#wheat and diabetes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Best Wheat for Diabetes
The chapati or roti are a ubiquitous accompaniment to every meal. Breakfast, lunch, and dinner just wouldn’t be the same without the humble chapati. And while it has gained much acceptance as a low-calorie food, given its lower Glycemic Index, not all varieties are equal, nor good for diabetics.
Read more to know wheat varieties for diabetics: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/best-wheat-for-diabetes/2904
#wheat for diabetes#is wheat good for diabetes#is wheat chapati good for diabetes#wheat flour for diabetes#best wheat variety in india#best wheat variety#wheat and diabetes#wheat flour and diabetes#wheat and diabetes connection
0 notes
Text
Best Wheat for Diabetes
This article is originally published on Freedom from Diabetes website, available here. When considering the best wheat options for individuals with diabetes, it’s important to focus on whole grains and those with a lower glycemic index. Lets understand 100 grams of wheat contain,Carbohydrates: 72 grams, Sugar 0.4 grams Protein: 13.2 grams,Water: 10 – 11%,Calories: ~ 340, Fiber: 12- 15% (bran).

Advantages and Disadvantages of Wheat:
Where diabetics are concerned, wheat in moderation makes a good addition to the diet, for the following reasons. 1.Heart-healthy- Whole wheat’s high fiber content helps reduce cholesterol, it help to down the risk of heart related problem.
2.Good for digestion- Fiber is present in the wheat, which is help in digestion.
Improves BSL- The fiber in wheat helps slow down the absorption of glucose, keeping your blood sugar levels from spiking.
4.Energy booster - Wheat's low GI and carbohydrate content ensure a steady and controlled release of calories.
What are the Disadvantages of wheat?
Digestion problem- Wheat's high fiber content is good for digestion, but some people have celiac disease, a chronic condition where gluten triggers digestive and immune problems.
Raises cholesterol level- Wheat contains a lot of carbohydrates, which, if eaten in excess, causes blood sugar to rise, and that can be bad for your LDL levels.
Wheat varieties for diabetics:
All wheat varieties are not equal. Which is good news for diabetics, because some varieties are proven to help lower blood sugar and provide other health benefits too. These are recommended wheat varieties for diabetes
Khapli (emmer wheat)
Spelt wheat
Durum wheat
Bansi wheat
Red wheat
At Freedom From Diabetes, we strongly recommend shifting from regular wheat to these varieties, for the following reasons. They have a lower GI, which makes them suitable for the diabetic diet. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals that offer a variety of health benefits from regulating blood sugar levels to improving cardiovascular health. If you can’t think of going without chapatti, we highly recommend shifting from chapattis made from regular wheat flour to flour made from khapli (emmer), Brum, jungli, Bansi, spelt, or indeed any of the ancient wheat varieties. To read more, click here.
Also please connect with me on my Website, Facebook page, and YouTube if you want to stay in touch or give me any feedback!
#Wheat for diabetes#is wheat good for diabetes#is wheat chapati good for diabetes#wheat flour for diabetes#best wheat variety in india#best wheat variety#wheat and diabetes#wheat flour and diabetes#wheat and diabetes connection#Regular wheat flour#Ancient wheat varieties#Khapli flour#Emmer wheat#Brum wheat#Wheat substitutes
0 notes
Text
Peanut Butter Banana Sandwich with Hemp Seeds
Here is a recipe for a peanut butter banana sandwich with hemp seeds and honey: Ingredients: 2 slices of whole-wheat bread 1 tablespoon peanut butter 1 banana, sliced 1 tablespoon hemp seeds 1 teaspoon honey Instructions: Toast the bread to your desired degree of crispiness. Spread the peanut butter on one slice of bread. Top with the banana slices. Sprinkle with the hemp seeds and…

View On WordPress
#Banana#chocolate chips#cinnamon#decadent treat#Easy recipes#healthy snack#hemp seeds#honey#improved heart health#Peanut butter#Peanut butter Banana Sandwich#quick and easy recipe#Raisins#reduced risk of diabetes#regulated blood pressure#ripe bananas#weight loss#whole-wheat bread
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
The Most Dangerous Foods for Your Health (Especially After 50!) | Dr. Eric Berg
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide derived from starch hydrolysis and used as a thickener and filler in processed food. Maltodextrin is regarded as inert and generally is regarded as safe by the US Food and Drug Administration.
loss of B1 keeps blood sugar high (pre-diabetic/diabetic); there are 4 different tissues that are going to age a lot faster than they should, which has to do with a lack of B1 but also bc when sugar gets stuck to protein in your body, it makes sticky protein & then it builds up in the body. This creates all sorts of problems, especially to the lense of the eye, that is when you get cataracts.
it really ages your skin & you get wrinkles, and then you lose elasticity. This is why as ppl get older, they can't sprint like they used, they don't have that bounce in their step.
Some other foods you want to also avoid: Barbecued Anything, where they add sugar sauce to meat then they cook it, deadly.
Think about it: How many restaurants add sugar to meat or even deep fried donuts/french fry?
This is going to really age you, and it also affects the cognitive function, mood, and also the heart; so the elasticity is affected, hardening the arteries.
The silica mineral, if you want strong bones/hair/skin that is elastic, silica is s/t you don't want to become deficient in. So what is high is silica: horsetail/bamboo/spring water/silica supplement.
Another food we consume that ages us is seed oils, which tends to get stored in our membranes of our cells, so they start to replace all the membranes in our brain & nervous system.
It take 1.5 years to get it out, once you stop eating these seed oils.
You don't want these industrial refined ranchid fats stored in your body bc it creates inflammation in your brain; it's in all the deepfried foods, it's in a lot of junk foods. But do not cook in seed oils. Use olive oil, but not other fats that can remain solid at room temperature like butter or lard or tallow oil [hydrogenated/saturated fats problematic].
Your body needs healthy fats for energy and other functions. But too much saturated fat can cause cholesterol to build up in your arteries (blood vessels). Saturated fats raise your LDL (bad) cholesterol. High LDL cholesterol increases your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Consume a lot of fish oil to replace that lower quality fat in your brain & nervous system.
youtube
#4: Refined Soy Products, especially Soy Protein: Avoid [4:15]
It's in a lot of protein bars, it's very refined but it is not that clean bc we don't know this for sure but there are reports that there is residue of hexane.. in order to make that you have to use a solvent, and you don't want to be consuming such a refined unnatural protein. When I was in practice, a lot of ppl were doing ideal protein, and I noticed when they lost weight they also looked really old & unhealthy & dried out. Their hair was bad, and brittle & breaking..
Their skin looked older, they had a lot of gallbladdar & liver problems, I really think it is that soy protein isolate, so you want to avoid it.
5.] Avoid Anything Low-Fat: One important nutrient is K2, that is in fatty cheese & goose liver, when you go low-fat you can deprive yourself of this nutrient that can make your bones really solid by taking the calcium out of the arteries & keeping the calcium out of your joints so you don't have Arthritis.
If you have those problems of calcium in your arteries/joints & a lot of stiffness, you may want to take a vitamin K2 supplement; or lower the acidity in your food consumption, which you can hear all about from Barbara O'Neill [worst things to make your blood acidic is caffeine/sugar/dairy, so you might want to rethink your cup of joe].
6.] Aid Sleep with Magnesium: Recommend Magnesium Glycinate, in powder for better absorption. But a high level of calcium, especially when magnesium intake is low, can impair magnesium balance and potentially lead to magnesium deficiency.
Calcium and Magnesium Competition: Calcium and magnesium compete for absorption and transport in the gut.
High Calcium, Low Magnesium: If calcium intake is significantly higher than magnesium intake, it can hinder magnesium absorption and lead to a negative magnesium balance.
Magnesium Deficiency Implications: Magnesium deficiency can have various health consequences, including muscle cramps, fatigue, and even more serious issues like heart problems.
Supplementation Considerations: If you are taking calcium supplements, it's important to ensure you are also getting adequate magnesium, either through diet or supplementation, to maintain a balanced ratio.
Optimal Ratio: Some authorities recommend a 2:1 ratio of calcium to magnesium (by weight) for both supplementation and overall daily intake. [this is bc we tend to lean towards acidic blood levels, ie pollution/lack of sleep/stress, do you see the infinite loops yet?]
Kidney Function: High calcium intake can also lead to increased urinary excretion of magnesium
Interactions with other nutrients: Dietary protein and phosphate can also influence magnesium absorption and excretion. Calcium and Magnesium Competition: Calcium and magnesium compete for absorption and transport in the gut.
High Calcium, Low Magnesium: If calcium intake is significantly higher than magnesium intake, it can hinder magnesium absorption and lead to a negative magnesium balance.
Magnesium Deficiency Implications: Magnesium deficiency can have various health consequences, including muscle cramps, fatigue, and even more serious issues like heart problems.
Supplementation Considerations: If you are taking calcium supplements, it's important to ensure you are also getting adequate magnesium, either through diet or supplementation, to maintain a balanced ratio.
Optimal Ratio: Some authorities recommend a 2:1 ratio of calcium to magnesium (by weight) for both supplementation and overall daily intake. [this is bc we tend to lean towards acidic blood levels, ie pollution/lack of sleep/stress, do you see the infinite loops yet?]
Kidney Function: High calcium intake can also lead to increased urinary excretion of magnesium
Interactions with other nutrients: Dietary protein and phosphate can also influence magnesium absorption and excretion.
High calcium results in a chain reaction to stress, which strips calcium from our bones to balance the acidic blood level:
Stress can increase acidic levels in the blood through several mechanisms, including increased breathing rate (hyperventilation) leading to lower carbon dioxide levels, and the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can lead to metabolic acidosis.
Hyperventilation: During stressful situations, people often breathe faster and deeper, a state called hyperventilation. This rapid breathing leads to the expulsion of more carbon dioxide from the body than usual.
Carbon Dioxide and pH: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a key player in maintaining the body's acid-base balance. When CO2 levels drop, the blood becomes more alkaline (less acidic).
Stress Hormones and Metabolism: Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can lead to changes in metabolism, including increased glucose and fatty acid mobilization.
Metabolic Acidosis: In some cases, stress can lead to metabolic acidosis, a condition where the blood becomes too acidic. This can occur if the body is unable to remove enough acid or if it produces too much acid.
Renal and Respiratory Compensation: The body has mechanisms to compensate for changes in blood pH, including the kidneys excreting or reabsorbing bicarbonate and the lungs adjusting breathing rate. However, these mechanisms can be overwhelmed in severe cases.
Does stress make your body more acidic?
Stress is another factor that causes an excessive production of stomach acid which can bring on acid reflux disease. Some food and drinks can cause the esophagus muscle to relax. These include high fat foods, caffeinated drinks, alcohol and peppermint.
Why does blood become more acidic?
Blood acidity increases when people ingest substances that contain or produce acid or when the lungs do not expel enough carbon dioxide. People with metabolic acidosis often have nausea, vomiting, and fatigue and may breathe faster and deeper than normal.
People with respiratory acidosis often have headache and confusion, and breathing may appear shallow, slow, or both. Tests on blood samples typically show pH below the normal range.
If an increase in acid overwhelms the body's acid-base control systems, the blood will become acidic. As blood pH drops (becomes more acidic), the parts of the brain that regulate breathing are stimulated to produce faster and deeper breathing (respiratory compensation). Breathing faster and deeper increases the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled, which raises the blood pH back toward normal.
The kidneys also try to compensate by excreting more acid in the urine. However, both mechanisms can be overwhelmed if the body continues to produce too much acid, leading to severe acidosis and eventually heart problems and coma.
The acidity or alkalinity of any solution, including blood, is indicated on the pH scale.
Blood pH
Acidity and alkalinity are expressed on the pH scale, which ranges from 0 (strongly acidic) to 14 (strongly basic or alkaline). A pH of 7.0, in the middle of this scale, is neutral.
Blood is normally slightly basic, with a normal pH range of 7.35 to 7.45. Usually the body maintains the pH of blood close to 7.40. The blood pH is below 7.35 in people with acidosis and above 7.45 in those with alkalosis.
Causes of Acidosis
Acidosis is categorized depending on its primary cause as metabolic & respiratory.
1.] Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis develops when the amount of acid in the body is increased through ingestion of a substance that is, or can be broken down (metabolized) to, an acid—such as wood alcohol (methanol), antifreeze (ethylene glycol), or large doses of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Many other medications and poisons can cause acidosis.
Metabolic acidosis can also occur as a result of abnormal metabolism. The body produces excess acid in the advanced stages of shock (lactic acidosis) and in poorly controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus (diabetic ketoacidosis).
Even the production of normal amounts of acid may lead to acidosis when the kidneys are not functioning normally (kidney failure) and are therefore not able to excrete sufficient amounts of acid in the urine.
Metabolic acidosis also develops when the body loses too much base. For example, bicarbonate can be lost through the digestive tract due to diarrhea.
2.] Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory acidosis develops when the lungs do not expel carbon dioxide adequately (inadequate ventilation), a problem that can occur in disorders that severely affect the lungs (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD], severe pneumonia, heart failure, and asthma).
Respiratory acidosis can also develop when disorders of the brain or of the nerves or muscles of the chest (such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) impair breathing. In addition, people can develop respiratory acidosis when their breathing is slowed due to oversedation as a result of opioids (narcotics), alcohol, or strong medications or drugs that induce sleep (sedatives). As a result of the slowed breathing, the level of oxygen in the blood may be low.
Sleep-disordered breathing (for example, sleep apnea) can repeatedly pause breathing long enough to cause temporary respiratory acidosis.
Symptoms of Acidosis
In mild metabolic acidosis, people may have no symptoms but usually experience
Fatigue
Nausea
Vomiting
Breathing becomes deeper and slightly faster (as the body tries to correct the acidosis by expelling more carbon dioxide). As the acidosis worsens, people begin to feel extremely weak and drowsy and may feel confused and increasingly nauseated. Eventually, in severe cases, heart problems may develop and blood pressure can fall, leading to shock, coma, and death.
In respiratory acidosis, the earliest symptoms are
Drowsiness
Headache
Drowsiness may progress to unresponsiveness and coma as the oxygen in the blood becomes inadequate. Stupor and coma can develop within moments if breathing stops or is severely impaired, or over hours if breathing is less dramatically impaired.
Diagnosis of Acidosis
Blood tests: The diagnosis of acidosis generally requires the measurement of blood pH and carbon dioxide in a sample of arterial blood, usually taken from the radial artery in the wrist. Arterial blood is used because venous blood is generally not as reliable when measuring the body’s pH status. To learn more about the cause of the acidosis, doctors also measure the levels of bicarbonate in the blood. Additional blood tests are then done to help determine the specific cause.
Treatment of Acidosis
Treatment of the cause
Rarely fluids with bicarbonate given by vein
Almost always, treatment of acidosis is directed at reversing the cause. Doctors rarely simply give alkaline medications, such as bicarbonate, to reverse the acidosis.
In metabolic acidosis, treatment depends primarily on the cause. For instance, treatment may be needed to control diabetes with insulin or to remove the toxic substance from the blood in cases of poisoning.
In respiratory acidosis, treatment aims at improving the function of the lungs. Medications that open the airways (bronchodilators, such as albuterol) may help people who have lung diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Sedation due to medications and other substances can sometimes be reversed by antidotes. People who have severely impaired breathing or lung function, for whatever reason, may need mechanical ventilation to aid breathing.
Severe acidosis may also be treated directly when it does not respond to efforts to treat the cause. In such cases, bicarbonate may be given intravenously. However, bicarbonate provides only temporary relief (treatment of the cause should continue) and may cause harm—for instance, by overloading the body with sodium and water.
youtube
The True Cause of Diseases | Barbara O’Neill
Alkalosis
ByJames L. Lewis III, MD, Brookwood Baptist Health and Saint Vincent’s Ascension Health, Birmingham | Reviewed Mar 2025
Alkalosis is excessive blood alkalinity (a measure of blood pH) caused by an overabundance of bicarbonate in the blood or a loss of acid from the blood (metabolic alkalosis), or by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from rapid or deep breathing (respiratory alkalosis).
Causes: Loss of Acid or Low Level of carbon dioxide
Symptoms: irritability/twitching&cramps/tingling extremities
Diagnosis: blood/urine test
Treatment: [1] Metabolic alkalosis is treated by correcting the cause and replacing water and mineral salts such as sodium and potassium (electrolytes). [2] Respiratory alkalosis is treated by correcting the cause, making sure the person is getting enough oxygen, and slowing rapid breathing.
(See also Overview of Acid-Base Balance.)
Causes of Alkalosis
If too much bicarbonate in the blood, a loss of acid from the blood, or a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood overwhelms the body's acid-base control systems, the blood will become alkalotic. Alkalosis is categorized depending on its primary cause as
Metabolic
Respiratory
Metabolic alkalosis
Metabolic alkalosis develops when the body
Loses too much acid
Gains too much base
For example, stomach acid is lost during periods of prolonged vomiting or when stomach acids are suctioned with a stomach tube (as is sometimes done in hospitals).
In rare cases, metabolic alkalosis develops in a person who has ingested too much base from substances such as baking soda (bicarbonate of soda).
In addition, metabolic alkalosis can develop when excessive loss of fluids and electrolytes (such as sodium or potassium) affects the kidneys' ability to maintain the blood's acid-base balance. For instance, loss of potassium sufficient to cause metabolic alkalosis may result from an overactive adrenal gland or the use of diuretics (for example, hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide, or ethacrynic acid).
Respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis develops when
Rapid, deep breathing (hyperventilation) causes too much carbon dioxide to be expelled from the bloodstream
The most common cause of hyperventilation, and thus respiratory alkalosis, is anxiety. Other causes of hyperventilation and consequent respiratory alkalosis include pain, low levels of oxygen in the blood, fever, and aspirin overdose (which can also cause metabolic acidosis).
Symptoms of Alkalosis
Alkalosis may cause
Irritability
Muscle twitching and cramps
Tingling in the fingers and toes and around the lips
Tingling (paresthesia) is a common complaint in hyperventilation due to anxiety. Sometimes alkalosis causes no symptoms at all. If the alkalosis is severe, painful muscle spasms (tetany) can develop.
Diagnosis of Alkalosis
Blood / Urine tests: A doctor evaluates a person's acid-base balance by measuring the blood pH and levels of carbon dioxide (an acid) and bicarbonate (a base) in the blood. To learn more about the cause of the alkalosis, doctors also measure levels of electrolytes in samples of blood and urine.
Treatment of Alkalosis
Treatment of cause
In metabolic alkalosis, replacement of water and electrolytes
In respiratory alkalosis, giving oxygen if necessary or providing calming reassurance to a person who is hyperventilating due to anxiety
Almost always, treatment of alkalosis is directed at reversing the cause. Rarely, doctors give acid, such as hydrochloric acid, to reverse the alkalosis.
Metabolic alkalosis is usually treated by replacing water and electrolytes (sodium and potassium) while treating the cause. Rarely, when metabolic alkalosis is very severe, dilute acid is given intravenously.
In respiratory alkalosis, the first step is to ensure that the person has enough oxygen. The doctor then looks for a serious cause, such as an infection. If pain is causing the person to breathe rapidly, relieving the pain usually suffices.
When respiratory alkalosis is caused by anxiety or a panic attack, a conscious effort to relax and slow breathing may make the condition disappear. Calming reassurance and emotional support can help. Sometimes people try to slow down their breathing by breathing into a paper bag, which may help raise the carbon dioxide level in the blood as the person breathes carbon dioxide back in after breathing it out. However, this technique is not usually recommended because it may lead to other problems (for example, worsening heart or lung problems because of breathing less oxygen).
youtube
True Cause of Disease P2 | Barbara O'Neill
Hyperaldosteronism
By Ashley B. Grossman, MD, University of Oxford; Fellow, Green-Templeton College | Reviewed/Revised Feb 2024
In hyperaldosteronism, overproduction of the hormone aldosterone leads to fluid retention and increased blood pressure, weakness, and, rarely, periods of paralysis.
Topics:
Hyperaldosteronism can be caused by a tumor in the adrenal gland or may be a response to some diseases.
High aldosterone levels can cause high blood pressure and low potassium levels. Low potassium levels may cause weakness, tingling, muscle spasms, and periods of temporary paralysis.
Doctors measure the levels of sodium, potassium, and aldosterone in the blood.
Sometimes, a tumor is removed, or people take medications that block the action of aldosterone.
(See also Overview of the Adrenal Glands.)
Aldosterone, a hormone produced and secreted by the adrenal glands, signals the kidneys to retain more sodium and excrete more potassium. Aldosterone production is regulated partly by the hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, also known as corticotropin), which is secreted by the pituitary gland, but mainly through the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (see figure Regulating Blood Pressure). Renin, an enzyme produced in the kidneys, controls the activation of the hormone angiotensin, which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce aldosterone.
Hyperaldosteronism can be caused by a tumor (usually a noncancerous one, called an adenoma) in an adrenal gland (a condition called Conn syndrome or primary hyperaldosteronism), although sometimes both glands are involved and are overactive. Sometimes hyperaldosteronism is a response to something else (a condition called secondary hyperaldosteronism), for example, certain disorders, such as narrowing of one of the arteries to the kidneys.
Eating large amounts of real licorice can cause all the symptoms of hyperaldosteronism. Real licorice contains a chemical (called glycyrrhizin) that can act as though there is too much aldosterone. However, many candies sold as "licorice" are artificially flavored and contain little or no real licorice.
Symptoms of Hyperaldosteronism
Doctors suspect hyperaldosteronism in people with high blood pressure who are found to have low potassium levels. Low potassium levels often cause no symptoms but may lead to weakness, tingling, muscle spasms, and periods of temporary paralysis. Some people become extremely thirsty and urinate frequently.
Diagnosis of Hyperaldosteronism
Measurement of sodium, potassium, and hormone levels in the blood
Imaging tests of the adrenal glands
Doctors who suspect hyperaldosteronism test the levels of sodium and potassium in the blood to see whether the potassium level is low. However, sometimes people with hyperaldosteronism have a normal potassium level. The sodium level may be mildly increased.
Doctors also measure renin and aldosterone levels. If the aldosterone level is high, spironolactone or eplerenone, medications that block the action of aldosterone, may be given to see if the levels of sodium and potassium return to normal. Doctors also measure the levels of renin. In Conn syndrome, the levels of renin are also very low because they are suppressed by high levels of aldosterone. In secondary hyperaldosteronism, the levels of renin are high, and they stimulate production of aldosterone.
When too much aldosterone is being produced but renin levels are very low, doctors examine the adrenal glands for a noncancerous tumor (adenoma). Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be helpful, but sometimes blood samples from each of the adrenal glands must be tested to determine the source of the hormone.
Treatment of Hyperaldosteronism
For tumors of the adrenal glands, removal of the tumor
Sometimes aldosterone-blocking medications
If a tumor is found, it can usually be surgically removed. When the tumor is removed, the low potassium level almost always returns to normal, while blood pressure returns to normal about 50 to 70% of the time.
If no tumor is found and both glands are overactive, partial removal of the adrenal glands may not control high blood pressure, and complete removal will cause adrenal insufficiency, requiring treatment with corticosteroids for life. However, spironolactone or eplerenone can usually control the symptoms, and medications for high blood pressure are readily available (see table Antihypertensive Medications). Because spironolactone can block the effects of testosterone and often causes breast enlargement (gynecomastia), decreased sex drive, and erectile dysfunction, it is usually avoided in men. Eplerenone is chemically related to spironolactone, but it does not block testosterone and only rarely causes these side effects.
Rarely do both adrenal glands have to be removed.
youtube
Better Than Ozempic! STOP Your Cravings | Feb 12, 2025
Avoiding cravings is not up to sheer willpower. In this video, I’ll share the foods and habits that act as natural appetite suppressants to stop hunger and reduce cravings. Discover the best foods to suppress your appetite naturally so you can lose weight, feel good, and look good!
0:00 Introduction: The best foods to suppress appetite 0:43 Hunger and appetite explained 1:05 The best natural appetite suppressants 5:51 Other ways to curb hunger
Hunger and appetite don’t start with your stomach. Did you know that your microbes and gut bacteria can manipulate your brain and cause you to eat the wrong thing? In this video, I'm going to help you reduce cravings for sugar, refined carbs, MSG, alcohol, and ultra-processed foods. Here’s a list of the best foods to suppress your appetite naturally. These foods contain potent compounds to leave you feeling full and satisfied, and prevent insulin spikes to help stabilize your blood sugar.
1. Coffee 2. Avocado 3. Dark chocolate 4. Cayenne pepper 5. Apple cider vinegar 6. Green tea 7. Bone broth 8. Protein-rich meals 9. Ginger 10. Dark leafy green vegetables 11. Olive oil 12. MCT oil 13. Turmeric 14. Zinc 15. Kombucha tea 16. Grapefruit 17. Arugula 18. Full-fat protein
Eating fatty protein or fat with protein prevents a high insulin spike, which lowers your blood sugar. Avoiding this dip in blood sugar can reduce cravings and curb hunger. Eating fiber also helps buffer the insulin response. Light exercise, like a long walk, is excellent for your blood sugar and can help reduce cravings. An extra 30 minutes of sleep significantly reduces cortisol, stabilizing blood sugar and suppressing appetite naturally.
Minimize stress with exercise, physical work, sleep, a healthy diet, and stretching. Ashwagandha is also beneficial, along with magnesium glycinate before bed.
What does ashwagandha do to the body?
Ashwagandha is an ancient medicinal herb with various possible health benefits. Study findings suggest that it may help reduce anxiety and stress, support restful sleep, and even improve cognitive functioning in certain populations. Ashwagandha is likely safe for most people in the short term. [nice caveat, what's the long-term?]
reduce mucus: [cinnamon/honey/olive oil/lemon/water]
#Dr. Eric Berg#sticky protein#Barbara O'Neill#WARNING#Blood pH#blood acidity#acidosis#Barbara O’Neill#forever chemicals in water source = cancer/kidney & liver problems/diabetes; plastics accumulate in brain to affect cognitive function#plastics keeps your brain inflamed#solution water filter that prevents forever chemicals#zinc makes hydrochloric acid; in older ppl they can't kill off microbes or digest proteins or absorb nutrients#refined carbs depletes zinc = lowers testosterone#starches / maltodextrin / modified food starch / even wheat flour = processed food; all deplete you of zinc & vitamin B1
1 note
·
View note
Text
#What is a good substitute for bread for diabetics#What is the best sourdough bread for diabetics#Is white sourdough bread good for diabetics#Best bread for diabetics to eat#How to make sourdough bread for diabetics#Is sourdough bread better than whole wheat for diabetes#Whole grain sourdough bread
1 note
·
View note
Text
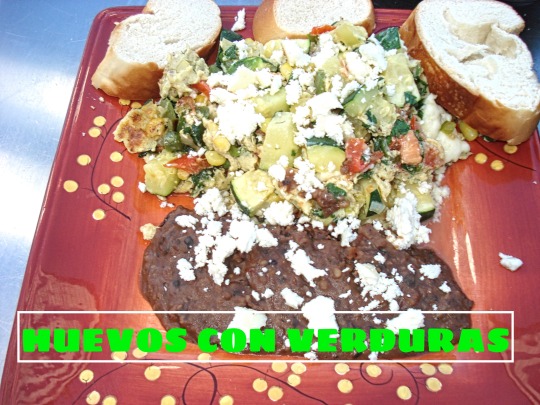
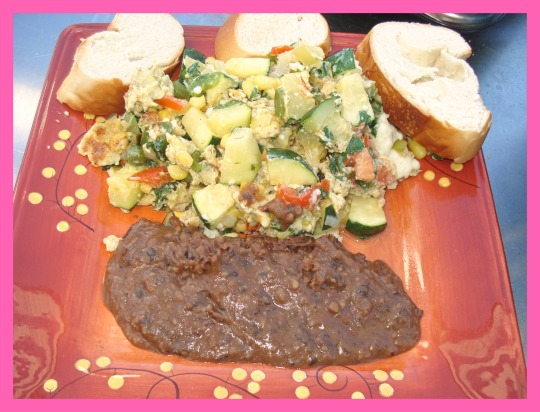
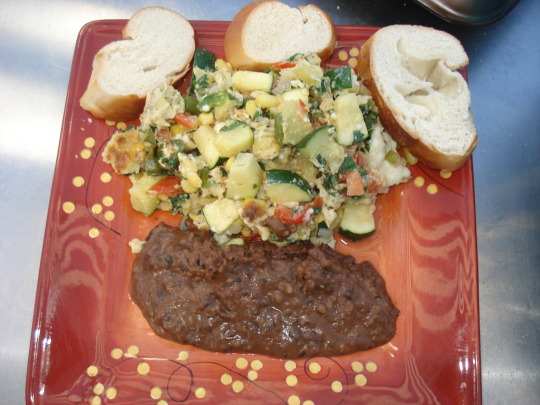
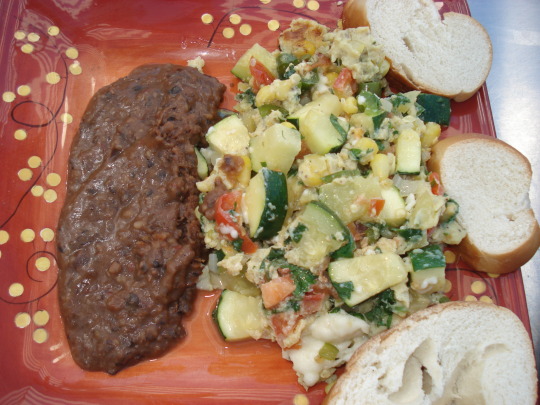















un desayuno balanceado para diabeticos. nutritivo. https://youtu.be/Ufm_3Y7Dl8o Descubre el Secreto para Cocinar verduras Perfectas cada Vez
recetas faciles y deliciosas. paso a paso. https://bit.ly/3jDlXCF EN LA COCINA CON ERNESTO.
0 notes
Text
The Best Ways to Add Wheat to Your Diet In Diabetes: Tips for Healthy Eating
Introduction Wheat, frequently alluded to as the “brilliant grain,” plays had a crucial impact in molding human civilization for millennia. As one of the most generally developed and consumed crops around the world, wheat has sustained endless populaces as well as affected social, monetary, and social parts of social orders across the globe. This article intends to dig into the complex meaning…

View On WordPress
#Add Wheat to Your Diet#Diet In Diabetes#Health#healthylife#Prepare and Cook Wheat for Diabetics#Recipe for Controlling Diabetes#Tips for Healthy Eating#treatment for constipaion
0 notes
Text

Best Wheat for Diabetes
Breakfast, lunch, and dinner just wouldn’t be the same without the humble chapatti. And while it has gained much acceptance as a low-calorie food, given its lower Glycemic Index, not all varieties are equal, nor good for diabetics.
Click here to read more: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/best-wheat-for-diabetes/2904
#wheat for diabetes#is wheat good for diabetes#is wheat chapati good for diabetes#wheat flour for diabetes#best wheat variety in india#best wheat variety#wheat and diabetes#wheat flour and diabetes#wheat and diabetes connection
0 notes
Text
Is Vegan Carrot Cake Good for Diabetics?
When we think of dishes made from carrots, Gajar ka Halwa usually tops the list. But did you know there’s another delicious and healthier option? Yes, it’s the carrot cake—and not just any version, but a Vegan Carrot Cake that’s perfect for diabetics too!

What is a Carrot?
Carrots, known scientifically as Daucus carota, are root vegetables most commonly seen in orange but also found in red, purple, and yellow. Originally from Persia, they’re now grown across Asia and Europe. Carrots are loaded with beta-carotene, fiber, and antioxidants—making them a great choice for health-conscious individuals.
Why Try Vegan Carrot Cake?
Carrot cake is a wonderful way to enjoy the natural sweetness and texture of carrots. And now, you can do it the healthy way! Our vegan version is made without eggs, milk, or any dairy products. It’s also free from refined sugar, making it ideal for people managing diabetes or following a plant-based diet.
What’s more, this recipe includes khapli wheat flour, known for its low glycemic index, and soft dates for natural sweetness. The result? A moist, soft, and flavorful cake that’s healthy without compromising on taste. You can also make mini cupcakes with the same batter for easy snacking.
Get the Full Recipe
Ready to try this wholesome dessert? Click here to explore the full Vegan Carrot Cake Recipe with detailed instructions and ingredients.
https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/vegan-carrot-cake-recipe/1448
Whether you’re vegan, diabetic, or just love nutritious baking, this cake is sure to win your heart—and your taste buds!
#vegan carrot cake recipe#diabetic carrot cake#eggless carrot cake recipe#healthy carrot cake for diabetes#sugar-free carrot cake#khapli wheat carrot cake#vegan dessert for diabetics#no sugar carrot cake#plant-based carrot cake#carrot cake without eggs and milk#carrot cake using dates
0 notes
Text
Going Gluten-Free, Dairy-Free and Healthier: Never a Better Time than Now!
Going Gluten-Free, Dairy-Free and Healthier: Never a Better Time than Now! disclaimer: I NEITHER WORK FOR, BENEFIT FROM, NOR EARN MONEY FROM PROMOTING ANY PRODUCTS AND THIS BLOG DOES NOT ACCEPT ADS. Got migraines? Eczema? Suffer from allergies that cause rhinitis (runny nose), itchy eyes and nose, chronic coughs or sinus infections? What about weird rashes, bloating, weight gain, high glucose…

View On WordPress
#A1#changing diet#dairy#dairy free#dairy-free#diabetes#diet#dietary#fat#gluten#gluten free#gluten-free#health#oils#wheat#wheat free#wheat-free
0 notes
Text
Ten Tips for an Easy Yom Kippur Fast
Fasting doesn’t necessarily mean suffering. There’s quite a bit we can do to alleviate the bodily and mental stress that normally accompanies a fast. The day before the fast, follow the following guidelines:
1. Cut down your caffeine intake to minimize headaches. That means stop drinking coffee, tea, and cola at least eight hours before the fast, and preferably twenty-four hours before the fast.
2. Avoid salty, spicey, and fried foods on the day before the fast.
3. Avoid white sugar, white flour, and white rice. Eat whole-grained foods such as brown rice and whole-wheat bread or challa.
4. Drink a lot of water all day long.
5. Eat a good breakfast that includes fruits, veggies, eggs or sardines, and whole grains.
6. The pre-Yom Kippur meal (se’uda mafseket) should include baked or broiled fish, a veggy salad, consomme, a small portion of chicken or turkey, and a side dish of complex carbohydrates. Substitute sweet deserts with watermelon or other water-retaining fresh fruit, and a cup of herb tea with a whole-grain cookie.
On Yom Kippur:
7. The more you immerse yourself in prayer, the less you’ll think about food.
8. Rest between prayers. Don’t run around outside, especially in the hot sun. Save your voice for prayers. Idle talking will make you thirstier, and will detract from the holiness of the day.
After the fast:
9. Drink two glasses of water, and then eat solids gradually, so as not to shock the digestive system. Begin with fruit, like plums or grapes. The worst thing people do is to consume pastries and soft drinks, or “lekach un bronfan” (cake and liquor) right after the fast (these are unhealthy anytime, all the more so right after the fast when they give your body a shock of glucose).
10. Forty-five minutes to an hour afterwards, one can eat a balanced meal with protein, carbohydrates, and vegetables. After eating, relax for an hour with your favorite book (preferably Gemara of the laws of Succoth from Shulchan Oruch) and your favorite beverage, then begin constructing your Succa.
Attention diabetics, heart patients, folks with high blood pressure, and people whose health depends on regular medication - you must be especially careful to ask your doctor if you are capable of fasting, and then consult with your local rabbi, giving him the doctor’s exact opinion. For many such people, it is a mitzva not to fast on Yom Kippur.
242 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you know how our understanding and treatment of diabetes has changed through history?
Oooh good question, anon!
As you may guess, diabetes mellitus is not new.

We've known about it since at least the Ebers Papyrus (1550 BCE) when the disease and a treatment was first described. This treatment was: "a liquid extract of bones, grain, grit, wheat, green lead and earth." I did not look these up, but I would guess they did not do a whole lot for the treatment of diabetes.
Later during the 6th century BCE it was first given a name when it was described by Hindu physician Sushruta as madhumeh or "honey urine."
Honey urine is a very apt descriptor for diabetes. In any type, one of the most measurable symptoms is that the person urinates a lot, and the urine tastes sweet (or, if one didn't feel like tasting, that it ferments, or that it attracts ants). This was also the first test for diabetes.
The reason for the sweetness of the urine (as well as a lot of other general info about diabetes) is spelled out more clearly in my "Don't Be That Guy Who Wrote Hansel and Gretel: Witch Hunters" post.
A Greek physician Apolonius of Memphis named it Diabetes, meaning "to siphon" (referring to the large amount of urine lost).
Roman physician Aretaeus later made the first precise description of diabetes. This included the classic symptoms of incessant thirst, copious urination, and constant hunger leading to emaciation and death. He also notes that if deprived of water, the patient will continue to urinate until they become so dehydrated that they die.
The term "Mellitus" was not added until the 1600s by an English physician Thomas Willis. This was again due to the sweetness of the expressed urine. Willis prescribed a diet of "slimy vegetables, rice, and white starch. He also suggested a milk drink which was distilled with cypress tops and egg whites, two powders (a mixture of gum arabic and gum dragant), rhubarb and cinnamon". Supposedly his patients improved if they kept to this diet, though few managed it long term. I honestly don't know how it would have worked, even temporarily.
A major breakthrough came in 1889 when it was discovered that if you removed the pancreas from a dog, the dog would become diabetic (particularly, that it would urinate large quantities of sweet urine). Up until this point it was thought that diabetes stemmed from the kidneys and bladder, or perhaps the lungs. This was the first time it had been shown experimentally that the pancreas was the problem.
Speaking of this, this was also part of a series of experiments where an English physician named Merkowski implanted a small amount of pancreas in the pancreas-less dog's fat, which reversed the diabetes temporarily. This proved that the pancreas was making something that helped regulate blood (and thus urine) sugar.
What this was wasn't figured out until 1921, when Canadian scientists Banting and Best (with help from McLeod and Collip) isolated something they called insletin (after the islets of langerhans, where the substance was being produced). It's important to note that all of these scientists hated each other so much they almost refused a Nobel Prize over it. Later, Collip would refine the substance and McLeod would rename it insulin.
Prior to insulin existing there was basically 1 vaguely useful treatment for diabetes. Unfortunately, that was starvation. So you could either die a slow and painful death by diabetes or you could die a slightly less slow but still painful death due to eating about 500 calories per day. Either way, diabetes was fatal, usually within a couple of years of diagnosis.
By 1923, the first commercial insulin product, Iletin, had been developed. Iletin was a U10 insulin (10 units per 1 milliliter- less potent than today's U100 and U500 insulins) and was made from pork pancreases. It took nearly a ton of pork pancreas to make 1oz of insulin. Fortunately, as a byproduct of the meat industry, pancreases were readily available.
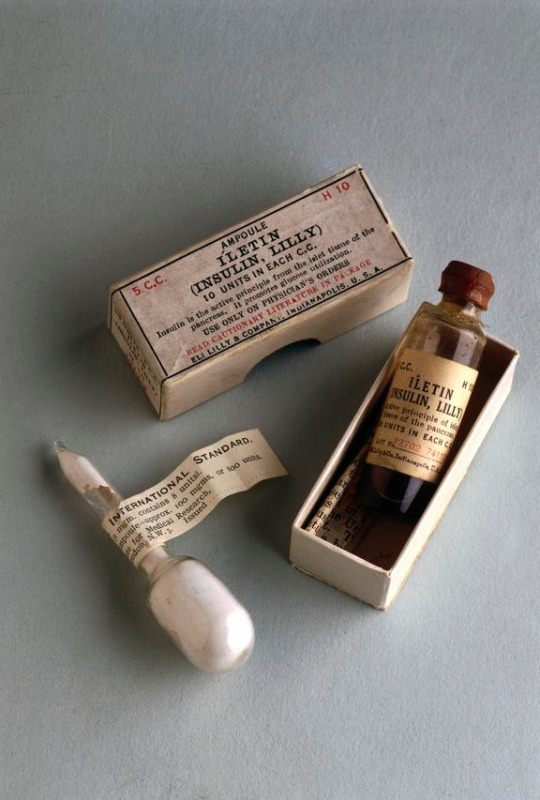
Now, you might be thinking- no one has mentioned type 1 or type 2 yet in this entire post!
Well, you would be right, because diabetes wouldn't be split into 2 forms (insulin-dependent and non-insulin dependent) until 1979, and wouldn't be classified as types 1 and 2 until 1995. That's right- some of you were alive when there was only one kind of diabetes out there.
Now, there's more about the types in the Hansel and Gretel post, but essentially type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas itself stops producing insulin, usually in childhood. When this happens, the body stops being able to use sugar (insulin, a hormone, acts as a "key" to let sugar into cells for use). Without replacing that insulin, the person dies because their cells starve.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas still produces insulin, but the cells stop responding to it correctly. This causes high sugar levels in the blood, which causes longer-term complications (infections, ulcers, blindness, neuropathy, heart and kidney disease, hyperosmolar syndrome, etc..) which eventually lead to death.
We started discovering oral drugs that worked on what would later become type 2 in the 1950s. Particularly those that worked by increasing the insulin output of the pancreas, but only when the pancreas was still producing some insulin.
Predicting which diabetics would benefit from oral therapies was challenging, but it was recognized that when the onset of diabetes was slow and came on in adulthood, the oral agents would work, while if it came on suddenly in childhood, the oral agents wouldn't. Terms like "adult onset" and "maturity onset" were common:

(Side note: if you have ever read Alas, Babylon (1955) there is a diabetic character who by today's standards clearly has type 1 diabetes, but wants to switch to the "new oral pill" (called "orinase" in the book, though they are likely referring to diabinese pictured above).)
From 1923 into the 1980s, insulin was given once or twice per day, and not particularly titrated to blood sugar. This was probably just because we didn't have a great way to measure blood sugar in real time. Pre-1970s, there was no way to test blood sugar outside of a lab setting.
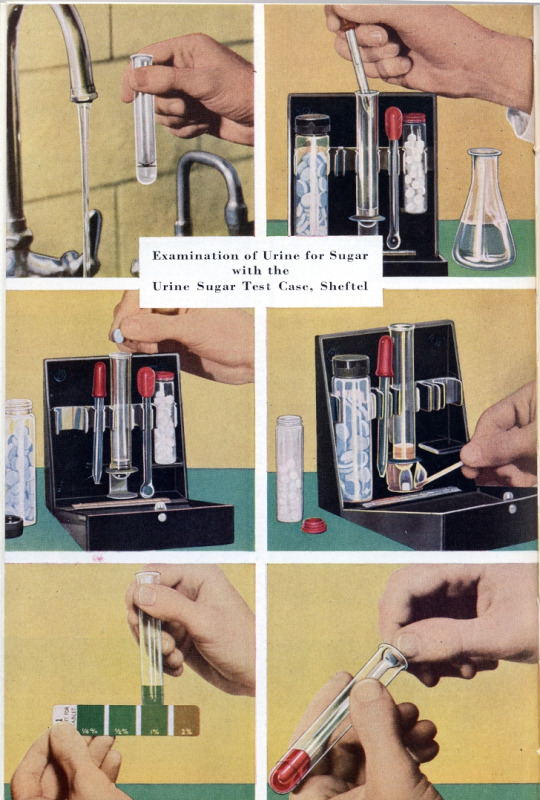
Urine testing was common starting in the 1940s, but was cumbersome as it required a flame for heating the urine. By the 1950s, a test had been developed that didn't require a flame, but was still not practical for home use. In the 1960s, paper strips were developed that changed color for different amounts of sugar in the urine. The problem with this was that the strips couldn't change color until there was sugar in the urine- a blood sugar level of over 200 by today's measurements. Low blood sugar readings were impossible at this time, and had to be treated based on symptoms.
In the 1970s, blood sugar could finally be measured by putting a drop of blood on a test strip, wiping it off, and matching the color of the test strip to a chart. While less cumbersome than urine tests, this was still something that would generally only be done at a doctor's office.

In 1983, the first home blood glucometer is developed. Finally, it was practical to take one's sugar multiple times per day, and it becomes possible to experiment with "sliding scale" insulin injections that keep tighter control of blood sugar. By the late 90s, continuous glucose monitors became available- though unlike today's CGMs that allow readings in real time on a smartphone or monitor, these had to be downloaded to a computer at regular intervals.
The 1980s were the first decade where insulin pumps become widely available. The very first pump was large and had to be carried in a backpack, but it represented a huge step forward in glucose control, as it more closely mimicked the function of a working pancreas than once-daily injections.
For the next 30 or so years you really had to work to qualify for an insulin pump, but recently it's been found that pumps greatly improve compliance with blood glucose control whether or not the person had good compliance before getting the pumps, and insurance has gotten better about covering them (though CGMs are still a pain to get insurance to cover).
The 1980s was also the decade that recombinant human insulin (insulin made by genetically modified bacteria) was first used. Up until that point the only insulins were pork and beef insulins, which some people had allergic reactions to. Recombinant insulin was closer to regular human insulin than beef or pork, and represented a big change in how insulin was made.
Today for people who take insulin to manage their diabetes, insulin is usually given as a single injection of a long-acting basal insulin, coupled with smaller doses of ultra-short-acting insulins with meals or snacks. This is the closest we've gotten to mimicking the way a pancreas would work in the wild, and keeps very tight control of blood sugar. This can be done by fingerstick blood sugar tests and individual injections of insulin, or it can be done with a CGM and pump- it just depends on the resources available to the person and their personal preference.
117 notes
·
View notes
Note
I went diabetic earlier this year, since then I've had far more serious health concerns to really focus on it. I've listened to my primary care and reduced my average a1c from 13 to 7. I've recently been looking into diets and what not that are the best. Currently, I'm trying to cut out all carbs, on my doctor's orders. What I'm seeing though is that a plant based diet is best. It looks like a ketogenic diet is what my doctor wants me to follow? I've watched videos on both diets and I don't know, I agree with you that keto is evil. What are your thoughts about this?
I am not a medical professional so i can't give you medical advice, but I'd say that you should ask your doctor for a referral to a dietician (an RD or an RDN, NOT a "nutritionist" - RD/RDN are protected terms that mean they have completed specific training and have specific board certification) and ask the dietician for advice on your specific dietary needs for your specific medical conditions.
What I can say is that trying to cut all carbs is pretty dangerous - not only is it a macronutrient that our body uses as the most available fuel for your body processes (we *can* get fuel from protein and fat, and ketones can *theoretically* replace sugars for energy but nobody is actually sure how long our bodies can do that and we know it's a LOT less efficient, it's supposed to be less efficient, and what that means is it makes a lot of people feel exhausted when they try it because they literally have less available energy) but also there are certain nutrients that are fortified in the US that are going to be hard to get if you're cutting carbs completely. The example that I always use is folate, because when I had to cut wheat out of my diet (i have grain allergies and celiac disease) I didn't know to supplement it and ended up with a form of anemia and stuff like "fainting" and "dizziness" and "low oxygen saturation."
Which is part of why massive diet changes should be undertaken with the assistance of a dietician! That's why I started studying nutrition! Because nobody supervised my medically necessary diet changes and it went very poorly!
Your GP very likely doesn't have a ton of training on nutrition, and is even less likely to have training on nutrition specific to your condition. If your GP is telling you to cut all carbs, they are telling you to do something dangerous and not nutritionally sound (even really restrictive keto diets call for 20g of carbs a day). Ask either them or your endocrinologist for a referral to a dietician (again, you are looking for a Registered Dietician or a Registered Dietician Nutritionist, RD or RDN, NOT just 'nutritionist') who is familiar with helping diabetics manage their nutrition.
Now, all of that said, in the choice between two fairly restrictive diets I will always say to try the one that requires less effort. It is much easier to eat a plant-based diet long term than a keto diet, and it is vanishingly unlikely that you are going to end up protein deficient (the primary concern for most people who are starting plant based diets, and it's just not all that likely - we need a lot less protein than a lot of people seem to think; though if you're going completely vegan you do need to be careful to supplement your B vitamins and to ensure that you're getting plenty of omega fats)
Because the thing is, for a diet to "work" you have to be on that diet forever. If you stop being on that diet, and stop adhering to its restrictions, whatever benefits exist for that diet go away. So the best diet for *anybody* is one that will provide them with the nutrients they need in a way that they can access regularly and affordably, that they enjoy eating and can comfortably maintain for long periods of time, and that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables because the only diet advice that is nearly universally applicable is that people should be eating more fruits and vegetables and they should be eating a wider variety of them.
I am not a fan of "diets" as a concept and I think that people should think of nutrition in terms of "my diet" not "the diet that is meant to be one-size-fits-all for millions of people that I am attempting." Your diet is what you eat and drink, and that is what you should be looking at adjusting. If you want to reduce carbs in your diet it's better to tweak your consumption than it is totally replace your diet with a one size fits all keto diet. If you want to increase fat in your diet it is better to tweak your consumption than it is to replace your diet with a one size fits all atkins diet. If you want to go plant based I think it is better to start by adjusting your diet to include more plants and to slowly replace animal based products than by trying a one size fits all vegan diet right out of the gate. You can always (and should!) make adjustments to what you eat as circumstances change and you may end up at a vegan diet or a low carb high fat diet and find that that works for you, but part of the reason that I think nutrition studies on diets are so screwy and hard to pin down is because your body is going to *flip the fuck out* when you change from, say, an average american diet to a study-provided Mediterranean diet for a 12 week experiment. If you drastically change your diet all at once and get good results immediately it's very hard to say if those results will be lasting because your body may just adjust to the "new normal" of your diet six months down the line.
But like seriously if your GP is telling you to cut all carbs you need to see a person who specializes in nutrition, and to prepare for your appointment with that person you should make a list of your goals (for you it sounds like you want to manage your blood sugar levels, reduce a1c, and *ask about* low carbs if that is something that interests you), a list of things you think that you'll have trouble with or that you want to include in your diet because they're important to you (if you really like nuts but have to be on a low fat diet, ask if there's a way to work around that with your needs, for example; if there is a cultural staple that you will find difficult to cut from family meals, TELL THEM THAT), a list of questions that you have about different types of diets, and *VERY IMPORTANTLY* information about your food budget and cooking skills. Be clear about it if you can't cook. Be clear about it if you can't afford certain ingredients.
Anyway. Once again, not medical advice, please speak to a medical professional, good luck.
194 notes
·
View notes
Text

Whole Wheat Chapati: A Diabetic's Delight or Disaster?
Whole wheat is rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals while contributing to better digestion and overall health. Fiber, plays a crucial role in slowing down the absorption of glucose, helping to manage blood sugar levels. Whole wheat has a lower GI compared to refined grains, which means it has a more gradual impact on blood sugar.
Here are tips for a Diabetic-Friendly Chapati: https://www.freedomfromdiabetes.org/blog/post/whole-wheat-chapati-a-diabetic's-delight-or-disaster/3735
#whole wheat chapati#chapati calories#chapati nutrition#is chapati good for weight loss#carbs in chapati#Sugar Free Atta for Diabetics#Diabetic Care Atta
0 notes
Text

Can Diabetics Eat Puran Poli? Yes, with a few changes, diabetics can enjoy puran poli! A regular puran poli is high in calories and sugar. But when made with khapli wheat, date paste instead of sugar or jaggery, and natural sweeteners like stevia, it becomes a much healthier option. Eat in moderation, and it can be a part of your diabetes-friendly diet.
Read more, visit blog.
#puran poli for diabetics#diabetic friendly puran poli recipe#can diabetics eat puran poli#is puran poli good for diabetes#how to make puran poli for diabetics#khapli wheat puran poli#puran poli with date paste#no sugar puran poli recipe#puran poli with stevia#healthy puran poli ingredients#traditional sweets for diabetes#low calorie Indian sweets#modified puran poli recipe
0 notes
Text
I'm having a really rough time and I really don't want to say anything, but at the same time I feel like I want to say something and I have like nowhere I can really say it because I feel like I don't know people personally in the community, but I also know I spend most of my time on Tumblr, some of the time, blogging my Sims so I felt like I could post this here rather than my personal blog.
I don't know how much more I can actually take.
I am doing the best I can with my diabetic and high blood pressure diagnosis after losing my dad to stomach cancer. And I get talked to like I'm a fucking idiot by my doctor who I have only had since September, at my physical today.
I am just sitting here at home like crying my fucking eyes out on and off since 11am this morning.
But I'm just fucking tired. I am mentally and emotionally tired after losing my dad in 2022, and dealing with my diagnosis for one year now.
I have had a fear of doctors since I literally came out of my mother's womb. She and my dad had the roughest time with me all through my youth and teenage years about going to the doctor while my older brother put them through NO hell about it.
I don't know where this fear came from, but I don't see it going away any time soon and each visit I have had since my diagnosis has been a terrible experience. And I have to go back every 3 to 4 months to check my sugar levels and my blood pressure and every last fucking thing.
I am tired of pricking my finger every single day. I am tired of taking my medicine. I am tired of the side effects. I am tired of the fucking blood pressure monitor. I am tired of it all.
Now it's off to the fucking eye doctor, then there, then here. I can't stand doctors and now you are forcing me to go to more doctors outside of my PCP office because "diabetes can mess with your eyes" and "check your feet because diabetes could take your limbs" -- I fucking know this. My mother's been a diabetic since I was 3 fucking years old. I've known how to deal with diabetes since I was 15, until at age 37 I now have to deal with it for myself and for the rest of my life.
I am just so fucking bent it's not even funny.
I am the lowest I have ever been in my life and honestly, I've felt pretty low during moments in my life for the amount of shit I've gone through. No matter how much effort I make, nothing is working. I try so fucking hard and nothing even moves in the right direction like I'm fucking cursed or something.
I feel lost and I feel alone and that's NOT the fucking person I am so that kills me inside. I never ask for help, I'm always there helping others.
Like literally everything, I blame myself for everything. It's like it's my fault I'm sick with these things. I know that's stupid and totally not true, but that's what I tell myself.
I am doing the best that I can do, but some days I just don't want to do it. Some days I'm just so slow going about everything.
I eat healthy. Sure I splurge like others, but since I've gotten sick? If I splurge for one meal once every month, it's a lot. I can't even fucking eat a piece of bread with a can of tuna without thinking what the bread might do to my sugar level.
It's like I love food so much and suddenly I'm like developing a fucking eating disorder over what every single piece of food could be doing to me.
I can't eat salt, I can't eat sugar. I can't eat fucking oatmeal. I can't eat cheerios. I can't even eat fucking wheat chex which is full of fiber. I can't eat fucking dairy. I can't eat fucking fruit.
I'm eating green veggies every single day and I can't seem to just be at normal fucking numbers or down to what they want me to be.
I've got side effects from the medication. I have to eat something with the medication. Now my entire system is slowing down so fiber up, but it still does nothing to move things along. Then I have to make sure I'm taking vitamins to supplement for all the shit the meds are depleting.
I'm fucking just tired of it all like JFC. I'm doing the literal best that I feel that I can do and I've got people coming at me like scolding me for shit that's not even my fucking fault and judging me.
Even my dad was a diabetic, but later on in his life. He was the one with the high blood pressure since he was like 29 years old -- and even that didn't kill him, the fucking stomach cancer did. The man ate healthier than anyone I knew once he hit like 55 years old -- and he fucking died of stomach cancer. Go fucking figure.
It's like you walk into the doctor's office and you get diagnosed with 5 things. They literally size you up and add shit to your chart you don't even want on there or you don't even know what they are.
It's like the dumbest shit to even say, but I sometimes feel like I've just been forgotten about. Like I'm being tested to see how much I can take before I just fucking crack and it's like I can't take any more. Maybe I could years ago or maybe I could before my dad died, but I can't take any more right now. I just want space and a fucking break so I can breathe and I feel like I'm being constantly monitored and forced to do shit that I don't want to do.
Anyone that knows how I blog here knows I'm a pretty silly and upbeat type of person -- and sarcastic as hell some of the time, too, but I'm really having a really tough time these days. I just try to put my best foot forward, but clearly, that isn't working at the moment.
I also hold a lot of stuff inside -- I always have since I was a kid so it's extremely painful for me to admit to how I honestly am feeling, but I'm just really down because I'm trying so fucking hard and it's like life just is like let's just fuck with her a little more and see how she does.
And through it all I can't call up my dad and be like hey Dad, can you believe this crap?! Or hey Dad, what should I do? Or hey Dad, how's the weather? I can't call him for any fucking thing anymore and that's a feeling I never expected to feel early into my life, and so suddenly.
I'm doing my best, but I'm also just fucking tired. Like something's got to give, but fucking when? I'm the most patient person in the world, but fuck -- when is something finally gonna fucking give?
10 notes
·
View notes