydrate-rich foods was largely driven by economic constraints, as they offered a cost-effective solution to meet the basic dietary needs of a growing population.
Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes:
As India underwent urbanization and economic development, lifestyles began to change. The influence of globalization brought about an increased awareness of diverse culinary practices and a growing interest in health and nutrition. This shift in mindset paved the way for a more conscious approach to food choices.
Rise of Nutrient-Rich Foods:
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in awareness about the importance of a balanced and nutrient-rich diet. With an increasing focus on health and well-being, traditional Indian foods like millets, quinoa, and a variety of locally sourced fruits and vegetables have gained popularity. The diversification of food choices reflects a growing understanding that a diet rich in nutrients is essential for overall health and longevity.
Revival of Regional Cuisines:
One of the remarkable trends in the evolution of India's food preferences is the revival of regional cuisines. People are rediscovering the diverse culinary traditions that the country boasts, emphasizing the use of locally grown and seasonal ingredients. This trend not only contributes to preserving cultural heritage but also promotes sustainable and eco-friendly food practices.
Globalization and Culinary Crossroads:


In an era of increased globalization, India's culinary horizons have expanded beyond traditional boundaries. Exposure to international cuisines through travel, media, and the internet has sparked a curiosity for diverse food options. Urban centers now boast a fusion of global flavors, with international food chains becoming a commonplace sight. As Indians explore and embrace the world on their plates, the demand for exotic ingredients and unique culinary experiences continues to rise.
Diverse Ingredients on the Plate: One of the most palpable effects of globalization on India's food produce preferences is the inclusion of a wide array of international ingredients in everyday cooking. Once considered exotic, ingredients like avocados, quinoa, and sriracha sauce are now finding their way into Indian kitchens, contributing to an exciting amalgamation of global and local flavors. The availability of these ingredients has expanded through both traditional markets and online platforms, offering consumers unprecedented access to a global pantry.
International Culinary Influences: The rise of international food chains and the popularity of cooking shows from around the world have played a pivotal role in introducing Indians to new culinary techniques and flavor profiles. From Japanese sushi to Mexican tacos, these global influences have transcended novelty to become integrated elements in urban Indian dining experiences. Restaurants, cafes, and street food vendors now proudly showcase a diverse menu inspired by global culinary trends, creating a melting pot of flavors.
Culinary Tourism and Travel Experiences: Globalization has not only brought the world to Indian kitchens but has also inspired Indians to explore global cuisines firsthand through travel. Culinary tourism has gained momentum, with food enthusiasts embarking on gastronomic journeys to savor authentic flavors and bring them back home. This exchange of culinary experiences has further fueled the cross-pollination of global and local food preferences.
Culinary Innovation and Fusion: The fusion of traditional Indian recipes with international culinary techniques has given rise to a new wave of innovative dishes. Chefs across the country are experimenting with flavor combinations, presenting a creative blend of local and global elements. This culinary innovation is not confined to high-end restaurants; street food vendors, too, are embracing globalization by infusing traditional snacks with a contemporary twist, showcasing the adaptability of Indian cuisine.
The Rise of Health and Wellness:


Health consciousness is reshaping Indian food choices, with a growing emphasis on fresh produce, organic options, and plant-based diets. Superfoods once considered niche, like quinoa, chia seeds, and kale, are gaining popularity as consumers become more attuned to the nutritional benefits of their diets. This shift towards healthier eating reflects a societal awareness of the profound connection between food and well-being.
Embracing Wholesome Choices: The rise of health and wellness in India's food produce preferences is characterized by a growing preference for fresh, locally sourced produce. Consumers are increasingly seeking out fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, recognizing the intrinsic nutritional value of these ingredients. From bustling urban markets to quaint rural stalls, the emphasis on offering wholesome, unprocessed foods is reshaping the way Indians approach their daily meals.
The Power of Superfoods: Superfoods, once considered exotic or niche, have found a prominent place on Indian plates. Quinoa, chia seeds, kale, and other nutrient-rich options have gained popularity as individuals become more aware of their health benefits. These superfoods are not just embraced for their nutritional density but are also celebrated for their versatility, seamlessly integrating into traditional recipes and adding a modern, health-conscious twist.
Plant-Based Diets on the Rise: A notable trend in the health and wellness movement is the increasing adoption of plant-based diets. Whether driven by ethical considerations, environmental concerns, or health-conscious choices, more Indians are exploring the benefits of a predominantly plant-centric lifestyle. This shift is reflected not only in individual dietary choices but also in the growing availability of plant-based alternatives in restaurants and grocery stores.
Mindful Eating Practices: Beyond the selection of ingredients, the rise of health and wellness is fostering a culture of mindful eating. From savoring each bite to recognizing the importance of portion control, individuals are becoming more attuned to their bodies' nutritional needs. This shift towards mindful eating goes hand-in-hand with an awareness of food as more than just sustenance, but as a means to nourish the body and mind.
Local and Organic Movements: The health and wellness trend is intertwined with a growing interest in supporting local farmers and embracing organic produce. Farmers' markets, organic stores, and community-supported agriculture initiatives are gaining traction, providing consumers with access to fresh, pesticide-free fruits, vegetables, and other produce. This movement not only promotes healthier eating but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices.
Innovations in Healthy Cooking: The rise of health and wellness is driving innovations in healthy cooking techniques. From air frying and steaming to experimenting with ancient grains, chefs and home cooks alike are exploring ways to retain the nutritional integrity of ingredients while creating delicious and satisfying meals. Cooking classes, online tutorials, and wellness-focused cookbooks are empowering individuals to make informed and health-conscious choices in their kitchens.
Rediscovering Regional and Local Gems:
India's culinary heritage is a treasure trove of regional delights, each with its unique set of ingredients. In recent times, there has been a resurgence of interest in indigenous grains, vegetables, and fruits that were once overshadowed by more mainstream choices. Consumers are now championing local produce, fostering a renewed appreciation for the diversity of India's agricultural landscape.
Celebrating Diversity: India's regional cuisines are a kaleidoscope of flavors, each telling a unique story of culture, history, and geography. In the quest to rediscover regional gems, there is a renewed celebration of this diversity. From the piquant flavors of South Indian spices to the hearty comfort of North Indian dals, people are increasingly seeking out and appreciating the rich tapestry of regional delicacies that paint the Indian culinary canvas.
Indigenous Grains and Pulses: A noteworthy aspect of this culinary renaissance is the revival of indigenous grains and pulses that were once staples but gradually faded into the background. Millets, sorghum, and heirloom varieties of rice are experiencing a renaissance as people rediscover their nutritional benefits and unique flavors. The resurgence of these grains not only adds diversity to diets but also contributes to sustainable farming practices.
Forgotten Vegetables and Local Produce: As global influences introduced new vegetables to Indian markets, some local and traditional varieties took a backseat. However, there is a noticeable shift as people rediscover and celebrate forgotten vegetables and indigenous produce. From the earthy sweetness of yams to the unique textures of local greens, chefs and home cooks alike are incorporating these local treasures into their recipes, adding depth and authenticity to their dishes.
Local Markets and Community Initiatives: The resurgence of regional and local gems is intricately linked with the thriving ecosystem of local markets and community initiatives. Farmer's markets, where local producers showcase their bounty, have become hubs for discovering and procuring unique ingredients. Community-supported agriculture programs are forging connections between farmers and consumers, fostering a sense of community and sustainability.
Preserving Culinary Heritage: In the rush towards modernity, there was a risk of losing some of India's culinary heritage. However, the rediscovery of regional and local gems is also a preservation effort. Families are delving into their ancestral recipes, passing down cooking traditions, and safeguarding the authenticity of regional dishes. Culinary enthusiasts are documenting these recipes, contributing to the preservation of India's rich gastronomic legacy.
Culinary Tourism and Regional Specialties: India's diverse culinary map is attracting culinary tourists eager to explore regional specialties. From the seafood delights of coastal regions to the robust flavors of the Himalayan foothills, culinary tourism is contributing to the rediscovery of local gems. This not only boosts local economies but also creates a dialogue around the importance of preserving and celebrating regional culinary identities.



Advancements in technology and changing lifestyles have given rise to a demand for convenience in food consumption. Ready-to-cook and ready-to-eat options are gaining popularity, offering busy urbanites quick and hassle-free meal solutions. The advent of online food delivery services and meal kit subscriptions has revolutionized the way Indians access and enjoy their food, making culinary experiences more accessible than ever.
Online Grocery Shopping and Meal Kits: The advent of technology has revolutionized the way Indians procure ingredients. Online grocery shopping platforms have made it convenient for consumers to access a vast array of products from the comfort of their homes. Additionally, meal kit subscriptions are gaining popularity, offering pre-portioned ingredients and step-by-step recipes, catering to individuals seeking convenient yet homemade meal options amidst their busy lives.
Smart Kitchen Appliances: The rise of smart kitchen appliances is transforming the cooking experience. From intelligent ovens that can be controlled remotely to smart refrigerators that help manage inventory, technology is seamlessly integrated into the culinary process. These appliances not only streamline tasks but also contribute to energy efficiency and sustainability, aligning with the changing attitudes towards eco-friendly living.
Mobile Apps for Recipe Inspiration: As smartphones become ubiquitous, mobile apps are playing a crucial role in inspiring and guiding home cooks. Recipe apps offer a treasure trove of culinary ideas, catering to various tastes, dietary preferences, and skill levels. These apps not only provide a convenient way to discover new recipes but also empower individuals to experiment with diverse cuisines and techniques.
Online Cooking Communities and Classes: Technology has facilitated the creation of vibrant online cooking communities and classes. Social media platforms and dedicated cooking forums bring together enthusiasts, allowing them to share experiences, tips, and recipes. Virtual cooking classes, conducted by chefs and culinary experts, offer an interactive and educational experience, fostering a sense of community among aspiring cooks.
Food Delivery Services and Virtual Restaurants: The hustle and bustle of contemporary life have led to an increased reliance on food delivery services. The convenience of having restaurant-quality meals delivered to one's doorstep has reshaped dining habits. Furthermore, the rise of virtual restaurants, establishments that operate solely through online platforms, caters to changing preferences for diverse and specialized culinary experiences.
Digitalization of Culinary Education: Aspiring chefs and culinary enthusiasts are leveraging digital platforms for education. Online courses and webinars cover a spectrum of culinary topics, from mastering specific techniques to understanding global cuisines. This digitalization of culinary education not only democratizes access to knowledge but also allows individuals to pursue their culinary passions at their own pace and convenience.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations:
Local Sourcing and Seasonal Ingredients: At the heart of the sustainability movement in Indian cuisine is a return to local sourcing and seasonal eating. Restaurants and home kitchens alike are increasingly prioritizing ingredients sourced from nearby farms, reducing the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. Seasonal menus celebrate the natural abundance of each period, connecting consumers with the rhythm of local ecosystems.
Reducing Food Waste:India's culinary landscape is tackling the challenge of food waste head-on. From innovative recipes that repurpose leftovers to campaigns encouraging responsible portioning, chefs and home cooks are finding creative ways to minimize waste. The adoption of composting practices and collaborations with food rescue organizations further contribute to a collective effort to curb unnecessary food disposal.
Plant-Based Initiatives and Sustainable Proteins: As awareness of the environmental impact of meat production grows, there is a discernible shift towards plant-based diets in India. Sustainable proteins, such as legumes, pulses, and plant-based alternatives, are gaining prominence. This not only aligns with health-conscious choices but also addresses concerns about deforestation, water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional meat production.
Zero-Waste Cooking and Circular Economy: The concept of zero-waste cooking is gaining traction, emphasizing the utilization of every part of an ingredient to minimize waste. Root-to-stem cooking and nose-to-tail practices with meat showcase the potential for creative and sustainable culinary approaches. Additionally, embracing a circular economy in the culinary sector involves reusing, recycling, and repurposing materials to minimize environmental impact.
Energy-Efficient Cooking Practices: Sustainability in Indian cuisine extends beyond ingredient choices to encompass energy-efficient cooking practices. From the use of energy-efficient appliances to the promotion of traditional cooking methods that minimize energy consumption, kitchens are exploring ways to reduce their ecological footprint. Solar cooking, in particular, is gaining popularity as a sustainable alternative in certain regions.
Community Gardens and Urban Farming: Urban spaces are witnessing the emergence of community gardens and urban farming initiatives, where individuals cultivate their produce. These projects not only foster a sense of community but also contribute to sustainable living by reducing the need for extensive transportation of produce and promoting local, organic agriculture.
Education and Awareness: A key driver of the sustainability movement in Indian cuisine is education and awareness. Culinary schools, workshops, and online platforms are focusing on educating chefs and home cooks about the environmental impact of food choices. This increased awareness is empowering individuals to make informed decisions that align with sustainable and ethical principles.
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, Indians are becoming increasingly mindful of the impact their food choices have on the planet. Sustainable and eco-friendly options are gaining traction, with a noticeable shift towards plant-based diets. Consumers are recognizing the importance of supporting local farmers and choosing produce with a lower ecological footprint.
Government Initiatives and Cultural Celebrations:
Government initiatives promoting agriculture and food processing industries play a pivotal role in shaping food preferences. Policies supporting local farmers and traditional crops contribute to a sustainable and diverse food landscape. Additionally, cultural celebrations and festivals significantly influence food choices, with a surge in demand for specific ingredients and traditional dishes during festive seasons.
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra): Defra is the lead government department for agriculture in the UK. It is responsible for developing and implementing policies that support the sustainable growth of the agricultural sector. Defra also provides funding for a range of agricultural support schemes.
Rural Payments Agency (RPA): The RPA is responsible for administering the Basic Payment Scheme and other agricultural support schemes in the UK. It also provides advice and guidance to farmers on how to claim these payments.
Food Standards Agency (FSA): The FSA is responsible for protecting public health by ensuring that food is safe and nutritious. It also sets standards for food production and labeling.
Animal Health and Plant Regulatory Agency (APHRA): APHRA is responsible for protecting animal and plant health in the UK. It also controls the movement of animals and plants into and out of the UK.
Their Roles in the Greenhouse Agriculture Sector
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra):
Policy Development and Implementation: Defra formulates and implements policies that encourage the adoption of greenhouse technologies, promote sustainable greenhouse practices, and enhance the competitiveness of greenhouse-grown produce.
Defra provides financial support to greenhouse farmers through grants, subsidies, and tax breaks, reducing the initial investment costs and encouraging the expansion of greenhouse operations.
Defra funds research and development initiatives aimed at improving greenhouse technologies, developing new crop varieties, and enhancing energy efficiency in greenhouse production systems.
Rural Payments Agency (RPA)
Administration of Support Schemes: The RPA administers various agricultural support schemes, including capital grants for greenhouse infrastructure development and technology upgrades.
Advice and Guidance: The RPA provides guidance and support to greenhouse farmers on eligibility criteria, application procedures, and documentation requirements for accessing financial assistance.
Streamlined Processes: The RPA strives to simplify and streamline the application process for greenhouse farmers, ensuring timely access to funding and reducing administrative burdens.
Food Standards Agency (FSA):
Regulatory Framework: The FSA establishes and enforces food safety regulations that apply to greenhouse-grown produce, ensuring that consumers have access to safe and wholesome food.
Risk Assessment and Monitoring: The FSA conducts risk assessments and monitors the safety of greenhouse-grown produce to identify and address potential hazards, such as pesticide residues or microbial contamination.
Consumer Education: The FSA provides information and guidance to consumers on the safety and nutritional value of greenhouse-grown produce, promoting informed food choices.
Animal Health and Plant Regulatory Agency (APHRA):
Biosecurity Measures: APHRA implements biosecurity measures to protect animals and plants within greenhouse facilities, preventing the introduction and spread of pests and diseases.
Import and Export Controls: APHRA regulates the movement of animals and plants into and out of the UK, ensuring that greenhouse-grown produce meets import and export requirements.
Conclusion:
India's changing food produce preferences reflect a captivating journey through time, encompassing a myriad of influences from globalization to health trends and environmental considerations. The culinary landscape is evolving, with Indians embracing a diverse array of flavors while simultaneously celebrating their rich heritage. As the kaleidoscope of Indian cuisine continues to turn, the nation's evolving palate promises an exciting and flavorful future.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#IndianFoodTrends hashtag#EvolvingFoodChoices hashtag#ChangingIndianCuisine hashtag#ModernIndianDiet hashtag#GlobalizationAndFood hashtag#IndianFoodShift hashtag#CulturalDietChanges hashtag#TraditionalVsModernFood hashtag#RegionalFoodVariations hashtag#PopularIndianIngredients
0 notes
Text
The Prosperous Dutch Entrepreneurial Ventures

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
The Netherlands, renowned for its picturesque landscapes and windmills, is also gaining recognition as a hotspot for entrepreneurial endeavors. The Dutch entrepreneurial spirit is thriving, and the current market conditions reflect a dynamic landscape that is conducive to innovation, growth, and prosperity.
Amidst the enchanting landscapes adorned with windmills and vibrant tulip fields, the Netherlands stands as a testament to not only natural beauty but also to a dynamic entrepreneurial spirit that defines its current market. As we step into 2024, the Dutch business landscape continues to thrive, marked by innovation, resilience, and a unique ecosystem that propels entrepreneurs to unprecedented heights. In this exploration of the prosperous Dutch entrepreneurial scene, we delve into the supportive environment, technological frontiers, and global connectivity that make the Netherlands a haven for business visionaries. Join us on this journey as we unravel the layers of success within the Dutch entrepreneurial tapestry.

Figure: Dutch Market Growth 2019 - 2022
Dutch Ecosystem:

One of the key factors contributing to the success of Dutch entrepreneurs is the supportive ecosystem. The Netherlands boasts a business-friendly environment, with a well-established legal framework, transparent regulations, and a government that actively encourages entrepreneurship. The Dutch government's initiatives, such as tax incentives and funding programs, provide a solid foundation for businesses to flourish.
In the vibrant landscape of Dutch startups, a dynamic business ecosystem serves as the fertile soil where innovation, collaboration, and growth flourish. The Netherlands, with its progressive policies and entrepreneurial culture, has become a nurturing ground for startups, fostering an environment where new ideas are not only welcomed but actively supported.
Government Initiatives: The Dutch government plays a pivotal role in creating a conducive environment for startups. Various initiatives, including tax incentives and grants, are designed to alleviate the financial burden on emerging businesses. Regulatory frameworks are crafted with flexibility, enabling startups to navigate administrative processes more efficiently.
Incubators and Accelerators: The presence of numerous incubators and accelerators across the country provides startups with invaluable support. These organizations offer mentorship, resources, and networking opportunities, accelerating the development of fledgling enterprises. Notable hubs like YES!Delft and Rockstart have gained international recognition for their contributions to the startup ecosystem.
Access to Funding: The Netherlands boasts a diverse funding landscape, ensuring startups have access to capital at various stages of their growth. Venture capital firms, angel investors, and crowdfunding platforms contribute to a robust financial ecosystem. Government-backed programs, such as the Dutch Venture Initiative, actively invest in promising startups, fueling their ambitions.
Innovation Hubs: Major cities like Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and Eindhoven have emerged as bustling innovation hubs, drawing talent and investment. These urban centers provide startups with a collaborative environment, proximity to key stakeholders, and a pool of skilled professionals. The concentration of like-minded individuals fosters a culture of innovation and knowledge-sharing.
Research and Development Collaboration: Dutch startups benefit from strong ties with research institutions and universities. Collaborations with academia facilitate access to cutting-edge research, fostering innovation in sectors such as technology, biotech, and renewable energy. The synergy between startups and research institutions creates a unique ecosystem where ideas seamlessly transition from the lab to the market.
Global Connectivity: The Netherlands' strategic geographical location and excellent transportation infrastructure position startups for international success. The country's well-connected airports and ports facilitate easy access to global markets, enabling startups to expand their reach and tap into a diverse customer base.
Sustainability Focus: Many Dutch startups place a strong emphasis on sustainability, aligning with the country's commitment to environmental responsibility. The green energy sector, circular economy initiatives, and eco-friendly technologies are areas where startups thrive, addressing global challenges while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Innovation Hubs:
Cities like Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and Eindhoven have emerged as vibrant innovation hubs, attracting startups and established businesses alike. Amsterdam, in particular, has positioned itself as a European tech hub, with a flourishing tech scene and a high concentration of innovative startups. Eindhoven, known as the "Brainport" region, is a hotspot for technology and design, fostering collaboration between businesses, research institutions, and the government.
Amsterdam: Tech Capital of Europe: Amsterdam stands tall as the indisputable tech capital of Europe, housing a diverse and thriving ecosystem of startups, scale-ups, and multinational tech giants. The city's historic charm is complemented by a modern outlook that embraces innovation. The presence of co-working spaces, accelerators, and research institutions such as the Amsterdam Science Park fosters an environment where ideas flourish. The annual Amsterdam Innovation Award celebrates and showcases the city's commitment to pushing the boundaries of technological advancements.
Eindhoven: The Brainport Region: Known as the Brainport Region, Eindhoven has carved a niche for itself in technology and design. Home to major companies like Philips and ASML, Eindhoven's innovation ecosystem is characterized by collaborations between industry, academia, and government. High-tech campuses, such as the High Tech Campus Eindhoven, serve as epicenters for research and development, attracting talent and investment. The city's commitment to fostering a creative atmosphere is evident in events like the Dutch Design Week, which draws innovators from around the world.
Rotterdam: Maritime and Sustainable Innovation Hub: Rotterdam, with its bustling port and modern skyline, is not only a key player in maritime trade but also an innovation hub with a focus on sustainability. The Port of Rotterdam serves as a testing ground for smart logistics and cutting-edge technologies. Startups and established companies collaborate on initiatives related to clean energy, circular economy, and urban resilience. The Rotterdam Science Tower and the Cambridge Innovation Center contribute to the city's vibrant innovation landscape.
Utrecht: Health and Life Sciences Hub: Utrecht has positioned itself as a hub for health and life sciences innovation. The Utrecht Science Park is home to research institutions and companies at the forefront of medical advancements. Startups in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and medical research find a supportive environment in Utrecht, with initiatives like UtrechtInc providing crucial resources and mentorship. The city's commitment to healthcare innovation is reflected in events like the Health Valley Event.
Groningen: Northern Tech Hub: In the northern part of the country, Groningen has emerged as a tech hub with a focus on innovation in the energy and information technology sectors. The presence of the Groningen Digital Business Centre and the Energy Academy Europe underscores the city's commitment to cutting-edge technologies. The Startup in Residence program encourages collaboration between startups and local government, fostering innovative solutions to societal challenges.
Technology and Sustainability:
The Dutch entrepreneurial landscape is increasingly characterized by a focus on technology and sustainability. Startups in fields like renewable energy, agritech, and smart logistics are gaining traction. The emphasis on sustainable practices aligns with the Dutch commitment to environmental responsibility and positions businesses for long-term success in a global market increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly solutions.
Smart Cities and Sustainable Urban Planning:
Dutch cities are embracing technology to enhance sustainability through smart urban planning. Initiatives include the implementation of smart grids, energy-efficient buildings, and intelligent transportation systems. Amsterdam's Smart City program, for instance, leverages data and technology to optimize energy consumption, reduce traffic congestion, and minimize environmental impact.
Renewable Energy Solutions:
The Netherlands is a pioneer in the development and implementation of renewable energy solutions. Wind energy, in particular, has seen significant investment, with offshore wind farms contributing to the country's goal of becoming carbon-neutral. The Gemini Wind Park, one of the largest in the world, exemplifies the Dutch commitment to harnessing clean energy sources.
Circular Economy Initiatives:
Circular economy principles, aimed at minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency, have found a fertile ground in the Dutch business landscape. Technology plays a pivotal role in enabling circular practices, from innovative waste management systems to the use of blockchain for supply chain transparency. Companies like Philips are actively involved in circular design, emphasizing product life extension and material recycling.
AgriTech Advancements:
The agricultural sector in the Netherlands has embraced technology for sustainable farming practices. Precision agriculture, utilizing data analytics and sensor technologies, enables farmers to optimize resource usage, reduce environmental impact, and increase crop yields. Dutch AgriTech startups are at the forefront of developing innovative solutions for sustainable and efficient agriculture.
Water Management and Climate Resilience:
Given its geographical challenges with water, the Netherlands has become a global leader in water management. Innovative technologies, including smart dikes, water sensors, and flood prediction models, contribute to effective flood control and climate resilience. The Delta Works project, a marvel of engineering, showcases the Dutch commitment to safeguarding against rising sea levels.
E-Mobility and Sustainable Transportation:
The Netherlands is fostering a shift towards sustainable transportation with a focus on electric mobility. Electric vehicle infrastructure, including charging stations and incentives for electric vehicle adoption, is widespread. Cities like Rotterdam are experimenting with innovative solutions such as e-mobility hubs that integrate electric vehicles with public transportation.
Green Tech Startups and Innovation Hubs:
The innovation hubs across Dutch cities actively support and incubate Green Tech startups. These startups focus on developing technologies that address environmental challenges and contribute to a sustainable future. Government initiatives and investment programs play a crucial role in propelling these startups from ideation to market implementation.
Access to Funding:
Access to funding is a crucial factor for the prosperity of entrepreneurs, and the Netherlands excels in this regard. The country has a well-developed financial infrastructure, with numerous venture capital firms, angel investors, and government-backed programs providing funding opportunities for businesses at various stages of development. This abundance of financial support allows entrepreneurs to turn their innovative ideas into reality.
Global Connectivity:
The Netherlands' strategic geographical location and excellent transportation infrastructure make it a gateway to Europe and beyond. Dutch entrepreneurs benefit from easy access to international markets, creating opportunities for global expansion. Moreover, the country's multilingual and highly skilled workforce enhances its global competitiveness.
Dutch Agencies and Programs for Startups
The Netherlands is a thriving hub for startups, offering a strong support system through various agencies and programs. Here's an overview of some key resources, including Dutchbasecamp:
Governmental Agencies:
Netherlands Enterprise Agency (RVO): Provides financial support, coaching, and access to networks for innovative startups. They offer grants and subsidies like the Proof of Concept (POC) grant and SME Instrument grant.
TechLeap: Focuses on accelerating growth in the Dutch tech sector, supporting startups in areas like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and fintech. They offer programs like TechLeap Ignite for early-stage startups and ScaleUpFast for growth-stage companies.
Incubators and Accelerators:
Dutchbasecamp: Dutchbasecamp specifically supports startups looking to expand into the European market. They offer market access, mentorship, and funding opportunities tailored to the needs of Indian companies.
Rockstart: One of the leading accelerators in Europe, with programs focused on specific sectors like fintech, foodtech, and energy. They provide funding, mentorship, and access to their extensive network.
Startupbootcamp: Runs industry-specific accelerator programs across various locations in Europe, including Amsterdam. They offer intensive support for startups to validate, refine, and scale their businesses.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the Dutch entrepreneurial landscape is flourishing, it is not without challenges. The competitive nature of the market demands continuous innovation and adaptability. Additionally, the impact of global events, such as economic downturns or geopolitical shifts, can influence the business environment.
Despite challenges, the current market in the Netherlands presents ample opportunities for entrepreneurs willing to embrace change, leverage technology, and contribute to sustainable practices. The Dutch entrepreneurial spirit, coupled with a supportive ecosystem, positions businesses for success in an ever-evolving global market.
Conclusion:
The prosperous Dutch entrepreneurial scene is a testament to the country's commitment to innovation, sustainability, and creating a conducive environment for businesses to thrive. As technology continues to reshape industries and sustainability becomes a priority, Dutch entrepreneurs are well-positioned to lead the way in shaping the future of business. The tulips may symbolize beauty, but it's the resilience and ingenuity of Dutch entrepreneurs that truly define the landscape of prosperity in the Netherlands.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#DutchEntrepreneurs hashtag#NetherlandsBusinessSuccess hashtag#DutchStartupCulture hashtag#EntrepreneurialVenturesNL hashtag#SuccessfulDutchBusinesses hashtag#DutchEntrepreneurshipTrends hashtag#InnovationInDutchStartups hashtag#DutchBusinessLeaders hashtag#NetherlandsEconomicGrowth hashtag#DutchEntrepreneurialEcosystem hashtag#StartupsInTheNetherlands hashtag#DutchBusinessAchievements hashtag#DutchEntrepreneurialSpirit hashtag#GrowingBusinessesNL hashtag#DutchSuccessStories hashtag#EntrepreneurshipInHolland hashtag#DutchBusinessLandscape hashtag#DutchSmallBusinessSuccess hashtag#DutchInnovationEntrepreneurship hashtag#DutchStartupScene
0 notes
Text
The Tech Boom in Africa and Middle East

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region has emerged as a dynamic and rapidly growing market, attracting attention from investors, businesses, and researchers alike. With diverse economies, cultures, and landscapes, the MEA region presents unique opportunities for growth and development across various sectors. In this article, we will delve into the current market trends and identify the booming sectors that are driving economic expansion in the Middle East and Africa.
The sun shines bright on the Middle East and Africa (MEA) as market research paints a picture of vibrant economies and burgeoning prospects. While certain sectors have always been robust, a closer look reveals some new stars rapidly eclipsing established players

The Middle East market presents a dynamic landscape with diverse opportunities across various sectors. While some traditional sectors remain strong, some others are experiencing a significant boom as we can see in the above figure.

Technology and Innovation:
One of the most significant trends in the MEA region is the rapid adoption of technology and innovation across various industries. The technology sector, in particular, has experienced substantial growth, with countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia, and South Africa leading the way. Investments in artificial intelligence, blockchain, and cybersecurity are on the rise, creating a fertile ground for startups and established companies alike.
Renewable Energy:
The MEA region has abundant sunlight and vast untapped renewable energy potential, making it an ideal hub for the development of solar and wind energy projects. Countries like Morocco and the UAE have made significant strides in harnessing renewable energy sources, attracting global investments and fostering sustainability initiatives. The renewable energy sector is on a steady rise, driven by the increasing emphasis on environmental consciousness and the need for alternative energy sources.
E-commerce and Digital Services:
The rise of e-commerce and digital services has transformed the retail landscape in the Middle East and Africa. With a growing young population and increasing internet penetration, consumers are shifting towards online platforms for shopping, entertainment, and financial services. E-commerce giants are expanding their presence in the region, capitalizing on the demand for convenience and the growing middle-class population.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals:
The healthcare sector in the MEA region is witnessing substantial growth, driven by increased government investments and a growing awareness of healthcare needs. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of a robust healthcare infrastructure, leading to increased funding for hospitals, medical research, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The demand for innovative healthcare solutions and pharmaceuticals is on the rise, creating opportunities for both local and international players.
Infrastructure Development:
Several countries in the MEA region are heavily investing in infrastructure development projects, including transportation, telecommunications, and urban development. The construction sector is booming, with mega projects such as the NEOM city in Saudi Arabia and the development of smart cities in the UAE. Infrastructure development not only enhances connectivity but also stimulates economic growth by creating jobs and fostering business activities.
Agriculture and Agribusiness:
Agriculture remains a vital sector in many African countries, and there is a growing focus on modernizing and enhancing productivity. Investments in agribusiness, including agrotech and food processing, are gaining momentum. Governments and private entities are working together to promote sustainable agriculture practices, improve supply chain efficiency, and address food security challenges.
Financial Technology (Fintech):
The financial technology sector is gaining traction in the Middle East and Africa, revolutionizing traditional banking and financial services. Fintech companies are introducing innovative solutions such as mobile banking, digital wallets, and peer-to-peer lending, catering to the unbanked and underbanked populations. Governments in the region are also supportive of fintech initiatives, creating regulatory frameworks to encourage entrepreneurship and financial inclusion.
Tourism and Hospitality:
Tourism has long been a significant contributor to the economies of countries in the Middle East, such as the UAE, Qatar, and Egypt. With a focus on diversifying their revenue streams, these nations are investing heavily in tourism infrastructure, including hotels, resorts, and entertainment complexes. Africa, with its rich cultural and natural attractions, is also witnessing a surge in tourism, presenting opportunities for the hospitality and travel sectors.
Education Technology (EdTech):
The education sector in the MEA region is undergoing a digital transformation, with EdTech gaining prominence. The demand for online learning platforms, e-learning content, and virtual classrooms has surged, driven by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the desire to enhance educational access. Governments are investing in technology-driven education solutions to improve learning outcomes and equip the workforce with the skills needed for a rapidly evolving global economy.
Consumer Goods and Retail:
The consumer goods and retail sector in the Middle East and Africa is experiencing a shift in consumer preferences and buying behavior. There is an increasing demand for high-quality products and a growing middle class with disposable income. International brands are expanding their presence in the region, and local businesses are exploring opportunities to meet the evolving needs of consumers. The rise of shopping festivals and online marketplaces further fuels the growth of this sector.
Space and Satellite Technology:
Countries in the Middle East, such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, are making significant strides in space exploration and satellite technology. The UAE, with its Mars mission success, has positioned itself as a player in the space industry. Investments in satellite communication, Earth observation, and space research are on the rise, offering opportunities for collaboration and partnerships with international space agencies and private space companies.
Mining and Extractive Industries:
Africa is rich in natural resources, and the mining and extractive industries play a crucial role in many African economies. The demand for minerals, including copper, gold, and rare earth elements, continues to grow globally. Countries like South Africa, Nigeria, and Ghana are major players in the mining sector, attracting investments in exploration, extraction, and processing of mineral resources.
In conclusion, the Middle East and African markets present a diverse landscape of booming sectors, each offering unique opportunities for growth and investment. From cutting-edge technology to traditional industries, the region's economic dynamics are evolving rapidly. As businesses and investors navigate this dynamic landscape, a thorough understanding of market trends, regulatory environments, and local nuances will be essential for sustainable success in the Middle East and Africa.
Business Ecosystem in the Middle East:
The business ecosystem in the Middle East is characterized by a combination of traditional industries and a growing emphasis on innovation and technology. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, including Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar, are at the forefront of economic diversification efforts.
Government Initiatives: Governments in the Middle East are actively promoting entrepreneurship and innovation through strategic initiatives. Vision 2030 in Saudi Arabia, UAE Vision 2021, and Vision 2022 in Qatar are comprehensive roadmaps that aim to reduce dependence on oil, stimulate private sector growth, and foster a knowledge-based economy.
Free Zones and Business Hubs: The region hosts numerous free zones and business hubs that provide favorable conditions for foreign investment and business setup. Dubai's Jebel Ali Free Zone, for example, has played a pivotal role in attracting international companies, offering tax incentives, full ownership rights, and streamlined business processes.
Venture Capital and Startups: The startup ecosystem is thriving in cities like Dubai and Riyadh, where government-backed funds and private venture capital firms actively support innovative ventures. Co-working spaces, incubators, and accelerators are contributing to the growth of a vibrant startup culture, with a focus on technology, fintech, and renewable energy.
Business Ecosystem in Africa:
Africa's business landscape is diverse, reflecting the continent's varied economies and markets. While challenges like infrastructure gaps and regulatory complexities exist, there's a palpable sense of growth and opportunity.
Regional Economic Blocs: Africa is home to various regional economic blocs, such as the African Union (AU) and the East African Community (EAC). These blocs aim to promote economic integration, intra-African trade, and harmonized business regulations, fostering a collaborative approach to regional development.
Agriculture and Agribusiness: In many African countries, agriculture remains a key component of the business ecosystem. Governments are actively supporting agribusiness initiatives to enhance food security, create jobs, and boost export revenues. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) further facilitates trade in agricultural products.
Informal Economy: In several African nations, a significant portion of economic activity takes place in the informal sector. Informal businesses, ranging from street vendors to small-scale enterprises, contribute substantially to employment and income generation. Governments are working to formalize and integrate these businesses into the mainstream economy.
Mining and Natural Resources: The extractive industries, including mining and oil production, play a pivotal role in many African economies. Countries like Nigeria, South Africa, and Ghana are key players in the global supply chain for minerals and energy resources, attracting investments from multinational corporations.
15. Cross-Border Collaboration:
Both the Middle East and Africa are witnessing increased cross-border collaboration to leverage synergies and enhance economic ties. Bilateral trade agreements, joint ventures, and strategic partnerships are becoming more common as businesses look to expand their reach beyond national borders.
Logistics and Transportation: Investments in logistics and transportation infrastructure are crucial for facilitating cross-border trade. The development of ports, railways, and road networks is a priority, reducing trade barriers and enabling more efficient movement of goods and services.
Digital Connectivity: The growth of digital connectivity is breaking down geographical barriers, fostering collaboration across borders. E-commerce platforms, digital payment systems, and cross-border fintech solutions are contributing to the seamless flow of business transactions.
In conclusion, the business ecosystems in the Middle East and Africa are evolving rapidly, driven by a mix of government initiatives, technological advancements, and a focus on sustainable development. As these regions continue to position themselves on the global stage, businesses will find diverse opportunities for growth, collaboration, and investment. A nuanced understanding of local nuances, regulatory frameworks, and cultural dynamics will be essential for navigating and thriving in these vibrant markets.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#hashtag#AfricanTechLandscape hashtag#MiddleEastTechnologyTrends hashtag#DigitalInnovationinAfrica hashtag#TechStartupsintheMiddleEast hashtag#ConnectivityinAfrica hashtag#MiddleEastEcommerceExpansion hashtag#FintechGrowthinAfrica hashtag#ArtificialIntelligenceintheMiddleEast hashtag#BlockchainAdoptioninAfrica hashtag#SmartCitiesintheMiddleEast hashtag#IoTinAfricaandtheMiddleEast hashtag#CybersecurityChallengesintheRegion hashtag#EntrepreneurshipintheMiddleEast hashtag#EdTechinAfricaandtheMiddleEast hashtag#SustainableTechPracticesinAfrica hashtag#RegionalCollaborationinTechnology hashtag#InvestmentOpportunitiesinAfricanTech hashtag#GovernmentTechInitiativesintheRegion hashtag#5GTechnologyDeploymentinAfrica hashtag#TechTalentDevelopmentintheMiddleEast
0 notes