#Iran Fars province
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Tomb Raider would be Eager for Journey in Iran.

The following article outlines the arcaeological value of Iran.And whether guys would refuse it,or not it's True:Tomb Raider would be Eager for aJourney in Iran.
Below:Our beloved action girl,and archaeologist iss in grand adventures:

Nothing can stop her.It's real wholesome:)

TEHRAN – Deep within the heart of Iran lies the awe-inspiring site of Tang-e Chogan, a captivating testament to the grandeur of the Sassanid Empire (224–651).
Visiting Tang-e Chogan (literary meaning “Chogan gorge”) is an immersive experience, allowing travelers to traverse the corridors of time and witness the grandeur of an ancient empire. The journey to this historical site involves navigating through awe-inspiring landscapes, adding to the allure of the excursion.
The site is located near Bishapur (“Shapur’s City”) of Fars province. As visitors explore the ruins, guided tours, and informational placards offer invaluable context, unraveling the mysteries of the Sassanid era. Additionally, the serene surroundings and picturesque vistas create an ambiance that transports visitors to a bygone era, making Tang-e Chogan an unforgettable destination for history enthusiasts and culture aficionados alike.
Tang-e Chogan is home to six reliefs related to Shapur I and Bahram I and II. There is also a large statue of Shapur I, which is six meters high, located in the Shapur Cave, at a height of about 700 meters from the river bed.
Furthermore, the site embraces larger and more crowded reliefs than any other Sassanid era reliefs, with three of them being more than 30 square meters in size and a body of more than 30 persons in each relief.
The first relief, which is larger and more crowded than any other one, is a scene celebrating Shapur I’s victory over the Roman Empire. Shapur I can be seen in the center of the relief riding on a horse and Gordianus’s corpse is under the feet of Shapur’s horse, Valerian’s hands are held captive in Shapur’s hand and Philip kneels in front of Shapoor’s horse and demands peace. The Persian military and officers are also behind Shapur in five rows of horses and the Roman officers and noblemen are seen in 5 rows carrying gifts and offerings in front of King Shapur I.
The second one represents the victory of King Bahram II over the Arabs. On the left is Bahram on horseback, and the Arabs are led by Iranian commanders to offer the king horses and camels.
The third bas-relief shows the ceremony of the Bahram I receiving a royal ring from Ahura Mazda. The engraving of this amazing relief is very artistic and even the wrinkles and the details of the clothes and so on are all beautifully illustrated. Everything in this relief fits in amazingly well. Even the physical details of the horse and the veins on the horse’s legs have been shown.
The fourth one depicts the scene of the victory of Bahram II over the rebels, in which the king sits on the throne in the center, while on his right side stand the Iranian commanders and soldiers with respect, and the rebels and captivates on the left. They are brought by Iranian soldiers to the presence of the king.
The fifth bas-relief located on the right side of the gorge is the most intact and complete relief among the others. It is about Shapur’s victory over the Roman Empire.
The sixth one depicts the ceremony of Shapur I receiving a royal ring from Ahura Mazda, as well as his victory in the war against the Romans. In this relief, both King and Ahura Mazda (the creator and highest deity of Zoroastrianism) are shown riding on horses and facing each other.
The Sassanid era is of very high importance in the history of Iran. Under the Sassanids, Persian art and architecture experienced a general renaissance. Architecture often took grandiose proportions, such as the palaces at Ctesiphon, Firuzabad, and Sarvestan, which are amongst the highlights of the ensemble.
Crafts such as metalwork and gem engraving grew highly sophisticated, yet scholarship was encouraged by the state. In those years, works from both the East and West were translated into Pahlavi, the language of the Sassanians.
Rock-carved sculptures and bas-reliefs on abrupt limestone cliffs are widely deemed as characteristics and striking relics of Sassanian art, top examples of which can be traced at Bishapur, Naqsh-e Rostam and Naqsh-e Rajab in southern Iran.
In 2018, UNESCO added an ensemble of Sassanian historical cities in southern Iran — titled “Sassanid Archaeological Landscape of Fars Region”-- to its World Heritage list. The ensemble comprises eight archaeological sites situated in three geographical parts of Firuzabad, Bishapur, and Sarvestan. It reflects the optimized utilization of natural topography and bears witness to the influence of Achaemenid and Parthian cultural traditions and Roman art, which later had a significant impact on the architecture and artistic styles of the Islamic era.
The Sassanid archaeological landscape also represents a highly efficient system of land use and strategic utilization of natural topography.
source: https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/493561/Tang-e-Chogan-a-peek-into-enigmatic-legacy-of-Sassanids
#culture#Iran Archaeology#Tomb Raider Lara Croft#Iran#ancient Persia#Iran Fars province#Sassanid Empire#UNESCO#Tang-e Chogan Iran#Iran Persepolis#ایران#ایران باستان#باستان شناسی#نقش برجسته#امپراتوری ساسانی#historical site#مهاجم مقبره#مهاجم مقبره لارا کرافت#Naqsh-e Rostam#نقش رستم#トゥームレイダー#古代ペルシャ#考古学#Iran Tehran#イラン テヘラン#ایران تهران#Tehrantimes
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

ARDASHIR PAPAKAN PALACE - IRAN
182 notes
·
View notes
Text

gerash, fars province, iran
by m.y.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
IRAN - Gathering at Kamjan International Wetland.

The rehabilitated wetland of Kamjan, Fars province, Iran. On this day, the people and wetland rehablitators sit next to the wetland to discuss the continuation of the wetland rehabilitation activities, the needs of the wetland and the effects that can help its sustainability and development. Reading poetry while cleansing, holding each other's hands, they consider themselves the permanent supporters of the wetland.
Country : Iran Organizer : Kamjan International Wetland Rehabilitators (NGO), Sirous Zare
#wetland rehablitators#Iran#wet meadows#sustainability#wetland of Kamjan#Fars province#Kamjan International Wetland Rehabilitators#events#exhibits
0 notes
Text

Ketubah (Jewish marriage contract) from Golpayegan, Iran, 1838
Golpayegan, which stands in Parsi for fortress of flowers and land of tulips, is one of the oldest towns in the Isfahan province. The history of its Jewish community goes back as far as 2,700 years. More than 10,000 Jews lived in Golpayegan before the Iranian revolution, forming the majority of the population and speaking a dialect known as Judeo-Golpaygani. When they arrived in Israel, their Iranian passports got confiscated and they were forbidden to return to their hometown. With no Jews left, both the numerous synagogues and the Jewish cemetery have been razed to the ground.
671 notes
·
View notes
Text

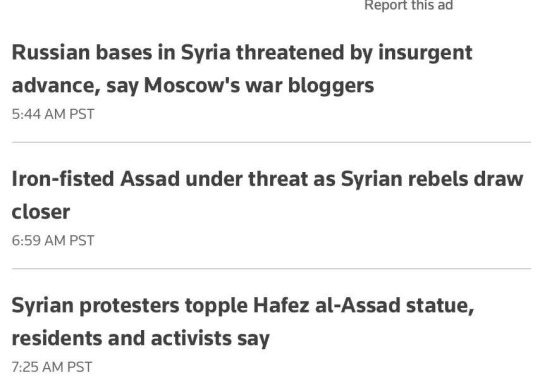
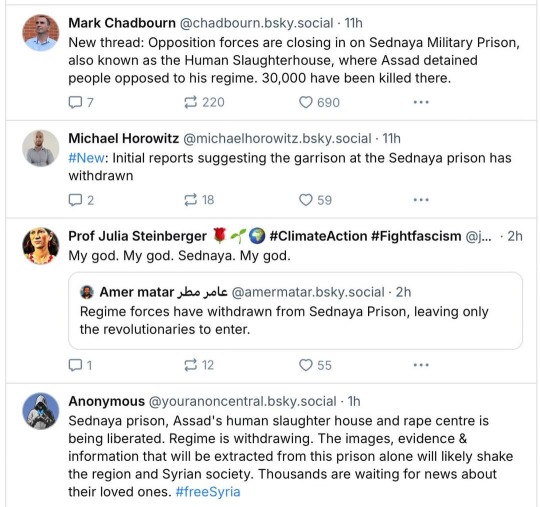
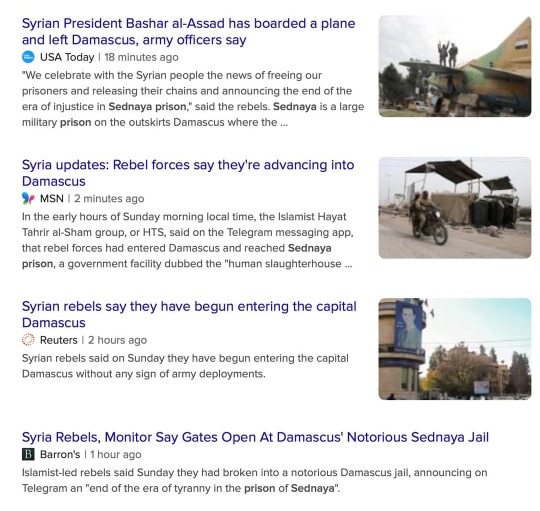
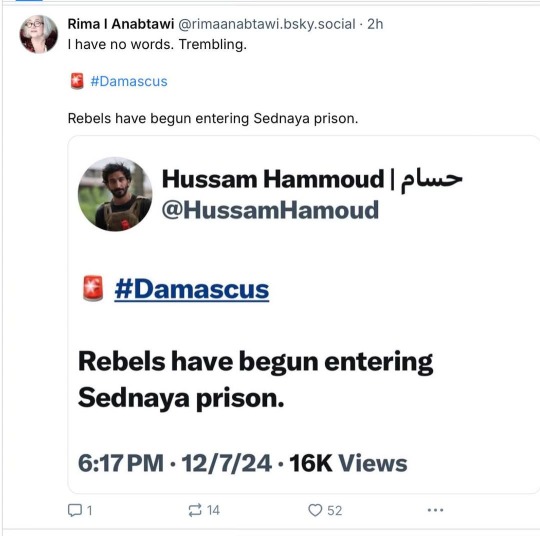
From Rebecca Solnit:
"My God. I was out all day today. Bashar Al Assad, the Butcher of Syria, has fled, his infamous prison/death camp/torture center has been freed, and rebels have taken Syria as far as I can tell. What a week. Insurrectionary Georgia. Coup-repelling South Korea. Now this.
The Guardian reports: When Islamist militants swept into her home town of Aleppo little over a week ago, Rama Alhalabi sheltered indoors as fear engulfed her. Forces loyal to president Bashar al-Assad, who had sought to reassure residents that nothing was happening, suddenly deserted the city. But as the insurgency pushed south, rapidly seizing control of the city of Hama on the road to Damascus, Alhalabi’s fears about life under militia rule have slowly ebbed. Instead they have been replaced by fears that her friends in the army will be abandoned by their commanding officers as Assad’s regime loses its grip.
“People in Aleppo are feeling more comfortable now we’re further from the areas under the regime’s control,” said the 29-year-old, while still using a pseudonym in fear Assad could retake the city.
“At the same time, I have many friends serving in the army and I don’t want them to get hurt. People with power inside the regime will protect themselves, and they will leave the poor fighters who were forced to join the army to face their awful fate alone.
“Things changed insanely fast,” she added. “We can barely believe what’s happening.”
As militants spearheaded by the group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) massed outside the city of Homs and rebel forces said they had entered the vast southern suburbs of the capital, rapid change swept across Syria. The Syrian army declared it had “redeployed,” its forces in two restive provinces south of Damascus in the latest thinly-veiled message of retreat, days after they withdrew from Hama. In under a week, five provincial capitals across the country were suddenly no longer under Assad’s control.
“We can hear the bombing nearby, and we are praying, hoping – and waiting,” said Um Ahmad, an elderly native of Homs, sheltering with her husband at home as the fighting drew close enough to be audible.
Assad loyalists fled the city, while people who stayed only have a couple of hours’ electricity each day and what goods are left in the shops are unaffordable. Those remaining in Homs waited to see if this might be the end of Assad’s rule, while an insurgent commander told his regime’s forces inside the city that this was their “last chance to defect before it’s too late”.
Um Ahmad was consumed by a single thought, that she might finally be able to see her sons again after a decade of separation and exile. “Most people are frightened but they fear the regime’s revenge more than anything else,” she said, as Russian and Syrian airstrikes pummelled the countryside around Homs and Hama.
When a popular uprising swept cities across Syria in 2011 calling for Assad to go, it initially looked as if demonstrations could topple another regional autocrat. But the Syrian leader swiftly turned the state’s weapons on his own people to crush dissent. As the uprising slowly morphed into a civil war, Assad freed jihadist prisoners from his fearsome detention system to alter the forces rising up against him, before relying heavily on his allies in Russia and Iran to provide the military muscle he used to reclaim control.
The civil war killed over 300,000 people in 10 years of fighting, with some estimates putting the true toll at twice that number. Tens of thousands remain in detention, including 100,000 believed missing or forcibly disappeared in Assad’s prisons since 2011, and subject to what United Nations monitors have described as systematic torture. Over 12 million people have been displaced.
Assad kept control of Syria’s major cities for years, as battle lines from the country’s years-long proxy war hardened. HTS ruled over a mountainous pocket in the northwest, cut off from the outside world. The group appeared a dim threat to Assad until they suddenly launched an offensive that saw them take control of Aleppo within days.
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/dec/07/syria-assad-damascus-hayat-tahrir-al-sham-insurgents
42 notes
·
View notes
Text

Elisabet Bclan
Persepolis, Iran // August 2018
Persepolis (/pərˈsɛpəlɪs/; Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, romanized: Pārsa; New Persian: تخت جمشید, romanized: Takht-e Jamshīd, lit. 'Throne of Jamshid') was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire (c. 550–330 BC). It is situated in the plains of Marvdasht, encircled by the southern Zagros mountains, Fars province of Iran. It is one of the key Iranian cultural heritage sites and a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1979. - Wikipedia
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
Six years ago, the Syrian regime conquered the southern province of Daraa, popularly known by millions of Syrians as the “cradle of the revolution.” That military victory represented a pivotal moment for Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. After all, it was the last time the regime captured a sizable swath of opposition territory, and in doing so in July 2018, its impunity was laid bare for all the world to see. On paper, Daraa had been designated a “de-escalation zone” after months of intensive international diplomacy in which the United States had played a central role.
Despite that protected status, regime forces with heavy Russian military assistance proceeded to besiege Daraa; shell it to rubble; and after weeks of brutal violence, coerce it into surrendering. Washington’s most reliable umbrella of opposition allies, the Southern Front, was abandoned—advised to surrender by U.S. officials. Since then, the regime’s status has never been in question, as international actors have methodically backed away, fatigued and disinterested. Since that decisive moment, as far as many were concerned, Assad had won and Syria’s crisis was over, its effects contained.
In truth, Assad never “won,” —he merely survived, thanks to the consistently strong support of Russia and Iran, but also to that international disengagement. In the years since, the world’s interest in working to resolve Syria’s debilitating crisis has completely evaporated. In Washington today, the mere suggestion of doing anything more on Syria in policymaking circles draws exasperated gasps and sarcastic laughs, not attention.
And yet, in many ways, the situation in Syria is worse than it’s ever been. There are clear and sustained signs of an Islamic State recovery; a multibillion-dollar regime-linked international drugs trade; and ongoing geopolitical hostilities involving Israel, Iran, Turkey, Russia, and the United States. The regime’s grip over areas under its control has never looked more frail and unconvincing.
Southern Syria offers a notable example. Six years after bombing the cradle of the revolution into submission, Assad’s rule in the south is fraying at the seams.
While Assad and his Russian sponsor intended for the south to embody a stabilized Syria that was “cleansed” of opponents, the region has been the most consistently unstable anywhere in Syria since 2018. As documented by Syria Weekly, at least 47 people have been killed in Daraa and Suwayda provinces between mid-June and mid-July alone, in a torrent of daily assassinations, ambushes, raids, and kidnappings and hostage executions. Daraa in particular is the embodiment of lawlessness and chaos.
Beyond the crippling disorder, former opposition fighters and other local armed factions in the regime-held southern provinces of Daraa and Suwayda have grown increasingly bold in challenging the regime’s abuses in recent weeks. From mid-June to mid-July, armed fighters—most of them former opposition—have kidnapped at least 25 Syrian military officers in retaliation for the regime’s arbitrary arrest of civilians from their areas. The hostages have then been successfully used as leverage to force the regime into releasing the civilian detainees. Never before has the regime been so consistently challenged and forced to submit.
Local armed factions that on paper are considered “reconciled” have now also taken to launching direct attacks on the Assad regime’s military checkpoints and buildings in retaliation for abuses. For example, when a Syrian woman from the Daraa town of Inkhil was detained while trying to renew her passport in Damascus on July 10, former opposition fighters in Inkhil launched coordinated attacks on three regime checkpoints and the local intelligence headquarters. When regime forces fired back, including with mortars and artillery, local fighters ambushed a regime armored vehicle arriving as reinforcement, destroying it with rocket-propelled grenades. Later that day, the woman was released.
Next door in the province of Suwayda, where locals have now held more than 330 days of consecutive protests demanding Assad’s downfall, regime forces unexpectedly established a new security checkpoint at the main entrance to the provincial capital on June 23. Within hours, at least six local armed factions had mobilized and launched attacks on regime positions, engaging in 48 hours of heavy fighting that drew in regime reinforcements from Damascus.
By June 25, the regime had been forced to back down, reverting the heavily fortified checkpoint into a post with no local authority. Such a direct challenge to regime security policy was remarkable, particularly for a province that never fell under opposition control.
That incident generated considerable regional attention, highlighting the regime’s capitulation. This may explain why one of the most prominent anti-regime armed group leaders in Suwayda, who had commanded many of the above-mentioned attacks, was assassinated in his home at dawn on July 17. Murhaj Jarmani, who went popularly by Abu Ghaith, was shot in the head through his living room window by a hit man equipped with a silencer. His wife had been in their home, but never even heard the shot.
During the same month-long time period, local armed groups in southern Syria have also kidnapped four regime intelligence operatives accused of a variety of abuses, including murder, torture, and organized crime. All four were themselves tortured, forced to confess to their crimes on camera, and then executed—their confession videos then disseminated locally and on social media. On top of that, the right-hand man of Daraa’s infamous military intelligence chief Luay al-Ali was assassinated in the heart of the provincial capital on July 13. The target, known commonly as Abu Luqman, had reportedly overseen nearly a decade of torture in Daraa’s largest detainee holding and interrogation facility.
Insights like these offer a glimpse into the true reality of regime rule in the 14th year of Syria’s crisis. Far from consolidating control, Assad’s authority appears to be crumbling. Meanwhile, the regime continues to fail in its intermittent effort to challenge a resurgent Islamic State. In the past month alone, at least 69 regime security force personnel have been killed in near-daily Islamic State attacks across Syria’s central desert. And that’s amid a month-long regime “clearance operation” against the jihadi group. Meanwhile, Assad’s senior advisor Luna al-Shibl died on June 3 in a mysterious car crash that some believe was an inside job, while a core backbone of the regime economy, Mohammad Bara Qaterji, was killed in an Israeli airstrike on June 15. And so much more.
Despite facing a regime so notorious for stopping short of nothing to eradicate opposition, the people of southern Syria appear to have had enough. From Suwayda’s nearly year-long popular uprising to the recent trend for local fighters to directly challenge regime abuses and security policy, this does not look anything like a resolved crisis, but rather an evolving and potentially escalating one, once again.
35 notes
·
View notes
Text










Alaska (No. 4)
The state is bordered by Canada's Yukon and British Columbia to the east (making it the only state to only border a Canadian territory); the Gulf of Alaska and the Pacific Ocean to the south and southwest; the Bering Sea, Bering Strait, and Chukchi Sea to the west; and the Arctic Ocean to the north. Alaska's territorial waters touch Russia's territorial waters in the Bering Strait, as the Russian Big Diomede Island and Alaskan Little Diomede Island are only 3 miles (4.8 km) apart. Alaska has a longer coastline than all the other U.S. states combined. Alaska's size compared with the 48 contiguous states (Albers equal-area conic projection)
At 663,268 square miles (1,717,856 km2) in total area, Alaska is by far the largest state in the United States. Alaska is more than twice the size of the second-largest U.S. state (Texas), and it is larger than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. Alaska is the seventh largest subnational division in the world. If it was an independent nation, it would be the 18th largest country in the world; almost the same size as Iran.
With its myriad of islands, Alaska has nearly 34,000 miles (55,000 km) of tidal shoreline. The Aleutian Islands chain extends west from the southern tip of the Alaska Peninsula. Many active volcanoes are found in the Aleutians and in coastal regions. Unimak Island, for example, is home to Mount Shishaldin, which is an occasionally smoldering volcano that rises to 10,000 feet (3,000 m) above the North Pacific. The chain of volcanoes extends to Mount Spurr, west of Anchorage on the mainland. Geologists have identified Alaska as part of Wrangellia, a large region consisting of multiple states and Canadian provinces in the Pacific Northwest, which is actively undergoing continent building.
One of the world's largest tides occurs in Turnagain Arm, just south of Anchorage, where tidal differences can be more than 35 feet (10.7 m).
Alaska has more than 409,000 natural lakes at least one hectare or bigger. Marshlands and wetland permafrost cover 188,320 square miles (487,700 km2) (mostly in northern, western and southwest flatlands). Glacier ice covers about 28,957 square miles (75,000 km2) of Alaska. The Bering Glacier is the largest glacier in North America, covering 2,008 square miles (5,200 km2) alone.
Source: Wikipedia
#Captain William Moore Bridge#Alaska#travel#original photography#vacation#tourist attraction#landmark#landscape#countryside#flora#nature#Last Frontier#clouds#Alaska Panhandle#Yukon Highway 2#Alaska Route 98#Klondike Highway#Coast Mountains#forest#woods#tree#snow#summer 2023#Captain William Moore Bridge Lookout
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yemen’s Iran-backed Houthi militia, a US-designated terrorist organization that has disrupted global shipping to display its support for Palestinians in the Gaza conflict, is now offering a place for students suspended from US universities after staging pro-Hamas, anti-Israeli protests.
For more than two weeks, university students have been amassing in the hundreds at a growing number of schools, taking over sections of campuses by setting up “Gaza Solidarity Encampments” and refusing to leave unless administrators condemn and boycott Israel. Footage of the protests has shown demonstrators chanting in support of Hamas, the Palestinian terrorist organization that Israel is fighting in Gaza; calling for the destruction of Israel; and even threatening to harm members of the Jewish community on campus. In many cases, activists have also lambasted the US and Western civilization more broadly.
The protests initially erupted across the US but have since spread to university campuses around the world, primarily in the West.
Many of the schools, including Ivy League Columbia University in New York City, have called in police to quell the protests.
“We are serious about welcoming students that have been suspended from US universities for supporting Palestinians,” an official at Sanaa University, which is run by the Houthis, told Reuters. “We are fighting this battle with Palestine in every way we can.”
Sanaa University had issued a statement applauding the “humanitarian” position of the students in the United States and said they could continue their studies in Yemen.
“The board of the university condemns what academics and students of US and European universities are being subjected to, suppression of freedom of expression,” the board of the university said in a statement, which included an email address for any students wanting to take up their offer.
The US and Britain returned the Houthi militia to a list of terrorist groups this year as their attacks on vessels in and around the Red Sea hurt global economies. Houthi military spokesman Yahya Sarea said in a televised speech on Friday that the terrorist group will target ships heading to Israeli ports in any area that is within their range.
“We will target any ships heading to Israeli ports in the Mediterranean Sea in any area we are able to reach,” he said.
The rebel movement — whose slogan is “death to America, death to Israel, curse the Jews, and victory to Islam” — has also claimed responsibility for attempted drone and missile strikes targeting Israel.
The Houthi’s offer of an education for US students sparked a wave of sarcasm by ordinary Yemenis on social media. One social media user posted a photograph of two Westerners chewing Yemen’s widely-used narcotic leaf Qat. He described the scene as American students during their fifth year at Sanaa University.
In a similar move to the Houthis earlier this week, the head of a major Iranian university reportedly offered scholarships to students expelled from US and European universities over the anti-Israel protests, which have involved students and faculty holding unauthorized demonstrations, occupying school buildings, and in some cases blocking Jews from entering parts of campus.
Mohammad Moazzeni, who runs Shiraz University in the Fars province, made the announcement to show “solidarity” with the anti-Israel agitators.
37 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gate of All Nations The Gate of Xerxes -UNESCO World Heritage (r. 486 – 465 BC) Persepolis - IRAN
The bronze trumpets that once signaled the arrival of important foreign delegations to Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the mighty Achaemenid Empire, may now be silent, but it is still possible to capture the sense of awe while visiting the colossal Gate of Xerxes.
Built during the reign of Achaemenid king Xerxes I , who called this his Gate of All Nations, the pillared entrance is guarded by bearded and hoofed mythical figures in the style of Assyrian gate-guards.
On arrival at Persepolis one is confronted by an imposing wall, completely smooth and plain, about 15 meters tall: this is the artificial terrace on which the palaces were built. This vast terrace of Persepolis, some 450 meters long and 300 meters wide, was originally fortified on three sides by a tall wall. The only access was from the monumental staircase, which leads to the Gate of All Nations.
The gateway bears a cuneiform inscription in Old Persian, Neo-Babylonian, and Elamite languages declaring, among other things, that Xerxes is responsible for the construction of this and many beautiful wonders in Persia. Centuries of graffitists have also left their mark, including explorer Henry Morton Stanley.
A pair of colossal bulls guarded the western entrance; two man-bulls stood at the eastern doorway. Engraved above each of the four colossi is a trilingual inscription attesting to Xerxes having built and completed the gate. The doorway on the south, opening toward the Apadana, is the widest of the three.
According to sources, pivoting devices found on the inner corners of all the doors indicate that they must have had two-leaved doors, which were probably made of wood and covered with sheets of ornamented metal.
Persepolis, also known as Takht-e Jamshid, whose magnificent ruins rest at the foot of Kuh-e Rahmat ("Mountain of Mercy"), was the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire. It is situated 60 kilometers northeast of the city of Shiraz in Fars Province.
Persepolis was the seat of the government of the Achaemenid Empire, though it was designed primarily to be a showplace and spectacular center for the receptions and festivals of the kings and their empire.
The royal city ranks among the archaeological sites which have no equivalent, considering its unique architecture, urban planning, construction technology, and art.
The city was burnt by Alexander in 330 BC apparently as revenge to the Persians
The immense terrace of Persepolis was begun about 518 BC by Darius the Great, the Achaemenid Empire’s king. On this terrace, successive kings erected a series of architecturally stunning palatial buildings, among them the massive Apadana palace and the Throne Hall (“Hundred-Column Hall”).
This 13-ha ensemble of majestic approaches, monumental stairways, throne rooms (Apadana), reception rooms, and dependencies is classified among the world’s greatest archaeological sites.
#art#design#doorway#architecture#heavensdoorways#gateway#entryway#iran#persepolis#bull#royal#royal city#style#history#gates of xerses#unesco world heritage#monumental#gate of all nations#achaemenid#persia#xerxes#front door#architrave
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
They achieved the impossible!

TEHRAN – It took 45 years for a Sassanid-era (224–651) petroglyph to be deciphered, ILNA reported on Saturday.
Forty-five years after its discovery in Naqsh-e Rostam, a royal rock-hewn necropolis in southern Fars province, the Sassanid petroglyph has been translated, Iranian archaeologist Abolhassan Atabaki said.
Raising goats in pastures is the subject of the petroglyph, he mentioned.
The petroglyph also mentions a nearby hydro structure that the residents of the region used for drinking and cattle water, he noted.
This rock drawing is one of the most important and largest petroglyphs discovered by the archaeologists during their previous survey of the area, he explained.
The petroglyph has been homogenized by rainwater because it was exposed to the open air, causing a large number of limestone sediments to slowly form a layer of the upper surface, resulting in the destruction of stone inscriptions, and the loss of parts of the letters, he added.
One of the wonders of the ancient world, Naqsh-e Rostam, is home to spectacular massive rock-hewn tombs and bas-relief carvings. Moreover, it embraces four tombs where Persian Achaemenid kings are laid to rest, believed to be those of Darius II, Artaxerxes I, Darius I, and Xerxes I (from left to right facing the cliff), although some historians are still debating this.
The Achaemenid necropolis is situated near Persepolis, itself a bustling UNESCO World Heritage site near the southern city of Shiraz. Naqsh-e Rostam, meaning “Picture of Rostam” is named after a mythical Iranian hero who is most celebrated in Shahnameh and Persian mythology. Back in time, natives of the region had erroneously supposed that the carvings below the tombs represent depictions of the mythical hero.
There are stunning bas-relief carvings above the tomb chambers that are similar to those at Persepolis, with the kings standing on thrones supported by figures representing the subject nations below. There are also two similar graves situated on the premises of Persepolis probably belonging to Artaxerxes II and Artaxerxes III.
Beneath the funerary chambers are dotted with seven Sassanian eras (224–651) bas-reliefs cut into the cliff depict vivid scenes of imperial conquests and royal ceremonies; signboards below each relief give a detailed description in English.
At the foot of Naqsh-e Rostam, in the direction of the cliff face, stands a square building known as Ka’beh-ye Zardusht, meaning Kaaba of Zoroaster. The building, which is roughly 12 meters high and seven meters square, probably was constructed in the first half of the 6th century BC, although it bears a variety of inscriptions from later periods. Though the Ka’beh-ye Zardusht is of great linguistic interest, its original purpose is not clear. It may have been a tomb for Achaemenian royalty or some sort of altar, perhaps to the goddess Anahiti, also called Anahita believed to be associated with royalty, war, and fertility.
In many ways, Iran under Sassanian rule witnessed tremendous achievements in Persian civilization. Experts say that the art and architecture of the nation experienced a general renaissance during Sassanid rule. In that era, crafts such as metalwork and gem engraving grew highly sophisticated, as scholarship was encouraged by the state; many works from both the East and West were translated into Pahlavi, the official language of the Sassanians.
Of all the material remains of the era, only coins constitute a continuous chronological sequence throughout the whole period of the dynasty. Such Sassanian coins have the name of the king for whom they were struck inscribed in Pahlavi, which permits scholars to date them quite closely.
The legendary wealth of the Sassanian court is fully confirmed by the existence of more than one hundred examples of bowls or plates of precious metal known at present. One of the finest examples is the silver plate with partial gilding in the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York. The dynasty was destroyed by Arab invaders during a span from 637 to 651.
The ancient region, known as Pars (Fars), or Persis, was the heart of the Achaemenid Empire founded by Cyrus the Great and had its capital in Pasargadae. Darius I the Great moved the capital to nearby Persepolis in the late 6th or early 5th century BC. Alexander the Great defeated the Achaemenian army at Arbela in 331 and burned Persepolis apparently as revenge against the Persians because it seems the Persian King Xerxes had burnt the Greek City of Athens around 150 years earlier.
Persis became part of the Seleucid kingdom in 312 after Alexander’s death. The Parthian empire (247 BC– 224 CE) of the Arsacids (corresponding roughly to the modern Khorasan in Iran) replaced the Seleucids' rule in Persis during 170–138 BC. The Sasanid Empire (224 CE–651) had its capital at Istkhr. Not until the 18th century, under the Zand dynasty (1750–79) of southern Iran, did Fars again become the heart of an empire.
Source:https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/483667/Sassanid-petroglyph-deciphered-after-45-years
#Iran#arcaelogy#Iranian archaeologists#Naqsh-e Rostam#Sassanid petroglyph#Zoroaster persia#UNESCO World Heritage#UNESCO#fars province#Iran Tehran#Achaemenid necropolis
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

NASIR AL-MULK MOSQUE - (Pink Mosque) - Fars Province, Shiraz, IRAN
121 notes
·
View notes
Text

Syria :: David Rowe
"If the United States was still going to be run by the competent next month, we would now be on the verge of destroying Russia as a competitor and letting Xi Jinping know how far he can go, along with ending the Iranian-backed opposition in the Middle East. The “authoritarian alternative to democracy” would be gasping for air. That may not sound “pretty” to political idealists, but since neither Nirvana nor Utopia is likely to be proclaimed in my lifetime, I damn sure prefer us to them.
Literally, the only thing that can now save Putin is the Orange Clusterfuck’s desire to surrender to his tender mercies and tear us apart because his sick, twisted psyche is so damaged by the fact civilized society saw him as the piece of shit he was born to be and left him with his nose pressed to a glass door that was never going to be opened to the likes of him. That we are expected hand this country over to traitors who campaigned on a promise to commit this destruction enrages me beyond my ability to put it in words."
[TCinLA]
+
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
December 8, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Dec 09, 2024
Late last night, the White House said in a statement that “President Biden and his team are closely monitoring the extraordinary events in Syria and staying in constant touch with regional partners.”
Early this morning, the Syrian government of Bashar al-Assad fell to armed opposition.
According to Jill Lawless of the Associated Press, the forces that toppled Assad are led by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham, or HTS, a coalition of Islamic groups formerly associated with al-Qaeda’s branch in Syria and currently designated a terrorist group by the U.S. and the United Nations, although its leaders have tried to distance themselves from al-Qaeda.
President Bashar al-Assad succeeded his father to the Syrian presidency in July 2000, establishing a totalitarian dictatorship. In 2011, Assad cracked down on protesters who were part of the Arab Spring, sparking a civil war of a number of factions fighting Assad’s troops, which by 2015 relied on support from Russia and Iran.
That war has turned half of Syria’s prewar population of 23 million (a little more than the population of Florida) into refugees and killed more than half a million people. With Russian and Iranian support, Assad managed to regain control of most of the country, with rebels pushed back to the north and northwest.
A stalemate that had lasted for years ended abruptly on November 27.
Iran and Hezbollah have been badly weakened by the ongoing fight of Israel against Iran-backed Hamas, Hezbollah, and the Houthis. On November 27, Israel and Lebanon signed a ceasefire agreement that made it clear that Hezbollah had been tied down in Lebanon and that its ability to fight had been severely compromised. At the same time, Russia has been badly weakened by almost three years of war against Ukraine, and the Russian ruble fell sharply again in late November after additional U.S. sanctions targeted Russia’s third-largest bank, creating more economic hardship in Russia and undercutting Putin’s insistence that he is winning against the West.
When opposition forces began an offensive on November 27, they took more than 15 villages in Aleppo province that day. Journalist Lawless recounted a quick history of the next 11 days, recording how the insurgents swept through the country with little resistance, taking Syria’s largest city, Aleppo, on the 29th. The Syrian military launched a counterattack on December 1, but the insurgents continued to gain ground, and by December 7 they had captured Syria’s third-largest city, Homs. They announced they were in the “final stage” of their offensive.
Today, December 8, Assad fled with his family to Moscow, where Russian president Vladimir Putin has offered him asylum. As Nick Paton Walsh of CNN put it, “Without the physical crutches of Russia’s air force and Iran’s proxy muscle Hezbollah, [Assad] toppled when finally pushed.”
In Damascus, crowds are praying and celebrating, and opposition forces have liberated the prisoners held in the notorious Saydnaya military prison. More than 100,000 detainees are unaccounted for, and their families are hoping to find them, or at least to find answers.
Meanwhile, after Assad’s regime fell, the U.S. Air Force struck more than 75 ISIS-related targets in Syria. “ISIS has been trying to reconstitute in this broad area known as the Badiya desert,” a White House senior official told reporters. “We have worked to make sure they cannot do that. So when they try to camp there, when they try to train… we take them out.”
National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan explained at the Reagan National Defense Forum in Simi Valley, California, that the U.S. will work to prevent the resurgence of ISIS. It will also make sure “that our friends in the region, Israel, Jordan, Iraq, others who border Syria, or who would potentially face spillover effects from Syria, are strong and secure.” Finally, he said, the U.S. wants to make sure “that this does not lead to a humanitarian catastrophe.”
Speaking to the nation this afternoon, President Joe Biden announced: "At long last, the Assad regime has fallen. This regime brutalized and tortured and killed literally hundreds of thousands of innocent Syrians." He called the fall of Assad’s regime a “fundamental act of justice” and “a moment of historic opportunity for the long-suffering people of Syria to build a better future for their proud country.”
But it is also “a moment of risk and uncertainty,” the president said. He noted that the U.S. is “mindful” of the security of Americans in Syria, including freelance journalist Austin Tice, who was kidnapped in 2012 and imprisoned by Assad’s regime. “[W]e believe he is alive,” Biden told reporters. “We think we can get him back, but we have no direct evidence of that yet.”
Biden noted that Syria’s main backers, Iran, Hezbollah, and Russia, could not defend “this abhorrent regime in Syria” because they “are far weaker today than when I took office.” He continued: “This is a direct result of the blows that Ukraine [and] Israel” have landed on them “with the unflagging support of the United States.”
In contrast to Biden’s comments, President-elect Donald Trump’s social media accounts took Russia’s side in the Syrian events. Noting that the insurgents looked as if they would throw Assad out, Trump’s account said that “Russia, because they are so tied up in Ukraine, and with the loss there of over 600,000 soldiers, seems incapable of stopping this literal march through Syria, a country they have protected for years.” The account blamed former president Barack Obama for the crisis of 2011 and said that Russia had stepped in then to stop the chaos. The Trump account suggested that Assad’s defeat might be “the best thing that can happen to” Russia, because “[t]here was never much of a benefit in Syria for Russia, other than to make Obama look really stupid.”
“In any event,” the account continued, “Syria is a mess, but is not our friend, & THE UNITED STATES SHOULD HAVE NOTHING TO DO WITH IT. THIS IS NOT OUR FIGHT. LET IT PLAY OUT. DO NOT GET INVOLVED!”
In contrast to Trump’s focus on Russia, journalist Anne Applebaum, a scholar of autocracy, took a much broader view of the meaning of Assad’s fall. In dictatorships, she wrote in The Atlantic, “cold, deliberate, well-planned cruelty” like Assad’s “is meant to inspire hopelessness. Ludicrous lies and cynical propaganda campaigns are meant to create apathy and nihilism.” Random arrests create destabilizing waves of refugees that leave those who remain in despair.
Authoritarian regimes seek “to rob people of any ability to plan for a different future, to convince people that their dictatorships are eternal. ‘Our leader forever’” she points out, was the slogan of the Assad dynasty. But soldiers and police officers have relatives who suffer under the regime, and their loyalty is not assured, as Assad has now learned.
The future of Syria is entirely unclear, Applebaum writes, but there is no doubt that “the end of the Assad regime creates something new, and not only in Syria. There is nothing worse than hopelessness, nothing more soul-destroying than pessimism, grief, and despair. The fall of a Russian- and Iranian-backed regime offers, suddenly, the possibility of change. The future might be different. And that possibility will inspire hope all around the world.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Letters From An American#Heather Cox Richardson#TCinLA#David Rowe#Authoritarian regimes#Russia#Anne Applebaum#Syria#Assad#Iran#Hezbollah
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
“The Syrian government fell early Sunday in a stunning end to the 50-year rule of the Assad family after a sudden rebel offensive sprinted across government-held territory and entered the capital in 10 days.
Syrian state television aired a video statement by a group of men saying that President Bashar Assad has been overthrown and all detainees in jails have been set free.
(…)
The statement emerged hours after the head of a Syrian opposition war monitor said Assad had left the country for an undisclosed location, fleeing ahead of insurgents who said they had entered Damascus following the remarkably swift advance across the country.
(…)
It was the first time opposition forces had reached Damascus since 2018, when Syrian troops recaptured areas on the outskirts of the capital following a yearslong siege.
(…)
The night before, opposition forces took the central city of Homs, Syria’s third largest, as government forces abandoned it. The city stands at an important intersection between Damascus, the capital, and Syria’s coastal provinces of Latakia and Tartus — the Syrian leader’s base of support and home to a Russian strategic naval base.
The rebels had already seized the cities of Aleppo and Hama, as well as large parts of the south, in a lightning offensive that began Nov. 27. Analysts said rebel control of Homs would be a game-changer.
(…)
The advances in the past week were by far the largest in recent years by opposition factions, led by a group that has its origins in al-Qaida and is considered a terrorist organization by the U.S. and the United Nations. In their push to overthrow Assad’s government, the insurgents, led by the Hayat Tahrir al-Sham group, or HTS, have met little resistance from the Syrian army.
(…)
Syrian Prime Minister Mohammad Ghazi al-Jalali said Sunday he does not know where Assad or the defense minister are. He told Saudi television network Al-Arabiyya early Sunday that they lost communication Saturday night.
He has had little, if any, help from his allies. Russia is busy with its war in Ukraine. Lebanon’s Hezbollah, which at one point sent thousands of fighters to shore up Assad’s forces, has been weakened by a yearlong conflict with Israel. Iran has seen its proxies across the region degraded by regular Israeli airstrikes.
U.S. President-elect Donald Trump on Saturday posted on social media that the United States should avoid engaging militarily in Syria. Separately, President Joe Biden’s national security adviser said the Biden administration had no intention of intervening there.”

“A fast-advancing rebel offensive in Syria threatens to dislodge Russia from a strategic linchpin that Moscow has used for a decade to project power in the Middle East, in the Mediterranean and into the African continent.
It also challenges Russian President Vladimir Putin’s efforts to portray Moscow as a flag bearer for an alternative global order to rival Western liberalism, and his defense of the Syrian regime as evidence of successful pushback against American dominance in the region.
(…)
Russia intervened in Syria’s civil war in 2015 to prop up President Bashar al-Assad against an armed uprising prompted by the Arab Spring, giving it a role as an influential foreign power in the Middle East. It sought to leverage its relations with rival powers such as Iran and Israel, as well as Turkey and Gulf states, to mediate conflicts and claim status as a regional power broker.
(…)
Syria has partly been an ideological project for Putin. The intervention in Syria became a way for Russia to extend its vision of a multipolar world opposed to the Western liberal order, said Nicole Grajewski, fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace and author of a coming book on Russia’s relationship with Iran, including in Syria.
“To see Russian planes leave Syria as rebel forces move onward towards their air bases, and their assets in Damascus fall, this would be so devastating for the Russian image of itself,” she said. “It would be akin to a Saigon moment for them.”
Putin’s assistance was instrumental to Assad’s survival, and showed Moscow’s allies far beyond the Middle East that Russian intervention could help push back popular uprisings, said a former Russian official. African leaders began to invite Russia, and specifically contractors from the Wagner paramilitary group who also played a critical role in Syria, to help stabilize their regimes.
Syria holds significant strategic value for Russia as well. The Khmeimim air base near the coastal city of Latakia serves as a logistical hub for flights to Libya, the Central African Republic, and Sudan, where Russian private contractors and soldiers have operated for years.
A naval base in the port city of Tartus serves as the only replenishment and repair point for the Russian navy in the Mediterranean, where it has brought in goods by bulk through the Black Sea. Tartus has granted Putin access to a warm water port, something Russian rulers for centuries before him sought in the Middle East. The port could also potentially connect Russia to Libya—like Syria, a Soviet-era ally—where it seeks a naval base to extend its reach into sub-Saharan Africa. A rebel takeover of those Syrian coastal positions could jeopardize Russia’s global-power projection.
“Syria provided so many advantages at a low cost,” said Anna Borshchevskaya, senior fellow at the Washington Institute think tank and author of a book on Putin’s war in Syria. “Losing Syria would be a big strategic defeat that would reverberate beyond the Middle East. It would have global repercussions.”
(…)
“One way to see Putin’s ambition in Syria is as part of his larger imperial vision,” said Borshchevskaya. “That’s what Ukraine is, that’s what [the invasion of] Georgia was in 2008, and to some extent that’s what Syria was,” she said. “Now in 2024, Russia finally finds itself overstretched.”
(…)
The Russian intervention in the civil war turned the tide in Assad’s favor and helped Iran consolidate its military foothold all the way to the Israeli border. Western attempts to isolate Moscow and Tehran through sanctions have pushed them closer together.”
“For years, Syria’s complicated battlefields have been populated by shifting groups of militants battling a range of enemies, including each other, and proxies backed by outside powers. Iran and Russia have propped up the autocratic Assad regime for more than a decade, while Turkey and the United States have troops on the ground in areas outside government control, and each support local proxies.
News reports and videos posted on social media indicate U.S.-backed rebels, supported by American airstrikes, may now be battling Syrian government forces as part of renewed fighting in the east.
That U.S. backing means boots on the ground. Around 900 U.S. troops are deployed in Syria alongside private military contractors, in what one expert calls “arguably the most expansive abuse” of the war powers granted to the executive branch in the wake of 9/11 — and those troops have, on average, come under fire multiple times each week since last October, according to new Pentagon statistics obtained by The Intercept.
Since the war in Gaza began last year, U.S. forces have been under sustained attack by Iran-backed militants across the Middle East, with the Pentagon’s Syrian bases being the hardest hit. Since October 18, 2023, there have been at least 127 attacks on U.S. forces in Syria, according to Lt. Cmdr. Patricia Kreuzberger, a Pentagon spokesperson, and information supplied by U.S. Central Command, or CENTCOM. On average, that’s about one attack every three days.
(…)
Brian Finucane, a former State Department lawyer now with the International Crisis Group, said the ongoing bombardment of U.S. bases should prompt hard questions in America’s halls of power. “Why are U.S. troops in Syria? What is the mission? What is the endgame? And is this legally authorized?” are the questions that need answers, he said. “The administration doesn’t want to have that debate. Congress also seems perfectly fine avoiding it. And so, the legislative and executive branches are content to muddle along, avoiding their constitutional responsibilities — the need for congressional authorization — and really debate the merits of this conflict.”
THE U.S. MILITARY has been conducting operations in Syria since 2014. America’s bases there and in neighboring Iraq ostensibly exist to conduct “counter-ISIS missions,” despite the fact that the Pentagon concluded in 2021 that the Islamic State in Syria “probably lacks the capability to target the U.S. homeland.”
Around 900 U.S. troops — including commandos from Combined Special Operations Joint Task Force-Levant — and an undisclosed number of private military contractors are operating in Syria. In 2022, The Intercept revealed the existence of a low-profile 127-echo counterterrorism program in Syria targeting Islamist militants. Under the 127e authority, U.S. Special Operations forces arm, train, and provide intelligence to small groups of elite foreign troops. But unlike traditional foreign assistance programs, which are primarily intended to build local capacity, 127e partners are dispatched on U.S.-directed missions, targeting U.S. enemies to achieve U.S. aims.
The Syrian Democratic Forces, a Kurdish-led militant group based in the country’s northeast is America’s main proxy force in Syria. While the SDF fights Islamist extremists with U.S. support, it also battles Turkey and Turkish-backed militants. Turkey, America’s longtime NATO ally, opposes the SDF due to that group’s ties to the Kurdistan Workers’ Party, a Kurdish nationalist militant group that both the Turkish and U.S. governments, among others, have designated a terrorist group.
(…)
The future of America’s escalating war in Syria may face renewed scrutiny early next year. President-elect Donald Trump showed antipathy to the U.S. war in Syria and withdrew U.S. forces from the north of the country in 2019, opening the door to a Turkish invasion.
“When Trump ordered the removal of U.S. forces from Syria in late 2018, there was a scramble within the government to try to figure out what that meant and whether there were ways to walk it back,” said Finucane, the former State Department lawyer. “The Pentagon was fine to pull out U.S. troops from al Tanf because there was really no counter-ISIS mission. But in his memoir, [Trump’s national security adviser] John Bolton said he wanted to keep troops there to counter Iran.”
For four years, experts say the Biden administration has continued this shadow effort aimed at Iran under the guise of a counter-ISIS mission, fending off several congressional efforts to force the removal of U.S. troops from Syria. Last year, a bid by Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky., to compel the withdrawal of all U.S. troops from Syria within 30 days also failed. “The American people have had enough of endless wars in the Middle East,” Paul told The Intercept at the time. “Yet, 900 U.S. troops remain in Syria with no vital U.S. interest at stake, no definition of victory, no exit strategy, and no congressional authorization to be there.” Those troops may be increasingly drawn into the Syrian civil war in support of their SDF allies.
“This is arguably the most expansive abuse of the 2001 AUMF in the history of the law,” said Erik Sperling of Just Foreign Policy, an advocacy group critical of mainstream Washington foreign policy, referring to the 2001 Authorization for Use of Military Force, enacted in the wake of the September 11 attacks. “We know from Biden administration leaks that the U.S. presence in Syria was part of an anti-Iran proxy war strategy but after Congress started voting to remove troops, they cracked down on those leaks and they said it’s only about terrorism.”
(…)
U.S. troops have, however, been relentlessly attacked across the Middle East since last October. There have been at least 208 attacks against U.S. forces in the region — two in Jordan, 79 in Iraq, and 127 in Syria — according to Kreuzberger and CENTCOM. In addition to coming under fire about once every other day, U.S. troops have been killed or seriously injured in these attacks. In January, three U.S. soldiers were killed and more than 40 other personnel were injured in an attack on a base in Jordan near the Syrian border. Eight U.S. troops also suffered traumatic brain injuries and smoke inhalation from an August 9 drone attack on the Rumalyn Landing Zone in northeastern Syria.”

“Israeli ground forces advanced beyond the demilitarized zone on the Israel-Syria border over the weekend, marking their first overt entry into Syrian territory since the 1973 October War, according to two Israeli officials speaking anonymously to discuss sensitive developments.
(…)
Israeli forces took control of the mountain summit of Mount Hermon on the Syrian side of the border, as well as several other locations deemed essential for stabilizing control of the area.
Lt. Gen. Herzi Halevi, the Israeli military chief of staff, appeared to confirm on Saturday night that Israeli forces had gone beyond a demilitarized buffer zone in the Golan Heights, saying Israel had “deployed troops into Syrian territory,” although he did not elaborate further.
(…)
More recently, the Israeli military has been more explicit about striking sites and people there, saying it was targeting Hezbollah’s supply lines. But the deployment of ground troops beyond the demilitarized zone in Syria marks a significant shift in policy as the first overt entry of Israeli military forces into Syrian territory since the 1974 cease-fire agreement that officially ended the last war between Israel and Syria.
The Israeli Air Force over the weekend was also striking targets in Syria to destroy government military assets that could fall into the hands of rebel forces and are considered strategic threats by Israel, the two officials said.
(…)
The targets included small stockpiles of chemical weapons, primarily mustard gas and VX gas, which remained in Syrian possession despite prior agreements to disarm, according to the officials. The Israeli military also targeted radar-equipped batteries and vehicles of Russian-made air defense missiles, as well as stockpiles of Scud missiles, according to the two officials.
(…)
Israel captured the Golan Heights during the Middle East war of 1967 and annexed much of the territory in 1981. The rest is controlled by Syria. Most of the world views this area as Israeli-occupied Syrian territory, though Donald J. Trump recognized Israeli sovereignty there in 2019 during his first term as president.”
#syria#assad#assad regime#ba’ath#ba’athism#baathism#middle east#arab#civil war#al qaeda#russia#putin#ukraine#iran#trump#biden#israel#golan heights#hezbollah#hamas
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
All of these stories about femicide are within the last week.
On Jan. 9, Liliana Concha Perez was found dead in Durham alongside her former boyfriend, who was described by Perez's family as jealous, possessive and obsessive. On Jan. 24, an argument between María Teresa Meraz-Cruz and her boyfriend, Miguel Angel Ventura, ended in Ventura killing her in a murder-suicide. On Feb. 7, police arrested Tammy Lynn Hodges’s husband after she was found dead inside her home.
These women are just three recent examples of a tragic, yet growing, epidemic in North Carolina: femicide.
See rest of article
Sherele counts female victims of violence. This is what she wants you to know
Violence against women is on the rise, and one of the key sources of up-to-date victim data is a lone journalist, not a government body.
Thirty-four Australian women have been killed by violence so far this year.
This figure wasn't put calculated by a government body or advocacy organisation; it was collated by journalist Sherele Moody.
During her 27 years in the media, Moody has won accolades for her reporting and research, which has involved verifying and cataloguing women and children who have died in violent incidents.
See rest of article
Last summer, Belgium adopted a pioneering European law on femicide, which aims to make up for lost time in collecting data on gender-based violence. However, feminist associations fear that it will not be enough to effectively curb the problem.
Théo Anberrée, Agathe Decleire – Le Soir April 30th, 2024
Their names were Laurence, Ingrid, Marie-Anne and Stéphanie. All four died this year in Belgium at the hands of their husbands. They were victims of femicide, i.e. the murder of a woman because she is a woman.
Like those women, more than 14,143 women were intentionally killed in Europe between 2012 and 2022. At least 4,334 died at the hands of their partner, and 2,472 at the hands of a family member. These are the numbers taken from Eurostat statistics, supplemented and studied by fifteen European media partners of EDJNet, including Le Soir.
See rest of article
Samira Akbari, a 35-year-old woman, lost her life at the hands of her ex-husband in the city of Bardeskan, Razavi Khorasan province.
Having separated from her husband three years prior, Samira was murdered in a horrifying act of violence.
According to a report by the human rights organization Hengaw, Samira Akbari was fatally attacked by her ex-husband, Mohammad Zahedi.
Samira, who was also the custodian of their children, fell victim to this assault.
Although Zahedi was apprehended following the incident, detailed information regarding his motive remains undisclosed.
Samira Akbari's case adds to a disturbing trend of femicide in Razavi Khorasan province, marking the seventh such incident in the past four months.
The human rights organization "Hengaw" revealed in a report that over the last hundred days, at least 50 cases of femicide have been documented across various cities in Iran.
Twenty percent of these cases were driven by so-called "honor" motives.
Shargh newspaper, in a report citing official statistics last year, reported that in less than two years, at least 165 women in Iran were killed by a male member of their family, 41 of which were in and around the capital, Tehran.
Eleven months on from her shocking disappearance, the investigation into Cecilia Strzyzowski’s suspected femicide in Chaco Province has been sent to trial.
The case, which rocked politics in the northern region, was referred for oral trial proceedings by the special investigative team probing the missing 28-year-old’s death.
Juan Martín Bogado, Jorge Cáceres Olivera and Nelia Velázquez, of the EFE Special Prosecution Team of Chaco Province, on Tuesday deemed the pre-trial investigation over and a jury trial for the defendants.
Strzyzowski’s former partner, César Sena, is accused of carrying out the murder, which prosecutors say was aggravated by their relationship and in a context of gender-based violence.
See rest of article
In August 2023, in Gradacac, a small town in Bosnia-Herzegovina (B-H), Nermin Sulejmanović brutally murdered his ex-wife, Nizama Hecimovic, during a live stream, with their child in the room. On the morning of August 11th, the bodybuilder started the live stream with the chilling words that viewers were about to witness a murder. Having killed his wife, Sulejmanović went on to kill two other people before committing suicide.
Over 10,000 people watched the live stream, some even encouraging the violence. The victim had reported the perpetrator to the official institutions, which decided to ignore his previous violence. Indeed, in the live video Sulejmanović cited the fact that she had reported him as a reason for the killing.
In B-H, one in two women has experienced violence since turning 15. Violence against women, particularly in the home, remains a pervasive social issue. Despite the advocacy efforts of non-governmental organisations to enhance legal protection for women against violence in public and private domains, it continues to enjoy alarmingly wide social acceptance.
See rest of article
#Femicide#North Carolina#Australia#Belgium#Iran#Rest In Peace Liliana Concha Perez#Rest In Peace María Teresa Meraz-Cruz#Rest In Peace Tammy Lynn Hodges#Sherele Moody is doing the work that the Australian government should already be doing.#Rest In Peace Laurence#Rest In Peace Ingrid#Rest In Peace Marie-Anne#Rest In Peace Stephanie#Rest In Peace Samira Akbari#Honor killing#Argentina#Rest In Peace Cecilia Strzyzowski#Bosnia-Herzegovina#Nizama Hecimovic
13 notes
·
View notes