#interleukin-6
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
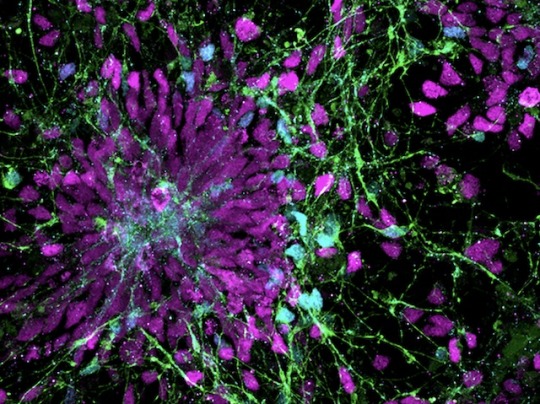
Culture of Disorder
Human neural progenitor cells generated from induced pluripotent stem cells – cells from reprogrammed mature cells – for modelling effects of pro-inflammatory molecule IL-6 released in maternal immune activation, a potential contributor to neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring
Read the published research paper here
Image from work by Kseniia Sarieva and colleagues
Hertie Institute for Clinical Brain Research, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in and cover image of Disease Models & Mechanisms, November 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
https://bundas24.com/read-blog/112096_interleukin-6-il-6-inhibitors-market-size-analysis-and-forecast-2031.html
The Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors Market in 2023 is US$ 33.3 billion, and is expected to reach US$ 77.41 billion by 2031 at a CAGR of 11.12%.
#Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors Market#Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors Market Scope#Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Inhibitors Market Share
0 notes
Text
data analysis is so draining but man i have correlations!!
1 note
·
View note
Text
Reference preserved in our archive
Abstract Background: COVID-19 emerged in December 2019 and rapidly became a global pandemic. It has since been associated with the progression of various endocrine disorders, including thyroid disease. The long-term effects of this interplay have yet to be explored. This review explores the relationship between COVID-19 and thyroid diseases, emphasizing thyroid gland function and the clinical implications for managing thyroid disorders in infected individuals.
Objectives: This narrative review intends to provide insight into the scope of research that future clinical studies may aim to address regarding the long-term effects of COVID-19 infection on thyroid health.
Methods: Keywords including “thyroid disease”, “COVID-19”, and “long-term” were used to search PubMed and Google Scholar for updated and relevant clinical research.
Results: COVID-19 affects the thyroid gland multifacetedly and includes direct viral invasion, immune-mediated damage, and hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis disruption. Approximately 15% of COVID-19 patients experience thyroid dysfunction, which can present as thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, or non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTI). Noteworthy findings include inflammatory thyroiditis. Long-term effects, including those observed in children, include persistent hypothyroidism and exacerbated pre-existing thyroid-autoimmune conditions. Management of thyroid disorders in COVID-19 patients requires consideration: anti-thyroid drug (ATD) therapy used to treat hyperthyroidism in COVID-19 patients may need adjustment to prevent immunosuppression. Radioactive iodine (ROI) alternatives and interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor antagonists could offer potential benefits and should be further explored.
Conclusion: Longitudinal follow-ups post-COVID-19 for patients with new and pre-existing thyroid disorders can improve disease outcomes. In addition, pathophysiological research on thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19 may help develop strategies to prevent and alleviate thyroid gland abnormalities post-COVID-19.
#mask up#pandemic#covid#wear a mask#public health#wear a respirator#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2#long covid
48 notes
·
View notes
Note
The Doctor from Darkwood…


⭐️ The Doctor from Darkwood is a Shar Pei.
Traditionally kept as a property guardian, the shar pei was driven to the brink of extinction in the 20th century. The breed was once very popular, but war and political turmoil in China caused it to nearly disappear in the 1970s. When the Guinness Book of World Records released a book naming it the rarest dog in the world, demand increased in America, and breeders began mixing Shar Pei with other dogs such as bull terriers to sell them to unknowing buyers. This gave them softer mouths, and they became known as “meat-mouth” shar peis while the originals are called “bone-mouth” shar peis. The Shar-pei is predisposed to several skin conditions including: allergic skin disease, cutaneous mucinosis, intertrigo, otitis externa, and vasculopathy, as well as Shar Pei fever, a swelling of the hocks due to more prominent anti-inflammatory genes ( interleukin 6 ). As long as he doesn’t try to lock everyone in a church again, am I right? .. too soon?
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cytokines are so cute, you know those weird numbers you see in medical text? The one you'll likely see around is Interleukin, shortned to IL. The name literally means 'Cell communication', they're chemicals that cells release to speak to one another, depending what interleukin you find in a test, you can deduce what these little guys are planning and doing at the moment
The most common ones are TNF-a (tumor necrosis alpha) and IL-6, both stimulate inflammation in damaged area. Inflammation is just the cells setting up the battlefield, the redness is due to bloodflow in the area bringing more immune cells in, the pain is that sometimes the area increases, pressing onto nerves. It's your body telling you that you need to stop using that part.
IL-6 and TNF-a are the cytokines that the cells use to call one another, kind of a "I need backup here" signal. Some of these cytokines are pyrogenic, which is what we call the ones that go to the brain and tell it to raise body temperature!
You also have interferons (shortned to IFN), those are what cells produce to warn others in a "I'm infected with something, stay away" kind of way, this tells the other cells that they need to protect themselves, it also calls some cells responsible to kill infected cells to do their jobs
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Anemia of Chronic Disease?

Anemia of Chronic Disease (ACD), also known as anemia of inflammation or anemia of inflammation and chronic disease, is a prevalent condition often associated with chronic illnesses that last longer than three months and cause sustained inflammation. This form of anemia is particularly challenging because it not only stems from the chronic disease itself but also exacerbates the overall health burden on affected individuals.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of ACD is closely linked to the body’s inflammatory response. Chronic inflammation, which is a hallmark of many autoimmune diseases and long-term illnesses, significantly alters iron metabolism. Normally, iron is recycled from old red blood cells and used in the production of new ones. However, in ACD, inflammatory cytokines, particularly interleukin-6 (IL-6), stimulate the production of hepcidin, a hormone that regulates iron homeostasis. Hepcidin inhibits iron absorption in the gut and traps iron in macrophages, making it unavailable for red blood cell production, leading to a functional iron deficiency. Additionally, chronic inflammation can suppress erythropoiesis (the production of red blood cells) and reduce the lifespan of existing red blood cells, compounding the severity of anemia.
Epidemiology and Affected Populations
ACD is the second most common type of anemia after iron-deficiency anemia, particularly in populations over the age of 65. It is often seen in individuals with chronic conditions such as cancer, chronic kidney disease (CKD), heart failure, and a range of autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The prevalence of ACD in these populations highlights the importance of understanding and managing this condition effectively to improve overall patient outcomes.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical symptoms of ACD are often subtle and can overlap with those of the underlying chronic disease. Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pallor, shortness of breath, and dizziness. These symptoms may be exacerbated during physical activity. However, the mild nature of ACD symptoms means that the condition is often underdiagnosed or attributed solely to the chronic disease without recognizing the contribution of anemia.
Diagnosis and Laboratory Findings
Diagnosing ACD involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Blood tests are crucial for identifying the characteristic features of ACD, including low hemoglobin levels, normal or elevated serum ferritin (reflecting adequate iron stores), low serum iron, and low transferrin saturation. The reticulocyte count is typically low, indicating reduced erythropoiesis. In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be conducted to assess iron stores directly and rule out other causes of anemia.
Management and Treatment Strategies
The primary approach to managing ACD is to address the underlying chronic condition. Effective treatment of the chronic disease often leads to an improvement in anemia. However, in cases where the anemia is severe or the chronic disease is difficult to control, additional interventions may be necessary. These can include:
Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs): Synthetic forms of erythropoietin (EPO) can be administered to stimulate red blood cell production. This is particularly useful in patients with chronic kidney disease or cancer, where endogenous EPO production is impaired.
2 .Iron Therapy: Although oral iron supplementation is typically less effective in ACD due to hepcidin-induced iron sequestration, intravenous iron therapy may be beneficial, particularly when combined with ESAs.
3 .Blood Transfusions: In cases of severe anemia, blood transfusions may be required to rapidly increase hemoglobin levels. However, this is generally considered a short-term solution due to the potential risks of iron overload and transfusion-related complications.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications
While ACD itself may not be preventable due to its association with chronic diseases, patients can take steps to support overall health and potentially mitigate the severity of anemia. A balanced diet rich in iron (from sources such as lean meats and dark leafy greens), folate, vitamin B12, and vitamin C can support healthy red blood cell production. Regular monitoring of iron levels and timely medical intervention are essential in managing ACD effectively.
In conclusion, Anemia of Chronic Disease is a complex condition that requires a broad approach to diagnosis and management. Understanding the interplay between chronic inflammation and iron metabolism is key to effectively treating this form of anemia. Through careful management of the underlying disease and appropriate use of adjunct therapies, healthcare providers can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of this condition.
As academic students and researchers navigate the challenges of their assignments and research endeavors, Expert Academic Assignment Help stands ready to provide professional guidance and assistance. Whether you require support with assignment writing, research paper assistance, or essay help, our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve academic excellence. Reach out to us today at [email protected] and let us support you on your academic journey. We wish you success and professional excellence.
#assignment help#medical students#healthcare#nursing school#nursing student#medicine#medical help#university student#medical university#university life#university#academic assignments#studying#student life#study blog#study inspiration#studyblr community#clinicalstudy#clinical research#phd research#research paper#pharmacy student#pharmacology
1 note
·
View note
Text
Millions missing
Knapp 1 1/2 Jahre sind vergangen, seit dem ersten Verdacht, an ME/CFS erkrankt zu sein. Und dem langsamen Verschwinden, aus meinem eigenen Leben.
Kurze Zeit später fand ich raus, dass überdurchschnittlich viele, eine positive EBV Anamnese haben. Ein Virus, das meiner Meinung nach jahrzehntelang unterschätzt wurde. Dabei setzt diese Erkrankung so viele von uns, völlig außer Gefecht und befördert einige ins Krankenhaus, wie auch mich, damals mit 13 Jahren.
Angegriffene Organe, der gesamte Organismus völlig aus dem Gleichgewicht. Lebenslanges Risiko der Reaktivierung, Chronifizierung und mögliche Ursache, einer am Ende unheilbaren Erkrankung. Aber wer hätte das schon ahnen können? Am allerwenigsten ich selbst.
8 Monate, seit ich geschwächt bei meiner Hausärztin saß und ihr berichtete, dass ich nach einem schweren, aber unklaren Infekt im Sommer 2020, nicht wieder auf die Beine kam; dass ich mich mittlerweile seit Monaten krank fühle. Tägliche Grippesymptome, neurologische und motorische Ausfälle, eine bleierne Erschöpfung und starke Schmerzen.
Sie hat mich nicht ernst genommen. Der Klassiker. Schließlich war ich untergewichtig und steckte wieder tief in der Essstörung.
Für sie war mein Fall völlig klar.
Thema abgeschlossen.
Für mich allerdings nicht.
Ich kämpfte mich wieder raus aus dem Untergewicht, aber nichts hat sich dadurch verändert oder gar verbessert. Denn ich wusste, dass mit meinem Körper etwas nicht stimmt. Ich konnte es spüren.
6 Monate, seit ich mir eingestehen musste, dass mein altes Leben, so wie ich es kannte, nicht mehr existiert.
Der Versuch eine Balance zu finden zwischen Ärzte-Odyssee, Ausschlussdiagnostik und „das bildest du dir doch eh bloß ein“ Gedanken in meinem verdrehten Kopf.
3 Monate, seit ich einen anderen Arzt fand, der sich auskennt und vor allem: der mich ernst nahm.
1 Monat, seit der immunologischen Laboruntersuchung und den erschreckenden Ergebnissen mit erhöhten GPCR Autoantikörper, Interleukin Werten und dem eindeutigen Nachweis, einer Autoimmunreaktion.
3 Wochen, seit der offiziellen ME/CFS Diagnose meines Arztes, der von Anfang an wusste, dass ich zwar eine ganze Palette an psychischen Erkrankungen mitbringe, aber das akute Problem, eindeutig körperlicher Natur ist.
Seit dem. Steht alles still.
Denn mit der Diagnose, kam die Depression. Die nackte Angst, die pure Verzweiflung.
Nie war mein Blogname passender. Aber diesmal, gibt es kein Weg raus. Die auszeitstille, ist nicht mehr nur eine Auszeit. Die Stille wird bleiben, so lange, bis die Politik endlich hinsieht. Wir brauchen Forschung, Akzeptanz, Therapie und bitte bitte bitte irgendwann eine Heilung.
Egal wer das hier liest: bitte sieh hin, werde laut. Erkundige dich über ME/CFS, kläre auf und trage unsere Botschaft in die Welt hinaus. Wir sind sichtbar, wir wollen leben.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Neuromyelitis optica "taken out of Breg": lymphocyte and cytokine signatures will grant the treatment conditions
No autoimmune diseases can currently be cured, only treated, and this is also true for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NEMOSD). Neuromyelitis optica disorder spectrum is one of them and it causes inflammation of the central nervous system, leading to vision and sensory loss, weakness and bladder dysfunction. The condition, which sometimes flares up in waves, has a treatment consisting of…
View On WordPress
#autoimmune disease#B lymphocytes#interleukin-10#interleukin-6#monoclonal antibody#neuromyelitis optica#satralizumab
0 notes
Text
Tofacitinib mechanism of action
Tofacitinib is a medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases, primarily rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis. Its mechanism of action involves targeting specific molecules and pathways in the immune system to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response. Here's an overview of how tofacitinib works:
Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibition: Tofacitinib drug belongs to a class of known as Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors. JAKs are enzymes that play a crucial role in transmitting signals within immune cells. By inhibiting specific JAK enzymes, tofacitinib interferes with the signaling pathways that lead to inflammation and immune system activation.
Cytokine Inhibition: JAK enzymes are involved in the signaling of various cytokines, which are small proteins that regulate immune responses. Tofacitinib primarily inhibits JAK1 and JAK3, which are associated with signaling by cytokines like interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-7 (IL-7), interleukin-15 (IL-15), and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). By blocking these cytokine signals, tofacitinib helps reduce inflammation and control immune system activity.
Immune System Modulation: Tofacitinib helps modulate the immune response by reducing the activity of certain immune cells, particularly T cells and B cells, which are involved in autoimmune diseases. It can also affect other immune cells like natural killer (NK) cells and dendritic cells.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Motivation Drain
When a person feels ill, their mental and physical motivation can often diminish. Short term, such feelings may be beneficial, promoting rest and recuperation. But, with chronic illnesses, the reduced motivation may develop into severe apathy and depression – an extreme version of this being seen in cancer patients with cachexia (wasting syndrome). Recently, scientists have identified the brain circuitry behind this illness-induced motivation slump. Using a mouse model of cachexia, they showed that the neurons (green) of a brain region called the area postrema (pictured) were responsive to interleukin 6 – an inflammatory cytokine (type of small protein) found at unusually high levels in cachexia. In turn, these neurons inhibited the release of the feel-good factor dopamine in a key part of the brain’s reward system – thus sapping the animals’ drive. Importantly, blocking this inflammation-neuronal circuitry, restored motivation in the cachectic mice, providing hope that such a strategy might benefit cancer patients too.
Written by Ruth Williams
Image by Aelita Zhu, Washington University in St. Louis - from work by Xiaoyue Aelita Zhu (朱晓悦) & Sarah Starosta et al
Department of Neuroscience, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA
Image copyright held by Washington University in St. Louis
Research published in Science, April 2025
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter, Facebook and Bluesky
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
From the article:
The American Academy of Pediatrics FALSELY states that “Vaccines are not associated with autism.”
Following is a list of abstracts from 212 papers demonstrating the multiple associations between vaccines and autism.
Autism is a largely immune mediated condition, and the purpose of a vaccine is to change the behavior of the immune system. Vaccines and their ingredients can cause the underlying medical conditions that are commonly found in children who have been given an autism diagnosis. These conditions include immune system impairment, autoimmune conditions, neuroinflammation, gastrointestinal damage, neurological regression, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, glial cell activation, interleukin-6 secretion dysregulation, damage to the blood–brain barrier, seizures, dendritic cell dysfunction, mercury poisoning, aluminum toxicity, gene activation and alteration, glutathione depletion, impaired methylation, impaired thioredoxin regulation, impairment of the opioid system, cellular apoptosis, endocrine dysfunction, and other disorders.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
"Just a cold" that increases intercranial abnormalities
By Nikhil Prasad
Medical News: A groundbreaking study conducted at San Marco University Hospital in Catania, Sicily, Italy, has revealed new insights into the potential impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on newborns. Researchers from this hospital and the University of Ferrara carried out an ultrasonographic analysis on newborns exposed to the virus, highlighting a significant incidence of minor intracranial abnormalities compared to unexposed infants. The findings raise important questions about the long-term neurological implications for children born during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Study at a Glance This Medical News report delves into the research conducted by Bruna Scalia, Marco Andrea Nicola Saporito, and their colleagues, investigating cranial ultrasonography (cUS) findings in infants born to mothers who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy or at delivery. The team analyzed data from 278 newborns, evenly split between exposed and unexposed cohorts. The study adhered to stringent observational protocols to ensure the reliability of results.
Key Findings Among the 139 newborns exposed to SARS-CoV-2, 23% exhibited intracranial abnormalities on cUS, compared to 16.5% in the unexposed group. Minor abnormalities were most prevalent and included subependymal cysts (SEPCs), choroid plexus cysts (CPCs), frontal horn cysts (FHCs), and lenticulostriate vasculopathy (LV). Major abnormalities, such as cerebellar hemorrhages and arachnoid cysts, were rare but noteworthy.
Interestingly, infants exposed to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy had a higher rate of abnormalities (38.4%) than those exposed at birth (19.5%). The second trimester emerged as a particularly critical period, with the majority of abnormalities observed in this subgroup.
Why These Findings Matter The study's results are alarming for public health professionals and expectant mothers. While SARS-CoV-2's immediate risks to newborns have been considered minimal, this research suggests subtle yet significant neurological effects. These abnormalities, although classified as minor, may carry long-term implications for cognitive and behavioral development.
The link between maternal inflammation and fetal development is not new, but the cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2 appears to heighten this risk. The researchers hypothesize that inflammatory markers like interleukin-6 could cross the placenta, affecting the fetal brain and potentially disrupting synaptogenesis.
Methodology Details All newborns in the study underwent cranial ultrasonography within their first week of life. The scans were conducted using standardized equipment by experienced neonatologists. The findings were categorized as normal, minor, or major abnormalities. To exclude confounding factors, the study excluded infants with other infections or genetic disorders.
Demographic factors, such as gestational age and birth weight, were comparable across both groups. However, premature birth and maternal complications, such as gestational diabetes and hypertension, were noted as potential contributors to the observed abnormalities.
Implications for Future Research The findings call for more extensive, longitudinal studies to understand the long-term effects of these abnormalities. Current evidence suggests a potential association between minor abnormalities like SEPCs and neuropsychiatric conditions such as autism and ADHD. Further investigation could clarify whether these cUS findings are precursors to such outcomes.
What Experts Are Saying The study's authors emphasize caution, noting that minor intracranial abnormalities do not necessarily predict adverse outcomes. However, they recommend routine cranial ultrasonography for newborns exposed to SARS-CoV-2 as a precautionary measure. "The cost-effectiveness and non-invasive nature of cUS make it a valuable tool in monitoring these infants," said lead researcher Bruna Scalia.
Limitations and Strengths of the Study One limitation of the study was its relatively small sample size, particularly for subgroups like prenatally exposed infants. Additionally, the lack of serological testing for unexposed mothers could have introduced undetected cases into the control group. However, the study's rigorous methodology and use of a well-matched control group lend credibility to its conclusions.
Study Conclusions The research underscores a statistically significant increase in minor intracranial abnormalities among SARS-CoV-2-exposed newborns. These findings are particularly pronounced in infants exposed during the second trimester of pregnancy. While the abnormalities observed in the study were predominantly minor, their potential impact on long-term neurological outcomes cannot be overlooked. The researchers advocate for the following:
-Routine cUS Screening: Cranial ultrasonography should be performed on all newborns exposed to SARS-CoV-2 to identify abnormalities early.
-Long-Term Follow-Up: Exposed infants should be enrolled in neurodevelopmental follow-up programs to monitor their progress and intervene if necessary.
-Expanded Research: Larger, multicenter studies are needed to confirm these findings and explore the mechanisms behind SARS-CoV-2's impact on fetal brain development.
By highlighting these abnormalities, the study adds a critical layer to our understanding of COVID-19's broader implications, particularly for future generations.
The study findings were published in the peer-reviewed Italian Journal of Pediatrics. link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13052-024-01826-3
#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#wear a respirator#covid#covid 19#still coviding#coronavirus#sars cov 2
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Autoimmune Registry adds Long COVID to its List of Diseases
The Autoimmune Registry has determined that biomarkers of immune system activity similar to those seen in many autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases justify the inclusion of Long COVID on its list of diseases.
High levels of antibodies to the immune-system proteins called type I interferons (IFNs) have been associated with severe COVID-19. Other studies have shown that severely ill patients tend to have a high concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6, compared to those who are moderately ill.
The Autoimmune Registry has decided to include Long COVID in its list of autoimmune diseases to support research into this emerging chronic condition.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Bioanalysis in Immunology: Monitoring Immune Responses to New Treatments

In recent years, the field of immunology has witnessed a transformative evolution, driven by the rise of biologics, cell and gene therapies, monoclonal antibodies, and personalized immunotherapies. These advancements offer powerful tools in the treatment of cancer, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and allergies. However, they also demand rigorous and precise evaluation of immune responses during clinical development. This is where clinical bioanalysis plays a critical role.
Clinical bioanalysis in immunology enables the quantification and characterization of drug concentrations, biomarkers, and immunogenicity-related factors in biological matrices. It helps researchers and clinicians monitor how the immune system responds to new treatments, ensuring both efficacy and safety.
Understanding Clinical Bioanalysis in the Context of Immunology
Clinical bioanalysis refers to the scientific discipline focused on the measurement of drugs, biological molecules, and biomarkers in human samples. In immunology, the focus expands to include:
Cytokines and chemokines (signaling proteins)
Antibody levels (therapeutic and anti-drug antibodies)
T-cell and B-cell markers
Immune complexes
Inflammatory mediators
Vaccine titers and immune memory markers
The goal is to obtain a comprehensive profile of how the immune system is activated, suppressed, or altered in response to therapeutic intervention.
Key Applications of Clinical Bioanalysis in Immunological Studies
1. Monitoring Therapeutic Antibody Levels
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are increasingly used in autoimmune diseases and cancer immunotherapy. Clinical bioanalysis quantifies circulating mAb concentrations to ensure that therapeutic levels are achieved and maintained.
LC-MS/MS and ligand-binding assays (LBAs) such as ELISA or electrochemiluminescence (ECL) are commonly used to quantify antibodies in serum or plasma.
Accurate measurement guides dose adjustments and supports pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) analyses.
2. Immunogenicity Assessment
One of the biggest challenges in immunological treatments is the potential for the body to generate anti-drug antibodies (ADAs), which can reduce drug efficacy or cause adverse effects.
Clinical bioanalysis helps detect binding and neutralizing ADAs using multi-tiered testing approaches.
Screening assays identify the presence, confirmatory assays verify specificity, and neutralization assays assess functional impact.
Immunogenicity profiling is critical for regulatory approval of biologics and biosimilars.
3. Biomarker Monitoring for Treatment Efficacy
Biomarkers such as interleukins (e.g., IL-6, IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) are indicators of immune activation or suppression.
Elevated cytokine levels may suggest an inflammatory response, cytokine release syndrome, or efficacy in activating immune cells.
Clinical bioanalysis enables multiplex detection of biomarkers to evaluate the immune landscape in real time.
4. Cellular Immune Response Analysis
Clinical bioanalysis also extends to flow cytometry and immunophenotyping methods to track immune cell populations:
T-cell and B-cell profiling helps assess vaccine responses or immune checkpoint therapy effectiveness.
Natural Killer (NK) cell activity, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and dendritic cells are often monitored in immuno-oncology studies.
These insights allow researchers to tailor immunotherapies for better patient outcomes.
5. Vaccine Development and Evaluation
Vaccines rely on generating strong and lasting immune responses. Clinical bioanalysis evaluates:
Antibody titers post-vaccination (e.g., IgG, IgM)
Neutralization assays to assess protection
Cell-mediated responses, including T-cell activation and memory formation
This data is vital for selecting appropriate formulations, adjuvants, and dosing schedules.
Analytical Techniques Used in Immunological Bioanalysis
Ligand-Binding Assays (ELISA, MSD, Gyrolab): For quantification of proteins, cytokines, and antibodies.
Flow Cytometry: For immune cell enumeration and phenotyping.
Luminex Multiplexing: For the simultaneous detection of multiple cytokines or biomarkers in one sample.
qPCR and RT-PCR: For measuring gene expression related to immune pathways.
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR): For binding kinetics and affinity analysis of antibodies.
Each technique is selected based on sensitivity, specificity, throughput needs, and nature of the therapeutic being analyzed.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH have issued clear guidance on clinical bioanalysis, especially regarding biologics and immunogenicity assessment:
FDA’s Immunogenicity Testing Guidance (2019) outlines strategies for ADA testing, cut point determination, and assay validation.
Bioanalytical method validation must adhere to GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) and ensure parameters such as accuracy, precision, specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility are met.
Proper documentation and data integrity are essential for regulatory submissions and clinical trial approvals.
Challenges in Clinical Bioanalysis for Immunology
Despite technological advancements, several challenges persist:
High Biological Variability: Immune responses vary widely between individuals, complicating biomarker interpretation.
Matrix Interference: Biological samples such as serum or plasma can interfere with assay specificity, especially in multiplex setups.
Assay Sensitivity: Detecting low concentrations of cytokines or ADAs requires ultra-sensitive platforms, which must be rigorously validated.
Stability Issues: Immune proteins may degrade over time, necessitating careful sample handling and storage.
Addressing these challenges requires robust assay design, quality control measures, and continuous method optimization.
The Future of Clinical Bioanalysis in Immunology
As immunology becomes more central to precision medicine, the demand for high-quality bioanalytical data is increasing. Future developments include:
Automation and AI-driven analytics for faster, more accurate data interpretation.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) integrated with immune profiling.
Digital biomarker platforms for remote patient monitoring and real-time immune surveillance.
Personalized immuno-monitoring kits for at-home use in chronic immunotherapies.
These innovations promise to enhance the granularity and accessibility of immune response data in clinical research.
Conclusion
In the era of precision immunotherapy and advanced biologics, clinical bioanalysis is not just a supporting discipline—it is a cornerstone of immunological research and therapeutic development. By enabling the accurate measurement of immune responses, it allows scientists and clinicians to understand treatment effects, ensure safety, optimize dosing, and demonstrate efficacy.
As the immunology landscape continues to evolve, clinical bioanalysis will remain vital in ensuring that new treatments are not only effective but also immunologically safe and tailored to individual patient needs.
1 note
·
View note