#3D Printing Materials Future
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
3D Printing Materials Market Valued at USD 2,836.6 Million in 2025

Exploring the Dynamic World of 3D Printing Materials Market 2034
The world of 3D Printing Materials Market has come a long way since its inception, evolving from a niche technology to a mainstream manufacturing process. At the heart of this transformation is the ever-expanding universe of 3D printing materials. These materials are not just a means to an end; they are pivotal in defining what can be created, how it can be produced, and what industries can benefit from this cutting-edge technology. In this blog, we will delve into the key aspects of the 3D printing materials market, exploring the types, applications, and future trends shaping this exciting field.
Sample copy report:
https://wemarketresearch.com/reports/request-free-sample-pdf/3d-printing-materials-market/1338
Types of 3D Printing Materials
Thermoplastics: Thermoplastics are among the most widely used materials in 3D printing. They are known for their ease of use, affordability, and versatility. Popular thermoplastics include:
PLA (Polylactic Acid): Known for its eco-friendly nature and ease of printing, PLA is a favorite among hobbyists and beginners.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): This material offers greater strength and durability, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Combining the ease of printing with durability, PETG is commonly used in applications requiring resistance to impact and moisture.
Resins: Resins are liquid materials that solidify under UV light and are used primarily in SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) printers. They offer high resolution and detail, making them suitable for applications such as jewelry and dental products. Key types include:
Standard Resins: Ideal for detailed models and prototypes.
Tough Resins: Engineered for increased durability and impact resistance.
Flexible Resins: Designed to produce parts with rubber-like properties.
Metals: Metal 3D printing is used for high-performance applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. Metal powders, such as titanium, aluminum, and stainless steel, are used in processes like SLM (Selective Laser Melting) and EBM (Electron Beam Melting). Metal 3D printing offers:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Essential for aerospace and automotive components.
Complex Geometries: Allows for the creation of intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
Composites: Composite materials combine thermoplastics with reinforcing fibers, such as carbon fiber or glass fiber, to enhance strength and rigidity. These materials are used in applications where lightweight and high strength are critical, including in the automotive and sports equipment industries.
Innovations Driving the 3D Printing Materials Market
The 3D printing materials market is experiencing rapid innovation, driven by advancements in technology and changing industry needs. Here’s a closer look at some of the latest innovations that are transforming the landscape of 3D printing materials:
Nanomaterials: Nanotechnology is making waves in the 3D printing industry by enabling the creation of materials with enhanced properties at the nanoscale. Nanomaterials can improve strength, durability, and thermal resistance, making them ideal for high-performance applications. For example, incorporating nanoparticles into polymers can enhance their mechanical properties, leading to more robust and reliable printed parts.
Bio-inks and Bioprinting: Bioprinting is revolutionizing the medical and research fields by enabling the creation of living tissues and organs. Bio-inks, which are made from natural and synthetic biopolymers, are used in this process to print cellular structures. These materials can be tailored to support cell growth and tissue development, opening up new possibilities for regenerative medicine and personalized healthcare.
Applications of 3D Printing Materials Market
The versatility of 3D printing materials market has led to their adoption across various sectors:
Aerospace: Lightweight and durable materials are used to manufacture complex parts and components, reducing overall weight and fuel consumption.
Healthcare: Custom prosthetics, implants, and dental products are tailored to individual patients using biocompatible materials.
Automotive: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and production of lightweight parts, enhancing vehicle performance and reducing time-to-market.
Consumer Goods: Customized products, from eyewear to home decor, benefit from the flexibility and personalization offered by 3D printing.
Future Trends in 3D Printing Materials Market
As the 3D printing industry continues to evolve, several trends are likely to shape the future of 3D printing materials:
Biodegradable and Sustainable Materials: There is a growing focus on developing eco-friendly materials that reduce environmental impact. Innovations in biodegradable plastics and recycling processes are set to make 3D printing more sustainable.
Advanced Metal Alloys: The development of new metal alloys with enhanced properties will open up new possibilities for high-performance applications in industries such as aerospace and defense.
Multi-Material Printing: Advances in multi-material printing technologies will allow for the creation of complex objects with varying properties in a single print, expanding the range of applications and functionalities.
Smart Materials: The integration of materials that respond to environmental changes (such as temperature or pressure) will lead to the development of "smart" products with adaptive capabilities.
Benefits of 3D Printing Materials Market Report:
Analyst Support: Get your query resolved by our expert analysts before and after purchasing the report.
Customer Satisfaction: Our expert team will assist with all your research needs and customize the report.
Inimitable Expertise: Analysts will provide deep insights into the reports.
Assured Quality: We focus on the quality and accuracy of the report.
Conclusion
The 3D printing materials market is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field, driven by continuous innovation and Technological Advancements. From thermoplastics and resins to metals and composites, the variety of materials available today provides limitless possibilities for creators and manufacturers alike. As we look to the future, emerging trends and new material developments promise to further revolutionize the industry, offering exciting opportunities for growth and transformation across various sectors. Whether you're a hobbyist, a designer, or an industry professional, staying informed about these advancements will be key to leveraging the full potential of 3D printing technology.
#3D Printing Materials Analysis#3D Printing Materials Demand#Market Insights 3D Printing#3D Printing Materials Future
0 notes
Text
The Science Behind 3D Printing and Its Innovations
Introduction Alternative term for additive manufacturing: in this process, objects are conceptualized in another manner, changing how the objects are thought of by using 3D printing. One such technology is making creation from prototyping to final products more flexible and efficient. At TechtoIO, we deep dive into the science of 3D printing and the innovations that fuel this groundbreaking technology. Read to continue link
#Science Explained#Tags3D printed houses#3D printed prosthetics#3D printing applications#3D printing benefits#3D printing education#3D printing future#3D printing in automotive#3D printing in fashion#3D printing in healthcare#3D printing materials#3D printing prototyping#3D printing science#3D printing technology#additive manufacturing#aerospace 3D printing#bioprinting#construction 3D printing#custom 3D printing#innovations in 3D printing#Technology#Science#business tech#Adobe cloud#Trends#Nvidia Drive#Analysis#Tech news#Science updates#Digital advancements
1 note
·
View note
Text
3D Printing for Food: The Culinary Revolution
Introduction to 3D Printing Technology
Discover the world of 3D printing technology – its history, applications, advantages, challenges, and future trends. Learn how 3D printing is reshaping industries and driving innovation.
In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a revolutionary technology that has transformed various industries. It allows the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital files through additive manufacturing processes. Unlike traditional subtractive methods, where material is removed to create an object, 3D printing adds layers upon layers of material to form the final product.
History of 3D Printing
The roots of 3D printing can be traced back to the 1980s when the first functional 3D printer was developed by Chuck Hull, the co-founder of 3D Systems Corporation. Initially used for rapid prototyping in manufacturing, 3D printing technology has evolved significantly over the years, becoming more accessible and diverse in its applications.
How 3D Printing Works
In 3D printing, the process begins with a digital model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. This model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers, which serve as a blueprint for the 3D printer. The printer follows these instructions layer by layer, selectively depositing material to build the object from the bottom up.
Additive Manufacturing Process
The additive manufacturing process allows for precise control over the final product's shape and geometry. It enables the production of complex designs and intricate structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods.
Materials Used in 3D Printing
A wide range of materials can be used in 3D printing, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological substances like living cells. Each material offers unique properties and characteristics suited to specific applications.
Applications of 3D Printing
3D printing has found applications across various industries, revolutionizing the way products are designed, prototyped, and manufactured.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, 3D printing is used to create customized implants, prosthetics, and medical devices tailored to individual patients' needs. It has also facilitated advancements in surgical planning and medical training.
Aerospace
In aerospace, 3D printing is utilized to produce lightweight components with complex geometries, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency in aircraft and spacecraft.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, 3D printing is employed for rapid prototyping, tooling, and the production of customized parts and accessories.
Architecture
In architecture, 3D printing enables architects to create intricate models and prototypes, allowing for more efficient design iterations and better visualization of projects.
Advantages of 3D Printing
One of the primary advantages of 3D printing is its ability to reduce waste by only using the exact amount of material needed to create an object. This efficiency not only minimizes environmental impact but also lowers production costs.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing
Despite its many benefits, 3D printing still faces several challenges, including limited material options, slow production speeds, and issues related to quality control and scalability.
Future Trends in 3D Printing
The future of 3D printing holds tremendous potential, with ongoing advancements in materials science, printer technology, and design software paving the way for new applications and innovations.
Impact of 3D Printing on the Manufacturing Industry
3D printing is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, decentralizing production and enabling greater customization and localization of products.
Environmental Considerations of 3D Printing
While 3D printing offers environmental benefits in terms of reduced waste and energy consumption, it also raises concerns about the environmental impact of materials used and disposal methods.
Cost Considerations in 3D Printing
The cost-effectiveness of 3D printing depends on various factors, including material costs, equipment expenses, and labor requirements. While initial investments may be high, long-term savings can be significant, especially in industries with high customization needs.
Accessibility and Education in 3D Printing
Efforts to improve accessibility and education in 3D printing are underway, with initiatives aimed at making the technology more user-friendly and inclusive across different age groups and skill levels.
Legal and Ethical Issues in 3D Printing
The rise of 3D printing raises complex legal and ethical questions related to intellectual property rights, safety regulations, and liability issues, requiring careful consideration and policy development.
Comparison with Traditional Manufacturing Methods
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing offers advantages in terms of design flexibility, customization, and rapid prototyping, but it also has limitations in terms of material selection and production speed.
Innovations and Breakthroughs in 3D Printing Technology
Recent innovations in 3D printing technology include advancements in multi-material printing, bioprinting, and large-scale construction, opening up new possibilities across various industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing technology represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing and design, offering unprecedented flexibility, efficiency, and customization capabilities. While challenges remain, the potential of 3D printing to revolutionize industries and transform the way we create and consume products is undeniable.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of 3D printing?
How does 3D printing contribute to sustainability?
What are the limitations of 3D printing technology?
How affordable is 3D printing for small businesses and individuals?
What are some emerging applications of 3D printing in healthcare?
#3D printing technology#Additive manufacturing#History of 3D printing#Applications of 3D printing#Advantages of 3D printing#Challenges in 3D printing#Future trends in 3D printing#Sustainability in manufacturing#Customization in manufacturing#3D printing materials
0 notes
Text

Morehshin Allahyari - Material Speculation: ISIS
My series Material Speculation: ISIS is a 3D modeling and 3D printing project focused on the reconstruction of 12 selected statues from the Roman period city of Hatra and Assyrian artifacts from Nineveh that were destroyed by ISIS in 2015 in a series of highly-publicized YouTube videos. The series goes beyond metaphoric gestures and digital and material forms of the artifacts by including a flash drive and a memory card inside the body of each 3D-printed object. Like time capsules, each object is sealed (though accessible) for future civilizations. The information in these flash drives includes images, maps, PDF files, and videos gathered on the artifacts and sites that were destroyed.
0 notes
Text
Tiny Homes Take on Tomorrow: A Look at the Future of Tiny Living
Tiny homes have become increasingly popular in recent years as people have embraced a simpler, more sustainable way of living. As we look to the future, it’s clear that tiny homes will continue to play an important role in our lives. In this blog post, we’ll take a look at some of the trends and innovations that we can expect to see in the world of tiny homes in the coming years. Smart Homes As…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
The Future of Textile Designing
Textile designing has come a long way from its traditional roots. Today, designers are using cutting-edge technologies, materials, and techniques to create innovative and sustainable textile products. In this blog, we will explore the future of textile designing, the trends shaping the industry, and the role of technology in this field. Sustainable Materials: One of the most significant trends…

View On WordPress
#3D printing#biodegradable materials.#collaborative design#custom-fit garments#Design#Designer#digital printing#eco-friendly materials#future#Graphic design#innovative#LaiqQureshi#laiqverse#natural dyes#smart textiles#Sustainability#Technology#textile#textile designing#unique products
1 note
·
View note
Text
6 MOST POPULAR INDUSTRIES TO USE METAL 3D PRINTING
The beauty of art lies not only in what all elements we add to it but also in, what elements we take out from it. This is what vests under the concept of Metal Additive Manufacturing, in common terms, referred to as Metal 3D Printing. It is an output of the biggest leap in technology that produces three-dimensional parts layer by layer from a metal material. In the modern era of technological innovations, there is no point in asking if it is possible to 3D print items from metal. The technology of Metal Additive Manufacturing makes it possible in the best way. Let us know how metal additive manufacturing works, the different types of metal 3D printing, its likely advantages and possible applications.
What is Metal 3D Printing?
A laser-based technology in manufacturing that uses powdered metals can be termed metal 3D printing. A vast variety of materials are available in powdered form for metal 3D printing in India including titanium, steel, stainless steel, aluminium, copper, cobalt chrome, tungsten and nickel-based alloys. They are known as 3D printing metal powders. Precious metals like gold, platinum and silver are also attainable. They are now recognised as 3D printing precious metals. So metal powder is the backbone of metal 3D printing. It is difficult and dangerous to handle in its raw state yet very widely used because of its unique features.
Types of Metal 3D Printing
As metal 3D printing technology uses powdered metals, the differences in metal 3D printing types are based on how they fuse the powder into metal parts. These methods vary considerably. It ranges from using high-energy lasers to fuse the loose powder to extruding bound metal powder filament. The most common type and widely used method is the powder bed fusion technique. In this method, machines distribute a fine layer of powder over a build plate and selectively melt a cross-section of the part into the powder layer. It is of two types: Selective Laser Melting and Electron Beam Melting. SLM machines use high-powered lasers to fuse metal layers into parts. EBM machines use an electron beam instead of a laser to fabricate parts. Then there is another method called Direct energy deposition that uses metal feedstock and a laser to fabricate parts. Another method is the EBAM technique where the Wire DED machines use a laser to melt feedstock, which is a metal wire instead of blown powder. There is the Binder Jetting method which is a large-scale, high-fidelity method of metal 3D printing. Bound Powder Extrusion (BPE) is the newest method of metal additive manufacturing. Here, the powder is bound together in waxy polymers which makes it much safer and easier to use than loose powder. Then there is the latest concept of FDM 3D metal printing which is Fused Deposition Modelling which is a plastic extrusion process. In addition to plastics, some FFF/FDM 3D printers are capable of printing metal filaments.
Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
The main advantage of Metal 3D printing is that it saves time and cost, which is very important to the manufacturing sector. Metal 3D printing uses simulation to improve the quality of the part manufactured and thus minimizes the risk of production failure. In discrete manufacturing processes, this is very much important. Another advantage of Metal 3D printing lies in its adaptability for customization. The technology can produce structures as per customer needs. The process is highly recommended to design complex components cost-effectively, create functional designs without manufacturing limitations, cut the investment in manufacturing tools, shorten the time to market and eliminate stock-related costs and risks.
Metal 3D printing Applications
Every technology has its potential applications. Metal 3D printing is no different. The typical 3D metal printing applications include fully functional prototyping, creating production tools, tooling for moulds or inserts, housings, ductwork, heat exchangers and heatsinks. It is well suited to manufacturing relatively small yet complex parts, including prototypes. It can also facilitate tooling for conventional manufacturing technologies in a much more cost-effective manner. Besides, It has wide applications in various sectors like Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering. The flexibility of 3D printing combined with the mechanical properties of metal makes this technology a boom and has found its space across the industry.
Let's Sum Up
As the world extends its dimensions, we need to extend ours too. As 3D metal printing is now available to home users also, it is now easy to print a wide variety of 3D objects. Because this metal additive manufacturing is time-consuming, complicated and expensive, it is difficult for it to be a common process. But as the technology develops, the constraints shrink and there will be a time when Metal 3D printing is widely used to change the dimensions of the world. Let us hope for such a moment where we can affordably do a lot of innovative 3D printing as commonly as now we do the printing on paper. Now regarding the cost of metal 3D printing, it can be incredibly cost-effective for the first 200 to 20,000 parts. Direct metal laser melting is a productive method for low-cost 3D metal printing. Apart from cost, metal 3d printing in India depends on factors such as the volume of your 3D model, complexity and the type of finishing that you use. Nowadays, there is a newer aspect of liquid metal 3D printing. It uses a laser to cure liquid photopolymer resin into solid isotropic parts. They produce an output having sharp edges, a smooth surface finish,dmls 3d printing service
and minimal visible layer lines.
#3d metal printing companies#3d metal printing machine#3d metal printing machine manufacturers#3d metal printing near me#3d metal printing prototyping#3d priniting post processing services#3d printing in defence industry#additive laser manufacturing#additive manufactured products#additive manufacturing 3d printing#additive manufacturing advantages#additive manufacturing aerospace#additive manufacturing application#additive manufacturing companies in bangalore#additive manufacturing company#additive manufacturing company in india#additive manufacturing future#additive manufacturing material#additive manufacturing metal parts#additive manufacturing near me#additive manufacturing process#additive manufacturing service in india#additive manufacturing technique#additive manufacturing types#additive metal 3d printing#advantages of 3d printers#automotive industry 3d printing#benefit of metal 3d printing#best 3d printing companies in bangalore#dmls 3d printer
0 notes
Text
at what point does something stop being made by a person and start being made by a machine? is someone creating a photoshop action so the computer will run code to edit a photo they found online all that different from someone inputting words into a human made algorithm trained on human made images to generate a photo? if i use a knitting machine to make something does it count as human made or machine made or both? if i design a program that knits the object without me having to manually operate the machine does it still hold emotional value? what if i allow others to use that program to do the same thing and they input a sentence into the program articulating what they want made and the machine creates it? is 3d printing art? is technology itself capable of being art? if we define 'what gets to be art' by the % of machine involvement at what % does it stop being art? does this entire argument not feel a bit futile and arbitrary to you?
everyone will have a different answer just like how everyone has a different answer on 'what is art' and that's an argument we've been having for ages and will continue to have for the foreseeable future. i'm a weaver and an artist and my tendency is to lean toward the romantic, but in my efforts to be a materialist i ultimately find these questions largely unhelpful on the topic of 'should generative ai art be forbidden' because if we're only talking about how things make us feel and how we want the world to be and not the actual material impacts of things from a practical perspective we'll never get anything done. it's why i said that arguments against generative ai that take this stance are unconvincing and if you try to critique ai from an angle that isn't materialist you will run yourself in circles.
#these are fun questions to discuss and think about but there will never be a conclusion to them and there will always be another argument#but they are unhelpful in practical terms for precisely that reason
132 notes
·
View notes
Text
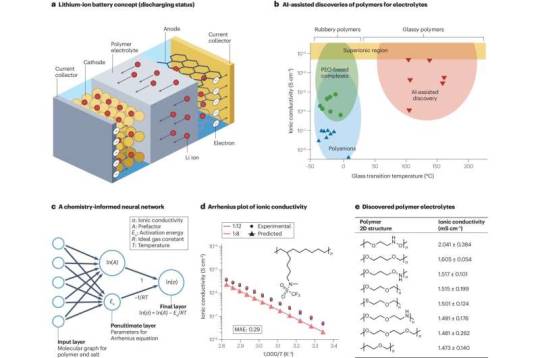
AI accelerates discovery of next-gen polymers
Nylon, Teflon, Kevlar. These are just a few familiar polymers—large-molecule chemical compounds—that have changed the world. From Teflon-coated frying pans to 3D printing, polymers are vital to creating the systems that make the world function better. Finding the next groundbreaking polymer is always a challenge, but now Georgia Tech researchers are using artificial intelligence (AI) to shape and transform the future of the field. Rampi Ramprasad's group develops and adapts AI algorithms to accelerate materials discovery. This summer, two papers published in the Nature family of journals highlight the significant advancements and success stories emerging from years of AI-driven polymer informatics research.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Polymers#Artificial intelligence#Computational materials science#Machine learning#Georgia Tech
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Swiss researchers develop robotic additive manufacturing method that uses earth-based materials—and not cement
Researchers at ETH Zurich, a university in Switzerland, have developed a new robotic additive manufacturing method to help make the construction industry more sustainable. Unlike concrete 3D printing, the process does not require cement.
According to a press statement from ETH Zurich, the robotic printing process, called impact printing, uses cheap, abundant, and low-carbon earth-based materials such as clay or excavated earth. Currently, the robotic additive manufacturing method uses a mix of excavated materials, silt, and clay. Most of the custom material is common waste product sourced locally from Eberhard Unternehmungen, a Swiss construction company. In the future, the process could use other materials.
With ETH Zurich’s method, a robot deposits material from above, gradually building a wall. On impact, the pieces of material bond together, with minimal additives. Whereas concrete 3D printing creates layers, ETH Zurich’s method extrudes and drops the material one bit at a time at velocities of up to 10 meters per second. The fast speed allows the material to bond quickly.
youtube
ETH Zurich’s process can build full-scale, freeform structures, including one- or two-story walls and columns. The printing tool has been used to build structures as tall as almost 10 feet. The process results in walls with a bumpy texture, but robotic surface finishing methods can achieve a smoother finish.
The custom printing tool can be integrated with multiple robotic platforms. As a result, the tool can build walls in both offsite facilities and onsite construction projects. At ETH Zurich’s Robotic Fabrication Laboratory, the tool has been integrated with a high-payload gantry system. The hardware can be mounted on an autonomous legged excavator to build walls on sites with variable terrain.
ETH Zurich says it aims to increase the cost competitiveness of sustainable building materials through efficient and automated production.
#solarpunk#solarpunk business#solarpunk business models#solar punk#solarpunk innovation#earth based construction#switzerland#3D printing#additive manufacturing#Youtube
34 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you guys have any info about what exactly Future-Tec is? I remember seeing some stuff in the 76 Atomic shop about it, but I can't really find any good info on what it is and what role it plays in the lore.
Heyo, thanks for the ask! I'm happy to answer anything I can!
So first, let's establish every game or publication Future-Tec is mentioned in (to my knowledge). Future-Tec is mentioned in the Vault Dweller's Survival Guide (Fallout's manual), Fallout 76 and lastly, Fallout: The Roleplaying Game!
In the Vault Dweller's Survival Guide, Future-Tec is stated to be a division of Vault-Tec, and presents an advertisement for the Garden of Eden Creation Kit (mind you, this is before the GECK was in a game too).

In Fallout 76, several Future-Tec Atomic Shop C.A.M.P. items appear, all with unique descriptions. The description for the Future-Tec Week Flag states the following:
Future-Tec was once a secret branch of Vault-tec tasked with investigating top-secret and alien technologies. Fly their flag in your C.A.M.P. with the Future-Tec Week Flag.
Additionally, the terminal entries for Vault 51 show that ZAX 1.3c copied Dr. Stanislaus Braun's writing and speaking style, in order to obtain a Hellfire Prototype Power Armor unit. The entry reveals that Braun was the department head of Future-Tec!
//SEARCHING: Hellfire Prototype Power Armor //SEARCHING: Future-Tec //SEARCHING: Department head //SEARCHING: Dr. Stanislaus Braun //ANALYZING: Dr. Stanislaus Braun published research and speaking history //COPYING: Dr. Stanislaus Braun writing & speaking style ........ Success; Probability of direct match 99.6% //SENDING: Hellfire Prototype Power Armor Requisition Request ........ Success; message delivered.
In Fallout 3, we also learn that Braun is the creator of the GECK!
Lastly, in Fallout: The Roleplaying Game, we get this short blurb about the GECK:
Devised by Vault-Tec’s Future-Tec division, this terraforming device uses matter recombination technology to transform irradiated or otherwise polluted earth into fertile soil. It also included force-field schematics and 3D printing arrays to make everything from buildings to clothing from the raw materials of the earth.
Now that we have our sources put together, let's piece together all that we know about Future-Tec, as a division of Vault-Tec.
Future-Tec was a division of Vault-Tec, headed by Dr. Stanislaus Braun. Described as a secret branch of the company, the division was responsible for investigating "top-secret and alien technologies." The Garden of Eden Creation Kit was devised by the department, with Dr. Braun being responsible for developing the device itself.
Hope this helps! Of course, sometimes I do miss a source or two, but I'm confident that that is all the info we have on Future-Tec. This was a nice little writing exercise, so I'd love to answer any more asks people have! :D
With this post, all info I've stated has been added to our Future-Tec page, which you can check out here:
https://fallout.wiki/wiki/Future-Tec
#fallout wiki#independent fallout wiki#fallout#fallout series#fallout 3#fallout 76#fallout 1#vault dweller#fallout the roleplaying game#fallout rpg#fallout ttrpg#fallout tabletop#fo76#fo3#fo1#forpg#vault tec#vaults#fallout wiki ask#fallout wiki facts#fallout facts
72 notes
·
View notes
Text
Print the Future: a 3D Micro-Optics Revolution - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/print-the-future-a-3d-micro-optics-revolution-technology-org/
Print the Future: a 3D Micro-Optics Revolution - Technology Org
In a recent publication in the scientific journal Trends in Chemistry from Cell Press, researchers from the University of Twente delve into the potential of 3D printing ceramics in micro-optics. These tiny ceramic structures can potentially be used to generate light and store information. “Let’s make ceramics so small they can manipulate light.”
Light – illustrative photo. Image credit: Pixabay (Free Pixabay license)
As with many publications, the article began with curiosity-driven students. J.P. Winczewski (former Ph.D.), J. Arriaga-Dávila (Nanotechnology master), and C. Rosero-Arias (Ph.D.) dove into 3D printing ceramics beyond our eyesight. “Instead of printing something massive, we decided to go the other way around and make extremely small printed structures”, says Arturo Susarrey-Arce, assistant professor at the Mesoscale Chemical Systems research group of the University of Twente.
Ceramics for micro-optics
Ceramics are very powerful in the micro-optics field due to their light-matter interaction properties. The speed of light in a vacuum is known to be unbeatably fast. However, glass and ceramics have a higher refractive index, meaning light gets slowed down while propagating through the suitable material. “Looking at the future, 3D-architected ceramics can contribute to optical communication and light circuits with the right material combination and composition,” says Susarrey-Arce.
As the name suggests, 3D printing implies accurately shaping micro-optics in all three dimensions. “Miniaturisation typically occurs in 2D, but there is still much space in the third dimension”, explains Susarrey-Arce. However, to advance, there are still challenges to overcome. For example, 3D ceramic printing should comply with key characteristics. To integrate 3D ceramic printing into low-temperature micro-optics, the researchers have to achieve perfect microarchitectures at the highest spatial precision. This aspect partially relies on the availability of various resins that change their properties when exposed to light, permitting them to print them simultaneously. Developing such resins remains a challenge for synthetic chemists, a challenge we engage daily in the lab.
More information
Dr. Arturo Susarrey-Arce is an assistant professor at Mesoscale Chemical Systems (Faculty of S&T). His work focuses on the micro(nano)fabrication of structured materials. Together with three other young creative researchers, he recently published an article entitled “Tailoring Chemistry for inorganic 3D micro-optics” in the scientific journal Trends in Chemistry. The exciting work has been highlighted on the cover of the journal’s February edition.
DOI: 10.1016/j.trechm.2023.12.005
Source: University of Twente
You can offer your link to a page which is relevant to the topic of this post.
#2023#3d#3D printing#amp#Article#cell#ceramics#challenge#change#chemical#chemistry#Chemistry & materials science news#communication#Composition#curiosity#dimensions#Fabrication#Faculty#Featured technology news#Future#interaction#Light#Link#material#materials#matter#micro-optics#Nanotechnology#optical communication#Optics
0 notes
Text
So I work with a lot of thermoplastic (I don't have a 3d printer yet, I use a heat gun and pellets) and I want everyone who's on the plastic hate train to know and understand a bit o' nuance.
Thermoplastics are generally extremely reusable and recyclable. The thermo plastic I work with is Techleo poly morph and it comes in meltable pellet form, but 3D printing filament uses a similar substance in the thermoplastics family. Other thermoplastic materials include: Worbla products, Polly plastics, and Instamorph.
There's a chemistry part of this I won't bore you with, but the lower the melt temp, usually the weaker the plastic. Worbla requires a higher temp than polymorph for instance. Cold, cured polymorph is softer and more scratchable, where as Worbla isn't.
Anyway-
Please stop getting mad at people with 3D printers because the waste from these printers is absolutely reusable and more importantly: it's easy for a layman to recycle and reuse a thermoplastic at home, now more than ever because of the rise of 3D printers.
Having a recycling plan if you own a 3D printer is a better message to rally behind. Use your 3D printer to recycle what companies won't. Buy recycled filament, create a demand for recycling.
3d printing brings recycling right into your home. Look up how to process bottles into filament and you'll see what I mean. You could make homewares out of your trash easily with just a few extra steps before the print process. A bottle that was cut into a continuous strip, melted into filament and then printed into a knick knack for your shelf is a bottle not in the ocean.
Recycling plastic has now become waaaay more accessible to regular people because of 3d printers. It changes the attitude people have towards recycling as a whole too.
Environmental conversation when it comes to plastic is not entirely an individual responsibility thing as we know and 3d printers are not an enemy. We are having so many more conversations about how to recycle plastic and I know 3d printers are teaching regular people about plastic production and that sets us up with an expectation that companies can do better about waste so they should.
Plastic isn't going away. It is unfortunately a curse of an extremely useful substance with no comparable alternative. Don't hate on plastic indiscriminately, hate on plastic that is not used to its fullest potential. Demand systems of recycling that make sense. Heck, bacteria that can break down plastic is the future right now so maybe artists that create beautiful things with plastic aren't your enemy
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
Maybe this sounds random, but on Tik Tok I saw a lot of people using AI to make their Arcane lookalike character, and I just wanted to say that if you do so you didn't understand anything this show offers.
The quality of Arcane comes obviously from a really good writing but also from the amazing character designs, worldbuilding choices, scene composition and obviously animation; those are works that take a lot of fucking time to the amazing artists, animators and directors, and using a technology that actively threatens this working positions is not only disrespectful but also stupid. Actively feeding AI with the unique artstyle of arcane is first of all helping this abomination evolve into becoming even more precise in stealing and copying specifics artworks, and also it's teaching it how to replicate Arcane lookalike art pieces that could be used to mass produce merch or prints putting a profit in the pockets of the wrong people; not only that but since we live in a time where profits are basically the only interest to big companies, who can guarantee us that once the AI products are good enough they will not be used for the actual series and products. I know that right now it doesn't seem like a possibility for this franchise because it has given us a genuine and fantastic work of art, but seeing what is happening in the world of animation (thinking for exaple Disney pushing only corporations slabs such as live action remakes or souless films, Pixar employees given less and less creative liberty, DreamWorks Co founder Katzemberg basically declaring that animators can be replaced by AI, and all the strikes the animators in the USA are doing because of the inadequate salaries and threatens to their positions) it's not an impossible scenario, maybe the fact that the arcane/league animation projects are done by a studio based in France, [were because of EU regulations AI is more limited (kinda, but also not really lol)], can keep it safe for now, but I wouldn't be so sure about it in the future.
This is to say that there are real people in the animation industry wich are suffering the direct consequences of the capitalistic mentality of their executives, and the real threat of AI replacing their labor, you chosing to use this technology is only giving this capitalist machine free fuel.
Also it's insulting to the amazing visual work done in the show, the art of animation is finally taking a different path in big industries than the iperrealism of Disneys 3D backgrounds; let's think about Spiderverse by sony, or the lates Ninja Turtles by nickelodeon, or even better Nimona, finally there has been a path of experimentation with this form of art recognized by the general pubblic, and Arcane is yet another example of this new and diverse path. The characters flow in the scenes, everyone of them has a unique style of combat reflecting their personality, the use of color as symbols but also as enanchment of the scenes, the raw strokes and blurred edges, the use of light to convey the scenes depth, the character designs, the writing, it's a work of art, a humanmade work of art, not one done by some click on a computer and a prompt. This is a tipe of work that an AI should struggle to replicate, it easy for an artificial intelligence to remake a Disney 3D style, because it's clean, boring and all the same therefore it's easy for a company like that to start rely on this technology to feed us with all the more shit ass stories and all the same animations, let's not make it easy for an AI to replicate something like Arcane, let's not feed this machine great material to steal and reuse to take away work from the people who give us this masterpieces in the first place.
Without obviously starting the discourse about how harmful it is for the environment, but this post is already a chapter, so maybe another time.
Section with spoilers:
Last thing is I saw a girl talking about the artstyle choices in the scene where Viktor and Jayce destroy the excore, where the excore products are all kinda fucked up and uncanny like something an AI could make, and then where the two of them fucking explode (rip to them I'll miss those gay boys) everything becomes more flat like a traditional human made drawing. So maybe the glorious evolution of mankind through AI it's a lot like how it's portraid in the show: souless, all the same, lacking personal freedom of choice and creativity, therefore if we put on our thinking caps maybe it's not the best path to go down. I dunno I just wanted to throw it out there because it fits a lot.
Just my thoughts. If there are grammatical errors I'm sorry, but clearly I don't want to use an AI to correct them lol.





19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Blaidd Cosplay project I worked on during May 2022


Elden Ring was the hype, I wanted to be a good turtle. I originally wanted to get this cosplay ready by Otakuthon 2022, but I never did finish it. I do want to finish this cosplay one day!
Now let ramble about my progress on it! :readmore:
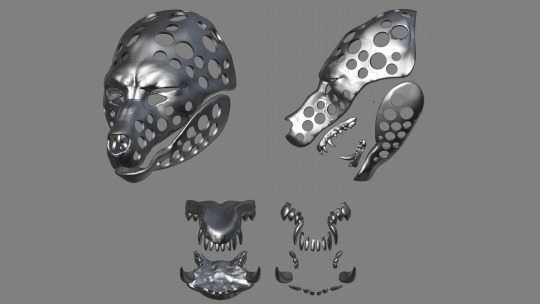
When it comes to video game cosplay, I take the easier route and rip models from the game, then modify them for cosplay. I 3D modelled a few Kamen Rider suits before and all that was a pain in general. For my sanity's sake, I plan to model as little as possible for future cosplays.
Lucky, the in-game model was well made, so I didn't have to make a lot of modifications. I had to separate some pieces, subdivide and give it some volume.
The head was given a lot of holes, so it would be lighter to wear. I had to separate the teeth and the gums because I will paint them individually.
I let my 3D printer work. Meanwhile....

Eyeballs! Molded with moldable plastic pellets. The iris part of the eye hollows inwards for a bit of that 3D look. The whole thing then got covered in 2-part epoxy to fill the cavity and make the eye shiny.
There's usually a few steps involved when it comes to painting. That is priming and then taking your time to paint something with the medium of your choice. Well, I skipped all that and decided to draw on the eye with sharpie and markers. Results were... satisfactory enough.

Time to work on the gummy teethies! I've been saving up for years on an airbrush set and I got really excited to try them for the first time.
FDM 3D prints don't come out perfect usually, so I brushed some XTC-3D (fancier 2-part epoxy) on them, and let it cure first.
With a bit of filler primer and airbrushing magic...

Teeth! Dentists in the Lands Between will make a KILLING if they ever move there.
Pretty happy with the process! I didn't bother to shade the gums because we won't see a lot of that anyway.

Did I ever tell you sewing is my least favorite part of cosplay? My specialty is more on props and armor. This image should've been flipped upside-down!
I tried to sew gloves using a free-to-use pattern I found on the internet (forgot where I got them). First one was too tight, second on was better, but still feel weird to wear. I will get these right one day!!

I bought some FUR! I shopped for a WHOLE hour at the fabric store for the right faux fur, and none of them felt like a match to Blaidd's fur. His fur was darker (than the fur in the picture, left side), with a hint of blue.
I tried to dye the fur a little bit to darken it, but not too much because I didn't want the white part of the fur to turn too dark. I used a dye for synthetic fibers. Right side of the image the the fur after soaking in hot dye solution for a few minutes (still wet)
Results? I there was only a subtle difference between then non-dyed and dyed furs! I either didn't let it bathe in the solution long enough, or I did not put enough dye in the solution.
ANYWAY I decided to just used the furs as is and airbrush the details at the end.

Now for the cloak? I was planning on tying some crochet threads together, then separate the ends with a fur brush, resulting in some fluffy ends the add on to the cape.
However, after re-examining Blaidd's cloak, I'm considering on scrapping this process because I feel like there's better materials to give out the look I want.
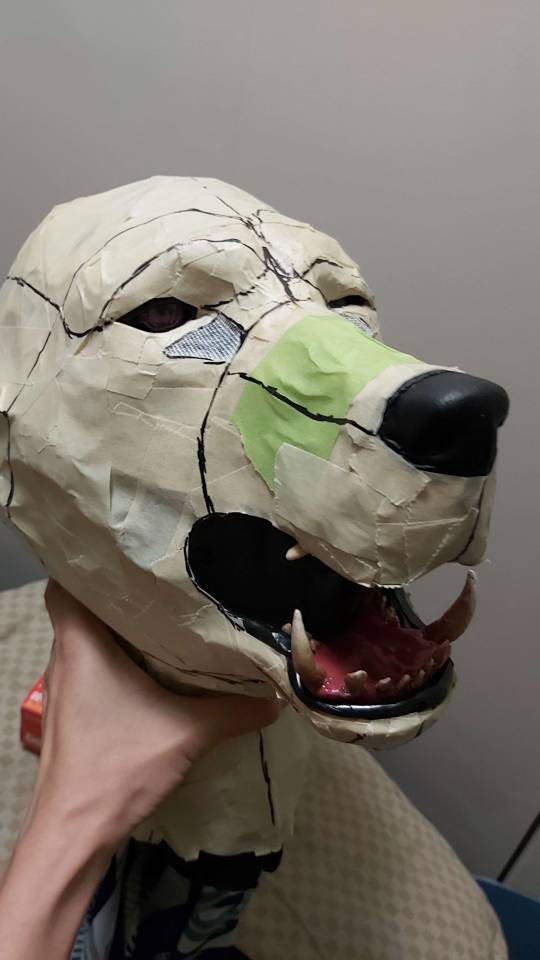

After assembling the mouth parts/eyes/nose, adding the lips with black moldable plastic and adding the hinge (to make the mouth movable), it's off to furring the head!
With the help of masking tape and sharpie, I went to pattern the fur. I then cut the appropriate shapes to sew.
I knew I had to cut the fabrics a bit bigger to make things fit and all, so I did that. My mistake? I realized after finishing the snout part, that I've cut the shapes TOO BIG! It did not fit the print!
So that's another thing I have to redo. Sewing is my passion (sarcasm).
This concludes part 1 of my Blaidd cosplay journal. Will there be a part 2? I don't know. It started snowing a few days ago and Winter is generally not a good time for cosplay-making. I'll have to see about this when Spring/Summer comes!
#cosplay#cosplay journal#okay well the readmore didnt work but got expand instead but ill just leave it there anyway
55 notes
·
View notes
Text

Arcane Jinx Progress thread
I started work on this months ago, so I'll briefly catch up what I've been working on then try to remember to post here when I have updates. I'm aiming to finish this for Dragoncon, so I have 47 days (46 technically since we fly out). AHHH
Current status Wig: Done (needs some fixes in the future, but good for now) Top: Done (again, small future fixes, but wearable) Gloves: In progress, like 50% done Tattoos: 0% Belt: 0% Pants: Done (yet again, small future fixes, but wearable) Bandage: 0% Boots: 5% (materials purchased, 3d-printed parts printed)
14 notes
·
View notes