#public sector regulations
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Government Imposes Strict Ban on Social Media Use by Civil Servants
Islamabad: The government has imposed a significant ban on the use of social media by civil servants, prohibiting them from using any media platforms without explicit permission. This new regulation was communicated through an official directive from the Establishment Division, instructing federal secretaries and other relevant authorities to ensure strict compliance.According to the directive,…
#civil servants#disciplinary action#Establishment Division#Government ban#information security#official directive#Pakistan government#public sector regulations#social media policy#social media restrictions
0 notes
Text
so: masking: good, unequivocally. please mask and please educate others on why they should mask to make the world safer for immune compromised people to participate in.
however: masking is not my policy focus and it shouldn't be yours, either. masking is a very good mitigation against droplet-born illnesses and a slightly less effective (but still very good) mitigation against airborne illnesses, but its place in the pyramid of mitigation demands is pretty low, for several reasons:
it's an individual mitigation, not a systemic one. the best mitigations to make public life more accessible affect everyone without distributing the majority of the effort among individuals (who may not be able to comply, may not have access to education on how to comply, or may be actively malicious).
it's a post-hoc mitigation, or to put it another way, it's a band-aid over the underlying problem. even if it was possible to enforce, universal masking still wouldn't address the underlying problem that it is dangerous for sick people and immune compromised people to be in the same public locations to begin with. this is a solvable problem! we have created the societal conditions for this problem!
here are my policy focuses:
upgraded air filtration and ventilation systems for all public buildings. appropriate ventilation should be just as bog-standard as appropriately clean running water. an indoor venue without a ventilation system capable of performing 5 complete air changes per hour should be like encountering a public restroom without any sinks or hand sanitizer stations whatsoever.
enforced paid sick leave for all employees until 3-5 days without symptoms. the vast majority of respiratory and food-borne illnesses circulate through industry sectors where employees come into work while experiencing symptoms. a taco bell worker should never be making food while experiencing strep throat symptoms, even without a strep diagnosis.
enforced virtual schooling options for sick students. the other vast majority of respiratory and food-borne illnesses circulate through schools. the proximity of so many kids and teenagers together indoors (with little to no proper ventilation and high levels of physical activity) means that if even one person comes to school sick, hundreds will be infected in the following few days. those students will most likely infect their parents as well. allowing students to complete all readings and coursework through sites like blackboard or compass while sick will cut down massively on disease transmission.
accessible testing for everyone. not just for COVID; if there's a test for any contagious illness capable of being performed outside of lab conditions, there should be a regulated option for performing that test at home (similar to COVID rapid tests). if a test can only be performed under lab conditions, there should be a government-subsidized program to provide free of charge testing to anyone who needs it, through urgent cares and pharmacies.
the last thing to note is that these things stack; upgraded ventilation systems in all public buildings mean that students and employees get sick less often to begin with, making it less burdensome for students and employees to be absent due to sickness, and making it more likely that sick individuals will choose to stay home themselves (since it's not so costly for them).
masking is great! keep masking! please use masking as a rhetorical "this is what we can do as individuals to make public life safer while we're pushing for drastic policy changes," and don't get complacent in either direction--don't assume that masking is all you need to do or an acceptable forever-solution, and equally, don't fall prey to thinking that pushing for policy change "makes up" for not masking in public. it's not a game with scores and sides; masking is a material thing you can do to help the individual people you interact with one by one, and policy changes are what's going to make the entirety of public life safer for all immune compromised people.
#dyspunktional#cripple punk#actually disabled#cripplepunk#a lot of these are major concessions for me personally as i'm an anarchist and loathe to support further concentrations of state power#but if you're gonna be operating within the structure of the system. here you go. handing you a cheat sheet for what you should demand.
12K notes
·
View notes
Text
The CFPB is genuinely making America better, and they're going HARD

On June 20, I'm keynoting the LOCUS AWARDS in OAKLAND.

Let's take a sec here and notice something genuinely great happening in the US government: the Consumer Finance Protection Bureau's stunning, unbroken streak of major, muscular victories over the forces of corporate corruption, with the backing of the Supreme Court (yes, that Supreme Court), and which is only speeding up!
A little background. The CFPB was created in 2010. It was Elizabeth Warren's brainchild, an institution that was supposed to regulate finance from the perspective of the American public, not the American finance sector. Rather than fighting to "stabilize" the financial sector (the mission that led to Obama taking his advisor Timothy Geithner's advice to permit the foreclosure crisis to continue in order to "foam the runways" for the banks), the Bureau would fight to defend us from bankers.
The CFPB got off to a rocky start, with challenges to the unique system of long-term leadership appointments meant to depoliticize the office, as well as the sudden resignation of its inaugural boss, who broke his promise to see his term through in order to launch an unsuccessful bid for political office.
But after the 2020 election, the Bureau came into its own, when Biden poached Rohit Chopra from the FTC and put him in charge. Chopra went on a tear, taking on landlords who violated the covid eviction moratorium:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/04/20/euthanize-rentier-enablers/#cfpb
Then banning payday lenders' scummiest tactics:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/01/29/planned-obsolescence/#academic-fraud
Then striking at one of fintech's most predatory grifts, the "earned wage access" hustle:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/01/usury/#tech-exceptionalism
Then closing the loophole that let credit reporting bureaus (like Equifax, who doxed every single American in a spectacular 2019 breach) avoid regulation by creating data brokerage divisions and claiming they weren't part of the regulated activity of credit reporting:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/16/the-second-best-time-is-now/#the-point-of-a-system-is-what-it-does
Chopra went on to promise to ban data-brokers altogether:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/13/goulash/#material-misstatement
Then he banned comparison shopping sites where you go to find the best bank accounts and credit cards from accepting bribes and putting more expensive options at the top of the list. Instead, he's requiring banks to send the CFPB regular, accurate lists of all their charges, and standing up a federal operated comparison shopping site that gives only accurate and honest rankings. Finally, he's made an interoperability rule requiring banks to let you transfer to another institution with one click, just like you change phone carriers. That means you can search an honest site to find the best deal on your banking, and then, with a single click, transfer your accounts, your account history, your payees, and all your other banking data to that new bank:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/21/let-my-dollars-go/#personal-financial-data-rights
Somewhere in there, big business got scared. They cooked up a legal theory declaring the CFPB's funding mechanism to be unconstitutional and got the case fast-tracked to the Supreme Court, in a bid to put Chopra and the CFPB permanently out of business. Instead, the Supremes – these Supremes! – upheld the CFPB's funding mechanism in a 7-2 ruling:
https://www.scotusblog.com/2024/05/supreme-court-lets-cfpb-funding-stand/
That ruling was a starter pistol for Chopra and the Bureau. Maybe it seemed like they were taking big swings before, but it turns out all that was just a warmup. Last week on The American Prospect, Robert Kuttner rounded up all the stuff the Bureau is kicking off:
https://prospect.org/blogs-and-newsletters/tap/2024-06-07-window-on-corporate-deceptions/
First: regulating Buy Now, Pay Later companies (think: Klarna) as credit-card companies, with all the requirements for disclosure and interest rate caps dictated by the Truth In Lending Act:
https://www.skadden.com/insights/publications/2024/06/cfpb-applies-credit-card-rules
Next: creating a registry of habitual corporate criminals. This rogues gallery will make it harder for other agencies – like the DOJ – and state Attorneys General to offer bullshit "delayed prosecution agreements" to companies that compulsively rip us off:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/about-us/newsroom/cfpb-creates-registry-to-detect-corporate-repeat-offenders/
Then there's the rule against "fine print deception" – which is when the fine print in a contract lies to you about your rights, like when a mortgage lender forces you waive a right you can't actually waive, or car lenders that make you waive your bankruptcy rights, which, again, you can't waive:
https://www.consumerfinance.gov/about-us/newsroom/cfpb-warns-against-deception-in-contract-fine-print/
As Kuttner writes, the common thread running through all these orders is that they ban deceptive practices – they make it illegal for companies to steal from us by lying to us. Especially in these dying days of class action suits – rapidly becoming obsolete thanks to "mandatory arbitration waivers" that make you sign away your right to join a class action – agencies like the CFPB are our only hope of punishing companies that lie to us to steal from us.
There's a lot of bad stuff going on in the world right now, and much of it – including an active genocide – is coming from the Biden White House.
But there are people in the Biden Administration who care about the American people and who are effective and committed fighters who have our back. What's more, they're winning. That doesn't make all the bad news go away, but sometimes it feels good to take a moment and take the W.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/10/getting-things-done/#deliverism
#pluralistic#cfpb#consumer finance protection board#rohit chopra#scotus#bnpl#buy now pay later#repeat corporate offenders#fine print deception#whistleblowing#elizabeth warren
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
More good things the Biden administration is doing: OSHA heat safety rules for workers
Remember when Texas and Florida passed laws preventing local and municipal governments from implementing their own heat safety rules and said that if heat is such a big problem, OSHA should make rules that apply to everyone? If not, NPR can remind you. OSHA has now accepted the challenge, moving much faster than they usually do:
OSHA National News Release U.S. Department of Labor July 2, 2024 Biden-Harris administration announces proposed rule to protect indoor, outdoor workers from extreme heat WASHINGTON – The U.S. Department of Labor has released a proposed rule with the goal of protecting millions of workers from the significant health risks of extreme heat. If finalized, the proposed rule would help protect approximately 36 million workers in indoor and outdoor work settings and substantially reduce heat injuries, illnesses, and deaths in the workplace. Heat is the leading cause of weather-related deaths in the U.S. Excessive workplace heat can lead to heat stroke and even death. While heat hazards impact workers in many industries, workers of color have a higher likelihood of working in jobs with hazardous heat exposure. “Every worker should come home safe and healthy at the end of the day, which is why the Biden-Harris administration is taking this significant step to protect workers from the dangers posed by extreme heat,” said Acting Secretary of Labor Julie Su. “As the most pro-worker administration in history, we are committed to ensuring that those doing difficult work in some of our economy’s most critical sectors are valued and kept safe in the workplace.” The proposed rule would require employers to develop an injury and illness prevention plan to control heat hazards in workplaces affected by excessive heat. Among other things, the plan would require employers to evaluate heat risks and — when heat increases risks to workers — implement requirements for drinking water, rest breaks and control of indoor heat. It would also require a plan to protect new or returning workers unaccustomed to working in high heat conditions. “Workers all over the country are passing out, suffering heat stroke and dying from heat exposure from just doing their jobs, and something must be done to protect them,” said Assistant Secretary for Occupational Safety and Health Douglas L. Parker. “Today’s proposal is an important next step in the process to receive public input to craft a ‘win-win’ final rule that protects workers while being practical and workable for employers.” Employers would also be required to provide training, have procedures to respond if a worker is experiencing signs and symptoms of a heat-related illness, and take immediate action to help a worker experiencing signs and symptoms of a heat emergency. The public is encouraged to submit written comments on the rule once it is published in the Federal Register. The agency also anticipates a public hearing after the close of the written comment period. More information will be available on submitting comments when the rule is published. In the interim, OSHA continues to direct significant existing outreach and enforcement resources to educate employers and workers and hold businesses accountable for violations of the Occupational Safety and Health Act’s general duty clause, 29 U.S.C. § 654(a)(1) and other applicable regulations. Record-breaking temperatures across the nation have increased the risks people face on-the-job, especially in summer months. Every year, dozens of workers die and thousands more suffer illnesses related to hazardous heat exposure that, sadly, are most often preventable. The agency continues to conduct heat-related inspections under its National Emphasis Program – Outdoor and Indoor Heat-Related Hazards, launched in 2022. The program inspects workplaces with the highest exposures to heat-related hazards proactively to prevent workers from suffering injury, illness or death needlessly. Since the launch, OSHA has conducted more than 5,000 federal heat-related inspections. In addition, the agency is prioritizing programmed inspections in agricultural industries that employ temporary, nonimmigrant H-2A workers for seasonal labor. These workers face unique vulnerabilities, including potential language barriers, less control over their living and working conditions, and possible lack of acclimatization, and are at high risk of hazardous heat exposure.
#biden harris administration#biden administration#osha#heat safety#worker safety#biden 2024#biden harris 2024#vote for democrats#vote blue#vote biden#us politics#us law
981 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a world flush with hazardous air pollutants, there is one that causes far more cancer than any other, one that is so widespread that nobody in the United States is safe from it.
It is a chemical so pervasive that a new analysis by ProPublica found it exposes everyone to elevated risks of developing cancer no matter where they live. And perhaps most worrisome, it often poses the greatest risk in the one place people feel safest: inside their homes.
As the backbone of American commerce, formaldehyde is a workhorse in major sectors of the economy, preserving bodies in funeral homes, binding particleboards in furniture and serving as a building block in plastic. The risk isn’t just to the workers using it; formaldehyde threatens everyone as it pollutes the air we all breathe and leaks from products long after they enter our homes. It is virtually everywhere.
Federal regulators have known for more than four decades that formaldehyde is toxic, but their attempts to limit the chemical have been repeatedly thwarted by the many companies that rely on it.
This year, the Biden administration finally appeared to make some progress. The Environmental Protection Agency is expected to take a step later this month toward creating new rules that could restrict formaldehyde.
But the agency responsible for protecting the public from the harms of chemicals has significantly underestimated the dangers posed by formaldehyde, a ProPublica investigation has found.
205 notes
·
View notes
Text
Things Biden and the Democrats did, this week #10
March 15-22 2024
The EPA announced new emission standards with the goal of having more than half of new cars and light trucks sold in the US be low/zero emission by 2032. One of the most significant climate regulations in the nation’s history, it'll eliminate 7 billion tons of CO2 emissions over the next 30 years. It's part of President Biden's goal to cut greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030 on the road to eliminating them totally by 2050.
President Biden canceled nearly 6 Billion dollars in student loan debt. 78,000 borrowers who work in public sector jobs, teachers, nurses, social workers, firefighters etc will have their debt totally forgiven. An additional 380,000 public service workers will be informed that they qualify to have their loans forgiven over the next 2 years. The Biden Administration has now forgiven $143.6 Billion in student loan debt for 4 million Americans since the Supreme Court struck down the original student loan forgiveness plan last year.
Under Pressure from the administration and Democrats in Congress Drugmaker AstraZeneca caps the price of its inhalers at $35. AstraZeneca joins rival Boehringer Ingelheim in capping the price of inhalers at $35, the price the Biden Admin capped the price of insulin for seniors. The move comes as the Federal Trade Commission challenges AstraZeneca’s patents, and Senator Bernie Sanders in his role as Democratic chair of the Senate Health Committee investigates drug pricing.
The Department of Justice sued Apple for being an illegal monopoly in smartphones. The DoJ is joined by 16 state attorneys general. The DoJ accuses Apple of illegally stifling competition with how its apps work and seeking to undermining technologies that compete with its own apps.
The EPA passed a rule banning the final type of asbestos still used in the United States. The banning of chrysotile asbestos (known as white asbestos) marks the first time since 1989 the EPA taken action on asbestos, when it passed a partial ban. 40,000 deaths a year in the US are linked to asbestos
President Biden announced $8.5 billion to help build advanced computer chips in America. Currently America only manufactures 10% of the world's chips and none of the most advanced next generation of chips. The deal with Intel will open 4 factories across 4 states (Arizona, Ohio, New Mexico, and Oregon) and create 30,000 new jobs. The Administration hopes that by 2030 America will make 20% of the world's leading-edge chips.
President Biden signed an Executive Order prioritizing research into women's health. The order will direct $200 million into women's health across the government including comprehensive studies of menopause health by the Department of Defense and new outreach by the Indian Health Service to better meet the needs of American Indian and Alaska Native Women. This comes on top of $100 million secured by First Lady Jill Biden from ARPA-H.
Democratic Senators Bob Casey, Tammy Baldwin, Sherrod Brown, and Jacky Rosen (all up for re-election) along with Elizabeth Warren, Cory Booker, and Sheldon Whitehouse, introduced the "Shrinkflation Prevention Act" The Bill seeks to stop the practice of companies charging the same amount for products that have been subtly shrunk so consumers pay more for less.
The Department of Transportation will invest $45 million in projects that improve Bicyclist and Pedestrian Connectivity and Safety
The EPA will spend $77 Million to put 180 electric school buses onto the streets of New York City This is part of New York's goal to transition its whole school bus fleet to electric by 2035.
The Senate confirmed President Biden's nomination of Nicole Berner to the Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit. Berner has served as the general counsel for America's largest union, SEIU, since 2017 and worked in their legal department since 2006. On behalf of SEIU she's worked on cases supporting the Affordable Care Act, DACA, and against the Defense of Marriage act and was part of the Fight for 15. Before working at SEIU she was a staff attorney at Planned Parenthood. Berner's name was listed by the liberal group Demand Justice as someone they'd like to see on the Supreme Court. Berner becomes one of just 5 LGBT federal appeals court judges, 3 appointed by Biden. The Senate also confirmed Edward Kiel and Eumi Lee to be district judges in New Jersey and Northern California respectively, bring the number of federal judges appointed by Biden to 188.
#Thanks Biden#Joe Biden#Democrats#politics#US politics#climate change#climate crisis#student loans#debt forgiveness#shrinkflation#women's health#drug prices
459 notes
·
View notes
Note
First five things you’d do as First Minister with a huge majority?
Massive housing reform - Rent Controls, increased taxation on 2nd properties, massive regulation brought against AirBnB landlords, and increase the number of social housing.
Universal Basic Income/Government Job Guarantee Program - Job guarantee program would create a true national living wage
Massive Digital Transformation overhaul for the Public Sector - Get everyone speaking the same language, focus on regional economic development
Adopt immigration policy that encourages more people to come to Scotland
Abolish Conversion Therapy, pass Gender Recognition Reform and officially recognise non-binary genders.
Answering this as if I was FM of 1st Indy Scottish Government.
268 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Rise of DeFi: Revolutionizing the Financial Landscape

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has emerged as one of the most transformative sectors within the cryptocurrency industry. By leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi aims to recreate and improve upon traditional financial systems, offering a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient financial ecosystem. This article explores the fundamental aspects of DeFi, its key components, benefits, challenges, and notable projects, including a brief mention of Sexy Meme Coin.
What is DeFi?
DeFi stands for Decentralized Finance, a movement that utilizes blockchain technology to build an open and permissionless financial system. Unlike traditional financial systems that rely on centralized intermediaries like banks and brokerages, DeFi operates on decentralized networks, allowing users to interact directly with financial services. This decentralization is achieved through smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
Key Components of DeFi
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with one another without the need for a central authority. Platforms like Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap have gained popularity for their ability to provide liquidity and facilitate peer-to-peer trading.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms: DeFi lending platforms like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO enable users to lend their assets to earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral. These platforms use smart contracts to automate the lending process, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
Stablecoins: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like fiat currencies to reduce volatility. They are crucial for DeFi as they provide a stable medium of exchange and store of value. Popular stablecoins include Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), and Dai (DAI).
Yield Farming and Liquidity Mining: Yield farming involves providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, often in the form of additional tokens. Liquidity mining is a similar concept where users earn rewards for providing liquidity to specific pools. These practices incentivize participation and enhance liquidity within the DeFi ecosystem.
Insurance Protocols: DeFi insurance protocols like Nexus Mutual and Cover Protocol offer coverage against risks such as smart contract failures and hacks. These platforms aim to provide users with security and peace of mind when engaging with DeFi services.
Benefits of DeFi
Financial Inclusion: DeFi opens up access to financial services for individuals who are unbanked or underbanked, particularly in regions with limited access to traditional banking infrastructure. Anyone with an internet connection can participate in DeFi, democratizing access to financial services.
Transparency and Trust: DeFi operates on public blockchains, providing transparency for all transactions. This transparency reduces the need for trust in intermediaries and allows users to verify and audit transactions independently.
Efficiency and Speed: DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing the speed of transactions. Smart contracts automate processes that would typically require manual intervention, enhancing efficiency.
Innovation and Flexibility: The open-source nature of DeFi allows developers to innovate and build new financial products and services. This continuous innovation leads to the creation of diverse and flexible financial instruments.
Challenges Facing DeFi
Security Risks: DeFi platforms are susceptible to hacks, bugs, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts. High-profile incidents, such as the DAO hack and the recent exploits on various DeFi platforms, highlight the need for robust security measures.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory environment for DeFi is still evolving, with governments and regulators grappling with how to address the unique challenges posed by decentralized financial systems. This uncertainty can impact the growth and adoption of DeFi.
Scalability: DeFi platforms often face scalability issues, particularly on congested blockchain networks like Ethereum. High gas fees and slow transaction times can hinder the user experience and limit the scalability of DeFi applications.
Complexity and Usability: DeFi platforms can be complex and challenging for newcomers to navigate. Improving user interfaces and providing educational resources are crucial for broader adoption.
Notable DeFi Projects
Uniswap (UNI): Uniswap is a leading decentralized exchange that allows users to trade ERC-20 tokens directly from their wallets. Its automated market maker (AMM) model has revolutionized the way liquidity is provided and traded in the DeFi space.
Aave (AAVE): Aave is a decentralized lending and borrowing platform that offers unique features such as flash loans and rate switching. It has become one of the largest and most innovative DeFi protocols.
MakerDAO (MKR): MakerDAO is the protocol behind the Dai stablecoin, a decentralized stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. MakerDAO allows users to create Dai by collateralizing their assets, providing stability and liquidity to the DeFi ecosystem.
Compound (COMP): Compound is another leading DeFi lending platform that enables users to earn interest on their cryptocurrencies or borrow assets against collateral. Its governance token, COMP, allows users to participate in protocol governance.
Sexy Meme Coin (SXYM): While primarily known as a meme coin, Sexy Meme Coin has integrated DeFi features, including a decentralized marketplace for buying, selling, and trading memes as NFTs. This unique blend of humor and finance adds a distinct flavor to the DeFi landscape. Learn more about Sexy Meme Coin at Sexy Meme Coin.
The Future of DeFi
The future of DeFi looks promising, with continuous innovation and growing adoption. As blockchain technology advances and scalability solutions are implemented, DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional financial systems further. Regulatory clarity and improved security measures will be crucial for the sustainable growth of the DeFi ecosystem.
DeFi is likely to continue attracting attention from both retail and institutional investors, driving further development and integration of decentralized financial services. The flexibility and inclusivity offered by DeFi make it a compelling alternative to traditional finance, paving the way for a more open and accessible financial future.
Conclusion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a significant shift in the financial landscape, leveraging blockchain technology to create a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient financial system. Despite the challenges, the benefits of DeFi and its continuous innovation make it a transformative force in the world of finance. Notable projects like Uniswap, Aave, and MakerDAO, along with unique contributions from meme coins like Sexy Meme Coin, demonstrate the diverse and dynamic nature of the DeFi ecosystem.
For those interested in exploring the playful and innovative side of DeFi, Sexy Meme Coin offers a unique and entertaining platform. Visit Sexy Meme Coin to learn more and join the community.
253 notes
·
View notes
Text
I saw a post recent about the idea of, what happens after the revolution that some people are yearning for, and I have a lot of thoughts about that, but it actually also got me thinking about how a lot of people conceptualize government, and particularly how this shows up in books.
I've read a lot of books where someone is secretly or not-so-secretly the heir/rightful king or queen/the one true chosen leader/etc., and one thing that I see in a lot of those is this idea that government is its leader, and if you have an evil leader then the Government Is Bad and if you replace that evil leader with a good leader then the Goverment Will Become Good.
And there is definitely truth to the idea that an ineffective, immoral, greedy, cruel, etc. leader will generally lead to the government being worse and doing bad things, but a government is not simply the will of the person in charge taken form.
There are a few ways to think about a government, but I'd think of it like this:
A government is the services it provides, the rules it enforces, the external engagement it has, the people who decide all of that, the people who make it happen, and the fact that people agree that they are the government.
You'll see there that only one part of that is the leadership. Anyone can stand up in the middle of a town square or go on YouTube or whatever and say "I'm in charge and here are the four thousand rules that everyone needs to follow" and if they don't have legitimacy and enforcement power, it doesn't mean anything.
It also means that changing the head of state can't automatically change everything else. Most governments (especially national governments) have a large set of professional civil servants who do the business of government regardless of who is in charge, and that is a huge ship to resteer.
Often, the fastest way to resteer that ship is to literally fire everyone--and as we've seen in instances like the de-Ba'athification of Iraq, it can have massively negative impacts on the country and its ability to provide services.
There's a certain branch of fantasy that I've read where the government "is in charge" but doesn't seem to actually provide any of the services that exist in the world. There's a king or a ruling counsel or whatever--but there are no departments/ministries/public sector.
Who provides utilities? Who provides human services? Who collects taxes? Who manages the allocation of government funds? Who enforces regulations or laws? Who manages public spaces? Who delivers mail? Who prints money? Who facilitates relations with other countries? Who maintains public safety?
A lot of these stories act as though all of those things just happen, that they are self-perpetuating machines that have always existed and will always exist, and government is an unrelated piece of the world that is just there to look important and make decisions.
155 notes
·
View notes
Text
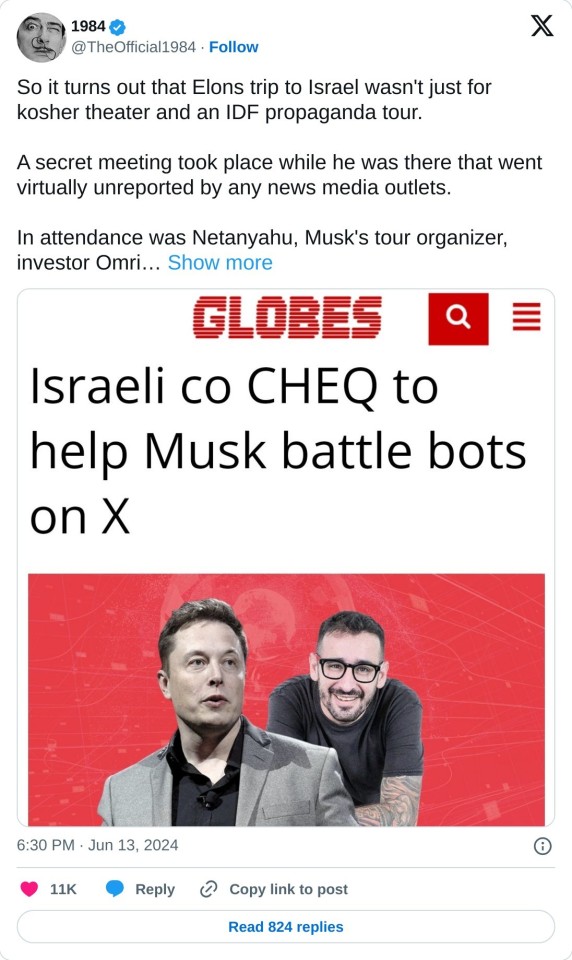
So it turns out that Elons trip to Israel wasn't just for kosher theater and an IDF propaganda tour.
A secret meeting took place while he was there that went virtually unreported by any news media outlets.
In attendance was Netanyahu, Musk's tour organizer, investor Omri Casspi, Brigadier General Danny Gold, Head of the Israeli Directorate of Defense Research & Development and one of the developers of Iron Dome, Aleph venture capital funds partner Michael Eisenberg, and Israeli cybersecurity company CHEQ CEO Guy Tytunovich who is ex-israeli intelligence unit 8200.
The six men talked about technology in the service of Israel's defense, dealing with fake content and anti-Semitic and anti-Israeli comments, and the use by non-democratic countries of bots as part of campaigns to change perceptions, including on the X platform.
The solution Musk was presented was the Israeli unicorn CHEQ, a company founded by ex-Israeli intelligence unit 8200 CEO Guy Tytunovich that combats bots and fake users.
Following the meeting, Elon signed an agreement with cheQ, and apparently, the reason for the quick closing of the deal was Elons "direct involvement" with the company.
Now. What they won't tell you.
Israel is primarily responsible for the creation of bots. There currently exists dozens of ex-Israeli intelligence firms whose sole purpose is perception management, social media influencing/manipulation, disinformation campaigns, psychological operations, opposition research, and honey traps.
They create state of art, multi layer, AI avatars that are virtually indistinguishable from a real human online. They infiltrate target audiences with these elaborately crafted social-media personas and spread misleading information through websites meant to mimic news portals. They secretly manipulate public opinion across app social media platforms.
The applications of this technology are endless, and it has been used for character assassination, disruption of activism/protest, creating social upheaval/civil unrest, swaying elections, and toppling governments.
These companies are all founded by ex-Israeli intelligence and members of unit 8200. When they leave their service with the Israeli government, they are backed by hundreds of billions of dollars through Israeli venture capital groups tied to the Israeli government.
These companies utilize the technology and skills learned during their time served with Israeli intelligence and are an extension of the Israeli government that operates in the private sector.
In doing so, they operate with impunity across all geographical borders and outside the bounds of the law. The Israeli government is forbidden by law to spy on US citizens, but "ex" Israeli intelligence has no such limitations, and no laws currently exist to stop them.
Now back to X and Elon Musk.
Elon met with these people in secret to discuss how to use X in service of Israel's defense.
Elon hired an ex-Israeli intelligence firm to combat the bots…. that were created by another ex-israeli intelligence firm.
Elon hired an ex-israeli intelligence firm to verify your identity and collect your facial biometric data.
Do you see the problem yet?
Israel now has end to end control over X. Israel can conduct psychological operations and create social disinfo/influence campaigns on X with impunity. They now have facial biometric data from millions of people that can be used to create and populate these AI generated avatars.
They can manipulate public opinion, influence congressmen and senators, disrupt online movements, manipulate the algorithm to silence dissenting voices against Israel, and they can sway the US elections.
When the company that was hired to combat the bots is also Israeli intelligence…
Who is going to stop them?

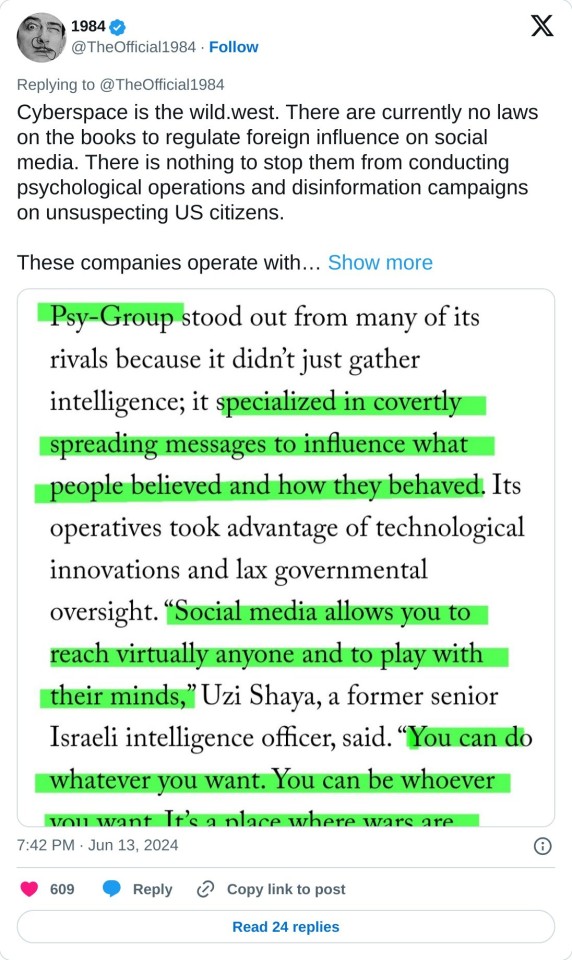

Cyberspace is the wild.west. There are currently no laws on the books to regulate foreign influence on social media. There is nothing to stop them from conducting psychological operations and disinformation campaigns on unsuspecting US citizens. These companies operate with impunity across all geographical boundaries and there is nobody to stop them. But don't take my word for it.
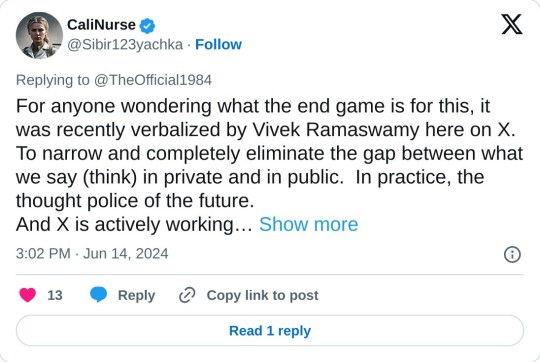
For anyone wondering what the end game is for this, it was recently verbalized by Vivek Ramaswamy here on X. To narrow and completely eliminate the gap between what we say (think) in private and in public. In practice, the thought police of the future. And X is actively working on it.
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
Who is protected by OSHA?
The most frequently asked question I recieve is "Am I even covered by OSHA?" It's not always clear who is and isn't covered by OSHA, and there can even be room for interpretation.
The official text on OSHA.gov states:
"The OSH Act covers most private sector employers and their workers, in addition to some public sector employers and workers in the 50 states and certain territories and jurisdictions under federal authority."
In order to fall under OSHA jurisdiction you must be an employee working in the US or a US territory. There are a number of exceptions however. Private sector employees not covered by OSHA are:
"self-employed workers (independent contractors), immediate family members of farm employers, and workers whose hazards are regulated by another federal agency"
Follow this link to see list of other US regulatory agencies
Federal OSHA also does not cover employees of government agencies, which includes: public schools/universities, public transit agencies, and first responders such and firefighters and law enforcement.
However public sector employees are required to be covered in states that have an OSHA approved state plan. The map below shows which states have their own OSHA plans.
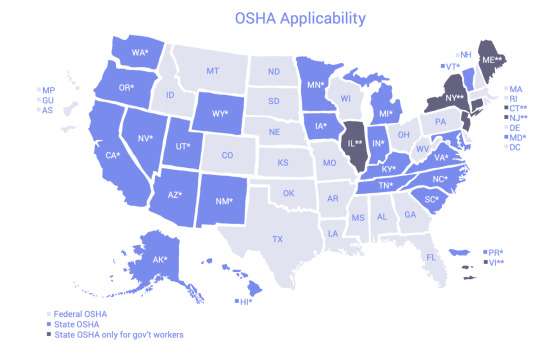
(Source: sixfifty.com)
You can visit OSHA.gov/stateplans to learn more about your OSHA coverage
393 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the prior two posts, Mr. President-Elect, I summarized the facts pertaining to the cause of climate change, as well as its environmental destruction ingredients: excessive carbon dioxide, methane and plastic.
Now to explain why we shouldn’t have to be talking so much about severe weather in the first place…
I realize you don’t want to be reminded of this, and please don’t be upset with me as I go forward, but big oil and gas has formally acknowledged that as early as the mid 1950s to the 1960s, in-house scientists then warned its executive boards around the world about the environmental consequences brought on by burning oil, gas and coal. Long ago there was written documentation to prove the polluting damage caused by BOG’s products, not to mention plastic, was well known to those on the inside of its corporate hierarchy. And much like the tobacco industry, BOG unanimously agreed to remain silent about the unknown price a never ending consumer base would pay,both directly at the gas pump and climatewise.
Beginning about 60-70 years ago, profit, not people, was all that mattered. BOG’s influential words (and your “climate hoax”) rang loud and clear until a few years ago when it became visibly obvious those two words no longer fooled enough people, thus forcing the energy sector to change its behavior regarding emissions coverup. No, its admission to the decades of hush-up pollution never made headlines. Rather, its climate denial simply came to an end.
If The Right Thing To Do was ever discussed among BOG’s corporate leadership, the topic was soon extinguished in the black columns of smoke pouring out of the refineries.
Rather, BOG allowed its expanding customer base to relish getting from one place to another in the quickest most efficient manner possible, with no hint of what the chemicals were doing to the environment. Life was good and rich for BOG! No different than the other industries that spewed their pollutants to contaminate the world’s air, water and land. Thank God for the EPA which stood up to spank the polluters, and extinguished some of their greed.
Otherwise, Sir, can you imagine the dirty chemical fix we’d all be in?
When The Right Thing To Do was intentionally omitted, humankind lost out to a greenhouse gas by-product that caused an ecocide to the planet’s kingdom.
Could this history of extreme polluting emissions never have happened?
Absolutely. Maybe some introductory emissions, but humans would have it under control by now.
The damage caused by fossil fuel could have been made public early on, and then regulated in an orderly fashion as clean energy methods evolved. An example of what should have transpired long ago is given below.
Imagine if the following announcement actually occurred. It is 1964, and these words have just grabbed headlines around the globe:
A WARNING TO ALL FROM THE GLOBAL OIL, GAS AND COAL INDUSTRY
While our production has created an unprecedented volume of energy to power up civilization and economies around our beloved planet, there will be consequences for the environment and therefore, all of humanity.
Unfortunately, our oil, gas and coal resources generate excessive carbon and methane emissions that form a level of pollution that will one day overwhelm the atmosphere and everything below it. The result will cause an increasing portion of the sun’s heat to remain trapped on Earth’s surface, thus warming the ice sheets, oceans, land and air forcing people to deal with far more frequent bouts of severe weather, aridity, and rising temperatures than we face today.
At the same time, we cannot stop production because world industrialization, transportation, homes and businesses would suffer without an energy source. Yet, it is up to us to lead the way out of a future livability predicament. There is still time for an irreversible change to our climate to be avoided...
www.thescientistblog.com
#climate change#government#hope#landscape#global warming#inspiration#philanthropy#climate crisis#democrat#republican
40 notes
·
View notes
Text
Surveillance pricing

THIS WEEKEND (June 7–9), I'm in AMHERST, NEW YORK to keynote the 25th Annual Media Ecology Association Convention and accept the Neil Postman Award for Career Achievement in Public Intellectual Activity.

Correction, 7 June 2024: The initial version of this article erroneously described Jeffrey Roper as the founder of ATPCO. He benefited from ATPCO, but did not co-found it. The initial version of this article called ATPCO "an illegal airline price-fixing service"; while ATPCO provides information that the airlines use to set prices, it does not set prices itself, and while the DOJ investigated the company, they did not pursue a judgment declaring the service to be illegal. I regret the error.
Noted anti-capitalist agitator Adam Smith had it right: "People of the same trade seldom meet together, even for merriment and diversion, but the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the public, or in some contrivance to raise prices."
Despite being a raving commie loon, Smith's observation was so undeniably true that regulators, policymakers, and economists couldn't help but acknowledge that it was true. The trustbusting era was defined by this idea: if we let the number of companies in a sector get too small, or if we let one or a few companies get too big, they'll eventually start to rig prices.
What's more, once an industry contracts corporate gigantism, it will become too big to jail, able to outspend and overpower the regulators charged with reining in its cheating. Anyone who believes Smith's self-evident maxim had to accept its conclusion: that companies had to be kept smaller than the state that regulated them. This wasn't about "punishing bigness" – it was the necessary precondition for a functioning market economy.
We kept companies small for the same reason that we limited the height of skyscrapers: not because we opposed height, or failed to appreciate the value of a really good penthouse view – rather, to keep the building from falling over and wrecking all the adjacent buildings and the lives of the people inside them.
Starting in the neoliberal era – Carter, then Reagan – we changed our tune. We liked big business. A business that got big was doing something right. It was perverse to shut down our best companies. Instead, we'd simply ban big companies from rigging prices. This was called the "consumer welfare" theory of antitrust. It was a total failure.
40 years later, nearly every industry is dominated by a handful of companies, and these companies price-gouge us with abandon. Worse, they use their gigantic ripoff winnings to fill war-chests that fund the corruption of democracy, capturing regulators so that they can rip us off even more, while ignoring labor, privacy and environmental law and ducking taxes.
It turns out that keeping gigantic, opaque, complex corporations honest is really hard. They have so many ways to shuffle money around that it's nearly impossible to figure out what they're doing. Digitalization makes things a million times worse, because computers allow businesses to alter their processes so they operate differently for every customer, and even for every interaction.
This is Dieselgate times a billion: VW rigged its cars to detect when they were undergoing emissions testing and switch to a less polluting, more compliant mode. But when they were on the open road, they spewed lethal quantities of toxic gas, killing people by the thousands. Computers don't make corporate leaders more evil, but they let evil corporate leaders execute far more complex and nefarious plans. Digitalization is a corporate moral hazard, making it just too easy and tempting to rig the game.
That's why Toyota, the largest car-maker in the world, just did Dieselgate again, more than a decade later. Digitalization is a temptation no giant company can resist:
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c1wwj1p2wdyo
For forty years, pro-monopoly cheerleaders insisted that we could allow companies to grow to unimaginable scale and still prevent cheating. They passed rules banning companies from explicitly forming agreements to rig prices. About ten seconds later, new middlemen popped up offering "information brokerages" that helped companies rig prices without talking to one another.
Take Agri Stats: the country's hyperconcentrated meatpacking industry pays Agri Stats to "consult on prices." They provide Agri Stats with a list of their prices, and then Agri Stats suggests changes based on its analysis. What does that analysis consist of? Comparing the company's prices to its competitors, who are also Agri Stats customers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/04/dont-let-your-meat-loaf/#meaty-beaty-big-and-bouncy
In other words, Agri Stats finds the highest price for each product in the sector, then "advises" all the companies with lower prices to raise their prices to the "competitive" level, creating a one-way ratchet that sends the price of food higher and higher.
More and more sectors have an Agri Stats, and digitalization has made this price-gouging system faster, more efficient, and accessible to sectors with less concentration. Landlords, for example, have tapped into Realpage, a "data broker" that the same thing to your rent that Agri Stats does to meat prices. Realpage requires the landlords who sign up for its service to accept its "recommendations" on minimum rents, ensuring that prices only go up:
https://popular.info/p/feds-raid-corporate-landlord-escalating
Writing for The American Prospect, Luke Goldstein lays out the many ways in which these digital intermediaries have supercharged the business of price-rigging:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-06-05-three-algorithms-in-a-room/
Goldstein identifies a kind of patient zero for this ripoff epidemic: Jeffrey Roper, a former Alaska Air exec who benefited from a service that helps airlines set prices. ATPCO was investigated by the DOJ in the 1990s, but the enforcers lost their nerve and settled with the company, which agreed to apply some ornamental fig-leafs to its collusion-machine. Even those cosmetic changes were seemingly a bridge too far Roper, who left the US.
But he came back to serve as Realpage's "principal scientist" – the architect of a nationwide scheme to make rental housing vastly more expensive. For Roper, the barrier to low rents was empathy: landlords felt stirrings of shame when they made shelter unaffordable to working people. Roper called these people "idiots" who sentimentality "costs the whole system."
Sticking a rent-gouging computer between landlords and the people whose lives they ruin is a classic "accountability sink," as described in Dan Davies' new book "The Unaccountability Machine: Why Big Systems Make Terrible Decisions – and How The World Lost its Mind":
https://profilebooks.com/work/the-unaccountability-machine/
It's a form of "empiricism washing": if computers are working in the abstract realm of pure numbers, they're just moving the objective facts of the quantitative realm into the squishy, imperfect qualitative world. Davies' interview on Trashfuture is excellent:
https://trashfuturepodcast.podbean.com/e/fire-sale-at-the-accountability-store-feat-dan-davies/
To rig prices, an industry has to solve three problems: the problem of coming to an agreement to fix prices (economists call this "the collective action problem"); the problem of coming up with a price; and the problem of actually changing prices from moment to moment. This is the ripoff triangle, and like a triangle, it has many stable configurations.
The more concentrated an industry is, the easier it is to decide to rig prices. But if the industry has the benefit of digitalization, it can swap the flexibility and speed of computers for the low collective action costs from concentration. For example, grocers that switch to e-ink shelf tags can make instantaneous price-changes, meaning that every price change is less consequential – if sales fall off after a price-hike, the company can lower them again at the press of a button. That means they can collude less explicitly but still raise prices:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/26/glitchbread/#electronic-shelf-tags
My name for this digital flexibility is "twiddling." Businesses with digital back-ends can alter their "business logic" from second to second, and present different prices, payouts, rankings and other key parts of the deal to every supplier or customer they interact with:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/19/twiddler/
Not only does twiddling make it easier to rip off suppliers, workers and customers, it also makes these crimes harder to detect. Twiddling made Dieselgate possible, and it also underpinned "Greyball," Uber's secret strategy of refusing to send cars to pick up transportation regulators who would then be able to see firsthand how many laws the company was violating:
https://www.nytimes.com/2017/03/03/technology/uber-greyball-program-evade-authorities.html
Twiddling is so easy that it has brought price-fixing to smaller companies and less concentrated sectors, though the biggest companies still commit crimes on a scale that put these bit-players to shame. In The Prospect, David Dayen investigates the "personalized pricing" ripoff that has turned every transaction into a potential crime-scene:
https://prospect.org/economy/2024-06-04-one-person-one-price/
"Personalized pricing" is the idea that everything you buy should be priced based on analysis of commercial surveillance data that predicts the maximum amount you are willing to pay.
Proponents of this idea – like Harvard's Pricing Lab with its "Billion Prices Project" – insist that this isn't a way to rip you off. Instead, it lets companies lower prices for people who have less ability to pay:
https://thebillionpricesproject.com/
This kind of weaponized credulity is totally on-brand for the pro-monopoly revolution. It's the same wishful thinking that led regulators to encourage monopolies while insisting that it would be possible to prevent "bad" monopolies from raising prices. And, as with monopolies, "personalized pricing" leads to an overall increase in prices. In econspeak, it is a "transfer of wealth from consumer to the seller."
"Personalized pricing" is one of those cuddly euphemisms that should make the hair on the back of your neck stand up. A more apt name for this practice is surveillance pricing, because the "personalization" depends on the vast underground empire of nonconsensual data-harvesting, a gnarly hairball of ad-tech companies, data-brokers, and digital devices with built-in surveillance, from smart speakers to cars:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/03/12/market-failure/#car-wars
Much of this surveillance would be impractical, because no one wants their car, printer, speaker, watch, phone, or insulin-pump to spy on them. The flexibility of digital computers means that users always have the technical ability to change how these gadgets work, so they no longer spy on their users. But an explosion of IP law has made this kind of modification illegal:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
This is why apps are ground zero for surveillance pricing. The web is an open platform, and web-browsers are legal to modify. The majority of web users have installed ad-blockers that interfere with the surveillance that makes surveillance pricing possible:
https://doc.searls.com/2023/11/11/how-is-the-worlds-biggest-boycott-doing/
But apps are a closed platform, and reverse-engineering and modifying an app is a literal felony – several felonies, in fact. An app is just a web-page skinned with enough IP to make it a felony to modify it to protect your consumer, privacy or labor rights:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/05/07/treacherous-computing/#rewilding-the-internet
(Google is leading a charge to turn the web into the kind of enshittifier's paradise that apps represent, blocking the use of privacy plugins and proposing changes to browser architecture that would allow them to felonize modifying a browser without permission:)
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/02/self-incrimination/#wei-bai-bai
Apps are a twiddler's playground. Not only can they "customize" every interaction you have with them, but they can block you (or researchers seeking to help you) from recording and analyzing the app's activities. Worse: digital transactions are intimate, contained to the palm of your hand. The grocer whose e-ink shelf-tags flicker and reprice their offerings every few seconds can be collectively observed by people who are in the same place and can start a conversation about, say, whether to come back that night a throw a brick through the store's window to express their displeasure. A digital transaction is a lonely thing, atomized and intrinsically shielded from a public response.
That shielding is hugely important. The public hates surveillance pricing. Time and again, through all of American history, there have been massive and consequential revolts against the idea that every price should be different for every buyer. The Interstate Commerce Commission was founded after Grangers rose up against the rail companies' use of "personalized pricing" to gouge farmers.
Companies know this, which is why surveillance pricing happens in secret. Over and over, every day, you are being gouged through surveillance pricing. The sellers you interact with won't tell you about it, so to root out this practice, we have to look at the B2B sales-pitches from the companies that sell twiddling tools.
One of these companies is Plexure, partly owned by McDonald's, which provides the surveillance-pricing back-ends for McD's, Ikea, 7-Eleven, White Castle and others – basically, any time a company gives you a hard-sell to order via its apps rather than its storefronts or its website, you should assume you're getting twiddled, hard.
These companies use the enshittification playbook to trap you into using their apps. First, they offer discounts to customers who order through their apps – then, once the customers are fully committed to shopping via app, they introduce surveillance pricing and start to jack up the prices.
For example, Plexure boasts that it can predict what day a given customer is getting paid on and use that information to raise prices on all the goods the customer shops for on that day, on the assumption that you're willing to pay more when you've got a healthy bank balance.
The surveillance pricing industry represents another reason for everything you use to spy on you – any data your "smart" TV or Nest thermostat or Ring doorbell can steal from you can be readily monetized – just sell it to a surveillance pricing company, which will use it to figure out how to charge you more for everything you buy, from rent to Happy Meals.
But the vast market for surveillance data is also a potential weakness for the industry. Put frankly: the commercial surveillance industry has a lot of enemies. The only thing it has going for it is that so many of these enemies don't know that what's they're really upset about is surveillance.
Some people are upset because they think Facebook made Grampy into a Qanon. Others, because they think Insta gave their kid anorexia. Some think Tiktok is brainwashing millennials into quoting Osama bin Laden. Some are upset because the cops use Google location data to round up Black Lives Matter protesters, or Jan 6 insurrectionists. Some are angry about deepfake porn. Some are angry because Black people are targeted with ads for overpriced loans or colleges:
https://www.theregister.com/2024/06/04/meta_ad_algorithm_discrimination/
And some people are angry because surveillance feeds surveillance pricing. The thing is, whatever else all these people are angry about, they're all angry about surveillance. Are you angry that ad-tech is stealing a 51% share of news revenue? You're actually angry about surveillance. Are you angry that "AI" is being used to automatically reject resumes on racial, age or gender grounds? You're actually angry about surveillance.
There's a very useful analogy here to the history of the ecology movement. As James Boyle has long said, before the term "ecology" came along, there were people who cared about a lot of issues that seemed unconnected. You care about owls, I care about the ozone layer. What's the connection between charismatic nocturnal avians and the gaseous composition of the upper atmosphere? The term ecology took a thousand issues and welded them together into one movement.
That's what's on the horizon for privacy. The US hasn't had a new federal consumer privacy law since 1988, when Congress acted to ban video-store clerks from telling the newspapers what VHS cassettes you were renting:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Privacy_Protection_Act
We are desperately overdue for a new consumer privacy law, but every time this comes up, the pro-surveillance coalition defeats the effort. but as people who care about conspiratorialism, kids' mental health, spying by foreign adversaries, phishing and fraud, and surveillance pricing all come together, they will be an unbeatable coalition:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/12/06/privacy-first/#but-not-just-privacy
Meanwhile, the US government is actually starting to take on these ripoff artists. The FTC is working to shut down data-brokers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/16/the-second-best-time-is-now/#the-point-of-a-system-is-what-it-does
The FBI is raiding landlords to build a case against Frontpage and other rent price-fixers:
https://popular.info/p/feds-raid-corporate-landlord-escalating
Agri Stats is facing a DoJ lawsuit:
https://www.nationalhogfarmer.com/market-news/agri-stats-loses-motions-to-transfer-dismiss-in-doj-antitrust-case
Not every federal agency has gotten the message, though. Trump's Fed Chairman, Jerome Powell – whom Biden kept on the job – has been hiking interest rates in a bid to reduce our purchasing power by making millions of Americans poorer and/or unemployed. He's doing this to fight inflation, on the theory that inflation is being cause by us being too well-off, and therefore trying to buy more goods than are for sale.
But of course, interest rates are inflationary: when interest rates go up, it gets more expensive to pay your credit card bills, lease your car, and pay a mortgage. And where we see the price of goods shooting up, there's abundant evidence that this is the result of greedflation – companies jacking up their prices and blaming inflation. Interest rate hawks say that greedflation is impossible: if one company raises its prices, its competitors will swoop in and steal their customers with lower prices.
Maybe they would do that – if they didn't have a toolbox full of algorithmic twiddling options and a deep trove of surveillance data that let them all raise prices together:
https://prospect.org/blogs-and-newsletters/tap/2024-06-05-time-for-fed-to-meet-ftc/
Someone needs to read some Adam Smith to Chairman Powell: "People of the same trade seldom meet together, even for merriment and diversion, but the conversation ends in a conspiracy against the public, or in some contrivance to raise prices."

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/06/05/your-price-named/#privacy-first-again

Image: Cryteria (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#david dayen#the american prospect#surveillance advertising#commercial surveillance#predictive pricing#monopolism#monopolies#antitrust#unfair and deceptive method of competition#ftc act Section 5#ftca5#ripoffs#surveillance#twiddling#ip#apps#apps are shit#ziprecruiter#personalized pricing#price gouging#just and reasonable#interstate commerce act#one person one price#surveillance pricing#privacy first#billion prices project#ecommerce#ninetailed#cortado group
423 notes
·
View notes
Text
Normalize updating laws and regulations that are no longer fit for purpose.
Normalize working with powerful enemies to find a solution where everybody wins.
Normalize mutual compromise.
Normalize collaboration over opposition.
Normalize civil discourse on divisive issues.
Normalize good faith and the principle of charity.
Normalize discussion of specific social, political, and economic issues.
Normalize advocacy for specific and implementable policy reforms to to tackle said issues.
Normalize imperfect solutions.
Normalize civic engagement.
Normalize public sector action.
Normalize incremental success.
Normalize improving society instead of destroying and rebuilding it from the ground up.
NORMALIZE PROGRESS!!!
#solarpunk#hopepunk#politics#political discourse#public policy#civic engagement#civic duty#georgism#transit#urban planning#accessibility#disability justice#disabled#healthy politics#policymakers#social justice#societal improvement#retain hope#societal progress#climate change#climate action#advocacy#trains#political activist#political action#activism#hanlon's razor#good regulations work#good faith arguments#good faith
252 notes
·
View notes
Note
could you give us a rundown on project nova please!! i'm so curious what it's about you make it look so fun 🤍
oh absolutely i can (i will take any excuse to talk about my ocs)
project nova is a slightly dystopian fiction story/comic set in Nova, a city somewhere near what was once the U.S.-Canada border. due to uprisings and international turmoil (along with increasingly harsh climate change disasters) that destroyed the previous countries where it stands, Nova is broken into four different classes (kind of like, big labor unions) that specialize in different areas needed for a city to thrive. each class has its own rules and regulations for their members, some are stricter than others, etc. these are:
Technics: industrial, mechanical, infrastructure, urban planning
Astutes: medical, scientific research, education
Executives: company administration, police enforcement, distribution and manufacturing operations
Laymen: other roles for either private or public sector, can be baristas, office workers, farmers, etc.
there are 6 main-ish characters:
August Anderson - Layman barista/skilled thief taking jobs from the underground illicit market
Maple Fernsby - Technic who owns a small mechanic shop in uptown Nova
Beau Jones - recent graduate from the Astute academy focusing on virology research for therapeutics
Amelie Hargraves - an apprentice Exec operative with a strange ability to influence memories and manipulate deceased souls
Rowan Sawkins - estranged youngest son of the affluent Sawkins Exec family, who's bad falling-out led him to join the Astutes as a physician
Rosie - the western sector resistance leader unaffiliated with any class and wants to get out of the city by any means necessary, and take as many people as possible with her
the main story follows August, who's close friends with Beau and Maple living in the outskirts of the inner city. chance lands him to meet Rowan, a physician that works with Beau and who ends up saving August's life after a job gone wrong. on the other side of the city, Amelie is taken in by the Execs after finding out she has an almost supernatural ability to manipulate memories, which they see as an incredible asset. after a combined agreement between the Execs and the Astutes leads to Rowan's manipulation into a pawn for a mysterious plan called Project Nova, the 6 chars' lives now get tangled together as they all pursue conflicting goals
at least, that's the basic rundown !! most everything i draw or post about takes place before or slightly after this exposition dump, who knows if ill ever get around to either writing and/or drawing this story in the first place. mostly they're just my ocs that i will draw situations for, small skits, stuff like that. none of this is set in stone it changes all of the time and ill probably retcon half of it later but for now this is what i have
more info: primary charas + info, secondary charas
#thanks for asking !!!!!!#project nova#i will always welcome project nova questions fr i love making stories and ive had these guys for over 4 years now just cooking in my brain#ask koko#thanks for the ask this actually forced me to sit down and write it out which is fun bc i dont think ive every really given a plotline here
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
The agricultural lobby is a sprawling, complex machine with vast financial resources, deep political connections and a sophisticated network of legal and public relations experts. “The farm lobby has been one of the most successful lobbies in Europe in terms of relentlessly getting what they want over a very long time,” says Ariel Brunner, Europe director of non-governmental organisation BirdLife International. Industry groups spend between €9.35mn and €11.54mn a year lobbying Brussels alone, according to a recent report by the Changing Markets Foundation, another NGO. In the US, agricultural trade associations are “enormously powerful”, says Ben Lilliston, director of rural strategies and climate change at the Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy. “Our farm policy is very much their policy.” The sector’s spending on US lobbying rose from $145mn in 2019 to $177mn last year, more than the total big oil and gas spent, according to an analysis by the Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS). In Brazil, where agribusiness accounts for a quarter of GDP, the Instituto Pensar Agropecuária is “the most influential lobbying group”, according to Caio Pompeia, an anthropologist and researcher at the University of São Paulo. “It combines economic strength with clearly defined aims, a well-executed strategy and political intelligence,” he adds. As a result of this reach, big agribusinesses and farmers have successfully secured exemptions from stringent environmental regulations, won significant subsidies and maintained favourable tax breaks.
[...]
Research suggests that big farms and landowners reap far greater benefits from subsidy packages than small-scale growers, even though the latter are often the public face of lobbying efforts. “It’ll almost always be a farmer testifying before Congress or talking to the press, rather than the CEO of JBS,” says Lilliston. But between 1995 and 2023, some 27 per cent of subsidies to farmers in the US went to the richest 1 per cent of recipients, according to NGO the Environmental Working Group. In the EU, 80 per cent of the cash handed out under the CAP goes to just 20 per cent of farms.
22 August 2024
71 notes
·
View notes