#Aerospace Industry
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Thsu is really important and shouldn't be ignored or looked over, these workers have been underpaid and without health insurance for some time now. What's worse is that people will demonize them for the crime of understanding the value of their labor and wanting better, as usual those people view workers from industrial manufacturers to service workers to be invisible or inhuman beings that do stuff for them. If anything I'm lucky Boeing has an awful reputation right which might sound strange but hesr me out, with everything going on with the suspicious deaths and widespread visible safety failures you'd look really bad defending Boeing in this strike given their current reputation, though you'll always have corporate stooges who love the taste of leather in their mouth. Dontate to the strikers if you can and promote the news regarding it, the more eyes and ears the better, don't let this simply fade from the news cycle!!!
#progressive#eat the rich#leftism#us politics#tax the rich#culture#the left#communism#corporate greed#politics#striking#boeing#Boeing is a bastard#Airplane#plane#flying#airbus#aerospace engineering#aerospace industry#aviation#labor rights#workers rights#unions#unionize#capitalism#billionaires should not exist#billionaire#markets#capital#financial updates
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
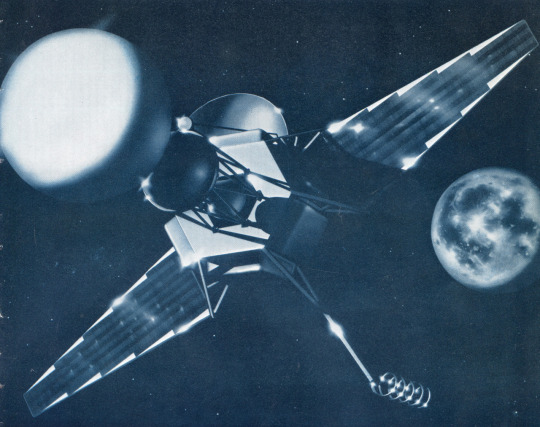
To while away time on its journey to the Moon the space probe blew bubbles to while away the time.
Aerospace Engineering Magazine - 1961
#vintage illustration#illustration#1961#1960s#1960's#aerospace#aerospace industry#space probe#funny#humor#humour
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Carbon Fiber Market- Unleashing Potential in Carbon Composites
Carbon fiber yarns containing up to 95% carbon appeared in markets around the 1970’s. Manufacturing processes also improved over the period. In the 1990s and 2000 engineers further scrutinized carbon fiber characteristics to explore more applications. This quest has resulted in skyrocketed market growth in recent years.
Beginning from military applications to aircraft and sports carbon fibers have gained traction of momentum in recent years. Certainly, its strength and light weight are key characteristics attracting growth. The carbon fiber market evolved to a much bigger size since then acquiring a horizon of applications across many industries.
Carbon fiber reduces the weight of aircraft and increases its fuel efficiency. Carbon fiber is strong enough to increase the safety of aircraft. The only restraining factor in the use of carbon fiber in aircraft is its price. Being more expensive than traditional materials companies may find it difficult to repair. However, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks of carbon fiber in aerospace.
Cycle manufacturers are foreseen to reap benefits from the procurement of carbon fiber in the coming decade. Growing emphasis on active lifestyle is bound to increase cycling activities among Americans leading to growth in demand for light weight cycles. Growing carbon fiber applications indicate promising ROIs for manufacturers investing in the carbon fiber market.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
#youtube video#Aircraft Preservation#Air Force Heritage#tucson#Aircraft Maintenance#arizona#Aviation Enthusiasts#Aerospace Engineering#davis-monthan air force base#Arizona Air Force Base#Aircraft Restoration#aviation#air force#usaf#boneyard#Military History#Aircraft Parts#aircraft#aircraft preservation#aircraft maintenance#aviation enthusiasts#aerospace preservation#aerospace industry#military history#aircraft parts#aircraft collection#us air force#aircraft boneyard#Youtube
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aero India 2025: भारत में एयरोस्पेस उद्योग के लिए नए अवसरों का द्वार
Aero India 2025, एशिया का सबसे बड़ा एयरोस्पेस शो, 10 से 14 फरवरी 2025 तक बेंगलुरु के येलहांका एयरफोर्स स्टेशन पर आयोजित होने जा रहा है। “द रनवे टू ए बिलियन ऑपर्च्युनिटीज़” थीम के तहत आयोजित होने वाले इस शो का उद्देश्य वैश्विक और भारतीय कंपनियों के बीच साझेदारियां स्थापित करना और स्वदेशीकरण की प्रक्रिया को गति देना है। यह कार्यक्रम न केवल सैन्य विमानन की दुनिया के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण अवसर है, बल्कि…
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
A launchpad for entrepreneurship in aerospace
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/a-launchpad-for-entrepreneurship-in-aerospace/
A launchpad for entrepreneurship in aerospace


At age 22, aerospace engineer Eric Shaw worked on some of the world’s most powerful airplanes, yet learning to fly even the smallest one was out of reach. Just out of college, he could not afford civilian flight school and spent the next two years saving $12,000 to earn his private pilot’s license. Shaw knew there had to be a better, less expensive way to train pilots.
Now a graduate student at the MIT Sloan School of Management’s Leaders for Global Operations (LGO) program, Shaw joined the MIT Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics’ (AeroAstro) Certificate in Aerospace Innovation program to turn a years-long rumination into a viable solution. Along with fellow graduate students Gretel Gonzalez and Shaan Jagani, Shaw proposed training aspiring pilots on electric and hybrid planes. This approach reduces flight school expenses by up to 34 percent while shrinking the industry’s carbon footprint.
The trio shared their plan to create the Aeroelectric Flight Academy at the certificate program’s signature Pitchfest event last spring. Equipped with a pitch deck and a business plan, the team impressed the judges, who awarded them the competition’s top prize of $10,000.
What began as a curiosity to test an idea has reshaped Shaw’s view of his industry.
“Aerospace and entrepreneurship initially seemed antithetical to me,” Shaw says. “It’s a hard sector to break into because the capital expenses are huge and a few big dogs have a lot of influence. Earning this certificate and talking face-to-face with folks who have overcome this seemingly impossible gap has filled me with confidence.”
Disruption by design
AeroAstro introduced the Certificate in Aerospace Innovation in 2021 after engaging in a strategic planning process to take full advantage of the research and ideas coming out of the department. The initiative is spearheaded by AeroAstro professors Olivier L. de Weck SM ʼ99, PhD ʼ01 and Zoltán S. Spakovszky SM ʼ99, PhD ʼ00, in partnership with the Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship. Its creation recognizes the aerospace industry is at an inflection point. Major advancements in drone, satellite, and other technologies, coupled with an infusion of nongovernmental funding, have made it easier than ever to bring aerospace innovations to the marketplace.
“The landscape has radically shifted,” says Spakovszky, the Institute’s T. Wilson (1953) Professor in Aeronautics. “MIT students are responding to this change because startups are often the quickest path to impact.”
The certificate program has three requirements: coursework in both aerospace engineering and entrepreneurship, a speaker series primarily featuring MIT alumni and faculty, and hands-on entrepreneurship experience. In the latter, participants can enroll in the Trust Center’s StartMIT program and then compete in Pitchfest, which is modeled after the MIT $100K Entrepreneurship Competition. They can also join a summer incubator, such as the Trust Center’s MIT delta v or the Venture Exploration Program, run by the MIT Office of Innovation and the National Science Foundation’s Innovation Corps.
“At the end of the program, students will be able to look at a technical proposal and fairly quickly run some numbers and figure out if this innovation has market viability or if it’s completely utopian,” says de Weck, the Apollo Program Professor of Astronautics and associate department head of AeroAstro.
Since its inception, 46 people from the MIT community have participated and 13 have fulfilled the requirements of the two-year program to earn the certificate. The program’s fourth cohort is underway this fall with its largest enrollment yet, with 21 postdocs, graduate students, and undergraduate seniors across seven courses and programs at MIT.
A unicorn industry
When Eddie Obropta SM ʼ13, SM ʼ15 attended MIT, aerospace entrepreneurship meant working for SpaceX or Blue Origin. Yet he knew more was possible. He gave himself a crash course in entrepreneurship by competing in the MIT $100K Entrepreneurship Competition four times. Each year, his ideas became more refined and battle-tested by potential customers.
In his final entry in the competition, Obropta, along with MIT doctoral student Nikhil Vadhavkar and Forrest Meyen SM ’13 PhD ’17, proposed using drones to maximize crop yields. Their business, Raptor Maps, won. Today, Obropta serves as the co-founder and chief technology officer of Raptor Maps, which builds software to automate the operations and maintenance of solar farms using drones, robots, and artificial intelligence
While Obropta received support from AeroAstro and MIT’s existing entrepreneurial ecosystem, the tech leader was excited when de Weck and Spakovszky shared their plans to launch the Certificate in Aerospace Innovation. Obropta currently serves on the program’s advisory board, has been a presenter at the speaker series, and has served as a mentor and judge for Pitchfest.
“While there are a lot of excellent entrepreneurship programs across the Institute, the aerospace industry is its own unique beast,” Obropta says. “Today’s aspiring founders are visionaries looking to build a spacefaring civilization, but they need specialized support in navigating complex multidisciplinary missions and heavy government involvement.”
Entrepreneurs are everywhere, not just at startups
While the certificate program will likely produce success stories like Raptor Maps, that is not the ultimate goal, say de Weck and Spakovszky. Thinking and acting like an entrepreneur — such as understanding market potential, dealing with failure, and building a deep professional network — are characteristics that benefit everyone, no matter their occupation.
Paul Cheek, executive director of the Trust Center who also teaches a course in the certificate program, agrees.
“At its core, entrepreneurship is a mindset and a skill set; it’s about moving the needle forward for maximum impact,” Cheek says. “A lot of organizations, including large corporations, nonprofits, and the government, can benefit from that type of thinking.”
That form of entrepreneurship resonates with the Aeroelectric Flight Academy team. Although they are meeting with potential investors and looking to scale their business, all three plan to pursue their first passions: Jagani hopes to be an astronaut, Shaw would like to be an executive at one of the “big dog” aerospace companies, and Gonzalez wants to work for the Mexican Space Agency.
Gonzalez, who is on track to earn her certificate in 2025, says she is especially grateful for the people she met through the program.
“I didn’t know an aerospace entrepreneurship community even existed when I began the program,” Gonzalez says. “It’s here and it’s filled with very dedicated and generous people who have shared insights with me that I don’t think I would have learned anywhere else.”
#000#Aeronautical and astronautical engineering#aeronautics#aerospace#aerospace industry#aircraft#airplanes#approach#artificial#Blue#board#Building#Business#carbon#carbon footprint#change#Classes and programs#college#Community#Companies#competition#course#courses#crash#Crop Yields#curiosity#disruption#dog#dogs#drone
0 notes
Text
The Ascending Aerostat Market: A Comprehensive Analysis
The aerostat market is surging, incorporating its high diversity of airborne platforms such as airships, blimps, and tethered balloons, driven by the combination of technological breakthroughs with growing demand across various fields. Aerostats have benefits toward surveillance and communications, scientific research, and even advertising, thereby offering unique advantages over traditional aircraft as well as drones.
The aerostat market is expected to rise from US$ 8.45 billion in 2023 to US$ 16.70 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period of 2023–2031.
Market Dynamics
Key Drivers
Improved Surveillance Capabilities: Aerostats are used for persistent, wide-area surveillance for border security, disaster management, and law enforcement purposes.
Telecommunications Infrastructure: The equipment can be used for rapid or permanent installation of the telephone network in sparsely populated or disaster-hitting areas.
Scientific Research: The Aerostat is put to practical applications for atmospheric and climatic studies and space explorations. Advertising and Marketing: Aerostats offers an adventurous and glamorous way of showing brands and products.
Market Restraints
Adverse weather factors could increase the sensitivity of operating such aerostats which in turn include strong winds along with heavy rains.
High Upfront Investment: Building and launching aerostat systems demand a lot of upfront investment.
Strict Airspace and Aviation Safety Regulations: Aerostat operations are bound by regulations that regulate airspace and ensure aviation safety.
Market Segmentation
By Product Type
Airships
Balloons
Hybrid Aerostat
HAPS
By Payload
Surveillance Radar
Navigation System
Communication Relays
By Application
Military and Commercial
By Region
North America
Europe
Asia-Pacific
South and Central America
Middle East and Africa
Key Players
Aero
Allsopp Helikites Ltd
ILC Dover
Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd
Lindstrand Technologies Inc
Lockheed Martin Corporation
Raven Industries Inc
Raytheon Company
RT
Future Outlook
Aerostat Market to grow with immense momentum ahead, considering the developments and advancements in technology, raising demand for surveillance and communication solutions, and the newer applications that are coming along. Key trends to keep an eye on include AI and IoT integration - integration of artificial intelligence and Internet of Things will further empower aerostats by giving advanced data analysis capabilities and autonomous operation.
Hybrid Airships- Incorporating into the airships the advantages of aircraft for improved performance and efficiency.
Increased Use in Renewable Energy: Aerostats can carry heavy elements of renewable energy projects to reduce transportation costs while saving the environment.
Conclusion-
The aerostat market is dynamic and highly evolving. With the help of technological advancement and overcoming regulatory challenges, this industry is very well poised to play a critical role in the future of aviation and aerospace. Frequently Asked Questions-
Which is the largest regional market for Aerostat?
Ans: - North America is the largest regional market for Aerostat.
Which companies have the maximum share in the Aerostat market?
Ans: - Aeros, Allsopp Helikites Ltd, ILC Dover, Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), Lindstrand Technologies Limited, Raven Industries Inc, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, RT, and TCOM LP are some top companies that hold maximum market shares.
What is the growth rate expected for this market during the period from 2023 to 2031?
Ans: - The Aerostat market is expected to grow at a growth rate of 8.9% during the forecast period.
How big is the Aerostat market?
Ans: - The global market size for Aerostat reached US$ 8.45 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach US$ 16.70 billion by 2031.
What are the different segments in the Aerostat market?
Ans: The Aerostat market is segmented into Product Type, Payload, Application, and region.
About Us-
The Insight Partners is among the leading market research and consulting firms in the world. We take pride in delivering exclusive reports and sophisticated strategic and tactical insights into the industry. Reports are generated through a combination of primary and secondary research, solely aimed at giving our clientele a knowledge-based insight into the market and domain. This is done to assist clients in making wiser business decisions. A holistic perspective in every study undertaken forms an integral part of our research methodology and makes the report unique and reliable.
0 notes
Text
BIS Research continuously monitors the developments in the aircraft and drone market and actively maintains an in-house database of participants and market developments. The research practice covers the entire aircraft/drone ecosystem, including urban air mobility (UAM)/advanced air mobility (AAM) infrastructure, eVTOLs, drones, related services, and regulatory frameworks to support clients across diverse market intelligence requirements.
#Aircraft and Drones Market#Aircraft and Drones Industry#Aircraft and Drones Market Reports#Aerospace Industry#BIS Research#Aircraft Market
0 notes
Text

Bolts: The Incredible Mechanics Behind Fastener and How They Revolutionized Construction
Bolts Fastener are one of the most simple and ubiquitous fasteners used in construction and mechanical assemblies. At their core, fastener are cylindrical rods with threads on one end that can be tightened or loosened by turning. When fitted through holes and tightened with a nut, fastener securely join two or more components together. Different Types of Bolts There are many varieties of fastener used for different applications. Bolts are commonly used to join metal parts and feature hexagonal heads that can be driven with a wrench. Lag fastener, also called coach screws, have large, cylindrSical heads and sharp threads that allow them to grip into wood or similar materials. Carriage fastener have a rounded head that sits flush and a square shoulder under the head to prevent rotation. Stove fastener are short fastener used to join thin sheets of metal, often found in appliances. Socket head cap screws feature a spherical head that can be driven with a hex key or socket tool. Allen fastener have a hexagonal socket in the head that is tightened with an Allen wrench. Material Composition Fastener are most commonly made of steel or stainless steel. Carbon steel fastener are inexpensive and strong for general construction use. Stainless steel holds up well to corrosion and is commonly used in wet or saltwater environments. Other materials may include brass, aluminum, titanium and specialty alloys depending on the application requirements and operating environment. Higher grades of steel such as alloy steels provide better strength characteristics but at increased cost. The material selection depends on factors like tensile strength needed, operating temperature range, and resistance to corrosion or wear expected. Thread Standards and Specifications Thread standards ensure fastener and nuts from different manufacturers properly interface. Fastener are identified by their diameter, length, thread type, class or grade of material. Common thread standards include unified coarse (UNC), unified fine (UNF), and metric threads. Fastener may have additional specifications for plating, finish, strength class or grade based on standards set by organizations like ASME, SAE, and ISO. Proper specifications ensure fastener reliably provide the clamping force and performance needed for particular engineering applications. Advantages of Bolted Joints There are several advantages that make bolted joints a popular mechanical fastening method: - Versatility - Fastener can join a wide variety of materials and assembly configurations from light fixtures to heavy machinery. - Removability - Bolted connections allow easy disassembly without damaging components for maintenance, repair, or replacement. - Adjustability - Fastener can be tightened or loosened to precisely control clamping force and preload on joints. - Strength - Properly selected and installed fastener provide very high tensile and shear strength for securely joining parts. - Tolerance for error - Bolted joints still function properly despite minor variations in hole alignment or part dimensions. - Economy - Fastener provide strong connections at relatively low cost compared to other joining methods like welding. Fastener in Construction In construction, fastener play a crucial structural role. Anchor fastener secure wooden framing members to concrete or masonry foundations. Lag fastener join beams, joists, and decking to walls or support posts. Machine fastener assembly prefabricated structural members and connect rebar in reinforced concrete slabs and footings. Carriage fastener hold together window and door frames, siding panels, and roofing sheets. Stove fastener install appliance panels and fasten thin gauge sheet metal. Due to their versatility, strength, economy and removability— fastener represent one of the most important innovations that enabled modern construction techniques. Get more insights on, Bolts
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want.
French
German
Italian
Russian
Japanese
Chinese
Korean
Portuguese
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Full Screw Bolt#Half Screw Bolt#Construction Sector#Automotive Industry#Aerospace Industry#Raw Material Price Volatility#Technological Advancements
0 notes
Text
#Aviation#Aerospace#aviation industry#aerospace industry#aerospace engineering#virtual reality#vr training
0 notes
Text
India: The Emerging Global Hub for Manufacturing, Maintenance, and Logistics
Imagine a world where India isn’t just the land of vibrant cultures, ancient history, and spicy curry but also the backbone of global manufacturing, maintenance, and logistics. This vision is rapidly becoming a reality, transforming India’s role in the global economy and military alliances. As this transformation unfolds, the implications are profound, setting the stage for India to become an…
#2024#aerospace industry#allied nations#armed forces#defense sector#digital transformation#diplomatic ties#economic development#economic growth#geopolitical significance#global hub#Global Supply Chain#India#Indo-Pacific#industrial corridors#infrastructure#international partnerships#Logistics#maintenance#Make in India#Manufacturing#maritime services#non-alignment#QUAD#regional-security#repairs#skilled labor#strategic location#Strategic-Alliances#technological advancements
0 notes
Text
High-Performance Adhesives for Aircraft Manufacturing
In the aerospace industry, the demand for high-performance adhesives has never been greater. As aircraft designs evolve, the need for materials that can withstand extreme conditions while ensuring structural integrity and safety is paramount. High-performance adhesives have become integral to aircraft manufacturing, providing exceptional strength, durability, and reliability.
One of the primary reasons aerospace adhesives are indispensable is their ability to bond various materials such as metals, composites, and plastics. These adhesives offer a seamless bonding solution, reducing the need for mechanical fasteners, which in turn decreases the aircraft's weight and enhances fuel efficiency. Among the various types of adhesives used, epoxy adhesives stand out for their remarkable properties. Epoxy adhesive manufacturers in India are at the forefront of developing formulations that cater specifically to the aerospace sector's rigorous requirements.
In addition to strength, electrically conductive adhesives are gaining traction in aircraft manufacturing. These adhesives ensure reliable electrical conductivity while providing robust mechanical bonding, making them ideal for electronic components within aircraft. The ability to conduct electricity without compromising on bond integrity is a game-changer for the industry, paving the way for more efficient and reliable aerospace systems.
As an adhesive manufacturer in India, Kohesi Bond is dedicated to producing high-quality aerospace adhesives that meet international standards. Our range of epoxy adhesives is designed to endure extreme temperatures, resist environmental degradation, and maintain superior performance under stress. We understand the critical role these adhesives play in ensuring the safety and efficiency of aircraft, and our products reflect this commitment to excellence.
In conclusion, the advancements in aerospace adhesives are revolutionizing aircraft manufacturing. With the expertise of epoxy adhesive manufacturers in India and the innovative solutions provided by companies like Kohesi Bond, the future of aerospace construction is set to soar to new heights.
For more information about our high-performance adhesives, visit Kohesi Bond.
#Aerospace adhesives#Aircraft manufacturing#High-performance adhesives#Epoxy adhesives#Electrically conductive adhesive#Adhesive manufacturer in India#Epoxy adhesive manufacturers in India#Aerospace industry#Structural adhesives for aircraft#Aviation bonding solutions#Lightweight aircraft materials#Kohesi Bond aerospace adhesives#Advanced adhesive technologies
1 note
·
View note
Text
Airbus Nearing Decision on H125 Helicopter Assembly Site in India
Airbus Helicopters is close to finalizing the location for its new final assembly line (FAL) in India, intended for the H125 helicopter. Eight potential sites are currently under evaluation, according to top Airbus Helicopters officials.

Expansion Plans in India
The proposed FAL, a collaboration between Airbus Helicopters and Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL), aims to meet the growing demand in India and South Asia. The decision on the location is expected soon, with the groundbreaking ceremony planned for late 2024 and the first H125 helicopter rolling out by 2026.
Olivier Michalon, Executive Vice President Global Business of Airbus Helicopters, emphasized that the final decision will consider factors like employee attractiveness, industrial activity, logistics, and regulations. “We are still in the final assessment stage but stay tuned, we should be in a position to announce shortly,” Michalon told reporters at Airbus Helicopters’ headquarters in Marignane, near Marseille.
Strategic Partnership
This FAL will be the first in the private sector in India, marking a significant milestone for Airbus and TASL. It follows the announcement made on India’s Republic Day during the French President Emmanuel Macron’s state visit to India. This is the second aircraft FAL by Airbus and TASL, with the first being the C295 military aircraft FAL in Vadodara.
Production Capacity and Future Prospects
Initially, the India FAL will have an annual production capacity of 10 H125 helicopters. Currently, the H125 is manufactured at Airbus Helicopters’ headquarters in Marignane, as well as in the US and Brazil. Although starting with a modest production capacity, Michalon mentioned the potential for significant expansion based on market demand. “Starting from scratch, it is not negligible. It could very well be 20, 30, or 50 in some years,” he noted.
Market Potential in India
India’s civil helicopter market, while currently small, holds immense potential due to its large population and economic growth. Airbus anticipates that producing the H125 in India will boost the usage of helicopters across various sectors.
Sunny Guglani, Head of Airbus Helicopters South Asia, highlighted the flexibility to ramp up production in response to demand. He cited a projected demand for 500 H125 class helicopters in India and neighboring countries over the next 20 years. “We have approximately 140 Airbus Helicopters in the region, with 100 in India alone,” Guglani stated, noting Airbus’s 40% market share in civil and para-public helicopters in the region.
Broader Implications
Michalon described the current market as “embryonic” but ripe for expansion. He pointed out that India’s growing middle and upper classes will drive demand for various services, including emergency medical services, law enforcement, firefighting, and disaster management. “We had two possibilities: either we wait for the sky to fully open, or we demonstrate our trust and the recognition of the potential of India and be ready to invest,” Michalon explained.
The H125, known for its versatility in missions like emergency medical services, law enforcement, and aerial work, is well-suited to meet India’s diverse needs. With around 7,200 H125 helicopters in operation worldwide, it is one of Airbus Helicopters’ most popular models.
Looking Ahead
Although smaller in scale, the H125 FAL in India will adhere to the same processes and standards as Airbus’s flagship facility in Marignane. The helicopters produced will carry the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) certification and will be competitively priced. Airbus is confident that this strategic move will enhance its global footprint and address the growing demand in the South Asian region.
In conclusion, Airbus’s decision to establish an H125 FAL in India is a testament to the country’s potential as a major hub for helicopter manufacturing and use. Stay tuned for the official announcement of the site location, which promises to be a significant development in the aerospace industry.
#Airbus Helicopters#H125 Helicopter#India Assembly Line#Tata Advanced Systems Limited#Aerospace Industry
0 notes
Text
Semiconductor Parts in the Aircraft Industry: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
In the fast-paced world of aviation, where precision, reliability, and safety are paramount, the role of semiconductor components cannot be overstated. These tiny yet powerful devices form the backbone of modern aircraft systems, enabling critical functions that ensure smooth operations from takeoff to landing. Let’s explore some key semiconductor parts and their contributions to the aerospace industry.
Diodes: Directing Current Flow with Precision
Diodes are fundamental semiconductor components in aircraft systems. They primarily serve to control the direction of electric current, ensuring that electricity flows in only one direction. In aviation, diodes are used in various applications such as power supplies, switching circuits, and voltage regulation. They play a crucial role in protecting sensitive electronic equipment from reverse voltage spikes and ensuring stable operation of essential systems.
Triacs: Controlling AC Power
Triacs are semiconductor devices that enable the precise control of AC (alternating current) power. They are extensively used in aircraft for applications such as dimming lights, controlling heating elements, and managing motor speed. Triacs allow for efficient and reliable adjustment of power levels, contributing to energy savings and operational flexibility in onboard systems.
Transistors: Switching and Amplification
Transistors are perhaps the most versatile semiconductor devices found in aircraft electronics. They serve dual roles as switches and amplifiers, crucial for controlling signals and power in avionics systems. Transistors enable efficient switching of digital signals, amplification of weak signals from sensors, and modulation of radio frequencies in communication systems. Their reliability and performance under varying environmental conditions make them indispensable in aerospace applications.
Bridge Rectifiers: Converting AC to DC
Bridge rectifiers are semiconductor assemblies used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). In aircraft, where numerous systems and equipment rely on DC power, bridge rectifiers play a critical role in converting power from generators and other AC sources into a usable form. They ensure a steady and reliable supply of DC voltage for avionics, navigation instruments, communication devices, and other essential onboard systems.
SCRs (Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers): Ensuring Power Regulation
SCRs are semiconductor devices used for precise control of large electrical currents. They excel in applications requiring high current regulation and are commonly found in aircraft power management systems. SCRs ensure efficient power distribution, voltage regulation, and protection against overcurrent conditions. Their robust design and ability to handle high-power loads make them essential for maintaining the reliability and safety of critical aircraft systems.
Challenges and Innovations in Semiconductor Technology
The aerospace industry poses unique challenges for semiconductor technology. Aircraft operate in extreme environmental conditions, including wide temperature ranges, high altitude, and electromagnetic interference. Semiconductor manufacturers continually innovate to develop components that meet stringent aerospace standards for reliability, durability, and performance under such demanding conditions.
Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques are key to producing semiconductor parts capable of withstanding the rigors of flight. Specialized coatings, ruggedized designs, and enhanced thermal management techniques ensure that semiconductor devices maintain optimal performance throughout their operational lifespan.
Future Directions and Beyond
Looking forward, semiconductor technology will continue to drive innovation in the aerospace industry. Advancements in materials science, miniaturization, and integration will enable more compact and energy-efficient aircraft systems. The ongoing development of smart sensors, artificial intelligence, and connectivity solutions will further enhance aircraft performance, safety, and passenger comfort.
In conclusion, semiconductor components are integral to the evolution of aviation technology, enabling aircraft to operate more efficiently, safely, and reliably. As aerospace engineering continues to push boundaries, semiconductor innovation will play a central role in shaping the future of air travel, ensuring that aircraft remain at the forefront of technological advancement in the 21st century and beyond.
#semiconductors#aircraft parts#aviation industry#aerospace#aviation parts#aerospace industry#industrial parts supplier
1 note
·
View note
Text
Aramid Fiber Market: A Comprehensive Overview
The global aramid fiber market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. Aramid fibers are a class of synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and abrasion resistance, making them an essential component in various applications.
Market Size and Growth
The global aramid fiber market size was valued at USD 4.3 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 9.6 Billion by 2033, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% during the forecast period 2024 – 2033. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for aramid fibers in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, defense, and infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
The global aramid fiber market is segmented based on type and application. Para-aramid fibers dominated the market in 2021, accounting for the largest market share of 57% and market revenue of USD 2.06 Billion. Meta-aramid fibers are also gaining popularity due to their unique properties, such as flame resistance, electrical insulation, and chemical stability.
Applications of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers have a wide range of applications across various industries. Security and protection equipment is the largest application segment, accounting for 27% of the market share in 2021. Other significant applications include frictional materials, optical fibers, rubber reinforcement, tire reinforcement, aerospace, and electrical insulation.
Market Drivers and Restraints
The growth of the aramid fiber market is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries, the growing need for safety and protection equipment, and the rising demand for eco-friendly and sustainable materials. However, the high cost of production and investment in research and development (R&D) are some of the key restraints hindering the growth of the market.
Regional Analysis
The global aramid fiber market is segmented into North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific (APAC), Latin America (LATAM), and Middle East and Africa (MEA). APAC is expected to be the fastest-growing region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India.
Competitive Landscape
The global aramid fiber market is highly competitive, with several key players operating in the market. Teijin Aramid B.V., DowDuPont Inc., Yantai Tayho Advanced materials Co. Ltd, KOLON Industries Inc., Huvis, Kermel, JSC Kamenskvolokno, China National Bluestar (Group) Co. Ltd., Hyosung Corp., and Toray Chemicals South Korea Inc. are some of the major players operating in the market.
Future Prospects
The global aramid fiber market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. The market is expected to witness significant growth in the APAC region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global aramid fiber market is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for lightweight and high-strength materials in various industries. The market is expected to witness significant growth in the APAC region, driven by the growing demand for aramid fibers in countries such as China and India. The competitive landscape is highly competitive, with several key players operating in the market.
#aramid fiber market#aramid fibers#synthetic fibers#lightweight materials#high strength materials#aerospace industry#automotive industry#defense industry#infrastructure industry#electrical insulation#frictional materials#optical fibers#rubber reinforcement#tire reinforcement#security and protection equipment
0 notes