#DNA
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
"Once thought to be extinct, black-footed ferrets are the only ferret native to North America, and are making a comeback, thanks to the tireless efforts of conservationists.
Captive breeding, habitat restoration, and wildlife reintegration have all played a major role in bringing populations into the hundreds after near total extinction.
But one other key development has been genetic cloning.
In April [2024], the United States Fish and Wildlife Service announced the cloning of two black-footed ferrets from preserved tissue samples, the second and third ferret clones in history, following the birth of the first clone in December 2020.
Cloning is a tactic to preserve the health of species, as all living black-footed ferrets come from just seven wild-caught descendants. This means their genetic diversity is extremely limited and opens them up to greater risks of disease and genetic abnormalities.

Now, a new breakthrough has been made.
Antonia, a black-footed ferret cloned from the DNA of a ferret that lived in the 1980s has successfully birthed two healthy kits of her own: Sibert and Red Cloud.
These babies mark the first successful live births from a cloned endangered species — and is a milestone for the country’s ferret recovery program.
The kits are now three months old, and mother Antonia is helping to raise them — and expand their gene pool.
In fact, Antonia’s offspring have three times the genetic diversity of any other living ferrets that have come from the original seven ancestors.

Researchers believe that expanded genetic diversity could help grow the ferrets’ population and help prime them to recover from ongoing diseases that have been massively detrimental to the species, including sylvatic plague and canine distemper.
“The successful breeding and subsequent birth of Antonia's kits marks a major milestone in endangered species conservation,” said Paul Marinari, senior curator at the Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute.
“The many partners in the Black-footed Ferret Recovery Program continue their innovative and inspirational efforts to save this species and be a model for other conservation programs across the globe.”
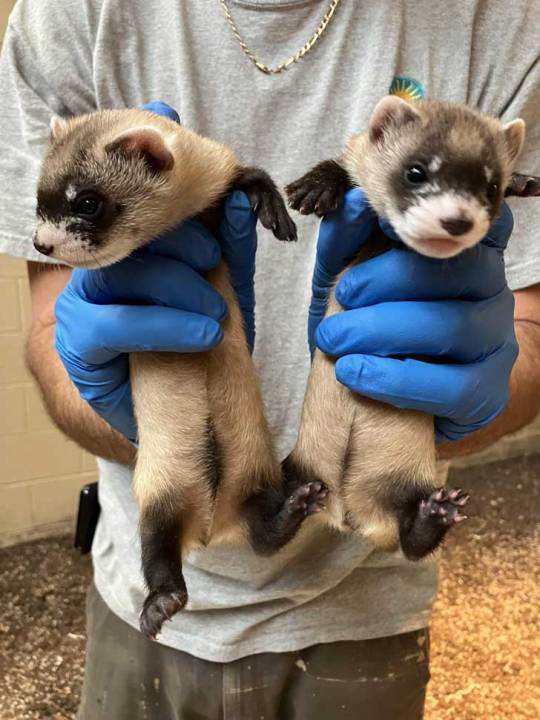

Antonia actually gave birth to three kits, after mating with Urchin, a 3-year-old male ferret. One of the three kits passed away shortly after birth, but one male and one female are in good health and meeting developmental milestones, according to the Smithsonian.
Mom and babies will remain at the facility for further research, with no plans to release them into the wild.
According to the Colorado Sun, another cloned ferret, Noreen, is also a potential mom in the cloning-breeding program. The original cloned ferret, Elizabeth Ann, is doing well at the recovery program in Colorado, but does not have the capabilities to breed.
Antonia, who was cloned using the DNA of a black-footed ferret named Willa, has now solidified Willa’s place as the eighth founding ancestor of all current living ferrets.
“By doing this, we’ve actually added an eighth founder,” said Tina Jackson, black-footed ferret recovery coordinator for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, in an interview with the Colorado Sun.
“And in some ways that may not sound like a lot, but in this genetic world, that is huge.”

Along with the USFWS and Smithsonian, conservation organization Revive & Restore has also enabled the use of biotechnologies in conservation practice. Co-founder and executive director Ryan Phelan is thrilled to welcome these two new kits to the black-footed ferret family.
“For the first time, we can definitively say that cloning contributed meaningful genetic variation back into a breeding population,” he said in a statement.
“As these kits move forward in the breeding program, the impact of this work will multiply, building a more robust and resilient population over time.”"
-via GoodGoodGood, November 4, 2024
#ferret#ferrets#mustelid#black footed ferret#conservation#endangered species#conservation biology#biodiversity crisis#dna#genetics#cloning#good news#hope#hope posting#hopecore#hopepunk
10K notes
·
View notes
Note
pls do the lyrics of DNA. by Kendrick Lamar
It would be so funny
Bc you do DNA so y'know
String identified: gtgtgtgtatgtatAatcgtaaacAgtaaAgtttgatAatctacatccttattaaatctattatTaTtattttTtatgtgtgtgtatcatAgtgtcAgtagttattAgtgttatAtagatagaatatagattatgaaCtttttataaaatcAatatctAatctagAactttagaggttttattttgTaatccttgaaatcaatataagaaaaAaAtattcctcgaacttattaAttcattatAgtatcattActattaAatattcaAttcAaatgaatcaTaatattttttagtatgtatAtatataaagtgAcaAcagtatgtatAattacTaacctagtatgtatAaTtagatttatccaaagTtggaatccatttattatttAttatAaaatTttatgtaatAtacttagtgaaaaGaaatatcatactttatgatgagagaaaatgtcaaatatagtcaaagaaattctaaatcatacatatcattcttattataTattttatctagtatgttaatttatatttatctatatcgttatcgttttaatTtctgaatGaatgaatactttttatA
Closest match: Myripristis murdjan genome assembly, chromosome: 24 Common name: Pinecone Soldierfish

(image source)
#tumblr genetics#genetics#biology#science#asks#requests#sent to me#throatofdelusion12#kendrick lamar#dna#fish#ocean#pinecone soldierfish#some members of this family are venomous!#they life in reefs and are known to give painful wounds
4K notes
·
View notes
Text




https://www.instagram.com/ya_xeel/
#yaxeel#dna#surreal#organism#weirdcore#scary#creepy#horror#spooky#aesthetic#unrealistic#unreal#strangecore#oddcore#fake gore#esoteric#fleshcore#meatcore#horror art#ai art#skeletrix#edwardskeletrix#alien#virus#xenomorph#bacteria#biology#cyber#cybercore#liminal aesthetic
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Yep, we were waiting for this. :/
890 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Lovers
This drawing is a tribute to the shared origins of humanity, a reminder of the ancient ties that bind us across time. In contemplating deep time, the vast stretches of history that have shaped us, I feel a profound sense of connection to those who came before us, whether our direct ancestors or other early hominids. The Neanderthals, along with other early hominids, coexisted with us and were not so different; they loved, they dreamed, and they faced the world with curiosity and wonder. This connection is even imprinted in our DNA, a living testament to the bonds we share with these ancient relatives.
By reflecting on our similarities, I am reminded that the essence of our humanity has always been rooted in relationships, in the bonds we forge with others. This connection extends beyond just the human lineage, reaching back to the many hominids who once walked this Earth, and even to our living relatives among the primates. We are part of a vast, interconnected family, linked by our shared journey through deep time.
In this image, I seek to capture the timeless nature of love and the shared journey of our species and our kin. This is not just a story of survival, but one of enduring connection, of two souls meeting across the millennia. In their embrace, I see a reflection of our own struggles and hopes, a reminder that despite the passage of time, the essence of what makes us human and what connects us to all life, remains unchanged.
We are all part of a continuous, unbroken lineage, connected by the deep and ancient roots of our existence. Prints are available: https://artofmaquenda.etsy.com/listing/1786867243/the-lovers-lustre-print-hominid-sapiens Thank you all for your kind messages and support on my WIP posts! It took me a while to finally dive into this piece, but it just needed the right moment to come together. <3
The lettering is done by the kind Urukins / Antiqueuru
#hominids#sapiens#neanderthalensis#neanderthal#homo sapiens#evolution#nature#venus von willendorf#flute#tree of life#dna#the lovers#tarot#paleo art#paleo#skeletons#primates#art#artofmaquenda#maquenda
864 notes
·
View notes
Text
A small, seemingly unremarkable fern that only grows on a remote Pacific island was on Friday crowned the Guinness World Record holder for having the largest genome of any organism on Earth. The New Caledonian fern, Tmesipteris oblanceolata, has more than 50 times more DNA packed into the nucleus of its cells than humans do. If the DNA from one of the fern's cells -- which are just a fraction of a millimeter wide -- were unraveled, it would stretch out to 106 meters (350 feet), scientists said in a new study. Stood upright, the DNA would be taller than the tower that holds London's famous Big Ben bell. The fern's genome weighed in at a whopping 160 gigabase pairs (Gbp), the measurement for DNA length. That is seven percent larger than the previous record holder, the Japanese flowering plant Paris japonica.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Plants#Biology#Molecular Biology#DNA#Genomes#Fern#New Caledonian Fern#Tmesipteris Oblanceolata#Guinness World Record
834 notes
·
View notes
Text








Organs and DNA by Animation Factory
295 notes
·
View notes
Text
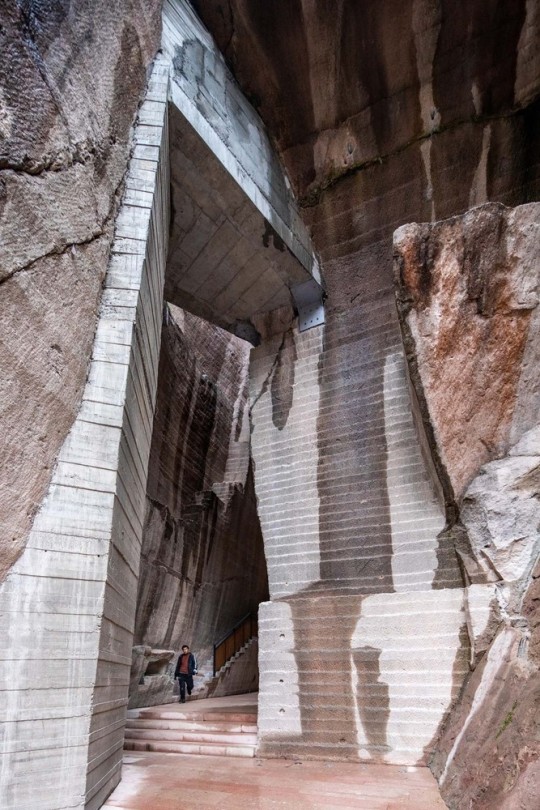
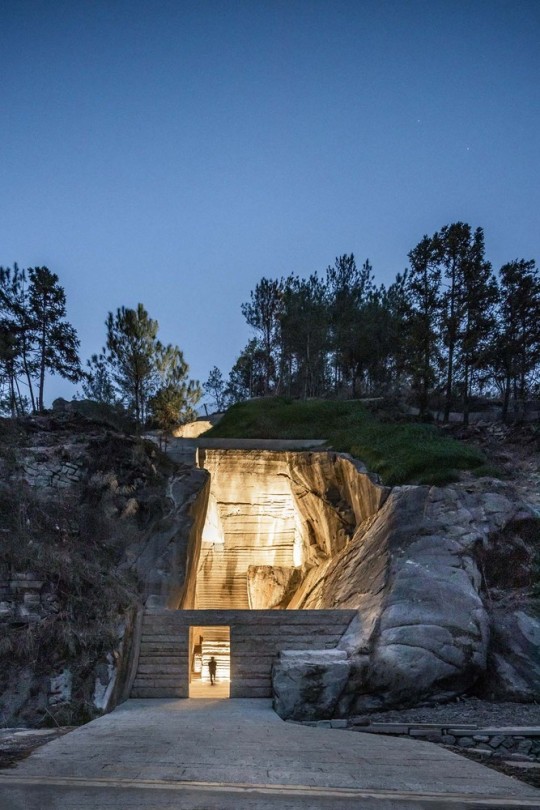
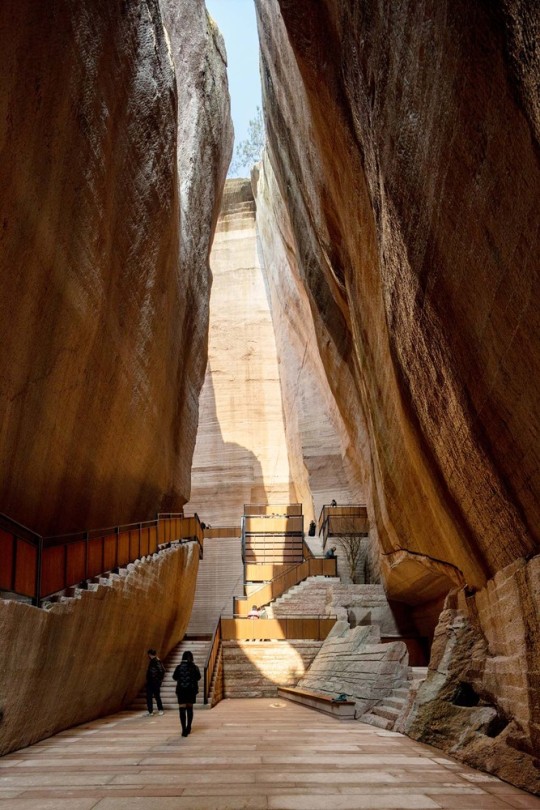
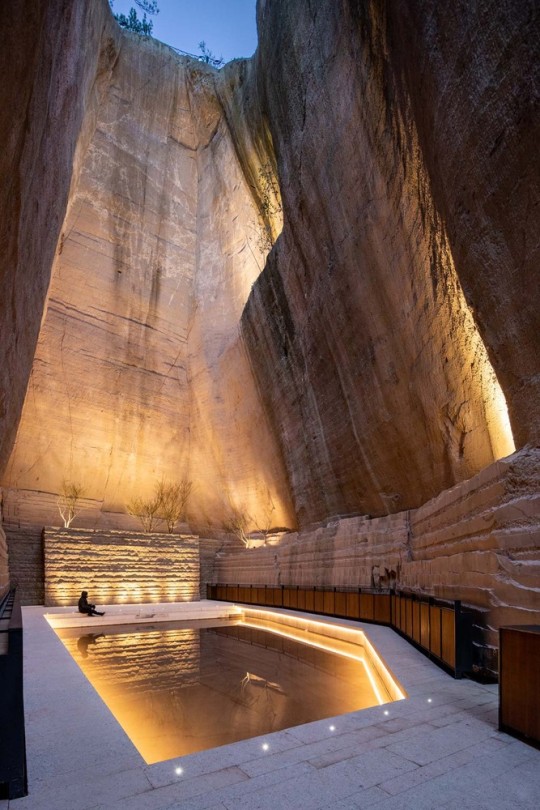







Quarry No. 8 & 9, Lishui, China - DnA
#DnA#architecture#design#building#modern architecture#minimal#modern#concrete#stone#stone building#stairs#quarry#adaptive reuse#inventive#amazing design#amazing places#landscape#tall#light#library#book shelves#books#reading spot#china#theatre#cultural#chinese architecture#design blog
172 notes
·
View notes
Text







Blade Runner 2049 (2017)
#blade runner 2049#scifiedit#science fiction#computing#scifi aesthetic#cyberpunk aesthetic#graphic design#glitch#user interface#user interaction#gifs#gifset#dennis villeneuve#genetics#dna#computers#flashing gif#uxdesign#ui ux design#uidesign
581 notes
·
View notes
Text

Connected forever ✨
#mine#my art#kidcore#nostalgia#lgbt#nostalgiacore#2000s kid#cottagecore#cat#sabertooth tiger#science#dna
151 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ashayana Deane: Language, Tones, patterns of light, Fire Letters, DNA strands and the number 12. Does this chart look similar to the astrological wheel? Video from the 90’s before she was into Earth as a realm. 🤔
#pay attention#educate yourselves#educate yourself#reeducate yourselves#knowledge is power#reeducate yourself#think about it#think for yourselves#think for yourself#do your homework#do your research#do your own research#do some research#ask yourself questions#question everything#dna#hidden knowledge#hidden wisdom#you decide#news#frequencies
276 notes
·
View notes
Text


https://www.instagram.com/ya_xeel/
#yaxeel#dna#surreal#organism#weirdcore#scary#creepy#horror#spooky#aesthetic#unrealistic#unreal#strangecore#oddcore#fake gore#esoteric#fleshcore#meatcore#horror art#ai art#skeletrix#edwardskeletrix#alien#virus#xenomorph#bacteria#biology#cyber#cybercore#liminal aesthetic
566 notes
·
View notes
Text

Scientists develop groundbreaking method for detecting DNA of invasive snakes in Florida
Scientists at the University of Florida have developed a pioneering tool to bolster Florida's defenses against invasive species: a DNA-based environmental monitoring test that can pinpoint where they've been, aiding eradication efforts.
Once a nonnative species gets into an environment, it is often too late to get rid of it, and the focus shifts to containment or long-term management. Both approaches come with heavy costs concerning native wildlife and funding, explained Melissa Miller, lead author on the study and an invasion ecologist at the UF/IFAS Fort Lauderdale Research and Education Center (UF/IFAS FLREC). "We hope this novel eDNA sampling tool we have designed will help increase efficiency in invasive species management, allowing for early detection and rapid removal of nonnative species," she said...
Read more:
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/11/241122130344.htm
#invasive species#herpetology#florida#animals#nature#science#eDNA#DNA#environment#conservation#snake#reptile
206 notes
·
View notes

