#Electronics Manufacturing Jobs
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
To empower individuals and Electronics industry companies by providing career and recruitment solutions and services as per career choice and market needs.

We will continuously provide superior value to our users and customers by delivering best-in-class solutions and services through leveraging our expertise in Industry, Technology, Sales and Service.
Learn more: https://www.memjobs.com/
#MEM jobs#career opportunities#job portal#job alerts#Top job portals in India#online job portal#free job alerts#looking for a job#job search#find job#job postings#job sites#job websites#find jobs near me#job search websites#Free Job Posting Sites#Best Electronics Jobs In India#Electronics Jobs In India#Electronics Manufacturing Jobs#Electronics Jobs In Hyderabad
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
If reddit says "japanese business practices" One more time I'm gonna break smth can't believe you guys have me defending corporations tonight
#it's just racism!#sorry but those 'japanese business practices' are the ones that have worked so well so far#since the inception of motogp as a series non japanese manufacturers have won like twice#in TWENTY THREE YEARS#it did not become incorrect overnight I dont think it's not a problem at allll or whateve#but the reason honda yamaha are bad is prob a combination of factors such as the new regs and adaptations (every sport has this)#covid hitting them harder. less number of bikes overall. being halfway across the world for most races and riders.#and all the tyre pressure and electronics stuff I barely understand#i dont even like honda yamaha all that much they're very much companies first and foremost making excuses for them is not my job#but some people are getting too comfortable saying honda yamaha's problem is that theyre Japanese
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) Recruitment 2025
January 31, 2025 Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) Recruitment 2025 is a Miniratna Category-I Public Sector Enterprise under the Ministry of Defence, Government of India. BDL has invited applications from eligible candidates for multiple positions in various disciplines. Important Post: Broadcast Engineering Consultants India Limited (BECIL) Recruitment 2025 Total Vacancies: 49 Job Post: Multiple…
#Apply Online BDL#BDL Exam 2025#BDL Recruitment#BDL Recruitment 2025 Bharat Dynamics Limited Jobs Government Jobs 2025 PSU Jobs 2025 Defence Sector Jobs Engineering Jobs 2025 Management Tr#Bharat Dynamics Limited#Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) Recruitment 2025#Central Government Jobs#Civil Engineering Jobs Mechanical Engineering Jobs Electronics Engineering Jobs Cyber Security Jobs Finance Jobs 2025 HR Jobs 2025 Public Se#Cyber Security Job Openings#Defence Manufacturing Jobs#Electrical Engineer Government Jobs#Engineering Government Jobs#Finance Job Notification#Government Jobs Notification#HR Career in Government#IT Jobs 2025 MBA Jobs in Government Sector Law Jobs in PSU Central Government Jobs Sarkari Naukri 2025 BDL Online Application Job Vacancies#IT Jobs in PSU#Latest Job Openings 2025#Management Trainee Vacancy#Mechanical Jobs PSU#Ministry of Defence Jobs#PSU Recruitment 2025#Public Sector Employment#Sarkari Exam BDL
0 notes
Text

Ontario PNP conducted 2 OINP draws for applicants under the Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream on April 23rd, 2024 On the 23rd of April 2024, Ontario PNP conducted a draw under the Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream, inviting several NOCs. This Ontario PNP latest draw invited applicants with a score of 53 and a job offer letter.
Illustrated below is the result of the latest Ontario PNP draw 2024 result for Ontario’s Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker Stream:Date of drawNumber of NOI’s issuedScoreApril 23, 2024n/a53
Your Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream: skilled trades occupations must mention one of the following NOCs as your primary NOC based on your work experience:
NOC 22212 – Drafting technologists and technicians
NOC 22301 – Mechanical engineering technologists and technicians
NOC 22302 – Industrial engineering and manufacturing technologists and technicians
NOC 22311 – Electronic service technicians (household and business equipment)
NOC 22312 – Industrial instrument technicians and mechanics
NOC 70010 – Construction managers
NOC 70011 – Home building and renovation managers
NOC 70012 – Facility operation and maintenance managers
NOC 72010 – Contractors and supervisors, machining, metal forming, shaping and erecting trades and related occupations
NOC 72011 – Contractors and supervisors, electrical trades and telecommunications occupations
NOC 72012 – Contractors and supervisors, pipefitting trades
NOC 72013 – Contractors and supervisors, carpentry trades
NOC 72014 – Contractors and supervisors, other construction trades, installers, repairers and servicers
NOC 72020 – Contractors and supervisors, mechanic trades
NOC 72021 – Contractors and supervisors, heavy equipment operator crews
NOC 72022 – Supervisors, printing and related occupations
NOC 72024 – Supervisors, motor transport and other ground transit operators
NOC 72100 – Machinists and machining and tooling inspectors
NOC 72101 – Tool and die makers
NOC 72102 – Sheet metal workers
NOC 72103 – Boilermakers
NOC 72104 – Structural metal and plate work fabricators and fitters
NOC 72105 – Ironworkers
NOC 72106 – Welders and related machine operators
NOC 72200 – Electricians (except industrial and power system)
NOC 72201 – Industrial electricians
NOC 72203 – Electrical power line and cable workers
NOC 72204 – Telecommunications line and cable installers and repairers
NOC 72205 – Telecommunications equipment installation and cable television service technicians
NOC 72300 – Plumbers
NOC 72301 – Steamfitters, pipefitters and sprinkler system installers
NOC 72302 – Gas fitters
NOC 72310 – Carpenters
NOC 72311 – Cabinetmakers
NOC 72320 – Bricklayers
NOC 72321 – Insulators
NOC 72400 – Construction millwrights and industrial mechanics
NOC 72401 – Heavy-duty equipment mechanics
NOC 72402 – Heating, refrigeration and air conditioning mechanics
NOC 72403 – Railway carmen/women
NOC 72404 – Aircraft mechanics and aircraft inspectors
NOC 72406 – Elevator constructors and mechanics
NOC 72410 – Automotive service technicians, truck and bus mechanics and mechanical repairers
NOC 72422 – Electrical Mechanics
NOC 72423 – Motorcycle, all-terrain vehicle and other related mechanics
NOC 72500 – Crane operators
NOC 73100 – Concrete finishers
NOC 73101 – Tilesetters
NOC 73102 – Plasterers, drywall installers finishers and lathers
NOC 73110 – Roofers and shinglers
NOC 73111 – Glaziers
NOC 73112 – Painters and decorators (except interior decorators)
NOC 73113 – Floor covering installers
NOC 73200 – Residential and commercial installers and servicers
NOC 73201 – General building maintenance workers and building superintendents
NOC 73202 – Pest controllers and fumigators
NOC 73209 – Other repairers and servicers
NOC 73400 – Heavy equipment operators
NOC 73402 – Drillers and blasters – surface mining, quarrying and construction
NOC 82031 – Contractors and supervisors, landscaping, grounds maintenance and horticulture services
NOC 92100 – Power engineers and power systems operators
Ontario PNP conducted another draw for the Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream:
Economic Mobility Pathways Project (EMPP) candidates invited two targeted immigrants to apply on April 23, 2024, to people who would be eligible for the Employer Job Offer: Foreign Worker stream.
We are there for you:
If you want to learn more about the latest draw for the Ontario Provincial Nomination Program, our Canadian immigration consultants can help you out. You can reach them at 750 383 2132 or 928 928 9006. Additionally, you can visit our website at www.aptechvisa.com/ontario-pnp for further details and updates.
#2024#Ontario PNP conducted a draw under the Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream#inviting several NOCs. This Ontario PNP latest draw invited applicants with a score of 53 and a job offer letter.#Illustrated below is the result of the latest Ontario PNP draw 2024 result for Ontario’s Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker Stream:#Date of draw#Number of NOI’s issued#Score#April 23#n/a#53#Your Employer Job Offer Foreign Worker stream: skilled trades occupations must mention one of the following NOCs as your primary NOC based#NOC 22212 – Drafting technologists and technicians#NOC 22301 – Mechanical engineering technologists and technicians#NOC 22302 – Industrial engineering and manufacturing technologists and technicians#NOC 22311 – Electronic service technicians (household and business equipment)#NOC 22312 – Industrial instrument technicians and mechanics#NOC 70010 – Construction managers#NOC 70011 – Home building and renovation managers#NOC 70012 – Facility operation and maintenance managers#NOC 72010 – Contractors and supervisors#machining#metal forming#shaping and erecting trades and related occupations#NOC 72011 – Contractors and supervisors#electrical trades and telecommunications occupations#NOC 72012 – Contractors and supervisors#pipefitting trades#NOC 72013 – Contractors and supervisors#carpentry trades#NOC 72014 – Contractors and supervisors
0 notes
Text
Have you ever noticed how weird it is that microwaves all cook in roughly the same time? Sure, if you squint, you'll notice that some microwaves will say on their fronts 700 watts, others 1500 watts, but this increased power doesn't make a material difference in your life. You'll still be waiting about two minutes for your corndog to become screechingly hot, an eternity when you're hungry. There's only one notable exception: the giant, intimidating, stainless-steel microwave at your corner convenience store.
You might think that this is easy to fix. Go to the bankruptcy auction for a convenience store, buy one. Have you ever seen a convenience store go bankrupt? They are basically money printers, and any region in which they go under will already have had the microwave picked clean by gangs of near-feral copper thieves. The manufacturers won't talk to you, either: why would they bother with your dumb domestic ass, and your crybaby questions about "what kind of cord does this take," when they could use the same phone call to sell fifty more microwaves to 7-Eleven?
No, it's just like my grandfather used to say: if you want a job done right, you have to half-ass it yourself and then claim victory anyway. I would have to understand how to make a microwave. With the help of my local librarian, I was able to check out some useful books, such as Electronics For The Precocious Nine-Year-Old and its sequel, Advanced Electronics For The Nine-Year-Old Orphan. It takes a village to raise a child, or more accurately, to produce a twenty-five thousand watt, V8-powered microwave that can cook a frozen potato to "atomized" in just over seventeen seconds.
We're going to market some time next year, but in the meantime, you can buy my plans and build one yourself. All you need is an undefended electrical substation near you, some wire cutters, and absolutely no self-preservation instinct. Hey, it's an investment. Think of how much extra time you've been wasting waiting for a breakfast burrito to cook. You could use that time trying to get bail instead.
484 notes
·
View notes
Text
Out of bounds . JJK

↳ 𝐬𝐲𝐧𝐨𝐩𝐬𝐢𝐬; his love subjected you to the true extent of deception, a merciless lie wrapped in the illusion of paradise, until the truth tore it apart - he was always out of bounds.
↳ Jungkook x reader
↳ 𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐬: ongoing
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Chapter Twenty Two
The low hum of machinery greeted me as I walked into the expansive manufacturing wing of the design company. The air smelled faintly of metal, oil, and fresh leather, and the large overhead lights cast a bright sheen over the nearly finished car sitting in the center of the room. My car—or, rather Jungkook’s.
The sight of it sent a mixture of pride and anxiety coursing through me. This was the culmination of months of work, countless sleepless nights, and hours upon hours of pouring my heart into every detail. And now, I was here to oversee the final stages of its creation.
Workers moved swiftly around the room, their movements practiced and precise. Each of them had a specific task to complete, and despite the occasional buzz of conversation, there was an air of focused determination. I could feel the weight of their dedication, and it made me stand a little taller. This wasn’t just my accomplishment—it was ours.
As I walked closer to the car, my breath caught. Even under the industrial lighting, it looked stunning. The sleek lines of the exterior, the way the shape of it seemed to embody both power and elegance—it was everything I had imagined and more. I circled the car, my eyes scanning over the interior through the slightly ajar door.
The seats were perfectly crafted, their stitching precise and clean. The dashboard was minimalistic but functional, with a subtle touch of sophistication. Everything about it screamed luxury, but not in an overwhelming or gaudy way. It was balanced.
I exhaled slowly, a faint smile forming on my lips. Seeing it in front of me, so close to completion, filled me with a sense of accomplishment I hadn’t felt in years.
“Excuse me,” I called softly to a worker nearby, a middle-aged man hunched over a leather seat, inspecting the stitching.
He glanced up at me and immediately straightened, brushing his hands against his uniform. “Yes, ma’am?”
I gestured toward the car. “How’s everything coming along? Any issues I should be aware of?”
The man smiled faintly, his face lined with both age and experience. “It’s coming along well. We’re finishing the interior fittings now, making sure everything is secure. Once that’s done, we’ll do a final check on the engine and electronics. Shouldn’t be much longer now.”
I nodded, impressed. “That’s great to hear. You’ve all done an incredible job. It’s one thing to see it on paper, but to see it here…” I trailed off, gesturing toward the car. “It’s amazing.”
His smile grew a little wider, a hint of pride in his expression. “Thank you, ma’am. That means a lot coming from you.”
I spent the next hour moving around the room, talking to the workers, asking questions, and offering input where it felt necessary. Each person I spoke to was polite and respectful, but there was also a quiet pride in the way they discussed their work. They weren’t just building a car—they were bringing my vision to life.
But just as I began to feel a sense of ease, the sound of the door opening cut through the room.
It wasn’t a loud sound, but it was enough to stop everyone in their tracks. The workers who had been bustling about suddenly froze, their conversations dying mid-sentence. All eyes turned toward the entrance as a man in a sharp black suit and dark sunglasses stepped inside.
The air shifted immediately. There was an unspoken tension that seemed to ripple through the room, and I couldn’t help but glance around, confused.
One by one, the workers began to bow, their heads lowering in a show of respect.
I stood there awkwardly, unsure of what to do. Who was this man, and why was everyone acting like this?
The man’s gaze swept across the room, cold and assessing, before landing on me. His expression hardened, and he raised an eyebrow, clearly unimpressed.
“Do you have any manners?” he asked sharply, his voice cutting through the silence like a knife.
I blinked, caught completely off guard. “I—uh—”
Before I could say anything coherent, the worker next to me leaned in, his voice low. “That’s the CEO,” he whispered urgently.
My stomach dropped. My eyes widened as realisation dawned, and I immediately bowed deeply, my heart pounding in my chest. “I’m so sorry, sir,” I stammered, my voice shaking slightly.
The CEO didn’t respond. He didn’t even acknowledge me, his gaze already moving past me as he walked further into the room. His presence was commanding, and the sound of his polished shoes against the floor seemed unnaturally loud in the tense silence.
He stopped in front of the leading worker, a tall man who looked visibly nervous under the CEO’s gaze.
“How’s the car?” the CEO asked, his tone clipped and to the point.
The worker swallowed hard before answering. “It’s on schedule, sir. We’re just finalising the details now.”
The CEO’s lips pressed into a thin line. “It better be perfect,” he said coldly. “If there’s a single flaw, you’ll all be out of a job. Do you understand?”
“Yes, sir,” the worker said quickly, bowing his head.
The CEO lingered for a moment longer before turning back toward me. His expression was unreadable behind his sunglasses, but I could feel his gaze on me as he approached.
“And who the hell are you?” he asked, his tone sharp and demanding.
I straightened up, forcing myself to meet his gaze despite the lump forming in my throat. “I’m the designer of this car, sir,” I said, keeping my voice steady.
For a moment, he said nothing. Then, slowly, a smirk formed on his lips. “So, you’re the girl Jeon took pity on.”
The words hit me like a punch to the gut. I opened my mouth to respond, to defend myself, but no words came out. I was too stunned, too confused.
The CEO didn’t wait for a response. He turned and walked away, his presence lingering in my mind long after he left the room.
I stood there in silence, his words echoing in my head. Took pity on me? What did he mean by that?
By the time the workers and I wrapped things up, the weight of the interaction was still pressing heavily on my chest. I thanked the team for their hard work, offering them a small smile despite the storm of emotions swirling inside me.
As I stepped out of the building, the cool evening air brushed against my skin, bringing with it a fleeting moment of clarity. The quiet hum of the city in the background, the faint scent of rain lingering from earlier in the day—all of it felt distant, like the world was moving around me but I wasn’t really part of it.
I paused for a moment, standing on the pavement, trying to steady my breathing. I should’ve gone straight to Jungkook’s house. That was the plan. But my feet felt heavy, unwilling to move in that direction. Instead, as if pulled by some invisible thread, I found myself wandering aimlessly toward a nearby park.
The park was deserted, the fading light of the evening casting long, soft shadows across the pathways. Everything was painted in shades of orange and purple, the sky above shifting into the twilight. There was a tranquility here, a stillness that felt almost sacred, but it did nothing to ease the storm brewing inside me.
I spotted a bench tucked beneath a tall oak tree, its branches stretching out like arms offering solace. Without thinking, I sank onto it, the weight of the day pressing down on me. Leaning back, I closed my eyes, hoping for even a brief reprieve from the chaos in my mind.
But there was no escaping it.
It all came rushing back at once—the piercing disappointment in my mother’s voice when I first told her I wanted to be a designer, the sharp sting of her words as she dismissed my dreams as childish and impractical. I could still hear her telling me that I was throwing my life away, that I would regret wasting my potential.
And then there was the CEO. The way he looked at me, as if I was nothing. As if my presence there was an insult. His words replayed in my mind on an endless loop.
I clenched my fists, my nails digging into my palms. Was that really how people saw me? Someone to be pitied? Was all of this—my work, my effort, my passion—just some act of charity in their eyes?
The thought made my chest tighten, the air around me feeling suddenly suffocating. I groaned softly, leaning forward and burying my face in my hands.
I had worked so hard to put myself out there, to prove that I was more than what people thought of me. But no matter how far I came, it felt like there was always someone ready to tear me down, to remind me that I wasn’t good enough. That I didn’t belong.
The more I thought about it, the heavier it felt, like a weight pressing down on my chest, making it harder and harder to breathe. My eyes stung with the threat of tears, but I forced them back, refusing to let them fall.
I pushed myself to stand, hoping that moving would help clear my mind. My steps were slow at first, the crunch of gravel beneath my feet barely registering. I focused on the sound, letting it ground me, each step a small reminder that I was still here, still moving forward, even if it felt like the world was trying to pull me back.
The trees around me swayed gently in the evening breeze, their leaves rustling softly like whispers of comfort. I tried to focus on that—the beauty of the moment, the quiet rhythm of nature—but it was like trying to hold onto water. Every time I thought I had a grip on it, it slipped through my fingers, leaving me with nothing but my thoughts.
The sky was darker now, the last remnants of sunlight fading into the horizon. The park was growing quieter, the faint sound of crickets beginning to fill the air. I stopped walking, taking a deep breath and letting the cool air fill my lungs.
But then, a quiet sob caught my attention.
Turning toward the sound, I saw a little girl sitting on the edge of a fountain, her shoulders shaking as she cried.
I hurried over, crouching down beside her, my heart squeezing at the sight of her small, trembling frame. “Hey, sweetheart,” I said softly, keeping my voice calm and gentle so I wouldn’t scare her. “Are you okay? What’s wrong?”
She sniffled, looking up at me with wide, tear-streaked eyes. Her face was flushed from crying, and she kept wiping at her nose with the back of her tiny hand. “I… I can’t find my mommy,” she said, her voice shaking as fresh tears welled up in her eyes.
“Oh no,” I murmured, feeling a pang of sadness for her. “It’s okay. We’ll find her, I promise. Can you tell me your name?”
“Sophia,” she whispered, hiccupping slightly.
“That’s a beautiful name, Sophia,” I said, offering her a small, reassuring smile. “I’m going to help you find your mom, okay? Do you remember what she looks like or what she’s wearing?”
She nodded, sniffing again as she rubbed at her eyes with her sleeve. “She… she’s wearing a blue dress. And she has long hair, like mine.”
I smiled softly, reaching out to gently touch her shoulder. “That’s really helpful. Thank you for telling me. Let’s walk around the park together, and we’ll find her in no time. Does that sound good?”
She hesitated for a moment, her big eyes searching mine for reassurance. Finally, she nodded and slipped her small, trembling hand into mine. I gave her hand a gentle squeeze, hoping it would make her feel a little safer.
We began walking slowly along the gravel path, my eyes scanning the park for any sign of a woman in a blue dress. The park wasn’t too crowded, but there were still enough people wandering around to make the search challenging. I could feel Sophia’s grip on my hand tightening with every passing moment.
“Do you come to this park often?” I asked, trying to distract her from her growing anxiety.
She nodded shyly. “Mommy and I come here after school sometimes,” she said, her voice small. “But today, I was playing on the slide, and then I couldn’t find her anymore.”
“It’s okay,” I said gently, my thumb brushing over the back of her hand. “You didn’t do anything wrong. Sometimes we just get turned around. But I promise we’ll find her soon, and everything will be okay.”
We continued walking, stopping now and then to look around. I crouched down once to check behind the playground equipment, but there was no sign of anyone matching her description. The more time passed, the more I could feel her unease.
“What’s your mommy’s name?” I asked, glancing down at her.
“Emma,” she said quietly, her grip tightening on my hand.
“That’s a lovely name,” I said with a smile. “You know, Sophia, you’re really brave. Not everyone would stay so calm in a big park like this. Your mommy is going to be so proud of you when we find her.”
She looked up at me, her tears momentarily forgotten as a tiny, bashful smile appeared on her lips.
We walked a little further when suddenly, a woman’s voice rang out, panicked and desperate. “Sophia! Sophia, where are you?”
Sophia froze, her head snapping up at the sound. Her eyes widened, and she let go of my hand, spinning around. “Mommy!” she cried, her small voice cutting through the air as she bolted in the direction of the voice.
A woman came running toward us from across the park, her face pale and tear-streaked, her hair disheveled as if she’d been frantically searching. She was wearing a flowing blue dress, and her eyes immediately locked onto Sophia.
The woman’s steps faltered for a brief moment, her body trembling as relief washed over her. Then she ran forward and scooped Sophia into her arms, holding her so tightly it was as if she was afraid to let go.
“Oh my God,” the woman sobbed, her voice breaking as she buried her face in Sophia’s hair. “I thought I lost you. I thought—” She couldn’t even finish her sentence, her words dissolving into quiet cries of relief.
Sophia clung to her mother’s neck, her tiny arms wrapping around her tightly. “I’m sorry, Mommy,” she whispered, her voice muffled.
“No, no, sweetheart,” the woman said, pulling back to cup her daughter’s face. “You didn’t do anything wrong. I was so scared…” Her voice cracked again as she pulled Sophia close once more.
I stayed back for a moment, watching the reunion with a soft smile. There was something so raw and beautiful about the way they held onto each other, as if the world around them didn’t exist.
Sophia eventually turned her head, pointing toward me. “Mommy, the pretty lady helped me. She found me.”
The woman’s tearful gaze shifted to me, and she took a hesitant step forward, still holding Sophia close. “You… you helped her?”
I nodded, feeling a little shy under her emotional gaze. “She told me she couldn’t find you, so we walked around the park together until we did. I’m just glad you’re both okay.”
The woman’s eyes filled with fresh tears, and she stepped closer, clutching Sophia with one arm while reaching out to me with the other. “Thank you,” she said, her voice trembling with gratitude. “Thank you so much. I don’t even know what I would’ve done if…” She trailed off, shaking her head as her voice broke.
I gave her a reassuring smile. “There’s no need to thank me. I’m just happy Sophia is safe and that you’re back together. That’s all that matters.”
The woman gave me a watery smile, her grip on Sophia tightening protectively. “Is there… is there anything I can do to repay you? Anything at all?”
I shook my head, feeling genuinely touched by her gratitude. “No, really. You don’t need to do anything. Just seeing you two together again is enough.”
She nodded, her expression softening as she looked at me. “Thank you,” she said again, her voice quieter this time but no less sincere.
With a final smile, I gave a small wave to Sophia, who waved back shyly before resting her head on her mother’s shoulder. They turned and walked away, their silhouettes bathed in the soft glow of the setting sun.
I watched them until they disappeared into the distance, a faint pang of something bittersweet tugging at my chest. For a moment, I let myself think about what it must feel like to have someone love you so fiercely, to hold you as if letting go was impossible.
A memory of my mother and I flashed through my mind—her laughing as she spun me around in the park when I was a child, the warmth of her embrace as she told me I was her little miracle. I couldn’t stop the small smile that spread across my lips.
But just as quickly, the smile faded. That version of her—the mother who adored me, who believed in me—felt like a distant dream now. The reality of her disappointment, her harsh words, and the cold distance between us slammed into me like a wave, leaving me breathless.
I shoved those thoughts aside, forcing myself to focus on the present. There was no point dwelling on what I couldn’t change.
The park had grown quieter, the sun now just a faint glow on the horizon. I turned toward the exit, shoving my hands into my pockets as I walked. My steps felt heavier, weighed down by the emotions swirling inside me, but for now I just needed to keep moving.
When I finally reached the front door of Jungkook’s house, I slipped inside as quietly as I could, the weight of the day pressing down on me like a heavy blanket. All I wanted was to sneak into my room, collapse onto the bed, and maybe sort through my tangled thoughts later. But the moment the door clicked shut, a voice rang out, sharp and cutting.
“Where the fuck have you been?”
I froze in place, my hand still on the doorknob. Slowly, I turned to see Jungkook standing in the hallway, his tall frame illuminated by the faint glow of the light above. His hair was a mess, as if he’d been running his hands through it repeatedly. He was dressed in a black tank top that showed the strain of his tense shoulders and joggers that hung low on his hips, but it was the look on his face that stopped me cold. His jaw was clenched so tight I could see the muscle twitch, and his dark eyes burned with fury—and something else I couldn’t place.
“Why weren’t you answering your phone?” he demanded, his voice low but brimming with restrained anger. Each word felt like it had been bitten out, dripping with frustration.
I blinked at him, too taken aback to respond right away. “I needed to get some air,” I said trying to move past him.
His brow furrowed deeper, his gaze hardening. “That’s your excuse?” He scoffed, his tone incredulous. “Do you have any idea how long you’ve been gone? How many fucking times I tried to call you? I—” He stopped abruptly, his lips pressing into a thin line as though he refused to finish the thought.
“I didn’t think it was a big deal,” I mumbled, avoiding his piercing stare.
“Not a big deal?” His voice rose slightly, his anger breaking through his usual composure. He took a step closer, his presence overwhelming. “Disappearing for hours without a word and ignoring your phone isn’t a big deal to you? Do you know how irresponsible that is?”
“I didn’t do it on purpose!” I snapped, my own frustration bubbling to the surface. “I just needed to be alone for a while, okay? Is that such a crime?”
He let out a sharp, humorless laugh, shaking his head. “It’s not about whether it’s a crime,” he shot back. “It’s about the fact that I’m responsible for you.”
That stopped me in my tracks. “Responsible for me?” I repeated, my voice laced with disbelief.
“Yes,” he said, his voice firm. “You’re working under me, which means your safety is my responsibility. And you disappearing like that without a word? It puts me in a position I shouldn’t have to be in.”
I stared at him, caught off guard by the sheer force of his conviction. But instead of backing down, my irritation flared. I didn’t need anyone to feel responsible for me—not after everything I’d been through. “I don’t need a babysitter,” I said sharply, crossing my arms over my chest. “And I definitely don’t need you to pity me.”
“Pity you?” His eyes flashed, and he took another step closer, his voice dropping to a dangerous low. “You think this is pity?”
“Isn’t it?” I countered, my voice trembling but defiant. “You’re acting like I can’t handle myself, like I’m some helpless kid you have to look after.”
“That’s not what this is,” he snapped, his frustration boiling over. “This is about you being reckless. Do you even realise how selfish that is? You didn’t think about anyone else—about how your actions might affect the people around you.”
For a moment, the only sound in the hallway was the sharpness of our breathing. His words cut deep, not because they were cruel but because they were true in a way I wasn’t ready to admit.
I shook my head, stepping back from him. “Stop with your fucking pity,” My voice cracked, but I refused to let him see the vulnerability clawing at me. “I don’t need it.”
His jaw tightened, the tension radiating off him in waves. “Again with this bullshit,” he growled, his voice sharp as a blade. “Stop putting words in my mouth. I don’t pity you.”
I scoffed, turning on my heel, trying to walk past him and toward the stairs. “Just leave me alone—”
Before I could take another step, his hand shot out, grabbing my arm with enough force to spin me around. His grip wasn’t painful, but it was firm, and it sent a shiver down my spine. His dark eyes burned into mine, his expression a storm of frustration and something I couldn’t quite name.
“Don’t act like a brat,” he snapped, his tone low but dangerous. “And stop twisting this into something it’s not. You want to keep throwing that word around? Fine. I’ll show you pity.”
I blinked, confused and alarmed. “What—”
“Move,” he interrupted, his voice leaving no room for argument.
I opened my mouth to protest, shaking my head instinctively. “No. I’m not—”
He turned his head sharply, his eyes narrowing as he looked back at me. His tone was like ice. “I won’t repeat myself.”
Something in his voice made my breath hitch. I exhaled sharply, my mind racing, but I forced my legs to move. My body betrayed me, drawn to the intensity radiating off him despite every warning screaming in my head.
I followed him up the stairs in silence, my heart pounding in my chest. His broad shoulders were tense, his muscles flexing with every step. When we reached his room, he pushed the door open with more force than necessary, stepping inside. I hesitated at the threshold, feeling a mix of trepidation and anticipation curling in my stomach.
“Inside,” he commanded, not even looking back at me as he stepped further into the room.
I bit the inside of my cheek, taking a shaky step inside. The moment I was in, he turned and shut the door behind me with a sharp click. The sound echoed in the tense silence, and I felt like the air had been sucked out of the room.
He didn’t say anything as he turned to face me. Instead, he grabbed the hem of his tank top and pulled it off in one fluid motion, tossing it aside. My eyes widened, immediately drawn to the ink decorating his skin, the way his muscles shifted and flexed with every movement.
“Get on the bed,” he said, his voice low and rough.
I froze, my breath catching. “Jungkook—”
“Do it,” he interrupted, his tone brooking no argument.
A part of me wanted to argue, to push back against his dominance, but another part of me—the part that was drowning in the overwhelming intensity of the moment—couldn’t move. Slowly, I took a step back, then another, until the backs of my knees hit the edge of the bed.
I sank down onto it, my mind spinning, my body trembling with a confusing mix of fear and desire.
He stepped closer, his eyes locked on mine, his gaze like a predator sizing up its prey. “You want to say that I took you in out of pity?” he asked, his tone mocking. “Then fine, I’ll fuck you like the pitiful bitch you are.”
I stared back at him, my chest rising and falling as a chaotic mix of fear and arousal tangled itself inside me. His gaze was unrelenting, pinning me in place, and I hated how much I wanted to crumble under it.
Every rational part of me screamed that this was wrong, that I shouldn’t be turned on by the dominance in his eyes or the subtle edge of danger in his voice, but my body betrayed me. It was maddening, the way my pulse quickened, the way heat pooled low in my stomach.
My breath hitched, my skin alive with anticipation, and before I could think, before I could stop myself or question the consequences, the words slipped past my lips like a challenge I wasn’t even sure I wanted to win.
“Do it then.”
Next
#jungkook#jungkook fanfic#enemies to lovers#jeon jungkook#jungkook smut#bts jungkook#racer#slow burn#bts#f1 x reader#bts jung jungkook#bts angst#bts x reader#bts fluff#bts jungguk#bts smut#bts army#bts fanfic#writing#jungkook scenarios#jeon jeongguk#jjk#f1 imagine#f1 fanfic#bad boys#designer#cars
48 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finished reading Cobalt Red by Siddharth Kara and he does a good job showing how the cobalt supply chain is inextricable from incredible human suffering, near-slavery, rampant exploitation, environmental devastation, and child labor. And it’s very clear that no promise a tech or battery manufacturer makes that their supply chain is clean means literally anything bc industrially and artisanally mined cobalt are mixed into the same supply untraceably. And the book also covers the fact that cobalt supplies are finite and when the DRC’s cobalt is exhausted the industry will move elsewhere, rinse and repeat, and the people in the Congo will be left with the ongoing and unremediated -maybe irremediable - damage. All of this so that we can have smartphones, electric vehicles, iPads, electric scooters, almost anything with a rechargeable battery.
It’s also clear that the tech and battery industries are interested in good PR and making empty statements about human rights when they should be taking responsibility for the working conditions of small-scale miners (and minors) dying at the bottom of their supply chains. What Kara doesn’t really address is the demand side of this equation, not just the demand by companies whose products use cobalt-containing batteries but also the consumers sustaining that demand, who buy every new smartphone and eagerly pin their hopes on electric vehicles to let us keep our car-dependent world without the fossil fuel guilt. The book takes it for granted that cobalt will be required in high quantities for consumer electronics and for “green” tech, and to some extent this is true - as in, none of those demands or uses will cease overnight and in the meantime we should worry about how to address industrial and business practices and government corruption in order to treat Congolese miners as human beings.
But it feels incomplete without also asking questions like: should that demand continue? Can it? Do we need this many devices? What costs are acceptable? Can we really have our cake (smartphones, EVs, etc) and eat it too (slavery-free, non-exploitative supply chains that don’t kill the people at the bottom and lay waste to the environment)? What if - as the book would seem to suggest - we really cannot? If one goal of the book is for people to realize what conditions underlie the extraction of cobalt, what action is then incumbent upon us? Personal consumer choice will not undo all this harm, but it is a necessary step in rethinking or attempting other ways to live. Is it a right to have a smartphone, a new one every year or two, if it comes at the price of other people’s human rights? At what point do we say that it is not an acceptable cost that the extractive industries are perpetuating neocolonialism and near-slavery in order that we should have comfortable lives?
We know we have to stop relying on fossil fuels or we’ll burn down the planet (to a greater degree than is already locked in) but the “green energy transition” is not clean at all. Capitalism seeks the lowest price for labor and the highest profits; obviously these extractive relationships owe a lot of their horror to being conducted in a capitalist milieu. But even thinking about, say, a socialist world instead, if it aspires to still provide smartphones and electric vehicles en masse and maintain the comforts and conveniences of the “Western” lifestyle then we would still be relying on massive amounts of resource extraction with no guarantee of less suffering. The devices are themselves part of the problem. The demand for them and the extent to which “modern” life in “developed” countries relies upon them is part of the problem. It is unsustainable. It is built on blood and it makes a mockery of purported values of dignity, equality, and human rights. The lives of Congolese cobalt miners are tied to how we in the “developed” or colonizer countries live and consume. I do not think their lives will change substantially unless ours do.
#will look for good quotes from the book too#it’s a good book I just think it lets consumers off the hook a bit#and assumes that we will need all this cobalt no matter what#sorry still posting abt resource extraction let’s see how badly ppl take it this time#cobalt#cobalt red#resource extraction#skravler
96 notes
·
View notes
Text

Name: Sheep Man
Debut: Mega Man 10
Most of the Robot Masters are too "Man" for my tastes. But this one? This one is Sheep! And that makes him so awesome. Sheep Man was created to be a sheep herding robot, which is rather silly, since humans have already created a guy to help with sheep herding. That guy's name is "Dog", and he loves to do it! Sheep Man, however, left this job to work as a circuit board tester, which makes more sense. I don't think any dog breeds have been developed to do that yet.
Sheep Man's job at the circuit board manufacturer was in their static resistance test division, since he noticed static buildup in his wool. And this got me thinking, is there really truth to the Electric Sheep concept? I mean in the sense of static wool, of course. I am well aware that, unfortunately, regular sheep cannot use Zap Attacks. Wool is indeed likely to give up electrons and take on a positive charge, but it is also great at retaining moisture, and thus can in fact prevent static cling from occurring! I guess Sheep Man must be inhabiting some very dry environments!

Considering his stage is a sort of Cyber's World, I guess it is a very dry environment? I don't know. I've never been in a digital world. Let me know if you have, and know how moist they are!
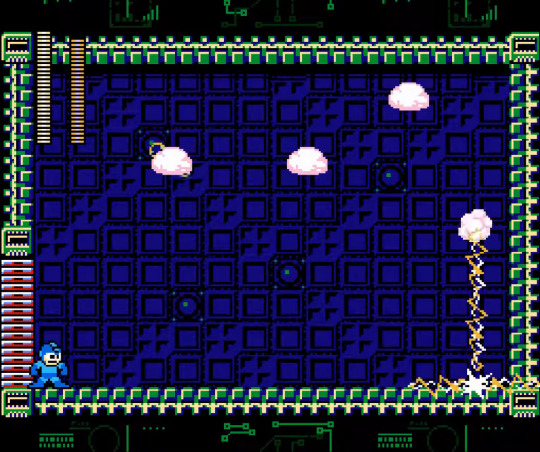
Unfortunately, as a Robot Master, you probably know that Sheep Man is sort of a Bad Guy. But it's just because he is sick, infected with Roboenza, and can be cured! I am happy that this funny sheepborg is typically a nice fellow. In battle, he demonstrates the awesome power of Sheep, by turning into four clouds of wool that float independently and zap the ground! (Shouldn't the metal ground be zapping him, if anything?) He's like a four-pack of wool dryer balls for reducing static in your clothing. When the first three do their zappies, they disappear, and the fourth turns back into Sheep Man. I'm over here trying to apply real-world physics to Sheep Man, and there he goes, generating infinite matter!
At least there is a bit of Physics Phun in that his weakness is the Rebound Striker, a rubber ball weapon. It hurts him extra because it's stealing his electrons! Give those back!

Generally, Robot Masters are "pretty neat at most" to me. You know me! I love creatures, and when robots are funny little guys that don't look like humans! So it is no surprise that I am VERY happy with the final Sheep Man design we got. The sleepy eyes are cute, yes, but I am so glad he was decided to be so much more Sheep than Man. It even looks like the design process was basically to give him more wool until he had no visible torso! Congratulations on your cephalothorax! A very excellent Man!
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

[W]e live in a society in which spurious realities are manufactured by the media, by governments, by big corporations, by religious groups, political groups. . . . So I ask, in my writing, What is real? Because unceasingly we are bombarded with pseudo-realities manufactured by very sophisticated people using very sophisticated electronic mechanisms. I do not distrust their motives; I distrust their power. They have a lot of it. And it is an astonishing power: that of creating whole universes, universes of the mind. I ought to know. I do the same thing. It is my job to create universes, as the basis of one novel after another. And I have to build them in such a way that they do not fall apart two days later.
—Philip K Dick, “How To Build A Universe That Doesn’t Fall Apart Two Days Later” (1978)
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another good one from Vox about the upcoming Trump Tariffs, and what they might mean for your near-future spending.
The first thing to understand is that tariffs absolutely do not do what Trump thinks they do. Trump has pitched tariffs as a way to lower prices, which is simply...wrong. He also seems to be under the impression that tariffs are a way to make foreign companies pay taxes to the United States. That is also wrong.
A tariff is a tax on imported goods. The usual reason for imposing a tariff is to protect domestic production from being undercut by cheaper imported goods--if Domestic Company A can produce widgets for $10 a dozen, but Foreign Company B can do it for $8 a dozen, you impose a 20% widget tariff, and Company A and Company B's widgets both end up on the domestic market at the same price. That way, Company A has no particular reason to move their widget factory to another country where it might be cheaper to operate, thus keeping jobs, wages, and prices at the current level.
Economists debate whether tariffs are actually a good way to achieve these goals; however, even if we assume it does, you can probably see a few problems. First, and most obviously, lowering prices is nowhere in the definition of what people who really like tariffs say that they do. On the contrary, they are intended to prevent prices from dropping due to cheaper imports, and they do that because the tariff is paid not by the foreign manufacturer, but by the domestic distributor, who typically passes that cost directly to the consumer.
Second, if we were going to use tariffs to support American manufacturing, it would have been a good idea to do that back when there was some American manufacturing left to protect. Like around the time Trump was in kindergarten, would have been a great time to start. Even 1980 might not have been too late.
If--and this is a big if--heavy tariffs on imported goods are maintained for a long time, it could happen that tariffs eventually slowly start to bring manufacturing, and manufacturing jobs, back to the US. It could happen.
But if it did, it would take a lot longer than four years. And what happens in the meantime, is that prices on everything we import will skyrocket. And what we import includes most of our clothing, electronics, household items, large appliances, small appliances, cars, children's toys--just about anything you can name. And a fair bit of our food. (We also export a lot of food, so unless climate change wallops us real hard in the next few years, we don't have to worry a whole lot about actual food shortages, but it will not be surprising if we see higher prices and less selection as a result of tariffs, let alone other policies that Trump has discussed.) While Trump has been (of course) light on policy specifics, some numbers he's floated are 10-20% tariffs on imported goods in general, rising to 60% on Chinese goods, and 100% on imports from Mexico.
Some sources are suggesting that, since tariffs are such a completely boneheaded idea that will not do any of the things Trump claims to believe* they will do, surely someone will manage to explain this in a way that he can understand, before he actually imposes them. The author of the Vox article above thinks that's unlikely, and that having made such a big deal about tariffs on the campaign trail, Trump will charge ahead with them anyway. I don't know.
However, the point is, if you're thinking about a major purchase, you might want to do that before January 20. Especially if it's something where the manufacturing is concentrated in China, like laptops, phones, that kind of thing. According to the article, the Consumer Technology Association is saying prices in that category could go up as much as 40%, if Trump follows through on what he's floated.
And he might not! We simply do not know. However, my laptop has started doing that thing where you have to wiggle the charging cable to get it to connect; in the before-times, I'd figure I have a few months before I really have to worry about it, but as things are, I'm keeping an eye on the Black Friday sales.
(*There's some speculation that what Trump actually wants to do is weaken China's economy, which happens to be something that Putin would like to see. Another possibility is that he has some idea about reducing America's reliance on/relationships with other countries, as a way of furthering some goal of his. Or maybe he just wants to start selling Trump-branded phones, IDK.)
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
With the exceptions of North Korea and Cuba, the communist world has merged onto the capitalist highway in a couple different ways during the twenty-first century. As you’ve read, free-trade imperialism and its cheap agricultural imports pushed farmers into the cities and into factory work, lowering the global price of manufacturing labor and glutting the world market with stuff. Forward-thinking states such as China and Vietnam invested in high-value-added production capacity and managed labor organizing, luring links from the global electronics supply chain and jump-starting capital investment. Combined with capital’s hesitancy to invest in North Atlantic production facilities, as well as a disinclination toward state-led investment in the region, Asian top-down planning erased much of the West’s technological edge. If two workers can do a single job, and one worker costs less, both in wages and state support, why pick the expensive one? Foxconn’s 2017 plan to build a U.S. taxpayer–subsidized $10 billion flat-panel display factory in Wisconsin was trumpeted by the president, but it was a fiasco that produced zero screens. The future cost of labor looks to be capped somewhere below the wage levels many people have enjoyed, and not just in the West.
The left-wing economist Joan Robinson used to tell a joke about poverty and investment, something to the effect of: The only thing worse than being exploited by capitalists is not being exploited by capitalists. It’s a cruel truism about the unipolar world, but shouldn’t second place count for something? When the Soviet project came to an end, in the early 1990s, the country had completed world history’s biggest, fastest modernization project, and that didn’t just disappear. Recall that Cisco was hyped to announce its buyout of the Evil Empire’s supercomputer team. Why wasn’t capitalist Russia able to, well, capitalize? You’re already familiar with one of the reasons: The United States absorbed a lot of human capital originally financed by the Soviet people. American immigration policy was based on draining technical talent in particular from the Second World. Sergey Brin is the best-known person in the Moscow-to-Palo-Alto pipeline, but he’s not the only one.
Look at the economic composition of China and Russia in the wake of Soviet dissolution: Both were headed toward capitalist social relations, but they took two different routes. The Russian transition happened rapidly. The state sold off public assets right away, and the natural monopolies such as telecommunications and energy were divided among a small number of skilled and connected businessmen, a category of guys lacking in a country that frowned on such characters but that grew in Gorbachev’s liberalizing perestroika era. Within five years, the country sold off an incredible 35 percent of its national wealth. Russia’s richest ended the century with a full counterrevolutionary reversal of their fortunes, propelling their income share above what it was before the Bolsheviks took over. To accomplish this, the country’s new capitalists fleeced the most vulnerable half of their society. “Over the 1989–2016 period, the top 1 percent captured more than two-thirds of the total growth in Russia,” found an international group of scholars, “while the bottom 50 percent actually saw a decline in its income.” Increases in energy prices encouraged the growth of an extractionist petro-centered economy. Blood-covered, teary, and writhing, infant Russian capital crowded into the gas and oil sectors. The small circle of oligarchs privatized unemployed KGB-trained killers to run “security,” and gangsters dominated politics at the local and national levels. They installed a not particularly well-known functionary—a former head of the new intelligence service FSB who also worked on the privatization of government assets—as president in a surprise move on the first day of the year 2000. He became the gangster in chief.
Vladimir Putin’s first term coincided with the energy boom, and billionaires gobbled up a ludicrous share of growth. If any individual oligarch got too big for his britches, Putin was not beyond imposing serious consequences. He reinserted the state into the natural monopolies, this time in collaboration with loyal capitalists, and his stranglehold on power remains tight for now, despite the outstandingly uneven distribution of growth. Between 1980 and 2015, the Russian top 1 percent grew its income an impressive 6.2 percent per year, but the top .001 percent has maintained a growth rate of 17 percent over the same period. To invest these profits, the Russian billionaires parked their money in real estate, bidding up housing prices, and stashed a large amount of their wealth offshore. Reinvestment in Russian production was not a priority—why go through the hassle when there were easier ways to keep getting richer?
While Russia grew billionaires instead of output, China saw a path to have both. As in the case of Terry Gou, the Chinese Communist Party tempered its transition by incorporating steadily increasing amounts of foreign direct investment through Hong Kong and Taiwan, picking partners and expanding outward from the special economic zones. State support for education and infrastructure combined with low wages to make the mainland too attractive to resist. (Russia’s population is stagnant, while China’s has grown quickly.) China’s entry into the World Trade Organization, in 2001, gave investors more confidence. Meanwhile, strong capital controls kept the country out of the offshore trap, and state development priorities took precedence over extraction and get-rich-quick schemes. Chinese private wealth was rechanneled into domestic financial assets—equity and bonds or other loan instruments—at a much higher rate than it was in Russia. The result has been a sustained high level of annual output growth compared to the rest of the world, the type that involves putting up an iPhone City in a matter of months. As it has everywhere else, that growth has been skewed: only an average of 4.5 percent for the bottom half of earners in the 1978–2015 period compared to more than 10 percent for the top .001 percent. But this ratio of just over 2–1 is incomparable to Russia’s 17–.5 ration during the same period.
Since the beginning of the twenty-first century, certain trends have been more or less unavoidable. The rich have gotten richer relative to the poor and working class—in Russia, in China, in the United States, and pretty much anywhere else you want to look. Capital has piled into property markets, driving up the cost of housing everywhere people want to live, especially in higher-wage cities and especially in the world’s financial centers. Capitalist and communist countries alike have disgorged public assets into private pockets. But by maintaining a level of control over the process and slowing its tendencies, the People’s Republic of China has built a massive and expanding postindustrial manufacturing base.
It’s important to understand both of these patterns as part of the same global system rather than as two opposed regimes. One might imagine, based on what I’ve written so far, that the Chinese model is useful, albeit perhaps threatening, in the long term for American tech companies while the Russian model is irrelevant. Some commentators have phrased this as the dilemma of middle-wage countries on the global market: Wages in China are going to be higher than wages in Russia because wages in Russia used to be higher than wages in China. But Russia’s counterrevolutionary hyper-bifurcation has been useful for Silicon Valley as well; they are two sides of the same coin. Think about it this way: If you’re a Russian billionaire in the first decades of the twenty-first century looking to invest a bunch of money you pulled out of the ground, where’s the best place you could put it? The answer is Palo Alto.
Malcolm Harris, Palo Alto
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
anyway, I sent google gemini feedback about it's product and I think you should too if you want :)
I don't want this useless feature. google and all its employees have blood on their hands from the expanse of computing based on child slavery and warfare. "Apple, Dell, Google, Microsoft, and Tesla were all named in the federal class-action lawsuit filed in 2019, in Washington, D.C. It stated that the companies were “knowingly benefiting from and aiding and abetting the cruel and brutal use of young children in the Democratic Republic of the Congo to mine Cobalt,” which is found in every lithium-ion battery used to recharge the electronic devices that these five American companies manufacture."
The Role of Tech in the Congo’s Silent Genocide
i'm never going to forget when you removed "don't be evil" as your company tag line. we knew you were bullshit then and we know it now. quit your job <3
to submit feedback on gemini: on a computer, go to gemini.google.com . at the bottom, click Help twice, go to the bottom to "Report a Problem".
Friends of the Congo are calling for people in the US to send letters to their representatives to stop supporting Rowanda in this conflict. there is a call for a global embargo of Congo's minerals. but I figured y'all hate AI so much you would probably enjoy getting started by giving the middle finger to Google (and all of the other complicit megacorps) :)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
The new tariffs imposed by the U.S. on China, Mexico, and Canada will have widespread effects on American goods and services. Here’s how they are likely to impact different aspects of the economy:
1. Higher Costs for Businesses and Consumers
Many American businesses rely on imported materials, components, and products from these countries. Tariffs increase the cost of these imports, forcing companies to either absorb the costs (reducing profits) or pass them on to consumers.
Industries such as automotive, electronics, manufacturing, and retail will see price hikes, making everyday goods more expensive for American consumers.
2. Inflationary Pressure
Tariffs function like a tax on imported goods, leading to higher prices across the board.
If companies pass increased costs to consumers, inflation could rise, making goods and services more expensive and potentially prompting the Federal Reserve to reconsider interest rate policies.
3. Supply Chain Disruptions & Business Uncertainty
Companies that rely on raw materials, electronics, and auto parts from these countries may face delays and shortages, forcing them to find alternative suppliers or move production, which takes time and money.
Some businesses might restructure their supply chains by sourcing materials from other countries or increasing domestic production, but this transition isn't immediate and could further increase costs.
4. Retaliation from Trading Partners
Canada, Mexico, and China have signaled that they may impose their own tariffs on U.S. exports, which could hurt American industries that depend on international trade, such as agriculture, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Farmers, in particular, could face declining demand for crops like soybeans, corn, and dairy products, which were previously targeted in retaliatory tariffs during the Trump-era trade war.
5. Impact on the Stock Market & Business Investment
Investors dislike uncertainty. If businesses anticipate lower profits due to higher costs or potential trade disruptions, stock markets may react negatively.
Companies may delay hiring or expansion plans due to concerns over higher operational costs and shifting trade dynamics.
6. Possible Job Losses in Affected Industries
If businesses face significantly higher costs and declining demand due to retaliatory tariffs, some industries could see layoffs or reduced hiring.
Manufacturing and export-dependent sectors, such as automotive, steel, and agriculture, may be hit the hardest.
Potential Silver Linings
Some industries, like domestic manufacturing and steel production, could see short-term gains if companies decide to shift production back to the U.S. instead of relying on imports.
The government may use tariff revenues to invest in domestic industries or subsidies, potentially offsetting some negative effects.
Bottom Line
The new tariffs will likely increase costs for businesses and consumers, contribute to inflation, and create uncertainty in financial markets and supply chains. While some domestic industries might benefit, the risk of retaliatory tariffs and economic slowdown poses a challenge for the broader U.S. economy.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
The three-day [Conference on Women and the Workplace, convened in 1976] featured traditional presentations and livelier discussion periods. The medical director of Dow Chemical, Harold Gordon, fretted that his company could be held liable for discrimination if it excluded fertile women from certain high-risk jobs, and for harm to their offspring if it didn't. Dow was trying to do the right thing, Gordon said, but there were many questions: "What is the population at risk? How is it identified? What specific agents need to be considered? How are they identified? What restrictions are needed? When do they apply? To whom do they apply?" The [Oil, Chemical, and Atomic Workers]'s Tony Mazzocchi was unsympathetic. "There isn't a single worker, including those at Dow, who knows what the hell he works with in the first place," he said. "No industry has allowed us to look at the monitoring data.... We aren't being told what is carcinogenic or what is teratogenic. We are learning after the fact." It was the union's position, he said, that neither women nor men should have to be removed from a job to protect the unborn; "our position is to make the workplace safe for everyone." ...
For workers like Yvette Flores [whose child was born with severe intellectual disabilities after her exposure to dangerous solvents and lead-based solution in her job manufacturing lasers for Spectra-Physics], the most germane speaker was Andrea Hricko with the Labor Occupational Health Program at the University of California, Berkeley. Hricko had been investigating, with growing alarm, the electronics industry, which then employed some 271,000 workers in the United States. More than three-quarters of these workers were women, she said, and many were "nonwhite. A higher percentage do not speak English. And few of them are organized." Hricko said she'd heard from some California workers that "dark-skinned women, including Filipinos, Chicanos and Blacks, are often assigned to certain departments in electronics plants where chemicals are used that cause skin rashes. This is done because the skin rashes are not as obvious on the dark skin and, therefore, the workers don't complain as much as the company doesn't have to deal with the complaints." Some plants didn't allow languages other than English to be spoken, "even in departments where the majority of women are non-English-speaking," Hricko said. Intimidation was common. Women in one Silicon Valley plant who'd prepared a warning leaflet on trichloroethylene "had to leave copies of it in the women's rest room so that the male management people would not snatch the copies away."
Jim Morris, Cancer Factory: Industrial Chemicals, Corporate Deception, and the Hidden Deaths of American Workers (2024), Chapter 20
#workplace safety#chemical safety is a huge problem & it has not been resolved! mazzocchi said that before we passed right-to-know laws#but those laws are difficult to enforce & many workers are still primarily told brand names for chemicals#or are not given the appropriate information to assess their own safety. the real problem of course is that you cannot make safety choices#when you are deciding between nebulous chemical exposure risk & losing your job! disclosure is insufficient!#this is especially egregious in agriculture where pesticide & herbicide use is horrifically dangerous to workers & broader ecosystems#OSHA standards only regulate one chemical at a time after extensive & slow testing & review; efforts in the 70s to block regulate#by functional group were comprehensively shot down. so what standards we do have are fifty years out of date & many newer compounds#are functionally unregulated. OSHA itself says this & refers people to NIOSH & the state of california!
9 notes
·
View notes
Text



Conn - Multi-Vider
"All the way back in 1967, C.G. Conn wanted in on the decidedly nascent effects scene, and they wanted to do so with a bang. The company partnered with Jordan Electronics of Alhambra, CA to release an octave effect for wind instruments. The resulting circuit is a truly interesting piece of gear history. It needs to be said that Conn went into manufacturing, thereby ending its partnership with Jordan (at least according to all the paperwork) and the result was two different MultiViders. The differences on the surface are minute: the first model is grey and looks like a piece of dictation equipment, offering “bright” and “dark” input modes, a top-mounted Sensitivity control, and a plethora of battery gadgets. By contrast, the much cooler-looking model “914” did away with the frequency selector, opting for a switch called Unison and a power supply input.
Both models contain “Soprano,” “Bass” and “Sub Bass” switches, and corresponding volume for each. The 914’s Unison mode is essentially a dry signal control. The “grey box” model is a little more convoluted about it but the job is effectively identical. However, the way these two models go about these identical tasks in different—yet similar—ways.
This original “grey box” model contains a duo of ersatz flip-flop circuits, which the unit relies on for its octave down effects. The circuit utilizes some rather intense gain staging to convert the signal to a crude square wave and then use the flip-flops to divide the frequency in half and then in half again. In the later 914 model, much of this circuit is switched to a CD4013 chip, an all-in-one CMOS device. It’s interesting that the first draft of the MultiVider contains what amounts to a discrete imagining of the CD4013, and what it all adds up to is the first-ever octave effect for an electronic instrument. There’s also a wah inductor on the 914, which is connected to the sub-octave circuit somehow; I dare not remove the board due to extreme rocker switch fragility. I love stuff like this.
For as cool as this whole thing sounds, there are some drawbacks, as one might expect with the first pedal of any type. As previously stated, the MultiVider is a horns-only instrument, as is to be used with Conn’s proprietary woodwind pickup. While the “grey box” model serves up a battery option, the 914 is adapter-only, and it’s a doozy—only a 12-volt eighth-inch style phone plug will do. Thankfully there are workarounds for both; if you can solder, the power situation is a cinch and the microphone issue can be circumnavigated by hitting the MultiVider with a hotter input signal. Even then, a large belt clip on the back of the unit dictates its preferred method of implementation. With all that said, synth players are at an automatic advantage with modernizing the MultiVider.
Of course, the MultiVider was an advanced device for its time, and so it was used by artists that had explored brass instruments to their fullest. In particular, the MultiVider was used by Zappa’s band, the Mothers of Invention. It was also used by Miles Davis on 1970’s The Complete Jack Johnson Sessions. Of course there are others, but with a resume like that, stick to your strengths."
cred: catalinbread.com/blogs/kulas-cabinet/conn-multivider
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
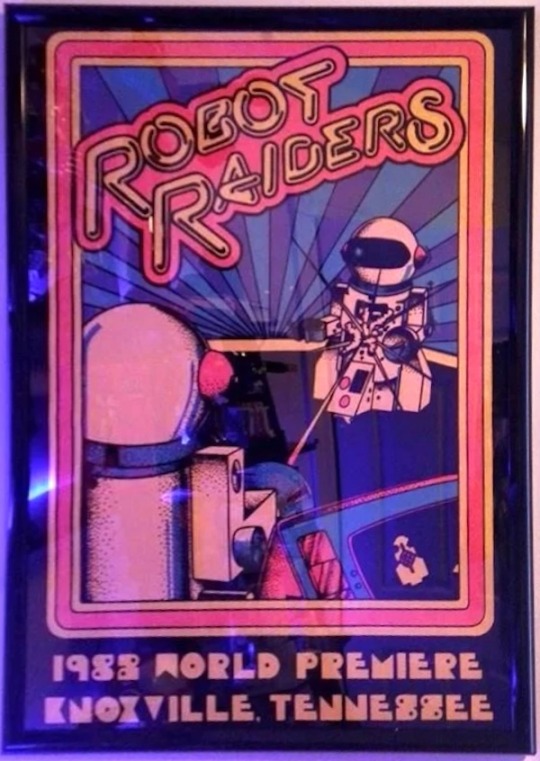



Robot Raiders, Video Expo Arcade, 1982 World’s Fair, Knoxville, TN. "Eight waist-high robots dashing around a ring zapping each other with light beams to the beat of rock music at the 1982 World's Fair have added a new dimension to electronic games. But the game, which costs $1.50 to play for about two minutes, may be just the "horse and buggy" of robot wars of tomorrow, its developers say. The game, called Robot Raiders, is played much like a video arcade game, except the action involves real robots, operated by remote control, in an octagonal ring. The eight humans at the controls fight their mini-war to the beat of hard rock music. As the lights flash and the music pounds, the robots race around firing light beams from their outstretched arms. The object is to hit an opponent in a a panel that registers the shot and transmits it by radio frequency to a scoreboard. "The guy says 'Go.' and everybody kind of comes up with lasers blazing," said Joe Stewardson, a photographer who says he played the game several times at the fair in Knoxville, Tenn. The robots, which are about about 3 feet tall, are "kind of your traditional robot," he said. The control stick moves left, right, forward and backward "just like a fighter pilot's," he said. While the game is getting its first public exposure at the fair, the gnome-sized warriors have been in the works for years at Sound Spectrum, an Orange County manufacturer. "What we wanted to do is extend the game beyond the cathode ray tube and develop a game that not only appealed to young people. but also adults as well…” said Gary Taylor, the head of Sound Spectrum. Dan Laughlin, another owner of the exhibit, said the players can visually track their hits by watching the light, which shows up something like a flashlight on the robot. "There are lights flashing on the floor, above and around the robots," Laughlin said. The show includes black lights and music with different frequency sounds that come from each of the robots as they shoot. Laughlin said the players, using remote-control "joy sticks," move the robots in an 18-foot radius from control podiums on the corners of the octagon. "They are inside what is almost like a cockpit of a fighter plane," he said. "They have a console where the hits are recorded, with a button on top their joy stick to shoot. While the game is popular, the owners concede it is expensive. But,” says Kail, "If a kid wants to play, he's going to pay the money. A lot of them are off on summer vacation, and have summer jobs." It's more of a main attraction, not for the average video parlor, more for theme parks and major shopping centers," he said." – Robot Raiders involves real, remote control robots, by Dolores Wood, Santa Ana, CA.
"They paid a quarter million for the world's first robot arcade game. There were eight robots but they did not work. We spent the last two months of the Fair engineering and building new robots. We had a few completed by the time the Fair closed." – Doug Dotson.
16 notes
·
View notes