#Gaelic/Irish
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
I think it’s just kinda ironic that Hozier released a song dedicated to the destruction of native culture and language, and most of you seem to be allergic to referring to the Irish language as Irish.
Gaelic is an umbrella term that describes many languages, mainly Irish, Welsh, and Scots Gaelic. Gaelic is not an actual language (or at least not anymore). All three are distinct languages with their own spellings and grammar. In the De Selby bts video Hozier himself refers to it as Irish.
You would not refer to Spanish as romantic when it could also mean French and Italian. Show some respect.
10K notes
·
View notes
Text










Kneecap (2024)
Dir. Rich Peppiatt
#kneecap#film#movie#drama#comedy#rap#hip hop#Irish#Irish film#Gaelic#rap group#2024 movies#rich peppiatt#belfast#mo chara#moglai bap#dj provai#michael fassbender
537 notes
·
View notes
Text
did you hear there’s a new short film that is GAY?? LESBIAN, even???
AND it’s filmed in a minority language?? a CELTIC language, one might say??
AND that it’s available for FREE, with SUBTITLES in both irish AND english??

“FAN” (2024) dir. cúnla ní bhraonáin morris
watch here 🫶
#fan#fan film#short film#irish film#irish short film#gay short film#lesbian#gay#irish#gaeilge#irish language#langblr#minority language#endangered language#gaelic#irish art#irish gaelic#stay#gearrscannán#gael#celtic#irish langblr#bloc tg4#romcom#comedy#lighthearted#romance#gay romance#lesbian romance#fan 2024
657 notes
·
View notes
Text
My most controversial take is that I think if youre going to be any kind of culturally based polytheist, you should a) learn the language and b) learn to do scholarly research.
I wont use the word "must", and call me a gatekeeper all you like, but there is so much misinformation out there that if you care about your practice being authentic/culturally sensitive AT ALL you need to learn how to sift through the centuries of romanticism and neopagan-speculation-sold-as-fact (looking at you, Wiccans).
Not saying your practice must be reconstructionist in nature, but if you can't tell what is supported by the data, what is conjecture, and what is outright fabrication, you are doing the material, your practice, and yourself a disservice.
#gaelpol#gaelic paganism#gaelic polytheism#celtic polytheism#heathenism#heathenry#norse paganism#norse polytheism#hellenic polythiest#hellenic pagan#hellenic polytheism#paganachd#irish paganism#celtic paganism
351 notes
·
View notes
Note
I dare YOU 🫵 to make Bonnie x the proxy doodles cause I think it would be cute (only if you want to though jdjdjsksksks)

They get paid under the table at Bonnie’s papas farm. Toby harasses her for extra money and food
#anon I adore you.#sweetart#creepypasta#creeped#creepypasta fanart#ticci toby#Kate the chaser#Bonnibel Hayes#imma be honest I named Bon before I realized Kate’s other last name#cuz I read that Hayes meant fire in irish/gaelic#n Bon used to have a backstory with a forest fire till I scrapped that#LMAOOO#so that’s my bad. copying Kate
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
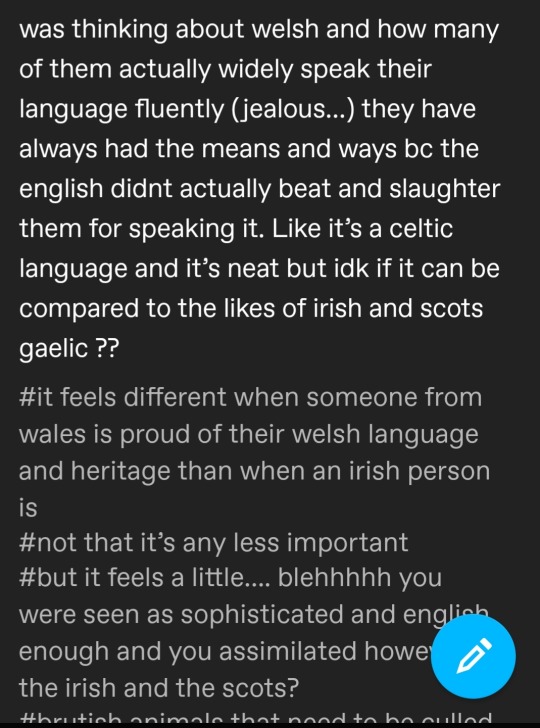
I'd like to preface this with that this is a screenshot of a post I saw a few days ago in the #welsh tag and that the OP has since deleted this post, but the sentiment is something I'd like to address since I see a lot of parallels with this kind of thinking in other contexts, such as in LGBTQIA+ rights conversations.
So, the most obvious elephant in the room is the idea that Welsh is super widely spoken in Wales now and that it isn't in as much danger as other Celtic languages. This idea is wishful thinking at best and erases the very real danger that Welsh is in and that it could be lost just as easily as Irish or Scottish Gaelic. Cornish (which is related to Welsh) actually did die out and has had to be revived. To make a metaphor out of this, we classify languages on a scale of non-threatened to endangered in a similar way to how we classify species.


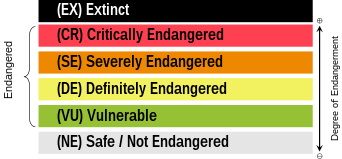
Here are the statuses of Welsh and Irish as of 2010 (above) and the statuses of Lions and Tigers (below).

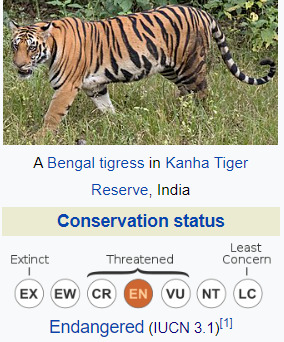
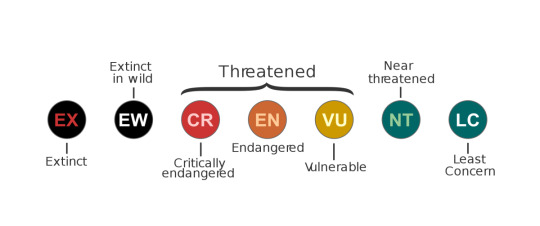
On paper tigers are more 'in danger' than lions. But that does not mean that lions are suddenly not in danger at all. The little bracket above CR, EN and VU labels all of these classifications as threatened. It isn't (and definitely shouldn't) be a competition of 'who is most in danger' because you do not want the thing you care about (whether it be a species or a language) to be in danger.

To come back to the original screenshot "they* [Welsh speakers] have always had the means and the ways because the English didn't beat or slaughter them for speaking it"- on the most basic of levels, this is just incorrect. The Welsh Not was a wooden token hung around schoolchildren's necks if they spoke Welsh in school. If someone else spoke Welsh the Not would be hung around their neck. At the end of the school day, whoever was wearing the Not would be beaten and caned by their teachers. I needn't go into much detail but there have been concerted efforts to beat Welsh out of schoolchildren. With the lions vs tigers metaphor, making the claim Welsh speakers have never been beaten for speaking Welsh because they always had the means and ways, while Irish speakers were beaten and never had the means or ways is like claiming poachers have never shot lions, only tigers. Bottom line is, lions and tigers are both victim to poaching and both species have suffered as a result. Similarly, Welsh and Irish have both suffered language loss and both need conservation efforts in order to survive.
(*sidenote- the consistent use of 'them' and 'they' in the original post is definitely indicative of a 'us vs them' sentiment which is a deeply unhelpful attitude to have when it comes to endangered languages and the Celtic languages in particular)
I see parallels with LGBTQIA+ rights in this situation. When equal marriage came in for gay and lesbian couples in the UK in 2014, many allies began to act like gay rights had now been achieved and that gay issues had been done, they're solved. Except, they really weren't (and aren't). Progress has been made in Wales and undeniably Welsh is doing the best out of the living Celtic languages. But that doesn't mean Welsh has been saved or that full equality for Welsh speakers has been achieved. It very much hasn't. The sentiment of the post in the screenshot is not conducive to helping Irish or Scottish Gaelic. Putting down Welsh speakers and erasing Welsh-language history will not save Irish or Scottish Gaelic. Pretending Welsh has had it easy in some kind of lap of luxury is a deeply harmful and bogus claim.
I'll address the tags under the cut as this post is getting long.
To address the tags, personal feelings ≠ an accurate reading of a situation. Nor is it praxis, for that matter. Why is pride in Welsh different/less good than pride in Irish? Is it the assumed proximity to England? If so, that's a terrible claim to make. Not only that, but Scotland is also next to England- does that make pride in Scottish Gaelic the same as pride in Welsh according to this metric? It's a ludicrous thing to say and deeply insensitive to the needs of Scottish Gaelic and Welsh speakers, who cannot help any current or former proximity to England.
Additionally, proximity to England ≠ worse. I know it's a popular internet joke to hate on England because of English attempts to eradicate the Celtic languages, but when the joke becomes praxis, it does not help. England ≠ a place devoid of Celtic languages either. Many English counties near the Welsh border actually have communities of Welsh speakers, such as Oswestry (Croesoswallt) in Shropshire. Cornwall is also home to many speakers of revived Cornish. It does a disservice to Celtic speakers in England to insinuate that proximity to England taints or corrupts them somehow. This is how ethnonationalism starts and we ain't about that.
And "#it feels a little.... blehhhhh you were seen as sophisticated and english enough and you assimilated however the Irish and the Scots? #brutish animals that need to be culled". So, this is arguably one of the worst things to say about a Celtic language- or any threatened language in general. First of all, the 'you were seen as' - 'you' is very telling. The switch from 'them', 'they' to 'you' indicates that this sentiment is aimed at Welsh speakers directly. This was likely a subconscious thing that OP wasn't thinking about when they wrote this. But it does indicate unhealthy feelings of jealousy and bitterness unfairly directed at Welsh speakers, who are also struggling. This righteous anger at the decline of Irish and Scottish Gaelic would be better directed at efforts to help promote those languages- some useful things to get involved with are LearnGaelic, similar to DysguCymraeg but for Scottish Gaelic or supporting channels such as Irish channel TG4 by watching their programmes.
The idea that Welsh speakers were or are 'sophisticated and english enough' is insulting and carries with it a lot of baggage of how any of these assumptions came about. Welsh speakers were definitely not seen as sophisticated. Where Welsh was 'tolerated', it was treated as a curiosity, a relic of a bygone age. Classic museification which all Celtic languages and cultures suffer from as well. Welsh was not tolerated in any legal sense since 1535- with English becoming the only valid administrative language and the language of Welsh courts after England annexed Wales into its Kingdom. Monolingual Welsh speakers suddenly had no access to any legal representation, unless they learned English. This is no voluntary assimilation- it is an act of survival for many speakers of minoritised languages to 'assimilate' into the dominant culture, or else risk losing access to legal security and other kinds of infrastructure. You need only ask any non-native English speaker living in an Anglophone country what that process is like. Welsh people did not see English incursion as an opportunity to become 'sophisticated and english enough', they had to assimilate in order to survive.
The "Irish and the Scots? #brutish animals that need to be culled" is also painfully misrepresenting a very complex social and political process that unfolded over the span of hundreds of years. The phrasing itself of 'brutish animals that need to be culled' speaks to righteous anger at the damage done to these languages and cultures, but it reinforces negative stereotypes about the Irish and Scots themselves. It also is more complicated than a simple English hatred of anything non-Anglo, since the English conception of particularly the Irish changed a lot over the centuries. It was (and still is) rarely consistent with itself. See: the enemy is both strong and weak. The very earliest Celticists were by and large, Anglos or French.
Ernest Renan (1823-1892) for example, was an early French Celticist who published La Poésie des races celtiques (Poetry of the Celtic Races- English translation) in which he says:
"... we must search for the explanation of the chief features of the Celtic character. It has all the failings, and all the good qualities, of the solitary man; at once proud and timid, strong in feeling and feeble in action, at home free and unreserved, to the outside world awkward and embarrassed. It distrusts the foreigner, because it sees in him a being more refined than itself, who abuses its simplicity. Indifferent to the admiration of others, it asks only one thing, that it should be left to itself. It is before all else a domestic race, fitted for family life and fireside joys. In no other race has the bond of blood been stronger, or has it created more duties, or attached man to his fellow with so much breadth and depth"
Yeah. This guy (unsurprisingly) was a white supremacist. Note that this sentiment is being applied to all people considered Celtic by Renan- Irish, Welsh, Breton, Scottish, Cornish, Manx etc. None unscathed by the celtophobia of the day. In this period, Celticity was romanticised (yet disparaged at the same time). It is less 'brutish animals' and more 'archaic, time-frozen peoples' in this period. Of course, 'brutish animals' attitudes towards Celticity did still exist, but it is disingenuous to act as if it was this attitude alone which drove English celtophobia. Like many things, it is always more complicated and never clear cut as it might seem.
I'll bring this to a close shortly, but returning to OP's suggestion that the Welsh assimilated and the Scots and Irish did not, is also incorrect in that some Scots did have to assimilate to survive as well. The Statutes of Iona (1609) required Scottish Gaelic speaking Highland chiefs to send their sons away to be educated in Scots and/or English in Protestant schools. Many did as the statutes required, which led to further language loss in the Highlands of Scottish Gaelic. These are acts of survival- and not ones always taken willingly.
This has been a long post but it's one which I felt I wanted to address. There's no need for infighting between speakers of Celtic languages over who has it worse. There isn't any answer to that question, nor is it a good use of time or energy. All in all, the Celtic languages have suffered greatly over the years and its only just now that some of them are turning a corner. If you care about these languages, put your energy into something good. Only through active work will these languages be saved for generations to come.
#long post#lukes originals#cymraeg#gaelige#gaidhlig#Irish#Welsh#Scottish Gaelic#politik#not dictionary related#Celticist#Celtic Studies#This took a lot of energy to write so if you found this post useful please consider reblogging
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Gàidhlig vs Gaeilge
The languages Scots Gaelic* (Gàidhlig) and Irish Gaelic (Gaeilge, also known in English as simply “Irish”) are two separate languages, yet in English they are often both called Gaelic.
However, they are pronounced completely differently.
Gaelic (Scottish) rhymes with Alec
Gaelic (Irish) sounds like Gay-lick
As a fun fact, it's easy to tell apart Scots Gaelic and Irish Gaelic visually because in Gàidhlig 🏴 all the accents are grave - “welcome to Scotland”, which you'll see driving over the border, is “fàilte gu Alba” - while in Gaeilge 🇮🇪 all the accents are acute - “welcome to Ireland” is “fáilte go hÉirinn”.
This has been a very friendly PSA from a Scot who has heard Scots Gaelic mispronounced as “Gaylick” too many times - and now you can go on your merry linguistic way confident in your pronunciation of these two words which look identical but sound totally different and refer to two separate things.
*not to be at all confused with the Scots language, which is its own separate thing and very much not included under “Gaelic”
#langblr#languages#learning languages#language learning#linguistics#gaelic#scots gaelic#gàidhlig#irish language#irish gaelic#gaeilge#my posts
403 notes
·
View notes
Text
Something about... fields... (in Irish)
I've been recommended a lot of posts regarding my endemic language, Irish Gaelic (an Ghaeilge), in recent times on this site (much to my joy), so I thought I'd make a post about something related that continues to tickle my brain. I don't know if many other languages have this kind of distinction, but in Irish, we have a lot, and I mean a lot, of words for field. Around 30 or so words. Though, in a good few modern dictionaries, the distinction between each term isn't really explained. Manchán Magan wrote about this in one of his more recent books, which is what made me think about start thinking about this again.
A general word for field we Irish people would learn in school would be páirc, which is from the same root as English park, but I find that word a bit dull. Here's a couple more specific words you mightn't know:
gort - a more rural field, used to grow crops such as corn or wheat.
geamhar - another crop field, this time used for corn grass.
garraí - yet another one, reserved for potatoes.
réidhleán - a field reserved for parties, game and dance.
fásach - a field consumed by the wilderness. Love exploring those.
póicín - a very small field - something to make you think "why even?"
cathairín - a field with a fairy dwelling in it - best keep away.
cluain - a meadowy field (or just a meadow, but whatever.)
tuar - a sheep run, or a pasture for animals to stay in overnight.
buaile - a summer pasture, or in posh terms, a shieling.
branar - a fallow field. Not too out there.
mothar - a field completely overrun, akin to a full-on jungle. Cool.
maigh - a normal, level, plain field. Nothing special.
cuibhreann - an enclosed/fenced field. Again, not too special
If you're learning Irish, I hope you maybe learned a thing or two. If you already know Irish enough to know those, I pass my respects to you. (and if I spelt something wrong as I usually do, please don't nag me about it ;-; I'll probably notice it at some point)
Go maire sibh an lá, a chairde.
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did the ancient Celts really paint themselves blue?
Part 2: Irish tattoos
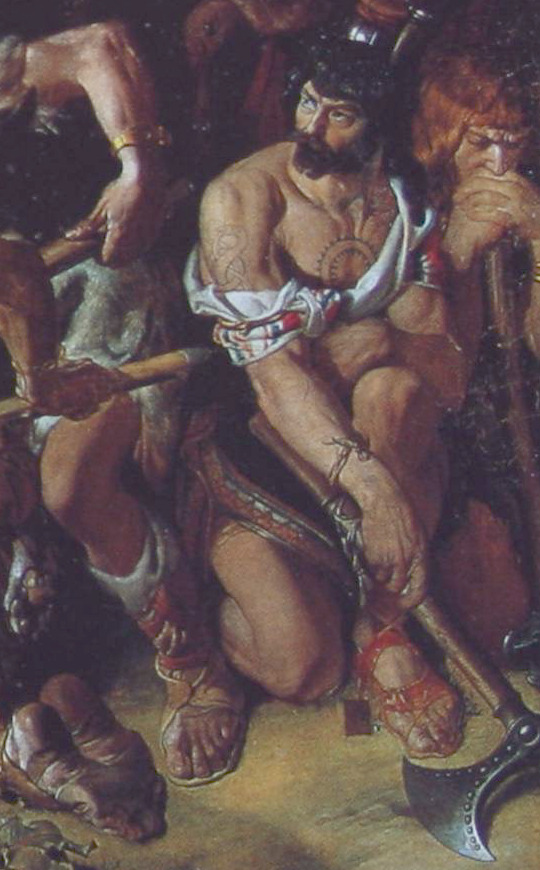
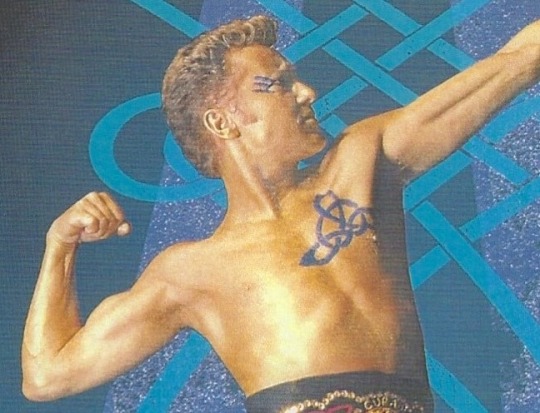
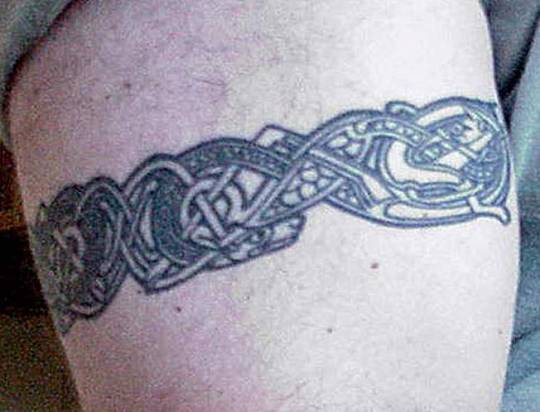




Clockwise from top left: Deirdre and Naoise from the Ulster Cycle by amylouioc, detail from The Marriage of Strongbow and Aoife by Daniel Maclise, a modern Celtic revival tattoo, Michael Flatley in a promotional image for the Irish step dance show 'Lord of the Dance'
This is my second post exploring the historical evidence for our modern belief that the ancient and medieval Insular Celts painted or tattooed themselves with blue pigment. In the first post, I discussed the fact that body paint seems to have been used by residents of Great Britain between approximately 50 BCE to 100 CE. In this post, I will examine the evidence for tattooing.
Once again, I am looking at sources pertaining to any ethnic group who lived in the British Isles, this time from the Roman Era to the early Middle Ages. The relevant text sources range from approximately 200 CE to 900 CE. I am including all British Isles cultures, because a) determining exactly which Insular culture various writers mean by terms like ‘Briton’, ‘Scot’, and ‘Pict’ is sometimes impossible and b) I don’t want to risk excluding any relevant evidence.
Continental Written Sources:
The earliest written source to mention tattoos in the British Isles is Herodian of Antioch’s History of the Roman Empire written circa 208 CE. In it, Herodian says of the Britons, "They tattoo their bodies with colored designs and drawings of all kinds of animals; for this reason they do not wear clothes, which would conceal the decorations on their bodies" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). Herodian is probably reporting second-hand information given to him by soldiers who fought under Septimius Severus in Britain (MacQuarrie 1997) and shouldn't be considered a true primary source.
Also in the early 3rd century, Gaius Julius Solinus says in Collectanea Rerum Memorabilium 22.12, "regionem [Brittaniae] partim tenent barbari, quibus per artifices plagarum figuras iam inde a pueris variae animalium effigies incorporantur, inscriptisque visceribus hominis incremento pigmenti notae crescunt: nec quicquam mage patientiae loco nationes ferae ducunt, quam ut per memores cicatrices plurimum fuci artus bibant."
Translation: "The area [of Britain] is partly occupied by barbarians on whose bodies, from their childhood upwards, various forms of living creatures are represented by means of cunningly wrought marks: and when the flesh of the person has been deeply branded, then the marks of the pigment get larger as the man grows, and the barbaric nations regard it as the highest pitch of endurance to allow their limbs to drink in as much of the dye as possible through the scars which record this" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
This passage, like Herodian's, is clearly a description of tattooing, not body staining or painting. That said, I have no idea of tattoos actually work like this. I would think this would result in the adult having a faded, indistinct tattoo, but if anyone knows otherwise, please tell me.
The poet Claudian, writing in the early 5th c., is the first to specifically mention the Picts having tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). In De Bello Gothico he says, "Venit & extremis legio praetenta Britannis,/ Quæ Scoto dat frena truci, ferroque notatas/ Perlegit exanimes Picto moriente figuras."
Translation: "The legion comes to make a trial of the most remote parts of Britain where it subdues the wild Scot and gazes on the iron-wrought figures on the face of the dying Pict" (from MacQuarrie 1997).
Last, and possibly least, of our Mediterranean sources is Isidore of Seville. In the early 7th c. he writes, "the Pictish race, their name derived from their body, which the efficient needle, with minute punctures, rubs in the juices squeezed from native plants so that it may bring these scars to its own fashion [. . .] The Scotti have their name from their own language by reason of [their] painted body, because they are marked by iron needles with dark coloring in the form of a marking of varying shapes." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
Isidore is the earliest writer to explicitly link the name 'Pict' to their 'painted' (Latin: pictus) i.e. tattooed bodies. Isidore probably borrowed information for his description from earlier writers like Claudian (MacQuarrie 1997).
In the 8th century, we have a source that definitely isn't Romans recycling old hearsay. In 786, a pair of papal legates visited the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria (Story 1995). In their report to Pope Hadrian, the legates condemn pagans who have "superimposed most hideous cicatrices" (i.e gotten tattoos), likening the pagan practice to coloring oneself "with dirty spots". The location of the visit indicates that these are Anglo-Saxon tattoos rather than Celtic, but some scholars have suggested that the Anglo-Saxons might have adopted the practice from the Brittonic Celts (MacQuarrie 1997).
A gloss in the margin of the late 9th c. German manuscript Fulda Aa 2 defines Stingmata [sic] as "put pictures on the bodies as the Irish (Scotti) do." (translation from MacQuarrie 1997).

Fulda Aa 2 folio 43r The gloss is on the left underlined in white.
Irish Written Sources:
Irish texts that mention tattoos date to approximately 700-900 CE, although some of them have glosses that may be slightly later, and some of them cannot be precisely dated.
The first text source is a poem known in English as "The Caldron of Poesy," written in the early 8th c. (Breatnach 1981). The poem is purportedly the work of Amairgen, ollamh of the legendary Milesian kings. In the first stanza of the poem, he introduces himself saying, "I being white-kneed, blue-shanked, grey-bearded Amairgen." (translation from Breatnach 1981)

The text of the poem with interline glosses from Trinity College Dublin MS 1337/1
The word garrglas (blue-shanked) has a Middle Irish (c. 900-1200) gloss added by a later scribe, defining garrglas as: "a tattooed shank, or who has the blue tattooed shank" (Breatnach 1981).
Although Amairgen was a mythical figure, the position ollamh was not. An ollamh was the highest rank of poet in medieval Ireland, considered worthy of the same honor-price as a king (Carey 1997, Breatnach 1981). The fact that a man of such esteemed status introduces himself with the descriptor 'blue-shanked' suggests that tattoos were a respectable thing to have in early medieval Ireland.
The leg tattoos are also mentioned c. 900 CE in Cormac’s Glossary. It defines feirenn as "a thong which is about the calf of a man whence ‘a tattooed thong is tattooed about [the] calf’" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997)
The Irish legal text Uraicecht Becc, dated to the 9th or early 10th c., includes the word creccoire on a list of low-status occupations (Szacillo 2012, MacNeill 1924). A gloss defines it as: crechad glass ar na roscaib, a phrase which Szacillo interprets as meaning "making grey-blue sore (tattooing) on the eyes" (2012). This sounds rather strange, but another early Irish text clarifies it.
The Vita sancti Colmani abbatis de Land Elo written around the 8th-9th centuries (Szacillo 2012) contains the following episode:
On another time, St Colmán, looking upon his brother, who was the son of Beugne, saw that the lids of his eyes had been secretly painted with the hyacinth colour, as it was in the custom; and it was a great offence at St Colmán’s. He said to his brother: ‘May your eyes not see the light in your life (any more). And from that hour he was blind, seeing nothing until (his) death. (translation from Szacillo 2012).
The original Latin phrase describing what so offended St Colmán "palpebre oculorum illius latenter iacinto colore" does not contain the verb paint (pingo). It just says his eyelids were hyacinth (blue) colored. This passage together with the gloss from the Uraicecht Becc implies that there was a custom of tattooing people's eyelids blue in early medieval Ireland. A creccoire* was therefore a professional eyelid tattooer or a tattoo artist.
A possible third reference to tattooing the area around the eye is found in a list of Old Irish kennings. The kenning for the letter 'B' translates as 'Beauty of the eyebrow.' This kenning is glossed with the word crecad/creccad (McManus 1988). Crecad could be translated as cauterizing, branding, or tattooing (eDIL). McManus suggests "adornment (by tattooing) of the eyebrow" as a plausible interpretation of how crecad relates to the beauty of the eyebrow (1988). The precise date of this text is not known (McManus 1988), but Old Irish was used c. 600-900 CE, meaning this text is of a similar date to the other Irish references to tattoos.

Kenning of the letter 'b' with gloss from TCD MS 1337/1
There is a sharp contrast between the association of tattoos with a venerated figure in 'The Caldron of Poesy', and their association with low-status work and divine punishment in the Uraicecht Becc and the Vita. This indicates that there was a shift in the cultural attitude towards tattoos in Ireland during the 7th-9th centuries. The fact that a Christian saint considered getting tattoos a big enough offense to punish his own brother with blindness suggests that tattooing might have been a pagan practice which gradually got pushed out by the Catholic Church. This timeline is consistent with the 786 CE report of the papal legates condemning the pagan practice of tattooing in Great Britain (MacQuarrie 1997).
There are some mentions of tattooing in Lebor Gabála Érenn, but the information largely appears to be borrowed from Isidore of Seville (MacQuarrie 1997). The fact that the writers of LGE just regurgitated Isidore's meager descriptions of Pictish and Scottish (ie Irish) tattooing without adding any details, such as the designs used or which parts of the body were tattooed, makes me think that Insular tattooing practices had passed out of living memory by the time the book was written in the 11th century.
*There is some etymological controversy over this term. Some have suggested that the Old Irish word for eyelid-tattooer should actually be crechaire. more info Even if this hypothesis is correct, and the scribe who wrote the gloss on creccoire mistook it for crechaire, this doesn't contradict my argument. The scribe clearly believed that eyelid-tattooer belonged on a list of low-status occupations.
Discussion:
Like Julius Cesar in the last post, Herodian of Antioch c. 208 CE makes some dubious claims of Celtic barbarism, stating that the Britons were: "Strangers to clothing, the Britons wear ornaments of iron at their waists and throats; considering iron a symbol of wealth, they value this metal as other barbarians value gold" (translation from MacQuarrie 1997). If the Britons wore nothing but iron jewelry, then why did they have brass torcs and 5,000 objects that look like they're meant to attach to fabric, Herodian?
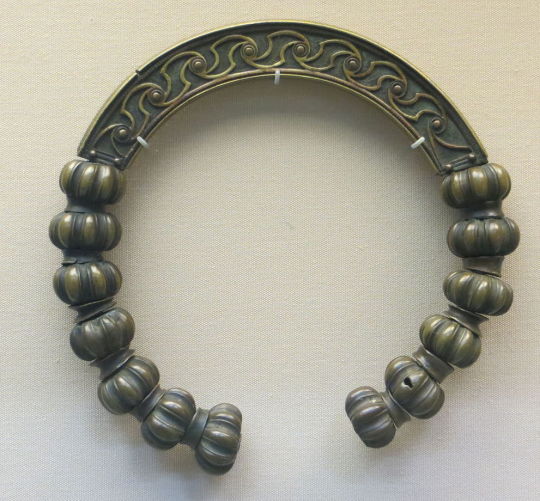
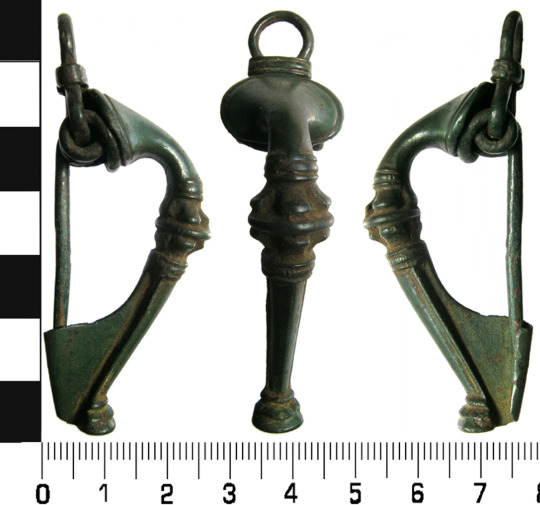


Brass torc from Lochar Moss, Scotland c. 50-200 CE. Romano-British trumpet brooch from Cumbria c. 75-175 CE. image from the Portable Antiquities Scheme.
Trumpet brooches are a Roman Era artifact invented in Britain, that were probably pinned to people's clothing. more info
Although Herodian and Solinus both make dubious claims, there are enough differences between them to indicate that they had 2 separate sources of information, and one was not just parroting the other. This combined with the fact that we have more-reliable sources from later centuries confirming the existence of tattoos in the British Isles makes it probable that there was at least a grain of truth to their claims of tattooing.
There is a common belief that the name Pict originated from the Latin pictus (painted), because the Picts had 'painted' or tattooed bodies. The Romans first used the name Pict to refer to inhabitants of Britain in 297 CE (Ware 2021), but the first mention of Pictish tattoos came in 402 CE (Carr 2005), and the first explicit statement that the name Pict was derived from the Picts' tattooed bodies came from Isidore of Seville c. 600 CE (MacQuarrie 1997). Unless someone can find an earlier source for this alleged etymology than Isidore, I am extremely skeptical of it.
Summary of the written evidence:
Some time between c. 79 CE (Pliny the Elder) and c. 208 CE (Herodian of Antioch) the practice of body art in Great Britain changed from staining or painting the skin to tattooing. Third century Celtic Briton tattoo designs depicted animals. Pictish tattoos are first mentioned in the 5th century.
The earliest mention of Irish tattoos comes from Isidore of Seville in the early 6th c., but since it seems to have been a pre-Christian practice, it likely started earlier. Irish tattoos of the 8-9th centuries were placed on the area around the eye and on the legs. They were a bluish color. The 8th c. Anglo-Saxons also had tattoos.
Tattooing in Ireland probably ended by the early 10th c., possibly because of Christian condemnation. Exactly when tattooing ended in Great Britain is unclear, but in the 12th c., William of Malmesbury describes it as a thing of the past (MacQuarrie 1997). None of these sources give much detail as to what the tattoos looked like.
The Archaeology of Insular Ink:
In spite of the fact that tattooing was a longer-lasting, more wide-spread practice in the British Isles than body painting, there is less archaeological evidence for it. This may be because the common tools used for tattooing, needles or blades for puncturing the skin, pigments to make the ink, and dishes to hold the ink, all had other common uses in the Middle Ages that could make an archaeologist overlook their use in tattooing. The same needle that was used to sew a tunic could also have been used to tattoo a leg (Carr 2005). A group of small, toothed bronze plates from a Romano-British site at Chalton, Hampshire might have been tattoo chisels (Carr 2005) or they might have been used to make stitching holes in leather (Cunliffe 1977).
Although the pigment used to make tattoos may be difficult to identify at archaeological sites, other lines of evidence might give us an idea of what it was. Although the written sources tell us that Irish tattoos were blue, the popular modern belief that woad was the source of the tattoo pigment is, in my opinion, extremely unlikely for a couple of reasons:
1) Blue pigment from woad doesn't seem to work as tattoo ink. The modern tattoo artists who have tried to use it have found that it burns out of the person's skin, leaving a scar with no trace of blue in it (Lambert 2004).
2) None of the historical sources actually mention tattooing with woad. Julius Cesar and Pliny the Elder mention something that might have been woad, but they were talking about body paint, not tattoos. (see previous post) Isidore of Seville claimed that the Picts were tattooing themselves with "juices squeezed from native plants", but even assuming that Isidore is a reliable source, you can't get blue from woad by just squeezing the juice out of it. In order to get blue out of woad, you have to first steep the leaves, then discard the leaves and add a base like ammonia to the vat (Carr 2005). The resulting dye vat is not something any knowledgeable person would describe as plant juice, so either Isidore had no idea what he was talking about, or he is talking about something other than blue pigment from woad.
In my opinion, the most likely pigment for early Irish and British tattoos is charcoal. Early tattoos found on mummies from Europe and Siberia all contain charcoal and no other colored pigment. These tattoos range in date from c. 3300 BCE (Ötzi the Iceman) to c. 300 CE (Oglakhty grave 4) (Samadelli et al 2015, Pankova 2013).
Despite the fact that charcoal is black, it tends to look blueish when used in tattoos (Pankova 2013). Even modern black ink tattoos that use carbon black pigment (which is effectively a purer form of charcoal) tend to look increasingly blue as they age.
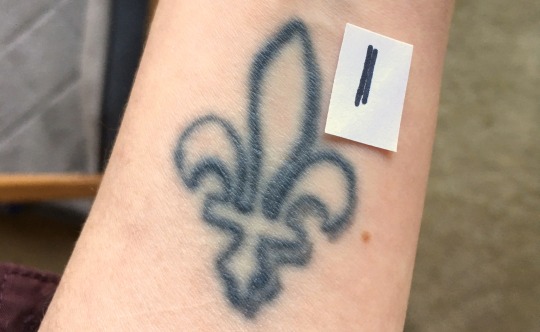
A 17-year-old tattoo in carbon black ink photographed with a swatch of black Sharpie on white printer paper.
The fact that charcoal-based tattoo inks continue to be used today, more than 5,000 years after the first charcoal tattoo was given, shows that charcoal is an effective, relatively safe tattoo pigment, unlike woad. Additionally, charcoal can be easily produced with wood fires, meaning it would have been a readily available material for tattoo artists in the early medieval British Isles. We would need more direct evidence, like a tattooed body from the British Isles, to confirm its use though.
As of June 2024, there have been at least 279 bog bodies* found in the British Isles (Ó Floinn 1995, Turner 1995, Cowie, Picken, Wallace 2011, Giles 2020, BBC 2024), a handful of which have made it into modern museum collections. Unfortunately, tattoos have not been found on any of them. (We don't have a full scientific analysis for the 2023 Bellaghy find yet though.)
*This number includes some finds from fens. It does not include the Cladh Hallan composite mummies.
Tattoos in period art?
It has been suggested that the man fight a beast on Book of Kells f. 130r may be naked and covered in tattoos (MacQuarrie 1997). However, Dress in Ireland author Mairead Dunlevy interprets this illustration as a man wearing a jacket and trews (Dunlevy 1989). Looking at some of the other figures in the Book of Kells, I agree with Dunlevy. F. 97v shows the same long, fitted sleeves and round neckline. F. 292r has long, fitted leg coverings, presumably trews, and also long sleeves. The interlace and dot motifs on f. 130r's legs may be embroidery. Embroidered garments were a status symbol in early medieval Ireland (Dunlevy 1989).
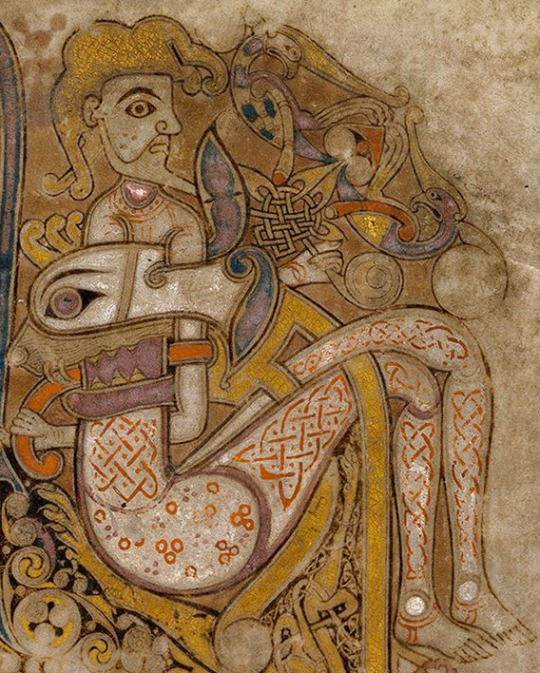


Left to right: Book of Kells folios 130r, 97v, 292r
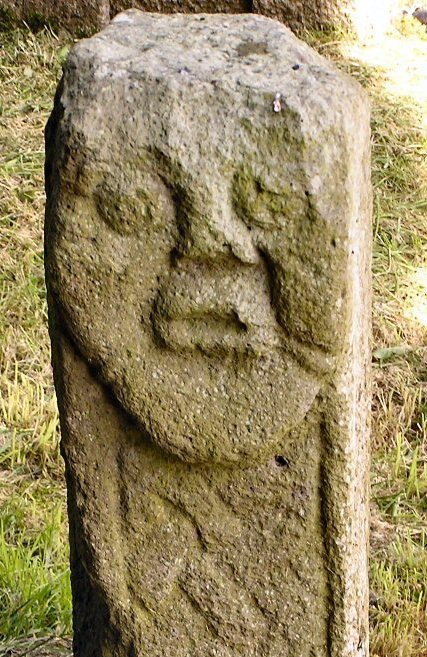
A couple of sculptures in County Fermanagh might sport depictions of Irish tattoos. The first, known as the Bishop stone, is in the Killadeas cemetery. It features a carved head with 2 marks on the left side of the face, a double line beside the mouth and a single line below the eye. These lines may represent tattoos.
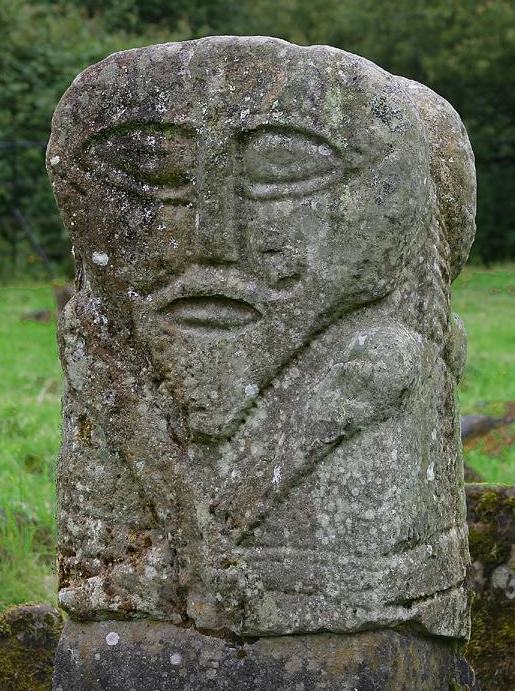


The second sculpture is the Janus figure on Boa Island. (So named because it has 2 faces; it's not Roman.) It has marks under the right eye and extending from the corner of the left eye that may be tattoos.
I cannot find a definitive date for the Bishop stone head, but it bears a strong resemblance to the nearby White Island church figures. The White Island figures are stylistically dated to the 9th-10th centuries and may come from a church that was destroyed by Vikings in 837 CE (Halpin and Newman 2006, Lowry-Corry 1959). The Janus figure is believed to be Iron Age or early medieval (Halpin and Newman 2006).
Conclusions:
Despite the fact that tattooing as a custom in the British Isles lasted for more than 500 years and was practiced by at least 3 different cultures, written sources remain our only solid evidence for it. With only a dozen sources, some of which probably copied each other, to cover this time span, there are huge gaps in our knowledge. The 4th century Picts may not have had the same tattoo designs, placements or reasons for getting tattooed as the 8th c. Irish or Anglo-Saxons. These sources only give us fragments of information on who got tattooed, where the tattoos were placed, what they looked like, how the tattoos were done, and why people got tattooed. Further complicating our limited information is the fact that most of the text sources come from foreigners and/or people who were prejudiced against tattooing, which calls their accuracy into question.
'The Cauldron of Posey' is one source that provides some detail while not showing prejudice against tattoos. The author of the poem was probably Christian, but the poem appears to have been written at a time when Pagan practices were still tolerated in Ireland. I have a complete translation of the poem along with a longer discussion of religious elements here.
Leave me a tip?
Bibliography:
BBC (2024). Bellaghy bog body: Human remains are 2,000 years old https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-northern-ireland-68092307
Breatnach, L. (1981). The Cauldron of Poesy. Ériu, 32(1981), 45-93. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007454
Carey, J. (1997). The Three Things Required of a Poet. Ériu, 48(1997), 41-58. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30007956
Carr, Gillian. (2005). Woad, Tattooing and Identity in Later Iron Age and Early Roman Britain. Oxford Journal of Archaeology 24(3), 273–292. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0092.2005.00236.x
Cowie, T., Pickin, J. and Wallace, T. (2011). Bog bodies from Scotland: old finds, new records. Journal of Wetland Archaeology 10(1): 1–45.
Cunliffe, B. (1977) The Romano-British Village at Chalton, Hants. Proceedings of the Hampshire Field Club and Archaeological Society, 33(1977), 45-67.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
eDIL s.v. crechad https://dil.ie/12794
Giles, Melanie. (2020). Bog Bodies Face to face with the past. Manchester University Press, Manchester. https://library.oapen.org/viewer/web/viewer.html?file=/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/46717/9781526150196_fullhl.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Halpin, A., Newman, C. (2006). Ireland: An Oxford Archaeological Guide to Sites from Earliest Times to AD 1600. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://archive.org/details/irelandoxfordarc0000halp/page/n3/mode/2up
Hoecherl, M. (2016). Controlling Colours: Function and Meaning of Colour in the British Iron Age. Archaeopress Publishing LTD, Oxford. https://www.google.com/books/edition/Controlling_Colours/WRteEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
Lambert, S. K. (2004). The Problem of the Woad. Dunsgathan.net. https://dunsgathan.net/essays/woad.htm
Lowry-Corry, D. (1959). A Newly Discovered Statue at the Church on White Island, County Fermanagh. Ulster Journal of Archaeology, 22(1959), 59-66. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20567530
MacQuarrie, Charles. (1997). Insular Celtic tattooing: History, myth and metaphor. Etudes Celtiques, 33, 159-189. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecelt.1997.2117
McManus, D. (1988). Irish Letter-Names and Their Kennings. Ériu, 39(1988), 127-168. https://www.jstor.org/stable/30024135
Ó Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Pankova, S. (2013). One More Culture with Ancient Tattoo Tradition in Southern Siberia: Tattoos on a Mummy from the Oglakhty Burial Ground, 3rd-4th century AD. Zurich Studies in Archaeology, 9(2013), 75-86.
Samadelli, M., Melisc, M., Miccolic, M., Vigld, E.E., Zinka, A.R. (2015). Complete mapping of the tattoos of the 5300-year-old Tyrolean Iceman. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 16(2015), 753–758.
Story, Joanna (1995). Charlemagne and Northumbria : the in
fluence of Francia on Northumbrian politics in the later eighth and early ninth centuries. [Doctoral Thesis]. Durham University. http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/1460/
Szacillo, J. (2012). Irish hagiography and its dating: a study of the O'Donohue group of Irish saints' lives. [Doctoral Thesis]. Queen's University Belfast.
Turner, R.C. (1995). Resent Research into British Bog Bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 221–34). British Museum Press, London. ISBN: 9780714123059
Ware, C. (2021). A Literary Commentary on Panegyrici Latini VI(7) An Oration Delivered Before the Emperor Constantine in Trier, ca. AD 310. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://www.google.com/books/edition/A_Literary_Commentary_on_Panegyrici_Lati/oEwMEAAAQBAJ?hl=en&gbpv=0
#early medieval#roman era#pict#tattoos#ancient celts#apologies to people who wanted a shorter post#archaeology#art#anecdotes and observations#statutes and laws#irish history#gaelic ireland#medieval ireland#anglo saxon#insular celts#romano british
109 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sétanta & the Hound 🐺🩸
This print is exclusive right now to my monthly postcard club! If you’re interested in art and learning more about Irish myths and folklore, consider checking it out here.
Sign up before end of July 2024 to get a print!
#irish mythology#artists on tumblr#irish folklore#celtic mythology#illustration#amylouioc art#fantasy illustration#irish myths#irish#cu chulainn#ulster cycle#gaelic mythology#ireland
137 notes
·
View notes
Text
Daily Irish Lesson 14
To say 'I love you' in Irish we say 'Tá mé chun tú a mharú'
Pronunciation: taw may kun too ah vah-roo
#irish#gaeilge#i love you#language#langblr#ireland#dublin#gaelic#irish language#hii#daily irish lesson#qsoc#endangered languages
77 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Bardic Tradition
I made a long thread explaining in detail all the symbolism in this piece when I first posted it. That's lost to time now, thanks Elon. I'll try to rewrite it to the best of my ability in an abridged form.
The basic gist is that its a visual representation of the ancient Gaelic bardic tradition. Seated in the center is St. Colmcille, composing an old Irish hymn to St. Brigid, "Brigit bé bithmaith". He is holding hazel nuts, symbols of knowledge / inspiration in Irish legend. On the two pillars on either side of him are King David (left) and Orpheus (right), two famous poets from antiquity. Two legendary poets from Irish legend, Oisín and Amergin, are situated above each pillar respectively. The two fish are seen swimming "upstream" (as in the legend of the Salmon of Knowledge) toward a sheela na gig, a architectural feature / grotesque of early Irish churches which some consider to be symbols of femininity, meant to ward off evil. At the top of the image, hands from a cloud (representing God) release a white dove (representing the Holy Spirit) down to St. Brigid. She owes her angelic appearance to her being considered both a pagan goddess and Christian saint. She is guarding a flame, which symbolises poetic inspiration, and which can be seen floating above the heads of all the other figures.
#celtic#irish#poetry#celtic mythology#irish mythology#irish culture#ireland#celtic culture#celtic christianity#druidry#druidism#bardic inspiration#imbas#imbas forosnai#celtic revival#gaelic#st brigid#saint brigid#mythology#digital art#mediaeval#medieval art#medieval manuscripts#illuminated manuscript#celtic design#irish history#awen#esotericism#spirituality#paganism
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Which deities do you personally associate with change/transformation?
#hellenic polytheism#norse polytheism#kemetic polytheism#celtic polytheism#gaelic polytheism#irish polytheism#welsh polytheism#roman polytheism#slavic polytheism#gaulish polytheism#deity work#deity worship#pop culture polytheism
101 notes
·
View notes
Text

The song of the sea, Tomm Moore, 2021
I ended up in tears
#selkie#the song of the sea#animated movies#mythical creatures#mythology#sea aesthetic#Tomm Moore#gaelic#irish mythology#folklore#the secret of kells#wolfwalkers
59 notes
·
View notes
Text
Calling Irish "Gaelic" is fine actually
I used to think it was just a thing that uninformed Americans did, but I was wrong, so let's talk about it.
There are Irish people (notably, native Irish speakers) who call it "Gaelic", when speaking English. (All video clips are timestamped, but it seems like timestamps don't work on mobile? So I'll write them as well) 8:27
youtube
4:36
youtube
In the name for the language in Irish varies across the dialects, but in Donegal, it's usually said as "Gaeilic"*, as you can hear here. (Bhí an Ghaeilic thar timpeall achan áit)
0:32
youtube
Or in the recording here from teanglann.ie:
It's fine to call it "Irish" as well, or "Irish Gaelic", but there's nothing wrong with just saying "Gaelic".
Notes
*I spelt it as Gaeilic for the sake of showing the pronunciation here, but really this comes from Gaeilg with the final consonant being devoiced in a similar way to how you see with Pádraig -> Pádraic
Some people will argue that you shouldn't call it "Gaelic" because there are several Gaelic languages, and it lacks specificity. It's true that it lacks specificity, but that is also how they're spoken about in the Gaelic languages themselves, e.g. "Gaeilge na hÉireann, Gaeilge na hAlban, Gaeilge Mhanann" (The Gaelic of Ireland, The Gaelic of Scotland, the Gaelic of Man) in Irish. There was, and still is to some degree, mutual intelligibility between these languages/dialects and it should be remembered that the difference between language and dialect is largely political.
#gaeilge#irish language#dialects#irish dialects#learning irish#gaelic#gaeilic#gaeilg#this is gonna be my biggest discourse post#I see people correcting others on this all the time#hopefully this can spread some info about the fact that gaelic is in fact fine
70 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok but what if David, Angel, Asher and Babe all leave before everyone at the wedding reception does thinking you know the rest of the people there will only be there another hour or so and so they go to bed only to wake up in the morning to be approached by a member of staff that tells them that there were still guests in the reception hall and when they go to check it’s Darlin and Sweetheart asleep on top of each other on the dance floor and Sam and Milo sleeping on chairs leaning against each other with the music still playing (I think Fireball would be funny)
They standing there looking at them like 😐😬😧😁
#this HC was brought to you while I was listening to Fireball#this is also basically every Irish wedding ever#Erik idk if your just Irish or really into Gaelic culture but either way#it freaks me out#I’m waiting for one of the characters of say ahh sure you know yourself#redacted audio#redacted asmr#redactedverse#redacted david#redacted sam#redacted asher#redacted darlin#redacted angel#redacted milo#redacted babe#redacted sweetheart#redacted shaw pack#redacted headcanons#redacted wedding#redacted shitpost
45 notes
·
View notes