#phosphate group activation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

The Science Notebooks of Satyendra Sunkavally, page 61.
#herbivores#protein synthesis#protein catabolism#primates#alcoholic fermentation#phosphate group activation#tibet#pectin#latent heat of vaporization#ribose#hydroxyl group#RNA solubility#sulfur deficiency#plants#X-rays#ice#opacity#John Torrington
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Marvels of Biological Macromolecules: The Molecular Machinery of Life (Part 3)
Proteins and Enzymes: Catalysts of Molecular Reactions
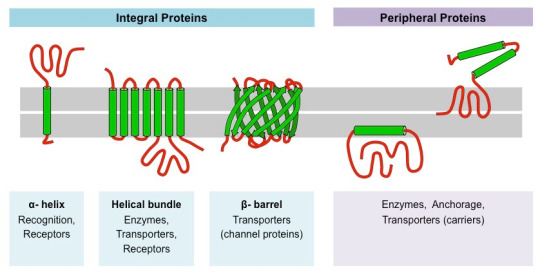
Proteins are the central players in macromolecular interactions. Enzymes, a specialized class of proteins, catalyze biochemical reactions with remarkable specificity. They bind to substrates, facilitate reactions, and release products, ensuring that cellular processes occur with precision.
Protein-Protein Interactions: Orchestrating Cellular Functions
Proteins often interact with other proteins to form dynamic complexes. These interactions are pivotal in processes such as signal transduction, where cascades of protein-protein interactions transmit signals within cells, regulating diverse functions such as growth, metabolism, and immune responses.
Protein-Ligand Interactions: Molecular Recognition
Proteins can also interact with small molecules called ligands. Receptor proteins, for instance, bind to ligands such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or drugs, initiating cellular responses. These interactions rely on specific binding sites and molecular recognition.
Protein-DNA Interactions: Controlling Genetic Information
Transcription factors, a class of proteins, interact with DNA to regulate gene expression. They bind to specific DNA sequences, promoting or inhibiting transcription, thereby controlling RNA and protein synthesis.
Membrane Proteins: Regulating Cellular Transport
Integral membrane proteins participate in macromolecular interactions by regulating the transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes. Transport proteins, ion channels, and pumps interact precisely to maintain cellular homeostasis.
Cooperativity and Allosteric Regulation: Fine-Tuning Cellular Processes
Cooperativity and allosteric regulation are mechanisms that modulate protein function. In cooperativity, binding one ligand to a protein influences the binding of subsequent ligands, often amplifying the response. Allosteric regulation occurs when a molecule binds to a site other than the active site, altering the protein's conformation and activity.
Interactions in Signaling Pathways: Cellular Communication
Signal transduction pathways rely on cascades of macromolecular interactions to transmit extracellular signals into cellular responses. Kinases and phosphatases, enzymes that add or remove phosphate groups, play pivotal roles in these pathways.
Protein Folding and Misfolding: Disease Implications
Proteins must fold into specific three-dimensional shapes to function correctly. Misfolded proteins can lead to Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and prion diseases. Chaperone proteins assist in proper protein folding and prevent aggregation.
References
Voet, D., Voet, J. G., & Pratt, C. W. (2016). Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. Wiley.
Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2017). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman.
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry. W. H. Freeman
#science#college#biology#education#school#medicine#student#doctors#health#healthcare#proteins#molecular biology#molecular structure#chemestry#chemistry
96 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sorry but I’m gonna smack u all with my ‘tism stick
Have my favourite spider, favourite crystals, favourite poisons and favourite mushrooms

African Black Velvet: eresidae gandanameno sp. “Pretoria” - I want to keep one as a pet, desperately. 10/10 perfect spider.



CHICKEN OF THE WOODS (laetiporus cincinnatus) - if I ever found one of these I would bash my head off a tree in excitement and glee
Fly Agaric (Amanita Muscaria) - I found a few of these while out walking with my uni group 2 years ago and accidentally held up the whole group with a TED Talk. Luckily they were all also mentally ill / autistic /nd art students so I didn’t bore anybody
Ghost Fungus!!!!! (Omphalotus Nidiformis) - if I had the money I would 100000% fly to australia and venture out into the blue mountains at night just to see these beauties bioluminesce.


Vivianite: anyone who brings up crystals around me has probably heard me go “DO YOU KNOW VIVIANITE GROWS OUT OF CORPSES” at some point. It’s a ferrous iron phosphate mineral that grows in a monoclinic crystal system and thrives in anaerobic boggy environments. It forms when the hydroxyapatite in your bones (major source of phosphate) reacts with water from a waterlogged tomb and the iron in any surrounding rocks, resulting in cool shit like blue skeletons and crystals growing out yer teef
Grape Agate: it’s not agate. It’s not chalcedony. It’s not amethyst. It’s a variety of quartz silica which are commonly termed as ‘amethystine’, and instead of taking on the macrocrystalline monoclinic formations typical of normal quartz, it’s made up of up micro crystals that grow radially in a botryoidal form. Also comes in green and white. It’s only found in the Manakarra Beach in Indonesia.



Strychnine: (Strychnos Loganiaceae, Nux Vomica) - the one that leaves you with a hideous grin. It causes violent muscle contractions, enough to make the body bend back to an unnatural degree before the victim finally dies of asphyxiation. Particularly horrid as the victim remains conscious throughout the ordeal and is very much aware of what is happening. In fact, the victim is hyperaware. Nasty stuff. It inhibits your postsynaptic glycine receptors in your spinal cord, which causes the intensely painful and involuntary contortions. Also it’s mentioned in the Herbal of Rufinus as ‘good for helping to balance the phlegmatic and choleric humours’ through purging (vomiting, hence why it’s called the ‘vomiting nut’), and was a medicine to be used with great caution.
Giant Hogweed (Heracleum Apiaceae, Mantegazzianum): all parts of this plant are toxic. man fuck this stuff, if you touch it you’re literally gonna be burning and blistering every time the sun touches your skin for months and possibly even years after coming into contact with this hellspawn plant. Its active constituents are furanocoumarins, which basically mutate your skin cells to become incredibly sensitive to light. It’s a mutagenic and possibly carcinogenic photoactive compound.
Mandrake (Mandragora Officinarum): it’s in the nightshade family (Solanaceae)! Revered in folklore for the way its roots look like a person, said to ‘scream and cause death’ upon being uprooted. It’s a powerful narcotic, hallucinogenic and emetic plant, meaning that you try and eat this shit and you’ll be absolutely off your tits and vomming your guts up before you kick it.
Other honourable mentions that make for interesting reading:
Orpiment, Gasteracantha Cancriformis, Gasteracantha Arcuata, Sugar Fluorite, Jelly Lichens, Monkshood (Aconitum), Bleeding Tooth Fungus, Amorphophallus Titanium
Stupid fact about me: I have, in fact, ingested wormwood (Artemisia Absinthium) to see what sort of effect it would have out of curiosity, but didn’t get very far as it tasted fucking awful (I made a tea). Tastes like nail polish remover, 0/10 do not recommend. Didn’t ingest enough to feel any sort of thujone effect and my little experiment was safely conducted. I did, however, burn some to see if that would do anything and it made me feel rank in the tummy. No hallucinogenic effect. Again. 0/10 do not recommend.
#autism special interest#cw arachnophobia#cw spiders#spiders#arachnophobia#cw poison#poisonous plants#crystals#fungi#mushrooms
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Nucleosome: DNA's Fancy Packaging and Party Trick!
Imagine cramming two meters of yarn into a pea-sized box. Sounds impossible, right? Well, that's the impressive feat that cells pull off every single day with DNA! They use a clever structure called the nucleosome to pack this massive genetic blueprint into the tiny nucleus.
The journey began in 1974 when Don and Ada Olins, peering through an electron microscope, spotted repeating beads – the first glimpse of nucleosomes. Roger Kornberg, building upon this observation, proposed the now-iconic "subunit theory," envisioning DNA wrapped around histone protein cores. This theory, later solidified by Pierre Oudet's term "nucleosome," laid the groundwork for further exploration. The 1980s witnessed a flurry of activity, with Aaron Klug's group using X-ray crystallography to reveal the left-handed superhelical twist of DNA around the histone octamer. But the true masterpiece arrived in 1997 when the Richmond group, armed with advanced techniques, unveiled the first near-atomic resolution crystal structure of the nucleosome. This intricate map, showcasing the precise interactions between DNA and histones, remains a cornerstone of our understanding.
The Players:
DNA: The star of the show, carrying our genetic code in the form of a double helix.
Histones: Protein spools around which DNA tightly winds. Imagine eight of them forming a core, like a mini-protein drum set.
Linker DNA: Short stretches of DNA connecting the spools, like the spaces between beads on a necklace.
The Steps:
Wrap and Roll: Picture DNA gracefully wrapping around the histone core, like thread around a spool. Each nucleosome holds about 146 base pairs of DNA, making about 1.67 turns.
Connect and Repeat: Linker DNA bridges the gap between nucleosomes, forming a "beads-on-a-string" structure. Think of it as pearls strung between the spools.
Compact and Condense: This repetitive unit folds further, creating intricate 30-nanometer fibers. Imagine these as twisted strands of pearls!
Here's the coolest part: histones aren't static. They can be chemically modified, like adding or removing phosphate groups. These modifications act like tiny flags that tell the cell how tightly to wrap the DNA, essentially throwing a "party" for specific genes by making them more accessible. This fine-tuning allows cells to respond to their environment and express the right genes at the right time. Understanding the nucleosome model is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of gene regulation and diseases like cancer. By studying how modifications affect nucleosome structure and gene access, scientists can develop new therapies to target specific genes and potentially treat diseases at the root cause.
While the nucleosome model is the foundation, the story gets even more intriguing. Different histone types and modifications create variations, influencing chromatin structure and function. Think of it as different music genres influencing the dance moves! Additionally, other proteins interact with the nucleosome, adding another layer of complexity to this fascinating choreography.
The nucleosome model is more than just a neat way to package DNA. It's a testament to the intricate dance between molecules that orchestrates life's processes. By understanding this fundamental structure, we gain deeper insights into cellular function, paving the way for advancements in medicine and beyond.
Remember, this is just the beginning! The world of nucleosomes and chromatin is vast and ever-evolving. So, keep exploring, keep questioning, and keep dancing to the rhythm of DNA!
#molecular biology#biology#science sculpt#life science#science#dna#biotechnology#genetics#Histone#Nucleosome#chromatin
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
how is psilocybin metabolized?
To metabolize is to breakdown a chemical to its simpler component forms for cells to use. Psilocybin is a psychedelic compound found in fungi of several genera including Psilocybe, Panaeolus, and Copelandia. Inside the body, it influences the functional molecular mechanisms of several organs, mainly the brain, kidneys, and liver. On its own psilocybin is not as effective. To produce its infamous hallucinogenic effect in the brain, it must be converted to psilocin. Psilocin is the main active molecule, which is derived from the prodrug psilocybin.
There are two ways of getting these metabolites inside the body: oral ingestion (for example, eating the "magic mushrooms") and intravenous injection. When orally ingested, the mushrooms are digested in the usual way. Eventually, the psilocybin in the mushrooms reaches the liver where it is converted to psilocin. An enzyme, alkaline phosphatase, acts on psilocybin such that its phosphate group (PO₄³⁻) is replaced with a hydroxyl group (−OH). Psilocin is further acted upon by diverse enzymes to obtain products which are either excreted through urine or contribute to other functions in hepatocytes (liver cells) as psilocin metabolites.
There is a format to convert chemical equations to sentences. Nevertheless, I firmly believe that one must have the convenience of remembering their organic chemistry without having a stroke. Behold,
psilocin + monoamine oxidase = 4-hydroxyindole-3-acetaldehyde
psilocin + glucuronosyltransferase = psilocin glucoronide (PCG)
psilocin + aldehyde reductase = 4-hydroxytryptophol
psilocin + aldehyde dehydrogenase = 4-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (4HIAA)
The fates of each of these products are an elaborate article on their own, and I will be happy to write them should you be interested. Let me know!
Now, we remember that the primary effects due to which human beings consume psilocybin-containing mushrooms are caused by psilocin in the brain. The exact step-by-step mechanism has not yet been outlined; however, general molecular interactions have been found in studies. This psychoactive compound shows an interesting resemblance to serotonin the neurotransmitter. The psilocin binds to 5-HT2A (a molecule in a cell membrane which responds specifically to serotonin i.e., a serotonin receptor) with high affinity, which is believed to be essential for hallucinogenic effect. It also binds to other receptors with varying affinities, although their significance is yet to be understood.
Psilocybin and its metabolized products are completely removed from the body after 24 hours of consumption. The kidneys take pride in detoxifying circulating blood by creating the waste product urine; psilocin consumed can be detected in blood plasma 6-8 hours after consumption. Majority of the psilocin excreted through urine is in the form of psilocin-O-glucoronide. Psilocybin that remains psilocybin is also excreted through urine by the kidneys.
Introducing psilocybin in the body through veins produces effects of similar intensity as the former method. Whereas it remains as an active compound in the blood for a shorter duration. Turton et. al. conducted an fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) study to compare the subjective experience of intravenous psilocybin injection interestingly explains how their participants’ descriptions of their experiences were influenced by the MRI scanner environment and the 1960s, when psychedelics were first introduced to western culture.
bibliography:
Passie T, Seifert J, Schneider U, Emrich HM. The pharmacology of psilocybin. Addiction biology. 2002 Oct;7(4):357-64.
Tylš F, Páleníček T, Horáček J. Psilocybin–summary of knowledge and new perspectives. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Mar 1;24(3):342-56.
Turton S, Nutt DJ, Carhart-Harris RL. A qualitative report on the subjective experience of intravenous psilocybin administered in an FMRI environment. Current Drug Abuse Reviews. 2014 Aug 1;7(2):117-27.
#psilocybe cubensis#psilocybe azurescens dried#psilocybe semilanceata#magic mushies#magic mushrooms#metabolites#mushrooms#altered my brain chemistry#psilocybin research#science side of tumblr#science side explain#science side help me
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Water is life's matter and matrix, mother and medium. There is no life without water.”
Albert Szent-Gyorgyi
Remember headlines similar to this?
“England’s rivers, lakes and streams ‘among worst in Europe’ amid concern over sewage and farm pollution.” (Independent: 15/09/21)
And more recently:
“Sewage entered rivers and seas on average 825 times a day last year Water companies released raw sewage into rivers and seas in England for more than 1.75 million hours last year. (BBC News: 31/03/23)
Does our Tory government care? No, not one jot. This is what we read in the media today.
“Michael Gove is set to announce a weakening of water pollution rules placed on housing developers in England, in a move that has angered groups across the UK’s green economy.” (edie.net: 29/08/23)
Gove is doing this to encourage more house building which up until now has been supposedly held back by anti-pollution laws and the cost this has for housing developers. From now on the building industry will not be held accountable for increases in nitrates and phosphates into out waterways.
In October 2021 the Tory government published a paper entitled: Nitrates: challenges for the water environment. In it they listed the dangers of too much nitrate in our waterways:
Risk to human health
Eutrophication of lowland surface waters (Eutrophic waters are often murky and may support fewer large animals, such as fish and birds, than non-eutrophic waters.)
Acidification and eutrophication of upland waters
Adverse impact on Groundwater Dependent Terrestrial Ecosystems.
In short, nitrates poison the water both above and below ground and can be a risk to human health as well as to birds, animals and aquatic life in general.
In December 2022, the government published another report:.
It found that phosphates cause eutrophication in the same way nitrates do:
“Eutrophication increases the cost of drinking water abstraction and treatment, adversely affects angling, water sports and other recreational activities, and causes the loss of sensitive plants and animals in rivers and lakes.” (Environment Agency: Phosphorus and freshwater eutrophication: challenges for the water environment./ December 2022)
So, we have a government who knows the dangers of increasing the levels of nitrates and phosphates in our waterways yet they decide to relax laws controlling these chemicals regardless of the environmental consequences.
Why!
The answer is, as is so often the case, “follow the money”.
Craig Bennett, Chief Executive of the Wildlife Trust had this to say on the Today programme this morning.
“I've been at the last few Conservative Party conferences over the last few years, and when you walk into the exhibition space, the biggest, fanciest exhibitions are by the big house building organisations. The most lavish parties and receptions put on at the Conservative Party conference over the last few years have been from the house building industry. They seem to have plenty of money when it comes to them lobbying, and guess what? - we discover this morning that money talks.”
To back up this claim, we find that in 2021, "property developers gave Tories £892,00 in the first three months of that year. And in May this year we read that:
“Millions in Tory donations at risk as property developers hit back. Housebuilders and developers - who in the past have accounted for around a fifth of all donations - have turned off the taps.”(Independent: 30/05/23)
There is a sneaking suspicion that the relaxation of water pollution laws has more to do with Tory Party funding than the housing shortage. Given the housing industry is one of the Conservative Party’s biggest donors, is it any wonder that under the new law, developers will no longer have to dip into their profits to offset nutrient pollution from new homes.
And just to prove the Tory Party has a sense of humour, not only will our waterways be more polluted than ever before but:
“Scrapping housebuilder water pollution rules in England to cost taxpayer £140m” (Guardian: 29/08/23)
#uk politics#water pollution#corruption#payoffs#michael gove#phosphate#nitrate#environment#humn health#waterways
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vitamin B3, niacin (from tobacco)
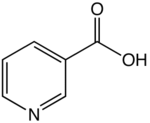
Nicotinic acid (Na) is one of the three structural isomers of pyridinecarboxylic acid. Nicotinic acid and nicotinamide are collectively called niacin. Niacin corresponds to vitamin B3 in the vitamin B group.
history
In 1867, it was discovered as a carboxylic acid obtained by oxidizing the alkaloid nicotine, and was given the common name nicotinic acid. In 1911, Umetaro Suzuki and C. Funk isolated it from living organisms as a pellagra-preventive factor. In 1937 C.A.Elvehjem revealed that nicotinic acid is a vitamin. Around the end of the 20th century, annual global production of nicotinic acid reached more than 10,000 tons[2]. However, most of it was produced for feed, and nicotinic acid for human food additives and pharmaceuticals was less than 10% of the total production.
Manufacturing method/Biosynthesis
It is obtained by oxidizing pyridine derivatives such as β-picoline with a side chain at the 3-position with strong oxidizing agents such as nitric acid and potassium permanganate. It is also synthesized by a method of constructing a pyridine ring. Salts of nicotinic acid and copper are sparingly soluble in water.
In animals and fungi, it is synthesized in vivo from tryptophan via kynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid, while in plants and bacteria it is biosynthesized from aspartic acid and the C3 unit, a glycerol-related metabolite.
physiological activity
Main article: Niacin
In vivo, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate containing nicotinic acid in a partial structure are hydrogen acceptors of oxidoreductases and are important as coenzymes.
ニコチン酸(ニコチンさん、英: nicotinic acid、Na)とは、ピリジンカルボン酸(英語版)の3つの構造異性体の中の1つである。ニコチン酸とニコチン酸アミドを総称してナイアシンと呼ばれる。ナイアシンは、ビタミンB群の中のビタミンB3に当たる。
歴史
1867年にアルカロイドのニコチンを酸化して得られるカルボン酸として発見され、ニコチン酸という慣用名が与えられた。1911年に鈴木梅太郎およびC.Funkらが生体より抗ペラグラ因子(こうペラグラいんし、pellagra‐preventive factor)として単離した。ニコチン酸がビタミンであることは、1937年にC.A.Elvehjemによって明らかにされた。 20世紀末頃で世界中の1年間のニコチン酸の生産量を合算すると、1万トン以上に達していた[2]。ただし、その大部分は飼料用として生産されていた物であって、ヒトに用いる食品添加物や医薬品用のニコチン酸は、全生産量の1割にも満たない量であった。
製法・生合成
3位に側鎖を持つβ-ピコリンなどピリジン誘導体を、硝酸や過マンガン酸カリウムなど強い酸化剤で酸化すると得られる。また、ピリジン環を構築する方法でも合成される。ニコチン酸と銅との塩は、水に溶けにくい。
動物・菌類では生体内で、トリプトファンからキヌレニン、3‐ヒドロキシアントラニル酸を経由して、一方、植物や細菌ではアスパラギン酸とグリセロール近縁代謝物質であるC3ユニットから生合成される。
生理活性
詳細は「ナイアシン」を参照
生体内では、ニコチン酸を部分構造に含むニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドやニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチドリン酸が、酸化還元酵素の水素受容体であり、補酵素として重要である。
Wikipediaより
Smoke (tobacco) is an indispensable material for human beings.
Rei Morishita
#Vitamin B3#Niacin#tobacco#nicotinic acid#coenzymes#Wikipedia#Rei Morishita#Smoke (tobacco) is an indispensable material for human beings.#smoke
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
HEREDITARY FORM OF EPILEPSY ASSOCIATED WITH PYRIDOXAMINE 5'-PHOSPHATE OXIDASE DEFICIENCY IN A CHILD by Plotnikova I.A in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences
SUMMARY
The article presents a clinical case of focal epilepsy with a status course of seizures associated with a genetic mutation in exon 1 of the PNPO gene, which led to pyridoxamine-5'-phosphate oxidase deficiency. The diagnosis was made late due to the misinterpretation of symptoms, which complicated the course of the disease. Despite the fact that the first symptoms in the form of seizures appeared at the age of 1 month, only at the age of 5 the diagnosis was verified by doing targeted DNA sequencing. At the moment, the patient is receiving substitution therapy in the form of pyridoxal phosphate 300 mg/day, which enabled unstable clinical remission. Right now, it is impossible to achieve complete control over the convulsive syndrome without a strict diet: dairy-free, meat-free, egg-free and low-protein fat-free food. Currently, further search for treatment methods continues to improve the patient's quality of life and ensure stable remission. A detailed analysis was given for further genetic verification based on the amino acid profile of the patient, and the rehabilitation potential was determined based on topical neuropsychological diagnostics performed on a non-verbal child.
Key words: focal epilepsy; Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; vitamin B6; PNPO; vitamin B6-dependent epilepsy, neuropsychological diagnostics.
INTRODUCTION
Vitamin B6-dependent epilepsies are aheterogeneous group of autosomal recessive diseases that are caused by mutations of five different genes involved in vitamin B6 metabolism [1]. Vitamin B6 is present in many forms in the human diet, but only pyridoxal-5 -phosphate (PLP) plays a vital role in the metabolism of a number of neurotransmitters, especially the inhibitory mediator gamma-aminobutyric acid. Code errors leading to a lack of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate manifest as B6-dependent epilepsy, including pyridoxamine-5-phosphate oxidase (PNPO) deficiency, which affects the synthesis and recycling of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate [2,3]. Neonatal manifestation in the form of acute encephalopathy with biphasic epileptic seizures (or status epilepticus) is the main symptom of the disease. The first phase (early attacks) is accompanied by fever and a temporary recovery of consciousness and the development; the second phase is a global cognitive dysfunction (late attacks).
Resistance to traditional antiepileptic therapy requires patient's lifelong treatment by pharmacological doses of vitamin B6 in the form of pyridoxine (PN) or a biologically active form of pyridoxal-5’-phosphate [1,4].
Case reports of PLP deficiency, verified not only clinically, but also by exome sequencing, are quite rare as well as the methods for studying molecular markers of alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde and pipecolic acid in body fluids [5–7]. The complexity of diagnosis is caused by multiple disorders in newborns, especially in case of a slow and incomplete response to pyridoxine [8].
Recent studies have shown that the main enzyme defect in pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy is caused by alpha-aminoadipic acid semialdehyde dehydrogenase in the pathway of cerebral lysine degradation. The accumulating compound, alpha-aminoadipine semialdehyde (alpha-AASA), is in equilibrium with delta-1-piperidine-6-carboxylate (P6C). P6C inactivates pyridoxal-5’-phosphate, causing severe cerebral insufficiency. Although treatment of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate deficiency can successfully control seizures, most patients develop some degree of disability, regardless of early diagnosis and treatment. Very few patients with normal intelligence have been reported [7].
Objective: to analyze the course of epilepsy with pyridoxamin-5’-phosphate oxidase deficiency in an 8-year-old patient with diagnosis verification by clinical exome sequencing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS OF RESEARCH.
The analysis of primary medical documentation from 2013 to 2021 of a patient born in 2013 was performed. We reviewed the materials on the topic using PubMed search engines for the period 2014-2021, correlation of literature data with a specific clinical case.
RESEARCH RESULTS AND THEIR DISCUSSION.
A clinical case
Girl, 8 years old, was born from IV pregnancy of a woman with a burdened obstetric history. At the age of 1 month, tonic-clonic convulsions were first noted during sleep: gaze adversion to the left, lasting 30 seconds - 1 minute; afterwards there was up to 4 seizures per day, daily. At the age of 1 year, she was hospitalized 4 times on an emergency basis for convulsive seizures. The child was observed by a neurologist-epileptologist with a diagnosis of perinatal damage to the central nervous system, recovery period. Valproic acid was prescribed at a dosage of 50 mg/kg per day, oxcarbazepine 300 mg/day, without an effect of therapy. At the age of 2 years, she was hospitalized three times in the intensive care unit due to the status course of an epileptic seizure with a rise in temperature to febrile numbers. Neurological diagnosis at that time was: symptomatic epilepsy with complex partial seizures, status course of generalized convulsive seizures. On electroencephalography (EEG): moderate diffuse changes in the bioelectric activity (BEA) of the brain in a disorganized type. The patient's condition worsened. At the age of 3 years, she was observed in the State Autonomous Healthcare Institution of the Sverdlovsk Region "Children's City Clinical Hospital No. 9, Yekaterinburg" with the same diagnosis; the dose of oxcarbazepine was increased to 500 mg/day, valproic acid to 300 mg/day with no significant clinical effect. At the age of 4 years, she was hospitalized three times in the intensive care unit about epileptic seizures, without the effect of anticonvulsant therapy. Concomitant diseases at age 4 were: severe osteoporosis of the visible parts of the skeleton; pathological compression fracture of the body Th11; hepatomegaly; moderate expansion of the common hepatic, common bile ducts; enlargement of the gallbladder; a pronounced increase in the size of the kidneys, pancreas; diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the kidneys, a single cyst of the right kidney; unspecified form of caries; chronic gingivitis. Computed tomography of the abdominal aorta and its branches showed no evidence of hepatic artery stenosis. Autonomic dysfunction of the sinus node was noted: sinus arrhythmia with episodes of bradycardia. There were also small anomalies in the development of the heart: a functioning foramen ovale, additional chords of the cavity of the left ventricle.
DNA sequencing was carried out in 2017. Genetic mutations that were identified are described in patients with epilepsy associated with pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate oxidase deficiency and, based on the totality of information, regarded as pathogenic - a mutation in exon 1 of the PNPO gene (chr17: 46019139A> T, rs370243877), leading to amino acid replacement at position 33 of the protein (p.Asp33Val, NM-018129.3, mutation frequency in the ExAC control sample 0.0235%); as probably pathogenic - a previously undescribed heterozygous mutation in intron 3 of the PNPO gene (chr17:46022086G>A, rs766037058), leading to disruption of the splicing site and synthesis of the full-length protein (c.363+5G>A, NM_018129.3, OMIM: 610090, the value of the algorithm for predicting its influence on the function of AdaBoost splicing sites is 1.000).
A heterozygous mutation was also found in exon 4 of the EARS2 gene (chr16:23546678A>T), leading to a premature translation termination site at codon 163 (p.Tyr163Ter, NM_001083614.1). Such mutations have been described in patients with combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency type 12 (OMIM: 614924). In this case (when no second mutation in the gene is detected), the result is regarded as an option with uncertain clinical significance, however, the mutation may be related to the phenotype. The parents did not undergo a genetic examination.
Prescribed treatment was: pyridoxine hydrochloride intramuscularly, then - pyridoxal phosphate at the rate of 10-50 mg / kg /day. On the 7th day after the start of treatment, the patient's consciousness was assessed as clear, she was able to sit up independently and stand with support. Her seizures stopped, appetite improved, during rehabilitation positive dynamics in neuropsychic development was noted with an expansion of the range of motor activity, the appearance of gaming activity, emotions and attempts to pronounce individual sounds.
At the age of 5 years 1 month there was a new epileptic seizure. The dose of pyridoxal phosphate was increased to 600 mg/day, convulsive attacks stopped. Concomitant diseases at age 5 were perianal dermatitis, vulvitis, continuously recurrent leukocyturia. Subsequent courses of medical rehabilitation was prescribed with positive dynamics.
In 2019, hyperkinesis (blinking), tremor, restlessness reappeared; in the summer were tonic-clonic seizures with vocalization, lasting 15-20 minutes and the status course of an attack, operculations, loss of appetite. By the end of the year, there was constant nausea and a gag reflex at the sight of food, vomiting with yellow mucus and a sour smell once every 5-7 days, accompanied by febrile fever, the smell of "rotten cheese" from the scalp and excrements during attacks. Motor clonic seizures appeared with a frequency of once every 1-2 months, symmetrical chill-like tremor - up to 3-5 times a day. Periodic episodes of psychomotor agitation, stereotyped movements were also noted.
Neurological status. There are bradypsychia, delayed psycho-motor development, coordination disorder. Patient does not pronounce words, speech is active only during the game-vocalisms, self-service skills are not formed. Autism spectrum disorders with general speech underdevelopment of level 1, psychomotor alalia were noted. Cerebral, meningeal symptoms are negative. The gait is uncertain. Cerebellar tests are negative. Cranial nerves: palpebral fissures D=S, pupils D=S, pupil reaction to light: direct D=S, consensual D=S. The volume of movement of the eyeballs is complete D=S, there is no nystagmus. The face is symmetrical D=S. There is no language deviation. Swallowing, phonation are not disturbed. Muscle tone: arms - reduced D=S, legs - normal D=S. Tendon reflexes: from the arms and legs increased D=S. There are no pathological foot signs, pelvic functions are preserved. Patient shows signs of slightly asymmetrical (with an accent on the left) motor awkwardness, reduced nutrition (Body weight 21,5 kg).
Results of instrumental and laboratory studies. The following disorders were detected on the EEG prior to the start of etiological therapy: Epileptiform activity in the form of "peak-wave" complexes in the frontal and central-temporal leads, more on the right; slowing down of activity in the temporal zone.
In the biochemical analysis of blood the level of amino acids (µmol/l) is low: alanine 119.30; glutamic acid 72.00; glycine 86.50; ornithine 22.10; proline 87.00. Activity of alanine aminotransferase is 24.9 U/l (reference values 0-29 U/l), aspartate aminotransferase - 26.4 U/l (reference values 0-48 U/l).
Control visit. After the diagnosis was verified by exome sequencing, the patient was prescribed etiotropic therapy: pyridoxal phosphate 300 mg/day. The pre-elevated (1070 nmol/l) plasma concentration of vitamin B6 (pyridoxal-5-phosphate) normalized. EEG data - video monitoring showed moderately severe violations of BEA of the brain; the main rhythm is formed by age; registered regional slowing of the rhythm in the right central-parietal region. Epileptiform activity, clinical paroxysms, EEG patterns of epileptic seizures were not registered.
Final diagnosis: Genetic focal epilepsy due to a mutation in the PNPO gene (chr17: 46019139A> T, rs370243877). The type of attack is focal with impaired consciousness. PNPO developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Cognitive impairment. Alalia. Motor awkwardness.
Psychological status. Diagnostics of cognitive activity showed that the girl is accessible to contact; she does not speak and comprehension of the speech is shown only in the form of understanding simple commands and simple instructions for the task. The child's object-sensory activity is carried out 100% through visual perception and shape perception, the perception of size is developed by 50%, spatial perception - 12%, color perception is completely absent. The insufficiency of these afferentations is a consequence of the decrease in the “zone of actual development”, which may be attributed to pedagogical neglect. In the motor sphere, gross motor skills are fully formed, fine motor skills are developed by 54%, objective activity is formed by 9%, taking into account the skills of game and constructive praxis, speech function is developed by 25%, self-service skills - by 60%, socialization – by 40%. Psychological diagnostics of the state of higher mental functions was carried out by depicting the structural and functional features of the brain, as a result of which topical insufficiency of brain areas was revealed. Figure 1 shows the level of formation of brain zones.
Figure 1: The degree of formation of brain departments that implement sensory and motor skills.
Despite the pronounced cognitive deficit in the child, the implementation of the program of psychological rehabilitation may expand the "zone of actual development" in the structure of the sensory, subject and pedagogical profile (since there are preserved components of cognitive activity)
DISCUSSION
Patient’s clinical diagnosis was established only at the age of 5 years, based on clinical manifestations and exome sequencing. The primal reduction of the dose of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate provoked a relapse of status epilepticus and a regression of acquired cognitive skills. A subsequent increase of treatment in combination with dietary therapy provided an unstable clinical remission without further improvement in the patient's condition. Such a response to the therapy has also been demonstrated in other studies [6,7].
Although in patients with a typical course of the disease, there is a several-fold increase in the level of glycine and glutamic acid in the blood plasma [1,5–7,9], in our case there is a decrease in glycine to 86,50 µmol/l (norm: 100-400 µmol /l) and other amino acids. Hypoglycinemia is an extremely rare condition, it occurs only in severe hereditary aminoacidopathy, but in our patient, tandem mass spectrometry was performed twice (including against the background of an attack) in 2016 and did not show any data of hereditary aminoacidopathy, organic aciduria, defects β-oxidation of fatty acids. The girl has a positive reaction to the oral intake of amino acid complexes and glycine separately, therefore, additional genetic analysis can be performed for 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency, the clinical manifestations of which may be encephalopathy and seizures unresponsive to anticonvulsants [10]. Symptoms of this disease can be stopped by joint intake of serine and glycine so this diet may be developed for our patient. The study of vitamin B6 metabolites in de novo serine biosynthesis by Ramos et al (2017) had one group of rats which received a pyridoxine-deficient diet, while the diet of the control group of rats contained a normal amount of pyridoxine. This study has demonstrated a decrease in serine biosynthesis in Neuro-2a cells in vitamin B6 deficient rats. The pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT, EC 2.6.1.52) cannot function fully in conditions of vitamin B6 deficiency, and likely reduces the synthesis of phosphoserine and serine in animals on a pyridoxine-deficient diet. The production of glycine depends on the availability of serine and on the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme SHMT, which catalyzes part of the transformation of glycine, and the simultaneous deficiency of serine and pyridoxal-5'-phosphate can reduce its activity and lead to a decrease in the content of glycine in blood plasma [9].
Some authors reported EEG changes in patients with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy [11]. In our patient, no clear epileptiform activity was registered either before or after the start of treatment with pyridoxal-5'-phosphate; this variant of EEG was also described by other researchers [5,6]. Changes in the brain during magnetic resonance imaging in patients with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy may vary from normal to diffuse atrophy of the gray and white matter of the hemispheres [2]; in our case no changes were detected.
According to Plecko B. Et al., with late diagnosis stable remission after the appointment of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate is observed only in a few patients [1]. Early treatment is critical to prevent irreversible damage to the central nervous system and shows positive results [1,5,6]. Patients with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy require lifelong supplementation with pyridoxal-5'-phosphate. Therapeutic doses of the drug vary from 15 to 30 mg/kg/day [1]. The daily requirement for vitamin B6 in infancy is 0.1–0.3 mg. Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate doses up to 500 mg/day are considered safe in children with classical vitamin B6 deficiency, but higher doses may cause reversible sensory and rare motor neuropathy [1], so total daily doses of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate, should not exceed 200-300 mg. There are no data on the optimal dose of the vitamin for long-term treatment. In experimental animals, doses of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate >50mg/kg/d induce ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, and muscle weakness; histological examination demonstrates neuronal damage with loss of myelin and degeneration of sensory fibers in peripheral nerves, dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and descending tract of the trigeminal nerve. In most cases of peripheral neuropathy, the total dose of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is >1000 mg/day. Some children who take high concentrations of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate develop a persistent increase in transaminases with progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma [3]. To avoid side effects, a fixed effective dose should be used. However, studies showed that daily doses up to 1100 mg/day and 50 mg/kg/day to achieve a state without epileptic seizures did not cause any side effects when they were divided into 4–5 doses per day [12]. In our case the doses of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate less than 600 mg/day induces epileptic seizures and cognitive disfunction. Some mutations in the genes encoding of pyridoxamine-5-phosphate oxidase may require the combined treatment with pyridoxal-5'-phosphate and pyridoxine [12,13]. It is possible that such treatment will have a positive response in our patient as well.
Another interesting feature of this clinical case is an intolerance of the patient to many products: remission occurs only on a low-protein, low-fat diet with the exclusion of dairy, meat products and eggs. Similar dietary restrictions are observed in ALDH7A1 deficiency (antiquitin deficiency), which often accompanies PNPO gene mutation. In our case ALDH7A1 deficiency was excluded by exome sequencing [13,14]. However, a lysine-restricted diet can also be effective for homozygous mutations in the PNPO gene in some patients [14]. As an example of a diet, the recommendations of Koelker and Ross on glutaric aciduria type I can be used [15].
The patient also has a high content of vitamin B6 in plasma (775.0 nmol/l), which is typical response to an intake of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (described levels of vitamin B6 in plasma: 400 nmol/l, 1060 nmol /l and 624 nmol/l) [12,18]. It is not known why some patients continue to have seizures even when taking high doses of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate, while others grow almost normally [1,7,19]. The long-term prognosis for this patient remains unclear. For our patient a clarifying genetic study with modification of pharmacological treatment and diet is required, considering that the girl does not tolerate protein hydrolysates and an unstable clinical remission only on a low-protein low-fat diet with the exclusion of dairy, meat products and eggs.
CONCLUSIONS
DNA diagnostics using the method of sequencing of exome regions of the genome is a key method for early verification of the diagnosis of epilepsy in newborns and young children, which in combination with the therapy can improve the prognosis.
The presence of heterozygous mutations in this clinical case suggests other metabolic deficits, which complicates the selection of treatment and requires additional examination of the exome.
To ensure stable remission, nutritional correction is required to compensate for deficient conditions during severe elimination measures, as well as the selection of the minimum sufficient dosage of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate in combination with pyridoxine hydrochloride.
Topical neuropsychological diagnostics and psychological correction based on intact higher mental functions makes the recovery of the patient possible.
Conflict of Interest: The authors of this article have confirmed that there are no conflicts of interest or financial support to report.
For more information: https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/about-us/
For more submission : https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/
#focal epilepsy#Pyridoxal 5#phosphate#vitamin B6#PNPO#vitamin B6-dependent epilepsy#neuropsychological diagnostics#DNA#aheterogeneous#alpha-aminoadipine#semialdehyde#Plotnikova I.A#jcrmhs
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'd love to! It's always something I forget to talk about having done. A few years ago (maybe... 3-4 now?) the ISS hosted a competition where middle, high school, and university students could submit an experiment proposal to be done aboard the ISS called the Student Spaceflight Experiments Program, which was perfect for since at the time i wanted to study both earth and space sciences (and couldnt choose).
The theming was pretty much... anything? As long as you could find a way for it to be justified as being helpful with Mars exploration. I was given the competition application by my astronomy teacher at the time and partnered with a friend.
We spent weeks researching and developing 3 different experiment proposals (honestly the hardest part was they had to be properly written and formatted as professional proposals and as a high schooler I had never encountered that sort of writing for myself before). As mentioned, one was on rock phosphate fertilizer cultivation and usage, another centered on a certain sort of fungal decomposition (I WISH I remembered which one) and the last was the epiphyte experiment!
To cheat it a little I'm pretty sure we were the only school with entries in our area. Typically pre-college experiments were made by big groups of like... 100+ kids for max engagement but it was just me and my friend lol. The epiphyte experiment really was centered on how epiphyte growth shape, size, and chronology would be affected in low gravity without the same gravity markers. I don't think I have the proposal document anymore unfortunately, but I know I was really interested in root growth and efficiency in this environment.
Our proposal involved sending a small seed and soil up in a lil test tube to then be planted and cultivated and having detailed documentation of its growth and flowering, including the size, shape, and timing of leaves, roots, any flowering, etc.
Honestly, I graduated before hearing much back about the proposal (launch is late spring), and since it was done through the teacher and not my own email I never heard anything further. However there's almost always ongoing experiments on the ISS centered around plant growth! Considering they weren't obligated to contact me, I truly have no idea what became of it or if a similar experiment ended up being conducted (and cant find any information on my submission year anyway, to be fair it WAS COVID so its very possible the program ended up being postponed or cancelled that year after submission and the teacher forgot to mention it between our other active projects). Right now i think it's currently centered on tomato cultivation 🍅
I started with succulents like everyone else but tbh orchids are rapidly becoming my plant blorbos. Everyone takes care of them wrong and it's not your FAULT because the care instructions that come with them are!! Incorrect!!! If you do what they say then your orchid will die!!!! If you give them the right environment they're SO easy. They're such easy plants to grow. They have been UNFAIRLY SLANDERED by a MISINFORMATION campaign. They don't deserve this.
#it was a lot of fun to work on!#and very eye opening as a prospective science student lol#god is proposal writing a hellscape#at the time we also did dust storm imaging on mars and radio telescope black hole tracking#the latter of which is where i actually spent most of my time
38K notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Structural Optimization Design of New Energy Vehicle Power Battery Packs
As the “heart” of new energy vehicles, the power package is the primary power source of the car and one of the key assemblies of electric vehicles; it plays a decisive role in the vehicle’s performance, and the battery pack’s performance is affected by parameters like the number of cells, energy density, and the box.
There is still a certain gap in the range of pure electric vehicles compared to traditional fuel vehicles, and users are concerned about the safety of battery packs. The global power battery pack industry chain has developed rapidly in tandem with the development trend of new global energy vehicles.

1. Studying the Optimization Design of the Power Battery Pack Structure of Pure Electric Vehicles is of Great Significance
Basic Requirements For the Design of a Power Battery Pack: within a limited space volume, based on meeting the power storage capacity to meet the needs, minimizing the damage to drivers and passengers by traffic accidents, and making them as lightweight as possible.
Structural Design Requirements of Power Battery Pack: structural strength, collision safety, fatigue reliability, ventilation and heat dissipation, insulation, and waterproofing, electromagnetic compatibility, etc.
The Research Direction of Power Battery Pack: Based on giving priority to the selection of appropriate high-energy ratio monomer cells, it is also an urgent need to study and optimize from the perspective of battery pack structure design to develop power battery packs with higher range, higher safety, and wider environmental temperature application range.
2. The Development Status of Power Battery Packs at Home and Abroad
Globally, leading automakers are actively creating new energy-electric vehicles, and one of the key elements determining how competitive these auto markets are is the longevity of power batteries.
International Mainstream Vehicle-Mounted Power Battery Pack
The premium all-electric model, which has a NEDC range of more than 600 kilometers and is backed by ternary lithium battery cells, is a product of the major automakers in the US, Germany, Japan, and South Korea. Mainstream automakers now prioritize using batteries made by Panasonic, LG, Samsung, and other Japanese and Korean companies.
Tesla introduced a battery pack based on 46800 single cells and improved the pack in line with the trend of increasing capacity and decreasing the number of single cells. The battery pack’s overall energy density has significantly increased due to the reduction of single cells to 960.
Domestic Mainstream Vehicle Power Battery Pack
Domestic mainstream automakers typically switch from using high-end models of batteries to ternary lithium batteries over time. The majority of the models in the middle and lower price range are lithium iron phosphate monomer cells, but overall the selection is not as high as the international advanced level.
A “blade battery” based on lithium iron phosphate was released by BYD. It combines the integrated design of the battery pack structure and the chassis to achieve flattening and lengthening of the cell by decreasing the thickness and lengthening the cell.
Cell Batteries of Domestic and Foreign Automobile Enterprises
An onboard power battery package that is correctly grouped into a single lithium-ion battery cell and integrated into the box body is the power battery that is most frequently used. The majority of current research on battery pack structure design concentrates on temperature field simulation, dynamic analysis, and structural optimization design. Numerous high-performance power battery packs have been developed as a result of these studies, which have also reliably supported the mass production of battery packs technically.
3. Mechanical Structure Design of Battery Pack

To meet the requirements of battery pack safety and onboard environmental excitation, the module must have high structural stability, strength, and stiffness. Its size should also be restricted to fit inside the battery box and allow for the installation of necessary electrical components. Additionally, the battery pack’s mechanical structure features a “⊥” type and an “earth” font. The installation location and the vehicle layout’s envelope space size impose restrictions on the design of the battery pack structure. Combining the integrated body and chassis design is the standard design approach. The vehicle structure indicates that the squeeze impact of the battery pack body can, to a certain extent, lessen the likelihood of collision safety accidents.
4. High-Voltage Electrical Design of Battery Pack

5. Thermal Management Design of Battery Pack
Maintaining the battery temperature within the proper working range of 10°C to 40°C is the goal of thermal management design, particularly to prevent or reflect local overheating. To regulate the lithium-ion battery pack’s internal temperature on schedule, a suitable thermal management system must be designed. Phase change cooling, liquid cooling, and forced air cooling are the three main components of the thermal management system.
Air Cooling Method: low cost, average heat dissipation effect, difficult to meet requirements under extreme conditions.
Phase Change Cooling: expensive and not suitable for current market demand.
Liquid Cooling Method: good heat dissipation effect and good heat dissipation and heating conversion, which is the main application method at present.
6. Integrated Design of Battery Pack
Power battery technology and related integrated management technologies have emerged one after another in tandem with the swift development of new energy vehicles. New technologies in the areas of material science (cobalt-free materials, for example), process science (blade batteries, etc.), integrated technologies (CTP, etc.), and management science (bullet batteries, etc.) have amassed material factories and batteries. The most recent R&D and application outcomes from auto factories.
The electric vehicle’s power source is the battery pack, of which the battery cell is the smallest component. Currently, the market is dominated by two structural methods: MTP (Module to Pack) and CTP (Cell to Pack). The newest battery system technology, CTC (Cell to Chassis), is used by Tesla, BYD, and Zero Run.
There is still space for improvement in the power battery pack of domestic automakers, as it is impacted by various factors like the low energy density of the battery cell, structural design flaws in the battery pack, and insufficient efficiency of the battery thermal management system. The integrated structure design and battery pack power, from the monomer to the system, are the main influencing factors. Therefore, by choosing suitable high-energy ratio monomer cells, it can be examined and optimized from the standpoint of battery pack structure design.
#battery packs#electric vehicles#lithium ion battery cell#lithium ion battery packs#lithium ion power battery packs#power battery packs
0 notes
Text
The X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Market Will Grow At Highest Pace Owing To Increasing R&D Investments

X-linked Hypophosphatemia is a rare, inherited disorder affecting bone mineralization characterized by abnormal bone development and low levels of phosphate in the blood. The condition is caused by mutations in the PHEX gene which lead to increased levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) that regulates phosphate metabolism and vitamin D activation. Some key signs and symptoms include bone pain, skeletal abnormalities, short stature and fractures. Treatment involves lifelong supplementation with oral phosphate and active vitamin D to normalize blood levels of phosphate and promote bone mineralization.
The X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 1.5 Bn in 2024 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 9.4% over the forecast period 2024-2031.
Key Takeaways
Key players - Key players operating in the X-linked Hypophosphatemia are Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin, Ascendis Pharma, Pfizer, and Chiesi Farmaceutici. Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical markets burosumab under the brand name Crysvita for treatment of XLH.
Growing demand - Rising prevalence of rare genetic conditions and growing access to specialized treatments is fueling demand for novel treatment options for XLH management. According to public health data, around 1 in 20,000 people are affected by XLH worldwide annually.
Technological advancement - Advancements in gene therapies and development of newer drug delivery technologies is anticipated to revolutionize XLHP treatment landscape in the coming years. Companies are investing heavily in R&D of recombinant protein and gene therapies to provide sustainable symptom relief.
Market Trends
Pipeline strength - Strong product pipeline with over ten candidates in clinical trials including gene therapies is boosting market growth prospects. If approved, these novel therapies can address unmet needs and become standard of care options.
Increasing awareness - Growing patient advocacy initiatives by non-profit groups along with rising medical education regarding genetic conditions is raising awareness about early diagnosis and management of XLH. This is encouraging more patients to seek long-term treatment.
Market Opportunities
Emerging markets - Underpenetrated developing regions of Asia Pacific and Latin America with growing healthcare infrastructure present significant commercialization opportunities for industry players.
Novel formulations - Demand for improved oral and injectable dosage forms to enhance patient adherence and compliance presents lucrative R&D opportunities in the market.
Impact Of COVID-19 On X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Market Growth
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the growth of the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market in various ways. During the pre-COVID times, the market was growing steadily owing to the availability of effective drugs and supportive care. However, during the pandemic, the market experienced slower growth initially due to several factors such as travel restrictions affecting supply chains, reduced demand due to decline in discretionary spending on healthcare and postponement of non-urgent treatments. This led to a short-term decline in revenues for key players.
However, post-COVID trends indicate that the market is recovering gradually and is projected to witness steady growth over the forecast period. With restrictions easing in most parts of the world, healthcare facilities and providers are gearing up to cope with the backlog in treatments. Several manufacturers are focusing on expanding their production capacities and restarting supply chains to meet the rising demand for drugs. Moreover, governments in various countries are prioritizing healthcare to prevent disruption of essential services. Telehealth and teleconsultation have also emerged as favorable alternatives for routine check-ups and medication compliance during such times. Overall, the medium to long term outlook for the market remains positive due to the availability of advanced treatment options and supportive initiatives.
Geographical Concentration In X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Market
In terms of value, North America represents the largest regional market for X-linked hypophosphatemia currently. This is attributed to factors such as high healthcare expenditure, strong reimbursement policies, presence of major market players and adoption of advanced therapies. Within the region, the United States captures the major share due to large patient pool and sophisticated medical infrastructure.
Europe follows North America as the second largest regional market owing to government support for orphan disease research and availability of medications through public healthcare programs across several countries. However, over the forecast period, Asia Pacific is projected to demonstrate the fastest growth rate in the global market due to rising medical tourism, increasing disposable incomes and expansions of coverage under universal healthcare initiatives in various developing nations.
Fastest Growing Region In X-Linked Hypophosphatemia Market
Asia Pacific is currently the fastest growing region in the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market and is expected to continue exhibiting strong growth prospects till 2031. This rapid expansion can be attributed to multiple factors like rising health awareness, growing per capita incomes, improving access to advanced healthcare services in emerging Asian countries like India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines and Thailand. Moreover, various companies are also focusing on expanding their footprint in the region through collaborations with local players and strategic initiatives like setting up manufacturing units. The rising middle class patient pool, favorable government policies supporting medical research and presence of low-cost generics are further expected to drive the Asia Pacific market during the forecast period.
Get more insights on this topic: https://www.trendingwebwire.com/x-linked-hypophosphatemia-treatment-market-is-estimated-to-witness-high-growth-owing-to-advancements-in-gene-therapy/
About Author:
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement. (LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)
What Are The Key Data Covered In This X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Report?
:- Market CAGR throughout the predicted period
:- Comprehensive information on the aspects that will drive the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market's growth between 2024 and 2031.
:- Accurate calculation of the size of the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market and its contribution to the market, with emphasis on the parent market
:- Realistic forecasts of future trends and changes in consumer behaviour
:- X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Industry Growth in North America, APAC, Europe, South America, the Middle East, and Africa
:- A complete examination of the market's competitive landscape, as well as extensive information on vendors
:- Detailed examination of the factors that will impede the expansion of X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market vendors
FAQ’s
Q.1 What are the main factors influencing the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market?
Q.2 Which companies are the major sources in this industry?
Q.3 What are the market’s opportunities, risks, and general structure?
Q.4 Which of the top X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market companies compare in terms of sales, revenue, and prices?
Q.5 Which businesses serve as the X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market’s distributors, traders, and dealers?
Q.6 How are market types and applications and deals, revenue, and value explored?
Q.7 What does a business area’s assessment of agreements, income, and value implicate?
*Note: 1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research 2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it
#X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Trend#X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Size#X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Information#X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Analysis#X-linked Hypophosphatemia Market Demand
0 notes
Text
In modern agricultural production, bamboo is an important cash crop, and its growth quality and yield are directly affected by soil fertility. In order to improve the growth effect of bamboo, the development and use of bamboo special organic fertilizer is particularly important. This paper will discuss the development process of bamboo special organic fertilizer and its effect evaluation in practical application.
1. Development basis of organic fertilizer
The development of organic fertilizer needs to consider the growth needs of bamboo and soil characteristics. The nutrients needed by bamboo mainly include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other elements. NPK Fertilizer Production Line plays an important role in the development of organic fertilizer, It can mix nitrogen fertilizer (Urea), Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate (Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate) and Potassium Chloride according to different ratios to meet the nutritional needs of bamboo at different growth stages.

2. Granulation process of organic fertilizer
In order to improve the efficiency and convenience of fertilizer application, organic fertilizers usually need to be granulated. Fertilizer Granules Compaction Machine and Flat-Die Pellet Machine in the fertilizer granules compaction machine series are commonly used granulation equipment. These devices are capable of compressing organic fertilizer feedstock into a granular form for easy storage and application.

3. Compost fermentation of organic fertilizer
Organic fertilizers need to go through the compost fermentation process before application to improve their fertilizer efficiency and safety. The Windrow Compost Turning Machine plays a key role in this process. By turning the compost material, it promotes air circulation and microbial activity, accelerating the decomposition and conversion of organic matter.

4. Evaluation of the effect of organic fertilizer
After the application of organic fertilizer, its effectiveness needs to be evaluated. The evaluation measures include bamboo growth rate, leaf color, root development, etc. Compared with the control group without organic fertilizer, the effect of organic fertilizer on bamboo growth can be seen directly.
Conclusion
The development and application of bamboo special organic fertilizer can not only improve the growth quality and yield of bamboo, but also improve the soil structure and promote the sustainable development of agriculture. By using NPK Fertilizer Production Line, Fertilizer Granules Compaction Machine, Flat-Die Pellet Machine, Windrow Compost Equipment such as Turning Machine can effectively improve the production efficiency and application effect of organic fertilizer. In the future, with the continuous advancement of organic fertilizer technology, bamboo planting will be more efficient and environmentally friendly.

#NPK Fertilizer Production Line#Fertilizer Granules Compaction Machine#Windrow Compost Turning Machine#Flat-Die Pellet Machine
0 notes
Text
Understanding Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate: Applications, Benefits, and Trend

In the vast world of chemical compounds, Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate stands out as a versatile and essential ingredient in various industries. Known for its wide range of applications and beneficial properties, this compound plays a crucial role in everything from food production to pharmaceuticals and water treatment. But what makes Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate so significant, and how does it impact our daily lives? Whether you are a professional in the field or simply curious about the compounds that touch our lives, learn from Annexe Chem Pvt. Ltd. as we delve into the fascinating world of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate.
What is Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate?
Chemical Composition of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate:
Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate, chemically represented as Na2HPO4·7H2O, is composed of two sodium (Na) atoms, one hydrogen (H) atom, one phosphate (PO4) group, and seven water (H2O) molecules. This heptahydrate form means it includes seven molecules of water of crystallization, which is integral to its structure and properties.
Physical Properties of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate:
This compound typically appears as a white, crystalline powder or granules. It is highly soluble in water, making it an excellent candidate for applications that require a quick and efficient dissolution. Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is stable under normal conditions but should be stored in a cool, dry place to maintain its efficacy and prevent it from absorbing moisture from the air.
Applications of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate Across Various Industries
Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate in Food Industry: Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is a key player in the food industry, valued for its multifunctional properties. As a pH regulator, it helps maintain the desired acidity or alkalinity in various food products, ensuring they have the right taste and texture. Its role as an emulsifier is equally important, as it enables the blending of ingredients that would otherwise separate, such as oil and water. Additionally, as a stabilizer, it helps maintain the consistency and appearance of food products, preventing them from breaking down over time.
You can find Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate in a variety of food items. It is commonly used in processed cheese to ensure a smooth texture and prevent separation. It’s also found in powdered dairy products like milk and creamers to improve solubility and flow properties. In bakery products, it helps with leavening and maintaining the desired pH for optimal texture and shelf life.
Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate in Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, this is an essential ingredient in drug formulations. Its buffering capacity is crucial in maintaining the pH balance of various medications, ensuring their efficacy and stability. It helps in adjusting the pH to the desired level, which is vital for the stability and bioavailability of many drugs.
One of the significant advantages of using Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate in pharmaceuticals is its ability to improve the stability and medicine shelf life. Maintaining a stable pH environment, prevents the degradation of active pharmaceutical ingredients, thus extending the product’s effectiveness and longevity. This stability is particularly important in liquid formulations and injectables, where precise pH control is critical.
Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate in Water Treatment: Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate plays a vital role in water treatment processes, especially in water softening. It effectively binds to calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, preventing them from forming scale and deposits. This process not only softens the water but also enhances the efficiency of detergents and soaps.
In industrial applications, Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is used to prevent scale formation in pipes, boilers, and other equipment. Inhibiting the precipitation of scale-forming minerals helps maintain the efficiency and longevity of these systems, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
Other Uses of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate
Cleaning Products: In the cleaning industry, Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is a valuable component of many detergents and cleaning agents. Its ability to soften water and stabilize pH makes it effective in improving the cleaning performance of these products. It helps remove dirt, grease, and stains more efficiently, enhancing the overall effectiveness of household and industrial cleaners.
Agriculture: In agriculture, Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is used as a component of fertilizers and soil treatment products. It provides essential phosphates that are vital for plant growth and development. Improving the nutrient content of the soil helps boost crop yields and enhance the health of plants. Additionally, its buffering properties help maintain optimal soil pH levels, promoting better nutrient uptake and plant growth.
Benefits of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate
Versatility: Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate is celebrated for its versatility, finding applications in diverse industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, cleaning products, and agriculture. Its multifunctional nature allows it to act as a pH regulator, emulsifier, stabilizer, buffering agent, and water softener, making it an invaluable component in many products and processes.
Effectiveness: Even in small quantities, Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate proves to be highly effective. Its potent chemical properties mean that a little goes a long way, whether it’s stabilizing a food product, enhancing the stability of a pharmaceutical formulation, or softening water. This effectiveness ensures that minimal amounts are required to achieve the desired results, contributing to its widespread use.
Cost-Effectiveness: This compound offers a cost-effective solution for many industrial and commercial applications. Its efficiency in small doses translates to lower usage rates, reducing overall material costs. Additionally, its ability to perform multiple roles in various applications means that manufacturers can rely on a single ingredient to meet multiple needs, further driving down costs and simplifying supply chains.
Environmental Impact: Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate has a relatively low environmental footprint. It is biodegradable and breaks down into harmless substances, reducing the risk of environmental pollution. Its use in water treatment and agriculture also promotes sustainable practices by improving water quality and soil health without leaving harmful residues. This eco-friendly profile makes it a responsible choice for companies aiming to minimize their environmental impact.
Future Trends and Developments Related to Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate
Innovations in Applications: Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate continues to evolve with new and emerging applications. Innovations in the food industry are exploring its use in novel food processing techniques and functional foods, enhancing both product quality and nutritional value. In pharmaceuticals, researchers are investigating its role in advanced drug delivery systems and novel therapeutic formulations. Additionally, advancements in water treatment technologies are focusing on using this compound for more efficient and sustainable water purification methods.
Research and Development: Ongoing research is delving into the potential of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate to address modern challenges. Scientists are exploring its application in new areas such as biotechnological processes, where its buffering and stabilizing properties could support innovative manufacturing techniques. Research is also focused on improving its efficiency and sustainability, with efforts to develop greener synthesis methods and enhanced formulations.
Market Trends: The demand for Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate remains strong across various sectors. The growing emphasis on food safety and quality, coupled with advancements in pharmaceutical and water treatment technologies, is driving market growth. Additionally, increasing awareness of environmental sustainability is boosting the demand for compounds with minimal ecological impact. Market trends indicate a steady rise in the use of this compound, reflecting its continued relevance and versatility in meeting the needs of diverse industries.
Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate proves to be a highly versatile and essential compound with significant applications across various industries, from food and pharmaceuticals to water treatment and agriculture. Its multifunctional properties, effectiveness in small quantities, and cost-efficiency make it a valuable asset in modern manufacturing and industrial processes. As research and innovations continue to explore new uses and improvements, this compound’s importance is set to grow. For those seeking high-quality Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate, Annexe Chem Pvt Ltd stands out as the leading manufacturer in India, offering reliable and efficient solutions to meet diverse industry needs.
Check out the Original Article
#Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate#benefits of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate#application of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate#advantages of Di Sodium Hydrogen Phosphate Heptahydrate
0 notes
Text
Kinases are essential enzymes involved in the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP or other sources to a wide array of molecules in cells. They are essential for many cellular functions, such as regulating the activity of proteins, enzymes, and other molecules. Thus, kinases play a vital role in the activity of cells, impacting a wide range of biological processes. Kinases also play an important role in maintaining homeostasis, or the physiological equilibrium of the body.
Homeostasis is essential for both human health and survival. Kinases can act as switching points for cell signaling pathways when certain conditions are disturbed, as well as when homeostasis needs to be maintained. Kinases can also regulate a variety of processes, such as metabolism, cell development, and immune responses. By controlling these processes, kinases are able to create a balance between different signals and ensure homeostasis.
Kinases also play an important role in the protection of the land. For example, kinases are involved in controlling the growth of pathogenic microbes, which can wreak havoc on soil ecosystems. Additionally, kinases help regulate the physiological responses of plants, allowing them to better tolerate changes in the environment. Finally, kinases are essential for basic cellular functions, including transport and energy production, which are necessary for maintaining healthy soils and ecosystems.
In summary, kinases are important enzymes essential for homeostasis in both humans and their environments. Kinases help regulate processes, such as cell signaling, metabolism, cellular development, and immune responses, all of which are key for maintaining the health and stability of lands.
0 notes
Text
Trichoderma asperellum TR3 Viability Formulation: Packaging Variations

Abstract
Trichoderma asperellum TR3 has been applied as a biopesticide and Plant Growth Promotion Fungi (PGPF) but in the form of a suspension and substrate without the addition of carriers and adhesives so for long-term use and short shelf life. This study aims to obtain the right packaging formulation and have good viability, as well as a long storage time using talc and tapioca flour as the basic ingredients. The isolate collection was rejuvenated by growing in PDA medium, after completion of incubation for 48 hours, the growing fungal colonies were counted, isolated and purified, then made in the form of a powder starter. Test of various formulations of T. asperellum TR3 fungal powder packaging was carried out by viability test using a Completely Randomized Design (CRD), with packaging treatment on the formulation: P1 = Aluminum foil plastic, P2 = Bottle and P3 = Cetic plastic. Each treatment was repeated 3 times to obtain a combination of 9 treatment units. Furthermore, all packaging combinations were stored at room temperature. In the first month, 1 pack was taken for regrowth which aims to determine the viability of the conidia and then every two weeks for 12 weeks. The results showed that the average number of conidia colonies growing on various packages gave different viability results, but had no significant effect between formulations of various packages and viability. The average number of colonies that grew on aluminum foil plastic packaging was more in each observation of storage time compared to bottle and plastic packaging.

Introduction
The use of microorganisms as biological control agents has been widely carried out and provides benefits for increasing agricultural production in Indonesia (Hanudin and Marwoto 2012; Nur Amin et al., 2015; Ratna et al., 2020; Ratnawati et al., 2020). However, reports on the use of local or local microorganisms that have potential have not been widely carried out. Local microorganisms work more effectively, because they are supported by various appropriate environmental factors and do not result in ecosystem changes and implementation in the field is easier. According to Cook & Baker (1983), efforts to overcome plant diseases with biological practices provide good opportunities because the microorganisms are already available in the field and their activities can be controlled by the environment and the host.
The group of microorganisms, especially fungal microbes that are able to suppress pathogens, is in the Moniliales family, such as Verticillum sp., Trichoderma sp and Gliocladium sp. The genus Trichoderma sp. it is known that several species can parasitize other fungi and have the potential to be used as biological control (Santoso et al., 2007; Ratnawati et al., 2019; Ratnawati et al., 2020).
Microbes that are useful as components of natural habitats have important roles and functions in supporting the implementation of environmentally friendly agriculture through various processes such as decomposition of organic matter, mineralization of organic matter, besides that microbes are positioned as producers of nutrients for plants. Budiarti & Nurhayati (2014), reported that plants and microbes will interact and stimulate each other caused by the presence of root exudates. Fungi are heterotrophs, dominant on acid soils although they are also found in neutral or alkaline soils and some of them are sensitive to pH 9.0 but this sensitivity is important in overcoming plant diseases. The presence of fungi and bacteria as antagonist agents is able to influence the activity of microorganisms so that it is important to take into account the suppression of disease. In addition, many antagonist agents can stimulate plant growth because they are able to produce growth hormones, fix nitrogen, dissolve phosphate, and produce siderophores (Siti Hardiyanti et al., 2017).
Antagonistic microbes found in the rhizosphere and rhizoplan areas that can act as controlling agents include the genus Trichoderma sp, Penicillium sp and Asperigillus sp (Agrios., 2005), while Nirwanto & Mujoka (2009) reported that the microbes found in the phyllosphere were the genus Penicillium sp., Fusarium sp. , Trichoderma sp. , Stemphylium sp., Rhizopus sp., Curvularia sp. and Gliocladium sp. Furthermore, Sayang (2009) reported that microbial antagonists that are effective as biological controllers include Bacillus sp, Trichoderma sp, Penicillium sp and Clostridium sp.
Nur Amin et al. (2015) suggested that the application of non-pathogenic fungi to various types of plants would increase the resistance of the host plant to pathogen attack and be able to induce resistance in the upper part of the plant. The use of beneficial microbes in improving soil texture and structure by increasing its aggregation and stability (Rashid et al., 2016). The interaction between microbes and plants is an indicator of soil fertility (Hayat et al., 2010).
Many studies using the fungus Trichoderma sp. as an effective biological agent to control various pathogens, however, it is still experiencing obstacles related to storage time (Suhera et al., 2018). Trichoderma sp. is a group of fungi that are always associated with plants and soil. If this fungus is in plant tissue, it is called an endophytic fungus (Nur Amin et al., 2017). Trichoderma sp. is one of the endophytic fungi that can live in all parts of plant tissue both below ground and above ground, namely roots, stems and leaves (Kusari et al., 2012; Rosmana et al., 2018).
Ratnawati's previous research (2020) was in vitro starting from the microbial isolation stage, identification of microbes both macroscopically and microscopically, microbial screening, molecular identification, compatibility tests, antagonist tests, until superior and potential microbes were found as biopesticides and as plant growth microbes. Promotion Fungi (PGPF) obtained as many as 9 microbes that could potentially be used as biological agents. One of them is Trichoderma asperellum TR3.
Trichoderma asperellum TR3 is one of the rhizosphere fungi which is known as an antagonist fungus in both in vitro and in vivo tests which has the ability to suppress various types of pathogens in various plants. T.asperellum TR3 is a fungus with biopesticide and PGPF properties (Suhera 2018; Ratnawati et al., 2020; Ismail et al., 2020). T. asperellum (TR3) has been applied as a biopesticide and PGPF but in the form of a suspension and substrate without the addition of carriers and adhesives so that it is for long term use and has a short shelf life. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a formulation in powder form with various forms of packaging which will then be monitored for viability during storage.
Based on the description above, it is necessary to conduct research on the development of powder formulations of the fungus T.asperellum strain TR3 isolate in various forms of packaging formulations to determine the viability of the fungal formulation. This study aims to obtain the right packaging formulation and have good viability, with a duration of storage.
Source : Trichoderma asperellum TR3 Viability Formulation: Packaging Variations | InformativeBD
1 note
·
View note
Text
20 Adenosine Diphosphate Examples
What is Adenosine diphosphate? Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is a molecule composed of adenosine and two phosphate groups. It is a fundamental component of the energy currency within living cells. ADP is an intermediate molecule in the process of transferring and storing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In simpler terms, when cells need energy for various activities, they…
0 notes