#Ancient Arab civilization
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
Explore the fascinating world of Pre-Islamic Arabia with our latest YouTube video! Dive into the rich history of the Arabian Peninsula, where ancient Arab civilization, nomadic lifestyles, and unique desert environments shaped a crossroads of civilizations. Discover the historical Arab culture, interactions with Romans and Persians, and the rise of Islam led by Prophet Muhammad. Join us on this journey through Arabian heritage, cultural transformations, historical poetry, and the intriguing artifacts that tell the tale of this captivating era.
Lost Islamic History Series Ep 1: A Short Journey Through Pre-Islamic Arabia
#Pre-Islamic Arabia#Arabian Peninsula history#Ancient Arab civilization#Nomadic lifestyle#Arab tribes#Historical Arab culture#Ghassanids#Lakhmids#Kingdom of Aksum#Rise of Islam#Prophet Muhammad#Islamic history#Arabian heritage#Early Islamic civilization#Islamic Golden Age#Islamic empires#Islamic conquests#Islamic caliphates#Islamic culture#Islamic dynasties#Islamic expansion#Islamic theology#Islamic caliphs#Islamic heritage#Islamic historical figures#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy " Eid Al fitr" (Muslims celebrate breakfast after fasting the holy month of Ramadan) and "Sham al Naseem festival" ( an ancient Egyptian celebration of harvest ).
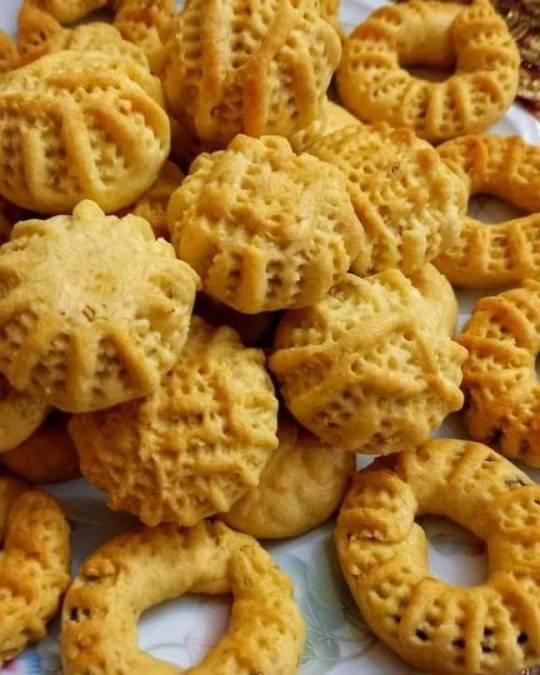

Kahk (coptic word) is round to represent the round desk of the sun ☀ the symbol of the ancient Egyptian god "Raa"
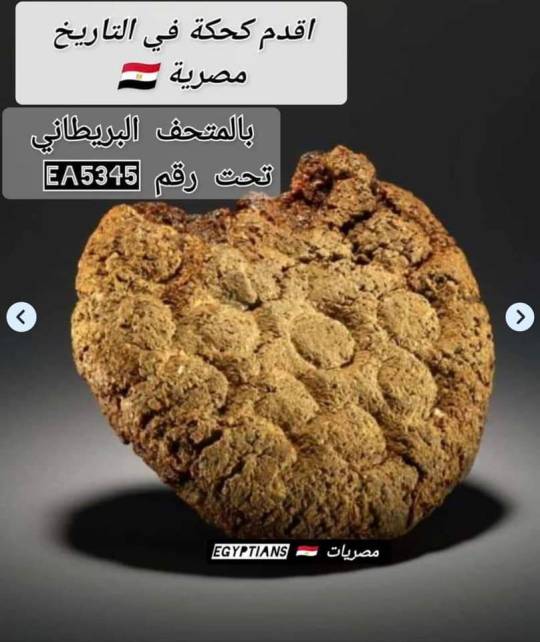
The eid cookies (kahk) is the oldest cookie in the world (British museum)
(we still make them today! The filled ones (kahk) in Eid. And the hollow ones (bracelet cookies) in funerals
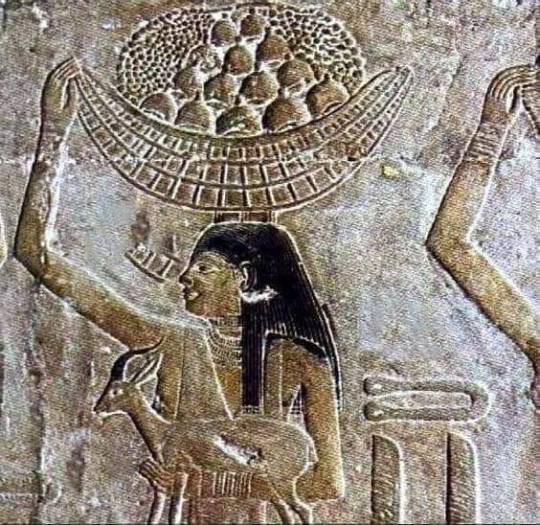


Our ancestors bringing kahk as symbolic sacrifice to Raa

Speaking of Easter.. Did you know that Sham al Naseem is the og Easter?
But in Egypt we postpone it so that Christians can eat fish (after fasting themselves) 🥰
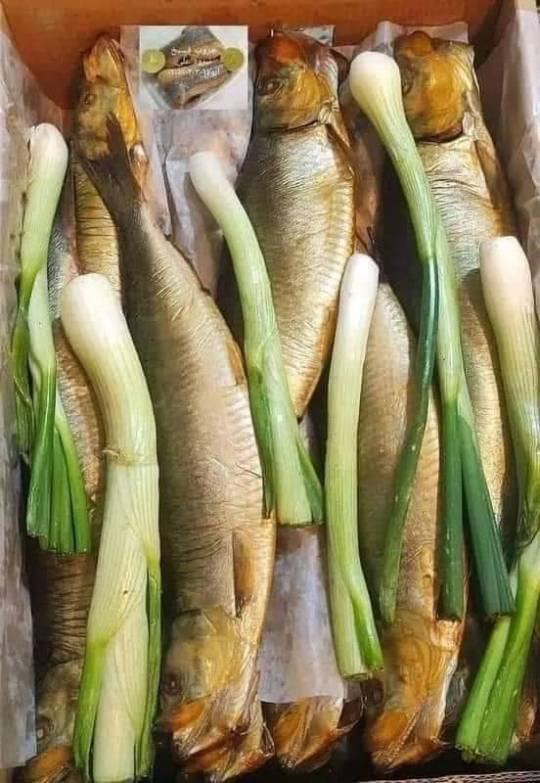





I can talk about our traditions and civilization all day long but nothing is compared to experiencing Egypt yourself. So don't be a stranger to the mother of the world 🥰❤️🇪🇬
#egypt#eid mubarak#eid al fitr#Sham al Naseem#ancient egypt#folclore#culture#civilization#no one can erase our traditions#not colonization#not arabization#we are the descendants#Kahk#Proud of my heritage#Proud of my religion#part of me#festival#fesikh#easter#easter eggs#green onions#food#cultural food#egyptian#history#muslims#christians#orthodox christianity#coptic#religious harmony
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
i've got a fourth of the book left so who knows this thought may change, but so far my biggest takeway from the agatha christie memoir is that the weird problematic parts and occasional slurs and shit that show up in her books aren't so much raging hateful bouts of racism in the style of young hp lovecraft or raymond chandler
but more an old victorian woman basted in colonialist propaganda and strict classism from birth and surrounded by awful people being politely ignorant and uneducated, and also being very blunt in her quoting real people and writing particular characters
like obviously a lot of that shit is still 100% problematic and deserves criticism and acknowledgement, no question there at all and no being apologist, but it is a bit of a relief that a lot of it is her writing what she saw around her and not necessarily her own personal screeds (chandler was a good noir writer but also so fucking racist holy shit)
#agatha christie#aside from a bit of bewildered culture clash there's been zero slurs or hatred on her personal part in the memoir towards anyone#there's commentary on beautiful turkish women and how polite arabic men are and the beauty of the middle east/egypt and their architecture#and how much she loves studying the ancient history of human civilization in those places#though of course the british relationship with archeology is a whole 'nother kettle of problematic fish#book stuff
1 note
·
View note
Text
AI translates 5,000-year-old cuneiform tablets into English
#linguistique#historical linguistics#linguist#linguistic#linguistics#languages#language#langblr#cuneiform#sumerian#akkadian#arabic#hebrew#ancient history#archeology#translator#translation#mesopotamia#ancient civilizations#ancient artifacts#writing#writing systems#ai#artificial intelligence#ai tools#ai technology
1 note
·
View note
Text
#fox news#wall streeet journal#ancient civilizations#history#sky news#historical#my journal#journal#booklr#washington#journaling#bbc news world#cnn fast facts#cnn news#cnn arabic#cnn#republican#cnnslot#cnn tonight#bbc merthur#bbc merlin#america#america was never great#british gp 2023#british royal family#britney spears#britain#british columbia#usa#made in usa
1 note
·
View note
Text
I want to take a few minutes to talk about my connection to Israel, as a Jew. I want to do that because some people desperately need to understand this, and also I'm procrastinating on uni homework.
Some years ago there were calls to return artifacts from the British Museum to the countries they're from. I know Britain pretty much went anywhere and took anything they wanted, but it got me thinking about cultural identities and their connection over time.
The middle east was home to some of the world's most ancient civilizations, and I'm sure most people living there could trace their lineage back to those civilizations (theoretically of course, we don't have data going that far). But how are they related to them? Do modern day Iraqis have any connection to Babylonians? They don't have a common language, religion, holidays, costumes… there is no cultural connection there. Babylonians happened to live in the same place, but other than that…
But this is not the case for Jews. Wherever Jewish people ended up throughout time, we kept a direct connection to ancient Israelites. I speak the same language they did thousands of years ago, I celebrate the holidays they celebrated. Our holy book is localized to Israel. We have holidays where we use local flora as decorations. We remembered our home, wherever we were, and waited to return.
The city I grew up in has flooding every winter. The whole area does (the Sharon region). It's because it used to be a swamp. There are 3 limestone ridges blocking the rivers from getting to the ocean, and when the early Zionist pioneers bought lands in this area (which were uninhabited swampland at the time) they had to open up tunnels through the limestone and drain the swamps before people could live here.
Why am I telling you this? Because we already did it before. Ancient Israelites already dug tunnels and drained swamps and lived here. There was a prayer during Yom Kippur specifically for the safety of people living here. All of the towns in the Sharon were razed by the Mamluks in the 13th century, and it became a swamp again. Until we returned.
To anyone who call us "colonizers": These "ancient" Israelites don't just share a religion with us, they ARE us. We were expelled from our homeland, but we kept our identity, we refused to let go, we kept wishing to come back home. We were always indigenous to Israel. We don't belong anywhere but here.
And now they're are trying to tell us that some people with a name invented by Rome to erase Judea and Israel, with a religion and language from Arabia, who didn't have a distinct cultural identity other than "Arab" until a few decades ago, belong here more than we do? I don't think so.
677 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monte Melqonyan/Մոնթե Մելքոնյան (1957-1993)
Honestly, I don't even know where to begin. He's one of those extraordinary individuals about whom countless books could be written and numerous movies could be made, yet still, so much would remain untold. You might wonder, "He's a National Armenian Hero—cool, but why should I know about him?" My answer is simple: if the world had more people like him, especially in today's times, it would be a much better place. He fought for justice, embodied culture and education, and radiated a deep love for his people and humanity as a whole. I believe everyone should aspire to have a little bit of Monte's spirit within them, regardless of their nationality.
Now, it's important to note that some things written about him in the Western press can be questionable and inaccurate. So, I would advise taking most of the information from those sources with a grain of salt.

Monte was born on November 25, 1957, into an Armenian family in Visalia, California, that had survived the Armenian Genocide. From 1969 to 1970, his family traveled through Western Armenia, the birthplace of his ancestors. During this journey, Monte, at the age of twelve, began to realize his Armenian identity. While taking Spanish language courses in Spain, his teacher had posed him the question of where he was from. Dissatisfied with Melkonian's answer of "California", the teacher rephrased the question by asking "where did your ancestors come from?" His brother Markar Melqonyan remarked that "her image of us was not at all like our image of ourselves. She did not view us as the Americans we had always assumed we were." From this moment on, for days and months to come, Markar continues, "Monte pondered [their teacher Señorita] Blanca's question Where are you from?"
In high school, he excelled academically and struggled to find new challenges. Instead of graduating early, as suggested by his principal, Monte found an alternative - a study abroad program in East Asia. The decision to go to Japan was not random. He had been attending karate clubs and was the champion of the under-14 category in California. He also studied Japanese culture, including taking Japanese language courses. After completing his studies at a school in Osaka, Japan, he went to South Korea, where he studied under a Buddhist monk. He later traveled to Vietnam, witnessing the war and taking numerous photographs of the conflict. Upon returning to America, he had become proficient in Japanese and karate.

Having graduated from high school, Monte entered the University of California, Berkeley, with a Regents Scholarship, majoring in ancient Asian history and archaeology. In 1978, he helped organize an exhibition of Armenian cultural artifacts at one of the university's libraries. A section of the exhibit dealing with the Armenian Genocide was removed by university authorities at the request of the Turkish consul general in San Francisco, but it was eventually reinstalled following a campus protest movement. Monte completed his undergraduate work in under three years. During his time at the university, he founded the "Armenian Students' Union" and organized an exhibition dedicated to the Armenian Genocide in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Turkey.
Upon graduating, he was accepted into the archaeology graduate program at the University of Oxford. However, Monte chose to forgo this opportunity and instead began his lifelong struggle for the Armenian Cause.

In the fall of 1978, Monte went to Iran and participated in demonstrations against the Shah. Later that year, he traveled to Lebanon, where the civil war was at its peak. In Beirut, he participated in the defense of the Armenian community. Here, he learned Arabic and, by the age of 22, was fluent in Armenian, English, French, Spanish, Italian, Turkish, Persian, Japanese, and Kurdish.
From 1980, Monte joined the Armenian Secret Army for the Liberation of Armenia (ASALA – I promise to tell you more about them later) and quickly became one of its leaders. In 1981, he participated in the planning of the famous Van operation. In 1981, he was arrested at Orly Airport in France for carrying a false passport and a pistol. During his trial, Monte declared, "All Armenians carry false passports—French, American—they will remain false as long as they are not Armenian." Over the following years, he perfected his military skills at an ASALA training camp, eventually becoming one of the group's principal instructors.

Monte with his wife Seda
After being released from a French prison (once again) in 1989, Monte arrived in Armenia in 1991, where armed clashes between Armenians and azerbaijanis had already begun. He founded the "Patriots" unit and spent seven months in Yerevan working at the Academy of Sciences, writing and publishing the book "Armenia and its Neighbors." In September of the same year, he went to the Republic of Artsakh to fight for his fatherland and its people. Due to his military expertise, he was appointed Chief of Staff of the Martuni defense district in 1992. His sincerity and purity quickly won the love and respect of the local population and the Armenian community as a whole.
Throughout his conscious life, Monte fought for the rights of Armenians, recognition of the Armenian Genocide, and the reclamation of Armenian homeland.
There are various versions of Monte Melqonyan's death circulating in both Armenian and azerbaijani media. According to official Armenian information, Monte was killed on June 12, 1993, by fire from an azerbaijani armored vehicle.
Monte remains a lasting testament to the incredible potential unleashed when the Armenian patriotic heart unites with sharp intellect.
youtube
In case you'd like to put a voice to the face and hear about the Artsakh struggle directly from Monte, here he is speaking about it in English.
#so many things have been left out#but I guess this is a good starting point#I promise to tell you more about ASALA and Van Operation in near future#monte melqonyan#armenia#armenian history#armenian culture#world history#artsakh#artsakh is armenia#translated literature#մոնթե մելքոնյան
283 notes
·
View notes
Note
sorry if this is ignorant, but how are palestinians the oldest christians when palestinians didn't exist before?
The Arabs that inhabited the land are descendants of Jewish people since biblical times, in fact, they're descendants of the ancient Canaanites. This is attested in archeological and geneological findings, even so by Israeli archeologists. The earliest Christians were Jewish converts to the religion and upheld their 2000 year old tradition throughout periods of civil unrest, invasions, wars and etc. With the Arab expansion, there was a process of Arabization in the Holy Land. Some Christians converted, either forcefully or willingly. Either way, the Christians survived and thrived beyond the crusades. The Muslim Arab community would intermingle with the native Jewish, Samaritan and Christian community, some would adopt each other's religions, customs and much more, creating an entirely distinct identity. This is why the Arabs in Palestine are historically known to have been Arabized with their own distinct set of customs and traditions, which set them apart from other Arabs.
Christianity remained in the pre-arabized people and its traditions would go on beyond the Islamization and Arabization of the Holy Land, hence why Palestinians are known to be the oldest custodians of the oldest Christian traditions in the world.
280 notes
·
View notes
Text
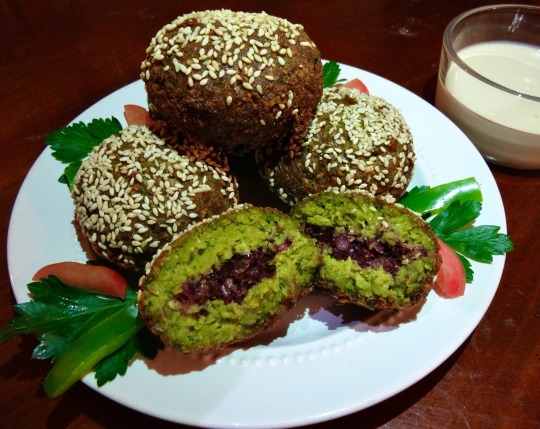
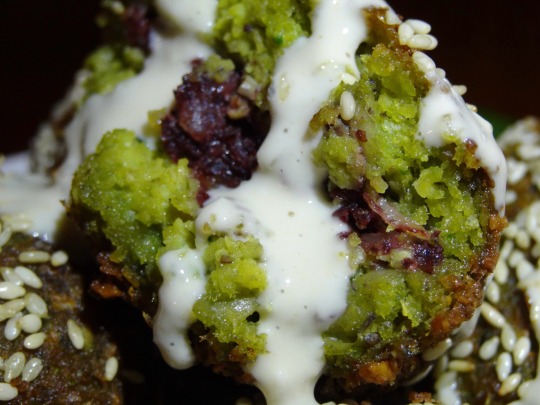


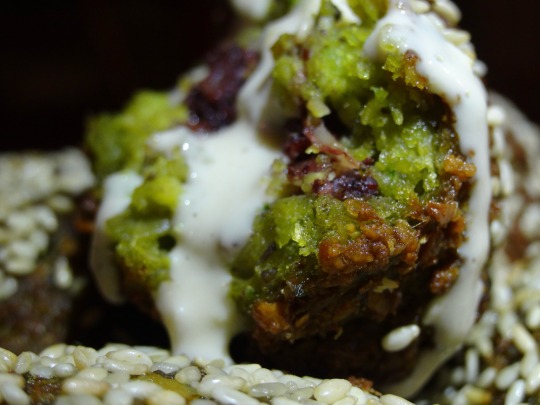
[ID: First image shows large falafel balls, one pulled apart to show that it is bright green and red on the inside, on a plate alongside green chilis, parsley, and pickled turnips. Second image is an extreme close-up of the inside of a halved falafel ball drizzled with tahina sauce. End ID]
فلافل محشي فلسطيني / Falafel muhashshi falastini (Palestinian stuffed falafel)
Falafel (فَلَافِل) is of contested origin. Various hypotheses hold that it was invented in Egypt any time between the era of the Pharoahs and the late nineteenth century (when the first written references to it appear). In Egypt, it is known as طَعْمِيَّة (ṭa'miyya)—the diminutive of طَعَام "piece of food"—and is made with fava beans. It was probably in Palestine that the dish first came to be made entirely with chickpeas.
The etymology of the word "falafel" is also contested. It is perhaps from the plural of an earlier Arabic word *filfal, from Aramaic 𐡐𐡋𐡐𐡉𐡋 "pilpāl," "small round thing, peppercorn"; or from "مفلفل" "mfelfel," a word meaning "peppered," from "فلفل" "pepper" + participle prefix مُ "mu."
This recipe is for deep-fried chickpea falafel with an onion and sumac حَشْوَة (ḥashua), or filling; falafel are also sometimes stuffed with labna. The spice-, aromatic-, and herb-heavy batter includes additions common to Palestinian recipes—such as dill seeds and green onions—and produces falafel balls with moist, tender interiors and crisp exteriors. The sumac-onion filling is tart and smooth, and the nutty, rich, and bright tahina-based sauce lightens the dish and provides a play of textures.
Falafel with a filling is falafel مُحَشّي (muḥashshi or maḥshshi), from حَشَّى (ḥashshā) "to stuff, to fill." While plain falafel may be eaten alongside sauces, vegetables, and pickles as a meal or a snack, or eaten in flatbread wraps or kmaj bread, stuffed falafel are usually made larger and eaten on their own, not in a wrap or sandwich.
Falafel has gone through varying processes of adoption, recognition, nationalization, claiming, and re-patriation in Zionist settlers' writing. A general arc may be traced from adoption during the Mandate years, to nationalization and claiming in the years following the Nakba until the end of the 20th century, and back to re-Arabization in the 21st. However, settlers disagree with each other about the value and qualities of the dish within any given period.
What is consistent is that falafel maintains a strategic ambiguity: particular qualities thought to belong to "Arabs" may be assigned, revoked, rearranged, and reassigned to it (and to other foodstuffs and cultural products) at will, in accordance with broader trends in politics, economics, and culture, or in service of the particular argument that a settler (or foreign Zionist) wishes to make.
Mandate Palestine, 1920s – early '30s: Secular and collective
While most scholars hold that claims of an ancient origin for falafel are unfounded, it was certainly being eaten in Palestine by the 1920s. Yael Raviv writes that Jewish settlers of the second and third "עליות" ("aliyot," waves of immigration; singular "עליה" "aliya") tended to adopt falafel, and other Palestinian foodstuffs, largely uncritically. They viewed Palestinian Arabs as holding vessels that had preserved Biblical culture unchanged, and that could therefore serve as models for a "new," agriculturally rooted, physically active, masculine Jewry that would leave behind the supposed errors of "old" European Jewishness, including its culinary traditions—though of course the Arab diet would need to be "corrected" and "civilized" before it was wholly suitable for this purpose.
Falafel was further endeared to these "חֲלוּצִים" ("halutzim," "pioneers") by its status as a street food. The undesirable "old" European Jewishness was associated with the insularity of the nuclear family and the bourgeois laziness of indoor living. The קִבּוּצים ("Kibbutzim," communal living centers), though they represented only a small minority of settlers, furnished a constrasting ideal of modern, earthy Jewishness: they left food production to non-resident professional cooks, eliding the role of the private, domestic kitchen. Falafel slotted in well with these ascetic ideals: like the archetypal Arabic bread and olive oil eaten by the Jewish farmer in his field, it was hardy, cheap, quick, portable, and unconnected to the indoor kitchen.
The author of a 1929 article in דאר היום ("Doar Hyom," "Today's Mail") shows unrestrained admiration for the "[]מזרחי" ("Oriental") food, writing of his purchase of falafel stuffed in a "פיתה" ("pita") that:
רק בני-ערב, ואחיהם — היהודים הספרדים — רק הם עלולים "להכנת מטעם מפולפל" שכזה, הנעים כל כך לחיך [...].
("Only the Arabs, and their brothers—the Sepherdi Jews—only they are likely to create a delicacy so 'peppered' [a play on the פ-ל-פ-ל (f-l-f-l) word root], one so pleasing to the palate".)
Falafel's strong association with "Arabs" (i.e., Palestinians), however, did blemish the foodstuff in the eyes of some as early as 1930. An article in the English-language Palestine Bulletin told the story of Kamel Ibn Hassan's trial for the murder of a British soldier, lingering on the "Arab" "hashish addicts," "women of the streets," and "concessionaires" who rounded out this lurid glimpse into the "underground life lived by a certain section of Arab Haifa"; it was in this context that Kamel's "'business' of falafel" (scare quotes original) was mentioned.
Mandate Palestine, late 1930s–40s: A popular Oriental dish
In 1933, only three licensed falafel vendors operated in Tel Aviv; but by December 1939, Lilian Cornfeld (columnist for the English-language Palestine Post) could lament that "filafel cakes" were "proclaiming their odoriferous presence from every street corner," no longer "restricted to the seashore and Oriental sections" of the city.
Settlers' attitudes to falafel at this time continued to range from appreciation to fascinated disgust to ambivalence, and references continued to focus on its cheapness and quickness. According to Cornfeld, though the "orgy of summertime eating" of which falafel was the "most popular" representative caused some dietary "damage" to children, and though the "rather messy and dubious looking" food was deep-fried, the chickpeas themselves were still of "great nutritional value": "However much we may object to frying, — if fry you must, this at least is the proper way of doing it."
Cornfeld's article, appearing 10 years after the 1929 reference to falafel in pita quoted above, further specifies how this dish was constructed:
There is first half a pita (Arab loaf), slit open and filled with five filafels, a few fried chips [i.e. French fries] and sometimes even a little salad. The whole is smeared over with Tehina, a local mayonnaise made with sesame oil (emphasis original).
The ethnicity of these early vendors is not explicitly mentioned in these accounts. The Zionist "תוצרת הארץ" "totzeret ha’aretz"; "produce of the land") campaign in the 1930s and 1940s recommended buying only Jewish produce and using only Jewish labor, but it did not achieve unilaterial success, so it is not assured that settlers would not be buying from Palestinian vendors. There were, however, also Mizrahi Jewish vendors in Tel Aviv at this time.
The WW2-era "צֶנַע" ("tzena"; "frugality") period of rationing meat, which was enforced by British mandatory authorities beginning in 1939 and persisting until 1959, may also have contributed to the popularity of falafel during this time—though urban settlers employed various strategies to maintain access to significant amounts of meat.
Israel and elsewhere, 1950s – early 60s: The dawn of de-Arabization
After the Nakba (the ethnic cleansing of broad swathes of Palestine in the creation of the modern state of "Israel"), the task of producing a national Israeli identity and culture tied to the land, and of asserting that Palestinians had no like sense of national identity, acquired new urgency. The claiming of falafel as "the national snack of Israel," the decoupling of the dish from any association with "Arabs" (in settlers' writing of any time period, this means "Palestinians"), and the insistence on associating it with "Israel" and with "Jews," mark this time period in Israeli and U.S.-ian newspaper articles, travelogues, and cookbooks.
During this period, falafel remained popular despite the "reintegrat[ion]" of the nuclear family into the "national project," and the attendant increase in cooking within the familial home. It was still admirably quick, efficient, hardy, and frequently eaten outside. When it was homemade, the dish could be used rhetorically to marry older ideas about embodying a "new" Jewishness and a return to the land through dietary habits, with the recent return to the home kitchen. In 1952, Rachel Yanait Ben-Zvi, the wife of the second President of Israel, wrote to a South African Zionist women's society:
I prefer Oriental dishes and am inclined towards vegetarianism and naturalism, since we are returning to our homeland, going back to our origin, to our climate, our landscape and it is only natural that we liberate ourselves from many of the habits we acquired in the course of our wanderings in many countries, different from our own. [...] Meals at the President's table [...] consist mainly of various kinds of vegetable prepared in the Oriental manner which we like as well as [...] home-made Falafel, and, of course vegetables and fruits of the season.
Out of doors, associations of falafel with low prices, with profusion and excess, and with youth, travelling and vacation (especially to urban locales and the seaside) continue. Falafel as part and parcel of Israeli locales is given new emphasis: a reference to the pervasive smell of frying falafel rounds out the description of a chaotic, crowded, clamorous scene in the compact, winding streets of any old city. Falafel increasingly stands metonymically for Israel, especially in articles written to entice Jewish tourists and settlers: no one is held to have visited Israel unless they have tried real Israeli falafel. A 1958 song ("ולנו יש פלאפל", "And We Have Falafel") avers that:
הַיּוֹם הוּא רַק יוֹרֵד מִן הַמָּטוֹס [...] כְבָר קוֹנֶה פָלָאפֶל וְשׁוֹתֶה גָּזוֹז כִּי זֶה הַמַּאֲכָל הַלְּאֻמִּי שֶׁל יִשְׂרָאֵל
("Today when [a Jew] gets off the plane [to Israel] he immediately has a falafel and drinks gazoz [...] because this is the national dish of Israel"). A 1962 story in Israel Today features a boy visiting Israel responding to the question "Have you learned Hebrew yet?" by asserting "I know what falafel is." Recipes for falafel appear alongside ads for smoked lox and gefilte fish in U.S.-ian Jewish magazines; falafel was served by Zionist student groups in U.S.-ian universities beginning in the 1950s and continuing to now.
These de-Arabization and nationalization processes were possible in part because it was often Mizrahim (West Asian and North African Jews) who introduced Israelis to Palestinian food—especially after 1950, when they began to immigrate to Israel in larger numbers. Even if unfamiliar with specific Palestinian dishes, Mizrahim were at least familiar with many of the ingredients, taste profiles, and cooking methods involved in preparing them. They were also more willing to maintain their familiar foodways as settlers than were Zionist Ashkenazim, who often wanted to distance themselves from European and diaspora Jewish culture.
Despite their longstanding segregation from Israeli Ashkenazim (and the desire of Ashkenazim to create a "new" European Judaism separate from the indolence and ignorance of "Oriental" Jews, including their wayward foodways), Mizrahim were still preferable to Palestinian Arabs as a point of origin for Israel's "national snack." When associated with Mizrahi vendors, falafel could be considered both Oriental and Jewish (note that Sephardim and Mizrahim are unilaterally not considered to be "Arabs" in this writing).
Thus food writing of the 1950s and 60s (and some food writing today) asserts, contrary to settlers' writing of the 1920s and 30s, that falafel had been introduced to Israel by Jewish immigrants from Syria, Yemen, or Morocco, who had been used to eating it in their native countries—this, despite the fact that Yemen and Morocco did not at this time have falafel dishes. Even texts critical of Zionism echoed this narrative. In fact, however, Yemeni vendors had learned to make falafel in Egypt on their way to Palestine and Israel, and probably found falafel already being sold and eaten there when they arrived.Meneley, Anne2007 Like an Extra Virgin. American Anthropologist 109(4):678–687
Meanwhile, "pita" (Palestinian Arabic: خبز الكماج; khubbiz al-kmaj) was undergoing in some quarters a similar process of Israelization; it remained "Arab" in others. In 1956, a Boston-born settler in Haifa wrote for The Jewish Post:
The baking of the pittah loaves is still an Arab monopoly [in Israel], and the food is not available at groceries or bakeries which serve Jewish clientele exclusively. For our Oriental meal to be a success we must have pittah, so the more advance shopping must be done.
This "Arab monopoly" in fact did not extent to an Arab monopoly in discourse: it was a mere four years later that the National Jewish Post and Opinion described "Peeta" as an "Israeli thin bread." Two years after that, the U.S.-published My Jewish Kitchen: The Momales Ta'am Cookbook (co-authored by Zionist writer Shushannah Spector) defined "pitta" as an "Israeli roll."
Despite all this scrubbing work, settlers' attitudes towards falafel in the late 1950s were not wholly positive, and references to the dish as having been "appropriated from the [Palestinian] Arabs" did not disappear. A 1958 article, written by a Boston-born man who had settled in Israel in 1948 and published in U.S.-ian Zionist magazine Midstream, repeats the usual associations of falafel with the "younger set" of visitors from kibbutzim to "urban" locales; it also denigrates it as a “formidably indigestible Arab delicacy concocted from highly spiced legumes rolled into little balls, fried in grease, and then inserted into an underbaked piece of dough, known as a pita.”
Thus settlers were ambivalent about khubbiz as well. If their food writing sometimes refers to pita as "doughy" or "underbaked," it is perhaps because they were purchasing it from stores rather than baking it at home—bakeries sometimes underbake their khubbiz so that it retains more water, since it is sold by weight.
Israel and elsewhere, late 1960s–2010s: Falafel with even fewer Arabs
The sanitization of falafel would be more complete in the 60s and 70s, as falafel was gradually moved out of separate "Oriental dishes" categories and into the main sections of Israeli cookbooks. A widespread return to כַּשְׁרוּת (kashrut; dietary laws) meant that falafel, a פַּרְוֶה (parve) dish—one that contained no meat or dairy—was a convenient addition on occasions when food intersected with nationalist institutions, such as at state dinners and in the mess halls of Israeli military forces.
This, however, still did not prohibit Israelis from displaying ambivalence towards the food. Falafel was more likely to be glorified as a symbol of Jewish Israel in foreign magazines and tourist guides, including in the U.S.A. and Italy, than it was to be praised in Israeli Zionist publications.
Where falafel did maintain an association with Palestinians, it was to assert that their versions of it had been inferior. In 1969, Israeli writer Ruth Bondy opines:
Experience says that if we are to form an affection for a people we should find something admirable about its customs and folklore, its food or girls, its poetry and music. True, we have taken the first steps in this direction [with Palestinians]: we like kebab, hummous, tehina and falafel. The trouble is that these have already become Jewish dishes and are prepared more tastily by every Rumanian restaurateur than by the natives of Nablus.
Opinions about falafel in this case seem to serve as a mirror for political opinions about Palestinians: the same writer had asserted, on the previous page, that the "ideal situation, of course, would be to keep all the territories we are holding today—but without so many Arabs. A few Arabs would even be desirable, for reasons of local color, raising pigs for non-Moslems and serving bread on the Passover, but not in their masses" (trans. Israel L. Taslitt).
Later narratives tended to retrench the Israelization of falafel, often acknowledging that falafel had existed in Palestine prior to Zionist incursion, but holding that Jewish settlers had made significant changes to its preparation that were ultimately responsible for making it into a worldwide favorite. Joan Nathan's 2001 Foods of Israel Today, for example, claimed that, while fava and chickpea falafel had both preëxisted the British Mandate period, Mizrahi settlers caused chickpeas to be the only pulse used in falafel.
Gil Marks, who had echoed this narrative in his 2010 Encyclopedia of Jewish Food, later attributed the success of Palestinian foods to settlers' inventiveness: "Jews didn’t invent falafel. They didn’t invent hummus. They didn’t invent pita. But what they did invent was the sandwich. Putting it all together. And somehow that took off and now I have three hummus restaurants near my house on the Upper West Side.”
Israel and elsewhere, 2000s – 2020s: Re-Arabization; or, "Local color"
Ronald Ranta has identified a trend of "re-Arabizing" Palestinian food in Israeli discourse of the late 2000s and later: cooks, authors, and brands acknowledge a food's origin or identity as "Arab," or occasionally even "Palestinian," and consumers assert that Palestinian and Israeli-Palestinian (i.e., Israeli citizens of Palestinian ancestry) preparations of foods are superior to, or more "authentic" than, Jewish-Israeli ones. Israeli and Israeli-Palestinian brands and restaurants market various foods, including falafel, as "אסלי" ("asli"), from the Arabic "أَصْلِيّ" ("ʔaṣliyy"; "original"), or "בלדי" ("baladi"), from the Arabic "بَلَدِيّ" ("baladiyy"; "native" or "my land").
This dedication to multiculturalism may seem like progress, but Ranta cautions that it can also be analyzed as a new strategy in a consistent pattern of marginalization of the indigenous population: "the Arab-Palestinian other is re-colonized and re-imagined only as a resource for tasty food [...] which has been de-politicized[;] whatever is useful and tasty is consumed, adapted and appropriated, while the rest of its culture is marginalized and discarded." This is the "serving bread" and "local color" described by Bondy: "Arabs" are thought of in terms of their usefulness to settlers, and not as equal political participants in the nation. For Ranta, the "re-Arabizing" of Palestinian food thus marks a new era in Israel's "confiden[ce]" in its dominance over the indigenous population.
So this repatriation of Palestinian food is limited insofar as it does not extend to an acknowledgement of Palestinians' political aspirations, or a rejection of the Zionist state. Food, like other indicators and aspects of culture, is a "safe" avenue for engagement with colonized populations even when politics is not.
The acknowledgement of Palestinian identity as an attempt to neutralize political dissent, or perhaps to resolve the contradictions inherent in liberal Zionist identity, can also be seen in scholarship about Israeli food culture. This scholarship tends to focus on narratives about food in the cultural domain, ignoring the material impacts of the settler-colonialist state's control over the production and distribution of food (something that Ranta does as well). Food is said to "cross[] borders" and "transcend[] cultural barriers" without examination of who put the borders there (or where, or why, or how, or when). Disinterest in material realities is cultivated so that anodyne narratives about food as “a bridge” between divides can be pursued.
Raviv, for example, acknowledges that falafel's de-Palestinianization was inspired by anti-Arab sentiment, and that claiming falafel in support of "Jewish nationalism" was a result of "a connection between the people and a common land and history [needing] to be created artificially"; however, after referring euphemistically to the "accelerated" circumstances of Israel's creation, she supports a shared identity for falafel in which it can also be recognized as "Israeli." She concludes that this should not pose a problem for Palestinians, since "falafel was never produced through the labor of a colonized population, nor was Palestinian land appropriated for the purpose of growing chickpeas for its preparation. Thus, falafel is not a tool of oppression."
Palestine and Israel, 1960s – 2020s: Material realities
Yet chickpeas have been grown in Israel for decades, all of them necessarily on appropriated Palestinian land. Experimentation with planting in the arid conditions of the south continues, with the result that today, chickpea is the major pulse crop in the country. An estimated 17,670,000 kilograms of chickpeas were produced in Israel in 2021; at that time, this figure had increased by an average of 3.5% each year since 1966. 73,110 kilograms of that 2021 crop was exported (this even after several years of consecutive decline in chickpea exports following a peak in 2018), representing $945,000 in exports of dried chickpeas alone.
The majority of these chickpeas ($872,000) were exported to the West Bank and Gaza; Palestinians' inability to control their own imports (all of which must pass through Israeli customs, and which are heavily taxed or else completely denied entry), and Israeli settler violence and government expropriation of land, water, and electricity resources (which make agriculture difficult), mean that Palestine functions as a captive market for Israeli exports. Israeli goods are the only ones that enter Palestinian markets freely.
By contrast, Palestinian exports, as well as imports, are subject to taxation by Israel, and only a small minority of imports to Israel come from Palestine ($1.13 million out of $22.4 million of dried chickpeas in 2021).
The 1967 occupation of the West Bank has besides had a demonstrable impact on Palestinians' ability to grow chickpeas for domestic consumption or export in the first place, as data on the changing uses of agricultural land in the area from 1966–2001 allow us to see. Chickpeas, along with wheat, barley, fenugreek, and dura, made up a major part of farmers' crops from 1840 to 1914; but by 2001, the combined area devoted to these field crops was only a third of its 1966 value. The total area given over to chickpeas, lentils and vetch, in particular, shrank from 14,380 hectares in 1966 to 3,950 hectares in 1983.
Part of this decrease in production was due to a shortage of agricultural labor, as Palestinians, newly deprived of land or of the necessary water, capital, and resources to work it—and in defiance of Raviv's assertion that "falafel was never produced through the labor of a colonized population"—sought jobs as day laborers on Israeli fields.
The dearth of water was perhaps especially limiting. Palestinians may not build anything without a permit, which the Israeli military may deny for any, or for no, reason: no Palestinian's request for a permit to dig a well has been approved in the West Bank since 1967. Israel drains aquifiers for its own use and forbids Palestinians to gather rainwater, which the Israeli military claims to own. This lack of water led to land which had previously been used to grow other crops being transitioned into olive tree fields, which do not require as much water or labor to tend.
In Gaza as well, occupation systematically denies Palestinians of food itself, not just narratives about food. The majority of the population in Gaza is food-insecure, as Israel allows only precisely determined (and scant) amounts of food to cross its borders. Gazans rely largely on canned goods, such as chickpeas (often purchased at subsidized rates through food aid programs run by international NGOs), because they do not require scarce water or fuel to prepare—but canned chickpeas cannot be used to prepare a typical deep-fried falafel recipe (the discs would fall apart while frying). There is, besides, a continual shortage of oil (of which only a pre-determined amount of calories are allowed to enter the Strip). Any narrative about Israeli food culture that does not take these and other realities of settler-colonialism into account is less than half complete.
Of course, falafel is far from the only food impacted by this long campaign of starvation, and the strategy is only intensifying: as of December 2023, children are reported to have died by starvation in the besieged Gaza Strip.
Support Palestinian resistance by calling Elbit System’s (Israel’s primary weapons manufacturer) landlord; donating to Palestine Action’s bail fund; buying an e-sim for distribution in Gaza; or donating to help a family leave Gaza.
Equipment:
A meat grinder, or a food processor, or a high-speed or immersion blender, or a mortar and pestle and an enormous store of patience
A pot, for frying
A kitchen thermometer (optional)
Ingredients:
Makes 12 large falafel balls; serves 4 (if eaten on their own).
For the فلافل (falafel):
500g dried chickpeas (1010g once soaked)
1 large onion
4 cloves garlic
1 Tbsp cumin seeds
1 Tbsp coriander seeds
2 tsp dill seeds (عين جرادة; optional)
1 medium green chili pepper (such as a jalapeño), or 1/2 large one (such as a ram's horn / فلفل قرن الغزال)
2 stalks green onion (3 if the stalks are thin) (optional)
Large bunch (50g) parsley, stems on; or half parsley and half cilantro
2 Tbsp sea salt
2 tsp baking soda (optional)
For the حَشوة (filling):
2 large yellow onions, diced
1/4 cup coarsely ground sumac
4 tsp shatta (شطة: red chili paste), optional
Salt, to taste
3 Tbsp olive oil
For the طراطور (tarator):
3 cloves garlic
1/2 tsp table salt
1/4 cup white tahina
Juice of half a lemon (2 Tbsp)
2 Tbsp vegan yoghurt (لبن رائب; optional)
About 1/4 cup water
To make cultured vegan yoghurt, follow my labna recipe with 1 cup, instead of 3/4 cup, of water; skip the straining step.
To fry:
Several cups neutral oil
Untoasted hulled sesame seeds (optional)
Instructions:
1. If using whole spices, lightly toast in a dry skillet over medium heat, then grind with a mortar and pestle or spice mill.
2. Grind chickpeas, onion, garlic, chili, and herbs. Modern Palestinian recipes tend to use powered meat grinders; you could also use a food processor, speed blender, or immersion blender. Some recipes set aside some of the chickpeas, aromatics, and herbs and mince them finely, passing the knife over them several times, then mixing them in with the ground mixture to give the final product some texture. Consult your own preferences.
To mimic the stone-ground texture of traditional falafel, I used a mortar and pestle. I found this to produce a tender, creamy, moist texture on the inside, with the expected crunchy exterior. It took me about two hours to grind a half-batch of this recipe this way, so I don't per se recommend it, but know that it is possible if you don't have any powered tools.
3. Mix in salt, spices, and baking soda and stir thoroughly to combine. Allow to chill in the fridge while you prepare the filling and sauce.
If you do not plan to fry all of the batter right away, only add baking soda to the portion that you will fry immediately. Refrigerate the rest of the batter for up to 2 days, or freeze it for up to 2 months. Add and incorporate baking soda immediately before frying. Frozen batter will need to be thawed before shaping and frying.
For the filling:
1. Heat olive oil in a skillet over medium heat. Fry onion and a pinch of salt for several minutes, until translucent. Remove from heat.
2. Add sumac and stir to combine. Add shatta, if desired, and stir.
For the tarator:
1. Grind garlic and salt in a mortar and pestle (if you don't have one, finely mince and then crush the garlic with the flat of your knife).
2. Add garlic to a bowl along with tahina and whisk. You will notice the mixture growing smoother and thicker as the garlic works as an emulsifier.
3. Gradually add lemon juice and continue whisking until smooth. Add yoghurt, if desired, and whisk again.
4. Add water slowly while whisking until desired consistency is achieved. Taste and adjust salt.
To fry:
1. Heat several inches of oil in a small or medium pot to about 350 °F (175 °C). A piece of batter dropped in the oil should float and immediately form bubbles, but should not sizzle violently. (With a small pot on my gas stove, my heat was at medium-low).
2. Use your hands or a large falafel mold to shape the falafel.
To use a falafel mold: Dip your mold into water. If you choose to cover both sides of the falafel with sesame seeds, first sprinkle sesame seeds into the mold; then apply a flat layer of batter. Add a spoonful of filling into the center, and then cover it with a heaping mound of batter. Using a spoon, scrape from the center to the edge of the mold repeatedly, while rotating the mold, to shape the falafel into a disc with a slightly rounded top. Sprinkle the top with sesame seeds.
To use your hands: wet your hands slightly and take up a small handful of batter. Shape it into a slightly flattened sphere in your palm and form an indentation in the center; fill the indentation with filling. Cover it with more batter, then gently squeeze between both hands to shape. Sprinkle with sesame seeds as desired.
3. Use a slotted spoon or kitchen spider to lower falafel balls into the oil as they are formed. Fry, flipping as necessary, until discs are a uniform brown (keep in mind that they will darken another shade once removed from the oil). Remove onto a wire rack or paper towel.
If the pot you are using is inclined to stick, be sure to scrape the bottom and agitate each falafel disc a couple seconds after dropping it in.
4. Repeat until you run out of batter. Occasionally use a slotted spoon or small sieve to remove any excess sesame seeds from the oil so they do not burn and become acrid.
Serve immediately with sauce, sliced vegetables, and pickles, as desired.


#Palestine#Israel#vegetarian recipes#Palestinian#falafel#chickpeas#sumac#onions#garlic#parsley#cilantro#dill seeds#sesame seeds#tahina#yoghurt#long post /
801 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi opencommunion - you are one of my favourite Tumblrs and I love hearing about Lebanese history from you. You say you are antiPhoenicianist - I hope you would tell us more about it. Hope you're having a great day.
aww thanks, I love your blog too <3
Phoenicianism is a Lebanese ethnonationalist ideology that basically argues that Lebanese people are ethnically/culturally unrelated to (and, implicitly or explicitly, superior to) not only other Arabs but other Levantine peoples. It's a secular ideology but it's extremely Islamophobic, so it posits that Lebanese Christians (especially Maronites) are the "purest" Lebanese people with a direct line of descent from the Phoenicians, who are portrayed as an almost supernaturally heroic and advanced culture who were supplanted by savage Arabs from the south (you probably recognize this as a Zionist talking point; more on that later). It's a narrative of Lebanese history that originates from rich European-educated Lebanese and their French & English orientalist buddies, and it bears all the hallmarks of European ethnonationalism and scientific racism. In my experience ascribing to Phoenicianism is associated with class and it doesn't represent the majority of Lebanese Maronites, who do consider ourselves Arabs. My family are dyed-in-the-wool Maronites from Wadi Qadisha, the cradle of Maronite culture, and for as far back as our family histories go we've always described ourselves as Arabs, with religion being the only difference—and an unimportant difference—between us and our Druze and Muslim neighbors. Phoenicianism predates the Zionist occupation but it started to take shape around the same time as Zionism, and is based in the same core orientalist myth: that the ancient Levant was populated by strictly separate and homogenous ethnocultures with exclusive claim over portions of the land, which were later supplanted by Arab Muslim invaders who oppressed a tiny remaining local population. (In reality, of course, SWANA cultures have always been internally diverse and mutually influential, and "Arabization" in the Levant was characterized by organic cultural shifts among local populations, with Arab culture influencing and combining with local cultures rather than replacing them). So when the Zionist settler project arrived they found easy allies in Phoenicianism. This relationship eventually culminated with the settler state backing the fascist Lebanese Phalanges Party (Kataeb in Arabic, a direct translation of Falange, the Spanish fascist party that inspired its founders) in the Lebanese Civil War. Israel used the Phalanges as a proxy to fight the Palestinian resistance in Lebanon, and it was Phalangists who collaborated with IOF to carry out the Sabra and Shatila massacres. This is the cruelest and ugliest moment in Lebanon's history and Phoenicianism enabled it; Phoenicianism enabled the cognitive dissonance necessary for Lebanese to participate in the occupation's genocide against our siblings and act as footsoldiers for the European fascist agenda in our region. The Phalangists and Zionists lost the war but there is still a Phalangist presence in the Lebanese government, and Phoenicianism is unfortunately alive and well among the Lebanese right wing at home and in the diaspora
382 notes
·
View notes
Photo

As the cradle of European civilization and a meeting place of diverse cultures, Crete is a magical island that stands apart in the heart of the Mediterranean sea. Its prominent place in world history dates back to the mysterious and fascinating Bronze Age civilization of the Minoans, who were building lavish labyrinth-like palaces at a time when Athens was just a village. In the Odyssey, Homer describes Crete as a rich land, filled with countless people who speak several languages. The location of this mountainous island, at a crossroad of three continents, has been a natural outpost of consecutive invaders, including the Greeks, Romans, Venetians, and Ottomans, who have left their mark on Cretan culture. Remainders of Crete's extraordinary past are scattered all over the island. Today, travellers come to explore and discover not only its five-millennium-old history but also its extraordinary natural beauty and diversity. As I journeyed through the Cretan landscape, I visited its most important ancient sites, including the famous Minoan palaces, but also veered off the beaten track to explore the lesser-known archaeological remains. In this tour of western Crete, I invite you to delve into the long and rich history of this fascinating island. The Minoan civilization emerged on the island of Crete in the Early Bronze Age at the end of the third and beginning of the second millennium BCE. It flourished from c. 2000 BCE until c. 1500 BCE with the establishment of centres, called "palaces" by modern archaeologists, that concentrated political and economic powers, as well as artistic activities. Of particular significance was the religious role played by the palaces in the cult of the Mother Goddess. These impressive edifices were built at Knossos and Malia in the northern part of the island, at Phaistos in the south, and Zakros in the east, all sites with a rich agricultural hinterland and direct access to the most important sea routes of the time. The British archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans discovered the first of these palaces in Knossos in 1900 CE and named the people who built them after the legendary King Minos. It was King Monos who, according to tradition, ordered the construction of a labyrinth in Knossos to hold the Minotaur, the mythical half-man, half-bull creature. The Minoan culture spread throughout the entire eastern Mediterranean world and its stunning art and architecture deeply influenced the Mycenaean Civilization (1600-1100 BCE) that would succeed it. After the downfall of the Mycenaeans, Crete was ruled by various ancient Greek city-states until the Romans conquered the island in 69 BCE and made Gortyn their capital. Under Roman rule, Crete re-emerged as a major cultural centre and became the joint province of Crete and Cyrenaica and a centre of early Christianity. When the Roman Empire split into two, Crete was made part of the Eastern Empire. It continued to prosper during the Byzantine era until it faced repeated Arab raids and, ultimately, full conquest in the 820s CE. Today the central and western parts of the island are blessed with archaeological treasures which include the famous sites of Knossos, Phaistos and Gortyn but also Aptera, Phalasarna and Eleutherna, all with significant architectural remains as compelling evidence of Crete's long and varied history.
135 notes
·
View notes
Text
palestinians poets: summer farah
summer farah is a palestinian american poet, editor, and critic. she is currently the outreach coordinator for the radius of arab american writers and sends out the occasional essay at evening conversations. she writes the poetry double features column at palette poetry, putting two collections in conversation each month.
IF YOU READ ONLY ONE PIECE BY SUMMER FARAH, MAKE IT THIS ONE: "the moon is pro-palestine"
OTHER POEMS ONLINE I LOVE BY SUMMER FARAH
"what it's called when israel destroys a palestinian village because there's allegedly an ancient jewish civilization under it" at sumuo mag
"noooo don’t be a birthright apologist you’re so sexy ahha" at bahr magazine // بحر issue 1
"at the met cloisters" at the rumpus
"for lorelai gilmore, cece parekh, & all the girls who take to the wilderness" at violet indigo blue etc
432 notes
·
View notes
Text
Quick worldbuilding hack, if you want to make a coherent political system for your fantasy world:
Basically, between the fall of Rome and early modern times, in Europe* most political organization wasn't actually kingdoms ruled by One True King like it's usual in fantasy, but something like this:
Feudalism: here, the center of power was not the nation (there was little concept of such thing) or the state, and not even the King, but the landowners (from kings to dukes to counts...) and their network of vassalages to each other. There were no "countries" but rather hereditary titles, and the people who held them. There was little of a true state besides what individual rulers did; they didn't even have formal armies as such, but rather the vassals who provided them, they and could have multiple allegiances. Examples are of course the Holy Roman Empire (neither holy, etc. etc.) France (note that the 100 Years War was a dispute about titles rather than France vs. England), Spain (actually a bunch of kingdoms and crowns rather than a country), etc...
"Empires": A state where a central goverment exerts power over other territories and peoples. These are rather familiar to us, because a formal state exists here, and the ruler is more powerful and often does have a standing arming and administration instead of relying on vassals. Here, there is a bureacracy and a claim to rule a territory, and while they might have vassals and prominent artistocratic families (everyone did) their administration was state-based, not allegiance based. The Roman Empire is the most imperial empire, as well as its cringefail successor the Byzantine Empire, but note that the great Islamic empires also had this kind of administration, with governors appointed and confirmed by the imperial court.
City-States: Basically a powerful city (though they were often the size of small towns, still, very rich) ruled by a local aristocracy, sometimes hereditary, sometimes elected from a few families or guilds, or a mix of both, and in some cases ruled by religious authorities. These could be independent or organized in alliances, but were often vassals of more powerful goverments such as above. Cities are in many way the building brick of larger states; of note, in the Ancient Mediterranean before Rome conquered it all, leagues of city-states were the main powers. Medieval and Early Modern independent city states were the Italian city states of course, and a famous league was the Hansa (many of its members themselves vassals of other powers)
Tribes and Clans: Every culture is different with this, but basically here the centre of power is the relationships between families and kinship. If this sounds familiar to Feudalism, you've been paying attention; Feudalism is what happened when the Roman empire and administration fell, and it was replaced by landowners and their ties of vassalage and allegiances.
Now, besides the history lesson, why is this important? Because there are reasons why rulers had their power, and you should know that.
A king never ruled alone. He was only the head of nobles tied by vassallage (feudalism), or the head of a inherited state bureaucracy and army ("empire"). If you killed the king, another one would rise from the prominent families. Often by bloody civil wars or conquest yes, but the system overall would stay. A king did not reign by its own power or virtue, but because the system itself supported him, and of course, he maintained the system.
A new king who wants to replace the bad old king (a common fantasy storyline) needs to also deal with the allegiances of all its vassals (who would probably rather kill him and take the throne themselves) or build a bureaucracy and an army, supremely expensive endeavors in those times, which took decades if not centuries to build. In fact, the Byzantines and the Arabs inherited most of their state aparatus, in one way or the other, from the Romans.
This is also why these systems lasted so long, too. The appearance of modern republics and other systems of goverment needed the coordination of people and revolutions that did not just kill the king, but also replace it with something else, and for that you need literacy, economic changes, an empowered populace... But that's for another time.
I hope this is fucking helpful because I don't want to spell allegiance ever again.
*I would love to do more about goverments outside Europe, especially Precolombine American ones like the redistrubitionist state-based economy of the Incas, or the Mesoamerican city-states. But that's for another time.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
#bbc news world#bbc merthur#bbc arthur#cnn fast facts#cnn بالعربية#cnn arabic#cnn heroes: sharing the spotlight cnn#wall streeet journal#washington post#fox news#my journal#journal#history#ancient civilizations#civilization collapse#western civilization#civilization as we know it ‘is ending’ and humans could face biggest extinction event since dinosaurs#lost civilization#civilizable#clash of civilizations#illegal civilization#harappan civilization#civilization vi#ancient rome#ancient#the noble and most ancient house of black#ancient greece#the ancient magus bride#ancient history#ancient origins
0 notes
Text
Druze and Judaism, a thread 🧵(remastered)
🟥The Druze venerate many Jewish figures as sages, including Isaac, Jacob, Joseph, Reuben, Benjamin, David, Elijah, Isaiah, Jeremiah, Ezekiel, Daniel... Solomon and Jethro are highlighted as manifestations of the Universal Mind.
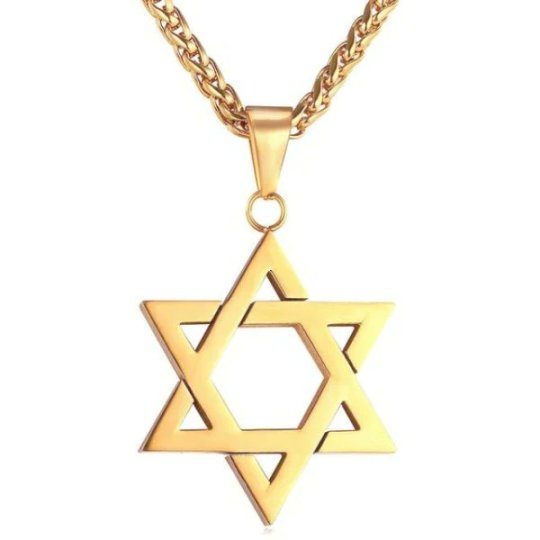


🟥 The Hexagram or six pointed star is very significant to Druze as well, and is often portrayed in books of Exegesis. It is understood as the Seal of Solomon, but also for its pre-Judaic ancient symbolism, as a symbol of the Union of Opposites.


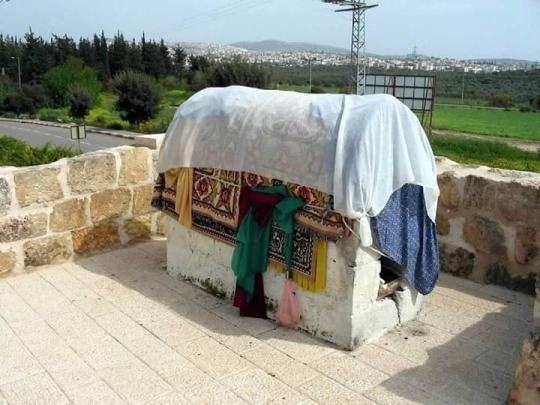
🟥Druze shrines in Carmel and Galilee echo the ancient Jewish shrine tradition, i.e. natural stone mound. Some are architecturally Jewish tombs, with descending staircases into caves. A Sheikh's striped cloak and the multicolored flag are said to resemble the coat of Joseph.


🟥Esoteric Judaism, or Kabballah, is most similar to Druze esotericism. Especially in its Neoplatonism, Gematria, Belief in Reincarnation(gilgul), Ein Sof. The Hasidic sect also stresses on Ascetism. Their highest soul Yechidah is akin to Tawheed. Batin Al Batin, their Chassidut.

🟥Druze and Jews have lived relatively harmoniously with circumstantial conflicts like the Safed Rebellion being exceptions. Jews in Druze areas were among the nobles in Prince Fakhreddin's entourage. Their Synagogues thrived in Bhamdoun and Aleyh without persecution.

🟥 Jewish communities in Deir al Qamar and Barouk were also rich land owners. The "blood bond" between Jews and Druze of Israel is one of the strongest the Druze have done with any another sect. Has been strong for 80 years. Agreed to regardless if one is Zionist or not.

🟥 Druze Sheikh Daoud Bessis who was imprisoned with the British Army while fighting the Nazis and sent to Germany, would smuggle food to Jewish prisoners during the Holocaust with his fellow Druze Prisoners.


🟥 During the recent Anti-Jewish pogroms in Amsterdam. A Druze man tried his best to save the Jews and conceal them from their pursuers. Highlighting the willingness of both communities to protect each other.


🟥 Druze have no occupied territory in Israel, or any encroached on Holy Land or Site. Therefore enmity to the Jews is not justified except on Islamist grounds or leftist brainwashing. Israeli Druze are much better off socially and economically than their peers in Arab countries


🟥 Druze ultimately derive their idea of the Messiah from the Jews and also the Messianic Era. Psalm 37's "The meek will inherit the Earth". Therefore they've avoided belief in Heaven and Hell and Rapture, and taken a reward/punishment in this realm approach, similar to Jews.

🟥 Druze Founder Imam Hamza Ibn Ali, had written in the Epistle to the Israelites, that 2 and a half of the 12 Jewish tribes(Asbat Al Haq) had accepted the Druze faith. This explains the genetic similarity, as Druze tend to cluster next to Ashkenazi and Persian/Kurdish Jews.

🟥 The Return of the Jews is foretold in Druze Scripture as one of the first signs of the end times. Druze 15th century scholar Al Amir Al Sayyed Al Tanukhi expounds that ownership would return to the children of Israel. Thus the creation of Israel lies within Druze Prophecy.

🟥 In the Druze description of Judgment Day in the Epistles of Wisdom, it is said the Druze Five Bound Army will be joined by the lost tribes of Israel. The named tribes are the "Pure of Al Benjamin and Al Naphtali".
🟥 Druze grievances with the State of Israel are bureaucratic, such as the Kaminitz law in civil development, or the nation state law which lacks a Druze exception. Which we hope are settled. Unlike with other central states, like Lebanon & Syria where grievances are existential.
🟥 The current violent tapestry of the Middle East presents Druze and Jews as natural allies. With Political Armed Islam being the common enemy of both. To come out of manufactured Arabist identity, is to embrace the tribal nature of the Middle East. And the need to save oneself

Druze Founder Baha'ldeen Al Muqtana**
Link
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Henry vs Julian
I have been thinking about this a lot. While Henry clearly admires and models his scholar self on Julian, their essential difference is in how they perceive the Ancient Greeks.
Julian's interest in the Ancient Greeks is true interest, he admires their high and exalted values. For him, the Greeks were the highest point of human civilization, and the closer he comes to his own time the more his disdain increases - the Roman Catholic Church he holds in contempt but it's still a 'worthy enemy' not as bad as the Presbyterian Church. It isn't mentioned but he must hold modernism and it's philosophy with disdain - modernist moral vacousness being a direct contradiction of the idealist values loyalty, honor, chastity etc. that were so exalted by the Greeks. Which is why he is always cherry picks, sees only what he wants to see, and invents what he can't - both for himself (his ambiguous involvement with the Isrami government) or for his students (encouraging Richard to lie about his life in California). Since he can't time travel back to Greece himself, he must try to live that life as much as he can and believe himself a character in a Greek play. But it comes, not from a place of wanting to escape his current reality, but true admiration of the ancient Greek way of seeing and doing things.
Henry is a true modernist. The monologue about feeling dead is central to his understanding his character:

Maybe it stems from his near death experience but he sees the world as inherently meaningless, God is dead and heaven and hell have been revealed to be man-made constructs, there is no punishment for evil and since there is no moral line. I think he subconsciously realised all of this before coming to Hampden, but to truly accept it would have been soul-crushing. So he tries to escape it by immersing himself in the Greeks, I imagine the absolutist values, vague representational ideas pertaining to each god might have interested him but really, it could have been anything else, the Medieval Age or the Victorians, anything. He just needed something to be obsessed with, to give meaning to his existence which he subconsciously knew to be meaningless. So is his adoration of Julian, he admired and wanted Julian's ability to almost half-live in another time when, in his view, things mattered more (we have divinity in our midst). It also explains the Bacchanal which is otherwise so out of character for him. The appeal was to escape the soul crushing knowledge of meaninglessness - even if for a while. To worship and call on Dinosiyus with the blind belief of the Ancient Greeks, a kind of belief that simply cannot exist anymore in the postmodern, post-Neitzche world. His harebrained plans also came from the same impulse, including the poison plan, and the one way ticket to Argentina.
I suspect that what subconsciously drove him to murder bunny, aside from the obvious fear of getting caught - is the same thing that drove Mersault to murder the Arab - it's the old existentialist question, if good and bad are relative and there is no punishment for evil, how far can one go? Bunny's murder was Henry's existentialist experiment with himself. And, I think in a way it confirmed for him what he already knew, they escaped unscathed and he didn't feel any of the fear or remorse he expected to feel. While it did give him the momentary sense of power, the feeling that he could now do whatever he wanted if he can be clever enough to not get caught, since he won't be punished for it otherwise. While it gave him enough courage to go get the girl he always wanted - it did confirm for him the inherent meaninglessness of the world. Also, conversely, Camilla could have been another experiment - something must matter, was it love? Camilla was the only girl he knew and he was fond of her - he may not even have thought of her romantically before considering he never cared to act on it in all the time he had known her. But either way, Julian's abandonment broke him.
Coming back to Julian, Julian's abandonment omakes perfect sense to me - he was disgusted by the modernist moral vacousness in his students. He himself was a moral man, but his morals operated on his own standards. He based it on the Greek sense of Honour, not the more modern sense of Justice. His basic instinct was the preservation of his own purity - he couldn't possibly keep on as their teacher. But also, to turn them in would be against his sense of honour - he must have very little respect for the police and law enforcement as institutions being the kind of person he is. Not to mention it would mean his having to be in frequent contact with the police and court. From his point of view atleast, leaving is the only thing he could have done, really.
For Henry however, he sees that his obsession with the Greeks as well as his admiration for Julian as the sham that it really was, is disillusioned with the world, shattered. Except for his fondness for Camilla he didn't really have anyone he loved, he saw his friends as pawns, wasn't close to his family, didn't have any goals in life with everything in his reach with his father's money - the only person he had really loved was Julian, and there he was betrayed. His obsession with the ancient Greeks was also thus tainted with Julian's betrayal - since it wasn't true interest at all, only a disguised attempt at escapism - it wavered and fell apart, and he didn't have a reason to live anymore.
.
Side note : Richard falls between the two. Like Julian, he had a real interest in the ancient Greeks, but he didn't put them on a pedestal like Julian did. He realised that like his own time, and like all other times in history the Greek civilization too had its own good and bad aspects, and he wanted to learn about it for its own sake. But he doesn't make it his life, or use it to escape his own reality - outside of his classes he was very much rooted in his own time.
#the secret history#tsh#donna tartt#henry winter#julian morrow#richard papen#camilla macaulay#charles macaulay#francis abernathy#bunny corcoran#tina rambles#lit
475 notes
·
View notes