#Amino Energy and Energy Supplements
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Spirulina powder is a nutrient-dense superfood that is high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Rich in protein, it boosts vitality and aids in muscle growth and repair. Spirulina also helps with heart health, cleansing, and immune system boosting by reducing cholesterol levels. Its high antioxidant content also reduces irritation illnesses, prevents oxidative stress, and enhances general health. Drinks, beverages, and foods all benefit from the inclusion of spirulina powder, which gives you an easy way to increase your daily nutrient intake. Please visit our website or amazon page to explore our organic supplements products.
#natural#organic#all natural#spirulina#spirulina powder#algae supplement#antioxidants#detox supplement#energy boost#green powder#immuneboost#nutrient-rich#organic spirulina#pure&organic#superfood#veganproduct#plant-based nutrition#healthy life style#weight management#essential amino acids#spirulina benefits#natural supplement#raw spirulina#digestive health#sustainable food#brain health#metabolism support#green super food
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Text
Amino Acid Analyzer
Labtron Amino Acid Analyzer is an automatic unit comprised with host and post-column derivatization system, (HPLC) system is designed with meticulous attention to detail, offering a pulsation rate of less than 1% or 0.1 MPa and a versatile flow rate ranging from 0.001 to 10 ml/min with an impressive flow accuracy of ±0.2%.The system is robust, with a maximum withstand voltage of 9000 Psi,and includes a built-in four-channel online vacuum degassing machine for efficient solvent degassing.Additionally, it features automatic cleaning of the plunger rod and anti-salt precipitation functionality, enhancing reliability and maintenance ease.

0 notes
Text
Essential Amino Acids: The Building Blocks for Optimal Health and Wellness

What are Essential Amino Acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. Protein-rich foods like meat & eggs are excellent sources of amino acids. Certain amino acids are also taken as supplements by some people looking for a natural way to improve athletic performance, muscle growth and recovery.There are over 20 different amino acids, and 8 of them cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet. These are called the "Essential Amino Acids," which include isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine—all of which are essential to human health, athletic performance, and general well-being. These essential amino acids play important roles in various processes in the body, including protein synthesis, immune function, and hormone regulation.
In this blog, we will explore and focus on the benefits of essential amino acids and how they can support optimal health and performance. From improved muscle building and recovery to better mental clarity and energy, essential amino acids offer a wide range of benefits that cannot be ignored. So if you want to feel your best and perform at your peak, read on to learn more about the power of essential amino acids!
1. Protein Synthesis
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in the synthesis of proteins, which are needed for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues and organs. When you consume protein, your body breaks it down into individual amino acids, which are then used to build and repair tissues in the body. This process is especially important for athletes, as exercise can cause microtears in muscle tissue. Getting enough protein and essential amino acids can help repair these tears and promote muscle growth and recovery. They also help make enzymes, hormones, and other substances that your body needs to function well.
2. Energy Production
Essential amino acids are used by the body to produce energy. When the body needs energy, it breaks down stored fats and sugars and uses them as fuel. Amino acids can also be used as an energy source, especially during prolonged exercise or when the body is in a fasting state primarily through a process called gluconeogenisis. However, it is important to note that ATP*, glycogen*, and fats are the primary sources of energy for the body, and a diet that includes a variety of micronutrients is important for overall health and energy production.
*ATP is a substance present in all living cells that provides energy for many metabolic processes.
*Glycogen is a form of glucose, a source of energy that your body stores primarily in your liver and muscles.
3. Immune System Function
Essential amino acids are necessary for the proper functioning of the immune system and are involved in the production of antibodies, immune cells, and other immune system components. For example, the amino acid lysine has been shown to support immune system function by inhibiting the replication of viruses and helping to reduce inflammation. Supplements with lysine are becoming widely recognized as a natural aid to improving the body's immune system. Additionally, other essential amino acids such as tryptophan and arginine have been shown to have immune-boosting effects.
4. Brain Function
Essential amino acids can help with brain function in several ways. They are crucial for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain and play a vital role in mood, cognition, and behavior. According to ��Lieberman, U.S. Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, the central nervous system requires a number of amino acids found in protein foods. Amino acids such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and arginine are used by the brain for the synthesis of various neurotransmitters and neuromodulators.
Essential amino acids also play a role in the development and maintenance of brain cells, including neurons and glial cells. They are involved in the production of proteins that are essential for brain function, such as myelin, which is a protective layer around nerve fibers that helps with the transmission of nerve impulses. Additionally, essential amino acids have been shown to have a positive effect on mood and cognitive function, possibly due to their role in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. Overall, maintaining an adequate intake of essential amino acids is important for optimal brain function and overall health.
5. Heart Health
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in maintaining the proper function of the cardiovascular system by helping to regulate blood pressure and heart rate, as well as aiding in the production of proteins that are necessary for healthy heart function. Some specific essential amino acids that may be particularly beneficial for heart health include arginine, which helps to dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow, and taurine, which helps to regulate heart contractions and maintain electrolyte balance in the body. Additionally, consuming a diet rich in essential amino acids may help to lower the risk of developing certain cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension and coronary artery disease.
6. Muscle Growth and Repair
Essential amino acids are essential for the growth and repair of muscles. They are involved in the production of collagen, which is a protein that helps to hold muscles together while also helping to reduce muscle breakdown during exercise or injury. In addition, essential amino acids stimulate the production of hormones, such as insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and leucine in particular, increases MTOR signaling leading to higher MPS - muscle protein synthesis. Both are very crucial for muscle growth. Therefore, adequate intake of essential amino acids is important for optimizing muscle growth and repair.
7. Hormone Production
Some essential amino acids, such as tryptophan, tyrosine, and lysine, are precursors for the synthesis of various hormones, including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, thyroid hormones, and growth hormone. These hormones play important roles in various bodily functions, including mood, energy, metabolism, and growth. Therefore, sufficient intake of essential amino acids is important for maintaining proper hormone balance and function.
8. Bone Health
Essential amino acids play a crucial role in bone health. They help to form and maintain bone tissue by providing the building blocks for bon collagen and other bone proteins. These amino acids also help to regulate bone metabolism and promote bone formation. Essential amino acids, such as lysine and methionine synthesize collagen, a major component of bone tissue, while arginine and histidine have been shown to have a positive effect on bone growth and repair. Essential amino acids also help to prevent bone loss and osteoporosis by improving bone density and strength. It is important to consume a high protein diet that includes all essential amino acids to support optimal bone health.
9. Skin Health
Certain key and essential amino acids can help with skin health by supporting the synthesis of proteins that are important for maintaining the structure and function of the skin. Lysine synthesizes collagen, a protein that helps to maintain the structural integrity of the skin; methionine synthesizes keratin, a protein that helps to protect and strengthen the skin; histidine synthesizes histamine, a chemical that helps to regulate inflammation in the skin; and arginine synthesizes nitric oxide, a molecule that helps to maintain blood flow to the skin and improve its elasticity while playing an important role in the maintenance and regulation of the skin and the integrity of its environment.
10. Weight Management
Essential amino acids can potentially help with weight management in a few ways: A) Essential amino acids play a vital role in the synthesis of protein in the body. When you consume enough protein, your body is better able to build and repair tissues, including muscles. This can help increase metabolism and promote weight loss. B) Essential amino acids can also help increase feelings of fullness and satisfaction after a meal, which can lead to reduced food intake and weight loss. C) Additionally, essential amino acids are involved in the production of various hormones, including ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite and energy expenditure.
Consuming enough essential amino acids can help regulate these hormones and potentially promote weight loss. It's important to note that while essential amino acids may have some weight management benefits, they should not be relied upon as a sole means of weight loss. A high protein, nutrient dense diet and regular physical activity are crucial for weight management.
11. Sleep
There is some evidence to suggest that essential amino acids may help improve sleep quality. According to Medical News Today, tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is important for the production of serotonin in the body. It is also key to brain function and has a role in healthy sleep. People cannot make tryptophan in their bodies, so must obtain it from their diet. Additionally, GABA (a neurotransmitter that is synthesized from the amino acid glutamine) has been shown to have a calming effect on the brain and may help to promote sleep.
12. Mood and Mental Health
Essential amino acids can potentially have a positive effect on mood and mental health. Some essential amino acids, such as tryptophan and tyrosine, have been shown to have a positive effect on mood and mental health. Tryptophan is converted to serotonin in the body, which is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in mood regulation. Tyrosine is converted to dopamine, another neurotransmitter that is involved in motivation and pleasure. Low levels of certain essential amino acids have been linked to conditions such as depression and anxiety. Supplementing these amino acids may help improve mood and mental health in some individuals.
SURPO Takeaways
Essential amino acids play a vital role in maintaining overall health and wellness. They help to build and repair tissues, produce hormones and enzymes, and support a strong immune system. They are also necessary for muscle growth and maintenance, and can even help with weight loss efforts. While essential amino acids can be obtained through a high protein diet, they can also be supplemented through EAA drinks and protein powders. Amino Hydrate+ by SURPO has an EAA formula which results in significantly higher absorption rates than any protein powder or other EAA drink. Overall, incorporating essential amino acids into your diet can provide numerous benefits for both physical and mental health.
Amino Hydrate +
Amino Hydrate+ helps replenish lost minerals & electrolytes while supplementing all the key amino acids your body needs to perform at its best. This combination will help you stay hydrated, prevent muscle breakdown, aid in athletic recovery, boost energy levels, & support muscle growth & overall health.
Higher Athletic Performance
When you engage in strenuous or prolonged physical activity, your body depletes its energy reserves & starts to break down muscle protein to convert its essential amino acids into energy. This process also leads to a decrease in muscle protein production, resulting in muscle weakness & reduced exercise performance. Amino Hydrate + replenishes lost electrolytes needed for energy & endurance while supplementing all the key amino acids needed to prevent muscle breakdown.
Optimum Hydration
The negative effects of dehydration can be avoided through proper hydration. Hydration involves not only drinking water but also replenishing the body with essential electrolytes. Amino Hydrate + offers better hydration over water alone. It enhances muscle water absorption & retention and replaces the vital electrolytes that are lost due to sweating. Our amino acid powder fully hydrates your body, keeping you fueled to tackle even the most intense workout while reaching your greater Survival Potential!
Workout Recovery and Muscle Growth
Essential Amino Acids activate a certain pathway in the body that stimulates muscle protein synthesis while decreasing muscle soreness & exercise fatigue. Our unique Amino Hydrate+ formula has been thoughtfully designed to replenish lost electrolytes while supplementing all the key amino acids in your body. This combination will help you to prevent muscle breakdown, support muscle growth, and is perfect any time during the day your muscles need extra recovery.
SURPO exists to help people fundamentally obtain higher levels of survival across all aspects of life and that experience begins with physical health. We strive to empower individuals to live a healthier, more active lifestyle through the promotion of proper nutrition. Our supplement is specifically designed to help you reach your health and fitness goals. Good hydration and high-quality supplements make all the difference in the world and have the power to transform your life.
#Amino Hydrate+Sale#Amino Hydrate+ formula#Surpo Nutrition#Amino Hydrate+#Sale Amino Hydrate+#Amino Hydrate+ Sale#Amino Acids multivitamins#Amino Acids Vitamins#Higher Athletic Endurance#Amino Acids supplements#Optimum Hydration#Caffeine Free Energy#high-quality supplements#Increased MPS#Essential Amino Acids#Essential Electrolytes#workout#running#nutrition#meal prep#marathon#healthy eating#bodybuilding
0 notes
Text
XXTRM OPTIMAL BCAAs 2:1:1 | GLUTAMINE | ELECTROLYTES (300G/0.66LB) | BOLT NUTRITION
XXTRM is An Amino Blast formula that contains GLUTAMINE, Optimal BCAAs ratio of 2:1:1 (Leucine, Isoleucine, and Valine) Plus Electrolyte blend a Performance driven Amino Blast Formula. You can fuel your workout with XXTRM Amino Blast which provides faster nutrient absorption into the bloodstream, hydration, and instant energy.
#BCAAs#glutamine#electrolyte#electrolytes#leucine#isoleucine#valine#glutamine powder#branched chain amino acids#bcaa amino acids#glutamine supplement#glutamine price#use of glutamine#electrolytes are#leucine amino acid#isoleucine amino acid#energy booster#energy boost#boost energy#energy boost supplement#stay hydrate#hydrated#keep yourself hydrated#keep hydrated#Muscle recovery#muscle recovery supplements#best muscle recovery supplements#intense workout#protein synthesis#muscle protein synthesis
0 notes
Text
Supplements & Vitamins
Here's a list of some of the most commonly used supplements and their benefits. Please remember that while supplements can be beneficial for certain people, everyones nutritional needs are different. It's always a good idea to consult with a specialist before adding any new supplements to your routine, as individual needs may vary.
Multivitamin: Provides a range of essential vitamins and minerals to support overall health and fill potential nutrient gaps in your diet.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promote heart health, brain function, and reduce inflammation. Typically derived from fish oil or algae.
Vitamin D: Supports bone health, immune function, and may have a positive impact on mood. It's commonly obtained through sun exposure, but supplements can be useful, especially in winter or for those with limited sun exposure.
Probiotics: Help promote a healthy gut microbiome, aiding digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Magnesium: Important for muscle and nerve function, bone health, and energy production. It may also help with relaxation and sleep.
B vitamins: Help convert food into energy, support brain function, and maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails.
Vitamin C: Boosts immune function, acts as an antioxidant, supports collagen production, and aids in iron absorption.
Zinc: Essential for immune function, wound healing, and cell division. It also supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence.
Iron: Required for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia and fatigue, but it's essential to get iron levels checked before supplementing.
Calcium: Crucial for bone health and muscle function. It's often combined with vitamin D for better absorption.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Plays a vital role in energy production within cells and acts as an antioxidant. It may benefit heart health and cellular energy metabolism.
Curcumin (Turmeric extract): Possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, potentially supporting joint health and cognitive function.
Ashwagandha: An adaptogenic herb that may help reduce stress, promote relaxation, and support cognitive function.
Green Tea Extract: Contains antioxidants and may support cardiovascular health, weight management, and cognitive function.
Glucosamine: Commonly used for joint health and may help alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Chondroitin: Often taken alongside glucosamine, it may help reduce joint pain and improve joint mobility.
Probiotics for Gut Health: Certain strains of probiotics can help restore and maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, supporting digestion and immune function.
Melatonin: A hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, melatonin supplements can help with insomnia or jet lag.
Vitamin E: An antioxidant that supports immune function and may help protect against cellular damage.
Ginseng: An adaptogenic herb that may help increase energy, reduce stress, and support cognitive function.
Prebiotics: These are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, supporting gut health and digestion.
Magnesium: In addition to its previous benefits, magnesium may help reduce muscle cramps, improve mood, and promote relaxation.
Probiotics for Vaginal Health: Certain strains of probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of vaginal flora, reducing the risk of infections.
Cranberry Extract: Often used for urinary tract health, cranberry extract may help prevent urinary tract infections.
Resveratrol: Found in grapes and berries, resveratrol has antioxidant properties and may support heart health and longevity.
L-theanine: An amino acid commonly found in green tea, L-theanine may promote relaxation, improve focus, and reduce anxiety.
#vitamins#supplements#health tips#healthy diet#health is wealth#healthy living#health and wellness#healthy lifestyle#health#clean girl#glow up tips#level up journey#wellness
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Foods that promote gut health
Maintaining a healthy gastrointestinal (GI) tract is vital for overall health, given its role in nutrient absorption, immune regulation, and maintaining a balanced microbiome. Gastrointestinal irritation can lead to dysbiosis, inflammation, and impaired barrier function, which can have systemic consequences. This article explores specific foods that have been shown to support gut health at the biochemical level and to alleviate GI irritation.

1. Chicken bone broth
A SOURCE OF COLLAGEN AND AMINO ACIDS
Chicken bone broth is rich in collagen, gelatin, and various amino acids, including glycine and proline, which play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of the gut mucosa. Collagen and gelatin are broken down in the stomach to release these amino acids, which are then utilized in the synthesis of extracellular matrix components. Glycine, in particular, has anti-inflammatory properties and contributes to the stabilization of the intestinal epithelial barrier by promoting tight junction integrity. This supports mucosal healing and reduces permeability, thereby mitigating the symptoms of leaky gut syndrome.
Additionally, bone broth contains glutamine, a conditionally essential amino acid that serves as a primary fuel source for enterocytes, the cells lining the gut. Glutamine supplementation has been shown to reduce intestinal permeability and inflammation, making bone broth a beneficial dietary component for repairing a compromised gut lining.


2. Vegetable soups
RICH IN PREBIOTIC FIBERS
Vegetable soups, especially those made from high-fiber vegetables like carrots, celery, and leafy greens, provide an abundance of prebiotic fibers, such as inulin and pectin. Prebiotics are non-digestible carbohydrates that resist digestion in the upper GI tract and reach the colon intact, where they undergo fermentation by the gut microbiota. This fermentation process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate, which serve as an energy source for colonocytes and have anti-inflammatory effects.
Butyrate, in particular, has been shown to strengthen the gut barrier by enhancing the expression of tight junction proteins and by modulating the immune response within the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). Additionally, SCFAs lower the pH of the colon, creating an environment that is less favorable for pathogenic bacteria, thus promoting a balanced microbiome.

3. Miso soup
A PROBIOTIC POWERHOUSE
Miso, a fermented product made from soybeans, rice, or barley, is rich in probiotics, particularly strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. These beneficial bacteria contribute to the maintenance of a healthy gut microbiome by outcompeting pathogenic bacteria for resources and attachment sites on the intestinal epithelium.
Probiotics in miso also produce antimicrobial substances like bacteriocins and lactic acid, which inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. Additionally, these microbes can enhance the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines and reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby modulating the gut immune response and reducing intestinal inflammation.
The fermentation process of miso also results in the production of bioactive peptides, which have been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, further contributing to the healing of the GI tract.

4. Nettle Tea
ANTI-INFLAMMATORY PHYTOCHEMICALS
Nettle (Urtica dioica) is a medicinal plant known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties, largely attributed to its high content of polyphenolic compounds, flavonoids, and carotenoids. These bioactive compounds inhibit the activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX), thereby reducing the production of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
Nettle also contains high levels of vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals such as iron and magnesium, which are essential for maintaining cellular functions and supporting the immune system. The antioxidative properties of nettle’s polyphenols help to mitigate oxidative stress, a key factor in gut inflammation and irritation.


5. Fermented vegetables
ENHANCING MICROBIAL DIVERSITY
Fermented vegetables like sauerkraut and kimchi are rich sources of live probiotics and their metabolites, which play a crucial role in maintaining gut health. The fermentation process not only preserves the vegetables but also enriches them with beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus plantarum and Leuconostoc mesenteroides, which can colonize the gut and enhance microbial diversity.
These probiotics have been shown to improve the gut’s mucosal barrier function by increasing the expression of mucin genes and enhancing the production of SCFAs. Moreover, the metabolites produced during fermentation, such as lactic acid and bacteriocins, exert antimicrobial effects against pathogens, thereby promoting a balanced and healthy microbiome.


6. Oats and whole grains
PREBIOTIC SOLUBLE FIBER
Oats are rich in beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that acts as a prebiotic, selectively stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. The fermentation of beta-glucan by colonic bacteria results in the production of SCFAs, which, as previously mentioned, have anti-inflammatory and gut-protective effects.
In addition to their prebiotic properties, beta-glucans modulate the immune system by binding to receptors on immune cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, thereby enhancing their ability to respond to pathogens while reducing unnecessary inflammatory responses. This immune-modulating effect is particularly beneficial in managing conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
[photos from Pinterest]
#it girl#that girl#clean girl#hyper feminine#becoming that girl#glow up tips#healthy girl#pink pilates girl#this is what makes us girls#weight loss#healthy diet#healthy food#healthy eating#health and wellness#wellness and health#health & fitness#healthylifestyle#italian foods#food#that girl tips#that girl aesthetic#that girl moodboard#fitness tips#health tips#beauty tips#girlhood#clean girl aesthetic#weight loss blog#wellness blog#girl blogger
136 notes
·
View notes
Note
Wait if the human body needs fats for protein absorption, do you have any idea what someone who can't process fat at all is supposed to do? I'm currently being evaluated for all kinds of possible diagnoses but so far my physician isn't sure what's wrong with me and if it's curable, but the gist is that I literally can't eat anything even slightly fatty without becoming severely sick and immediately having to run to the bathroom. So I can't eat any meat that isn't lean, I can't eat cheese, can't drink milk, I can't eat yoghurt that isn't advertised as 0 fat, and I can't use oils at all either.
From what you're saying about fats, that sounds...less than ideal. Considering I don't know for how long I'll be forced to live this way or if there's anything that can fix it at all, do you know if there's anything I can do to prevent the rabbit starvation you speak of?
(referring to this post) Oh, wow! I’m sorry, that sounds frustrating and stressful.
I want to be clear: I’m an archaeologist, and my primary understanding of this comes from an archaeological and evolutionarily perspective, not a modern nutritional one. Your doctor and your nutritionist will know a lot more about your case than I do.
That said, rabbit starvation/protein poisoning is only really a concern when lean meat makes up the majority of your diet. Not the majority of the meat in your diet, the majority of your diet, period. It’s a topic of interest among archaeologists in particular because it would have been a perennial concern in the winters during the Ice Age: when hunting animals with lean meats would have made up a large portion of early humans’ and Neanderthals’ diets during a Paleolithic winter. Historically, this tends to happen only in the winter in tundra and subarctic regions when grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fish aren’t available. There’s a reason it’s also called mal de caribou.
Carbohydrates, sugars, fruit, and vegetables give you a much more balanced diet and help make up for deficiencies in other areas. And modern nutritional supplements, fortified foods, and multivitamins also help stave off many historical areas of malnutrition. If you are eating a modern spread of foods, even without fat, you are very unlikely to get protein poisoning. You might get constipated when you eat the meat, though.
My understanding is: proteins get digested faster than fats. So if you eat high-protein lean meats, they can move through your system quickly, without your body having time to extract all the amino acids and all the nutrients from them. And then the undigested bits can build up in your colon and make you feel constipated. Fat is digested more slowly, and when eaten with protein, allows your body more time to extract more and fuller suite of nutrients from the protein. Possibly there is also an emulsification aspect going on as well, I’m not positive and it’s hard to find good explanations that aren’t diet-culture-focused. (Fat also does other important things in your body with providing long-term slow-burning energy, padding your organs so they don’t impact against other parts of your body, and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and such; again, I’m not a nutritionist, and I don’t super understand the details.)
But dietary fiber can also slow down digestion, and can help give some of those same digestive effects. (Nixtamalized) corn+beans+squash is a very traditional diet of the Americas because it gives the whole suite of necessary amino acids without requiring a whole lot of external additions. Also, I get the sense that fish like salmon work differently because of omega-3 fatty acids? So there are for sure things you can supplement with.
My post wasn’t intended to make people worry; modern nutrition and food availability means that there is a lot of flexibility you can have in your diet if you’re allergic to one aspect of it. It was meant to say, even “unhealthy” fats have an important place in a balanced diet, and can do good things for you besides just tasting good, and that craving it may well mean there’s something in there that your body wants. But if fat genuinely isn’t good for you for medical reasons, there are absolutely ways of dealing with that. Ultimately, variety is the most important part.
#I AM NOT A DOCTOR#I want to make it clear that my understanding comes from an archaeological place#And the evolutionarily needs we developed as humans#Definitely ask your doctor or a nutritionist how to stay healthy#But I really don’t think you need to worry about rabbit starvation if you are eating plenty of grains and fruits and vegetables as well#asks#featherymainffins#Good luck though that sounds stressful
13 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hello 👋 when I was trying to get muscles a few years back I struggled with getting enough protein (I was aiming for 1gm/pound of bodyweight). As a vegetarian how much do you rely on supplements vs your regular meals?
Also if you ever wanna share some of your fav vegetarian recipes I’d appreciate it.
Hi!
To me it looks like you might actually have been aiming for too much protein. The most efficacious amount of protein that you can consume is 70% of your desired body weight in grams of protein. While soy is a complete protein, it is important to consider other sources of protein that have complimentary amino acid profiles. Whey protein is a decent compliment to soy, and eggs are the gold standard for anabolic proteins.
Consistency is key to any sort of anabolism. You should be training your muscle groups to total failure at least one time per week. You should also avoid any systemic inflammation reduction (i.e., from NSAIDs like ibuprofen) as inflammation is the key mediating factor that leads to muscle growth. Additionally, check your hormones and consider hormonal optimization. 9 hours of sleep, avoidance of stress, plenty of sex, and the right window of calories is key. You should be eating between 250-500 calories more than you burn in order to have enough energy left over to build muscle. Good fats are very important as they improve HDL cholesterol which is the number one source of cholesterol for hormone synthesis. Finally, if your body is screaming for rest, do not exercise. It's key to rest when you need to rest so your muscle building can catch up. Overworking yourself will kill your body's ability to recover, meaning that there won't be any muscle growth.
Omelets and tofu are the best. Press out all the water in the tofu, put on soy sauce and a little corn starch that you season, and toss it in the air fryer with a vegetable. Smoothies are also great because they allow you to ingest a lot of protein powder (just make sure to drink them slowly). Typically I have one protein bar and 2-4 scoops of whey protein per day in addition to everything else.
Hope this helps,
Drew
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
how do human recreational drugs affect gallifreyans? are there any gallifreyan recreational drugs or alien recreational drugs that have interesting effects on gallifreyans?
How do recreational drugs affect Gallifreyans?
🌍 Human Recreational Drugs on Gallifreyans Info on Gallifreyan drug use is there but it's limited, so these are more theoretical effects.
While Gallifreyan biology is similar to human biology in many ways, it reacts a bit differently to human recreational drugs. It’s important to note that Gallifreyans require double the dose of any human drug to feel its effects, and these effects take twice as long to kick in.
1️⃣ Stimulants (e.g., Cocaine, Amphetamines)
Effects: Increased alertness and energy.
Gallifreyan Response: Mild doses likely just give a bit of a mental and physical pep like humans, but due to their dual-heart system and efficient metabolism, higher doses could cause dangerously elevated heart rates and cardiovascular strain, leading to arrhythmias or hearts attacks. Additionally, their heightened sensory perception might lead to overstimulation, causing distress and potentially harmful feedback loops in their nervous system.
2️⃣ Depressants (e.g., Alcohol, Barbiturates)
Effects: Relaxation and reduced inhibition.
Gallifreyan Response: Gallifreyans metabolise these substances quickly, reducing their intended calming effects. However, excessive use might disrupt their chronopsionic sense centres, leading to impaired time-sensing and telepathic abilities..
3️⃣ Hallucinogens (e.g., LSD, Psilocybin)
Effects: Altered perception and hallucinations.
Gallifreyan Response: Hallucinogens could potentially amplify a Gallifreyan’s already complex perception of time and space, providing some wild insights. High doses will probably cause severe disorientation and intense psychotropic episodes - their enhanced neural networks likely make them more susceptible to prolonged or intense hallucinations.
4️⃣ Opioids (e.g., Heroin, Morphine)
Effects: Pain relief and euphoria.
Gallifreyan Response: Due to their natural resistance to pain and efficient healing capabilities, opioids are more supplemental to their natural abilities, but extremely high doses might overwhelm their systems, potentially leading to respiratory failure or inducing a deep regenerative coma. Their bodies could also quickly develop a tolerance, necessitating even higher doses to achieve the same effect, increasing the risk of addiction and overdose.
👽 Gallifreyan Drugs
Gallifrey has a couple of naturally found drugs.
1️⃣ Cerub Nuts
Effects: Mildly hallucinogenic and taste like truffles.
Description: Cerub nuts come from Gallifreyan Cerub trees. When consumed, they induce mild hallucinations, possibly disrupting the senses, resulting in them seeing vibrant colours and patterns.
2️⃣ Mount Cadon Snow
Effects: Hallucinogenic, giving visions of the past or future.
Description: The snow on Mount Cadon is known for its powerful hallucinogenic properties. Ingesting or possibly even inhaling the fine particles of this snow can give Gallifreyans vivid visions of their past or possible futures. The effect becomes stronger the closer you get to the peak.
🥑 Overabundance of Nutrients
As a side note, due to their incredibly efficient ability to absorb nutrients, an overabundance of certain substances might cause unexpected effects in Gallifreyans.
Tyrosine: Found in foods like chicken, peanuts, avocados, and bananas, tyrosine is a precursor to dopamine, the 'feel-good' neurotransmitter. Gallifreyans' supercharged ability to synthesise amino acids means a diet rich in tyrosine could lead to a spike in dopamine levels, causing an elevated mood, increased pleasure, and incessant giggling.
Tryptophan: Present in turkey, cheese, and nuts, tryptophan is a precursor to serotonin, another neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation. Overconsumption might lead to excessive calmness, lethargy, and an unnaturally positive disposition.
Phenylalanine: Found in soy products, fish, and eggs, phenylalanine is another amino acid that can influence mood by increasing levels of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine. Excessive intake could cause heightened alertness, restlessness, and even anxiety.
Of course, these would need to be consumed to absolute excess to achieve these results, or if something in their digestive process is a little wonky.
🏫 So ...
So, while Gallifreyans can be affected by human recreational drugs, their unique physiology requires higher doses and longer onset times. The effects can range from mild stimulation to severe physiological and psychological problems. Stay safe, Gallifrey!
Related:
How much sugar causes hyperactivity In Gallifreyans?: Overview of the sugar metabolism in Gallifreyans and theoretical limitations.
Do Gallifreyans control how quickly their body processes alcohol?: Gallifreyan alcohol processing, its limitations, and the dangers of ginger.
How much caffeine can a Gallifreyan handle?: Caffeine tolerance, with theoretical limits and symptoms of overconsumption.
Hope that helped! 😃
Any purple text is educated guesswork or theoretical. More content ... →📫Got a question? | 📚Complete list of Q+A and factoids →😆Jokes |🩻Biology |🗨️Language |🕰️Throwbacks |🤓Facts →🫀Gallifreyan Anatomy and Physiology Guide (pending) →⚕️Gallifreyan Emergency Medicine Guides →📝Source list (WIP) →📜Masterpost If you're finding your happy place in this part of the internet, feel free to buy a coffee to help keep our exhausted human conscious. She works full-time in medicine and is so very tired😴
#gil#gallifrey institute for learning#dr who#dw eu#ask answered#whoniverse#doctor who#gallifreyan biology#time lord biology#gil biology
18 notes
·
View notes
Text

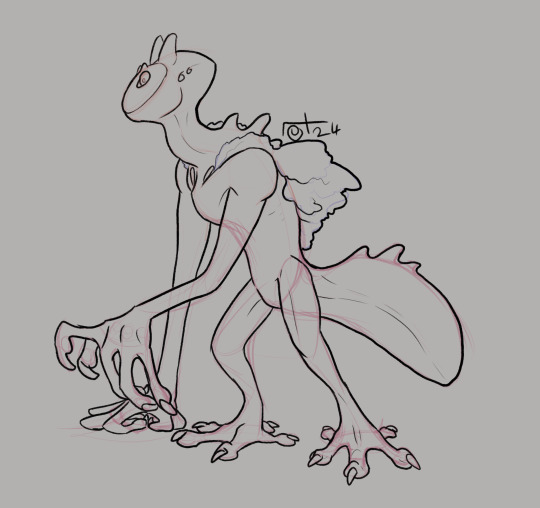
[ID: Two pictures digitally drawn on grey canvases.
Picture 1: The bust of an alien in profile with several blue circles behind it serving as a background. The alien has a white faceplate, pale eyes, and ink-black smooth skin. Its head is slightly elongated and egg-shaped. It has a bent neck, three knobby spines on its back, and two sets of short horns on its head. There are two sets of paired orifices on the side of the head behind the face plate and a pair of orifices on the chest.
Picture 2: The same species of alien as a full-body drawing with visible colored sketch lines underneath the black line art. The alien is a vaguely gecko-like semi-humanoid creature. It has five digits at the end of each limb, stands on its hind legs, and has a fat tail with three knobby spines near the base. On its back is a blobby symbiotic organism. /End ID]
The Draken.
My brain threw Osmosians (Ben 10), those psychic panda newts (Scavengers Reign), and the Phils (Oban Star Racers) in a blender with an alien not-fungus selkie style skinsuit symbiote dealing I was working on for something to make a new alien species.
Psychic powers (short-range mindreading/hypnosis, telepathy, and sort-range telekinesis), can near freely alter their proportions. Can absorb/manipulate matter and energy. Their symbiote can sample and transform into shells that resemble other species/prey.
Facultative navivores and facultative parasites that spend most of their time basking and passively consuming sunlight. Can forcefully drain energy from special pads on their hands and feet. Those same pads can absorb matter to be used as a protective skin spread over the body that increases durability and also aid in stealth. Can consume solid and liquid matter to supplement their diet with vitamins, minerals, amino acids. While capable of hunting for themselves they thrive better living in groups and having hypnotized thralls gather/hunt food for them.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Mediterranean diet contains nutrients that are known to enhance longevity and has other health benefits that are backed by peer-reviewed, scientific studies. Broccoli is one of nature's most nutrient-dense foods, with only 30 calories per cup and contains fibre and polyphenols — antioxidants that detoxify cell-damaging chemicals in your bodying.
A Spanish study found a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil reduced the incidence of major cardiovascular events among patients with a history of heart disease.
Quinoa contains a good dose of protein to help build muscle. Yet including any type of whole grain in your diet — from barley to brown rice — will aid in weight loss by filling you up for fewer calories.
Blueberries is a kind of superfood because studies have shown they aid in everything from fighting cancer to lowering cholesterol. But all berries, including raspberries, strawberries and blackberries, contain antioxidants and phytonutrients.
Studies show that eating a handful of nuts several times a week can prevent heart disease and ultimately help you shed pounds since they fill you up and stop you from snacking on other things. Almonds, in particular, contain lots of monounsaturated fats and fibre.
Salmon is also a good source of lean protein. With this diet, doctors suggest eating fish at least two times a week. Salmon provides a high dose of omega-3 fatty acids, which studies show significantly lower the risk of heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids fight back by reducing inflammation and slowing the rate of plaque buildup in blood vessels.
Black, kidney, white and garbanzo beans (also known as chickpeas) are good for fibre and protein. They fill you up and provide muscle-building material without any of the fat that meat can add to your meal.
Eating a breakfast high in protein is a good way to keep hunger at bay throughout the day. Eggs are full of choline, a nutrient that helps block fat from being absorbed in the liver. Choline may also help in preventing memory loss.
Spinach is a great source of iron, which is a key component in red blood cells that fuel our muscles with oxygen for energy. But researchers in Sweden identified another way in which these greens might keep you charged: Compounds found in spinach actually increase the efficiency of our mitochondria, the energy-producing factories inside our cells.
Walnuts are packed with tryptophan, an amino acid your body needs to create serotonin. They're digested slowly which contributes to mood stability and can help you tolerate stress.
Asparagus is one of the best sources of folate, a B vitamin that could help keep you out of a mental slump. Folate is important for the synthesis of the neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine; all of these are crucial for mood.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can I build muscle and lose fat at the same time?

Yes, it is possible to build muscle and lose fat simultaneously, though it can be challenging and typically requires a well-structured approach. This process is often referred to as “recomping” (short for recomposition). Here are some key strategies to achieve this:
1. Nutrition
Caloric Balance: Aim for a slight caloric deficit to lose fat while providing enough nutrients to support muscle growth. This typically means consuming slightly fewer calories than your body needs to maintain its current weight.
Protein Intake: Ensure a high protein intake (1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight) to support muscle repair and growth.
Macronutrient Balance: Balance your diet with a good mix of carbohydrates and fats to provide energy and support overall health.
2. Strength Training
Progressive Overload: Continuously challenge your muscles by increasing the weight, reps, or intensity of your workouts over time.
Compound Movements: Focus on compound exercises (squats, deadlifts, bench presses) that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Consistency: Maintain a regular workout schedule, typically 3–5 times per week, to consistently stimulate muscle growth.
3. Cardio
Moderation: Incorporate moderate cardio to support fat loss without compromising muscle gains. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) can be particularly effective.
Timing: Consider doing cardio on non-lifting days or after strength training sessions to prioritize muscle preservation.
4. Recovery
Sleep: Ensure adequate sleep (7–9 hours per night) to allow your body to recover and grow.
Rest Days: Incorporate rest days to prevent overtraining and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Consistency and Patience
Long-Term Commitment: Body recomposition is a gradual process that requires consistent effort over time. Patience and persistence are crucial.
Monitor Progress: Track your progress with measurements, photos, and performance in the gym rather than just focusing on the scale.
6. Individual Factors
Starting Point: Beginners or individuals returning after a long break often see more dramatic changes in body composition.
Genetics: Genetic factors can influence how easily you gain muscle or lose fat.
7. Nutrient Timing
Pre-Workout Nutrition: Consume a meal or snack rich in protein and carbohydrates about 1–2 hours before your workout to fuel performance.
Post-Workout Nutrition: Have a post-workout meal or shake with protein and carbs within 30–60 minutes after your workout to aid recovery and muscle growth.
8. Hydration
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for overall health, performance, and recovery. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, particularly before, during, and after workouts.
9. Supplementation
Protein Supplements: Whey or plant-based protein powders can help you meet your daily protein requirements.
Creatine: Creatine monohydrate is a well-researched supplement that can enhance strength, power, and muscle mass.
Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): These can help reduce muscle soreness and promote muscle protein synthesis, particularly when training in a fasted state.
10. Mind-Muscle Connection
Focus on Form: Pay attention to proper form and technique to maximize muscle engagement and prevent injury.
Contraction: Emphasize the contraction of the target muscles during each exercise to improve muscle activation.
11. Variation in Training
Periodization: Incorporate different phases in your training program, such as strength, hypertrophy, and endurance phases, to continually challenge your muscles and prevent plateaus.
Exercise Variety: Regularly change your exercises, rep ranges, and workout routines to keep your muscles guessing and promote continuous adaptation.
12. Tracking and Adjustment
Regular Assessments: Keep track of your body composition, strength levels, and overall progress. Adjust your diet and training plan based on these assessments to ensure continued progress.
Listen to Your Body: Be mindful of signs of overtraining or injury. Adjust your training intensity and volume as needed to prevent burnout and maintain long-term progress.
13. Metabolic Rate and Muscle Mass
Muscle Increases Metabolism: Building muscle increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR), helping you burn more calories even at rest, which aids in fat loss.
14. Hormonal Balance
Manage Stress: High-stress levels can lead to elevated cortisol, which can negatively impact muscle growth and fat loss. Incorporate stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Hormonal Health: Ensure adequate intake of essential fats and micronutrients to support hormonal health, which is crucial for muscle growth and fat loss.
15. Support System
Accountability: Having a workout partner, or coach, or joining a fitness community can provide motivation, accountability, and support.
Education: Continuously educate yourself about nutrition, training, and recovery to make informed decisions and optimize your body recomposition efforts.
By paying attention to these important factors, you can further enhance your ability to build muscle and lose fat simultaneously. Remember, consistency, patience, and a holistic approach are key to achieving long-term success in body recomposition.
#weightloss#health#weight loss#fatloss#lose weight#healthy#diet to lose weight#fat loss#losing weight#fatlosstips#how to lose weigth fast#weigthloss#lose stomach weight#weight loss tips#weight loss motivation#weight loss success stori#weightwatchers#i wanna lose weight#i need to lose so much weight#gaining weight on purpose#i need to lose this weight#diet#weight loss journey#how to lose weight#muscles#bodybuilder#muscular#flexing
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
9 Essential Amino Acids: Function, Health Benefits, and Food Sources

As health enthusiasts, we understand the importance of having a balanced diet that includes all the essential nutrients our body needs to function properly. Among these essential nutrients are Amino Acids, which play a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
Amino acids are the fundamental components of proteins and are essential for many critical functions in the body. These compounds are responsible for the formation of important structures such as proteins, hormones, and neurotransmitters. To obtain enough amino acids, it is important to consume protein-rich foods like meat, fish, and seafood. Additionally, some individuals take amino acid supplements as a natural way to boost their mood and/or enhance their athletic performance.
Our bodies require a diverse range of amino acids to maintain optimal health and function. Although there are approximately 500 different amino acids found in nature, only 20 of these are used to create the proteins found within the human body. Though each of these amino acids plays a crucial role in our well-being, 9 of them are deemed particularly essential for our survival.
These 9 essential amino acids include leucine, valine, isoleucine, lysine, threonine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, methionine, and histidine. In this blog, we will be discussing the definition, health benefits, and food sources of these essential amino acids to help you understand the significance of including them in your diet.
1. Leucine
Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)** along with isoleucine and valine. It plays a vital role in protein synthesis, making it important for muscle growth and repair. It can help preserve muscle mass during periods of caloric restriction or increased physical activity. Leucine is also involved in the regulation of blood sugar levels and the stimulation of wound healing. Additionally, studies have suggested that leucine may have the potential to improve bone health, and may play a role in preventing obesity.
A wide variety of healthy, tasty foods contain leucine, including eggs, beef, tuna, and salmon. These good food sources of leucine are all easy to incorporate into your diet. Leucine is also available in supplement form and is often used by athletes, bodybuilders, and other fitness enthusiasts to enhance muscle growth and recovery via a BCAA or EAA drink.
**BCAAs are a group of three amino acids that have a distinct branching structure at the molecular level. These amino acids are metabolized by the body and used as a source of energy for muscle tissue. BCAAs, which are found in high concentrations of muscle protein, have been recently recognized as vital to muscle health.
2. Valine
Like leucine, valine is classified as a branched-chain amino acid (BCAA). This essential amino acid is commonly used by athletes and bodybuilders as it helps prevent muscle breakdown, enhances athletic performance, and helps supply the muscles with extra glucose for energy production during intense exercise or workouts.
Valine promotes the growth and repair of muscle tissue, which can lead to an increase in muscle mass and strength. It also helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes during intense exercise. Additionally, valine helps to stimulate the formation of hormones, which can aid in the body's overall health and well-being.
Valine can be found in a variety of food sources, including red meat like lamb and beef & dairy products too, especially cottage cheese and yogurt. Eggs, turkey, and chicken; fish, including wild-caught salmon and trout are some other good sources. To ensure that you're getting enough valine, be sure to incorporate these foods into your diet regularly.
Additionally, supplements like Amino Hydrate + which contains Valine, among the other essential amino acids, are commonly taken by weightlifters and performance athletes as part of their workout routines.
3. Isoleucine
Isoleucine, as one of the BCAAs, is also critical to the physiological functions of your whole body. It helps with growth, immunity, protein metabolism, and fatty acid metabolism. Isoleucine has a role in the detoxification of nitrogenous waste like ammonia, which is then excreted from the body by the kidneys. It is also necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin and the production of red blood cells, making it a crucial amino acid in the process of recovering from blood loss or anemia.
Isoleucine is also commonly taken by some bodybuilders and athletes, as it helps decrease post-workout muscle damage and soreness. According to a systemic review published in 2017 in the Journal of Nutrients, some studies have shown that BCAA supplementation can be successful at reducing exercise-induced muscle damage. Moreover, according to Annie Price, a Certified Holistic Health Coach, the isoleucine amino acid is also believed to mediate glucose uptake into a cell and break it down into energy. This specific isoleucine function is why it may help enhance athletic performance.
Animal-based isoleucine food sources include yogurt, tuna, lean chicken breast, lean pork chops, beef, cod, and haddock.
4. Lysine
Lysine is an essential amino acid that helps build muscle tissue, prevent cold sores, maintain a healthy immune system, produce enzymes, antibodies, and healthy hormones, and even reduce feelings of anxiety and levels of the stress hormone cortisol in some people.Additionally, lysine also plays a crucial part in the synthesis of collagen, a protein necessary for bones and connective tissues, including skin, hair, tendons, and cartilage, keeping your skin, hair, and bones healthy.
Other benefits include preventing osteoporosis and bone loss, regulating blood pressure, mitigating artery plaque buildup, assisting athletes in recovering from strenuous workouts, and building and developing muscle among bodybuilders.
Foods that will help people meet their daily lysine requirements include chicken, cottage cheese, parmesan, brewer’s yeast, red meat, fish such as tuna, cod, or sardines, eggs, seafood such as mussels, prawns, and oysters to name a few.
Moreover, supplements are also a common source of amino acids because they're convenient to use and easy to find at health food stores or online. Supplements usually come in powder form, like Surpo Amino Hydrate +, just add 1 scoop to 12-16 oz of water and you will get the dose of lysine your body needs for maximum performance and overall health. This product can be taken at any time of the day or on an empty stomach.
5. Threonine
Threonine is an essential amino acid that plays a vital role in the formation of structural proteins such as collagen and elastin, which are important for maintaining the strength and elasticity of skin, hair, and nails. Threonine is important for the proper functioning of the nervous system and has been shown to promote a healthy immune system. Additionally, threonine helps to maintain the proper balance of proteins in the body and aids in the absorption of nutrients.
It is important to consume adequate amounts of threonine through diet, as a deficiency can lead to poor immune function, skin and hair issues, and problems with the liver and nervous system. Some food sources of threonine include chicken, fish, dairy products, and eggs.
6. Phenylalanine
The human body requires phenylalanine, an essential amino acid, in order to function properly. It is a building block of proteins and is important for the formation of important neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are responsible for regulating mood and behavior. Phenylalanine can help improve memory and concentration. It also plays a role in the production of melanin, a pigment that gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes.
Phenylalanine has been found to improve mood and cognitive function, making it beneficial for those with depression or anxiety. It may also help reduce pain and inflammation in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Additionally, phenylalanine has been found to improve wound healing and skin health, making it beneficial for those with skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis.
Food sources high in phenylalanine include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. It's also important to note that phenylalanine can be found in a different form called aspartame, which is commonly used in artificial sweeteners. People with phenylketonuria (PKU) are advised to avoid foods containing aspartame, as their bodies cannot break down the phenylalanine in the sweetener, leading to a buildup of the amino acid in the body.
7. Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that is a precursor to the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is involved in regulating mood, sleep, and appetite. Tryptophan is responsible for healthier and better-quality sleep, relief from depression and anxiety, increased emotional well-being and strengthened pain tolerance. Tryptophan supplementation improves muscle development, and it has previously been shown that it has a significant impact on muscle mass via its metabolite serotonin.
Tryptophan is found in meats such as turkey and chicken. It is also found in eggs, bananas, cheese, fish, chocolate, dried dates, and milk. Tryptophan is often found in high-protein foods such as these, but it can also be taken as a dietary supplement. The amount of l-tryptophan in these foods is small compared to supplements.
However, it is important to note that supplementing with tryptophan alone may not be as effective as getting it from food sources or as part of a balanced diet, and high doses of tryptophan supplements can be harmful. It's always best to consult a healthcare professional if you are considering taking this supplement.
8. Methionine
Methionine is an essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including protein synthesis, detoxification, and the production of other essential nutrients like glutathione and creatine. Methionine is involved in the detoxification of heavy metals, pesticides, and other harmful substances. It also helps to prevent the buildup of fat in the liver. It is also essential for the production of new proteins, which are important for the growth and repair of tissues.
Additionally, methionine is necessary for the production of collagen, which is a protein that provides structure to skin, hair, and nails, and is involved in the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a role in mood regulation.
Some of the best sources of methionine, with high concentrations, are found in red meat, chicken, and turkey. It is also found in eggs, dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt, some nuts, and seeds, like sesame seeds and sunflower seeds. It's important to note that a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein sources will provide enough methionine for most people. However, those who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to pay extra attention to their methionine intake.
9. Histidine
Histidine is a nutritionally essential amino acid that plays a vital role in a variety of pathophysiological and physiological processes. It plays a crucial role in the maintenance of myelin sheaths that protect your nerve cells while metabolizing the key wake-promoting neurotransmitter called histamine. Histamine supports and reinforces your immune system and inflammatory response, and is vital for gastric secretion, sexual functions, and the production of blood cells. Additionally, histidine also plays a key role in the formation of collagen, which is necessary for maintaining healthy skin and hair.
Histidine is an amino acid that was traditionally considered non-essential, meaning that it could be produced by the body from other amino acids. However, recent research has shown that histidine may play a crucial role in certain physiological processes, such as immune function, blood vessel health, and neurotransmitter production. As a result, histidine is now considered to be conditionally essential, meaning that under certain conditions (such as during growth or development) the body may not be able to produce enough histidine on its own and it may need to be obtained from the diet.
Histidine can be made by the body by converting other amino acids, such as lysine and methionine, into histidine. However, this process can be limited by the availability of these other amino acids, as well as other nutrients such as vitamin B6 and zinc. By consuming adequate amounts of the original 8 essential amino acids, as well as other key nutrients, the body can produce enough histidine to meet its needs.
It's important to note that while histidine is considered conditionally essential, it is not considered as essential as the other 8 amino acids that are required in larger amounts and cannot be synthesized by the body. Therefore, it's important to include a variety of protein sources in the diet to obtain all essential amino acids.
Foods rich in histidine are generally protein-rich foods such as meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. It is also present in some spices and herbs, like basil, thyme, and oregano.
SURPO Takeaways
Essential amino acids are an important component of a healthy diet. They are essential because our bodies cannot produce them on their own and must obtain them through our diet. These essential amino acids play a vital role in maintaining optimal health and well-being. From helping to build and repair muscles to supporting the immune system, these amino acids are necessary for many bodily functions.
Food sources such as eggs, fish, poultry, beef, and dairy products are excellent sources of essential amino acids. However, vegetarians and vegans can also obtain these essential amino acids through plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, and seeds.
It's essential to note that a balanced diet is crucial for obtaining all the essential amino acids. Therefore, it's essential to consume a variety of foods that are rich in these nutrients. If you're concerned about your dietary intake, it's always best to speak with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional.
Amino Hydrate +
Amino Hydrate+ intra workout & hydration powder replenishes lost minerals and electrolytes needed for endurance and physical and mental energy. Formulated with 8 Essential Amino Acids (EAAs), this Pre Workout Powder & Post Workout Recovery Drink assists in muscle recovery and growth, fueling your fitness journey! Amino Hydrate’s EAAs have an unparalleled 99% absorption rate and are already broken down in the correct ratios for optimal utilization, making it ideal to consume while training.
This hydration drink is an amino acids supplement for men and women that allows you to train harder and longer in the gym or on the field—an ideal hydration electrolyte and amino-heavy pre-workout with no stimulants and for an after-workout recovery drink! Our hydration supplements for men and women fully hydrate your body, keeping you fueled to tackle even the most intense workout.
Unlike ordinary hydration electrolytes and amino acid nutritional supplements, this workout powder will help you reach your body and fitness goals. Our EAA Supplement (which contains the bcaas) increases metabolic rate and muscle protein synthesis and provides 99% NNU (amino acid absorption) to support athletic recovery and overall performance!
#Amino Hydrate+Sale#Amino Hydrate+ formula#Surpo Nutrition#Amino Hydrate+#Sale Amino Hydrate+#Amino Hydrate+ Sale#Amino Acids multivitamins#Amino Acids Vitamins#Higher Athletic Endurance#Amino Acids supplements#Optimum Hydration#Caffeine Free Energy#high-quality supplements#Increased MPS#Essential Amino Acids#Essential Electrolytes#bodybuilding#gymmotivation#workout#runspo#running#nutrition#meal prep#marathon#healthy eating#runblr
0 notes
Text
can my cat be vegan?
This is a very long article but it is comprehensive and will answer all your questions if you’re thinking of putting your cat on a vegan diet. I hope it will be helpful.
the obligate carnivore
Not all carnivores are obligate carnivores.In fact, most aren’t. But all members of the cat family are.
As obligate carnivores, they cannot digest plant-based foods efficiently. Eating meat is a biological necessity.
One of the defining characteristics of an obligate carnivore is a requirement for a high amount of protein in the diet. They are so dependent on protein that if their diet is lacking an adequate amount to supply their energy needs, they will break down their own body muscle and organs.
The true carnivore will occasionally eat other foods, but the primary nutritive source must be meat for them to survive. This is because the protein in animal tissue has a complete amino acid profile.
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Plant proteins do not contain all the amino acids critical for the health of obligate carnivores, and unlike humans who have the physiological ability to turn plant proteins into the missing pieces needed for a complete amino acid profile, cats don’thave that capacity.
Cats need the amino acid taurine in their food to prevent blindness and certain kinds of heart disease. Cats cannot produce taurine in their own bodies; rather, they must eat foods containing taurine to obtain it.
Taurine is supplied almost exclusively by meat and seafood and little to none from vegetables.
Cats require approximately 200-300mg of taurine per meal, which is easily supplied by a diet that is more than half raw meat.
Ornithine, another amino acid, is manufactured in the body and is necessary because it binds the ammonia produced from the breakdown of protein. Most animals manufacture the amino acid ornithine through various processes, some of which require arginine.
In cats, the only method of producing ornithine is to convert it from arginine. Arginine helps remove by-products of the broken-down protein in their diet. arginine is only found in low amounts in plant-based diets.
An arginine deficiency will lead to drooling, lethargy and convulsions due to the toxicity built up from the protein – and even death.
Cats also lack the enzyme which can convert beta-carotene to retinol, the active form of Vitamin A. Therefore, they require a pre-formed Vitamin A, which is present only in foods of animal origin, and is usually included in cat foods as retinyl palmitate or acetate. Deficiencies of Vitamin A are rare, but signs include night blindness, retarded growth, and poor-quality skin and coat.
Arachidonic acid is one of the essential fatty acids. Cats cannot manufacture arachidonic acid from linoleic acid or gamma-linolenic acid, so it must be supplemented in their food. Arachidonic acid is necessary to produce an inflammatory response. It also helps to regulate skin growth, is necessary for proper blood clotting, and is necessary for the reproductive and gastrointestinal systems to function properly. Arachidonic acid is found in animal fats as well as peanut oil.
Cats on a vegan diet can develop abnormally alkaline (high pH) urine due to the more alkaline pH of plant based proteins in comparison to the acidic pH of meat-based foods which cats have evolved to eat.
When the urine pH becomes too alkaline, there is an increased risk of formation of bladder crystals and/or stones.
Such stones can create irritation and infection of the urinary tract and require veterinary treatment. In male cats the stones can cause an obstruction of the urethra, so the cat cannot urinate. This is a life-threatening emergency requiring immediate veterinary care.
the cat’s biological make-up
The feline digestive tract is short and is unable to process the nutrients contained in plant matter. It also causes them to need a highly digestible diet. Not only is the cat’s diet necessarily full of highly digestible proteins and fat, the proteins and fat can be very quickly digested as opposed to plant matter, which is slowly digested.
Cats have scissor-like teeth and generally, strong jaws made for grasping and tearing up their prey. Their jaws do not allow motions for actual chewing or masticating; rather, they are made to cut their prey and eat them quickly. They do not chew their prey because they can mostly digest them in their stomachs. Their tongues are raspy because they use them to scrape the meat from the bones.
Domestic cats did not evolve much further beyond their ancestral need to eat an all-meat diet because they thrived on this particular diet. They were physically and powerfully designed to eat primarily meat.
the risks of commercial pet food
However, questions must be asked about the origins of the commercial meat-based foods we are feeding our pets.
The domestication of the house cat together with the growth of the commercial pet food industry, has changed the food we feed our cats, especially in the past 50 years or so. In the quest to profit from slaughterhouse waste products, owners developed meat by-products, digests, and meals.
Over time other non-animal products were blended as filler to help make the pet foods even more profitable. It has only been in the past 20 years or so that commercial pet food manufacturers have started looking at pet nutrition seriously. However, much commercial pet food is made up of meat products not fit for human consumption simply because it makes financial sense.
Even if we are not going to cross over to a vegan diet for our feline friends, we must make sure that we are not feeding them the “excesses” of factory farming. Apart from the obvious desire to feed our cats a high - quality food, it is worth spending more on a scientifically based diet that may lead to a long and healthy life.
attention to possible health issues
Is it possible to raise your cat vegan? Only if proper attention is given to providing a food that is nutritionally balanced and complete. Supplementation of taurine and arginine is absolutely essential. Cats also requireconsiderable amounts of Vitamin A.
In the case of commercial vegan cat foods, a urinary pH level of 6.5 is should be targeted.
Cats on a vegan diet can develop abnormally alkaline (high pH) urine due to the more alkaline pH of plant based proteins in comparison to the acidic pH of meat-based foods which cats have evolved to eat. When the urine pH becomes too alkaline, there is an increased risk of formation of struvite (also known as magnesium ammonium phosphate) bladder crystals and/or stones.
advice from vegancats.com
“Unless you are very committed to following the advice outlined on our site by feeding your cat a properly balanced diet as per the information below, we recommend that you mitigate the risk of urinary tract problems by feeding males cats a 25-75% vegan diet and females a 50-100% vegan diet. Of course, many cats (both male and female) will thrive on a simple vegan diet and never have any complications from urinary tract infections or crystal formations, but you need to be prepared to adjust the diet accordingly for cats who may be prone to such issues”.
We do not believe in making companion animals suffer through recurring health complications simply because we’d like to feed them an exclusively vegan diet; rather, we believe that people should do the best they can to find a balance that keeps their companions healthy while reducing dependency on meat products to the greatest extent.”
Whatever you decide – it is, of course, your decision - it is advisable to research the pros and cons and to discuss your options with your vet. It may turn out to be healthier for your cat to not eat the way you do. In the long run, it is best to give your feline companion a long happy life than to make him/her conform to your choices.
Jennifer Larsen, DVM, PhD, veterinary nutritionist and assistant professor of clinical nutrition at the University of California, Davis Veterinary School says the following guidelines should be followed if you are considering a vegan diet for your cat:
· Only consider or feed commercial diets that have gone through feeding trials and meets the requirements for AAFCO (Association of American Feed Control Officials) compliance.
· Consult with a veterinary nutritionist who can analyse your commercial or homemade vegetarian pet diet and make recommendations for additional health safeguards.
· Schedule more frequent wellness exams, including blood work, with your family veterinarian - at least twice a year, even for young pets eating vegetarian diets.
what the experts say
Pet care professionals who warn against vegetarian diets for cats empathize with pet owners’ concerns that lead to these decisions. Believing its biologically or physiologically ok to switch your cat to one of these diets is to deny all the science proving otherwise.
Below you will find some of the leading veterinarians in the world stating their opinion on a vegan diet for your cat:
Lew Olson, PhD, author of Raw and Natural Nutrition for Dogs, makes this analogy: “Trying to feed a cat a vegan diet would be like me feeding my horses meat. You’re taking a whole species of animal and trying to force it to eat something that it isn’t designed to handle.
“People do this to make themselves happy,” says Olson, who worked in psychotherapy before changing careers in the early 1990s. “It’s not about the animal. When people tell me they want to feed a vegan diet, I say, ‘Get a hamster, get a rabbit.’”
“For cats, it’s really inappropriate. It goes against their physiology and isn’t something I would recommend at all, “says Cailin Heinze, VMD, a board-certified veterinary nutritionist and assistant professor of nutrition at Tufts Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine.
Vitamins A and D: Dogs and cats cannot make vitamin D in their skin, so it needs to be in their diet. And the vitamin D needs to be D3, which comes from animal sources, not D2, which comes from plant-based sources. “People and dogs can use D2 to some extent, but cats really need D3,” Heinze says.
the risks of feeding your pet a vegetarian or vegan diet
· Inadequate total protein intake (less than the 25 grams per 1,000 calories recommended).
· Imbalance of the certain amino acids, such as taurine and L-carnitine (dogs and cats) or essential fatty acids arachidonic acid (cats only), in particular.
· Deficiency in vitamins and minerals (such as B vitamins, calcium, phosphorus, and iron) that are obtained ideally, or only, through meat or other animal products.
· If allowed to continue long enough, these dietary problems can lead to serious and sometimes irreversible medical conditions. The one veterinarians mention most often is taurine-related dilated cardiomyopathy (enlarged heart with weak contractions and poor pumping ability). Low taurine can also lead to reproductive failures, growth failures, and eye problems.
· For the sake of your cat’s health, wellness and longevity do not make the mistake of putting them through this slow death. The chances of you seeing the sign of their immune system and organs shutting down before it’s too late is very slim.
Veterinarian Marla McGeorge, a cat specialist at Portland, Oregon’s Best Friends Veterinary Medical Centre, argues that the problem with forcing your cat to be vegetarian or vegan is that such diets fail toprovide the amino acids needed for proper feline health and are too high in carbohydrates that felines have not evolved to be able to process. As to those powder-based supplements intended to bridge the nutritional gap, McGeorge says that such formulations may not be as easily absorbed by cats’ bodies as the real thing.
With thanks to Veg Family, Feline Nutrition, catsanswers.com, cattime.com, veganhealth.org, Huffington Post, Well - Minded Pets, PetNutritionSystems & vegancats.com

5 notes
·
View notes
Text
When to Take 5-HTP and Molly: A Guide to Timing, Safety, and Recovery

Introduction
Molly, the common street name for MDMA, is a popular recreational drug known for inducing euphoria, heightened emotions, and a sense of connection. However, its use comes with a significant downside: the depletion of serotonin, a key neurotransmitter that regulates mood and well-being. As a result, many users experience a "comedown" after the effects wear off, which can include depression, anxiety, and fatigue.
To mitigate these effects, some individuals turn to 5-HTP (5-hydroxytryptophan), a supplement that is a precursor to serotonin. The idea is that taking 5-HTP before or after using Molly could help replenish serotonin levels and ease the negative aftereffects. However, the timing of when to take 5-HTP in relation to Molly is crucial, as improper use could result in harmful side effects.
In this article, we’ll explore what Molly and 5-HTP are, how they work, and the best practices for using 5-HTP to help mitigate the effects of Molly. We will also discuss potential risks and how to use these substances safely.
What Is Molly?
Molly is the street name for MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine), a synthetic drug that acts as a stimulant and hallucinogen. It is commonly used at parties, festivals, and social events for its ability to produce a sense of euphoria, increased energy, emotional warmth, and sensory perception. These effects are primarily driven by a massive release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain.
The Effects of Molly on Serotonin
MDMA triggers the release of large amounts of serotonin, which is responsible for many of the drug’s pleasurable effects. However, this surge of serotonin also depletes the brain’s natural reserves, leading to the negative comedown that users often experience in the days following. Symptoms of a comedown include:
Depression or low mood
Anxiety
Fatigue and lethargy
Difficulty sleeping
Difficulty concentrating or brain fog
The depletion of serotonin is one of the main reasons people seek out supplements like 5-HTP to aid in recovery after using Molly.
What Is 5-HTP?
5-HTP (5-hydroxytryptophan) is a naturally occurring amino acid that acts as a precursor to serotonin. It is found in foods like turkey, bananas, and certain seeds, but is commonly taken in supplement form to support serotonin production in the brain. 5-HTP supplements are often used to manage conditions like depression, anxiety, and insomnia, as these are related to serotonin imbalance.
By taking 5-HTP, users hope to boost serotonin levels and alleviate symptoms like low mood and fatigue that follow after the body’s serotonin stores are depleted by substances like Molly.
How 5-HTP Works
5-HTP is converted into serotonin in the brain. By increasing serotonin production, 5-HTP can improve mood, enhance sleep quality, and reduce feelings of anxiety. It is important to note that while 5-HTP can support serotonin production, it does not have an immediate effect like MDMA. Instead, it gradually increases serotonin levels over time, making it more suitable for long-term mood stabilization and recovery.
When to Take 5-HTP and Molly: Understanding the Timing
Timing is essential when it comes to taking 5-HTP in relation to Molly use. Taking 5-HTP too early—while Molly is still active in the system—can lead to unwanted side effects, including serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by excessive serotonin levels in the brain.
Should You Take 5-HTP Before Molly?
It is generally not recommended to take 5-HTP before or during Molly use. This is because MDMA already triggers a massive release of serotonin. Adding 5-HTP into the mix while MDMA is still active could further increase serotonin levels to dangerous levels, increasing the risk of serotonin syndrome.
Serotonin syndrome can cause symptoms such as:
Agitation or restlessness
Rapid heart rate
High blood pressure
Confusion or disorientation
Muscle rigidity
Sweating and tremors
Severe cases of serotonin syndrome can be fatal, so it’s critical to avoid combining 5-HTP and Molly too closely.
When to Take 5-HTP After Molly
The safest and most effective time to take 5-HTP is after Molly’s effects have worn off, typically 24 hours after use. By waiting until MDMA is fully metabolized, you reduce the risk of serotonin syndrome while allowing your body to start replenishing its serotonin reserves.
Here’s a general guideline for taking 5-HTP after Molly:
Day of Molly use: Avoid taking 5-HTP. Allow the body to metabolize the MDMA naturally.
24 hours after Molly: Begin taking 50-100mg of 5-HTP to support serotonin recovery. Some people start with smaller doses to avoid overstimulation.
For the next few days: Continue taking 50-100mg of 5-HTP once or twice daily for up to three days. This helps replenish serotonin and may reduce symptoms of the comedown.
Why Timing Matters
Timing is crucial because the body needs time to reset after the surge of serotonin caused by MDMA. By taking 5-HTP after the body has had time to metabolize the Molly, you give your brain a chance to safely rebuild its serotonin levels without overwhelming it with too much serotonin at once.
Potential Risks of Using 5-HTP with Molly
While 5-HTP can help ease the comedown from Molly, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks involved, especially if used improperly.
1. Serotonin Syndrome
As mentioned earlier, combining 5-HTP with Molly too soon can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. This condition can be life-threatening, so it's important to wait at least 24 hours after using Molly before introducing 5-HTP into your system.
2. Overstimulation
Some people report feeling overstimulated or jittery when taking high doses of 5-HTP. If you are sensitive to supplements or medications, start with a lower dose of 5-HTP (such as 50mg) and increase slowly if needed.
3. Interactions with Other Medications
5-HTP can interact with medications that affect serotonin levels, such as antidepressants (SSRIs) or MAOIs. If you are on any medications that affect serotonin, consult with a healthcare professional before using 5-HTP, especially in combination with Molly.
4. Gastrointestinal Issues
Some users experience nausea, upset stomach, or diarrhea when taking 5-HTP. If you experience these side effects, consider reducing your dose or taking the supplement with food to minimize discomfort.
Additional Tips for Recovery After Molly
In addition to taking 5-HTP, there are several other strategies you can use to support your body and mind after using Molly:
1. Stay Hydrated
Molly use can lead to dehydration, especially if you’ve been dancing or exerting yourself. Drink plenty of water during and after using Molly to stay hydrated and support your recovery.
2. Eat Nutrient-Dense Foods
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help support serotonin production and overall well-being. Foods like turkey, bananas, and nuts contain tryptophan, an amino acid that is a precursor to serotonin.
3. Get Plenty of Rest
Sleep is essential for recovery after using Molly. Make sure to prioritize rest and allow your body time to recuperate. If you experience difficulty sleeping, consider natural supplements like melatonin to help regulate your sleep cycle.
4. Take Antioxidants
Molly use can increase oxidative stress in the brain. Taking antioxidant supplements like vitamin C or N-acetylcysteine (NAC) may help reduce oxidative damage and support recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding when to take 5-HTP and Molly is key to safely managing the aftereffects of MDMA use. While 5-HTP can be a helpful supplement for replenishing serotonin and easing the comedown, it’s important to wait at least 24 hours after Molly use before taking it. This reduces the risk of serotonin syndrome and allows your body to recover naturally.
If used responsibly and in the correct dosage, 5-HTP can be a valuable tool in supporting mood, reducing fatigue, and speeding up recovery after Molly use. However, it’s always important to prioritize safety, stay hydrated, eat well, and get plenty of rest to ensure your body recovers fully.
2 notes
·
View notes