#life science
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
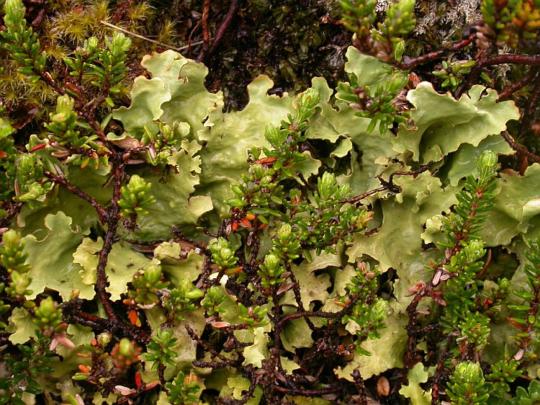
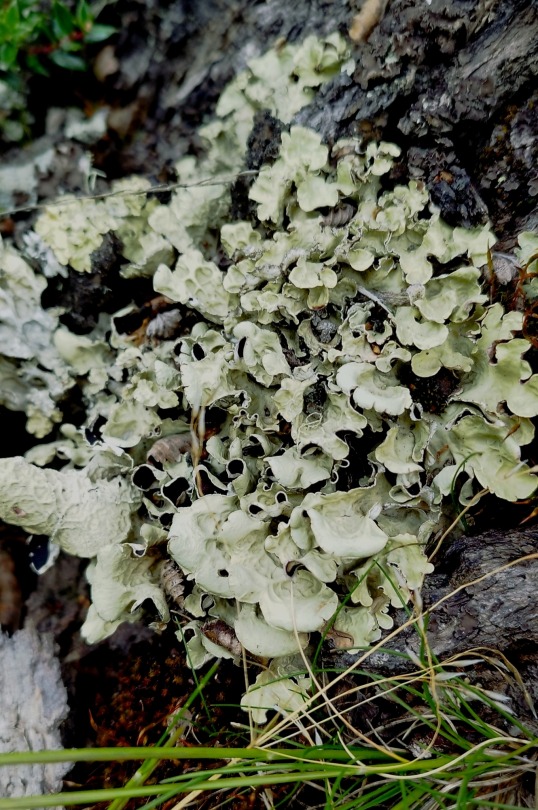
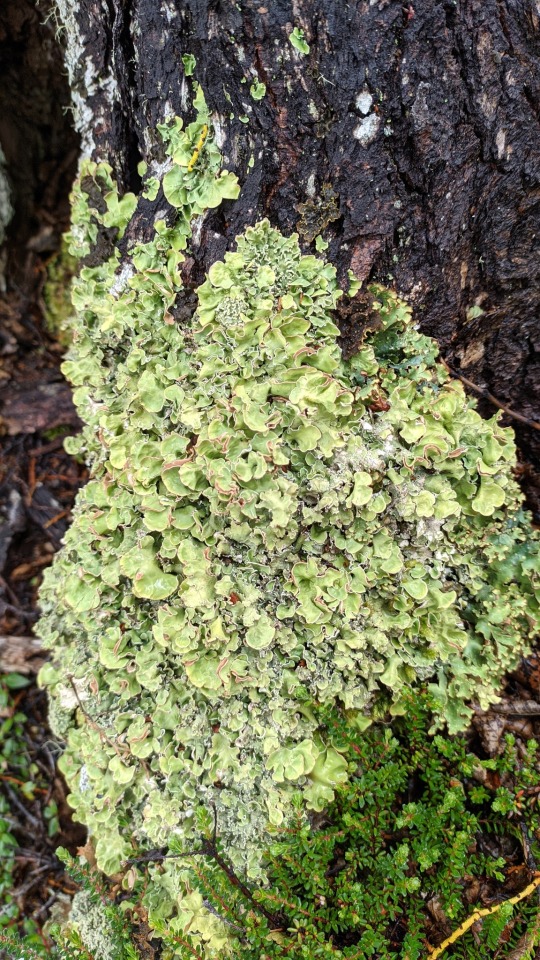
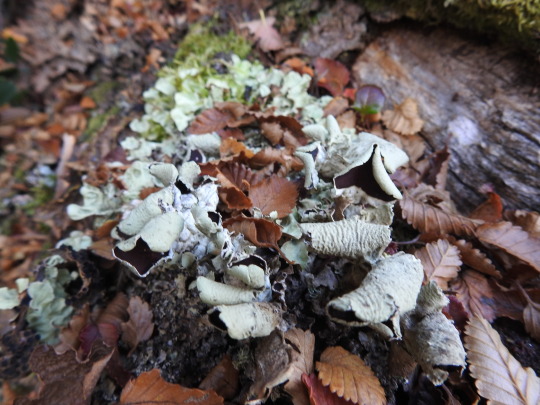
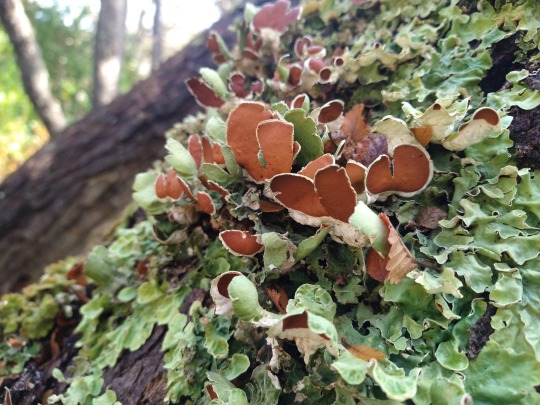
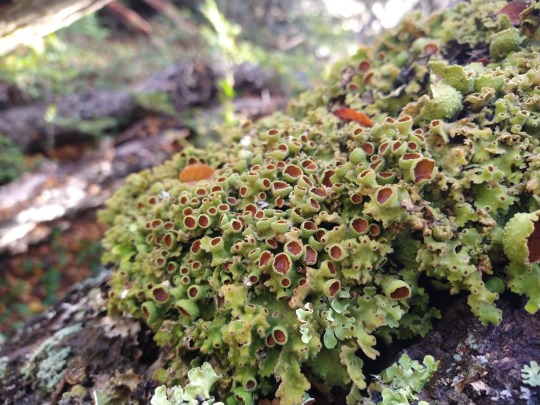
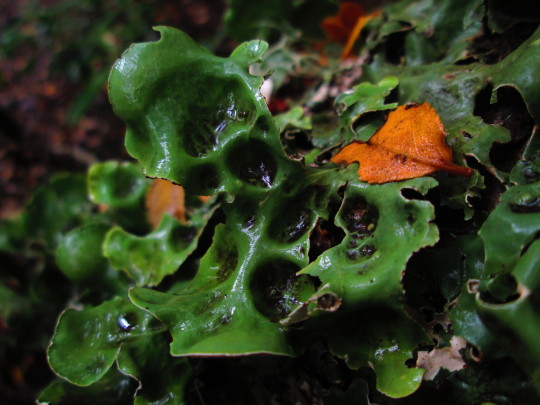









Nephroma antarcticum
images: source | source
#lichen#lichens#lichenology#lichenologist#mycology#ecology#biology#fungi#fungus#symbiosis#symbiotic organisms#algae#I'm lichen it#lichen a day#daily lichen post#lichen subscribe#trypo#trypophobia#Nephroma antarcticum#Nephroma#foliose lichen#life science#environmental science#natural science#the natural world#beautiful nature#weird nature
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
My absolute favourite thing about nature is how NOTHING is set in stone and everything is on a spectrum.
Species ? They're not as clear as you'd think. Tell me when the first human was, or who would've counted as one. It's hard to say because it's a Gradient from one species to another rather than seperate boxes. Chicken or the egg ?
Sex ? Not as binary as it seems. Individuals are usually one or the other extreme but no one thing defines sex, it's usually just determined by how many characteristics match one extreme, and sometimes you can't, and it's neither one or the other !! Many animals and other species are hermaphrodites, having both gametes and sexual organs, many can be gynandromorphs and humans can be intersex.
Disorders ? Similar to sex, where they're usually defined by how many symptoms seem to fit a label.
Individuals ? While fairly easy to define in things like mammals, there are animals like siphonophores, which are colonies of animals that work like specialised cells but the colony itself functions as an individual as well. Which is the animal in that case, the colony or the parts of it ?
Thinking in black and white just means you're missing out on so much wonderful complexity in nature and the world around you, grey comes in many more shades than black and white and can make the world infinitely more interesting to view.
144 notes
·
View notes
Text
Join Biodiverse!
Biodiverse is an LGBT+ centered science Discord server where we welcome science lovers from all fields and levels of expertise. Casual science enjoyers, certified professionals, and anyone in between are all welcome to join and talk about their passions!
Here are some of the things we offer:
🧪Channels for a variety of science topics - There is a focus on natural sciences (biology, botany, mycology), as well as topics covering lots of different fields of science (astronomy, geology, chemistry). There's something for everyone!
🔍 Identification Help - Encounter a critter or plant you don't know the name of? We'll try to help you out with our handy identification help pings that connect you to people who might recognize your find.
📽️Movie nights - We have (mostly) weekly movie nights on Saturday evenings, as well as impromptu movies throughout the month. 🧠Events & Activities - Stay tuned for events we might host, such as birding competitions or art contests! We also host Trivia where everyone is welcome to participate, and a study session ping if you need someone to body double with you in a voice chat!
😸Custom Emotes - Cute animal themed emotes, drawn by me and unique to the server!
If any of this sounds interesting to you, or you just need a place to yap about your favorite topics and look at cool animals, please consider joining our Discord server!
#biology#zoology#mycology#botany#geology#ecology#microbiology#paleontology#astronomy#medicine#vulture culture#environmental science#entomology#ornithology#icthyology#science#lgbt discord server#science discord#natural science#life science#marine biology#spec evo#spec bio
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Epigenetics: A Journey Through Inheritance Beyond Genes
For centuries, scientists have been fascinated by the mysteries of heredity and how traits are passed down from generation to generation. DNA, the molecule that stores our genetic code, was once thought to be the sole determinant of our characteristics. However, a new frontier in biology, revealing a captivating layer of complexity beyond the DNA sequence itself: Epigenetics.
What is Epigenetics?
The term "epigenetics" was first coined in the 1940s by British biologist Conrad Waddington, but it wasn't until the late 20th century that its significance truly blossomed. Epigenetics, literally meaning "above genetics," refers to the study of heritable changes in gene expression that occur without alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Imagine DNA as the musical score, but epigenetics are the conductor and musicians who determine how the music is played. Through chemical modifications and adjustments to the proteins around DNA, epigenetics dictates which genes are turned on or off, influencing how cells function and ultimately shaping our health, development, and even behavior. Think of your DNA as the hardware: it contains the basic instructions for building and running your body. But epigenetics acts like the software, fine-tuning those instructions and determining which genes get turned on or off at specific times and in specific cells. These modifications, like chemical tags or changes in the packaging of DNA, don't alter the underlying code itself, but they can have a profound impact on how it's read and interpreted.
The Key Players:
DNA methylation: This process involves adding a methyl group to DNA, essentially silencing the gene it's attached to. Imagine it like putting a dimmer switch on a light bulb.
Histone modifications: Histones are proteins that package DNA, and changes in their structure can make genes more or less accessible to the cellular machinery needed for expression. Think of it like adjusting the curtains around a window - open wide for full light, slightly closed for filtered light.
Non-coding RNAs: These are molecules that don't code for proteins but can regulate gene expression in various ways. They're like the backstage crew in a play, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
The Power of Epigenetic Regulation
Epigenetic regulation plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including:
Development: During embryonic development, different cell types emerge from the same DNA blueprint by activating or silencing specific gene sets through epigenetic modifications.
Cellular differentiation: Specialized cells like muscle or nerve cells have unique functions due to differences in their active genes, controlled by epigenetic mechanisms.
Learning and memory: Epigenetic changes in brain cells are thought to be essential for learning and forming memories.
Aging: As we age, our epigenome accumulates changes that can contribute to age-related decline and disease.
Environmental influences: Diet, exercise, stress, and exposure to toxins can leave epigenetic marks on our genes, potentially impacting our health and even the health of future generations.
Epigenetics reminds us that we are not simply products of our genes. Our environment, choices, and experiences leave their mark, shaping who we are and potentially influencing our children's health. This deeper understanding of ourselves opens doors for self-awareness, empowerment, and potentially reshaping our narratives – not just as individuals, but as a species with the potential to leave a healthier legacy for generations to come.
#life science#biology#science sculpt#molecular biology#biotechnology#epigenetics#daily dose of science#dna#genetic inheritance#genetics#decoding dna#genetic code#science#double helix
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hermit crabs all over the world, which scavenge shells as armour for their bodies, are turning increasingly to plastic waste instead. The conclusion is based on analysis of photos, taken by wildlife enthusiasts, and published online. Scientists said they were "heartbroken" to see the extent to which the animals were living in our rubbish. They said two-thirds of hermit crabs species were pictured in "artificial shells" - items that humans discarded. The discovery is published in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
Continue Reading.
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
i’m an ecology major because nothing terrifies transphobes like life sciences taught beyond the 7th grade level
#trans pride#trans#trans people in stem#queer#queer stem#queer scientists#ecology#biology#advanced biology#forestry#life science#bio major#anti transphobes
58 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the Shadows of Slime: Uncovering the Role of Sporangia in Slime Mold Life

Imagine walking through a damp, moss-covered forest floor, when you suddenly spot something strange: a bright, glistening mass of yellow-orange goo. It looks like something out of a science fiction movie, but it’s actually a plasmodial slime mold, one of nature’s most bizarre and fascinating creatures. These organisms are neither fungi nor plants, but something entirely different, existing in a world all their own.
One of the most mind-blowing aspects of plasmodial slime molds is their method of reproduction, which involves the formation of sporangia. But what exactly are sporangia? Simply put, they are spore-producing structures that serve as the slime mold’s way of multiplying and spreading its species. These sporangia usually emerge at the end of the plasmodial stage, after the slime mold has spent time exploring its environment, moving across surfaces like a slow, undulating wave.
Now, here’s the kicker: the slime mold’s plasmodium is a giant, multi-nucleated mass of protoplasm, which doesn’t have individual cells like most organisms do. It's essentially one big, living blob that “decides” when to form sporangia. This decision is made in response to environmental conditions—often when food is scarce or the mold has completed its spread. The plasmodium’s ability to adapt and respond in such a complex way, without a brain, is what scientists find so captivating. The slime mold "chooses" the right moment to produce sporangia, which will release spores that can survive harsh conditions and begin the cycle again.
In a sense, plasmodial slime molds are like tiny, living puzzle pieces, piecing together an ancient survival strategy. Their ability to create sporangia and spread spores helps them survive and thrive in unpredictable environments. And even though these creatures don’t have a brain or nervous system, they exhibit an incredible form of “intelligence” when it comes to solving problems like finding food or navigating through mazes.
So the next time you find yourself lost in the woods, take a moment to appreciate the strange and wonderful world of plasmodial slime molds. With their sporangia, they’re not just a blob of goo—they’re survivors, masters of adaptation, and proof that intelligence can come in many forms.
#nature#biology#microbiology#microorganisms#protists#slime molds#slime mold#myxogastria#myxomycota#myxomycetes#fungi#mycology#natural history#life science#science#science class#microscopic#microscope#microscopic life#microscopic organisms
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
70 days of productivity

Seventy days of mastery—every second bent to my will.

- 50+ chapters expertly - consistent workout - natural skincare + artificial skincare - haircare - mind detox - breathing & mindfulness - nature bath - math & other skills - hydration - gradual productivity increase

@crownedinscrubs on Tumblr : my secondary blog
#academic#medblr#med school#med student#med studyblr#university#uni student#notes#medical notes#med notes#biology#bio#bio notes#biology notes#life science#science#sciblr#scienceblr#100 days of productivity#academia#studyblr#bibliophile#studyspo#study aesthetic#study motivation
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
There are some weird growths by bacteria but this was by far the most ridiculous I've seen. Creeped the shit out of me till I got used to seeing it. It was slimy/moist af
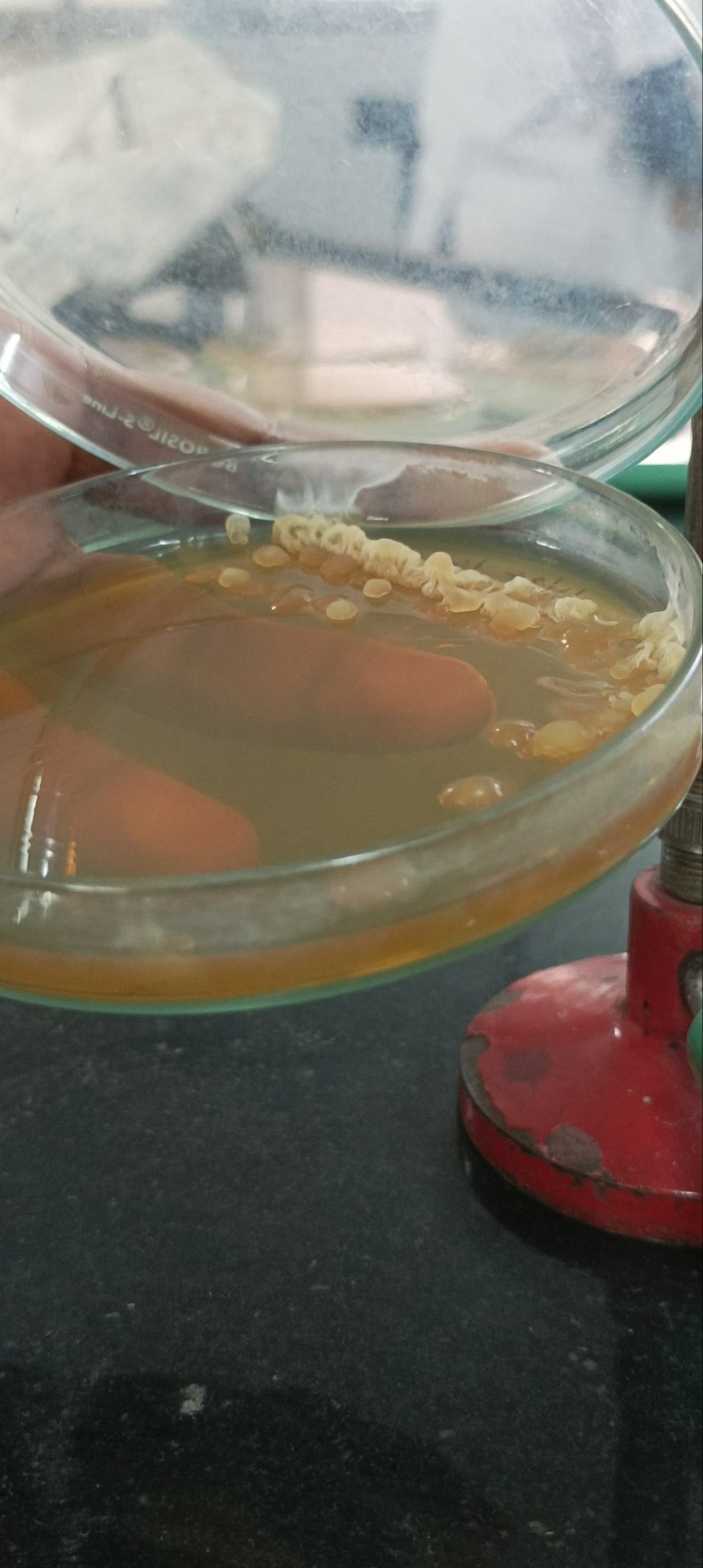
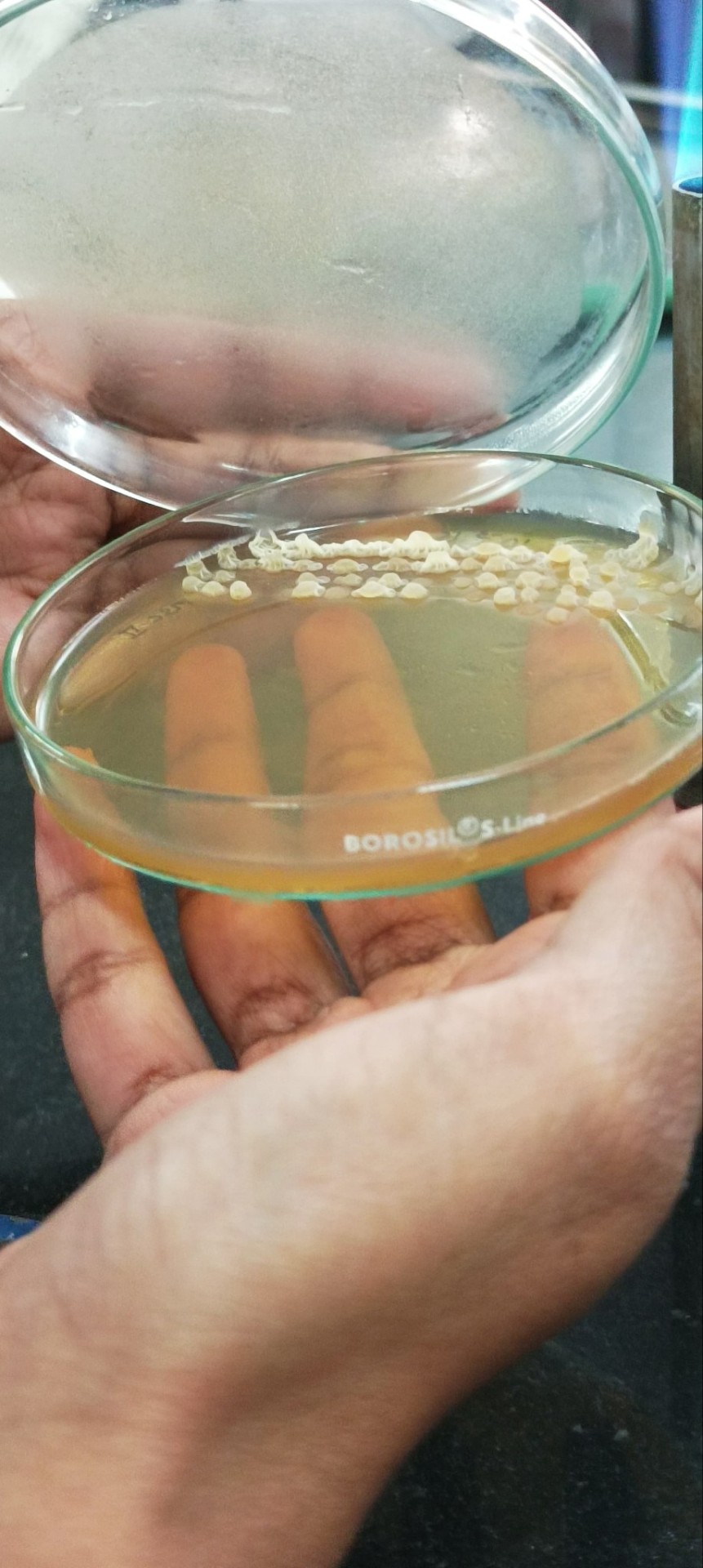

Isolated from yoghurt sample.
For reference, the image below is what bacteria usually grow as
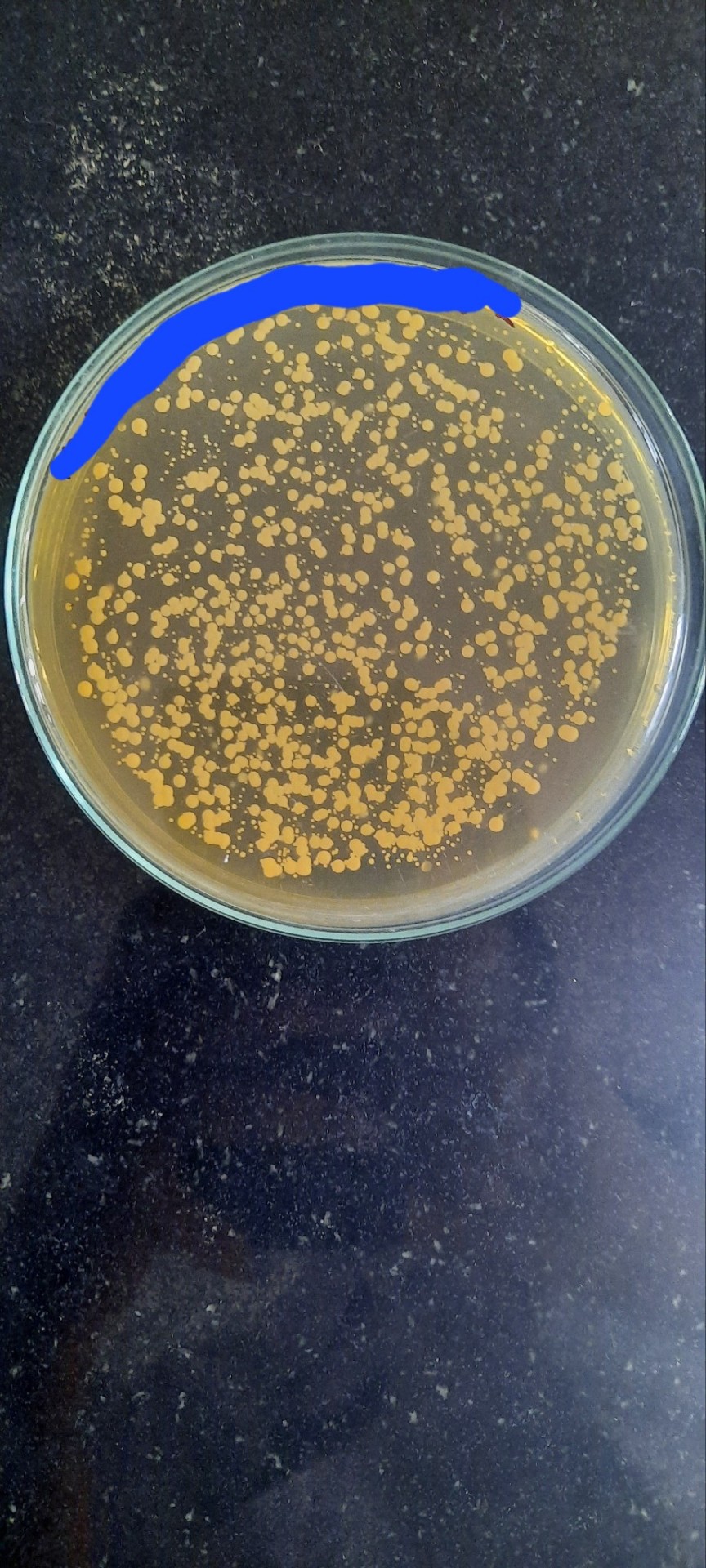
Just small circles, sometimes in color.
Anyone know what the top one can be?
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
THE TREE OF NATURAL SCIENCE

LIFE SCIENCE -> Any science concerned with the study of living organisms
THE BRANCHES OF LIFE SCIENCE:
BIOLOGY
This branch of life science will study living organisms, and it will be divided into many specialized branches that cover their morphology, physiology, anatomy, behavior, origin, and distribution.
THE BRANCHES OF BIOLOGY:
CONSERVATION
This branch of biology will study environmental conservation and biodiversity on Earth.
■Wildlife Management is a branch of conservation that will specialize in the concern for the management process influencing the interaction between wildlife, its habitat, and people in order to achieve the pre-defined impact.
ECOLOGY
This branch of biology will study how organisms interact with the environment around them.
■Autecology is a branch of ecology that will specialize in studying a specific organism of a species.
■Synecology is a branch of ecology that will specialize in studying an ecosystem.
EVOLUTION
This branch of biology will study any evolutionary process with its regard to diversification and adaptation over many years.
GENETICS
This branch of biology will study genes, genetic variation, and heredity.
MARINE BIOLOGY
This branch of biology will study marine organisms.
■Ichthyology is a branch of marine biology that will specialize in studying fish.
MEDICINE
This branch of biology will study managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of an injury or disease, and promoting the health of a patient through such mentioned practice.
■Psychiatry is a branch of medicine that will devote itself to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of deleterious mental conditions.
□Addiction psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will focus on the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of people who have one or more disorders related to addiction.
□Forsenic psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will be applied in a legal context involving any civil, criminal, correctional, regulatory, or legislative issues.
□Neuropsychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will examine both organic and psychological aspects as a cause for illness.
□Occupational psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will use the extension of psychiatric knowledge and skill to the day-to-day functioning of individuals in the workplace and their organizations, with the goal of helping both function better.
□Geriatric psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will center itself on prevention, evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of mental and emotional disorders in the elderly.
□Child psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will be concerned with the study and treatment of mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders of childhood.
□Adolescent psychiatry is a branch of psychiatry that will be interested in the diagnosis and the treatment of disorders of thinking, feeling, and/or behavior affecting children, adolescents, and their families.
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
This branch of biology will study the chemical structure and any biological process of a molecule.
PHYSIOLOGY
This branch of biology will study how the human body functions.
BOTANY
This branch of biology will study plants.
■Mycology is a branch of botany that will focus on the study of fungi, including their taxonomy, genetics, physiology, and any ecological role.
ZOOLOGY
This branch of biology will study the entire animal kingdom.
■Anthrozoology is a branch of zoology that will study the interaction between any human and another animal.
■Arachnology is a branch of zoology that will handle the study of spiders and any related species known as arachnids.
■Cetology is a branch of zoology that will be interested in the study of marine mammals.
■Entomology is a branch of zoology that will focus on the study of insects.
1. COLEOPTEROLOGY is the sub-branch of entomology that will concern itself with the study of the beetle.
2. DIPTEROLOGY is the sub-branch of entomology that will study all types of flies.
3. ISOPTEROLOGY is the sub-branch of entomology concerned with the study of the termite.
MICROBIOLOGY
This branch of biology will study any microorganism.
CHEMISTRY ->
The study of the identification of the substances that which matter is comprised; the investigation of their properties and the methods in which they interact, combine, and change; and the use of these processes to form new substances.
THE BRANCHES OF CHEMISTRY:
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry that's concerned with the study of an organic substance and compound.
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry that will examine the properties and behavior of inorganic compounds, which would include any metal, mineral, and organometallic compound.
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry concentrated on the application of technique and theory of physics to the study of the chemical system.
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry interested in obtaining, processing, and communicating information about the composition and structure of matter.
STEREOCHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry illustrating the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and molecules and its effect on the chemical reaction.
BIOCHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry that will evaluate the chemical and physicochemical processes and substances that occur within the living organism.
GEOCHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry that will study the chemical composition of the earth and its rocks and minerals.
FORENSIC CHEMISTRY
The branch of chemistry that will use the application of chemistry to help law enforcement catch their criminal.
PHYSICS ->
The study of the structure of matter and how the fundamental constituents of the universe interact.
THE BRANCHES OF PHYSICS:
OPTICS
The branch of physics that will study the sense of sight and the behavior of light, or the properties of transmission and deflection of other forms of radiation.
ELECTROMAGNETISM
The branch of physics that will investigate the interaction of electric currents or fields and magnetic fields.
RELATIVITY
The branch of physics that will examine special relativity and general relativity. For example, special relativity will apply to all physical phenomena in the absence of gravity, but general relativity will explain the law of gravitation and its relation to any force of nature.
THERMODYNAMICS
The branch of physics that will illustrate the energy and work of a system.
ACOUSTICS
The branch of physics that will vocalize the study of sound for us to hear it.
QUANTUM PHYSICS
The branch of physics that will focus on the study of matter and energy at the most fundamental level.
MECHANICS
The branch of physics that will examine the relationship between force, matter, and motion among a physical object. To define this, this force, when applied to an object, will result in the displacement or change of an object's position relative to its environment.
EARTH SCIENCE ->
See previous post regarding this topic.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
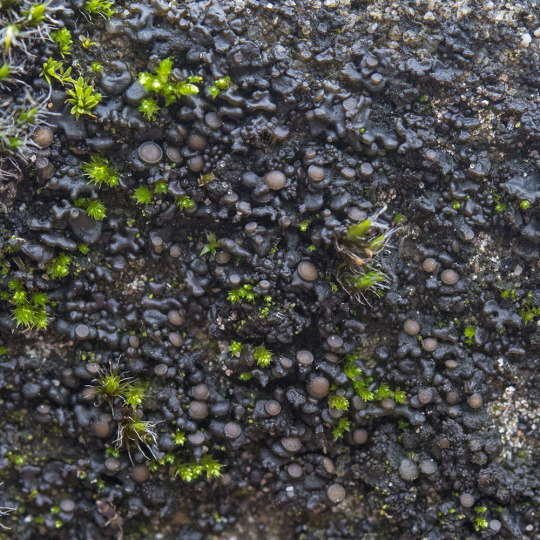
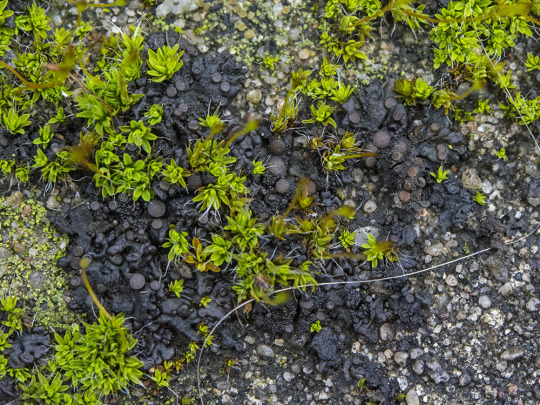
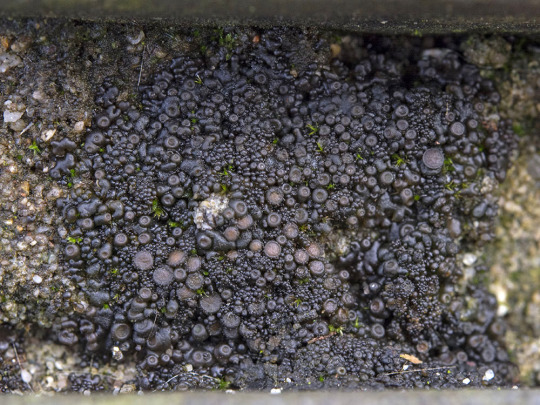
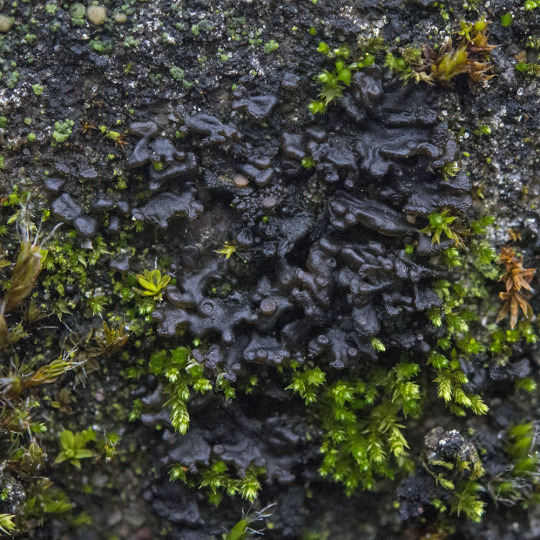
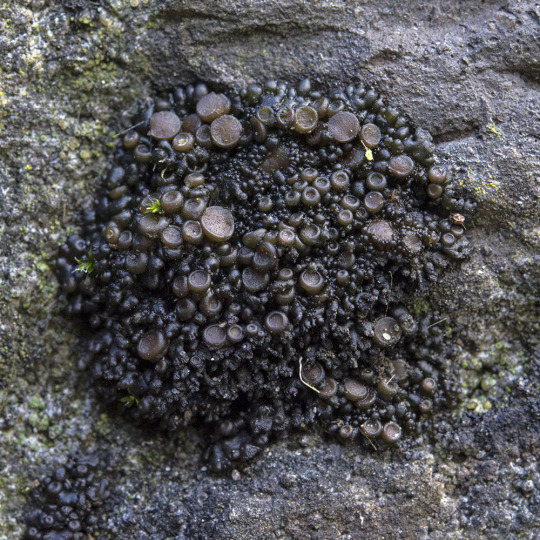







Scytinium turgidum
When I see people tag my lichen posts with #plant, I have to admit, a part of me dies inside. Because like, cyanolichens like S. turgidum have to plants parts. This guy is composed of an ascomycete fungi and a cyanobacteria -- no plants involved whatsoever. This jelly lichen grows on calcareous rock often inundated with runoff. It has shiny red-black to blackish-olive lobes which are wrinkled and thin when dry, thick and gelatinous when wet. The upper surface is covered in granular isidia, and often brownish-red apothecia. S. turgidum has a Nostoc photobiont.
images: source
info: source | source
#lichen#lichens#lichenology#lichenologist#mycology#ecology#biology#fungi#fungus#symbiosis#symbiotic organisms#cyanobacteria#nostoc#Scytinium turgidum#Scytinium#trypo#trypophobia#nature#the natural world#beautiful nature#weird nature#life science#environmental science#I'm lichen it#lichen a day#daily lichen post#lichen subscribe
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
since animal science turned out to be a very popular option on the last poll--
#studyblr#animal science#vetblr#medblr#veternary science#veterinary medicine#vet med#vetmed#surgery#zoology#zoological science#wildlife biology#conservation#environmental science#vet surgery#vet sci#vet science#animals#pharmacology#biology#bio#ecology#polls#tumblr polls#science#scienceblr#sciblr#life science#microbiology#virology
40 notes
·
View notes
Text


Life Science Library: Planets (1972)
#books#70s#nature#animals#life on earth#time life#life science library#life science#hologram parade#1970s#physical media
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
hello hello everyone! just here to tell you all again about our wonderful server, Biodiverse!
Biodiverse is an LGBT+ science discord server! everyone from all science fields and levels of expertise are welcome! you don’t need to be a scientist to join, just as long as you love science and want to know more about it!
we have text channels for a wide variety of science topics! there is a focus on natural sciences (mycology, botany, biology, etc.) as well as topics like chemistry and astronomy; there’s something for everyone!
there’s also fun events and community projects! this includes weekly trivia contests, occasional movie/documentary streams, study sessions, and art contests to celebrate server milestones! and honestly whatever random fun activity we feel like doing LOL
we recently started a community project forum, where members can share in depth information about any science topic of their choosing. it’s basically an info-dump channel, and personally i’m very excited to read everyone’s entries!
OH ALSO. we have custom emojis! lovingly hand drawn by yours truly. here’s a few of them :3c
if any of this sounds interesting to you, please consider checking us out! we’d love to have you!
#biology#zoology#mycology#botany#geology#ecology#microbiology#paleontology#astronomy#medicine#vulture culture#science#lgbt discord server#science discord#natural science#life science#marine biology
296 notes
·
View notes
Text
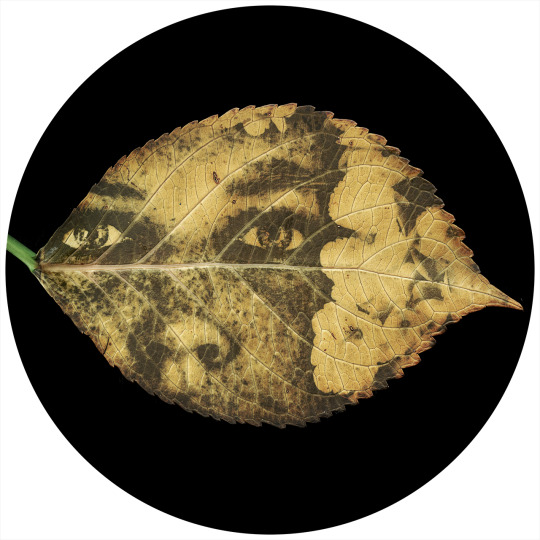

Untitled Chlorophyll Print (A. with Hydrangea) - chlorophyll print photogram (7 hour solar exposure) - hydrangea leaf - robert matejcek - 2023
“She seemed a compound of the autumn leaves and the winter sunshine...” - Virginia Woolf - Night and Day
tags:
#robert matejcek#photography#analog#chlorophyll print#alternative photographic processes#alternative photography#contact printing#solar printing#hydrangea leaf#plants#botanical#biology#science#life science#portrait#found objects#experimental#art#my art#artists on tumblr#photographers on tumblr
31 notes
·
View notes