#cryptobiosis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: tardigrades
Last week on Wet Beast Wednesday I covered the largest animals to ever exist on our planet. This week I'm going to pull a full 180 and cover the smallest animals yet on this series. Meet the tardigrade, the internet's favorite micro-animal the is said to be basically immortal. How true is that? Let's see.

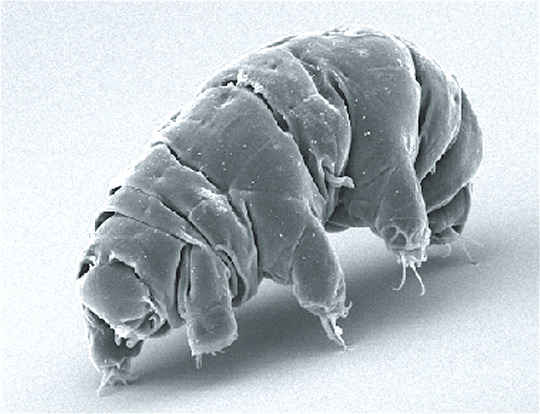
(Image: an electron microscope image of a tardigrade. It looks a lot like a potato with eight stubby legs tipped with long claws. At the front is a small, circular mouth. It has no other discernable features. In the background are bits of plant matter that look like seaweed at this scale. End ID)
The tardigrades are 1,300 known species (and probably a lot of unknown ones too) in the phylum Tardigrada. They are also part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa, which are animals that grow by molting their outer cuticles or exoskeletons. In particular, the tardigrades are believed to be a sister group of the arthropods, the group that contains crustaceans, insects, isopods, and a lot of other things. Tardigrades are truly tiny, the largest species reaching a whopping 1.5 millimeters in length, though most species reach no more than 0.5 mm. They have round, segmented bodies with four pairs of legs that end in either claws or suction discs. The body segments consist of a head, three body segments with a pair of legs each, and a caudal segment with the final pair of legs. The first three legs are used for movement while the final pair points backwards and is used for grabbing onto substrate. All of the body segments except for the final one correspond to segments found in the head section of insects. Tardigrades are missing many hox genes, genes that direct the body plan during development. Their ancestors may have had a body plan more similar to insects, but the loss of the hox genes has compressed them into walking heads with a bit of butt. The mouth is tubular and sucks in food. In the mouth are stylets, needle-like structures used to pierce food objects. Once food is drawn into the mouth, a structure called the buccopharyngeal apparatus activates. This is a combination of spines and muscle that acts like an inner jaw that pulls food into the digestive tract. The buccopharyngeal apparatus is distinct enough to be used as a major identifying feature between species. Tardigrades are translucent and many images you've seen of them have false color to show the details or are 3D models based on scanning electron microscope imagery of them. Tardigrades molt their exoskeletons multiple times (up to 12) during their lifecycle. Some species are unable to poop normally and instead all their waste is discarded during the molt. It was formerly believed that tardigrades could exchange genes with each other without mating, a process called horizontal gene transfer that is seen in bacteria, archaea, and other micro-organisms. It has since been discovered that while still capable of horizontal gene transfer, it is quite a bit rarer in tardigrades than we thought.

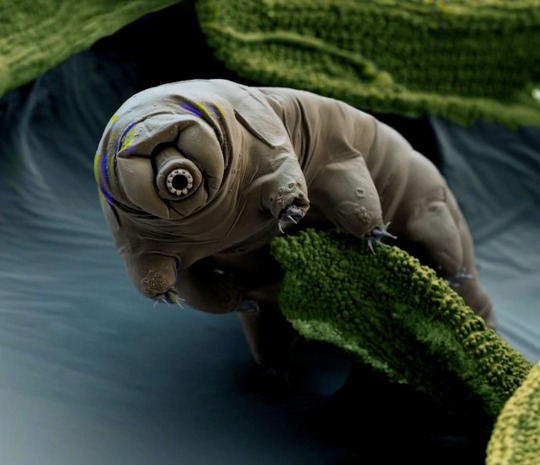
(Image: an electron microscope image of a tardigrade standing on a bit of plant matter. This one has a closed mouth with a ring of triangular tooth-like structures. It also has two simple eyes that look like black dots. End ID)
The name "tardigrade" means "slow walker", which is fitting as, despite their eight legs, tardigrades have a slow and awkward gait. This is the result of their legs being unjointed, only able to pivot at their connection to the body. Their gait has been compared to that of bears, hence why they are often called water bears and their discoverer, Johann August Ephraim Goeze, called them "kleiner wasserbär", meaning "little water bear". Tardigrades are found worldwide and have inhabited virtually every habitat, from the tops of mountains to the deep sea, from hot springs to the antarctic, from freshwater to saltwater. The one thing they have in common is a need to stay wet. Tardigrades can survive out of water as long as they can stay moist and are often found in mosses, hence another common name: moss piglets. The majority either eat plants or bacteria, but some will feed on smaller tardigrades or other micro-animals. Their famous survivability makes it easy for tardigrades or their eggs to be carried to new habitats by larger animals or other phenomena. Tardigrades are one of the first micro-animals to colonize a new habitat and they are a pioneer species, the first species to colonize a new environment and whose presence makes that environment fore suitable for other species to follow. Tardigrades are a major food source to other micro-animals and larger organisms. Most species have distinct males and females, though a few reproduce through parthenogenesis. In most cases, molting female will lay her eggs in her shed cuticle and males will them fertilize them. Other species have a form of internal reproduction. Males and females will court each other before mating and females will usually allow multiple males to fertilize her eggs. Female tardigrades are typically larger and more abundant than males. Eggs can take up to 14 days (species dependent) before hatching. All tardigrades of the same species have the exact same number of cells as each other. They are also born with the same number of cells they will have as an adult. Their growth is driven by enlargement of the existing cells rather than cellular reproduction making new cells. The lifespan ranges between a few months to a few years, depending on species.
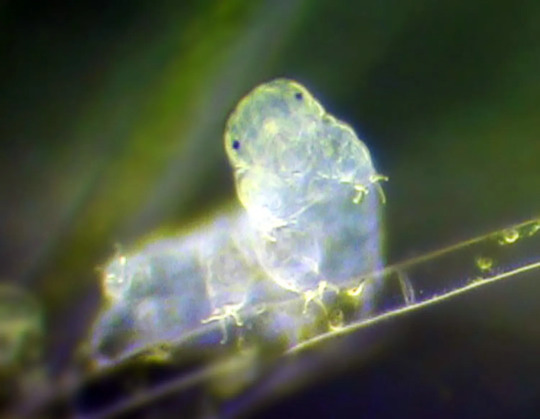
(Image: a color photo of a tardigrade. It is a pale, translucent white, making it hard to make out details. Its body is curved, with the front end pointing at the camera. It has two simple eyes. End ID)
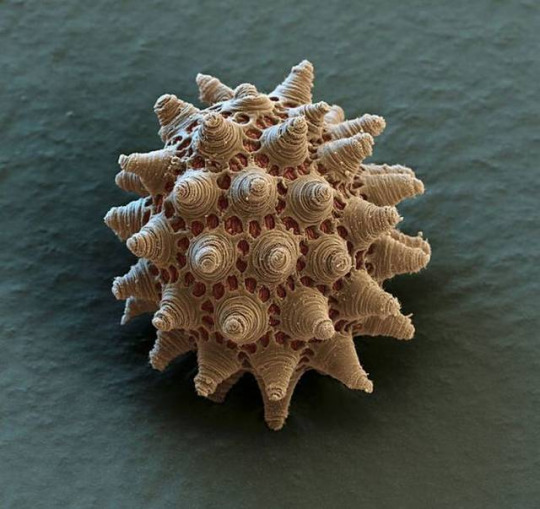
(Image: an electron microscope image of a tardigrade egg. It is round but covered in small pores and conical structures. End ID)
The most famous feature of tardigrades is their legendary durability. It is commonly said that tardigrades can survive just about anything (except for the things that are actually trying to kill them. They are prey to a lot of species after all). Among the things they can survive is extreme heat, extreme cold, dehydration, extremely high and low pressure, exposure to ionizing radiation (that's the scary kind), low oxygen environments, environmental toxins, heavy impacts, and the vacuum of fucking space. While the can survive in extreme conditions, tardigrades are not considered extremophiles. True extremophiles thrive in extreme environments and are negatively impacted by leaving them. Tardigrades can survive in extreme environments, but are negatively impacted and can't survive as well there as they can in less extreme places. The main trait that has allowed tardigrades to survive all five mass extinctions in history is cryptobiosis. Cryptobiosis is the rare ability for an animal to enter a state of dormancy where their metabolic processes come to an almost complete stop. While in cryptobiosis, metabolic activity drops to 0.01% normal and water content drops to 1% normal. In this state, the tardigrade is called a tun. Tardigrades usually enter cryptobiosis in response to arid conditions. One experiment showed that a species of tardigrade could last for at least 30 years in this state and return to normal lifestyle functions when exposed to water. Tardigrades will also enter cryptobiosis in response to low oxygen, toxic chemical exposure, increased or decreased temperature, and excessive salt content in the water. Tardigrades also show extreme resistance to both high and low pressure. They can live in 0 atmospheres of pressure and some species can survive up to 6,000 atmospheres, more than double the pressure at the bottom of the Marianas trench. More interesting is their ability to survive dangerous radiation. They can survive 1,000 times the dose of gamma radiation that humans can. Early tests focused on tardigrades in cryptobiosis and concluded that the extremely low water content of a cryptobiotic tardigrade doesn't leave much opportunity for the radiation to react with the animal. However it was later found that active and fully hydrated tardigrades are still considerably resistant to radiation. Studies into this resistance indicate that tardigrades can very efficiently repair damaged DNA and have unique proteins called Dsup that provides additional protection. Dsup introduced to human cells has provided additional protection against x-rays.
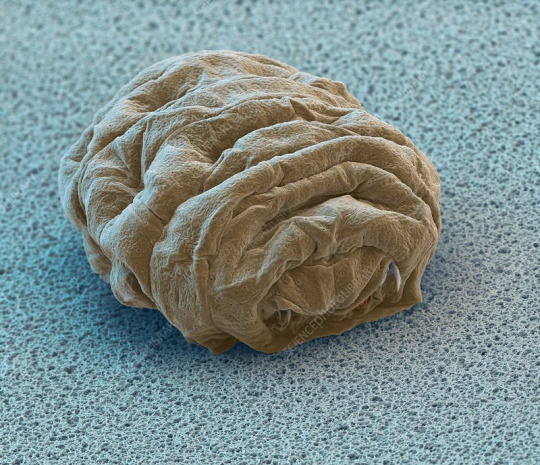

(Image: an electron microscope image of a tun - a tardigrade in cryptobiosis. It is smaller and very wrinkly, with the legs and mouth retracted into the body. End ID)
Tardigrades were the first animals to be exposed to the vacuum of space. They were exposed for 10 days, some in a state of cryptobiosis at the time of exposure and some still active. It was found that they were able to survive the vacuum when shielded from the sun's ultraviolet radiation, with those already in cryptobiosis doing better. Upon being rehydrated, many were able to resume normal life functions and successfully reproduce, though others died after being rehydrated. Those that were exposed to UV radiation fared much worse, with only a few hydrated individuals surviving. The individuals in cryptobiosis had a lower survival rate when exposed to UV than those not exposed to UV and were less successful at reproducing afterwards. Studies of tardigrade's space survival abilities and resistance to radiation could go a long way in helping human space travel. One of the largest dangers of space travel is that space is full of nasty radiation from the sun that Earth's magnetic field protects us from. Some scientists speculate about the possibility of accidentally seeding other planets or moons with tardigrades or other space-resistant organisms. This is a problem because introducing Earth life to other world has the potential to damage any native ecosystems and if we find life in space in the future we don't want to have to figure out if it's something we accidentally put there. While tardigrades could likely survive on other planets, they would eventually die without a food source. Some sources reported that tardigrades may have colonized the moon after an experiment with them crashed. Unfortunately, the moon is not crawling with tardigrades now. It's way too dry for them to exit cryptobiosis even if they survived the crash, which they probably didn't.

(Image: art of a tardigrade floating in the vacuum of space. End ID. Source: University of California - Santa Barbara)
#wet beast wednesday#tardigrade#water bear#moss piglet#micro animal#microbiology#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#informative#science#space#astrobiology#radiation#cryptobiosis#tun#image described
197 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frozen Worm continues to live after 40,000 years of Cryptobiosis | Earth.com
https://www.earth.com/news/frozen-worm-comes-back-to-life-after-46000-years/ “Life – uhm – finds a way.” (Jeff Goldblum as “Malcolm” in Jurassic Park) // In a recent breakthrough, researchers determined that a worm which had been frozen for about 46,000 years had survived and remained alive.Dr. Philipp Schiffer, a group leader in the Institute of Zoology at the University of Cologne, and his…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text

TSRNOSS, p 816.
#capillary damage produced by glucose#longevity of women#superoxide dismutase#DNA repair#toxins#malaria#Red Tide#herbivores#cryptobiosis#spores#lngfish#Brownian motion#thermal conductivity of ice#satyendra sunkavally#theoretical biology#manuscript#cursive handwriting#notebooks#diaries
0 notes
Text
youtube
#Meet the incredible tardigrades#the microscopic marvels of resilience! 🌟 In this video#we dive deep into the unique characteristics that make these tiny creatures stand out in the natural world. Discover how tardigrades surviv#' allowing them to endure the harshest environments imaginable. From the depths of the oceans to the highest mountains#learn how these amazing organisms thrive everywhere on Earth. Don't forget to like and share this video with science enthusiasts!#Tardigrades#MicroscopicMarvels#ExtremeSurvivors#Cryptobiosis#scienceexplained Tardigrades: Microscopic marvels#these eight-legged wonders boast near-mythical resilience. They can withstand radiation hundreds of times higher than what would kill a hum#entering a dormant state called a tun to wait out the danger Stop Googling#Deep dives#explained simply#start learning. Smash that subscribe button and level up your knowledge! and Join our community of curious minds. Let's explore knowledge t#natures#life#marvels#microscopic#tardigrades The clock is ticking to join the knowledge revolution Like this video? Hit subscribe and join the adventure!#Youtube
0 notes
Text
Cryptobiosis - Humanity's hope in climate crisis, space travel?
A recent paper on a roundworm that survived 46,000 years frozen in ice, has renewed interest in the field of cryptobiosis that has the potential to change the galaxy writes Satyen K. Bordoloi. Read More. https://www.sify.com/science-tech/cryptobiosis-humanitys-hope-in-climate-crisis-space-travel/
0 notes
Text
Thank you Op, I would love to live in this forest...
Just beware of the Tardigrades...
aka WATER BEARS!!

Aka MOSS PIGLETS!!

But also, this:
Cryptobiosis..god damn it, I love science.


Wouldn't you want to live in a forest of common haircap moss? 🌱

#moss forest#beware of the moss bears#tardigrades#cryptobiosis#cryptids#moss#science is awesome#goblincore#gremlincore#crowcore#ravencore#cryptidcore#nature
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tired of gender? Try becoming a tardigrade today!

·They can't die from hypothermia!
·They survive without food or water!
·Actually, they're almost immortal
·And they can even survive without oxygen.
·Can the terfs do that? I don't think so.
·Also they're cute and everyone loves them. Especially people who study quantum physics.
See, being a tardigrade is the coolest shit ever. So why are you still hesitating to reject your mortal flesh?
#Tardigrades#They're just amazing little things from the unknown side of the world#Also they can make quantum connections in cryptobiosis#Biophysics facts#Don't mind me I just post stupid stuff at 3 am
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Australian Pokemon - new evolutions
Another set of my Fakemon designed for my original Goorda Region based on a combination of Australia and Aotearoa/New Zealand. This time I'm designing new evolutions for older Pokemon, plus a bonus convergent line. Links to previous entries below.

Factortry, the Industry Pokemon, fire/steel type, an evolution of Torkoal. It started eating metal as well as coal and its internal heat melted the metal into slag. The slag has started covering its shell, increasing its defense, but the smoke it releases is toxic. During the industrial revolution, Factortry were used for metal refining, but the practice was banned after it produced too much pollution.
Factortry is based on a coal-burning refinery and industrial age factories, with all the pollution that came with them. Industrial pollution has been reduced thanks to regulations, such as the ones that banned Factortry for use in refining. Its name comes from "factory" and "tortoise".

Castla, the Coral Pokemon, water/rock type, an evolution of Corsola. Its branches have grown together into a fortress-like structure that is virtually unbreakable. It has a symbiotic relationship with small Pokemon that live in its fortress. It defends them from predators while they help clean it. It needs clean water to live in and the populations has dropped considerably due to pollution.
I figured that if Galarian Corsola gets an evolution, the original should too. Like the original, this Castla is based on staghorn coral, but also castles. A castle is a type of barrier and Australia famously has the great barrier reef. Reefs are famous as habitats and are essentially ecosystems based on symbiosis, just like Castla. Like the great barriier reef, pollution and global warming is signaling hard times ahead for poor Castela. Its name comes from "Corsola" and "Castle"

Glideon, the Sugar Glider Pokemon, flying type, an evolution of Eevee. Glideon live in trees and glide around their rainforest homes on flaps of skin between their legs. Using their tails as rudders, Glideon are very proficient gliders and they will perform aerial tricks to impress each other and attract mates. Trainers should be aware that Glideon are highly social and need a diet high in sugar.

Wormeon, the Velvet Worm Pokemon, Bug type, an evolution of Eevee. Wormeon are reclusive beings that live deep in the forest and are rarely seen. Their fuzzy pelt is so soft people can get addicted to petting them. Wormeon bodies are soft and fragile, so they defend themselves by spitting out sticky slime and powerful acid.
If Gamefreak won't make new Eeveeloutions then dammit I will. Glideon is based on sugar gliders and Wormeon is based on velvet worms. Sugar gliders are a type of possum that glide around on skin flaps called patagia and have a very fruit-heavy diet. They are found in Australia and have been exported as exotic pets. Unfortunately, the biggest provider of sugar gliders is pretty unethical. Velvet worms are members of a unique phylum and can be described as worms with legs. They are very soft, hence the name, and spit slime for offense and defense like Wormeon. There are many species of velvet worm in Aotearoa. I may end up revising the Wormeon design as I'm not totally sold on it. I don't think it looks enough like an Eevee for my liking.

Frozosis, the Cryptobiosis Pokemon, ice type. It was once thought to be a regional variant of Solosis, but is now known to be unrelated. These strange Pokemon are found frozen under the ice on high mountains, where the cold keeps them in stasis. Scientists believe they froze themselves possibly millions of years ago to survive a mass extinction and are only now beginning to thaw out. Those who thaw out often roll down the mountains to be found in the lowlands.

Frozosis evolves to Frozuion, the Cryptobiosis Pokemon, ice type. Despite being frozen to the point where biological activity should cease, Frozuion are still capable of moving and feeding. Scientists suspect they are in a sleepwalking-like state of half-stasis and that if one were to fully thaw out, it would have mysterious powers, though nobody knows how to do it safely.

Frozuion evolves to Reunifroz, the Cryptobiosis Pokemon, ice type. They have some strange power that allows them to levitate and act alive, despite being frozen so cold that no conventional life could exist. Scientists are unsure of what would happen if one were to thaw out as they are so cold even molten magma cannot warm them. It is possible that a thawed Reunifroz would have powers unlike any other Pokemon.
The Frozosis line is convergent to the Solosis line. They are based on cryptobiosis, a state of near-death stasis that certain living things can enter to survive extreme conditions. The Solosis line are based on embryo development and the Frozosis line are based on frozen embryos. The first successful pregnancy from a frozen embryo happened in Australia. Because it's frozen and in cryptobiosis, the cell in the Frozosis line doesn't develop like the one in the Solosis line. Frozuion and Reunifroz are based on micro-animals. Some species of micro-animal can enter cryptobiosis to survive changing conditions. Frozuion is based on a tardigrade (the poster child for cryptobiosis) while Reunifroz is based on a rotifer. Their names come from "frozen" and the Solosis line's names.
Previous entries in this series. Misc 4, misc 3, single-stages, non-natives, regional standards, creepy lines, regional variants, birds, early-game standards, misc 2, misc 1, starter variants, starters
#pokemon#fakemon#original pokemon#oc pokemon#australia#aotearoa#new zealand#new pokemon evolutions#torkoal#corsola#eevee#eeveelution#convergent pokemon#tortoise#factory#industrial revolution#coral#coral reef#great barrier reef#sugar glider#velvet worm#cryptobiosis#frozen embryo#tardigrade#rotifer
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aliens are floored by tardigrades
Life is pretty resilient. It has to be, especially if the rest of the Galaxy thinks we're from a Deathworld. In comparison then, if their planets are not as demanding, would life there ever be under enough pressure to survive to go to the extreme lengths that some Earth creatures do? I think one of the most profound things aliens might learn from Earth and Humanity is just how powerful life itself can be.
That itself could shake their understanding of themselves - a billion year old civilization could never even conceive of a thing we accept as simple fact, ushering a revolution in thinking not seen in eons.
___________________________
The Galactic Coalition scientists are busying themselves with obtaining, analyzing, categorizing, and integrating the libraries of information Humanity has brought with them as they incorporate into the greater space faring matrix of civilizations.
A good grasp of Physics, though lacking in certain fields for now; unmatched Engineering doctrines, they really do think of everything, although, perhaps, better to say - they really do attempt everything, then take notes and improve for the next attempt.
Chemistry is another fine addition to the collective knowledge base, a disproportionate part of the catalogue is comprised entirely of explosive reagents and combinations - always good to know more about what NOT to do.
And Biology. Oh boy. What a chaotic but beautiful but also disturbing mess. Life on most planets has a long period of just chugging along, surviving as best it can, until eventually something has the bright idea to evolve the ability to have bright ideas. Then in almost no time at all (on a cosmic scale) a dominant intelligence emerges and civilization alongside it, and in the blink of an eye it finds itself exploring the stars.
A similar pattern happened on Earth, but interrupted alarmingly often by utter catastrophes. Humans call them Mass Extinctions. It is exceedingly rare to find life that can talk about its own extinction events. Kind of deflates the term a bit. Life on planets as inhospitable (by Galactic norms) as Earth tends to be found only as fossils, and almost always on the microscopic level - very rarely do they get the chance to form more complex and advanced lifeforms before the planet with its harsh conditions and scarce resources kills it just as randomly as it spawned it.
We were incredibly saddened to learn from the Humans that the biodiversity of Earth had dwindled by roughly 85% since they accidentally created that giant hole on their planet, and that it had already been on a steady decline before then. Even so, when they revealed there were still 2.4 million species alive on Earth was a shockingly high number. Most are on the brink of extinction, yes, but the fact remains that Earth is easily one of the most biodiverse planets in the Galaxy.
Then we started looking at each individual species and learned about the Tardigrade.
what
It is literally the toughest creature ever discovered, and it's not even close. At least, so far, we haven't looked at absolutely everything Earth has or had yet.
It can just... basically turn itself off and then back on again when the outside becomes livable again - Cryptobiosis, or suspending their metabolism, something we considered only possible through artificial means. And the levels of various extreme they can endure and still be alive would just be utterly ridiculous if they didn't give us samples to confirm for ourselves.
Then we came across the term Extremophile and just decided to take a day off.
#earth is weird#earth is space australia#earth is a deathworld#nature is weird#tardigrade#that's how my brain works#I too learned of that term only now#so it was time to stop before things got out of hand#carionto
445 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Science Research Manuscripts of S. Sunkavally, p 713.
#pterodactyls#humidity#Northern fish#oxygen content of cold waters#Kleiber's law#dinosaurs#island life#growth hormone#gigantism#plants under stress#ethylene#crocodiles#anaesthetics#cryptobiosis#hibernation#magnesium ion#nitric oxide
0 notes
Text
Microscopic tardigrades—plump, eight-legged arthropod relatives—are nearly indestructible, and their durability superpower may have helped them weather the deadliest mass extinction in Earth’s history, according to a new fossil analysis.
Tardigrades, also called water bears, can withstand extreme heat, cold, pressure and radiation. Two major tardigrade lines survive hostile environments through a process called cryptobiosis, in which they lose most of their body’s water and enter a suspended metabolic state.
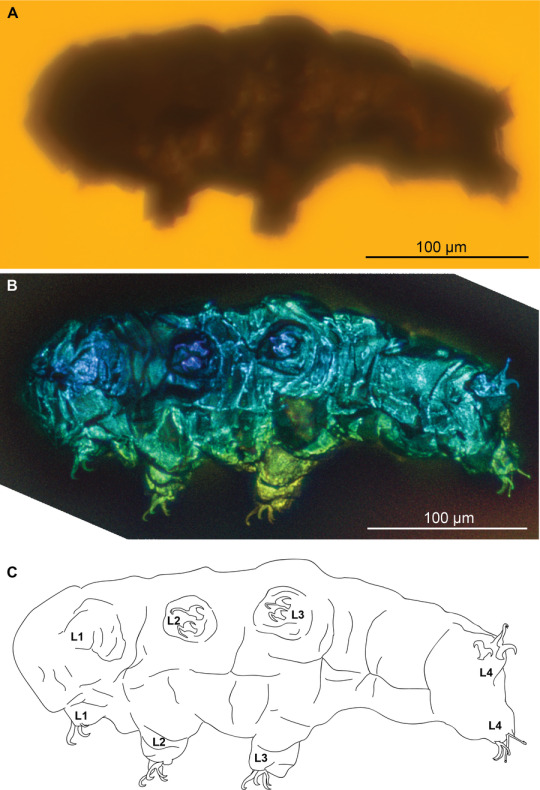
The tardigrade Beorn leggi, photographed with transmitted light under a compound microscope (A), photographed with autofluorescence under a confocal microscope (B) and represented as a schematic drawing (C).
For a new study in Nature Communications Biology, Mapalo and his colleagues used high-contrast microscopy to uncover previously unseen details in both specimens’ claws, “which are very important taxonomic characteristics in tardigrades,” Mapalo says. Tardigrade body plans have varied little for millions of years, so the small visible differences in claw shape offered crucial information about where in the tardigrade family tree these amber-trapped fossils belonged, says University of Chicago organismal biologist Jasmine Nirody (whose own work has also examined tardigrade claws).
The authors determined the smaller tardigrade was a new genus and species: Aerobius dactylus. They also revised B. leggi’s description and classification based on its claw joints. Both species were placed in the same tardigrade superfamily Hypsibioidea, and B. leggi was moved into the family Hypsibiidae. Reclassifying B. leggi based on previously unseen details clarified its relationship to living tardigrades.
The resulting family tree recalibration allowed the researchers to calculate when the two tardigrade lines that perform cryptobiosis could have diverged—putting a latest date on the likely acquisition of that skill. Their work suggests cryptobiosis appeared in tardigrades during the Carboniferous period (359 million to 299 million years ago), predating a deadly event known as the Permian extinction, or the “Great Dying,” which occurred about 252 million years ago. The authors suggest that cryptobiosis may have helped tardigrades survive the event, which wiped out 96 percent of marine life and 70 percent of life on land.
Cryptobiosis’s evolution is challenging to study, partly because tardigrade fossils are so scarce, Mapalo says. Additional fossil discoveries will help scientists pin down details about the appearance of this unique survival strategy. By sharing this result, he says, “we hope we will entice other people to be aware that fossil tardigrades exist and there are still more to be found.”
Editor’s Note (9/16/24): This article was edited after posting to correct the descriptions of the how the findings helped researchers reclassify the tardigrade family tree and when Beorn leggi was first described.
#article#science#fossils#scientific american#tardigrade#water bear#evolution#Carboniferous period#biology
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
just found out the drying skin rolling up entering water for revival in the three body problem thing is similar to cryptobiosis in species like tardigrades
#jkriordanverse#kinda interesting tbh#luna if ur reading this#girl watch thte 3 body probem#best sci fi show#honestly plot not as thrilling as stranger things#BUT OH MY GODS
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
By: Colin Wright
Published: Dec 2, 2024
In the annals of academic absurdity, there are moments that make even seasoned critics pause in awe. “Loving the Brine Shrimp: Exploring Queer Feminist Blue Posthumanities to Reimagine the ‘America’s Dead Sea’” is one such moment. This is not a parody—though it reads like one—but a “serious” paper, or so the author insists. In what is best described as a surrealist love letter to brine shrimp, the author, Ewelina Jarosz (she/they), wades through a soup of critical theory, environmental activism, and performance art, asking the reader to reconsider their relationship with brine shrimp—not as mere crustaceans but as symbols of queer resilience, ecological ethics, and, somehow, hydrosexual love.
This paper is part of a growing tradition of postmodern scholarship that prioritizes ideological signaling over intellectual rigor. Following in the footsteps of infamous works like the 2016 “Feminist Glaciology” paper—which posited that glaciers are gendered—“Loving the Brine Shrimp” sets a new standard for academic ridiculousness. Its culmination in a cyber wedding to augmented reality brine shrimp makes feminist glaciers seem like a grounded scientific pursuit by comparison. But before we arrive at the nuptial climax, let’s examine how this spectacle unfolds.
Love at First Shrimp
The article begins innocuously enough, discussing the ecological crisis facing Utah’s Great Salt Lake. However, it doesn’t take long before it veers into woke lunacy with concepts like “hydrosexuality,” which refers to a “more-than-human sensuality and sexuality emphasizing fluidity and relationality” that “offers a cultural understanding of water as a non-binary substance connecting all bodies of water on the planetary scale.” Hydrosexuality, she argues, challenges the “hegemonic notion of the autonomous and bounded human subject” by embracing “watery thinking.”
If you’re struggling to imagine what any of this means, join the club. The author’s language is a masterclass in obfuscation, using terms like “hydrophilic logic” and “multispecies ethics” to mask the fact that she’s anthropomorphizing liquid.
The absurdity intensifies when she links hydrosexuality to the brine shrimp, praising these creatures for their “swirly sexuality” and reproductive versatility. Apparently, the shrimp’s ability to reproduce via live birth or parthenogenesis (which the author incorrectly calls “pathogenesis” throughout the paper) is a triumph over binary thinking, making them paragons of queer resilience that subvert the oppressive structures of settler-colonial science. Yes, really.
Settler Science and Capitalist Cysts
The paper is rife with accusations against “settler science,” a term the author uses to describe any scientific practice associated with Western colonialism. She argues that early studies of the Great Salt Lake objectified its ecosystem, reducing the brine shrimp to mere commodities. Even the shrimp’s Latin name, Artemia franciscana, is critiqued as a tool of imperial domination. Naming a species, she asserts, reflects a “biology of empire” that erases Indigenous ways of knowing. By this logic, taxonomy itself is a colonial plot.
The author also condemns the commercialization of brine shrimp, particularly their use as fish food and their reinvention as the whimsical “Sea-Monkeys” pet marketed to children. This, they say, constitutes “environmental violence,” a term that appears to mean anything they dislike about human interaction with water-based ecosystems.
Drawing from perspectives offered by queer death studies (Radomska et al. 2021, p. 2), the brine shrimp’s ambiguous status and reproductive agentiality, hovering between the “living” and “non-living” in a state scientifically referred to as cryptobiosis, were reinvented for entertainment, concealing environmental violence.
To support their critique, the author invokes “low-trophic theory,” a concept they describe as prioritizing the ethical interdependence of organisms in an ecosystem. While the principle itself might have some use, the author’s application of it veers into parody. She laments the capitalist exploitation of the shrimp’s reproductive system, framing the harvesting of brine shrimp cycts as a form of ecological oppression. This is all delivered in the impenetrable prose of critical theory, with phrases like “queer ethical field studies” and “feminist blue posthumanities” sprinkled heavily throughout.
The Cyber Wedding to the Brine Shrimp
The paper reached peak woke in a section titled “Loving the Brine Shrimp,” which recounts a performance art piece called Cyber Wedding to the Brine Shrimp. This event, staged on the receding shores of the Great Salt Lake, involved artists, scientists, and augmented reality brine shrimp. Participants made vows to the crustaceans, marched in a procession, and capped it off with a communal bath in the lake. The author describes this as “making love to the lake,” a phrase that may haunt frequent swimmers of the Great Salt Lake for the rest of their lives.
The wedding was not merely symbolic; it was, according to the author, an act of environmental advocacy. By expressing love and commitment to the brine shrimp, the participants hoped to challenge capitalist commodification and foster “multispecies solidarity.” The participants even asked the brine shrimp for their consent to marry, which the shrimp apparently gave telepathically to some participants, while the author seemed content in problematically assuming their consent after proclaiming, “I didn’t hear a no.”
The use of augmented reality (AR) technology added another layer of surrealism. Instead of interacting with real brine shrimp, participants directed their vows toward a giant AR projection of the creatures.
The author describes the procession and bath as transformative, blurring the boundaries between human and non-human bodies. For most readers, however, this spectacle is less an example of profound ecological insight and more a testament to the unchecked excesses of woke performance art masquerading as legitimate scholarship.
I am not sure if you’re sufficiently prepared for this, but below I present to you Cyber Wedding to the Brine Shrimp in its entirety, which has been appropriately overlaid with Mystery Science Theater 3000 silhouettes by my good friend Dr. Rollergator.
[ Watch: "Cyber Wedding to the Brine Shrimp" ]
A Crisis of Peer Review
While the paper’s content is laughable, its publication raises serious questions about the state of academic peer review. How did this article, brimming with jargon and palpably absurd, make it through the editorial process? Are journals so desperate to appear progressive that they’ll publish anything cloaked in the language of decolonization and queerness? The answer appears to be “yes.”
However, one thing is certain: the academic community must reckon with the consequences of allowing such work to proliferate. At a time when public trust in science is already dismal, papers like this undermine the credibility of legitimate scholarship. When even the most basic standards of coherence and relevance are abandoned in favor of ideological grandstanding, the credibility of academia itself is at stake.
* * *
As we reflect on the surreal spectacle of Cyber Wedding to the Brine Shrimp and its academic context, one thing becomes clear: we need a term to capture the moment when scholarly work crosses the line from odd to outright ludicrous. I propose “marrying the shrimp” as the academic world’s answer to “jumping the shark.” From now on, this phrase will signify a project so absurd, so detached from reality, that it becomes a parody of itself.
Let’s explore how this term might find its place in academic vernacular:
“Oh Steve? Yeah, he really married the shrimp with his last research project.”
“Yeah Sally, your thesis wasn’t groundbreaking, but at least you didn’t marry the shrimp.”
“That journal used to have standards, but now they’re marrying the shrimp left and right.”
The phrase could also be used preemptively, as a warning to those teetering on the edge: “Careful, Karen. Your proposal on the patriarchal dynamics of Tupperware parties is dangerously close to marrying the shrimp.” Or, as a compliment when someone narrowly avoids absurdity: “I thought your case study on the history of medieval cheese wheels was going to marry the shrimp, but you really pulled it together!”
In an era where intellectual rigor often takes a backseat to performative absurdity, it’s important to keep a sense of humor about the bizarre trajectory of academic publishing. After all, what else can we do when purportedly serious scholars convene weddings for brine shrimp or ascribe nonbinary identities to water?
Alas, these are the times we live in.
--



==
How did we ever let these mentally ill retards gain institutional and societal-wide power?
#Colin Wright#brine shrimp#sea monkeys#hydrosexuality#academic fraud#academic corruption#corruption of education#higher education#queer theory#feminism#feminist theory#defund gender studies#gender studies#religion is a mental illness
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
Phylum #14: Tardigrada, the water bears!
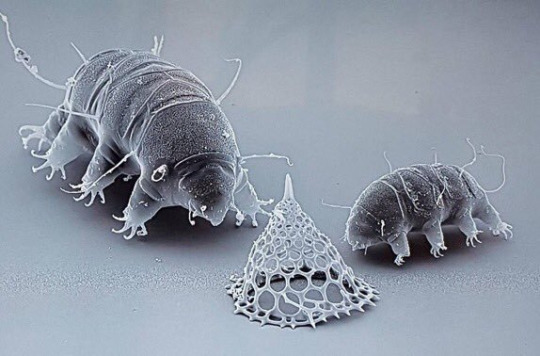
With humans, the only creatures to have reached the Moon alive are small, inconspicuous eight-legged creatures. But they are not spiders, or arthropods for that matter. While still their ancient relatives, tardigrades have followed a very different evolutionary path.
Tardigrades are part of our third and last ecdysozoan group, panarthropods - with a segmented body bearing multiple pairs of limbs. However, most of the tardigrade body isn't homologous to the arthropod one! Instead, most of their limbs correspond to what would become antennas and mouthparts in arthropods, functionally making them a giant head with two back limbs!
Most famous for surviving extreme conditions, from near-absolute zero temperatures to immense pressures or the vacuum of space, tardigrades achieve this thanks to a special capability called cryptobiosis. By entering a dehydrated "tun state", they preserve themselves while nearly stopping their metabolism, and can be revived decades later in perfect health! While they survived on the surface of the Moon, they do not thrive in those extreme conditions, only being dormant - in fact, they prefer moist environments like mosses or hot springs!
Fancy a mystery? Tardigrades today are divided into two main classes - the plump Eutardigrada and the armored Heterotardigrada. However, a third class, Mesotardigrada, was discovered in 1937, with a single specimen found in a hot spring near Mount Unzen, Japan. Of unique appearance among tardigrades, it was never found again despite repeated searches, and the type locality was destroyed years later.




62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh, sorry... I didn't think there was anyone in here... *enters a state of cryptobiosis in the hopes that conditions are less awkward in the future*
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
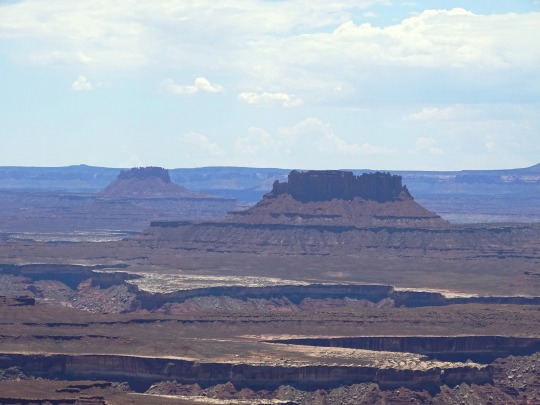
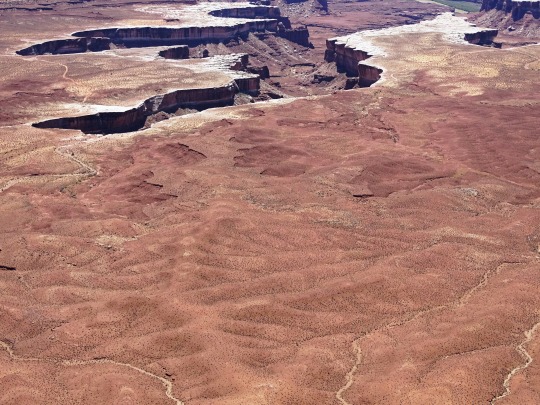
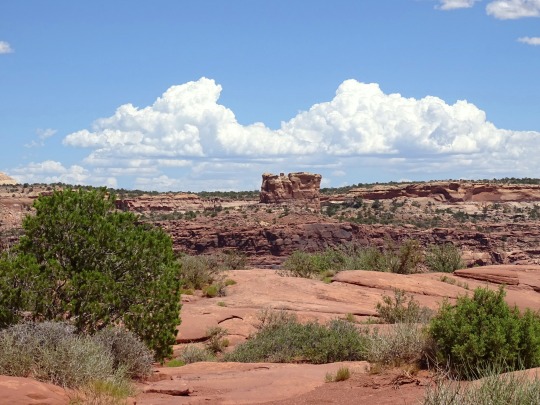
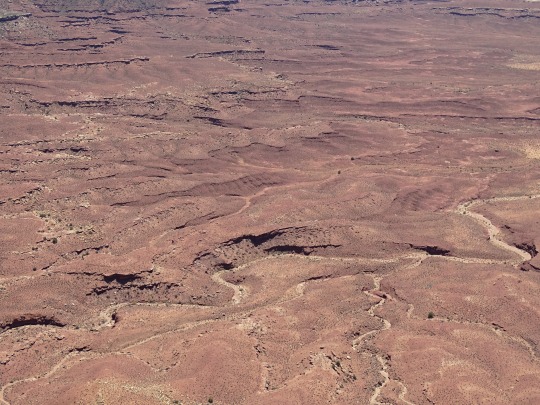
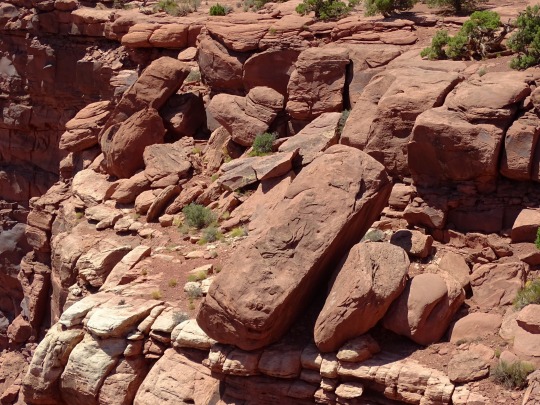
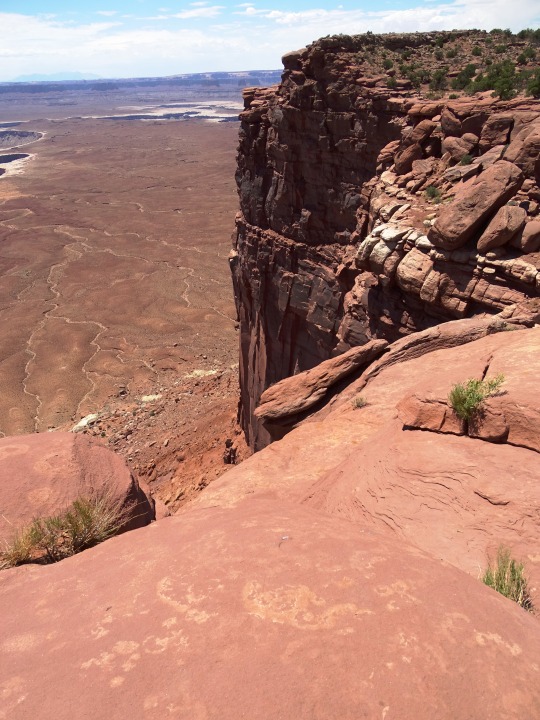










Green River Overlook, Canyonlands National Park (No. 3)
Drought Tolerators
Drought tolerators are able to withstand losing much of their total body water content, in some cases up to 92 percent (e.g. rotifers, tadpole and fairy shrimp eggs). This process is known as cryptobiosis. Remarkably, many cryptobiotic species can be rehydrated and become fully functional in as little as half an hour. Cryptobiosis is accomplished by a command center in the organism that remains hydrated. Throughout the rest of the organism, water is replaced by sugar molecules. Changing water to sugar helps the organism’s cells keep shape. Many species are only tolerant during one stage in their life cycle (e.g. egg, larva) and will die if a pool dries up during another life cycle stage.
Source
#Willow Flat#Green River Overlook#desert#landscape#red rock#geology#rock formation#Island in the Sky#flora#nature#Canyonlands National Park#White Rim Sandstone#bush#grass#original photography#summer 2022#view#La Sal Mountains#Utah#Western USA#USA#vacation#travel#rocks#cliff#mesa#butte#dead wood#Colorado Plateau
43 notes
·
View notes