#Ultrasonic Technology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

https://bit.ly/3S9egpW An anti-gravity air moisturizer is a type of humidifier that uses advanced technology to suspend a water reservoir in mid-air, creating the illusion that it is floating or levitating. This unique design not only adds a futuristic and stylish look to any room but also eliminates the need for a bulky base or stand, making it a space-saving option. Additionally, the device releases a fine mist of water vapor into the air, which helps to increase humidity levels and alleviate dry air symptoms such as dry skin, chapped lips, and sinus congestion. Overall, an anti-gravity air moisturizer is a functional and visually striking way to humidify the air in your home or office.
#Anti-gravity#Humidifier#Air Purifier#Dehumidifier#Portable#Quiet#Ultrasonic Technology#Essential Oil Diffuser#Aromatherapy#Healthy living#Home comfort#Energy efficient#Easy to use#Automatic shut-off#LED light#Health and wellness#Innovative technology#Allergies#Asthma#Dry air#Indoor air quality#Moisture control#Compact design#Mist output control.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dolphitech pioneers ultrasonic technology in non-destructive testing, setting new standards with precise inspection solutions for aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries.
0 notes
Text

Clear Away Algae With Ultrasonic Technology
Revolutionize water management with our cutting-edge Ultra-Sonic technology! Safely control algae For more info, visit: https://puroxi.com/ultra-sonic-algae-treatment/
0 notes
Text
Ultrasonic Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Ultrasonic sensors are devices that use ultrasonic waves, which are sound waves with frequencies higher than the audible range for humans (typically above 20,000 hertz), for various applications.
These sensors operate on the principle of sending out ultrasonic waves and measuring the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. This information can then be used to determine the distance or presence of the object.
Ultrasonic Sensors Working Principle
The working principle of ultrasonic sensors is based on the transmission and reception of ultrasonic waves. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how these sensors operate:
Generation of Ultrasonic Waves:
Ultrasonic sensors consist of a transducer, typically a piezoelectric crystal, that can convert electrical energy into ultrasonic waves. When an electrical voltage is applied to the crystal, it vibrates and generates ultrasonic waves in the frequency range beyond human hearing (typically above 20,000 hertz).
Wave Emission:
The ultrasonic sensor emits a short burst of ultrasonic waves into the surrounding environment. This burst of waves travels outward from the sensor.
Wave Propagation:
The ultrasonic waves move through the air until they encounter an object in their path. The waves continue to propagate until they hit a surface.
Reflection of Ultrasonic Waves:
When the ultrasonic waves strike an object, they are reflected back towards the sensor. The reflection occurs because the ultrasonic waves encounter a change in the medium (from air to the object’s surface), causing the waves to bounce back.
Reception of Reflected Waves:
The same transducer that emitted the ultrasonic waves now acts as a receiver. It detects the reflected waves returning from the object.
Time Measurement:
The sensor measures the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel from the sensor to the object and back. This time measurement is crucial for determining the distance to the object.
Distance Calculation:
Using the known speed of sound in the air, which is approximately 343 meters per second (at room temperature), the sensor calculates the distance to the object. The formula for distance (D) is given by D = (Speed of Sound × Time) / 2.
Output Signal:
The calculated distance information is then processed by the sensor’s electronics, and the output is provided in a suitable format, often as an analog voltage, digital signal, or distance reading.
These sensors work by emitting ultrasonic waves, detecting their reflections from objects, measuring the time taken for the round trip, and using this time information to calculate the distance to the objects in their detection range. This working principle is fundamental to various applications, including distance measurement, object detection, and obstacle avoidance.
Ultrasonic Sensors Pins Configurations
The pin configurations of ultrasonic sensors may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. However, We will discuss general overview of the typical pin configuration for a commonly used ultrasonic sensor module, like the HC-SR04. This module is widely used in hobbyist and educational projects.
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor typically has four pins:
VCC (Voltage Supply):
This pin is used to provide power to the sensor. It typically requires a voltage in the range of 5V.
Trig (Trigger):
The Trig pin is used to trigger the start of the ultrasonic pulse. When a pulse of at least 10 microseconds is applied to this pin, the sensor emits an ultrasonic wave.
Echo:
The Echo pin is used to receive the ultrasonic waves that are reflected back from an object. The duration of the pulse received on this pin is proportional to the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel to the object and back.
GND (Ground):
This pin is connected to the ground (0V) of the power supply.
Read More: Ultrasonic Sensors
#ultra sonic#ultrasonic sensors#ultrasonic technology#sensor technology#sensor applications#non-contact measurement#distance measurement#level measurement#flow measurement#object detection#obstacle avoidance#industrial automation#automotive industry#robotics#healthcare#home automation#smart homes#IoT#internet of things#technology#innovation#engineering#science#research#development#education#learning#acoustics#sound waves#frequency
0 notes
Text
#Anti-gravity#Humidifier#Air Purifier#Dehumidifier#Portable#Quiet#Ultrasonic Technology#Essential Oil Diffuser#Aromatherapy#Healthy living#Home comfort#Energy efficient#Easy to use#Automatic shut-off#LED light#Health and wellness#Innovative technology#Allergies#Asthma#Dry air#Indoor air quality#Moisture control#Compact design#Mist output control.
0 notes
Text
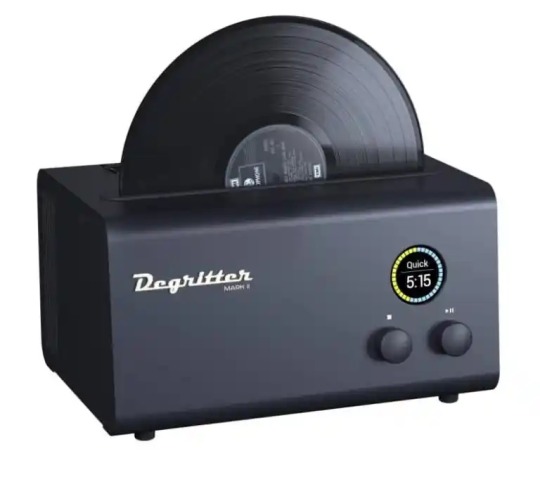

#audiophile#hifi#audio#audio system#hifidelity#technology#vinyl#new#news#listen#reviews#review#Degritter#ultrasonic#cavitation#clean#cleaner
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
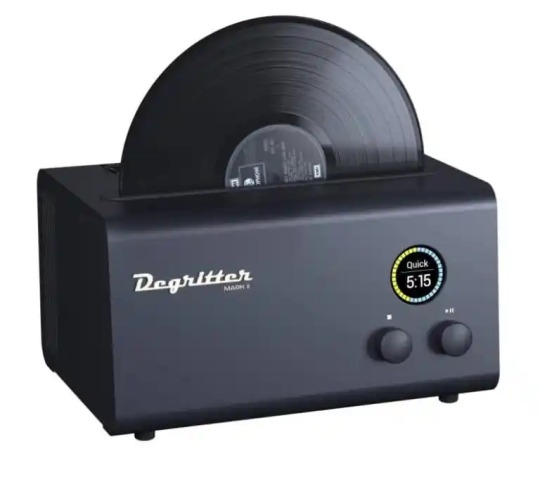

#audiophile#review#reviews#hifi#technology#audio#tech#listen#stereo#new#vinyl#Degritter#ultrasonic#clean#cleaner#cavitation#accessories#accessory
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
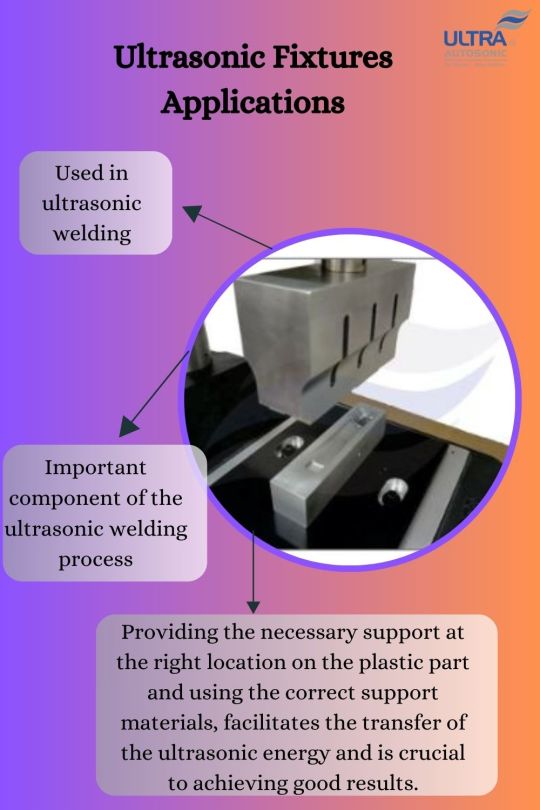
The main purpose of Ultrasonic Fixtures is to securely hold the workpieces or components in place while transmitting ultrasonic vibrations through them. This ensures that the vibrations are concentrated at specific points, optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of the ultrasonic process.
#Ultrasonic#supplier#technology#business#manufacture#pune#fixtures#innovation#weldinglife#processing#cutting#bonding#Stability#Accuracy
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Precision and Power: Spire’s Ultrasonic Heat Meters Transform Industrial Heat Management
Nowadays, demand for IoT enabled Ultrasonic flowmeters are increasing day by day. Accurate heat meter measurements are essential for effectively measuring the performance of heat generating technologies. Ultrasonic Heat meters are measuring accurate energy consumption and very effective from mechanical meters. Advanced Ultrasonic Heat Meters are required for most of industrial measurement. There…
0 notes
Text
dental fluoride treatments
#dental technology really has come a long way. the fluoride treatment used to taste terrible and stick too hard and now it tastes sweet#they used to have to scrape the plaque off with the metal hooks but now they have ultrasonic cleaners#if only they could make tooth polish that actually tastes like what flavor it says it is#i think i saw somewhere once that too much fluoride when the teeth are developing causes discoloration#yeah yeah dental fluorosis i was right. bet thats what happened to my cheesy tooth rip :( i did used to eat toothpaste
0 notes
Text

Enhance your dairy operations with Prompt Sanchay – the 3-in-1 digital solution designed to make milk collection process fast, effortless, and precise. Experience the next level of efficiency in dairy collection. To know more, visit https://www.promptdairytech.com/prompt-sanchay
#prompt#Sanchay#digital solution#mobile milk collection#milk collection system#built-in thermal printer#Ultrasonic stirrer#3 in 1 solution#technology#accuracy
0 notes
Text

https://bit.ly/3S9egpW An anti-gravity air moisturizer is a type of humidifier that uses advanced technology to suspend a water reservoir in mid-air, creating the illusion that it is floating or levitating. This unique design not only adds a futuristic and stylish look to any room but also eliminates the need for a bulky base or stand, making it a space-saving option. Additionally, the device releases a fine mist of water vapor into the air, which helps to increase humidity levels and alleviate dry air symptoms such as dry skin, chapped lips, and sinus congestion. Overall, an anti-gravity air moisturizer is a functional and visually striking way to humidify the air in your home or office. Anti-gravity, Humidifier, Air Purifier, Dehumidifier, Portable, Quiet, Ultrasonic Technology, Essential Oil Diffuser, Aromatherapy, Healthy living, Home comfort, Energy efficient, Easy to use, Automatic shut-off, LED light, Health and wellness, Innovative technology, Allergies, Asthma, Dry air, Indoor air quality, Moisture control, Compact design, Mist output control.
#https://bit.ly/3S9egpW#An anti-gravity air moisturizer is a type of humidifier that uses advanced technology to suspend a water reservoir in mid-air#creating the illusion that it is floating or levitating. This unique design not only adds a futuristic and stylish look to any room but als#making it a space-saving option. Additionally#the device releases a fine mist of water vapor into the air#which helps to increase humidity levels and alleviate dry air symptoms such as dry skin#chapped lips#and sinus congestion. Overall#an anti-gravity air moisturizer is a functional and visually striking way to humidify the air in your home or office.#Anti-gravity#Humidifier#Air Purifier#Dehumidifier#Portable#Quiet#Ultrasonic Technology#Essential Oil Diffuser#Aromatherapy#Healthy living#Home comfort#Energy efficient#Easy to use#Automatic shut-off#LED light#Health and wellness#Innovative technology#Allergies#Asthma#Dry air#Indoor air quality
1 note
·
View note
Text
Dolphitech's Dolphicam2+ NDT Ultrasonic Technology elevates inspection performance with its rugged tablet design, advanced imaging software, and user-friendly interface. Offering high-resolution imaging and real-time analysis, it enhances efficiency and accuracy in non-destructive testing processes for various industries.
0 notes
Text
Plastic structure design 7 - other design requirements
To read previous article, please refer to Plastic structure design 6 —part gaps, buckles and stops.This article mainly introduces requirements for penetration and penetration positions, ultrasonic welding, bottom scraping and surface scraping in design of plastic structures. See below for details; 1. Insertion position and penetration position Insertion position is often encountered in design…

View On WordPress
#Design of plastic products#Flat welding surface#Grooved welding surface#injection molding#plastic products#Plastic structure design#plastic structures#plastic welding#Stepped welding surface#Ultrasonic welding design#ultrasonic welding technology#Welding surface design
0 notes
Text
Ultrasonic Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Ultrasonic sensors are devices that use ultrasonic waves, which are sound waves with frequencies higher than the audible range for humans (typically above 20,000 hertz), for various applications.
These sensors operate on the principle of sending out ultrasonic waves and measuring the time it takes for the waves to bounce back after hitting an object. This information can then be used to determine the distance or presence of the object.
Ultrasonic Sensors Working Principle
The working principle of ultrasonic sensors is based on the transmission and reception of ultrasonic waves. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how these sensors operate:
Generation of Ultrasonic Waves:
Ultrasonic sensors consist of a transducer, typically a piezoelectric crystal, that can convert electrical energy into ultrasonic waves. When an electrical voltage is applied to the crystal, it vibrates and generates ultrasonic waves in the frequency range beyond human hearing (typically above 20,000 hertz).
Wave Emission:
The ultrasonic sensor emits a short burst of ultrasonic waves into the surrounding environment. This burst of waves travels outward from the sensor.
Wave Propagation:
The ultrasonic waves move through the air until they encounter an object in their path. The waves continue to propagate until they hit a surface.
Reflection of Ultrasonic Waves:
When the ultrasonic waves strike an object, they are reflected back towards the sensor. The reflection occurs because the ultrasonic waves encounter a change in the medium (from air to the object’s surface), causing the waves to bounce back.
Reception of Reflected Waves:
The same transducer that emitted the ultrasonic waves now acts as a receiver. It detects the reflected waves returning from the object.
Time Measurement:
The sensor measures the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel from the sensor to the object and back. This time measurement is crucial for determining the distance to the object.
Distance Calculation:
Using the known speed of sound in the air, which is approximately 343 meters per second (at room temperature), the sensor calculates the distance to the object. The formula for distance (D) is given by D = (Speed of Sound × Time) / 2.
Output Signal:
The calculated distance information is then processed by the sensor’s electronics, and the output is provided in a suitable format, often as an analog voltage, digital signal, or distance reading.
These sensors work by emitting ultrasonic waves, detecting their reflections from objects, measuring the time taken for the round trip, and using this time information to calculate the distance to the objects in their detection range. This working principle is fundamental to various applications, including distance measurement, object detection, and obstacle avoidance.
Ultrasonic Sensors Pins Configurations
The pin configurations of ultrasonic sensors may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. However, We will discuss general overview of the typical pin configuration for a commonly used ultrasonic sensor module, like the HC-SR04. This module is widely used in hobbyist and educational projects.
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor typically has four pins:
VCC (Voltage Supply):
This pin is used to provide power to the sensor. It typically requires a voltage in the range of 5V.
Trig (Trigger):
The Trig pin is used to trigger the start of the ultrasonic pulse. When a pulse of at least 10 microseconds is applied to this pin, the sensor emits an ultrasonic wave.
Echo:
The Echo pin is used to receive the ultrasonic waves that are reflected back from an object. The duration of the pulse received on this pin is proportional to the time it takes for the ultrasonic waves to travel to the object and back.
GND (Ground):
This pin is connected to the ground (0V) of the power supply.
Read More: Ultrasonic Sensors
#ultrasonic sensors#ultrasonic technology#sensor technology#sensor applications#non-contact measurement#distance measurement#level measurement#flow measurement#object detection#obstacle avoidance#industrial automation#automotive industry#robotics#healthcare#home automation#smart homes#IoT#internet of things#technology#innovation#engineering#science#research#development#education#learning#acoustics#sound waves#frequency#amplitude
0 notes
Text
#Anti-gravity#Humidifier#Air Purifier#Dehumidifier#Portable#Quiet#Ultrasonic Technology#Essential Oil Diffuser#Aromatherapy#Healthy living#Home comfort#Energy efficient#Easy to use#Automatic shut-off#LED light#Health and wellness#Innovative technology#Allergies#Asthma#Dry air#Indoor air quality#Moisture control#Compact design#Mist output control.
0 notes