#high polyunsaturated fats
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
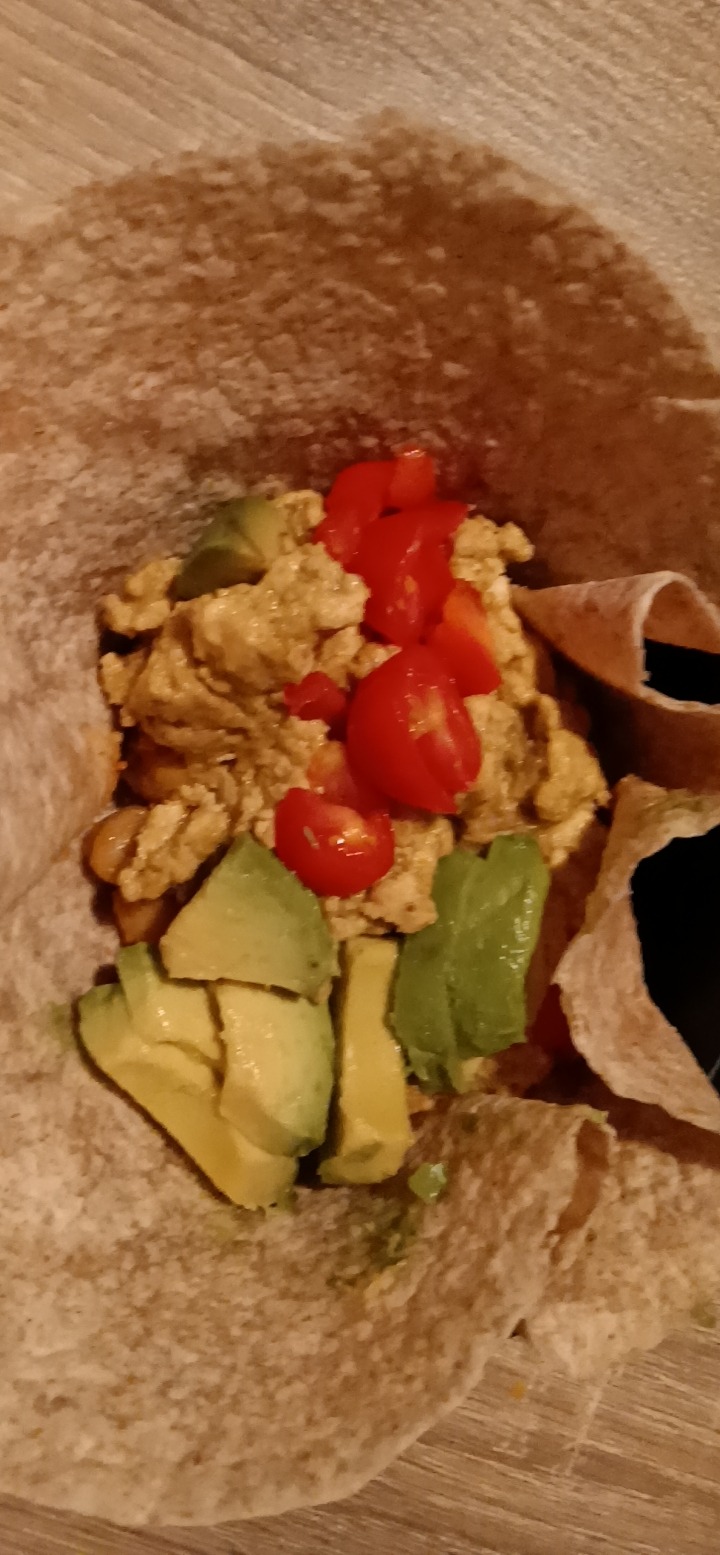
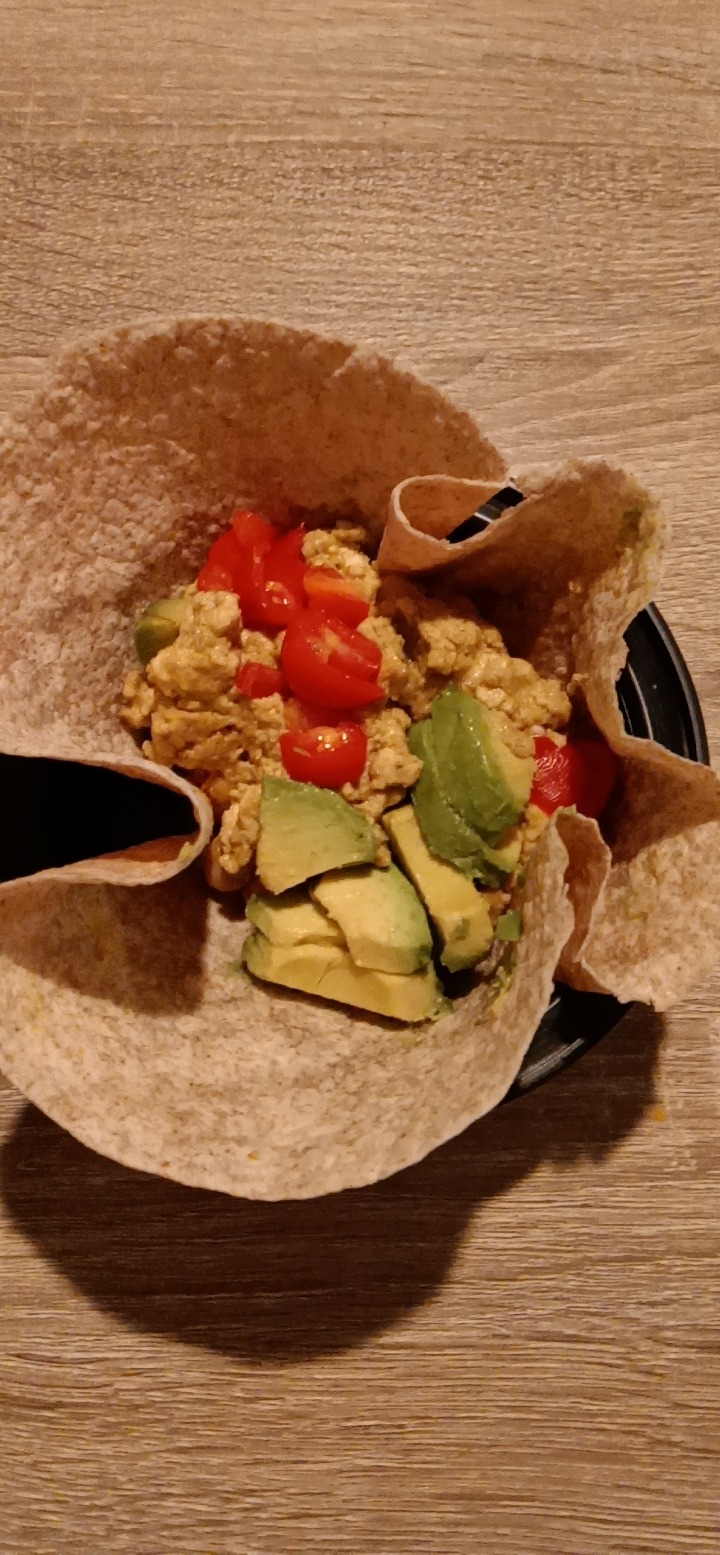
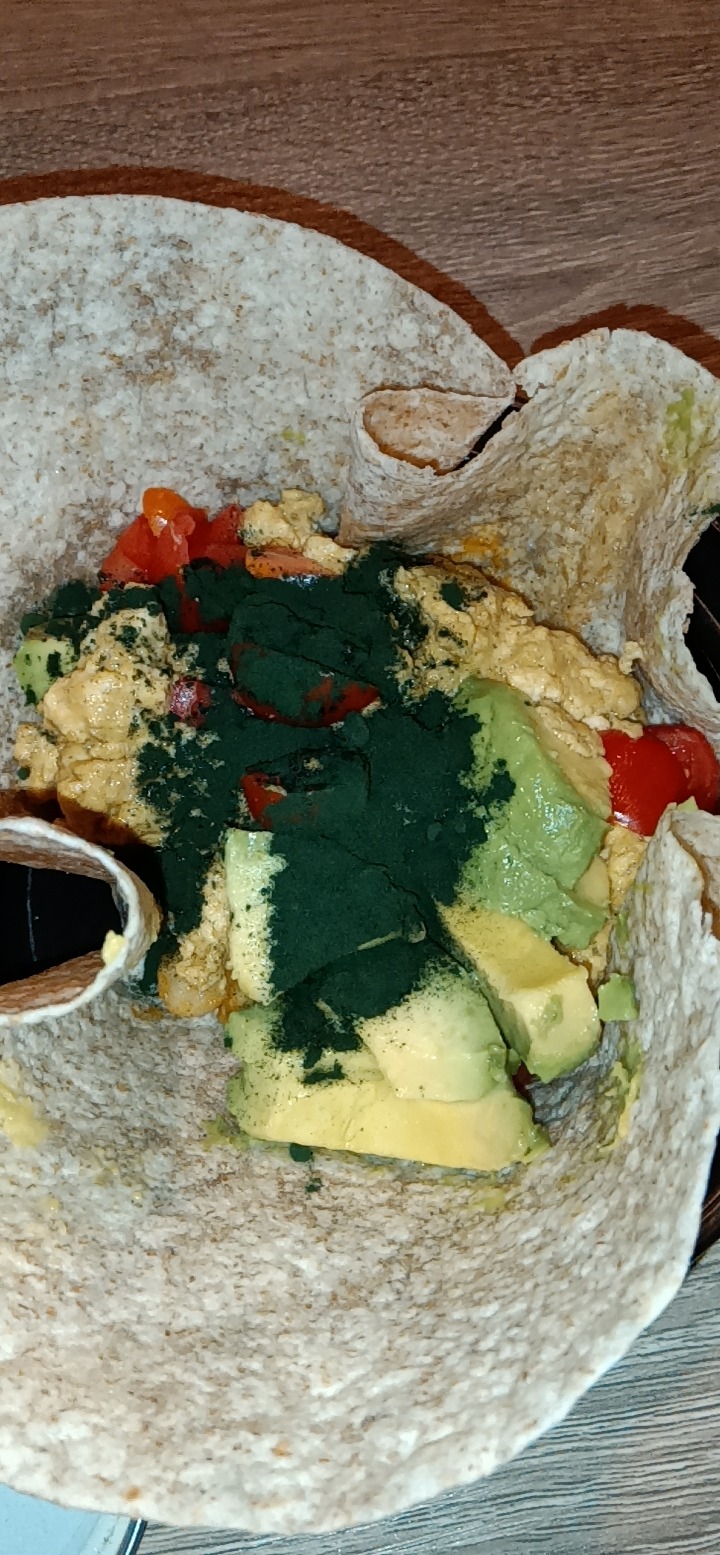




I will post my chickpeas recipe and tofu scrambled eggs
#veganlife#vegan eats#diet plan#high protein#high polyunsaturated fats#high monounsaturared fats#health and wellness
1 note
·
View note
Photo

…So as medical practitioners, we have to make sure our message is clear and irrefutable: if you replace saturated fat in your diet with refined grains and sugar—the largest source of calories in the United States diet—your risk of heart disease remains relatively high. But if you replace those saturated fats with starch from whole grains, whole potatoes or sweet potatoes, whole beans, polyunsaturated fat, or monounsaturated fat in the form of olives, nuts, or other higher-fat plant foods, your risk of heart disease is significantly reduced.
excerpt from Oversaturated by Evan Allen
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
You need to consume unsaturated fats or you'll feel slow, fatigued, and never want to do anything.
You have to learn the healthy fats and eat the healthy fats if you're committed to being vegetarian or vegan. Or you will be tired forever, and not the type of tired where you can push through it, but the type of tired where you feel like you have to stay in bed all day and your heart feels like it's being sucked through a straw.
Fatty acids are what lipids in our bodies are made mostly up of. Fatty acids are responsible for energy storage, brain development, blood clotting, and controlling inflammation. They are necessary for your body to be able to absorb vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K. They are necessary for your body to produce sex hormones like testosterone and estrogen. Not having enough of these fats can cause muscle pain, night blindness, infertility, easy bruising, dry hair, hair loss, loose teeth, depression and anxiety, and dermatitis (presenting as dry and scaly rashes).
You need unsaturated fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These are good fats. Saturated fats and trans fats are bad, these are what raise your risk of heart attacks and strokes. Diets high in saturated fats might also lead to chronic pain.
35% of your caloric intake should be fats. This can be added to the list on why the diet industry is so cruel. Manufacturers and organizations paired with the pornography and cosmetic industry pushing dieting and beauty norms on women and girls for decades impressed the seriously dangerous and false idea that consuming fats was bad. Denying healthy fats means denying healthy brain development, energy and motivation, better ability to heal from injuries, and preventing depression and anxiety.
Balsamic and olive oil together (and you can add some minced garlic if you like) tastes fantastic with warm bread and can be made in 12 minutes.
Cooking with the oils above instead of butter can also introduce fatty acids in your diet (might not be enough though, you need 1-2 tablespoons a day).
Sometimes if I'm in a hurry I just eat a plain avocado a day.
You can sprinkle chia seeds on yogurt. Add flax seed to smoothies.
Just eat 1/4th of pumpkin seeds too (which are also super high in magnesium). That's basically a handful a day, make it part of your morning routine.
Almonds, walnuts, and pecans are also high in good fats.
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
Story at-a-glance
BPH is not just a part of aging — While prostate enlargement becomes more common with age, research shows that metabolic dysfunction is also a key driver of disease progression
Inflammation fuels prostate growth — Men with BPH have higher levels of inflammatory lipids that promote tissue remodeling and chronic inflammation
Metabolic dysfunction worsens BPH severity — Research shows that men with both BPH and metabolic syndrome experience faster disease progression and greater symptom severity
Omega-6 fats are a hidden culprit — Excess linoleic acid, the primary omega-6 fat in vegetable oils, fuels chronic inflammation and disrupts hormone balance. Studies suggest that a diet high in omega-6 fats drives prostate enlargement
Targeting metabolic health helps slow or reverse BPH — Optimizing metabolic health by addressing polyunsaturated fat intake, hormonal imbalances and chronic inflammation is a more effective strategy than conventional symptom management
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Debunking Wellness Trends: Seed Oils
One aspect of the growing wellness trends on social media is the idea that seed oils are poisoning the population and need to be avoided to reach better health/heal health conditions/conserve fertility/etc. They’re being called “the hateful eight”, and there’s a lot of people doing the #seedoilfree lifestyle. Seed oils are being blamed for headaches, low immunity, disrupted attention and thinking, diabetes, and more.
(Seed oils include canola, corn, cottonseed, grapeseed, rice bran, safflower, soy and sunflower oil)
Toxicity Claims
Current scientific evidence does NOT support claims that seed oils are “toxic”.
Now, if you begin to cut out foods such as fried foods (like fries) or packaged snacks, you may feel better. A lot of people are attributing this feeling to removing seed oils, but these foods are usually high in refined carbohydrates, sodium and sugar which is why they’re associated with more negative health outcomes.
Another fear is that the “toxicity” comes from production byproducts. Heat and solvents like hexane are used to extract oil from seeds, which apparently introduces chemical additives and unstable molecules, which then can turn polyunsaturated fats into harmful trans fats. Realistically, hexane is a bigger threat to the environment and workers in case of inhalation – trace amounts in the oil are still being studied, but so far there’s no concerning data. They’re also heated for short periods, and actually have fewer trans fats than products like milk or butter.
Omega-6
Additionally, omega-6 (found in nuts and seeds, and a dominant polyunsaturated fat in seed oils) is also not “toxic”. In fact, it’s been scientifically linked to lower cholesterol, lower blood sugar and reduced heart disease risk. The argument against omega-6 is that it’s responsible for chronic inflammation – omega-6 linoleic acid is converted into arachidonic acid in the body, which is a component of inflammatory compounds. Only 0.2% of linoleic acid we eat turns into arachidonic acid, and not all the compounds cause inflammation – arachidonic acid is a complex molecule, and it also has some anti-inflammatory effects. Linoleic acid is also an essential fatty acid that our body can’t make itself, and we use it to produce cell membranes and for skin health.
Another claim is that our omega-3: omega-6 ratio is out of balance, and that this is because our ancestors ate a much more balanced ratio than we do today. We DO eat more omega-6 fats than omega-3, but the claim that we eat 20 to 50x more is misinformation – it’s closer to 10:1. Instead of cutting omega-6, the better solution is to try and introduce more omega-3 fats into your diet.
Realistically, a lot of the online discourse about seed oils is misunderstanding scientific reports + deliberate fear-mongering. If you do have concerns about something in your diet causing health issues, seek advice from a trained medical professional who can give you evidence-based ideas and solutions to help you!
(Some articles to start if you want to know more on this topic 1 2 3)
#ive been promising to say something about this forever lmao i finally got to it#wellness trends#<- my tag for this stuff#i honestly feel bad for people who i see getting anxious about these kinds of things!!! :((#katie rambles
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
Best Peanut Butter for Gym and Muscle Gain – High-Protein Options
If you are hitting the gym regularly and aiming to build lean muscle, you know the importance of fueling your body with the right nutrients. Among all the high-protein snacks available, peanut butter stands out as a popular and effective choice. Packed with protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients, high-protein peanut butter is a must-have in every fitness enthusiast's diet.

In this blog, we shall explore how peanut butter helps in muscle gain, what makes it ideal for gym-goers, and how to buy peanut butter in India wisely. We shall also take a look at some of the top peanut butter brands in India and guide you on choosing the best peanut butter in India to complement your fitness journey.
Why Peanut Butter is Great for Muscle Gain
Whether you are bulking up or looking to stay lean while gaining muscle, peanut butter offers a powerful punch of protein and calories in a small serving. Here is why fitness professionals and athletes include it in their diet plans:
1. High Protein Content
Peanut butter is naturally rich in plant-based protein, which helps repair and build muscle tissue after a workout. High protein peanut butter offers around 8–10g of protein per 2-tablespoon serving, making it a convenient protein source between meals or pre/post-workout.
2. Healthy Fats for Energy
The healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats in peanut butter provide a sustained energy boost, perfect for long workouts. These fats also support hormone production, which is essential for muscle growth.
3. Calorie Dense
Gaining muscle requires a caloric surplus, and peanut butter can help you achieve this without stuffing yourself. A couple of tablespoons add 180-200 calories, perfect for increasing your intake effortlessly.
4. Versatile and Delicious
From smoothies to sandwiches, oatmeal to protein bars – peanut butter can be incorporated into nearly every meal, making it easy to consume regularly.
Choosing the Best Peanut Butter in India for Gym and Muscle Gain
With so many options available in the market, selecting the right peanut butter can be confusing. To help you buy peanut butter in India wisely, consider these factors:
1. Check the Ingredients
The best peanut butter contains just peanuts and maybe a pinch of salt. Avoid options with added sugar, hydrogenated oils, or preservatives.
2. Go for High Protein Variants
Look for labels that say “high protein peanut butter” or ones that are blended with whey protein for an added muscle-building boost.
3. Natural vs. Commercial
Natural peanut butter is less processed and usually free from unnecessary additives. For fitness purposes, natural options are often superior.
4. Crunchy vs. Creamy
Both types offer similar nutritional value. Choose the texture that best suits your recipes or personal preference.
Best Peanut Butter Company in India – Why Choose Master Farmer?
When it comes to high-quality nutrition, Master Farmer takes pride in offering some of the best quality peanut butter in the market. As a trusted peanut butter company in India, Master Farmer focuses on delivering premium products made with 100% roasted peanuts, no added sugar, and zero trans fats.
Here is what makes Master Farmer a standout among the top peanut butter brands in India:
High protein content perfect for gym-goers and athletes
No preservatives or artificial flavors
Available in various delicious flavors (classic, chocolate, honey)
Crunchy and creamy textures to suit every preference
Innovative peanut butter combo pack options for value buying
If you are searching for the best peanut butter brand in India, Master Farmer ticks all the right boxes for quality, taste, and nutrition.
Benefits of Including Peanut Butter in Your Gym Diet
Supports Muscle Recovery
After intense workouts, your muscles need protein for repair. A peanut butter protein smoothie can be a quick and effective post-workout meal.
Easy to Digest
Unlike some protein bars or powders that may cause bloating, peanut butter is generally easy on the stomach while being highly satiating.
Affordable and Easily Available
Compared to other high-protein snacks, peanut butter offers great value. You can easily buy peanut butter in India through online stores or health food retailers.
Best Ways to Enjoy Peanut Butter for Muscle Gain
Looking to spice up your fitness diet with peanut butter? Here are some smart and tasty ideas:
Peanut Butter Banana Smoothie: Blend one banana, a scoop of high protein peanut butter, whey protein, and almond milk.
Peanut Butter Oatmeal: Stir a spoonful into your morning oats for a protein boost.
Pre-Workout Toast: Whole-grain bread with peanut butter gives slow-digesting carbs and fats for long-lasting energy.
Post-Workout Shake: Mix with milk and protein powder for muscle recovery.
Energy Balls: Combine oats, peanut butter, honey, and flax seeds for homemade protein bites.
Do not forget to explore peanut butter combos that offer different variants in one pack – ideal for mixing flavors and getting the most out of your purchase.
Peanut Butter Combos – Smart Buying for Smart Fitness
For those serious about their gym routine, peanut butter combo pack options are a great way to stock up on different flavors and textures. Many top peanut butter brands in India offer combo packs that include creamy, crunchy, chocolate, or honey-infused versions – giving you variety without compromising on nutrition.
Master Farmer’s peanut butter combos are especially curated for fitness lovers, offering:
Better value for money
More variety in your diet
Easy options for pre/post-workout meals
Perfect gifting options for fitness friends
Next time you plan to buy peanut butter in India, go for a combo pack to get more in one go!
Final Thoughts – Best Peanut Butter in India for Gym and Muscle Gain
Building muscle is not just about lifting weights – it is also about feeding your body with the right nutrients. Incorporating high protein peanut butter into your fitness diet is a smart, tasty, and convenient way to support muscle gain.
When choosing the best quality peanut butter, always go for trusted brands that prioritize health, purity, and performance. Master Farmer stands tall as one of the top peanut butter brands in India, offering premium peanut butter that meets the demands of gym-goers and health-conscious individuals.
So, whether you are starting your fitness journey or are a seasoned athlete, make peanut butter your go-to gym companion. Check out Master Farmer’s wide range of natural, protein-rich options and buy peanut butter in India that truly works for your gains!
Get Started Today! Explore Master Farmer’s peanut butter combo packs, try different flavors, and power up your workouts with the best fuel for muscle growth.
Fuel your fitness. Feed your muscles. Go Master Farmer.
#Buy peanut butter in India#Best peanut butter in India#Top peanut butter brands in India#Best peanut butter company in India#High protein peanut butter#Best peanut butter brand in India#Best quality peanut butter
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Nutrition and Wellness: Separating Fact from Fiction
In the age of social media influencers, fad diets, and self-proclaimed well-being authorities, it’s more difficult than ever to separate nutrition data from fiction. Misinformation spreads quick, frequently packaged in aesthetically alluring posts or sensational headlines. While some pointers and traits are rooted in technological know-how, many aren't—and they can do extra damage than top. In this newsletter, we’ll dive into commonplace myths surrounding nutrients and well being and highlight what the technological know-how definitely says.

separating nutrition facts from fiction"
Myth #1: Carbs Are Bad for You
Fiction: Carbohydrates make you gain weight and should be averted.
Fact: Carbohydrates are a number one supply of power for your body and mind. Not all carbs are created same, and the secret is distinguishing between simple and complicated carbohydrates.
Simple carbs (like delicate sugars in sweet or white bread) can spike blood sugar and contribute to weight benefit if consumed excessively.
Complex carbs (like entire grains, culmination, and greens) provide fiber, nutrients, and lengthy-lasting power.
In fact, entire grains and fiber-rich foods were associated with lower dangers of coronary heart ailment, kind 2 diabetes, and obesity. Carbs handiest end up difficult whilst consumed in extra or whilst sourced from fantastically processed ingredients.
Myth #2: You Need to Detox Your Body with Juice Cleanses
Fiction: Juice cleanses flush out pollutants and reset your body.
Fact: Your body already has an extremely effective detox machine—your liver, kidneys, skin, and lungs. There's no medical proof that juice cleanses or detox teas enhance this natural manner. In truth, excessive cleanses can lead to nutrient deficiencies, blood sugar imbalances, and digestive issues.
While juices may be nutrient-dense if crafted from complete end result and vegetables, they regularly lack fiber and are high in sugar. A better approach? Support your frame with a balanced food regimen, hydration, normal workout, and sleep.
Myth #3: Fat Makes You Fat
Fiction: Eating fat causes weight advantage.
Fact: Dietary fat is critical for fitness. It helps mobile increase, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. What matters most is the form of fats you consume.
Healthy fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat located in avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish) can lessen irritation and decrease the danger of coronary heart disorder.
Unhealthy fats (trans fats and excessive saturated fat) can make a contribution to cardiovascular problems and need to be constrained.
Eating fat moderately as part of a balanced weight-reduction plan does no longer immediately cause weight advantage—in reality, healthy fats can boom satiety and assist adjust urge for food.
Myth #four: High-Protein Diets Are Dangerous
Fiction: Eating too much protein harms your kidneys and bones.
Fact: For most healthful individuals, a high-protein weight-reduction plan is not harmful. This fable likely originated from research in human beings with preexisting kidney disease, for whom excessive protein consumption can be dangerous. But in wholesome individuals, there’s no strong evidence that a high-protein food plan causes kidney harm.
Protein plays a key position in muscle repair, immune feature, and hormone manufacturing. It's specially critical for active individuals, older adults, and those looking to lose fats while keeping lean muscle mass.
That stated, "high-protein" doesn't mean all-meat diets. Good protein sources encompass legumes, dairy, eggs, hen, fish, and plant-primarily based options like tofu and quinoa.
Myth #5: Natural or Organic Means Healthy
Fiction: If it’s labeled “natural” or “natural,” it ought to be excellent for you.
Fact: Labels may be misleading. "Natural" is a loosely regulated time period and doesn’t assure a product is unfastened from preservatives, introduced sugars, or dangerous fat. Similarly, "organic" refers to how components are grown (without artificial pesticides or fertilizers), not to the product’s dietary fee.
For instance, organic cookies might also nonetheless be loaded with sugar and energy. Always study the vitamins label and elements list as opposed to counting on advertising buzzwords.
Myth #6: You Should Eat Small Meals Every 2–three Hours
Fiction: Frequent consuming boosts metabolism and enables with weight reduction.
Fact: While some humans do nicely with frequent meals, there may be no customary gain to eating each 2–three hours. Your metabolism does not appreciably speed up with extra frequent eating.
What’s extra essential is general calorie intake and meals nice over the direction of the day. For a few, intermittent fasting or 3 balanced food an afternoon is probably extra sustainable and beneficial, specially for urge for food control and blood sugar law.
Myth #7: Supplements Can Replace Food
Fiction: Taking nutrients and supplements is simply as top as ingesting nutrient-wealthy ingredients.
Fact: Supplements may be useful, mainly for filling unique dietary gaps (like diet D in winter or B12 for vegans). But they are able to’t fully mirror the complexity of whole meals, which give a synergistic blend of fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals.
Relying totally on dietary supplements can deliver a false sense of safety and might even lead to nutrient imbalances or toxicities if overused. Whenever possible, prioritize entire, minimally processed meals.
Myth #8: You Must Be Perfect to Be Healthy
Fiction: One dangerous meal or missed workout ruins your development.
Fact: Consistency beats perfection. A healthy lifestyle isn’t about never indulging—it is approximately developing sustainable conduct that support your well-being through the years. One meal or one lazy day won’t undo weeks or months of proper selections.
Allowing flexibility in your ordinary promotes a more healthy relationship with meals and motion. Mental well-being is a part of the photo, too, and stressing over perfection can cause burnout, disordered eating, or anxiety.
Evidence-Based Wellness Tips
Now that we’ve busted some common myths, right here are a few actionable, evidence-subsidized pointers to assist nutrition and typical wellbeing:
Eat quite a few entire meals: Include veggies, fruits, entire grains, lean proteins, and wholesome fat.
Stay hydrated: Water is important for metabolism, digestion, and energy.
Get enough sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours in line with night to aid hormone balance, urge for food regulation, and recovery.
Move your frame frequently: Exercise facilitates lessen stress, enhance temper, and help cardiovascular and metabolic fitness.
Limit ultra-processed meals: These regularly incorporate excessive quantities of brought sugar, sodium, and bad fats.
Practice mindful eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, and enjoy meals without distractions.
Manage pressure: Chronic strain can negatively have an effect on digestion, appetite, and irritation.
Benefits Of Meditation
Immediate Benefits Of Plant Based Diet
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
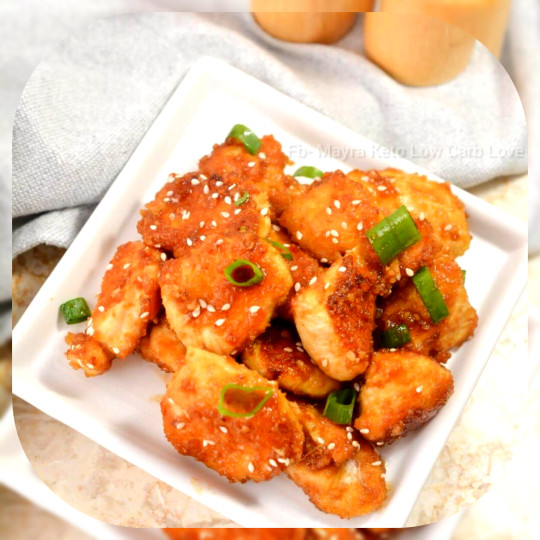

Keto Orange Chicken 🍗😋
Prep Time: 20minutes minutesCook Time: 30minutes minutesTotal Time: 50minutes minutes Servings: 4 Calories: 328
🙏 𝔽𝕠𝕝𝕝𝕠𝕨 𝕗𝕠𝕣 𝕞𝕠𝕣𝕖 🔃 𝕊𝕙𝕒𝕣𝕖 𝕨𝕚𝕥𝕙 𝕗𝕣𝕚𝕖𝕟𝕕𝕤 𝕒𝕟𝕕 𝕗𝕒𝕞𝕚𝕝𝕪 𝕞𝕖𝕞𝕓𝕖𝕣𝕤 𝕨𝕙𝕠 𝕟𝕖𝕖𝕕 𝕚𝕥.
Ingredients
▢1 ½ pounds boneless skinless chicken breast cut into bite sized pieces
▢1 ½ cups pork rind crumbs
▢2 large eggs
▢2 tablespoons heavy whipping cream
▢salt and pepper to taste
▢oil for frying
Sauce:
▢2 teaspoons minced garlic
▢1 teaspoon ginger paste
▢½ teaspoon sesame oil
▢3 tablespoons water
▢2 tablespoons soy sauce
▢⅓ cups brown sugar substitute
▢zest from one orange
▢2 tablespoons fresh orange juice
▢¼ cup white vinegar
Instructions
Cover the bottom of a large skillet with oil, and heat over medium high heat.
Combine eggs and heavy whipping cream in a small bowl.
Dip the chicken pieces into the egg mixture and then dredge in the pork rind crumbs.
Place the chicken into the heated oil, and season with salt and pepper to taste. Saute until browned and cooked through.
Remove the chicken and set aside.
In a bowl, combine the ingredients for the sauce.
Remove the excess oil from the skillet and reduce the heat to medium.
Pour in the sauce mixture and simmer until thickened.
Toss the chicken in the sauce, and allow to cool slightly before serving garnished with sesame seeds and chopped green onions.
Notes
Cut the chicken evenly. This will help it all cook at the same rate so you don't have some pieces burning while others are undercooked.
Make sure the chicken is fully cooked. The safe cooking temperature of chicken breasts is 165°F.
Easily thicken your sauce if it is too thin. Just simmer the sauce on low in order to thicken it.
Use your favorite garnish. Garnish the chicken with sesame seeds after you toss it in the orange sauce.
Use fresh squeezed orange juice. It will give your keto orange chicken the most incredible flavor.
Use coconut aminos. It's gluten free and perfect for those who have a soy sensitivity.
Nutrition
Calories: 328 | Carbohydrates: 2g | Protein: 47g | Fat: 13g | Saturated Fat: 5g | Polyunsaturated Fat: 1g | Monounsaturated Fat: 3g | Trans Fat: 1g | Cholesterol: 211mg | Sodium: 1510mg | Potassium: 708mg | Fiber: 1g | Sugar: 1g | Vitamin A: 302IU | Vitamin C: 7mg | Calcium: 36mg | Iron: 1mg
Additional Info
Net Carbs: 1 g | % Carbs: 1.3 % | % Protein: 60.8 % | % Fat: 37.9 % |
6 notes
·
View notes
Text


This is my lunch it’s super healthy and low cal 🌷
1. Eggplant (180g): 35 calories
2. Broccoli (200g): 70 calories
3. Mini cucumbers (5, ~100g total): ~15 calories (average ~3 calories per mini cucumber)
4. Olive oil (1 teaspoon): 40 calories
5. Tomato salsa (100g)**: ~25 calories
Total Calories:
35 + 70 + 15 + 40 + 25 = 185 calories
Here’s a detailed nutritional breakdown for your meal. Values are approximate and based on averages for each ingredient.
Nutrition break-down 🎀
Eggplant (180g)
- Carbohydrates: 8.6g
- Fiber: 2.5g
- Sugar: 3.2g
- Protein: 0.8g
- Fat: 0.2g
- Vitamins/Minerals: Good source of potassium (240mg) and some vitamin C.
Broccoli (200g)
- Carbohydrates: 13.7g
- Fiber: 5.6g
- Sugar: 3.3g
- Protein: 5.6g
- Fat: 0.7g
- Vitamins/Minerals:
- High in vitamin C (200% of daily value)
- Good source of vitamin K (220% of daily value)
- Contains folate, calcium, and iron.
Mini Cucumbers (5, ~100g)
- Carbohydrates: 3.6g
- Fiber: 0.7g
- Sugar: 2g
- Protein: 0.6g
- Fat: 0.1g
Hydrating (95% water) + vitamin k
Olive Oil (1 teaspoon)
- Carbohydrates: 0g
- Protein: 0g
- Fat: 4.5g
- Saturated fat: 0.6g
- Monounsaturated fat: 3.3g
- Polyunsaturated fat: 0.5g
- Vitamins/Minerals: Contains vitamin E and antioxidants.
Tomato Salsa (100g)
- Carbohydrates: 4g
- Fiber: 1g
- Sugar: 3g
- Vitamins/Minerals: Good source of vitamin C and some lycopene.
Meal Nutritional Breakdown:
Ingrédients:
- 180g Eggplant
- 200g Broccoli
- 5 Mini Cucumbers (~100g)
- 1 Teaspoon Olive Oil
- 125g Tomato Salsa (~25 calories)
Totals:
- Calories: 185 kcal
- Carbohydrates: 30g
- Fiber: 9.5g
- Sugar: 11g
- Protein: 7.5g
- Fat: 5.5g
- Saturated Fat: 0.6g
- Monounsaturated Fat: 3.3g
- Polyunsaturated Fat: 0.5g
Vitamins & Minerals:
Vitamin C ~280% of daily value
Vitamin K ~220% of daily value
Potassium ~850mg
Folate ~20% of daily value
Calcium ~100mg
Iron ~2mg
🌷H I G H L I G H T S 🌷
- High in fiber and vitamins (notably C & K)
- Low-calorie and nutrient-dense
- Contains healthy fats from olive oil
#nutrition#nutrients#food#health and wellness#low calorie meals#glow up#glowingskin#recipe#low cal meal
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Vegan and Kosher Omega-3 Supplements

In today’s health-conscious world, many individuals are looking for supplements that align with their dietary choices and ethical values. Whether you follow a vegan diet, prefer kosher-certified products, or need vegetarian-friendly options, finding the right omega-3 supplement is essential. Omega-3 fatty acids are critical for overall health, playing a vital role in heart function, brain health, and reducing inflammation. This article explores the best options for vitamins vegan supplement, kosher omega-3 supplements, vegetarian omega-3 capsules, and veg omega 3 capsules to help you make an informed choice.
Why Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Essential
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that the body cannot produce on its own. These include EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), and ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). While EPA and DHA are predominantly found in fish oil, ALA is abundant in plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids include:
Improved cardiovascular health
Enhanced brain function and reduced cognitive decline
Anti-inflammatory properties that alleviate joint pain
Better skin and eye health
If you follow a vegan, kosher, or vegetarian lifestyle, you’ll need omega-3 supplements derived from non-animal sources or those that meet religious dietary laws.
Vegan Omega-3 Supplements
Vegan omega-3 supplements are derived from plant-based sources like algae, flaxseeds, or chia seeds. Algae oil is particularly significant as it provides both DHA and EPA, making it a superior option for vegans who may struggle to get these nutrients from their diet.
Benefits of Vegan Omega-3 Supplements:
Sustainability: Algae farming is environmentally friendly compared to fish oil production.
Purity: Algae oil is free from ocean contaminants such as mercury and heavy metals.
Allergen-Free: Ideal for individuals with fish allergies or sensitivities.
Look for brands that explicitly mention "vegan omega-3 capsules" on their labels to ensure they meet your dietary needs.
Kosher Omega-3 Supplements
kosher omega 3 supplements are produced according to Jewish dietary laws and certified by recognized kosher organizations. These products cater to those who observe kashrut and require supplements free from non-kosher ingredients, such as shellfish or certain animal derivatives.
Features to Look For:
Certification from a reputable kosher agency.
Non-animal-based sources, such as algae or flaxseed oil.
Kosher supplements often overlap with vegan or vegetarian products, making them versatile for multiple dietary requirements.
Vegetarian Omega-3 Capsules
For vegetarians who do not consume meat or fish but include dairy and eggs, vegetarian omega 3 capsules derived from plant-based sources are an excellent option. These capsules often contain ALA from flaxseeds or chia seeds, or DHA and EPA from algae.
Why Choose Vegetarian Omega-3 Capsules?
Perfect for supplementing plant-based diets.
Affordable and widely available.
Suitable for individuals who may not follow a strict vegan lifestyle but avoid fish-based products.
Conclusion
Whether you're vegan, vegetarian, or require kosher-certified supplements, there are plenty of options available to meet your dietary and health needs. Vegan omega-3 supplements derived from algae provide high-quality DHA and EPA, while kosher omega-3 supplements cater to religious dietary requirements. For those following a vegetarian diet, vegetarian omega-3 capsules offer an excellent way to include these essential fatty acids without compromising on values or taste preferences.
1 note
·
View note
Text
What Is Hemp?
It’s A Trillion Dollar Cash Crop.
youtube
Hemp is a name given to a strain of the cannabis plant.
Hemp is a name given to cultivars of the cannabis plant (Cannabis sativa) that have been selected over many generations for fiber and seed production. Most hemp cultivars contain less than 1.5% THC, a narcotic compound that has the potential for abuse in high concentrations. Cannabis sativa cultivars selected and developed for their drug properties, referred to as marijuana, or dagga, can have a THC content of 3%-25%. Hemp is a bast fiber, producing its fibers in the stalk similar to flax, kenaf, and sun hemp.
Multiple Uses
Hemp fiber and seed are used to produce a wide range of commodities including food and beverage products, fiberboard, insulation, paper, composites, textiles, carpets, animal bedding and feed, cosmetics, body-care products, soaps, paints, fuels, and medicines.
Hemp Seed Food and Beverage Products
Hemp seed contains about 25% protein, 30% carbohydrates, & 15% insoluble fiber. Hemp seed is reported to contain more easily digestible protein than soybeans. Hemp seed contains all 8 amino acids essential to human nutrition. Hemp seed is high in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, carotene, sulfur, iron and zinc, as well as Vitamins A, E, C, B1, B2, B3, and B6.
Hemp seed imported into the United States or Canada must be steam sterilized at between 180 degrees F and 212 degrees F for 15 minutes to prevent sprouting. Many US facilities receive imported viable seed under customs bond, steam it, and release it to the consignee or customer with a Certificate of Sterilization.
Hemp food and beverage products include hemp oil and seed, flour, pasta, cheese, tofu, salad dressings, snacks, sweets, hemp protein powders, soft drinks, beer, and wine. Hemp beer can be made from the seed, flowers, sprouts, and seed cake that is a by-product of oil pressing. Hemp beer is produced and sold in Europe and the United States of America.
Hemp Oil
Hemp seed is 25% to 35% oil, and is one of the oils lowest in saturated fats (8%). Hemp seed oil is the richest source of polyunsaturated essential fatty acids (80%). Hemp seed oil is the only common edible seed oil containing Omega-6 Gamma-Linolenic Acid. Hemp seed oil is very fragile and not suitable for cooking.
Pressed hemp seed oil must be bottled immediately under oxygen-free conditions, and must be refrigerated in dark, airtight containers.
Fiberboard
Hemp fiberboard tested by Washington State University Wood Materials and Engineering Laboratory proved to be two and one half times stronger than wood MDF composites, and the hemp composite boards were three times more elastic.
Hemp herds can be used in existing mills without major changes in equipment. Russia, Poland and other Eastern European countries already manufacture composite boards from hemp and other plant materials.
Pulp and Paper
The major use of hemp fiber in Europe is in the production of specialty papers such as cigarette paper, archival paper, tea bags, and currency paper. The average bast fiber pulp and paper mill produces 5,000 tons of paper per year. Most mills process long bast fiber strands, which arrive as bales of cleaned ribbon from per-processing plants located near the cultivation areas.
Composites
Until the 1930’s, hemp-based cellophane, celluloid and other products were common, and Henry Ford used hemp to make car doors and fenders. Today hemp herds can be used to make new plastic and injection-molded products or blended into recycled plastic products. Hemp fibers are introduced into plastics to make them stiffer, stronger and more impact resistant. Hemp plastics can be designed that are hard, dense, and heat resistant, and which can be drilled, ground, milled, and planed.
Hemp plastic products currently made include chairs, boxes, percussion instruments, lampshades, bowls, cups, spectacles, jewelry, skateboards, and snowboards.
Hemp Animal Care
Hemp horse bedding and cat litter are produced and sold in Europe. After oil is extracted from the hemp seed, the remaining seed cake is about 25% protein and makes an excellent feed for chicken, cattle, and fish. Chickens fed hemp seed on a regular basis have been found to produce more eggs, without the added hormones used in most poultry plants.
Fuels
Hemp seed oil can be combined with 15% methanol to create a substitute for diesel fuel which burns 70% cleaner than petroleum diesel. Hemp stalks are rich in fiber and cellulose, making them conducive for conversion into ethanol and methanol fuels that have a higher octane than gasoline and produce less carbon monoxide. These biomass fuels are also free from sulfur, and do not require the addition of lead and benzene used to boost octane and improve engine performance in fossil fuels. Ethanol holds condensation, eliminating oxidation and corrosion, and is reported to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by more than 30%.
Hemp has been studied in Ireland as a biomass fuel to generate electricity. Hemp has been reported to yield 1000 gallons of methanol per acre year. Hemp stalk can be converted to a charcoal-like fuel through a thermochemical process called pyrolysis. Henry Ford operated a biomass pyrolitic plant at Iron Mountain, Michigan in the mid-20th.
Paints and Varnishes and Binders
Until the 1930's, most paints were made from hemp seed oil and flax seed oil. Hemp oil makes a durable, long lasting paint that renders wood water-resistant. Hemp herds have the potential to make glues for composite construction products that are non-toxic and superior to binders currently used. With this technology, industry can produce composite products where all components are derived from hemp.
Markets for Hemp Pulp
Some paper manufacturers already have the equipment to process decorticated hemp fiber into paper. The leading European supplier of non-wood pulp, Celesa, currently produces about 10,000 tons per year of pulp from hemp. The use of hemp pulp in blends with recycled fiber of other non-wood fibers is growing. Tests by several European pulp and paper producers suggest that hemp pulp may replace cotton cost effectively in several specialty paper applications.
Potential Markets for Medical Application of Low-THC Hemp Cultivars
Many cannabis medicines have been produced using cannabis cultivars high in THC, and there has been medical research into cannabis that is low in THC and high in CBD. CBD is a cannabinoid that does not have many of the psychoactive effects associated with THC. CBD has been used to treat the following medical conditions: epilepsy, dystonic movement disorders, inflammatory disorders, pain, chronic insomnia, chorea, cerebral palsy, and Tourette's syndrome. According to a July 1998 report by the National Institute of Health, CBD may hold promise for preventing brain damage in strokes, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and even heart attacks and has been found to prevent brain cell death in an experimental stroke model.
Please share this with your friends.
youtube
#hemp farming#hemp foods#hemp fuel#industrial hemp#hemp plastic#hemp paper#hemp fibers#hemp seeds#hemp prohibition
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Modern science confirms that dairy fats, which are naturally high in saturated fat and low in polyunsaturated fats, are beneficial to human health. But Big Dairy has developed “rumen-protected fats” that bypass the cow’s natural digestive processes, which increases polyunsaturated fatty acid content and decreases beneficial saturated fats by up to 20%.
by Dr. Joseph Mercola
February 6, 2025
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
An unintended consequence of partial hydrogenation of the alkene groups in polyunsaturated oils is the isomerisation of a small proportion of the cis alkenes to trans alkenes. These are known as trans-fats and are of concern as they are believed to increase the risk of coronary heart disease. These trans-fats do occur naturally, although only to a small extent. Canola oil naturally has a relatively high level of trans-fats, but most other natural oils have very little trans-fat. Lamb and mutton also naturally contain moderate levels of trans-fats.
"Chemistry" 2e - Blackman, A., Bottle, S., Schmid, S., Mocerino, M., Wille, U.
#book quote#chemistry#nonfiction#textbook#unintended consequences#hydrogenation#alkene#polyunsaturated#oils#isomerization#cis#trans#trans fat#coronary heart disease#risks#canola oil#natural oil#lamb#mutton
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Unveiling the Health Benefits of Cashew Nuts: A Nutritional Treasure Trove
Cashew nuts, commonly referred to as "Kaju" in various regions worldwide, are renowned not only for their delightful taste but also for the plethora of health benefits they offer. With their nutrient-rich composition and potential positive impact on health, cashews have solidified their status as a versatile dietary staple. In this comprehensive analysis, with guidance from PTI Nuts And Spices, we'll explore the multifaceted advantages of incorporating Cashew Nuts into your diet.

Nutritional Profile:
Cashew nuts boast an impressive array of nutrients, contributing significantly to overall well-being. Serving as an excellent source of healthy fats, including beneficial monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats crucial for heart health, cashews are also packed with protein, dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a wholesome choice for snacks or meal accompaniments.
Heart Health:
Among the multitude of benefits associated with cashew nuts, their positive impact on heart health is particularly noteworthy. The presence of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats in cashews has been linked to lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides, along with an increase in HDL (good) cholesterol. This favorable lipid profile helps reduce the risk of heart disease and promotes overall cardiovascular well-being.
Weight Management:
Despite their calorie density, Cashew Nuts can be beneficial for weight management when consumed judiciously. Their unique blend of protein, healthy fats, and dietary fiber promotes feelings of fullness and satiety, effectively curbing cravings and preventing overeating. By incorporating cashews into your diet, you can effectively regulate appetite and progress towards weight loss or maintenance goals.

Bone Health:
Cashews emerge as champions in promoting bone health, thanks to their abundance of essential minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium. These minerals are instrumental in bone formation, density, and overall skeletal integrity. Regular consumption of cashew nuts may significantly contribute to improved bone density and reduced susceptibility to osteoporosis and fractures, especially as individuals age.
Antioxidant Benefits:
Cashew nuts exhibit remarkable antioxidant properties, characterized by vitamins E and K, as well as minerals like copper and zinc. Antioxidants play a crucial role in neutralizing harmful free radicals within the body, thereby reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage. By combating oxidative stress, cashews have the potential to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
Hair and Skin Health:
The abundance of vitamins and minerals in cashew nuts, particularly copper and zinc, plays pivotal roles in maintaining healthy hair and skin. Copper aids in melanin production, responsible for hair and skin coloration, while zinc supports collagen synthesis, wound healing, and skin integrity. Incorporating cashews into your diet can contribute to stronger, shinier hair and clearer, more radiant skin.
Blood Sugar Control:
Emerging research suggests that integrating cashew nuts into a balanced diet may offer benefits for blood sugar control, particularly in individuals with or at risk of type 2 diabetes. The combination of protein, healthy fats, and dietary fiber in cashews helps regulate sugar absorption into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood glucose levels. This may reduce the risk of insulin resistance and promote improved glycemic control over time.
Digestive Health:
Cashews are valuable allies in promoting digestive wellness, thanks to their high fiber content. Dietary fiber adds bulk to stool, softens it, and facilitates regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and supporting overall digestive health. By incorporating cashews into your diet, you can ensure adequate fiber intake and cultivate a healthy gut microbiome.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations:
Despite their numerous health benefits, it's essential to consume cashew nuts in moderation due to their calorie density. Excessive intake may lead to weight gain and other adverse effects. Additionally, individuals allergic to cashews or other tree nuts should exercise caution and avoid consumption to prevent allergic reactions.
Incorporating Cashew Nuts Into Your Diet:
The culinary versatility of cashew nuts offers a plethora of delicious options for integration into a nutritious diet. Whether enjoyed raw or roasted as a convenient snack, added to salads, stir-fries, or grain bowls for extra flavor and texture, or blended into creamy sauces and dressings, cashew nuts enhance the culinary experience. Cashew butter, a delightful alternative to peanut butter, provides versatility as a spread or dip.
Conclusion:
In summary, cashew nuts emerge as nutritional powerhouses, offering a wealth of health benefits beyond their delicious taste. From supporting heart health and aiding in weight management to fortifying bones and enhancing hair and skin health, cashews contribute to overall well-being. By incorporating cashew nuts into your diet in moderation, you can enjoy their exquisite flavor while reaping the diverse rewards they offer. Let PTI Nuts And Spices guide you on the journey to optimal health through the inclusion of Cashew Nuts in your diet.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Peanuts: A nutrient-rich and versatile snack with many health benefits

Peanuts are a type of legume that is native to South America. They are one of the most popular snack foods in the world, and for good reason. Peanuts are packed with nutrients and have been linked to a number of health benefits.
**Nutritional value of peanuts:**
Peanuts are a good source of:
* Protein: Peanuts are a good plant-based source of protein, making them a good choice for vegetarians and vegans. One ounce of peanuts contains approximately 6 grams of protein.
* Healthy fats: Peanuts contain mostly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are good for heart health. Monounsaturated fats can help to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and raise HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Polyunsaturated fats can also help to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
* Fiber: Peanuts are a good source of fiber, which can help to keep you feeling full and satisfied. Fiber can also help to improve digestion and regularity. One ounce of peanuts contains approximately 3 grams of fiber.
* Vitamins and minerals: Peanuts contain a variety of vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E, magnesium, potassium, and niacin. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that can help to protect cells from damage. Magnesium is important for muscle and nerve function. Potassium is important for blood pressure regulation. Niacin is important for energy metabolism and skin health.

**Health benefits of peanuts:**
Peanuts have been linked to a number of health benefits, including:
* Reduced risk of heart disease: The healthy fats and antioxidants in peanuts can help to lower cholesterol levels and improve blood vessel health. A study published in the journal *Circulation* found that people who ate peanuts or peanut butter at least five times per week had a 14% lower risk of death from heart disease than those who did not eat peanuts or peanut butter.
* Improved blood sugar control: Peanuts have a low glycemic index, meaning they do not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. This makes them a good snack option for people with diabetes or prediabetes. A study published in the journal *Diabetes Care* found that people with type 2 diabetes who ate peanuts or peanut butter as part of a healthy diet had lower blood sugar levels and less insulin resistance than those who did not eat peanuts or peanut butter.
* Weight management: Peanuts are high in protein and fiber, both of which can help you to feel full and satisfied. This can lead to reduced calorie intake and weight loss over time. A study published in the journal *Obesity* found that people who ate peanuts or peanut butter as part of a low-calorie diet lost more weight and body fat than those who did not eat peanuts or peanut butter.
* Cancer prevention: Some research suggests that peanuts may help to protect against certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer and breast cancer. A study published in the journal *Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention* found that people who ate peanuts or peanut butter at least twice per week had a 27% lower risk of developing colon cancer than those who did not eat peanuts or peanut butter. A study published in the journal *Breast Cancer Research and Treatment* found that women who ate peanuts or peanut butter at least five times per week had a 22% lower risk of developing breast cancer than those who did not eat peanuts or peanut butter.

**How to incorporate peanuts into your diet:**
Peanuts can be eaten raw, roasted, or salted. They can also be used to make peanut butter, peanut oil, and other peanut products. Peanuts can be incorporated into a variety of dishes, including salads, soups, stews, and stir-fries.
Here are some tips for incorporating peanuts into your diet:
* Add a handful of peanuts to your breakfast cereal, oatmeal, or yogurt.
* Spread peanut butter on whole-wheat bread or crackers for a healthy snack or sandwich.
* Add peanuts to salads, soups, stews, and stir-fries.
* Snack on peanuts instead of unhealthy snacks like chips or candy.
* Make your own peanut butter at home using raw peanuts and a blender.
**Conclusion:**
Peanuts are a nutritious and versatile snack food with many health benefits. They are a good source of protein, healthy fats, fiber, and vitamins and minerals. Peanuts have been linked to a number of health benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, improved blood sugar control, weight management, and cancer prevention. Peanuts can be easily incorporated into a variety of dishes, making them a healthy and convenient food choice for everyone.
#healthy#health#help#healthcare#headlines today news#headline news#self healing#heartbreak#healthy diet#business news#breaking news#blog#latest news#natural remedy#nutritious#world news#nature#news#money#beautiful#beauty#low cal diet#weight loss diet#life#love#long reads#liveblogging#literature#journal#gorgeous
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thank you for the recipe @crows-and-crowns 🖤
Ingredients
2 cups red lentils soaked, and drained*
½ cup whole psyllium husks (or 1 cup flaxseed meal)
2 tablespoons neutral flavored oil (optional)
½ cup water (use ¼ cup water for flaxseed meal)
¾ teaspoon salt or to taste
1 ¼ teaspoons baking soda
1 tablespoon apple cider vinegar
2 teaspoons sesame seeds for garnish (optional)
Instructions
Rinse the lentils: Transfer the red lentils to a medium bowl and add water to cover. Use your hands to rinse them thoroughly. Drain the lentils into a mesh sieve and discard of the cloudy water.
Soak the lentils: Rinse the bowl. Return the lentils back to the bowl and add water to cover by about 2 inches high. Soak them for at least 3 hours, but preferably overnight before draining. Discard of the water.
Preheat the oven to 360ºF.
Process: Transfer the lentils, psyllium husk, oil, water, salt, and baking soda to the canister of a food processor. Then pour the apple cider vinegar directly onto the baking soda. The bubbling reaction between these two ingredients is what allows for the dough to rise, so it is important to move quickly from this point on. Process the ingredients until just combined.
Remove the lentil dough from the canister and transfer it to a cutting board. Roll the dough into a ball and divide it into two roughly equal parts. Shape both parts in a log, and cut each log into 4 roughly equal parts for a total of 8 pieces. (Use a sharp knife or a bench scraper.)
Roll each piece into a ball and transfer them to a large nonstick baking sheet, leaving about 2 inches between each ball. Sprinkle sesame seeds onto each ball, if using.
Bake for about 20 minutes on the middle rack, or until golden brown on top. Set aside to cool for at least 10 minutes before slicing.
Notes
For 4 rolls: Simply half the quantities listed in the recipe. It works equally well.
To make vegan lentil bread with flaxseed meal, use 1 cup flaxseed meal and ¼ cup water. The dough will be sticky but don't panic. It works great. Bake at 360ºF for about 17 minutes, or until golden brown. Use golden flaxseed meal for a milder flavor.
*Soak rinsed lentils in water to cover by about 2 inches high for at least 3 hours, but preferably overnight. Drain and rinse.
Use psyllium husks, and not psyllium powder.
Make sure your baking soda is not expired or they will not rise well.
Storage: Store any remaining rolls in an airtight container for up to 2 days. Or freeze in a freezer-safe container for up to 3 months.
Nutrition
Calories: 282kcal | Carbohydrates: 33g | Protein: 15g | Fat: 11g | Saturated Fat: 1g | Polyunsaturated Fat: 6g | Monounsaturated Fat: 3g | Trans Fat: 0.01g | Sodium: 180mg | Potassium: 594mg | Fiber: 19g | Sugar: 1g | Vitamin A: 18IU | Vitamin C: 2mg | Calcium: 77mg | Iron: 5mg
4 notes
·
View notes