#5 June 1944
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text


Ladies and gentlemen, eighty years ago today, Field Marshal Montgomery – Commander in Chief of the Allied Ground Forces – wrote in his message to all soldiers on the eve of D-Day:
‘To us is given the honour of striking a blow for freedom, which will live in history; and, in the better days that lie ahead, men will speak with pride of our doings’.
Today, we come together to honour those nearly one hundred and sixty thousand British, Commonwealth and Allied troops who, on 5th June 1944, assembled here and along these shores to embark on the mission, which would strike that blow for freedom and be recorded as the greatest amphibious operation in history.
Those who gathered here in Portsmouth would never forget the sight. It was by far the largest military fleet the world has ever known.
Yet all knew that both victory and failure were possible, and none could know their fate.
Aircrew flying overhead, sailors manning warships; or troops in assault craft battering their way through the stormy swell to the shore; whether dropping by parachute, landing in a wooden glider, or taking that terrible leap of faith onto the beaches... all must have questioned whether they would survive and how they would respond when faced with such mortal danger.
The poet Keith Douglas, who was killed in action three days later, wrote of the embarkation:
"Actors waiting in the wings of Europe, we already watch the lights on the stage and listen to the colossal overture begin.
For us entering at the height of the din, it will be hard to hear our thoughts, hard to gauge how much our conduct owes to fear or fury."
At this remove, eight decades later, it is a near impossible task to imagine the emotion of that day:
The pride of being part of so great an enterprise, the anxiety of in some way not coming up to scratch, and the fear of that day being their last.
I recently myself spoke to veterans who, to this day, remember with such heartbreaking clarity the sight of those many soldiers lying on the beach, who drowned before they could even engage in combat.
The stories of courage, resilience and solidarity which we have heard today, and throughout our lives, cannot fail to move us, to inspire us, and to remind us of what we owe to that great wartime generation – now, tragically, dwindling to so few.
It is our privilege to hear their testimony, but our role is not purely passive:
It is our duty to ensure that we, and future generations, do not forget their service and their sacrifice in replacing tyranny with freedom.
Our rights, and the liberty won at such terrible cost, bring with them responsibilities to others in the exercise of that liberty.
The Allied actions of that day ensured the forces of freedom secured, first, a toehold in Normandy, then liberated France, and ultimately, the whole of Europe from the stranglehold of a brutal totalitarianism.
And as we remember, with humility, pride and gratitude, let us never forget that the soldiers who fought in the campaign launched from this place came from thirty nations, from across the United Kingdom, the Commonwealth and Allied countries; while elsewhere in Europe, Allied forces continued to make vital progress in their successful Italian campaign; and while halfway around the world, at that same moment, the critical battles of Imphal and Kohima raged on in what was then Burma.
The 1944 Victoria Cross roll of honour includes Sikh, Muslim and Hindu soldiers – a reminder that events that year shaped our world then, and the society we share today.
While it was the frontline troops who faced the greatest personal dangers, the privations and sacrifices of war were endured by so many more.
The Allied victory was a truly collective effort, born of the fortitude and hard work of those who remained on the Home Front, toiling in factories, under our land in the mines, out in the fields, or working in secret – men and women alike.
Their collective industry, ingenuity and commitment helped our soldiers, sailors and airmen to prevail.
So, as we give thanks for all those who gave so much to win the victory, whose fruits we still enjoy to this day, let us, once again, commit ourselves always to remember, cherish and honour those who served that day and to live up to the freedom they died for by balancing rights with civic responsibilities to our country. For we are all, eternally, in their debt.
Source: Royal UK
youtube
A speech by The King at the UK's National Commemorative Event in Portsmouth to mark #DDay80
5 June 2024
The King addresses veterans, serving forces and and members of the public at the UK's National Commemorative Event in Portsmouth to mark the 80th anniversary of the D-Day Landings.
#Youtube#D-Day#D-Day 1944#UK National Commemorative Event#Portsmouth#5 June 1944#D-Day Landings#Field Marshal Montgomery#Allied Ground Forces#Keith Douglas#1944 Victoria Cross#Allied Forces#World War II#war heroes#war veterans#King Charles III#Queen Camilla#British Royal Family
9 notes
·
View notes
Text

On June 5, 1944, two members of the ‘Filthy Thirteen’ with the 101st Airborne Division, Clarence Ware applies war paint to Charles Plauda, before jumping into Normandy.
The Filthy Thirteen was the name given to the 1st Demolition Section of the Regimental Headquarters Company of the 506th Parachute Infantry Regiment, 101st Airborne Division. They were ordered to secure or destroy the bridges over the Douve River during the Normandy Invasion of Europe in June 1944. Half were either killed, wounded or captured, but they accomplished their mission.
This unit was best known for the famous photo which appeared in Stars and Stripes, showing two members wearing Indian-style “mohawks” and applying war paint to one another. The inspiration for this came from unit sergeant Jake McNiece, who was part Choctaw.
#filthy thirteen#101st airborne#us army#world war 2#wwii#dday#operation overlord#normandy#military#history
724 notes
·
View notes
Text
i think its really funny when people say that it's unrealistic for will AND mike AND robin AND vickie to all be gay in the 80s cuz clearly they have never even looked back to the past. people in the 1900s were gay as hell! and heres some examples
james dean (1931-1955) bisexual !
marlon brando (1924-2004) bisexual !
rock hudson (1925-1985) very gay
leslie gore (1946-2015) lesbian
dusty springfield (1939-1999) lesbian
norma tanega (1939-2019) lesbian
(dusty springfield and norma tanega dated)
elton john (1947-present) gay
freddie mercury (1946-1991) gay
george michael (1963-2016) gay
david bowie (1947-2016) bi
crazy that david and elton were born the same year and george and david passed the same year
john lennon (1940-1980) bi im pretty sure unless yoko was lying for some reason
joan jett (1958-present) bi but google ai wants to argue with me about it
janis joplin (1943-1970) bi
whitney houston (1963-2012) bi?? maybe
debbie harry (blondie) (1945-present) bi (or ex bi LMAO)
billie holiday (1915-1959) bi
im lovin all the bi people
andy fraser (free) (1952-2015) gay
i do NOT like boy george at all but unfortunately hes an iconic gay artist and i have to add him (1961-present) gay 🙄
ray and dave davies from the kinks (1944+1947-present) ima just say that theyre both bisexual cuz its a bit confusing
art garfunkel (1941-present) bi. i just found this out like last year but ive always known in my soul. simon and garfunkel are like frog and toad or bert and ernie. you just know.
4/5 members of the b-52's are queer
little richard (1932-2020) gay
mick jagger (1943-present) bi? probably? idk but please go watch the mick jagger david bowie dancing in the street music video its the gayest thing ive ever seen
pete townshend (the who) (1945-present) pansexual
chuck panozzo (styx) (1948-present) gay
lou reed (velvet underground) (1942-2013) prooobably bi but google is giving me super confusing answers that are different since the last time i checked
morrissey 🙄 (this smiths) (1959-present) im diagnosing him as pan cuz all google says is "humansexual"
pete burns (dead or alive) (1959-2016) queer
jane wiedlin (the gogos) (1959-present) bi
june millington and alice de buhr of the band fanny are gay and nickey barclay is bi. (alice is one of my biggest drummer inspirations and i totally forgot she was gay)
neil tennant (pet shop boys) gay
marianne faithfull, katharine hepburn, ian mckellen, divine, rupaul, andy warhol, frankie goes to hollywood, soft cell probably, tab hunter, stephen fry, anthony perkins, cristopher walken, sal mineo, sister rosetta tharpe, billie joe armstrong, drew barrymore, jodie foster, fiona shaw, angelina jolie, etc
i have more but im tired
but these are just some people that are confirmed queer. i could go ooon and ooon and ooon about "not gay" people doing gay ass things
if you're going to make silly statements about the past please actually do a bit of research
not to mention the lesbians and the same sex kiss in the 1927 movie wings



#byler#rovickie#forgot that they were the point of the post#gay#queer#lesbian#bisexual#80s#70s#60s#50s#40s#stranger things#history#gay history#music history#film history#cinema history#gay celebs#will byers#mike wheeler#robin buckley#vickie stranger things
115 notes
·
View notes
Text

American troops of the 1ST ID leaving the port of Weymouth, Dorset in Southern England en route to Omaha Beach in Normandy. June 5 1944. (Photo by Robert Capa)
(Colorized by Jecinci )
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
D-Day was 80 years ago today!
D-Day was the first day of Operation Overlord, the Allied attack on German-occupied Western Europe, which began on the beaches of Normandy, France, on 6 June 1944. Primarily US, British, and Canadian troops, with naval and air support, attacked five beaches, landing some 135,000 men in a day widely considered to have changed history.
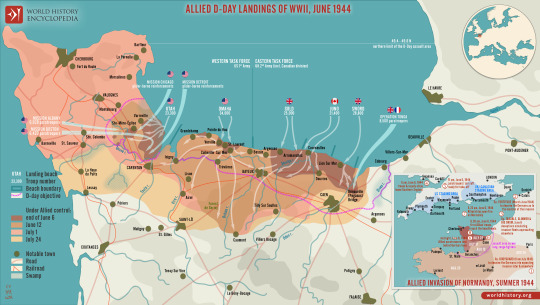
Where to Attack?
Operation Overlord, which sought to attack occupied Europe starting with an amphibious landing in northwest France, Belgium, or the Netherlands, had been in the planning since January 1943 when Allied leaders agreed to the build-up of British and US troops in Britain. The Allies were unsure where exactly to land, but the requirements were simple: as short a sea crossing as possible and within range of Allied fighter cover. A third requirement was to have a major port nearby, which could be captured and used to land further troops and equipment. The best fit seemed to be Normandy with its flat beaches and port of Cherbourg.
The Atlantic Wall
The leader of Nazi Germany, Adolf Hitler (1889-1945), called his western line of defences the Atlantic Wall. It had gaps but presented an impressive string of fortifications along the coast from Spain to the Netherlands. Construction of gun batteries, bunker networks, and observation posts began as early as 1942.
Many of the German divisions were not crack troops but inexperienced soldiers, who were spending more time building defences than in vital military training. There was a woeful lack of materials for Hitler's dream of the Atlantic Wall, really something of a Swiss cheese, with some strong areas, but many holes. The German army was not provided with sufficient mines, explosives, concrete, or labourers to better protect the coastline. At least one-third of gun positions still had no casement protection. Many installations were not bomb-proof. Another serious weakness was naval and air support. The navy had a mere 4 destroyers available and 39 E-boats while the Luftwaffe's (German Air Force's) contribution was equally paltry with only 319 planes operating in the skies when the invasion took place (rising to 1,000) in the second week.

Neptune to Normandy
Preparation for Overlord occurred right through April and May of 1940 when the Royal Air Force (RAF) and United States Air Force (USAAF) relentlessly bombed communications and transportation systems in France as well as coastal defences, airfields, industrial targets, and military installations. In total, over 200,000 missions were conducted to weaken as much as possible the Nazi defences ready for the infantry troops about to be involved in the largest troop movement in history. The French Resistance also played their part in preparing the way by blowing up train lines and communication systems that would ensure the defenders could not effectively respond to the invasion.
The Allied fleet of 7,000 vessels of all kinds departed from English south-coast ports such as Falmouth, Plymouth, Poole, Portsmouth, Newhaven, and Harwich. In an operation code-named Neptune, the ships gathered off Portsmouth in a zone called 'Piccadilly Circus' after the busy London road junction, and then made their way to Normandy and the assault areas. At the same time, gliders and planes flew to the Cherbourg peninsula in the west and Ouistreham on the eastern edge of the planned landing. Paratroopers of the 82nd and 101st US Airborne Division attacked in the west to try and cut off Cherbourg. At the eastern extremity of the operation, paratroopers of the 6th British Airborne Division aimed to secure Pegasus Bridge over the Caen Canal. Other tasks of the paratrooper and glider units were to destroy bridges to impede the enemy, hold others necessary for the invasion to progress, destroy gun emplacements, secure the beach exits, and protect the invasion's flanks.
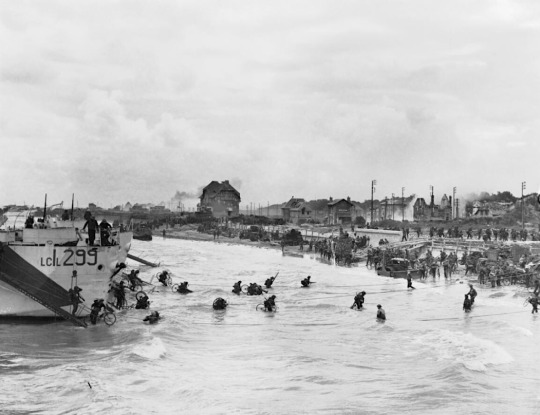

The Beaches
The amphibious attack was set for dawn on 5 June, daylight being a requirement for the necessary air and naval support. Bad weather led to a postponement of 24 hours. Shortly after midnight, the first waves of 23,000 British and American paratroopers landed in France. US paratroopers who dropped near Ste-Mère-Église ensured this was the first French town to be liberated. From 3.00 a.m., air and naval bombardment of the Normandy coast began, letting up just 15 minutes before the first infantry troops landed on the beaches at 6.30 a.m.
The beaches selected for the landings were divided into zones, each given a code name. US troops attacked two, the British army another two, and the Canadian force the fifth. These beaches and the troops assigned to them were (west to east):
Utah Beach - 4th US Infantry Division, 7th US Corps (1st US Army commanded by Lieutenant General Omar N. Bradley)
Omaha Beach - 1st US Infantry Division, 5th US Corps (1st US Army)
Gold Beach - 50th British Infantry Division, 30th British Corps (2nd British Army commanded by Lieutenant-General Miles C. Dempsey)
Juno Beach - 3rd Canadian Infantry Division (2nd British Army)
Sword Beach - 3rd British Infantry Division, 1st British Corps (2nd British Army)
In addition, the 2nd US Rangers were to attack the well-defended Pointe du Hoc between Utah and Omaha (although it turned out the guns had never been installed there), while Royal Marine Commando units attacked targets on Gold, Juno, and Sword.
The RAF and USAAF continued to protect the invasion fleet and ensure any enemy ground-based counterattack faced air attack. As the Allies could put in the air 12,000 aircraft at this stage, the Luftwaffe's aerial fightback was pitifully inadequate. On D-Day alone, the Allied air forces flew 15,000 sorties compared to the Luftwaffe's 100. Not one single Allied aircraft was lost to enemy fire on D-Day.
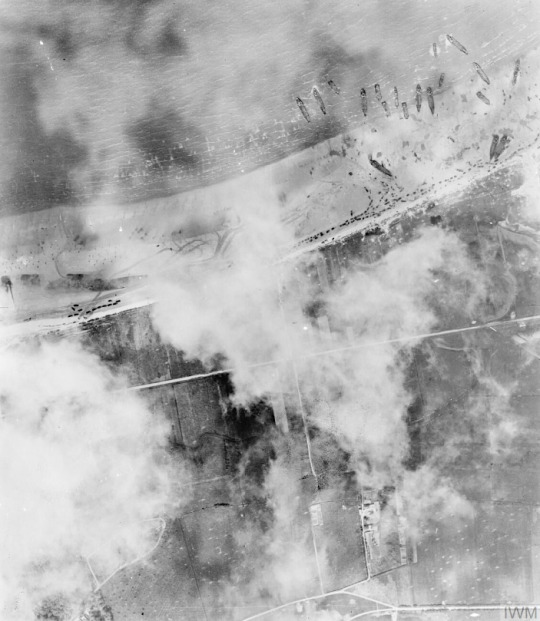

Packing Normandy
By the end of D-Day, 135,000 men had been landed and relatively few casualties were sustained – some 5,000 men. There were some serious cock-ups, notably the hopeless dispersal of the paratroopers (only 4% of the US 101st Air Division were dropped at the intended target zone), but, if anything, this caused even more confusion amongst the German commanders on the ground as it seemed the Allies were attacking everywhere. The defenders, overcoming the initial handicap that many area commanders were at a strategy conference in Rennes, did eventually organise themselves into a counterattack, deploying their reserves and pulling in troops from other parts of France. This is when French resistance and aerial bombing became crucial, seriously hampering the German army's effort to reinforce the coastal areas of Normandy. The German field commanders wanted to withdraw, regroup and attack in force, but, on 11 June, Hitler ordered there be no retreat.
All of the original invasion beaches were linked as the Allies pushed inland. To aid thousands more troops following up the initial attack, two artificial floating harbours were built. Code-named Mulberries, these were located off Omaha and Gold beaches and were built from 200 prefabricated units. A storm hit on 20 June, destroying the Mulberry Harbour off Omaha, but the one at Gold was still serviceable, allowing some 11,000 tons of material to be landed every 24 hours. The other problem for the Allies was how to supply thousands of vehicles with the fuel they needed. The short-term solution, code-named Tombola, was to have tanker ships pump fuel to storage tanks on shore, using buoyed pipelines. The longer-term solution was code-named Pluto (Pipeline Under the Ocean), a pipeline under the Channel to Cherbourg through which fuel could be pumped. Cherbourg was taken on 27 June and was used to ship in more troops and supplies, although the defenders had sunk ships to block the harbour and these took some six weeks to fully clear.
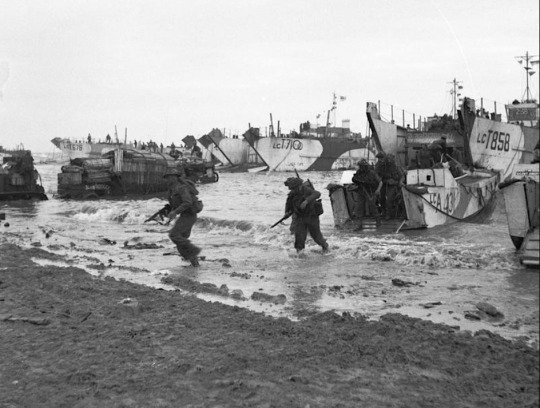

Operation Neptune officially ended on 30 June. Around 850,000 men, 148,800 vehicles, and 570,000 tons of stores and equipment had been landed since D-Day. The next phase of Overlord was to push the occupiers out of Normandy. The defenders were not only having logistical problems but also command issues as Hitler replaced Rundstedt with Field Marshal Günther von Kluge (1882-1944) and formally warned Rommel not to be defeatist.
Aftermath: The Normandy Campaign
By early July, the Allies, having not got further south than around 20 miles (32 km) from the coast, were behind schedule. Poor weather was limiting the role of aircraft in the advance. The German forces were using the countryside well to slow the Allied advance – countless small fields enclosed with trees and hedgerows which limited visibility and made tanks vulnerable to ambush. Caen was staunchly defended and required Allied bombers to obliterate the city on 7 July. The German troops withdrew but still held one-half of the city. The Allies lost around 500 tanks trying to take Caen, vital to any push further south. The advance to Avranches was equally tortuous, and 40,000 men were lost in two weeks of heavy fighting. By the end of July, the Allies had taken Caen, Avranches, and the vital bridge at Pontaubault. From 1 August, Patton and the US Third Army were punching south at the western side of the offensive, and the Brittany ports of St. Malo, Brest, and Lorient were taken.
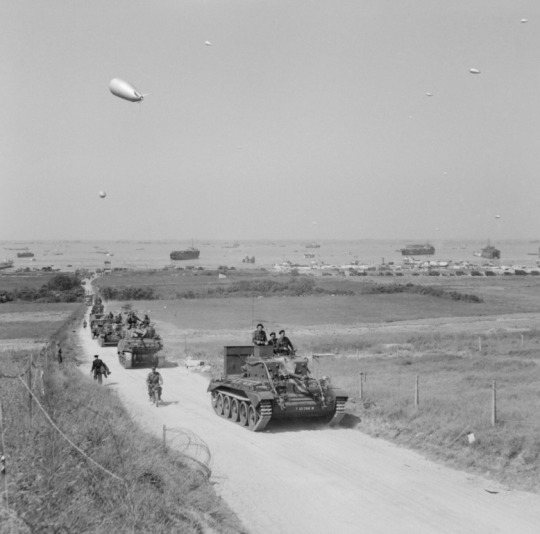

German forces counterattacked to try and retake Avranches, but Allied air power was decisive. Through August 1940, the Allies swept southwards to the Loire River from St. Nazaire to Orléans. On 15 August, a major landing took place on the southwest coast of France (French Riviera landings) and Marseille was captured on 28 August. In northern France, the Allies captured enough territory, ports, and airfields for a massive increase in material support. On 25 August, Paris was liberated. By mid-September, the Allied troops in the north and south of France had linked up and the campaign front expanded eastwards pushing on to the borders of Germany. There would be setbacks like Operation Market Garden of September and a brief fightback at the Battle of the Bulge in December 1944, but the direction of the war and ultimate Allied victory was now a question of not if but when.
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

Soldier of the US 34th Infantry Division armed with a bazooka on the outskirts of Rome, 5 June 1944.
94 notes
·
View notes
Text
D-DAY ANNIVERSARY
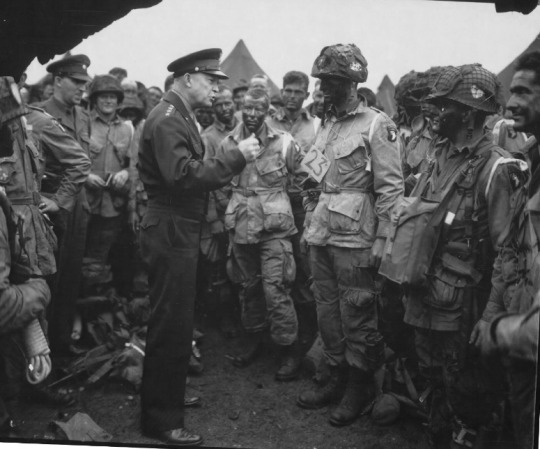

“You are about to embark upon the Great Crusade, toward which we have striven these many months. The eyes of the world are upon you. The hopes and prayers of liberty-loving people everywhere march with you…” With these words, Gen. Dwight D. Eisenhower issued the “Order of the Day” just before the 1944 Allied assault on Normandy Beach. It’s been 80 years since that historic day, and less than one percent of Americans who served in WWII are still alive. However, the impact of their service and sacrifice will live on forever.

Code named Operation Overlord, planning for D-Day began after France fell to the Nazis in 1940. It involved Allies from several countries and was the largest amphibious invasion in military history. As H-Hour approached (5:30 a.m. local time) on June 6, 1944, demolition teams had already blasted out underwater obstacles planted by German forces. Rangers were already scaling the cliffs to knock out coastal guns, and American and British airborne divisions had been dropped in hedgerows behind the beaches overnight. Soon, the first waves of Infantry would hit the beach.

Leonard T. Schroeder, Jr. served in the 2nd Battalion, 8th Infantry, Fourth Division, where he was the commanding officer of Company F.
He has the distinction of being the first man ashore at Utah Beach, the first beachhead, landing fewer than 60 seconds after H-Hour. Recalling the day, Schroeder said that Allied aircraft had bombed the beach heavily, creating craters that could be used as cover. Some of those craters were offshore and hidden by water. When Schroeder’s landing craft pulled ashore, he jumped off and into a water-filled crater six feet deep. He came up sputtering and struggled to rush ashore. Working his way up the beach, he was wounded by shrapnel but continued to fight. He commanded his company for three hours before collapsing into unconsciousness. He woke up at an aid station and was later evacuated to England. Schroeder received the Silver Star.

Pvt. Carlton W. Barrett served in the 18th Infantry, 1st Infantry Division and participated in the Normandy Invasion. His unit was in the third wave of Allied soldiers to come ashore at Omaha Beach, landing at about 10:00 a.m. Germans had planted mines on the beach about a foot apart, and the beach was strewn with bodies of soldiers. Barrett landed under heavy enemy fire, wading through neck-deep water. He noticed fellow soldiers around him floundering in the water and rushed to save them from drowning. Once on the beach, Barrett carried dispatches back and forth along the exposed beach while under heavy fire. He also carried wounded soldiers to an offshore evacuation boat. For his dauntless courage, Barrett was awarded the Medal of Honor.

The Allies landed over 160,000 troops on June 6, 1944, with an estimated 10,000 casualties, more than half of which were American. Today, a visit to the Normandy American Cemetery is the final resting place for 9,387 Americans and a sobering reminder of selfless service and the ultimate sacrifice made 80 years ago.
84 notes
·
View notes
Text
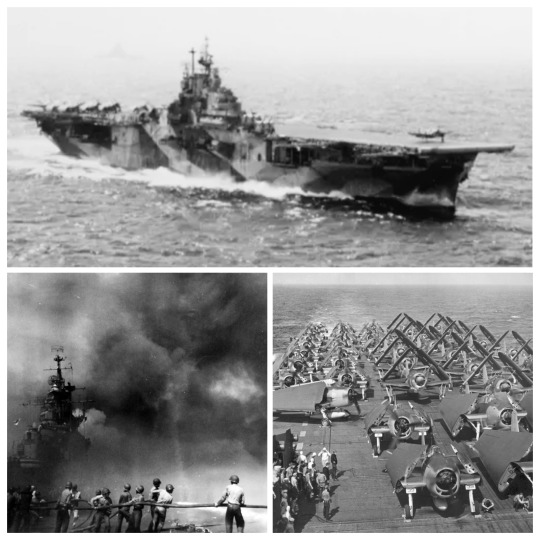

• USS Intrepid
USS Intrepid (CV/CVA/CVS-11), also known as The Fighting "I", is one of 24 Essex-class aircraft carriers built during World War II for the United States Navy. She is the fourth US Navy ship to bear the name. Commissioned in August 1943, Intrepid participated in several campaigns in the Pacific Theater of Operations. Because of her prominent role in battle, she was nicknamed "the Fighting I", while her frequent bad luck and time spent in dry dock for repairs—she was torpedoed once and hit in separate attacks by four Japanese kamikaze aircraft—earned her the nicknames "Decrepit" and "the Dry I".
The keel for Intrepid was laid down on December 1st, 1941 in Shipway 10 at the Newport News Shipbuilding & Dry Dock Co., Newport News, Virginia, days before the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and the United States' entrance into World War II. She was launched on April 26th, 1943, the fifth Essex-class aircraft carrier to be launched. She was sponsored by the wife of Vice Admiral John H. Hoover. In August 1943, she was commissioned with Captain Thomas L. Sprague in command before heading to the Caribbean for shakedown and training. She thereafter returned to Norfolk, before departing once more on December 3rd, bound for San Francisco. She proceeded on to Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, arriving there on 10 January, where she began preparations to join the rest of the Pacific Fleet for offensive operations against the Imperial Japanese Navy.
Intrepid joined the Fast Carrier Task Force, then Task Force 58 (TF 58), for the next operation in the island-hopping campaign across the Central Pacific: the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign. On January 16th, 1944, Intrepid, her sister ship Essex, and the light carrier Cabot left Pearl Harbor to conduct a raid on islands in the Kwajalein Atoll from January 29th to February 2nd. The three carriers' air group destroyed all 83 Japanese aircraft stationed on Roi-Namur in the first two days of the strikes, before Marines went ashore on neighboring islands on January 31st, in the Battle of Kwajalein. That morning, aircraft from Intrepid attacked Japanese beach defenses on Ennuebing Island until ten minutes before the first Marines landed. The Marines quickly took the island and used it as a fire base to support the follow-on attack on Roi. After the fighting in the Kwajalein Atoll finished, on February 3rd, Intrepid and the rest of TF 58 proceeded to launch Operation Hailstone, a major raid on the main Japanese naval base in the Central Pacific, Truk Lagoon. From the 17th to 19th of February, the carriers pounded Japanese forces in the lagoon, sinking two destroyers and some 200,000 GRT (gross register tonnage) of merchant ships.
The strikes demonstrated the vulnerability of Truk, which convinced the Japanese to avoid using it in the future. Intrepid did not emerge from the operation unscathed, however; on the night of 17th–18th of February, a Rikko type Torpedo Bomber from the 755th Kōkūtai (Genzan Air Group) flying from Tainan attacked and torpedoed the carrier near her stern. The torpedo struck 15 ft (5 m) below the waterline, jamming the ship's rudder to port and flooding several compartments. Sprague was able to counteract the jammed rudder for two days by running the port side screw at high speed while idling the starboard screw, until high winds overpowered the improvised steering. The crew then jury-rigged a sail out of scrap canvas and hatch covers, which allowed the ship to return to Pearl Harbor, where she arrived on February 24th. Temporary repairs were effected there, after which Intrepid steamed on March 16th, escorted by the destroyer USS Remey, to Hunters Point Naval Shipyard in San Francisco for permanent repairs, arriving there six days later. The work was completed by June, and Intrepid began two months of training around Pearl Harbor. Starting in early September, Intrepid joined operations in the western Caroline Islands; the Fast Carrier Task Force was now part of the Third Fleet under Admiral William Halsey Jr., and had been renamed Task Force 38. On September 6th and 7th, she conducted air strikes on Japanese artillery batteries and airfields on the island of Peleliu, in preparation for the invasion of Peleliu. On the 9th and 10th of September, she and the rest of the fleet moved on to attack airfields on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines, followed by further strikes on bases in the Visayan Sea between the 12th and 14th of September. On September 17th, Intrepid returned to Pelelieu to provide air support to the Marines that had landed on the island two days before.
Intrepid and the other carriers then returned to the Philippines to prepare for the Philippines campaign. At this time, Intrepid was assigned to Task Group 38.2. In addition to targets in the Philippines themselves, the carriers also struck Japanese airfields on the islands of Formosa and Okinawa to degrade Japanese air power in the region. On October 20th, at the start of the Battle of Leyte, Intrepid launched strikes to support Allied forces as they went ashore on the island of Leyte. By this time Halsey had reduced the carriers of TG 38.2, commanded by Rear Admiral Gerald F. Bogan aboard Intrepid, to just Intrepid, Cabot, and the light carrier Independence. Between the 23rd and 26th of October, the Japanese Navy launched a major operation to disrupt the Allied landings in the Philippines, resulting in the Battle of Leyte Gulf. On the morning of October 24th, a reconnaissance aircraft from Intrepid spotted Vice Admiral Takeo Kurita's flagship, Yamato. Two hours later, Intrepid and Cabot launched a strike on Kurita's Center Force, initiating the Battle of the Sibuyan Sea; this included eight Curtiss SB2C Helldiver dive bombers from Intrepid. One 500-pound (230 kg) bomb struck the roof of Turret No. 1, failing to penetrate. Two minutes later, the battleship Musashi was struck starboard amidships by a torpedo from a Grumman TBF Avenger, also from Intrepid. The Japanese shot down two Avengers. Another eight Helldivers from Intrepid attacked Musashi again at around noon, scoring two more hits, with two Helldivers shot down. Further strikes from Essex and Lexington inflicted several more bomb and torpedo hits, 37 aircraft from Intrepid, the fleet carrier Franklin, and Cabot attacked Musashi, hitting her with 13 bombs and 11 torpedoes for the loss of three Avengers and three Helldivers. In addition to the loss of Musashi, many of Kurita's other ships, including battleships Yamato, Nagato and Haruna, and heavy cruiser Myōkō were damaged in the attacks, forcing him to break off the operation temporarily. After Kurita's force began to withdraw, Halsey ordered TF 38 to steam north to intercept the aircraft carriers of the Northern Force, commanded by Vice Admiral Jisaburō Ozawa. Bogan correctly perceived that Ozawa's force was intended to lure TF 38 away from the landing area to allow Kurita to attack it, but Halsey overruled him and several other Task Group commanders who voiced similar concerns. Early on October 25th, aircraft from Intrepid and the other carriers launched a strike on the Japanese carriers. Aircraft from Intrepid scored hits on the carrier Zuihō and possibly the carrier Zuikaku. Further strikes throughout the morning resulted in the sinking of four Japanese aircraft carriers and a destroyer in the Battle off Cape Engaño. Halsey's preoccupation with the Northern Force allowed Kurita the respite he needed to turn his force back to the east, push through the San Bernardino Strait, where it engaged the light forces of escort carriers, destroyers, and destroyer escorts that were directly covering the landing force in the Battle off Samar. Kurita nevertheless failed to break through the American formation, and ultimately broke off the attack.
On October 27th, TG 38.2 returned to operations over Luzon; these included a raid on Manila on the 29th. That day, a kamikaze suicide aircraft hit Intrepid on one of her port side gun positions; ten men were killed and another six were wounded, but damage was minimal. A Japanese air raid on November 25th, struck the fleet shortly after noon. Two kamikazes crashed into Intrepid, killing sixty-nine men and causing a serious fire. The ship remained on station, however, and the fires were extinguished within two hours. She was detached for repairs the following day, and reached San Francisco by December. In the middle of February 1945, back in fighting trim, the carrier steamed for Ulithi, arriving by March. She set off westward for strikes on Japan on March 14th, and four days later launched strikes against airfields on Kyūshū. That morning a twin-engined Japanese G4M "Betty" kamikaze broke through a curtain of defensive fire, turned toward Intrepid, and exploded 50 ft (15 m) off Intrepid's forward boat crane. A shower of flaming gasoline and aircraft parts started fires on the hangar deck, but damage control teams quickly put them out. Intrepid's aircraft joined attacks on remnants of the Japanese fleet anchored at Kure damaging 18 enemy naval vessels, including battleship Yamato and carrier Amagi. The carriers turned to Okinawa as L-Day, the start of the most ambitious amphibious assault of the Pacific war, approached. The invasion began on the 1st of April. Intrepid aircraft flew support missions against targets on Okinawa and made neutralizing raids against Japanese airfields in range of the island. On April 16th, during an air raid, a Japanese aircraft dived into Intrepid's flight deck; the engine and part of the fuselage penetrated the deck, killing eight men and wounding 21. In less than an hour the flaming gasoline had been extinguished; three hours after the crash, aircraft were again landing on the carrier. On April 17th, Intrepid retired homeward via Ulithi. She made a stop at Pearl Harbor on 11 May, arriving at San Francisco for repairs on May 19th. On June 29th, the carrier left San Francisco. On August 6th, her aircraft launched strikes against Japanese on bypassed Wake Island. Intrepid arrived at Eniwetok on the next day. On August 15th, when the Japanese surrendered, she received word to "cease offensive operations." Intrepid got under way on August 21st to support the occupation of Japan.
In February 1946, Intrepid moved to San Francisco Bay. The carrier was reduced in status to "commission in reserve" in August, and she was decommissioned on March 22nd, 1947. After her decommissioning, Intrepid became part of the Pacific Reserve Fleet. On February 9th, 1952, she was recommissioned. Intrepid later severed as an attack carrier (CVA), and then eventually became an antisubmarine carrier (CVS). In her second career, she served mainly in the Atlantic, but also participated in the Vietnam War. She was the recovery ship for a Mercury and a Gemini space mission. She was decommissioned for the second time in 1974, she was put into service as a museum ship in 1982 as the foundation of the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum Complex in New York City. Intrepid earned five battle stars and the Presidential Unit Citation during World War II, and a further three battle stars for Vietnam service.
#second world war#world war 2#world war ii#wwii#military history#american history#naval history#naval warfare#aircraft carrier#intrepid museum#pacific campaign#pearl harbor#us navy
39 notes
·
View notes
Text
Princess Anne reading the memoirs of her husbands uncle, Sub-Lieutenant Keith Symons, who at aged 20 was in command of three landing crafts at gold beach on the first wave of D-Day, at the Commonwealth War Graves Commissions ‘Great Vigil’ at Bayeux War Cemetery in France on 5th June 2024.
The full speech:
At 04.15 hours on 5th June 1944, General Eisenhower, Supreme Commander Allied Forces, took the momentous decision to launch Operation overlord - what we now call D-Day - the largest sea and airborne invasion the world has ever seen. After 5 years of war, all that time training and waiting, who knows what those Sailors, Soldiers and Airmen felt. 80 years ago today, charged with storming the Normandy coastline and beginning the campaign to free Western Europe from Nazi tyranny.
One of those sailors was my husband's uncle, Sub-Lieutenant Keith Symons who, at the age of 20 was in command of three landing craft at Gold Beach in the first wave on D-Day.
Recalling in his memoirs the evening of 5th June he wrote:
"At last it was time for our briefing. Our confidence was dented by predictions that casualties in the first wave were likely to be heavy. Everyone was quite subdued, but it was all very matter-of-fact. They were in those days. After supper we sat around making light conversation and listening to the chaplain playing his violin.
My cabin companion was a Captain in the Green Howards, a charming man who had been a solicitor before the war. We talked about what we would do when the war was over. Sadly he was killed in France only a few weeks later."
Bayeux was close to the landing beaches and it was the first city to be liberated by the British on 7th June. The City's hospitals were soon full of the wounded from the surrounding battlefield. For those who could not be saved, this was their final resting place.
It is the largest Commonwealth cemetery of the Second World War in France and contains four thousand one hundred and forty allied graves. It is my honour as President of the Commonwealth War Graves Commission to continue to protect their legacy.
The epitaphs on the headstones here capture the grief of those who loved these men. One mother's words are:
"HE IS NOT DEAD WHOSE MEMORY LIVES IN HEARTS THAT KNOW AND LOVED HIM."
80 years on, let their memory still live on in our hearts.
#ill replace this with a better recording when i get chance#thank you random Twitter user 😅#PDA PDA PDA 😭😭😭#my heart#princess anne#princess royal#tim laurence#timothy laurence
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

American troops being ferried to larger ships in preparation for the allied invasion of Normandy. Weymouth, Dorset. June 1–5, 1944
Photo: Robert Capa
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
HOMESTUCKS, GRAB YOUR SWIM GEAR. IT'S TIME TO GO TO THE BEACH!!!

Hey there, lovely readers! This past month, our Coalition has been hard at work with our latest Competition: Beach Day! We invite you to join us in reading these works and partake in Voting between now and July 14th! You can choose Best in Romance, Best in Fluff, Best in Comedy, and more!
There were 8 entries, featuring everything from post-SBURB to humanstuck AUs. List below the cut, for your perusal. I hope you read them all!
[edited artwork by our lovely admin @arealpeople ]
(1) The Beach Day Will Continue Until Morale Improves
Or: Don't let the Terezi drive the bus.
(2) Beachside Epitaph
Rose danced in the firmaments of reality, playing god with a game built to crown one. Kanaya looked for a beach to reclaim a sense of normality in a universe gone mad. At least conversation framed with lapping waves was ‘close enough.’
(3) Ever Forward
Your name is John Egbert. You were drafted. Due to mishaps, you are on a boat on June 6, 1944 with a squad that you've never met before, headed for Omaha beach.
(4) Karkat's Awesome Beach Day Saving John's Lusus-Guardian
Karkat gets invited to go down to the beach with John and all his friends. Unfortunately, John doesn't seem to know the first thing about keeping his lusus safe at the beach. Guess it's up to Karkat to keep the poor boy from becoming an orphan.
(5) Notion
A nice day for a group of friends on the beach
(6) Obligatory Beach Episode
June and her pals visit the beach…but now that there's time to just…slown down and appreciate life, silly old fears come back.
(7) ShoreTrip
Vriska and her friends go to the beach, shenanigans occur, tags are ur friend.
(8) Swim
It’s earth C’s first beach day! But Vriska isn't so sure she'll enjoy it...
Special shoutout to our authors: @arealpeople ; @madam-melon-meow ; @meowloudly15 ; @ambrosianlullaby ; @aspen1185 ; @june-egbert-official ; @timelessambivalence and @bralsradoesfanfiction !
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

1942 04 10 The Texas Hurricane - Roy Grinnell
Hurricane IIb, BE171, 17 Sqn Flown by Sergeant John 'Tex' Barrick, RCAF, on 7th February 1942.
Barrick, born in Sweetwater, Texas, joined the RCAF in late 1940. Having finished his training at 55 OTU in the UK he was posted to the Middle East with 17 Sqn in September 1941. Following the Japanese attacks in December the squadron was rerouted to Burma. Seeing significant action during the retreat, he claimed two Nakajima Ki-27 'Nates' destroyed and another damaged in BE171. 17 Sqn ended up at Loiwing, China and from here on 10th April 'Tex' made his last claim. This was a Ki-43, which he foolishly watched go down. He was then set upon by three more, and crash landed, striking his face on the gunsight. Getting clear of his aircraft he saw it strafed before AVG Tomahawks drove of his attackers.His injuries were initially seen to by missionary doctors, but he was eventually moved to Colonel Chennault's and flown back to India. Once recovered he rejoined the squadron and in August received the DFM and promotion to Warrant Officer. In November Barrick was commissioned and became a flight commander in May 1943 .During June and July he and 17 were involved in numerous ground attack sorties over the Arakan, but in August they moved to Ceylon.Ending his tour in December 1943, Barrick returned to the UK before going to Canada to become an instructor. Finally in October 1944 he joined 135 Sqn, RCAF at Patricia Bay, British Columbia, where he stayed until demobilized on 2nd October 1945. His score stood at 5 destroyed, 2 damaged, and 2 destroyed on the ground.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here’s something I’ve been translating on and off for the past week or so! I was looking at old German youth magazines in order to find interesting articles about classic rock bands (specifically Pink Floyd) and came across this in the 01/1978 issue of BRAVO magazine (One of the most famous teen/young adult magazines in Germany that’s been there since 1958 and is still going strong today!) A lot of youth magazines back in the day had articles and posters about rock bands because, well, that’s the people who were celebrities at that time! This page includes both short descriptions of the band members and a short history of the band up until that point when the issue came out! Enjoy ;)

Here’s the original picture
And here is the translation! (Italized text are context comments added by me to add to the understanding of this text!)
Warning: Some of the information here is obviously incorrect!
Pink Floyd: Their profiles
Nick Mason:
Born on the 27th of January 1945 in London, plays drums, has black hair, brown eyes, is 1,72 m tall (for non metric peeps it’s approximately 5 foot 8), is married to Lindy, has two daughters, owns a vineyard and collects old cars (old timers in German means old/vintage cars)
Rick Wright:
Born on the 28th of July 1945 in London, plays the organ/keyboard, piano, cello, and Moog-synthesizer; has blonde hair, blue eyes, is 1, 74 m tall (approximately 5 foot 9), is married to Juliette, has a son named Jamie, and a daughter named Gaia, loves football (or soccer for American peeps)
Roger Waters:
Born on the 6th of September 1944 in Great Bookham near Cambridge, plays bass, Moog-synthesizer, and sings as well; has blonde hair, grey eyes, is 1,83 m tall (approximately 6 feet), is married to Caroline, and has a 15 month old son named Harry.
David Gilmour:
Born on the 6th of March 1946 in Cambridge, plays lead guitar and sings; has brown hair, blue eyes, is 1,78 m tall (approximately 5 foot 10), is married to Ginger, and has a 2 year old daughter named Alice.
The diary/summary of their career; All their albums
1965
The three architecture students Roger Waters, Rick Wright, and Nick Mason meet and get to know each other, establishing the band Sigma 6.
1966
February: Sigma 6 gets their first fee for a performance in the London Marquee Club and mostly cover popular rock and blues songs. During this time they meet art student Syd Barrett. He writes songs and joins the band as a guitarist and singer. Under his influence Sigma 6 evolve into their own music style: The group does electronic experiments and uses spotlights, reversal film, and recorded footage as part of their stage shows. Thus psychedelic music is born. Syd Barrett is as well (psychedelic), who now comes up with new names for the band almost every month — they call themselves “T-Set,“ “Abdabs” — and in this group a girl sings as well from time to time: Juliette Gale. She later marries keyboardist Rick Wright.
June: The group could pay for a band bus for approximately 200 Mark (the German currency at the time of this article), but decide to separate for the time instead. No one is interested in performing, since the boys want to enjoy the semester holidays as well as after them improve and work harder on their studies; music is fun but a real job is more important. Syd Barrett then has a new idea for a band name: The Pink Floyd Sound. He comes up with his idea through combining the names of two American blues singers: Pink Anderson and Floyd Council. The owner of an artist agency, Peter Jenner, sees a performance from The Pink Floyd Sound in the Marquee, and then from there on decides to manage the band, not knowing the band wanted to break up.
July: Peter Jenner gets the band gigs, and thus Pink Floyd stays together.
October: Pink Floyd are now the stars of the London Underground. They perform in the Roundhouse to 2000 fans, with even Paul McCartney being there to see them.
December: On the 23rd of December the UFO club opens, with Pink Floyd performing there daily henceforth.
1967
January: The English music magazine “Melody Maker” write an article about Pink Floyd, which makes record companies curious about the band. The band accepts the best offer, and as they sign the record label contract, they cash in an advance payment of 40 000 Mark.
February: The first single “Arnold Layne” gets recorded.
March: Arnold Layne goes to the English hit charts.
April: The single is on number 20 in the charts and then falls off. But this beginning success gives them the push they needed to record their first album “The Pipers at the Gates of Dawn.“ Norman “Hurricane” Smith serves as producer for this album, and began his career as a recording engineer for the Beatles. While Pink Floyd work on their album in studio 3 of Abbey Road studios, the Beatles work on their album “Sgt. Pepper’s Lonely Hearts Club Band” at the same time in studio 2; two decade defining groups working next door.
June: Pink Floyd join as a supporting act along with Jimi Hendrix and the Move (runner up band to Electric Light Orchestra) for an England tour, but only get to play 17 minutes.
July: The second single “See Emily Play,“ becomes part of the English hit charts, coming in at number 6, and the first album “The Pipers at the Gates of Dawn” releases.
September: See Emily Play also goes into the German hit charts and reaches number 28. Syd Barrett at this time also creates a speaker system which is still useful today, where the speaker boxes are placed all around the room.
1968
At this time, it is practically impossible for Pink Floyd to continue performing with Syd Barrett. He is more and more off in his own world and mind, often not knowing where he is. Out of necessity, the band thus searches for a second guitarist who could join the band.
February: David Gilmour joins Pink Floyd. Syd is still part of the band, but during concerts his amps are often not even turned on, so that the audience doesn’t know any better about his mistakes.
April: On the 6th of April Syd definitively leaves the band, with manager Peter Jenner going with him. Pink Floyd begin working on their second album “A Saucerful of Secrets.“
June: At a free open air concert on the 29th in the London Hyde Park the band officially announces and debuts David Gilmour as their new lead (and only) guitarist. On the same day the new album releases as well.
1969
July: The soundtrack album Pink Floyd worked on for the film “More,” releases.
October: Pink Floyd have their first concert in Germany on the 11th of October at the Pop and Blues Festival in the Essen Grugahalle venue. On this day, Deep Purple celebrate their first concert in Germany as well.
November: The double album “Ummagumma” releases and makes the group successful worldwide for the first time.
1970
March: The soundtrack album Pink Floyd worked on for the film “Zabriskie Point” releases.
June: Pink Floyd perform the title track of their upcoming new album “Atom Heart Mother” worldwide at open air festivals with recorded footage, dry ice fog, and light bombs as part of their special effects on stage.
October: The album “Atom Heart Mother” releases and leads the album charts in England and America.
1971
The album “Meddle” comes out. This year Pink Floyd is particularly busy; they go from one concert to the next and have multiple tours worldwide.
1972
The soundtrack album Pink Floyd worked on for the film “La Vallée” releases under the title “Obscured by Clouds” as their new album. The rest of the year the band spends inside the studio.
1973
March: The album “Dark Side of the Moon” releases and is on the English and American album charts for over two years, and also goes gold in Germany. It is to this day the band’s most sold album.
October: Pink Floyd perform their last German concert for a long time on the 12th of October at the Olympiahalle in Munich, and it becomes the sensation of the year. Pink Floyd also make their way into the English and German single charts again with the single “Money.”
1974
Pink Floyd are tired of success and go back to their private family lives, with rumors appearing that the group will break up. In autumn, the double album “A nice pair” comes out, which is a rerelease of their first two albums.
1975
September: The album “Wish You Were Here” releases.
1976
This year, Pink Floyd doesn’t appear publicly that much as well, except for some performances at festivals.
1977
January: In Dortmund Pink Floyd start their first German tour since 3 years ago on the 23rd. They have 2 concerts each for Dortmund, Frankfurt, and Berlin, with Munich having 3. All concerts were sold out 2 months before the tour started. Simultaneously the 11th album of the band, “Animals” releases. Even before the album released, “Animals” goes gold, with 250 000 records being preordered. This German tour is also the starting point of a months long worldwide tour — the most comprehensive one that Pink Floyd have undertaken yet.
Written originally by: K. E. Siegfried
Translated from German to English by: me! (Vik)
(Btw my source to where I found this is the Internet archive, love that place!)
also here are some pictures that were included in the magazine of the band!
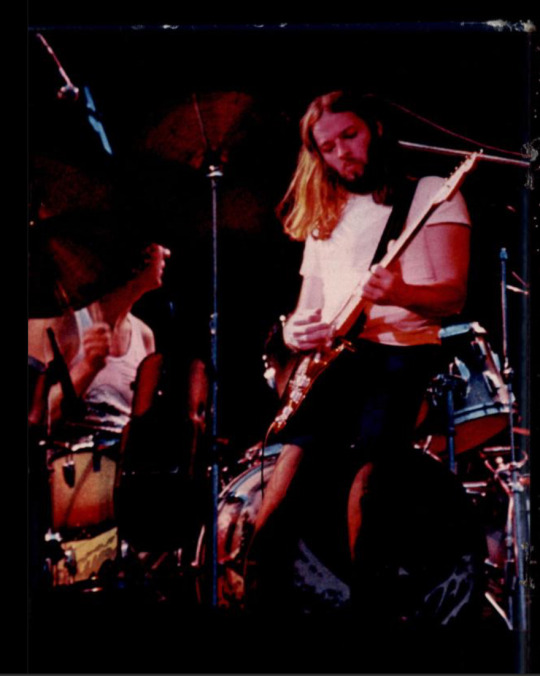
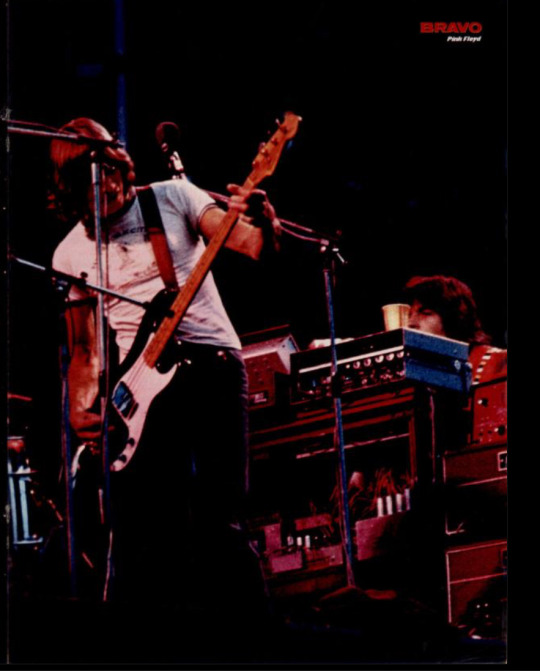


#Pink Floyd#rock photography#classic rock#60s#60s rock#70s#70s rock#roger waters#david gilmour#nick mason#rick wright#richard wright#syd barrett#rock history#music history#60s music#70s music#translation#magazine article#old magazines
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
Review of Official MCU Timelines: Phase One Official Timeline
My (unofficial) but logical (correct) detailed timeline of Phase One
Now that we have a timeline with evidence from the movies, we can compare it to the official timelines. Yes, there's more than one, and they contradict each other.
First, I'll look at the official Phase One timeline (the "old timeline"), created by Brad Winderbaum shortly before The Avengers came out.

In this timeline, Marvel used "BIM" (Before "I am Iron Man") and "AIM" (After "I am Iron Man"). So the starting point in both directions is May 25, 2008, although this date is not defined in this timeline, but it is defined in the new official timeline, as well as in my timeline.
Correct dates are highlighted in blue, questionable or too vague - in orange, and incorrect ones - in red.

Odin fought the Frost Giants on Earth and adopted Loki - 1000 years BIM (old timeline)/965 AD ("Thor", new timeline, my timeline):
The old timeline uses a vague "1000 years BIM", which, to be precise, corresponds to 1008 AD, not 965 AD.

Odin hid the Tesseract on Earth - 600 years BIM (old timeline)/ "undetermined time" (movies, new timeline, my timeline):
Then we have a date that only appears in the old timeline - 600 BIM, which corresponds to 1408 AD. The new timeline mentions the event, but also says that it is unknown when it happened.

Hydra stole the Tesseract; Rogers became a super soldier - 67 years BIM (old timeline)/March 1942 and June 1943 (CA:TFA, new timeline, my timeline):
2008 minus 67 is 1941. According to the movie (CA:TFA), Schmidt invaded Norway in March 1942. Steve Rogers became a super soldier in June 1943.

Valkyrie crash, Rogers frozen in Arctic - 64 years BIM (old timeline)/January 1945 (my timeline):
"64 years BIM" in the old timeline is also not quite true. If we were to believe that, we would have Rogers going into suspended animation in the Arctic in 1944. We found out that was early 1945, which also corresponds the new timeline. My timeline narrows it down to January.

Creation of the Hulk - 5 years BIM (old timeline)/March 2004 (my timeline):
According to the old timeline, this would have been 2003. More detailed analysis gave me March 2004.

Tony's kidnapped in Afghanistan - 9 months BIM (old timeline)/4 months BIM (IM1, new timeline, my timeline):
Tony was kidnapped in late January or early February 2008. He spent 3 months in captivity and then almost a month at home before the famous press conference. See IM1 timeline.

Events of "Iron Man 2: Public Identity" tie-in - 3 months AIM (old timeline)/Never (movies, new timeline, my timeline):
The old timeline includes events from the Iron Man 2: Public Identity comics, which are absent from the new official timeline and the movies (it also contradicts them). As such, for now, I will not consider Public Identity canon and will not include the events in the timeline. I will review the comics in the future.

Chase after Bruce Banner in Rio; Tony is attacked by Ivan Vanko in Monaco - 6 months AIM (old timeline)/~September 4, 2009 and May 23, 2010 (my timeline):
Absolutely no way it could be 6 months AIM, just as there was no way it could be 9 months BIM before. See IM2 timeline, part 1.
Those movies even took place in different years. Thanks to Fury's Big Week, we got an abomination in the timeline.
Fury's Big Week will be reviewed in detail in another post.
Review of The MCU Guidebook timeline
#marvel#mcu#tony stark#iron man#the avengers#iron man 2#steve rogers#captain america#mcu timeline#bruce banner#the incrediable hulk#hulk#thor#captain america the first avenger
24 notes
·
View notes
Text

Brigadier General Anthony McAuliffe of the US 101st Airborne Division, gives his glider pilots last minute instructions before take-off for the D-Day landings in Normandy - June 5, 1944
125 notes
·
View notes
Text

JACK DANIELS HOLSCLAW (1918-1998)
Tuskegee Airman Jack Daniels Holsclaw was born in Spokane, Washington, on March 21, 1918. His father, Charles, was a clerk in a downtown store, and his mother, Nell, was a manager at Pacific Telephone and Telegraph. Holsclaw attended North Central High School in Spokane, where he excelled both academically and athletically. When he was 15, he became the first black person in Spokane to earn the Eagle Scout badge.
Holsclaw entered Whitworth College in 1935 but transferred to Washington State College (now Washington State University) in 1936 to play baseball. Beginning in his junior year, he played center field and helped the Cougars finish as co-champions of the Northern Division, Pacific Coast Conference. He was the second African American earn a varsity letter in baseball at the college.
In 1939, Holsclaw transferred to a chiropractic program at Western States College in Portland, Oregon, where he met his wife, Bernice Williams. They had one son, Glen. Holsclaw completed the chiropractic program in 1942 and passed the Oregon state board examination.
While there, he enrolled in a government sponsored Civilian Pilot Training Program at Multnomah College and earned his pilot’s license. On October 5, 1942, he enlisted in the army as a private and entered flight school, training at Tuskegee Army Airfield, Alabama. After completing his training, he received his wings and was commissioned as a 2nd Lieutenant on July 28, 1943. Lieutenant Holsclaw received advanced training at Selfridge Field near Detroit, Michigan before his squadron was shipped to Italy in December 1943.
Lieutenant Holsclaw flew in the 100th Fighter Squadron, 332d Fighter Group, an all-black pursuit squadron. Holsclaw named his favorite P-51 “Bernice Baby” in honor of his wife. The 332d Fighter Group had distinctive red tails giving them the nickname “Red Tails.” The 332d Fighter Group escorted bombers on their runs over enemy territory, shielding them from German fighters. To the bomber crews that were protected by them they were the “Red Tail Angels.”
On July 18, 1944, in an aerial battle over Italy, Holsclaw shot down two German fighters. For this action he received the Distinguished Flying Cross. By December 1944, Holsclaw had completed 68 combat missions, nearing the limit of 70, when he became Assistant Operations Officer, an important administrative position that included aerial mission planning. In January 1945, Holsclaw was promoted to captain.
Captain Holsclaw returned to the United States in June 1945 to serve as assistant base operations officer at Godman Field, Fort Knox, Kentucky. He served as an Air Force ROTC instructor at Tuskegee Institute and then Tennessee State College.
From 1954 to 1957, Holsclaw was assigned to Japan, and from May 1962 to the end of 1964, he served as chief of the training division, Sixth Air Force Reserve Region at Hamilton Air Force Base, California. He directed the preparation of two textbooks to guide incoming air force personnel. Holsclaw retired from the Air Force on December 31, 1964 as a Lieutenant Colonel.
From 1965 to 1973 Holsclaw served as a manager in the Marin County Housing Authority, California. In 1973, he and Bernice returned to Washington where Holsclaw joined the staff at the People’s National Bank in Bellevue. He remained there until his second retirement in 1983. He and Bernice took up residence in Arizona, where Jack Holsclaw died on April 7, 1998, at the age of 80.
In August 2019, the Jonas Babcock Chapter, NSDAR, dedicated a historical marker in the memory of Lt. Col. Holsclaw at the site of his childhood home in Spokane.
146 notes
·
View notes