#striatum
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

by Elizabeth Johnson-Wold
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Depression "under pressure": the better we know mechanisms, the better come out managements
Deporession ad public health emergency Depression is a growing mental health concern and is associated with significant levels of disability across the world. Depressive symptoms, such as persistent low mood, fatigue, cognitive impairments, anhedonia, or a lack of interest or pleasure in the activities of life, are categorized as interest-activity symptoms. These symptoms contribute substantially…
#depression#dopamine#interleukin-1#interleukin-6#neuroinflammation#Parkinson disease#public health#striatum#TNF-alpha
0 notes
Text
Bağırsak Bakterileri Egzersiz Yapma Motivasyonunu Artırabilir
Bağırsak Bakterileri Egzersiz Yapma Motivasyonunu Artırabilir Pensilvanya Üniversitesi Perelman Tıp Fakültesi’ndeki araştırmacılar tarafından fareler üzerinde yürütülen bir araştırmaya göre, bağırsakta yaşayan bazı bakteri türleri, egzersiz yapma isteğini artırmak için bağırsaktaki sinirleri harekete geçiriyor. Bağırsak Bakterileri Egzersiz Yapma Motivasyonunu Artırabilir Araştırmada,…

View On WordPress
#bağırsak bakteri popülasyonu#Bağırsak Bakterileri Egzersiz Yapma Motivasyonunu Artırabilir#bağırsak bakterileri hareket etme üzerine etkili#bağırsak bakterisi#bağırsak bakterisi ve hareket etme#bağırsak mikrobiyomu#Bağırsak v eğzersiz#bağırsak ve beyin ilişkisi#Christoph Thaiss#Coprococcus eutactus#egzersiz yapma alışkanlığı#egzersiz yapma isteği ve bağırsak#Eubacterium rectale#hareket ve bağırsak ilişkisi#metabilitler#Striatum
0 notes
Text

This weird plant is the recently described Bolivian endemic Gorgonidium striatum. Endemic means it's native to only one place and nowhere else - in this case, tropical rainforests on the eastern Andean slopes in Bolivia. As a member of the family Araceae, it has a spadix and spathe inflorescence, which means it has a spike of many tiny flowers (here they're dark purple-brown) surrounded by a big bract (modified leaf), which here is both mottled and striped with green, cream, and a bit of purple. It's an interesting one!
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
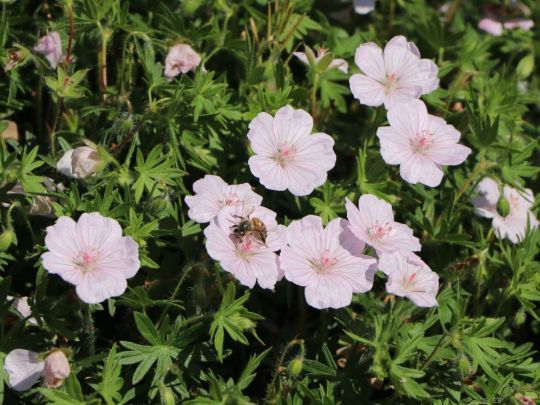
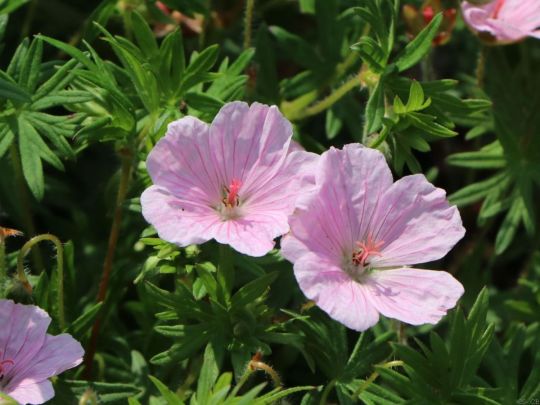


Der Blut-Storchschnabel 'Apfelblüte' erfreut sich immer größerer Beliebtheit. Die einzeln wachsenden Blüten sind weiß bis zartrosa und erinnern an die Blüte des Apfelbaumes. Die schalenförmigen Blüten sind zart geädert. Daher wirkt die Blüte von (bot.) Geranium sanguineum var. striatum 'Apfelblüte' besonders filigran und zerbrechlich. Sie bietet reichlich Nektar und Pollen für Bienen, Hummeln und Schmetterlingen an. The Blood Cranesbill 'Apple Blossom' is becoming increasingly popular. The individually growing flowers are white to pale pink and are reminiscent of apple tree blossom. The cupped flowers are delicately veined. This makes the flower of (bot.) Geranium sanguineum var. striatum 'Apple Blossom' look particularly delicate and fragile. She offers plenty of nectar and pollen for bees, bumblebees and butterflies.
#Blut-Storchschnabel Apfelblüte#Geranium sanguineum var. striatum 'Apfelblüte'#Blood Cranesbill Apple Blossom#Geranium sanguineum var. striatum 'Apple Blossom#Garden#Nature#Wild Life Nature
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo

シランの蕾(4月3日)
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Feeling a little overly perceived by Dr. Dodson right now, not gonna lie.
I'll throw a transcript under the cut, but both reading the transcript and listening to the video can be difficult as it's quite long, so here's some highlights. As always, these are the opinions of a specialist but only one specialist, so take with a grain of salt, and if you have research to add to this, please feel free to comment or reblog with it. I believe this presentation is from sometime in 2022.
ADHD appears to derive from issues in the corpus striatum in the brain. In most people, the corpus striatum filters out all but the most important input AND output; with ADHD, the things normally handled "outside of awareness" must be handled consciously.
People with ADHD don't see their emotions coming. Emotion is immediate, intense, and unfiltered, making therapies like CBT or ACT difficult, because you can learn the technique but you won't have time to employ it. Because people with ADHD have impulse control issues, expressing emotions "inappropriately" is common, leading people with ADHD to believe they can't trust themselves.
One function of ADHD-typical dysregulation is Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria, which nobody understands even a little. People who have it can't even adequately describe it to people who want to study it. It is intense, painful, and apparently impossible to control. Prevention is based in maladaptive behaviors designed to avoid it entirely (perfectionism, people pleasing, generalized withdrawal). The only currently known treatment is alpha agonist medication.
Lastly, by the age of twelve, a child with ADHD has likely received twenty thousand more "negative or corrective" messages than their neurotypical peers. (This isn't relevant to the rest, I just found it sufficiently horrifying to warrant inclusion. Fortunately for me, if I got 20,000 negative or corrective messages, I wasn't paying attention for most of them.)
Anyway, here's the transcript of the first half. I did this by copying and cleaning up the auto-transcript on YouTube, but I stopped at Question Time, so this is only the first half (the presentation). Transcription of the second half is available at YouTube.
There is suddenly a very large interest in the whole subject of emotional dysregulation and ADHD. That has been driven oddly enough by the Food and Drug Administration, which has just opened up several pathways that drug companies can study emotional dysregulation and whether or not their medications can get an FDA indication for emotional dysregulation. So it's sort of follow the money. Up until then, there was not a great deal of interest for ADHD emotional dysregulation.
We have to understand that the ADHD diagnostic criteria were not made for people like you and me, either practitioners or people who have ADHD or their families. They were designed for and made by people who do research and pretty much that's it. People who do research have to have criteria that they can physically see and count. "Little Johnny was up and out of his chair three times in the last hour," and you can write a three on your clipboard. Things which are invisible, not always there, hard to count, or even hidden by the patient, don't lend themselves to research very easily and so tend to be ignored. And so consequently this is one of the main reasons why emotional dysregulation -- until there was some other motive provided -- was pretty much ignored and disregarded.
Consequently ADHD right now, if you look at the 18 diagnostic criteria, are almost entirely behavioral criteria. What is the person doing? Not how is the person thinking, what is the patient feeling, how are they controlling their emotions, how are they sleeping. Things that are all very, very important to the person who has ADHD but which is essentially ignored by the diagnostic criteria.
Why should you care? Who really cares about this? Well, the definition of what ADHD is and isn't defines who and what will be studied. It defines who will actually get into a study and what questions will be asked. It defines who will be diagnosed with ADHD and who will not. One of the most common problems I get is with a secondary referral to me -- somebody clearly has ADHD but they're not pinging off the walls, they can sit and do their work, especially when they get into a hyperfocus, and so they're told they couldn't possibly have ADHD. When really they just have the inattentive subtype and they're not being driven by their behavior, their overt behavior. Therefore it defines who will get treatment, who will get insurance coverage for that treatment, and who will get accommodations in school when they're young and at the workplace when they're older.
Consequently we should also care because the other major components of ADHD get ignored. These are the ones that if you really stand back and look at it cause the greatest amount of impairment, the greatest amount of embarrassment, the greatest amount of just…problems in general. We're talking about cognition and thinking, that people with ADHD fundamentally think in a different way than do neurotypical people. They are able to engage with the tasks of their lives in a totally different way. Their ability to control their emotions and their behavior, control their emotional responses, tremendously affects their self-esteem and their self-definition. Who am I? What am I worth? What am I valued? Why am I valued in a certain way? What do other people think of me?
It affects tremendously the nature and healthiness of relationships. How you respond emotionally to the people in your realm makes a great deal of difference about the healthiness and gratification you get from your relationships. Being highly dysregulated in terms of your energy and emotions also affects deeply how well you sleep, how easy it is to fall asleep and awake refreshed, and of course it affects emotional dysregulation.
And this is probably, when you look at it in the long term and especially with adults, probably the most impairing part of the ADHD syndrome. The vast majority of people with ADHD have found ways around their academic and work performance, but they haven't found their way around their emotional reactions to the people and events of their lives.
At all points in the life cycle -- child, adolescent, adult, and elderly -- people who have ADHD nervous systems lead intense, passionate lives. Their highs are higher, their lows are lower, all of their emotions are much more intense. And that really is what we're talking about: not really the quality of the emotions -- people who have ADHD have the same types of emotions for the same reasons that everybody else does. What we're talking here, in terms of dysregulation, is two things: one, the expression of emotions, being able to choose whether or not you let an emotion out. And then, when you do decide to express it, how intensely that emotion is experienced and expressed by you as a unique individual.
Consequently just about everybody with ADHD, but especially little children, are always at some sort of risk of being overwhelmed by their own emotions from within themselves. This is something that needs to be really emphasized: a lot of people with ADHD grow up not being able to trust themselves.
So why is this happening, especially to people with ADHD? I think that just about everybody now would agree that ADHD is primarily a problem of insufficient inhibition, being able to slow down and keep things from happening. If you look at the mass of the human brain, 85% of all the nerves in your brain and out in your nervous system are inhibitory in function. We happen to be aware of the other 15% because we can see what happens when those nerves are used: they create movement, they create emotions, they create our experience and memory. We have to remember they are a minority of the actual mass of the human brain.
Most of what happens inside the brain occurs outside of awareness. What happens is the brain starts something, it gets it moving, and then uses inhibition to guide that toward the destination it wants. It's like shooting off a rocket -- shooting it off is the easy part, guiding it to where you want it to go is the hard part.
When you look at where stimulant class medications work, they work solely in the deep areas of the brain down in the basal ganglia, and especially in an area called the corpus striatum, which is just Latin for a "striped body". That's how it looks when you look at it -- it's got many very fine stripes in it. This area, the corpus striatum, is almost entirely inhibitory in function. What it does is that it inhibits neurological input and output to just the one piece of information or one action that happens to be most important at that time. Everything else gets handled, but it gets handled out of awareness.
Probably the easiest place to see this in action is when we're driving a car. Driving a car is the most difficult thing that the average human being ever has to learn how to do. It's a very difficult process, if anybody has ever had an adolescent learning to drive. But once we learn how to drive a car we do it largely outside of our own conscious awareness. We can drive along, talk to the person on the seat next to us, think about what we're going to have for dinner, sing along to the radio, and not really pay attention, conscious attention, to what's going on around us. But if suddenly something is out in front of the car, even before our conscious brain can process what that thing is, our corpus striatum has already handled it. Slam on the brakes, swerve to miss it, start to question that person's parentage, in the twinkling of an eye. The corpus striatum has been scanning everything, handling everything.
So basically what ADHD is, is that relative lack of inhibition that should be there. Inattention, which is a cardinal feature of ADHD, is the relative lack of the inhibition of other inputs or distractions. When we look at physiologically what's happening, we don't actually pay attention to one thing. Neurologically, we suppress every other thing we might engage with except the one thing that we want. It is maximally inefficient in that way.
Impulsivity is a relative lack of inhibition, of the expression of actions and emotions before you can think about them and make decisions about that expression. Hyperactivity is the relative lack of inhibition of physical and mental activity. When the physical activity of the hyperactive little boy who's pinging off a wall goes away in adolescence, they're still very much mentally active in their own brains.
So what? The “so what” for most of us is that when this area of the brain is not working as it should, people cannot regulate the experience and expression of their emotions. Emotions are experienced as completely unmodified and unscreened. The word that most people use is that they are raw. They come out without any modification at all, they go in without any modification at all. People can see this in hyperacusis, where somebody chewing or the conversation across the restaurant comes in loud and clear because it can't be screened out.
All this is tremendously overwhelming. We get overwhelmed by entirely too much input, and the impulse to have entirely too much output. It's exhausting, and when it does get inappropriately expressed it's embarrassing, so consequently people with ADHD must always be vigilant of themselves.
Now, when we look at the traditional therapies that have been used, or tried to be used, with ADHD, they have had very very poor track records. They're largely ineffective in helping people control the expression of what they think and feel. The reason for this is that people with ADHD don't see their own emotions, their own actions, coming. They find out about their emotions and actions the same way everybody else does: it's already out there before they even know that it's coming. Consequently they don't have the time and the warning to use the techniques and new skills that they may have learned in behavior modification therapy, or in cognitive therapy. They learned them, learned them perfectly well, but the cat’s out of the bag before they can make use of them.
Right now, as we sit here today, medications are the only thing we have to offer that have a proven track record, because they're there all the time. We have two basic groups: we have the stimulant class medications which are amphetamine, methylphenidate, et cetera, which help directly with inhibition. They help slow things down, they help inhibit both input that would distract us and output. It gives you the same two seconds that everybody else has, to see an emotion or an action coming up, to play it out in your mind. “If this happens then this will happen, then that'll happen. Oh, I don't want that to happen, I'll redirect it.”
The alpha agonist, of which we have two -- guanfacine and clonidine -- inhibit the energy driving the speed and intensity of response. Interesting enough, when we look at just clean effectiveness, when we measure how effective is this treatment, the alpha agonists are significantly more effective than are the stimulants. Usually that's kind of a false choice, because most people end up taking both classes of medication.
A very special type, I think, of emotional dysregulation is -- again a terrible technical term -- what's called Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria. We actually don't know what it is. It's much too early to tell. But it does seem to be a thing with which many people with ADHD identify. There was a brief article from ADDitude that got posted on Reddit, on their subreddit on ADHD; that particular posting got twice as many responses, in less than a month, than any other posting that had ever been put on that subreddit. It really touched a lot of people in a strong way.
In my own checklist, when I'm asking about Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria, the question I have is: “For your entire life, in other words going all the way back into childhood, have you always been much more sensitive than other people you know to rejection, teasing, criticism, or your own perception that you’ve failed or fallen short?” This is directly from a psychiatric textbook, an old one, and it's the definition of a technical term, for psychiatrists called Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria.
It's important to note, this is all a matter of degree. No one likes being rejected or criticized. Everybody hates it when we fail, we fall short, especially in front of other people. Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria is much more intense, and is much more than this universal discomfort.
When they were originally doing the research on this particular idea, 45 years ago, they wanted to get that intensity right up there in the name, and so they chose the word dysphoria -- which unfortunately happens to be Greek -- but it means “unbearable”. Because that was the description they were getting from people over and over and over again. Again, for reasons unknown, people with rejection sensitivity have trouble describing what the intense emotion is all about. They can describe its intensity -- “it's awful, it's terrible, it's catastrophic,” -- but not the quality of the mood. And so, over and over again, these research subjects would finally just tell the researcher, “Look, man, back off. I can't find words to tell you what this awful feeling feels like, but I want you to know I can hardly stand it.” And so that's where the word dysphoria came from. A researcher at Harvard who decided to put it into Greek, but that unbearable quality is very much a part of what's going on, a part of the experience of Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria.
It's extremely common in people with ADHD; my guess is that about 95% of my patients report it as a significant impairment, and about a third of my patients say that it is by far the most impairing part of their ADHD. For the majority of people, and most occurrences, it is not that particularly disruptive, but when it hits, it turns your life upside down.
So how is rejection sensitivity experienced? There's no warning. It hits out of the blue; there's no way to protect yourself from it. It happens all at once, it goes from zero to a hundred percent instantaneously. It is commonly experienced as being physically painful, as if someone just punched you in the chest or punched you in the stomach -- there's an aching in the core of your being.
Once it gets started it seems to be largely uncontrollable until it's run its course, whatever it is. The quality of the mood is indescribable. Most people struggle to find any words at all to describe this feeling, even though it's massively intense. The duration can be a few minutes to several months. It's a very potent experience and can make it very difficult to risk ever being rejected or criticized again.
If this very intense emotional reaction is internalized, it looks for all the world like an instantaneous major depression, complete with suicidal thinking. And so a lot of times people do get a diagnosis of major depression, because the clinician they're working with fails to pick up the triggered, instantaneous nature of the onset of that depressive-looking syndrome. If it's externalized, it presents as a rage that is directed at the person or situation that wounded them so terribly. In fact, being “wounded” is is a very common description. This sort of sudden trigger change, with an intense emotional response, not uncommonly leads to a misdiagnosis of borderline character organization.
So if you can't see it coming, and you can't do anything once it's happened, how do people try and protect themselves from episodes of rejection sensitivity happening in the first place? Some people use perfectionism; they try to be above reproach. They feel driven to be the very best at everything they do. These are the penultimate overachievers. It works, but it's also an absolutely terrible, driven way in which to live.
By far the most common response is that people become people pleasers. They are constantly scanning everybody around them and trying to figure out what that person wants or would approve of, and that's what they give them, so much so that it is the to the exclusion of what they want for their own lives. These are people who take care of others, please others, to the exclusion of any sort of gratification in their own lives.
Another very common way that people try to deal with this is that they give up trying anything new, giving up anything in which they might fail or be embarrassed. I have hundreds of patients who have never been able to apply for a job or ask someone of the opposite sex out for a date. Just the imagination of being told no is so frightening, so devastating, that they just say, “No, I'm not going there. I'll sit this one out.”
One of the most effective ways of dealing with this are the alpha agonist medications, and when they work they can be almost completely effective. Alpha agonist again is a tongue twisting name, but it's not as tongue-twisting as the full name, which is alpha-2 selective adrenergic agonists. So you can see why we shorten it a bit. They were originally blood pressure medications that came on the market in the early 1980s. They worked very poorly -- when they did work, at most they lowered blood pressure about 10%, which was measurable but it still required other things that needed to be done in order to get most people's blood pressure down into a therapeutic range.
We have two of them, guanfacine which was marketed both as immediate release and extended release under the name of Intuniv, and clonidine, which was marketed under the trade name of Kapvay, both as an immediate release product and as a delayed release product. They have been used as a treatment of the hyperactive component of ADHD for more than 30 years, so these are not new medications for the field of ADHD. They're very much the treatment of choice for the “hyperactive, disruptive, and obnoxious little boy” that is what most people have in their minds when they consider the notion of “What does a person with ADHD look like?”
The exact mechanism of action of these medications both in ADHD and especially in rejection sensitivity is highly unclear. We really don't know -- we have a couple of ideas but they are very definitely theoretical. The only thing that we know for sure is that the stimulants don't work by stimulating anything, and that the alpha agonists don't work by being alpha agonists. How they do work is completely unknown.
We have two medications, they seem to work equally well, so there's nothing that would lead you to choose one over the other. The problem is that the robust response that we're looking for that really changes people's lives, is disappointingly low -- at about 30% to either molecule. Luckily that 30% is a different 30% of people, so that 30% of people get a good response to guanfacine but it's largely a different 30% that get a response to clonidine. So if the first medication tried does not work, it makes good clinical sense that that one should be stopped and the other one tried. There was an unfortunately worded sentence in an article I wrote for ADDitude several years ago that gave the impression that you could use the two medications together; they should not be used together. You try one, if that doesn't work you try the other.
The typical dose of either one is in the range of three milligrams of guanfacine per day or about three tenths of a milligram of clonidine per day. If you take all the people who get a good robust response to either one of these medications, about 80% are going to end up at these doses, so it's by far the most common dose.
There are of course side effects. Anything that's going to adjust the adrenaline system of the body is going to have the potential for sedation as a side effect, and this does occur for about 25% of people. It's usually mild and it does go away -- over a period of several months. So a person has to be fairly patient with that. It can cause dry mouth, and it's by a different mechanism then the stimulants can cause dry mouth, so the two of them together can really make your mouth cottony dry. And the third one is an accentuation of a universal experience we've all had, when we stand up quickly and suddenly and we get dizzy, get kind of a head rush, vision goes a bit gray. The technical term for it is orthostasis. And this can happen more frequently when you take the alpha agonist medications.
The benefits of the alpha agonist medications take a while to develop. When you change the dose it takes five days for the benefits to develop, so once again they're not like the stimulants where what you see is what you get at one hour. It takes a while for these medications to work and to see all that they can do.
Now just as a side note, Strattera has been looked at in two studies for emotional dysregulation and the results have been what they call mixed. If they did work it was only to a very minimal degree, almost undetectable, so Strattera does not seem to be a medication one could use and expect to have it help with emotional dysregulation.
So in summary, emotional dysregulation is a basic feature of ADHD, is almost universal in ADHD, and it should be considered as a core symptom of ADHD that ought to be evaluated in every initial evaluation. Rejection sensitivity…it's unclear yet -- this is an old concept that has only been brought up in the last couple of years. Its exact nature is still unclear. It does seem to be a specific form of emotional dysregulation, especially in regard that it does respond very well to medication. But again, how it fits into emotional dysregulation is completely unclear at this point. It does seem to be something that's really important, though. It is a thing that resonates with a large number of people with ADHD.
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Anorexia nervosa is a gut-wrenching eating disorder that may be linked to the 'blunted' release of a particular chemical in the brain, an animal study suggests. Male mice engineered to harbor a rare genetic variant found in some people with eating disorders (and substance use disorders too) were found to be deficient in a neurotransmitter, called acetylcholine, in a part of the brain, the striatum, involved in learned behaviors, cravings, and reward. Although further validation and human studies are required, the work "identifies a mechanism and a potential treatment to alleviate these severe psychiatric disorders," Mathieu Favier, a neuroscientist at McGill University in Montreal, and colleagues write in their published paper.
Continue Reading.
87 notes
·
View notes
Text

poor mr.silhouette about to get murdered by a ton of bullsquids
anyway heres a size chart with all the bois i have drawn so far
sepiotherium horribilis and striatum are both typically around 330cm long. sepiotherium agilis is around 260cm long and sepiotherium viridis tends to be just 200cm long. lolligosuchus imperator is 550cm long
i havent drawn the olm bullshit yet but that thing is about 15cm max.
#half life#art#my art#doodle#half life 2#halflife fanart#bullsquid#scarlet creaturetag#creatures#creature
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
Preserved in our archive
A research letter from 2022 highlighting the effects of even "mild" covid on the brain.
Dear Editor,
A recent study published in Nature by Douaud and colleagues1 shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with longitudinal effects, particularly on brain structures linked to the olfactory cortex, modestly accelerated reduction in global brain volume, and enhanced cognitive decline. Thus, even mild COVID-19 can be associated with long-lasting deleterious effects on brain structure and function.
Loss of smell and taste are amongst the earliest and most common effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, headaches, memory problems, confusion, or loss of speech and motility occur in some individuals.2 While important progress has been made in understanding SARS-CoV-2-associated neurological manifestations, the underlying mechanisms are under debate and most knowledge stems from analyses of hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19.2 Most infected individuals, however, develop mild to moderate disease and recover without hospitalization. Whether or not mild COVID-19 is associated with long-term neurological manifestations and structural changes indicative of brain damage remained largely unknown.
Douaud and co-workers examined 785 participants of the UK Biobank (www.ukbiobank.ac.uk) who underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) twice with an average inter-scan interval of 3.2 years, and 401 individuals testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection between MRI acquisitions (Fig. 1a). Strengths of the study are the large number of samples, the availability of scans obtained before and after infection, and the multi-parametric quantitative analyses of serial MRI acquisitions.1 These comprehensive and automated analyses with a non-infected control group allowed the authors to dissect consistent brain changes caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection from pre-existing conditions. Altogether, the MRI scan processing pipeline used extracted more than 2,000 features, named imaging-derived phenotypes (IDPs), from each participant’s imaging data. Initially, the authors focused on IDPs involved in the olfactory system. In agreement with the frequent impairment of smell and taste in COVID-19, they found greater atrophy and indicators of increased tissue damage in the anterior cingulate cortex, orbitofrontal cortex and insula, as well as in the ventral striatum, amygdala, hippocampus and para-hippocampal gyrus, which are connected to the primary olfactory cortex (Fig. 1b). Taking advantage of computational models allowing to differentiate changes related to SARS-CoV-2 infection from physiological age-related brain changes (e.g. decreases of brain volume with aging),3 they also explored IDPs covering the entire brain. Although most individuals experienced only mild symptoms of COVID-19, the authors detected an accelerated reduction in whole-brain volume and more pronounced cognitive declines associated with increased atrophy of a cognitive lobule of the cerebellum (crus II) in individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to the control group. These differences remained significant when 15 people who required hospitalization were excluded. Most brain changes for IDPs were moderate (average differences between the two groups of 0.2–2.0%, largest for volume of parahippocampal gyrus and entorhinal cortex) and accelerated brain volume loss was “only” observed in 56–62% of infected participants. Nonetheless, these results strongly suggest that even clinically mild COVID-19 might induce long-term structural alterations of the brain and cognitive impairment.
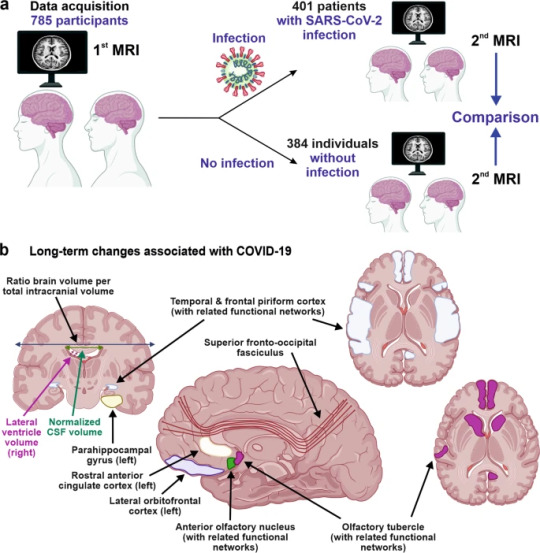
The study provides unique insights into COVID-19-associated changes in brain structure. The authors took great care in appropriately matching the case and control groups, making it unlikely that observed differences are due to confounding factors, although this possibility can never be entirely excluded. The mechanisms underlying these infection-associated changes, however, remain to be clarified. Viral neurotropism and direct infection of cells of the olfactory system, neuroinflammation and lack of sensory input have been suggested as reasons for the degenerative events in olfactory-related brain structures and neurological complications.4 These mechanisms are not mutually exclusive and may synergize in causing neurodegenerative disorders as consequence of COVID-19.
The study participants became infected between March 2020 and April 2021, before the emergence of the Omicron variant of concern (VOC) that currently dominates the COVID-19 pandemic. During that time period, the Alpha and Beta VOCs dominated in the UK and all results were obtained from individuals between 51 and 81 years of age. It will be of great interest to clarify whether Omicron, that seems to be less pathogenic than other SARS-CoV-2 variants, also causes long-term brain damage. The vaccination status of the participants was not available in the study1 and it will be important to clarify whether long-term changes in brain structure also occur in vaccinated and/or younger individuals. Other important questions are whether these structural changes are reversible or permanent and may even enhance the frequency for neurodegenerative diseases that are usually age-related, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. Previous findings suggest that cognitive disorders improve over time after severe COVID-19;5 yet it remains to be determined whether the described brain changes will translate into symptoms later in life such as dementia. Douaud and colleagues report that none of top 10 IDPs correlated significantly with the time interval between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the 2nd MRI acquisition, suggesting that the observed abnormalities might be very long-lasting.
Currently, many restrictions and protective measures are relaxed because Omicron is highly transmissible but usually causes mild to moderate acute disease. This raises hope that SARS-CoV-2 may evolve towards reduced pathogenicity and become similar to circulating coronaviruses causing mild respiratory infections. More work needs to be done to clarify whether the current Omicron and future variants of SARS-CoV-2 may also cause lasting brain abnormalities and whether these can be prevented by vaccination or therapy. However, the finding by Douaud and colleagues1 that SARS-CoV-2 causes structural changes in the brain that may be permanent and could relate to neurological decline is of concern and illustrates that the pathogenesis of this virus is markedly different from that of circulating human coronaviruses. Further studies, to elucidate the mechanisms underlying COVID-19-associated neurological abnormalities and how to prevent or reverse them are urgently needed.
REFERENCES (Follow link)
#public health#wear a mask#covid 19#pandemic#covid#wear a respirator#mask up#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid#covid conscious#covid is airborne
27 notes
·
View notes
Text

by Elizabeth Johnson-Wold
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Striatum and cerebellum as related and damaged partners in Huntington's disease: a matter of vulnerability
In patients with Huntington’s disease, neurons in a part of the brain called the striatum are among the hardest-hit. Degeneration of these neurons contributes to patients’ loss of motor control, which is one of the major hallmarks of the disease. As many as 10 years ahead of the motor diagnosis, Huntington’s patients can experience mood disorders, and one possibility is that the striosomes might…

View On WordPress
#cell cycle#cellular replication#cerebellum#clinical prognosis#dopamine#Huntington disease#neurodegeneration#neuronal damage#neuronal death#striatum#striosomes
0 notes
Text
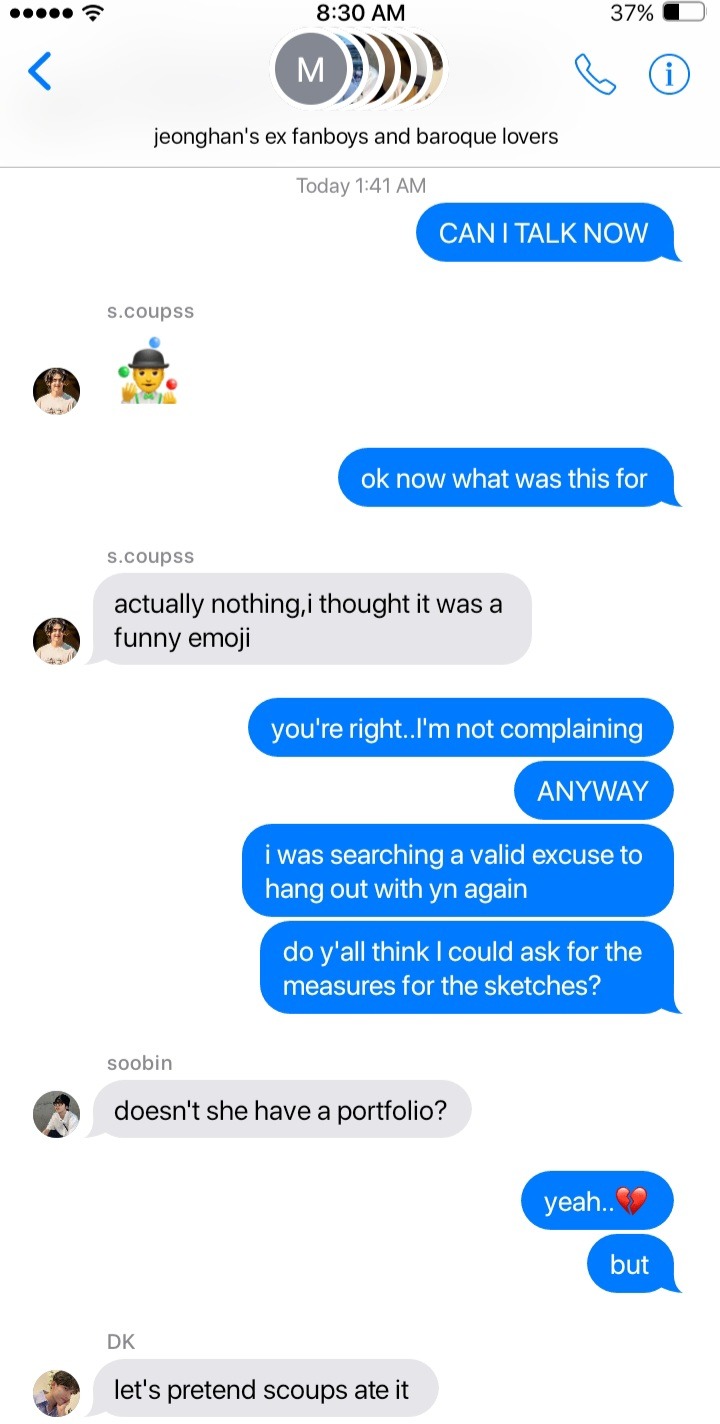
LOVE GUIDE (SAY YES) chap12

yunjin and chaewon were waiting for you to speak, as you sat outside the bathroom door in complete silence. you could even hear your breathing and your heart beating so fast?
on that night, you finally admitted to yourself, and to your best friends that kwon soonyoung was more than just a project partner…
indeed, during the time you spent with him, you noticed that your heart might have skipped a few beats (let's not forget that he fainted after receiving your gifts) and that every time you told him something, he made an extreme effort not to stare mesmerized at your moving lips.
also you could always feel your real happiness when you texted each other at night, and when you couldn't stop laughing together.
your conversations were at ease, and in that short time, you discovered numerous similarities between you two - you understood that he had no idea what "baroque" was; you were similar in many ways, not all.
again, it was during that night that you admitted to your friends that you had let him pretend to be an expert in that art movement just so that you could observe him trying to pronounce the correct name, and show his "deep knowledge" in the days to follow.
you also planned to show your gratitude to him in an indirect way. you were ready to suggest that he also use the concept of animals, keeping in a sketch the tiger's striatum as the main theme (when you had first met, the third thing after his name and a failed pick-up line had been that he loved tigers).
his ability to make you smile and blush had touched your heart, which you had worked so hard to keep safe for fear of the awful consequences. you were afraid that opening yourself to love would end up in a lonely frigid cold; nevertheless, he was able to make you feel a comfortable warmth that seemed endless.
"is this "falling in love"? am I now ready and willing to change myself to be loved? to let the old me die to be reborn and achieve the completeness given by love? should I then take this step, trusting the only way to fully live is to love?"
you had spoken those words all in one breath. so fast that your friends were still looking confused in the first few minutes, they were still trying to understand exactly what you had said.
"All right! I'm thankful you said it out loud girl… you seem to be questioning your existence. However, I can tell you based on my little experience that yes, this is this love," yunjin said.
"that's where you overthink must come from." chaewon added.
they both appeared calm, and such a reassuring smile - you could sense the unconditional love in their gaze.
"anyway…it is not that serious, right?" you uttered, a little afraid of ruining the moment.
you three started laughing and nodding, and rather, the tension in the room dissipated. your anxiety at openly declaring that you liked Hoshi faded, and instead, it was finally starting to give you that satisfying rush of nervousness. the faint thrill you get in the early stages of a crush, when your hopes are as high as the mountains and the sun, a metaphor for love, gets to embrace you close.
"I like him. I like Hoshi."
you instantly chuckled as the girls drew near to you, and hugged you while wearing mock-surprised expressions; many of your worries from the previous few weeks also suddenly disappeared.
it was already late at night, and you were too tired to even consider the possible consequences of a relationship between you and your crush. before the final project, you would have spent many days together, so there was plenty of time for everything to work out, right?

chap11 // chap13 ; m.list
。 ✧ ⁺ 。
summary: It is clear to everyone that Kwon Soon-young has a huge crush on the model student Yn. But can Hoshi, a passionate and funny stylist make her fall in love in just a month? What if he followed a weird LOVE GUIDE, that he found in the school bathroom?
。 ✧ ⁺ 。
a.n. HII after a rlly long break i am back!! hope y'all missed a bit this funny smau, and i hope you will like this chapter. we are slowly reaching the end, but i promise there's still a funny plot twist who's waiting for our protagonists,, (text + 0.6k wc)
taglist(33/50): @alsktudy @kissesfrmwonwoo @marsstarxhwa @haohyo @wonwooz1 @wonwoos-wineparty @mhlsymlysn @nishloves @punkhazardlaw @manooffline @kflixnet @minhui896 @azkahanif @woozixo
@chimmy-bts @luvhuihui @wonraiwoo @keeboismine @teenyfinds @ninetiesbitches @astro-doll-the-star @bangantokchy @meowwyoong @dahbee8 @ivehypnosis @chweverni @miriamxsworld @cottoncheol @caratboy
@gigiiiiislife @isabellah29 @forrhoshi
send an ask or comment under THIS post to be part of it !!
#love guide (say yes)#k labels#seventeen#seventeen x reader#hoshi#hoshi smau#hoshi fluff#hoshi svt#hoshi seventeen#hoshi x reader#hoshi scenario#seventeen hoshi#seventeen smau#svt#svt smau#kwon soonyoung smau#kwon soonyoung fluff#kwon soonyoung x reader#kwon soonyoung#kwon hoshi#svt funny#svt fic#svt scenarios#svt hoshi#hoshi x yn
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Brain pathways that control dopamine release may influence motor control
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/brain-pathways-that-control-dopamine-release-may-influence-motor-control/
Brain pathways that control dopamine release may influence motor control


Within the human brain, movement is coordinated by a brain region called the striatum, which sends instructions to motor neurons in the brain. Those instructions are conveyed by two pathways, one that initiates movement (“go”) and one that suppresses it (“no-go”).
In a new study, MIT researchers have discovered an additional two pathways that arise in the striatum and appear to modulate the effects of the go and no-go pathways. These newly discovered pathways connect to dopamine-producing neurons in the brain — one stimulates dopamine release and the other inhibits it.
By controlling the amount of dopamine in the brain via clusters of neurons known as striosomes, these pathways appear to modify the instructions given by the go and no-go pathways. They may be especially involved in influencing decisions that have a strong emotional component, the researchers say.
“Among all the regions of the striatum, the striosomes alone turned out to be able to project to the dopamine-containing neurons, which we think has something to do with motivation, mood, and controlling movement,” says Ann Graybiel, an MIT Institute Professor, a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research, and the senior author of the new study.
Iakovos Lazaridis, a research scientist at the McGovern Institute, is the lead author of the paper, which appears today in the journal Current Biology.
New pathways
Graybiel has spent much of her career studying the striatum, a structure located deep within the brain that is involved in learning and decision-making, as well as control of movement.
Within the striatum, neurons are arranged in a labyrinth-like structure that includes striosomes, which Graybiel discovered in the 1970s. The classical go and no-go pathways arise from neurons that surround the striosomes, which are known collectively as the matrix. The matrix cells that give rise to these pathways receive input from sensory processing regions such as the visual cortex and auditory cortex. Then, they send go or no-go commands to neurons in the motor cortex.
However, the function of the striosomes, which are not part of those pathways, remained unknown. For many years, researchers in Graybiel’s lab have been trying to solve that mystery.
Their previous work revealed that striosomes receive much of their input from parts of the brain that process emotion. Within striosomes, there are two major types of neurons, classified as D1 and D2. In a 2015 study, Graybiel found that one of these cell types, D1, sends input to the substantia nigra, which is the brain’s major dopamine-producing center.
It took much longer to trace the output of the other set, D2 neurons. In the new Current Biology study, the researchers discovered that those neurons also eventually project to the substantia nigra, but first they connect to a set of neurons in the globus palladus, which inhibits dopamine output. This pathway, an indirect connection to the substantia nigra, reduces the brain’s dopamine output and inhibits movement.
The researchers also confirmed their earlier finding that the pathway arising from D1 striosomes connects directly to the substantia nigra, stimulating dopamine release and initiating movement.
“In the striosomes, we’ve found what is probably a mimic of the classical go/no-go pathways,” Graybiel says. “They’re like classic motor go/no-go pathways, but they don’t go to the motor output neurons of the basal ganglia. Instead, they go to the dopamine cells, which are so important to movement and motivation.”
Emotional decisions
The findings suggest that the classical model of how the striatum controls movement needs to be modified to include the role of these newly identified pathways. The researchers now hope to test their hypothesis that input related to motivation and emotion, which enters the striosomes from the cortex and the limbic system, influences dopamine levels in a way that can encourage or discourage action.
That dopamine release may be especially relevant for actions that induce anxiety or stress. In their 2015 study, Graybiel’s lab found that striosomes play a key role in making decisions that provoke high levels of anxiety; in particular, those that are high risk but may also have a big payoff.
“Ann Graybiel and colleagues have earlier found that the striosome is concerned with inhibiting dopamine neurons. Now they show unexpectedly that another type of striosomal neuron exerts the opposite effect and can signal reward. The striosomes can thus both up- or down-regulate dopamine activity, a very important discovery. Clearly, the regulation of dopamine activity is critical in our everyday life with regard to both movements and mood, to which the striosomes contribute,” says Sten Grillner, a professor of neuroscience at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, who was not involved in the research.
Another possibility the researchers plan to explore is whether striosomes and matrix cells are arranged in modules that affect motor control of specific parts of the body.
“The next step is trying to isolate some of these modules, and by simultaneously working with cells that belong to the same module, whether they are in the matrix or striosomes, try to pinpoint how the striosomes modulate the underlying function of each of these modules,” Lazaridis says.
They also hope to explore how the striosomal circuits, which project to the same region of the brain that is ravaged by Parkinson’s disease, may influence that disorder.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Saks-Kavanaugh Foundation, the William N. and Bernice E. Bumpus Foundation, Jim and Joan Schattinger, the Hock E. Tan and K. Lisa Yang Center for Autism Research, Robert Buxton, the Simons Foundation, the CHDI Foundation, and an Ellen Schapiro and Gerald Axelbaum Investigator BBRF Young Investigator Grant.
#anxiety#author#autism#Behavior#Biology#Brain#Brain and cognitive sciences#brain research#career#cell#cell types#Cells#classical#clusters#Disease#effects#emotion#Foundation#Health#how#human#human brain#it#Labyrinth#learning#life#LISA#Matrix#McGovern Institute#mit
19 notes
·
View notes
Note
I did see your photo and I have been looing for a long time for this one. Do you have bulbs of Gorgonidium striatum?
No, we do not have bulbs of Gorgonidium striatum - and if we did, we would not share them. Gorgonidium striatum is limited to small patches of cloud forest in Bolivia, and although a formal conservation assessment hasn't been done, this species is quite likely endangered. Furthermore, Bolivia has pretty comprehensive laws to protect wild plants from export. Removing and selling parts of G. striatum for anything other than scientific research is unethical and likely illegal.
When it comes to rare plants, unless you are a conducting research with a permit, it is always better to look but not touch - and certainly not take. Given the unusual climatic conditions in this area, this plant would likely simply die if you tried to keep it at home.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Interesting Papers for Week 49, 2024
Psychometrics in experimental psychology: A case for calibration. Bach, D. R. (2024). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 31(4), 1461–1470.
Cellular and circuit architecture of the lateral septum for reward processing. Chen, G., Lai, S., Jiang, S., Li, F., Sun, K., Wu, X., … Zhu, Y. (2024). Neuron, 112(16), 2783-2798.e9.
Prediction-error signals in anterior cingulate cortex drive task-switching. Cole, N., Harvey, M., Myers-Joseph, D., Gilra, A., & Khan, A. G. (2024). Nature Communications, 15, 7088.
An essential role for the latero-medial secondary visual cortex in the acquisition and retention of visual perceptual learning in mice. Consorti, A., Sansevero, G., Di Marco, I., Floridia, S., Novelli, E., Berardi, N., & Sale, A. (2024). Nature Communications, 15, 7322.
Abstract representations emerge in human hippocampal neurons during inference. Courellis, H. S., Minxha, J., Cardenas, A. R., Kimmel, D. L., Reed, C. M., Valiante, T. A., … Rutishauser, U. (2024). Nature, 632(8026), 841–849.
Dopamine biases decisions by limiting temporal integration. Gautham, A. K., Miner, L. E., Franco, M. N., Thornquist, S. C., & Crickmore, M. A. (2024). Nature, 632(8026), 850–857.
Slow ramping emerges from spontaneous fluctuations in spiking neural networks. Gavenas, J., Rutishauser, U., Schurger, A., & Maoz, U. (2024). Nature Communications, 15, 7285.
Task-specific invariant representation in auditory cortex. Heller, C. R., Hamersky, G. R., & David, S. V. (2024). eLife, 12, e89936.3.
Replay-triggered brain-wide activation in humans. Huang, Q., Xiao, Z., Yu, Q., Luo, Y., Xu, J., Qu, Y., … Liu, Y. (2024). Nature Communications, 15, 7185.
Temporal resolution relates to sensory hyperreactivity independently of stimulus detection sensitivity in individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Kaneko, A., Atsumi, T., & Ide, M. (2024). Perception, 53(9), 585–596.
Partial blindness: Visual experience is not rich, but not sparse. Kim, C., & Chong, S. C. (2024). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 31(4), 1558–1569.
Amygdala and Cortex Relationships during Learning of a Sensory Discrimination Task. Levitan, D., & Gilad, A. (2024). Journal of Neuroscience, 44(34), e0125242024.
Slow-wave sleep drives sleep-dependent renormalization of synaptic AMPA receptor levels in the hypothalamus. Liu, J., Niethard, N., Lun, Y., Dimitrov, S., Ehrlich, I., Born, J., & Hallschmid, M. (2024). PLOS Biology, 22(8), e3002768.
How aging shapes our sense of agency. Mariano, M., Kuster, N., Tartufoli, M., & Zapparoli, L. (2024). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 31(4), 1714–1722.
Individual thalamic inhibitory interneurons are functionally specialized toward distinct visual features. Müllner, F. E., & Roska, B. (2024). Neuron, 112(16), 2765-2782.e9.
Predictions enable top-down pattern separation in the macaque face-processing hierarchy. Nigam, T., & Schwiedrzik, C. M. (2024). Nature Communications, 15, 7196.
Signatures of hierarchical temporal processing in the mouse visual system. Rudelt, L., Gonz��lez Marx, D., Spitzner, F. P., Cramer, B., Zierenberg, J., & Priesemann, V. (2024). PLOS Computational Biology, 20(8), e1012355.
Dopamine Release in the Nucleus Accumbens Core Encodes the General Excitatory Components of Learning. Taira, M., Millard, S. J., Verghese, A., DiFazio, L. E., Hoang, I. B., Jia, R., … Sharpe, M. J. (2024). Journal of Neuroscience, 44(35), e0120242024.
Non-invasive stimulation of the human striatum disrupts reinforcement learning of motor skills. Vassiliadis, P., Beanato, E., Popa, T., Windel, F., Morishita, T., Neufeld, E., … Hummel, F. C. (2024). Nature Human Behaviour, 8(8), 1581–1598.
Short-latency preference for faces in primate superior colliculus depends on visual cortex. Yu, G., Katz, L. N., Quaia, C., Messinger, A., & Krauzlis, R. J. (2024). Neuron, 112(16), 2814-2822.e4.
#neuroscience#science#research#brain science#scientific publications#cognitive science#neurobiology#cognition#psychophysics#neurons#neural computation#neural networks#computational neuroscience
14 notes
·
View notes