#water sanitation workers
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Jal Sahias Demand Better Conditions in Chaibasa Protest
Water Workers Stage Dharna at Minister’s Residence, Submit 5-Point Memorandum Jharkhand State Jal Sahia Sangh advocates for improved compensation and job security for essential water service providers. CHAIBASA – Jal Sahias from multiple blocks in the Chaibasa assembly constituency staged a protest on Sunday, presenting a five-point memorandum to Minister Deepak Birua at his residence. The…
#राज्य#Chaibasa assembly constituency#community health initiatives#government worker benefits#Jal Sahia protest Chaibasa#Jharkhand State Jal Sahia Sangh#Jharkhand water workers#lr#Minister Deepak Birua#Rural Development Jharkhand#rural employment issues#state#water sanitation workers
0 notes
Text

"It May Be War, But Housewives Are Riled Over Flooding of Street," Windsor Star. August 1, 1942. Page 3, 5 & 10. ---- THERE'S water, water everywhere on Central avenue, near Tecumseh-road and the residents of the wartime house in the muddy flooded area are threatening to refuse to pay their rent until something is done to take the water away. Picture at top left shows neighborhood children splashing over the original roadway. The mud will be tracked into houses and round into new carpets, housewives say. At top right, a car is shown moving at moderate speed through a puddle. The spray covers the sidewalks and lawns, ruins clothes and automobile finishes, as well as all the neighborhood tempers. Below, company has called at one of the houses and the occupants of the car are having a hard time trying to find a place to bring their car to dock.
Housewives Are Militant ---- Men on Central Avenue Also Fighting Mad About Flood --- Occupants of Wartime Housing homes on Central avenue, near Tecumseh road, are ready to do battle over muddy water which has an in the street for two weeks Some are refusing to pay their rent until the muddy flood is taken away, House wives are militant over mud-tracked rugs. Some attribute sore throats to the flood, and a few of those inclined to take the situation less seriously have spoken of building landing docks. WATER AND MUD A reporter and photographer of The Windsor Star plowed through the yellow-brown sea of Central avenue 13 hours after the heavy rain had stopped yesterday. In some places the sidewalk is buried under mud throw up by swashbuckling auto automobiles. In me places the water is almost a foot deep All boulevards are mires. Mud has been splashed half-way up the front walk of the trim little homes out there. Housewives stand in doorways with a gleam in their eyes that bodes no good for someone each time a car cleaves the water. There are sewers on Central Avenue. But the sewers are placed at each end of the block, and the roadway has sagged in the centre, so that the sewers gleam as freshly as when installed, while only a few feet away, children splash, sail boats, and distraught parents scream at them to get out of the mud and into a tub immediately. There are threats on the smouldering battlefront of Central avenue sea today. They're the threats of a legion of women who are fed up with having to clean house every day with a mop: the threats of young women who no longer dare walk down the sidewalk that are covered by mud, for fear of finding their white summer clothes spotted with brown by passing cars; there are threats from men whose cars need rewashing each time they leave home; there are threats from those who want to entertain company and are ashamed of their neighborhood: there are threats from distraught mothers who blame the condition of the streets for sore throat. WOMEN INDIGNANT Several of the women are going to swing into action today. They said their rents are due now, but that no. one is going to get a penny until the street is fixed and their homes become "decent places to live in, instead of pigpens." "My little girl has bronchitis," said the occupant of one house. "She's three years old, and when she goes out to play she gets in all that filth. There is mud everywhere. I don't think we should stand for it." "It's a mess" complained a second. "My husband went down to the board of health and they told him they couldn't do anything about it. I'll tell anyone that wartime housing is certainly far from healthy. Why I had company here, and I was so ashamed. They got stuck in the mud. We're not going to pay our rent until this street is fixed. My husband cut a downhill drain for part of the street, but that doesn't help much. Everyone gets splashed with mud. It gets tracked into the house. I'm just sick about it." "It's a disgrace," said a third. "All my children have had infected throats since then floors came, and I blame that water out there for it. It's terrible. It isn't healthy. I had a boy guest visiting here from Pleasant Ridge. He comes from a fine home. They have a maid. Every time he went outside, he came in covered with that filth from head to foot, and I had to put him in the tub. It's been this way for two weeks. I'm not going to buy a carpet until that street is fixed. I'm polishing floors all day long." MOTORIST ANGERED "I've got a good mind to send some- one the bill for washing my car," said an irate motorist, who had just met another ca. in midstream. "Every time I go through here, the car is coated with muck from bumper to bumper. If any windows are open, it's even worse."
"It's awful," said a fifth. "I came here last March from the West, and I couldn't even get out of the taxi. I ruined my shoes. They should have decent drains here. I can't keep my rug cleaned. It's always full of mud. I can't even let my children come in their own home the front way, they get so messy from just walking on the sidewalk. The Wartime Housing people say it's up to the city to fix, and the city passed the buck to the Wartime Housing. Let me tell you, it's going to be just too bad for the city if I get sick as a result of this. I'd be ashamed for my friends out West to see the way we have to live. I have to pay my rent tomorrow, and I don't think I will, until this is fixed. There's no road. There's not even a side-walk. It's all mud. Mud everywhere!" Said a sixth: "You might as well be living on the battlefront. They say that the men in factories are the men behind the men behind the guns. I agree with them. We live in mud too. What's the use of trying to look clean and dainty when all you have to do is to step outside your house when a car passes and get drenched in that awful smelly stuff."
And a seventh: "Cars are getting stalled in that goo all the time. We aren't even sure of our deliveries any more. We women out here are tired of talking. It's about time we had some action. If the city won't take the action, and the Wartime Housing won't take the action, then we women will!"
#windsor#wartime housing#public housing#low income housing#muddy waters#flooded streets#sewage system#sanitation issue#women in revolt#housewives#war workers#women workers#women in history#canada during world war 2
1 note
·
View note
Text
If anyone has taken their eyes off what's happening to federal workers in the US right now, here's some highlights that we're hearing from our comrades across the government who have not yet been fired:
In one building (hosting multiple agencies), the locks on the bathroom were changed so employees no longer have any access to a bathroom during the workday. People are peeing in trash cans.
Elsewhere, multiple agencies have reported that hand soap is no longer being supplied in the bathrooms.
Toilet paper supplies have not been adjusted to meet the needs of a vastly increased number of in-office employees.
Employee-owned coffee and coffee makers have been stolen or thrown away without notice (it was already illegal for taxpayer dollars to be spent on supplying federal employees with amenities like coffee, so many offices have coffee supplied by pooled employee funds).
Meanwhile, many offices don't even have potable drinking water (recurrent legionella outbreaks), so employees have to bring their own water from home.
Despite an explosion in the number of workers in offices, cleaning budgets have been slashed and many offices are not being cleaned regularly enough to remain sanitary. Pests like roaches and rats are a problem.
The firings continue, legal and illegal. Entire programs are being cut. Managers have no idea when they might lose staff. Employees are getting fired at 6pm on a weekend or finding out when they're unable to log into their computer or when they receive a shipping label in the mail to return their equipment.
Through all of this, the DOGE employees in federal workplaces are enjoying incredible and expensive luxury: AI-powered sleep pods, entire dormitories so they can live in federal buildings, nurseries for their children on site, free food and beverages, laundry services, and who knows what else. They have special security to restrict access to their areas of the buildings, including armed guards.
And I'm not just saying this to lament how bad it is for federal workers. I'm saying this because, as workers are reporting this to one another, the response is, inevitably: "This is illegal." "Yes, but who would I report it to? OPM? They're a DOGE puppet. OSHA? They've cut OSHA. The Inspectors General? Cut. The NLRB? Cut. My union? No longer recognized."
There is no one left to enforce these laws, so taking away access to basic sanitation is now effectively legal. They are doing this to federal workers, who historically have been some of the best-protected workers in the country. They are doing this specifically because it demonstrates to the public sector that it is now legal to do these things to their own workers.
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
so: masking: good, unequivocally. please mask and please educate others on why they should mask to make the world safer for immune compromised people to participate in.
however: masking is not my policy focus and it shouldn't be yours, either. masking is a very good mitigation against droplet-born illnesses and a slightly less effective (but still very good) mitigation against airborne illnesses, but its place in the pyramid of mitigation demands is pretty low, for several reasons:
it's an individual mitigation, not a systemic one. the best mitigations to make public life more accessible affect everyone without distributing the majority of the effort among individuals (who may not be able to comply, may not have access to education on how to comply, or may be actively malicious).
it's a post-hoc mitigation, or to put it another way, it's a band-aid over the underlying problem. even if it was possible to enforce, universal masking still wouldn't address the underlying problem that it is dangerous for sick people and immune compromised people to be in the same public locations to begin with. this is a solvable problem! we have created the societal conditions for this problem!
here are my policy focuses:
upgraded air filtration and ventilation systems for all public buildings. appropriate ventilation should be just as bog-standard as appropriately clean running water. an indoor venue without a ventilation system capable of performing 5 complete air changes per hour should be like encountering a public restroom without any sinks or hand sanitizer stations whatsoever.
enforced paid sick leave for all employees until 3-5 days without symptoms. the vast majority of respiratory and food-borne illnesses circulate through industry sectors where employees come into work while experiencing symptoms. a taco bell worker should never be making food while experiencing strep throat symptoms, even without a strep diagnosis.
enforced virtual schooling options for sick students. the other vast majority of respiratory and food-borne illnesses circulate through schools. the proximity of so many kids and teenagers together indoors (with little to no proper ventilation and high levels of physical activity) means that if even one person comes to school sick, hundreds will be infected in the following few days. those students will most likely infect their parents as well. allowing students to complete all readings and coursework through sites like blackboard or compass while sick will cut down massively on disease transmission.
accessible testing for everyone. not just for COVID; if there's a test for any contagious illness capable of being performed outside of lab conditions, there should be a regulated option for performing that test at home (similar to COVID rapid tests). if a test can only be performed under lab conditions, there should be a government-subsidized program to provide free of charge testing to anyone who needs it, through urgent cares and pharmacies.
the last thing to note is that these things stack; upgraded ventilation systems in all public buildings mean that students and employees get sick less often to begin with, making it less burdensome for students and employees to be absent due to sickness, and making it more likely that sick individuals will choose to stay home themselves (since it's not so costly for them).
masking is great! keep masking! please use masking as a rhetorical "this is what we can do as individuals to make public life safer while we're pushing for drastic policy changes," and don't get complacent in either direction--don't assume that masking is all you need to do or an acceptable forever-solution, and equally, don't fall prey to thinking that pushing for policy change "makes up" for not masking in public. it's not a game with scores and sides; masking is a material thing you can do to help the individual people you interact with one by one, and policy changes are what's going to make the entirety of public life safer for all immune compromised people.
#dyspunktional#cripple punk#actually disabled#cripplepunk#a lot of these are major concessions for me personally as i'm an anarchist and loathe to support further concentrations of state power#but if you're gonna be operating within the structure of the system. here you go. handing you a cheat sheet for what you should demand.
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
Too hot after your bath? Oh no!
Don't fear, I have the solution!
Eat 2.5 popsicles, you will go from "too hot" (bypassing"comfy" far too rapidly to register) to "way too cold oh no now my fingers are cold also my lips and I have the chills" really quickly!
Also it helps to already be sick and have a stupid temperature gauge anyway
#I'm finishing this popsicle bc i did the adult thing#nd washed my other blanket so I can get warm fast#sickness update#i will be miserable at home and take drugs about it for work#but before you get all super crank#I have been wearing a mask for nearly 4 years when I am not in my house out of my bedroom#anytime I touch my face I use hand sanitizer before I touch anything else#and I disinfect my workspace before anybody else gets into it after I'm done my shift#i move my mask up slightly to drink water from the straw in my personal bottle#i cannot afford to miss work#and at least two other co-workers are out with medical issues#so there's nobody else
1 note
·
View note
Text
I love you garbage truck workers I love you janitors I love you waste water treatment workers I love you sanitation workers I love you
#lizard screaming#worlds most underappreciated jobs fr!!!!!#add on if you want#same level of importance as doctors you cant change my mind#repetition
9K notes
·
View notes
Text
"India's efforts and progress in reducing preventable child deaths have been lauded as an "exemplar" by the United Nations, which cited the example of health initiatives such as Ayushman Bharat, and said the country has saved millions of young lives through strategic investments in its health system.
The United Nations Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation report, released Tuesday, cited the example of five “exemplar countries” in achieving child mortality reduction -- India, Nepal, Senegal, Ghana and Burundi -- highlighting diverse strategies that have accelerated progress in reducing preventable child deaths.
The report said these countries illustrate that with "political will, evidence-based strategies and sustained investments, even resource-constrained settings facing unique challenges can achieve substantial reductions in mortality, bringing the world closer to an end to preventable child deaths".
On India, the report said the country has made gains through health system investment...
The report highlighted that since 2000, India achieved an under-five mortality reduction of 70 per cent and a neonatal mortality reduction of 61 per cent, “driven by overlapping measures to increase health coverage, enhance available interventions and develop health infrastructure and human resources", the report said.
It cited the example of Ayushman Bharat, the world's largest health insurance scheme which provides annual coverage of nearly USD 5,500 per family per year.
It noted that every pregnant woman is entitled to free delivery (including caesarean section), and infant care provides free transport, medications, diagnostics and dietary support in public health institutions.
To ensure comprehensive coverage and equitable access to health services, India has strengthened infrastructure via the establishment of maternity waiting homes, maternal and child health wings, newborn stabilisation units, sick newborn care units, mother care units and a dedicated programme for birth defect screening, the report said...
“This ensures millions of healthy pregnancies and thriving live births each year. India has also prioritised the training and deployment of skilled birth attendants, such as midwives and community health workers, to provide appropriate maternal and child health services,” it said.
The report noted that additionally, data systems and digital surveillance of maternal, newborn and child health indicators are continuously improved to support evidence-based decision-making...
Other Countries that Did Well
The UN agency also said that several low and lower-middle-income countries have surpassed the global decline in under-five mortality since 2000.
Angola, Bhutan, Bolivia, Cabo Verde, India, Morocco, Senegal, Tanzania and Zambia have all cut their under-five mortality rate by more than two thirds since 2000.
In 2000, the country with the highest burden of under-five measles mortality was India, with only 56 per cent of infants vaccinated for measles and 189,000 deaths from measles.
By 2023, the infant measles vaccination rate had increased to 93 per cent, and under-five deaths due to the disease decreased by 97 per cent to 5,200 measles-related deaths...
Since 2000, child deaths [globally] have dropped by more than half and stillbirths by over a third, fuelled by sustained investments in child survival worldwide...
"Millions of children are alive today because of the global commitment to proven interventions, such as vaccines, nutrition, and access to safe water and basic sanitation,” UNICEF Executive Director Catherine Russell said.
-via India Today, March 27, 2025
#india#asia#child death#cw child death#infant mortality#measles#vaccination#vaccines#vaccinate your kids#maternal health#public health#children#good news#hope
479 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dear President Biden and Vice President Harris, We are 99 American physicians, surgeons, nurse practitioners, nurses, and midwives who have volunteered in the Gaza Strip since October 7, 2023. Combined, we spent 254 weeks volunteering in Gaza’s hospitals and clinics. We worked with various nongovernmental organizations and the World Health Organization in hospitals and clinics throughout the Strip. In addition to our medical and surgical expertise, many of us have a public health background, as well as experience working in humanitarian and conflict zones, including Ukraine during the brutal Russian invasion. Some of us are veterans and reservists. We are a multifaith and multiethnic group. None of us support the horrors committed on October 7 by Palestinian armed groups and individuals in Israel.
We are among the only neutral observers who have been permitted to enter the Gaza Strip since October 7. Given our broad expertise and direct experience of working throughout Gaza we are uniquely positioned to comment on several matters of importance to our government as it decides whether to continue supporting Israel’s attack on, and siege of, the Gaza Strip. Specifically, we believe we are well positioned to comment on the massive human toll from Israel’s attack on Gaza, especially the toll it has taken on women and children.
This letter and the appendix show probative evidence that the human toll in Gaza since October is far higher than is understood in the United States. It is likely that the death toll from this conflict is already greater than 118,908, an astonishing 5.4% of Gaza’s population. Our government must act immediately to prevent an even worse catastrophe than what has already befallen the people of Gaza and Israel. A ceasefire must be imposed on the warring parties by withholding military support for Israel and supporting an international arms embargo on Israel and all Palestinian armed groups. We believe our government is obligated to do this, both under American law and International Humanitarian Law. We also believe it is the right thing to do.
With only marginal exceptions, everyone in Gaza is sick, injured, or both. This includes every national aid worker, every international volunteer, and probably every Israeli hostage: every man, woman, and child. While working in Gaza we saw widespread malnutrition in our patients and our Palestinian healthcare colleagues. Every one of us lost weight rapidly in Gaza despite having privileged access to food and having taken our own supplementary nutrient-dense food with us. We have photographic evidence of life-threatening malnutrition in our patients, especially children, that we are eager to share with you. Virtually every child under the age of five whom we encountered, both inside and outside of the hospital, had both a cough and watery diarrhea. We found cases of jaundice (indicating hepatitis A infection under such conditions) in nearly every room of the hospitals in which we served, and in many of our healthcare colleagues in Gaza. An astonishingly high percentage of our surgical incisions became infected from the combination of malnutrition, impossible operating conditions, lack of basic sanitation supplies such as soap, and lack of surgical supplies and medications, including antibiotics. Malnutrition led to widespread spontaneous abortions, underweight newborns, and an inability of new mothers to breastfeed. This left their newborns at high risk of death given the lack of access to potable water anywhere in Gaza. Many of those infants died. In Gaza we watched malnourished mothers feed their underweight newborns infant formula made with poisonous water. We can never forget that the world abandoned these innocent women and babies. We urge you to realize that epidemics are raging in Gaza. Israel’s continued, repeated displacement of the malnourished and sick population of Gaza, half of whom are children, to areas without running water or even toilets available is absolutely shocking. It was and remains guaranteed to result in widespread death from viral and bacterial diarrheal diseases and pneumonias, particularly in children under the age of five. Indeed, even the dreaded polio virus has reemerged in Gaza due to a combination of systematic destruction of the sanitation infrastructure, widespread malnutrition weakening immune systems, and young children having missed routine vaccinations for nearly an entire year. We worry that unknown thousands have already died from the lethal combination of malnutrition and disease, and that tens of thousands more will die in the coming months, especially with the onset of the winter rains in Gaza. Most of them will be young children. Children are universally considered innocents in armed conflict. However, every single signatory to this letter saw children in Gaza who suffered violence that must have been deliberately directed at them. Specifically, every one of us who worked in an emergency, intensive care, or surgical setting treated pre-teen children who were shot in the head or chest on a regular or even a daily basis. It is impossible that such widespread shooting of young children throughout Gaza, sustained over the course of an entire year is accidental or unknown to the highest Israeli civilian and military authorities.
#yemen#jerusalem#tel aviv#current events#palestine#free palestine#gaza#free gaza#news on gaza#palestine news#news update#war news#war on gaza#gaza genocide#genocide#children of gaza#epidemics#famine#genocide joe#joe biden
880 notes
·
View notes
Text
pretty boy
| Jung Wooyoung - oneshot|



|☆pairing:piercer!reader x collegestudent!wooyoung!
|☆summary: Everyone in the friend group knew that wooyoung had a crush on the cute piercer who did hongjoongs piercings. After weeks of convincing, he finally decides to make an appointment to get his lip pierced.
|☆ genre: smut, fluff, both had crushes on each other
|☆ warnings: smut, lowercase intended, piercing needles, a bit of blood, oral (m receiving), unprotected sex, sex in a public setting, dacryphilia, switch reader! switch woo!, overstimulation, woos a head pusher, yes.. they did hear everything, uh not proofread (yet), let me know if I missed anything!
⋆⁺₊⋆ ━━━━⊱༒︎ • ༒︎⊰━━━━ ⋆⁺₊⋆
"whatttt no way you finally booked the appointment??" jongho said as he sat on the sofa in the living room next to wooyoung.
"yup it's at 3, wanna come with me?" wooyoung said, clicking on the confirmation email for his appointment before looking at jongho.
"sure, I'm not busy, we should tell hongjoong to come too."
And as if he summoned the devil himself
"go where," hongjoong said as he walked into the shared apartment.
"woo finally made the appointment to get his lip pierced with y/n today at 3" he snickered slightly.
he stopped dead in his tracks, turning to face woo.
"i'm coming just so I know you won't give her a hard time, since you know that's my friend," hongjoong said, side eyeing wooyoung before he headed upstairs to get changed.
"ugh im not gonna give her a hard time," wooyoung whined before dragging himself up to go shower before the appointment. afterall he was not going to risk smelling like ass around you. no way in hell.
turing on the hot water, he stood under the running stream debating if he really wanted to go through with this. he knew damn well that his mom was going to murder him when she found out. but he kinda didn't care. plus, even if this was just an excuse to see you, he has wanted a lip piercing for a while.
after the quick shower, he changed into some baggy sweats and his hoodie before fixing his hair just a bit. walking downstairs to see jongho and hongjoong waiting for him.
"let's go I refuse to let you be late" hongjoong said grabbing his keys as the 3 headed out the apartment and on their way to the shop.
after a 25-minute drive, they pull up to the small piercing and tattoo studio that was on the other side of town. it was owned by their mutual friends, yunho and mingi. the shop was small but comfortable, and each worker had their own designated space that was decorated to their liking.
"ah hongjoong? did you have an appointment today?" You asked confused as you made your way to the front seeing your longtime friend.
"ah nah not me today actually. woo has an appointment to get his lip pierced" hongjoong spoke as the three men walked up to the counter.
"ah I see wooyoung?" You spoke looking at the two standing next to hongjoong. the one with semi long black hair and a mole under his eye steps forward. "nice to meet you wooyoung, im y/n your piercer today. if you can just sign these forms while I go get set up, and seonghwa will take a copy of your id" you smiled handing him a clip board with the necessary paperwork as seonghwa came back from his break.
you weren’t dumb you knew exactly who wooyoung was. you’d seen him hanging with hongjoong on his stories and you’d always thought he was hot but, you never asked hongjoong about him as much as you wanted to.
you walked back into the small space you had, sanitizing everything down and taking out the necessary tools. it didnt take long before everything was ready and you made your way to the front once more. "okay you guys can come back" you beamed and the three men followed you.
"so this is your first facial piercing, I see," you say softly as you slip on the pink latex gloves. "you nervous?"
woo sits down in the chair fidgeting with his fingers, the nerves finally setting in. "a bit but i've wanted a lip piercing for forever now" he says smiling at you.
"don't worry ill take good care of you pretty boy" you say as you adjust how he's sitting. his cheeks flush with a slight pink color that he’s praying you don’t notice. "which side did you want the piercing on?' you question.
"right side" he said quickly
you nod as you take in his features to see what placement would look the best on him. god he really was a pretty boy, the way his lips were so pink and plump. his seductive eyes that make him look unapproachable, his hooked nose god. you had to restrain yourself from running ur finger down the bridge of his nose
after the analyzing his face, you place a dot on the skin, handing him a mirror to see if he liked the placement.
“do you like it? or do you wanna move it. because I can move it as many times as you want hun”you say reassuringly.
“I like it there” he said with a smile as he handed back the small mirror.
“perfect” you say as you take the alcohol pad and sanitize the area. “okay this is gonna sting just a bit but i’m going to have you take a deep breath in. ” you say lining up the clamp and needle to his skin. “and deep breath out” as he exhales you push the needle through along with the jewelry. screwing it on tight before you go back and clean the little bit of blood.
you once again hand him the small hand held mirror, “what do you think?”
he took the mirror from ur hand examining the piercing. god he loved it. not just because the piercing suited him but it was done by someone he deemed the most beautiful girl he’s ever seen. “I love it”he beamed. causing you to smile like an idiot.
you giggle as you give him the piercing care kit that comes with the appointment, going over what he can and can’t eat for the first 2 weeks, how to clean the piercing etc.
“now you’ll have to come back in 4-6 weeks so we can downsize the jewelry. because eventually this bar is going to be too long and it’ll get caught in ur teeth” you explain to him as he listens attentively to ur instructions.
hongjoong and jongho snicker quietly as they see him looking like a desperate puppy looking up at you.
“oh and not to be weird but ur actually really cute here’s my number. now I have to go on my break before yunho murders me. seonghwa can take payment up front” you smiled handing him a piece of paper with your number on it before getting up to walking towards the door, but you pause and turn to him once more “text me pretty boy”.
hongjoong and jongho’s jaws drop. there is no way in hell that just happened. hongjoong specifically was in shock, he never would’ve thought wooyoung out of all his friends would be ur type. if anything they had bet on you ending up with mingi.
wooyoung finds himself shocked, he didn’t even get a chance to process it fully before he started to giggle like a maniac.
“there is no way” hongjoong spoke as he walked over to looked at the piece of paper, and sure enough it was your actual phone number.
before woo can freak out they go to the front and pay, chatting a bit with seonghwa and yeosang before heading out.
“she thinks i’m cute??” woo squeals as he skips happily to the car
“no way in hell did I think he’d have a chance” hongjoong whispered to jongho
“me neither”
wooyoung immediately took his phone out to send you a quick text to make sure you saved his number.
as for you, you sat in the break room in shock that u mustered up the courage to give him ur number in the first place. while sitting in shock your phone dings, an unknown number texting you “ur pretty one y/n” and your cheeks flush a bright red as you squealed and kicked ur feet. Mingi walking in with a face mixed of concern and amusement?
“what are you all happy about on a wednesday” he said walking over to the counter to grab a bag of chips to snack on.
“yk your cute friend wooyoung” you said looking over at mingi who nods slowly knowing you had a crush on woo. “he came in today for a lip piercing. I may or may not have given him my number and called him cute to his face”you say, cheeks flushing red all over again.
“damn look at you go y/nnie”
“and now he’s texting me and I omg”you freak out again, because you genuinely didn’t think you stood a chance.
“what’s the hyena saying anyways?” mingi ask coming closer to try and look at your phone.
“he asked me out for a date on next friday” you smiled brightly showing him the message.
“well good luck with that” he snickered as he walked out.
*fast forward to friday*
you sat at your vanity messing with your hair one last time before standing up to look at your outfit in the mirror. baggy washed out jeans, a band tee that had the collar cut off, and your docs. layers of necklaces adorn your neck, and stacks of bracelets on both wrist. the outfit was casual but that’s how woo told you to dress. he promised he had a fun surprise for this first date.
looking at your phone, the time reading 5:28. which meant he would be there soon, as he told u to specifically be ready by 5:30. and just in time you hear a horn honk outside, following a quick text from wooyoung “i’m hereee”.
you grab your purse and head out letting san know you’ll be back later.
as soon as wooyoung sees you step out of the apartment he got out of the car to open the door for you.
“well aren’t you a gentleman” you tease as you kiss his cheek before getting into the car.
wooyoung is stunned a bit at the fact you kissed his cheek, taking a moment to compose himself before getting back into the driver side.
“so where are we going?” you question as he begins too drive
“we are going to an amusement park” he grins turning to look at you, and u beamed. how on earth did he know you loved amusement parks?
"oh my god no fucking way" you squeal and look at him, "I love amusement parks, did joong tell you?" you question
"maybe he did mention it, and also these are for you," he says as he reaches into the back seat, grabbing a bouquet of stargazer lilies and handing it to you.
you melted even more, the flowers were beyond beautiful. "oh woo, they're gorgeous" the words slip past your lips turning into a smile.
"good, I'm glad you like them," he smiled as he took a quick peek at you before focusing back on the road.
you smiled as the music filled the car, falling into a comfortable silence. it was odd how comforting wooyoungs presence was to you.
it wasn't long before you made it to your destination, that night was one of the most exhilarating nights you've lived. running like little kids from ride to ride, woo and you trying to win the rigged carnival games. in the end woo was able to win a big gloomy bear for you. walking hand and hand to the end of the pier, admiring the sunset.
"I really enjoyed tonight" you spoke lightly as you rested your head on his lap.
"I did too," he smiled, looking down at you, admiring how beautiful you were, and how the inside seemed just as beautiful.
the conversation flowed as effortlessly as the waves. the two of you getting to know each other more and more, there was no denying how right this felt.
*4 weeks later*
you get startled when you hear a knock on the door, it was past closing hours when you turn around to see seonghwa with a person behind him.
"you scared me shitless hwa"you pant, hand covering your chest "whos here so late? we're closed" you say.
"ah sorry, woos here for his downsize" he said before dismissing himself and allowing woo to walk into the room.
"close the door," you say absent-mindedly, getting out the new jewlery and gloves.
woo smiles as he closes the door before walking over to the leather chair in the corner of the room.
"'I've missed you, y/nnie," he said as you turned to come closer to him, positioning yourself between his legs as you grabbed his face to make him look up at you.
"i've missed you too woo, im sorry I've been so busy"you said in an apologetic tone.
"I know, I just miss my gorgeous girlfriend" he pouts, "but can we please change this jewlery, it is getting caught every 20 minuets" he whines and you let go laughing at his whine.
"of course, pretty boy, let me sanitize the piercing first," you said, grabbing an alcohol pad and cleaning the new stud. slipping on your gloves you grab a q-tip with some saline spray and clean around his piericng before taking it out and replacing it with the shorter bar.
"there you go baby" you say cleaning the area and giving a quick peck to his nose which caused him to laugh.
"come here let me hold you" he said grabbing your waist and pulling you in close. you wrap your arms around him and rest your hea don his, taking in how good he smelled. and suddenly an idea popped in to your head.
"I think I know how to apologize to you, baby," you say slowly, getting out of his grip to walk over and lock the door.
woo straightens up on the chair, eyeing the way you walk back over slowly and get on your knees in between his legs.
"you sure about this? here?" he asks, hand snaking to the side of your cheek rubbing it slightly.
" 'm sure pretty boy" you say as your hand trails over wooyoung covered thighs, slowly making your way to his hard on her had. slipping your hands to the side of his waist to pull his pants and boxers down. you take him into your hands, teasing slightly before putting him in your mouth.
'oh fuck baby" he groans as he grips the top of your hair, causing a sting that felt so nice as you suck him off.
you felt how wet it made you to make him feel this good. knowing he was a panting, whiny mess because of you all, because of you, and how perfect your lips felt around him.
"f-fuck baby I'm close"he whines, pushing your head to his stomach, making you gag and tear up as he finishes down your throat. making you swallow every drop as he pulled you up and looked at what a mess you were.
"what do we say baby" he cooed yanking your hair just a bit.
"ah- thank you, sir," you moan, looking up at him with hazy eyes.
"good girl," he whispers as he kisses your head and helps you stand up. you smirk as you settle over his lap, guiding him inside of you so you can ride him.
"ah-ah my turn, pretty boy" you moan out as you start to ride him at a fast pace.
causing woo to immediately fell apart, desperate pleas and whines fall from his lips out of overstimulation. "ah baby, I-it's too much," he chokes out.
"you can take it for just a bit longer pretty boy" you say as you pant against his neck, trying to not be loud.
tears form in his eyes as he reaches another climax that was more intense than the previous.
"g-gonna cum"he whined into your ear, wrapping his arms around you as he takes control and thrust into you roughly, losing any sense of control he had.
"f-fuck come w-with me" you moan out as you feel yourself get close to the edge, knots forming in your stomach.
and with just a couple more more thrust before he comes undone in you. filling you up as you hit your climax.
"f-fcuk woo" you whine as you slump into his arms, your limbs feeling like jello.
"that was amazing princess"he says, holding you close to let you catch your breath.
"this really feels so right" you pant out as tears well in ur eyes, you haven't felt his happy in so long and nothing could ruin it.
"BE MORE QUIET NEXT TIME," mingi yells as he walks past the door, causing both of you to burst out laughing, not ready to face everyone after what you just did... in ur piercing room, nonetheless.
"im so glad I met you pretty boy" you smile kissing his nose and holding him tight.
#ateez#wooyoung#wooyoung smut#ateez x reader#ateez oneshot#ateez smut#ateez fanfic#hongjoong#jongho#seonghwa#yeosang#mingi#san#yunho#ateez fic#jung wooyoung#atiny#slutforwoo materlist
145 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anti-Larva Spraying Intensifies to Combat Dengue in Jamshedpur
Municipal Corporation fines Rs. 10,500 for water logging violations Jamshedpur Municipal Corporation steps up efforts to prevent dengue spread with daily anti-larva spraying and awareness programs. JAMSHEDPUR – The Jamshedpur Municipal Corporation has escalated its anti-dengue initiatives by undertaking daily anti-larva spraying in numerous regions and imposing penalties for water logging…
#anti-larva spraying Municipal Corporation#जनजीवन#community health education Jamshedpur#dengue awareness program Workers College#dengue prevention Jharkhand#Jamshedpur dengue prevention#Jamshedpur Public Health Initiatives#Life#monsoon health precautions Jamshedpur#Mosquito Control Measures#urban sanitation drive#water logging fines Jamshedpur
0 notes
Note
I see your fancy bat tech post and I raise you: when left without resources the bats can do some absolutely terrifying low tech shit with whatever is on hand.
The idea that immediately springs to mind is spark gloves as used in haunted houses. It's just the spark plate off common razor scooter mod duct taped to some gloves with metal fingers made from plumbing connectors and E5000. In the dark they're terrifying.
Lost all your bat tech to an EMP? If nobody else got you, hardware store got you.
They’re really, really good at scavenging for supplies and making weapons/resources out of limited materials. Trapped in an empty room with a Bat? They’re yanking open the vents and walls to find wires and cables and doing some weird shit to make a lock pick and/or a shiv. Need water on a desert planet? They’ve got a still going in less than an hour. Stuck walking in a Gotham sewer to lay low after an EMP? They know where the sanitation workers keep their kits and pilfer them for supplies.
257 notes
·
View notes
Text
so... i'm seeing a lot of activism (like, actual activism, not just tumblr posts--letters & scripts to us senators, for example, copy written for press, etc) focusing on improving ventilation & filtration as primarily an access issue for immunocompromised people. basically, presenting the argument as "this is in service of this demographic, who is blocked from public access currently."
this is like. true. of course. it is the main reason i want clean air and i think it is the most pressing reason overall for it. but i think it's the wrong tack for building a clean air movement and getting legislation passed.
like, unfortunately, the vast majority of people in power--and of americans in general, tbh--are not immunocompromised and do not have immunocompromised roommates or family members. should you have to have this experience to understand that public access is a big fucking deal for, like, staying alive? no! you shouldn't! but most people straight up will not understand whatsoever unless they have personal experience with immune compromisation.
trying to change hearts and minds to have cognitive sympathy for disabled people takes a long time, decades' worth of work to just change a handful of people; meanwhile, getting legislation passed is 1) imminently important, 2) while still a lengthy process, takes significantly less time if it doesn't hinge on first converting the majority of the population to have sympathy for a marginalized demographic they have no contact with (and yes, they have no contact with us because we are barred from public access to begin with, again, i am aware of how fucked up this is).
here's some arguments for passing clean air legislation that are designed to appeal to a normative, conservative-leaning crowd:
air filtration is a public health and sanitation baseline just like running water. we provide clean water to drink and wash our hands in as a baseline for public life; we should also be providing clean air to breathe similarly.
improved ventilation and filtration in schools results in less sick days for students, meaning better attendance and less time off work for parents.
improved ventilation and filtration in the workplace results in workers taking less sick days. it also makes it less troublesome when a coworker comes in sick; it's less likely you will have to take sick leave as a result.
improved ventilation and filtration in hospitals, doctors' offices, etc, helps combat the health care worker shortage by reducing the amount of sick leave health care workers need. it additionally makes hospitals safer overall; for example, it makes it safer for cancer patients to be in the same building with patients with highly infectious airborne illnesses such as chickenpox.
improved ventilation and filtration in public buildings at large could improve the economy, as less workers stay home, more people enter the workforce, more people begin attending public businesses like bars and venues, etc.
if government programs to upgrade ventilation and filtration are created, this could create jobs for blue-collar workers, further improving the economy.
the last note i have is that, as much as this sucks shit, don't mention covid as much as you can avoid it. covid has become a massive culture war thing in the usa and as soon as you bring it up, the entire discussion becomes about virtue-signaling and showing in-group affinity--it doesn't matter what you're saying about covid, anyone who thinks "covid is over" will immediately shut down and become incapable of listening to anything else you have to say. and unfortunately, a majority of the population does, in fact, think covid is an irrelevant concern even for immunocompromised people in 2024.
importantly, all general air sanitation improvements will improve the covid situation significantly. in this context, you do not have to talk about covid in order to make real, material changes limiting the spread of covid. system-level changes that limit the spread of things like the flu and chickenpox are equally effective in limiting the spread of covid. take advantage of that!
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
i've been reading about the case of asia bibi and it got me thinking how pakistani christians' oppression is also rooted in casteism in addition to religious discrimination.
christians make up roughly 1.6% of pakistan's population. 90% of christians are also dalit. despite having a small population, pakistani christians make up 80% of sanitation workers. this is rooted in the belief that lower castes such as dalits should perform "unclean" jobs.
these sanitation workers are paid meagre wages with no benefits. on top of that they also face abuse from people who look down on them as "unclean". which is again, rooted in casteist beliefs that dalits are "polluted". like the case of shafique masih, who was cast out by even his own relatives for his job as a sanitation worker. he's only one of the many sanitation workers who face discrimination on the basis of both religion and caste in pakistan.
the case of asia bibi, one of the most famous blasphemy cases in pakistan, started after she stopped to take a drink of water with a cup she found lying near the well. this angered a neighbour of hers who told her that it was "forbidden" for christians and muslims to drink from the same cup and that by touching the cup, she had made it "unclean".
this echoes the notion of untouchability, that lower castes and upper castes mustn't use the same utensils lest those utensils become "unclean" or "polluted". i'm going to quote the below article which summarizes perfectly the casteism aspect of the asia bibi case
In fact, even the case of Asia Bibi – the Christian woman who was accused of blasphemy, sentenced to death and then acquitted by the Supreme Court on October 31, resulting in protests across Pakistan – has at its essence the continuation of caste hierarchy. In Punjab, Christianity is frequently referred to as a caste as well as a religion, and many Muslims refuse to share utensils with Christians. It was Asia Bibi’s use of a utensil that led to an altercation with her Muslim neighbours, which eventually resulted in the alleged blasphemy. While the case led to a global discussion about Pakistan’s blasphemy laws, the caste hierarchy and discrimination based on it received no attention.
there is a misconception that casteism is purely a hindu concept and other religions are free of it. however casteism is deep rooted in both indian and pakistani societies, regardless of religion. whether it be hindu, muslim, christian, or even atheist, the caste system is alive and manifests in violent ways, infused with these religions. for example, upper caste pakistani muslims argue that lower caste hindu and christian minorities eat "haram" food to justify their oppression of them
so denying the existence of casteism in modern times or painting it as a hindu only aspect does a disservice to lower caste these lower caste minorities in pakistan oppressed by upper caste muslims, both on the basis of religion and caste.
373 notes
·
View notes
Text
A greasy-haired teenager sat alone in a dark bedroom, pointing his wand at the ceiling, shooting down flies...
never given this line much thought before but it fits with what Bellatrix says about Spinner's End being a "Muggle dunghill" and the dirty river etc, on top of the infamous collection of information in Two Up, Two Down post I love so much.
what follows is another moment for me of realising just how hard snape had it and the likely conditions he grew up in
he didn't have any older siblings (that we know about) to borrow clothes from, which was why he was in his parents' clothing; the fact that he wasn't loaned any clothes that fit marginally better or were even for boys from the neighbours suggests that the Snapes weren't particularly close to the other families, and i expect a large number of flies in the house (enough to be shooting down, enough to spot when harry only saw the memory fleetingly) suggests poor sanitation in the home
It's not just a case of Bellatrix being judgy about a Muggle neighbourhood, currently falling apart with houses on the cobbled streets boarded up and with broken windows, and a dirty, smelly river; Snape's home growing up was considered "a poor recommendation" even when he was a child. Two up, two down houses were, in that period (and even before) often falling apart, known for being unsanitary and unsafe, as well as damp and cramped together. they were never intended to be nice; they were thrown up so that workers could be near the factories, and that was about the only concern at the time
There's some really vivid descriptions of living in these sorts of houses around, but I've just found this one from facebook (with images I've added from flashbak.com):
The house had no electric supply and relied solely on gas for everything.
One wall in each room had one gas mantle fitted to it for light and when the mantle became faulty it would smell and the light would become less bright and eventually cease to do the job and need replacing.
There was a coal fire grate in each room but only the living room fire was kept lit to keep the costs down because although people worked long hours wages were low and money was in short supply.
In the kitchen the heat from the stove when cooking provided some warm that also made its way upstairs into the bedrooms.
During the winter months when the house was particularly cold overcoats were placed over the blankets on the beds for extra warmth for the children in the front bedroom. While the parents slept in the smaller back bedroom.


There was only one water tap in the house situated in the kitchen and the kettle or pans had to be filled when hot water was required. They were heated on the stove and because there was no bathroom the young children were washed in the large sink or a tin bath while others went to the public baths situated nearby, local to the area.
The toilet was in the back yard and was also unlit, leaving the gas light from the kitchen to light up the yard through the window.
Toilet paper was old newspapers that had been cut up into squares and made ready for use.
All flooring in the house was covered with lino with the exception of the living room that had a rug in the centre for comfort and to help prevent wear and tear. Since the end of the world war II there had been shortages and many households struggled to get basic food stuff and clothing.

The black market had been active for some years and those that had the money would get what they needed, while for those that had little depended on the rationing system introduced by the government to make sure that everyone got at least basic food stuff.
The I.D. card had been introduced because of the war and was proof of who you were and was used for the benefit of rationing. There were often queues at the butchers and many families got the scrag ends and scraps that were left over.
When it came to clothing, families would put aside what was worn by one child until the next child had grown enough to wear them and every item including shoes were cleaned and repaired if possible and put away and saved for later use.
In those days children at play preferred to play outside and regularly would play along the canal and the neighbourhood streets and alleyways. There were very few cars around and despite the unclean air from the surrounding factories they would play all day outside until they were called in.
In those days there were very little restrictions on pollution and it was normal to wake up in the mornings to smog that sometimes lasted all week. A real pea souper as they say
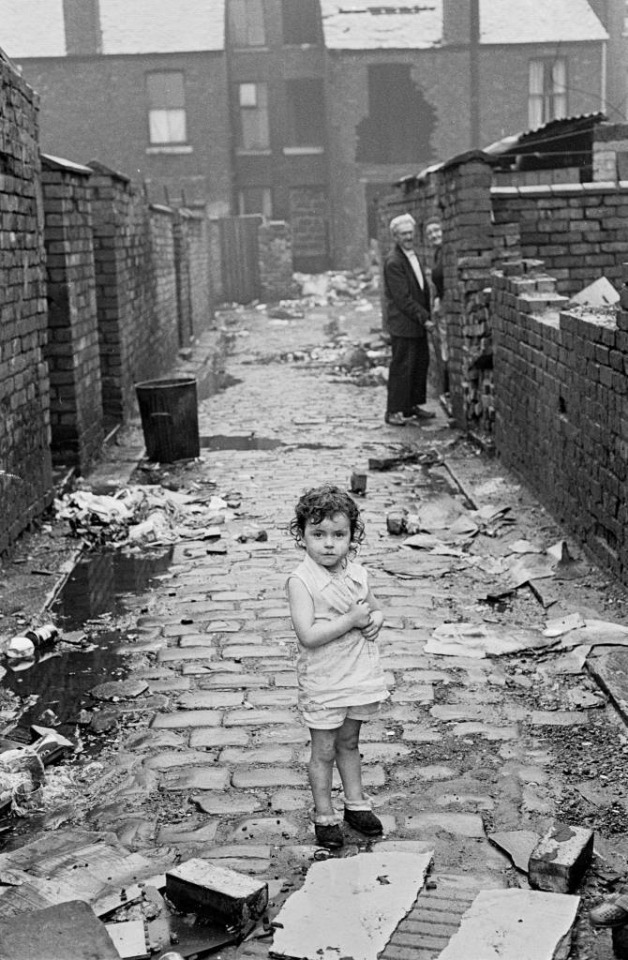


but like... imagine snape growing up there, like that, with no sense of community and parents who couldn't afford to or weren't able to care for him properly. this is so far beyond 'weasley poor' with their warm, cosy home and plenty to eat; this is gaunt poor, improper housing, and conditions that regularly made people ill
perhaps the Snapes had to rely on the black market to even eat enough, if they could afford it; I'm picturing chest infections and frost on the insides of the windows over the winters, and flies crawling in the house in the summers - and apparently limited use of magic at the time snape was growing up to rectify any of it, else the descriptions wouldn't be so consistently negative (and evocative) with a potential swarm of flies in his bedroom
(wonder if he was underage here, and using his wand since his mother would've had one, or whether it's a snippet of post-hogwarts snape; the next memory is of snape on a broomstick, so presumably that's at hogwarts, and he was underage in the fly memory, trapped/hiding/sulking in his room)
then he gets to hogwarts with the likes of the malfoys, who have a whole mansion and peacocks and house elves and can afford anything they want, and they look down on the weasleys and their comfortable one-'moderate'-income supporting a seven-child home as if they were cockroaches. what on earth would they have thought of snape, if they knew? he had factual knowledge of the magical world, but i doubt he had that "raised in the magical world" vibe they so desperately want to protect
#severus snape#pro snape#snape#snape fandom#professor snape#pro severus snape#young snape#spinner's end#need to stop thinking about snape when i have things to do
109 notes
·
View notes
Text
Also preserved on our archive
SARS-CoV-2 is now circulating out of control worldwide. The only major limitation on transmission is the immune environment the virus faces. The disease it causes, COVID-19, is now a risk faced by most people as part of daily life.
While some are better than others, no national or regional government is making serious efforts towards infection prevention and control, and it seems likely this laissez-faire policy will continue for the foreseeable future. The social, political, and economic movements that worked to achieve this mass infection environment can rejoice at their success.
Those schooled in public health, immunology or working on the front line of healthcare provision know we face an uncertain future, and are aware the implications of recent events stretch far beyond SARS-CoV-2. The shifts that have taken place in attitudes and public health policy will likely damage a key pillar that forms the basis of modern civilized society, one that was built over the last two centuries; the expectation of a largely uninterrupted upwards trajectory of ever-improving health and quality of life, largely driven by the reduction and elimination of infectious diseases that plagued humankind for thousands of years. In the last three years, that trajectory has reversed.
The upward trajectory of public health in the last two centuries Control of infectious disease has historically been a priority for all societies. Quarantine has been in common use since at least the Bronze Age and has been the key method for preventing the spread of infectious diseases ever since. The word “quarantine” itself derives from the 40-day isolation period for ships and crews that was implemented in Europe during the late Middle Ages to prevent the introduction of bubonic plague epidemics into cities.
Modern public health traces its roots to the middle of the 19th century thanks to converging scientific developments in early industrial societies:
The germ theory of diseases was firmly established in the mid-19th century, in particular after Louis Pasteur disproved the spontaneous generation hypothesis. If diseases spread through transmission chains between individual humans or from the environment/animals to humans, then it follows that those transmission chains can be interrupted, and the spread stopped. The science of epidemiology appeared, its birth usually associated with the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak in London during which the British physician John Snow identified contaminated water as the source of cholera, pointing to improved sanitation as the way to stop cholera epidemics. Vaccination technology began to develop, initially against smallpox, and the first mandatory smallpox vaccination campaigns began, starting in England in the 1850s.
The early industrial era generated horrendous workplace and living conditions for working class populations living in large industrial cities, dramatically reducing life expectancy and quality of life (life expectancy at birth in key industrial cities in the middle of the 19th century was often in the low 30s or even lower). This in turn resulted in a recognition that such environmental factors affect human health and life spans. The long and bitter struggle for workers’ rights in subsequent decades resulted in much improved working conditions, workplace safety regulations, and general sanitation, and brought sharp increases in life expectancy and quality of life, which in turn had positive impacts on productivity and wealth.
Florence Nightingale reemphasized the role of ventilation in healing and preventing illness, ‘The very first canon of nursing… : keep the air he breathes as pure as the external air, without chilling him,’ a maxim that influenced building design at the time.
These trends continued in the 20th century, greatly helped by further technological and scientific advances. Many diseases – diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, etc. – became things of the past thanks to near-universal highly effective vaccinations, while others that used to be common are no longer of such concern for highly developed countries in temperate climates – malaria, typhus, typhoid, leprosy, cholera, tuberculosis, and many others – primarily thanks to improvements in hygiene and the implementation of non-pharmaceutical measures for their containment.
Furthermore, the idea that infectious diseases should not just be reduced, but permanently eliminated altogether began to be put into practice in the second half of the 20th century on a global level, and much earlier locally. These programs were based on the obvious consideration that if an infectious agent is driven to extinction, the incalculable damage to people’s health and the overall economy by a persisting and indefinite disease burden will also be eliminated.
The ambition of local elimination grew into one of global eradication for smallpox, which was successfully eliminated from the human population in the 1970s (this had already been achieved locally in the late 19th century by some countries), after a heroic effort to find and contain the last remaining infectious individuals. The other complete success was rinderpest in cattle9,10, globally eradicated in the early 21st century.
When the COVID-19 pandemic started, global eradication programs were very close to succeeding for two other diseases – polio and dracunculiasis. Eradication is also globally pursued for other diseases, such as yaws, and regionally for many others, e.g. lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, measles and rubella. The most challenging diseases are those that have an external reservoir outside the human population, especially if they are insect borne, and in particular those carried by mosquitos. Malaria is the primary example, but despite these difficulties, eradication of malaria has been a long-standing global public health goal and elimination has been achieved in temperate regions of the globe, even though it involved the ecologically destructive widespread application of polluting chemical pesticides to reduce the populations of the vectors. Elimination is also a public goal for other insect borne diseases such as trypanosomiasis.
In parallel with pursuing maximal reduction and eventual eradication of the burden of existing endemic infectious diseases, humanity has also had to battle novel infectious diseases40, which have been appearing at an increased rate over recent decades. Most of these diseases are of zoonotic origin, and the rate at which they are making the jump from wildlife to humans is accelerating, because of the increased encroachment on wildlife due to expanding human populations and physical infrastructure associated with human activity, the continued destruction of wild ecosystems that forces wild animals towards closer human contact, the booming wildlife trade, and other such trends.
Because it is much easier to stop an outbreak when it is still in its early stages of spreading through the population than to eradicate an endemic pathogen, the governing principle has been that no emerging infectious disease should be allowed to become endemic. This goal has been pursued reasonably successfully and without controversy for many decades.
The most famous newly emerging pathogens were the filoviruses (Ebola, Marburg), the SARS and MERS coronaviruses, and paramyxoviruses like Nipah. These gained fame because of their high lethality and potential for human-to-human spread, but they were merely the most notable of many examples.
Such epidemics were almost always aggressively suppressed. Usually, these were small outbreaks, and because highly pathogenic viruses such as Ebola cause very serious sickness in practically all infected people, finding and isolating the contagious individuals is a manageable task. The largest such epidemic was the 2013-16 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, when a filovirus spread widely in major urban centers for the first time. Containment required a wartime-level mobilization, but that was nevertheless achieved, even though there were nearly 30,000 infections and more than 11,000 deaths.
SARS was also contained and eradicated from the human population back in 2003-04, and the same happened every time MERS made the jump from camels to humans, as well as when there were Nipah outbreaks in Asia.
The major counterexample of a successful establishment in the human population of a novel highly pathogenic virus is HIV. HIV is a retrovirus, and as such it integrates into the host genome and is thus nearly impossible to eliminate from the body and to eradicate from the population (unless all infected individuals are identified and prevented from infecting others for the rest of their lives). However, HIV is not an example of the containment principle being voluntarily abandoned as the virus had made its zoonotic jump and established itself many decades before its eventual discovery and recognition, and long before the molecular tools that could have detected and potentially fully contained it existed.
Still, despite all these containment success stories, the emergence of a new pathogen with pandemic potential was a well understood and frequently discussed threat, although influenza viruses rather than coronaviruses were often seen as the most likely culprit. The eventual appearance of SARS-CoV-2 should therefore not have been a huge surprise, and should have been met with a full mobilization of the technical tools and fundamental public health principles developed over the previous decades.
The ecological context One striking property of many emerging pathogens is how many of them come from bats. While the question of whether bats truly harbor more viruses than other mammals in proportion to their own species diversity (which is the second highest within mammals after rodents) is not fully settled yet, many novel viruses do indeed originate from bats, and the ecological and physiological characteristics of bats are highly relevant for understanding the situation that Homo sapiens finds itself in right now.
Another startling property of bats and their viruses is how highly pathogenic to humans (and other mammals) many bat viruses are, while bats themselves are not much affected (only rabies is well established to cause serious harm to bats). Why bats seem to carry so many such pathogens, and how they have adapted so well to coexisting with them, has been a long-standing puzzle and although we do not have a definitive answer, some general trends have become clear.
Bats are the only truly flying mammals and have been so for many millions of years. Flying has resulted in a number of specific adaptations, one of them being the tolerance towards a very high body temperature (often on the order of 42-43ºC). Bats often live in huge colonies, literally touching each other, and, again, have lived in conditions of very high density for millions of years. Such densities are rare among mammals and are certainly not the native condition of humans (human civilization and our large dense cities are a very recent phenomenon on evolutionary time scales). Bats are also quite long-lived for such small mammals – some fruit bats can live more than 35 years and even small cave dwelling species can live about a decade.
These are characteristics that might have on one hand facilitated the evolution of a considerable set of viruses associated with bat populations. In order for a non-latent respiratory virus to maintain itself, a minimal population size is necessary. For example, it is hypothesized that measles requires a minimum population size of 250-300,000 individuals. And bats have existed in a state of high population densities for a very long time, which might explain the high diversity of viruses that they carry. In addition, the long lifespan of many bat species means that their viruses may have to evolve strategies to overcome adaptive immunity and frequently reinfect previously infected individuals as opposed to the situation in short-lived species in which populations turn over quickly (with immunologically naive individuals replacing the ones that die out).
On the other hand, the selective pressure that these viruses have exerted on bats may have resulted in the evolution of various resistance and/or tolerance mechanisms in bats themselves, which in turn have driven the evolution of counter strategies in their viruses, leading them to be highly virulent for other species. Bats certainly appear to be physiologically more tolerant towards viruses that are otherwise highly virulent to other mammals. Several explanations for this adaptation have been proposed, chief among them a much more powerful innate immunity and a tolerance towards infections that does not lead to the development of the kind of hyperinflammatory reactions observed in humans, the high body temperature of bats in flight, and others.
The notable strength of bat innate immunity is often explained by the constitutively active interferon response that has been reported for some bat species. It is possible that this is not a universal characteristic of all bats – only a few species have been studied – but it provides a very attractive mechanism for explaining both how bats prevent the development of severe systemic viral infections in their bodies and how their viruses in turn would have evolved powerful mechanisms to silence the interferon response, making them highly pathogenic for other mammals.
The tolerance towards infection is possibly rooted in the absence of some components of the signaling cascades leading to hyperinflammatory reactions and the dampened activity of others.
An obvious ecological parallel can be drawn between bats and humans – just as bats live in dense colonies, so now do modern humans. And we may now be at a critical point in the history of our species, in which our ever-increasing ecological footprint has brought us in close contact with bats in a way that was much rarer in the past. Our population is connected in ways that were previously unimaginable. A novel virus can make the zoonotic jump somewhere in Southeast Asia and a carrier of it can then be on the other side of the globe a mere 24-hours later, having encountered thousands of people in airports and other mass transit systems. As a result, bat pathogens are now being transferred from bat populations to the human population in what might prove to be the second major zoonotic spillover event after the one associated with domestication of livestock and pets a few thousand years ago.
Unfortunately for us, our physiology is not suited to tolerate these new viruses. Bats have adapted to live with them over many millions of years. Humans have not undergone the same kind of adaptation and cannot do so on any timescale that will be of use to those living now, nor to our immediate descendants.
Simply put, humans are not bats, and the continuous existence and improvement of what we now call “civilization” depends on the same basic public health and infectious disease control that saw life expectancy in high-income countries more than double to 85 years. This is a challenge that will only increase in the coming years, because the trends that are accelerating the rate of zoonotic transfer of pathogens are certain to persist.
Given this context, it is as important now to maintain the public health principle that no new dangerous pathogens should be allowed to become endemic and that all novel infectious disease outbreaks must be suppressed as it ever was.
The death of public health and the end of epidemiological comfort It is also in this context that the real gravity of what has happened in the last three years emerges.
After HIV, SARS-CoV-2 is now the second most dangerous infectious disease agent that is 'endemic' to the human population on a global scale. And yet not only was it allowed to become endemic, but mass infection was outright encouraged, including by official public health bodies in numerous countries.
The implications of what has just happened have been missed by most, so let’s spell them out explicitly.
We need to be clear why containment of SARS-CoV-2 was actively sabotaged and eventually abandoned. It has absolutely nothing to do with the “impossibility” of achieving it. In fact, the technical problem of containing even a stealthily spreading virus such as SARS-CoV-2 is fully solved, and that solution was successfully applied in practice for years during the pandemic.
The list of countries that completely snuffed out outbreaks, often multiple times, includes Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Bhutan, Cuba, China, and a few others, with China having successfully contained hundreds of separate outbreaks, before finally giving up in late 2022.
The algorithm for containment is well established – passively break transmission chains through the implementation of nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as limiting human contacts, high quality respirator masks, indoor air filtration and ventilation, and others, while aggressively hunting down active remaining transmission chains through traditional contact tracing and isolation methods combined with the powerful new tool of population-scale testing.
Understanding of airborne transmission and institution of mitigation measures, which have heretofore not been utilized in any country, will facilitate elimination, even with the newer, more transmissible variants. Any country that has the necessary resources (or is provided with them) can achieve full containment within a few months. In fact, currently this would be easier than ever before because of the accumulated widespread multiple recent exposures to the virus in the population suppressing the effective reproduction number (Re). For the last 18 months or so we have been seeing a constant high plateau of cases with undulating waves, but not the major explosions of infections with Re reaching 3-4 that were associated with the original introduction of the virus in 2020 and with the appearance of the first Omicron variants in late 2021.
It would be much easier to use NPIs to drive Re to much below 1 and keep it there until elimination when starting from Re around 1.2-1.3 than when it was over 3, and this moment should be used, before another radically new serotype appears and takes us back to those even more unpleasant situations. This is not a technical problem, but one of political and social will. As long as leadership misunderstands or pretends to misunderstand the link between increased mortality, morbidity and poorer economic performance and the free transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the impetus will be lacking to take the necessary steps to contain this damaging virus.
Political will is in short supply because powerful economic and corporate interests have been pushing policymakers to let the virus spread largely unchecked through the population since the very beginning of the pandemic. The reasons are simple. First, NPIs hurt general economic activity, even if only in the short term, resulting in losses on balance sheets. Second, large-scale containment efforts of the kind we only saw briefly in the first few months of the pandemic require substantial governmental support for all the people who need to pause their economic activity for the duration of effort. Such an effort also requires large-scale financial investment in, for example, contact tracing and mass testing infrastructure and providing high-quality masks. In an era dominated by laissez-faire economic dogma, this level of state investment and organization would have set too many unacceptable precedents, so in many jurisdictions it was fiercely resisted, regardless of the consequences for humanity and the economy.
None of these social and economic predicaments have been resolved. The unofficial alliance between big business and dangerous pathogens that was forged in early 2020 has emerged victorious and greatly strengthened from its battle against public health, and is poised to steamroll whatever meager opposition remains for the remainder of this, and future pandemics.
The long-established principles governing how we respond to new infectious diseases have now completely changed – the precedent has been established that dangerous emerging pathogens will no longer be contained, but instead permitted to ‘ease’ into widespread circulation. The intent to “let it rip” in the future is now being openly communicated. With this change in policy comes uncertainty about acceptable lethality. Just how bad will an infectious disease have to be to convince any government to mobilize a meaningful global public health response?
We have some clues regarding that issue from what happened during the initial appearance of the Omicron “variant” (which was really a new serotype) of SARS-CoV-2. Despite some experts warning that a vaccine-only approach would be doomed to fail, governments gambled everything on it. They were then faced with the brute fact of viral evolution destroying their strategy when a new serotype emerged against which existing vaccines had little effect in terms of blocking transmission. The reaction was not to bring back NPIs but to give up, seemingly regardless of the consequences.
Critically, those consequences were unknown when the policy of no intervention was adopted within days of the appearance of Omicron. All previous new SARS-CoV-2 variants had been deadlier than the original Wuhan strain, with the eventually globally dominant Delta variant perhaps as much as 4× as deadly. Omicron turned out to be the exception, but again, that was not known with any certainty when it was allowed to run wild through populations. What would have happened if it had followed the same pattern as Delta?
In the USA, for example, the worst COVID-19 wave was the one in the winter of 2020-21, at the peak of which at least 3,500 people were dying daily (the real number was certainly higher because of undercounting due to lack of testing and improper reporting). The first Omicron BA.1 wave saw the second-highest death tolls, with at least 2,800 dying per day at its peak. Had Omicron been as intrinsically lethal as Delta, we could have easily seen a 4-5× higher peak than January 2021, i.e. as many as 12–15,000 people dying a day. Given that we only had real data on Omicron’s intrinsic lethality after the gigantic wave of infections was unleashed onto the population, we have to conclude that 12–15,000 dead a day is now a threshold that will not force the implementation of serious NPIs for the next problematic COVID-19 serotype.
Logically, it follows that it is also a threshold that will not result in the implementation of NPIs for any other emerging pathogens either. Because why should SARS-CoV-2 be special?
We can only hope that we will never see the day when such an epidemic hits us but experience tells us such optimism is unfounded. The current level of suffering caused by COVID-19 has been completely normalized even though such a thing was unthinkable back in 2019. Populations are largely unaware of the long-term harms the virus is causing to those infected, of the burden on healthcare, increased disability, mortality and reduced life expectancy. Once a few even deadlier outbreaks have been shrugged off by governments worldwide, the baseline of what is considered “acceptable” will just gradually move up and even more unimaginable losses will eventually enter the “acceptable” category. There can be no doubt, from a public health perspective, we are regressing.
We had a second, even more worrying real-life example of what the future holds with the global spread of the MPX virus (formerly known as “monkeypox” and now called “Mpox”) in 2022. MPX is a close relative to the smallpox VARV virus and is endemic to Central and Western Africa, where its natural hosts are mostly various rodent species, but on occasions it infects humans too, with the rate of zoonotic transfer increasing over recent decades. It has usually been characterized by fairly high mortality – the CFR (Case Fatality Rate) has been ∼3.6% for the strain that circulates in Nigeria and ∼10% for the one in the Congo region, i.e. much worse than SARS-CoV-2. In 2022, an unexpected global MPX outbreak developed, with tens of thousands of confirmed cases in dozens of countries. Normally, this would be a huge cause for alarm, for several reasons.
First, MPX itself is a very dangerous disease. Second, universal smallpox vaccination ended many decades ago with the success of the eradication program, leaving the population born after that completely unprotected. Third, lethality in orthopoxviruses is, in fact, highly variable – VARV itself had a variola major strain, with as much as ∼30% CFR, and a less deadly variola minor variety with CFR ∼1%, and there was considerable variation within variola major too. It also appears that high pathogenicity often evolves from less pathogenic strains through reductive evolution - the loss of certain genes something that can happen fairly easily, may well have happened repeatedly in the past, and may happen again in the future, a scenario that has been repeatedly warned about for decades. For these reasons, it was unthinkable that anyone would just shrug off a massive MPX outbreak – it is already bad enough as it is, but allowing it to become endemic means it can one day evolve towards something functionally equivalent to smallpox in its impact.
And yet that is exactly what happened in 2022 – barely any measures were taken to contain the outbreak, and countries simply reclassified MPX out of the “high consequence infectious disease” category in order to push the problem away, out of sight and out of mind. By chance, it turned out that this particular outbreak did not spark a global pandemic, and it was also characterized, for poorly understood reasons, by an unusually low CFR, with very few people dying. But again, that is not the information that was available at the start of the outbreak, when in a previous, interventionist age of public health, resources would have been mobilized to stamp it out in its infancy, but, in the age of laissez-faire, were not. MPX is now circulating around the world and represents a future threat of uncontrolled transmission resulting in viral adaptation to highly efficient human-to-human spread combined with much greater disease severity.
While some are better than others, no national or regional government is making serious efforts towards infection prevention and control, and it seems likely this laissez-faire policy will continue for the foreseeable future. The social, political, and economic movements that worked to achieve this mass infection environment can rejoice at their success.
Those schooled in public health, immunology or working on the front line of healthcare provision know we face an uncertain future, and are aware the implications of recent events stretch far beyond SARS-CoV-2. The shifts that have taken place in attitudes and public health policy will likely damage a key pillar that forms the basis of modern civilized society, one that was built over the last two centuries; the expectation of a largely uninterrupted upwards trajectory of ever-improving health and quality of life, largely driven by the reduction and elimination of infectious diseases that plagued humankind for thousands of years. In the last three years, that trajectory has reversed.
The upward trajectory of public health in the last two centuries Control of infectious disease has historically been a priority for all societies. Quarantine has been in common use since at least the Bronze Age and has been the key method for preventing the spread of infectious diseases ever since. The word “quarantine” itself derives from the 40-day isolation period for ships and crews that was implemented in Europe during the late Middle Ages to prevent the introduction of bubonic plague epidemics into cities1.
Rat climbing a ship's rigging. Modern public health traces its roots to the middle of the 19th century thanks to converging scientific developments in early industrial societies:
The germ theory of diseases was firmly established in the mid-19th century, in particular after Louis Pasteur disproved the spontaneous generation hypothesis. If diseases spread through transmission chains between individual humans or from the environment/animals to humans, then it follows that those transmission chains can be interrupted, and the spread stopped. The science of epidemiology appeared, its birth usually associated with the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak in London during which the British physician John Snow identified contaminated water as the source of cholera, pointing to improved sanitation as the way to stop cholera epidemics. Vaccination technology began to develop, initially against smallpox, and the first mandatory smallpox vaccination campaigns began, starting in England in the 1850s. The early industrial era generated horrendous workplace and living conditions for working class populations living in large industrial cities, dramatically reducing life expectancy and quality of life (life expectancy at birth in key industrial cities in the middle of the 19th century was often in the low 30s or even lower2). This in turn resulted in a recognition that such environmental factors affect human health and life spans. The long and bitter struggle for workers’ rights in subsequent decades resulted in much improved working conditions, workplace safety regulations, and general sanitation, and brought sharp increases in life expectancy and quality of life, which in turn had positive impacts on productivity and wealth. Florence Nightingale reemphasized the role of ventilation in healing and preventing illness, ‘The very first canon of nursing… : keep the air he breathes as pure as the external air, without chilling him,’ a maxim that influenced building design at the time. These trends continued in the 20th century, greatly helped by further technological and scientific advances. Many diseases – diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, etc. – became things of the past thanks to near-universal highly effective vaccinations, while others that used to be common are no longer of such concern for highly developed countries in temperate climates – malaria, typhus, typhoid, leprosy, cholera, tuberculosis, and many others – primarily thanks to improvements in hygiene and the implementation of non-pharmaceutical measures for their containment.
Furthermore, the idea that infectious diseases should not just be reduced, but permanently eliminated altogether began to be put into practice in the second half of the 20th century3-5 on a global level, and much earlier locally. These programs were based on the obvious consideration that if an infectious agent is driven to extinction, the incalculable damage to people’s health and the overall economy by a persisting and indefinite disease burden will also be eliminated.
The ambition of local elimination grew into one of global eradication for smallpox, which was successfully eliminated from the human population in the 1970s6 (this had already been achieved locally in the late 19th century by some countries), after a heroic effort to find and contain the last remaining infectious individuals7,8. The other complete success was rinderpest in cattle9,10, globally eradicated in the early 21st century.
When the COVID-19 pandemic started, global eradication programs were very close to succeeding for two other diseases – polio11,12 and dracunculiasis13. Eradication is also globally pursued for other diseases, such as yaws14,15, and regionally for many others, e.g. lymphatic filariasis16,17, onchocerciasis18,19, measles and rubella20-30. The most challenging diseases are those that have an external reservoir outside the human population, especially if they are insect borne, and in particular those carried by mosquitos. Malaria is the primary example, but despite these difficulties, eradication of malaria has been a long-standing global public health goal31-33 and elimination has been achieved in temperate regions of the globe34,35, even though it involved the ecologically destructive widespread application of polluting chemical pesticides36,37 to reduce the populations of the vectors. Elimination is also a public goal for other insect borne diseases such as trypanosomiasis38,39.
In parallel with pursuing maximal reduction and eventual eradication of the burden of existing endemic infectious diseases, humanity has also had to battle novel infectious diseases40, which have been appearing at an increased rate over recent decades41-43. Most of these diseases are of zoonotic origin, and the rate at which they are making the jump from wildlife to humans is accelerating, because of the increased encroachment on wildlife due to expanding human populations and physical infrastructure associated with human activity, the continued destruction of wild ecosystems that forces wild animals towards closer human contact, the booming wildlife trade, and other such trends.
Because it is much easier to stop an outbreak when it is still in its early stages of spreading through the population than to eradicate an endemic pathogen, the governing principle has been that no emerging infectious disease should be allowed to become endemic. This goal has been pursued reasonably successfully and without controversy for many decades.
The most famous newly emerging pathogens were the filoviruses (Ebola44-46, Marburg47,48), the SARS and MERS coronaviruses, and paramyxoviruses like Nipah49,50. These gained fame because of their high lethality and potential for human-to-human spread, but they were merely the most notable of many examples.
Pigs in close proximity to humans. Such epidemics were almost always aggressively suppressed. Usually, these were small outbreaks, and because highly pathogenic viruses such as Ebola cause very serious sickness in practically all infected people, finding and isolating the contagious individuals is a manageable task. The largest such epidemic was the 2013-16 Ebola outbreak in West Africa, when a filovirus spread widely in major urban centers for the first time. Containment required a wartime-level mobilization, but that was nevertheless achieved, even though there were nearly 30,000 infections and more than 11,000 deaths51.
SARS was also contained and eradicated from the human population back in 2003-04, and the same happened every time MERS made the jump from camels to humans, as well as when there were Nipah outbreaks in Asia.
The major counterexample of a successful establishment in the human population of a novel highly pathogenic virus is HIV. HIV is a retrovirus, and as such it integrates into the host genome and is thus nearly impossible to eliminate from the body and to eradicate from the population52 (unless all infected individuals are identified and prevented from infecting others for the rest of their lives). However, HIV is not an example of the containment principle being voluntarily abandoned as the virus had made its zoonotic jump and established itself many decades before its eventual discovery53 and recognition54-56, and long before the molecular tools that could have detected and potentially fully contained it existed.
Still, despite all these containment success stories, the emergence of a new pathogen with pandemic potential was a well understood and frequently discussed threat57-60, although influenza viruses rather than coronaviruses were often seen as the most likely culprit61-65. The eventual appearance of SARS-CoV-2 should therefore not have been a huge surprise, and should have been met with a full mobilization of the technical tools and fundamental public health principles developed over the previous decades.
The ecological context One striking property of many emerging pathogens is how many of them come from bats. While the question of whether bats truly harbor more viruses than other mammals in proportion to their own species diversity (which is the second highest within mammals after rodents) is not fully settled yet66-69, many novel viruses do indeed originate from bats, and the ecological and physiological characteristics of bats are highly relevant for understanding the situation that Homo sapiens finds itself in right now.
Group of bats roosting in a cave. Another startling property of bats and their viruses is how highly pathogenic to humans (and other mammals) many bat viruses are, while bats themselves are not much affected (only rabies is well established to cause serious harm to bats68). Why bats seem to carry so many such pathogens, and how they have adapted so well to coexisting with them, has been a long-standing puzzle and although we do not have a definitive answer, some general trends have become clear.
Bats are the only truly flying mammals and have been so for many millions of years. Flying has resulted in a number of specific adaptations, one of them being the tolerance towards a very high body temperature (often on the order of 42-43ºC). Bats often live in huge colonies, literally touching each other, and, again, have lived in conditions of very high density for millions of years. Such densities are rare among mammals and are certainly not the native condition of humans (human civilization and our large dense cities are a very recent phenomenon on evolutionary time scales). Bats are also quite long-lived for such small mammals70-71 – some fruit bats can live more than 35 years and even small cave dwelling species can live about a decade. These are characteristics that might have on one hand facilitated the evolution of a considerable set of viruses associated with bat populations. In order for a non-latent respiratory virus to maintain itself, a minimal population size is necessary. For example, it is hypothesized that measles requires a minimum population size of 250-300,000 individuals72. And bats have existed in a state of high population densities for a very long time, which might explain the high diversity of viruses that they carry. In addition, the long lifespan of many bat species means that their viruses may have to evolve strategies to overcome adaptive immunity and frequently reinfect previously infected individuals as opposed to the situation in short-lived species in which populations turn over quickly (with immunologically naive individuals replacing the ones that die out).
On the other hand, the selective pressure that these viruses have exerted on bats may have resulted in the evolution of various resistance and/or tolerance mechanisms in bats themselves, which in turn have driven the evolution of counter strategies in their viruses, leading them to be highly virulent for other species. Bats certainly appear to be physiologically more tolerant towards viruses that are otherwise highly virulent to other mammals. Several explanations for this adaptation have been proposed, chief among them a much more powerful innate immunity and a tolerance towards infections that does not lead to the development of the kind of hyperinflammatory reactions observed in humans73-75, the high body temperature of bats in flight, and others.
The notable strength of bat innate immunity is often explained by the constitutively active interferon response that has been reported for some bat species76-78. It is possible that this is not a universal characteristic of all bats79 – only a few species have been studied – but it provides a very attractive mechanism for explaining both how bats prevent the development of severe systemic viral infections in their bodies and how their viruses in turn would have evolved powerful mechanisms to silence the interferon response, making them highly pathogenic for other mammals.
The tolerance towards infection is possibly rooted in the absence of some components of the signaling cascades leading to hyperinflammatory reactions and the dampened activity of others80.
Map of scheduled airline traffic around the world, circa June 2009 Map of scheduled airline traffic around the world. Credit: Jpatokal An obvious ecological parallel can be drawn between bats and humans – just as bats live in dense colonies, so now do modern humans. And we may now be at a critical point in the history of our species, in which our ever-increasing ecological footprint has brought us in close contact with bats in a way that was much rarer in the past. Our population is connected in ways that were previously unimaginable. A novel virus can make the zoonotic jump somewhere in Southeast Asia and a carrier of it can then be on the other side of the globe a mere 24-hours later, having encountered thousands of people in airports and other mass transit systems. As a result, bat pathogens are now being transferred from bat populations to the human population in what might prove to be the second major zoonotic spillover event after the one associated with domestication of livestock and pets a few thousand years ago.
Unfortunately for us, our physiology is not suited to tolerate these new viruses. Bats have adapted to live with them over many millions of years. Humans have not undergone the same kind of adaptation and cannot do so on any timescale that will be of use to those living now, nor to our immediate descendants.
Simply put, humans are not bats, and the continuous existence and improvement of what we now call “civilization” depends on the same basic public health and infectious disease control that saw life expectancy in high-income countries more than double to 85 years. This is a challenge that will only increase in the coming years, because the trends that are accelerating the rate of zoonotic transfer of pathogens are certain to persist.
Given this context, it is as important now to maintain the public health principle that no new dangerous pathogens should be allowed to become endemic and that all novel infectious disease outbreaks must be suppressed as it ever was.
The death of public health and the end of epidemiological comfort It is also in this context that the real gravity of what has happened in the last three years emerges.
After HIV, SARS-CoV-2 is now the second most dangerous infectious disease agent that is 'endemic' to the human population on a global scale. And yet not only was it allowed to become endemic, but mass infection was outright encouraged, including by official public health bodies in numerous countries81-83.
The implications of what has just happened have been missed by most, so let’s spell them out explicitly.
We need to be clear why containment of SARS-CoV-2 was actively sabotaged and eventually abandoned. It has absolutely nothing to do with the “impossibility” of achieving it. In fact, the technical problem of containing even a stealthily spreading virus such as SARS-CoV-2 is fully solved, and that solution was successfully applied in practice for years during the pandemic.
The list of countries that completely snuffed out outbreaks, often multiple times, includes Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, Vietnam, Thailand, Bhutan, Cuba, China, and a few others, with China having successfully contained hundreds of separate outbreaks, before finally giving up in late 2022.
The algorithm for containment is well established – passively break transmission chains through the implementation of nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as limiting human contacts, high quality respirator masks, indoor air filtration and ventilation, and others, while aggressively hunting down active remaining transmission chains through traditional contact tracing and isolation methods combined with the powerful new tool of population-scale testing.
Oklahoma’s Strategic National Stockpile. Credit: DVIDS Understanding of airborne transmission and institution of mitigation measures, which have heretofore not been utilized in any country, will facilitate elimination, even with the newer, more transmissible variants. Any country that has the necessary resources (or is provided with them) can achieve full containment within a few months. In fact, currently this would be easier than ever before because of the accumulated widespread multiple recent exposures to the virus in the population suppressing the effective reproduction number (Re). For the last 18 months or so we have been seeing a constant high plateau of cases with undulating waves, but not the major explosions of infections with Re reaching 3-4 that were associated with the original introduction of the virus in 2020 and with the appearance of the first Omicron variants in late 2021.
It would be much easier to use NPIs to drive Re to much below 1 and keep it there until elimination when starting from Re around 1.2-1.3 than when it was over 3, and this moment should be used, before another radically new serotype appears and takes us back to those even more unpleasant situations. This is not a technical problem, but one of political and social will. As long as leadership misunderstands or pretends to misunderstand the link between increased mortality, morbidity and poorer economic performance and the free transmission of SARS-CoV-2, the impetus will be lacking to take the necessary steps to contain this damaging virus.
Political will is in short supply because powerful economic and corporate interests have been pushing policymakers to let the virus spread largely unchecked through the population since the very beginning of the pandemic. The reasons are simple. First, NPIs hurt general economic activity, even if only in the short term, resulting in losses on balance sheets. Second, large-scale containment efforts of the kind we only saw briefly in the first few months of the pandemic require substantial governmental support for all the people who need to pause their economic activity for the duration of effort. Such an effort also requires large-scale financial investment in, for example, contact tracing and mass testing infrastructure and providing high-quality masks. In an era dominated by laissez-faire economic dogma, this level of state investment and organization would have set too many unacceptable precedents, so in many jurisdictions it was fiercely resisted, regardless of the consequences for humanity and the economy.
None of these social and economic predicaments have been resolved. The unofficial alliance between big business and dangerous pathogens that was forged in early 2020 has emerged victorious and greatly strengthened from its battle against public health, and is poised to steamroll whatever meager opposition remains for the remainder of this, and future pandemics.
The long-established principles governing how we respond to new infectious diseases have now completely changed – the precedent has been established that dangerous emerging pathogens will no longer be contained, but instead permitted to ‘ease’ into widespread circulation. The intent to “let it rip” in the future is now being openly communicated84. With this change in policy comes uncertainty about acceptable lethality. Just how bad will an infectious disease have to be to convince any government to mobilize a meaningful global public health response?
We have some clues regarding that issue from what happened during the initial appearance of the Omicron “variant” (which was really a new serotype85,86) of SARS-CoV-2. Despite some experts warning that a vaccine-only approach would be doomed to fail, governments gambled everything on it. They were then faced with the brute fact of viral evolution destroying their strategy when a new serotype emerged against which existing vaccines had little effect in terms of blocking transmission. The reaction was not to bring back NPIs but to give up, seemingly regardless of the consequences.
Critically, those consequences were unknown when the policy of no intervention was adopted within days of the appearance of Omicron. All previous new SARS-CoV-2 variants had been deadlier than the original Wuhan strain, with the eventually globally dominant Delta variant perhaps as much as 4× as deadly87. Omicron turned out to be the exception, but again, that was not known with any certainty when it was allowed to run wild through populations. What would have happened if it had followed the same pattern as Delta?
In the USA, for example, the worst COVID-19 wave was the one in the winter of 2020-21, at the peak of which at least 3,500 people were dying daily (the real number was certainly higher because of undercounting due to lack of testing and improper reporting). The first Omicron BA.1 wave saw the second-highest death tolls, with at least 2,800 dying per day at its peak. Had Omicron been as intrinsically lethal as Delta, we could have easily seen a 4-5× higher peak than January 2021, i.e. as many as 12–15,000 people dying a day. Given that we only had real data on Omicron’s intrinsic lethality after the gigantic wave of infections was unleashed onto the population, we have to conclude that 12–15,000 dead a day is now a threshold that will not force the implementation of serious NPIs for the next problematic COVID-19 serotype.
UK National Covid Memorial Wall. Credit: Dominic Alves Logically, it follows that it is also a threshold that will not result in the implementation of NPIs for any other emerging pathogens either. Because why should SARS-CoV-2 be special?
We can only hope that we will never see the day when such an epidemic hits us but experience tells us such optimism is unfounded. The current level of suffering caused by COVID-19 has been completely normalized even though such a thing was unthinkable back in 2019. Populations are largely unaware of the long-term harms the virus is causing to those infected, of the burden on healthcare, increased disability, mortality and reduced life expectancy. Once a few even deadlier outbreaks have been shrugged off by governments worldwide, the baseline of what is considered “acceptable” will just gradually move up and even more unimaginable losses will eventually enter the “acceptable” category. There can be no doubt, from a public health perspective, we are regressing.
We had a second, even more worrying real-life example of what the future holds with the global spread of the MPX virus (formerly known as “monkeypox” and now called “Mpox”) in 2022. MPX is a close relative to the smallpox VARV virus and is endemic to Central and Western Africa, where its natural hosts are mostly various rodent species, but on occasions it infects humans too, with the rate of zoonotic transfer increasing over recent decades88. It has usually been characterized by fairly high mortality – the CFR (Case Fatality Rate) has been ∼3.6% for the strain that circulates in Nigeria and ∼10% for the one in the Congo region, i.e. much worse than SARS-CoV-2. In 2022, an unexpected global MPX outbreak developed, with tens of thousands of confirmed cases in dozens of countries89,90. Normally, this would be a huge cause for alarm, for several reasons.
First, MPX itself is a very dangerous disease. Second, universal smallpox vaccination ended many decades ago with the success of the eradication program, leaving the population born after that completely unprotected. Third, lethality in orthopoxviruses is, in fact, highly variable – VARV itself had a variola major strain, with as much as ∼30% CFR, and a less deadly variola minor variety with CFR ∼1%, and there was considerable variation within variola major too. It also appears that high pathogenicity often evolves from less pathogenic strains through reductive evolution - the loss of certain genes something that can happen fairly easily, may well have happened repeatedly in the past, and may happen again in the future, a scenario that has been repeatedly warned about for decades91,92. For these reasons, it was unthinkable that anyone would just shrug off a massive MPX outbreak – it is already bad enough as it is, but allowing it to become endemic means it can one day evolve towards something functionally equivalent to smallpox in its impact.
Colorized transmission electron micrograph of Mpox virus particles. Credit: NIAID And yet that is exactly what happened in 2022 – barely any measures were taken to contain the outbreak, and countries simply reclassified MPX out of the “high consequence infectious disease” category93 in order to push the problem away, out of sight and out of mind. By chance, it turned out that this particular outbreak did not spark a global pandemic, and it was also characterized, for poorly understood reasons, by an unusually low CFR, with very few people dying94,95. But again, that is not the information that was available at the start of the outbreak, when in a previous, interventionist age of public health, resources would have been mobilized to stamp it out in its infancy, but, in the age of laissez-faire, were not. MPX is now circulating around the world and represents a future threat of uncontrolled transmission resulting in viral adaptation to highly efficient human-to-human spread combined with much greater disease severity.
This is the previously unthinkable future we will live in from now on in terms of our approach to infectious disease.
What may be controlled instead is information. Another lesson of the pandemic is that if there is no testing and reporting of cases and deaths, a huge amount of real human suffering can be very successfully swept under the rug. Early in 2020, such practices – blatant denial that there was any virus in certain territories, outright faking of COVID-19 statistics, and even resorting to NPIs out of sheer desperation but under false pretense that it is not because of COVID-19 – were the domain of failed states and less developed dictatorships. But in 2023 most of the world has adopted such practices – testing is limited, reporting is infrequent, or even abandoned altogether – and there is no reason to expect this to change. Information control has replaced infection control.
After a while it will not even be possible to assess the impact of what is happening by evaluating excess mortality, which has been the one true measure not susceptible to various data manipulation tricks. As we get increasingly removed from the pre-COVID-19 baselines and the initial pandemic years are subsumed into the baseline for calculating excess mortality, excess deaths will simply disappear by the power of statistical magic. Interestingly, countries such as the UK, which has already incorporated two pandemic years in its five-year average, are still seeing excess deaths, which suggests the virus is an ongoing and growing problem.
It should also be stressed that this radical shift in our approach to emerging infectious diseases is probably only the beginning of wiping out the hard-fought public health gains of the last 150+ years. This should be gravely concerning to any individuals and institutions concerned with workers and citizens rights.
This shift is likely to impact existing eradication and elimination efforts. Will the final pushes be made to complete the various global eradication campaigns listed above? That may necessitate some serious effort involving NPIs and active public health measures, but how much appetite is there for such things after they have been now taken out of the toolkit for SARS-CoV-2?
We can also expect previously forgotten diseases to return where they have successfully been locally eradicated. We have to always remember that the diseases that we now control with universal childhood vaccinations have not been globally eradicated – they have disappeared from our lives because vaccination rates are high enough to maintain society as a whole above the disease elimination threshold, but were vaccination rates to slip, those diseases, such as measles, will return with a vengeance.
The anti-vaccine movement was already a serious problem prior to COVID-19, but it was given a gigantic boost with the ill-advised vaccine-only COVID-19 strategy. Governments and their nominal expert advisers oversold the effectiveness of imperfect first generation COVID-vaccines, and simultaneously minimized the harms of SARS-CoV-2, creating a reality gap which gave anti-vaccine rhetoric space to thrive. This is a huge topic to be explored separately. Here it will suffice to say that while anti-vaxxers were a fringe movement prior to the pandemic, “vaccination” in general is now a toxic idea in the minds of truly significant portions of the population. A logical consequence of that shift has been a significant decrease in vaccination coverage for other diseases as well as for COVID-19.
This is even more likely given the shift in attitudes towards children. Child labour, lack of education and large families were the hallmarks of earlier eras of poor public health, which were characterized by high birth-rates and high infant mortality. Attitudes changed dramatically over the course of the 20th century and wherever health and wealth increased, child mortality fell, and the transition was made to small families. Rarity increased perceived value and children’s wellbeing became a central concern for parents and carers. The arrival of COVID-19 changed that, with some governments, advisers, advocacy groups and parents insisting that children should be exposed freely to a Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome virus to ‘train’ their immune systems.
Infection, rather than vaccination, was the preferred route for many in public health in 2020, and still is in 2023, despite all that is known about this virus’s propensity to cause damage to all internal organs, the immune system, and the brain, and the unknowns of postinfectious sequelae. This is especially egregious in infants, whose naive immune status may be one of the reasons they have a relatively high hospitalization rate. Some commentators seek to justify the lack of protection for the elderly and vulnerable on a cost basis. We wonder what rationale can justify a lack of protection for newborns and infants, particularly in a healthcare setting, when experience of other viruses tells us children have better outcomes the later they are exposed to disease? If we are not prepared to protect children against a highly virulent SARS virus, why should we protect against others? We should expect a shift in public health attitudes, since ‘endemicity’ means there is no reason to see SARS-CoV-2 as something unique and exceptional.
We can also expect a general degradation of workplace safety protocols and standards, again reversing many decades of hard-fought gains. During COVID-19, aside from a few privileged groups who worked from home, people were herded back into their workplaces without minimal safety precautions such as providing respirators, and improving ventilation and indoor air quality, when a dangerous airborne pathogen was spreading.
Can we realistically expect existing safety precautions and regulations to survive after that precedent has been set? Can we expect public health bodies and regulatory agencies, whose job it is to enforce these standards, to fight for workplace safety given what they did during the pandemic? It is highly doubtful. After all, they stubbornly refused to admit that SARS-CoV-2 is airborne (even to this very day in fact – the World Health Organization’s infamous “FACT: #COVID19 is NOT airborne” Tweet from March 28 2020 is still up in its original form), and it is not hard to see why – implementing airborne precautions in workplaces, schools, and other public spaces would have resulted in a cost to employers and governments; a cost they could avoid if they simply denied they needed to take such precautions. But short-term thinking has resulted in long-term costs to those same organizations, through the staffing crisis, and the still-rising disability tsunami. The same principle applies to all other existing safety measures.
Worse, we have now entered the phase of abandoning respiratory precautions even in hospitals. The natural consequence of unmasked staff and patients, even those known to be SARS-CoV-2 positive, freely mixing in overcrowded hospitals is the rampant spread of hospital-acquired infections, often among some of the most vulnerable demographics. This was previously thought to be a bad thing. And what of the future? If nobody is taking any measures to stop one particular highly dangerous nosocomial infection, why would anyone care about all the others, which are often no easier to prevent? And if standards of care have slipped to such a low point with respect to COVID-19, why would anyone bother providing the best care possible for other conditions? This is a one-way feed-forward healthcare system degradation that will only continue.
Finally, the very intellectual foundations of the achievements of the last century and a half are eroding. Chief among these is the germ theory of infectious disease, by which transmission chains can be isolated and broken. The alternative theory, of spontaneous generation of pathogens, means there are no chains to be broken. Today, we are told that it is impossible to contain SARS-CoV-2 and we have to "just live with it,” as if germ theory no longer holds. The argument that the spread of SARS-CoV-2 to wildlife means that containment is impossible illustrates these contradictions further – SARS-CoV-2 came from wildlife, as did all other zoonotic infections, so how does the virus spilling back to wildlife change anything in terms of public health protocol? But if one has decided that from here on there will be no effort to break transmission chains because it is too costly for the privileged few in society, then excuses for that laissez-faire attitude will always be found.
And that does not bode well for the near- and medium-term future of the human species on planet Earth.
(Follow the link for more than 100 references and sources)
#mask up#covid#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#public health#coronavirus#sars cov 2#still coviding#wear a respirator
129 notes
·
View notes
Text

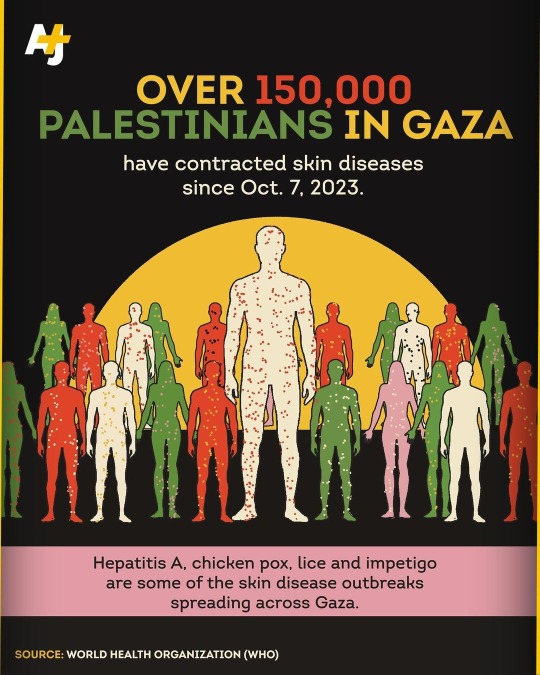







Infectious skin diseases are spreading rapidly in Gaza – and part of the reason is because Israel is blocking soap from entering the enclave.
Limited access to water, unhygienic conditions in cramped tents and the destruction of Gaza’s sewage and sanitation system is making it even worse.
Israel is restricting humanitarian organizations from delivering soap into Gaza, and aid workers who try to bring it in have had it confiscated.
…
Producer: Aina J. Khan
Senior Video Editor: Ben Angeloni
#Gaza #IsraeliBlockade #IsraeliOccupation #Palestine
#palestine#human rights#free palestine#gaza#israel#free gaza#gaza genocide#cleanliness#cleancore#clean girl#soap#health#self care#hygiene#skincare#skin#medicine#ethnic cleansing#war crimes#israel is committing genocide#israeli war crimes#stop arming israel#arms embargo now#boycott divest sanction#boycott israel
58 notes
·
View notes