#Westminster Declaration
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
"Deeply concerned about increasing censorship."
by Dr.Harald Wiesendanger– Klartext What the mainstream media is hiding The human right to freedom of expression is in extreme danger. The “Westminster Declaration” urgently warns against this, signed by 137 personalities from science, culture, and the media. The right to freely express one’s own opinion and disseminate it unhindered is a cornerstone of democracy. But he falters. Governments,…

View On WordPress
#Censorship#Censorship-Industrial Complex#Corona crisis#Disinformation#Fake News#free opinion#Freedom of expression#industrial censorship complex#UDHR#Universal Declaration of Human Rights#Westminster Declaration
0 notes
Text
“The Benediction of Life Together” at Westminster Presbyterian Church
On September 10, 2023, Rev. Tim Hart-Andersen. Senior Pastor at Minneapolis Westminster Presbyterian Church, delivered the sermon, “The Benediction of Life Together,” which was the first of his last seven sermons before his retirement at the end of October. Scripture Psalm 1: 1-3: “Blessed is the one who does not walk in step with the wicked or stand in the way that sinners take or sit in the…
View On WordPress
#"God is good --All the time"#"God of Grace and God of Glory"#&039;Yonder Come Day&039;#African-American worship#‘All Creatures of Our God and King&039;#‘O God Beyond All Praising&039;#‘What a Fellowship What a Joy Devine&039;#Barmen Declaration#Belhar Confession#benediction#Christianity#Confession of Belhar#Dietrich Bonhoeffer#Irenaeus#Jacksonville (Alabama)#Jesus Christ#John 10: 7-10 14-16#Minneapolis Westminster Presbyterian Church#Montgomery Alabama#Morocco#Paul Granlund#Presbyterian Church (USA) Consitution#Psalm 1: 1-3#Rev. Dr. Arnold Lowe#Rev. Dr. Timothy Hart-Andersen#Sculpture "The birth of Freedom"#St. Augustine
0 notes
Note
I have no clue if you've done this already, but I would love some royal-related vocabulary!! I write about a royal family (one in the middle ages) and it gets tiring looking for all the correct terms😅
Some Medieval Vocabulary
Amercement - financial penalty imposed by the King or his justices for various minor offences. The word comes from the fact that the offender is said to be ‘in mercy’.
Assize - meeting of feudal vassals with the King, and the edicts issued from it. It comes to have a legal context of court; but then in the early days the king’s court was just that – a place where law was made and justice executed. Hence the double meaning of the word court.
Borough - town with the right of self government granted by royal charter
Chamber - the financial office of the royal household
Chamberlain - officer of the royal household, responsible for the Chamber. He was therefore responsible for administration of the household and the private estates of the King.
Chancellor - officer of the Royal Household who originally served as the monarch’s secretary or notary, managing the Chancery, filled with clerks who produced writs and written instructions and records.
Chivalry - the knightly class of feudal times. The primary sense of the term in Europe in the Middle Ages is “knights,” or “fully armed and mounted fighting men.” Thence the term came to mean the gallantry and honour expected of knights. Later the word came to be used in its general sense of “courtesy.”
Constable - the title of an officer given command in an army or an important garrison. Also the High Constable was the officer who commanded in the King’s absence and commanded the King's army.
Destrier - warhorse; so called because it would be led using the right hand
Diadem - a royal crown
Eyre - the king and his justices would traditionally travel through the kingdom to deliver justice. As the king became more centred at Westminster, justices would continue to travel – and were called Justices in Eyre. From the French errer, "to travel".
Heir apparent - the declared heir to the throne, normally the king’s eldest son
Heir presumptive - the presumed heir to the throne in the event of the king dying without an heir apparent
Justiciar - head of the royal judicial system and the King’s viceroy during his absence from the country
League - somewhere between 1½ to 3 miles. Traditionally, the distance a person or horse can walk in one hour.
Mark - money, worth thirteen shillings and four pence, i.e. two thirds of £1
Mead hall - in the Middle Ages in Northern Europe and Scandinavia, a large building with just one room that was used as a central place for entertainment and as a living place for a lord/king
Minstrel - a traveling musician and singer common between the 11th and 15th centuries
Ordeal - a method of trial in which the accused was given a physical test which could be met successfully only if they were innocent (e.g., ordeal by fire)
Purveyance or prise - in early medieval days, the lord had the right to be entertained by his followers, at their expense. And of course this applied to the greatest lord of all – the king. Over time, the king travelled less, but still wanted the benefit of being able to have him and his household live at someone else's expense – and so he exercised the right to take goods and food in lieu of being there. It was the policy to pay – but payment was often small and late.
Saga - a long story about Scandinavian history, written in the Old Norse language in the Middle Ages, mainly in Iceland
Steward - man responsible for running the day to day affairs of the manor or castle in absence of the lord
Subinfeudation - in medieval Europe, the process by which a vassal (i.e., a man who lived on land given to him by a powerful land owner in exchange for agreeing to fight for him) allowed someone else to use or live on part of their land
Sumpter - packhorse, pony, mule or other animal
Thegn - military companion to the king
Sources: 1 2 3 4 5 6
Here's what I found for you. Hope this helps! Would love to read your work if it does—sounds like the kind of writing I enjoy :)
More: Medieval-Related Vocabulary ⚜ Word Lists
#anonymous#terminology#medieval#middle ages#writeblr#writing reference#spilled ink#dark academia#writing inspiration#langblr#words#linguistics#history#literature#writers on tumblr#poets on tumblr#writing prompt#creative writing#fiction#light academia#poetry#writing resources
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey hi hello to any fellow Brits reading this.
You probably know we have a general election coming up, which by the way, make sure you're registered to vote and have the qualifying photo ID.
And hey maybe you're a fence-sitter who doesn't want to vote for Labour for whatever reason.
Well, this post is giving you a reason to vote for Labour (or any party other than Tory if the candidate actually has a chance to win the seat).
You might have noticed that a lot of local and city councils have either gone bankrupt recently or are teetering on the edge, and that officially, it's the councils themselves that have been blamed, and uh yeah, that's horseshit.
The majority of a local council's funding comes from core grants given out by Westminster.
There's actually a limit on funding that local councils can raise via taxes, and like a whole lot of issues in the UK, that comes down to Margaret fucking Thatcher. It's also thanks to her that local councils don't have as much power over the local area as you'd ideally want them to.
(That's been eased a little since, but if a local council ain't got the money, they can't exercise that power.)
Suffice to say, local councils are very much dependent on funding from the central government.
And as you might imagine, 14 years of Tory government has just made it worse. From 2010 to 2020, that funding was cut by 40%.
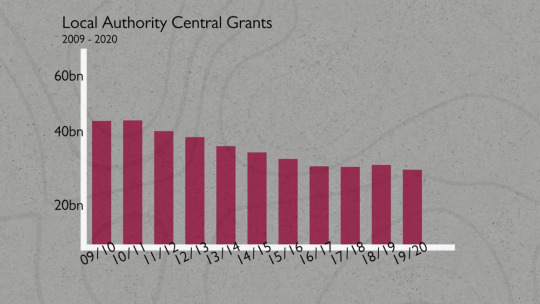
Wanna know why hundreds of libraries have closed down? Or why public services like bin collections are almost entirely ran by corporations? Or why bin collections are now once a fortnight rather than once a week? Or why council houses haven't been built? Or why public toilets are being closed? Or why you have to Tokyo Drift on the drive to work because it's been 2 years and no one's done shit about that goddamn pothole? Or why parks seem to now be maintained by Big Foot and by the way Big Foot has also declared bankruptcy? Or why local arts have had their budget of 17 paperclips and a whistle reduced down to 10 paperclips and no whistle? Or why your local museum is effectively a mausoleum?
It is all down to this.
Your local council runs on a shoestring budget because Tory rule has deprived local councils of the funding that they need.
If the Tories win in July, this problem is just gonna get worse and worse and worse.
More councils are going to go bankrupt; more public services are going to be cut or underfunded; more vulnerable kids are going to fall through the cracks; more local services will be privatised; more pressing issues will be ignored because there's no money left over to fix it.
You might not like the current Labour party, but hi hello welcome to harm reduction politics. Maybe a Labour government won't fix this, but another 5 years of Tory rule is going to break this country.
So for god's sake, get over yourself and your leftist purity bullshit, and just fucking vote for Labour as a vote against the Tories.
[Information for this post comes from this video by Tom Nicholas]
#britpol#british politics#uk politics#britposting#tories#fuck the tories#uk general election#general election#margaret thatcher#politics#i dont know what to tag this as#but i just saw another stupid fucking ''no its actually enlightened to just not vote'' post#and im angry#and frustrated#and for fucks fucking sake#if you really care about all the issues you claim to care about#then for gods fucking sake go fucking votw#the glorious revolution is not fucking happening#especially with you not doing jackshit toward it#so for fucks sake actually engage with reality as it is and vote for labour as to vote the fucking tories out
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
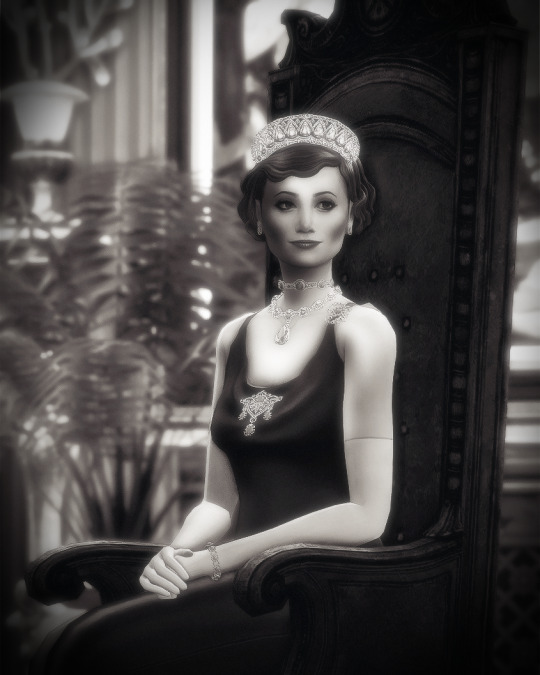
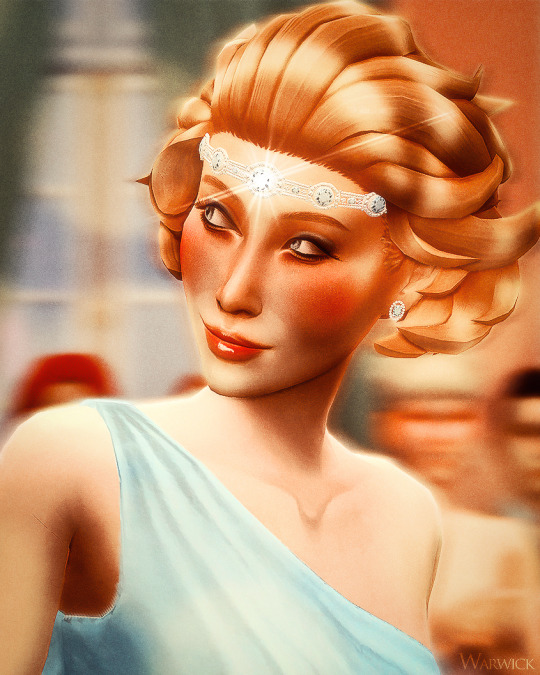




Sunderland's Royal Jewel Vault (27/∞) ♛
↬ The Westminster Aquamarines
The Sunderlandian royal family has several magnificent parures of aquamarine jewellery. One of these collections, the Westminster Aquamarines, features some of the royal family’s oldest and most iconic jewels; uncovering their history takes us back nearly two hundred years. In 1830s, Sunderland was a lone constitutional monarchy in North America, bordered by the United States in the northeast and Mexico to the southwest. The early 19th century had seen the country’s steady expansion westward thanks to territorial acquisitions from the Spanish and British. This period of territorial and economic growth, however, was cut short by the early death of Sunderland’s Hereditary Prince in 1835. Hereditary Prince Frederick James was just shy of thirty, the only son of King Louis III and his beloved first wife, Princess Amelia of the United Kingdom. Freddie was also the only legitimate male-line grandson of King Louis II, as a result, his death complicated Sunderland’s succession. The question of who would succeed Louis III ignited a fierce rivalry among the King’s younger brothers, as they scrambled to marry and produce an heir to the throne. The Duke of Lennox and St. George, the King’s first brother and heir presumptive, married an obscure German princess. The Duke of Glencairn, the King’s second brother, married the daughter of a wealthy British statesman. But it was the King’s fifth brother, Prince Augustus, the Duke of Westminster, who looked for a bride closer to home. Lady Martha Whitley was twenty years younger than her husband-to-be, a descendant of the Prussian nobility that migrated to Sunderland following the election of Prince Heinrich of Prussia as King Louis I of Sunderland, Martha hailed from one of Sunderland’s oldest aristocratic families. Unlike some of her foreign, and significantly younger, sisters-in-law Martha was shrewd and held a deep familiarity of Sunderland's court life, this was reflected in her impressive jewelry collection. On her wedding day, Martha was gifted a small box of aquamarine pendants of various shapes and sizes. As Martha’s prominence at court grew, the aquamarines became known as the Duchess of Westminster’s Aquamarines. Over the years, the Duchess incorporated the aquamarines into a few pieces of jewelry including a necklace and a pair of earrings. The tensions surrounding Sunderland’s succession died down when the British-born Prince George of Glencairn became king in 1860. By then Westminsters had three children, Prince Louis, who became Duke of Westminster following his father’s death in 1877; Prince Thomas, and Princess Elizabeth Anne. The family was popular with nobility and the public alike, but they weren’t without their scandals. After Prince Louis enraged King George by marrying without permission, his subsequent children were declared illegitimate and barred from inheritance. Finding a suitable wife for Prince Thomas, now heir to the Westminster Dukedom, became a top priority. In 1876, Prince Thomas met and fell in love with Princess Marie of Hanover, a male-line great-granddaughter of King George III and therefore a British princess. The couple married in 1880, but struggled to have children. In 1887, their only surviving child was born in the presence of Queen Alexandra. The little princess, given the lengthy name Alexandra Anne Martha Georgina Dagmar Gloriana Marie, would be known to history as Princess Anne of Westminster. Growing up, Anne was placed in the direct care of her Dear Granny Martha.
My grandmother was magnificent. She was kind but strict, with old-fashioned ideas about how a princess should be brought up. - Queen Anne of Sunderland, circa 1953
The Duchess of Westminster had high hopes for her only male-line granddaughter. Indeed, Anne’s maternal cousins were well-connected to the British and Danish royals, as well as the Imperial families of Russia and Germany. By the time Anne was twenty, she’d been taken on several trips to Europe, excursions she came to loathe. Anne’s anxiety worsened when she was rejected by several families. After her mother died in Austria, Anne returned from Europe “alone and feeling rather sorry for myself”. Back in Sunderland, Anne made friends with her second cousin once-removed, Prince George, the Duke of Woodbine and eldest son of the Prince and Princess of Danforth. Over the years, the pair’s friendship developed into a romance and in 1911, King George allowed the couple to marry. That same year, the Duchess of Westminster died, and Anne inherited the largest jewel collection in the royal vault, aquamarines included. Anne and George married in 1913. Anne, now Duchess of Woodbine, was one the most dynastically important ladies at court and she set to work reworking her grandmother’s jewels into spectacular works of art. For King George and Queen Alexandra’s 1920 Diamond Jubilee, Anne commissioned Garrard to work the aquamarines into a parure that included a necklace, a choker, two brooches, and a pair of earrings. The parure paired nicely with the aquamarine Georgiyevna Tiara, which entered the family in the early 1920s. To this day, the Georgiyevna aquamarines are often mistaken for those of the Westminster set, showing how ubiquitous they’ve become with the main-line royal family’s collection. When Anne became Queen in 1930, she wore the aquamarines. Despite her overflowing jewellery box, the aquamarines were evidently her favourite and became synonymous with her name and legacy. The Westminster aquamarines have remained iconic long after Queen Anne’s time. Queen Irene became another famous wearer of the suite, wearing the choker as both a necklace and a headband in the 1980s. Queen Anne was an important figure to Irene during the early years of her marriage, and she wears nearly all of the jewels her grandmother-in-law left to her. In the 2010s, Tatiana, then the Princess of Danforth was seen in bits and pieces of the suite, notably the choker, signalling that the jewels will be carried on into the next generation.
Queen Anne of Sunderland, wife of King George II, wears the Westminster aquamarines with the Georgiyevna tiara for a promotional image, circa 1930
Queen Irene of Sunderland, wearing a powder blue satin evening gown along with the Westminster aquamarine choker as a headband, attends a gala dinner on April 30, 1984 in Auckland, New Zealand
#warwick.jewels#✨#not a tiara technically i don't care leave me alone#ts4#ts4 story#ts4 royal#ts4 storytelling#ts4 edit#ts4 royal legacy#ts4 legacy#ts4 royalty#ts4 monarchy#ts4 screenshots
50 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Edward VI of England
Edward VI of England reigned as king from 1547 to 1553 CE. Succeeding his father Henry VIII of England (r. 1509-1547 CE), Edward was only nine years old at the time and so the kingdom was ruled by a council of nobles, foremost among whom was Edward's maternal uncle, Edward Seymour (l. c. 1500-1552 CE) until he was replaced by John Dudley, the Earl of Northumberland (l. 1504-1553 CE). During Edward's reign, Protestant religious reforms continued as the Church of England broke further away from the traditions of the established Catholic Church directed by the Pope. There were also popular uprisings as the economy faltered and inflation was rampant. Edward's reign was short as he died of tuberculosis aged just 15. He was succeeded by his cousin Lady Jane Grey (1537-1554 CE) until what the majority of the people and nobility regarded as the rightful heir, his elder half-sister, was installed nine days later as Mary I of England (r. 1553-1558 CE).
Henry VIII & The Succession
Henry VIII married six times but it was his first three marriages that each produced a future monarch. With Catherine of Aragon (1485-1536 CE), Henry had a daughter, Mary (b. Feb. 1516 CE). With Anne Boleyn (c. 1501-1536 CE), there was another daughter, Elizabeth (b. Sep. 1533 CE). With wife number three, Jane Seymour, who was a lady-in-waiting at court, Henry had his first and last legitimate son, Edward, born on 12 October 1537 CE in Hampton Court Palace. At the joyous news, there followed 2,000 cannon shots let off in the Tower of London, bells rang out across England and there were 24 hours of parties and feasts but, tragically, Jane died 12 days after giving birth, most likely from post-natal fever.
As the first marriage was annulled to permit the second and Anne Boleyn was executed on charges of adultery, so each of their children was disinherited and it was Edward who became the official heir to the throne. As more wives came and went and no more children were forthcoming, Henry changed his mind in 1544 CE and declared that Edward could be succeeded by his half-sister Mary with Elizabeth next in line.
Henry VIII's health declined rapidly in his later years as the king became seriously overweight and suffered a badly ulcerated leg. The king died on 28 January 1547 CE at Whitehall Palace in London; he was 55 years old. Henry was buried in Saint George's Chapel at Windsor Castle, next to his late third wife, Jane Seymour, and he was duly succeeded by Edward who became Edward VI at his coronation in Westminster Abbey on 20 February 1547 CE. Henry, having split the Church in England from Rome to acquire his first marriage annulment and gone on a massive spending spree on palaces and wars, left his son an impoverished kingdom split over religious issues and, particularly, whether or not to press on with reforming the Church.
Continue reading...
24 notes
·
View notes
Text


On December 12th 1574, Anne of Denmark, the wife of King James VI, was born.
Anne was the second child of Frederick II, King of Denmark and Sophia of Mecklenburg. Her father was reportedly so angry at the birth of a second daughter that he stormed into the birthing chamber to remonstrate his wife.
She was sent to live in Mecklenburg for the first four years of her life, before returning to Denmark, where she lived under her mother’s care until her marriage. She received a good education for a Princess of her rank.
In as early as 1586, the possibility of marriage was raised between Denmark and Scotland, but it wasn’t Anne who was the subject of debate, it was her sister Elizabeth. However, their dying father showed little interest in a match, and the Scots went home without a new Queen. Frederick died in 1588 and was succeeded by Anne’s brother Christian. Elizabeth became betrothed to the Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel in 1689, and the attention shifted to Anne. Her mother had taken over as matchmaker and negotiations were concluded quickly. Anne married James by proxy on 20 August 1589.
Anne set sail from Denmark on 5 September, but a storm scattered the fleet and Anne was stuck at sea for several days. The fleet was eventually forced to return to Denmark before setting off again. Once again, Anne didn’t make it to Scotland. On 24 September a public feast day was declared, and James ordered that prayers be said for Anne’s safe arrival. By early October, James despatched a ship to look for her and found her in Norway. Anne had been forced to go to Oslo to wait out the winter weather. James decided to go in person and sailed to Norway at the end of October. They were married in person in Oslo on 23 November, and during the ceremony, Anne was described as “a Princess both godly and beautiful … she giveth great contentment to his Majesty.” They travelled by sledge to Denmark, where Anne was reunited with her family. They spent three months in Denmark and even stayed for Elizabeth’s wedding.
Anne and James landed in Scotland on 1 May 1590, and she was given a grand ceremonial entry to Edinburgh, and she was crowned Queen of Scotland on 17 May. She may have converted to Catholicism within a few years of their marriage.
She gave birth to her first child in February 1594, a son named Henry Frederick. She was pregnant a total of 9 times, but she had two miscarriages, and four children died in infancy. Only Henry Frederick, Charles and Elizabeth survived to adulthood. Anne’s refusal to be separated from her eldest son, who was to be raised in Stirling Castle by the Earl of Mar is said to have caused a miscarriage.
On 24 March 1603, James succeeded to the throne of England and immediately headed towards England. Anne followed him but more slowly. She stopped at Stirling Castle and demanded to see her son. After a furious discussion, Anne suffered yet another miscarriage, and she was even dangerously ill for a while. James wanted her with him in London and finally allowed her to travel to England with both Henry and Elizabeth.
Anne and James were crowned together on 25 July 1603 in Westminster Abbey, and Anne threw herself into her new role as Queen of England. She spent a lot of time producing and performing in masquerades, which became more costly as her husband’s reign went on.
Tragedy struck in 1612 when her eldest son died, and Anne never recovered from the shock. Her grief became even greater when her daughter Elizabeth left for Germany to be married in 1613. Anne’s relationship with James was cordial, but they rarely saw each other. Anne’s health began to steadily deteriorate, and over Christmas 1618 she was too ill to attend the court festivities. James was afraid of disease and refused to visit Anne, but her son Charles remained by her side. Anne died in the early hours of 2 March 1619 at Hampton Court Palace in the same chamber where Jane Seymour had died.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text



Royal Autumn 2024 Photo Challenge
Day 13: Favorite Photos of Royals with Ancestors
Photos 1 and 2; Princess Margaret and Prince Arthur of Connaught, children of Prince Arthur Duke or Connaught and Grandchildren of Queen Victoria, dressing up as distant ancestors King Edward V of England and Prince Richard Duke of York for a Tableaux
Photo 3: Drawing of King Edward V and Prince Richard done by descendant Princess Alice Grand Duchess of Hesse and By Rhine, third child of Queen Victoria
A brief history of these two brothers, most commonly known as “The Princes In The Tower” is as followed: When King Edward IV died, his eldest son Edward automatically became king but as he was only 12 years old, a regent monarch would need to rule until he became an adult. Edward and his party started to make the journey from Wales (where he was being educated to be the future king) to London but were intercepted by Richard Duke of Gloucester’s party who took custody and control of him and his party. Richard, who was King Edward IV’s brother and Edward V’s paternal uncle, was declared regent after the dying Edward IV wished it to be so and eventually had three members of Edward V’s party executed and placed Edward V in the Tower of London to have complete control over the young king. Despite pleas from mother Elizabeth Woodville, who took her remaining children into sanctuary at Westminster Abbey, her younger son Richard was eventually taken away from her and was placed in the tower with his brother. This was in May of 1483. A coronation for Edward was to be immediately planned as this is what would allow Richard to be a legal protectorate but it was repeatedly postponed by Richard himself.
In June of 1483, it was declared from parliament that all children of Edward IV and Elizabeth Woodville were illegitimate and the same with the children of brother of the former king George Duke Of Clarence (who was already dead at this time) so Richard was seen as the legitimate king and a day later acceded to the throne as Richard III. After Richard became king, the princes were taken into the inner apartments of the Tower and were seen less and less until the Autumn of 1843 when they disappeared from public view entirely. After the young princes disappearance, it was widely accepted that they were killed on the orders of their Uncle Richard and were smothered to death in their sleep, this theory is most accurate because Richard had complete access to them and men so loyal that they would do anything for their king.
In 1674, close to two hundred years later, two sets of skeletons resembling two children were found by workers who were rebuilding a staircase in the Tower. King Charles II ordered that the bones be placed in an urn marked with the children’s names on it which was located in Westminster Abbey until 1933 when it was reopened to be examined under the orders of King George V. Some animal bones were found within these two sets of children’s skeletons and since in 1933 modern DNA testing wasn’t invented yet, the tomb was closed. Further reopening the tomb and testing has been denied, so ultimately we still do not factually know if these are the true Princes in the Tower
~
#royal autumn 2024 challenge#the princes in the tower#princes in the tower#king Edward v#prince Richard#Duke or York#british royal family#brf#princess Alice#princess alice grand duchess of hesse#princess margaret of connaught#crown princess margaret of sweden#prince arthur of connaught#1800s#Victorian era#1483#king richard iii#1400s
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
THIS DAY IN GAY HISTORY
based on: The White Crane Institute's 'Gay Wisdom', Gay Birthdays, Gay For Today, Famous GLBT, glbt-Gay Encylopedia, Today in Gay History, Wikipedia, and more … November 29



1628 – John Felton, murderer of George Villiers (King James I's lover) was hanged. Villiers was the last in a succession of handsome young favorites on whom the king lavished affection and patronage, although the personal relationship between the two has been much debated.


1764 – Percy Jocelyn (d.1843) was Anglican Bishop of Clogher in the Church of Ireland from 1820 to 1822. He was forced from his position due to claims of homosexual practices.
In 1811, Bishop Percy's brother John Jocelyn's coachman, James Byrne, accused Percy of 'taking indecent familiarities' with him (possibly buggery) and of 'using indecent or obscene conversations with him'. The bishop survived this accusation, instead suing the coachman for libel. Byrne was convicted and was sentenced to two years in jail and also to public flogging. Recanting his allegations at the prompting of the bishop's agent, the floggings were stopped. A public subscription was raised in 1822 after Jocelyn's fall from grace to raise money for Byrne to try to make up for this miscarriage of justice.
On 19 July 1822, Percy Jocelyn was caught in a compromising position with a Grenadier Guardsman, John Moverley, in the back room of The White Lion public house, St Albans Place, off The Haymarket, Westminster. He and Moverley were released on bail, provided by the Earl of Roden and others. Jocelyn broke bail and moved to Scotland where he worked as a butler under an assumed name. He was declared deposed in his absence by the Metropolitan Court of Armagh in October 1822 for "the crimes of immorality, incontinence, Sodomitical practices, habits, and propensities, and neglect of his spiritual, judicial, and ministerial dutie."

A political cartoon of the time
Jocelyn was the most senior British churchman to be involved in a public homosexual scandal in the 19th century. It became a subject of satire and popular ribaldry, resulting in more than a dozen illustrated satirical cartoons, pamphlets, and limericks, such as:
The Devil to prove the Church was a farce Went out to fish for a Bugger. He baited his hook with a Soldier's arse And pulled up the Bishop of Clogher.
The scandal was so great, that in the days following, "it was not safe for a bishop to show himself in the streets of London", according to Charles Manners-Sutton, Archbishop of Canterbury at the time. In August 1822, Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh, who was both the Foreign Secretary and Leader of the House of Commons, had an audience with King George IV saying he was being blackmailed, and that "I am accused of the same crime as the Bishop of Clogher."


1931 – Leo Martello (d.2000) was an American Wiccan priest, gay rights activist, and author. He was a founding member of the Strega Tradition, a form of the modern Pagan new religious movement of Wicca which drew upon his own Italian heritage. During his lifetime he published a number of books on such esoteric subjects as Wicca, astrology, and tarot reading.
Born to a working-class Italian American family in Dudley, Massachusetts, he was raised Roman Catholic although became interested in esotericism as a teenager. He later claimed that when he was 21, relatives initiated him into a tradition of witchcraft inherited from their Sicilian ancestors; this conflicts with other statements that he made, and there is no independent evidence to corroborate his claim.
During the 1950s, he was based in New York City, where he worked as a graphologist and hypnotist. After beginning to publish books on paranormal topics in the early 1960s, he publicly began identifying as Wiccan in 1969, and stated that he was involved in a New York coven.
After the Stonewall riots of 1969, Martello – himself a gay man – involved himself in gay rights activism, becoming a member of the Gay Liberation Front (GLF). Leaving the GLF following an internal schism, he became a founding member of the Gay Activist Alliance (GAA) and authored a regular column, "The Gay Witch", for its newspaper.
In 1970 he founded the Witches International Craft Associates (WICA) as a networking organization for Wiccans, and under its auspices organized a "Witch In" that took place in Central Park at Halloween 1970, despite opposition from the New York City Parks Department. To campaign for the civil rights of Wiccans, he founded the Witches Anti-Defamation League, which was later renamed the Alternative Religions Education Network.
In 1973, he visited England, there being initiated into Gardnerian Wicca by the Gardnerian High Priestess Patricia Crowther. He continued practicing Wicca into the 1990s, when he retreated from public life, eventually succumbing to cancer in 2000.


1968 – Jonathan Knight is an American singer. Knight is part of the boyband New Kids on the Block. The band also includes Donnie Wahlberg, Joey McIntyre, Danny Wood and Jonathan's younger brother Jordan. He is the oldest member of the group and was the first to leave the group in 1994 prior to their official disbanding. The band reunited briefly in 2008.
Jonathan Knight was born in Boston, Massachusetts, to Canadian parents. (His father, an Episcopal priest, is from Meaford, Ontario; his mother is from Dunnville, Ontario.) He is one of six children, including Allison, Sharon, David, Christopher and Jordan.
In the early 1990s, Knight was linked to teen pop singer Tiffany. Both denied dating at the time. In 2009, The National Enquirer published an article from a man claiming to be Knight's ex-boyfriend, and outing him as gay. In a January 2011 interview, singer Tiffany stated that Knight is gay, which Knight then confirmed, saying "I have lived my life very openly and have never hidden the fact that I am gay." n a statement on the NKOTB blog, he added "Apparently the prerequisite to being a gay public figure is to appear on the cover of a magazine with the caption 'I am gay'. I apologize for not doing so if this is what was expected!"
Since 2008, Knight has been in a relationship with Harley Rodriguez, best known for playing Manny Lopez in the Sweet Valley High television series. The two participated in the 26th season of the reality competition series The Amazing Race, which aired on CBS in early 2015, where they placed 9th. On November 15, 2016, while vacationing in Africa, the two became engaged when Knight proposed to Rodriguez. In March 2021, Knight began hosting the HGTV television show Farmhouse Fixer, in which he restores old New England farmhouses for clients.
On August 25, 2022, it was revealed that Knight and Rodriguez had married.


1971 – Steve May is a former politician from Arizona, where he served in the Arizona House of Representatives. He was openly gay when he ran for and served in the legislature. He was nevertheless recalled to active duty in the military. He came to national attention in 1999 when the U.S. Army attempted to discharge him from the United States Army Reserve under the gay-exclusionary law known as "don't ask, don't tell" (DADT).
May was born and grew up in a Mormon household in Phoenix, Arizona, in the district he later represented in the state legislature. He was an Eagle Scout. He entered the Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps in 1989 at the age of 17 at Claremont McKenna College and received his commission as an U.S. Army officer in 1993. He served for two and a half years at Fort Riley, Kansas. His assignments included managing the integration of women into an all-male platoon. He left the Army with an honorable discharge in 1995. May ran unsuccessfully for the House in 1996 before winning a seat in 1998, as a Republican. He ran as an openly gay man and had secured the endorsement of the Gay & Lesbian Victory Fund, a political action committee dedicated to helping elect openly LGBT candidates to public office. He and his family have engaged in protracted lawsuits about their competing business interests.
On February 3, 1999, May spoke to a committee of the Arizona House about pending legislation that would prevent local jurisdictions from providing benefits to the domestic partners of their employees. He said:
I know many of you expected me to sit quietly in my office, but I cannot sit quietly in my office when another member attacks my family and attempts to steal my freedom. And furthermore if this legislature intends to take my gay tax dollars, which work just as well as your straight tax dollars, then treat me fairly under the law.
A few weeks later, as the Kosovo crisis was developing, he was recalled by the Army Reserves, where he attained the rank of First Lieutenant. He returned to duty in April and in May a local magazine reported on him under the headline "Gay Ring Wing Mormon Steve May is a Walking Talking Contradiction". In July the Army notified him that he was under investigation for homosexuality.
An Army spokesman commented in August: "I don't think that the individual has been, shall we say, keeping this under wraps, as to his sexual orientation." In March 2000, the Army asked him to resign and he refused.
He said of this period:
That was in December of 1999 and I continued to serve my soldiers and my unit. My soldiers were very cooperative. They treated me just like they would any other officer, gay or straight. In March, I sent 18 kids off to Kosovo. When I came home from sending those kids out, I received a letter from the Army “inviting” me to resign. Not only did they invite me to resign, they wrote a letter of resignation for me. I wasn’t about to let the Army have the satisfaction of me just going away. The fact is, the Army called me back into service when they felt they needed me. I was willing to give my life for my country and now the Army was telling me that my life was no longer worthy to give. Not because of anything that I did, but because of who I am. Well, they should have known who I was before they asked me to me back. I refused to resign.
On September 17, 2000, an Army panel recommended May be given an honorable discharge under DADT. May fought to remain in service and in January 2001 the Army terminated its discharge proceedings. May received an honorable discharge in May 2001 at the scheduled conclusion of his term of service.
During his time in office, May served as the chairman of the House Ways and Means committee and was instrumental in getting Arizona's sodomy law repealed.In 2002, May lost his bid for re-election. In 2010, May joined the race for Arizona's 17th District House seat as a write-in candidate. Following the revelation of a 2009 guilty plea to a charge of driving under the influence of alcohol, for which May served ten days in jail and received three years of probation, May dropped out of the race.


1981 – John Milhiser is an American actor and comedian. Milhiser first garnered attention for his work as a member of the Upright Citizens Brigade sketch group Serious Lunch, before achieving widespread success for his brief stint as a cast member on the NBC sketch comedy series Saturday Night Live for the 2013–2014 season.
He has been a regular performer at the Upright Citizens Brigade Theater since 2005, where he was a member of the sketch comedy group Serious Lunch, who have been featured on Late Night with Jimmy Fallon and Attack of the Show. Milhiser is a native of Belle Mead, New Jersey and he graduated in 2000 from Montgomery High School in Skillman, New Jersey. He later attended Hofstra University, where he graduated in 2004 as a Film Studies and Production major and was a member of Sigma Pi fraternity.
Milhiser made his debut on Saturday Night Live on the September 28, 2013, season premiere hosted by Tina Fey. His celebrity impressions included Jon Cryer, Matthew McConaughey, Verne Troyer (as Mini-Me from the Austin Powers movies), and Billie Joe Armstrong. On July 15, 2014, it was announced that Milhiser's contract with SNL was not renewed and he would not be returning as a cast member.
In 2014, Milhiser appeared in a supporting role in the indie film Camp Takota. He has also made guest appearances on television programs such as Adam Ruins Everything, 2 Broke Girls, Netflix Original Series Love, and Other Space.
Milhiser was Saturday Night Live's second openly gay male cast member (after Terry Sweeney), as well as the one of the few LGBTQ cast members overall.


1984 – Less than a month after being established as a city, West Hollywood approved a gay rights ordinance.

1990 – US President George H.W. Bush signs an immigration bill ending the gay ban.


8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Austerity has been biting since 2010, when George Osborne slashed the amount of money councils could receive from central government in one of his first acts as chancellor. Between 2010 and 2020, they lost more than 50% of their government grants in real terms. Six councils have already gone ‘bankrupt’ in the last two years while more than half of the rest say they could follow, meaning they could be taken over by Whitehall or replaced by new authorities.
[...]
Councils are responsible for 800 different services, including meeting Britain’s soaring demand for social care. They also run schools, public health, housing, planning and licensing. “Everyone thinks that councils [just] collect the bins and fix the roads,” said Revans. “We do so, so much more.” Most council services are mandatory, meaning they must legally be delivered. But others – including leisure centres, pest control, museums, and youth clubs – are discretionary, meaning councils can choose whether to offer them or not.
[...]
When David Cameron and Nick Clegg formed the coalition government in 2010, they declared that: “The time has come to disperse power more widely in Britain today.” A year later, the Localism Act became law, giving councils “the legal capacity to do anything that an individual can do”. In practice, that meant not a lot, because councils continue to be fiscally dependent on Westminster. London, for example, relies on strings-attached central government grants for 68.8% of its funding. New York, by comparison, only depends on central government for 26% of its budget, and Paris just 16.3%. Councils can also generate revenue from council tax and business rates, an equivalent tax on business premises. But the Localism Act prevents councils from raising council tax annually above a cap – which is currently 5% – set by the government. Austerity, then, has seemingly overridden any attempt at decentralisation. Fourteen years ago, your council could do a lot more for you, especially if you were in a tight spot. But year after year, it has pared back what it offers to the point that some campaigners fear residents expect less in the first place.
29 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hi! You think arthur wasn't premature? Do you think he was planned ?
Hi! Sorry for taking so long to reply! Honestly, I'm unsure whether Arthur was carried to term or genuinely premature. I've been meaning to make a poll about it because imo this is such an interesting speculation. The arguments in favour and against Arthur being premature would be, in general lines:
Arguments in favour:
Elizabeth of York seems to have been sick during her pregnancy. Preparations had been made for her arrival at York for the king's northern progress but she did not go. After her labour, she definitely became sick (she had an 'ague', as the herald recorded). Hyperemesis gravidarum could explain Elizabeth's sickness and possible preterm delivery.
The Earl of Oxford, one of Arthur's godparents, arrived late for Arthur's christening ceremony, delaying for a couple of days. If Arthur was born premature it could explain why Oxford had not made his way yet to Winchester by the time of his godchild's birth.
Henry VII was famously prudent, which was also talked about during his lifetime, and that might have hindered any premarital relations. He went to great lengths to have all the necessary marriage dispensations and to have his marriage formally recognised by parliament as a state necessity. Given the whole context of past accusations of illegitimacy against royal heirs, it would be out of character for him to risk having his heir born before they could get a papal dispensation and undergo a formal public wedding ceremony. Henry himself declared to the papal legate that 'he cannot fulfil such desire [marriage] without obtaining canonical dispensation'.
Arguments against:
Arthur was described as a 'fair prince and large of bones' at his birth. Being described as a big baby does not sound like someone who was born before his term. His parents waited a few days for his baptism thanks to Oxford's late arrival so they definitely thought him healthy enough to risk the possibility of him dying before getting him the sacrament. At that time, babies who died before baptism were considered unable to go to Heaven, and many hasty baptisms were performed by midwives soon after the child's delivery if their health was considered to be in danger. The herald who registered the proceedings of Arthur's birth and christening never once did mention that Arthur arrived early or that Elizabeth of York 'was delivered suddenly', like she was said to have the last time she gave birth (1503).
In medieval England, betrothals could be as binding as an actual marriage. Elizabeth of York was described as Henry VII's 'wife' since December 1485 and seems to have moved into the Palace of Westminster around that time, that is, they started cohabitating from then on. It's possible they became husband and wife in practical terms after a declaration of intention to marry followed by consummation (marriage per verba de praesenti).
Although Henry VII made sure to get all the necessary papal dispensations (3), the fact is that he did not wait for the arrival of all three dispensations and quickly married Elizabeth after the arrival of the first one — only two days later, in fact. Did they rush to get a public wedding because they had already been living as husband and wife? Did they do it because they feared Elizabeth could already have been pregnant at that time? Why couldn't they wait until March/April when the other dispensation, signed by the Pope himself this time, arrived?
The papal representative that gave them their first dispensation arrived in England in January. It's possible they already knew about his arrival back in December and knew that they could quickly get their first dispensation through him (they certainly did prepare for his audience), so cohabitating (and everything else it entailed) would not be as risky and imprudent of them as we might think nowadays. Alternatively, the papal legate might have already been in England by December but could only hold an audience in January once Advent/Christmastide was over.
Henry VII's prudence aside, they might have simply had the hots for each other. Thomas Stanley declared at the papal audience that he often heard Elizabeth and Henry talking together about their marriage ('often and at divers times treating and communing of and about a marriage to be contracted between them') and that Elizabeth had 'great and intimate love and cordial affection' for Henry. Stanley was the only witness to cite Elizabeth's love and affection when questioned, so it does not read as an argument line that was agreed upon between all the witnesses before the audience. Interestingly, in the ballad The Most Pleasant Song of the Lady Bessy, Thomas Stanley is portrayed as Elizabeth's trusted friend. Similarly, the Earl of Nottingham, who claimed to have known Henry for twenty years, was the only one to cite Henry's 'singular love which he bears to her'. The pregnancy calculator sets Arthur's full-term conception as 29 December-4 January, so could Arthur have been a Christmas/New Year's celebration baby, conceived during a time when court etiquette was particularly lax and the mood particularly festive?
This is all I can think now but there might be other arguments either in favour or against the theory. I've been meaning to read a new biography of Arthur Tudor recently published whose author seems to think Arthur truly was premature, so I'm curious to know why he thinks that. Of course, the theory that Arthur was premature does carry a certain weight. Every argument against it can be refuted, including for example, the idea that Arthur would have looked small on the day of his birth (20 September 1486) if he was conceived exactly on their parents' wedding night — he would only be a week short of his full time, then. If he was conceived later, though, he would have been even more premature. It's difficult to say.
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
As Reformation Day Approaches...
Many will wish to talk about Martin Luther. Which makes sense because he famously nailed the 95 theses to the church door at Wittenburg on October 31st.
But what better time to commemorate all of the OTHER important figures and reformers of the Protestant reformation? Of whom there were many.
Wikipedia lists 284 people burned in England under Queen Mary I, as she attempted to consolidate her power. Her new laws declared anyone teaching against Catholic doctrines to be guilty of heresy and subject to the death penalty. The Catholic church has never denounced these murders committed by its members on its behalf.
These laws affected famous and regular people alike. Over time I may make a series of posts with more detail about some of these persons.
Incomplete list of the protestant martyrs in England under the cut. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
Protestants executed under Mary I
1. John Rogers City of London clergyman – preacher, biblical translator, lecturer at St. Paul's Cathedral burnt 4 February 1555 Smithfield, London
2. Lawrence Saunders City of London clergyman – preacher, Rector of All Hallows Bread Street, London burnt 8 February 1555 Coventry, Warwickshire
3. John Hooper Gloucester and Worcester clergyman – Bishop of Gloucester and Worcester under Edward VI burnt 9 February 1555 Gloucester, Gloucestershire
4. Rowland Taylor Hadleigh, Suffolk clergyman – Rector of Hadleigh, Suffolk burnt 9 February 1555 Aldham Common, Nr Hadleigh, Suffolk[5]: p.98 [59]
5. Rawlins White Cardiff, Glamorgan fisherman burnt March 1555 Cardiff, Glamorgan[60]
6. Thomas Tomkins Shoreditch, London weaver burnt 16 March 1555 Smithfield, London[61]
7. Thomas Causton Horndon on the Hill or Thundersby, Essex gentleman burnt 26 March 1555 Rayleigh, Essex[62]
8. Thomas Higbed Horndon on the Hill or Thundersby, Essex gentleman burnt 26 March 1555 Horndon-on-the-Hill, Essex[62]
9. William Hunter Coleman Street Parish, London apprentice burnt 27 March 1555 (or 26 according to Foxe) Brentwood, Essex
10. Stephen Knight barber burnt 28 March 1555 Maldon, Essex[64]
11. William Pygot (or Pigot) butcher burnt 28 March 1555 Braintree, Essex[64]
12. [n 6] William Dighel burnt 28 March 1555 Banbury, Oxfordshire [65][66]
13. John Lawrence (or Laurence) clergyman – priest and former Blackfriar at Sudbury, Suffolk[50] burnt 29 March 1555 Colchester, Essex[64]
14. Robert Ferrar St David's, Pembrokeshire clergyman – Bishop of St David's under Edward VI burnt 30 March 1555 Carmarthen, Carmarthenshire[67]
15. George Marsh Dean, Lancashire clergyman – curate to Laurence Saunders and minister at Dean, Lancashire burnt 24 April 1555 Boughton, Cheshire[68]
16. William Flower Lambeth, London surgeon and teacher burnt 24 April 1555 Westminster[69]
17. John Cardmaker Wells, Somerset clergyman – prebendary of Wells Cathedral burnt 30 May 1555 Smithfield, London[70]
18. John Warne Walbrook, London upholsterer burnt 30 May 1555 Smithfield, London[70]
19. Thomas Hawkes (or Haukes) Essex gentleman burnt 10 June 1555 Coggeshall, Essex
20. Thomas Watts (or Wattes) Billericay, Essex linen draper burnt 10 June 1555 Chelmsford, Essex[7][72]
21. John Ardeley (or Ardite) Wigborough, Essex husbandman burnt 30 May 1555 (or 'about 10 June', according to Foxe) Rayleigh, Essex[7][73]
22. John Simson Wigborough, Essex husbandman burnt 30 May 1555 (or 'about 10 June', according to Foxe) Rochford, Essex[7][73]
23. Nicholas Chamberlain (or Chamberlaine) Coggeshall, Essex weaver burnt 14 June 1555 Colchester, Essex[7][74]
24. William Bamford (or Butler)[n 8]Coggeshall, Essex weaver burnt 15 June 1555 Harwich, Essex[7][74]
25. Thomas Ormond (or Osmande)[n 9]Coggeshall, Essex fuller burnt 15 June 1555 Manningtree, Essex[7][74]
26. John Bradford City of London clergyman – prebendary of St Paul's Cathedral burnt 1 July 1555 Smithfield, London[7][75][76]
27. John Leaf (or Jhon Least) Christ Church Greyfriars, London (born in Kirkby Moorside, Yorkshire) apprentice tallow chandler burnt 1 July 1555 Smithfield, London
Canterbury Martyrs of July 1555
28. John Bland (or Blande) Rolvenden, Kent clergyman – vicar of Rolvenden, Kent burnt 12 July 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][78]
29. Nicholas Shetterden (or Shitterdun) burnt 12 July 1555 Canterbury, Kent
30. John Frankesh Adisham, Kent clergyman – parson of Adisham, Kent burnt 12 July 1555 Canterbury, Kent
31. Humphrey Middleton Ashford, Kent burnt 12 July 1555 Canterbury, Kent
32. Nicholas Hall Dartford, Kent bricklayer burnt 19 July 1555 Rochester, Kent
33. Christopher Wade Dartford, Kent linen-weaver burnt July 1555 Dartford, Kent
34. Margaret (or Margery) Polley Pepeling, Calais widow burnt 17 July 1555 Royal Tunbridge Wells, Kent[80]
35. Dirick Carver (also spelt Deryk; also known as Dirick Harman) Brighthelmstone (now Brighton), Sussex beer-brewer burnt 22 July 1555, Lewes, East Sussex
36. John Launder Godstone, Surrey husbandman burnt 23 July 1555 Steyning, West Sussex
37. Thomas Euerson (or Iueson, Iverson or Iveson) Godstone, Surrey carpenter burnt (day unknown) July 1555 Chichester, West Sussex
38. Richard Hook (or Hooke) lame man [66] burnt unknown date in July 1555 Chichester, West Sussex
39. James Abbess Stoke-by-Nayland, Suffolk shoemaker burnt 2 August 1555 Thetford, Norfolk (or Bury, according to Foxe)
40. John Denley Maidstone, Kent gentleman burnt 8 August 1555 Uxbridge, Middlesex
41. Robert Smith Windsor, Berkshire clerk at the college in Windsor, Berkshire and painter burnt 8 August 1555 Uxbridge, Middlesex
Canterbury Martyrs of August 1555
42. William Coker burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][89]
43. William Hopper Cranbrook, Kent[79] burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][89]
44. Henry Laurence burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][89]
45. Richard Collier (or Colliar) burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent
46. Richard Wright Ashford, Kent[79] burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent
47. William StereAshford, Kent[79] burnt 23 August 1555 Canterbury, Kent
48. Elizabeth Warne (or Warren)[n 13]Walbrook, London widow of John Warne, upholsterer burnt 23 August 1555 Stratford-atte-Bow, London
49. Roger Hues (aliases: Curryer, Corier) St Mary's, Taunton, Somerset burnt 24 August 1555 Taunton, Somerset [66][7][91]
50. George Tankerfield London (born in York) cook burnt 26 August 1555 St Albans
51. Patrick Pakingham (aliases: Packingham, Pachingham, Patchingham or Pattenham) burnt 28 August 1555 Uxbridge, Middlesex [7][87]
52. John Newman Maidstone, Kent pewterer burnt 31 August 1555 Saffron Walden, Essex [7][87]
53. Robert Samuel (or Samuell) Barfold, Suffolk clergyman – minister at Barfold, Suffolk burnt 31 August 1555 Thetford, Norfolk[7][93]
54. Stephen HarwoodWare, Hertfordshire brewer burnt 30 August 1555 Stratford in Essex[7][94]
55. Thomas Fust (or Fusse) hosier, August 1555 In the environs of London or Ware
56. William Hale (or Hailes)Thorpe, Essex, late August 1555 In the environs of Barnet, London
57. William Allen Somerton, Norfolk labourer burnt early September 1555 Walsingham, Norfolk
58. Roger Coe (or Coo or Cooe) Melford, Suffolk shearman burnt date unknown September 1555 Yoxford, Suffolk
59. Thomas CobHaverhill, Suffolk butcher burnt date unknown September 1555 Thetford, Norfolk
Canterbury Martyrs of September 1555
60. George Catmer (or Painter) Hythe, Kent burnt about 6 September 1555, according to Foxe (or 12 July 1555) Canterbury, Kent
61. Robert Streater (or Streter) Hythe, Kent burnt about 6 September 1555, according to Foxe (or 12 July 1555) Canterbury, Kent
62. Anthony Burward Calete (possibly Calais) [98] burnt about 6 September 1555, according to Foxe (or 12 July 1555) Canterbury, Kent
63. George Brodbridge (or Bradbridge) Bromfield, Kent burnt about 6 September 1555, according to Foxe (or 12 July 1555) Canterbury, Kent
64. James Tutty (or Tuttey)Brenchley, Kent burnt about 6 September 1555, according to Foxe (or 12 July 1555) Canterbury, Kent
65. Robert Glover (or Glouer)Mancetter, Warwickshire gentleman burnt 14 September 1555 Coventry, Warwickshire
66. Cornelius Bongey (or Bungey) capper burnt 20 September 1555 Coventry, Warwickshire
67. Thomas Hayward (or Heywarde) burnt mid September 1555 Lichfield, Staffordshire
68. John Goreway Holy Trinity Parish, Coventry, Warwickshire [50] burnt mid-September 1555 Lichfield, Staffordshire Ely Martyrs
69. William WolseyUpwell, Norfolk constable, one of the Ely Martyrs burnt 16 October 1555 Cathedral Green, Ely, Cambridgeshire
70. Robert Pygot (or Pigot) Wisbech, Isle of Ely, Cambridgeshire painter, also an Ely Martyr burnt 16 October 1555 Cathedral Green, Ely, Cambridgeshire
Oxford Martyrs
71. Hugh Latimer (or Latymer) Baxterley, Warwickshire [103] clergyman – chaplain to King Edward VI burnt 16 October 1555 outside Balliol College, Oxford
72. Nicholas RidleyFulham Palace clergyman – Bishop of London under Edward VI burnt 16 October 1555 outside Balliol College, Oxford
Canterbury Martyrs of November 1555
73. John Webbe (or Web) gentleman burnt 30 November 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][105]
74. George Roper burnt 30 November 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][105]
75. Gregory Parke (or Paynter)[citation needed] burnt 30 November 1555 Canterbury, Kent [7][105]
76. John PhilpotWinchester, Hampshire clergyman – Archdeacon of Winchester burnt 18 December 1555 Smithfield, London[7][106]
77. Thomas Whittle (or Whitwell)Essex clergyman – priest or minister burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
78. Bartlett (or Bartholomew) GreenTemple, London – born in Basinghall, London gentleman and lawyer burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
79. Thomas BrownSt Bride's parish, Fleet Street, London – born in Histon, Cambridgeshire burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
80. John TudsonSt Mary Botolph parish, London – born in Ipswich, Suffolk artificer burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
81. John Went (or Winter or Hunt) Langham, Essex artificer burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
82. Isobella Forster (or Annis Foster) St Bride's parish, Fleet Street, London – Born in Greystoke, Cumberland wife of John Foster, cutler burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London[7][107]
83. Joan Lushford (or Jone Lashforde, or Warne) Little Allhallows parish, Thames Street, London maid burnt 27 January 1556 Smithfield, London
Canterbury Martyrs of 1556
84. John Lomas (or Jhon Lowmas) Tenterden, Kent burnt 31 January 1556 Wincheap, Canterbury [7][108]
85. Annes Snoth (or Annis Snod) Smarden, Kent widow burnt 31 January 1556 Wincheap, Canterbury [7][108]
86. Anne Wright (or Albright); alias Champnes burnt 31 January 1556 Wincheap,Canterbury [7][108]
87. Joan (or Jone) SoaleHorton, Kent wife burnt 31 January 1556 Wincheap, Canterbury [7][108]
88. Joan Catmer Hythe, Kent 'wife (as it should seem) of George Catmer', burnt in 1555 burnt 31 January 1556 Wincheap, Canterbury [108][n 15][7]Ipswich Martyrs of 1556
89. Agnes Potten Ipswich, Suffolk wife of Robert Potten burnt 19 February 1556 Ipswich, Cornhill [7][n 16][109]
90. Joan Trunchfield Ipswich, Suffolk wife of Michael Trunchfield, a shoemaker burnt 19 February 1556 Ipswich, Cornhill
91. Thomas Cranmer Lambeth Palace clergyman – Archbishop of Canterbury (former) burnt 21 March 1556 outside Balliol College, Oxford[7][110]
92. John Maundrel Beckhampton, Wiltshire – brought up in Rowde, Wiltshire husbandman burnt 24 March 1556 outside Salisbury, Wiltshire
93. William Coberly Wiltshire tailor burnt 24 March 1556 outside Salisbury, Wiltshire
94. John Spicer (or Spencer) Winston, Suffolk[50] freemason or bricklayer burnt 24 March 1556 outside Salisbury, Wiltshire
95. John Harpole (or Hartpoole) St Nicholas Parish, Rochester, Kent burnt 1 April 1556 Rochester, Kent[7][112]
96. Joan BeachTunbridge Wells, Kent widow burnt 1 April 1556 Rochester, Kent
97. John Hullier (or Hulliarde) Babraham, Cambridgeshire clergyman – curate of Babraham, Cambridgeshire burnt 16 April 1556 Cambridge, Cambridgeshire
98. William Tyms (or Timmes)Hockley, Essex clergyman – curate of Hockley, Essex burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London
99. Robert DrakeThundersley, Essex clergyman – minister or parson of Thundersley, Essex burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London
100. Richard SpurgeBocking, Essex shearman burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London[7][115]
101. Thomas SpurgeBocking, Essex fuller burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London[7][115]
102. George AmbroseBocking, Essex fuller burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London[7][115] 103. John Cavel (or Cauell)Bocking, Essex weaver burnt 24 April 1556 Smithfield, London[7][115]Colchester martyrs of April 1556
104. Christopher ListerDagenham, Essex husbandman burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex [7][116]
105. John MaceColchester, Essex apothecary burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex [7][116]
106. John SpencerColchester, Essex weaver burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex [7][116]
107. Simon Joyne sawyer burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex [116]
108. Richard NicolColchester, Essex weaver burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex
109. John HamondColchester, Essex tanner burnt 28 April 1556 Colchester, Essex [7][116]
110. Hugh Laverock (or Lauarocke) Barking, Essex painter, (a lame man) burnt 15 May 1556 Stratford in Essex
111. John Apprice (or Aprice) blind man burnt 15 May 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow or Stratford in Essex
112. Thomas Drowry blind boy burnt about 15 May 1556 Gloucester, Gloucestershire [7][n 18][118]
113. Thomas Croker bricklayer burnt about 15 May 1556 Gloucester, Gloucestershire [7][n 18][118]
114. Katherine HutBocking, Essex widow burnt 16 May 1556 Smithfield, London[7][117]
115. Elizabeth ThackvelGreat Burstead, Essex maid burnt 16 May 1556 Smithfield, London[7][117]
116. Joan (or Jone) HornsBillericay, Essex maid burnt 16 May 1556 Smithfield, London
117. Thomas Spicer Winston, Suffolk labourer burnt 21 May 1556 Beccles, Suffolk
118. John Deny (or Denny) (possibly a female Joan or Jone) Beccles, Suffolk burnt 21 May 1556 Beccles, Suffolk
119. Edmund PooleBeccles, Suffolk burnt 21 May 1556 Beccles, Suffolk
120. Thomas HarlandWoodmancote, Sussex carpenter burnt 6 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
121. John Oswald (or Oseward) Woodmancote, Sussex husbandman burnt 6 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
122. Thomas Reed Ardingly, Sussex burnt about 6 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
123. Thomas Avington (or Euington) Ardingly, Sussex turner burnt about 6 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
124. Adam Forster (or Foster) Mendlesham, Suffolk husbandman burnt 17 June 1556 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk [124][125]
125. Robert Lawson Mendlesham, Suffolk linen weaver burnt 17 June 1556 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk [124][125]
126. Thomas Wood clergyman – pastor burnt about 20 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
127. Thomas Milles Hellingly, Sussex burnt about 20 June 1556 Lewes, Sussex
128. Thomas Moor servant and husbandman burnt 26 June 1556 Leicester, Leicestershire
Stratford Martyrs, 11 men and 2 women.
129. Henry Adlington (or Addlinton) Grinstead, Sussex sawyer burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
130. Lawrence (or Laurence) ParnamHoddesdon, Hertfordshire smith burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
131. Henry WyeStanford-le-Hope, Essex brewer burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
132. William Holywell (or Hallywell)Waltham Holy Cross, Essex, smith. burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
133. Thomas Bowyer (or Bowier)Great Dunmow, Essex weaver burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
134. George Searle White Notley, Essex tailor burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
135. Edmond Hurst St James's Parish, Colchester labourer burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
136. Lion/Lyon Cawch City of London merchant/broker burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
137. Ralph Jackson Chipping Ongar, Essex, serving-man burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
138. John Derifall (or Dorifall) Rettendon, Essex labourer burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow[7][126]
139. John Routh/Roth Wickes, Essex labourer burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
140. Elizabeth Pepper St James's parish, Colchester wife of Thomas Pepper, weaver burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
141. Agnes George West Barefold, Essex wife of Richard George, husbandman burnt about 27 June 1556 Stratford-Atte-Bow
142. Roger Bernard Framsden, Suffolk labourer burnt 30 June 1556 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk [124][125]
143. Julins Palmer Reading, Berkshire schoolmaster burnt about 15 July 1556 'The Sand-pits', Nr Newbury, Berkshire
144. John Guin/Jhon Gwin shoemaker [66] burnt about 15 July 1556 'The Sand-pits', Nr Newbury, Berkshire[7][128]
145. Thomas Askin/Askue burnt about 15 July 1556 'The Sand-pits', Nr Newbury, Berkshire
Guernsey Martyrs – (Three women and one unborn male foetus)
146. Catherine Cauchés (sometimes spelt Katherine Cawches) St Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands burnt 18 July 1556 St Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands[129]
147. Perotine Massey (pregnant) St Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands wife of NormanCalvinist minister burnt 18 July 1556 St Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands[129]
148. Guillemine GilbertSt Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands burnt 18 July 1556 St Peter Port, Guernsey, Channel Islands
149. Thomas Dungate (or Dougate) East Grinstead, Sussex burnt 18 July 1556 Grinstead, Sussex
150. John Forman (or Foreman) East Grinstead, Sussex burnt 18 July 1556 Grinstead, Sussex
151. Anne Tree (or Try) West Hoathly, Sussex burnt 18 July 1556 Grinstead, Sussex
152. Joan WasteAll Hallows', Derby, Derbyshire blind woman burnt 1 August 1556 Derby, Derbyshire
153. Edward Sharp glover (possibly)[66] burnt early September 1556 Bristol, Gloucestershire/Somerset
154. Rose Pencell burnt 17 October 1555 Bristol
155. William Shapton weaver burnt 17 October 1555 Bristol[131]
156. John Kurde Syresham, Northamptonshire shoemaker burnt October 1556 or 20 September 1557 Northampton, Northamptonshire
157. John Noyes Laxfield, Suffolk shoemaker burnt 22 September 1556 or 1557 [133]
158. Thomas Ravensdale burnt 24 September 1556 Mayfield, Sussex[85][122]
159. John Hart burnt 24 September 1556 Mayfield, Sussex [85][122]
160. Unknown man shoemaker burnt 24 September 1556 Mayfield, Sussex [85]
161. Unknown man currier burnt 24 September 1556 Mayfield, Sussex [85]
162. Nicholas Holden Withyham, Sussex weaver burnt 24 September 1556 Mayfield, Sussex
163. Unknown man carpenter burnt 25 September 1556 Bristol, Gloucestershire/Somerset
164. John Horn burnt late September 1556 Wotton-under-Edge, Gloucestershire
165. John Phillpott Tenterden, Kent burnt 16 January 1557 Wye, Ashford, Kent
166. Thomas Stephens Biddenden, Kent burnt 16 January 1557 Wye, Ashford, Kent
Canterbury Martyrs of January 1557
167. Stephen KempeNorgate, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
168. William WatererBiddenden, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
169. William ProwtingThurnham, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
170. William LowickCranbrook, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
171. Thomas HudsonSelling, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
172. William HayHythe, Kent burnt 15 January 1557 Canterbury, Kent [136]
173. Nicholas Final Tenterden, Kent burnt 16 January 1557 Ashford, Kent
174. Martin Bradbridge Tenterden, Kent burnt 16 January 1557 Ashford, Kent
175. William Carman (or Carmen)[n 28] burnt day and month unknown 1557 [138]
176. Thomas Loseby burnt 12 April 1557 Smithfield, London
177. Henry Ramsey burnt 12 April 1557 Smithfield, London
178. Thomas Thyrtell (or Sturtle) burnt 12 April 1557 Smithfield, London
179. Margaret Hyde burnt 12 April 1557 Smithfield, London
180. Agnes Stanley (or Stanlye) burnt 12 April 1557 Smithfield, London
181. Richard Sharpe weaver burnt 7 May 1557 Cotham, Bristol[141]
182. Thomas Hale shoemaker burnt 7 May 1557 Cotham, Bristol[141]
183. Stephen Gratwick (or Steuen Grathwick) Brighthelmstone (now Brighton), Sussex burnt at end of May 1557 St. George's Fields, Southwark, Surrey
184. William Morant burnt at end of May 1557 St. George's Fields, Southwark, Surrey [7][142]: p. 272 [143]
185. Thomas King[66] burnt at end of May 1557 St. George's Fields, Southwark, Surrey
Maidstone martyrs
186. Joan (or Jone) Bradbridge Staplehurst, Kent Presumably a relative of Widow Bradbridge, burnt 19 June 1557[144] burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
187. Walter Appleby Maidstone, Kent burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
188. Petronil Appleby Maidstone, Kent wife of Walter Appleby burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
189. Edmund Allin (or Allen) Maplehurst Mill, Frittenden, Kent miller burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
190. Katherine Allin (or Allen) Maplehurst Mill, Frittenden, Kent Wife of Edmund Allin/Allen, miller burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
191. Joan (or Jone) Manning Maidstone, Kent burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]
192. Elizabeth (surname possibly 'Lewis') blind maid burnt 18 June 1557 Maidstone, Kent [7][145]Canterbury martyrs of June 1557
193. John Fishcock/Jhon Fiscoke burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [7][145]
194. Nicholas White burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [7][145] 195. Nicholas Pardue/Perdue burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [7][145]
196. Barbara Final burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [7][145]
197. Bradbridge's Widow (Bradbridge's Wife) Probably Tenterden, Kent Probably the widow of Martin Bradbridge, burnt 16 January 1557 burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [145]
198. Mistress Wilson (also referred to as 'Wilson's Wife') burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent [7][145]
199. Alice Benden, possibly also referred to as 'Benson's Wife' Staplehurst (or possibly Cranbrook), Kent[146] burnt 19 June 1557 Canterbury, Kent
Lewes Martyrs
200. Richard WoodmanWarbleton, Sussex iron-maker burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex [7][82][147]
201. George Stevens (or Steuens) Warbleton, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
202. William MainardMayfield, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
203. Alexander HosmanMayfield, Sussex servant of William Mainard burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
204. Thomasina WoodMayfield, Sussex maidservant of William Mainard burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
205. Margery Morris (or Morice) Heathfield, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
206. James Morris (or Morice) – son of Margery Heathfield, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
207. Denis Burcis (or Burgis) Buxted, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
208. Ann Ashdon (or Ashdown; also referred to as 'Ashdon's Wife') Rotherfield, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
209. Mary Groves (also referred to as 'Gloue's Wife') Lewes, Sussex burnt 22 June 1557 Lewes, Sussex
210. Simon Miller (or Milner) Lynn, Norfolk burnt 13 July 1557 Norwich, Norfolk
211. Elizabeth Cooper St Andrew's Church, Norwich, Norfolk wife of a pewterer burnt 13 July 1557 Norwich, Norfolk [7](which calls her 'a woman')
212. George Egles/Eagles hung, drawn & quartered, August 1557 Chelmsford, Essex[7][150]Colchester Martyrs of August 1557
213. William BongeorSt Nicholas Parish, Colchester, Essex glazier burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
214. William Purchase (or Purcas) Bocking, Essex fuller burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
215. Thomas Benhote (or Benold) Colchester, Essex tallow-chandler burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex
216. Agnes Silverside (or Smith) Colchester, Essex widow burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
217. Helen (or Ellen) EwringColchester, Essex wife of John Ewring, miller burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
218. Elizabeth Folk Colchester, Essex 'young maiden' and servant burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
219. William Munt (or Mount)Much Bentley, Essex burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex
220. Alice Munt (or Mount) Much Bentley, Essex wife of William Munt (or Mount) burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
221. Rose Allen (or Allin) Much Bentley, Essex spinster, daughter of Alice Mount burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
222. John JohnsonThorpe, Essex labourer burnt 2 August 1557 Colchester, Essex [151]
223. Richard Crashfield Wymondham, Norfolk burnt 5 August 1557 Norwich, Norfolk[7] which records 'one at Norwich' in July[152]
224. Father Fruier burnt August 1557 Rochester, Kent[7][150]
225. Robert Stevenson burnt August 1557 Rochester, Kent[153]
226. Sister of George Eagles burnt August 1557 Rochester, Kent
227. Unknown Woman burnt August 1557 Rochester, Kent[7]
228. Agnes Prest Boyton, Cornwall Spinner burnt 15 August 1557 Southernhay, Exeter [154]
229. Thomas Benion weaver burnt 27 August 1557 Bristol[141]
230. Joyce Lewis Mancetter, Warwickshire gentlewoman burnt September 1557 Lichfield, Staffordshire – may be the same as Joyce Bowes, August 1557 (the Regester)
231. Ralph Allerton/Rafe Glaiton Much Bentley, Essex burnt 17 September 1557 Islington
232. James Austoo (or Auscoo) burnt 17 September 1557 Islington
233. Margery Austoo (or Auscoo) burnt 17 September 1557 Islington[7][157]
234. Richard Roth (or Rooth) burnt 17 September 1557 Islington
235. Agnes Bongeor (also known as Bowmer's Wife), wife of Richard Bongeor (similar name but different death date) burnt 17 September (or unknown date July) Colchester, Essex (or March 1558, Colchester)
236. Margaret Thurston/Widow Thurston-similar name but different death date burnt 17 September (or unknown date July) Colchester, Essex [132](or March 1558, Colchester)
237. Cicely Ormes St Edmund's Parish, Norwich, Norfolk wife of Edmund Ormes, worsted-weaver burnt 23 September 1557 Norwich, Norfolk
238. Thomas Spurdance servant of the Queen burnt November 1557 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk
239. John Halingdale/Hallingdale/Hollingday carpenter burnt, 18 November/or day unknown October 1557, Smithfield, London
240. William Sparrow burnt, 18 November/or day unknown October 1557 Smithfield, London
241. Richard Gibson gentleman[66] burnt, 18 November/or day unknown October 1557 Smithfield, London
242. John Rough/Jhon Roughe London/Islington, Middlesex clergyman – minister at London/Islington, Middlesex burnt 22 December 1557 Smithfield, London
243. Margaret Maring (or Mering) burnt 22 December 1557 Smithfield, London
244. [Unknown forename ...] Lawton burnt March 1558 Huntingdon, Huntingdonshire
245. Cuthbert Symson/Symion London/Islington, Middlesex clergyman – deacon of the church in London/Islington, Middlesex died 28 March 1558 Smithfield, London
246. Hugh Foxe hosier[66] died 28 March 1558 Smithfield, London
247. John Devinish/Jhon Denneshe wool winder, died 28 March 1558 Smithfield, London
248. William Nichol burnt 9 April 1558 SM9515 Haverfordwest/Hwlffordd, Pembrokeshire/Sir Benfro
249. William Seaman (or Symon) Mendlesham, Suffolk husbandman burnt 19 May 1558 Norwich, Norfolk
250. Thomas Hudson Aylsham, Norfolk glover burnt 19 May 1558 Norwich, Norfolk[166] described as 'Glouer' in [7]
251. Thomas Carman[n 28] burnt 19 May 1558 Norwich, Norfolk
252. William Harris burnt 26 May 1558 Colchester[7][127]
253. Richard Day burnt 26 May 1558 Colchester, Essex [7][127]
254. Christian George (female) burnt 26 May 1558 Colchester, Essex her husband had previously been married to Agnes George, mentioned above
Islington Martyrs
255. Henry Pond (or Houde) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
256. Reinald Eastland (or Launder) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
257. Robert Southain (or Southam) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
258. Matthew Ricarby (or Ricarbie) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
259. John Floyd (or Flood) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
260. John Holiday (or Hollyday) burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
261. Roger Holland London (taken in or near St John's Wood) merchant tailor burnt 27 June 1558 Smithfield, London
262. Sir Richard Yeoman (or Yeman) Hadleigh, Suffolk clergyman – curate of Hadleigh, Suffolk burnt 10 July 1558 Norwich, Norfolk
Islington Martyrs (second group)
263. Robert Mills burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex [167]
264. Stephen Cotton burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex
265. Robert Dynes burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex [167]
266. Stephen Wight (or Wreight) burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex
267. John Slade burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex
268. William Pikes (aliases: Pikas, Peckes) tanner burnt 14 July 1558 Brentford, Middlesex [7][167]
269. John Cooke sawyer burnt about 25 July 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk [170]
270. Robert Milles (or Plummer) shearman burnt about 25 July 1558 Bury St Edmunds
271. Alexander Lane wheelwright burnt about 25 July 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk
272. James Ashley bachelor burnt about 25 July 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk
273. Thomas Benbrike/Benbridge gentleman burnt unknown day in July 1558 Winchester, Hampshire
274. John (or Richard) Snell Bedale, Yorkshire burnt 9 September 1558 Richmond, Yorkshire
Ipswich Martyrs of 1558
275. Alexander Gooch (or Geche, or Gouch) Woodbridge or Melton, Suffolk weaver of shredding-coverlets burnt 4 November 1558 Ipswich Cornhill
276. Alice DriverGrundisburgh, Suffolk wife of a husbandman burnt 4 November 1558 Ipswich Cornhill [173]
277. Philip Humphrey (or Humfrey) burnt November 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk
278. John David/Jhon Dauy (brother of Henry David) burnt November 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk
279. Henry David/H. Dauy (brother of John David) burnt November 1558 Bury St Edmunds, Suffolk [174]Canterbury Martyrs of 1558
280. John CornefordWrotham, Kent burnt 15 November 1558 Canterbury, Kent [175]
281. Christopher Brown Maidstone, Kent burnt 15 November 1558 Canterbury[175]
282. John HerstAshford, Kent burnt 15 November 1558 Canterbury, Kent
283. Alice Snoth burnt 15 November 1558 Canterbury, Kent [175]
284. Katherine Knight/Tynley an aged woman burnt 15 November 1558 Canterbury
#english reformation#history#protestant#now you will see me open up about my study of the english reformation#protestant martyrs
65 notes
·
View notes
Note
my baby fever is also … atrocious. would love to see anything with matty and a baby (or a dad to be matty) if you’re comfortable with that!
Literally cannot stop thinking about a tiny baby with curly hair in a Paddington Bear onesie. Look at what you’ve done!!! 😭😭😭
(Do not take a shot every time I say onesie). I hope you like it :)
Matty x Female reader

Onesie
‘She already has a bunch of onesies, love,’ you tell him gently but he’s lost in his excitement
‘She can always have more,’ his voice trails off as he’s already making his way into the newborn clothes aisle.
‘She’s not even out yet and she’s the most spoiled girl ever,’ you laugh.
‘And she should be!’ he calls out.
This is the first time he’s left you alone all day. He’s always there with his hand on the small of your back, making sure people don’t accidentally bump into you, making sure he’s there if you are in pain or start to feel dizzy or nauseous or any other disaster that you’re sure he’s thought of.
You take advantage of this alone time as you wander over to another rack. You gently run your fingers over the clothes, make sure they are as soft as they look. You rub a hand over your belly and ask her what colour she wants.
It’s not like she can respond to you but you love the idea that she’s contemplating the answer in there; that she will move and kick when you come across a colour she likes.
Out of the corner of your eye, you see Matty debating between two onesies—a sage green one with daisies on it and a lilac one with bumblebees. Then he shrugs his shoulders and grabs them both.
‘Look how excited Daddy is,’ you whisper to your stomach and start making your way to him.
Just as your eyes slide off the last rack, you freeze in your tracks.
In a sea of darker colours, the white onesie stands out like a beacon. And it is the best thing you’ve ever seen.
It’s patterned with little Paddington Bears doing various activities. There’s one that stands in front of Westminster Bridge, there’s one that’s leaning against a lamp post and there’s one that’s waving in excitement.
You can already feel the flood of incoming tears. Just as the first soft sob comes out of you, Matty’s already there.
‘Are you okay? Are you in pain?’ it’s the worry and concern in his voice that makes you cry harder.
‘No,’ you manage to take a deep breath, ‘it’s so stupid…but lo–look at the Paddington Bear onesie!’
‘Wha…ohhh,’ his face softens as realisation dawns on him.
It takes him one look before he’s also fallen hopelessly in love with the tiny thing in front of him. He takes a step forward and touches it in a daze as if he’s already imagining caressing his daughter’s cheek, tickling her tummy until she can’t stop giggling.
‘I think this one’s perfect,’ he whispers while trying not to sound all choked up.
Almost as if in response, you feel a familiar flutter in your stomach.
‘I think she likes it too,’ you laugh quietly while rubbing a hand on your belly.
He turns around, looks at you with quiet joy radiating off of him.
‘Is she kicking?’
‘Mm-hmm,’ you confirm and hold your hand out for his.
He eagerly obliges, waits until you place it on the exact spot and then caresses the spot gently. It never gets old for him. He’s felt the baby kick countless times before. Often at night, he sings to her—sings to both of you—while rubbing your belly but he’s always eager for more.
A few more tears escape your eyes as you think about what a good dad he’s going to be. He wastes no time in wiping them off and you focus on the callouses on his fingers, on the humdrum of the people, on this moment that feels like a core memory.
‘Let’s get this then,’ he declares.
‘Let’s get this,’ you confirm.
236 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Mick Hume
In one sense, of course, the posturing by European and American politicians makes no difference to the war, since the Israeli government and people have so far shown little inclination to buckle, despite the international opprobrium. When Starmer declared that the fighting must ‘stop now’ in February, he might as well have said ‘stop the world, I want to get off’. But such political posturing does increase Israel’s isolation in a hostile world.
More immediately, the impending abandonment of Israel really does matter here in the UK, Europe and the West. It signals that our leaders are giving up on the fight to defend democracy and freedom at home, and to resist the rising tide of anti-Semitism.
In the immediate aftermath of 7 October, the British Jewish playwright Tom Stoppard issued a cautionary warning that: ‘Before we take up a position on what’s happening now, we should consider whether this is a fight over territory or a struggle between civilisation and barbarism.’
Six months later, that is even more true. This remains a fundamental struggle between civilisation and barbarism. Not a ‘fight over territory’ or any two-state solutions. It is an existential battle about the survival of the only Western-style democracy in the Middle East – and the ability of Western society to defend its values against Islamist and allied barbarians who are not only within the gates of the citadel, but also projecting their pro-genocide message on to the Palace of Westminster. The unholy alliance of Islamist and left-wing anti-Semitism, united by their hatred for Western society, is the threat we face at home.
Anybody who wants to defend our democratic civilisation, warts and all, needs to stand foursquare with the Israeli people, and to remind the world of who they are fighting against and what they are fighting for. As spineless Western leaders risk losing the life-and-death war over there, and the struggle for democratic values at home, our message needs to be: No Surrender.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lia de Beaumont, Mademoiselle d'Éon, a French-born aristocrat, became the subject of a huge wager in London in 1776, printed in the Westminster Gazette:
This gentleman declares the d'Eon (alias the Chevalier d'Eon) a WOMAN in the clearest sense of the word; this declaration he supports with a bet of any such sum of money from one to five thousand guineas, or he proposes to any one, who will deposit five thousand guineas in the hand of his banker, to pay £10,000 if d'Eon proves herself either a MAN and HERMAPHRODITE or any other animal other than a WOMAN.
"Normal Women: 900 Years of Making History" - Philippa Gregory
#book quotes#normal women#philippa gregory#nonfiction#lia de beaumont#chevalier d'eon#french#aristocrat#wager#london#70s#1770s#18th century#westminster gazette#hermaphrodite#intersex
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
📍Westminster, London 🇬🇧🇵🇸!
Thousands participate in a protest in front of Parliament House in Westminster, London; To demand a ceasefire in Gaza.
From the homeland of the Foreign Minister who gave the Balfour Declaration to the Jews, just amazing!👌
|
#free palestine 🇵🇸#Palestine#free palestine#palestinian martyrs#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#gazaunderfire#help gaza#free gaza#gaza strip#gazaunderattack#gaza#gaza genocide#glory to all martyres#all world stand with gaza#i stand with gaza#i stand with palestine#save gaza#al aqsa flood#isreal is a terrorist state#israel is committing genocide#israel is bombing gaza hysterically#فلسطين#غزة تحت القصف#طوفان الأقصى#غزة تحت النار#شهداء غزة#غزة العزة#غزة الأبية#قطاع غزة#london
40 notes
·
View notes