#bronchiectasis
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
It's really cool and fun to find out they saw some unrelated to lymphoma things on my CT but nobody told me 🙃 what they think is mucous plugging in my main right bronchus - is this why I've been so breathless of late? Doesn't feel like my asthma though. Also I already have a diagnosis of mild bronchiectasis so does this infer it's worse? So many questions and zero answers because I just so happened to read about these findings on my cardiologists letter. Also kidney stones, none blocking anything but like, should I not again have been told this?
Maybe I'm reading too much into it but I'm a person that likes to know everything. I don't often worry about health things and definitely don't have health anxiety - I just like knowing the whole picture.
#chronic illness#fibromyalgia#chronic pain#polyarteritis nodosa#adrenal insufficiency#stills disease#chronic uti#asthma#bronchiectasis#mucous plugging
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bronchiectasis
-- chronic dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles
-- caused by inflammation
-- the inflammation process destroys the elasticity of smooth muscle in the airways
-- chronic infections occur in dilated areas
-- these dilated areas retain mucus and obstruct airways
-- can be localized or diffuse
-- sometimes associated with childhood diseases, influenza, or tuberculosis
#medblr#studyblr#notes#my notes#medical notes#med notes#medblr notes#anatomy and physiology#anatomy#physiology#anatomy notes#physiology notes#bronchiectasis#biology#biology notes#bio#bio notes
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mercury Poisoning And Toxicity Symptoms - Mercury Is A 2nd Most Toxic Heavy Metal Poison, Behind Plutonium
The Primitive Medical Practice that Refuses to Die… Set to be phased out, it instead just suffered a major setback. It involves a poison linked to vision and hearing problems, paralysis, tremors, emotional instability, and more. Yet these “experts” just labeled it “safe.” Don’t be their next unwitting victim… Could it be that at least some in the medical profession are trained to parrot or…

View On WordPress
#amalgam#asparesthesia#bioaccumulation#bronchiectasis#burning#chelation#faster-than-normal heart beat#fingertips and toes#fish#high blood pressure#hydrargyria#hypertension#increased salivation#insomnia#irritation#itching#Kawasaki disease#kidney damage#kidney dysfunction#king mackerel#loss of appetite#loss of hair#low sperm count#memory impairment#mercury poisoning#metallic taste#muscle twitching#muscle weakness#neuropsychiatric symptoms#peripheral neuropathy
1 note
·
View note
Text
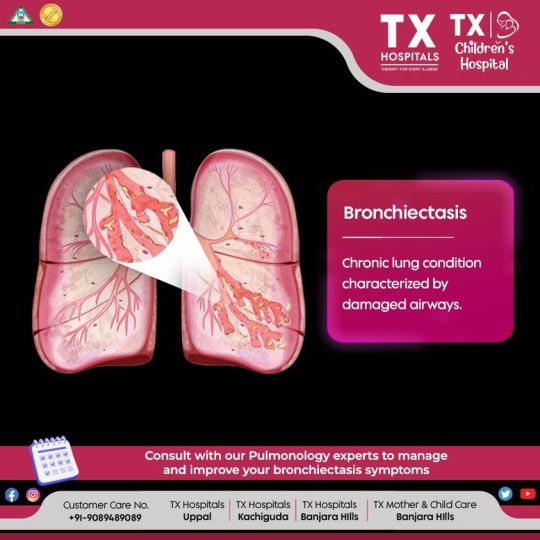
Damaged airways? It could be Bronchiectasis.
0 notes
Text
My Auto Immune Journey Reactive Hypoglycemia Hypothyroidism & Hashimotos Disease 2023
My Auto Immune Journey Reactive Hypoglycemia Hypothyroidism & Hashimotos Disease 2023 is the title of my blog post. An update as to what has happened to me since we spoke last. Unbelievably frustrating as you will find out... ❤️
For my dear family and friends who’ve been following my journey. I was diagnosed with Hypothyroidism in 2017. I was put on thyroid medicine, I was initially having regular blood tests to ensure I’m getting the correct dosage for me to be able to function normally. My former GP (an experienced semi-retired part-time GP who also taught other GPs) wasn’t sure what to say when I asked why did I have…

View On WordPress
#autoimmune#autoimmune disease#autoimmune health#autoimmune reactions#autoimmunity#Blog#blogger#blood#blood disorders#blood glucose#blood sugar#blood sugar levels#bowel health#bowel movements#bowel pain#Brain health#breathing#breathing problems#Bronchiectasis#children&039;s health#chronic disease#Chronic health#chronic illness#Chronic Illnesses#chronic stress#CIP#coeliac#coeliac disease#constipated#constipation
0 notes
Text
Andrew Tate: His Manager Sets the Record Straight on Lung Cancer Rumors
Andrew Tate, former kickboxer and reality TV star, has been diagnosed with bronchiectasis, a non-cancerous condition that affects the lungs. His manager refuted rumors of lung cancer and said Tate is receiving treatment.
#AndrewTate#Bronchiectasis#LungHealth#RealityTVStar#HealthScare#KickboxingLegend#NonCancerousCondition#RumorControl#andrewtatecancer
0 notes
Note
[PT: Obstructive Lung Disease Pride Flag. end PT]
Ooh! Can you do an OLD flag?
Obstructive Lung Disease Pride Flag

Obstructive lung disease is a category of respiratory disease characterized by airway obstruction. It is generally characterized by inflamed and easily collapsible airways, obstruction to airflow, problems exhaling. Types of obstructive lung disease include; asthma, bronchiectasis, bronchitis, cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Flag meanings:
pink: pride
cyan: obstructive lung diseases
white: difficulty breathing
green: inflammation of the lungs
#flags#disability flags#obstructive lung disease#theme: disability#asthma#bronchiectasis#bronchitis#cystic fibrosis#chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Bronchiectasis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, & Treatment Options
Learn the key symptoms of bronchiectasis & explore available treatment options to manage this chronic lung condition effectively. Stay informed for better health.
To know more: https://lalithachestandskinhospital.com/blog/bronchiectasis-awareness-identifying-symptoms-and-exploring-treatment-options/
lungs specialist in karimnagar,bronchiectasis treatment,lungs hospital near me,breathing specialist doctor near me,best chest physician near me

#lungs specialist in karimnagar#bronchiectasis treatment#lungs hospital near me#breathing specialist doctor near me#best chest physician near me
0 notes
Text
An Overview of Bronchiectasis Market: Trends and Insights
Bronchiectasis market, a chronic lung condition characterized by abnormally widened airways, is a significant global health concern.

Buy the Full Report to Know More About the Bronchiectasis Market Forecast Download a Free Sample Report
This market overview explores the key trends, drivers, and challenges shaping the bronchiectasis market.
Market Dynamics
Rising Prevalence: The increasing prevalence of bronchiectasis, driven by factors such as infections, cystic fibrosis, and autoimmune diseases, is a major driver of the market growth.
Improved Diagnosis: Advancements in diagnostic techniques, including high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), are enabling earlier detection and diagnosis of bronchiectasis.
Growing Awareness: Increased awareness of the condition among healthcare professionals and patients is leading to earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Therapeutic Innovations: The development of new therapeutic options, such as inhaled antibiotics and mucolytics, is expanding the treatment landscape for bronchiectasis.
Market Trends
Personalized Medicine: The focus on personalized medicine is driving the development of targeted therapies for bronchiectasis, considering individual patient factors and genetic variations.
Home Care and Telehealth: The increasing adoption of home care and telehealth services is providing convenient and accessible care for patients with bronchiectasis.
Disease Management Programs: Comprehensive disease management programs are being implemented to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Emerging Therapies: The development of novel therapies, including gene therapy and stem cell therapy, holds promise for addressing the underlying causes of bronchiectasis.
Challenges and Opportunities
Diagnostic Delays: Despite advancements in diagnostic techniques, delays in diagnosis can lead to disease progression and complications.
Treatment Limitations: Current treatments often focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the underlying causes of bronchiectasis.
Healthcare Costs: The management of bronchiectasis can be costly, placing a burden on healthcare systems.
Emerging Markets: Expanding access to bronchiectasis care in emerging markets presents significant opportunities for market growth.
Conclusion
The bronchiectasis market is characterized by growing awareness, advancements in diagnostic techniques, and the development of new therapeutic options. Addressing challenges such as diagnostic delays and treatment limitations will be crucial for improving patient outcomes and enhancing the market potential.
0 notes
Text
Comprehensive Analysis of Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Directions
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by the irreversible widening of the bronchi, leading to mucus accumulation, recurrent infections, and reduced lung function. While it is not as well-known as other respiratory diseases, bronchiectasis poses a significant burden on patients' quality of life and the healthcare system. In recent years, clinical trials have played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the disease, developing new treatments, and improving patient outcomes. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of recent bronchiectasis clinical trials, highlighting key advancements, challenges, and future directions in the field.
Key Advancements in Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials
Innovative Drug TherapiesRecent clinical trials have led to the development of new drug therapies aimed at reducing inflammation, preventing exacerbations, and improving mucus clearance in bronchiectasis patients. One notable example is the use of inhaled antibiotics, such as liposomal amikacin and tobramycin, which have shown promise in reducing bacterial load and exacerbation frequency. Additionally, macrolide antibiotics like azithromycin have been studied for their anti-inflammatory properties, leading to a reduction in exacerbations and improvement in lung function.
Targeted TherapiesThe emergence of targeted therapies has revolutionized the treatment landscape for bronchiectasis. Clinical trials focusing on biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies targeting specific inflammatory pathways, have shown potential in reducing disease progression. For example, studies on interleukin-5 (IL-5) inhibitors, like mepolizumab, have demonstrated significant reductions in sputum eosinophils and exacerbation rates in patients with eosinophilic bronchiectasis.
Non-Pharmacological InterventionsIn addition to drug therapies, clinical trials have explored non-pharmacological interventions to improve the quality of life for bronchiectasis patients. Pulmonary rehabilitation, airway clearance techniques, and exercise programs have been investigated for their effectiveness in enhancing lung function, reducing symptoms, and improving overall well-being. These trials emphasize the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to bronchiectasis management.
Challenges in Conducting Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials
Heterogeneity of the DiseaseBronchiectasis is a heterogeneous condition, with varying underlying causes, disease severity, and patient responses to treatment. This heterogeneity poses challenges in designing clinical trials that can accurately capture the effectiveness of new therapies across diverse patient populations. Stratifying patients based on disease phenotype and underlying causes is crucial for improving trial outcomes and developing personalized treatment approaches.
Limited Patient RecruitmentRecruiting sufficient numbers of patients for bronchiectasis clinical trials can be challenging due to the relatively low prevalence of the disease compared to other respiratory conditions. Additionally, the geographic distribution of patients and the need for specialized centers can limit access to trials. Innovative strategies, such as decentralized trials and virtual assessments, may help overcome these recruitment barriers.
Measuring Meaningful OutcomesDetermining the most relevant clinical outcomes for bronchiectasis trials remains a challenge. While traditional outcomes such as exacerbation rates and lung function are important, patient-reported outcomes, including quality of life measures and symptom burden, are increasingly recognized as vital for evaluating the overall impact of new therapies. Developing standardized outcome measures that capture both clinical and patient-centered aspects is essential for future trials.
Future Directions in Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials
Personalized MedicineThe future of bronchiectasis treatment lies in personalized medicine, where therapies are tailored to the individual patient's disease characteristics and genetic profile. Ongoing trials are investigating biomarkers that can predict treatment response and guide therapy selection. Personalized approaches hold the promise of optimizing treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Long-Term StudiesGiven the chronic nature of bronchiectasis, there is a need for long-term clinical trials that assess the sustained benefits and safety of new treatments. These studies will provide valuable insights into the durability of therapeutic effects and the potential for disease modification over time. Long-term data are also crucial for evaluating the cost-effectiveness of new interventions.
Exploring New Therapeutic TargetsAs our understanding of bronchiectasis pathophysiology continues to evolve, new therapeutic targets are being identified. Future trials are likely to explore novel anti-inflammatory agents, immune modulators, and treatments targeting airway remodeling. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies will be essential to accelerate the translation of these discoveries into clinical practice.
Buy the Full Report for More Regional Insights into the Bronchiectasis Clinical Trials Download a Free Sample Report
0 notes
Text
We got a *new sparkly diagnosis* today.
Not me saying for the last 18 months there's something up with my chest after that viral chest thing left me with bad asthma and a hospitalisation for a week. And doctors being like, we think you just have a breathing pattern disorder. And me being like 🙄🙄🙄🙄
Finally, today - bronchiectasis. Mild, so we chill for now I guess. But explains why I'm getting repeated chest infections. Just glad I finally have something to point at like -> it's this, believe me.
You'd think after like a lifetime of illness, and 14/15 years of chronic illness, I'd have found a way to better get doctors to listen. But no, it's not ME that needs to take better note, it's the doctor's. No wonder I have so much medical trauma under my belt huh.
#chronic illness#fibromyalgia#chronic pain#polyarteritis nodosa#adrenal insufficiency#stills disease#bronchiectasis
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global Bronchiectasis Market: Regional Growth and Market Dynamics
The global bronchiectasis market exhibits regional variations in terms of prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, and market dynamics.

For more sex segment insights, download a free report sample
Here's an overview of the regional growth and market dynamics in the context of bronchiectasis:
1. North America:
Market Dynamics: North America, particularly the United States, has a well-established healthcare infrastructure and a high prevalence of bronchiectasis. The market is characterized by extensive research and development activities, clinical trials, and collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and research institutions.
Prevalence: The prevalence of bronchiectasis in North America is influenced by factors such as aging populations, respiratory infections, and the presence of underlying conditions like cystic fibrosis.
Treatment Landscape: The region has access to a diverse range of treatment options, including antibiotics, airway clearance techniques, and emerging pharmacological therapies. Clinical trials for new drugs and therapies are frequently conducted in North America.
2. Europe:
Market Dynamics: Europe has a significant burden of bronchiectasis, and the market dynamics are influenced by the presence of well-established healthcare systems, research initiatives, and collaborations. European countries contribute to the development of treatment guidelines and standards.
Prevalence: Bronchiectasis prevalence varies across European countries, with some regions experiencing a higher incidence due to factors like respiratory infections, genetic predisposition, and environmental factors.
Treatment Landscape: European countries have access to a comprehensive range of treatment options, and there is a focus on adopting patient-centric approaches, including patient education and support services.
3. Asia-Pacific:
Market Dynamics: The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing increasing awareness of bronchiectasis, with a growing focus on research and development. The market dynamics are influenced by factors such as demographic changes, urbanization, and healthcare infrastructure development.
Prevalence: The prevalence of bronchiectasis in Asia-Pacific is influenced by factors such as infectious diseases, environmental exposures, and changing lifestyle patterns. Improved diagnostic capabilities contribute to better identification of cases.
Treatment Landscape: The treatment landscape in Asia-Pacific is evolving, with an increasing emphasis on adopting international treatment guidelines. Access to innovative therapies and technologies is expanding in the region.
4. Latin America:
Market Dynamics: Latin America faces challenges in terms of healthcare infrastructure discrepancies and economic constraints. However, there is a growing awareness of respiratory conditions, including bronchiectasis, leading to increased efforts in research and disease management.
Prevalence: The prevalence of bronchiectasis in Latin America is influenced by factors such as infectious diseases, environmental exposures, and socioeconomic factors. Limited access to healthcare services may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Treatment Landscape: Access to advanced treatment options may vary across countries in Latin America. Efforts are being made to enhance the availability of diagnostics and treatment modalities.
5. Middle East and Africa:
Market Dynamics: The Middle East and Africa face challenges related to healthcare infrastructure, but there is a growing recognition of respiratory diseases. Market dynamics are influenced by efforts to improve healthcare access and address the impact of infectious diseases.
Prevalence: The prevalence of bronchiectasis in the Middle East and Africa may be influenced by environmental factors, including air quality and exposure to pollutants. Limited access to healthcare services may contribute to underdiagnosis.
Treatment Landscape: Access to specialized treatments may vary, and efforts are needed to improve diagnostic capabilities and treatment options. Collaboration with international organizations may contribute to advancements in the region.
6. Global Collaborations:
Research Networks: Global collaborations and research networks play a crucial role in advancing bronchiectasis research and treatment. International conferences and collaborations facilitate the exchange of knowledge and expertise.
Clinical Trials: Multinational clinical trials contribute to a better understanding of bronchiectasis and the development of novel therapies. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is essential for global advancements.
In summary, the global bronchiectasis market exhibits regional variations in prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, and market dynamics. Efforts to improve awareness, enhance diagnostic capabilities, and advance treatment options are ongoing across regions, contributing to the overall management of bronchiectasis worldwide.
0 notes
Text
07/01/2023 is Tartan Day 🌏, Canada Day 🍁🇨🇦, Republic Day 🇬🇭, National Doctors' Day 👩⚕️👨⚕️🇮🇳, World Bronchiectasis Day 🌏, International Reggae Day 🇯🇲, Keti Koti 🇳🇱, National Creative Ice Cream Flavors Day 🍨🇺🇲, National Gingersnap Day 🇺🇲, National Postal Worker Day 🇺🇲, National U.S. Postage Stamp Day 🇺🇲, National Hot Dog Month 🌭🇺🇲, Picnic Month 🇺🇲, Berry Month 🍓🇺🇲, National Ice Cream Month 🍨🇺🇲, Hop-a-Park Day 🇺🇲, International Chicken Wing Day 🐓🇬🇧, International Day of Cooperatives 🇺🇳

#tartan day#canada day#republic day#national doctors day#world bronchiectasis day#international reggae day#keti koti#national creative ice cream flavors day#national gingersnap day#national postal worker day#national us postage stamp day#national hot dog month#picnic month#berry month#national ice cream month#hop a park day#international chicken wing day#international day of cooperatives
1 note
·
View note
Text


24.11.2024//Sunday
Day 6 of 12 day productivity challenge
Today was good.
Patho , I studied :
Bronchiectasis
Bronchial Asthma
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
After a very productive morning and afternoon. My plans of studying cephalisporins were destroyed by a very very bad stomach ache.
But I just read the topic .
Will study it tom .
Byeeeee
#studyblr#productivity#study motivation#study blog#med school#study hard#stdyblr#aesthetic#studtblr#study inspiration#study community#study challenge#productivity challenge#medical student#12 day productivity challenge#exam soon#exam season#study time#college studyblr#desi studyblr#medical school#med student#med studyblr#medblr#medical studyblr#medstudent#chaotic academic aesthetic#academia aesthetic#study inspo#studyblr community
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm sure someone has done this before but i'm pretty sure i've broken down the medical aspects of operator sickness
- direct exposure to the operator causes encephalitis + bronchiectasis which goes away once you're "out of range" (see coughing up blood, disorientation, headaches, vomiting)
- the operator picks people to expose on the regularity
- the regular exposure leads to some type of encephalopathy that has similar neurological symptoms as CJD but not the quickness of it, and instead of full blown dementia it's short term memory loss (in severe cases like Jay's, long term)
this also puts a point towards the operator as a fungus giving them fungal infections. :]
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
Some of Trans Rights fighters so often remind me of smoker patients in the Pulmonology department.
You tell a person, "You have bronchiectasis and/or COPD, you should stop smoking because it slowly kills your lungs" - but such patients are really hard to terrify, to convince to drop off their obsession. They genuinely believe nothing bad will happen if they secretly smoke one cigarette, and they can be pretty aggressive about that. They usually die the next year from cancer. At first, you throw all your strength to help the poor, to save them from such a terrible fate - but the more and more patients you have, the little by little lose your desire because you realise: such people actually don't need your help. Such people realise how deep in shit they are only when it's too late, and not a single living soul can prevent that. Such people often don't even realise that till death.
Doctors are also people, and we often want to use the George Carlin's language: Stop smoking, you idiot, or you will fucking die. You will die! Some of us, of course, understand that the habit can be only replaced with another habit and the ban will lead to nothing, and the doctor's goal is to convince the patient, "You and only you are responsible for your body" - but it's so exhausting. It's so exhausting - and the only thing you want to say is eventually, "You know, what? Keep killing yourself, I don't care." But you can't say so because you're a doctor.
Returning to the trans topic: when you see all those clinics who prescribe mastectomy and hormones to children and teens - children and teens, it's normal for them to be insecure in their own bodies, they are growing up and they have monstrously sharp changes in hormones and they have growing tissues, growing bones, growing bones hurt really fucking much, if only all adults remembered how it feels to have a growing body - you realise that first of all, such kids and teens, both trans and cis, need psychological support, someone who allows them to cry and scream and complain a lot because that's what their bodies scream for. Not hormones who will just make it worse, and not the mastectomy. But you can't say that because otherwise you're a transphobe and a terf, and even if you try to explain that, they throw you links on pseudoscientifical articles which often contradict each other.
And then, you want to say, "Yk what? Keep going, I don't care." And it's only a matter of time when people who were screaming of the holy properties of hormones/antidepressants/drugs for mental disorders and other stuff which any adequate pharmacist will prescribe only with lab results and only after all possible therapies have been tried and have had no effect - yes, it's only a matter of time when the collective silence appears with rare interspersed regrets and complaints about side effects of such treatment. Fortunately and not, most of humanity just needs the most hard-to-get medicine - the improved quality of life - more sleep, less social media, more good food, more physical activity, fresh air, more light, more water, more social interactions with people who make you feel good, more money - not the drugs. In fact, it's already happening. Maybe it explains why pseudofighters for trans rights are so aggressive.
Btw, when most people can't get themselves improved life quality, then we have wars. The more time people try to get themselves such medicine and fail - the more brutal wars we have. A restart mechanism that can not be avoided.
4 notes
·
View notes