#Intrauterine growth retardation
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Explore the meaning of high-risk pregnancy. Understand the factors and care needed for a healthy pregnancy journey. Learn about High Risk Pregnancy.
Do Read: https://www.drshubhragoyal.com/welcome/blogs/introduction-to-high-risk-pregnancy--what-does-it-mean
#High Risk Pregnancy#Pregnancy with heart disease#Rh incompatibility#Oligohydramnios#Uterine fibroids pregnancy#Pregestational diabetes#Cervical insufficiency#Pregnancy after 35#Recurrent miscarriages#Intrauterine growth retardation#Placental abruption#VBAC risks (Vaginal Birth After Cesarean)#Perinatal infections#Pregnancy-induced hypertension#Chronic kidney disease pregnancy#Antiphospholipid syndrome pregnancy#Congenital anomalies risk
1 note
·
View note
Text
Microcephaly is an underdevelopment of the skull and brain, accompanied by mental retardation and neurological abnormalities.
I will not consider the causes of microcephaly yet, because this is a very complex topic of chromosomal mutations, intrauterine infections and pathologies, birth injuries, etc.


I rely solely on the unofficial concept of Pyro's face, so looking at the concept of signs of microcephaly, what am I trying to pull on the arsonist:
1) The predominance of the facial skull over the cerebral one.
2) Narrow and sloping forehead, prominent brow ridges, large ears.
I also love fanon, that Pyro has big and sparse teeth, the wrong taste.
3) Disproportionate physique – a change in the parts of the figure (feet, hands) and their unexpected growth.
Further, what I can add from myself are possible signs:
a) A gross delay in speech development.
b) Indistinctness of articulation (articulate pronunciation) – is further complicated by tightening the face with a gas mask, the tongue and lips may not move well.
c) Limited vocabulary – exclamations and repetition of the same expressions heard earlier.
d) Violation of the understanding of the addressed speech – ignoring, misunderstanding that they are addressing him, "withdrawal into oneself".
I consider Pyro to be an erectile group of patients: hyperactivity, fussiness, mobility, unstable attention.
The degree of intellectual disability varies from imbecility to idiocy.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Troubled by Early Pregnancy Symptoms? Try These Adjustment Methods!
It also touches on the importance of prenatal care and provides guidance for expectant mothers. Additionally, it discusses considerations for multiple pregnancies and advanced maternal age. Throughout the article, we will also highlight the significance of maternity clothing and introduce the GoMamee brand as a trusted provider of stylish and comfortable maternity wear.

1.How Can I Tell I Am Pregnant?
For women with a history of sexual intercourse and regular menstruation, it is recommended that pregnancy should be suspected for more than 10 days after menstruation. It can be determined by early pregnancy reaction, early pregnancy test paper, or blood hCG test, and you can also check ultrasound test after 6 weeks of menopause.
2.I Don't Know If I'm Pregnant, But I Had a Chest X-Ray For a Medical Checkup. Will It Affect My Child?
Within 2 weeks of fertilization, or 4 weeks of pregnancy, most drugs or medical examinations have an "all or nothing" effect on the embryo. If there is an effect, it may die, miscarry or stop developing. If the fetus survives, there is nothing to worry about; secondly, the radiation exposure dose from x-ray examination is much lower than the dose that is harmful to the fetus. Therefore, please do not easily give a death sentence to life.
3.What Should I Do If My Early Pregnancy Reaction Is Too Severe?
Anorexia and vomiting are relatively normal early pregnancy reactions. Pregnant mothers should self-regulate their diet, try to choose foods that promote appetite, are rich in nutrients and easy to digest, eat less and more meals, and also take some vitamin B6 to reduce the symptoms of pregnancy vomiting.
If you still have very serious pregnancy vomiting after self-regulation, even accompanied by weight loss, it is recommended to go to the hospital for liver function, blood electrolyte test and urine ketone body test, which may require hospitalization, intravenous supplementation of water, electrolytes and heat card, and at the same time, let the stomach and intestines rest.
4.Can I Eat Seafood During Pregnancy?
Yes. Seafood itself will not affect the fetus, but seafood may have parasites, so it is important to eat fresh, hygienic and cooked seafood.
5.Do I Need To Reduce The Fetus If The Ultrasound Examination Indicates a Triplet Pregnancy?
In general, it is recommended to reduce the fetus if there are three or more fetuses alive. In addition, there is a high risk of hypertensive disorders such as pre-eclampsia in late pregnancy and complications such as postpartum hemorrhage during delivery, which endanger the life of mother and child. The risk of decompensation is mainly to cause miscarriage and preterm delivery. Early reduction is generally recommended to reduce complications in the middle and late stages of pregnancy.
6.What Should I Pay Attention To When I Am Pregnant At An Advanced Age?
The age of delivery ≥ 35 years old is an advanced pregnancy. Because after women reach 35 years old, many aspects of their bodies start to go downhill relatively, and pregnancy at this time will increase the incidence of baby malformations; at the same time, the risk of intrauterine growth retardation, miscarriage and premature birth increases, and advanced pregnant women are prone to combined heart disease of pregnancy, gestational hypertension disease and gestational diabetes. Therefore, extra attention should be paid to pregnancy care, and regular prenatal checkups should be ensured.
In addition to the routine 11-13+6 weeks NT ultrasound and 20-24 weeks ultrasound for major abnormalities, amniocentesis for fetal chromosomes is recommended directly after 18 weeks of gestation for older pregnant women. If you are not willing to perform amniocentesis or have contraindications to amniocentesis, you can also choose a non-invasive DNA test first, but you should understand the limitations of non-invasive DNA tests.

7.Can I Have a Fetus With Thickened Nt Value? It Needs To Be Determined On a Case-By-Case Basis.
The thickness of NT value is directly proportional to the incidence of chromosomal abnormalities and can better evaluate the risk of trisomy 21, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, etc.; it is also associated with congenital structural malformation of the fetal heart, which is the most common cause of non-chromosomal abnormal NT thickening. Secondly, NT thickening is also associated with other structural malformations of the fetus: such as malformations of the skeletal system, diaphragmatic hernia, anterior abdominal wall defects (umbilical bulge), and fetal dyskinesia syndrome. In addition, thickened NT is also associated with spontaneous abortion, etc.
A completely normal fetus may also have thickened NT. When you get the result of NT thickening, please do not be overly nervous and upset, but go to the hospital on time. We have professional experts to help you further investigate the possible risks.
8.What Do I Need To Pay Attention To Now That I Am Pregnant With My Second Child After My First Child Was Delivered By a Cesarean?
It is appropriate to have another pregnancy after cesarean section with an interval of more than 2 years and less than 10 years. The shorter the interval, the greater the risk of uterine rupture in another pregnancy. Pregnant mothers with scarred uterus can first have an ultrasound examination to understand the location of the embryo in relation to the scar. If the embryo lays on the scar, it is considered a "scarred pregnancy" and is at higher risk of uterine rupture and hemorrhage. If the bed site is not in the scar, pregnancy can continue, but there is still a risk of uterine rupture during pregnancy, so it is recommended to strengthen perinatal health care regularly.
9.Can I Play With Cell Phones And Computers During Pregnancy?
Yes. The radiation dose of daily electrical appliances is very small and will not cause harm to the mother and fetus. The normal use of cell phones for phone calls has no effect on the fetus, but it is not recommended to play on cell phones for a long time. It is recommended to take a walk outdoors more often during pregnancy to relax, pay attention to rest more, develop good habits of life and rest, don't stay up late, avoid straining and do regular maternity checkups.
10.How To Supplement Folic Acid During Pregnancy?
In order to prevent fetal neural tube malformation, the demand for folic acid during pregnancy is high.
Experts recommend starting oral folic acid 0.4 mg as early as three months prior to pregnancy preparation. Women with a history of births with neural tube defects, as well as those with diseases affecting folic acid metabolism such as diabetes, epilepsy, or those found to have genetic defects that impair folic acid metabolism, need to increase their folic acid intake as prescribed by their doctors on a case-by-case basis.

Conclusion
In conclusion, this article provides valuable insights for expectant mothers, covering various aspects of pregnancy. It emphasizes the importance of timely pregnancy confirmation and regular prenatal care. Additionally, it highlights the significance of choosing appropriate maternity clothing, and the GoMamee brand stands out as a reliable option offering fashionable and comfortable options for expectant mothers. By considering the information presented here and selecting quality maternity clothing from GoMamee, pregnant women can enhance their comfort and style during this special time in their lives.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) and Why It Matters?
It’s a well-known scientific fact that our genetics is the sum of our parents, a lesser-known fact is that sometimes their actions can heavily impact our genetics as well. One of these actions is responsible for causing the single most preventable cause of intellectual disability in children – Fetal alcoholic spectrum disorder (FASD), brought about when women consume alcohol during pregnancy.
I am sure alcohol needs no introduction, it is one of the most abused psychoactive drugs in the world while also being one of the most widely used in many diverse scenarios – social drinking, cooking, as a coping mechanism by addicts, etc. Among its many toxic effects (that most of us choose to be ignorant towards) a highly overlooked one is its ability to transmit these effects from a mother to her unborn child leading to the child having to suffer with FASD for life.
As we observe ‘International FASD Day’ this 9th of September, its vital to understand the workings of this 100% preventable disorder and our role in it.
I have aforementioned that the intake of alcohol by pregnant mothers is the cause of FASD in their offspring but how exactly does alcohol reach the baby and how does it affect it?
During pregnancy the mother’s body develops a specialized structure known as the placenta which acts as a sort of bridge between the maternal body and the developing fetus. A little-known fact about the placenta is that it's not just a temporary structure but a whole organ in and of itself thus alluding to its sheer importance and complexity. The placenta makes sure that the transport of nutrients, metabolites, blood gases and other vital substances happens seamlessly between the mother and the developing baby, it also protects the fetus from any harmful substances and toxins circulating within the mother’s bloodstream. Some toxic substances (termed teratogens) like alcohol and tobacco can readily pass through the placenta due to their nature and enter the baby’s bloodstream.
Babies do cannot process alcohol the same way we do due to their immature liver and that’s why high doses of alcohol are fatal to the unborn fetus. Moreover, alcohol can enter and concentrate within the amniotic fluid thus increasing the overall exposure of the fetus to it. If this occurs during the first trimester, the fetus is at increased risk of spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, and intrauterine growth retardation. When alcohol consumption occurs during the second trimester the fetus has a higher chance of survival but will be born with a range of adverse outcomes which fall under FASD.
How does someone suffering from FASD look like?
We have so far discussed how FASD comes about but haven't really gotten into the basic symptoms and appearance of FASD. As a teratogen alcohol brings about its effects by attacking important cells within the central nervous system which are responsible for a range of important functions from brain development to proper anatomical alignment of facial features and limbs. This led to the formation of FASD classification as follows - (1) Central nervous system damage and cognitive impairments, (2) Dysmorphic facial features, and (3) Behavioral and emotional deficits.
Physical dysmorphic features of people suffering from FASD are rare but can include – a thin upper lip, smooth hypoplastic philtrum, down-slanting short palpebral fissures, hypertelorism, microcephaly, epicanthal folds, and a receding chin. Although only a few of these features may be present in a single FASD patient at a time depending on the severity of the disease. The main FASD features involve the brain and therefore can lead to other disabilities later in life. These disabilities include, but are not limited to, academic failure, substance abuse, mental health problems, frequent contact with law enforcement, and inability to live independently and obtain and/or maintain employment—all of which have lifelong implications.
How do people suffering from FASD feel about it?
A study published in May of 2024 in the MDPI Journals titled ‘FASD: The Living Experience of People with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder—Results of an Anonymous Survey’ sought out to get a comprehensive understanding of how living with FASD has affected these people in the following major life areas – Sense of self, adversity, education, employment, finances, housing instability, memory issues, familial relationships, friendships, and criminal justice. They achieved this by conducting anonymous surveys among FASD patients targeting the aforementioned areas, they received 468 complete responses which were then included in the study. The results of the study proved to be very concerning -
Sense of self – On average respondents mentioned that they felt alienated and inferior in society which impacted their sense of self greatly. This was also brought about by the fact that the majority of them did not have a clear definition of FASD provided to them leading to internal conflict.
Adversity – This are of the study was divided into childhood and adult adversities. The most common childhood adversities mentioned were being involved with alcoholics in the household in an abusive or depressed manner. Adulthood adversities involved being easily manipulated and talked into doing things against their better judgement.
Education – The main takeaway from this section of the study is that 77% of respondents who did not complete their high school believe that they would have been able to complete their education had they been provided with more individualized support pertaining to their special needs.
Employment – Among those who were employed, majority of the respondents felt fulfilled and enjoyed their work but also felt heavy stress and disorientation leading to mental stress due to the nature of job stress itself. They felt like they did not do their job properly and would take extra care in this regard leading to more stress. Majority of the respondents also hid their diagnosis from their coworkers and employers due to the stigma surrounding it. Something more concerning this area of the study revealed was that majority of the respondents were laid off or quit at least thrice in their career journey.
Finances – Just over half of the respondents revealed that they received some sort of financial support (albeit small) from the government or their family members, this adds to their level of dependency.
Housing instability – Of those who had been evicted at least once in the past, they reported issues like not having enough finances to cover their rent or failing to remember that their rent was due.
Memory issues – The respondents indicated a number of problems arising due to memory issues which included failing to remember to pay rent, to eat, to maintain hygiene, and to take their medications.
Familial relationships – Only a very small percent of the respondents were raised by their birth family, the majority of them were raised in a variety of living situations. This had led to more childhood trauma in addition to already existing trauma.
Friendships – Majority of the respondents indicated that it was difficult for them to make friends and even more so to keep them. They also added that making and keeping friends was very exhausting and caused a lot of anxiety for them.
Is FASD treatable? To date, there is no known treatment to reverse alcohol-induced damage to the fetus. The only treatment options available deal with trying to reduce symptoms and increase support as much as possible.
It's scary to think of all these lifelong implications and problems caused by a disease which is 100% preventable. So, in the spirit of International FASD Day, Lets tackle the most important question now – How can we help in the battle against FASD?
We can further divide this problem into two smaller issues – How to help prevent FASD? And how to help those existing with FASD?
The aforementioned study actually answers the second problem very effectively in the following ten points -
Access to a mental health clinician who specializes in FASD.
Availability of a doctor or nurse practitioner who knows about FASD.
A person who can help when something goes wrong.
A person who can be trusted to give advice when needed.
Enough money to meet monthly needs.
Help with tasks of daily living such as cleaning and laundry.
Having a trusted person who, with permission, can speak and act for the person with FASD.
A trusted person to manage or help with money so that the person with FASD is less likely to be taken advantage of. This may also include being able to attend appointments so that there is someone present to support the person’s understanding of what has been said and recommended.
Help to obtain and sustain employment (this would be a person who understands what is and is not possible).
The ability to engage in activities that are important to the person.
When it comes to preventing FASD, remember that a pregnant woman almost never drinks alone so doing our best to engage with pregnant women who have a history of alcohol abuse and raising awareness among them during social gatherings or your inner circles goes a long way in preventing FASD.
You can also use this opportunity to reach out to anyone you know who suffers from FASD and give them the support they need.
1 note
·
View note
Text
A 12 Day- Old Female Infant Diagnosed with Pelvic Osteomyelitis in the Pediatric Emergency Department by Mehmet Ali Oktay in Journal of Clinical and Medical Images, Case Reports

Abstract
Osteomyelitis (OM) is a bacterial disease that is very rare in newborns and has devastating consequences. Neonatal OM is seen in 1-3 in 1000 babies. We presented a 12-day-old female baby who was brought to the Pediatric Emergency Department (PED). Because she could not move her leg. She did not have fever and septic appearance and had a history of hospitalization in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit; acute phase reactants were high and radiological imaging performed gradually was consistent with OM. Our patient is the youngest patient who was diagnosed with pelvic OM upon admission to the PED. Earlydiagnosis and treatment prevent complications and sequels. Keywords: Osteomyelitis; newborn; pediatric emergency
Introduction
Osteomyelitis often occurs secondary to the hematogenous spread of microorganisms into the blood-rich metaphysis of the developing bone. When left untreated, it leads to complications such as joint destruction and decreased range of motion [1]. Osteomyelitis (OM) of the hip is rare in newborns. Signs and symptoms are quite different compared to older children. This may cause difficulties/delays in diagnosis and permanent disability [2]. Successful management of OM in the neonatal period has been associated with rapid correct diagnosis and adequate correct treatment [2, 3]. The incidence of OM in the pediatric age group is 1/5000 cases. About 50% of pediatric OM cases are under the age of five. The incidence of neonatal OM is 1-3/1000 cases [3]. Although there are studies on patients diagnosed with osteomyelitis while staying in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) [1, 4, 5], cases diagnosed upon PED (Pediatric Emergency Department) admission are very rare [6]. In this article, the youngest case in literature who went to the PED and was diagnosed with pelvic and acetabulary OM is presented.
Case Report
A 12-day-old girl, born from the first pregnancy of a 28-year-old mother, was admitted to the PED with complaints of restlessness and inability to move her right leg. The day before the application, it was stated by her mother that she did not move her leg, that she was agitated when forced to move, and could not be consoled. The baby did not have a history of fever or trauma, her feeding was good, and her urine and defecation were normal. From her history, it was learned that she was born at 36 weeks and 3 days of gestation and had intrauterine growth retardation compatible with 31 weeks gestational age, and she was born by emergency cesarean section due to preeclampsia. The patient, who was hospitalized in the NICU due to temporary tachypnea of the newborn after birth, was discharged on the sixth postnatal day. During the follow-up in the NICU, umbilical catheterization was not applied to the patient. She had not received antibiotic treatment and no growth was detected in blood cultures taken before discharge.
At her evaluation in the Pediatric Emergency Department triage area, she was a restless baby with a good general appearance. Vital signs; body temperature was 37°C, heart rate was 140/min, respiratory rate was 42/min, pulse oximetry was 98%, and mean arterial pressure was 45 mmHg. There was no pathological finding in the physical examination, and it was observed that the patient's discomfort increased due to the position given to the hip and leg while changing the diaper. While abducting the right thigh from the hip in the supine position, there was limited range of motion compared to the left. No swelling or redness was detected on the joint surface.
Laboratory and radiological examinations were planned for the patient with a preliminary diagnosis of septic arthritis. In laboratory tests: hemoglobin (Hb) 14.6 g/dL, RBC (Erythrocyte) - 3.361 x10.e6/uL, hematocrit (Hct) 40.04%, white blood cell (WBC) 16.82 x10.e3/uL, neutrophil percentage 59.8%, C-reactive protein (CRP) 25.9 mg/L, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 51 mm/hr, procalcitonin (PCT) 2.95 ng/mL, IL-6 145.6 pg /mL detected. On direct radiographs of the lower extremity and pelvis, the right femoro-acetabular distance was observed to be increased (Figure 1). Long bone radiographs were normal. In the superficial tissue ultrasound (US) performed for the right hip joint, bilateral hip joints were compared with each other, and no significant effusion was observed on the right side. The patient was consulted to the Orthopedics and Traumatology department with a preliminary diagnosis of septic arthritis. MRI was requested from the patient for the differential diagnosis of septic arthritis.

Figure 1: There is an increase in the right acetofemoral distance compared to the left.
Bilateral hip MR imaging showed “The right femoral head is small and irregular in appearance, and an area of pathological signal change in the right femur proximal metaphysis, medullary bone marrow, and solid periosteal reaction in the lateral proximal section is observed. Widespread edema was observed in the surrounding muscle planes, fascial surface and subcutaneous adipose tissue adjacent to the hip joint. In addition, medullary bone marrow edema was observed in the right acetabulum (osteomyelitis). Areas of pathological signal changes consistent with diffuse edema are observed in the right obturator externus, pectineus, quadriceps muscles, gluteal muscle planes and iliacus muscle (myositis). Minimal free fluid was observed in the right hip joint space. Findings were primarily evaluated as compatible with osteomyelitis and myositis.” (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Osteomyelitis in the proximal metaphysis of the femur
Due to the history of hospitalization in the intensive care unit, the patient was diagnosed with OM secondary to hematogenous spread and, according to the age, to include possible infectious agents, vancomycin (15mg/kg/dosex3), ceftazidime (30 mg/kg/dose x 3), fluconazole loading (12 mg/kg/dose)) and maintenance (6 mg/kg/dose) treatment was started. Blood culture was taken before antibiotic treatment. Our patient, who received antibiotic doses only one day before the operation, was operated on the postnatal 13th day.
The patient was operated by the Orthopedics and Traumatology department and the intra-articular pus was drained. From the material; joint fluid culture, fungal culture, tuberculosis PCR, ARB staining, fungus search was sent. There was no growth in the blood culture, but because of the growth of ceftazidime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the joint fluid culture, ceftazidime was discontinued and meropenem (20 mg/kg/dosex3) treatment was started. Fluconazole was discontinued on the 8th day because there was no growth in the fungal culture. The patient was discharged with oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment after 25 days of vancomycin and 27 days of meropenem treatment. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was discontinued 22 days after discharge. The regression of the inflammation was seen in the MRI taken under the control of the outpatient clinic. verbal consent was obtained from the patient's parents for the publication of the article.
Discussion
This case demonstrates the importance of detailed investigation of newborn infants admitted to PED. Although OM in newborns is rare, there are difficulties in diagnosing and treating it. High suspicion is required for early diagnosis and observation of clinical signs is very important.
Risk factors for osteomyelitis in newborns are stated as immature host-defense mechanisms, invasive intervention such as umbilical catheterization. It has been shown that half of the cases diagnosed with neonatal OM have a history of umbilical catheterization. It has been observed that the pregnancy and delivery history of the mother is also important in the development of OM, and maternal complications such as maternal hypertension, preeclampsia, ablatio placentae, infection are present in approximately half of the infants who develop OM [7]. Particular attention should be paid to the evaluation of newborn cases, especially in PEDs where is crowded and the number of patient admissions is high. Newborns are among the patients at risk for PED and require special care. Application complaints and prenatal, natal and postnatal history should be questioned in detail. It was observed that the mother of our case had preeclampsia during pregnancy, but umbilical catheterization was not applied to the baby.
In studies conducted in newborns with neonatal osteomyelitis, the most common sites of involvement were reported as femur, humerus, and tibia, respectively [1, 4, 8]. The pelvis is a rare site of hematogenous disseminated OM for neonates. Pelvic OM constitutes 2.3% of all childhood osteomyelitis cases [3]. Our case also had pelvic (acetabular) OM, which is a rare site of OM involvement. Involvement was also demonstrated in the proximal region of the right femur.
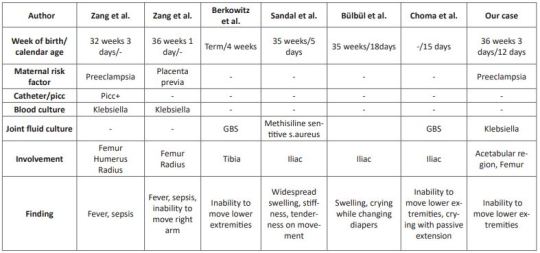
Pelvic OM was defined in three cases at 5, 15, and 18 days in the neonatal period [3, 9, 10]. In the literature, it has been observed that mostly cases hospitalized in the NICU were diagnosed with osteomyelitis [1, 3, 4, 8-10]. As far as we can find in the literature, a 4-week-old case with a diagnosis of distal tibial OM and culture of GBS has been reported, just like our case [6]. Our case is the youngest OM case diagnosed in the emergency department, except for the case in the literature. The clinical features, presentation symptoms, cultures and risk factors of cases diagnosed with neonatal osteomyelitis in the literature are shown in (Table 1)
Table 1: Comparison of cases with neonatal osteomyelitis in the literature.
Clinical symptoms are related to the bone or joint area involved in newborns. Swelling and local inflammation findings are common findings in the neonatal osteomyelitis group. Systemic findings such as fever are seen in fewer of these cases. A highly variable rate of fever was found in 9.1-76.5% of patients with extensive neonatal osteomyelitis. In addition, it has been shown that the WBC count, CRP and ESR levels are high in the cases [1, 4, 8, 11]. In our case, there was no fever, but there were complaints of inability to move her right leg and restlessness. Laboratory parameters were high and consistent with the literature. In cases with osteomyelitis, direct radiographs can guide the correct diagnosis, exclude other diagnostic possibilities, or provide clues for underlying pathological conditions [12]. Soft tissue swelling on plain radiographs can be seen within days of the onset of infection. It can also show periosteal reaction, lytic lesions, joint effusions and destructive bone changes 7-10 days after the onset of infection [13]. US findings begin with nonspecific swelling in the soft tissues adjacent to the bone. US can show thickening and elevation of periosteal and subperiosteal fluid collections as early as 3 days [14]. In a study comparing osteomyelitis groups, it was shown that the diagnostic value of US was statistically higher in the newborn group compared to the other groups, regarding the capacity of detecting subperiosteal abscesses [11]. In our case, however, an increased femoro-acetabular distance was observed on direct X-ray, but no finding was found on US. This supports the view that the primary step in the pediatric emergency department in patients with suspected osteomyelitis should be started with direct X-ray as recommended in the literature.
MR imaging is the most useful imaging technique for evaluating suspected OM, allowing early detection of osteomyelitis and assessment of the extent of involvement and disease activity. MRI is very sensitive in detecting OM 3-5 days after the onset of infection [12]. As seen in our case, it still remains the gold standard. However, we recommend hospitalization in order not to miss the newborn cases because MRI is difficult in emergency conditions.
In infants, osteomyelitis and septic arthritis often coexist. While Staphylococcus aureus is the most common organism causing osteomyelitis at all ages, GBS and Escherichia Coli are important pathogens to be considered in newborns [6]. Culture is found to be negative in 22-50% of the cases [15]. Antibiotics to be used in neonatal OM should be effective against these pathogens [16]. In our case, treatment with antibiotics covering these pathogens was applied and Klebsiella pneumoniae growth was observed in the pus culture.
We think that even with rapid diagnosis and aggressive treatment, there are orthopedic sequelae and inadequate treatment increases the risk of chronic osteoma [16], therefore, in cases who apply to the pediatric emergency department with these complaints, early diagnosis and treatment of neonatal OM should be planned in a timely manner to minimize long-term sequelae.
In conclusion, a detailed anamnesis should be taken and a careful physical examination should be performed in newborns who present to the PED with limited range of motion at joints. Neonatal OM cases mostly consist of cases diagnosed while staying in the NICU. Pelvic involvement is rare and our case is the youngest pelvic OM case diagnosed in the PED.
For more details : https://jcmimagescasereports.org/author-guidelines/
#Osteomyelitis#newborn#pediatric emergency#Pediatric Emergency Department#OM#PED#catheterization#RBC#C-reactive protein#hematocrit#Traumatology#Mehmet Ali Oktay#JCMICR
0 notes
Text
Impact Of Nutrition On The National Education And Healthy Growth

Education and health growth in a country are dependent on nutrition. A productive student is one that is healthy. A healthy diet is seen as an investment in human potential that will yield returns in the future. Bad nutrition is considered a treat for the nation. Wellnessbeing Four types of malnutrition are responsible for the global decline in social productivity between 1990 and 1990. stunting and other disorders due to vitamin A and iron deficiency. This equated to nearly 46 million years of productive disabilities. Free life nutrition increases returns on investments in education and healthcare.
Literature has shown that knowledge levels in Nigeria have declined significantly since the 1980s, in contrast to previous years. This decline was attributed to malnutrition from the civil war. One researcher found that Nigeria had the lowest percentage of indigenous engineers among Third World countries in the 1980s. Teaching English, the language used for instruction, was so poor that university faculty reported their inability understand written work from their students. This is due to the ineffective communication. There are many quack workers and graduates in Nigeria. In 1990, the education crisis was so severe that it was predicted that the country would run out of personnel in the next ten years. This is a problem that needs to be addressed before the country loses all its skilled labour force. These problems can be divided into two main nutritional factors: malnutrition and undernutrition. This article is a? This article is intended to examine the current and past effects of nutrition and the necessary steps to correct the situation. This report will provide solutions.
NUTRITIONAL PROBLEMS
Nigeria is plagued by undernutrition as well as micronutrients. Rest of the nutrients have very little impact and should be left for now. Inadequate intake of macronutrients is the hallmark of undernutrition. It can begin in the uterus and continue throughout life. It can also spread across generations. It can occur in pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence and can have a cumulative negative effect on future babies' birthweight. Baby born with intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), as a fetus, is in effect malnourished and has a higher chance of dying in childhood. Malnutrition can have serious consequences for adulthood. Infancy and young childhood are prone to frequent or prolonged infections, as well as inadequate nutrition intakes (especially energy, iron, protein and vitamin A). This can lead to stunting and underweight in preschool. After a period of exclusively breast-feeding, infants are given weaning, which consists of pap (akamu), ogi or koko. It is made of maize (Zee Mays), millet, pennisetum Americanum, and guinea corn. Because of socio-economic factors and ignorance, low income people rarely feed their infants meat, eggs, or seafood.
Agu, from Anambra State in Nigeria, observed that pap had 0.5% protein and less then 1% fat compared to 9% protein and 4% fat of the original corn. Poor processing is often the reason. Omotola and Akinele examined the energy and protein intakes of children in the low-income group and infants. The researchers found that around one-third to half of the infants were suffering from malnutrition, while 10% were stunted and wasted. The Demographic and Health Survey (DHS), Nigeria, conducted a more recent Nigerian National Survey in 1990. It found that underweight children aged under 5 years (those who are below a) were almost half of all those underweight. ?2SD weight for age was 36%, with 12% severely underweight. (below -3 SD). Stunting (below a) ?2 SD height for a?? Age) was 43%, with 22% severe stunting (below? 3SD), while the levels for severe wasting and wasting were 9% & 2%, respectively. DHS Survey of children 6 to 36 months old in Nigeria's Ondo State found 28% underweight prevalence, 32% stunting and 7% wasting.
Adults and older children can usually get adequate protein. You can increase your daily intake of low-nutrient starchy foods to increase your energy intake. The traditional diets may not be sufficient for infants or small children. For energy (740 Kcal and 13g protein), a baby four- to six months old would require 920g corn gruel. Given the size of an infant's stomach, this is a daunting task. ?s stomach.
President Chief Olusegun Obasanjo correctly observed that nearly half of Nigeria's children aged 7-13 are still underweight. Many children and adults are starved, and some only eat one meal per day that consists mainly of carbohydrates.
Another difficult problem in nutrition is micronutrient. It refers to a low intake of key vitamins or minerals. This can be seen in both urban and rural Nigerians. Inadequate vitamins and minerals can cause irreversible mental and physical impairments in the child's development. Micronutrient deficiencies in pregnancy can have severe consequences for the developing foetus, as well as indirect effects on the mother. Iodine deficiencies can cause foetus brain damage, still birth, mental retardation, delayed motor developmental and stunting. Folate and infantile iodine deficiencies can lead to a 10-15% drop in intelligence quotient. Foliate deficiencies can lead to neural tube defects, preterm births, or other birth defects. Iron deficiency and vitamin A deficiency could have serious implications for future infants. Their ability to focus, social interaction, and development are affected by their morbidity, mortality, vision, and cognitive development. Vitamin A deficiency affects 40% of children younger than 5 years old. Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of severe, preventable blindness and severe visual impairment in children. Pre-school children and pregnant women are most at risk. These two nutritional problems are huge in Nigeria and have a significant impact on the economy as well as the social life of the nation.
0 notes
Text
Birth Injury Attorneys California

An attorney specializing in birth injuries can help families pursue compensation when a child or mother is hurt during labor and delivery due to the negligence of a medical professional.
More than 25,000 American newborns are injured yearly due to complications during birth. The parents of a child who sustained injuries at birth due to medical malpractice may file a claim for damages to cover the costs of their kid's continued medical care.
Let's understand the Role of an Obstetrician and Other Workers in a Birthing Facility?
Obstetricians and other delivery room staff must keep a close eye on the woman and the baby during the entirety of the pregnancy and birth and be ready for any emergency. Medical malpractice occurs when doctors, nurses, and other medical staff fail to take necessary precautions to prevent birth damage.
However, there are many potential causes of birth injuries, and not all result from medical malpractice. Therefore, if either the mother or the newborn has been injured during birth, the parents should seek the advice of a medical malpractice lawyer with extensive experience with cases involving birth injuries.
Because a child who suffers catastrophic birth damage may need ongoing medical care — and the means to pay for that care — for the rest of their lives, their parents will need an attorney who will actively pursue the maximum compensation available from all parties and may be held liable.
Who Could Be Held Responsible for a Fetal Injury?
A birth injury malpractice claim is not always restricted to the delivering doctor. Medical malpractice claims can also be filed against a negligent clinic, hospital, anesthesiologist, nurse, or healthcare provider.
An applicant's credentials in education, licensure, and training must be verified before employment in a medical position at a hospital. The hospital could be held responsible for negligent supervision or employment if it fails to do so, and birth harm occurs as a result.
Even a doctor's qualifications must be checked before a hospital allows them to practice there. Hospitals are also responsible for ensuring enough nurses and other support workers available to treat patients at all hours of the night and day.
What factors contribute to the problem where babies are born with physical defects?
Cerebral palsy, Erb's palsy, mental retardation, and brachial plexus injury are all common results of subpar medical care during childbirth. What specific examples of bad medical care led to these wounds? All of the following can contribute, but they are not limited to:
Inadequate surveillance
Bad drugs and treatments
Birth Trauma
An undetected case of fetal distress
The infant suffers from hypoxia due to disruptions in oxygen delivery via the placenta or umbilical cord.
Too much time is spent with the infant in the delivery canal
IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction, is one of several pregnancy-related complications that might be missed until it's too late.
Complications from waiting too long to perform a C-section
Failure to properly employ a vacuum or forceps
The apparent separation of the placenta from the uterus (where the placenta separates from the wall of the womb causing the mother severe bleeding)
Untreated preeclampsia increases the risk of stroke and seizures in the mother and brain damage in the infant.
Suppose your child was injured during birth due to the negligence of a medical professional (such as a doctor, midwife, nurse, anesthesiologist, clinic, hospital, or HMO). In that case, you might be entitled to compensation.
Tips for Recognizing a Birth Injury
It might be difficult to determine whether or not a baby has suffered an injury during birth. However, your newborn may have suffered some birth damage if you detect any out-of-the-ordinary symptoms in their physical state, breathing, excessive crying, etc. If you have concerns about your child, it is important to take them to a doctor immediately.
When comparing birth injuries and congenital disabilities, what are the key distinctions?
Usually caused by chromosomal abnormalities or anatomical problems in the uterus, congenital disabilities manifest themselves while the baby is still developing inside the mother's body. In contrast, a birth injury occurs during the process of giving birth. A birth injury can occur either because of the carelessness of a medical professional or because it is an inevitable result of giving birth.
What Can the Stalwart legal firm do for you?
A medical malpractice attorney in California can investigate the circumstances surrounding a birth injury and determine who is at fault. Parents who suspect their child may have suffered a birth injury should consult an attorney without delay.
In order to determine the validity of a parent's claim and how the legislation in California pertains to their specific situation, the stalwart law firm provides a free initial consultation.
The Preferred Method of Seeking justice
When representing parents in a birth injury case, Stalwart Law Group will collaborate with relevant medical authorities and birthing experts to collect the testimony and evidence necessary for a successful case outcome.
Cases involving birth injuries are often complex. In-depth investigations and months of legal preparation are typical for cases of this nature. The best approach to seek justice and financial compensation for your kid and family is to work with a skilled Pasadena birth injury attorney.
Put your trust in the California birth injury experts at Stalwart law firm if you or a loved one has suffered because of medical negligence during labor or delivery.
The affected victims of negligence have benefited from the millions we have collected for them. Stalwart Law Group's award-winning lawyers have been helping customers for a long time, building a track record of success and a stellar reputation for legal prowess.
To set up a free initial consultation, parents struggling with a birth injury can phone or fill out the online form on the Stalwart Law group website.
0 notes
Text
Bile acid improves intrauterine growth retardation metabolism in piglets#Bile #acid #improves #intrauterine #growth #retardation #metabolism #piglets
Bile acid improves intrauterine growth retardation metabolism in piglets#Bile #acid #improves #intrauterine #growth #retardation #metabolism #piglets
Schematic diagram of bile acid metabolism in normal birth weight piglets and IUGR piglets. Credit: LIU Yang Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), defined as the impaired growth and development of a mammalian embryo/fetus or fetal organs during pregnancy, is a major concern in pig farming. IUGR animals exhibit impaired growth and development, lower meat quality, and higher morbidity and…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Reviewing questions:
Preeclampsia is diagnosed with new-onset hypertension occurring after 20 weeks' gestation with proteinuria. The combination of hypertension and proteinuria during pregnancy is diagnostic for preeclampsia until proven otherwise. Diagnostic criteria:
Hypertension:
Systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg on 2 occasions at least 4 hours apart after 20 weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive patient, or
If systolic blood pressure is ≥160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure is ≥110 mmHg, confirmation within minutes is sufficient
Proteinuria ≥0.3 g in a 24-hour urine specimen or protein (mg/dL)/creatinine (mg/dL) ratio ≥0.3 or dipstick 1+ if a quantitative measurement is unavailable
In patients with new-onset hypertension without proteinuria, the new onset of any of the following is diagnostic of preeclampsia:
-Platelet count 1.1 mg/dL or doubling of serum creatinine in the absence of other renal disease -Liver transaminases at least twice the normal concentrations -Pulmonary edema -Cerebral or visual symptoms
Preeclampsia usually occurs in the third trimester. If preeclampsia occurs before the third trimester, you should think of gestational trophoblastic disease. Preexisting hypertension increases the risk for intrauterine growth retardation and preeclampsia. Risk factors for preeclampsia include chronic renal disease, chronic hypertension, family history, multiple gestations, nulliparity, a very young woman with her first child, diabetes, and being African American. If the neonate is at term, definitive treatment is delivery. If the neonate is at preterm, the hypertension can be treated with hydralazine, methyldopa, or labetalol. Then, bedrest and observing the patient are advised.
Bottom Line: New-onset hypertension with proteinuria after 20 weeks' gestation is diagnosed as preeclampsia.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and most other organizations worldwide continue to recommend magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis and prevention of eclampsia, especially in patients with severe preeclampsia.
ACOG recommends that the decision of whether to use magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis in patients with preeclampsia without severe features be determined using shared decision-making on a patient-by-patient basis. Magnesium sulfate has been shown to be superior to other medical interventions for pregnant women with eclampsia in multiple trials.
Neuromuscular toxicity is the most consistently observed complication of hypermagnesemia. Magnesium is contraindicated in women with myasthenia gravis, as it has been shown to precipitate severe myasthenic crisis. Increased magnesium decreases impulse transmission across the neuromuscular junction. Decreased deep tendon reflexes are usually the first sign of magnesium toxicity and can be seen when the plasma magnesium concentration reaches 7 to 10 mEq/L.
If there is a magnesium drip, it should be stopped at this point. Other side effects of magnesium include respiratory paralysis (10–13 mEq/L), pulmonary edema, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, and cardiac arrest (greater than 25 mEq/L). Intravenous calcium gluconate can be administered to reverse severe magnesium sulfate toxicity.
Preeclampsia with severe features requires any one or more of the following factors:
1. Symptoms of central nervous system dysfunction:
New-onset cerebral or visual disturbance, such as:
Photopsia, scotomata, cortical blindness, retinal vasospasm Severe headache (ie, incapacitating, "the worst headache I've ever had") or headache that persists and progresses despite analgesics Altered mental status
2. Hepatic abnormality:
Severe, persistent, right upper quadrant or epigastric pain unresponsive to medication and not accounted for by an alternative diagnosis or serum transaminase concentration ≥ twice normal, or both
3. Severe blood pressure elevation:
Systolic blood pressure ≥160 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥110 mmHg on 2 occasions at least 4 hours apart while the patient is on bedrest (unless the patient is on antihypertensive therapy)
4. Thrombocytopenia:
Less than 100,000 platelets/μL
5. Renal abnormality:
Progressive renal insufficiency (serum creatinine greater than 1.1 mg/dL or doubling of serum creatinine concentration in the absence of other renal disease)
6. Pulmonary edema
Patients may also have HELLP syndrome, which stands for hemolysis, elevated liver function tests, and low platelets. Definitive treatment is delivery if the patient is at term. If preterm, delivery of the neonate is advised once the mother is stabilized to prevent the death of both mother and neonate.
The diagnosis of polyhydramnios is based upon sonographic visualization of increased amniotic fluid volume (AFV). It is diagnosed when there is a single deepest pocket ≥ 8 cm and an amniotic fluid index (AFI) ≥ 24 cm.
The most common cause of severe polyhydramnios are fetal anomalies (often associated with an underlying genetic abnormality or syndrome), while maternal diabetes, multiple gestation, and idiopathic factors are more often associated with milder cases. Polyhydramnios has been associated with fetal anomalies in most organ systems.
Vaginal bleeding is the most common symptom of a complete molar pregnancy and occurs when the molar tissue separates from the decidua. The uterus may also become distended by large pooling of blood, which can overflow into the vaginal vault. This symptom occurs in greater than 95% of cases. Other common symptoms of complete molar pregnancy include hyperemesis, nausea, and signs of hyperthyroidism such as tachycardia, tremor, and warm skin. These findings are a result of markedly elevated beta hCG associated with complete hydatidiform moles. Physical examination typically reveals a uterine size inconsistent with gestational age. Ultrasonography is the gold standard for diagnosis of both complete and partial molar pregnancies and elicits a classic “snowstorm pattern,” or "bunch of grapes" which is simply a mass of heterogenous echogenic material.
Bottom Line: Findings consistent of preeclampsia before 20 weeks, uterine enlargement, disproportional fundal height, and “snowstorm pattern” on ultrasound with no gestational sac all point to the diagnosis of complete molar pregnancy.
There are several key differences between complete and partial hydatidiform mole to be aware of when evaluating a patient with a potential molar pregnancy. Genetically, partial hydatidiform moles are triploid, usually as a result of two sperm fertilizing a normal ovum. Thus, you will see 69 chromosomes (for example, 69XXX or 69XXY) as opposed to a normal 46XY or 46XX in complete hydatidiform mole. Symptomatically, partial molar pregnancies will have fewer sequelae, such as hyperemesis, uterine enlargement or vaginal bleeding, as a result of lower hCG levels than complete molar pregnancies. Finally, a fetus, amniotic fluid and gestational sac can be seen on ultrasound with partial molar pregnancies (sometimes even with fetal heartbeat), whereas no fetus is seen in complete molar pregnancy.
Molar pregnancy tx: It is important to remember that hydatidiform moles are capable of developing into a malignant disease called gestational trophoblastic neoplasm. As such, evacuation of the uterus by dilatation and curettage (D+C) or dilation and evacuation (D+E) is always necessary following this diagnosis.
Clinical chorioamnionitis is an acute ascending, polymicrobial infection of the membranes and chorion of the placenta that can occur in women with prolonged rupture of membranes (defined as greater than 18 hours). Intraamniotic infection occurs in 15-25% of PPROM cases, with a higher incidence occurring at earlier gestational ages. Diagnostic criteria include maternal fever, maternal tachycardia, fetal tachycardia (fetal heart rate > 160/min), leukocytosis, or presence of purulent vaginal discharge. When chorioamnionitis is diagnosed, then IV antibiotics should be started and delivery should occur. In the absence of maternal decompensation or fetal distress, then prompt induction or augmentation of labor is recommended, with a c-section reserved for standard obstetric indications (history of prior CS, fetal distress, fetal malposition, labor dystocia, etc.).
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome occurs in monozygotic monochorionic twins and is the result of intrauterine blood transfusion from one twin to another. The donor twin will be small for gestational age; will develop hypovolemia, anemia, and oligohydramnios; and will be oliguric. The recipient twin will be large for gestational age, plethoric, and ruddy and have hypervolemia, polyhydramnios, jaundice, hypertension, and congestive heart failure. This is due to hypoperfusion of the donor twin and hyperperfusion of the recipient twin. Hemoglobin differences are typically greater than 5 g/dL. Hydrops fetalis can present in both twins. Treatment is a reduction amniocentesis.
Radiation exposure less than 50mGy (5 rads) in pregnancy provides negligible risk to the fetus. Radiographic, fluoroscopic, and CT examinations in areas of the body other than the abdomen and pelvis deliver minimal radiation doses to the fetus. Fetal radiation doses from radiographic, fluoroscopic, and CT examinations of the abdomen and pelvis and from nuclear medicine studies rarely exceed 25 mGy. The absolute risks of fetal effects, including childhood cancer induction, are small at conceptus doses of 100 mGy and negligible at doses of less than 50 mGy.
After giving methotrexate to treat an ectopic pregnancy, patients must be carefully followed. The day the methotrexate is given is considered day 1. The β-human chorionic gonadotropin (bHCG) will be checked again on day number 4 and day number 7. It is typical for the bHCG to increase between day 1 and day 4. If it rises during this point, nothing needs to be done. However, between day number 4 and day number 7, the bHCG must decrease by at least 15%. If the bHCG decreases by at least this much, then the bHCG will be checked every week until the level reaches 0. If the bHCG does not decrease by 15%, then another dose of methotrexate is warranted if the patient remains stable and there are no signs of rupture.
Bottom Line: Patients given methotrexate must have bHCG levels followed. From day 4 until day 7, the level must drop by 15%. If it does not, then a second dose of methotrexate is warranted.
COMBANK Insight: There is a single-dose and a two-dose regimen for methotrexate. In the two-dose regimen, a second dose of methotrexate is automatically administered on day 4; otherwise, the regimen steps are the same.
Primary postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) occurs in 1-3% of pregnancies and is defined as 1000 mL of blood loss along with signs of hypovolemia. Causes include uterine atony (most common), bleeding disorders, trauma, and retained placental tissue. Uterine atony can be suspected when there is a history of overdistension (multiple gestations, grand multiparty) or prolonged labor.
Initial treatment includes bimanual or fundic massage. If that fails, uterotonic medications should be given. Oxytocin is usually first-line with the addition of either methylergonovine or carboprost if needed. If that fails, balloon tamponade can be attempted. It is important to assess vitals, hemoglobin/hematocrit, platelets, and coagulation status and initiate volume resuscitation as needed.
When conservative measures fail, the best first approach is uterine artery embolization. This is minimally invasive and has less risk than surgical measures. Conservative surgical options include arterial ligations and compression sutures. Hysterectomy should only be performed if all other measures fail or are unavailable or if there is massive hemorrhage/hemodynamic instability.
#preeclampsia#polyhydramnios#molar pregnancy#chorioamnionitis#twin twin transfusion#ectopic pregnancy#OBGYN#postpartum hemorrhage
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
ICU- the Care unit
Intensive care units (ICUs) are special hospital zones that deliver medication and monitoring for people who are extremely ill and in emergency cases. They're staffed with specially trained healthcare experts and contain sophisticated monitoring equipment.
We at Laxmi Narasimha a Multi Speciality Hospitals In Warangal provide the best Care units. Our Neonatal Intensive Care Unit has the most advanced equipment in the world like GE Giraffe incubators and all compelled infrastructure to care for sick newborns including ventilation, HFOV, and Nitric Oxide, among other facilities. We do care for both mother and baby with the expertise fertility specialists and gynecologists over India
Patients will be insisted directly from an emergency ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or instantly after surgery if the surgery is very invasive. We at Laxmi Narasimha Hospitals are one of the list of Best Hospitals in Warangal and we take good care of our patients and children Types of ICU
• Coronary Care Unit
• Critical Care Unit
• Geriatric intensive-care unit
• High dependency unit
• Isolation intensive care unit
• Mobile intensive care unit
• Pediatric intensive care unit
• Psychiatric intensive care unit
• Surgical intensive care unit
Why do newborn babies and pregnant women need ICU?
• Prematurity (24 weeks gestation or more)
• Intrauterine growth retardation/small for gestational age
• Blood pressure variations and blood sugar level issues
• Respiratory issues
• Any kind of serious Infections
• Seizures
• Temperature fluctuation
• Assistance with feeding
Quality of care
• We appoint a special team of nurses, and doctors at the Fertility Hospitals in Hanamkonda and are equipped with advanced instruments to take extra care
• The unit of the neonatology will visit the baby every day and will be available 24/7 to monitor them
• Pediatric experts for Child Care Hospital in Hanamkonda for many departments comprising surgery, cardiology, nephrology, gastroenterology, genetics, pathology, radiology, and ultrasound are also available if the need arises.
Get consulted by the Best Multispeciality Hospitals in Warangal and we take utmost care for your children from delivery to post-pregnancy period
The best treatment is done by our doctors at one of the top Multi-Speciality Hospitals in Warangal For more details visit: http://www.laxminarasimhahospital.in/ | Contact us at: +91 -9550978696
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Introduction to High-Risk Pregnancy- What Does It Mean

Pregnancy can indeed be a joyous time, but it can also be overwhelming and stressful. Expectant mothers need to take care of themselves and their unborn babies. However, for some women, their pregnancy is considered high-risk.What is a high-risk pregnancy? It means the mother has an increased chance of experiencing complications during pregnancy, labor, delivery, and even after birth. Understanding this can help expectant mothers plan accordingly.Factors that contribute to high-risk pregnancy can vary from woman to woman. Some common factors include age, weight, medical history, and lifestyle choices. Awareness of these factors can help women make informed choices during this crucial time.So, let's dive deeper and understand what medical conditions can cause high-risk pregnancies and how to reduce the risks.So, let's get started!High Risk Pregnancy: Quick Overview!Pregnancy is a unique and beautiful journey, but it has challenges. As the name suggests, a high-risk pregnancy involves a higher likelihood of complications than a typical pregnancy. These complications can arise due to various factors, such as pre-existing medical conditions, age, or a history of pregnancy-related issues. Let's explore some common aspects that can categorize a pregnancy as high-risk.Factors that Contribute to High-Risk Pregnancy!Age is one of the factors that contribute to high-risk pregnancy. Women older than 35 are at increased risk. Other factors include Pre-existing medical conditions, Multiple pregnancies, substance abuse, and more.According to the insights, high-risk pregnancies accounted for 11.5% of all pregnancies, whereas moderate pregnancies accounted for 21.6%. 33.1% of pregnancies overall had high or medium risk.Pregnancy brings a lot of physical changes in a woman's body, making it more vulnerable to certain medical conditions. Some medical conditions that can cause high-risk pregnancy include hypertension, gestational diabetes, and preeclampsia.1. HypertensionHypertension or high blood pressure is a condition in which the mother's blood pressure is higher than the ideal range. Hypertension can lead to complications such as preterm labor, low birth weight...2. Gestational DiabetesGestational diabetes is a condition that can really affects pregnant women who didn't have diabetes before pregnancy. It indeed leads to high blood sugar levels, which can indeed cause complications such as preterm labor, macrosomia or a giant baby, and respiratory distress syndrome.3. PreeclampsiaPreeclampsia is a condition that affects pregnant women after 20 weeks of gestation. It leads to high blood pressure and damage to organs like the kidneys and liver. Preeclampsia can cause complications such as preterm delivery, low birth weight, and long-term health problems for both the mother and the baby.
Continue Reading: https://www.drshubhragoyal.com/welcome/blogs/introduction-to-high-risk-pregnancy--what-does-it-mean
#High Risk Pregnancy#Pregnancy with heart disease#Rh incompatibility#Oligohydramnios#Uterine fibroids pregnancy#Pregestational diabetes#Cervical insufficiency#Pregnancy after 35#Recurrent miscarriages#Intrauterine growth retardation#Placental abruption#VBAC risks (Vaginal Birth After Cesarean)#Perinatal infections#Pregnancy-induced hypertension#Chronic kidney disease pregnancy#Antiphospholipid syndrome pregnancy#Congenital anomalies risk
1 note
·
View note
Text
TAFAKKUR: Part 79
Medication, Pregnancy and God's Will
Pregnancy is a unique condition for women, and childbirth has always been considered to be one of the most important events in a woman’s life. Maternity has always been highly respected and esteemed. People have always regarded the birth of a child as a gift from God.
A wanted child brings happiness to a family; it is a gift from God. And, of course, every woman who wants to give birth wants to bring up a healthy and beautiful child. Unfortunately, the health index of the modern generation of women at child-bearing age is not very high (there are many chronic diseases, spiritual poverty, with a high vulnerability to different infections due to a variety of reasons). Due to this reason, medical interference in what is a natural process has become more frequent recently. Statistics show that more than 92% of women use different drugs at different stages of pregnancy. The question is to what extent this medication is safe for the future baby. This is a fundamentally important matter to investigate because a pregnant woman taking any chemicals is in essence applying a kind of experiment on her as well as the baby’s health which can have a variety of different consequences.
The problem of medical effects on the development of a fetus has recently become very acute. This is because there are many different medications that are common and easily available nowadays, and they are very often taken without a doctor’s prescription. Unfortunately, the consequences of this fact are not pleasant. Prenatal development is one of the most important and difficult stages in a person’s life. Just in 9 months an ovicell (an egg cell) and a sperm cell form an extremely complex living organism that consists of millions and billions of cells! Moreover, all these cells are combined into tissues, organs and systems that are always interacting. The fetus has a fascinating rate of growth to become a structure with an ever-increasing complexity. In addition, all these processes do not happen chaotically but in a strict order. This order is supplied by two factors: the first is a sound genetic program. It is obtained by the fetus from its parents and the decoding of the genome vividly denotes the existence of Divine Power. The second factor is the state of a maternal organism which supplies everything necessary for the realization of the genetic program and protects the fetus from the negative influence of the environment. In this way the failure of one of the mentioned factors can lead to different deviations and to the disturbance of the development, including the formation of congenital malformations of the fetus and even prenatal death.
The history of medicine shows that medications can be the most harmful etiological factor in relation to the fetus. Today, there are many examples proving this fact. One of the best-known is the thalidomide tragedy which happened in Europe in the 1950-60s. As a result of taking a poorly studied medicine (a light tranquilizer) the children of hundreds (!) of women were born with serious physical defects. Unfortunately, the list of drugs that causes fetal malformation is not short. Nowadays doctors are aware of syndromes caused by hydantoin, warfarin, aminopterin, and many other medications. Each of these has a specific effect on the fetus (mostly leading to serious abnormalities) when taken by a pregnant woman. In the past, people believed that such children were marked by Satan. But nowadays we say that it is the unpredictable effect of the medicine on the realization of the Creator’s program. Medical interference can lead to a disruption in the rate of development and affect the order of differentiation in the tissues and organs of fetus. Moreover, drugs can interrupt the blood circulation in the placenta, change the metabolic process between the fetus and the mother, causing a retardation of intrauterine growth or premature labor, or they can be the reason for a falloff in the health of the child in the first years of life.
The influence of drugs on the fetus depends on different factors, such as the term of gestation at which the drug is administered, the dosage, and the length of time that the medicine is taken, as well as the ways that the drug is excreted, the health of the mother and her inherited sensitivity to medicine, and, of course, the properties of the medicine itself. There are many drugs whose influence on the fetus have not yet been examined, as such research is very difficult, expensive, or in many cases simply impossible. If we understand this, we can see that the outlook for scientific interference in God’s creation of human beings is not good.
You may wonder why the wide-spread usage of medication by pregnant women throughout the whole world has not lead to a continuous increase in congenital malformations if it is really this dangerous. Thanks to a happy concourse of circumstances, this process has not become too wide-spread, as there are many factors that allow the fetus to “escape” medical danger. For example, there may be an inherited insensitivity on the part of the fetus to the influence of different medications, the placenta has its own inherent protective function, the medication may be taken in a small dosage, the developmental stage of the fetus may be at a “non-critical” period, plus many other factors. Doubtless, although this has not been proven, is the fact that the mother has a sincere faith in God and believes in God’s protection of her and her child, which has a positive influence on the development of the fetus.
The initial clustering of embryonic cells and the formation of all the fetus’ organs and systems occur in the first trimester of pregnancy. It is particularly in this period that the fetus is very sensitive to the influence of different factors, including different drugs.
It is quite common that the results of the use of some teratogens1 by pregnant women, which can have fatal effects, can simply go unnoticed in some cases, resulting in the death of the fetus during the first two weeks of development. In this case, the woman does not even know that she is pregnant. Such cases are not rare (according to some researchers, up to 70% of all pregnancies finish in the early death of the fetus).
What should a pregnant woman do if she is ill or feeling unwell? How can she effectively help herself and minimize the risk of any medications on her baby at the same time? It is never a good idea to self-medicate if you are pregnant, particularly in the case of little-known or untested medications. In any case, it is better to consult an experienced doctor or pharmacist. If for some reason this is impossible, please read the prospectus which is to be found with the medicine carefully. Which dangers the medicine can cause are probably mentioned on the prospectus, and it may be written that the drug should not be used if pregnant. If a drug has been used while being unaware of pregnancy (for example, during the first 2 weeks) then immediately consult a specialist about any possible negative effects there might be for the fetus as soon as you found out that your are pregnant. Going to see your doctor early will allow you the necessary time to avoid any dangers and allow you to arrive at a decision about this pregnancy. If the medicine has been prescribed by a doctor then be sure to ask about possible unwanted side effects for the fetus. Don’t hesitate to ask such questions. If it seems to you that your doctor’s attitude to this question is not serious enough (unfortunately, this happens quite often) then consult a competent specialist (a geneticist or a clinical pharmacist).
If you are just planning your pregnancy, then try to predict all the negative factors beforehand. If you have some chronic diseases which may become acute during the pregnancy, or if you have an allergic predisposition or high sensitivity to acute respiratory diseases, then you should consult a doctor. Preventive methods which have been worked out especially for you minimize the risk of the illness and the risk of using drugs that are potentially harmful to the fetus.
During early stages of ontogenesis the fetus has almost no adaptation mechanisms or specific reactions in its response to the influence of pathogenic agents. Only with time will the fetus’ main organs and systems become mature and the functions of the placenta fully form the morphological and functional backgrounds of the response characteristics peculiar to a new-born baby. We usually say that everything happens according to God’s Will but He has created us for a full, vivid, and creative life. And He wants us to understand and be attentive to the miracle that happens during pregnancy.
#allah#god#muhammad#prophet#sunnah#hadith#islam#muslim#muslimah#hijab#help#quran#ayat#revert#convert#religion#reminder#dua#salah#pray#prayer#welcome to islam#how to convert to islam#new muslim#new revert#new convert#revert help#convert help#islam help#muslim help
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo




What Are The Advantages of Electrospinning Nanofiber Anti-haze Window Screen?
#electrospinning #nanofiber #antihaze #window #screen #haze #prevention #sandwich #film #membrane #screens #PM2.5 #nanotechnology
Although we can't change outdoor air pollution, we can make indoor air safer.
The haze prevention window screen made of sandwich nanofiber film can simultaneously have five filtering mechanisms, such as screen, inertial collision, Brownian motion, interception, and electrostatic effect, etc., with low wind resistance and good haze prevention effect.
Ordinary window screens can only protect the house from insects. Nanofiber membrane window screens are dust-proof, smog-proof, breathable, and do not need to close the windows all year round. They can catch smog and PM2.5, pollen, dust, bacteria, and rain. Most importantly, it prevents mold and mold allergens from entering the house, which is often accessed through open windows and can cause dangerous diseases.
Harmfulness of PM2.5
PM2.5 goes directly to the alveoli.
Respiratory system: PM2.5 is easy to settle in the alveolar area and dissolve into the blood. Insoluble deposits in the lungs induce or exacerbate inflammation, causing cough, rhinitis, pharyngitis, asthma, and chronic bronchitis.
Cancer: Bacteria, viruses, and carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons enter the body with PM2.5, thus increasing the incidence of lung cancer and bladder cancer.
Blood and the cardiovascular system: PM2.5 enters the capillaries from the alveolar wall and then enters the whole blood circulation system, inducing the formation of thrombosis, causing coagulation abnormalities, and can directly reach the heart, causing arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, non-fatal heart disease, and premature death of cardiopulmonary patients.
Reproductive system: Many heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and other pollutants attached to PM2.5 cause placental blood toxicity in pregnant women, easily leading to fetal intrauterine growth retardation and congenital functional defects. Poisons can also pass through the placenta and directly poison the fetus.
Advantages:
Natural ventilation, good light transmittance, rainproof and moistureproof, antibacterial and odor removal, durable, easy to install.
Applications:
Can be widely used in home protection, office buildings and commercial air environment improvement, can effectively block the air including bacteria, PM2.5, dust, pollen, automobile exhaust particles, and other toxic and harmful substances, while ensuring the ventilation and lighting of the building interior, truly build a healthy, ventilated and breathable "nano barrier"!
Product features
1) Advanced nanotechnology;
2) Small fiber diameter, high porosity, low compression resistance, and high filtration efficiency;
3) Physical interception, long service life and high safety (no electrostatic attenuation);
4) Can effectively filter PM2.5 suspended particles, allergens, formaldehyde, peculiar smell, allergens, and other harmful substances;
5) Not only applicable to a variety of filtering application scenarios, but also effectively improve the dust capacity and service life in each application scenario.
Winnie Chan
International Trade Manager
Mob./Whatsapp: +86 18520902852
QQ: 1130008454
WeChat: QingziNano
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel.:+86 757-89956076
Web. : https://www.qingzitech.net/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/LeptonChina/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/?lang=zh-cn
#electrospinning#nanofiber#antihaze#window#screen#haze#prevention#sandwich#film#membrane#screens#pm2.5#nanotechnology
1 note
·
View note
Text
Growth and development of children
Growth: Growth is a measure of physical maturation, signifies an increase in size of the body and its various organs.
Definition: An increase in number and size of cells as they divide and synthesize new proteins; results in increased size and weight of the whole or any of its parts – Wong DL
It can be measured in terms of centimeters, and Kilograms.
Unlike in the adult, it is an essential feature of the child’s life.
Development: is a measure of functional or physiological maturation and myelination of the nervous system.
A gradual change and expansion; advancement from lower to more advanced stages of complexity; the emerging and expanding of the indl’s capacities through growth, maturation and learning.
It signifies the accomplishment of mental, emotional and social abilities.
Unlike growth, it is rather difficult to assess development.
Factors affecting growth and development
A number of factors influence growth and development.
1. Genetic heredity: The heredity of a man and a woman determines that of their children.
Eg: Tall parents are likely to have tall off springs
Members of the families bear physical resemblances to each other and a high degree of correlation of stature with weight among siblings exists. The rate of growth is more alike among siblings than among unrelated persons.
2. Sex: Sex is determined at conception. After birth, the male infant is both longer and heavier than the female infant. Boys maintain this superiority until about 13 years of age. Girls mature earlier, reach the period of accelerated growth earlier than boys are then taller on the average.
Bone development is more advanced in girls than in boys.
3. Racial and National c/cs
Race: Growth potential of children differ between different racial groups. Distinguishing c/c called racial/subracial developed in prehistoric humans
Nationality:
4. Nutritional
Nutritional deficiency of proteins, calories, minerals, vitamins and essential amino acids, both quantitative and qualitative, considerably retards physical growth and development.
Over nutrition, beyond a limit, may cause obesity.
5. Socio economic
Poverty is associated with diminished growth. Children from well-to-do families usually are better nourished
Prenatal factors
Environment
Postnatal
Prenatal period
Maternal (H) practices affect the growth and development of fetus. Maternal decreased nutrition and anemia may lead to IUR and small size offetus.
Diseases during pregnancy can retard the fetal growth. Administration of some drugs can adversely affect the embryo
Eg: Thalidomide
Hormonal Influence
Thyroxine ………………. Significantly retard. Skeletal maturation of fetus
Insulin – Stimulate fetal growth
Growth hormone - fetal / mat……… GH is not essential for fetal growth
Postnatal
1. Nutrition
2. Socio economic factors
3. Infection and diseases: Persistent and recurrent infections of the child will adversely affect the growth of the child.
Diseases of the heart, chest, kidneys, liver, neoplasms digve and absorptive disorders, may impair the growth
4. Emotional factors: Children from broken homes and orphanages do not grow and develop at an optimal rate
5. Cultural factors: Methods of child rearing and infant feeding in the community are determined by cultural habits and conventions. There may be religious factors against consumption of particular foods.
PRINCIPLES OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
Growth and development are continuous and orderly process that have predictable sequences.
Although the rates of progress vary all human beings, go through same stages on their way of growth and development to their physical increase in size and maturation of neuromuscular function.
Certain principles regulate the growth and development they are:
1. Directional trends
2. Sequential trends
3. Developmental pace
4. Sensitive periods
5. Individual differences
1. Directional trends:
Growth and development proceed in regular, related directions or gradients and reflect the physical development and maturation of neuromuscular functions.
a) Cephalocaudal (Head to tail) direction
The head end of the organism (Embryo) develop first before tail and end and is very large and complex, where as lower end is simple and takes shape at later period.
The physical evidence of the trend is most apparent during the period before birth, but it also applies to postnatal behavior development
Infants achieve structural control of the head before they have control of trunk and extremities, hold their back erect before they stand, use their eyes before their hands and gain control of their hands before they have control of their feet.
b) Proximodistal (Near - to -far) – applies to the midline to peripheral concept
In the early embryonic development of limb buds, which is followed by rudimentary fingers and toes.
In the infant shoulder control precedes mastery of the hands, the whole hand is used as a unit before the fingers can be manipulated, and the central nervous system develops more rapidly than the peripheral nervous system.
c) Differentiation: Describes development from simple operations to more complex activities and functions.
All areas of development proceed in this direction. Through the process of development and differentiation, early embryonal cells with vague, un differential functions progress to an immensely complex organism composed of highly specialized and diversified cells, tissues and organs
Gross, random muscle movements take place before fine muscle control.
2. Sequential trends
In all dimension of growth and development, there is predictable and definite sequence. Each child normally passing their every stage.
Children crawl before they creep, creep before stand, stand before they walk.
The child Babbles first than forms words and finally sentences, writing emerges from scribbling
3. Developmental pace
Although there is a fixed precise order to development, it does not progress at the same rate/ pace.
There are periods of accelerated growth and periods of decelerated growth in total body growth and growth of subsystem.
Rapid growth after birth gradually levels off throughout early childhood. Growth relatively slow during middle childhood and markedly increase at the beginning of adolescence and levels off in early adulthood.
4. Sensitive period
During the process of growth, at certain time organism will interact with particular environment in a specific manner. The quality of interaction determines whether the effects on organism will be beneficial / harmful.
Eg: Physiologic maturation of CNS is influenced by adequate nutrition and stimulation.
First 3 months of prenatal life are sensitive ……….. for physical growth of the fetus.
5. Individual differences
Each child grows in his/her own unique and personal way. Great individual differences exist in the age at ………….. developmental milestones are reached. The sequence is predictable but exact timing is not predictable.
Some children are fast growers and others are moderated and some are slower o reach maturity.
Periods of Growth (Stages of Growth and Development)
Intrauterine life / prenatal period
Extrauterine life or postnatal period
Prenatal period
Ovum - 0 to 14 days after conception
Embryo - 14 days to 8 weeks ( till 2 months)
Postnatal period
Newborn / Neonate - From birth to four weeks of life
Infancy - First year of life
Toddler - 1 to 3 years
Preschool child - 3 to 6 years (early childhood)
School going child (middle childhood)
6 – 10 years (for girls)
6 – 12 years (boys)
Adolescent – from puberty to adult hood
Pre pubescent (early adolescent) late child hood)
10 to 12 years (girls)
12 to 14 years (boys)
Pubescent (Middle adolescent)
12 to 14 years (girls)
14 to 16 years (boys)
Post pubescent (late adolescent)
14 to 18 years (girls)
16 to 20 years (boys)
Cognitive Development (Piaget) (1969)
Based on his observations and work with children, piaget formulated a theory of cognitive (intellectual) development. He believed that the children’s view the world is influences largely by age and maturational ability.
Given nurturing experiences, the child’s ability to think matures naturally. The child incorporates new experiences via assimilation and changes to deal with these experiences by the process of accommodation.
Eg: An example of assimilation occurs when the infant uses reflexes to suck on objects that touch the lips. With more experiences, the infant accommodates by realizing that not all objects are pleasant to suck, cognitive structures change to integrate and learn from the experiences of sucking.
Piaget proposed three stages of reasoning.
1. Initiative
2. Concrete operational
3. Formal operational
Each stage is derived from and buildson the accomplishments of the previous stage in a continuous orderly process.
Stages:
1. Sensorimotor (Birth – 2 years)
Infants learn about the world by input obtain through the senses and by their motor activity.
6 sub stages
a) Use of reflexes ( birth to 1 month)
The infant begins life with a set of reflexes such as sucking, rooting and grasping. By using these reflexes, the infant receives stimulation via touch, sound, smell and vision. The reflexes thus put the foundation for the subsequent stages
b) Primary circular reactions (1 to 4 months)
Beginning of the replacement of reflexive behavior with voluntary acts.
The beginning of accommodation is evident. Infants incorporate and adapt their reactions to the environment and recognize the stimulus that produced a response.
Previously they would cry until the nipple was brought to the mouth. Now they associate the nipple with the sound of the parent’s voice. They accommodate this new piece of information and adapt by ceasing to cry when they hear the voice-before receiving the nipple.
c) Secondary circular reactions (4-8 m)
In this stage the 1o circular reactions are repeated and prolonged for the response that results.
Grasping and holding now become shaking, banging and pulling. Shaking is performed to hear a noise, not solely for the pleasure of shaking “More” or “less” shaking produces different responses.
Causality, time, deliberate intention, and separateness from the environment begin to develop.
Three new process of human behavior occur.
Imitation: Requires the differentiation of selected acts from several events. By the second half of the first year, infants can imitate sounds and simple gestures.
Play: Becomes evident as they take pleasure in performing an act after they have mastered it. Much of infants’s working hours is absorbed in sensor motor play.
Affect (outward manifestations of emotion and feeling) is seen as infants begin to develop a sense of permanency
During the first 6 months, infants believe that an object exists only as long as they can visually perceive it / out of right = out of mind
d) Coordination of secondary schemas and their application to new situations (8-12 months)
This stage is largely transitional. Increasing motor skills allow for greater exploration of the environment. They begin to discover that hiding an objective does not mean that it is gone but that removing an obstacle will reveal the object.
They can experience an event by observing it, and they begin to associate symbols with events (bye-bye -> Mom / Dad goes to work), but the classified is purely their own.
e) Tertiary circular reactions (12 to 18 months)
Curiosity, experimentation, and exploration, predominate as the toddler tries out actions to learn results. Objects are turned in every direction, placed in the month, used for banging, and inserted in containers as their qualities and uses are explored.
f) Mental combinations (18 to 24 months)
Language provides a new tool for the toddler to use in understanding the world. Language enables the child to think about events and objects before or after they occur. Obj. permanence is now fully developed as the child actively searches for objects in various locations and out of view.
The child who has had successful separations from the parents followed by return, such as hours spent in another home, begins to understand that the missing parent will return
2. Preoperational (2 to 7 years)
a. Pre conceptual sub stage 2-4 years
Child thinks by using words as symbols. Vocabulary and comprehension increase greatly. Child shows egocentrism. Inability to see things from the perspective of another.
b. Intuitive sub stage 4-7 years
Child shows transductive reasoning (drawing conclusions from one general fact to another)
Cause and effect relationships are often unrealistic (all women with big bellies have babies
Intuitive ……………. Stars have to go to bed just as they do)
Magical thinking – The belief that events occur because of thoughts or wishes
Centration – The ability to consider only one aspect of a situation at a time
Animism – ascribing life to in animate objects because they move, make noise or have certain other qualities.
3. Concentrate operational (7 to 11 years)
Transductive reasoning has given way to a more accurate understanding of cause and effect. Child can reason quite well if concrete objects are used in teaching or experimentation.
Children are able to classify, sort, order and otherwise organize the facts about the world to use in problem solving. They develop the concept of permanence, conservation, that is they realize that physical factors such as volume, weight and no. remain the same even though outward appearances are changed.
Reasoning is inductive.
4. Formal operations (11 to 15 years)
Formal operational thought is characterized by adaptability and flexibility
Adolescents can think in abstract terms, use abstract symbols and draw logical conclusions from a set of observations.
1 note
·
View note
Text

We are aware of the strong connection between obesity & fertility, but what about those who are underweight. Will it impact my fertility?
In this blog, we will address the same concern of being thin & underweight and planning for pregnancy, and how it will affect the chances of fertility.
As we all know, the human body is made up of 5 essential elements. Fat, Protein, Carbohydrate, vitamins & minerals. All these elements along with tissue fluid form the weight of the body.
Protein is the basic component of tissues and is very important for bodily functions. There is a good amount of metabolism happening in the body like the generation of new cells & recycling of the old tissues. This process requires protein for cell development. Excess protein if ingested is stored as fat. The same is the case with carbohydrates. Fats are divided into healthy and unhealthy fats. Unhealthy fats constitute obesity.
Body weight simply means the weight of tissues, muscles, body fluids & blood elements.
The fertility journey is complex and any burden of health conditions can be reduced. One such burden is body weight. Being underweight also impacts the fertility journey.
Weight-driven infertility is just not confined to obesity. What about women with low BMI? Are they not healthy to have conception as a normal healthy person?
Being underweight affects your fertility. Generally speaking, better chances of conception occur with BMI ranging between 20 and 25. Body fat plays an important role in regulating hormones. Being underweight (BMI of 18.5 or less), often causes irregular menstrual cycles and may cause ovulation to stop altogether. Many underweight women cease to have periods due to the low estrogen level.
A BMI of 17.5 or less could point to an eating disorder.
Then, what is the ideal fertility BMI in the case of women?
If you are trying for pregnancy, the ideal BMI range for fertility is 18.5 to 24.9.
Ideal BMI to get pregnant: 18.5 – 24.9
Overweight: BMI>24.9
Underweight: BMI<18.5
When we achieve the ideal weight to get pregnant, there are numerous health benefits and the most important is reproductive outcomes.
Having periods even though underweight, will I have any issues regarding conceiving?
Having periods when you are underweight does not mean you will have an easy-going pregnancy process.
As the endocrine system is underperforming, it results in irregular ovulation. These underweight women may become pregnant but carry a higher risk of miscarriage, premature birth, stillbirth & having low-birth babies.
Loss of adipose tissues subsequently causes hormonal disturbances
Restoration of weight in underweight women often results in the resumption of menses and the resolution of infertility concerns.
Concerns of Underweight Women
Underweight women trying to conceive face a plethora of obstetric complications, which are primarily related to undernutrition for the mother and foetus.
This includes the risk of impaired weight gain by the foetus, intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), preterm delivery, low birth weight, postnatal complications and even an increased risk of chronic diseases in the offspring.
Being underweight directly links to ovulatory dysfunction. There are situations where women who exercise excessively or have a low caloric intake may have irregular menstrual cycles or no periods at all. This is typically due to a disruption in hormones that causes a deficiency of estrogen.
Women with low BMI are at increased risk of amenorrhoea &chronic anovulation may cause infertility.
How it affects my baby when I am underweight during pregnancy?
Babies born to underweight mothers (women with BMIs of 18.5) are at higher risk for health problems, including:
– Premature birth (also referred to as preterm birth)
– or childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy
– Low birth weight (smaller than 2.5 kg). These infants are at risk for health and development problems as they get older.
How to gain healthy weight status from being underweight?
•Try eating smaller & frequent meals by adding snacks into your routine as well.
•increase the use of foods that are rich in nutrients, like whole grains, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, nuts and seeds, and lean proteins.
•Pay more attention to how & when you’re drinking. Smoothies are better options than diet soda, coffee, and other beverages.
•If drinks decrease your appetite, consider going for it after you eat a meal & 30 min after a meal.
•Get more calories in your meals by adding nuts and seeds as toppings to main dishes.
•Start exercising. You can add muscle by exercising. Working out may also boost appetite and act as a mood enhancer.
Your weight is often an indicator of overall health. Being underweight can be just as detrimental as being overweight. Underweight women are more likely to have miscarriages than healthy-weight women. if you are underweight & planning to undergo IVF, it’s time to know more about how to optimize your likelihood of pregnancy. Weighing every parameter that improves the pregnancy outcome is very important. We at Pearl women’s hospital & Yash IVF are offering tailor-made solutions for underweight patients planning for pregnancies.
0 notes
Text
Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon

Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Growth denotes increase in physical size of the body and development denotes improvement in skills and function of an individual. Together they denote physical, intellectual, emotional and social well being of a person. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Normal growth and development is observed only if there is proper nutrition, without any recurrent episodes of infections and if there is freedom from adverse and environmental influences. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Determinants of growth and development Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Genetic inheritance - especially height, weight, mental, social development and personality. Nutrition before and after birth - Retardation in an infant indicates malnutrition. Age - Growth rate is maximum during fetal life, first two years of life and during puberty. Sex - Men usually are larger in size than women. During puberty girls grow fast and earlier than boys, but boys grow more. Infections and infestations - Infection with TORCH during intrauterine life retards growth of fetus. Recurrent infections like diarrhea and measles especially in a malnourished child will adversely affect the growth. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Physical surroundings - Sun shine, good housing, lighting ventilation have their effect on growth and development. Psychological factors - Love, tender care and proper child parent relationship are all found to influence growth in a child. Economic factors - Higher the family income better is the nutritional status of an infant. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Other factors - Birth order, Birth spacing, Education of parents (higher the educational level better the growth). Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Assessment of nutritional status 2.1 Normal growth In children, parameters used to measure growth are weight in kilograms, height in meters and head and chest circumferences. Assessment can be longitudinal where serial measurement of the same child is recorded over different periods of time or cross-sectional where recorded measurement is compared to that of his peers. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon In India, we are using the new WHO child Growth Standards (2006) for children. However values differ substantially among adults of different ethnic groups. We have ICMR values as Indian standard. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon 2.2 Physical growth 2.2.1 Weight Most widely used and simplest, reproducible anthropometric measurements for the evaluation of nutritional status. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon It indicates body mass It is sensitive to even small changes in nutritional status due to childhood morbidity like diarrhea. Rapid loss of weight indicates a potential malnutrition Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Serial weight recording is more valuable for progressive growth of a child when age of a child is not known. Technique for measurement To measure weight beam or lever accentuated scales with an accuracy of 50-100 g are preferred. Portable Salter scale (CMS Weighing Equipment, Ltd. England): the child is suspended from the scale which is hung from a branch or a tripod. Special "pants" are used to weigh babies. Robust, cheap, and easy to carry, these scales should be replaced after one year because of stretching of the spring and inaccurate readings. The model with readings up to 25 kg (x 100 g) is recommended. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Bathroom scales are not recommended as errors up to 1.5 kgs can occur with this. Precautions to be taken while weighing Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Zero error has to be adjusted. Minimal clothing should be worn and be without shoes. While recording the value do not lean against or hold anything. Preferably record under basal conditions in early morning. Most types of scales (especially beam scales) are sensitive to dust and mud. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Standards Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon On an average, a baby weighs double the birth weight by five months, trebles its birth weight by one year and quadruples its birth weight by two years. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon A baby should gain at least 500g per month in the first three months of life. If the growth is less than this it points to malnutrition. In different parts of India, the average birth weight is between 2.7 to 2.9 kgs. Weight for age is used to classify malnutrition. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon 2.2.2. Height Height of an individual is influenced by genetic as well as environmental factors. Maximum growth potential is decided by genetic factors. Nutrition and incidences of infection determine the extent of exploitation of that genetic potential. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Inadequate dietary intake and/ or infections reduce nutrients available at the cellular level.This results in growth retardation. A prolonged period of severe deprivation leads to stunting. Technique for measurement Children below two years are measured by using an infantometer. Baby is made to lie on the scale and crown heel length is measured. For children above two years and adults a vertical measuring rod anthropometer- is used and maximum height is measured. Measuring scale should be capable of measuring to an accuracy of 0.1 cm. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Standards Length of the baby at birth is 50 cm. By first year it increases by 50% to 75cm. By third year end it increases by 12cm. During puberty, growth spurt, boys add 20cm to their height and girls gain about 16 cm. Indian girls reach 98% of their final height by 16.5 yrs. and boys reach the same stage by 17.75 yrs. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Low height for age indicates nutritional stunting or dwarfing. It reflects past or chronic stunting. Cut off point for diagnosis of stunting is 90% NCHS values. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon 2.2.3. Mid upper arm circumference Mid upper arm circumference and calf circumference indicate the status of muscle development. Mid calf and mid upper arm are heavily muscled and is approximately circular. Mid upper arm circumference is simple, easily accessible in any age and sex and practical to measure. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Well-nourished children have a nearly constant arm circumference (about 16 cm) between 1 and 5 years. Undernourished children have a thinner upper arm and a smaller AC. Children can be classified as malnourished if their AC falls below an arbitrarily specified level. If ages are not known, AC can be related to height (arm circumference or height). Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon As poor musculature and wasting are cardinal features of PEM in early childhood, MUAC helps in identifying malnutrition and in determining mortality risk in children. It correlates well with weight, weight for height and clinical signs.( QUAC stick). Technique Usually left arm is measured. Arm is flexed at the elbow. The circumference is measured on the left upper arm half way between the end of the shoulder (acromion and the tip of the elbow (olecranon). To locate this point, the arm is flexed at a right angle. Then the arm is allowed to hang freely and a tape-measure (preferably of fibreglass) put firmly round it. Do not pull too tight. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Tapes or strips can be made locally from thin cardboard or X-ray films which are marked in centimeters. Special plastic tapes (insertion tapes) have been manufactured. Fibre glass tape is preferred to tailors cloth tape as it is seen to lose accuracy. 2.2.4 Body Fat Subcutaneous fat constitutes body's main store of energy reserves. Muscle and fat constitute the soft tissues that vary most with a deficiency of protein and calories. Many accurate and near accurate methods like densitometry and DEXA but physical anthropometry using skin-fold calipers are practicable in field circumstances to determine the nutritional status of a person. For this a standard skin fold caliper has to be used. The skin fold measured consists of a double layer of skin and subcutaneous fat. For adults multiple sites are selected like triceps, the abdomen and the sub scapular and subcostal sites. By using different formulae we can derive at the amount of total body fat. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaonIn young children, the triceps skin-fold is used. The site is exactly at the mid upper arm as determined by the method used for mid arm circumference. The technique needs prolonged supervised practice and repetition to obtain reliable and reproducible results. Values differ in different communities thus necessitating local standards for comparisons.Hence it is used mostly by researchers and academics in the field. Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon Growth monitoring in child in manesar gurgaon https://g.page/r/CS-wJ9nI0cIsEAE
0 notes