#China Covid outbreak
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
China says restrictions on its travellers abroad discriminatory: Warns countermeasures
#china covid measures#china coronavirus#restrictions on travellers abroad discriminatory#china#china news#china latest news#china covid surge#china covid outbreak#china passengers guidelines#china pasengers guidelines#China travel restrictions#Restrictions on chinese passengers#China covid cases#China zero covid policy#China covid cases today#World news#Latest world news#china travel restrictions from india
0 notes
Text
Taiwan offers support to China to deal with deadly Covid outbreak
Taiwan offers support to China to deal with deadly Covid outbreak
Taiwan has announced its decision to offer support to China to deal with the deadly Covid outbreak. Taiwan and China have repeatedly sparred over their respective measures to control the spread of Covid. New Delhi,UPDATED: Jan 1, 2023 11:50 IST A patient with Covid rests in a wheelchair in a hallway at Tangshan Gongren Hospital in China’s northeastern city of Tangshan. (Photo: AFP) By India…

View On WordPress
#China#china coronavirus outbreak#china covid#china covid lockdown#china covid news#china covid outbreak#china covid update#china zero covid policy#Covid#deadly#deal#offers#outbreak#support#Taiwan#taiwan china conflict#taiwan china covid#taiwan china covid outbreak#taiwan covid support china#taiwan support china
0 notes
Text
When China relaxed its zero-COVID policy at the start of December, international observers warned there would be mass outbreaksin the Chinese population, which, it was estimated, lacks sufficient herd immunity or vaccine protection.
One statistical model published by healthdata.org predicts that 300,000 people could die from COVID-19 infections by April 2023 and 1.6 million people could die by the end of the year.
"Infections are steeply on the rise and hospitals are overwhelmed. It's quite [certain] that the situation is spiraling out of control, at least in Beijing and other big cities," said Björn Alpermann, a sinologist at the University of Würzburg in Germany.
COVID wave in China 'thermonuclear bad'
On December 19, a prominent epidemiologist, Eric Feigl-Ding, tweeted that the situation was "thermonuclear bad."
Feigl-Ding predicted "over 60% of China's and 10% of the Earth's population likely infected over the next 90 days. Deaths likely in the millions — plural."
In scenes reminiscent of the early months of the pandemic in 2020, Feigl-Ding posted a video of what looks like an overcrowded hospital, with patients lying close next to each other on the floor.
Other reports suggest morgues and crematoriums are overloaded, with backlogs running into the thousands. "The reports that crematoriums are working 24/7 are deeply disturbing," said Alpermann.
How accurate are the statistics?
It's not known how many people are currently infected with COVID-19 in China or the number of those who have recently died from the disease.
Oliver Radtke who lives in Beijing and is the chief representative of the Heinrich Böll Foundation, an independent political foundation affiliated with Germany's Greens, said it was impossible to know how severe the current COVID wave was by reading the official statistics.
"Judging strictly from personal evidence, scrolling through WeChat [social media] and having conversations with colleagues and friends, I reckon about one third in the city is sick, one third is taking care of the sick and one third simply doesn't dare to venture out," Radtke told DW.
Alpermann said the Chinese government had more or less admitted that its statistics were artificially low when it said that it would only count COVID deaths that had happened due to lung failure. That's Alpermann's personal assessment, but it suggests that those statistics tell only a partial truth.
The lack of accurate statistics about the current COVID situation in China makes predictions about deaths and illness difficult.
"There are so many moving parts in models, so there's a lot of guess work. The subvariant [of omicron, BF.7] circulating in China now isn't well studied, and we don't know how fast people will get boosters this winter," Alpermann said.
Booster campaign to target elderly
So, how are Chinese health authorities responding to the situation? Radtke said authorities had placed responsibility on individuals to keep safe.
"The official slogan these days is 'everybody is responsible for the prevention and control of the pandemic,'" he said.
But the Chinese National Health Commission (NHC) has initiated a large vaccination and booster campaign, especially for the elder and other high-risk groups.
Many health experts outside China have been critical about the effectiveness of Chinese vaccines from Sinovac and Sinopharm compared to mRNA vaccines, such as the BioNTech-Pfizer and Moderna jabs — and the NHC is only administering vaccines made in China.
However, reports suggest they may include new nasal spray vaccines in the booster program. The hope is that the new vaccine types will reduce COVID transmission as well as the risk of severe COVID-19 symptoms.
"Worries about grandparents and older parents are high. Especially regarding family members in the countryside and [remote] provinces, where Intensive Care Unit beds are rare or non-existent," said Radtke.
What caused the latest COVID outbreak in China?
Experts say that the current infection and death rates in China may be because the country has a lower level of population immunity than that in other countries.
"The Chinese government boasted they won a victory against COVID with their zero-COVID strategy. For some time it looked that way in 2021, but with omicron the picture completely changed," said Alpermann.
China has pursued a zero-COVID policy since the pandemic began.
During zero-COVID, the government implemented mass testing, imposed strict lockdowns and quarantined those people with COVID-19 in special facilities.
Now that it has relaxed its lockdown rules, the population has been going out but with very little natural exposure to infection, especially the more contagious variants, such as omicron — because they were locked in for all that time. In any case, that is the theory you hear from health experts outside China.
Rates of booster vaccine uptake are estimated to be low in China, especially among older people who have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms — only about one-third of over-80s and two-thirds of over 60s have received their first booster shot, according to official data.
"In retrospect, it now looks like the Chinese government did not use the time during zero-COVID to their own advantage to get vaccination rates as high as they should have been. They did not import more advanced mRNA vaccines or approve mRNA vaccines created in China," Alpermann said.
The first of three waves
Speaking at a conference in Beijing on December 17, Zunyou Wu, a chief epidemiologist at the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, said that the current outbreak would peak this winter and run in three waves for about three months.
The modelling mentioned at the start of this article puts the potential death rate as high as 1.6 million people by the end of 2023. But that depends on whether COVID transmission can or will be contained with new lockdowns and by the success of vaccination programs.
"I am worried about what happens once the current wave reaches the lesser-developed parts of the country, especially in the western hinterland," said Radtke.
Whatever the exact figures, Chinese health authorities appear to be struggling to keep up with the spread of the disease, and that continues to cause concern outside of the country as well.
#nunyas news#What caused the latest COVID outbreak in China?#are you really so dense that you think people don't know the answer to that already
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dear God,
Thanks so much for tipping China to try to be truthful. BTW it doesn't help my very American sisters that they look Chinese in the States so please prevent the Communist country from moving in a way that might increase xenophobia internationally.
Lots of love & Happy Year of the Rabbit,
-- dnagirl
P. S. Thanks for granting my Christmas wish of taming our Rottweiler so he can come home.
22.01.2023
0 notes
Text
Opinion | Western Scientists Cheered On China's Covid Repression - The Wall Street Journal
Opinion | Western Scientists Cheered On China's Covid Repression – The Wall Street Journal
China’s zero-Covid policies have recently come under criticism from public-health leaders—including those at the World Health Organization—who once held them up as a model for the West. “China’s success rests largely with a strong administrative system that it can mobilise in times of threat, combined with the ready agreement of the Chinese people to… Read more
View On WordPress
#Beijing#C&E Executive News Filter#China#commentaries#Commentaries/Opinions#Content Types#COVID#Epidemics#experts#Factiva Filters#general news#Health#Infectious Diseases#lockdowns#Medical Conditions#Medicine#Novel Coronaviruses#Omicron#opinions#outbreaks#Outbreaks/Epidemics#pandemic#political#Political/General News#public health#Respiratory Tract Diseases#SYND#who#WSJ-PRO-WSJ.com#zero-covid
0 notes
Text
China announces rollback of strict anti-COVID-19 measures
China announces rollback of strict anti-COVID-19 measures
BEIJING — In a sharp reversal, China has announced a series of measures rolling back some of its most draconian anti-COVID-19 restrictions, including limiting harsh lockdowns and ordering schools without known infections to resume regular classes. The National Health Commission in a 10-point announcement on Wednesday stipulated that COVID-19 tests and a clean bill of health displayed on a…
View On WordPress
#asia#Business#China#coronavirus#COVID-19 pandemic#Disease outbreaks#Diseases and conditions#east asia#Economy#General news#Government and politics#Greater China#Health#infectious diseases#Lung disease#public health
0 notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
By Joshua Boscaini
In short:
Australia has recorded its first cases of the XEC COVID-19 variant that has been spreading in Europe this year.
The mutation is a "recombinant" variant that is a mix of two previous Omicron subvariants called KS 1.1 and KP 3.3.
What's next?
An infectious disease expert says the strain has the hallmarks of something that could lead to a "summer wave" of infections.
A new highly transmissible variant of COVID-19 has been detected in Australia, raising questions about whether it will lead to a wave of COVID-19 cases over summer.
The XEC strain has been reported in 29 countries including the United States, United Kingdom and China, according to global health data platform GISAID.
Here's what we know about the XEC variant and how many cases have been reported in Australia.
What do we know about XEC?
XEC is a "recombinant" COVID-19 variant, which means it's a mix of two previous Omicron subvariants called KS 1.1 and KP 3.3.
A recombinant variant is created when someone is infected with two strains of a virus that go on reproduce and create another strain.
There are conflicting reports about where the strain originated, but most suggest it was first detected in Germany in May or June.
Cases have been reported in 29 countries, according to GISAID, including Brazil, Canada, China, France, Spain and Japan.
The World Health Organization (WHO) classified XEC as a variant under monitoring in September so health authorities could give it more attention and investigate whether it presented an additional threat to global public health.
University of Queensland infectious diseases physician Paul Griffin told the ABC that XEC could become the dominant variant by the end of October.
"It is seeming to grow fairly quickly," Dr Griffin says.
"It's got a significant growth advantage in a number of countries around the world, including our own at the moment, so it does seem to be able to out compete some of the existing sub-variants."
How many cases of XEC are in Australia?
Australia recorded 23 known XEC COVID-19 infections as of September 23, according to the Department of Health's latest Australian Respiratory Surveillance Report.
Dr Griffin says the XEC strain makes up about 5 to 10 per cent of COVID-19 cases in Australia and the strain may have arrived in the country earlier than data suggests.
The National Notifiable Disease Surveillance Dashboard reports 12,037,101 cases of COVID-19 have been detected in Australia as of October 7, 2024 since the start of the pandemic.
But Dr Griffin says case numbers aren't a good indicator of how severe or easily transmissible the XEC variant is because fewer people are getting tested.
"The main things we monitor [for] … is things like cases and outbreaks in aged care, and hospitalisations, intensive care and death," he says.
"To date we haven't see any rise in any of those."
What are the symptoms and how is it transmitted?
Just like other COVID-19 variants, XEC can be transmitted from person to person by respiratory droplets or small airborne particles when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks.
Symptoms for the XEC variant are the same as most other COVID-19 strains and include fever, coughing, sore throat and shortness of breath.
While some people don't display any symptoms, the disease can be serious for older people, people with underlying health conditions and pregnant people, according to the Department of Health.
"At this stage there's nothing to indicate that it's going to cause any different kind of symptoms or presentations than what we've seen with the other similar sub-variants," Dr Griffin says.
"People can have very different presentations … it's one of those things that can cause such a variable illness in so many different people depending on their level of past exposure and immunity and what other conditions they might have."
The Department of Health says wearing a face mask, practising good hygiene and physical distancing can protect you from contracting the virus. Vaccinations also provide protection against severe illness.
How is XEC different from other COVID-19 variants?
Dr Griffin says the merger of the KS 1.1 and KP 3.3 variants have caused a change to the virus's spike protein, which makes the disease more transmissible.
But he says it's too early to know more about XEC's characteristics because scientists are still examining the virus's sequence.
"At the moment, this is a combination of two very significant sub-variants … that's why we've got a change in the spike protein and the growth advantage that we see."
Dr Griffin says while it's likely there will be more COVID-19 variants, people shouldn't get complacent.
"These changes are truly random. One of these sub-variants could, just by sheer chance, become more virulent, cause more severe disease or gain other properties like evading our testing or anti-virals."
"That's why we do need a level of vigilance to continue so we do keep monitoring, we do keep assessing and we do keep responding and that's really why we can't get complacent."
He says it's uncertain whether the variant will cause a "summer wave" of infections, like with Omicron.
"It certainly has the hallmarks of something that could lead to a significant wave but we could also get a new sub-variant any day or any time into the future from here that could account for that."
Do current vaccinations protect you against XEC?
Dr Griffin says changes to the virus can lead to immune evasion, which means that immunity generated from past infections or vaccination can be slightly less effective against the mutated virus.
He says an updated JN.1 COVID-19 vaccination under review by the Theraputic Goods Administration (TGA) will provide good levels of coverage against the new strain because it's a "closely related" sub-variant.
"We still anticipate those vaccines to be highly effective and the biggest determinant of how well they're going to work is how many people get them," he says.
"The JN.1 boosters that hopefully we'll have soon will be really important for protection in our country and we want really high levels of uptake."
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#sars cov 2#coronavirus#still coviding#wear a respirator#Australia#XEC
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
"The first session of the 118th Congress was one of the least productive in the body’s history. Only 22 bills were signed into law this year by the president — by far the lowest total since at least 1993, the first year for which the National Archives have data. (For comparison, the next least productive year during this timespan was in 2013, when 72 bills became law.) Despite the slow year, members nonetheless found time to introduce an abundance of bills relating to the threat of China, which was the focus of hearings in committees ranging from Financial Services to the Judiciary committee, and of legislation concerning everything from fentanyl distribution to TikTok. In 2023, members introduced 616 pieces of legislation that contain a variation of the word “China” — more than 3.5 for every day that Congress was in session on average. That’s already more than any two-year congressional session, except for the 117th Congress (2021-2022; 860 bills) and the 116th (2019-2020; 620 bills), according to a search of the congressional record. One of the few “accomplishments” in Congress this year was the formation of the Select Committee on the Strategic Competition Between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party — which was almost instantly dubbed the “tough on China committee” — in January."[...]
Members of Congress introduced at least nine bills aimed at restricting foreign ownership of agricultural land in the United States. As RS has explained, these efforts are not always logical, even if there are some legitimate national security concerns over China or other nations buying up farmland.[...]
Rep. Andy Ogles (R-Tenn.) and five co-sponsors introduced the “Defund China’s Allies Act” to “prohibit the availability of foreign assistance to certain countries that do not recognize the sovereignty of Taiwan,” aimed at 21 countries in Central America and the Caribbean. The bill argues that the “United States efforts to condemn these countries’ willing diplomatic shift toward a genocidal government is undermined by an incomprehensible adherence to the so-called ‘One China’ policy, on terms dictated by the Chinese Communist Party,” implicitly calling for an end to the policy that has maintained peace in the Taiwan Strait for decades.[...]
bills introduced by Sen. Marco Rubio (R-Fla.), Reps. John Curtis (R-Utah), and Chris Pappas (D-N.H.) [...] would have renamed the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office (TECRO) in Washington, D.C. to the Taiwan Representative Office, because it “better reflects its status as Taiwan’s de facto diplomatic mission to the United States.” That was only one of many bills that were purely symbolic and antagonizing, including one that demanded that Beijing “must be held financially liable for $16,000,000,000,000,” because of its responsibility in the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic and a resolution that declared China to be the biggest threat to freedom in the world. “Whereas it is the opinion of Congress that the Chinese Communist Party is the greatest threat to freedom and to the free world,” reads the text, introduced by Rep. George Santos (R-N.Y.). “Be it Resolved by the House of Representatives (the Senate concurring), That Congress agrees that the Chinese Communist Party is the greatest threat to freedom and to the free world.” That’s the entire resolution.
27 Dec 23
102 notes
·
View notes
Text
Xi Jinping urges steps to ‘protect’ lives as China battles Covid wave
Xi Jinping urges steps to ‘protect’ lives as China battles Covid wave
Chinese President Xi Jinping urged officials on December 26 to take steps to protect lives in his first public remarks on Covid-19 since Beijing dramatically loosened hardline containment measures this month. Chinese President Xi Jinping. (File photo/AP) By Agence France-Presse: Chinese President Xi Jinping urged officials on December 26 to take steps to protect lives in his first public…

View On WordPress
#battles#bf.7 variant#China#Chinese covid cases#chinese president#coronavirus outbreak#Covid#covid wave#Jinping#lives#protect#steps#urges#wave#xi jinping
0 notes
Text
The tulsi gabbard Appointment and The 2024 U.S. Elections Aren't The Only Times donald j. trump and his Russian Asset Republicans Worked With Russians Against United States' Interests: COVID-19, USA Patriot Act/USA Freedom Act Sabotage, The Massive Russian SolarWinds Hack of 33,000 U.S. Government and Private Sector Computer Networks, and Russian 2024 Election Day Interference (compiled from Wikipedia):

In November 2019, a security researcher notified SolarWinds that credentials to a third party FTP server had a weak password of "solarwinds123", warning that "any hacker could upload malicious [code]" that would then be distributed to SolarWinds customers. The New York Times reported SolarWinds did not employ a chief information security officer and that employee passwords had been posted on GitHub in 2019.
December 1, 2019: COVID-19 pandemic: First known human case of Coronavirus disease 2019, in Wuhan, Hubei, China.
December 5, 2019: Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives Nancy Pelosi asks the House Judiciary Committee to begin drafting the articles of impeachment against U.S. President Donald Trump.
December 9, 2019: The World Anti-Doping Agency votes unanimously to ban Russia from international sport for four years for doping offences, meaning it will be excluded from the 2020 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, the 2022 Winter Olympics in Beijing and the 2022 World Cup in Qatar.
December 10, 2019: Democrats in the United States House of Representatives announce formal charges against President Donald Trump, accusing him of abusing power and "obstructing Congress"; he becomes the third U.S. president in history to face impeachment.
December 18, 2019: The U.S. House of Representatives approves two articles of impeachment against President donald trump, making him the third president to be impeached in the nation's history.
December 29, 2019: The Taliban's ruling council agrees to a temporary cease-fire in Afghanistan, opening a door to a peace agreement with the United States.
In January and February 2020, U.S. intelligence agencies delivered over a dozen classified warnings in the President's Daily Brief about COVID-19, including its potential to inflict severe political and economic damage. President Donald Trump typically did not read daily briefs and often has "little patience" for oral summaries, The Washington Post reported. Each brief was also shared with other officials in the administration. The Office of the Director of National Intelligence, which produces the President's Daily Brief, denied that there were repeated mentions of COVID-19.
On January 8, 2020, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released a health advisory regarding an outbreak of pneumonia in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China, which was being caused by a yet-unidentified virus.
January 16, 2020: The first impeachment trial of the President of the United States, Donald Trump, begins in the U.S. Senate.
On January 27, 2020, Anthony Fauci, head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, predicted that "things are going to get worse before they get better". Three days later, Fauci stated that the COVID-19 outbreak "could turn into a global pandemic".
On February 10, 2020, Trump stated that "a lot of people think that [COVID-19] goes away in April with the heat … Typically, that will go away in April" (later, on April 3, he denied ever having given "a date" for the departure of the virus)
On February 13, 2020, CDC director Robert Redfield contradicted Trump, saying that the "virus is probably with us beyond this season, beyond this year". Redfield also predicted that it "will become a community virus at some point in time, this year or next year".
On February 16, 2020, Anthony Fauci warned that it was not necessarily true that COVID-19 would "disappear with the warm weather."
February 25, 2020, was the day that the CDC first warned the American public to prepare for a local outbreak. That day, Nancy Messonnier, head of the CDC's National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, said that "We are asking the American public to work with us to prepare for the expectation that this is going to be bad." Messonnier predicted that "we will see community spread in this country", and it was only a matter of time. As a result, "disruption to everyday life might be severe". Messonnier stated that the CDC is preparing, and "now is the time for hospitals, schools and everyday people to begin preparing as well."
On February 25, 2020, Anthony Fauci declared that given how COVID-19 was spreading in other nations, it was "inevitable that this will come to the United States" as well. On February 26, CDC Director Robert Redfield said it would be "prudent to assume this pathogen will be with us for some time to come".
On February 26, 2020, Trump contradicted Messonnier, stating: "I don't think it's inevitable" that a U.S. outbreak would occur, "It probably will, it possibly will … Whatever happens, we're totally prepared." Trump additionally declared that the number of infected was "going very substantially down, not up".
On February 27, 2020, The chairman of the Senate Intelligence Committee, Richard Burr, who helped to write the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Act (PAHPA), which forms the framework for the federal response, warned a private group of his constituents that COVID-19 is much more aggressive in its transmission than anything that we have seen in recent history, and is probably more akin to the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic. "There will be, I'm sure, times that communities, probably some in North Carolina, have a transmission rate where they say, 'Let's close schools for two weeks. Everybody stay home,' We're going to send a military hospital there; it's going to be in tents and going to be set up on the ground somewhere, It's going to be a decision the president and DOD make."
On February 27, 2020, Trump said of the virus: "It's going to disappear. One day it's like a miracle, it will disappear. And from our shores, you know, it could get worse before it gets better. Could maybe go away. We'll see what happens. Nobody really knows." Also on February 27, Trump declared that the risk to the American public from COVID-19 "remains very low".
February 27, 2020 stock market crash: Triggered by fears of the spreading of COVID-19, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) plunges by 1,190.95 points, or 4.4%, to close at 25,766.64, its largest one-day point decline at the time. This follows several days of large falls, marking the worst week for the index since the 2007–2008 financial crisis.
On February 29, 2020, Trump said that "additional cases in the United States are likely", but "there's no reason to panic at all." When a reporter asked Trump: "How should Americans prepare for this virus?" Trump answered: "I hope they don't change their routine".
February 29, 2020: A conditional peace agreement is signed between the United States and the Taliban. The U.S. begins gradually withdrawing combat troops from Afghanistan on March 10.
On March 4, 2020, donald trump appeared on Fox News's Hannity by phone, where he claimed a 3.4% mortality rate projected by the World Health Organization (WHO) was a "false number", and stated his "hunch" that the true figure would be "way under 1%". Trump also predicted that many people infected with COVID-19 would experience "very mild" symptoms, "get better very rapidly" and thus they "don't even call a doctor". Thus, there may be "hundreds of thousands of people that get better just by, you know, sitting around and even going to work—some of them go to work, but they get better."
From March 6 to March 12, 2020, donald trump stated on four occasions that the coronavirus would "go away". On March 10, Surgeon General Jerome Adams stated that "this is likely going to get worse before it gets better."
March 2020: The nightmare of empty grocery shelves begins. Stores capping/limiting purchases.
By March 11, 2020, the virus had spread to 110 countries, and the WHO officially declared a pandemic. The CDC had already warned that large numbers of people needing hospital care could overload the healthcare system, which would lead to otherwise preventable deaths. Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Anthony Fauci said the mortality from COVID-19 was ten times higher than the common flu. By March 12, diagnosed cases of COVID-19 in the U.S. exceeded a thousand. Trump declared a national emergency on March 13. On March 16, the White House advised against any gatherings of more than ten people. Three days later, the United States Department of State advised U.S. citizens to avoid all international travel.
The USA Freedom Act, which became law on June 2, 2015, reenacted the expired USA Patriot Act sections through 2019. However, Section 215 of the law was amended to disallow the National Security Agency (NSA) to continue its mass phone data collection program. Instead, phone companies will retain the data and the NSA can obtain information about targeted individuals with a federal search warrant.
On August 14, 2019, the outgoing Director of National Intelligence sent a letter to Congress stating the Trump Administration's intention to seek permanent extension of the provisions of FISA that under the terms of the USA FREEDOM Act are scheduled to expire on December 15, 2019, namely the "lone wolf" authority allowing surveillance of a suspected terrorist who is inspired by foreign ideology but is not acting at the direction of a foreign party, the roving wiretap authority regarding surveillance of a terrorist who enters the United States and the authority to allow the Federal Bureau of Investigation to obtain certain business records in a national security investigation, as well as the call detail records program undertaken by the NSA. In reference to the latter authority, the letter announced that "The National Security Agency has suspended the call detail records program that uses this authority and deleted the call detail records acquired under this authority."
Jurisdiction over the reauthorization of the expiring FISA provisions is shared by the Judiciary and Intelligence committees in the U.S. Senate and the U.S. House of Representatives; the House Committee on the Judiciary and the Senate Committee on the Judiciary held separate public hearings on the reauthorization in September 2019 and November 2019, respectively. Opposition to the call detail records program has led to some Congressional demands that the authority for the program not be renewed. Additional complications hindering reauthorization arose from a report of the US Department of Justice Inspector General finding fault with certain FISA applications in connection with the 2016 presidential campaign, which led some members of Congress to insist on reforms to FISA as a condition of reauthorizing the expiring USA FREEDOM Act provisions.With Congressional attention focused on dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States in 2020, the House of Representatives passed a long-term extension of the USA FREEDOM Act on March 11, 2020, just four days before the scheduled expiration of the Act on March 15, 2020, by a wide, bipartisan margin that kept the protections of the Act largely the same. Two months later, in May of 2020, the Senate passed an extension of the Act by an 80-16 vote that expanded some privacy protections, but the Senate version did not include protection of Americans’ internet browsing and search histories from warrantless surveillance, which was proposed by Sens. Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) and Steve Daines (R-Mont.) and failed by one vote.
According to former KGB major Yuri Shvets, donald trump became the target of a joint Czech intelligence services and KGB spying operation after he married Czech model Ivana Zelnickova and was cultivated as an "asset" by Russian intelligence since 1977: "Russian intelligence gained an interest in Trump as far back as 1977, viewing Trump as an exploitable target." Luke Harding writes that documents show Czechoslovakia spied on donald trump during the 1970s and 1980s, when he was married to Ivana Trump, his Czechoslovakia-born first wife. Harding writes that the Czechoslovakian government spied on donald trump because of his political ambitions and notability as a businessman. It is known that there were close ties between Czechoslovakia's StB and the USSR's KGB. Harding also describes how, already since 1987, the Soviet Union was interested in Trump. In his book Collusion, Harding asserts that the "top level of the Soviet diplomatic service arranged his 1987 Moscow visit. With assistance from the KGB." Then-KGB head Vladimir Kryuchkov "wanted KGB staff abroad to recruit more Americans". Harding proceeds to describe the KGB's cultivation process, and posits that they may have opened a file on Trump as early as 1977, when he married Ivana. "According to files in Prague, declassified in 2016, Czech spies kept a close eye on the couple in Manhattan, … [with] periodic surveillance of the trump family in the United States."
donald j. trump and His Republican Allies Allowed the USA PATRIOT ACT/FREEDOM ACT to Expire on March 15, 2020 and They Didn't Reinstate It until May of 2020.
March 2020: SolarWinds's Orion software hotfixes were released to 33,000 Orion customers.Hackers acquired superuser access to SAML token-signing certificates. This SAML certificate was then used to forge new tokens to allow hackers trusted and highly privileged access to networks. The attack used a backdoor in a SolarWinds library; when an update to SolarWinds occurred, the malicious attack would go unnoticed due to the trusted certificate. APT29, aka Cozy Bear, working for the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), was reported to be behind the 2020 attack. Victims of this attack include the cybersecurity firm FireEye, the US Treasury Department, the US Department of Commerce's National Telecommunications and Information Administration, as well as the US Department of Homeland Security. Prominent international SolarWinds customers investigating whether they were impacted include the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the European Parliament, UK Government Communications Headquarters, the UK Ministry of Defence, the UK National Health Service (NHS), the UK Home Office, and AstraZeneca.
December 13, 2020: SolarWinds begins notifying customers, including a post on its Twitter account, “SolarWinds asks all customers to upgrade immediately to Orion Platform version 2020.2.1 HF 1 to address a security vulnerability.”
December 15, 2020 SolarWinds Victims named and timeline moves back — Wall Street Journal reported that the U.S. Commerce and Treasury Departments, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), the National Institutes of Health, and the State Department were all affected. Various security officials and vendors expressed serious dismay that the attack was more widespread and began much earlier than expected. The initial attack date was now pegged to sometime in March 2020, which meant the attack had been underway for months before its detection.
December 17, 2020: New SolarWinds victims revealed — The Energy Department (DOE) and National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA), which maintains the U.S. nuclear weapons stockpile, were publicly named as victims of the attack.
On December 21, 2020, Attorney General William Barr, Secretary of State Mike Pompeo, the FBI, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, or CISA, and the Office of the Director of National Intelligence all agreed that Russia was engaged in “a significant and ongoing cybersecurity campaign” against the United States. Russian asset, donald j. trump, immediately replied: “The Cyber Hack is far greater in the Fake News Media than in actuality,” Trump wrote. “I have been fully briefed and everything is well under control. Russia, Russia, Russia is the priority chant when anything happens because Lamestream is, for mostly financial reasons, petrified of discussing the possibility that it may be China (it may!).”
March 16, 2020: stock market crash: The the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) falls by 2,997.10, the single largest point drop in history and the second-largest percentage drop ever at 12.93%, an even greater crash than Black Monday (1929). This follows the U.S. Federal Reserve announcing that it will cut its target interest rate to 0–0.25%.
On March 19, 2020, donald trump told journalist Bob Woodward that he was deliberately downplaying the risk when communicating with the public. "I wanted to always play it down," Trump said. "I still like playing it down, because I don't want to create a panic."
On March 24, 2020, donald trump argued that: "We lose thousands and thousands of people a year to the flu … But we've never closed down the country for the flu." On March 27, he stated: "You can call it a flu. You can call it a virus. You know you can call it many different names. I'm not sure anybody even knows what it is."
On March 24, 2020, donald trump declared that "we begin to see the light at the end of the tunnel"; a day later the U.S. surpassed 1,000 COVID-19 deaths.
Throughout March and early April, several state, city, and county governments imposed "stay at home" quarantines on their populations to stem the spread of the virus. By March 26, The New York Times data showed the United States to have the highest number of known cases of any country. By March 27, the country had reported over 100,000 cases.
From March 30 to April 7, 2020, Trump stated on four occasions that COVID-19 would "go away".
On March 31, 2020, contradicting his many previous comparisons of COVID-19 to the flu, Trump said: "It's not the flu … It's vicious". When reporters asked him if his initial dismissive comments on the virus had misled Americans, he replied: "I want to give people a feeling of hope. I could be very negative … You know, I'm a cheerleader for the country." Asked further if he had known—despite his claims that the outbreak was under control—that the situation would turn out so severe, Trump replied: "I thought it could be. I knew everything. I knew it could be horrible, and I knew it could be maybe good."
On November 5, 2024, during the official Election Day, several non-credible bomb threats that originated from Russia briefly disrupted voting in two polling places in Fulton County, Georgia. Both re-opened after about 30 minutes. Republican Georgia Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger said Russian interference was behind the Election Day bomb hoaxes. In a statement, the FBI said it was aware of non-credible bomb threats to polling locations in several states, with many of them originating from Russian email domains. The bomb threats were solely made against Democratic-leaning areas. On the same day, U.S. federal officials again reported that Russian sources were actively engaged in "influence operations", citing disinformation in specific videos that falsely claimed Kamala Harris had taken a bribe and false news stories about the Democratic Party and election fraud in Georgia.
On November 8, 2024 it was reported that one of the Russian email addresses behind Election Day bomb threats was used in June 2024 bomb threats targeting LGBTQ+ events in Massachusetts, Minnesota and Texas.
If you're an American who wants this matter and the anti-American traitors responsible investigated by the U.S. Department of Justice, please contact Democratic Leaders Schumer and Jeffries, Marc Elias and Democracy Docket, and Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics in Washington regarding enforcing donald j. trump's insurrectionist disqualification and electing Kamala Harris as the 47th President of the United States. If you want this matter investigated and prosecuted, the best person to do it is an experienced criminal prosecutor sitting as the U.S. President.
#2024 presidential election#2024 election#election 2024#kamala harris#harris walz 2024#donald trump#trump vance 2024#trump 2024#president trump#trump#republicans#gop#evangelicals#democrats#us elections 2024#us elections#us election 2024#us politics#politics#american politics#uspol
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello, dropping by to ask if you have any reading recomendation wrt the sinophobic history of linking flus to China? It's been on my mind given covid was dubbed as "the wuhan virus" or more broadly as a Chinese disease; but I also seem to recall that in the 2010s, outbreaks of aviary flu were also characterized as Chinese outbreaks. It interests me given the current strains of aviary flu ripping through USA poultry and cattle...
Thank u in advance
yes, as a good starting point i would recommend the following bibliographic essay by Robert Peckham and Mei Li: "Epidemic Histories in East Asia." this is open-access and intended to give a reader some footing in the secondary literature, with a particular focus on China; the footnotes and bibliography here will give you a lot more sources to look at, and the essay is mostly just a reading guide for those. Peckham & Li cover the 20th century flu pandemics and the imagining of (southern) China as a global epicenter of influenza, as well as the longer history of sinophobic colonial concerns about leprosy, smallpox, cholera, and plague, and the general narrative of contagious disease as inevitably moving east -> west and south -> north.
the special issue of IsisCB that Peckham & Li's article comes from is also entirely free and open-access, and has several other articles that touch on disease narratology and the western/global northern conception of pandemics as a foreign danger emerging from the global south/east. additionally, in the last few decades there has been a wave of scholarship on similar narratives specifically concerning the plague; if that's interesting to you I would recommend Monica Green's work and Nükhet Varlık's (including but not limited to her essay in the above special issue). most epidemic and pandemic diseases have similar colonial and imperial narratives attached to them so there's lots to poke around in here (eg, French medical views of cholera as a climate-linked disease originating from India; but we would be here all day if I tried to be exhaustive).
wrt flu and China specifically: Robert Peckham has also written more about this in the Journal of Global History 15.3 (DOI 10.1017/S1740022820000224). additionally there is this article by Lachlan Strahan on Australia and the 'Asian flu' epidemic of 1957 in Australian Historical Studies 26.103, though it's a bit dated now (DOI 10.1080/10314619408595959).
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
H5N1: What to know before fear spreads
What is H5N1?
H5N1 is a 1996 strain of the Spanish or Avian Flu first detected in Chinese birds before spreading globally across various avian species. H5N1 is similar to H1N1, but spreads slower and has a much higher mortality rate.
H5N1 may also be referred to as Influenza A. The American Association of Bovine Practitioners has seen fit to rename H5N1 to Bovine Influenza A Virus, or BIAV, and are encouraging others to use the same terminology.
I would not be surprised if the colloquial name among the public becomes Bovine Flu or American Flu in the coming months, and may be referred to as the Chinese Flu by the same folks who took the spark of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic as an excuse to be publicly racist to East Asian people without social repercussions.
BIAV is a virus, meaning that it is a (probably) non-living packet of self-replicating infectious material with a high rate of mutation. BIAV is structured similarly to SARS-CoV-2, having a packet of infectious material encased in a spherical shell with a corona, or crown, of proteins that can latch to living cells to inject RNA.
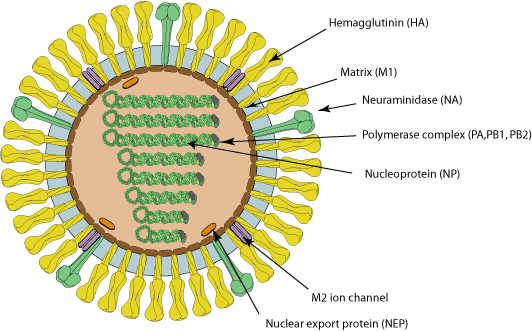
Image source with interactive model: ViralZone - H5N1 subtype
What is the history of BIAV?
In 1996 and 1997, an outbreak of BIAV occurred among poultry and infected 18 people in Hong Kong, 6 of which died. This seemingly isolated incident then infected ~860 people with a >50% death rate.
At the time, BIAV was known as Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza, or HPAI, and killed nearly 100% of chickens within a 48 hour period.
From 2003 to 2005, continual outbreaks occurred in China and other East Asian countries, before spreading to Cambodia, the Netherlands, Thailand, and Vietnam.
From 2014 to 2016, it began being detected in American fowl, as well as mutating the H5N6 (lethal in birds, no human to human transmission) and H5N8 (largely spread through turkeys, ducks had immunity) viruses.
BIAV has since evolved into a clade known as 2.3.4.4b, and was first detected in 2021 in wild American birds. This then caused outbreaks in 2022 among wild and domesticated birds (such as chickens) alike, but was largely being overshadowed by the pressing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic at the time.
From 2022 to 2023, it was observed to be spreading among various mammals, including humans. Now, in 2024, we're having the most concerning rapid outbreak of BIAV since 2003.
BIAV is known to spread from mammal to mammal, particularly between cows and humans. BIAV may also be spread from cow to cow (highly likely, but not confirmed - this is likely the reason the virus has spread to Idaho from Texan cattle), and is known to be lethal to domestic cats and birds within 48 hours.
How does BIAV spread?
BIAV spreads through fomites - direct contact with infected animals or infected surfaces and then touching parts of your face or other orifices - as well as through airborne particulates, which may be inhaled and enter the sinuses and lungs.
BIAV is known to spread through:
Asymptomatic Ducks, geese, swans, various shorebirds
Symptomatic, may be lethal Foxes, bears, seals, sea lions, polar bears, domestic cats, dogs, minks, goats, cows, (potentially human to human, but unconfirmed - there have only been 8 potential human to human cases in 2024).
How can I protect against BIAV?
As BIAV is a type of Influenza A, existing protocols should do fine.
Current recommendations are to wash your hands vigorously after interacting with birds (I would also recommend doing this with mammals), avoid touching your face or other open orifices, and wear N95 masks.
Avoid sick or dead animals entirely - I would also recommend reporting them to your local Animal Control or veterinary centre and warning them about the infection risk. People who work with animals are recommended to also wear full PPE such as N95 masks, eye protection, gloves, and partake in vigorous hand washing.
If you suspect you've caught BIAV, seek medical attention immediately. Existing medications such as oseltamivir phosphate, zanamivir, peramivir, and baloxavir marboxil can reduce BIAV's ability to replicate.
Standard flu shots will not protect against BIAV. Remember - symptoms of BIAV may not manifest for between 2 to 8 days, and potentially infected people should be monitored for at least 10 days.
How far has BIAV spread?
BIAV is currently a global virus, though the current infection location of note is the United States.
Image Key: Dark red - Countries with humans, poultry and wild birds killed by H5N1 Deep red - Countries with poultry or wild birds killed by H5N1 and has reported human cases of H5N1 Light red - Countries with poultry or wild birds killed by H5N1
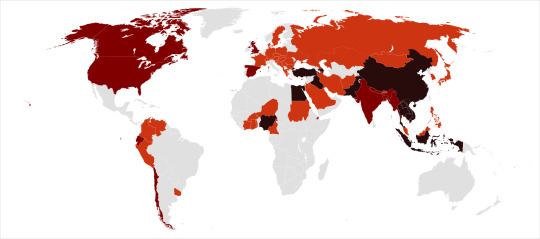
Image source: Wikipedia - Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 - File: Global spread of H5N1 map
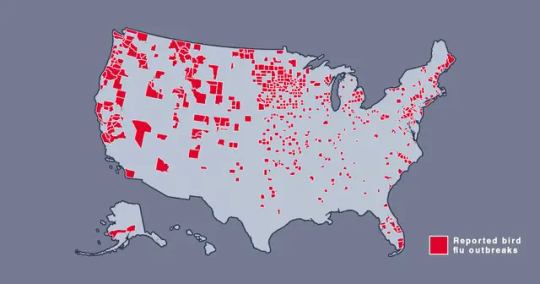
Image source: Metro.co.uk - Map shows where bird flu is spreading in US amid new warning - File: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s H5N1 bird flu detections map across the United States
Should I be afraid?
You needn't be afraid, just prepared. BIAV has a concerningly high lethality, but this ironically culls its spread somewhat.
In the event human to human transmission of BIAV is confirmed, this will likely mainly affect marginalized communities, poor people, and homeless people, who are likely to have less access to medical care, and a higher likelihood of working in jobs that require frequent close human contact, such as fast food or retail jobs.
Given the response to SARS-CoV-2, corporations - and probably the government - may shove a proper response under the rug and refuse to participate in a full quarantine, which may leave people forced to go to work in dangerous conditions.
If this does spread into an epidemic or pandemic, given our extensive knowledge about Influenza, and the US having a backup vaccine for a prior strain of H5N1, a vaccine should be able to be developed relatively quickly and would hopefully be deployed freely without charge - we won't have to worry about a situation like The Stand.
Wash your hands, keep clean, avoid large social gatherings where possible, wear an N95 mask if you can afford them (Remember: Cloth masks are the least protective, but are better than nothing. If you can't afford N95 masks, I recommend wearing a well-fitted cloth mask with a disposable face mask over it to prevent pneumonia from moisture buildup in the disposable mask), support the disabled, poor, and homeless, and stay educated.
We can do better this time.
Further things to check out:
YouTube: MedCram - H5N1 Cattle Outbreak: Background and Currently Known Facts (ft. Roger Seheult, M.D.)
Wikipedia - Influenza A virus subtype H5N1
Maine.gov - Avian Influenza and People
CDC.gov - Technical Report: Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Viruses
Wikipedia - H5N1 genetic structure
realagriculture - Influenza infection in cattle gets new name: Bovine Influenza A Virus (BIAV)
#H5N1#bird flu#avian flu#bovine flu#BIAV#pandemic#epidemic#COVID 19#coronavirus#spanish flu#long post#text post#no id#undescribed#news#politics#us news#us politics#american news#american politics#world news#global news#global politics#world politics#lgbt#lgbtq#queer#trans#communist#socialist
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
🚨HOLY… SHIT…🚨
Nathan Wolfe, Virologist, Metabiota founder, and Epstein associate, was a consultant for the film “Contagion” in 2011.
The film is about a new virus that starts at a wet market in China, then rapidly spreads worldwide killing millions…
Sound familiar?
This is the same guy who was hunting down animal viruses all over the world, was studying bat coronaviruses in Ukraine for 5 years PRIOR to the C19 outbreak, and was accused by the Russians of creating Covid-19 in Ukraine.
He helped make this movie… which was essentially fear porn to scare the American public about potential future pandemics.
If “Predictive Programming” is real… this is the proof.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is what Liberal insanity looks like.
youtube
If you or your loved one is a Democrat or feeling a bit more left then left-of-center, you may be suffering from DNC - Democratic Neurological Corruption. Seek professional help before it becomes TDS - Trump Derangement Syndrome. Sufferers of DNC and TDS may become violent, schizophrenic, and delusional, becoming a danger to themselves and everyone else.

Sufferers of TDS hallucinate and express delusions of persecution after a brief period of a DNC induced Christ Complex. These may be followed by random repetitive chanting and frothing at the mouth. Similar to COVID, it is spread through close proximity and is believed to have been released through a lab accident through a Communist bat from a swamp in China. If you encounter a person afflicted with TDS, take caution, evacuate the area, and notify the local law enforcement agency of the deranged individual.

One should not attempt to interact with the individual nor counteract their rantings with real facts. This may lead to an outbreak of others in close proximity. Liberals tend to form packs and congregate in mindless groups. Be vigilant and avoid situations where one or more white people in expensive clothing appear to be accompanied by a single person of color. The person of color may mouth the words, "Help me" or respond with the international sign of distress. There is nothing you can do for them, it's already too late and they have become a carrier.

Remember: Only you can take personal responsibility into your own hands and cure this plague by voting Republican this election year.

#just azure things#just azzy things#wicked bitch of the midwest#what the hell is wrong with you#you got some wicked tastes girl#dankmark#dank#youtube#shit azzy says#shit azure says#tds#dnc#biden administration#president biden#democratic party#hunter biden#trump derangement syndrome#trump 2024#trump#2024 presidential election#2024 election#donald trump#maga#drain the swamp#rnc#Youtube
37 notes
·
View notes
Text

A revolutionary “pessimistic” postscript in times of coronavirus
“The outbreak of the new strain of coronavirus (COVID-19), which has wrought havoc in China since the end of last year, has surged over borders and impacted the rest of the world, and with it, the imminent economic crisis has but further advanced. The world economy is in full-on crisis, the administrators of power are pending on immense financial relief, the bourgeoisie are beginning to close factories and lay off employees using the lucky pretext of the “quarantine” as excuse. The disaster is immanent. Nevertheless, it’s important to know that the monetary losses don’t signify the fall of the capitalist system. Capitalism will seek at every moment to restructure itself on the basis of austerity measures imposed on proletarians in order to palliate all the catastrophic consequences that it will bring along with it. And this is due to the fact that the “blows” that capitalism has been dealt due to these phenomena are simply losses in its rate of profit, but those losses don’t at all change its structure or its essence, meaning the social relations that allow it to remain standing: the commodity, value, the market, exploitation and wage labor. In fact, it’s in these structures that capitalism most reaffirms its necessities: sacrificing millions of human beings to the favor of economic interests, making the polarization between classes sharpen and revealing more forcefully in what position the dominant class is to be found, who will use all the efforts in their reach in order to preserve this state of things.
[…]
The ever-more contradictions heightened contradictions of this mode of production (crisis, war, pandemics, environmental destruction, pauperization, militarization), which exasperate our conditions of survival, won’t clear the way either mechanically or messianically for the end of capitalism. Or better said, such conditions, although they will be fundamental, won’t suffice. Because for capitalism to reach its end, it���s imperative for there to be a social force, antagonistic and revolutionary that manages to direct the destructive and subversive character towards something completely different from what we know and experience now.
If we want it or not, we can’t let a question as important as the revolution to drift aimlessly, to leave it to luck. It’s necessary to experience the resolution of this problem on the basis of the organization of tasks that can go on to present themselves, that’s to say, the grouping for the appropriation and defense of the most immediate necessities (not paying debts, rent, or taxes), but also, the rupture from all the dreams and mirages that carry us to manage the save miseries behind another facade.
[…]
It’s not necessary to wait for the dystopia or the hollywoodesque scenes of apocalypse, because these are already materially manifesting in different parts of the globe, and in fact they greatly surpass any attempt at representation by cinematic fiction.
The current pandemic of COVID-19 is one more stage in the degradation to which this society of commodity production brings us.
A stage before which it is reaffirmed that the true future only hangs from two strings:
Communist revolution or to perish in the twilight!”
Contra la Contra n.3 Collapse of the capitalist system? A few notes on current events. Mexico City March 2020
#freedom#ecology#climate crisis#anarchism#resistance#community building#practical anarchy#practical anarchism#anarchist society#practical#revolution#daily posts#communism#anti capitalist#anti capitalism#late stage capitalism#organization#grassroots#grass roots#anarchists#libraries#leftism#social issues#economy#economics#climate change#climate#anarchy works#environmentalism#environment
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved in our archive
By Tulio de Oliveira
Dr. Oliveira is the director of the Centre for Epidemic Response and Innovation in South Africa.
As a virus scientist in South Africa, I’ve been watching with dread as H5N1 bird flu spreads among animals in the United States. The pathogen poses a serious pandemic threat and has been detected in over 500 dairy herds in 15 states — which is probably an undercount. And yet, the U.S. response appears inadequate and slow, with too few genomic sequences of H5N1 cases in farm animals made publicly available for scientific review.
Failure to control H5N1 among American livestock could have global consequences, and this demands urgent attention. The United States has done little to reassure the world that it has the outbreak contained.
The recent infection of a pig at a farm in Oregon is especially concerning as pigs are known to be “mixing bowls” for influenza viruses. Pigs can be infected by both avian and human influenza viruses, creating a risk for the viruses to exchange genetic material and potentially speed up adaptation for human transmission. The H1N1 pandemic in 2009 was created and spread initially by pigs. Beyond the risks to its own citizens (there are over 45 cases of people in the United States getting the virus in 2024), the United States should remember that the country where a pandemic emerges can be accused of not doing enough to control it. We still hear how China did not do enough to stop the Covid-19 pandemic. None of us would want a new pandemic labeled the “American virus,” as this could be very damaging for the United States’ reputation and economy.
The United States should learn from how the global south responds to infectious diseases. Those of us working in the region have a good track record of responding to epidemics and emerging pandemics, and can help the United States identify new virus strains and offer insights into how to control H5N1. This knowledge has not come easily or without suffering; it has developed from decades of dealing with deadly diseases. We’ve learned one simple lesson: You need to learn your enemy as quickly as possible in order to fight it.
We did this during Covid. In November 2021, my colleagues and I, and others in Botswana, discovered the Omicron variant. We quickly and publicly warned the world that it could rapidly spread. This kind of transparency is not always easy because it can come at large economic cost. For example, after we shared our Omicron discovery, countries around the world imposed travel bans on South Africa ahead of December holidays, spurring backlash. Our team received death threats, and we needed security for our labs. One estimate suggests South Africa lost $63 million in canceled bookings from December to March.
But it was the right thing to do. That’s why it’s so frustrating that genomic sequences of H5N1 animal cases in the United States are not quickly made available. Sharing genomes of virus samples immediately is crucial for understanding the threat and giving the world time to prepare, including developing antivirals and vaccines. Rwanda, for example, was recently bold enough to go public with the detection of the deadly Marburg virus. Health responders there worked around the clock, and within about a month, they seem to have controlled the outbreak. Other countries in Africa have similarly and openly shared data about the spread of Mpox.
I’ve worked for decades with American scientists, and this summer I toured many of the country’s top scientific research institutions and was a speaker at one of its largest annual virology meetings. I know how flabbergasted many American scientists are about the country’s slow response to the H5N1. One highly respected American virologist, David O’Connor, told me that “it seems that the United States is addicted to gambling with H5N1. But if you gamble long enough, the virus may hit a jackpot.” A jackpot for the virus would fuel a global pandemic.
It is time to respond forcefully to this threat. The world’s scientists are here to help, in the same way as the United States has helped us so many times. Countries need to continue to support one another; we need an international scientific and medical force that can work together to respond to new epidemics and potential pandemics, including diagnosing and genetically analyzing every single sample of H5N1.
I understand that it’s not easy to persuade businesses, such as the meat and dairy industries, to allow the testing of all of their animals and staffs, and to make that data public quickly. But I also know that in the end, doing so protects lives, lessens economic damage and creates a safer world.
The world cannot afford to gamble with this virus, letting it spread in animals and hoping it never sparks a serious outbreak — or crossing our fingers that its effects won’t be serious in people. Time will tell. I hope we are not watching the start of a new pandemic unfold, with both the American and the international communities burying our heads in the sand rather than confronting potential danger.
19 notes
·
View notes