#Grand Saint Antoine
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo








Nouveau retour à mon projet de présenter la plupart de mes 55500 photos (et des brouettes). Plus trop loin du présent....
Le Musée d’Histoire
- Pomone en proue - XVIIIe
- Pierre de Libertat 1600
- “Le Cours de Marseille pendant la Peste", Rigaud d'après Serre
- ancre du Grand Saint-Antoine, le navire qui amena la Peste à Marseille en 1720
- chambre de studio en poirier de l'atelier Nadar - début XXe s.
- maquette du Pont Transbordeur
- Fortuné Lavastre - maquette en bois de Marseille pendant les insurrections de 1848
- Fortuné Lavastre - maquette en bois de Marseille pendant les insurrections de 1848
- François Ferry-Duclaux - maquette de Marseille en 1824, en liège
#souvenirs#marseille#musée d'histoire#renaissance#pierre de libertat#cours belsunce#peste de marseille#peste de 1720#peste#ancre#grand saint-antoine#fortuné lavastre#plan-maquette#insurrection de 1848#maquette#françois ferry-duclaux#pont transbordeur#pont à transpondeur#nadar#appareil photographique#chambre photographique
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
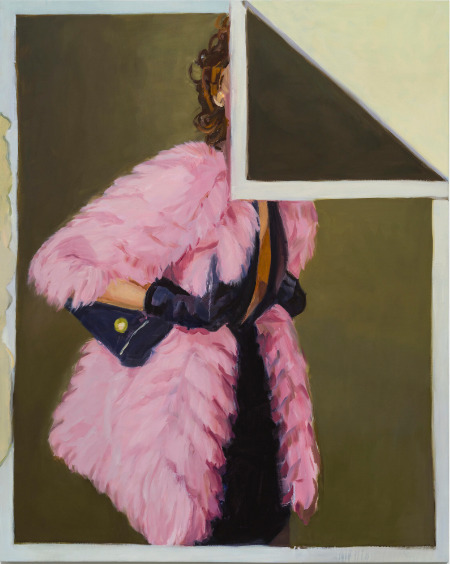
Janet Werner - Spiders and Snakes / Galerie Bradley Ertaskiran (ca)
Janet Werner / Feathers and fold Spiders and Snakes Jusqu’au 4 mai 2024 Bradley Ertaskiran a le plaisir de présenter Spiders and Snakes, une exposition solo de nouvelles peintures de Janet Werner. Ce corpus d’œuvres poursuit les explorations uniques et hybrides de l’artiste dans le genre du portrait, dans lesquelles elle crée ses propres règles en réunissant des représentations concurrentes de…

View On WordPress
#3550 rue Saint-Antoine Ouest#Association des galeries d&039;art contemporain (AGAC)#Galerie Bradley Ertaskiran#Janet Werner#Janet Werner - Spiders and Snakes / Galerie Bradley Ertaskiran (ca)#Montréal (Québec)#Paumé arts et littératures#Plural Foire d&039;art contemporain - Plural Contemporary Art Fair / Grand Quai du Port de Montréal (CA)#Spiders and Snakes
0 notes
Text
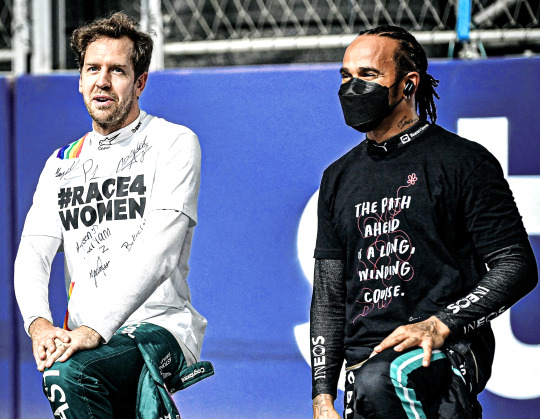
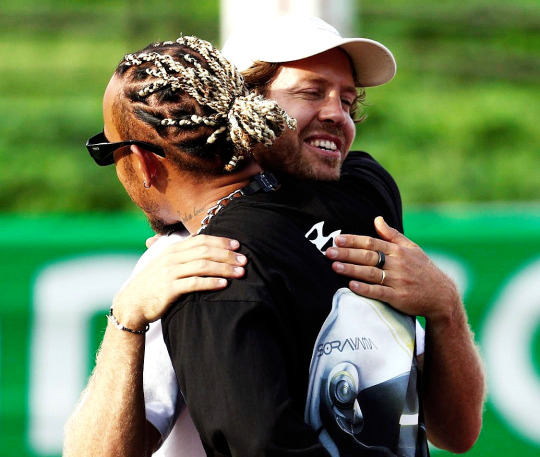















lewis, seb, and something bigger than themselves —
antoine de saint exupery, wind, sand and stars / mercedes amg formula 1, 'lewis hamilton reacts to iconic moments from 10 years with mercedes' (2023) / sports illustrated, lewis hamilton celebrates sebastian vettel 'not yet seen a driver as brave as him' (2023) / attitude magazine, sebastian vettel: formula 1 is ready for an out gay driver (2022) / planet f1, lewis hamilton claims 'no one in f1 history have done what vettel and i have done' (2022) / spanish grand prix (2020) / sebastian vettel, sebastian vettel: formula 1 is ready for an out gay driver (2022) / saudi arabian grand prix (2021) / lewis hamilton (2023) / pre japanese grand prix (2023) / jean paul sartre
#i love how men love (and save the earth)#lewis hamilton#sebastian vettel#sewis#web weaving#f1#*edit#*web weaving
500 notes
·
View notes
Text
All grown-ups were once children, but only few of them remember it.
Toutes les grandes personnes ont d'abord été des enfants, mais peu d'entre elles s'en souviennent.
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, The Little Prince / Le Petit Prince
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Deputy of Humanity
In August 1790, Robespierre, then deputy in the National Assembly, received a letter from a young man in Aisne. The subject of the letter was of little consequence in the grand scheme of things: the author was expressing his concern that the free monthly markets for grain and sheep in his village of Blérancourt might be moved to the rival village of Coucy.
The subject of the letter may have been trivial, but its author was not. Louis Antoine Saint-Just, not yet twenty-three, was quickly outgrowing local politics and had his eyes on debuting on the national stage. In around two years’ time, he would become one of Robespierre’s closest allies. But back in 1790, the young man only knew him “like God, through miracles” ("comme Dieu, par des merveilles"). This would be the first contact between the two men.
The letter has been widely translated, quoted, and speculated on. It is very well-written, with the effusive admiration and almost hero worship of the young man practically jumping off the page. Whether Saint-Just was entirely genuine or not is hardly consequential. Robespierre clearly found his admiration touching because he kept the letter until the end of his life.
The fact that Robespierre kept the letter is a sweet gesture that can be interpreted in a myriad of different ways. Perhaps he enjoyed the flattery, or maybe he wanted to keep a memento of the beginning of their friendship with Saint-Just. Maybe he simply forgot to throw it away. In my opinion, it's not very important.
What I find more interesting and revealing about Robespierre's character is that a young lieutenant colonel of the National Guard of the department of Aisne felt empowered to raise his provincial concerns to a deputy who wasn't even representing his constituency. Why would he do that? Setting aside Saint-Just's audacity and desire for recognition, the simple reason is that he knew he would be heard.
Since the days of the Estates General, Robespierre had not only been gaining popularity but was also notorious for standing up for the interests of the common man beyond his own province (later on department). For all the flattery, Saint-Just was right: Robespierre wasn’t only the deputy from Arras; he was “[the deputy] of humanity and the Republic (1)”. He frequently weighed in, as a dissenting voice, on matters of national importance, maintaining a consistent stance that always favoured the underdog. This was nothing new. His entire career in Arras had been built on helping the common man. On a national stage, he vocally continued that work.
He opposed the king's veto power over constitutional laws and emphasized the sovereignty of the nation over monarchical traditions. He also opposed the exclusion of "passive" citizens (2) from the National Guard and advocated for extending voting rights. All this, along with his defense of civic equality for various groups, including actors, Protestants, and Jews, solidified his position as a defender of the people.
Despite facing mockery from royalist publications and some of his peers, he remained steadfast in his dedication to the universal principles of the Revolution, with the most crucial principle being the sovereignty of the people. If the people are sovereign, then their grievances are significant. It's understandable that Saint-Just would reach out to him regarding the issue with the village market. He wasn't the only one.
For what it's worth, Robespierre probably didn’t intervene in the matter, but Blérancourt ultimately did retain its markets.
Translation (3)
Blérancourt, near Noyon, August 19, 1790
You who support the faltering homeland against the torrent of despotism and intrigue, you whom I know only, like God, through miracles; I address you, sir, to ask you to join me in saving my sad country.
The town of Coucy has transferred (so the rumour goes here) the free markets from the village of Blérancourt. Why should the cities swallow up the privileges of the countryside? Then, nothing will remain for the latter but the taille (direct tax) and taxes! Please, support with all your talent a petition that I am sending by the same mail, in which I ask for my inheritance to be joined to the national domains of the district so that my country may retain a privilege without which it must starve.
I do not know you, but you are a great man. You are not just the representative of a province; you are that of humanity and the Republic. Please ensure that my request is not scorned.
I have the honour of being, sir, your humble and obedient servant,
Saint-Just,
elector (4) in the department of Aisne.
Notes
(1) Here Saint-Just doesn't refer to Republic as a form of government, but uses the word as a substitute for nation/country. In 1790 France was a constitutional monarchy.
(2)Passive citizens were those who, for a variety of reasons (mostly tax related), were not allowed to vote. (3) The parts that are in bold, are underlined in the original . As usual, this is my own translation and you can surely find much better ones out there!
(4) Touchy subject...
(BONUS) The letter is Recto-Verso. The small red arrows in the image indicate where the back page starts. I edited the two sides in one image for ease of reading.
Source
I really like Saint-Just but his handwriting is just as bad as mine (yes. I can barely read mine either). The french text of the letter comes from:
Saint-Just, Louis Antoine Léon. Œuvres. Paris: Gallimard, 2014
#frev#french revolution#robespierre#maximilien robespierre#saint just#committee of public safety#history#amateurvoltaire's essay ramblings#the letter that launched 1000 speculations
145 notes
·
View notes
Note
How many relationships did Robespierre have and who were they? if you can tell a little about it
I’m currently working on compiling as much information as possible about Robespierre’s different relationships. Those I’ve done so far are:
The relationship between Robespierre and Saint-Just
The relationship between Robespierre and Desmoulins (btw, comparing the notes on this post and the SJ one, I think it’s pretty clear who has already won the shipping contest currently on…)
The relationship between Robespierre and Brissot
The relationship between Robespierre and Marat
The relationship between Robespierre (and his siblings) and the Duplay family
The relationship between Robespierre (and his sister) and Fouché
The relationship between Robespierre and Pétion (planning to remake this one)
I’m not an expert on any relationship beyond these yet, but when it comes to people of which it is established Robespierre was the personal friend (bc were we to talk about people he is confirmed to have had any form of contact/relationship at all with we would of course be here all night) this is basically what I’ve got so far (feel free to send an individual ask about those you consider more interesting, then it will be easier to give a more satisfying answer):
Pre-revolution
Robespierre and his five years younger brother Augustin grew up together at their grandparents’ house, but from 1769-1781 and 1781-1787 respectively the two spent the majority of the year studying in Paris and consequently saw very little of one another. Once the revolution rolled around Augustin came to visit his brother two times before being elected a deputy and permanently moving to Paris in 1792. We have several letters from Augustin in Arras to Maximilien in Versailles/Paris (but none the other way around). The two were evidently close, and when Maximilien was ordered arrested on July 27 1794, Augustin asked to share his fate.
After the death of their mother and disappearance of their father in 1764, Robespierre and his two years younger sister Charlotte grew up seeing each other only once a week until the former headed to Paris in 1769. After he graduated in 1781, he and Charlotte lived with each other up until the opening of the Estates General, after which Charlotte didn’t see him again for three years (save a short trip he made to Arras in 1791). According to Paul Villiers, who served as Maximilien’s secretary for a time, he sent a quarter of his fees to ”a sister in Arras whom he held a lot of affection for” during this period. In 1792 Charlotte moved to Paris with her younger brother where the two moved in with Maximilien’s host family. The three siblings got into a conflict and were seperated as enemies, different sources giving us different answers regarding exactly what for.
During his time as a lawyer in Arras, Robespierre and his siblings were close to his fellow lawyer Antoine Buissart and his family. They kept this contact up during the revolution, and we have several letters exchanged between Maximilien, Augustin and Antoine conserved. They did however eventually fall out with one another due to ”the terror” carried out in Arras in the spring of 1794, and after Robespierre’s execution Buissart was quick to abandon and denounce him.
During his time as a student at the college of Louis-le-Grand it would appear Robespierre gained a friend/school rival in the future dramatist and man of letters Beffroy de Reigny. In 1786 Robespierre sent him two of his most recent works to insert in his journal, Beffroy responding by celebrating his success and saying he ”perfectly remembers the role played at the College by his amiable study companion; a talent like his is not meant to be forgotten.” He did however quickly grow to dislike the revolution, and in works written in the years following Robespierre’s death he claimed to have never been his friend.
The Revolution
Robespierre and Danton were good friends, or at least good brothers in arms. In 1792 Danton offered his ”dear friend” a job at the Revolutionary Tribunal, and the next year Robespierre adressed what is probably the most sentimental of his conserved letters to Danton, consoling him over the loss of his wife and telling him ”I love you (tu) more than ever, until death.���
Robespierre had a good relation with the Roland couple, Mme Roland writing in her memoirs that she thought him ”an honest man” and that they sometimes dined together. They eventually fell out with each other over the war question, but not before Manon had written Robespierre a letter asking for a meeting so that they could sort out their differences.
Robespierre was also at first good friends with the ”girondin” and fellow National Assembly member François Buzot, who in his memoirs wrote that Robespierre had told him ”I esteem you, because I know you well” even in 1793. In his defense (1793), the girondin Gensonné wrote that ”In 1791 and 1792, Robespierre had the most intimate liasons with Pétion, Buzot and Roland, how can he accuse them today without accusing himself?”
Robespierre and Georges Couthon quickly got to know each other after the latter’s arrival in Paris in September 1791, although it’s possible they started out on less than friendly terms. We have a letter from Robespierre to Couthon dated August 9 1792 where he tells him he ”anxiously await news of your (votre) health.[…] May you soon return to your homeland and we await with equal impatience your return and your recovery.”
Robespierre was also good friends with Philippe Le Bas. The best source for their relationship is the memoirs of the latter’s wife Élisabeth, where she numerous times has the two say flattering things about one another. On 9 thermidor, Le Bas, like Augustin, volonteered to share Robespierre’s fate.
Robespierre was good friends with Collot d’Herbois, who also knew his host family (this can be observed via letters from Collot to Robespierre dated November 23 and December 1, and a letter from him to Maurice Duplay dated December 5). They eventually fell out with each other in 1794, but it’s unclear exactly when and why.
Robespierre had a friend in his doctor Joseph Souberbielle. In his Histoire de la Révolution française (1869) the historian Louis Blanc reported Souberbielle to have spoken warmly about him even decades after his death.
During his time on the Committee of Public Safety, Robespierre wrote a list containing the names of around 115 men he described as ”patriots with more or less talent,” many of which held (thanks to his list?) important functions. On first place on the list we find Martial Hermann, president of the revolutionary tribunal and later chairholder of the Commission of Civil Administration, Tribunals and Claude-François Payan, head of the Paris commune, who are both proven to sometimes have turned directly to Robespierre regarding things that concerned the entire Committee of Public Safety (1, 2, 3, 4), as well as François Dumas, president of the Revolutionary Tribunal April-July 1794 and Jean-Baptiste Coffinhall, judge at said tribunal, who both public procecutor Fouquier-Tinville and Barère, Billaud-Varennes and Collot-d’Herbois after thermidor would claim to everyday have gone home to Robespierre to discuss the tribunal’s upcoming affairs. If Robespierre was the personal friend of the four is harder to say, but all of them would nevertheless be executed as his ”accomplices.”
Another person on the list is the young Marc-Antoine Jullien who served as representative on mission 1793-1794 and often turned to Robespierre directly when reporting about things going on (according to From Jacobin to Liberal: Marc Antoine Jullien 1775-1848 (1993) by R.R Palmer: ”of Jullien’s known letters written during this period twenty-one were addressed to Robespierre, but eighteen were addressed to the CPS as a whole, and twenty-nine to four other members of the Committee.”) He was arrested right after thermidor and would deny having had any association with Robespierre, but it would still be more than a year before he was released. His mother Rosalie Jullien was her too a big admirer of Robespierre and dined with him a couple of times.
Another one of the people on the list is Jean Charles Guislain Mathon, an arragois childhood friend of Robespierre who, after the siblings fell out with each other, offered Charlotte asylum at his house ”in spite of [the brothers’] protests.” She moved in with him after their execution and stayed there for the rest of her life.
#robespierre#maximilien robespierre#ask#frev#being Robespierre’s friend basically means you can either choose between:#dying for him#dying with him#dying because of him#denounce him and pretend you never knew him so you can save yourself from dying
81 notes
·
View notes
Text
Idea for a Saintspierre Au:
Angel Saint-just and misunderstood demon Robespierre

My idea for the Au is that there are angels and demons (the other frev people are also included in this Au, so you decide which would be a demon, human or angel) and angels and demon have a rivalry, but humans don't see them because they are able to shape shift into humans.
Which is how this story starts, Robespierre is a devil who, unlike the others, doesn't want to cause any harm or do any mischief. He doesn't want to have a bad reputation just because he's a demon, so he often uses his human form to talk to humans.
One day, he meets Angel Saint-just, who was shifted into his human form, and I still haven't decided if he would know that Saint-just is an angel or not, hut they interact as humans, and eventually start dating, but when Saint-just finds out that Robespierre is a demon, he feels betrayed, and he breaks it off with him.
Robespierre tries really hard to impress Antoine and redeem himself, but Antoine still doesn't believe him, and the other other demons try to tell Maximilean to stop trying, while the other angels want him far away from Saint-just, but eventually, Robespierre redeems himself in some way by doing some grand act, and Saint-just wants to be with him, but he's not allowed to, so he becomes a fallen angel!
Got any recommendations for the Au?
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
La liberté ou la mort, extrait
Robespierre jouait à lancer des branches à Brount avec Elisabeth, à quelques distances devant eux. Il courrait pour entraîner le molosse derrière lui, et jetait le bâton de toutes ses forces, ne se souciant pas de voir s'il risquait de tacher ses bas blancs de boue. Brount partait comme un fou avec ses grandes pattes désordonnées, la langue pendant sur le côté et la queue frétillante. Quand il revenait avec le morceau de bois, Elisabeth et Maximilien devaient s'escrimer à le lui récupérer et tiraient de toutes leurs forces pour le lui arracher de la gueule. Le jeu recommençait ensuite, pour la plus grande joie des trois participants.
Saint-Just marchait les bras croisés dans le dos, au rythme d'Eléonore.
-Eléonore, maintenant que nous sommes bons amis, puis-je me permettre une question?
La jeune fille lui sourit d'un air indulgent.
- Voyons la question.
Saint-Just se racla la gorge et fixa son regard sur la pointe de ses bottes.
- Eh bien... je ne comprends pas que tu ne sois pas amoureuse de lui.
Eléonore laissa échapper un petit rire. Elle ne paraissait pas particulièrement vexée ou embarrassée par cette question indiscrète.
-Et pourquoi cela ? demanda-t-elle.
Saint-Just redressa la tête et fit un geste de la main vague vers Brount qui s'était mis à aboyer joyeusement, et Elisabeth qui faisait semblant de jeter le bâton pour la troisième fois.
- Je ne sais pas, regarde le... Tout à l'heure il faisait un travail de géant pour la patrie, et maintenant il se contente d'une récompense si simple ! Jouer avec son chien, nourrir ses oiseaux, manger le potage de ta mère ce soir, lire quelques pages de Rousseau au coin du feu...
-... quelques oranges, une visite de son cher Saint-Just...
- Si nous parvenons à installer et à protéger notre république, il ne cherchera aucune récompense pour lui même. Il ne faudra pas davantage que ces quelques plaisirs que nous avons évoqués pour faire son bonheur. Quand on en vient à le connaitre, il est si doux, si sincère. Parfois, cela me noue le coeur quand j'y pense.
- Certainement, approuva Eléonore en venant prendre le bras d'Antoine, et c'est pour cela que mes parents le considèrent comme leur fils et moi comme mon frère. Le sang ne me le rendrait pas plus cher.
- Un frère, oui...Mais imagine le comme époux, ne serait-ce pas mieux encore ? La voix de Saint-Just s'était réduite à un murmure rêveur. Il est si loyal, si dévoué. Non vraiment, tu ne trouveras pas mieux que lui.
-Pour ce qui est du physique... commença Eléonore
- Du physique ! répéta-t-il, le cri qu'il ne réussit par à réprimer attirant un instant l'attention de Brount vers lui. Comment peux tu parler du physique face à une telle âme ! Et puis de toute façon la physionomie de Maximilien n'a rien de désagréable, regarde, il est petit certes, mais il a les mollets bien fait, une mine intelligente, des yeux verts, un joli nez...
- Tu ne trouves pas qu'il a un style un peu démodé?
- Maximilien s'en fiche des fariboles de la mode! Il prends soin de ses vêtement et il est toujours bien mis. On ne peut pas en dire autant des trois quarts des députés qui siègent à la Convention avec les cheveux gras et les bottes crottées. Son style est très respectable.
Eléonore se mit à rire de bon coeur devant l'air révolté de Saint-Just.
-Antoine... Si moi je ne suis pas amoureuse de lui, rien ne t'empêche de l'être, toi.
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Belle Lettre d'amour... à lire......
Lettre de Consuelo de Saint-Exupéry à son mari Antoine St Exupery
Fin décembre 1944
Que j’aille très loin, en train, en avion, sous la mer, par la terre, j’ai l’impression que jamais je ne pourrai arriver jusqu’à toi.
Tonio, Tonito, mon homme, mon fils, mon clocher, fais sonner les grandes cloches parce que je ne peux pas respirer. J’ai grossi en attendant la houle qui va te ramener.
Je tombe avec les feuilles, avec la pluie, avec ma jupe de fête.
Je ne peux pas marcher à force d’attendre le moment où
je reverrai tes yeux, ronds comme des fleurs.
Tu ne vois pas que je ne peux pas arroser l’arbre de Noël pour le faire grandir. Mon mari des étoiles, j’ai de tout petits pieds et de toutes petites mains, il faut que tu reviennes m’aider.
Je ne sais pas comment j’ai marché depuis mon enfance jusqu’à aujourd’hui. Ma vie fut un immense vertige.
A présent, j’ai des cheveux gris, j’ai tellement de larmes dans ma bouche que cela me suffirait pour boire toute ma vie.
Pourquoi Tonio, mon Tonio, mon mari,
mon mal et mon bien, mon ciel et mon enfer,
es-tu parti pour ne jamais revenir ?
Je ne peux pas le croire, je ne veux pas le savoir, tu es parti dans ton avion, le 31 juillet, en mission de guerre et tu n’es pas revenu. Pas de nouvelles de toi et l’année va finir. Il faut que je l’accepte, et si je l’accepte, c’est pour t’aimer davantage.
Comme je t’aurais aimé si tu étais revenu ! Comme toi aussi tu aurais fait la même chose pour moi !
Seigneur à la couronne d’épines, arrache-moi le cœur pour qu’il ne me fasse plus mal.
Tu sais, toi, que Tonio est tout pour moi. Sans lui, je ne suis rien. Sur la table de ma chambre d’hôtel, j’ai un livre de lui, son portrait avec son manteau de soldat en cuir et ses fines mains d’homme comme des ailes et sa barbe pousse avec mes larmes.
Seigneur grand et miséricordieux, je te donne ma peine et ma douleur.
Mon Père, aide-moi. Je n’ai personne pour aimer, pour attendre, pour embrasser.
Ma maison est devenue petite, seule ma fenêtre reste ouverte pour faire entrer le ciel où il est parti en s’envolant pour ne pas revenir.
Rendez-le-moi mon Père, je vous en prie, faites un miracle.
Si vous me le rendez dans sa tendresse, je le coifferai, je le laverai, je l’embrasserai et ensemble nous irons jusqu’à vous

28 notes
·
View notes
Text
Friends, enemies, comrades, Jacobins, Monarchist, Bonapartists, gather round. We have an important announcement:
The continent is beset with war. A tenacious general from Corsica has ignited conflict from Madrid to Moscow and made ancient dynasties tremble. Depending on your particular political leanings, this is either the triumph of a great man out of the chaos of The Terror, a betrayal of the values of the French Revolution, or the rule of the greatest upstart tyrant since Caesar.
But, our grand tournament is here to ask the most important question: Now that the flower of European nobility is arrayed on the battlefield in the sexiest uniforms that European history has yet produced (or indeed, may ever produce), who is the most fuckable?
The bracket is here: full bracket and just quadrant I
Want to nominate someone from the Western Hemisphere who was involved in the ever so sexy dismantling of the Spanish empire? (or the Portuguese or French American colonies as well) You can do it here
The People have created this list of nominees:
France:
Jean Lannes
Josephine de Beauharnais
Thérésa Tallien
Jean-Andoche Junot
Joseph Fouché
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand
Joachim Murat
Michel Ney
Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte (Charles XIV of Sweden)
Louis-Francois Lejeune
Pierre Jacques Étienne Cambrinne
Napoleon I
Marshal Louis-Gabriel Suchet
Jacques de Trobriand
Jean de dieu soult.
François-Étienne-Christophe Kellermann
17.Louis Davout
Pauline Bonaparte, Duchess of Guastalla
Eugène de Beauharnais
Jean-Baptiste Bessières
Antoine-Jean Gros
Jérôme Bonaparte
Andrea Masséna
Antoine Charles Louis de Lasalle
Germaine de Staël
Thomas-Alexandre Dumas
René de Traviere (The Purple Mask)
Claude Victor Perrin
Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr
François Joseph Lefebvre
Major Andre Cotard (Hornblower Series)
Edouard Mortier
Hippolyte Charles
Nicolas Charles Oudinot
Emmanuel de Grouchy
Pierre-Charles Villeneuve
Géraud Duroc
Georges Pontmercy (Les Mis)
Auguste Frédéric Louis Viesse de Marmont
Juliette Récamier
Bon-Adrien Jeannot de Moncey
Louis-Alexandre Berthier
Étienne Jacques-Joseph-Alexandre Macdonald
Jean-Mathieu-Philibert Sérurier
Catherine Dominique de Pérignon
Guillaume Marie-Anne Brune
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan
Charles-Pierre Augereau
Auguste François-Marie de Colbert-Chabanais
England:
Richard Sharpe (The Sharpe Series)
Tom Pullings (Master and Commander)
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington
Jonathan Strange (Jonathan Strange & Mr. Norrell)
Captain Jack Aubrey (Aubrey/Maturin books)
Horatio Hornblower (the Hornblower Books)
William Laurence (The Temeraire Series)
Henry Paget, 1st Marquess of Anglesey
Beau Brummell
Emma, Lady Hamilton
Benjamin Bathurst
Horatio Nelson
Admiral Edward Pellew
Sir Philip Bowes Vere Broke
Sidney Smith
Percy Smythe, 6th Viscount Strangford
George IV
Capt. Anthony Trumbull (The Pride and the Passion)
Barbara Childe (An Infamous Army)
Doctor Maturin (Aubrey/Maturin books)
William Pitt the Younger
Robert Stewart, 2nd Marquess of Londonderry (Lord Castlereagh)
George Canning
Scotland:
Thomas Cochrane
Colquhoun Grant
Ireland:
Arthur O'Connor
Thomas Russell
Robert Emmet
Austria:
Klemens von Metternich
Friedrich Bianchi, Duke of Casalanza
Franz I/II
Archduke Karl
Marie Louise
Franz Grillparzer
Wilhelmine von Biron
Poland:
Wincenty Krasiński
Józef Antoni Poniatowski
Józef Zajączek
Maria Walewska
Władysław Franciszek Jabłonowski
Adam Jerzy Czartoryski
Antoni Amilkar Kosiński
Zofia Czartoryska-Zamoyska
Stanislaw Kurcyusz
Russia:
Alexander I Pavlovich
Alexander Andreevich Durov
Prince Andrei (War and Peace)
Pyotr Bagration
Mikhail Miloradovich
Levin August von Bennigsen
Pavel Stroganov
Empress Elizabeth Alexeievna
Karl Wilhelm von Toll
Dmitri Kuruta
Alexander Alexeevich Tuchkov
Barclay de Tolly
Fyodor Grigorevich Gogel
Ekaterina Pavlovna Bagration
Ippolit Kuragin (War and Peace)
Prussia:
Louise von Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Gebard von Blücher
Carl von Clausewitz
Frederick William III
Gerhard von Scharnhorst
Louis Ferdinand of Prussia
Friederike of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Alexander von Humboldt
Dorothea von Biron
The Netherlands:
Ida St Elme
Wiliam, Prince of Orange
The Papal States:
Pius VII
Portugal:
João Severiano Maciel da Costa
Spain:
Juan Martín Díez
José de Palafox
Inês Bilbatua (Goya's Ghosts)
Haiti:
Alexandre Pétion
Sardinia:
Vittorio Emanuele I
Lombardy:
Alessandro Manzoni
Denmark:
Frederik VI
Sweden:
Gustav IV Adolph
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Il n'y a pas de plus grande richesse que de savoir vivre dans la simplicité.
Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
9 notes
·
View notes
Text


Automne 1930 - Champs-les-Sims
4/4
J'ai montré ta lettre à Tante Rose, au sujet de ton père. Elle a secoué la tête d'un air navré avant d'ajouter qu'à ce stade, il n'y avait plus grand chose d'autre à faire. Elle ne veut pas que tu te fasse des illusions, mais malgré tout, elle a déjà vu des malades tenir ainsi plusieurs années. J'espère que ce sera le cas pour ton père. Je sais que ça doit être dur, mais j'espère que vous ne vous fâcherez pas avec lui, et que lui s'adoucira un peu, car ce sera dur pour tout le monde. Tante Rose t'envoie ses amitiés.
Sur un ton un peu plus joyeux, sache que Sélène n'est pas encore mariée. Dans ses lettres, ma soeur me dit qu'elle souhaite attendre encore un peu, mais elle ne sait pas combien de temps. Je me demande si ce n'est pas en partie pour calmer les ardeurs de sa belle-famille, il parait qu'ils ne font que parler de mariage.
Je suis assez surprise de ce que tu me dis sur Ada, mais passe lui tout de même le bonjour. C'est une femme qui gagne à être connue selon moi. Elle était bien intarissable d'anecdotes, et je ne doute pas qu'elle les tienne de ta mère. Nous avons eu avec elle un aperçu de la vie au Canada qui a rassasié notre curiosité pour un moment, surtout celle d'Antoine, qui a du passer pour un sacré bavard. J'espère que ma prochaine lettre te parlera de son mariage.
Bien à toi,
Noé
_____________________________________________________________
Cher Lucien,
Noé m'a bien montré la photographie de votre truite. Je pêche peu, mais certains de mes amis m'ont confirmé qu'il s'agit d'une très belle prise. Un de ces amis m'a même appris qu'il s'agissait d'une variété de truite brune originaire d'Eurasie et qui avait été sans doute introduite dans le Saint-Laurent pour la pêche sur glace. Il s'agit en tous cas de son humble avis.
Je n'avais quand à moi pas grand chose à répondre dans le cadre de ce rituel typiquement masculin de comparer ses prises respectives. Il aurait été inconvenant de ma part que vous envoie une photographie de mes propres prises, par respect pour mon épouse qui respecte autant mes inclinations que ma vie privée autant que pour les "prises" en question qui y auraient vu quelque chose de dégradant. Je ne pratique pas la chasse à courre ou le safari, et je n'ai aucun hobby qui puisse non plus rentrer dans le cadre d'un rituel social. Mes seules réelles fiertés en tant qu'homme sont mes filles, Anna et Elisabeth, alors je me suis dit que j'allais vous les montrer. J'ai assez d'images pour que vous puissiez tapisser votre salon, mais je doute que cela vous intéresse, alors en voici une seule. Elisabeth est à droite et Anna à gauche.
Avec l'assurance de ma plus fervente amitié,
Ange de Chastel

Transcription :
Aurore « Tu vois, quand tu veux. »
Marc-Antoine « Je risque d’en entendre parler longtemps n’est-ce pas ? »
Aurore « C’est possible. Monsieur de Chastel a eu beaucoup de mal à rester sérieux quand il m’a expliqué la situation. Je ne sais pas vraiment si j’ai été vexée ou si j’étais morte de honte. »
Marc-Antoine « Il nous a observé ? »
Aurore « Un certain temps, jusqu’à ce qu’il trouve trop cruel de ricaner dans son coin en t’observant me faire des demandes en mariage à mots couverts pendant que je ne comprenais rien. »
Marc-Antoine « Bon sang... »
Aurore « Pour se faire pardonner, il a promis de me laisser des gages supplémentaires en guise de cadeau de mariage. »
Marc-Antoine « Avec le père que j’ai, j’ai toujours imaginé que je serais à l’abri de ce genre de quiproquo. Je devrais avoir l’habitude. »
Aurore « Tu me compares à ton père ? »
Marc-Antoine « Non, chez lui c’est particulier. Vous n’avez pas grand-chose en commun, juste cette difficulté à démêler premier et second degré. »
Aurore « J’imagine que ta mère a été plus efficace que toi sur ce point, sinon tu te serais jamais né. »
Marc-Antoine « En fait, c’est mon père qui a pris les devants et l’a demandée en mariage, comme le veux l’usage. »
Aurore « J’aurais du aller contre l’usage. Nous nous serions mariés il y a déjà des mois. »
Marc-Antoine « N’exagère pas. Je n’ai commencé à pelleter de l’air il n’y a de que deux semaines. »
Aurore « Pelleter de… quoi ? »
Marc-Antoine « C’est une expression québecoise que m’a appris Ada Rumédier, ça veut dire perdre son temps. »
Aurore « Oui, enfin c’est bien ce que je dis. Entre toute cette parade et les mois qu’il t’a fallut pour trouver le courage, j’aurai du te le demander moi-même. J’aurai obtenu ce que je veux bien avant. »
Marc-Antoine « Tu veux dire que tu me trouves lent ? »
Aurore « Je veux dire que pour un politicien, tu as bien du mal à prendre les devants. »
#lebris#lebrisgens5#legacy challenge#history challenge#decades challenge#nohomechallenge#sims 3#simblr#ts3#sims stories#Arsinoé Le Bris#Lucien Le Bris#Marc-Antoine Le Bris#Aurore Laroche#Ange de Chastel#Anna Le Bris de Chastel#Elisabeth Le Bris de Chastel#Constantin Le Bris#Albertine Maigret#Ada Rumédier#Rose Le Bris#Jules Le Bris#Sélène Le Bris#Gilberto Bragança#Eugénie Bernard
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
M. Myriel Becomes M. Welcome
Les Mis Letters reading club explores one chapter of Les Misérables every day. Join us on Discord, Substack - or share your thoughts right here on tumblr - today's tag is #lm 1.1.2
The episcopal palace of D—— adjoins the hospital.
The episcopal palace was a huge and beautiful house, built of stone at the beginning of the last century by M. Henri Puget, Doctor of Theology of the Faculty of Paris, Abbé of Simore, who had been Bishop of D—— in 1712. This palace was a genuine seignorial residence. Everything about it had a grand air,—the apartments of the Bishop, the drawing-rooms, the chambers, the principal courtyard, which was very large, with walks encircling it under arcades in the old Florentine fashion, and gardens planted with magnificent trees. In the dining-room, a long and superb gallery which was situated on the ground floor and opened on the gardens, M. Henri Puget had entertained in state, on July 29, 1714, My Lords Charles Brûlart de Genlis, archbishop; Prince d’Embrun; Antoine de Mesgrigny, the capuchin, Bishop of Grasse; Philippe de Vendôme, Grand Prior of France, Abbé of Saint Honoré de Lérins; François de Berton de Crillon, bishop, Baron de Vence; César de Sabran de Forcalquier, bishop, Seignor of Glandève; and Jean Soanen, Priest of the Oratory, preacher in ordinary to the king, bishop, Seignor of Senez. The portraits of these seven reverend personages decorated this apartment; and this memorable date, the 29th of July, 1714, was there engraved in letters of gold on a table of white marble.
The hospital was a low and narrow building of a single story, with a small garden.
Three days after his arrival, the Bishop visited the hospital. The visit ended, he had the director requested to be so good as to come to his house.
“Monsieur the director of the hospital,” said he to him, “how many sick people have you at the present moment?”
“Twenty-six, Monseigneur.”
“That was the number which I counted,” said the Bishop.
“The beds,” pursued the director, “are very much crowded against each other.”
“That is what I observed.”
“The halls are nothing but rooms, and it is with difficulty that the air can be changed in them.”
“So it seems to me.”
“And then, when there is a ray of sun, the garden is very small for the convalescents.”
“That was what I said to myself.”
“In case of epidemics,—we have had the typhus fever this year; we had the sweating sickness two years ago, and a hundred patients at times,—we know not what to do.”
“That is the thought which occurred to me.”
“What would you have, Monseigneur?” said the director. “One must resign one’s self.”
This conversation took place in the gallery dining-room on the ground floor.
The Bishop remained silent for a moment; then he turned abruptly to the director of the hospital.
“Monsieur,” said he, “how many beds do you think this hall alone would hold?”
“Monseigneur’s dining-room?” exclaimed the stupefied director.
The Bishop cast a glance round the apartment, and seemed to be taking measures and calculations with his eyes.
“It would hold full twenty beds,” said he, as though speaking to himself. Then, raising his voice:—
“Hold, Monsieur the director of the hospital, I will tell you something. There is evidently a mistake here. There are thirty-six of you, in five or six small rooms. There are three of us here, and we have room for sixty. There is some mistake, I tell you; you have my house, and I have yours. Give me back my house; you are at home here.”
On the following day the thirty-six patients were installed in the Bishop’s palace, and the Bishop was settled in the hospital.
M. Myriel had no property, his family having been ruined by the Revolution. His sister was in receipt of a yearly income of five hundred francs, which sufficed for her personal wants at the vicarage. M. Myriel received from the State, in his quality of bishop, a salary of fifteen thousand francs. On the very day when he took up his abode in the hospital, M. Myriel settled on the disposition of this sum once for all, in the following manner. We transcribe here a note made by his own hand:—
NOTE ON THE REGULATION OF MY HOUSEHOLD EXPENSES.
For the little seminary - 1,500 livres
Society of the mission - 100”
For the Lazarists of Montdidier - 100”
Seminary for foreign missions in Paris - 200”
Congregation of the Holy Spirit - 150”
Religious establishments of the Holy Land - 100”
Charitable maternity societies - 300”
Extra, for that of Arles - 50”
Work for the amelioration of prisons - 400”
Work for the relief and delivery of prisoners - 500”
To liberate fathers of families incarcerated for debt - 1,000”
Addition to the salary of the poor teachers of the diocese - 2,000”
Public granary of the Hautes-Alpes - 100”
Congregation of the ladies of D——, of Manosque, and of Sisteron,<br> for the gratuitous instruction of poor girls - 1,500”
For the poor - 6,000”
My personal expenses - 1,000”
- ———
Total - 15,000”
M. Myriel made no change in this arrangement during the entire period that he occupied the see of D—— As has been seen, he called it <i>regulating his household expenses</i>.
This arrangement was accepted with absolute submission by Mademoiselle Baptistine. This holy woman regarded Monseigneur of D—— as at one and the same time her brother and her bishop, her friend according to the flesh and her superior according to the Church. She simply loved and venerated him. When he spoke, she bowed; when he acted, she yielded her adherence. Their only servant, Madame Magloire, grumbled a little. It will be observed that Monsieur the Bishop had reserved for himself only one thousand livres, which, added to the pension of Mademoiselle Baptistine, made fifteen hundred francs a year. On these fifteen hundred francs these two old women and the old man subsisted.
And when a village curate came to D——, the Bishop still found means to entertain him, thanks to the severe economy of Madame Magloire, and to the intelligent administration of Mademoiselle Baptistine.
One day, after he had been in D—— about three months, the Bishop said:—
“And still I am quite cramped with it all!”
“I should think so!” exclaimed Madame Magloire. “Monseigneur has not even claimed the allowance which the department owes him for the expense of his carriage in town, and for his journeys about the diocese. It was customary for bishops in former days.”
“Hold!” cried the Bishop, “you are quite right, Madame Magloire.”
And he made his demand.
Some time afterwards the General Council took this demand under consideration, and voted him an annual sum of three thousand francs, under this heading: <i>Allowance to M. the Bishop for expenses of carriage, expenses of posting, and expenses of pastoral visits.</i>
This provoked a great outcry among the local burgesses; and a senator of the Empire, a former member of the Council of the Five Hundred which favored the 18 Brumaire, and who was provided with a magnificent senatorial office in the vicinity of the town of D——, wrote to M. Bigot de Préameneu, the minister of public worship, a very angry and confidential note on the subject, from which we extract these authentic lines:—
“Expenses of carriage? What can be done with it in a town of less than four thousand inhabitants? Expenses of journeys? What is the use of these trips, in the first place? Next, how can the posting be accomplished in these mountainous parts? There are no roads. No one travels otherwise than on horseback. Even the bridge between Durance and Château-Arnoux can barely support ox-teams. These priests are all thus, greedy and avaricious. This man played the good priest when he first came. Now he does like the rest; he must have a carriage and a posting-chaise, he must have luxuries, like the bishops of the olden days. Oh, all this priesthood! Things will not go well, M. le Comte, until the Emperor has freed us from these black-capped rascals. Down with the Pope! [Matters were getting embroiled with Rome.] For my part, I am for Cæsar alone.” Etc., etc.
On the other hand, this affair afforded great delight to Madame Magloire. “Good,” said she to Mademoiselle Baptistine; “Monseigneur began with other people, but he has had to wind up with himself, after all. He has regulated all his charities. Now here are three thousand francs for us! At last!”
That same evening the Bishop wrote out and handed to his sister a memorandum conceived in the following terms:— EXPENSES OF CARRIAGE AND CIRCUIT.
For furnishing meat soup to the patients in the hospital - 1,500 livres
For the maternity charitable society of Aix - 250”
For the maternity charitable society of Draguignan - 250”
For foundlings - 500”
For orphans - 500”
- ——
Total - 3,000”
Such was M. Myriel’s budget.
As for the chance episcopal perquisites, the fees for marriage bans, dispensations, private baptisms, sermons, benedictions, of churches or chapels, marriages, etc., the Bishop levied them on the wealthy with all the more asperity, since he bestowed them on the needy.
After a time, offerings of money flowed in. Those who had and those who lacked knocked at M. Myriel’s door,—the latter in search of the alms which the former came to deposit. In less than a year the Bishop had become the treasurer of all benevolence and the cashier of all those in distress. Considerable sums of money passed through his hands, but nothing could induce him to make any change whatever in his mode of life, or add anything superfluous to his bare necessities.
Far from it. As there is always more wretchedness below than there is brotherhood above, all was given away, so to speak, before it was received. It was like water on dry soil; no matter how much money he received, he never had any. Then he stripped himself.
The usage being that bishops shall announce their baptismal names at the head of their charges and their pastoral letters, the poor people of the country-side had selected, with a sort of affectionate instinct, among the names and prenomens of their bishop, that which had a meaning for them; and they never called him anything except Monseigneur Bienvenu [Welcome]. We will follow their example, and will also call him thus when we have occasion to name him. Moreover, this appellation pleased him.
“I like that name,” said he. “Bienvenu makes up for the Monseigneur.”
We do not claim that the portrait herewith presented is probable; we confine ourselves to stating that it resembles the original.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text


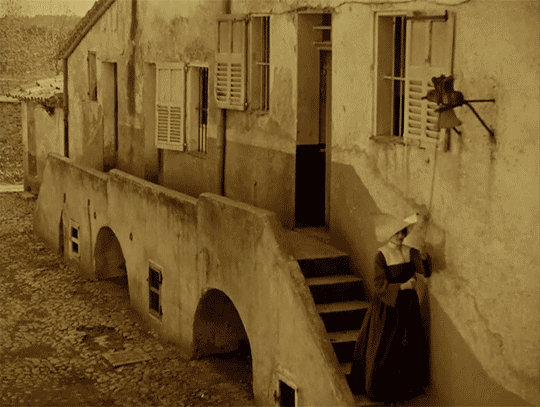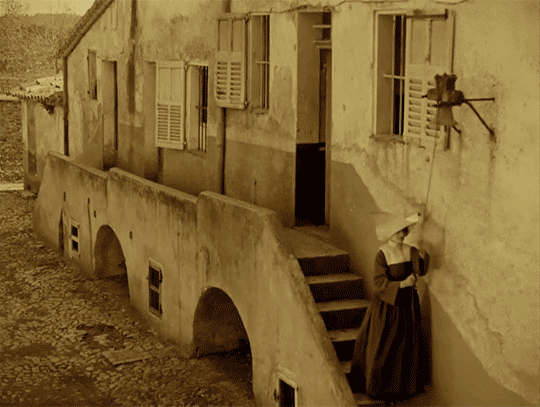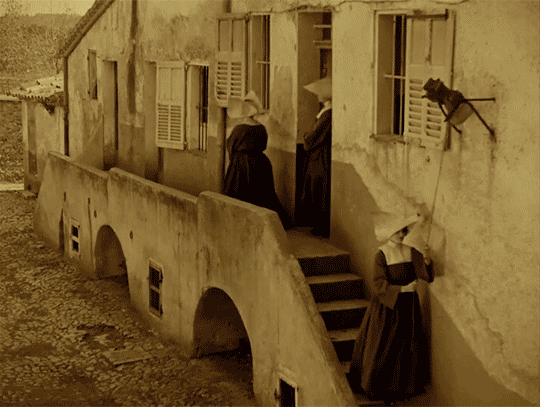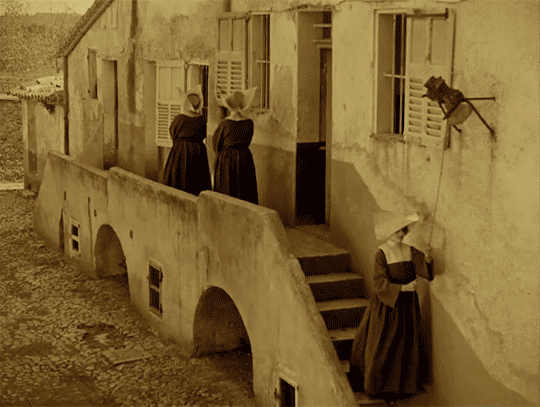



LES MIS LETTERS IN ADAPTATION - M. Myriel Becomes M. Bienvenu, LM 1.1.2 (Les Miserables 1925)
The episcopal palace of Digne adjoins the hospital. The episcopal palace was a huge and beautiful house, built of stone at the beginning of the last century by M. Henri Puget, Doctor of Theology of the Faculty of Paris, Abbé of Simore, who had been Bishop of Digne in 1712. This palace was a genuine seignorial residence. Everything about it had a grand air,—the apartments of the Bishop, the drawing-rooms, the chambers, the principal courtyard, which was very large, with walks encircling it under arcades in the old Florentine fashion, and gardens planted with magnificent trees. In the dining-room, a long and superb gallery which was situated on the ground floor and opened on the gardens, M. Henri Puget had entertained in state, on July 29, 1714, My Lords Charles Brûlart de Genlis, archbishop; Prince d’Embrun; Antoine de Mesgrigny, the capuchin, Bishop of Grasse; Philippe de Vendôme, Grand Prior of France, Abbé of Saint Honoré de Lérins; François de Berton de Crillon, bishop, Baron de Vence; César de Sabran de Forcalquier, bishop, Seignor of Glandève; and Jean Soanen, Priest of the Oratory, preacher in ordinary to the king, bishop, Seignor of Senez. The portraits of these seven reverend personages decorated this apartment; and this memorable date, the 29th of July, 1714, was there engraved in letters of gold on a table of white marble. The hospital was a low and narrow building of a single story, with a small garden.
#Les Mis#Les Miserables#Les Mis Letters#les Mis Letters in Adaptation#LM 1.1.2#Les Mis 1925#Les Miserables 1925#lesmisedit#lesmiserablesedit#lesmis1925edit#lesmiserables1925edit#pureanonedits#the SETS of 1925!!#I wish this kept the order and impact of the brick though.#Oh well.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me: Hugo isn't obsessed with details, you are just lazy fucks
Hugo: In the dining-room, a long and superb gallery which was situated on the ground-floor and opened on the gardens, M. Henri Puget had entertained in state, on July 29, 1714, My Lords Charles Brulart de Genlis, archbishop; Prince d'Embrun; Antoine de Mesgrigny, the capuchin, Bishop of Grasse; Philippe de Vendome, Grand Prior of France, Abbe of Saint Honore de Lerins; Francois de Berton de Crillon, bishop, Baron de Vence; Cesar de Sabran de Forcalquier, bishop, Seignor of Glandeve; and Jean Soanen, Priest of the Oratory, preacher in ordinary to the king, bishop, Seignor of Senez.
#bare minimum of world building#les mis letters#trying to join but with a huge delay#take notes fanfic writers#do you also have a century long backstory of one dining room that a minor oc visited once in the beginning of the story or are you normal#bishop myriel#les miserables#i guess i should tag this as#lm 1.1.2#?#victor hugo#aspa reads les mis
23 notes
·
View notes
Note
Were Danton and Camille really as close as almost every biography/novel/movie, etc. makes them out to be? For a long time I believed they were best friends, but I realize that I don't know much about what really happened (only that Camille mentioned him as a friend several times in his letters).
Sorry if a similar question has already been asked, and thank you for all your wonderful posts. I read each one with great interest.

Thank you! I’m throwing in their wives too for good measure.
As popular as the idea of Danton and Desmoulins being friends already before the revolution is among novelists (A Place of Greater Safety (1992) by Hilary Mantel, The Gods Are Thirsty (1996) by Tanith Lee) and even biographers (Danton (2012) by David Lawday, Georges-Jacques Danton (1987) by Frank Dwyer) I have not been able to discover any evidence indicating this to actually have been the case. The very first connection I’ve found between the two dates to December 12 1789, when Desmoulins for the very first time mentions Danton’s name in his recently founded journal Révolutions de France et de Brabant:
As I do not have the advantage of being from the illustrious Cordeliers District, I am addressing this motion [to make it forbidden to use the term Queen of the French in public acts] to it through this journal. I beg its worthy President M. d'Anton to propose it to the honorable members, to discuss it in their wisdom and address it to the fifty-nine others; I leave my motion on their desks, and I sign it... A Frenchman.
The second time Camille mentions Danton’s name in Révolutions de France et de Brabant is eleven numbers later (March 1 1790). In the number, Camille describes how he on February 24 for the very first time enters the Cordeliers district and enrolls himself as a member. The very same session, he, alongside Danton, Fabre d’Eglantine, Paré and Dufourny de Villiers are named commissioners for the editing of a report by the club requesting the construction of a building ”worthy the National Assembly” on the place of the destroyed Bastille. This is the earliest confirmed meeting between Danton and Desmoulins that I’ve been able to find.
By the end of the same month, in number 17 (March 20) and number 18 (March 29) of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Camille loudly protests against the fact Danton (”this lustrous president of the Cordeliers district”) has been decreed under arrest by le Châtelet de Paris, accused of having threatened to ring the tocsin in order to mobilize the Faubourg Saint−Antoine for the defense of his district when the National Guard came by:
If you put on trial a citizen who has put forward an extravagant opinion in his district, you will therefore also have to put on trial, with much more reason, the judge who, in his company, has opined in an extravagant manner; it will therefore be necessary to hang the judge who will have sentenced to death an accused whom the majority will have absolved, since this judge will have approved the death of an innocent person, which is much worse than making an extravagant motion in a district.
Desmoulins brings up Danton in Révolutions de France et de Brabant a few more times throughout the rest of 1790, calling him both ”the lustrous Danton” (number 31, June 28, number 35, July 26) as well as the more bombastic ”the most robust athlete of the patriots, the only tribune of the people who could have been heard in the Champ-de-Mars, and with his voice rally the patriots around the tribune, the only man whose veto the aristocracy had to fear, and in whom it could have found both the Gracchi brothers and a Marius.” (number 44, September 27). When Danton in the fall is appointed judge at Saint-Germain, Camille celebrates (number 47, October 18):
The Philoctetes of Hercules, d’Anton, is also appointed judge at Saint-Germain. He is well worthy of sitting next to M. Le Grand de Laleu. Honor to the city of Saint-Germain! Based on these two choices we can only augur well for the others. I would be tempted to believe that our patriarch Robe did so many readings of his poem on the revolution there, that he inflamed all the voters with a patriotism which dictated to them these excellent choices. The Parisians, ungrateful, forgot in the elections Danton, and Abbé Fauchet, and Brissot, and Carra, and Manuel; but it seems that the surrounding districts were responsible for the recognition.
On December 27 1790 Danton, alongside twelve other well known ”patriots,” signed the Desmoulins couple’s wedding contract. He was however not present for the actual wedding ceremony two days later, something which I suppose could be read as implying he and Desmoulins were not that close yet. On the other hand, the way Desmoulins does describe his wedding witnesses in a letter to his father written five days later (”Péthion [sic] and Robespierre, the elite of the National Assembly, M. de Sillery who wanted to be there, and my two colleagues Brissot de Warville and Mercier, the elite among the journalists”), it almost sounds like he’s chosen them less out of friendship and more out of prestige, so maybe this doesn’t have to mean that much either… After the wedding, Camille and Lucile moved to Rue du Théâtre 1 (today Rue de l’Odeon 28) roughly a ten minute walk from the Dantons’ apartment on 20 cour du Commerce-Saint-André (today destroyed). The ease with which they would come and go between these two apartments will be seen through Lucile’s diary 1792-1793.
In number 63 (February 7 1791) of Révolutions de France et de Brabant, Camille celebrates the fact that ”the excellent patriot Danton” has become a member of the department of Paris — ”If there is only one patriot of this caliber in the 83 departments, all the projects of our enemies from within and without will fail against his firmness, his ascendancy, his vigilance and his incorruptibility.” In a letter to La Marck dated March 10 1791, Mirabeau claimed to ”have evidence Danton was behind (a fait faire) the latest number of Camille-Desmoulins,” which, regardless of whether the charge was true, suggests a certain closeness between the two at this point. In number 72 (April 11) Camille exclaims: ”how the true jacobin Danton made blush the adulators that his excellency had already found.” Two numbers after that (April 25), he celebrates Danton’s actions the 18th the same month, the day the royal family tried to leave for Saint-Cloud but was stopped by a mob. In the number, Camille writes that Danton told him how he on the day in question had found himself at the Department when Bailly and La Fayette came there to demand permission to proclaim martial law and order the National Guards to fire on the crowd surrounding the royal family if necessary. Danton had successfully intervened and reduced them to silence. Camille praises this move in the number:
Courage, dear Danton! how much the patriotic writers must congratulate themselves today, who fought with obstinacy to praise you, and constantly nominated you for the votes of the people. By the parallel of your tribunitian eloquence, of your incorruptibility, of your masculine courage, with the academic and lachrymatory sentences of the courtier Bailly and his telescope which would have made us fall into the well with the astronomer in a scarf, continue to cover with shame all the citizens who gave him votes due to your patriotism.
In the same number, Camille also attributed to Danton and Kersaint an address placing the blame on what had happened on the 18th not on the people, but on the king: ”The same day the department of Paris presented the king with an address, the first, perhaps, which was written in the style of a free people. Also, it had been written by Danton and Kersaint: [transcription of the address].” According to Danton (1978) by Normann Hampson, Camille is however mistaken here, as the address had actually been written by Talleyrand and Pastoret…
In the next number (May 2 1791) Camille writes the following, which I’m not sure how to interpret, but which Hervé Leuwers reads as assassins having been after both Camille, Danton and Fréron when the three were walking home a week earlier: ”I have learned that four assassins waited for me Tuesday evening (April 26), until midnight. Me, D’anton [sic] and the Orator of the People (Fréron).” In number 81 (June 18 1791) he lifts Danton, Garran de Coulon and Manuel as ”the candidates whom I would most strongly recommend to the 83 departments, for the next legislature.”
In number 82 (June 27 1791), Camille writes that, eleven o’clock in the evening of June 20, ”I was walking home from the Jacobins together with Danton and other patriots. We only saw but one patrol the whole way. Paris seemed so abandoned to me that night that I could not help but remark on it. One of us (Fréron according to Leuwers) who had in his pocket a letter which I will speak about, which warned him that the King had to leave that night, wanted to observe the castle, he saw M. Lafayette enter it at 11 o'clock.” The next morning, Paris woke up to the discovery that the royal family had indeed left the capital during the night. The very same day, Camille goes to the Jacobin club and arrives in the middle of Robespierre holding a speech about the current situation which moves him deeply. After him, Danton mounts the rostrum, and about the same time Lafayette enters the club. Danton delivers a speech blaming him for the king’s flight and asking he explains himself that Camille records in the journal. At the end of the speech, Alexandre Lameth rises to support Lafayette, recalling that he has always thought Lafayette would fall at the head of the patriots in case of a counter-revolution.
Danton came back to sit down next to me. Is it possible? I said to him. Yes, [he answered], and rising up, he confirmed that M. Alexandre Lameth had always said this to him about M. La Fayette. My blood boiled. I was tempted to cry out to Alexandre Lameth: you used very different language with me; and I declare that almost everything I wrote at La Fayette, I wrote, if not under your dictation, at least under your guarantee. But Danton held me back.
While all of this was going down, Lucile Desmoulins and Gabrielle Danton was staying at the apartment of the latter, something which we know through a letter Lucile wrote her mother on either June 24 or June 25, when the royal family had been captured and was on their way back to Paris. Unfortunately I have not been able to transcribe it in its entirety, but these are all the places mentioning Gabrielle that I could find:
…Ever since papa came with [warnings?] to us madame Danton and I have not left each other. I would have [gone crazy?] had I remained alone. These three days we have left [her place?] only at 9 o’clock [in the evening?] Sometimes people came to tell us that we were lost, and when we were told good news, madame Danton, her eyes filled with tears, threw herself around my neck. I’ve supped at her place during this time and [with?] all the patriots. […] Oh God o God, I’m going to send your beautiful [p..?] to madame Danton.
On July 15 the Jacobins entrusted Brissot with writing a petition asking for the abdication of Louis XVI. The session was closed at midnight. Afterwards, Camille, Danton, Brune and La Poype all went over to Danton’s house to further discuss the petition (this was revealed by Brune in an interrogation held August 12 1791, published in number 34 (August 26) of the journal Gazette des nouveaux tribunaux). Two days later, the two were there once again, this time together with Fréron, Fabre, Santerre, Brune, Duplain, Momoro and Sergent-Marceau, and discussing the lynching of two men at the Champ-de-Mars the same morning, when, at nine o’clock, Legendre arrived and told the group that two men had come home to him and said: We are charged with warning you to get out of Paris, bring Danton, Camille and Fréron, let them not be seen in the city all day, it is Alexandre Lameth who engages this. Camille, Danton and Fréron follow this advice and leave, and were therefore most likely not present for the demonstration and shootings on Champ-de-Mars the very same day (this information was given more than forty years after the fact by Sergent-Marceau in volume 5 of the journal Revue rétrospective, ou Bibliothèque historique : contenant des mémoires et documens authentiques, inédits et originaux, pour servir à l'histoire proprement dite, à la biographie, à l'histoire de la littérature et des arts (1834)).
In the aftermath of the massacre on Champ de Mars, arrest warrants were issued against people deemed guilty for them. On July 22, the Moniteur reports that the journalists Suleau and Verrières have been arrested, and that the authorities have also fruitlessly gone looking for Fréron, Legendre, Desmoulins and Danton, the latter three, the journal assures, having already left Paris. Camille hid out at Lucile’s parents’ country house in Bourg-la-Reine together with Fréron, while Danton went to Arcis-sur-Aube, where he was sheltered by his friend Courtois, and then to Troyes (it’s also commonly stated he went to England during this period, but Hampson expresses some doubt over it). If Camille’s fellow journalist Louis Marie Prudhomme’s Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs, des fautes et des crimes commis pendant la Révolution (1797) is to be believed, on August 14, Danton told Camille and Fabre d’Églantine: the ”b.... won't have me; rather they will all be exterminated first.”
The rather flimsy charges against Danton and Camille — Danton was accused of having cheered on a crowd demanding Lafayette’s head on June 21, Camille of having made incendiary remarks at Café Procope café, saying that it was necessary to shoot the national guards — were however dropped after about six weeks, and in September 1791 they were both back in Paris to stand for election to the Legislative Assembly. Neither did however get in. Camille had also had to resign as journalist in the aftermath of the massacre on Champ-de-Mars.
In Histoire des Montagnards (1847) Alphonse Esquiros writes that Albertine Marat had told him that her brother, Danton and Desmoulins ”liked to come together, from time to time, to rest their souls in the sweet serenity of nature”:
In this contrast of the noise of revolutions with the silence, with the serious serenity of a sunset, under the trees, at the water's edge, a league from Paris, the three friends then had before their eyes the two faces eternal aspects of the world, history and nature, God in movement and God at rest. Danton, this eloquent thunderbolt, this large head of a genius on which smallpox had left big marks, Danton ordered dinner. Whatever efforts one agreed to make during the frugal meal, to keep irritating subjects out of the conversation, one was obliged to go there at dessert; because the company was too preoccupied with the dangers of the State not to mix public affairs with their most personal conversations.
When the question of war in December 1791 became the main topic of discussion, both Danton and Desmoulins joined the minority that cautioned against it. Already on December 16, right after Brissot had held his very first speech in favour of the idea, Danton, while praising the speaker as an excellent patriot, objected to the thought of a war right at the moment — ”I want us to have war; it is essential. We must have war. But above all, we have to exhaust the means that could save us from it.” Ten days later, December 26, Desmoulins did him too deliver a speech against war. Four days after that, after Brissot had just finished his second speech on the subject, Danton and Robespierre both demanded a change be made to a passage when it got printed. Following this moment, it would however appear Danton abandons the question. Camille on the other hand released the pamphlet Jean Pierre Brissot démasqué in February 1792, mocking Brissot and painting him as a fool. Danton’s name got mentioned three times throughout, Camille calling him and Robespierre ”the best citizens.” Danton also got mentioned a total of eight times in the journal La Tribune des Patriots Camille and Fréron published from April to June the very same year, but not in any way that could give us more insight into their relationship.
In her memoirs, Manon Roland claims that Danton and Fabre d’Églantine in the summer of 1792 often came home to her. At one point Fabre told her that “We have a newspaper project which we will call Compte rendu au Peuple souverain, and which will present the picture of the last revolution. Camille Desmoulins, Robert, etc, work on it.” Manon suggested they bring it to her husband for him to subsidise it, something which the two apparently never did, and there was no more talk of the journal again.
On June 23 1792 Lucile starts keeping a diary. The first time any of the Dantons show up in it is already on Wednesday June 27 — ”Madame D(anton) came, we played music.” A few days later Lucile gives this rather odd account: ”My head is spinning. I was madame D(anton) after dinner.” The day after that, July 6, she gives birth to her first child, and a week later, Camille writes to tell his father that said child ”was immediately sent to a wetnurse in Isle-Adam, with the little Danton” (François-Georges, born February 2 1792). If Camille and Lucile made a conscious choice of sending their son to the same wetnurse as Georges and Gabrielle’s (perhaps on the suggestion of their friends) one can only speculate in.
A week after Camille wrote his letter, Lucile traveled to her parents’ country house in Bourg-la-Reine. On July 25 Camille writes to tell her that ”I was brought to Chaville this morning by Panis, together with Danton, Fréron, Brune, at Santerre’s” (letter cited within Camille et Lucile Desmoulins: un rêve de république). Lucile returned to Paris on August 8. In a diary entry written four months later she reveals that she, in the afternoon of August 9, together with others went over to the Dantons. ”Her mother was crying, she was sad, her father looked dazed. D(anton) was resolute. As for me, I was laughing like a madwoman! They feared that the affair [the insurrection of August 10] would not take place; although I was not at all sure, I told them, as if I knew it well, that it would take place. “But can we laugh too?” mde D(anton) said to me. ”Alas, I said to her, that presages to me that I will perhaps shed a lot of tears this evening!” At the end of the day, Lucile, Gabrielle (and others?) go home to Gabrielle’s mother to go for a walk and eventually sit down next to a cafe with her. When groups of sans-culottes and troops on horseback pass by, Lucile gets scared and tells Gabrielle that they should go. ”She laughed at my fear, but by dint of telling her, she too became scared and we left. I say to her mother: ”Farewell! You will soon hear the toscin sound!” The two go back to Gabrielle’s apartment, where a scared Lucile eventually admits to Camille she doesn’t want him to get involved in the dangerous insurrection — ”He reassured me by telling me that he would not leave D(anton).” Lucile and Gabrielle are soon left alone in the apartment with Louise de Kéralio-Robert, but after only a little while Danton returns home and goes to bed. This eventually upsets Louise who tells Lucile that if her husband dies in the insurrection she will stick a knife in Danton. ”From that moment on I never left her. What did I know what could happen? To know what she was capable of…” Some additional time later Camille returns to the apartment and falls asleep on Lucile’s shoulder. Louise tells her that “I can’t stay here any longer! Madame D(anton) is unbearable to me, she seems to be calm, her husband does not want to expose himself!” Lucile therefore suggests she come with her and Camille to their apartment to get some rest. When they around noon go back to the Dantons’ place again ”Madame D(anton) ran up to us to see how we were, she was soon informed when she saw the silence of one and the tears of the other. We waited long enough without knowing anything. Finally they came to tell us that we were victorious.” In a letter to her mother penned down the very same day, Lucile, similarly to how she described them during the Flight to Varennes, writes: ”Mme Danton and I do not leave each other, when I would have liked to flee it would have been impossible, the women are kept from going out.” The following night Camille and Lucile sleep over at the Roberts. When Lucile returns home on the 12th she learns that Danton has been appointed minister of justice. ”These news gave me great pleasure, especially when C(amille) came to tell me that he was secretary.” One day later Camille writes a letter revealing the very same news to his father:
My friend Danton has become minister thanks to the canon. This bloody day could only end, for the two of us especially, in being raised or hoisted together. He said to the national assembly: If I had been defeated, I would have been a criminal. The cause of liberty has triumphed, and Danton has associated me to his triumph.
According to Prudhomme’s Histoire générale et impartiale… (1797), it was Camille and Fabre themselves who three o’clock in the morning announced to Danton that he had been named minister of justice, after which they demanded he make them his secretaries:
”But, are you sure that I am appointed minister?” [said Danton]. “Yes,” replied the two midshipmen; and we will not leave you until we have your word for these two places.” ”Right on time,” said Danton. And everything was arranged according to the wishes of the two revolutionary patriots; but all this does not praise their disinterestedness.
After Camille and Danton had gotten their new occupations, both families briefly went to live at Hôtel de Bourvallais. Lucile writes:
I really liked it there, but only one thing bothered me, it was Fréron. Every day I saw new progress and didn’t know what to do about it. I consulted Maman, she approved of my plan to banter and joke about it, and that was the wisest thing to do. Because what to do? Forbid him to come? He and C(amille) dealt with each other every day, we would meet. To tell him to be more circumspect was to confess that I knew everything and that I did not disapprove of him; an explanation would have been needed. I therefore thought myself very prudent to receive him with friendship and reserve as usual, and I see now that I have done well. Soon he left to go on a mission. I was very happy with it, I thought it would change him. But many other cares to be taken… I realized that D(anton)… Oh, of that one, I was suspicious! I had to fear the eyes of his wife with whom I did not want to be hurt. I did so well that one did not know that I had noticed it, and the other that it might be. We spent three months like this quite cheerfully. At the end of this time C(amille) was appointed deputy and we returned to our first home.
Somewhere during Camille and Danton’s time in the ministry we find the following undated letter ”from the minister of justice to citizen Desmoulins, national commissioner in Vervins” (Camille’s father). Charles Vellay, who published the letter in 1792, did however find it more likely for the author of the letter, unlike what the header leads you to believe, was Camille, seeing as it is in a secretary’s handwriting and the letter was found among his and not Danton’s papers:
I am pleased to learn, Citizen, that yielding to the wishes of your compatriots, you have accepted the position of Natal Commissioner at the Vervins District Tribunal. You could undoubtedly desire some rest after the long fatigues you have had and the feeling which invited you to retire was very legitimate; but it was worthy of your good citizenship to still make the sacrifice for your country, and I am convinced that it was not in the midst of the agitations which precede the most beautiful of centuries that you would have left without regret a career where you you still have services to render to public affairs for a long time to come. It is not fair, however, to forget that the more you redouble your efforts, the more it is in your fellow citizens' interest to prescribe reasonable limits for yourself, and it is also your duty to moderate your zeal and not to forbid you these considerations which can be reconciled with public service and the care of your health. Your colleagues will themselves urge you to give nature the moments of relaxation it needs; a few temporary absences can be infinitely useful to you, and certainly they will not harm the interests of business if some attention is given to the circumstances and replacement measures. I will approve the first of wise precautions which I feel the necessity of and sure of my attachment to your duties I will rely with confidence on your respect for this moral responsibility as sacred as the will of the laws to true republicans.
Danton would however not remain minister of justice for a long time, already on August 26 Camille reported to his father that:
It seems that several departments will nominate me and especially Danton [to the National Convention], and he will not hesitate for a moment to leave the ministry to be representative of the people. You can imagine that I would follow an example that I would have given him, if I were in his place. Danton is from Paris no more than I am, and it is a remarkable thing that among all the principal authors of the revolution and among all of our friends, we perhaps do not know a single one who was born in Paris.
However, before the opening of the National Convention, the so called September Massacres took place. In l’Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs… (1797) Prudhomme attributed big responsibility for the prison killings to both Danton and Desmoulins, portraying them as aware of what was going to happen already on September 2, the day before they began:
September 2, at midday, I go, hearing the noise of the tocsin and the cannon of alarm, to my section de l'Unité. People came to announce that the barriers had been closed. A general consternation was painted on all faces. At the news of the arrival of the Prussians in Paris, as well as of a conspiracy of the prisoners against the patriots (a vague rumor had been circulating about it for fifteen days), a number of citizens questioned me on this subject. ”Your profession as a journalist should enable you to know something,” one said to me. ”I know nothing,” I responded, ”but I’m going to visit someone who could tell me.” As I knew Camille Desmoulins since a long time back, I thought it a good idea to go to his house. I didn’t find him anywhere, one assured me that he was at Danton’s, minister of justice. It was about half past two in the afternoon, I went home to the minister, and told him: ”I have come, in the quality of pure patriotism and in my own name, to ask you what this canon of alarm, this toscin and the arrival of the Prussians to Paris.” ”Calm down, old friend of liberty,” Danton responded, ”it’s the toscin of victory.” ”But,” I told him, ”people talk about slitting throats.” ”Yes,” he told me, ”we were all about to have our throats cut this night, starting with the most patriotic. All those arisocrat rascals, who are in the prisons, had been provided with firearms and daggers. At a specified time next night, the gates were to be opened to them; they would have spread in different quarters to cut the throats of the wives and children of the patriots who will leave to march against the Prussians. We addressed ourselves principally, above all, to those who had demonstrated the principles of freedom.” ”All this comes off as a bit made up to me,” I responded, ”but what means are to be employed to prevent the execution of such a plot?” ”What means?” he said. ”The People, irritated and instructed in time, want to do justice themselves to all the bad subjects inside the prisons.” At these words I was seized with horror; I told him that such a measure appeared to me unworthy of a people who claimed to be free. At this moment, Camille Desmoulins entered. ”Hello there!” Danton said to him. ”Prudhomme just asked me what is to be done. ”Yes,” I said, ”and I am heartbroken after what I have just heard. ”So you (tu) didn’t tell him that one won’t mix up the innocent with the guilty? Camille said to Danton. ”All those who will be claimed by their sections will be returned.” ”Seems to me that we could take a less violent measure,” I responded. ”Spilling blood is an abominable act of which those who govern are responsible. The people will one day make those who make them commit this crime pay dearly. Let Paris march en masse against the Prussians. Send the wives and children of those who are to march at the enemy out of Paris to avoid them getting massacred by the prisoners, let us lock them up in fortified castles.” ”Any kind of moderate measure is useless,” Danton said. ”The anger of the people is at its height, there would even be danger in stopping it.” His first anger assuaged, one could make him listen to reason. ”But,” I say, ”if the Legislative body and the constituted authorities spread themselves through Paris, and harangued the people?” ”No, no,” replied Camille, ”that would be too dangerous; for the people, in their first wrath, might make victims in the person of their dearest friends.” I withdrew filled with pain.
Exiting Danton’s house, Prudhomme adds:
As I passed through the dining room, I saw the wives of Camille, Danton, Robert, etc, Fabre-d'Eglantine, and other guests. I did not know what to think of the tranquility that reigned at the house of the Minister of Justice; everything led me to believe that it was indeed impossible to stop the resentment of the People, at the news of a conspiracy hatched by the nobles and priests.
The next day, Prudhomme also claims that Théophile Mandar went over to Danton’s place, where he saw ”all ministers, with the exception of Roland, Lacroix, president [of the Assembly], Pétion, mayor of Paris, Robespierre, Camille-Desmoulins, Fabre d’Églantine, Manuel and several members of the so-called Commune of August 10. The presidents and commanders from each of the 48 sections had come as well.” Half past seven in the evening everyone sat down in Danton’s salon to discuss the means to save Paris, Danton staying firm in his conviction of what had just happened and was still happening as necessary.
On September 8, two days after the end of the massacres, the time had come for Camille to be elected to the National Convention. He did at first come under question for his friendship with the royalist journalist François Suleau, killed in the Insurrection of August 10. The journal Gazette nationale de France does however report that Camille after this ”was defended with a lot of energy and eloquence by M. Danton and his election was almost unanimous.” With that, Desmoulins became the sixth elected deputy representing Paris (Danton was the second).
In December 1792, Lucile returns to keeping a diary. On the 22nd she writes: ”I went to supper with little Brune at mde D(anton’s). How detestable she is!” It’s hard to tell if it’s Gabrielle or madame Brune she designates as detestable, and even harder to know what she had done in order to get called that… Two days later, December 24, Lucile documents the following:
We had dinner at mde D(anton's), mde R(obert), B(rune) and B(oyer) were there. After dinner the men asked themselves if they should go to the Jacobins. They said yes. We were asked if we would go. We say no. Madame D(anton) said to me: ”do you (vous) want to spend the evening with me?,” I said yes, but soon I did not know what to do. Brune suggested I go to the theater! It was very embarrassing. Madame Brune said aloud: “I have never been to the Jacobins, I would be very happy to go there.” "Well, I'm going with you," I tell her. Finally, here we are, all ready to leave, when I see Mme Brune and Boyer whispering in each other’s ears. I, like a fool, go to ask them what they’re saying to each other. Mde R(obert) told me that she was very embarrassed, that she would like to go with us to the Jacobins. I was very kind, I said a few words to her that meant nothing, then I went into the antechamber. She came there soon and told me to wait for her, that she was going to follow me, she came back near madame D(anton). Brune came and told me “let’s go”. I followed her saying: ”but mde R(obert) who wants to come?” Finally, we are hardly in the middle of the staircase when we hear someone who says “here they are, here they are!”, then we descend with astonishing speed, and when we are in the street we run even harder. We took a fairly long detour. God knows how we laughed! Nothing, too, was more comical.
Throughout the first two halves of January, Lucile goes to the Convention to follow the trial of Louis XVI every single day. If Gabrielle went with her to these sessions is not confirmed, but not disproven either. Danton was absent on a mission in Belgium for most of the trial, but on January 14 he returned to Paris and two days later he voted for death, just like Camille. One day after the execution of the king, January 22 1793, Lucile writes: ”I went to Robert’s. Danton came there. His jokes are as boorish as he is. Despite this, he is a good devil. Madame Ro(bert) seemed jealous of how he teased me…” Two days later she witnesses the funeral procession of the recently assassinated Michel Peletier from the window of Jeanne-Justine Boyer, an event which moves her deeply. Once all her guests have left for the evening ”I felt that I could not be alone and bear the horrible thoughts that were going to besiege me. I ran to D(anton’s). He was moved to see me still pale and defeated. We drank tea, I supped there.” A week later, January 29, Lucile reports that ”we had dinner at D(anton's), where I just laughed, because I was preventing Brune from eating by saying "poa, poa, poa". D(anton) too couldn't keep himself from laughing.” Four days after that, February 3, Lucile writes ”I went to see madame Danton. Sick.” Three days later, she goes back to see her friend — ”I went to see madame Danton… She is very ill.” Yet another three days later Lucile writes ”Madame Danton is ill. She has given birth to a girl.” and at last, the day after that: ”I had dinner with Maman. Madame Danton is dead.” Two days after the death of her friend, Lucile goes to visit Gabrielle’s mother together with madame Brune and Robert. Shortly after that, she and Camille do however leave for Essonne, the latter having been apointed to a mission there, while Georges returned to Paris after another mission in Belgium to receive the sad news. Lucile did however not forget about him, in a letter to her mother Annette dated February 16 she asks her to ”give us news regarding Danton.” Apropos of Annette eventually joining them in Essonne Lucile adds: ”I forgot to mention a facility that could be of use for you, it’s Danton’s carriage. No doubt he could still have it.”
On March 26 1793, Desmoulins and Danton were both elected for the so called Commission of Public Safety, alongside 23 others. The commission, which consisted of both fervent montagnards and fervent girondins, was however off to a rocky start, and already on April 6 it was put to death and replaced by the Committee of Public Safety. A little more than a month later, May 17, Desmoulins announced the release of his new pamphlet l’Histoire des Brissotins to the Jacobins. Danton’s name gets mentioned eleven times in it, but only one can be used to really say something about their relationship, and it’s when Camille on page 54 writes: ”Jérôme Pétion told Danton in confidence that ”what makes poor Roland saddest is the fact people will discover his domestic sorrows and how bitter being a cuckold is to the old man, troubling the serenity of that great soul.” This implies Danton went and shared Roland’s secret with Camille after Pétion had confided it to him. Two weeks later, on June 7, a ”member” is recorded to have voiced suspicion on Danton’s current sentiments — ”This deputy isn’t as revolutionary as he used to. He doesn’t come to the Jacobins anymore. He left me the other day to approach a general.” In response, Camille is recorded to have ”advocated Danton’s good citizenship.” In Lettre de Camille Desmoulins, député de Paris à la Convention, au général Dillon en prison aux Madelonettes released a few months later, Camille calls Robert Lindet, Robespierre and Danton ”the best citizens of the Convention.”
On October 30, 22 girondins were sentenced to death. In Les mysterès de la mère de Dieu dévoilès (1794) Joachim Vilate described a dramatic reaction from Camille’s part upon hearing the final verdict: ”hearing the juror's declaration, he suddenly threw himself into my arms, agitated, tormenting himself:”ah my god, my god, it's me who kills them: my Brissot dévoilé [sic], ah my god, it’s that which kills them.” If Dominique-Joseph Garat’s Memoirs of the revolution; or, an apology for my conduct, in the public employments which I have held (1795) are to be believed, Danton too was deeply moved by the fate of the girondins, to the extent it motivated him to, on October 12, ask for a leave of absence to go to Arcis-sur-Aube in order to recruit his health:
I could not convince myself that among all those who, since May 31, had retained great popularity, there was not one who did not still retain a little humanity, and I went to Danton. He was ill, it only took me two minutes to see that his illness was above all a deep pain and a great dismay at everything that was coming. ”I won't be able to save them (the girondins)”, were the first words out of his mouth, and, as he uttered them, all the strength of this man, who has been compared to an athlete, was defeated, big tears strolled down his face, whose shapes could have been used to represent that of Tartarus. […] When the fate reserved for the twenty-two [girondins] seemed inevitable, Danton already heard, so to speak, his death sentence in theirs. All the strength of this triumphant athlete of democracy succumbed under the feeling of the crimes of democracy and its disorders. He could only talk about the countryside, he was suffocating, he needed to escape from men in order to be able to breathe.
Danton’s absence did not go unnoticed. In a letter from Toulon written October 18, Fréron tells Lucile that ”I have been really worried about Danton. The public papers announce that he is ill. Let me know if he has recovered. Give him 1000 friendships from my part.” Through the next letter Fréron writes Lucile, dated December 11, we learn that Danton had a nickname within this inner circle of friends — ”I would like to have news of Patagon (Brune), Saturne (Duplain) and Marius (Danton).” It can be observed that Camille, as seen above, had likened Danton to Marius in Révolutions de France et de Brabant already in 1790.
Danton was however back in Paris again on November 22, when he is recorded to have spoken of ”the relief to be granted to abdicated priests” at the Convention. Two weeks later, December 3, he was accused of ”moderatism” by Coupé d’Oise for having opposed the suggestion of sending a group with a portable guillotine to Seine-Inférieure in order to deal with rebels fleeing the Vendée. Robespierre did however rise to defend Danton, saying that he had always seen him serve his homeland with zeal and ending by asking that everyone says what he sincerely thinks about Danton. Aside from Merlin de Thionville, who hailed Danton as the saviour of the republic, no one said anything, and Momoro therefore concluded this meant no one had anything to accuse Danton of. The discussion therefore ended with Danton embracing the president of the club amidst loud applause. Just two days later, the first number of Camille’s new journal, the Vieux Cordelier, was released. In the number, Desmoulins designates the session at the Jacobins on the 5th as the event that caused him to return to the journalistic pen:
Victory is with us because, amid the ruins of so many colossal civic reputations, Robespierre’s in unassailed; because he lent a hand to his competitor in patriotism, our perpetual President of the “Old Cordeliers,” our Horatius Cocles, who alone held the bridge against Lafayette and his four thousand Parisians besieging Marat, who now seemed overwhelmed by the foreign party. Already having gained stronger ground during the illness and absence of Danton, this party, domineering insolent in society, in the midst of the most sensitive places, the most compelling justification, in the tribunes, jeering, and in the middle of the meeting, shaking its head and smiling with pity, as in the speech of a man condemned by every vote. We have won, however, because after the crushing speeches of Robespierre, in which it seems that talent grows in pace with the dangers of the Republic, and the profound impression he has left in souls, it was impossible to venture to raise a voice against Danton without giving, so to speak, a public quittance of guineas of Pitt. […] I learned some things yesterday. I saw how many enemies we have. Their multitude tears me from the Hotel des Invalides and returns me to combat. I must write.
If Danton had a bigger role in the Vieux Cordelier than simply being part of the event that caused Camille to start writing it is debated. When Robespierre a little more than three months later was working out the dantonists’ indictment, he claimed that Danton had been the ”president” of the Vieux Cordelier, whose prints he had corrected and made changes to, and that Camille had been his and Fabre’s ”dupe.” In Memoirs of the revolution; or, an apology for my conduct… (1795) Garat claimed that Danton during his stay in Arcis-sur-Aube had been cooking up a ”conspiracy” with a goal to ”restore for the benefit of all the reign of justice and of the laws, and to extend clemency to his enemies,” and to which ”all of his friends,” including Desmoulins, entered into. In Histoire générale et impartiale des erreurs… (1797) Prudhomme claimed that Danton, Lacroix, Camille-Desmoulins and Fabre-d'Églantine made up a secret party wishing to overthrow the Committee of Public Safety, and that Camille, as part of this plan, got charged with a ”moral attack,” leading to the creation of the Vieux Cordelier. Danton’s friend Edme-Bonaventure Courtois wrote in Notes et souvenirs de Courtois de l’Aube, député à la Convention nationale (cited in La Révolution française: revue d’histoire moderne et contemporaine (1887), that ”it was in these painful moments that [Desmoulins] put to paper (in his Vieux Cordelier) the reflections that his indignation could no longer contain, and whose acrimony Danton, through his advice, softened in many places.” Finally, in his Camille Desmoulins And His Wife: Passages From The History Of The Dantonists (1876), Jules Claretie included the following passage:
I know, through information given to me by M. Labat the elder, that one evening in that mournful summer of 1793, Danton and Camille Desmoulins had walked to the Cour du Commerce, along the Seine, by the quay des Lunettes, and, thinking of that 31st of May, which was to end in the events of the 31st of October, Danton pointed out to Camille the great river in which the rays of the sun, setting behind the hill of Passy, were reflected so vividly that the river looked like blood. ”Look,” said Danton — and, like Garat, Camille saw the tribune's eyes fill with tears — ”see, how much blood! The Seine runs blood! Ah! too much blood has been spilt! Come, pick up your pen again; write and demand clemency, I will support you!”
However, considering Robespierre’s notes had an interest in wanting to paint the ”dantonists” as a unified grupp (and perhaps also to absolve Desmoulins of some responsibility), while all the other testimonies were reported after the fact, its hard to be sure of anything.
Danton went unmentioned in the rest of number 1, as well as number 2 (released December 10) of the Vieux Cordelier. When Camille on December 14 passed through the Jacobins ongoing scrutiny test, he regrettingly admitted that ”a well marked fatality willed that, among the sixty [sic] people who signed my wedding contract, I only have two friends left — Danton and Robespierre. All the others have emigrated or been guillotined.” In the Vieux Cordelier’s third number (released December 18), he wrote the following about Danton, apropos of underlining he was not asking for moderation:
In this duel between liberty and servitude, and in the cruel alternative of a defeat a thousand times more bloody than our victory, overruling the revolution therefore had less danger and was even better than remaining behind it, as Danton said, and it is necessary, above all, for the republic to secure the battlefield. […] Despite so many guineas (guinées) said Danton, name for me a single man strongly pronounced in the revolution, and in favor of the republic, who has been condemned to death by the revolutionary tribunal?
Danton went unmentioned again in number 4 (December 21), but in number 5 Camille brings him up seven times, writing that ”I said with Danton, that to outrage the revolution was less dangerous and even better than to remain within it; that, on the course taken by the vessel, it was better to approach the rock of exaggeration, than the sandbar of moderation,” insisting he has never ceased to ”conspire against the tyrants with Danton and Robespierre,” denouncing Hébert for having attacked him, Danton and nine other deputies and claiming to have heard Danton say that ”[Hébert’s] pipe resembles the trumpet of Jericho, when he has smoked three times around a reputation, it must fall of itself.” At one point he also accuses Barère of having discussed the arrest of Danton on June 2.
On January 7, Camille and Robespierre got into a fight at the Jacobin club after the latter had denounced the fifth number of Vieux Cordelier as counter-revolutionary, but insisting that its author had been ”led astray by bad company,” and therefore proposing that the Society forgive him and ”just” burn the latest numbers of the Vieux Cordelier. When Camille refused that ultimatum, exclaiming that ”burning isn’t answering,” the fight worsened until Danton stepped in to act as meditator between the two:
Danton: Camille mustn’t be frightened by the rather severe lessons Robespierre’s friendship has just given him. Citizens, let justice and cold-headedness always preside over our decisions. In judging Camille, be careful to not strike a deadly blow against the liberty of the press.
In a letter to Fréron dated January 13, Lucile regretfully reports that ”Marius is not listened to anymore, he loses courage and vigour.” Around the same time, her father was arrested and locked up in the Carmes prison due to a few objects decorated with fleurs-de-lys having been found in his home. On January 24 Camille protested against his arrest at the Jacobins, gaining the support of Bourdon d’Oise who asked that the Committee of General Security make a report about the case in three days. Danton did however object to this, but did make the more vague suggestion that ”the Convention consider ways to do justice to all the victims of arbitrary measures and arrests, without harming the action of the revolutionary government”:
I oppose the kind of distinction of privilege which would seem to be granted to Desmoulins' father-in-law. I want the Convention to deal only with general affairs. If we want a report for this citizen, we also need one for all the others. […] My colleague's complaint is fair in itself, but it would give rise to a decree unworthy of us. If we were to give priority, it would belong to citizens who do not find in their fortune and in their acquaintance with members of the Convention hopes and resources in the midst of their misfortune: it must be to the unfortunate, to the needy, that you should first hold out your hands. I ask that the Convention consider ways to do justice to all the victims of arbitrary measures and arrests, without harming the action of the revolutionary government. I would be careful not to prescribe the means here. I request the referral of this question to the consideration of the Committee of General Safety, which will consult with the Committee of Public Safety; that a report be made to the Convention, and that it be followed by a broad and in-depth discussion; because all the discussions of the Convention have resulted in the triumph of reason and liberty.
When Robespierre about two months later was preparing the dantonists’ indictment, he wrote that ”during this last visit [to my place], [Danton] spoke of Desmoulins with contempt. He attributed his deviances to a vice that is private and shameful, but absolutely foreign to the crimes of the conspirators to the Revolution. Laignelot was witness.” Robespierre used this as evidence Danton had ”an ungrateful and dark soul,” as he previously had ”highly recommended the last productions of Desmoulins.”
Both Danton and Camille were arrested in the night between March 30 and March 31. They were taken to the Luxembourg prison and placed in solitary confinement. On April 1, in his very last written letter, Camille regrettingly tells Lucile:
How to believe that a few jokes in my writings, against colleagues that had provoked me, have erased the memory of my services! I do not disguise the fact that I die as a victim of these jokes and my friendship with Danton. I thank my assassins for letting me die with him and Philippeaux. And since my colleagues have been cowardly enough to abandon us and listen to calumnies that I don’t know, but must be the most vulgar, I can say that we die as victims of our courage to denounce traitors, and of our love for the truth. We can well carry this testimony with us, that we die as the last republicans.
It would however appear Lucile wanted to do something about the situation. We have the following anecdote published in Histoire de la Révolution française (1850) by Nicolas Villiaumé, which, as far as I’m aware, is the only known connection we have between the Desmoulins couple and Danton’s second wife Louise-Sébastienne Gély (married June 14 1793):
[After the arrest of Danton and Desmoulins] Lucile ran to Madame Danton to suggest that she come with her to go find Robespierre, ask him for an explanation, and recall the feelings of friendship which had attached him to their husbands. Madame Danton refused, saying that she wanted nothing from a man who had showed himself to be the enemy of her husband. (I obtained this particularity from Madame Danton herself, who was then pregnant. She gave birth fifteen days after Danton's death, but her child did not live.)
On April 2, Danton, Desmoulins and seven other deputies were brought from the Luxembourg to the Conciergerie prison. If Mémoires d’un detenu pour servir à l’histoire de la tyrannie de Robespierre(1795) by Honoré Riouffe are to be believed, the accused were kept in seperate cells here as well. He writes:
Danton, placed in a cell next to Westermann, didn’t stop talking, less to be heard by Westermann than by us. […] Here are some phrases I retained: […] ”What proves Robespierre is a Nero, is that he never spoke as kindly to Desmoulins as on the day before his arrest.”
Their trial began the very same day. For three days, the accused defended themselves (or at least tried to) against the charges of ”complicity with d'Orléans and Dumourier, with Fabre d'Eglantine and the enemies of the Republic, of having been involved in the conspiracy tending to re-establish the monarchy, to destroy the national representation and the republican government” side by side. It did however not go that well, and on April 5, Danton, Desmoulins and thirteen others were sentenced to death. The execution took place the very same afternoon. Contrary to the myth of Danton and Camille sitting next to each other in the same tumbril as they were driven to Place de la Révolution, number 561(April 6 1794) of Suite du Journal de Perlet reports that ”they were in three tumbrils: in the first was Danton, next to Delacroix; Fabre near the executioner; Hérault opposite Chabot. In the second, Phelippeaux [sic], Westermann, Camille Desmoulins, Basire and Launai d’Angers [sic]. […] Danton […]seemed to pay little attention to the crowd around him: he was chatting with Lacroix and Fabre. […]Desmoulins spoke almost continually to the people; the courage he affected seemed like a painful effort, he was an actor who was studying to play his last part well.”
After the death of Camille and, eight days later, Lucile, their son Horace was taken in by his maternal grandparents and aunt, who then permanently retired to their country house in Bourg-la-Reine. Danton’s sons Antoine and François-Georges were they too adopted by their maternal grandfather and uncles. In 1805, the two moved from Paris to Arcis-sur-Aube where they instead got looked after by their paternal grandmother. I have not been able to find anything indicating the families stayed in touch to process the grief or let the children come together, something which we on the other hand know Lucile’s mother did with Philippeaux’s widow.
#danton#desmoulins#georges danton#camille desmoulins#frev friendships#lucile desmoulins#gabrielle danton#frev#ask#interesting how it’s to lucile (and albertine) we owe the best information for her husband’s friendship with danton…
65 notes
·
View notes