#hong kong university of science and technology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
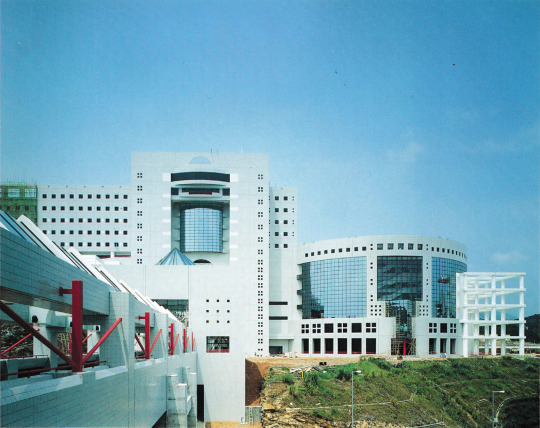


Pictured, in steps, is the roofed pedestrian walkway that connects the complexes in the campus site of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. Above we have the main building (administration and library. In between is the large skylit atrium, where escalators take you to the enormous walkway. In between is a pavillion.


Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, 1989 - 1992. Designed by Simon Kwan & Associates Ldt / Percy Thomas Partnership.
Scan
#scan#hong kong#Hong Kong University of Science and Technology#architecture#postmodern#postmodernism#1980s#eighties
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon
Researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a new integration technique for efficient integration of III-V compound semiconductor devices and silicon, paving the way for photonic integration at low cost, large volume, and high speed and throughput that could revolutionize data communications. Unlike conventional integrated circuits, or microchips, that use electrons, photonic integrated circuits use photons, or particles of light. Photonic integration combines light and electronics to speed up data transfer. Silicon photonics (Si-photonics), in particular, is at the forefront of this revolution as it enables the creation of high-speed, low-cost connections that can handle massive amounts of data at once. While silicon can handle passive optical functions, it struggles with active tasks, such as generating light (lasers) or detecting it (photodetectors)—both key components for data generation and readout. This necessitates the integration of III-V semiconductor (which uses materials from groups III and V of the periodic table) onto a silicon substrate for complete functionality and enhanced efficiency.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Semiconductors#Silicon#Electronics#Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

0 notes
Text
Random JSTOR Daily articles that looked interesting
#jstor#jstor daily#readings#history#snippets#Black in the USSR#Black Soviets#maps#asian maps#historical maps#murder#autopsy#medical history#chinatown#trans history#the danish girl#linksave
328 notes
·
View notes
Text
An international research team led by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has uncovered in a recent research project that people's beliefs in science and religion are primarily shaped by the words of others, rather than their personal experiences. The study could help enhance public understanding of people's belief formation in important scientific issues, such as climate change and vaccination. The team's findings, realized in collaboration with researchers at Harvard University, Union College, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology, were published in Trends in Cognitive Sciences. Conventionally, people are generally more confident about the existence of scientific phenomena, like oxygen, than religious phenomena, like God, as it is thought that people can experience oxygen, for instance, while it is harder to observe religious entities on one's own.
Continue Reading.
104 notes
·
View notes
Text
Growing Nervous
Regeneration after damage of the central nervous system is limited. This study finds that suppressing activity of a gene called Lipin1 leads to significant regrowth of sensory and motor nerve axons (the signal-transmitting projections) after spinal cord injury
Read the published research article here
Video from work by Weitao Chen, Junqiang Wu and Chao Yang, and colleagues
Biomedical Research Institute, Shenzhen Peking University–The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Medical Center, Shenzhen, China
Video originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), September 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elon Musk just dragged ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence programs into the Trump crosshairs by repeating his warning that current AI models are too “woke” and “politically correct.”
“A lot of the AIs that are being trained in the San Francisco Bay Area, they take on the philosophy of people around them,” Musk said at the Future Investment Initiative, a Saudi Arabia government–backed event held in Riyadh this week. “So you have a woke, nihilistic—in my opinion—philosophy that is being built into these AIs.”
Although Musk is himself a polarizing figure, he is right about AI systems harboring political biases. The issue, however, is far from one-sided, and Musk’s framing may help further his own interests due to his ties to Trump. Musk runs xAI, a competitor to OpenAI, Google, and Meta that could benefit if those companies become government targets.
“Musk clearly has a close, close relationship with the Trump campaign, and any comment that he’s making will hold a big influence,” says Matt Mittelsteadt, a research fellow at George Mason University. “At a maximum he could have some sort of seat in a potential Trump administration, and his views could actually be enacted into some sort of policy.”
Musk has previously accused both OpenAI and Google of being infected with “the woke mind virus.” When Google’s Gemini chatbot produced historically inaccurate images, including black Nazis and Vikings, in February, Musk saw it as proof of Google using AI to spread an absurdly woke outlook.
Musk is clearly no fan of government regulation, but he backed a proposed AI bill in California that would have required companies to make their AI models available for vetting.
The first Trump administration also targeted perceived bias at Big Tech companies with an executive order that sought to hold platforms such as Twitter, Google, and Facebook accountable for censoring information for political reasons. The pressure had a tangible impact, with Meta ultimately abandoning plans for a dedicated news section on Facebook.
Mittelsteadt notes that Trump’s VP pick, JD Vance, has also talked of reining in Big Tech companies and gone as far as to call Google “one of the most dangerous companies in the world.”
Mittelsteadt adds that Trump could punish companies in a variety of ways. He cites, for example, the way the Trump government canceled a major federal contract with Amazon Web Services, a decision likely influenced by the former president’s view of the Washington Post and its owner, Jeff Bezos.
It would not be hard for policymakers to point to evidence of political bias in AI models, even if it cuts both ways.
A 2023 study by researchers at the University of Washington, Carnegie Mellon University, and Xi’an Jiaotong University found a range of political leanings in different large language models. It also showed how this bias may affect the performance of hate speech or misinformation detection systems.
Another study, conducted by researchers at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, found bias in several open source AI models on polarizing issues such as immigration, reproductive rights, and climate change. Yejin Bang, a PhD candidate involved with the work, says that most models tend to lean liberal and US-centric, but that the same models can express a variety of liberal or conservative biases depending on the topic.
AI models capture political biases because they are trained on swaths of internet data that inevitably includes all sorts of perspectives. Most users may not be aware of any bias in the tools they use because models incorporate guardrails that restrict them from generating certain harmful or biased content. These biases can leak out subtly though, and the additional training that models receive to restrict their output can introduce further partisanship. “Developers could ensure that models are exposed to multiple perspectives on divisive topics, allowing them to respond with a balanced viewpoint,” Bang says.
The issue may become worse as AI systems become more pervasive, says Ashique KhudaBukhsh, an computer scientist at the Rochester Institute of Technology who developed a tool called the Toxicity Rabbit Hole Framework, which teases out the different societal biases of large language models. “We fear that a vicious cycle is about to start as new generations of LLMs will increasingly be trained on data contaminated by AI-generated content,” he says.
“I’m convinced that that bias within LLMs is already an issue and will most likely be an even bigger one in the future,” says Luca Rettenberger, a postdoctoral researcher at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology who conducted an analysis of LLMs for biases related to German politics.
Rettenberger suggests that political groups may also seek to influence LLMs in order to promote their own views above those of others. “If someone is very ambitious and has malicious intentions it could be possible to manipulate LLMs into certain directions,” he says. “I see the manipulation of training data as a real danger.”
There have already been some efforts to shift the balance of bias in AI models. Last March, one programmer developed a more right-leaning chatbot in an effort to highlight the subtle biases he saw in tools like ChatGPT. Musk has himself promised to make Grok, the AI chatbot built by xAI, “maximally truth-seeking” and less biased than other AI tools, although in practice it also hedges when it comes to tricky political questions. (A staunch Trump supporter and immigration hawk, Musk’s own view of “less biased” may also translate into more right-leaning results.)
Next week’s election in the United States is hardly likely to heal the discord between Democrats and Republicans, but if Trump wins, talk of anti-woke AI could get a lot louder.
Musk offered an apocalyptic take on the issue at this week’s event, referring to an incident when Google’s Gemini said that nuclear war would be preferable to misgendering Caitlyn Jenner. “If you have an AI that’s programmed for things like that, it could conclude that the best way to ensure nobody is misgendered is to annihilate all humans, thus making the probability of a future misgendering zero,” he said.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

VICE SCRIPT: Game Theory for The Venetian Macao, China (Trapping Aesthetic for Tennis) 14K
BIO
My Name is Adrian Blake-Trotman. I am Indo-Mediterranean Caribbean Born in Toronto but From Barbados and Haiti. I am a Beta-arbitrage Mergers & Acquisitions Banker that Specializes in Commodities. I have Understanding Financial Markets by Université de Genève and Monetary Policy in the Asian-Pacific by Hong Kong University of Science and Technology with No Gr. 12 Math or Intro to Linear Algebra; I built a mathematical learning style by using Japanese Candlesticks Bullish Engulfing Discounted Cash Flow Charts for Poker. I Operate TAX AVOIDANCE through Freelance Mergers & Acquisitions through an Enterprise Foundation and Investment Trust. My background is Agriculture Working Class, I've worked in Kitchens and Grocery Stores. My goal is to connect the Democratic Republic of the Congo to two tax havens; Haiti & Seychelles to stabilize the Diamond Trade and more Important the Commodities Market. Through Mercantilism Agriculture Hedge Fund as a Central Bank, Options Volatility Exchange, Lab Grown Re-sale Market, Decentralized Currency and Fiat Money, Hospitality & Gaming. Also To form a Socioeconomic Status Agriculture Working Class; Blue, Pink, and White Collar Jobs. I am Modelling my Cartel off of Wall Street for De Beers but is owned and operated by the Société des Bains de Mer (SBM); The Casino de Monte-Carlo is owned and operated by the Société des Bains de Mer (SBM), a public company in which the government of Monaco and the ruling princely family have a majority interest. The company also owns the principal hotels, sports clubs, food service establishments, and nightclubs throughout the Principality. The Société des Bains de Mer operates in the accommodation, dining, entertainment, and gambling services. SBM manages and owns casinos, hotels, restaurants, bars, nightclubs, spas, beach clubs, and golf clubs. Fifty-two of their fifty-eight properties are located in Monaco. The concept of state-corporate crime refers to crimes that result from the relationship between the policies of the state and the policies and practices of commercially motivated corporations. The term was coined by Kramer and Michalowski in 1990.
FUTURISM NUIT BLANCHE STRIP
Futurism was an artistic and social movement that originated in Italy, and to a lesser extent in other countries, in the early 20th century. It emphasized dynamism, speed, technology, youth, violence, and objects such as the car, the airplane, and the industrial city.
Nuit Blanche (White Night) is an annual all-night or night-time arts festival of a city. A Nuit Blanche typically has museums, private and public art galleries, and other cultural institutions open and free of charge, with the centre of the city itself being turned into a de facto art gallery, providing space for art installations, performances (music, film, dance, performance art), themed social gatherings, and other activities.
Tennis-Art Movement VICE SCRIPT: Culinary Arts** (Trampoline), Graffiti** (Trampoline), Olfactory Arts** (Trampoline), Photography** (Trampoline), Fashion Design, Dramatic Arts, Theater Arts (Short Film Series), Shibuya Punk/Jet Set Radio/Drive (2011 film) Video Game by Gran Turismo Series first-party video game development studio & Sports Book Celebrity Drift Racing Mini Airports, and Raves-Nuit Blanche Gambling Strip (Acid Gardens). Influence's Muesuem has Bobby Flay, Gordon Ramsy, Stussy-Patagonia-Billionaire Boys Club, Freebandz, Jean-Michel Basquiat, Jimi Hendrix, Nelson Mandela, Nigo, Pharrell, Kazunori Yamauchi, and Keiichi Tsuchiya.
THE ARNAULT MODEL: BALANCING FINANCIAL DISCIPLINE AND CREATIVITY
Over the next three decades, as he brought the best luxury brands in fashion, cosmetics, and beverages under the LVMH umbrella, Arnault proceeded to make “a series of brilliant business decisions” that “can only be called masterful.” Even his critics were impressed by “his ability to manage creativity for the sake of profit and growth.” Industry observers frequently credit his outstanding success in a highly competitive industry to the fact that—unlike other global CEOs—Arnault understands both the creative and the financial aspects of running a luxury business
Financed through Real Estate and Convertible Bonds
The Creation of Star Brands
In a 2001 Harvard Business Review interview, Arnault explained his famous business process, which—unlike the traditional fashion industry—requires financial discipline as well as creativity. The entire focus of Arnault's teams is the creation of “star brands” that must meet a high bar for four artistic and financial criteria: LVMH brands must be “timeless, modern, fast-growing, and highly profitable.” In practice, “profitable creativity” means that “star brands are born only when a company manages to make products that ‘speak to the ages’ but feel ‘intensely modern’ and ‘sell fast and furiously, all while raking in profits
Although the LVMH process begins with "radical innovation—an unpredictable, messy, highly emotional activity” on the creative end, as soon as “it comes to getting creativity onto shelves—chaos is banished,” and the company imposes "strict discipline on manufacturing processes, meticulously planning all 1,000 tasks in the construction of one purse.”
The genius of Arnault’s process is that, although the "front end of a star brand—the innovation…the creative process, the advertising—is very, very expensive,” the “back end of the process in the atelier (the factory)” is a place of "amazing discipline and rigor” that drives “high profitability behind the scenes.” Brands with “unbelievably high quality” require “unbelievably high productivity,” so “every single motion, every step of every process is carefully planned with the most modern and complete engineering technology.”
For example, when Arnault automated production at Vuitton, he drove that venerable old brand to the top spot on Fashionista’s list of the world's best-selling luxury brands in 2011, with a value of $24.3 billion—more than twice the amount of its nearest competitor.
As he spent “lavishly” on advertising, Arnault "rigorously" controlled costs by leveraging every possible synergy across the group: Kenzo manufactured a Christian Lacroix line; Givenchy manufactured a Kenzo perfume, and Guerlain created the first Vuitton perfume.
Creative Talent Management
As Arnault built LVMH into the world's largest luxury conglomerate, he hired new design talent for star brands that “speak to the ages” but “feel intensely modern”: from Céline, Kenzo, Guerlain, and Givenchy to Loewe, Thomas Pink, Fendi, and DKNY.
Because his model requires that “the counterbalance to creativity must be commerce,” Arnault “never hesitated to reign in, or outright terminate, creative executives who did not produce.” Since the early days at Dior, he has often replaced creative executives with non-traditional talent and then shuffled them across his brands to help him identify opportunities to drive profit—no matter how unpopular.
For example, at Givenchy in 1995, Arnault brought in a “fashion industry darling” and “notorious wild child,” British designer John Galliano, to replace Hubert de Givenchy, the industry icon “credited with defining simple elegance for an entire generation of women, (including) Audrey Hepburn, Jacqueline Kennedy, and the Duchess of Windsor.”
Within a year, Arnault moved Galliano, the first British designer in French haute couture, from Givenchy to Christian Dior to replace Gianfranco Ferré, the Italian couturier who had led Dior design since the late 1980s. Other non-traditional Arnault hires included installing 27-year-old Alexander McQueen (another British designer) at Givenchy and Marc Jacobs at Louis Vuitton, where he gave the American designer a mandate to challenge LVMH’s competitors, Prada and Gucci.
Although those iconoclastic designers later left LVMH, they had served Arnault’s purpose: interest in his traditional fashion houses had been jumpstarted by the early 21st century.
HOW TO STABILIZE THE DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO, CÔTE D'IVOIRE, MOROCCO, ALGERIA, TUNISIA, LIBYA, EGYPT, REPUBLIC OF CABO VERDE, SEYCHELLOIS, AND HAITIAN CURRENCY (SWISS CENTRAL BANKING CASE STUDY: INDIAN PREMIER LEAGUE DUAL SPORTS SYSTEM: INDIVIDUAL SPORT; COMMODITIES PURSE SYSTEM TENNIS/TEAM SPORTS; TECHNOLOGY TOURISM CRICKET) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FIRLA2X6WBM&t=22s FOR INES CHAIEB
Documentary: Bioeconomy Meta-Analysis/Case Study 25-Year (Chapters) Social Experiment; Agriculture Working Class Pegged to Loblaws-Joe Fresh Purse System Tennis-Art Movement for Dopamine, Ambush, Influencer Marketing, and Destroys Starving Artist
Biotechnology Central Hedge Fund with Bulge Brackets Oligopolistic System Hyper Inflation Vehicle Fiat Currency: Strict Negative Interest Rates for Investments; Debt/Equity Business Loan Period and Construction Loan/Tax Benefits Programs, Investment Trusts & Enterprise Foundations are Common Corporate Tax Avoidance Practices, and Raise Denominator of Currency & Print Currency for Insurance Companies for Building Process
Real Estate is Rental For Sociocultural Theory of Development to Challenge Trust Fund Kid Stereotypes
Paris-Bay Area, California AgriCivil Engineering
Agrichemical and Biotechnology Khakistocracy Monopolies
Latin and Mandarin are Languages
Car Purse System Tennis as National Sport: Free Internet with International Corporate Sponsor Purse Bid/Height Class System UBS/HSBC Tennis Gardens, Camps, Orphanages, Polytheist Churches; Attach to Commodities Market; and Gaming-Hospitality Beta Arbitrage, DCF +EV, Live Betting Options Trading Turf Accountant Gambling. Treat Tennis Tournaments as Car Shows and BE THE BUGATTI. Play on Lipolysis. Vertical Integration Trademark Collaborations are Restaurant Clientele Grocery Chain, Mattresses, Fougère with Mineral & Floral Bar Soap, High Fat-Mineral Shaving Cream, Deodorant, and Mineral Aftershave/Water. Uniform: Grafitti Graphic Mock Knightsneck (Turtleneck) Crew Neck, Drawstring Mesh Shorts, High Socks, Continental Grip Long Sleeve Trapeziod (Hex) Compression Garments, and Blade Runner Sneakers with Rubber Clog Interior. Rugby Union Influence Variants Rugby union has spawned several variants of the full-contact, 15-a-side game. The two most common differences in adapted versions are fewer players and reduced player contact.
Knightsneck Material: Viscose, Nylon, Elastane
Mercantilism Fiat Currency Pegging: Foreign Exchange Rate to Diamond Peg Currency
UBS & HSBC Market Extension Vertical Integration Bank Mergers Lottery Industries: STEM-Mergers & Acquisitions Agriculture Industry, Lobbyist, Culinary Arts, Photography, Design Technology, Market Volume Pegged Decentralized Finance, Real Estate Finance-Economics, Capital Gains Tax Haven, Corporate Tax Haven, Inheritance Tax Haven, Short Film Series Taxi Driver Lessons, Fragrance House, Art Ports, and Gaming-Hospitality
Diamond-Commodities Exchange Modelled Off of CBOE Volatility Index (VIX). Founded in 1973, the CBOE Options Exchange is the world's largest options exchange with contracts focusing on individual equities, indexes, and interest rates. Debit/Credit Spread Options, Cash-secured Puts, and Investment Trust the Commodities Market with Volatility Prediction.
Business Capital is a Collaborative Environment through Generalized Education (Agri STEM AND Agri M & A)
Socioeconomic Status Agriculture Working Class Immigrants; Replace Jury Duty to Construction Duty
Traditional Tennis Training (Fascia-Elastic Force); Supplement Hydrolyzed Collagen-HA Acid mTAA or BCAA (mTOR Amino Acid or Branched-chain Amino Acid), Tennis Specific Resistance HIIT Weighted Vest, Isometric-Plyometric Weighted Jump Rope, Isometric-Mobility Tennis (Pullup) Bands [Replace Boxing Bags] & Med Ball Hybrid Muscle Fibre Elasticity and Elastic Force: Something that is elastic can return to its original shape after being stretched or compressed. This property is called elasticity. As you stretch or compress an elastic material like a bungee cord, it resists the change in shape. It exerts a counterforce in the opposite direction. This force is called elastic force. The farther the material is stretched or compressed, the greater the elastic force becomes. As soon as the stretching or compressing force is released, the elastic force causes the material to spring back to its original shape. Collagen Athletes: Researchers found that a year of daily collagen peptides supplementation measurably increased bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and in the upper femur. The women also had higher levels of a blood biomarker that indicates bone formation. Collagen provides resistance to tension and stretch, which commonly occur in fascial tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, sheaths, muscular fascia, and deeper fascial sub-layers. mTOR controls the growth and production (or 'synthesis') of protein in various types of cells, including muscle cells (muscle fibers). Enlargement of muscle fibers (hypertrophy) relies upon mTOR signaling. It, therefore, plays an important role in muscle gains following exercise. Leucine and essential amino acids appear to stimulate human muscle protein synthesis primarily by activating the mTOR signaling pathway. Adequate mobility allows you to train optimally. Another one of the commonly acknowledged L-arginine benefits is its contribution to muscle growth, as it is needed for the synthesis of most proteins. While the muscle mass increases, L-arginine also signals muscle cells, encourages the release of growth hormone and promotes a fast metabolism. Vitamin K2 activates the osteocalcin proteins that put calcium into bones. Without Vitamin K2, calcium cannot do its job properly. Arginine is an important amino acid that plays a role in height growth. It promotes the multiplication of cells at the growth plate in bones to help bones grow longer. It creates the potential for you to train for strength and muscle mass in the most effective way possible. Without enough mobility, you will have to compromise on certain movement patterns and find workarounds to challenge muscles in certain positions.
The roles of gender and personality factors in vandalism and scrawl-graffiti among Swedish adolescents; Abstract: A total of 360 upper secondary school students in Sweden were divided into three grouping variables: gender (male, female), vandalism (involved, not involved), and scrawl-graffiti (involved, not involved). Relevant to the discussion of whether or not scrawl-graffiti may be construed as vandalism or art, the aim of the study was to explore whether or not personality factors known to be linked to vandalism in general (such as impulsivity, affectivity, emotional disability, and optimism) are related also to involvement in scrawl-graffiti, and, furthermore, how the gender factor relates to vandalism and scrawl-graffiti, respectively. The analysis showed that impulsiveness was a significant variable related to vandalism as well as to scrawl-graffiti. Further analysis indicated that vandalism was predicted by non-planning impulsiveness whereas scrawl-graffiti was predicted by motor impulsiveness. Analyses showed also that there were significant gender differences related to both vandalism and scrawl-graffiti, whereby male participants were significantly more involved in vandalism than female participants, while the latter were significantly more involved in scrawl-graffiti than the former.
Sports Book For UEFA Through Switzerland
Culinary Arts, Olfactory Arts, Graffiti, and Photography (COGP) as National Arts
Culinary Arts 2-Year Program With High School Diploma
Mediterranean Ingredients Italien-French Cuisine: Coconut, Nuts, or Cheese Roux (Culinary)
Planned Parenting For MAO-A Father: XYY or Triple X Syndrome, ACTN3 Gene, MSTN Gene, and Mercury Cusp Births for Artistic Athletes (Virgo-Leo, Virgo-Libra, Gemini-Taurus, and Gemini-Cancer)
**Alternative Sports Pairs: X Games-Volleyball, Golf-Baseball, Muay Thai-Rugby, Tour de France-Football
A ROUND OF PAR GAME THEORY NETWORK
Beta Arbitrage with Convertible Bonds Compounding
Key Ingredients
Player's: Futures Exchange and Investor
Actions: Issue payments under any circumstances
Payoffs: Exchange - Larger Market Volume, Investor - Larger Assets Under Management or Profits
Representation
Extensive Form includes timing of moves. Player's move sequentially, represented as a tree (timing). Chess: the white player moves, then the black player can see White's move and react
Theory
There's a common expression of higher the risk, higher the reward; but in finance it should be higher reward, higher risk because people's savings are involved. This is why I created The Round of Par Games Theory Network where the intended score should always be 0. Nobody wins and nobody loses between investor and stock exchange, just a nice friendly draw. The Investors assets under management grows and the Exchange's Market Volume Grows.
Let's break down the Components:
Beta Arbitrage
Investor: Beta Arbitrage involves longing in one market and shorting in a DIFFERENT market. The example is longing Company A in the stock market but then going to Company A in the options market and placing a put/short option. Either way the Investor earns a profit.
Exchange: The Futures Exchange benefits because now not only is equity on the stock market is being bought but the options market has a larger volume.
Convertible Bond Compounding
Investor: By compounding through Convertible Bonds not only are you going to be paid back your money because creditors are first on the company's bankruptcy list unlike investors, but it's an easier way to buy more shares for growth investing while not diving head first.
Exchange: The Futures Exchange benefits because now not only is equity on the stock market is being bought, but the bond market has a larger volume.
LANGUAGES
Mandarin
Latin
INDUSTRY WORTH FOR COMMODITIES (AGRICULTURE WORKING CLASS)
In 2012, Forbes reported that $21 trillion was Off-Shored
In 2017 the equivalent of at least 10% of the world’s GDP is in offshore banks, and that number is probably higher due to the opaqueness of the world’s global tax havens, according to a research report release this month by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
The estimated amount of money laundered globally in one year is 2 - 5% of global GDP, or $800 billion - $2 trillion in current US dollars.
Taxes in the US – The federal government collected revenues of $3.5 trillion in 2019—equal to about 16.3 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) (figure 2). Over the past 50 years, federal revenue has averaged 17.4 percent of GDP, ranging from 20.0 percent (in 2000) to 14.6 percent (most recently in 2009 and 2010).
The foreign exchange or forex market is the largest financial market in the world – larger even than the stock market, with a daily volume of $6.6 trillion, according to the 2019 Triennial Central Bank Survey of FX and OTC derivatives markets.
In 2019, for example, the sales value of rough diamonds amounted to some 13.9 billion U.S. dollars worldwide. After polishing, the value increased by nearly double to 26.7 billion U.S. dollars. In 2019, the global diamond jewelry market value was approximately 79 billion U.S. dollars.
Global Cut Flowers Market to Reach $41. 1 Billion by 2027.
The global coffee market was valued at USD 102.02 billion in 2020
According to the report published by Allied Market Research, the global cocoa market generated $12.8 billion in 2019, and is projected to reach $15.5 billion by 2027, witnessing a CAGR of 4.3% from 2021 to 2027
The global water and wastewater market was valued at 263.07 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. The market is projected to reach a value almost 500 billion U.S. dollars by 2028 at a CAGR of 7.3 percent in the 2021 to 2028 period.
For the year 2020, Worldwide Cotton Market was US$ 38.54 Billion. Global Cotton Market is expected to reach US$ 46.56 Billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 2.74% from 2020 to 2027.
The global waste management market size was valued at $1,612.0 billion in 2020, and is expected to reach $2,483.0 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 3.4% from 2021 to 2030
According to Brandessence Market Research, the Energy Drink market size reached USD 61.23 billion in 2020 and expected to reach USD 99.62 Billion by 2027.
LEGAL DEFENSE
Smurfing: Reverse Onus, Challenge Mens Rea and Actus Rea, Press Malicious Prosecution Charges, Financial Settlement
RICO Legal Disputes Trademark (30 for 30 Court): Undisclosed Settlement; 1 large sum ($30 million) broken into a 3-part settlement, Not going to trial settlement (guaranteed payment for being brought into court), Case being unsealed settlement (if the case gets reopened), and Testimony settlement (in court testimony in reopened case). The non-disclosure agreement (NDA); Agreement to 10 years jail time for every broken NDA, NDA on Case, NDA on Testifying, and NDA on Settlement. Sealed Federal Cases: Have legal matters sealed by the court to prevent leaked information to media and Precedence for RICO
CRIME COLLAR
White-Blue collar crime is a subgroup of white-collar crime White Collar Crime, a term reportedly first coined in 1939, is synonymous with the full range of frauds committed by business and government professionals. Blue-collar crime is a term used to describe crimes that are committed primarily by people who are from a lower social class. This is in contrast to white-collar crime, which refers to crime that is usually committed by people from a higher social class.
SOCIOCULTURAL THEORY OF DEVELOPMENT
Agriculture Working Class Immigrants Socioeconomic Status Focused Key Players in Commodities Market*
Polytheism (Zeus, Poseidon, and Ogou-Athena)*
Births: Mercury-Venus, MSTN Gene, ACTN3 Gene, XYY Syndrome, or Triple X Syndrome
Māori All Blacks Sports Culture and Tennis is National Sport*
Jumping for Cardio*
Poker Brain*
REITs/Real Estate ETF Investors with Index Credit or Debit Spreads Options Trading*
Mergers and Acquisitions Exploratory School System*
Sand-Based Calisthenics kallos sthenos (beautiful strength) Interval Training: Isometric-Plyometric, Circuit Training: Isometric-Isotonic, and Isometric-Mobility
Tofu is Protein of Choice
Fish/Seafood is Meat of Choice
Blueberry is consumed at every breakfast
Mineral Water instead of Spring Water
Coconut Syrup as Sugar Replacement
Business News is a part of The Cigar Culture
Sports Gambling for Extra Revenue Stream instead of Lottery Tickets when in Working Class
Hydrolyzed Collagen-BCAA is the Main Sports Medicine
Brokerage Accounts with First 10 Investments as Bond Funds and REITs
TAMMBRGC LIFESTYLE BRAND RACKET
Tennis (Trampoline)
Acting (Short Film Series: Aesthetic Taxi Game, Character: Expansive Mood Villain)
Modeling (Brand Activation Models)
Music (Psychedelic Festival Trap)
Ballet (Females Only)
Rings Gymnastics (Males Only)
Graffiti (Art)
Cooking (Endorsements)
LVMH-On Running and ONE Championship Collaboration Company For Tax Mergers Law; Market-extension merger: Two companies that sell the same products in different markets. 4.2.2 Corporate Taxation At the corporate level, the tax treatment of a merger or acquisition depends on whether the acquiring firm elects to treat the acquired firm as being absorbed into the parent with its tax attributes intact, or first being liquidated and then received in the form of its component assets.
What Is Vertical Integration? Vertical integration is a strategy that allows a company to streamline its operations by taking direct ownership of various stages of its production process rather than relying on external contractors or suppliers. A company may achieve vertical integration by acquiring or establishing its own suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retail locations rather than outsourcing them. However, vertical integration may be considered risky potential disadvantages due to the significant initial capital investment required.
Analysis Discounted Cash Flow (DCF): A key valuation tool in M&A, a discounted cash flow (DFC) analysis determines a company's current value, according to its estimated future cash flows. Forecasted free cash flows (net income + depreciation/amortization (capital expenditures) change in working capital) are discounted to a present value using the company's weighted average cost of capital (WACC). Admittedly, DCF is tricky to get right, but few tools can rival this valuation method.
VŒUX DE CHAMPAGNE SOGNI CAVIALI
Description: Beta-arbitrage Mergers & Acquisitions Cartel that commits Mediterranean-Caribbean and Afro-Mediterranean Socioeconomic Status Development Conflict Prevention and Reconstruction (CPR) Unit Charities, Protection Racket, Paramilitary Financing, Lobbyist-Investment Trust, Commodities Management, Gambling & Diamond Trafficking, Rolex Re-sale Market, Real Estate Brokerage, Graffiti Art Port, Smurfing, Nike Sports & Fashion Corporate Espionage and Larceny Business Model Reengineering, and AMMMBRGC Contract Racketeering Through Enterprise Foundations
Activities: Executive Council for Mayor, Culinary Arts, Grey Market Fashion, Trap Shooting Gambling Tournaments, Mixed Martial Arts, Corporate Sponsor EdTech, Grocery Insurance & Electronic Financial Data Interchange, Diamond Encrusted Accessories Collaboration with LVMH, OTC Beta-arbitrage Branch Bracket, OTC Exchange (Commodities, Sports Betting Investment Trust, Real Estate Investment Trust, Cuisine Real Estate Investment Trust, Forex Pairs Contract for Difference, Retail/Hospitality Real Estate Investment Trust, Credit Swap Options Endorsement Index), TAMMBRGC Youtube Distribution Channel (Gambling News Network, Noir Short Film Series [Shakespearean Crime], Cooking Channel, Sports Resort Real Estate, Sports/Modelling/Acting Business Case Study Video Essay, Brand Activation Modelling, Calisthenics Workout Class, Sports Science Lessons, Graffiti Tourism, Music Videos, Natural Resources Documentaries, Hype Beast Re-Sale Market, Rolex Business Case Study Video Essays, Business Conferences).
DIAMOND TRAFFICKING
The WFDB Trade And Business Committee
The Trade and Business Committee makes recommendations to the Executive Committee concerning industry relations with financial institutions worldwide, lab-grown diamonds, Know Your Customer and the System of Warranties.
Idea 1: Luxury Goods Encrusted Items Investment Service and Auction. Example: Hermès Bag, Investment System: Masterworks, Auction System: Information Catwalks with models then bidding in a separate room with Video Replay for YouTube.
Idea 2: A sightholder is a company on the De Beers Global Sightholder Sales's (DBGSS) list of authorized bulk purchasers of rough diamonds. De Beers Group made this list, the second largest miner of diamonds. DBGSS was previously known as DTC (Diamond Trading Company). In May 2006, DTC released a list of the 93 sightholders on its website. High Fashion Accessories Aggregator Business Model with Auction and Re-sale.
Business Model
The London Metal Exchange (LME) which is based in Hong Kong is a commodities exchange that deals in metals futures and options. It is the largest exchange for options and futures contracts for base metals, which include aluminum, zinc, lead, copper, and nickel. The exchange also facilitates trading of precious metals like gold and silver.
Originally known as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the exchange changed its name in 2017 as part of a rebranding effort by its holding company, CBOE Global Markets. Traders refer to the exchange as the CBOE ("see-bo"). CBOE is also the originator of the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), the most widely used and recognized proxy for market volatility.
ABC Exchange (Alumina, Beryllium, Carbon): There are four types of precious stones: diamonds, rubies, sapphires and emeralds. Each type has its own specific chemical and physical properties. Diamonds are made from carbon, rubies and sapphires from alumina and emeralds from beryllium.
Diamond Monopoly
What Is Vertical Integration? Vertical integration is a strategy that allows a company to streamline its operations by taking direct ownership of various stages of its production process rather than relying on external contractors or suppliers. A company may achieve vertical integration by acquiring or establishing its own suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retail locations rather than outsourcing them. However, vertical integration may be considered risky potential disadvantages due to the significant initial capital investment required.
My Vertical Integration Mergers: Company’s Diamond Mines, Merger Manufacturers, Company’s Distribution, and Merger Hospitality and Gaming Diamond Exchange
The Diamond Standard
Influence: Agricultural Bank of China is active in commercial banking, investment banking, and insurance services.
Mercantilism was a form of economic nationalism that sought to increase the prosperity and power of a nation through restrictive trade practices. Its goal was to increase the supply of a state's gold and silver with exports rather than to deplete it through imports. It also sought to support domestic employment.
The bio-economy is defined as the economic activity associated with the invention, development, production; and use of primarily bio-based products, bio-based production processes, and/or biotechnology-based intellectual property.
Industries Association; Hospitality and Gaming: Daily and Monthly Revenue Streams, Capital Gains Taxing: Create Offshore revenue through trading and Blockchain is a volatile market for good liquidity. FOREX Vehicle Currency: Low Interest Rates means currency will be traded against other currencies, Shorting own currency to get foreign currency and exchanging returns to domestic currency stabilize exchange rate and Currency Basket
Interest Rate Pegging: Environmental alternative to gold, Surplus item during Quantitative Easing, and Low Interest Rates lead to spending and loans for investment which means buying and trading diamonds will balloon
Mine Options: Credit spreads and debit spreads are different spread strategies that can be used when investing in options. Both are vertical spreads or positions that are made up entirely of calls or entirely of puts with long and short options at different strikes. They both require buying and selling options (with the same security) with the same expiration date but different strike prices.
Diamond Mine Investment Group: Mines can create private Investment Groups. Items within Group: diamond retail, diamond trading, industrial diamond manufacturing sectors
Lab-created diamonds are grown in controlled laboratory environments using advanced technology that replicates the conditions under which diamonds naturally develop beneath the Earth's crust. These lab-grown diamonds consist almost entirely of carbon atoms and are arranged in a diamond crystal structure.
Fougère INVESTMENT TRUST (EXAMPLE)
Description
Fougère Listing Through Discounted Cash Flow for Fougère Agriculture Investment Trust; Pay a minimum of 90% of taxable income in the form of shareholder dividends each year, and Give Sample Bottles to Each Investor.
Underwriting Products Value $200
Formula Appreciating In Value
Collector's Edition
Less than 5000 models made
Masterwork Investing Platform (reference)
Masterworks is making the world of art a little less exclusive by offering everyday investors the chance to own a fraction of these high-priced investments with a much smaller amount of money.
Through the fine art investing platform, users can purchase (and trade) shares in what the company has defined as "blue-chip" art: masterpieces from artists like Pablo Picasso, Claude Monet, Andy Warhol, Banksy, Kaws, Jean-Michel Basquiat and more.
How Masterworks functions (reference)
Masterworks provides an affordable way to invest in art. What was once an option reserved exclusively for wealthy investors is now accessible to investors of all types. Here's how the platform works:
Masterworks will purchase a painting and file it with the SEC as a public offering, or IPO, similar to how a company goes public. Shares of the painting are then made available for purchase on the Masterworks website for as little as $20 per share. The company says it launches about one new painting every four to five days.
The platform stands out, especially for using propriety data to determine which artist markets have the most momentum, focusing on the very high-end segment of the art market that has predictable returns, the company says. Meanwhile, its research team works in the background to calculate appreciation rates, correlation, and loss rates.
Masterworks even recently added a secondary market, too, where investors can trade shares in paintings. Plus, Masterworks lets you invest your IRA earnings into their fine art through its partnership with Alto IRA, an alternative asset investing platform.
Industrial Embassy
Business Model: Insurance companies base their business models around assuming and diversifying risk. The essential insurance model involves pooling risk from individual payers and redistributing it across a larger portfolio. Most insurance companies generate revenue in two ways: Charging premiums in exchange for insurance coverage, then reinvesting those premiums into other interest-generating assets. Like all private businesses, insurance companies try to market effectively and minimize administrative costs. Types of Insurance: Mining, Manufacturing, Retail, Logistics
Financing is the process of providing funds for business activities, making purchases, or investing. Financial institutions, such as banks, are in the business of providing capital to businesses, consumers, and investors to help them achieve their goals. The use of financing is vital in any economic system, as it allows companies to purchase products out of their immediate reach. Equity financing is the process of raising capital through the sale of shares. Companies raise money because they might have a short-term need to pay bills or have a long-term goal and require funds to invest in their growth. By selling shares, a company is effectively selling ownership in their company in return for cash. Advantages of Equity Financing; Funding your business through investors has several advantages, including the following: The biggest advantage is that you do not have to pay back the money. If your business enters bankruptcy, your investor or investors are not creditors. They are part-owners in your company, and because of that, their money is lost along with your company. You do not have to make monthly payments, so there is often more cash on hand for operating expenses. Investors understand that it takes time to build a business. You will get the money you need without the pressure of having to see your product or business thriving within a short amount of time.
Planning Permission and Building Regulations Courses: Planning permission assesses whether the development fits in with local and national policies and whether it would cause unacceptable harm, for example, to neighbours' quality of life. Whereas building control covers the structural aspects of development and progress throughout the construction
AFRO-MEDITERRANEAN PARAMILITARY FINANCING
Military Payments
Security Operations (SercOps) Payment: $150,000 yearly salary: Receives $100,000 salary; the other $50,000 is used for a branch-managed investment portfolio and investment trust
Discharge Payment: $75,000 yearly salary for Armoured Car Guard and Driver, Receives $50,000 salary; other $25,000 is used for branch-managed investment portfolio and investment trust
Military Funding: Bioeconomy Agriculture Central Hedge Fund Equity Given
Payment is in Fixed Currency
AFRO-MEDITERRANEAN SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS DEVELOPMENT CONFLICT PREVENTION AND RECONSTRUCTION (CPR) UNIT CENTERS
Corporate Sponsor: M & A Schools (Mergers and Acquisitions) & Retirement-preparatory School
Cross-Curriculum
STEM education is the cross-curricular study of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, and the application of those subjects in real-world contexts.
Studying Style
I use Interleaving Studying for Generalist Kinaesthetic Learners.
Transition to Interleaving Studying: Online PowerPoint Presentation, Video Essays, Case Studies & Meta-analyses over Books to present Information as a country, Less Paper Use, Courses on Different PowerPoint Studying Styles, Make country a Business & Finance Culture and Technological Advanced, Overview at Beginning; Program Learning Concept Check During Quizzes at the End for Courses, Spaced Learning on concept checks before exiting the course.
A great example of when to use interleaving is sports, for instance, tennis. Instead of just practicing backhands in one session, you can interleave backhands, forehands, and volleys to get increased results. Another great example can be found in science classes, where interleaving math, physics, and chemistry, for example, can provide you with an advanced understanding of all 3 fields.
Spaced learning is a learning method in which highly condensed learning content is repeated three times, with two 10-minute breaks during which distractor activities such as physical activities are performed by the students. It is based on the temporal pattern of stimuli for creating long-term memories reported by R. Douglas Fields in Scientific American in 2005.
Spacing boosts learning by spreading lessons and retrieval opportunities out over time so learning is not crammed all at once. By returning to content every so often, students' knowledge has had time to rest and be refreshed.
The two concepts are similar but essentially spacing is revision throughout the course, whereas interleaving is switching between ideas while you study. Although interleaving and spacing are different interventions, the two are linked because interleaving inherently introduces spacing. These two concepts will create student-athletes
The best part about interleaving is that it is almost a universal aid in learning
Evidence suggests that spaced practice is more effective for long-term retrieval.
Interleaving Studying forces the brain to continually retrieve because each practice attempt is different from the last, so rote responses pulled from short-term memory won’t work.
Multiple choice test is an example of measuring retrieval by A. reconstruction. B. recognition.
Chess
Increasing Intelligence: Fluid and crystallized intelligence are constructs originally conceptualized by Raymond Cattell. The concepts of fluid and crystallized intelligence were further developed by Cattell and his former student John L. Horn. Crystallized intelligence. This refers to your vocabulary, knowledge, and skills. Crystallized intelligence typically increases as you get older. Fluid intelligence, also known as fluid reasoning, fluid intelligence is your ability to reason and think abstractly. Fluid intelligence refers to basic processes of reasoning and other mental activities that depend only minimally on prior learning (such as formal and informal education) and acculturation. Horn notes that it is formless, and can "flow into" a wide variety of cognitive activities Tasks measuring fluid reasoning require the ability to solve abstract reasoning problems. Examples of tasks that measure fluid intelligence include figure classifications, figural analyses, number and letter series, matrices, and paired associates. Crystallized intelligence refers to learned procedures and knowledge. It reflects the effects of experience and acculturation. Horn notes that crystallized ability is a "precipitate out of experience," resulting from the prior application of fluid ability that has been combined with the intelligence of culture. Examples of tasks that measure crystallized intelligence are vocabulary, general information, abstract word analogies, and the mechanics of language.
Bullet Chess: The rules for bullet chess aren't different from those of a regular chess game. Bullet chess refers to games played with time controls that are faster than 3 minutes per player. The most popular forms of bullet chess are 1|0 (one minute with no increment per player) or 2|1 (two minutes with a one-second increment per player). Increment (also known as bonus and Fischer since former World Chess Champion Bobby Fischer patented this timing method)—a specified amount of time is added to the players main time each move, unless the player's main time ran out before they completed their move.
Chess Benefits: It has been suggested by different scientists that chess involves, and possibly boosts, cognitive abilities such as working memory, fluid intelligence, and concentration capacity. Besides, chess may be beneficial for mathematical ability and, more widely, academic achievement by enhancing concentration and problem-solving skills.
Life-History Strategy
Life history theory posits that behavioral adaptation to various environmental (ecological and/or social) conditions encountered during childhood is regulated by a wide variety of different traits resulting in various behavioral strategies. Unpredictable and harsh conditions tend to produce fast life history strategies, characterized by early maturation, a higher number of sexual partners to whom one is less attached, and less parenting of offspring. Unpredictability and harshness not only affects dispositional social and emotional functioning, but may also promote the development of personality traits linked to higher rates of instability in social relationships or more self-interested behavior. Similarly, detrimental childhood experiences, such as poor parental care or high parent-child conflict, affect personality development and may create a more distrustful, malicious interpersonal style. The aim of this brief review is to survey and summarize findings on the impact of negative early-life experiences on the development of personality and fast life history strategies. By demonstrating that there are parallels in adaptations to adversity in these two domains, we hope to lend weight to current and future attempts to provide a comprehensive insight of personality traits and functions at the ultimate and proximate levels.
The Savant Skills Curriculum
Savant gifts, or splinter skills, may be exhibited in the following skill areas or domains: memory, hyperlexia (ie, the exceptional ability to read, spell and write), art, music, mechanical or spatial skill, calendar calculation, mathematical calculation, sensory sensitivity, athletic performance, and computer ability. These skills may be remarkable in contrast to the disability of autism, or may be in fact prodigious when viewed in relation to the non-disabled person.
Learning Centers
Enrichment centers require you to be aware of your students' learning styles (Kinesthetic) as well as their knowledge about a topic. The enrichment center can provide individual students with varied activities or combination of activities that differ from those pursued by other students. As such, the center becomes an individualized approach to the promotion of the topic.
Skill Centers Skill centers are typically used at the elementary level, more so than at the secondary level. Students may work on math facts, phonics elements, or other tasks requiring memorization and/or repetition.
Interest and Exploratory Centers: Interest and exploratory centers differ from enrichment and skill development centers in that they are designed to capitalize on the interests of students. They may not necessarily match the content of the textbook or the curriculum; instead they provide students with hands-on experiences they can pursue at their own pace and level of curiosity. These types of centers can be set up throughout the classroom, with students engaging in their own selection of activities during free time, upon arrival in the morning, as a “free-choice” activity during the day, or just prior to dismissal. These centers allow students to engage in meaningful discoveries that match their individual interests.
Programmed Learning
The way a teaching machine works is: It asks you a question. If you give the right answer, it goes on to the next question. If you give the wrong answer, it tells you why the answer is wrong and tells you to go back and try again. This is called "programmed learning".
Programmed learning, educational technique characterized by self-paced, self-administered instruction presented in logical sequence and with much repetition of concepts. Programmed learning received its major impetus from the work done in the mid-1950s by the American behavioral psychologist B.F.
Exploratory Learning (Singapore Field Trips)
The Choice Theory Culture:
Is an expected way of being or living
Encourages positive choices which lead to healthy relationships
Is relationship based and collaborative
Is not about controlling behavior, rather promoting personal responsibility
Carol Dweck's Growth Mindset Theory
Growth Mindset: “In a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—brains and talent are just the starting point. This view creates a love of learning and a resilience that is essential for great accomplishment. With a growth mindset, students continually work to improve their skills, leading to greater growth and ultimately, success. The key is to get students to tune into that growth mindset.
Dweck writes, “In the fixed mindset, everything is about the outcome. If you fail—or if you’re not the best—it’s all been wasted. The growth mindset allows people to value what they’re doing regardless of the outcome. They’re tackling problems, charting new courses, working on important issues. Maybe they haven’t found the cure for cancer, but the search was deeply meaningful,” (Dweck, 2015).
Poker as Intro to Portfolio Building
Famous Fund Managers who played Poker
Steven A. Cohen (born June 11, 1956) is an American hedge fund manager and owner of the New York Mets of Major League Baseball since September 14, 2020, owning roughly 97.2% of the team. He is the founder of hedge fund Point72 Asset Management and now-closed S.A.C. Capital Advisors, both based in Stamford, Connecticut. Cohen grew up in Great Neck, New York, where his father was a dress manufacturer in Manhattan's garment district, and his mother was a piano teacher. He is the third of seven brothers and sisters. He took a liking to poker as a high school student, often betting his own money in tournaments, and credits the game with teaching him "how to take risks." Cohen graduated from John L. Miller Great Neck North High School in 1974, where he played on the school's soccer team. Cohen received an economics degree from the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania in 1978. While in school, Cohen was initiated as a brother of Zeta Beta Tau fraternity's Theta chapter where he served as treasurer. While in school, a friend helped him open a brokerage account with $1,000 of his tuition money.
Carl Icahn is one of the most recognisable and successful investors in the world, having far outperformed the market on an annualised basis since 1968; at a rate which, by some measures, has him ahead of Warren Buffett. Carl Icahn was born on the 16th February 1936 in Queens, New York. It was a beach neighbourhood and a poor area. His mother was a pianist, but dropped her dreams of pursuing it as a career and instead chose a more stable job as a school teacher. His father also became a substitute teacher. As you may expect with both parents involved in education, Carl was extremely studious. At high school, he didn’t involve himself in many activities such as sports and clubs, instead he had set himself the big goal of making it to an Ivy League university; something most people in his area had no chance of doing. His teacher didn’t even think it was worth him applying, but this made him even more determined to be different. He had a mind-set that he wanted to be the best at everything. Icahn’s parents said they would only pay for university if he got into one of the top Ivy League universities. Although no one thought he stood a chance, he managed to enrol at Princeton University and studied philosophy as his major. His parents fulfilled their promise and paid for his Princeton fees but couldn’t stretch to anything else such as his accommodation or food. Instead, Carl got himself a summer job at a Cabana club in his neighbourhood to fund his living costs. It was at the Cabana club that he learnt how to play poker and joined in the games regularly. He says at the start he didn’t know how to play, but then he read 3 poker books in 2 weeks and became the best player there, taking home huge winning each summer. He says: “To me, it was a big game, big stakes. Every summer I won about $2,000, which was like $50,000 back in the ‘50s”
Brain Training: How Regular Poker Play Could Help Soccer Stars Succeed: An athlete’s brain is their most vital organ. It controls how the body functions, and it needs to be cultivated and disciplined just like the muscles do. Those in the industry are constantly searching for new ways to help soccer players get their heads in the game, and it turns out that poker can help immensely. By sharpening cognitive function, increasing social awareness, and improving mental endurance, poker enables athletes to rise to the occasion for peak performance on the field.
Conflict Prevention & Reconstruction Unit Psychology
Reintegration of child soldiers should emphasize three components: family reunification, psychosocial support and education, and economic opportunity. Family reunification—or, where that is not possible, foster placement or support for independent living—is crucial to successful reintegration.
Children are reintegrated into community life through the provision of psychosocial support, life skills classes and basic vocational training. At the end of the program, participants are provided with small grants to start businesses.
Post-traumatic growth (PTG) is a theory that explains this kind of transformation following trauma. It was developed by psychologists Richard Tedeschi, PhD, and Lawrence Calhoun, PhD, in the mid-1990s, and holds that people who endure psychological struggle following adversity can often see positive growth afterward. Post-traumatic growth often happens naturally, Tedeschi says, but it can be facilitated in five ways: through education (rethinking ourselves, our world, and our future), emotional regulation (managing our negative emotions and reflecting on successes and possibilities), disclosure (articulating what is happening and its effects), narrative development (shaping the story of a trauma and deriving hope from famous stories of crucible leadership), and service (finding work that benefits others).
People who have experienced posttraumatic growth report changes in the following 5 factors: Appreciation of life; Relating to others; Personal strength; New possibilities; and Spiritual, existential or philosophical changes
Although posttraumatic growth often happens naturally, without psychotherapy or other formal intervention, it can be facilitated in five ways: through education, emotional regulation, disclosure, narrative development, and service.
Forgeard found that the form of cognitive processing was critical in explaining growth after trauma. Intrusive forms of rumination caused a decline in multiple areas of growth, whereas deliberate rumination led to an increase in five domains of posttraumatic growth. Deliberate rumination involves perceiving multilateral sides of the stressful experience including value, meaning, and significance (Calhoun et al., 2000; Cann et al., 2011), and may also decrease the discrepancy between global and situational meanings, as it promote finding meaning. Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) & Compassion-focused therapy (CFT) is a recommended psychotherapy
The two psychological traits which indicate a higher likelihood of experiencing post-traumatic growth are openness to experience and extraversion. Novelty seeking is positively associated with the Big Five personality trait of "extraversion," and to a lesser extent “openness to experience,” but is inversely associated with "conscientiousness." Online poker players are high sensation seekers who gamble to experience strong feelings and arousal, whereas impulsivity plays an important role in developing and maintaining pathological gambling.
CORPORATE SPONSOR: BETA-ARBITRAGE M & A EXAM
Poker Contest: Bankroll Budget*
Math Contest: Linear Algebra Contest, Probability and Ratios
Investment Management Contest: Decentralized Portfolio Building Simulation
Latin and Mandarin Technical Analysis Settings Fair: Year-Long Competition
Blues Ocean Strategy Game Theory Network Mergers & Acquisitions Contest: Macau Game Theory - The course includes modules in areas such as: Essentials of M&A, Due diligence training, Business valuation training, post-merger integration planning
Machine Learning Contest: Quantitative Aptitude
Winners Get a Full Ride to Internships (Licenes Courses I'm Gonna Make with Established Schools and Banks) Freshman Class is made of the contest winners: Mergers & Acquisitions Generalization with Corporate Sponsor; Understanding Capital Markets, Game Theory, Investment Model & Analysis, Quantitative Aptitude, Hedging Techniques, Foreign Language, Business Engineering, Business Models & Reengineering, Offshore Law, Blue Ocean Strategy, Investment Management with Python (Machine Learning)
Ages: 10, 12, 14, 17, 18, 20
SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS DEVELOPMENT CENTRES
Socioeconomic status is the social standing or class of an individual or group. It is often measured as a combination of education, income, and occupation.
EdTech
Business Model: Grants, corporate sponsorships, and recruiting business FutureLearn is another MOOC heavyweight with 210+ partners that include universities, humanitarian foundations, and large businesses. Some startups even rely on corporate sponsorship as their main business model
Generalist Education
TAMMBRGC: Tennis, Acting, Modelling, Music, Ballet (Female), Rings Gymnastics (Male), Graffiti (Art), Cooking (Gastronomy)
STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics
M&A: Merger, Acquisitions
Welfare Investment Program
Fund through Rental Properties: Bond Funds, REITs
Credit Building Program: Line of Credit Deposit Program
Job Placement for Agriculture Working Class
Agricultural Industry means an industrial activity involving the processing, cleaning, packing or storage of the results from agricultural production. The working class (or labouring class) comprises those engaged in manual-labour occupations or industrial work, who are remunerated via waged or salaried contracts. Working-class occupations (see also "Designation of workers by collar colour") include blue-collar jobs, and most pink-collar jobs. Members of the working class rely exclusively upon earnings from wage labour; thus, according to more inclusive definitions, the category can include almost all of the working population of industrialized economies, as well as those employed in the urban areas (cities, towns, villages) of non-industrialized economies or in the rural workforce.
As with many terms describing social class, working class is defined and used in many different ways. The most general definition, used by many socialists, is that the working class includes all those who have nothing to sell but their labour. These people used to be referred to as the proletariat. In that sense, the working class today includes both white and blue-collar workers, manual and menial workers of all types, excluding only individuals who derive their livelihood from business ownership and the labour of others. The term, which is primarily used to evoke images of laborers suffering "class disadvantage in spite of their individual effort," can also have racial connotations. These racial connotations imply diverse themes of poverty that imply whether one is deserving of aid.
COMMODITIES REAL ESTATE
Insurance Premium, Financial Electronic Data Interchange, Royalties, Lease, & Gross Sale Payments for Restaurant Clientele/Cook Book Meal Delivery Grocery Stores and Delivery Food Courts:
A lease payment is the equivalent of the monthly rent, which is formally dictated under a contract between two parties, granting one participant the legal right to use the other individual's real estate holdings, manufacturing equipment, computers, software, or other fixed assets, for a specified amount of time.
Gross sales refer to the grand total of all sales transactions over a given time period. This doesn't include the cost-of-sales or deductions (like returns or allowance). To calculate a company's gross sales, add up the total sales revenue for a specified period of time—monthly, quarterly, or annually.
A franchise (or franchising) is a method of distributing products or services involving a franchisor, who establishes the brand's trademark or trade name and a business system, and a franchisee, who pays a royalty and often an initial fee for the right to do business under the franchisor's name and system. Royalties are the amount someone pays you to use your property after you subtract the expenses you have for the property.
(My Name) Macaroni Au Gratin; Pot Roux: Soy Flour and Garlic-Basil Goat Butter, Cheese Sauce: Broccoli, Spinach, Seasoned Sundried Tomato, Sweet Onion, Goat Milk Kefit, Multi-Mix Cheese (Goat Brie-Aged Goat Gouda-Nababbo), Pumpkin Seeds; Stove Pasta: Soy Rigatoni; And Oven Crust Well Done: Diced Onion Aged Parmesan Panko-Chia Seed; How To Eat: Eat Rigatoni and Save Veggies For Left Over Roux
Goat Milk Kefir & Honey-Caramel Tofu Iced Espresso
Coconut Bowl Soy Sauce Fried Rice
Soy Cookies-Ice Goat Milk Vanilla Bean Kefir Sandwich
Specifically, goat butter contains plenty of fat-soluble vitamins, among which the most important vitamins are A, E and especially K2. Goat milk kefir presents a better-to-assimilate calcium for our bodies. This is because of the Vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 helps assimilate calcium. Bacterial fermentation (which happens in making kefir) produces vitamin K2.
CONFLUENCE FOREX & COMMODITIES BETA-ARBITRAGE FORMULA
Trading Psychology: Play Defense, Focus on preserving capital instead of gaining capital
Position Trading: Currency being used, Shorting Low-Interest Currency against High-Value Currency Or Currency Being used, Shorting Low Interest/High-Value Currency against High-Interest Currency. Examples: Carry-Roll Down Bonds, CFD Forex Gold
Swing Trading: Use mt4/mt5 With Heiken Ashi Charts, Setting at 14 or 21 Momentum Indicator above 0 as Divergence Oscillator and VSA as Reversal Oscillator and Trade when bullish candlesticks above 200 exponential moving average and/or 20 exponential moving average (EMA) on H1 (Hourly) Time Frame; use H4 (4 Hours) and D1 (1 Day) as reference. Works for Oil & Gold Commodities
Master Supply and Demand (S&D) Zones (banks use this)
Candlestick Patterns for Momentum: Bearish Engulfing, Hanging Man, Shooting Star Three Crows, Evening Star, (Short). Bullish Engulfing, The Bearish Inverted Hammer or Regular Hammer (Regardless of Colour), Morning Star, and Piercing Line (Long) are extremely Important
Candlestick Patterns for VSA When Volume Spikes Down and Price is Up Bearish: Shooting Star, Doji, Hanging Man, Doji-Star
Candlestick Patterns for VSA When Volume Spikes Up and Price is Down Bullish: Hammer, Inverted Hammer, Doji, Doji-Star
S&D Reversal Patterns: The Drop-Base-Rally is a bullish reversal pattern, The Rally-Base-Drop is a bearish reversal pattern
S&D Continuation patterns: The Rally-Base-Rally is a bullish continuation pattern, The Drop-Base-Rally is a bearish continuation pattern
Swing Trading Time Frame H1 (Hourly) Reference D1 and H4 to locate supply and demand zones Pivot Points and VSA
Heiken Ashi Candlesticks Much easier to read candlestick charts and analyze market trends
Using Pivot Points for Prediction A pivot point is a technical analysis indicator, or calculations, used to determine the overall trend of the market over different time frames Works for commodities
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) 200 Day 20 Day
Momentum Indicator Settings 14 or 21
Volume Spread Analysis (VSA Trading) Entry 4 Steps: Identify the trend, Identify the sign of weakness in an existing uptrend, Wait to test the weakness for confirmation for the continuation of the uptrend, Look for any bullish reversal candlestick pattern for entry.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum indicator. It is a single line ranging from 0 to 100 which indicates when the stock is overbought or oversold in the market. If the reading is above 70, it indicates an overbought market and if the reading is below 30, it is an oversold market. RSI is also used to estimate the trend of the market, if RSI is above 50, the market is an uptrend and if the RSI is below 50, the market is a downtrend.
Commodity Channel Index Commodity Channel Index identifies new trends in the market. It has values of 0, +100, and -100. If the value is positive, it indicates uptrend, if the CCI is negative, it indicates that the market is in the downtrend. CCI is coupled with RSI to obtain information about overbought and oversold stocks.
What is Cash-and-Carry-Arbitrage? Cash-and-carry-arbitrage is a market-neutral strategy combining the purchase of a long position in an asset such as a stock or commodity, and the sale (short) of a position in a futures contract on that same underlying asset. A cash-secured put is an income options strategy that involves writing a put option on a stock or ETF and simultaneously putting aside the capital to buy the stock if you are assigned.
What are Gold CFD? A contract for difference (CFD) is a popular type of derivative that allows you to trade on margin, providing you with greater exposure to the gold market. Instead of purchasing gold itself, you buy or sell units for a given financial instrument depending on whether you think the underlying price will rise or fall.
What is Quanto Option? The Quanto option is a cash-settled, cross-currency derivative in which the underlying asset has a payoff in one country, but the payoff is converted to another currency in which the option is settled.
Hedging Strategies: Forex and Commodities CFD, Crude Oil Cash-secured Put Options (Binary Options)
DAILY FANTASY SPORTS CONTEST TURF ACCOUNTANT
Beta-Arbitrage Parlay and Single Bets (PROFITS FOR BOOKMAKER)
+EV DCF Round Robin (Investment)
Live Betting Options Trading (Balance Sheets)
Draft Kings is My Influence
Global Sports Betting Market Will Reach USD 155.49 Billion By 2024: Zion Market Research
MY BOOKIE LIVE BETTING TRADEMARK
The Ladder
Modeled Off Of Shout Options, A shout option allows the holder to lock in a certain amount in profit while retaining future upside potential on the position. Multi-Leg Options, Multi-leg option strategies involve using two or more options in a single strategy and order. Leverage, leverage is any technique involving borrowing funds to buy things, hoping that future profits will be many times more than the cost of borrowing.
Bettor places a wage on an Over Base Amount. Multi-leg Upsides are met with discounted live betting that has full value. If the live bet isn't met the bettor loses the upside wager.
Helps with balance sheets
BRANCH BRACKET DISCOUNTED CASH FLOW PORTFOLIO BET SLIP
+EV Round Robin instead of WACC Portfolio
$5 Units
GAME THEORY OPTIMAL POKER WITH LOOSE AGGRESSIVE & GROWTH INVESTING
Growth Investing Strategy & Game Theory
Japanese Candlestick Charts: Bullish Engulfing
Discounted Cash Flow Model: EV (Expected Value replaces WACC)
Mixed Strategy
Fold Equity
Community Cards
Companies Charts and Historical Financials
Royal Flush
Straight Flush
4 of a Kind
Full House
Flush
Hands
FCF of Companies
Strategy
Every chart starts with a green candlestick
Depending on your hand the second candlestick is either green or red
Green for the top 5 hands: Listed above
Red for the bottom 5 hands
If it's green invest by betting
If it's red fold
The third candlestick depends on the Flop
The fourth candlestick depends on The Turn
As more money gets betted the Green candlestick gets larger
After The Flop risk-assessment and probability needs to be accounted for
After The Flop, The Turn, and The River it is possible for a red candlestick to appear because of a fold or a better hand because you lost money. Judge how much money you lost by the size of the candlesticks growth
Tony Dunst Tips
Learn to think in Big Blinds, Opponents are Effective Big Blinds
Identify Player Types then Adjust
Study Big Blind Defense Frequency (Hand Ranges)
Work on Bubble and Final Table Play (Independent Chip Model)
Build 3 Betting Ranges
AFRO-MEDITERRANEAN SOCIOECONOMIC STATUS & TENNIS SPORTS PERFORMANCE FOR KINAESTHETIC LEARNERS
Tennis Physiological Age System for Both Genders: Plyometric High-Intensity Interval Training Through Cross Training, Wingspan Through Cross Training, Unstable Surface Muscle Recruitment Contrast Training, Isometric-Plyometric-Sprint-or-Vertical Jump Contrast Conditioning, Intermittent Hypoxic Training (IHT) Weighted Jump Rope Respiratory Conditioning, Functional Threshold Power (FTP) Cycling, Fascia and Central Pattern Generator Skill Development, Stretch-Reflex Elastic Strength Training, Running-Based Anaerobic Sprint Test (RAST), Stimulus-Fatigue-Recovery-Adaptation for Supercompensation, Autophagy Recovery, High Fat and High Carb with Lipolysis Supplement Nutrition: 3 Fuels of Energy in Oxygen, Fat, and Glucose, Convert Hybrid Muscle Fibers
Stretch Goal of Having a Physiological Age of 25
Volleyball is an aerobic sport with additional anaerobic demands. This will require volleyball players to work both energy systems, making cardiorespiratory conditioning very important. The aerobic, or lower intensity training, will help build a strong cardio base that is needed for a long match. A study done on college athletes showed that gymnasts and volleyball players had significantly higher bone mineral density than swimmers, which is considered a low-impact sport.
Collagen Athletes: Researchers found that a year of daily collagen peptides supplementation measurably increased bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and in the upper femur. The women also had higher levels of a blood biomarker that indicates bone formation. Collagen provides resistance to tension and stretch, which commonly occur in fascial tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, sheaths, muscular fascia and deeper fascial sub-layers. Julio Jones and Cam Newton do Fascia Beach Workouts https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Unm5dvlcqL4
Anta Sports Fashion Collab Circuits (Graffiti Fashion Week and Trade Show): Key City Tournaments
Planned Pregnancy: Mercury-Venus Cusp, MSTN Gene, ACTN3 Gene, and XYY Syndrome or Triple X Syndrome
TENNIS POSITION
A Baseliner plays from the back of the tennis court, around/behind/within the baseline, preferring to hit groundstrokes, thereby allowing themselves more time to react to their opponent's shots, rather than to come up to the net (except in certain situations).
WORKOUT SPLITS
Upper/Lower-Offense/Defense, Upper/Lower-Defense/Offense
SUISSE CONTRAST SUPERSETS TRAINING
Wall Sit-Low Split Step/Squat Jack Weighted Jump Rope 10 sec:50 Reps
Tendon stiffness may influence the Rate Force of Development by affecting the time lag between muscle activation and muscle force production. For example, Waugh et al showed that the electromechanical delay was inversely correlated with tendon stiffness, while RFD was positively correlated to stiffness[8]. That study also found that tendon stiffness accounts for 35% of RFD variability in children. Plyometric and isometric training are commonly studied for their effects on musculotendinous stiffness. https://www.sportsmith.co/articles/combining-plyometrics-and-isometric-training-to-improve-tendon-stiffness-and-performance/#:~:text=Plyometric%20training%20is%20effective%20in,effective%20in%20improving%20tendon%20stiffness.
Pre-workout Supplement Hydrolyzed Collagen-BCAA to Build Fascia.
Fascia-Elastic Force Defensive Stance HIIT Isometric-Plyometric & Isometric-Mobility Acompany's Defensive Workout. Sauna Suits (Full Body), Gymnastic Rings (Upper Body), Battle Ropes (Upper Body), Med Ball (Core), Tennis [Resistance] Bands {Replaces Punching Bags} (Full Body), Sledgehammer (Ful Body), Weighted Vest (Full Body), and Weighted Jump Rope (Full Body). Keto BHB & Hydrolyzed Collagen HA Acid BCAA is Pre-Workout and Hydrolyzed Collagen HA Acid mTAA is Post Workout Supplement. This Will Be Known as Traditional Tennis Training and referred to as Tennis Physique.
TENNIS PSYCHOLOGY
Self ONE is the Organizer, Self TWO is the Doer
Initiative in a chess position belongs to the player who can make threats that cannot be ignored, thus putting the opponent in the position of having to spend turns responding to threats rather than creating new threats.
In chess, prophylaxis consists of a move or series of moves done by a player to prevent their opponent from taking some action. Such preventative moves, or prophylactic moves, aim not only to improve one's position but also to restrict the opponent in improving their own.
In chess, someone who is considered to be "losing", "has a worse position" or has a more "passive position" is going to try to stir up some trouble for the opponent.
RACKET POCKET DRILLS
Racket Pocket Check Position: Scapular Pinch, Palm Down; 2 Step Right-Left Priming Footwork showing the Bottom of the Shoe to Load Hips (Reverse for Backhand) [Chop Feet to get on Back Foot to Set Up Priming Footwork]): Back Hip Quick-Chest Safe (Shoulder Angle Side Arm), Power-Slice (Trophy Pose Knob Cast)
Creep Drill: Adjust the Tennis Ball Machine as Fast as Possible. Start From a Normal Distance and after Succesfull Contact Move Closer. When Speed Is Too Difficult, Do the Same Thing From That Spot Backwards.
Return Adjustability: Use 3 different colored balls. One represents a slow runner the other is a medium runner/well-hit ball and the third is a fast runner. The Central Pattern Generator is also neuroplastic. That is, the timing, sequence, and control of your movement patterns can be changed, refined, and perfected but this takes time. 75% intensity for 2-4 weeks
TENNIS TRACKING DEFENSE
Court Cutting:
Ball Tracking: Use a combination of “soft focus”, transition to “hard focus” and gentle “pursuit movement” to track each and every target. Start in a Dorsiflexion Tall Athletic Position, Shift Hips to an x not +, and Run a Route to a Spot to receive the Shot.
How to Attack the Ball: One-handed Striking (Make a Check Mark with Base and Racket Pocket as Check) Before the Contact Point, Keep Racket Arm Straight While Running, and Make Contact with the Ball in Front of Body. Generate momentum toward Bound Lines Before Making Contact Ball.
TENNIS SPIRAL STRIKES
Racket Pocket (Check Position): Back Hip Quick or Chest Safe (Shoulder Angle)
Scapular Pinch with Palm Down, 2 Step Right-Left Priming Footwork showing the Bottom of the Shoe to Load Hips (Reverse for Baackhand) [Chop Feet to get on Back Foot to Set Up Priming Footwork], Glute Pull, and Tricep Extension with Wrist Pronation or Supination. Flex Core Rotation from Rest to* Movement
SWEET SPOT CONTACT
Choke Up On Racket, Catch Ball In Sidearm Pronation/Supination Throwing Method, Racket Sweet Spot Is Extension Of Hand.
SPORTS INTERNATIONAL REPRESENTATION
Citizenship By Investment Mercantilism Program: Enterprise Foundations; Hospitality-Gaming Agriculture Vertical Integration & Real Estate, Offshore Biotechnology Holdings Company Investment Trust
HSBC/UBS TENNIS PURSE/HEIGHT CLASS SYSTEM SEMI-PRO LEAGUE
A remodeling of national tournament circuits for Business Purposes and the path to Turing Pro or International shows and tournaments, Mediterranean Games, and ultimately the Olympics. Rugby Union Influence Variants Rugby union has spawned several variants of the full-contact, 15-a-side game. The two most common differences in adapted versions are fewer players and reduced player contact. I added a Car Purse System; People are Investing in Car Shows. The Human System has 12 Systems, and a Car has 8. BE THE BUGATTI.
Starter Kit
10 Uniform Kits, 3 Pairs of Shoes, a Racket, a Tennis Ball Case, and a Defense Workout Bundle
Qualification
50 Wins, 13 Years Old Minimum
Development
Fascia Hybrid Fibre Type Bone Density Training: Isometric-Contrast Training, Jump Rope As Main Cardio, Calisthenics Dynamic Effort Method, Joint Preparation Exercises, Elastic Force-Stretch Shortening Cycle Tennis (Resistance) Bands, Straight Arm Exercises, and Tennis-Volleyball
Residency
1-year residency to simulate Olympic/School Lifestyle
Campus
Tennis-focused Campus: Medical Center, Tennisology Sports Science Building, Commodities Corporate Finance Building, Cafeteria, Fitness Center, Training Space, and Business Meetings Plaza
Education
Financial Times Triad: Psychology Sessions
Polgár Experiment: Operant Conditioning, Learning Centers, Programmed Learning
Monthly Tournament & Venues
Purse Qualifiers: This term refers to the amount of money, agreed upon before the fight, that each fighter is to be paid for completing the fight. The amount of money to be paid to each fighter can be different and can include different clauses. For example, one fighter may be entitled to a certain percentage of the pay-per-view revenue that the event may generate. Purse-Gambling: Beta-Arbitrage, DCF +EV, Live Betting Options Trading
Tournament Style Round Robin: Financial Incentives for Top 4 Finishers
Venue Location: Financial District
Membership
After residency tennis players go back to camps with experience but are now members
Members are invited to all tournaments
Tournament Spectator Invitation
Corporations
Real Estate Expos
ATP or WTA Tournament Host
Oligopolistic Banks
Scholarships
Any non-playing ESTJ personality receives a full scholarship to Tennis Gardens and an Inside track to Agri STEM & Mergers and Acquisitions Finance Hiring
ESTJ Personality is the Executive Personality
ESTJs typically thrive in leadership roles, and they have a reputation as reliable, highly organized entrepreneurs who love logic-driven policies and procedures. Sometimes referred to as The Executive, the ESTJ personality type includes natural-born leaders with the skills and work ethic required to succeed.
Business Engineering (Macroeconomics And Tribes Social Organism For Microeconomics Marketing)
Free To Play (F2P) Mean? Free to play (F2P) refers to a business model for online games in which the game designers do not charge the user or player in order to join the game. Instead, they hope to bring in revenue from advertisements or in-game sales, such as payment for upgrades, special abilities, special items, and expansion packs.
In a franchained business model (a short-term chain, long-term franchise), the company deliberately launched its operations by keeping tight ownership on the main assets, while those are established, thus choosing a chain model. Once operations are running and established, the company divests its ownership and opts instead for a franchising model.
**A Blue Sea strategy instead tries to redefine value, not for a whole market, but only for a small group of people craving for that value to be provided.
The aggregator business model is basically a network notion that connects a big number of unorganized merchants to a single major site with a unique corporate image. This platform connects providers with their customers but under a particular firm. Merchandising and/or speciality co-ops are often the actual clientele of such aggregator-based organizations. As a consequence of the aggregator business model, these specialist firms can obtain clients for a charge or reward.Generally, a B2C aggregator does not have its own manufacturing unit; instead, it depends on its power to make a site that allows buyers to compare prices and specifications of rival manufacturers before purchasing after completing comprehensive research.The Aggregator Business Model is built on the foundation of trust. For instance, if you're a provider, an aggregator will negotiate an agreement with you and offer your services to their customers under their identity. It is referred to as a network marketing scheme. Each of the services provided by the aggregator has its own network since the aggregator is a business. The services are standardized and structured, despite numerous providers providing them. Travel Industry Aggregators: A tourism aggregator is a service or application that analyses many web pages for savings and summarizes the output in one place. For instance, if you wished to book a cheap flight from Australia to Seattle, you could sit down and look at a lot of airline companies, which would take ages or you could also use a tool like Tripadvisor to look for thousands of flights in one go.
The razor-razorblade model is a pricing tactic in which a dependent good is sold at a loss (or at cost) and a paired consumable good generates the profits. Also known as a razor and blades business model, the pricing and marketing strategy is designed to generate reliable, recurring income by locking a consumer onto a platform or proprietary tool for a long period. It is often employed with consumable goods, such as razors and their proprietary blades. The concept is similar to the "freemium," in which digital products and services (e.g., email, games, or messaging) are given away for free with the expectation of making money later on upgraded services or added features.
Match NBA and FIFA shoe deals by allowing players to wear their own Leather Strapbacks. Rebrand Hat Culture to Loyalty Check Culture (LC or Loyalty Check for short)
Club Card (Starbucks Gift Card Remodeled)
Scan and Swipe Card
Treat as Monetary Policy for Bubble or Recession, Through Price Saving/Sale Percentage For Tribe
Keynesian: Keynesian economics was founded mainly based on the works of John Maynard Keynes and was the beginning of macroeconomics as a separate area of study from microeconomics. Keynesians focus on aggregate demand as the principal factor in issues like unemployment and the business cycle. Keynesian economists believe that the business cycle can be managed by active government intervention through fiscal policy, where governments spend more in recessions to stimulate demand or spend less in expansions to decrease it. They also believe in monetary policy, where a central bank stimulates lending with lower rates or restricts it with higher ones. Keynesian economists also believe that certain rigidities in the system, particularly sticky prices, prevent the proper clearing of supply and demand.
PayPal Influence: Scheduled Payments and Club member Discounts. At Restaurants and Ticket price match for raves plus discount
AGRICULTURE WORKING CLASS TENNIS-DEVELOPMENT GROCERY STORE TEMPLATE
Leadership Program
Put high quality employees on management track
Put minority supervisors in place for diverse equality
Offer di-biasing training to create fair opportunity for everyone
Collectivistic Culture Traits
A few common traits of collectivist cultures include:
Individuals define themselves in relation to others (for example, “I am a member of…”).
Group loyalty is encouraged.
Decisions are based on what is best for the group.
Working as a group and supporting others is essential.
Greater emphasis is placed on common goals than on individual pursuits.
The rights of Departments comes before those of the individual.
Work Week and Payroll System
4-Day Work Week: Monday, Tuesday, Thursday, Friday; Be realistic with tasks your giving people but shorter deadlines will lead to more productivity
Individual Project Days (IPD): Wednesday, Saturday, Sunday; Give people time to work on their own projects this will lead to my company growing and adding different departments
Two-Tier System: A two-tier system is a type of payroll system in which one group of workers receives lower wages and/or employee benefits than another. The employer wishes to establish a pay-for-performance or merit-pay wage scheme that compensates more productive employees without increasing overall wage costs.
Employee Relationship
Employee's titles are Independent Leader or Group Leader
Offer university certificate through customer training (MOOC)
Articulating the strategy in human terms—what capabilities the company will need to build, and what skills are required to do so—not only helps the company focus on how to develop the right talent, but it allows individuals to understand how their role fits into the overall strategy and allows them to see their work in a much more fundamentally connected way.
CORPORATE TIME MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
168 Hours
168 hours — that’s the number of hours there are in a week. And that’s how author Laura Vanderkam proposes we look at our schedule — one week at a time. By reorganizing your time according to your priorities, you can cut down on misused time that comes from misplaced priorities or excuses.
Vanderkam believes that we actually have more time than we think and so we can devote more time to the things we’ve always wanted to do but never quite found the time to do so.
Divergent Pomodoro Technique
Developed in the late 1980s by Francesco Cirillo, the Pomodoro Technique is centered on the idea that work should be broken down and completed in intervals separated by short breaks. That is, you work for 25 minutes, then take a five minutes break. Each of these 25-minute periods is called a “Pomodoro”, named after the Italian word for tomato. (Cirillo had used a tomato-shaped kitchen timer, hence the name.) After 4 Pomodori, you take a longer break of 15–20 minutes. Of course, nothing should interrupt an ongoing Pomodoro.
The philosophy behind this technique is simple — frequent breaks can improve mental agility, letting you feel refreshed and recharged, ready to tackle new tasks. More importantly, it minimizes any distractions, which these days come in the form of a Facebook message or a tweet. Pomodoro forces these distractions to wait so that you can focus on your task. This also translates to higher productivity in getting work done, and you can have more time to do other things.
Divergent thinking is a thought process or method used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions. It typically occurs in a spontaneous, free-flowing, "non-linear" manner, such that many ideas are generated in an emergent cognitive fashion. Many possible solutions are explored in a short amount of time, and unexpected connections are drawn. Following divergent thinking, ideas, and information are organized and structured using convergent thinking, which follows a particular set of logical steps to arrive at one solution, which in some cases is a "correct" solution. Activities that promote divergent thinking include Creating Lists of Questions*, setting aside time for thinking and meditation, Music/Intoxicated Brainstorming*, subject mapping, bubble mapping, Keeping a Journal*, playing tabletop role-playing games
The Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is a simple tool for considering the long-term outcomes of your daily tasks and focusing on what will make you most effective, not just most productive. It helps you visualize all your tasks in a matrix of urgent/important. All of your day-to-day tasks and bigger projects will fall into one of these four quadrants: Urgent & Important tasks/projects to be completed immediately; Not Urgent & Important tasks/projects to be scheduled on your calendar; Urgent & Unimportant tasks/projects to be delegated to someone else; Not Urgent & Unimportant tasks/projects to be deleted
In the real world, the distinction between urgent/non-urgent, important/not important is much murkier than under experimental conditions. Urgent matters are those that require immediate action. These are the visible issues that pop up and demand your attention NOW. Often, urgent matters come with clear consequences for not completing these tasks. Urgent tasks are unavoidable, but spending too much time putting out fires can produce a great deal of stress and could result in burnout. Important matters, on the other hand, are those that contribute to long-term goals and life values. These items require planning and thoughtful action. When you focus on important matters you manage your time, energy, and attention rather than mindlessly expanding these resources. What is important is subjective and depends on your own values and personal goals. No one else can define what is important for you.
SWOT Analysis
What Is a SWOT Analysis? SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, and so a SWOT analysis is a technique for assessing these four aspects of your business. SWOT Analysis is a tool that can help you to analyze what your company does best now, and to devise a successful strategy for the future.
HOW TO BUILD A SPORT-SPECIFIC WORKOUT FOR GROCERY PERFORMANCE CENTERS
Template
Pre-workout Supplement Hydrolyzed Collagen-BCAA and Wear 10lb Vest
Self Analysis: Scrimmage Plus/Minus System (Ranked Clients vs Non-Ranked Clients)
Report cards: Ontario report cards and fall progress report cards outline six learning skills and work habits throughout Grades 1 to 12: Responsibility, Organization, Independent work, Collaboration, Initiative, Self-regulation
The emphasis on these skills and habits reflect that students need to learn more than just facts if they want to succeed in postsecondary education and the world of work. At school students are learning to take initiative, think critically, solve problems, work independently, be self-reliant and work in a team.
Performance Center Grades Category (Chess Initiative Rally Percentage): Off Court; Initiative, Self-regulation, Independent Work/On Court (Test); Responsibility, Organization, Collaboration
Test Possession (Test within a Test) Offense, Tracking Defense
SWOT: Strengths, What you Are Good At; Weaknesses, What you Are Not Good At; Opportunities, Improve, Expand, and Grow; Threats, What can Keep You off the Court
Eisenhower Matrix: Urgent/Important (Threats), Urgent/Not Important (Weaknesses), Not Urgent/Important (Opportunities), Not Urgent/Not Important (Strenghts)
ATP & WTA TENNIS TOURNAMENT (DEBUT OPEN & FIRST TIER SERIES) [INVITE ONLY]
Debut Open locations: Rotating Key City Locations, Africa, India, Asia and South America
Locations: Bid to Host
Debut Open
Reason For Tournament
You see the NBA constantly replacing superstars and showcasing the next generation, this tournament brings tennis that opportunity.
Tournament Details
Participants are 23 years of age or younger
Hold tournament as the last tournament before the Australian open
Host during Christmas break
Equal Pay for men and women
High cash earnings for winners and low earnings for losers to offset high earnings for winning
Benefits Of Having A Grand Slam Outside of America and Europe
Increase global relations by gathering advertisements and sponsors for tournament
Broadcasting deal can be greater because if a cable company is owned
The core audience going forward for the next generation will be greater
This increases the network of fans
First Tier Series
Reason for Tournament
Tennis has tournaments all over the world but most people can't name the bottom 5 players of the top 10 rankings. This fixes that.
Tournament Details (First Tier Series) {all-star equivalent}
Point of the tournament is to show the world the difference between good and great
5 Game Series
Top 10 invite only
Teams of 5, every participant has 1 match three sets
All matches are played
Themes: Males vs Females, Mixed Male and Female Teams, Ranking Lottery Draft with Captains
Skills Competition: Hardest Serve, Accuracy Challenge, Best Return,
Fan Media Day
Player's kit endorser must make themed outfit
Player's Pay rates are by ranking
Profit Strategies (both)
Broadcasting Rights
Sponsorships/Advertisers
Ticket and Concession
Equal Pay and No Capital Gains Tax to attract star Women Players
No Capital Gains Tax so players lower their appearance fee
Pay Quarter Finalist to run to the 3-day clinic
Have a YouTube channel where players give fundamental tips, fitness tips, Diet tips, mental strategies, and book recommendations
Have an Umpire Clinic and application in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Attach hospitality and casino industries to tickets to draw crowds
LIVE BROADCASTING AND STREAMING COMPANY
Allow people to create their own highlights for social media and YouTube through streaming service but they have to purchase 1 Year Pass of live Broadcasting
In service editing software: Offer different graphics and effects; In Service Cost for Different Packages.Different camera angles; In Service Cost for Different Packages. Add in-rings mics to differentiate from sports network's highlights. Chapters Feature: Everytime a Significant Event in the Event Happens a Bookmark is Made for Highlight Creation, Easier to create highlights, and Subscribers can create their own bookmarks
Pre-made music to create fight mix: Take percentage of revenue from social media and YouTube highlights
Streaming Service: For an up front fee subscribers can get distribution rights to create highlights. Make money from: Live Broadcast, Highlights, Subscription, Distribution Rights, In Subscription Cost
Potential Hiring Process: People are paying to be content creators from all over the world this leads to more diverse content creating staff. Sell this as a way to hire people without a physical resume. YouTube can lead to employment
Bet Night Hour Program: Betting Analysis on Tournament, Predictions, Bets that were Placed Globally, Live Television
CARTEL THEORY
HSBC Bank Holding Company Equity Financing
What Is a Bank Holding Company? A bank holding company is a corporation that owns a controlling interest in one or more banks but does not itself offer banking services. Holding companies do not run the day-to-day operations of the banks they own. However, they exercise control over management and company policies. They can hire and fire managers, set and evaluate strategies, and monitor the performance of subsidiaries’ businesses.
What Is Equity Financing? Equity financing is the process of raising capital through the sale of shares. Companies raise money because they might have a short-term need to pay bills or have a long-term goal and require funds to invest in their growth. By selling shares, a company is effectively selling ownership in their company in return for cash. Equity financing comes from many sources: for example, an entrepreneur's friends and family, investors, or an initial public offering (IPO). An IPO is a process that private companies undergo to offer shares of their business to the public in a new stock issuance. Public share issuance allows a company to raise capital from public investors.
Palmiers Noirs Rivals
United Kingdom
Jews
Luxembourg (EU Blacklist Creator)
Latin Kings
Sinaloa Cartel
Sonora Cartel
Colombian Cartels
Neymar
Banker Title
Croupier Comptable: An investment banker who has experienced decadence through Casino Capitalism
Palmiers Noirs Structure
Clandestine Cell System
A clandestine cell system is a method for organizing a group of people (such as resistance fighters, sleeper agents, mobsters, or terrorists) such that such people can more effectively resist penetration by an opposing organization (such as law enforcement or military units).
In a cell structure, each of the small group of people in the cell know the identities of the people only in their own cell. Thus any cell member who is apprehended and interrogated (or who is a mole) will not likely know the identities of the higher-ranking individuals in the organization.
The structure of a clandestine cell system can range from a strict hierarchy to an extremely distributed organization, depending on the group's ideology, its operational area, the communications technologies available, and the nature of the mission.
Criminal organizations, undercover operations, and unconventional warfare units led by special forces may also use this sort of organizational structure.
Infrastructure cells
Any clandestine or covert service, especially a non-national one, needs a variety of technical and administrative functions, such as: Recruitment/training, Forged documents/counterfeit currency, Finance/Fundraising, Communications, Transportation/Logistics, Safehouses, Reconnaissance/Counter-surveillance, Operational planning, Arms and ammunition, and Psychological operations
A national intelligence service has a support organization to deal with services like finance, logistics, facilities (e.g., safehouses), information technology, communications, training, weapons and explosives, medical services, etc. Transportation alone is a huge function, including the need to buy tickets without drawing suspicion, and, where appropriate, using private vehicles. Finance includes the need to transfer money without coming to the attention of financial security organizations.
Cartel Definition
Cartel is an ambiguous concept, which usually refers to a combination or agreement between rivals, but – derived from this – also designates organized crime. The main use of ‘cartel’ is that of an anticompetitive association in the economy.
Price cartels engage in price fixing, normally to raise prices for a commodity above the competitive price level.
Cartel Theory
Cartel theory is usually understood as the doctrine of economic cartels. However, since the concept of 'cartel' does not have to be limited to the field of the economy, doctrines on non-economic cartels are conceivable in principle. Such exist already in the form of the state cartel theory and the cartel party theory. For the pre-modern cartels, which existed as rules for tournaments, duels and court games or in the form of inter-state fairness agreements, there was no scientific theory. Such has developed since the 1880s for the scope of the economy, driven by the need to understand and classify the mass emergence of entrepreneurial cartels. Within the economic cartel theory, one can distinguish a classical and a modern phase. The break between the two was set through the enforcement of a general cartel ban after the Second World War by the US government.
Constituent characteristics and exclusion criteria for cartels
Constituent criteria for cartels would be the following: The members are, at the same time, partners as well as competitors (so do e.g. enterprises, states, parties, duelists, tournament knights). These members can be individual persons or organizations. The members of a cartel are independent of each other, negotiating their interests with each other and against each other. So there have to be at least two participants and they determine their interests autonomously. The members of a cartel know each other; they have a direct relationship, in particular they communicate with each other.
Exclusion criteria for cartels would be the following: There is a "hierarchical" or other strong "dependency relationship among the participants": a drug mafia that is organized hierarchically and managed by a single boss can't be a drug cartel in the sense of a real "cartel". KLikewise, a business corporation can't be a "cartel" due to its central management, which controls its subsidiaries. Furthermore, an OPEC, in which all adherents would be dependent on the largest member (since long: Saudi Arabia) would no longer be a "cartel". Similarly, colonial empires from a motherland and colonies do not constitute a "state cartel". The union of competitors, in their entirety or via important members of its association, is dependent on an outside power. A strict, state-mandated compulsory cartel without freedom of choice between the partners would not be a (real) cartel. A suitable example is the "Deutsche Wagenbau-Vereinigung" (German Railway Cars Association), which was organized in the 1920s by the "Deutsche Reichsbahn" (German Imperial Railways) – its "market opponent". The combination takes place between actors of different levels. Thus, the concerted actions of employers’ associations and trade unions in some industrialized countries was not a cartel, because the allies there were no homogenous competitors. The alleged members of a suspected cartel do not know each other, but only randomly show a parallel behavior: “Cartels of the godless”, “cartels of maintenance deniers” or “silent cartels” are therefore usually no real cartels, but pure verbal abuse formulas.
MACAU ECONOMICS
Science
Science of Aesthetics
Nutritional Biochemistry
Vertical-Rotational Force Kinetic Chain
Biomechanics
Sports Medicine
Technology
Biotechnology
FinTeach
RealTeach
Merger & Acquisition EdTech
Engineering
Business Engineering (Tribes Organism and Keynesian Macroeconomics)
Construction Management
Business Model Reengineering
Mathematics (Decentralized Central Banking)
Investment Management
Monetary Policy & Central Banking
Wolf Packs are Generalist
David Epstein examined the world’s most successful athletes, artists, musicians, inventors, forecasters and scientists. He discovered that in most fields—especially those that are complex and unpredictable—generalists, not specialists, are primed to excel. Generalists often find their path late, and they juggle many interests rather than focusing on one. They’re also more creative, more agile, and able to make connections their more specialized peers can’t see.
Wolves are habitat “generalists,” meaning they can adapt to living in many kinds of habitat. They basically need two things to thrive: abundant prey and human tolerance.
Trophic Cascade, an ecological phenomenon triggered by the addition or removal of top predators and involving reciprocal changes in the relative populations of predator and prey through a food chain, which often results in dramatic changes in ecosystem structure and nutrient cycling. (Diamond Trafficking in Macau)
A keystone species is an organism that helps define an entire ecosystem. Without its keystone species, the ecosystem would be dramatically different or cease to exist altogether. Keystone species have low functional redundancy. (Diamonds Trafficking in Macau)
Unpredictable and harsh conditions tend to produce fast life history strategies, characterized by early maturation, a higher number of sexual partners to whom one is less attached, and less parenting of offspring.
MANDELA/BASQUIAT ARTS (PHOTOGRAPHY, OLFACTORY, CULINARY) YOUTH PRISON SYSTEM
Nelson Mandela spent the first 18 of his 27 years in jail at the brutal Robben Island Prison. Confined to a small cell without a bed or plumbing, he was forced to do hard labor in a quarry.
If you work in Agriculture You'll Always Have a Food Mindset.
THE MILLIONAIRE NEXT DOOR BY THOMAS J. STANLEY (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
What’s in it for me? Find out how wrong you are about the way millionaires live.
Millionaires are ostentatious. They live a glamorous life, with private jets and luxury cars, hidden away in enormous mansions in the exclusive Hollywood hills.
Or is that all fantasy? The truth is far from the bling and bright lights. Most millionaires in America actually live what most people would call a normal lifestyle. What’s more interesting, though, is that living modestly is what made them millionaires in the first place.
These blinks show you that if you’re dedicated and clever enough to plan your finances correctly, you too can follow the path to riches that many a millionaire has walked before you.
In these blinks, you’ll learn why the guy driving a Bentley probably earns less than you do; exactly when you should start saving your cash; and why lazy kids get the biggest piece of their millionaire parents’ pie.
Many millionaires don’t live the high life. They budget wisely to maintain their affluence.
If you were a millionaire, you wouldn’t hesitate to wear Prada and drink Champagne every day for breakfast, right? But despite the stereotypes, many actual millionaires purchase fewer expensive items than you do – and they are happy doing so.
If you want to become a millionaire, you’ve got to learn to save responsibly at the moment when you first start to earn more money than you need to live on.
The majority of self-made millionaires have modest backgrounds and achieved great wealth by saving their monthly earnings and avoiding spending cash on stuff they didn’t need. This simple rule is one way you too could become a millionaire, without ever actually making a million dollars a year.
People become millionaires by controlling their budget and maintaining their affluence in the same way. They’re also practiced at thinking long term and planning for the future.
A survey of millionaires found that for every 100 millionaires who weren't budgeting and thinking about their financial future, there were 120 millionaires who certainly were.
Planning and structuring expenses is key if you want to become a millionaire. To start, set a goal, such as having a certain amount of cash tucked away for retirement. Then budget your expenses, living costs and investments.
Mrs. and Mr. Rule are millionaires, and their main goal is to be financially independent when they’re ready to retire. By this time, they want to have saved some $5 million.
To make this happen, the couple cleverly allocates their time and money so that they can continue to invest in their business while earning and saving money that can be used toward real estate purchases or home renovation projects.
Millionaires know where and how to spend their cash. Invest in what you know!
How do millionaires choose what to invest in? Clever millionaires know that dishing out on medical care for their family and investing in methods to make a business more productive is the way to go.
Although these millionaires are often frugal in other respects, price is not an issue when it comes to buying investment services, getting tax advice or spending on medical care for themselves and their loved ones.
Likewise, they know to buy products or services that improve their businesses, such as additional office space or computer software.
Take millionaire Mr. South. He says he would never buy a Rolls Royce for himself, because in his lower-middle-class neighborhood, it would turn too many heads. Instead, he understands that using his money to pay for his grandchildren’s dental care makes far more financial sense. Smart spending also means smart planning. Millionaires spend a greater amount of time planning investments and often reap more benefits from them than those who neglect to plan. Moreover, if you want to increase your wealth by investing in specific businesses, you’ll need to plan as well as get some expertise. Everyone has at least one area in which they have considerable knowledge, so use this to your advantage when investing. For example, Mrs. Smith is an auctioneer who specializes in commercial real estate. Which industry should she invest in? Commercial real estate, of course. Mr. Long however knows a lot about antique furniture. Should he invest in high-tech securities? Probably not, as he should stick to what he knows best.
Many millionaires share their wealth with their children, even though it can hinder them.
We’ve seen how millionaires live, but what about the children of millionaires?
In most cases, millionaire parents don’t raise their kids with much financial support. Although many millionaires are thrifty, they spend a great deal on economic outpatient care. This means their children receive monthly cash gifts, have the costs of medical treatments and education covered, and so on.
But the more money adult children of affluent parents receive, the less they save, and vice versa.
By financially supporting adult children, some millionaires cause them to be financially dependent and hamper them from being able to budget intelligently.
Did you know that more than 46 percent of wealthy Americans support their adult children and/or grandchildren by offering gifts or cash of at least $15,000 each year?
For example, since she was married, Mary gets $15,000 annually from her parents. She and her husband are in their early 50s, own expensive cars, live in a great neighborhood, are country club members and are involved in a number of non-profit organizations.
From the outside, they look like millionaires, yet they’ve never earned more than $60,000 a year.
The amount of money you spend and save also influences your children’s purchasing behavior. Every family has their own do’s and don’ts for investing and purchasing, and these budgets affect children who emulate their parents’ financial habits.
So teach your children how to invest well and how to spend wisely!
For instance, John is an under-accumulator of wealth (UAW). Whenever he gets a paycheck, he spends the money on designer clothes, a habit he learned from his parents who used to shop every Saturday. They bought just for the sake of buying, and now so does John.
The most financially dependent children receive the largest share of the family inheritance.
Who will receive your money after you die? A lot of millionaires claim it will be divided equally between their children. But in reality, some people are more likely to inherit than others.
Housewives are one such group. Millionaires or affluent parents are aware of the fact that women tend to earn less than men, so they pass more money down to them. Especially housewives, who may have been “daddy’s girl” since childhood or didn’t finish college. They’re significantly more likely to receive a considerable inheritance.
Consider Alice, who was always her father’s favorite. When she married a man who earned only a modest income, and quit school to stay at home with her two children, her father started economic outpatient care because he wouldn’t allow his daughter to live in a home that didn’t measure up to his upper-middle class image.
In addition to women who stay at home, unemployed adult children often receive more cash gifts and inheritance than do working siblings.
In many cases, the children of millionaires are unemployed or “professional students” who have never held a job, choosing instead to study all their life. Parents regard these children as requiring more financial support than their more independent siblings.
Many cash gifts also are drawn from over-funded college savings accounts, which, when a child quits school, were no longer needed.
Take Paul and Peter, brothers and children of a millionaire couple. Paul became an entrepreneur and moved far away from home, and became financially independent as he refused cash from his parents.
Peter, however, moved back to his parents’ home after graduating from college as he didn’t want to be employed full-time. So now he receives cash gifts for housing, food, clothing and transportation from his parents.
It’s no surprise then, that after the death of their parents, the financially dependent Peter received the inheritance.
Final summary
The key message in this book: The typical millionaire isn’t all Hollywood glitz and glamour. Many live well below their means, saving and budgeting money diligently and spending it intelligently. If you consistently adhere to these simple standards, you too could become a millionaire.
THE POWER OF HABIT BY CHARLES DUHIGG (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
What’s in it for me? Learn to pick up or drop any habit you wish.
You’ve made the decision: no more cigarettes! Or maybe it’s: no more junk food! For a couple of weeks, things go swimmingly. You’re proud of yourself. But then, one day, the craving suddenly overpowers you – and, before you know it, you’re back to your old habits.
Sound familiar? If so, you already know the power of habits.
But where does the power of habits come from? As you’ll see in these blinks, habits go deep into the human brain and psyche and influence our lives in a myriad of ways. And while they make our lives a whole lot easier – just imagine if you had to figure out how to open a door every time you encountered one – habits can also cause problems and even ruin lives.
Luckily, by learning how habits work, you can begin to overcome their power. So let’s delve into the world of habits!
In these blinks, you’ll learn why anticipation is at the root of habit formation; what resisting marshmallows can tell us about habits; and what the LATTE method is.
Habits are simple cue-routine-reward loops that save effort.
In the 1990s, a group of researchers at MIT were studying mice to learn more about how habits are formed in the brain. The mice had to find their way to a piece of chocolate that’d been placed at the end of a T-shaped maze. Using special equipment, the researchers could monitor the brain activity of the mice as they sniffed their way to the chocolate.
When the mice were first put in the maze, their brain activity spiked. They could smell the chocolate and they began searching for it. When the researchers repeated the experiment, however, they noticed something interesting.
As the mice gradually learned where the chocolate was and memorized how to get there – go straight, then turn left – their brain activity decreased.
This process of turning a sequence of actions into an automatic routine is known as “chunking,” and it forms the basis of all habit formation. Its evolutionary role is clear and crucial: it allows the brain to save energy and perform common tasks efficiently.
Hence, even a complicated act that demands concentration at first, like finding a piece of chocolate in a maze or backing out of the driveway, eventually becomes an effortless habit. In fact, according to a 2006 paper by a researcher at Duke University, as many as 40 percent of the actions we perform each day are based on habit.
In general, any habit can be broken down into a three-part loop: First, you sense an external cue – say, your alarm clock ringing. This creates an overall spike in your brain activity as your brain decides which habit is appropriate for the situation. Next comes the routine, meaning the activity you’re used to performing when faced with this particular cue. You march into the bathroom and brush your teeth with your brain virtually on autopilot. Finally, you get a reward – a feeling of success and, in this case, a minty-fresh tingling sensation in your mouth. Your overall brain activity increases again as your brain registers the successful completion of the activity and reinforces the link between the cue and the routine.
Habits are incredibly resilient. In some cases, people with extensive brain damage can still adhere to their old habits. Just consider Eugene, a man with severe brain damage caused by encephalitis. When asked to point at the door leading to the kitchen from his living room, he couldn’t do it. But when asked what he would do if he were hungry, he walked straight into the kitchen and took down a jar of nuts from one of the cabinets.
Eugene could do this because learning and maintaining habits happens in the basal ganglia, a small neurological structure embedded deep in the brain. Even if the rest of the brain is damaged, the basal ganglia can function normally.
Unfortunately, this resilience means that, even if you successfully kick a bad habit, like smoking, you will always be at risk of relapsing.
Habits stick because they create craving.
Imagine this scenario: every afternoon for the past year, you’ve bought and eaten a delicious, sugar-laden chocolate-chip cookie from the cafeteria at your workplace. Call it a just reward for a hard day’s work.
Unfortunately, as a few friends have already pointed out, you’ve started putting on weight. So you decide to kick the habit. But how do you imagine you’ll feel that first afternoon, walking past the cafeteria without indulging? Odds are, you will either eat “just one more cookie” or you’ll go home in a distinctly grumpy mood.
Kicking a bad habit is hard because you develop a craving for the reward at the end of the habit loop. Research from the 1990s conducted by the neuroscientist Wolfram Schultz shows how this works at the level of the brain. Schultz was studying the brain activity of a macaque monkey named Julio, who was learning to perform various tasks. In one experiment, Julio was placed in a chair in front of a screen. Whenever some colored shapes were shown on the screen, Julio’s task was to pull a lever. When he did, a drop of blackberry juice (Julio loved blackberry juice) would drip down on his lips through a tube.
At first, Julio didn’t pay much attention to the screen. But when he happened to pull the lever at the right moment, thus triggering the blackberry-juice reward, his brain activity spiked, showing a strong pleasure response.
As Julio gradually grasped the connection between seeing the shapes on the screen, pulling the lever and getting the blackberry juice, he not only stared at the screen, but Schultz noticed that, as soon as the shapes appeared, there was a spike in Julio’s brain activity similar to when he actually received the reward. In other words, his brain had begun anticipating the reward. This anticipation is the neurological basis of craving and helps explain why habits are so powerful.
Schultz then altered the experiment. Now, as Julio pulled the lever, either no juice would come or it would come in a diluted form. In Julio’s brain, Schultz could now observe neurological patterns associated with desire and frustration. Julio got decidedly mopey when he didn’t get his reward, just as you might if you forewent your cherished end-of-the-day cookie.
The good news is that craving works for forming good habits as well. For instance, a 2002 study from New Mexico State University showed that people who manage to exercise habitually actually crave something from the exercise, be it an endorphin rush in the brain, a sense of accomplishment or the treat they allow themselves afterward. This craving is what solidifies the habit; cues and rewards alone are not enough.
Given the power of habits, it should come as no surprise that companies work hard to understand and create such cravings in consumers. A pioneer of this tactic is Claude Hopkins, the man who popularized Pepsodent toothpaste when countless other toothpaste brands had failed. He provided a reward that created craving: namely, the cool, tingling sensation that we’ve come to expect toothpaste to have. That sensation not only “proved” that the product worked in consumers’ minds; it also became a tangible reward that they began to crave.
To change a habit, substitute the routine for another and believe in the change.
As anyone trying to give up cigarettes will tell you, when the craving for nicotine hits, it’s hard to ignore. That’s why the golden rule for quitting any habit is this: don’t try to resist the craving; redirect it. In other words, you should keep the same cues and rewards, but change the routine that occurs as a result of the craving.
Several studies on former smokers have shown that, by identifying the cues and rewards around their smoking habit and replacing the routine with one that has a similar reward, such as doing some push-ups, eating a piece of Nicorette or simply relaxing for a few minutes, the chances of staying smoke-free increases significantly.
One organization that uses this method to great effect is Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), which may have helped as many as ten million alcoholics achieve sobriety.
AA asks participants to list what exactly they crave from drinking. Usually, factors like relaxation and companionship are far more important than the actual intoxication. AA then provides new routines that address those cravings, such as going to meetings and talking to sponsors for companionship. The idea is to replace drinking with something less harmful.
However, research on AA members shows that, although this method works well in general, it alone is not enough. In the early 2000s, a group of researchers at California’s Alcohol Research Group noticed a distinct pattern in their interviews with AA members. A frequent response was that the habit-replacement method worked wonders, but, as soon as a stressful event occurred, the old habit was simply too strong to resist, no matter how long the respondent had been in the program.
For example, one recovering alcoholic had been sober for years when his mother called to say she had cancer. After hanging up, he left work and went directly to a bar, and then, in his own words, was “pretty much drunk for the next two years.”
Further research has indicated that those who resist relapse and remain sober often rely on belief. This is why spirituality and God feature prominently in AA philosophy. But it’s not necessarily the religious component itself that helps people stay sober. Believing in God also helps participants believe in the possibility of change for themselves, which makes them stronger in the face of stressful life events.
Change can be achieved by focusing on keystone habits and achieving small wins.
When former government bureaucrat Paul O’Neill became the CEO of the ailing aluminum company Alcoa in 1987, investors were skeptical. And O’Neill didn’t improve matters when, during an investor meeting in a swanky luxury hotel in Manhattan, he declared that, rather than focusing on profits and revenues, he intended to make workplace safety his number-one priority. One investor immediately called his clients and said, “The board put a crazy hippie in charge and he’s going to kill the company.”
O’Neill tried to explain his reasoning to the lukewarm investors. No amount of talk would reduce injury rates at Alcoa, he argued. Sure, most CEOs claimed to care about workplace safety. But empty words would never lead to the formation of a company-wide habit, which is what would be necessary for real change.
O’Neill knew that habits exist in organizations. And he knew that changing an organization’s direction is a matter of changing its habits. He was also aware that not all habits are equal. Some habits, known as keystone habits, are more important than others because adhering to them creates positive effects that spill over into other areas.
By insisting that worker safety come first, managers and employees would have to think about how the manufacturing process could be safer and how safety suggestions could best be communicated to everyone. The end result would be a highly streamlined, and hence profitable, production organization.
Despite the investors’ initial doubts, O’Neill’s approach proved to be a huge success. By the time O’Neill retired in 2000, Alcoa’s annual net income had increased fivefold.
Keystone habits can help individuals change, too. For instance, research indicates that doctors have a hard time getting obese people to make a broad change in their lifestyle. However, when patients focus on developing one keystone habit, such as keeping a meticulous food journal, other positive habits start to take root as well.
Keystone habits work by providing small wins – that is, early successes that are fairly easy to attain. Developing a keystone habit helps you believe that improvement is possible in other spheres of life, too, which can trigger a cascade of positive change.
Willpower is the most important keystone habit.
In the 1960s, researchers at Stanford conducted what would become a very famous study. A large group of four-year-olds was brought, one by one, into a room. In the room, there was a table with a marshmallow on it. A researcher gave each child a choice: either eat the marshmallow now or wait a few minutes and have two marshmallows instead. The researcher then left the room for 15 minutes. Only about 30 percent of the children managed not to devour the marshmallow in the researcher’s absence.
But here’s the interesting part. When, years later, the researchers tracked down the study’s participants, who were now adults, they found that those who had exhibited the greatest willpower and waited the full 15 minutes had ended up with the best grades in school, were more popular on average and were less likely to have drug addictions. Willpower, it seemed, was a keystone habit that could be applied to other parts of life, too.
More recent studies have shown similar results. For instance, a 2005 study on eighth-graders showed that students exhibiting high levels of willpower had better grades on average and were more likely to get into selective schools.
So willpower is a key habit in life. However, as you might have noticed if you’ve ever tried to start exercising more, willpower can be highly inconsistent. Some days, hitting the gym is a breeze; on others, leaving the sofa is nigh impossible. Why is that?
It turns out that willpower is actually like a muscle: it can tire. If you exhaust it by concentrating on, say, a tedious spreadsheet at work, you might have no willpower left when you get home. But the analogy goes even further: by engaging in habits that demand resolution – say, adhering to a strict diet – you can actually strengthen your willpower. Call it a willpower workout.
Other factors can also affect your willpower. For example, Starbucks found that, on most days, all of its employees had the willpower to smile and be cheerful, regardless of how they felt. But when things became stressful – for example, when a customer began screaming – they would soon lose their cool. Based on research, executives at the company determined that if baristas mentally prepared for unpleasant situations and planned out how to overcome them, they could muster enough willpower to follow the plan even when under pressure.
To help them, Starbucks developed the aptly named LATTE method, which outlines a series of steps to take in a stressful situation: Listening to the customer, Acknowledging their complaint, Taking action, Thanking the customer, and, lastly, Explaining why the issue occurred. By practicing this method over and over, Starbucks baristas learn exactly what to do should a stressful situation arise, and can stay cool.
Other studies have shown that a lack of autonomy also adversely affects willpower. If people do something because they are ordered to rather than by choice, their willpower muscle will get tired much quicker.
Organizational habits can be dangerous, but a crisis can change them.
In November of 1987, a commuter at the King’s Cross station in London approached a ticket collector and said he’d just seen a piece of burning tissue by one of the building’s escalators. Rather than investigating the matter or notifying the department responsible for fire safety, the ticket collector did nothing. He simply returned to his workstation, thinking it was someone else’s responsibility.
This was perhaps not so surprising. Responsibilities in running the London underground were divided into several clear-cut areas, and, as a result, staff had formed an organizational habit of staying within departmental bounds. Over the decades, an intricate, hierarchical system of bosses and sub-bosses, each highly protective of his authority, had emerged. The nearly 20,000 employees of the London Underground knew not to encroach on each other’s terrain.
Under the surface, most organizations are like this: battlegrounds on which individuals clamor for power and rewards. So, in order to keep the peace, we develop certain habits, such as minding one’s own business.
Soon after the ticket collector returned to work as usual, a huge fireball erupted into the ticket hall. But no one present knew how to use the sprinkler system or had the authority to use the fire extinguishers. The rescuers, who were eventually called in after a long series of failures to act by several employees at the station, described passengers so badly burned that their skin came off when touched. In the end, 31 people lost their lives.
The failure at the heart of this tragedy was that, despite its complicated system of responsibility distribution, no single employee or department at the London Underground had an overview responsibility for the safety of passengers.
But even such tragedies can have a silver lining: crises offer a unique chance to reform organizational habits by providing a sense of emergency.
This is why good leaders often actively prolong a sense of crisis or even exacerbate it. In investigating the King’s Cross station fire, special investigator Desmond Fennel found that many potentially lifesaving changes had been proposed years earlier, but none had been implemented. When Fennel encountered resistance to his suggestions, too, he turned the whole investigation into a media circus – a crisis that enabled him to implement the changes. Today, every station has a manager whose main responsibility is passenger safety.
Companies take advantage of habits in their marketing.
Picture yourself walking into your local supermarket. What’s the first thing you encounter? In all likelihood, it’s fresh fruits and vegetables, laid out in lush piles. If you consider this for a second, it doesn’t make much sense. As fruit and veggies tend to be soft and are easily damaged by other products put in the cart, they ought to be displayed closer to the registers. But marketers figured out long ago that, if we begin our shopping by filling our carts with fresh, healthy items, we’re more likely to buy unhealthier products, like snacks and cookies, as we continue to shop.
This might seem pretty obvious. But retailers have figured out far subtler ways to influence customers’ purchasing habits. For example, here’s a surprising fact: most people instinctively turn right when entering a store. That’s why retailers put their most profitable products to the right of the entrance.
As sophisticated as these methods are, however, they have one big drawback; they’re all one-size-fits-all and don’t account for differences in the purchasing behavior of individual customers. Over the past few decades, however, increasingly sophisticated technology and data-collection have made it possible to target customers with breathtaking precision. One of the true masters of this game is the American retailer Target, which serves millions of shoppers annually and collects terabytes of data on them.
In the early 2000s, the company decided to use the full force of its data to target a particular segment of the population long known to be one of the most profitable: new parents. To get a leg up on its competitors, however, Target wanted to do more than market to new parents; it wanted to draw in expecting parents before their babies had even arrived. To accomplish this, it set out to determine pregnant women’s purchasing habits.
In the end, Target’s analysis worked so well that it marketed to a pregnant teenage girl who hadn’t yet told her family about her situation. Target sent her baby-related coupons, prompting her father to pay the local Target manager an angry visit: “She’s still in high school,” he said. “Are you trying to encourage her to get pregnant?!” When the truth came out, it was the abashed father’s turn to apologize.
But Target soon realized that people resented being spied upon. For its baby coupons to work, it figured out a clever way to bury them amid random and unrelated offers for things like lawnmowers and wine glasses; the offers had to seem like the familiar, untargeted ones.
Indeed, when trying to sell anything new, companies will do their best to make it seem familiar. For example, radio DJs can guarantee a new song becomes popular by playing it sandwiched between two existing hit songs. New habits or products are far more likely to be accepted if they don’t seem new.
Target got a lot of flack for its invasive approach to marketing, but that doesn’t mean it wasn’t a smashing success. Due in large part to its work with targeting pregnant women, the company’s revenues grew from $44 billion in 2002 to $65 billion in 2009.
Movements are born from strong ties, peer pressure and new habits.
In 1955, a black woman named Rosa Parks refused to give up her bus seat for a white man in Montgomery, Alabama. She was arrested and charged, and the events that followed made her a civil-rights icon.
Interestingly, her case, though it’s become the most famous, was neither unique nor the first. Many others had already been arrested for the same reason. So why did Parks’s arrest spark a bus boycott that lasted over a year?
First of all, Rosa Parks was especially well-liked in the community and had an unusually broad array of friends. She belonged to many clubs and societies and was closely connected to all kinds of people, from professors to field hands. For instance, she served as the secretary of the local NAACP chapter, was deeply involved in a youth organization at a Lutheran church close to where she lived and spent her spare time providing poor families with dressmaking services, all while still finding time to make gown alterations for young debutantes from wealthy white families. In fact, she was so active in her community that her husband would sometimes say she ate at potlucks more often than at home.
Parks had what is known in sociology studies as strong ties – that is, first-hand relationships with plenty of people from across different social segments of her community. These ties not only bailed her out of jail; they spread word of her arrest throughout Montgomery’s social strata, thus sparking the bus boycott.
But her friends alone could not have sustained a lengthy boycott. Enter peer pressure. In addition to strong ties, social spheres also comprise weak ties, meaning acquaintances rather than friends. It is mostly via weak ties that peer pressure is exerted. When a person’s larger network of friends and acquaintances support a movement, it is harder to opt out.
Eventually, commitment to the boycott began waning in the black community, as city officials began introducing new carpooling rules to make life without buses increasingly difficult. This is when the final component was added: a speech by Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. advocating nonviolence and asking participants to embrace and forgive their oppressors. Based on this message, people began to form new habits, such as independently organizing church meetings and peaceful protests. They made the movement a self-propelling force.
We bear the responsibility for changing our habits.
One night in 2008, Brian Thomas strangled his wife to death. Distraught, he promptly turned himself in and was prosecuted for murder. His defense? He was experiencing something scientists refer to as sleep terrors.
Research has shown that, unlike sleepwalking, during which people might get up from bed and start acting out impulses, when a person experiences sleep terrors, the brain effectively shuts down, leaving only the most primitive neurological regions active.
Since he was in this state, Thomas thought he was strangling a burglar who was attacking his wife. In court, the defense argued that the instant Thomas thought someone was hurting his wife, it triggered an automatic response – an attempt to protect her. In other words, he followed a habit.
Around the same time, Angie Bachman was sued by the casino company Harrah’s for half a million dollars in outstanding gambling debts. This was after she had already gambled away her home and her million-dollar inheritance.
In court, Bachman argued that she, too, was merely following a habit. Gambling felt good, so when Harrah’s sent her tempting offers for free trips to the casino, she couldn’t resist. (Note that Harrah’s knew she was a compulsive gambler who had already declared bankruptcy.)
In the end, Thomas was acquitted and many, including the trial judge, expressed great sympathy for him. Bachman, on the other hand, lost her case and was the object of considerable public scorn.
Both Thomas and Bachman could quite plausibly claim: “It wasn’t me. It was my habits!” So why was only one of them acquitted?
Quite simply, once we become aware of a harmful habit, it becomes our responsibility to address and change it. Thomas didn’t know he would hurt anyone in his sleep. Bachman, however, knew she had a gambling habit, and could have avoided Harrah’s offers by participating in an exclusion program that would’ve prohibited gambling companies from marketing to her.
Final summary
The key message in these blinks: Following habits is not only a key part of our lives but also a key part of organizations and companies. All habits comprise a cue-routine-reward loop, and the easiest way to change this is to substitute something else for the routine while keeping the cue and reward the same. Achieving lasting change in life is difficult, but it can be done by focusing on important keystone habits such as willpower.
BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY BY RENÉE MAUBORGNE AND W. CHAN KIM (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
What’s in it for me? Conquer uncontested market space.
Every business asks themselves the same question: how can we beat out the competition? And almost every business comes up with the same answer: we need to become bigger, better, and faster to outperform our rivals.
But what if your business didn’t have to beat the competition because there wasn’t any? What if you could enjoy unlimited growth without worrying about limited demand? This isn’t some idle fantasy but a strategic approach that a handful of successful businesses have already made reality. How did they do it? And how can your business do the same? This short Blink will give you a taste.
Escape your competition by setting sail to a blue ocean.
When you establish a new business, competition can be brutal. Whether you’re selling wine, audio books, or life insurance, the market for a product can only get so big. So you’re left to fight with hundreds of other companies for your share of a limited demand. No surprise that America’s most popular business TV show is called Shark Tank! Markets today are like oceans, swarming with hungry companies ready to kill each other. There’s so much blood in the water, we can call these markets red oceans.
But every once in a while, a company emerges that seems to sail past all the competition. These are businesses that rise fast, grow uncontested, and seem to play by their own rules. What are they doing differently?
Well, instead of fighting over scraps in red oceans, these businesses navigate uncharted territory: blue oceans. You can think of blue oceans as all the markets we haven’t yet discovered, for products and services that don’t yet exist. Demand isn’t limited because demand isn’t there – it has to be created. But this isn’t a handicap, it’s an opportunity. Because if the size of your market isn’t limited, neither are your growth and profits.
In blue oceans, the water isn’t bloodied by cut-throat competition. It’s deep, clear, and full of undiscovered potential. The blue ocean strategy gives you the methodology and tools to conquer such uncontested markets. The basic tenet is this: It’s true that the space in a certain industry might be limited. But who’s to say that a business can’t create an entirely new industry?
Let’s look at an example of this in action: famous Canadian circus company Cirque du Soleil. With its extraordinary variety shows, Cirque du Soleil has entertained millions of people worldwide. On top of that, it’s made record profits. Not something you would expect from a circus company! How did the company do it?
Well, Cirque du Soleil did two interesting things. First, it got rid of the old circus staple of animal acts. Then, it supplemented its human acts with live music and compelling storylines. The first move reduced costs while the second introduced exciting new elements into the world of circus. In effect, Cirque du Soleil created a blue ocean: it carved out an entirely new market for artistic theater experiences. And people love it.
Lower your costs and differentiate yourself.
Perhaps you find the example of a circus company a bit too eclectic? No problem. There are thousands of other businesses that have successfully implemented a blue ocean strategy. Companies like Ford, Nintendo, Netflix, Nespresso, Yellow Tail, Southwest Airlines, and even The Body Shop. In this section, we’ll take a closer look at how they succeeded.
But first, a few more words about red oceans. In red oceans – industries that are already established – everyone plays by agreed rules. Not so long ago, these rules might have looked something like this: “Movies can be bought or rented.” “Wine needs to have an air of sophistication.” “Air travel is expensive.” But in blue oceans, none of these rules apply. Blue oceans are actively shaped by the actions of the industry players who create them.
Let’s be clear – you don’t need to reinvent the wheel to establish a blue ocean. Often, a few little tweaks are enough to set a product apart from its competitors and create a new market. It’s really quite simple: Take a close look at your industry as it is right now. Then think about which factors you can Raise, Eliminate, Reduce, and Create. Let’s go through these points step-by-step with examples.
Raise. Think about how you can elevate the product quality, price point, or service standards of your industry. Southwest Airlines did this when it became the first US airline to make domestic flights quick, easy, and affordable for everyone.
Eliminate. Consider which aspects of your product or service can be cut completely. Remember how Cirque du Soleil got rid of costly and unethical animal acts? Every industry has some outdated practice they’d be better off abandoning.
Reduce. Look at which production processes, product features or service offers you can reduce. Australian wine brand Yellow Tail, for instance, decided to reduce its focus on prestigious vineyards and the aging process in favor of affordable wines with broad appeal.
Create. Brainstorm what new features you can offer your customers. Netflix is a premium example of this that barely needs an explanation: it was the first company to offer on-demand streaming for movies and TV shows.
Ideally, considering these questions will help you do two things: lower your costs and differentiate your business from the competition. And that’s really all you need to create a blue ocean. Even more so, if your company keeps addressing these four factors – that’s raise, eliminate, reduce, and create –, it will stay one step ahead of the competition at all times.
Final summary
In this short Blink, you’ve learned about the difference between red and blue oceans. Rather than competing for limited market space, successful businesses often capture new markets with unlimited potential. They’re discovered by raising, eliminating, reducing, and creating industry factors in a way that lowers costs and sets your business apart from the competition.
ORIGINALS BY ADAM GRANT (COURTESY OF BLINKIST) [THE HOW]
What’s in it for me? Embrace the original in you!
We have all heard of that elusive quality known as “originality.” But while it remains something highly coveted, referring to someone as an “original” can also bring up connotations of eccentricity or weirdness.
So, can there be originality without originals?
These blinks look at the ways in which you can be non-conformist and original without getting shunned, as well as some of the originals who have challenged the status quo and pushed innovation throughout history.
In these blinks, you’ll find out
how your choice of web browser can indicate whether you’re original or not; why advocating against your innovative idea is a great way to get people on board; and how procrastination paved the way for one of the most famous speeches in history.
Originality is your key to a fulfilling career.
Look in any dictionary and it’ll tell you that originality is the quality of having a unique or singular character. But what’s an original? In today’s context, originals are people who not only dream up novel ideas and shake up the status quo, but who also take the initiative to make their unique vision a reality.
Even the smallest things can identify an original. Economist Michael Housman discovered in his research that a certain percentage of customer service employees stayed in their jobs far longer than others. Seeking clues, he discovered a surprising link between how long someone kept their job and their choice of internet browser. Sounds crazy, right?
Get this: employees who installed browsers other than the default Internet Explorer were not only more likely to keep their jobs, they were also more likely to take initiative, confront challenges and find new solutions. In the end, the tendency to install Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox was tied to problem-solving abilities that, in turn, allowed these employees to stay in their jobs an average of 15 percent longer.
As for the other employees who simply used built-in browsers, they approached their roles in the same conventional way as they used the internet. They accepted the standards given to them and were unable to solve problems, which eventually made them sick of their jobs.
If you want to survive in the working world, your best bet is to become an original. The good news is, anyone can do it. Though we might not all be able to found our own companies, compose a musical masterpiece or alter the course of history with a stirring speech, we all have unique ideas with the potential to improve our work, our communities and our relationships.
Putting new ideas out there requires courage and the determination not to back down when you want change to happen. The first step toward becoming an original is overcoming your fear of taking action and standing up for your own ideas. But how? Find out in the next blinks.
Quantity leads to quality when it comes to generating great ideas.
Legend has it that physicist Isaac Newton was relaxing under a tree when an apple fell on his head. In a flash of brilliance, Newton was inspired to develop his law of universal gravitation. Unfortunately, great ideas like this usually don’t fall from trees; new ideas require hard work.
When it comes to idea generation, what’s more important – quantity or quality? As it happens, they’re equally important, specifically because quantity paves the way for quality in brainstorming. Psychologist Dean Simonton, renowned for his study of creative productivity, demonstrated in his research that highly creative individuals don’t necessarily produce better ideas; rather, they just make more of them.
By creating a larger volume of work, they had a higher probability of developing a small handful of brilliant ideas. For instance, Picasso’s entire body of work includes countless rugs and prints, 2,800 ceramics, 1,800 paintings, 1,200 sculptures and more than 12,000 drawings. And yet, only a small number of these pieces gave Picasso his success and status as an international art icon.
In other words, when it comes to quantity and quality, you can’t have one without the other!
Another of Simonton’s findings demonstrated that even geniuses can’t tell which of their works will become timeless classics and which ones will flop. So, again, the more you produce, the better. Simonton found that Beethoven judged his work quite differently than later experts did. Comparing letters where Beethoven rated 70 of his own compositions with the evaluations of contemporary critics, Simonton calculated that Beethoven had disagreed with them about 33 percent of the time!
Generating ideas, and lots of them, is the first step to unlocking your creative potential. But you shouldn’t see your brain as a creativity factory, pumping out original ideas the way cars are manufactured on an assembly line.
To create great ideas, we need to take it slow. That could mean taking a detour and procrastinating, or just making the time here and there to relax under a tree!
Procrastination can work creative wonders when you use it strategically.
Procrastinating, we’re told, is your productivity’s arch-nemesis; but is this really the case?
Leaving stuff to the last minute makes us more creative by forcing us to improvise. Would you have guessed that Martin Luther King Jr.’s most famous line was the result of procrastination? King was set to give a speech at the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, but didn’t even start writing the speech until the night before.
King’s iconic “I have a dream” line was partially improvised – gospel singer Mahalia Jackson cried out during King’s speech, imploring him, “Tell them about the dream, Martin! Tell them about the dream!” King abandoned his script and began to speak freely about his inspiring vision of the American future.
King’s speech is a fantastic example of the Zeigarnik effect. The phenomenon, named after Russian psychologist Bluma Zeigarnik, describes the way that our mind stays open to new ideas and insights, even after we attempt to finish a task and give up. Essentially, King’s unfinished speech left room for his brain to come up with brilliant lines.
For great originals, procrastination is a key strategy. It allows them to make gradual progress while remaining open to a range of possibilities. Leonardo da Vinci is another example of history’s prolific procrastinators. He began painting the Mona Lisa in 1503, then abandoned the project before returning to the painting some years later. The Mona Lisa was finally completed in 1519, 16 years later!
Historian William Pannapacker believes that this allowed da Vinci to procrastinate in a calculated way, experimenting with optical illusions and new painting techniques. Without this experimentation, and the procrastination that created the space for it, we may never have had the Mona Lisa or other brilliant works by original thinkers.
Admitting your weaknesses during a pitch will garner you more support.
Have you ever gotten a less-than-encouraging response to what you thought was your best idea yet? Rest assured, it’s not always because your idea is useless! There are a few common factors behind rejections.
For one thing, voicing an opinion that threatens to upset the status quo can be a threat to your business career and your network. A massive study conducted across nonprofit, service, retail and manufacturing companies revealed that the more frequently employees voiced their ideas and concerns to their superiors, the less likely they were to receive raises and promotions over a two-year period.
This is quite a troubling trend! So, what can you do to get people on board with your ideas? Strangely enough, your best option is to tell people why they should not accept your proposals. Start by being open about the shortcomings of your projects; this will surprise your audience and show them that you’re an honest person regardless of the situation.
This is what entrepreneur couple Rufus Griscom and Alisa Volkman did when presenting their online parenting magazine and blog network “Babble” to potential backers. To their audience’s great surprise, Griscom was up-front and told them that their website’s user engagement was lower than they’d expected, 40 percent of the news on the site was taken up by seemingly irrelevant celebrity gossip and their back end was in major need of an update.
Though it sounds like they were shooting themselves in the foot, investors were charmed by their approach. They trusted them, and Babble brought in $3.3 million in funding before being acquired by Disney in 2011.
Make radical ideas familiar by getting them out there often and finding common points of reference.
Do you think you look better in the mirror or in a candid photo? Most of us would prefer the reflection we see in the bathroom. Photos of ourselves can be cringeworthy and off-putting. Why is this? Well, because we’re seeing ourselves from an unfamiliar angle. It’s a classic human tendency to reject things that aren’t familiar to us – even our own images!
As you might have guessed, this presents another hurdle to dreaming up original ideas. But there are strategies you can implement to make even the most conventional coworker feel comfortable with your unorthodox solutions.
One of these is the mere exposure effect, where repeating yourself will give others time to warm up to your ideas. Research shows that exposing people to new ideas more often will make them more receptive over time. So, speak up and repeat yourself!
To make this easier, keep your ideas short and snappy, blend them with other ideas to show their different applications and be prepared to keep pushing your solutions for as long as necessary. Keep at it, and you’ll be surprised by how your peers’ responses improve!
Another useful strategy for making new ideas seem less controversial is to frame them in a familiar context. When the idea for the animated classic The Lion King was first pitched to Disney, producers were initially turned off by its dark storyline.
But in a meeting between scriptwriters and Disney executives, CEO Michael Eisner and producer Maureen Donley turned things around by highlighting the film’s similarities to Shakespeare’s King Lear and Hamlet. This was enough to persuade the producers, who were much more enthusiastic once the unconventional storyline was tied to a common point of reference.
The Lion King went on to become 1994’s highest-grossing film and the recipient of two Academy Awards. This example illustrates how great ideas can become a reality when their novelty is offset with familiar elements to win support.
The best collaborators are the ones that love to prove you wrong.
Regardless of what you’re pursuing, if you only listen to people who praise you, you probably won’t get very far. It might not be pleasant, but sometimes you need a bit of criticism to help you grow.
This was illustrated in a pivotal experiment by psychologist Charlan Nemeth. Groups of participants were asked to hire one of three possible job candidates. The first candidate, John, was presented as having the best skillset for the job.
Even so, some of the participants showed a preference for the less qualified candidate, Ringo. But when some participants argued in favor of the third candidate, George, the chance that the participants would end up hiring the best-qualified candidate quadrupled. How can we make sense of this?
By throwing a minority opinion into the mix that differs from the two leading views, the consensus is disrupted. Group members are then pushed to assess the situation for themselves and not simply follow what others are thinking. This is a great strategy to break up groupthink and encourage everyone to share their real opinions.
Groupthink occurs when people organized in groups prioritize avoiding conflict and reaching consensus over making the best choice possible. This concept, developed by Yale research psychologist Lester Irving Janis, is the underlying problem in poor team decision making. Another way to prevent groupthink hindering your own creativity is to surround yourself with people who constantly question your ideas.
This was the strategy used by Ben Kohlmann, a founding member of the Chief of Naval Operations’ Rapid Innovation Cell (CRIC), when his team began to work on innovative ideas for the navy. They succeeded in creating a whole range of creative solutions and were even the first to bring a 3D printer on a ship to print spare parts in case something broke while at sea.
This creativity wouldn’t have been possible without the powerful group dynamic that emerged as a result of Kohlmann’s calculated decision making. He chose junior officers with a track record of facing discipline as a result of challenging authority. Though these officers all had their own backgrounds and objectives, uniting their disruptive mindset with a common goal created the perfect environment for creativity.
Learn to disguise your ideas to get the supporters you need.
Though you might have a network of people who share the same goals and values as you, it’s no guarantee that they’ll support your ideas. If you want dependable allies, you need to win over your peers by hitting the right tone in your messaging. The trick is not to go over the top, but also to keep people interested.
Though we tend to think that common goals are what brings a team together, research has shown that the opposite is true. Dartmouth College psychologists Judith White and Ellen Langer illustrate this finding through the theory of horizontal hostility; this is a form of prejudice that surfaces in relationships between members of the same minority group.
For instance, the most dedicated members of radical political groups tend to attack each other more than they confront impostors and sell-outs within their movement, even though they share the same set of core values.
You can avoid horizontal hostility in your team by making your ideas seem a little less radical. To do this, you’ll need a disguise – or even a Trojan horse! The goal is, after all, not to convince people to change their attitudes entirely, but to connect with the values you know they already believe in.
Meredith Perry, the inventor of wireless power solutions for charging electronic equipment, received little support when she first presented her ideas to her physics professors and engineers. They all unanimously agreed that it was simply not possible at the time to charge electronic devices through waves passing through the air. So what did Perry do? She changed her tactics and used a Trojan horse.
By disguising her idea and telling people that she simply wanted to design a transducer, and not one that sent power wirelessly, she received a lot more support: her idea was interesting, but not too far-fetched. Collaborators and funders were much more willing to team up with her, and Perry was able to create her product and company, uBeam, which today provides innovative wireless charging solutions.
As we can see, it’s not enough simply to have creative ideas – you have to know how to find the right supporters and collaborators to make them a reality.
Final summary
The key message in this book: Unleash your creative potential by developing lots of ideas and sharing your best ones with others. To further boost your creativity, surround yourself with disruptive thinkers and make them feel comfortable about sharing their opinions. Learn to make your original idea seem familiar, accessible and appealing to get the support you need, and you’ll be ready to turn your unique plans into real-world solutions.
RANGE BY DAVID EPSTEIN (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
What’s in it for me? Learn why taking a wide-ranging approach to life will pay off.
In our complex and cutthroat world, there’s a lot of pressure to get a head start and specialize early. Many successful people, such as Tiger Woods, start to focus on one path early in life. But delve a little deeper, and it becomes clear that it’s generalists, not specialists, who are primed to excel.
Generalists may take a little longer to find their path in life, but they are more creative, can make connections between diverse fields that specialists cannot. This makes them more innovative and, ultimately, more impactful.
Drawing on examples from medicine to academia to sport, these blinks explore how breadth and range are far more powerful than specialized expertise. They also show that experts often judge their own fields more narrowly than open-minded, intellectually curious amateurs do.
In these blinks, you’ll learn; what comic books have to tell us about the ingredients of success, how the complexity of modern life has changed the way we think, and why you should be a Roger; not a Tiger.
Starting early and specializing is fashionable, but has dubious merit.
At the age of ten months old, Tiger Woods picked up his first miniature golf club. At two, he showed off his golf drive on national television. Later that same year, he entered and won his first tournament in the under ten category. Tiger Woods embodies a now popular idea that the key to success in life is to specialize, get a head start and practice intensively.
This trend toward specialization doesn’t only show up in the sports world. In fact, it’s also true of academia, our complex financial system and medicine. Oncologists, for example, now rarely focus on cancer alone. Rather, they specialize in cancer of a particular organ. The writer and surgeon Atul Gawande notes that when doctors joke about right-ear surgeons, we shouldn’t be so quick to assume they don’t actually exist.
But is specializing really the way to go? Simply put, no. In many walks of life, building up experience in just one field doesn’t help performance. In a 2009 paper, psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Gary Klein explored the connection between experience and performance.
Klein shows that experience counts in certain fields. For firefighters, for example, years of focused experience trains them to recognize patterns in the behavior of flames, which enables them to make 80 percent of their on-the-job decisions instinctively in seconds.
But Kahneman found that in other areas, experience counted for nothing. Studying the assessment of officer candidates in the Israeli Defence Forces, he found that recruiters’ predictions of a recruit’s future performance, based on physical and mental abilities, were no more reliable than guesswork. Crucially, as the recruiters received more and more feedback after multiple recruitment rounds, they didn’t get any better at making predictions. Kahneman concluded that there was a complete disconnect between experience and performance.
Some fields of life resemble golf or firefighting. While not necessarily easy, they offer recurring patterns or simple rules that govern decision-making. But there are many more fields of life, like army recruitment, that are much more nebulous and require the creativity and flexibility that generalization offers.
Experimentation is as reliable a route to expertise as early specialization.
In 2006, a now 31-year-old Tiger Woods watched Roger Federer win the US Open final for the third year in a row. Both were at the peak of their powers. As they sipped champagne together in the locker room afterward, Federer felt he had never connected with someone who understood his feeling of invincibility so well. They became firm friends. But, as Roger later told a biographer, his story was very different from Tiger’s.
Roger’s mom was a tennis coach, but if she ever felt tempted to coach him, she resisted it. As a young boy, he dabbled in squash, skiing, wrestling, skateboarding, basketball, tennis and badminton. Later, he gave credit to this range of sports experience for helping his hand-eye coordination and athleticism.
Over time, he found that he liked sports with balls. He moved toward tennis as a teenager, but not intensively. In fact, when his instructors recognized his talent and tried to move him to a group of older players, he asked to stay in the group with his friends. Roger Federer’s winding path to tennis success points to the fact that sampling, rather than specialization, can often be the best route to eventual success.
And plenty of evidence across multiple disciplines supports this. This is true even in an area like music, where plenty of outstanding musicians do specialize young. World-renowned cellist Yo-Yo Ma, for instance, started playing music at a very young age. But what many people don’t know is that Ma first tried violin and piano, and only moved to the cello because he didn’t like the first two.
Yo-Yo Ma isn’t alone in this. In a study of students at a British boarding school, music psychologist John Sloboda found that every one of the students who attended structured music lessons early in their development was categorized by the school as “average,” while not one was “exceptional.” In contrast, those children identified as exceptional were those who had tried out three instruments.
So, if you haven’t yet found your calling, experiment. You could take Vincent van Gogh as inspiration. He tried everything from working in bookstores to teaching and art dealing to preaching before finding his calling as an artist who changed painting forever.
Let’s find out how this works.
Living in a complex world has increased the average person’s IQ and ability to think abstractly.
In 1981, James Flynn, a professor of political studies from the beautiful hilly town of Dunedin in New Zealand, changed the way we think about thinking.
Flynn stumbled upon reports of IQ test scores of American troops that showed dramatic improvement between the two World Wars. The same score that placed a World War I soldier in the 50th percentile would only land him in the 22nd percentile of World War II troops. Intrigued, Flynn asked researchers in other countries for data. He received IQ test results from the Netherlands that showed similarly huge leaps from generation to generation. He then compiled data from 14 other nations.
In what’s now known as the Flynn effect, this research reveals an average three-point increase in IQ every decade in over 30 countries. But what causes this rapid rise? The work of a Russian psychologist, Alexander Luria, gives us an idea.
In 1931, the Soviet Union was changing rapidly. Remote, essentially premodern villages operating in ways unchanged for centuries were converted to collective farms with industrialized development, planned production and division of labor.
Luria capitalized on this rate of change to conduct unique studies. In one experiment, he asked villagers to sort wools into groups. In more modern villages, people would happily group similar pieces of wool, like those in different shades of blue. But in the remote, still premodern villages, participants simply refused to do so. According to them, each piece of wool was different – it was an impossible task!
Other questions involving conceptual thinking got a similar response. One villager, named Rakmat, was shown a picture of three adults and one child and asked which person did not belong. But Rakmat didn’t think about the question abstractly, as we would, and identify the child as different. Instead, he insisted that the boy must stay with the adults and help them with their work.
Luria’s findings were clear. The more exposure to modernization, the greater the ability to make conceptual connections between objects or abstract notions. Today, our minds are constantly dealing with abstract concepts. We glance at a download progress bar on our computer, for example, and instantly understand its meaning. Our minds are better at understanding a breadth of topics and making connections between ideas than ever before.
And yet, we continue to narrow our conceptual focus.
If you want it to stick, learning should be slow and hard, not quick and easy.
The teachers you liked the most in your educational career might be the ones who taught you the least. A study of teaching at the US Air Force Academy tracked the progress of thousands of students working with hundreds of different professors, starting with Calculus I classes. It found that the professors whose students’ got better grades on the exam were also highly rated in student evaluations. The professors whose students did not receive good grades received harsher student feedback.
But when the economists conducting the study looked at long-term results, there was a twist. The professors who received positive feedback had a net negative effect on their students in the long run. In contrast, those professors who received worse feedback actually inspired better student performance later on.
Rather than teaching to the test, these professors appeared to be facilitating a deeper understanding of underlying math concepts. It made their classes frustrating and difficult, hence the poor grades and student evaluations. But it paid off in the long run. Those professors were using desirable difficulties – harder, but ultimately more rewarding, ways to learn.
There are certain techniques we can all use that embrace desirable difficulties. One such technique is spacing, which means leaving time between learning something and practicing it. Consider a 1987 study in the Journal of Experimental Psychology. This study separated Spanish students into two groups, testing one group on vocabulary that they had learned the same day, and the other group weeks later. Eight years later, and with no further study in the interim, the two groups were tested again. The results showed that the latter group could remember over 200 percent more words.
Even short-term spacing is effective. In a 1972 study, researchers at Iowa State University read people a series of words. The first group of participants was asked to recite the words straight away. Another group was asked to recite them after being distracted for fifteen seconds by some simple math problems.
The first group did considerably better than the group that was distracted. But later the same day, the participants were asked to write down each word they could recall. This time, the group that previously performed worse did the best. The process of working hard to recall the information in the first instance had helped them move it from short-term to long-term memory.
So, don’t get too excited by quick progress when you learn. Embrace hard, slow learning. It will pay off in the long run.
A narrow focus is unhelpful, and a remedy for this is to think outside the box.
In some environments, dealing with specialists is desirable. If you need an operation, you probably want a doctor who specializes in the procedure and has done it many times before. However, as we benefit from more reflection and thinking, this narrow focus can be unhelpful.
For example, cardiologists use stents – metal tubes that hold blood vessels open – to treat chest pain so often that they often do so reflexively, even in situations that may be dangerous or inappropriate. This explains a 2015 study by Dr. Anupam Jena of Harvard Medical School. The study found that patients with cardiac arrest or heart failure were actually less likely to die if they were admitted to hospital while top cardiologists were away.
Other fields also point to the benefits of looking at problems with an outside view, rather than the inside view dictated by your own particular specialty.
In a study by University of Sydney professor Dan Lovallo, private equity investors were asked to provide a detailed assessment of businesses they were considering investing in, including their estimated return on investment. The investors were then asked to write notes about some other projects with broad similarities, like another tech start-up or an infrastructure project.
It turned out that the investors’ estimates of returns for the businesses they were actually planning to invest in were around 50 percent higher than for those alternative projects they had identified but not looked at in detail. The investors were shocked to discover the differences, and quickly slashed their estimated profit for their original potential investments.
As further psychological research has repeatedly shown, the more details we consider about something, the more extreme our judgments become. In one example, students rated a university higher when told that only certain science departments, rather than all science departments, were ranked in the national top ten.
Clearly, failing to see things from a broad perspective can lead to some bad calls.
A breadth of experience and interest drives innovation.
Comic books can tell us a surprising amount about range and success. When Dartmouth business professor Alva Taylor and Henrik Greve from the Norwegian School of Management decided to examine the impact of individual breadth on creative impact, they chose to study comics.
Tracking the careers of comic creators and the commercial success of thousands of comic books from 1971 onward, they made some predictions about what would boost the average value of a comic. They predicted that the more comics a creator made, the better the comics would be. Further, they thought that the more resources a publisher had, the higher quality and more successful its product would be.
All these assumptions were wrong. Neither experience nor financial resources bred success. What did drive success was the breadth of a comic creator’s experience across comic genres. Of 22 genres, the more a creator had worked in, from comedy to crime, fantasy to non-fiction, the more successful they were. But this link between breadth and success isn’t just the case in creative or artistic worlds.
Andy Ouderkirk, an inventor at the multinational company 3M, was named Innovator of the Year in 2013 and has been named on 170 patents, a proxy for creative success. He became fascinated with what generates successful and inventive teams, so he started to do some research. He found that the inventors who were most likely to succeed within 3M and win the company’s Carlton Award, which recognized innovation, were not specialists. They were polymaths, people with one area of depth, but a great deal of expertise in other areas as well.
These polymaths tended to have many patents in their area of focus, but also repeatedly took expertise gathered in one area and applied it to another. A study of prestigious scientists led by Robert Root Bernstein, a Professor of Psychology at Michigan State University, confirm Ouderkirk’s findings. Comparing Nobel prize-winning scientists to other scientists, the figures show that Nobel laureates are a full 22 times more likely to be an amateur actor, magician, dancer or performer.
So, for any hiring managers out there looking for fresh talent, here’s a plea. Don’t just look for people who fit into your clearly-defined slots. Make some space for those who don’t fit so clearly into any one category. Their breadth of experience might be invaluable.
The experts and pundits that our society listens to are usually hopeless at making predictions.
During 20 years of the Cold War, world-renowned forecasting expert Philip Tetlock collected and assessed the predictions of 284 experts. He concluded that experts are absolutely terrible at making predictions about anything.
Tetlock found that an expert’s years of experience, academic degree and even ability to access classified information made no difference. When experts said that some potential event was impossible, it happened in 15 percent of cases. Events declared to be an absolute sure thing failed to occur 25 percent of the time.
And worryingly for anyone who listens to cable news, Tetlock found that there was a perverse and inverse relationship between fame and accuracy. The more an expert appeared in the news, the more likely they were to be wrong, or as Tetlock famously put it, “roughly as accurate as a dart-throwing chimpanzee.”
One of the problems was that many of the experts’ focus was too narrow. Having spent entire careers studying a single issue – say, US-Soviet relations – they tended to have explicit theories about how it worked. So, what makes a better forecaster of future events? Well, researchers like psychologist Jonathan Baron point to active open-mindedness – a willingness to question your own beliefs. Most of us fail at this, and can’t override our strong instinct to cherry-pick evidence that confirms our existing beliefs.
Consider a study run by Yale professor Dan Kahan. Pro and anti-Brexit voters were first tasked with interpreting a set of statistics about the effectiveness of a skin cream. Most participants completed the task successfully. But when presented with the same numbers framed as the link between crime and immigration, many of the participants misinterpreted the statistics according to their political beliefs. The same study has yielded similar results in the US on the topic of gun control.
So, how exactly can we combat our tendency to stick to our existing beliefs, despite the evidence? Kahan argues that one personality feature is important if we want to stay open-minded and think clearly about the world around us. Instead of scientific knowledge – how much you know – emphasize scientific curiosity – a desire to learn more, willingness to look at new evidence and ability to think with a genuinely open mind.
Now, let’s consider how we can embrace this kind of curiosity.
To be more of a generalist, you need to change your attitude toward learning and success.
See if you can answer this question correctly. Disease X has a prevalence of one in 1,000 people. The test for the disease has a false positive rate of five percent. What is the chance that someone receiving a positive test result has the disease?
If your answer was two percent, or 1.96 to be precise, you got it right. And in doing so, you did better than the 75 percent of physicians and students at Harvard and Boston University who got it wrong. Their most frequent answer was 95 percent.
The problem is straightforward if you know how to think about it. In a sample of 10,000 people, ten will have the disease and get a true positive. Five percent, or 500 people, will get a false positive. So out of the 510 people with a positive result, only 10, or 1.96% are ill. Sadly, many students aren’t taught to think openly about such problems. And this, according to Arturo Casadevall – a star in the world of microbiology and immunology – has to change.
In a new role at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Casadevall is developing programs focused on an interdisciplinary understanding of topics such as philosophy, ethics, statistics and logic. One course, called “How do we Know What is True,” examines different types of evidence in various academic disciplines. “Anatomy of Scientific Error” encourages students to hunt for signs of misconduct or poor methodology in scientific research.
Casadevall hopes that, with a more rigorous grounding in reasoning and multidisciplinary thinking, students will be better prepared to make a real impact on our economy and society.
Of course, not all of us hold senior academic positions like Casadevall. What can we do to expand our range? Well, one thing is to embrace failure. Dean Keith Simonton, a creativity researcher, has shown that the more work creators produce, the more failures they produce, but they are also more likely to produce a superstar success. Thomas Edison, for instance, held over 1,000 patents, many of which were ultimately failures. But his successes, like the light bulb, were revolutionary.
Treading a wide-roaming, disorderly path of experimentation may not always bring instant results. But it may just be the best route to greatness in the end.
Final summary
The key message in these blinks: Embracing range, experimentation and breadth of experience is often a better road to success than specialization. Range demands patience, open-mindedness and scientific curiosity. If we can foster and exemplify these, the chances that we will generate major innovations and contribute significantly to our economy and society increase.
THINKING IN BETS BY ANNIE DUKES (COURTESY OF BLINKIST) CROUPIER COMPTABLE PSYCHOLOGY
Human minds tend to confuse decisions with their outcomes, which makes it hard to see mistakes clearly.
Super Bowl XLIX ended in controversy. With 26 seconds left in the game, everyone expected Seattle Seahawks coach Pete Carroll to tell his quarterback, Russell Wilson, to hand the ball off. Instead, he told Wilson to pass. The ball was intercepted, the Seahawks lost the Super Bowl, and, by the next day, public opinion about Carroll had turned nasty. The headline in the Seattle Times read: “Seahawks Lost Because of the Worst Call in Super Bowl History”!
But it wasn’t really Carroll’s decision that was being judged. Given the circumstances, it was actually a fairly reasonable call. It was the fact that it didn’t work.
Poker players call this tendency to confuse the quality of a decision with the quality of its outcome resulting, and it’s a dangerous tendency.
A bad decision can lead to a good outcome, after all, and good decisions can lead to bad outcomes
In fact, decisions are rarely 100 percent right or wrong. Our decision-making is like poker players’ bets. We bet on future outcomes based on what we believe is most likely to occur.
So why not look at it this way? If our decisions are bets, we can start to let go of the idea that we’re 100 percent “right” or “wrong," and start to say, “I’m not sure.” This opens us up to thinking in terms of probability, which is far more useful.Volunteering at a charity poker tournament, the author once explained to the crowd that player A’s cards would win 76 percent of the time, giving the other player a 24 percent chance to win. When player B won, a spectator yelled out that she’d been wrong. But, she explained, she’d said that player B’s hand would win 24 percent of the time. She wasn’t wrong. It was just that the actual outcome fell within that 24 percent margin.
If we want to seek out truth, we have to work around our hardwired tendency to believe what we hear.
We all want to make good decisions. But saying, “I believe X to be the best option” first requires good-quality beliefs. Good-quality beliefs are ideas about X that are informed and well thought-out. But we can’t expect to form good-quality beliefs with lazy thinking. Instead, we have to be willing to do some work in the form of truth-seeking. That means we have to strive for truth and objectivity, even when something doesn’t align with the beliefs we hold.
Focusing on accuracy and acknowledging uncertainty is a lot more like truth-seeking, which gets us beyond our resistance to new information and gives us something better on which to bet.
We can learn a lot from outcomes, but it’s difficult to know which have something to teach us.
The best way to learn is often by reviewing our mistakes. Likewise, if we want to improve our future outcomes, we’ll have to do some outcome fielding. Outcome fielding is looking at outcomes to see what we can learn from them.
To become more objective about outcomes, we need to change our habits.
Habits work in neurological loops that have three parts: cue, routine and reward. As Pulitzer-prize-winning reporter Charles Duhigg points out in his book The Power of Habit, the key to changing a habit is to work with this structure, leaving the cue and reward alone but changing the routine.
We can improve our decision-making by being part of a group, but it needs to be the right kind of group.
We’ve all got blind spots, which makes truth-seeking hard. But it’s a little easier when we enlist the help of a group. After all, others can often pick out our errors more easily than we can.
But to be effective, a group dedicated to examining decisions isn’t like any other. It has to have a clear focus, a commitment to objectivity and open-mindedness, and a clear charter that all members understand.
In a decision-examining group committed to objective accuracy, this kind of change is self-reinforcing. Increasing objectivity leads to approval within the group, which then motivates us to strive for ever-greater accuracy by harnessing the deep-seated need for group approval that we all share.
To work together productively, a group needs CUDOS.
Shared commitment and clear guidelines help define a good-quality decision-examining group. But once you’ve got that group, how do you work within it?
You can start by giving each other CUDOS.
CUDOS are the brainchild of influential sociologist Merton R. Schkolnick, guidelines that he thought should shape the scientific community. And they happen also to be an ideal template for groups dedicated to truth-seeking. The C in CUDOS stands for communism. If a group is going to examine decisions together, then it’s important that each member shares all relevant information and strives to be as transparent as possible to get the best analysis. It’s only natural that we are tempted to leave out details that make us look bad, but incomplete information is a tool of our bias. U stands for universalism – using the same standards for evaluating all information, no matter where it came from. When she was starting out in poker, the author tended to discount unfamiliar strategies used by players that she’d labeled as “bad.” But she soon suspected that she was missing something and started forcing herself to identify something that every “bad” player did well. This helped her learn valuable new strategies that she might have missed and understand her opponents much more deeply. D is for disinterestedness and it’s about avoiding bias. As American physicist Richard Feynman noted, we view a situation differently if we already know the outcome. Even a hint of what happens in the end tends to bias our analysis. The author’s poker group taught her to be vigilant about this. But, teaching poker seminars for beginners, she would ask students to examine decision-making by describing specific hands that she’d played, omitting the outcome as a matter of habit. It left students on the edge of their seats, reminding them that outcomes were beside the point! “OS” is for organized skepticism, a trait that exemplifies thinking in bets. In a good group, this means collegial, non-confrontational examination of what we really do and don’t know, which keeps everyone focused on improving their reasoning. Centuries ago, the Catholic church put this into practice by hiring individuals to argue against sainthood during the canonization process – that’s where we get the phrase “devil’s advocate.”
If you know that your group is committed to CUDOS, you’ll be more accountable to these standards in the future. And the future, as we’ll see, can make us a lot smarter about our decisions.
To make better decisions, we need to spend some time in the future.
Temporal Discounting – making decisions that favor our immediate desires at the expense of our future self – is something we all do.
We can also recruit our future feelings using journalist Suzy Welch’s “10-10-10.” A 10-10-10 brings the future into the present by making us ask ourselves, at a moment of decision, how we’ll feel about it in ten minutes, ten months and ten years. We imagine being accountable for our decision in the future and motivate ourselves to avoid any potential regret we might feel.
Backcasting, imagining a future in which everything has worked out, and our goals have been achieved, and then asking, “How did we get there?" This leads to imagining the decisions that have led us to success and also recognizing when our desired outcome requires some unlikely things to happen. If that’s the case, we can either adjust our goals or figure out how to make those things more likely.
Premortems are when we imagine that we’ve failed and ask, “What went wrong?" This helps us identify the possibilities that backcasting might have missed. Over more than 20 years of research, NYU psychology professor Gabrielle Oettingen has consistently found that people who imagine the obstacles to their goals, rather than achieving those goals, are more likely to succeed.
Final summary
The key message in these blinks: You might not be a gambler, but that’s no reason not to think in bets. Whether or not there’s money involved, bets make us take a harder look at how much certainty there is in the things we believe, consider alternatives and stay open to changing our minds for the sake of accuracy. So let go of “right” and “wrong” when it’s decision time, accept that things are always somewhat uncertain and make the best bet you can.
Side Note: I think there is a link between Poker and Financial Psychopathy & Cerebral Narcissism because of the Rewiring of the Brian Benefits of Poker through Dopamine Release.
PITCH ANYTHING BY OREN KLASS (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
PITCH ANYTHING is a fast-paced narrative packed with crystal clear examples illustrating the unique S.T.R.O.N.G. Method, which takes advantage of how the brain really works by Setting the Frame; Telling the Story; Revealing the Intrigue; Offering the Prize; Nailing the Hookpoint; and Getting a Decision.
You must tailor your pitch to the audience’s croc brains.
Everyone should learn to pitch ideas well. In every profession, from dentistry to investment banking, there comes a time when you must convince someone of something. Unfortunately, there is a gap between what we are trying to tell our audience and how they perceive it. To understand this gap and overcome it, we must look at the evolution of the human brain.
Basically, the human brain has evolved in three separate stages, resulting in three distinct parts: the primitive reptilian part, the croc brain, developed first. It’s a simple device primarily focused on survival and it can generate strong emotions, like the desire to flee a predator. Next, the midbrain developed. It allows us to understand more complex situations, such as social interactions. Finally, the sophisticated neocortex evolved, facilitating reasoning and analysis to understand complex things.
When you pitch, you use your neocortex to put into words the ideas you are trying to convey. Unfortunately, your audience doesn’t at first process these ideas with their neocortices. Instead, it is the audience’s primitive croc brains that receive the ideas and they ignore everything that is not new and exciting. Worse still, if your message seems abstract and unfathomable to the croc brain, it might perceive the message as a threat. This will make your audience want to flee to escape the situation.
This is why you must tailor your pitch to the croc brain. Since croc brains are simple, your message should be clear, concrete and focused on the big picture. You also need to ensure the croc brain sees your message as something positive and novel, which deserves to be passed on to the higher brain structures.
To secure your target’s attention, you must create desire and tension.
The one critical thing you need throughout your pitch is the attention of your target. To successfully attain this, research has shown that you must evoke two sensations in your pitch: desire and tension. Desire arises when you offer your target a reward, and tension arises when you show them they might lose something, like an opportunity, as a result of this social encounter. On a neurological level, this effectively floods your target’s brain with two neurotransmitters: dopamine and norepinephrine.
Dopamine is a chemical associated with anticipating rewards — desire. One such reward would be the pleasure of understanding something new, such as solving a puzzle. Thus, to increase the level of dopamine in your target’s brain, you must introduce novelty through a pleasant surprise, like an unexpected yet entertaining product demo.
Norepinephrine, on the other hand, is the chemical responsible for alertness and it creates tension in the target. If your pitch convinces them that there is a lot at stake here, their brains will be flooded with norepinephrine.
To create tension, you must create a bit of low level conflict with a push-pull strategy. This means first saying something to push the target away, like, “Maybe we aren’t a good match for each other.” You then counter this by pulling the target back toward you with something like, “But if we are, that would be terrific.”
This push-pull dynamic creates alertness in the target, as they sense that they might lose this opportunity. Depending on the situation, you may use very powerful push-pull statements, especially if you sense your target’s attention beginning to wane.
To control a meeting, you must first establish frame control.
Different people will see any given situation from a different perspective or point of view based on their intelligence, ethics and values. These perspectives are called frames, and they dictate how we perceive social situations such as meetings and sales pitches. Frames also determine who controls those situations.
When two people meet, their individual frames crash into each other. Only one frame can survive such an encounter — the stronger one. For example, let’s assume a cop pulls you over for speeding. He has a strong moral-authority frame and you only have a weak “I’m so sorry officer”-frame. It is clear that when your frames clash, his frame will prevail. This means he will control every aspect of the encounter: from its duration to its content and tone.
You will often face a similar clash of frames in a business environment; for example, a customer may be focused on the price of your product while you are focused on its quality. You will both try to get the other to focus on what you think is important.
If it is your frame that survives this clash, you will have frame control in the situation meaning your ideas and statements will be accepted as facts by the customer. This is a crucial advantage in any pitch. Without frame control, you are unlikely to convince anyone of anything.
You will often encounter the power frame, time frame and analyst frame, hence you must know how to counter them.
In a pitch or sales meeting you will often encounter certain archetypes of frames, and it is important you choose strong with which to counter them.
Typically, your target will use the power frame which exudes arrogance. You must not do anything that validates the other person’s power. Instead, use small acts of defiance and denial to bust the frame; for example, by yanking your presentation material away from the target if they do not seem to be taking it seriously.
Another oft-used frame is the time frame, where your customer asserts control over time: “I only have ten more minutes.” This is meant to push you off balance, but you can always counter with: “That’s fine, I only have five.”
A particularly lethal frame is the analyst frame, denoted by a fixation on details and numbers. If your opponent is in this frame, they will likely insist on drilling down into minor technical and financial details, effectively bogging down your pitch.
In such situations, give a direct but high-level answer to the question asked and get right back to your pitch. Analysis comes later. Before more questions come up, counter the analyst frame with your own intrigue frame. This basically means you tell a compelling personal story and leave it unfinished as a cliffhanger: “… so there we were, in a pitch black, falling airplane with no idea what was going to happen. Anyway, back to the pitch …" This redirects the focus of the room onto you and makes the discussion personal once again.
Use prizing to make the target seek your acceptance.
The most important frame you should be able to use is the prize frame, as it works in a variety of situations against many opposing frames.
Typically when you’re selling something or pitching an idea, your target will tend to see their money as the “prize” of the meeting, something you have to fight for. You must reframe the situation so that you are the prize and they would be lucky to do business with you.
Because people tend to want things they can’t have, prizing yourself will make your target work for your acceptance instead of the other way around. BMW does this with a special-edition M3. The company demands prospective buyers sign a contract assuring they will take proper care of the car, otherwise they cannot buy one.
In a pitching situation, never engage in behavior that makes it seem as if you are chasing the target, for example by agreeing to last minute schedule changes or trying to prematurely close the deal by saying things like, “So, what do you think so far?” Such behavior only reinforces the impression that the target is the prize. Instead, get your target to explicitly qualify themselves to you; for example, you could say, “I am very particular about with whom I work. Why should I do business with you?” This usually catches them off guard and they start trying to impress you.
Stack frames to trigger hot cognitions.
Contrary to popular belief, we are more prone to making choices instinctively than through rational analysis. In fact, we often make a decision about something before we even fully understand it and only later come up with reasons for that decision. These gut calls are called hot cognitions, whereas the decisions arrived at through rational reasoning are known as cold cognitions.
After you’ve introduced your big pitch idea, you want to trigger hot cognitions within your target. These will make him or her want what you have to offer in mere seconds, instead of analyzing your pitch for days to reach a rational, cold decision. You trigger the hot cognitions by stacking frames, meaning you introduce multiple frames in quick succession.
The first frame is the intrigue frame: you tell your target a compelling story, a personal narrative where a dilemma is solved. At the crucial juncture, you stop telling the story, leaving your target on the edge of their seat, ensuring their full attention.
Next, you pile on the prize frame, where you flip the tables on the target: instead of trying to impress them, make them qualify themselves to you. You could say something like, “This deal has so many investors after it, I have to choose who to take on board.”
After this, you stack on the time frame by adding time pressure to the pitch: “Unfortunately, this is a limited-time offer, and the train, so to speak, is leaving the station on Monday.” This will make the target feel like they are losing an opportunity, at which point they will want it even more.
By triggering all these hot cognitions in the target, you will leave them drooling for what you have to offer.
Don’t be needy – make the target chase you.
Neediness, otherwise known as validation-seeking behavior, is a sign of weakness and it can be absolutely fatal to your pitch. If you act needy, the audience will sense you are weak and their primitive croc brains will classify your proposal as a threat – to their money. This can easily push you into a vicious cycle where the audience becomes more and more distant due to your neediness, which in turn makes you anxious and even needier!
To negate neediness, you can use a simple three-step formula based on the movie The Tao of Steve, where the protagonist, Dex, follows a pseudo-Taoist philosophy to pick up women.
First, try to eliminate your desires, at least in the eyes of the target. If they have something you desperately want, this will translate as neediness in you. To negate this, make it clear to the target that you do not need them.
Second, focus on the things you do well, your strengths. Demonstrate something that showcases your excellence. Dex, for instance, was great with children and made sure the target of his affections saw this. Similarly, you must demonstrate excellence in front of your target.
Third, withdraw. At the crucial moment when your target expects you to chase them for their money, withdraw instead by saying something like, “I’m not totally convinced we’re a good match for each other.” This will make them chase you, much like the women in the Tao of Steve chased Dex.
To pitch effectively, you must attain situational alpha status.
Status plays a vital part in any social encounter. In any meeting, a dominant member known as an alpha emerges, while others take subordinate beta-positions. It is very difficult to be persuasive from a beta-position; hence, you must grab alpha status.
Though some elements of status, like your reputation or wealth, are quite stable, situational status can vary immensely; for example, while a successful surgeon has considerably higher social status than a golf teacher, the teacher is still the alpha during a golf lesson.
Often your pitch targets will lay so-called beta traps to force you into the situational beta position; for example, being made to wait in the lobby is a classic beta trap.
You must try to ignore these traps and avoid doing anything that enforces your opponent’s alpha status. Instead, use small acts of defiance and denial to grab the situational alpha status for yourself as soon as you can.
Say a customer has made you wait in the lobby. Once in the meeting room, you could begin examining some papers on the table in front of you. When the customer peeks at them, you could yank them away and say something like, “Nope, not until I’m ready.” If done in a good-natured, half-joking manner, this enforces your alpha position.
Once you have alpha status, you must then steer the discussion into a direction where you are the expert, much like the golf professional talks about golf, not heart surgery, when teaching the surgeon. To solidify your status, force your opponent to say something that reinforces your alpha position with a good-natured jest, like, “Remind me, why on earth should I work with you guys on this?”
Keep your pitch short and simple.
Before you begin any pitch, let your target know you will keep the presentation short. This will put them at ease. When Watson and Crick presented their Nobel Prize-winning idea of the DNA helix, they only needed five minutes. If you know what you are doing, you can pitch anything in twenty.
Start your pitch by introducing yourself. This does not mean rattling off your entire résumé but just outlining your greatest successes, like projects where you really did something impressive.
Most people will be tempted to jump right to the “big idea” for which they’re trying to get financing. But before you get to it, you should address one crucial concern in your target’s mind. Namely, you must explain why now is the right time to invest.
Rather than a long and complex analysis, simply outline the economic, social and technological forces which make your deal unmissable right now. Economic forces that benefit your pitch, for example, could be your target customers becoming wealthier and interest rates going down, the social forces could be the rising consumer concern for the environment, and the technological force could be the development of the electric car. You must present these forces in a way that shows a window of opportunity has recently opened but will not remain open forever.
The three forces set the stage and paint a backstory for your big idea, which should also be kept brief and simple. Use an established “recipe” for this: “For [target customers] who are dissatisfied with [current offerings on the market]. My product is a [new idea] that provides [solution to key problem] unlike [competing product]. My product has [key product features].”
That’s it. The time for details comes later.
Final summary
The key message in this book is: In any social encounter where you aim to be persuasive, it is vital that you seize control of the situation and ensure the target sees your pitch through the frame of mind you have chosen. At the same time, you must cater your pitch so that on a neurological level, the target’s brain works for you, not against you.
TRIBES BY SETH GODIN (COURTESY OF BLINKIST)
All Tribes Share 3 Components
A Group of People
A Common Cause
At least one Leader who Represents and Organizes the Tribe
The most important feature for a tribe is the shared cause.
A tribe’s shared cause leads its members to internalize the tribe’s values and ideas as their own. These internalized incentives make tribe members into driven believers instead of mere followers
Don’t engineer your ideas for the masses: make it exclusive and meaningful for a distinct group of people.
Apple set out to produce a new kind of phone that almost no one would initially like, but that a few people would really love.
With today’s technology, everyone can form and lead a tribe.
The first thing to know is that people need to be able to communicate intensely about their shared cause. This means that communication can’t just be vertical – between you (the leader) and the individual tribe members – more importantly, it must be horizontal, between tribe members.
With today’s technology, you have everything you need to facilitate both vertical and horizontal communication. Websites, blogs and social networks allow you not only to spread your cause, but also provide the room and the tools for your tribe to communicate, share ideas and organize. For example, you can use Basecamp to organize projects, and Twitter to share brief updates about developments. At the same time, these websites allow you to set ground rules for participation, and align everyone with your common vision by setting specific goals.
If you have a meaningful cause and the will to lead, people will follow.
Have you ever wondered how many people make up a movement? The answer is around 1,000: that’s the amount of true believers you need for a group to keep moving.
Creating a movement is about organizing an existing yearning into a way that tribe members can connect with each other, and form a movement under your leadership.
As former U.S. Senator Bill Bradley defines it, a movement contains three elements: A narrative that tells the story of the future you’re trying to build; a connection between the leader and the tribe and among the tribe members; and something to do – the fewer limits, the better.
When forming a tribe, don’t worry about making it grow – concentrate on tightening connections.
At least in the beginning, a tribe’s biggest advantage is not its size, but the multiple connections between the members, the leader and the outside world.
In fact, a tribe has four different directions of communication: Leader to tribe, tribe to leader, tribe members to one another and tribe member to outsider. Normal marketing pales in comparison, with communication generally only in one direction: company to market.
The most important of these directions is the communication between members. And this is where tightening a tribe comes in.
Tightening a tribe means bringing members closer together by facilitating communication and tightening their common bonds. You can do this by transforming a shared interest into one passionate goal, and by providing a platform for members to easily connect with each other.
Or you can harness the power of insiders and outsiders. To create a feeling of cohesion, you have to develop a culture of insiders – which inevitably excludes others. This allows the tribe to differentiate itself from other tribes, and create a stronger sense of internal identification.
Leadership is about stepping into a vacuum and creating motion.
For a tribe to form there has to be a particular change that people want to see made. This need for change has to come from a certain discomfort with the status quo, from a sense that there is something missing in the world. A leader steps right into this discomfort zone – the vacuum – and starts to organize so people will follow him.
Leaders do this despite the risks because of two things: they have faith in the cause and they know that innovation is always more effective the earlier it happens – so the sooner the better.
To make the world a better place, we need more heretics and less sheepwalkers.
What we need in the world are more heretics: people who question the status quo and the existing dogmas, and take action without asking for permission. Organizations need more heretics to advocate change from the inside: because if you hire amazing people and give them freedom, they will do amazing things. And tribes need heretics as leaders to break into new territory and help change the world.
SUISSE CAMBRIOLAGE
Scatter Site Shares Appreciation Rights Social Club
KEY MOTIFS
Mr. & Mrs. Smith, Physical Fitness, Force-Velocity Curve Stimulus-Fatigue-Recovery-Adaptation Performance Training, Circuits, Networking, Chaárms or Athena Venus-Mercury Cusp Births, Triple Decker Projects with Sand Rings, Brand Activation Modelling, Sports Larceny & Contract Racketeering, Sports for Orphans Charities, Short Film Series Acting, Polyglot, Industrial-Organizational Psychologist and Mergers & Acquisitions Bankers Advisory Team
KEY VALUES
Brass Knuckles as Weapons, Decadence, Socratic Methods Game Theory, Poker Country Clubs with Sports Betting Investment Trust, Red Bull Music Festivals, Athletic excellence, Sports Performance Centers, Med Spas, Patchwork Tattoos, Pastel Goth, Pastel Wavy Hair, Video Games, Real Estate Investment Groups, Scatter-site Share Appreciation Rights Social Club, Art House and Management Companies, Business Incubators and Startups Accelerators Collaboration Holding Company, Syncretism of Athena through Occult Magic to Warrior Spirits, Law Education EdTech Sponsor and Provider, Armed Robbery Sports Playbooks, Force-Velocity Curve Physique, Smurfing, Sports Betting, Poker Tournaments, Enterprise Foundations, Rental Properties, and Overview of the Nevada Economy: The top three sectors by total employment are Real Estate and Rental and Leasing, Accommodation and Food Services, Retail Trade, while the unemployment rate across the state in 2022 was 4.8%.
AESTHETIC THEORIES
Subjective
Based on or influenced by personal feelings, tastes, or opinions
Precarious Balance
Precariously: If something is happening or positioned precariously, it's in danger. A glass could be precariously balanced on the edge of a table. If something is on the verge of danger, then the word precariously fits.
Semblance
Semblance is generally used to suggest a contrast between outward appearance and inner reality.
Phantasmagorical
Having a fantastic or deceptive appearance
adjective. having a fantastic or deceptive appearance, as something in a dream or created by the imagination. having the appearance of an optical illusion, especially one produced by a magic lantern.
Law of Polarity in Relationships
In any successful relationship that has an intimate connection and sexual attraction, there is polarity. What does this mean exactly? Polarity in relationships is the spark that occurs between two opposing energies: masculine and feminine. Gender does not affect whether you have masculine or feminine energy.
Second Reflection
Burden Aesthetics with Intentions
The Second Reflection lays hold of the Technical Procedures
CRIMINOLOGY THEORIES
Choice Theory: The belief that individuals choose to commit a crime, looking at the opportunities before them, weighing the benefit versus the punishment, and deciding whether to proceed or not.
Classical Theory: Similar to the choice theory, this theory ascertains that people think before they proceed with criminal actions; that when one commits a crime, it is because the individual decided that it was advantageous to commit the crime.
Critical Theory: Critical theory upholds the belief that a small few, the elite of the society, decide laws and the definition of crime; those who commit crimes disagree with the laws that were created to keep control of them.
Labeling Theory: Those who follow the labeling theory of criminology ascribe to the fact that an individual will become what he is labeled or what others expect him to become; the danger comes from calling a crime a crime and a criminal a criminal.
Life Course Theory: The theory that a person’s “course” in life is determined by short (transitory) and long (trajectory) events in his life, and crime can result when a transitory event causes stress in a person’s life causing him to commit a crime against society.
Positivist Theory: The positivist rejects the idea that each individual makes a conscious, rational choice to commit a crime; rather, some individuals are abnormal in intelligence, social acceptance, or some other way, and that causes them to commit crime.
Rational Choice Theory: Reasons that an individual thinks through each action, deciding on whether it would be worth the risk of committing a crime to reap the benefits of that crime, whether the goal be financial, pleasure, or some other beneficial result.
Routine Activity Theory: Followers of the routine activity theory believe that crime is inevitable, and that if the target is attractive enough, crime will happen; effective measures must be in place to deter crime from happening.
Social Learning Theory: Social learning indicates that individuals learn from those around them; they base their morals and activities on what they see others in their social environment doing.
Strain Theory: The theory holds that individuals will turn to a life of crime when they are strained, or when they are unable to achieve the goals of the society, whether power, finance, or some other desirable goal.
Trait Theory: Those who follow the trait theory believe that individuals have certain traits that will contribute to whether or not they are capable of committing a crime when pushed in a certain direction, or when they are in duress.
Consensual or Victimless Crime: Consensual crime refers to crimes that do not directly harm other individuals or property. Rather, individuals choose to participate in risky behaviors that may be considered against the law. This includes indulging in drug use, prostitution, or obscenity.
VICE SCRIPT MOVEMENT
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
This day in history

THIS SATURDAY (July 20), I'm appearing in CHICAGO at Exile in Bookville.

#20yrsago Walkmen changed our social norms https://web.archive.org/web/20040803222231/http://www.belleville.com/mld/belleville/entertainment/music/9144361.htm
#20yrsago Ultima preservation efforts: a guide https://web.archive.org/web/20040721014058/http://www.nelson.monkey.org/~nelson/weblog/culture/games/ultimaPreservation.html
#15yrsago ATMs that spray attackers with pepper-spray https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/jul/12/south-africa-cash-machine-pepper-spray
#10yrsago TSA employee to security theater skeptics: “You don’t have shit for rights” https://memex.craphound.com/2014/07/18/tsa-employee-to-security-theater-skeptics-you-dont-have-shit-for-rights/
#10yrsago Documentary on the making of the Homeland audiobook with Wil Wheaton https://vimeo.com/100956787
#10yrsago Ontario police’s Big Data assigns secret guilt to people looking for jobs, crossing borders https://www.thestar.com/news/canada/police-chiefs-call-for-presumed-innocence-in-background-checks/article_f479a149-f184-5824-80ee-0427abfe4b71.html
#10yrsago UK government “dries out” its “water damaged” CIA torture files https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/northamerica/usa/10969535/Lost-US-extraordinary-rendition-files-have-dried-out-Foreign-Office-says.html
#5yrsago SAMBA versus SMB: Adversarial interoperability is judo for network effects https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2019/07/samba-versus-smb-adversarial-interoperability-judo-network-effects #5yrsago An Indian research university has assembled 73 million journal articles (without permission) and is offering the archive for unfettered scientific text-mining https://memex.craphound.com/2019/07/18/an-indian-research-university-has-assembled-73-million-journal-articles-without-permission-and-is-offering-the-archive-for-unfettered-scientific-text-mining/
#5yrsago How deceptive browser extensions snaffled up 4m users’ browsing history, including Nest videos, medical history and tax returns https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2019/07/dataspii-inside-the-debacle-that-dished-private-data-from-apple-tesla-blue-origin-and-4m-people/
#5yrsago Thousands of elderly Hong Kongers march in solidarity with young human rights activists https://hongkongfp.com/2019/07/17/no-rioters-tyrannical-regime-thousands-hong-kong-seniors-march-support-young-extradition-law-protesters/
#5yrsago Interactive map of public facial recognition systems in America https://www.banfacialrecognition.com/map/
#5yrsago Sony’s copyright bots remove a band’s own release of its new video https://memex.craphound.com/2019/07/18/sonys-copyright-bots-remove-a-bands-own-release-of-its-new-video/
#1yrago Let the Platforms Burn https://pluralistic.net/2023/07/18/urban-wildlife-interface/#combustible-walled-gardens

Support me this summer on the Clarion Write-A-Thon and help raise money for the Clarion Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers' Workshop!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
in their universe, harley stands alone at tony’s funeral. after ten years of having known each other, harley has to stand there. staring blankly hollowly ahead. shuffling uncomfortable in an ill-fitted suit. around a majority of people he has never met before as he mourns a mentor, a friend, a mechanic.
he has to stand there while people talk about tony stark — this larger than life man who has left behind a larger than life shadow cast on all of their lives, a footprint on all of their hearts — as he only ever thinks about tony the mechanic.
the man who crash - landed in his garage after everyone in the world thought he had died. the man who gave him a way to defend himself against bullies. the man who praised a throwaway idea he had on what the iron man suit could have even if he likely already thought it. the man who let him oversee and aid in the recovery of jarvis despite only being eleven. the man who took out the one thing keeping him alive just to try and save a kid he never met as harley had to scramble to put it back. the man who gave his garage an equipment makeover as a thank you. the man who would stay in his life and check up on him. the man who did more than his own father figure ever could.
in their universe, harley has to go back home and reconcile with the knowledge that the world got everyone back but the people standing in pained agonised silence at the stark lakehouse didn’t.
but in another universe, tony gets to do more.
he gets to be a constant in harley’s life by sending him equipment and checking up on him, but he gets to stay in his life, too.
in another universe, tony gets to see him grow up from this sarcastic child who might be a little too blunt for his age to a young adult who has finally had the opportunity to flourish away from a home that only ever stifled him. harley can credit tony for inspiring him, for making him want to explore his love for technology and mechanical engineering. harley developed a love for cars, and he chose to come back to work with tony. to return to working by his side in what used to be stark motors. to walk the same hallways where tony’s father tried to make the first flying car.
harley was enlisted by tony to join the worldwide engineering brigade. he got to attend stark expo in hong kong with doreen. he and doreen got so inspired by the iron wing and decided to create the web slinger vehicles because of it. he is accredited to making the automation system behind the vehicles and works in designing and debugging. he wanted to put heated seats and a potato gun attachment on the web slinger vehicles.
he made a repulsor blaster in both iron man and rescue colours. he still has dorky potato gun names inspired off of disney puns. he makes a whole assortment of potato - powered and potato - firing weapons including his own stun blaster gauntlet. his locker has a sticker of iron man and stark racing on it with his name spray - painted. it’s been 39 days since the last potato gun incident. he has a spider bot he uses to fight peter during their web battle potluck. his potato guns are all over avengers campus.
he gets to go to a school where he can learn and grow with people who think the way he does, who have a love of science the way he does. he is listed as one of the avengers’ allies, sorted under iron man’s allies.
in another universe, he’s the mechanic’s assistant.
#harley keener#tony stark#iron dad#marvel#iron man meta#anyways i'm not pretending to be okay i'm killing myself !!!#marvel theme park universe you will ALWAYS be famous.#can't believe mtpu had tony adopt harley /real !#i did this instead of working on my term paper. srry about my demons#ch: harley keener#ch: tony stark
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong, 1989 - 1992. Designed by Simon Kwan & Associates Ldt / Percy Thomas Partnership. Pictured above is student housing.
Scan
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
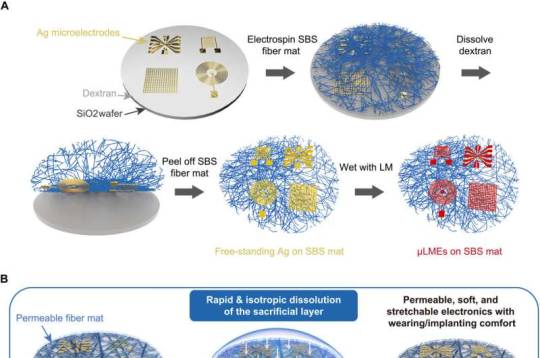
Team develops microelectrodes with soft, stretchable and permeable properties for implantable bioelectronic devices
Electronic devices that can be attached to the skin or even implanted in the body will become more and more prevalent in near-future technology. Such "implantable bioelectronics" are envisaged as having a wide range of uses from medical technology to the emerging field of augmented reality, and a research team led by The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) has developed a type of microelectrode that is uniquely suited to devices of this kind. Their pioneering study entitled "Wafer-patterned, permeable, and stretchable liquid metal microelectrodes for implantable bioelectronics with chronic biocompatibility" was recently published in Science Advances. Compared with conventional electronics, materials used for wearable or implantable bio-electronic technology require specific properties that are difficult to bring together. They must be stretchable, soft and permeable enough to survive in the human body without causing discomfort or harm to the user. Meanwhile, like everyday household devices, bioelectronics still depend on electrodes that are highly electrically conductive and can be patterned into microscale circuitry.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Electronics#Medical technology#Liquid metals#Biocompatible#Flexible electronics#Hong Kong Polytechnic University
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Only by not having children can I live the way I do now,” said Zheng, who has visited more than 50 countries. “I only have to think about myself, which is the part I enjoy most.”
“Considering global political and economic trends, if you don’t have a strong maternal instinct, you shouldn’t have a child just for the sake of it,” she said.
(Text under cut.)
TAIPEI, Taiwan —
Shorthand for gainfully employed U.S. couples whose only responsibilities were to themselves, the acronym DINK — dual income, no kids — was coined to capture the unabashed materialism of the 1980s.
Four decades later, the term has made a comeback, with millennials embracing it on social media to flaunt their free time, lavish spending habits and the other perks of choosing to be child-free.
It has taken off far beyond United States, including in one country where it would have been hard to imagine just a decade ago: China.
China’s population declined for the second year in a row last year; India overtook it as the world’s most populous nation.
Amid deep economic uncertainty, a growing number of Chinese are opting for another number: zero.
Many proudly refer to themselves as DINKs — using the acronym in English — or dingke, the phonetic translation in Mandarin.
Xu Kaikai, 29, said being DINKs gives her and her 36-year-old boyfriend a greater sense of control over their lives.
“It reduces some of the anxieties about age,” she said.
She works in advertising in Shanghai, where her boyfriend is a project manager for a construction company. “I used to talk about having a beautiful baby,” Xu said.
Now she calls herself a “drifting leaf” and gets so bored with people talking about children on social media that she follows only people without them.
A recent study from the Luoyang Institute of Science and Technology estimated that DINKs accounted for about 38% of Chinese households in 2020 — up from 28% a decade earlier — but those figures included large numbers of people living alone and the research did not look at whether couples were in fact dual-income.
Not that all Chinese adhere to a strict definition of the acronym. Some include anybody without children, while others don’t count people who still have a chance to change their minds — women of child-bearing age or men without vasectomies.
It’s also unclear how many DINKs there are in the United States. Some 44% of couples ages 18 to 49 surveyed by Pew Research in 2021 said it was unlikely they would have children — up from 37% in 2018.
After decades of enforcing a one-child policy to keep population growth in check, China’s government is now offering subsidies and financial support to encourage families to have more kids.
“It was just a high-class phenomenon,” said Yuying Tong, a professor of sociology at the Chinese University of Hong Kong who studies family life.
She said the number of DINKs is going up in large part because more people are delaying marriage.
The rejection of societal norms comes at an inopportune time for the Communist Party, which is struggling to stave off a demographic crisis in which there aren’t enough young people to support the elderly.
The country’s population declined for the second year in a row in 2023 — India surpassed it as the world’s most populous nation — and the birthrate fell 5.6% to a record low of 6.39 births per 1,000 people — a little more than half the U.S. rate, which has also declined in recent years.
Now the Chinese government is trying to motivate people to have kids, resorting to subsidies and even matchmaking services.
In March, Chinese officials announced plans to provide more support for child rearing and “work toward a birth-friendly society,” including improving parental leave policies and child-care options.
The government also appears to be trying to scare DINKs into changing their mindset.
Last month, China’s Twitter-like platform Weibo promoted an article about DINK couples in China who regretted not having kids because it had led to loneliness, marital strife or inheritance issues.
As economic growth has stalled, more Chinese couples are giving up on the idea of having kids. According to the Beijing-based Yuwa Population Research Institute, the average cost of raising a child in China was one of the highest in the world.
DINKs took issue with the characterization.
“Are all these examples being brought up to encourage people to have kids?” a popular entertainment blogger who goes by the moniker Jing Zhao Cha Mi responded on social media. “There are probably more people who regret their lifestyle with children.”
Hu Huiwen, a 38-year-old financial consultant who lives in the eastern city of Hangzhou, has heard all the warnings: Her husband will leave her. She will want children later and be too old to have them. Nobody will care for her in her old age.
But in the five years since she swore off having children, none of that has come to pass.
“It might become a minor sorrow, but not to the point of regret,” Hu said. “Even if I do regret it, then I can only bear it myself. What else can you do?”
She belongs to three different group chats for DINKs, where participants advise one another how to spend their leisure time. In video diaries, she shows herself reading or wandering through parks admiring the foliage.
In March, the Chinese government emphasized the need to support child rearing and “work toward a birth-friendly society.”
A recent study by the Beijing-based Yuwa Population Research Institute found that the average cost of raising a child in China was $74,600 — or 6.3 times the per capita GDP.
Of the 14 countries included in the study, the only place where it cost more relative to income was South Korea, which has the lowest birthrate in the world.
“At the end of the day, it’s still about the pressures and this very competitive environment that makes both marriage and childbearing untenable,” said Mu Zheng, an assistant professor of sociology at the National University of Singapore.
When Zheng Yu, a 47-year-old fashion consultant living in Shanghai, was in her 20s, her friends and family viewed her decision to not have children as a symptom of her rebellious nature.
Now with income inequality rising and seeing the pressure her niece is under to excel, she said she and her husband would make the same decision all over again.
“Only by not having children can I live the way I do now,” said Zheng, who has visited more than 50 countries. “I only have to think about myself, which is the part I enjoy most.”
“Considering global political and economic trends, if you don’t have a strong maternal instinct, you shouldn’t have a child just for the sake of it,” she said.
Vable Liu, a 29-year-old English teacher in Jinan, the capital of China’s Shandong province, said about a third of her friends are dinks.
Liu and her husband recently posted a short video defending their choice.
“Will DINKs miss out on the joy of children?” she asks him in the clip.
DINK couples account for about 38% of households in China as of 2020, according to one study, up from 28% in 2010.
They continued with their mock interview.
“What if your family pressures you?” “Stay away from them.”
“Who do you pass your wealth on to when you die?” “Squander it all before then.”
Special correspondent Xin-yun Wu in Taipei contributed to this report.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best of Web Development Courses: A Comprehensive Guide

Web development is a vital skill in today’s digital world. Whether you're aspiring to become a professional web developer or looking to enhance your skills, selecting the right web development course is crucial. With countless options available, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. This article provides a guide to the best web development courses available, helping you navigate through the top choices and find the one that suits your needs.
Why Take a Web Development Course?
Web development encompasses everything from creating basic websites to complex applications. The demand for skilled web developers is consistently high as businesses transition to digital platforms. By taking a web development course, you can:
Enhance your coding skills: Learn programming languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and more.
Gain practical experience: Hands-on projects help you build a portfolio to showcase your skills.
Stay updated with industry trends: Modern courses keep you informed on the latest technologies and best practices.
Open career opportunities: Web development is a versatile field with various career paths such as front-end, back-end, or full-stack development.
Now, let’s dive into the top 10 web development courses that will give you the edge you need.
Top 10 Web Development Courses
The Web Developer Bootcamp – UdemyOverview: This course, created by Colt Steele, is one of the most popular web development bootcamps available. It covers everything from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to more advanced topics like Node.js and Express.Why it stands out:
Over 63 hours of content.
Project-based learning with real-world applications.
Affordable pricing with regular discounts.
Ideal for: Beginners looking to get an in-depth introduction to web development.
Full-Stack Web Development with React – Coursera (offered by Hong Kong University of Science and Technology)Overview: This course focuses on the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express, React, Node). It's offered through Coursera by the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, which gives it a reputable edge.Why it stands out:
Covers both front-end (React) and back-end development.
Offers a certificate from a prestigious institution.
Focuses on responsive web design.
Ideal for: Learners who want to focus on full-stack web development.
The Odin ProjectOverview: The Odin Project is a free, open-source curriculum that takes you through the entire web development process. It focuses on Ruby on Rails, JavaScript, and offers plenty of hands-on projects.Why it stands out:
Completely free with a community of learners.
Comprehensive learning paths from beginner to advanced.
Emphasizes practical projects.
Ideal for: Self-motivated learners looking for a free, community-driven option.
CS50’s Web Programming with Python and JavaScript – edX (Harvard University)Overview: CS50 is Harvard’s famous computer science course, and this specific track focuses on web programming. You’ll learn about Python, Django, JavaScript, and SQL through this rigorous program.Why it stands out:
Offered by Harvard University.
Covers complex web development topics such as Django and security.
Highly challenging, suitable for intermediate to advanced learners.
Ideal for: Developers with some background looking to dive deeper into web programming.
Complete Web Development Bootcamp – Udemy (Dr. Angela Yu)Overview: Dr. Angela Yu’s bootcamp is highly rated on Udemy for its engaging teaching style and comprehensive approach. You’ll learn HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Node.js, React, and even a little bit of web design.Why it stands out:
Over 55 hours of content.
Fun and engaging style with a focus on building projects.
Regularly updated to reflect the latest technologies.
Ideal for: Beginners who want to build a solid foundation in web development.
Responsive Web Design – freeCodeCampOverview: FreeCodeCamp is known for offering free, self-paced coding lessons, and its Responsive Web Design certification is one of the most popular. You’ll learn HTML5, CSS3, and responsive design principles.Why it stands out:
Free and self-paced.
300 hours of content including hands-on projects.
Community support and real-world project building.
Ideal for: Those looking for a free, structured way to learn responsive web design.
Zero to Mastery Complete Web Developer – Udemy (Andrei Neagoie)Overview: Andrei Neagoie’s course takes a hands-on approach to web development, covering everything from HTML and CSS to advanced topics like React and Node.js.Why it stands out:
Covers both front-end and back-end development.
Real-world projects like building a chat application.
Regularly updated to reflect industry changes.
Ideal for: Beginners to intermediate learners looking for comprehensive training.
Modern React with Redux – Udemy (Stephen Grider)Overview: React is one of the most in-demand front-end technologies today, and Stephen Grider’s course is perfect for those looking to specialize in it. This course covers React and Redux, focusing on building dynamic web applications.Why it stands out:
Specialized focus on React and Redux.
Project-based learning.
Great for intermediate learners.
Ideal for: Developers looking to specialize in React.
Learn Web Development – Mozilla Developer NetworkOverview: MDN’s web development course is a comprehensive, free resource that covers all aspects of web development. It’s created by the Mozilla Developer Network, known for its high-quality documentation.Why it stands out:
Free and constantly updated.
Covers the basics to advanced topics.
Reliable and well-documented resources.
Ideal for: Learners who prefer self-paced study with extensive documentation.
JavaScript, HTML, and CSS for Web Developers – Coursera (Johns Hopkins University)
Overview: This course, offered through Coursera by Johns Hopkins University, focuses on the fundamentals of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS, which are essential building blocks for any web developer.
Why it stands out:
Covers core web technologies.
Earn a certificate from a well-known university.
Focus on building real-world projects.
Ideal for: Beginners looking to get certified in web development fundamentals.
What to Look for in a Web Development Course
When choosing the best web development course for your needs, consider the following:
Skill Level: Are you a beginner or do you have some coding experience? Courses like The Odin Project and freeCodeCamp are great for beginners, while more advanced developers might prefer CS50’s Web Programming or Modern React with Redux.
Specialization: Do you want to focus on front-end (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), back-end (Node.js, Django), or full-stack development? Choose a course based on your career goals.
Project-Based Learning: A good web development course should include hands-on projects to help you apply what you've learned. The more projects, the better your portfolio will look to potential employers.
Certification: If you’re looking for recognition, consider courses that offer certificates from reputable institutions, like those from Coursera or edX.
Price: While some courses are free, others may require a one-time fee or subscription. Many platforms like Udemy offer discounts, so be sure to check regularly.
Final Thoughts
Whether you're just starting your journey in web development or looking to advance your skills, there’s a course out there for you. The best web development courses offer a blend of hands-on projects, updated content, and engaging instruction. As you consider the top 10 web development courses, think about your current skill level, your career aspirations, and your learning preferences. With the right course, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a proficient web developer.
Remember, learning web development is a marathon, not a sprint. Choose a course that fits your pace, stay consistent, and you'll see significant improvement in no time!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Study finds health risks in switching ships from diesel to ammonia fuel
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/study-finds-health-risks-in-switching-ships-from-diesel-to-ammonia-fuel/
Study finds health risks in switching ships from diesel to ammonia fuel


As container ships the size of city blocks cross the oceans to deliver cargo, their huge diesel engines emit large quantities of air pollutants that drive climate change and have human health impacts. It has been estimated that maritime shipping accounts for almost 3 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions and the industry’s negative impacts on air quality cause about 100,000 premature deaths each year.
Decarbonizing shipping to reduce these detrimental effects is a goal of the International Maritime Organization, a U.N. agency that regulates maritime transport. One potential solution is switching the global fleet from fossil fuels to sustainable fuels such as ammonia, which could be nearly carbon-free when considering its production and use.
But in a new study, an interdisciplinary team of researchers from MIT and elsewhere caution that burning ammonia for maritime fuel could worsen air quality further and lead to devastating public health impacts, unless it is adopted alongside strengthened emissions regulations.
Ammonia combustion generates nitrous oxide (N2O), a greenhouse gas that is about 300 times more potent than carbon dioxide. It also emits nitrogen in the form of nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2, referred to as NOx), and unburnt ammonia may slip out, which eventually forms fine particulate matter in the atmosphere. These tiny particles can be inhaled deep into the lungs, causing health problems like heart attacks, strokes, and asthma.
The new study indicates that, under current legislation, switching the global fleet to ammonia fuel could cause up to about 600,000 additional premature deaths each year. However, with stronger regulations and cleaner engine technology, the switch could lead to about 66,000 fewer premature deaths than currently caused by maritime shipping emissions, with far less impact on global warming.
“Not all climate solutions are created equal. There is almost always some price to pay. We have to take a more holistic approach and consider all the costs and benefits of different climate solutions, rather than just their potential to decarbonize,” says Anthony Wong, a postdoc in the MIT Center for Global Change Science and lead author of the study.
His co-authors include Noelle Selin, an MIT professor in the Institute for Data, Systems, and Society and the Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS); Sebastian Eastham, a former principal research scientist who is now a senior lecturer at Imperial College London; Christine Mounaïm-Rouselle, a professor at the University of Orléans in France; Yiqi Zhang, a researcher at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology; and Florian Allroggen, a research scientist in the MIT Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics. The research appears this week in Environmental Research Letters.
Greener, cleaner ammonia
Traditionally, ammonia is made by stripping hydrogen from natural gas and then combining it with nitrogen at extremely high temperatures. This process is often associated with a large carbon footprint. The maritime shipping industry is betting on the development of “green ammonia,” which is produced by using renewable energy to make hydrogen via electrolysis and to generate heat.
“In theory, if you are burning green ammonia in a ship engine, the carbon emissions are almost zero,” Wong says.
But even the greenest ammonia generates nitrous oxide (N2O), nitrogen oxides (NOx) when combusted, and some of the ammonia may slip out, unburnt. This nitrous oxide would escape into the atmosphere, where the greenhouse gas would remain for more than 100 years. At the same time, the nitrogen emitted as NOx and ammonia would fall to Earth, damaging fragile ecosystems. As these emissions are digested by bacteria, additional N2O is produced.
NOx and ammonia also mix with gases in the air to form fine particulate matter. A primary contributor to air pollution, fine particulate matter kills an estimated 4 million people each year.
“Saying that ammonia is a ‘clean’ fuel is a bit of an overstretch. Just because it is carbon-free doesn’t necessarily mean it is clean and good for public health,” Wong says.
A multifaceted model
The researchers wanted to paint the whole picture, capturing the environmental and public health impacts of switching the global fleet to ammonia fuel. To do so, they designed scenarios to measure how pollutant impacts change under certain technology and policy assumptions.
From a technological point of view, they considered two ship engines. The first burns pure ammonia, which generates higher levels of unburnt ammonia but emits fewer nitrogen oxides. The second engine technology involves mixing ammonia with hydrogen to improve combustion and optimize the performance of a catalytic converter, which controls both nitrogen oxides and unburnt ammonia pollution.
They also considered three policy scenarios: current regulations, which only limit NOx emissions in some parts of the world; a scenario that adds ammonia emission limits over North America and Western Europe; and a scenario that adds global limits on ammonia and NOx emissions.
The researchers used a ship track model to calculate how pollutant emissions change under each scenario and then fed the results into an air quality model. The air quality model calculates the impact of ship emissions on particulate matter and ozone pollution. Finally, they estimated the effects on global public health.
One of the biggest challenges came from a lack of real-world data, since no ammonia-powered ships are yet sailing the seas. Instead, the researchers relied on experimental ammonia combustion data from collaborators to build their model.
“We had to come up with some clever ways to make that data useful and informative to both the technology and regulatory situations,” he says.
A range of outcomes
In the end, they found that with no new regulations and ship engines that burn pure ammonia, switching the entire fleet would cause 681,000 additional premature deaths each year.
“While a scenario with no new regulations is not very realistic, it serves as a good warning of how dangerous ammonia emissions could be. And unlike NOx, ammonia emissions from shipping are currently unregulated,” Wong says.
However, even without new regulations, using cleaner engine technology would cut the number of premature deaths down to about 80,000, which is about 20,000 fewer than are currently attributed to maritime shipping emissions. With stronger global regulations and cleaner engine technology, the number of people killed by air pollution from shipping could be reduced by about 66,000.
“The results of this study show the importance of developing policies alongside new technologies,” Selin says. “There is a potential for ammonia in shipping to be beneficial for both climate and air quality, but that requires that regulations be designed to address the entire range of potential impacts, including both climate and air quality.”
Ammonia’s air quality impacts would not be felt uniformly across the globe, and addressing them fully would require coordinated strategies across very different contexts. Most premature deaths would occur in East Asia, since air quality regulations are less stringent in this region. Higher levels of existing air pollution cause the formation of more particulate matter from ammonia emissions. In addition, shipping volume over East Asia is far greater than elsewhere on Earth, compounding these negative effects.
In the future, the researchers want to continue refining their analysis. They hope to use these findings as a starting point to urge the marine industry to share engine data they can use to better evaluate air quality and climate impacts. They also hope to inform policymakers about the importance and urgency of updating shipping emission regulations.
This research was funded by the MIT Climate and Sustainability Consortium.
#000#Accounts#Aeronautical and astronautical engineering#aeronautics#air#air pollution#air quality#America#ammonia#Analysis#approach#Asia#asthma#atmosphere#author#Bacteria#betting#burns#carbon#Carbon dioxide#carbon dioxide emissions#carbon emissions#carbon footprint#Center for Global Change Science#change#Cleaner industry#climate#climate change#college#container
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
R.I.P. William Anders.
William Anders, a NASA astronaut who was part of the 1968 Apollo 8 crew who were the first three people to orbit the moon, has died in a plane crash in Washington state, according to his son, Gregory Anders. He was 90 years old. My “dad passed in an aircraft incident in the San Juan Islands,” Anders told CNN Friday evening. “The family is devastated and grieving the loss of a great pilot,” he added. The San Juan County Sheriff’s Office said in a news release an aircraft went down off the coast of Jones Island. [ ... ] William Anders, born on October 17, 1933, in Hong Kong, graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1955 and after being commissioned in the US Air Force, he earned his pilot’s wings the following year, according to the US Naval Academy’s website. [ ... ] Anders and fellow astronauts Jim Lovell and mission commander Frank Borman, who died in November 2023, flew aboard the first lunar orbit mission in December 1968 on Apollo 8. Anders served as the lunar module pilot for the historic flight. From the spacecraft, Anders captured an iconic image of Earth showing the moon’s surface in the foreground during the Apollo 8 flight on Christmas Eve 1968, titled “Earthrise.” “We came all this way to explore the moon, and the most important thing is that we discovered the Earth,” Anders famously said.
Although the first moon landing by Apollo 11 in 1969 was a great technological achievement, I think the Apollo 8 mission in 1968 may have had a greater impact on the way humans think about our neck of the cosmos.
The first flight beyond low Earth orbit put our planet in perspective and made people understand how precious and vulnerable it is.
The Earthrise photo became instantly iconic. It gave momentum to the environmental movement and the first Earth Day was marked in 1970.

BTW, the Apollo 8 command module is now on display at Chicago's Museum of Science and Industry in the Hyde Park neighborhood which also includes University of Chicago.
#william anders#apollo 8#nasa#astronauts#space travel#usa#earthrise#lunar orbit#the environmental movement#chicago#museum of science and industry
2 notes
·
View notes