#ATF = Federal Bureau of Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
One of my favorite examples of "Deadpool's not actually an idiot."
Context: In this issue, Deadpool takes down a corrupt police department in very rural Georgia. Rather than kill 'em all (as suggested by the cops' mastermind), he invites the Feds to catch them all red-handed at their illegal moonshine distillery. Initially, he's cuffed and detained along with everyone else.
His little interaction with the ATF agents at the end is fantastic.


Love it. It's like...summary of my favorite version of Deadpool. He's heroic, he does good things, he doesn't kill anyone in this issue - but he's also dangerous, his good intentions don't erase his bad habits or volatile nature. He definitely wanted to kill the whole lot of 'em (in fairness, one of theirs killed him first, that's why he got involved) and had to dial it back to "wait, I don't do that anymore."
Plus - smart enough to turn his bad reputation into an advantage, sometimes. He probably wouldn't have hurt those agents (not on purpose), but they don't need to know that...
IDK I just love this sequence. :)
#deadpool (2008) issue 22#deadpool#wade wilson#ATF = Federal Bureau of Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms#genius to call them in bc actually proving these corrupt cops ran a crime ring robbing and terrorizing people could have taken forever#but caught red handed with an illegal distillery means the ATF could arrest every last one of them on the spot#ATF Agent is the smartest man on this page
148 notes
·
View notes
Text

Kash Patel sworn in as Director of the FBI by Attorney General Pam Bondi
#hey I know that guy 😉#the final jewel in the crown#kashyap patel#kash patel#federal bureau of investigation#fbi#fbi director#alcohol tobacco and firearms#atf#president trump#trump administration#trump 47#donald trump#american politics#us politics#united states#america#usa#🇺🇸#2025
36 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Tags:and Explosives (ATF)#Bureau of Alcohol#Constitutional Freedoms#facts#Federal Overreach#Firearm Legislation#Firearms#Gun Control Laws#Gun Ownership#Gun Rights#life#Podcast#Second Amendment#serious#State Regulations#Supreme Court Decisions#Tobacco#truth#upfront#website#Post navigation
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
GUYS!!! Stop saying Coyle is singing his ABCs wrong!!
"T, P, D, A, T, F, C, I, A, F, B, I, U, S, P, I, S, D, O, D, S, S, S, U, S, A."
He's not singing his ABCs he's just using the same tune, they're all acronyms
TPD = ?*
ATF = Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives
CIA = Central Intelligence Agency,
FBI = Federal Bureau of Investigation,
USPIS = United States Postal Inspection Service,
DOD = United States Department of Defense,
SSS = Selective Service System,
USA = United States of America
Okay? So let's all stop saying he's uneducated or illiterate because he's definitely not. Pre-Sinyala Coyle kept "obsessively complete notes" according to Clyde Perry's account, and furthermore just look at his pretty handwriting on the evidence boxes, that's not an uneducated scrawl. Coyle is willfully ignorant, but he's not lacking in basic literacy skills.

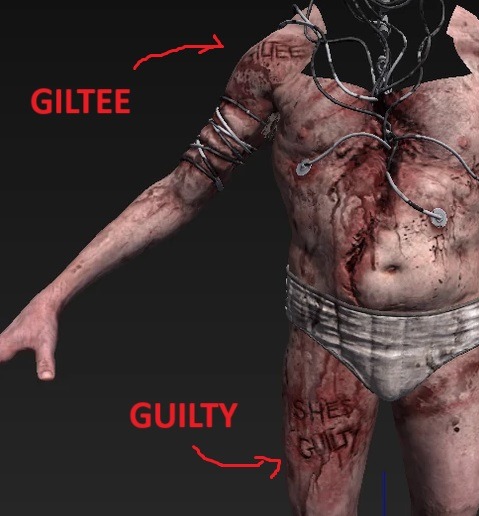
"But Leon, why did he misspell Guilty as Giltee on the Scapegoat?"
Well, friend, I don't entirely know. But as he's spelt it correctly in other places, he probably did it on purpose, matching his dialect to emphasise his point. Maybe he just forgot about the U and by the time he'd started carving the L he knew he needed to commit to his fuck up.
*Sooo I have some theories as to what TPD could stand for.
Total Permanent Disability. In one of Coyles' dialogues, he mentions his Father losing his foot in the Battle of Hürtgen Forest. That injury would likely see him permanently disabled and unable to work as he had before (it's implied that Coyles' parents were cattle ranchers), therefore he would be entitled to welfare checks.
Tulsa Police Department. Tulsa and Blackwell are within 2 hours drive of each other and it's very possible that Coyle completed his training at the Tulsa Police Academy before going on to work for the Blackwell Police Department. Tulsa also has history of violent racism, which would appeal to Coyle.
Tactical PSYOPS Detachment/United States Psychological Operations. There was extensive use of psychological operations in World War II, and given everything that the Outlast Trials are about I think this is a worthy contender.
Tobacco Products Directive. This was the only other thing I could think of that would make sense in conjunction with Coyle, but it's a European Union directive, and therefore I think it's unlikely this is what Coyle is referring to, but I still thought it was worth mentioning.
If you have any better ideas please feel free to share them!

A big big thank you to my friends in the Coyle Crew: @misa-bun @soggy-bean and @mortisdeth for their help in researching, theorising and giving me moral support when I thought I was about to lose it
#leland coyle#sergeant leland coyle#sergeant coyle#officer coyle#the outlast trials#outlast trials#outlast#friends stuff#its just a theory#backed up by evidence#Coyleology
338 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Attorney General Pam Bondi on Thursday fired Pamela Hicks, the general counsel for the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF).
“Earlier today, I was served official notice from the Attorney General of the United States that I was being removed from my position as the Chief Counsel of ATF and my employment with the Department of Justice terminated,” Hicks said in a statement on social media confirming the news.
“I have had the privilege of serving in the federal civil service for almost 28 years, including 23 as an attorney for the Department of Justice,” Hicks continued. “Serving as ATF Chief Counsel has been the highest honor of my career and working with the people at ATF and throughout the Department has been a pleasure.”
Gun Owners of America said that Hicks “oversaw the enforcement of every Biden infringement of the Second Amendment since taking the position in 2021.”
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heather Cox Richardson:
MAGA representatives have been introducing a slew of measures to the new Congress, many of which incorporate the plans of Project 2025 into legislation. They call for turning over immigration to the states, privatizing veterans’ healthcare, and repealing the 1993 National Voting Rights Act, the 2010 Affordable Care Act, and the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act.
Bills call for withdrawing the U.S. from the World Health Organization; increasing oil and gas production on federal lands; abolishing the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF), and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA); allowing states to spend federal education money on private school vouchers; and removing the protection of transgender rights from schools. Other measures would revoke security clearances for “certain former members of the intelligence community,” introduce a constitutional amendment to cap the Supreme Court at nine justices, and cut off federal funding to the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office (the office that successfully charged Trump with election interference) and the Fulton County (GA) District Attorney’s Office (the office that has charged Trump with criminal conspiracy). And MAGA Republicans have proposed a bill to impose a national abortion ban.
Is this what the country wants? More like the wet dream of a minority of a minority.
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) has run a secretive program for years where ICE agents have trained hundreds of civilian volunteers on how to operate multiple types of firearms, conduct investigations and surveillance of immigrants, and use lethal force on human beings. The program, known as Citizens Academies, includes role-play scenarios for civilians to conduct fictional raids on immigrants and is active in New York and in more than a dozen cities across the country. The program is run by Homeland Security Investigations, the branch of ICE in charge of intelligence, international affairs, and surveillance. [...] An ICE spokesperson confirmed to Documented that HSI’s Citizens Academies are still ongoing across the country. Similar initiatives are implemented by other law enforcement agencies, including the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), the spokesperson said.
So where's the FEMA academy?
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's the complete list of DHS flagged search terms. Don't use any of these on social media to avoid having the 3-letter agencies express interest in your activities!
DHS & Other Agencies
Department of Homeland Security (DHS)
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
Coast Guard (USCG)
Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
Border Patrol
Secret Service (USSS)
National Operations Center (NOC)
Homeland Defense
Immigration Customs Enforcement (ICE)
Agent
Task Force
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
Fusion Center
Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA)
Secure Border Initiative (SBI)
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
Alcohol Tobacco and Firearms (ATF)
U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (CIS)
Federal Air Marshal Service (FAMS)
Transportation Security Administration (TSA)
Air Marshal
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
National Guard
Red Cross
United Nations (UN)
Domestic Security
Assassination
Attack
Domestic security
Drill
Exercise
Cops
Law enforcement
Authorities
Disaster assistance
Disaster management
DNDO (Domestic Nuclear Detection Office)
National preparedness
Mitigation
Prevention
Response
Recovery
Dirty Bomb
Domestic nuclear detection
Emergency management
Emergency response
First responder
Homeland security
Maritime domain awareness (MDA)
National preparedness initiative
Militia
Shooting
Shots fired
Evacuation
Deaths
Hostage
Explosion (explosive)
Police
Disaster medical assistance team (DMAT)
Organized crime
Gangs
National security
State of emergency
Security
Breach
Threat
Standoff
SWAT
Screening
Lockdown
Bomb (squad or threat)
Crash
Looting
Riot
Emergency Landing
Pipe bomb
Incident
Facility
HAZMAT & Nuclear
Hazmat
Nuclear
Chemical Spill
Suspicious package/device
Toxic
National laboratory
Nuclear facility
Nuclear threat
Cloud
Plume
Radiation
Radioactive
Leak
Biological infection (or event)
Chemical
Chemical burn
Biological
Epidemic
Hazardous
Hazardous material incident
Industrial spill
Infection
Powder (white)
Gas
Spillover
Anthrax
Blister agent
Exposure
Burn
Nerve agent
Ricin
Sarin
North Korea
Health Concern + H1N1
Outbreak
Contamination
Exposure
Virus
Evacuation
Bacteria
Recall
Ebola
Food Poisoning
Foot and Mouth (FMD)
H5N1
Avian
Flu
Salmonella
Small Pox
Plague
Human to human
Human to ANIMAL
Influenza
Center for Disease Control (CDC)
Drug Administration (FDA)
Public Health
Toxic
Agro Terror
Tuberculosis (TB)
Agriculture
Listeria
Symptoms
Mutation
Resistant
Antiviral
Wave
Pandemic
Infection
Water/air borne
Sick
Swine
Pork
Strain
Quarantine
H1N1
Vaccine
Tamiflu
Norvo Virus
Epidemic
World Health Organization (WHO and components)
Viral Hemorrhagic Fever
E. Coli
Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure security
Airport
CIKR (Critical Infrastructure & Key Resources)
AMTRAK
Collapse
Computer infrastructure
Communications infrastructure
Telecommunications
Critical infrastructure
National infrastructure
Metro
WMATA
Airplane (and derivatives)
Chemical fire
Subway
BART
MARTA
Port Authority
NBIC (National Biosurveillance Integration Center)
Transportation security
Grid
Power
Smart
Body scanner
Electric
Failure or outage
Black out
Brown out
Port
Dock
Bridge
Canceled
Delays
Service disruption
Power lines
Southwest Border Violence
Drug cartel
Violence
Gang
Drug
Narcotics
Cocaine
Marijuana
Heroin
Border
Mexico
Cartel
Southwest
Juarez
Sinaloa
Tijuana
Torreon
Yuma
Tucson
Decapitated
U.S. Consulate
Consular
El Paso
Fort Hancock
San Diego
Ciudad Juarez
Nogales
Sonora
Colombia
Mara salvatrucha
MS13 or MS-13
Drug war
Mexican army
Methamphetamine
Cartel de Golfo
Gulf Cartel
La Familia
Reynose
Nuevo Leon
Narcos
Narco banners (Spanish equivalents)
Los Zetas
Shootout
Execution
Gunfight
Trafficking
Kidnap
Calderon
Reyosa
Bust
Tamaulipas
Meth Lab
Drug trade
Illegal immigrants
Smuggling (smugglers)
Matamoros
Michoacana
Guzman
Arellano-Felix
Beltran-Leyva
Barrio Azteca
Artistics Assassins
Mexicles
New Federation
Terrorism
Terrorism
Al Queda (all spellings)
Terror
Attack
Iraq
Afghanistan
Iran
Pakistan
Agro
Environmental terrorist
Eco terrorism
Conventional weapon
Target
Weapons grade
Dirty bomb
Enriched
Nuclear
Chemical weapon
Biological weapon
Ammonium nitrate
Improvised explosive device
IED (Improvised Explosive Device)
Abu Sayyaf
Hamas
FARC (Armed Revolutionary Forces Colombia)
IRA (Irish Republican Army)
ETA (Euskadi ta Askatasuna)
Basque Separatists
Hezbollah
Tamil Tiger
PLF (Palestine Liberation Front)
PLO (Palestine Libration Organization)
Car bomb
Jihad
Taliban
Weapons cache
Suicide bomber
Suicide attack
Suspicious substance
AQAP (Al Qaeda Arabian Peninsula)
AQIM (Al Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb)
TTP (Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan)
Yemen
Pirates
Extremism
Somalia
Nigeria
Radicals
Al-Shabaab
Home grown
Plot
Nationalist
Recruitment
Fundamentalism
Islamist
Weather/Disaster/Emergency
Emergency
Hurricane
Tornado
Twister
Tsunami
Earthquake
Tremor
Flood
Storm
Crest
Temblor
Extreme weather
Forest fire
Brush fire
Ice
Stranded/Stuck
Help
Hail
Wildfire
Tsunami Warning Center
Magnitude
Avalanche
Typhoon
Shelter-in-place
Disaster
Snow
Blizzard
Sleet
Mud slide or Mudslide
Erosion
Power outage
Brown out
Warning
Watch
Lightening
Aid
Relief
Closure
Interstate
Burst
Emergency Broadcast System
Cyber Security
Cyber security
Botnet
DDOS (dedicated denial of service)
Denial of service
Malware
Virus
Trojan
Keylogger
Cyber Command
2600
Spammer
Phishing
Rootkit
Phreaking
Cain and abel
Brute forcing
Mysql injection
Cyber attack
Cyber terror
Hacker
China
Conficker
Worm
Scammers
Social media
SOCIAL MEDIA?!
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Thorny Problem of Straw Purchases in U.S. Gun Law
by Cliff Montgomery - Feb. 15th, 2024
Yesterday’s mass shooting at a parade intended to celebrate the Kansas City Chiefs’ recent Super Bowl victory over the San Francisco 49s once again reminds us of the need for serious gun laws and gun law reform.
On February 9th, two short reviews on current federal gun laws were released by the Congressional Research Service (CRS). The CRS refers to itself as a “ non-partisan shared staff to congressional committees and Members of Congress.” In short, it prepares concise, easy-to understand reports on matters of the moment to members of the U.S. and their affiliated staff members.
We will cover those two short studies for our readers. Tonight, we look at the report Gun Control: Straw Purchase and Gun Trafficking Provisions in Public Law 117-159, better known as the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act.
Straw purchases are defined by the study as “illegal firearms transactions in which a person serves as a middleman by posing as the transferee, but is actually acquiring the firearm for another person.”
Below, we offer readers most of the central statements found in the CRS report:
“On June 25, 2022, President Joe Biden signed into law the Bipartisan Safer Communities Act (BSCA; S. 2938; P.L. 117-159). This law includes the Stop Illegal Trafficking in Firearms Act, provisions of which amend the Gun Control Act of 1968 (GCA, 18 U.S.C. §§921 et seq.) to more explicitly prohibit straw purchases and illegal gun trafficking. Related provisions expand federal law enforcement investigative authorities.
Federal Firearms Law
“The GCA is the principal statute regulating interstate firearms commerce in the United States. The purpose of the GCA is to assist federal, state, and local law enforcement in ongoing efforts to reduce violent crime.
“Congress constructed the GCA to allow state and local governments to regulate firearms more strictly within their own borders, so long as state law does not conflict with federal law or violate constitutional provisions.
“Hence, one condition of a federal firearms license for gun dealers, which permits the holder to engage in interstate firearms commerce, is that the licensee must comply with both federal and state law.
“Also, under the GCA there are several classes of persons prohibited from shipping, transporting, receiving, or possessing firearms or ammunition (e.g., convicted felons, fugitives, unlawful drug users). It was and remains unlawful under the GCA for any person to transfer knowingly a firearm or ammunition to a prohibited person (18 U.S.C. §922(d)). Violations are punishable by up to 10 years’ imprisonment.
“The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) is the principal agency that administers and enforces the GCA, as well as the 1934 National Firearms Act (NFA, 26 U.S.C. §§5801 et seq.).
“The NFA further regulates certain firearms deemed to be especially dangerous (e.g., machine guns, short-barreled shotguns) by taxing all aspects of the making and transfer of such weapons and requiring their registration with the Attorney General.
Straw Purchase Provision
“Straw purchases are illegal firearms transactions in which a person serves as a middleman by posing as the transferee, but is actually acquiring the firearm for another person.
“As discussed below, straw purchases are unlawful under two existing laws. Prosecutions under those provisions have been characterized by some as mere paperwork violations and, hence, inadequate in terms of deterring unlawful gun trafficking.
“P.L. 117-159 amends the GCA with a new provision, 18 U.S.C. §932, to prohibit any person from knowingly purchasing or conspiring to purchase any firearm for, on behalf of, or at the request or demand of any other persons if the purchaser knows or has reasonable cause to believe that the actual buyer
is a person prohibited from being transferred a firearm under 18 U.S.C. §922(d);
plans to use, carry, possess, or sell (dispose of) the firearm(s) in furtherance of a felony, federal crime of terrorism, or drug trafficking crime; or
plans to sell or otherwise dispose of the firearm(s) to a person who would meet any of the conditions described above.
“Violations are punishable by a fine and up to 15 years’ imprisonment. Violations made by a person knowing or having reasonable cause to believe that any firearm involved will be used to commit a felony, federal crime of terrorism, or drug trafficking crime are punishable by a fine and up to 25 years’ imprisonment.
Gun Trafficking Provision
“Gun trafficking entails the movement or diversion of firearms from legal to illegal channels of commerce in violation of the GCA. P.L. 117-159 amends the GCA with a new provision, 18 U.S.C. §933, to prohibit any person from shipping, transporting, causing to be shipped or transported, or otherwise disposing of any firearm to another person with the knowledge or reasonable cause to believe that the transferee’s use, carrying, or possession would constitute a felony.
“It would also prohibit the receipt of such firearm if the transferee knows or has reasonable cause to believe that receiving it would constitute a felony. Attempts and conspiracies to violate these provisions are proscribed as well. Violations are punishable by a fine and up to 15 years’ imprisonment. […]
GCA Interstate Transfer Prohibitions
“The GCA generally prohibits anyone who is not a Federal Firearms Licensee (FFL) from acquiring a firearm from an out-of-state source. [But] Interstate transfers among unlicensed persons may be facilitated through an FFL in the state where the transferee resides. […]
GCA Record-keeping and Straw Purchases
“Under the GCA (18 U.S.C. §926), Congress authorized a decentralized system of record-keeping allowing ATF to trace a firearm’s chain of commerce, from manufacturer or importer to dealer, and to the first retail purchaser of record. FFLs must maintain certain records, including ATF Forms 4473, on transfers to non-FFLs as well as a parallel acquisition/disposition log.
“As part of a firearms transaction, both the FFL and purchaser must truthfully fill out and sign the ATF Form 4473. The FFL must verify the purchaser’s name, date of birth, and other information by examining government-issued identification (e.g., driver’s license). The purchaser attests on Form 4473 that he or she is not a prohibited person and is the actual transferee/buyer. […]
“[However,] straw purchases are not easily detected because they only become apparent when the straw purchase is revealed by a subsequent transfer to a prohibited person.
Other GCA Gun Trafficking Prohibitions
“According to ATF, gun trafficking often entails an unlawful flow of firearms from jurisdictions with less restrictive firearms laws to jurisdictions with more restrictive firearms laws, both domestically and internationally.
“Such unlawful activities can include, but are not limited to, the following:
straw purchasers or straw purchasing rings in violation of the provisions described above;
persons engaging in the business of dealing in firearms without a license in violation of 18 U.S.C. §921(a)(1)(A), punishable by up to 5 years’ imprisonment;
corrupt FFLs dealing off-the-books in an attempt to escape federal regulation in violation of 18 U.S.C. §922(b)(5), punishable by up to 5 years’ imprisonment; and
trafficking in stolen firearms in violation of 18 U.S.C. §922(j), punishable by up to 10 years’ imprisonment.
“Under current law, offenders could potentially be charged with multiple offenses under both the preexisting GCA provisions such as those discussed above and 18 U.S.C. §§932 and 933.
“Since P.L. 117-159 went into effect on October 31, 2023, 250 defendants have been charged with gun trafficking, including 80 charged with violating the law’s straw purchase provision.
“In January 2024, the National Shooting Sports Foundation—an industry trade group for the firearms industry—noted that the ATF has yet to implement two parts of P.L. 117-159: ‘Firearm Handler Background Checks’ (FHCs) and instant point-of-sale background checks when an FFL buys from a private individual.
“The former would allow FFLs to use the NICS to background check FFL employees and has been in regulatory review since September 26, 2023. The latter would allow FFLs to instantly identify if a weapon is stolen at the point of sale by authorizing importers, manufacturers, and dealers of firearms to access records of stolen firearms in the National Crime Information Center; it has been in the interim final rule stage since May 17, 2023.”
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
Officials in Camden County, Missouri are refusing to cooperate with the ATF, local reports said.
The ATF asked for the zoning information of people applying to open new gun stores, per KCUR 89.3.
Officials cited a since-struck-down state law that kept police from enforcing federal gun laws.
Missouri officials in one county have refused to work with the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, or ATF, claiming that the government agency is unconstitutional.
Might I say…based.
Now, this does seem to be in reference to people applying for licenses to open new gun stores. Hopefully the Camden County officials will work with those entrepreneurs to make sure they can open their businesses without waiting on ATF approval.
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thousands of ads on Facebook and Instagram have promoted “fuel filters” using videos demonstrating how they can be easily modified into gun silencers—a process that, without federal approval, could lead to felony charges. Despite Meta’s policies banning ads for silencers on the company’s social networks, the promotions have persisted for years, driven by a what appears to be a single network of more than 100 Facebook pages marketing “fuel filters” that can be easily turned into gun silencers, WIRED has found. The devices sell for as little as $50.
Silencers, also known as suppressors, are heavily regulated under United States federal law. Purchasing one legally requires submitting fingerprints, passing a background check, and paying a fee to the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF). Federal law allows people to build their own suppressors, provided they register the device with the ATF. But the ads don’t mention this key stipulation, marketing silencers to buyers who may not understand the legal risks.
“You know those things that are definitely not suppressors, even though they look just like suppressors,” a man says in a video that appears in many of the ads. “Well, but they’re still not suppressors, because they don’t have a hole in the other end. So, you can legally own one without going through the paperwork to own a suppressor, because it isn’t one.”
The ads often recycle the same text, referencing “light and durable air-grade aluminum,” and use videos stitched together from a handful of YouTube clips featuring firearms influencers and enthusiasts. The original creators of these videos are likely unaware their content is being used; one tells WIRED they had deleted the footage from YouTube years ago.
One ad features a suppressor engraved with the words Black Collar Arms. A co-owner of Black Collar Arms, who goes by Jeremy McSorely, tells WIRED his company has no connection to the ad. McSorely explains that the footage was taken from a blog and YouTube video he had uploaded years ago but has since removed. “The photos you saw were screenshots taken from my video,” he says, emphasizing that the suppressor was legally manufactured and engraved with their corporate information to comply with ATF regulations.
In November 2023, the ATF warned federal firearms licensees about marketing silencers as “solvent traps,” or contraptions purportedly used to collect gun oil and residue during cleaning. The agency clarified that legality depends on functionality, not what you call a product, and stressed that even incomplete parts intended for silencers are regulated under federal law.
“The test for whether an item is a silencer is not the label a manufacturer or retailer applies. Rather, it is the way the statute written by Congress applies to the item,” the ATF wrote, referring to definitions of suppressors in the Gun Control Act and the National Firearms Act.
A WIRED analysis of more than 2,800 ads revealed they are linked to a network of hundreds of ecommerce websites. These sites often reuse code, share IP addresses, and peddle the same low-quality knockoff products alongside the “fuel filters.” At least one of the sites was flagged by Google as a likely phishing scam.
Experts believe the operation is based in China and relies on a drop-shipping scheme. “It’s likely just a reshipper selling controversial or illegal products,” says Zach Edwards, a senior threat researcher at cybersecurity firm Silent Push who specializes in online data ecosystems.
Typically, Edwards explains, drop-shippers wait for a customer to place an order, then purchase the item from inexpensive online retailers, repackage it, and ship it to the customers. Edwards says that the operator behind the network is likely creating hundreds of websites, applying a moderate markup to the products, and spinning up Facebook pages to promote their items. “Even if some sites or ads get caught and taken down, others keep running,” Edwards says. “It’s a spray-and-pray method.”
Meta explicitly bans ads promoting weapons, silencers, and related modifications. According to Meta, ads are reviewed by an automated system with support from human moderators. However, enforcement has been inconsistent: While at least 74 of the ad campaigns in our analysis were removed for violating the platforms’ terms, the rest appeared to have run successfully.
After WIRED reached out to Meta, the company said that it removed the ads and associated advertising accounts. However, a quick search of Meta’s Ad Library revealed that nearly identical ones have since been published.
“Bad actors constantly evolve their tactics to avoid enforcement, which is why we continue to invest in tools and technology to help identify and remove prohibited content,” Meta spokesperson Daniel Roberts wrote in a statement.
Roberts says that many of the ads flagged by WIRED had little to no engagement, suggesting few people ever saw this content. However, at least two ads reviewed by WIRED had thousands of comments, including accusations that it was an ATF honeypot, complaints from self-identified buyers whose products never arrived, and even testimonials from others claiming the item worked as advertised. WIRED reached out to several commenters who said they had purchased the product—none responded.
The ads have also drawn the attention of US Department of Defense officials. An internal presentation to Pentagon staff, viewed by WIRED, claims that the targeted ad for a fuel filter had been served to US military personnel on a government computer at the Pentagon. The presentation, which a source says was delivered to high-ranking general officers, including the US Army’s chief information officer, raised flags over how social media algorithms are being used to target service members.
Meta’s Ad Library provides limited transparency, leaving it unclear exactly how these ads are targeted. Researchers suggest that Meta’s powerful ad tools, which allow advertisers to find niche audiences using granular targeting options, could be exploited to reach gun enthusiasts or military personnel. While Roberts confirmed that Meta did not detect any indication that these ads were targeting the military, WIRED found that advertisers can easily target users who list their job title as “US Army” or “military” on their profiles—an audience that Meta estimates includes up to 46,134 people.
Meta’s platforms have long struggled to prevent the sale of firearms and related products. An October 2024 joint report by the Tech Transparency Project found that more than 230 ads for rifles and ghost guns had run on Facebook and Instagram in nearly three months. Many of these ads directed buyers to third-party platforms like Telegram to complete transactions. In 2024, two Los Angeles County men were charged with operating an “unlicensed firearm dealing business” that used Instagram accounts to advertise and market the sale of more than 60 firearms, which included some untraceable ghost guns and weapons with scratched-off serial numbers. Both individuals have since pleaded guilty.
Silencers are rarely used in crimes, but their use is on the rise—nearly 5 million are registered in the United States, up from 1.3 million in 2017. Last month, 26-year-old software engineer Luigi Mangione allegedly used a 3D-printed gun equipped with a silencer to fatally shoot UnitedHealthcare CEO Brian Thompson on a street in midtown Manhattan.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Chicago man has pleaded guilty to charges in a 2021 drive-by shooting of three undercover law enforcement officers that he mistook for rival gang members, federal prosecutors announced Wednesday.
Eugene "Gen Gen" McLaurin, 31, entered the plea Tuesday to three counts of assaulting a federal officer and two counts of using a firearm during a crime of violence, prosecutors said.
Each firearm count is punishable by 10 years to life in prison and each assault count is punishable by up to 20 years, prosecutors said. U.S. District Judge Manish Shah scheduled sentencing for March 13, 2024.
McLaurin has been detained in federal custody since his arrest in 2021.
The shootings occurred on the morning of July 7, 2021, when two agents from the U.S. Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives and an ATF Task Force officer were driving in an unmarked vehicle while conducting a covert federal investigation on the South Side.
McLaurin admitted in a plea agreement that he had mistakenly suspected the officers were members of an opposing gang. McLaurin drove alongside the vehicle and fired several shots, leaving the three officers seriously injured, prosecutors said.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
ATF Firearm Expert Demonstration
A “leading firearm expert” with the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives demonstrates the disassembly and assembly of firearms. Here’s how the government agency in charge of issuing Federal Firearm Licenses to gun dealers and gunsmiths does it.
youtube
View On WordPress
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
?;'
if you write "cis men dni" my ass isn't/ interacting ether. if you write "cis men dni" my ass isn't interacting ether.
\'
01=8-['p \\
]
'47]
'/.]\/5689+3
\
\
The ATF was formerly part of the United States Department of the Treasury, having been formed in 1886 as the "Revenue Laboratory" within the Treasury Department's Bureau of Internal Revenue. The history of the ATF can be subsequently traced to the time of the revenuers or "revenoors"[5] and the Bureau of Prohibition, which was formed as a unit of the Bureau of Internal Revenue in 1920. It was made an independent agency within the Treasury Department in 1927, was transferred to the Justice Department in 1930, and became, briefly, a division of the FBI in 1933.
When the Volstead Act, which established Prohibition in the United States, was repealed in December 1933, the Unit was transferred from the Department of Justice back to the Department of the Treasury, where it became the Alcohol Tax Unit (ATU) of the Bureau of Internal Revenue. Special Agent Eliot Ness and several members of The "Untouchables", who had worked for the Prohibition Bureau while the Volstead Act was still in force, were transferred to the ATU. In 1942, responsibility for enforcing federal firearms laws was given to the ATU.
In the early 1950s, the Bureau of Internal Revenue was renamed "Internal Revenue Service" (IRS),[6] and the ATU was given the additional responsibility of enforcing federal tobacco tax laws. At this time, the name of the ATU was changed to the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax Division (ATTD).
In 1968, with the passage of the Gun Control Act, the agency changed its name again, this time to the Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms Division of the IRS and first began to be referred to by the initials "ATF". In Title XI of the Organized Crime Control Act of 1970, Congress enacted the Explosives Control Act, 18 U.S.C.A. Chapter 40, which provided for close regulation of the explosives industry and designated certain arsons and bombings as federal crimes. The Secretary of the Treasury was made responsible for administering the regulatory aspects of the new law, and was given jurisdiction over criminal violations relating to the regulatory controls. These responsibilities were delegated to the ATF division of the IRS. The Secretary and the Attorney General were given concurrent jurisdiction over arson and bombing offenses. Pub.L. 91-452, 84 Stat. 922, October 15, 1970.
In 1972, the ATF was officially established as an independent bureau within the Treasury Department on July 1, 1972, this transferred the responsibilities of the ATF division of the IRS to the new Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms. Rex D. Davis oversaw the transition, becoming the bureau's first director, having headed the division since 1970. During his tenure, Davis shepherded the organization into a new era where federal firearms and explosives laws addressing violent crime became the primary mission of the agency.[7] However, taxation and other alcohol issues remained priorities as the ATF collected billions of dollars in alcohol and tobacco taxes, and undertook major revisions of the federal wine labeling regulations relating to use of appellations of origin and varietal designations on wine labels.
The ATF was formerly part of the United States Department of the Treasury, having been formed in 1886 as the "Revenue Laboratory" within the Treasury Department's Bureau of Internal Revenue. The history of the ATF can be subsequently traced to the time of the revenuers or "revenoors"[5] and the Bureau of Prohibition, which was formed as a unit of the Bureau of Internal Revenue in 1920. It was made an independent agency within the Treasury Department in 1927, was transferred to the Justice Department in 1930, and became, briefly, a division of the FBI in 1933.
When the Volstead Act, which established Prohibition in the United States, was repealed in December 1933, the Unit was transferred from the Department of Justice back to the Department of the Treasury, where it became the Alcohol Tax Unit (ATU) of the Bureau of Internal Revenue. Special Agent Eliot Ness and several members of The "Untouchables", who had worked for the Prohibition Bureau while the Volstead Act was still in force, were transferred to the ATU. In 1942, responsibility for enforcing federal firearms laws was given to the ATU.
In the early 1950s, the Bureau of Internal Revenue was renamed "Internal Revenue Service" (IRS),[6] and the ATU was given the additional responsibility of enforcing federal tobacco tax laws. At this time, the name of the ATU was changed to the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax Division (ATTD).
In 1968, with the passage of the Gun Control Act, the agency changed its name again, this time to the Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms Division of the IRS and first began to be referred to by the initials "ATF". In Title XI of the Organized Crime Control Act of 1970, Congress enacted the Explosives Control Act, 18 U.S.C.A. Chapter 40, which provided for close regulation of the explosives industry and designated certain arsons and bombings as federal crimes. The Secretary of the Treasury was made responsible for administering the regulatory aspects of the new law, and was given jurisdiction over criminal violations relating to the regulatory controls. These responsibilities were delegated to the ATF division of the IRS. The Secretary and the Attorney General were given concurrent jurisdiction over arson and bombing offenses. Pub.L. 91-452, 84 Stat. 922, October 15, 1970.
In 1972, the ATF was officially established as an independent bureau within the Treasury Department on July 1, 1972, this transferred the responsibilities of the ATF division of the IRS to the new Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms. Rex D. Davis oversaw the transition, becoming the bureau's first director, having headed the division since 1970. During his tenure, Davis shepherded the organization into a new era where federal firearms and explosives laws addressing violent crime became the primary mission of the agency.[7] However, taxation and other alcohol issues remained priorities as the ATF collected billions of dollars in alcohol and tobacco taxes, and undertook major revisions of the federal wine labeling regulations relating to use of appellations of origin and varietal designations on wine labels.
2654879/*+-9*-/"
sorry i was cleaning my keyboard
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
[T]he constitutionality of Section 922(g) might be bolstered by – and might even require – an additional form of tailoring. A potentially important but moribund provision of federal law, 18 U.S.C. § 925(c), allows those who are prohibiting from possessing firearms to "make application to the Attorney General for relief from the disabilities imposed by Federal laws." The "Attorney General may grant such relief if it is established to his satisfaction that the circumstances regarding the disability, and the applicant's record and reputation, are such that the applicant will not be likely to act in a manner dangerous to public safety and that the granting of the relief would not be contrary to the public interest." Section 925(c) also provides for judicial review of a denial of this application.
Taken seriously, this provision could do a great deal to render the various federal firearms provisions consistent with a hypothetical general-law dangerousness principle. Part of the standard for relief is basically a dangerousness principle ("likely to act in a manner dangerous to public safety") and so this might be the appropriate legal channel for anybody who would otherwise have an as-applied constitutional challenge to the federal prohibitions.
However, for over thirty years, Congress has blocked the implementation of Section 925(c). As the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives reports: "Although federal law provides a means for the relief of firearms disabilities, ATF's annual appropriation since October 1992 has prohibited the expending of any funds to investigate or act upon applications for relief from federal firearms disabilities submitted by individuals. As long as this provision is included in current ATF appropriations, ATF cannot act upon applications for relief from federal firearms disabilities submitted by individuals." And because ATF cannot review the petitions at all, the Supreme Court has held, judicial review is unavailable too. Implementing a general law approach through a dangerousness principle might force Congress to reconsider this intransigence and restore Section 925 to its original role, or else face the legal consequences.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
It Begins: 20 Heavily Armed IRS & ATF Agents Raid Great Falls Gun Store, Seize Firearm Purchase Records
In an unprecedented move, twenty armed Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) agents carried out a raid on a gun store in Great Falls, Montana, seizing all Form 4473s – documents that record buyer’s information during firearms transactions.
Tom Van Hoose, owner of Highwood Creek Outfitters, alleges that he has been under constant surveillance by state and federal agencies for over two years, KRTV reported.
On Wednesday, the gun shop owner reported an unexpected visit from 20 heavily armed IRS agents at his store.
The agents reportedly arrived at the shop early in the morning, as Van Hoose was opening for the day.
https://www.thegatewaypundit.com/2023/06/it-begins-20-heavily-armed-irs-atf-agents/
3 notes
·
View notes